User login
Severe Henoch-Schönlein Purpura Complicating Infliximab Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis
To the Editor:
Anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α treatments have radically improved the management of chronic inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and bowel diseases (eg, Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis [UC]). Because the number of patients treated with these agents has increased, uncommon adverse reactions have increasingly occurred. Cutaneous adverse reactions that have been reported with anti-TNF agents include immediate injection-site reaction, systemic infusion reactions, and delayed reactions.1 Among the delayed adverse reactions, psoriatic and eczematous eruptions as well as cutaneous infections are the most common, while cutaneous adverse effects related to an immune imbalance syndrome including vasculitis; lupuslike, lichenlike, and granulomatous eruptions; and skin cancer rarely are observed.1 Although most of the cutaneous adverse effects do not require anti-TNF treatment discontinuation and are resolved with symptomatic treatment, anti-TNF therapy must be stopped in more severe cases. We report the case of severe Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP) following treatment with infliximab.
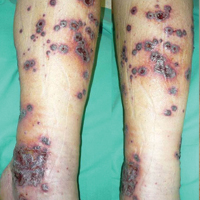
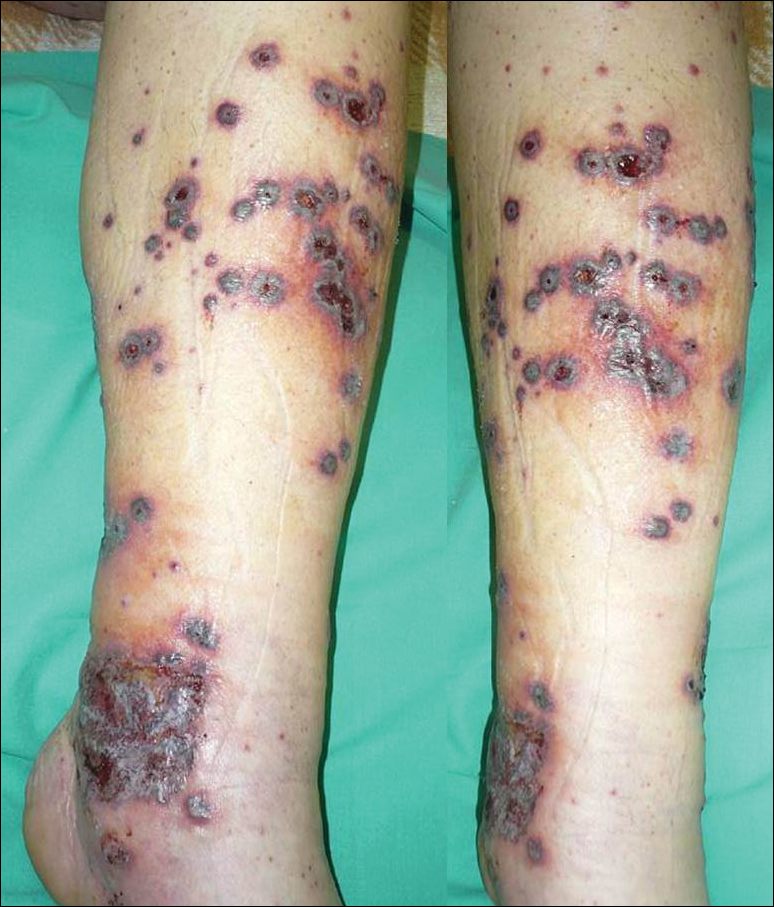
A 46-year-old man who was a nonsmoker with quiescent UC on infliximab for 30 months presented with palpable necrotic purpura on both legs (Figure) and arms as well as the abdomen of 10 days’ duration, along with diffuse joint pain and swelling. He had no history of infectious or gastrointestinal symptoms. The last infliximab infusion was performed 6 weeks prior to developing the purpura. His UC was diagnosed 10 years prior to the current presentation and was not associated with any extragastrointestinal manifestations. Since diagnosis, UC had failed to respond to therapies such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, and purinethol. The complete blood cell count was normal. The C-reactive protein level was 18.7 mg/L (reference range, <5 mg/L) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 30 mm/h (reference range, 0–20 mm/h). Electrolytes, urea, creatinine clearance, and liver function were normal, and a chest radiograph and radiographs of the swollen joints were unremarkable. The total IgA level was elevated at 4 g/L (reference range, 0.7–4 g/L), with IgG and IgM levels within reference range. There was no hematuria or proteinuria on urinalysis. Tests for antinuclear antibodies, rheumatoid factor, circulating immune complexes, and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody were negative. Total complement, C3, and C4 levels also were normal. A skin biopsy confirmed a leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with C3 deposition. Serologic tests for hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and human immunodeficiency virus were negative. Based on these findings, the diagnosis of HSP was made. Systemic corticosteroids—120 mg daily of intravenous methylprednisolone for 3 days, followed by 1 mg/kg daily of oral prednisone for 2 weeks—were then introduced with rapid clinical improvement. Henoch-Schönlein purpura and joint symptoms completely resolved, but UC relapsed with bloody diarrhea and severe abdominal pain. Oral prednisone was maintained (1 mg/kg daily). Because of the severity of cutaneous vasculitis (HSP), a multidisciplinary decision was taken to definitively stop the anti-TNF agents and to first add azathioprine (2 mg/kg daily for 2 months), then subcutaneous methotrexate (25 mg weekly). Colonoscopy did not show any dysplasia or adenocarcinoma and confirmed the diagnosis of UC. After 6 months of combined therapy, UC was still active and we decided to perform a total colectomy with ileostomy formation. Complete remission of UC was obtained and maintained after 28 months of follow-up.
Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a multisystem small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis with the deposition of immune complexes containing IgA. Clinical manifestations may include palpable purpura, arthritis, enteritis, and nephritis. Henoch-Schönlein purpura usually affects children. Adult onset is rare but associated with more severe symptoms and a poor prognosis.2 The criteria for HSP, as defined by the American College of Rheumatology,3 include palpable purpura, 20 years or younger at disease onset, bowel angina, and presence of vascular wall granulocytes on biopsy. At least 2 of these criteria are required for HSP diagnosis. Various viral or bacterial infections and drugs can trigger HSP, which also can be associated with autoinflammatory or autoimmune diseases. The association of HSP and UC is a rare event, as demonstrated by de Oliveira et al.4 Although only 2 cases of cutaneous vasculitis mimicking HSP have been described in UC,4 we cannot exclude a possible association between HSP and UC. However, our patient had UC for 10 years and never had clinical manifestations of vasculitis.
There are 5 reports of HSP following etanercept5,6 or adalimumab7-9 therapy and 1 following infliximab therapy.10 In all cases, HSP occurred after several months of anti-TNF therapy. However, there also are reports of cutaneous vasculitis associated with arthralgia and glomerulonephritis that resolved after withdrawal of anti-TNF agents.11,12 It is possible that some of these reactions may have been manifestations of undiagnosed HSP. In a series of 113 patients who developed cutaneous vasculitis after anti-TNF agents, visceral vasculitis was observed in 24% of patients. Treatment of vasculitis involved withdrawal of the anti-TNF therapy in 101 cases (89%).13 In these UC patients with few therapeutic alternatives, the continuation of anti-TNF agents should be discussed. In the previous series,13 of 16 patients who were rechallenged with the same or a different TNF antagonist, 12 (75%) experienced vasculitis relapse, suggesting a class effect of TNF inhibition. Because of the severity of cutaneous vasculitis and as previously suggested in a recent analytical and comprehensive overview on paradoxical reactions under TNF blockers,1 we decided not to re-expose our patient to infliximab or to other anti-TNF agents.
In conclusion, HSP may occur during anti-TNF therapy and physicians need to be aware of this potentially serious complication.
- Toussirot É, Aubin F. Paradoxical reactions under TNF-α blocking agents and other biological agents given for chronic immune-mediated diseases: an analytical and comprehensive overview. RMD Open. 2016;2:e000239.
- Saulsbury FT. Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13:35-40.
- Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Blanco R, Hernández JL, et al. Applicability of the 2006 European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) criteria for the classification ofHenoch-Schönlein purpura. an analysis based on 766 patients with cutaneous vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33(2, suppl 89):S44-S47.
- de Oliveira GT, Martins SS, Deboni M, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis in ulcerative colitis mimicking Henoch-Schönlein purpura [published online May 22, 2012]. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7:e69-e73.
- Marques I, Lagos A, Reis J, et al. Reversible Henoch-Schönlein purpura complicating adalimumab therapy. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:796-799.
- Rahman FZ, Takhar GK, Roy O, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura complicating adalimumab therapy for Crohn’s disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010;1:119-122.
- Lee A, Kasama R, Evangelisto A, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura after etanercept therapy for psoriasis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006;12:249-251.
- Duffy TN, Genta M, Moll S, et al. Henoch Schönlein purpura following etanercept treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006;24(2, suppl 41):S106.
- LaConti JJ, Donet JA, Cho-Vega JH, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura with adalimumab therapy for ulcerative colitis: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2016:2812980.
- Nobile S, Catassi C, Felici L. Herpes zoster infection followed by Henoch-Schönlein purpura in a girl receiving infliximab for ulcerative colitis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009;15:101.
- Mohan N, Edwards ET, Cupps TR, et al. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocking agents. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1955-1958.
- Simms R, Kipgen D, Dahill S, et al. ANCA-associated renal vasculitis following anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51:e11-e14.
- Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Muñoz S, et al. Autoimmune diseases induced by TNF-targeted therapies: analysis of 233 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:242-251.
To the Editor:
Anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α treatments have radically improved the management of chronic inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and bowel diseases (eg, Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis [UC]). Because the number of patients treated with these agents has increased, uncommon adverse reactions have increasingly occurred. Cutaneous adverse reactions that have been reported with anti-TNF agents include immediate injection-site reaction, systemic infusion reactions, and delayed reactions.1 Among the delayed adverse reactions, psoriatic and eczematous eruptions as well as cutaneous infections are the most common, while cutaneous adverse effects related to an immune imbalance syndrome including vasculitis; lupuslike, lichenlike, and granulomatous eruptions; and skin cancer rarely are observed.1 Although most of the cutaneous adverse effects do not require anti-TNF treatment discontinuation and are resolved with symptomatic treatment, anti-TNF therapy must be stopped in more severe cases. We report the case of severe Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP) following treatment with infliximab.
A 46-year-old man who was a nonsmoker with quiescent UC on infliximab for 30 months presented with palpable necrotic purpura on both legs (Figure) and arms as well as the abdomen of 10 days’ duration, along with diffuse joint pain and swelling. He had no history of infectious or gastrointestinal symptoms. The last infliximab infusion was performed 6 weeks prior to developing the purpura. His UC was diagnosed 10 years prior to the current presentation and was not associated with any extragastrointestinal manifestations. Since diagnosis, UC had failed to respond to therapies such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, and purinethol. The complete blood cell count was normal. The C-reactive protein level was 18.7 mg/L (reference range, <5 mg/L) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 30 mm/h (reference range, 0–20 mm/h). Electrolytes, urea, creatinine clearance, and liver function were normal, and a chest radiograph and radiographs of the swollen joints were unremarkable. The total IgA level was elevated at 4 g/L (reference range, 0.7–4 g/L), with IgG and IgM levels within reference range. There was no hematuria or proteinuria on urinalysis. Tests for antinuclear antibodies, rheumatoid factor, circulating immune complexes, and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody were negative. Total complement, C3, and C4 levels also were normal. A skin biopsy confirmed a leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with C3 deposition. Serologic tests for hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and human immunodeficiency virus were negative. Based on these findings, the diagnosis of HSP was made. Systemic corticosteroids—120 mg daily of intravenous methylprednisolone for 3 days, followed by 1 mg/kg daily of oral prednisone for 2 weeks—were then introduced with rapid clinical improvement. Henoch-Schönlein purpura and joint symptoms completely resolved, but UC relapsed with bloody diarrhea and severe abdominal pain. Oral prednisone was maintained (1 mg/kg daily). Because of the severity of cutaneous vasculitis (HSP), a multidisciplinary decision was taken to definitively stop the anti-TNF agents and to first add azathioprine (2 mg/kg daily for 2 months), then subcutaneous methotrexate (25 mg weekly). Colonoscopy did not show any dysplasia or adenocarcinoma and confirmed the diagnosis of UC. After 6 months of combined therapy, UC was still active and we decided to perform a total colectomy with ileostomy formation. Complete remission of UC was obtained and maintained after 28 months of follow-up.

Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a multisystem small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis with the deposition of immune complexes containing IgA. Clinical manifestations may include palpable purpura, arthritis, enteritis, and nephritis. Henoch-Schönlein purpura usually affects children. Adult onset is rare but associated with more severe symptoms and a poor prognosis.2 The criteria for HSP, as defined by the American College of Rheumatology,3 include palpable purpura, 20 years or younger at disease onset, bowel angina, and presence of vascular wall granulocytes on biopsy. At least 2 of these criteria are required for HSP diagnosis. Various viral or bacterial infections and drugs can trigger HSP, which also can be associated with autoinflammatory or autoimmune diseases. The association of HSP and UC is a rare event, as demonstrated by de Oliveira et al.4 Although only 2 cases of cutaneous vasculitis mimicking HSP have been described in UC,4 we cannot exclude a possible association between HSP and UC. However, our patient had UC for 10 years and never had clinical manifestations of vasculitis.
There are 5 reports of HSP following etanercept5,6 or adalimumab7-9 therapy and 1 following infliximab therapy.10 In all cases, HSP occurred after several months of anti-TNF therapy. However, there also are reports of cutaneous vasculitis associated with arthralgia and glomerulonephritis that resolved after withdrawal of anti-TNF agents.11,12 It is possible that some of these reactions may have been manifestations of undiagnosed HSP. In a series of 113 patients who developed cutaneous vasculitis after anti-TNF agents, visceral vasculitis was observed in 24% of patients. Treatment of vasculitis involved withdrawal of the anti-TNF therapy in 101 cases (89%).13 In these UC patients with few therapeutic alternatives, the continuation of anti-TNF agents should be discussed. In the previous series,13 of 16 patients who were rechallenged with the same or a different TNF antagonist, 12 (75%) experienced vasculitis relapse, suggesting a class effect of TNF inhibition. Because of the severity of cutaneous vasculitis and as previously suggested in a recent analytical and comprehensive overview on paradoxical reactions under TNF blockers,1 we decided not to re-expose our patient to infliximab or to other anti-TNF agents.
In conclusion, HSP may occur during anti-TNF therapy and physicians need to be aware of this potentially serious complication.
To the Editor:
Anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α treatments have radically improved the management of chronic inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, and bowel diseases (eg, Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis [UC]). Because the number of patients treated with these agents has increased, uncommon adverse reactions have increasingly occurred. Cutaneous adverse reactions that have been reported with anti-TNF agents include immediate injection-site reaction, systemic infusion reactions, and delayed reactions.1 Among the delayed adverse reactions, psoriatic and eczematous eruptions as well as cutaneous infections are the most common, while cutaneous adverse effects related to an immune imbalance syndrome including vasculitis; lupuslike, lichenlike, and granulomatous eruptions; and skin cancer rarely are observed.1 Although most of the cutaneous adverse effects do not require anti-TNF treatment discontinuation and are resolved with symptomatic treatment, anti-TNF therapy must be stopped in more severe cases. We report the case of severe Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP) following treatment with infliximab.
A 46-year-old man who was a nonsmoker with quiescent UC on infliximab for 30 months presented with palpable necrotic purpura on both legs (Figure) and arms as well as the abdomen of 10 days’ duration, along with diffuse joint pain and swelling. He had no history of infectious or gastrointestinal symptoms. The last infliximab infusion was performed 6 weeks prior to developing the purpura. His UC was diagnosed 10 years prior to the current presentation and was not associated with any extragastrointestinal manifestations. Since diagnosis, UC had failed to respond to therapies such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, and purinethol. The complete blood cell count was normal. The C-reactive protein level was 18.7 mg/L (reference range, <5 mg/L) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 30 mm/h (reference range, 0–20 mm/h). Electrolytes, urea, creatinine clearance, and liver function were normal, and a chest radiograph and radiographs of the swollen joints were unremarkable. The total IgA level was elevated at 4 g/L (reference range, 0.7–4 g/L), with IgG and IgM levels within reference range. There was no hematuria or proteinuria on urinalysis. Tests for antinuclear antibodies, rheumatoid factor, circulating immune complexes, and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody were negative. Total complement, C3, and C4 levels also were normal. A skin biopsy confirmed a leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with C3 deposition. Serologic tests for hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and human immunodeficiency virus were negative. Based on these findings, the diagnosis of HSP was made. Systemic corticosteroids—120 mg daily of intravenous methylprednisolone for 3 days, followed by 1 mg/kg daily of oral prednisone for 2 weeks—were then introduced with rapid clinical improvement. Henoch-Schönlein purpura and joint symptoms completely resolved, but UC relapsed with bloody diarrhea and severe abdominal pain. Oral prednisone was maintained (1 mg/kg daily). Because of the severity of cutaneous vasculitis (HSP), a multidisciplinary decision was taken to definitively stop the anti-TNF agents and to first add azathioprine (2 mg/kg daily for 2 months), then subcutaneous methotrexate (25 mg weekly). Colonoscopy did not show any dysplasia or adenocarcinoma and confirmed the diagnosis of UC. After 6 months of combined therapy, UC was still active and we decided to perform a total colectomy with ileostomy formation. Complete remission of UC was obtained and maintained after 28 months of follow-up.

Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a multisystem small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis with the deposition of immune complexes containing IgA. Clinical manifestations may include palpable purpura, arthritis, enteritis, and nephritis. Henoch-Schönlein purpura usually affects children. Adult onset is rare but associated with more severe symptoms and a poor prognosis.2 The criteria for HSP, as defined by the American College of Rheumatology,3 include palpable purpura, 20 years or younger at disease onset, bowel angina, and presence of vascular wall granulocytes on biopsy. At least 2 of these criteria are required for HSP diagnosis. Various viral or bacterial infections and drugs can trigger HSP, which also can be associated with autoinflammatory or autoimmune diseases. The association of HSP and UC is a rare event, as demonstrated by de Oliveira et al.4 Although only 2 cases of cutaneous vasculitis mimicking HSP have been described in UC,4 we cannot exclude a possible association between HSP and UC. However, our patient had UC for 10 years and never had clinical manifestations of vasculitis.
There are 5 reports of HSP following etanercept5,6 or adalimumab7-9 therapy and 1 following infliximab therapy.10 In all cases, HSP occurred after several months of anti-TNF therapy. However, there also are reports of cutaneous vasculitis associated with arthralgia and glomerulonephritis that resolved after withdrawal of anti-TNF agents.11,12 It is possible that some of these reactions may have been manifestations of undiagnosed HSP. In a series of 113 patients who developed cutaneous vasculitis after anti-TNF agents, visceral vasculitis was observed in 24% of patients. Treatment of vasculitis involved withdrawal of the anti-TNF therapy in 101 cases (89%).13 In these UC patients with few therapeutic alternatives, the continuation of anti-TNF agents should be discussed. In the previous series,13 of 16 patients who were rechallenged with the same or a different TNF antagonist, 12 (75%) experienced vasculitis relapse, suggesting a class effect of TNF inhibition. Because of the severity of cutaneous vasculitis and as previously suggested in a recent analytical and comprehensive overview on paradoxical reactions under TNF blockers,1 we decided not to re-expose our patient to infliximab or to other anti-TNF agents.
In conclusion, HSP may occur during anti-TNF therapy and physicians need to be aware of this potentially serious complication.
- Toussirot É, Aubin F. Paradoxical reactions under TNF-α blocking agents and other biological agents given for chronic immune-mediated diseases: an analytical and comprehensive overview. RMD Open. 2016;2:e000239.
- Saulsbury FT. Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13:35-40.
- Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Blanco R, Hernández JL, et al. Applicability of the 2006 European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) criteria for the classification ofHenoch-Schönlein purpura. an analysis based on 766 patients with cutaneous vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33(2, suppl 89):S44-S47.
- de Oliveira GT, Martins SS, Deboni M, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis in ulcerative colitis mimicking Henoch-Schönlein purpura [published online May 22, 2012]. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7:e69-e73.
- Marques I, Lagos A, Reis J, et al. Reversible Henoch-Schönlein purpura complicating adalimumab therapy. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:796-799.
- Rahman FZ, Takhar GK, Roy O, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura complicating adalimumab therapy for Crohn’s disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010;1:119-122.
- Lee A, Kasama R, Evangelisto A, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura after etanercept therapy for psoriasis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006;12:249-251.
- Duffy TN, Genta M, Moll S, et al. Henoch Schönlein purpura following etanercept treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006;24(2, suppl 41):S106.
- LaConti JJ, Donet JA, Cho-Vega JH, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura with adalimumab therapy for ulcerative colitis: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2016:2812980.
- Nobile S, Catassi C, Felici L. Herpes zoster infection followed by Henoch-Schönlein purpura in a girl receiving infliximab for ulcerative colitis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009;15:101.
- Mohan N, Edwards ET, Cupps TR, et al. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocking agents. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1955-1958.
- Simms R, Kipgen D, Dahill S, et al. ANCA-associated renal vasculitis following anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51:e11-e14.
- Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Muñoz S, et al. Autoimmune diseases induced by TNF-targeted therapies: analysis of 233 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:242-251.
- Toussirot É, Aubin F. Paradoxical reactions under TNF-α blocking agents and other biological agents given for chronic immune-mediated diseases: an analytical and comprehensive overview. RMD Open. 2016;2:e000239.
- Saulsbury FT. Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001;13:35-40.
- Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Blanco R, Hernández JL, et al. Applicability of the 2006 European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) criteria for the classification ofHenoch-Schönlein purpura. an analysis based on 766 patients with cutaneous vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015;33(2, suppl 89):S44-S47.
- de Oliveira GT, Martins SS, Deboni M, et al. Cutaneous vasculitis in ulcerative colitis mimicking Henoch-Schönlein purpura [published online May 22, 2012]. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7:e69-e73.
- Marques I, Lagos A, Reis J, et al. Reversible Henoch-Schönlein purpura complicating adalimumab therapy. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:796-799.
- Rahman FZ, Takhar GK, Roy O, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura complicating adalimumab therapy for Crohn’s disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010;1:119-122.
- Lee A, Kasama R, Evangelisto A, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura after etanercept therapy for psoriasis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006;12:249-251.
- Duffy TN, Genta M, Moll S, et al. Henoch Schönlein purpura following etanercept treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006;24(2, suppl 41):S106.
- LaConti JJ, Donet JA, Cho-Vega JH, et al. Henoch-Schönlein purpura with adalimumab therapy for ulcerative colitis: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2016:2812980.
- Nobile S, Catassi C, Felici L. Herpes zoster infection followed by Henoch-Schönlein purpura in a girl receiving infliximab for ulcerative colitis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009;15:101.
- Mohan N, Edwards ET, Cupps TR, et al. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocking agents. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1955-1958.
- Simms R, Kipgen D, Dahill S, et al. ANCA-associated renal vasculitis following anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51:e11-e14.
- Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Muñoz S, et al. Autoimmune diseases induced by TNF-targeted therapies: analysis of 233 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:242-251.
Practice Points
- Cutaneous adverse effects may occur in approximately 20% of patients treated with anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF) drugs.
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), a small-vessel vasculitis, is an extremely rare complication of anti-TNF treatment.
- Although most cutaneous adverse effects do not require anti-TNF treatment discontinuation and are resolved with symptomatic treatment, anti-TNF therapy must be stopped in more severe cases.