User login
Disparities in Palliative Care Utilization in Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumor: A National Cancer Database (NCDB) Study
Study Purpose/Background
Malignant mixed Mullerian tumor (MMMT), known as carcinosarcoma of the uterus, is a rare tumor consisting of malignant epithelial and mesenchymal components. Palliative care (PC) has been shown to enhance quality of life and improve outcomes in patients with advanced or incurable cancer. Patients with MMMT may benefit from PC. The project’s objective is to describe disparities in PC utilization among MMMT patients using the National Cancer Database (NCDB).
Methods/Design
A total of 14,085 patients, diagnosed with MMMT, were identified utilizing the NCDB ICD-O-3 histology code 8950. Demographic factors (race, income, facility type, insurance, geographic location, grade, and Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score) were studied in relation to the receipt of PC using multivariate logistic regression.
Results
3.10% of the study cohort received PC (437/14085). Participants with a median income of ≥ $63,000 (2.74%) were less likely to receive PC than participants making < $38,000 (3.93%), P = .049. Participants treated at an academic/research program (2.48%) were less likely to receive PC compared to patients treated at a community cancer program (4.44%), P = .023. Those with private insurance (2.50%), were less likely to receive PC than those with no insurance (3.56%), P = .032. Participants who received treatment at a facility located in the South Atlantic (2.25%), East North Central (3.11%), West South Central (2.73%) or Pacific (1.36%), were less likely to receive PC than patients who received treatment at a New England facility (4.42%), P < .001, P = .031, P = .017, and P < .001, respectively. Those with tumors that were undifferentiated, anaplastic (3.52%) were more likely to receive PC than those with well-differentiated tumors (1.01%), P = .040.
Conclusions/Implications
PC is underutilized in patients with private insurance, received treatment at an academic/research program, had well-differentiated tumors, and were in the South Atlantic, East North Central, West South Central, and Pacific regions. By highlighting disparities that exist, our study can aid clinicians in addressing PC underutilization to help provide more comprehensive care for patients.
Study Purpose/Background
Malignant mixed Mullerian tumor (MMMT), known as carcinosarcoma of the uterus, is a rare tumor consisting of malignant epithelial and mesenchymal components. Palliative care (PC) has been shown to enhance quality of life and improve outcomes in patients with advanced or incurable cancer. Patients with MMMT may benefit from PC. The project’s objective is to describe disparities in PC utilization among MMMT patients using the National Cancer Database (NCDB).
Methods/Design
A total of 14,085 patients, diagnosed with MMMT, were identified utilizing the NCDB ICD-O-3 histology code 8950. Demographic factors (race, income, facility type, insurance, geographic location, grade, and Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score) were studied in relation to the receipt of PC using multivariate logistic regression.
Results
3.10% of the study cohort received PC (437/14085). Participants with a median income of ≥ $63,000 (2.74%) were less likely to receive PC than participants making < $38,000 (3.93%), P = .049. Participants treated at an academic/research program (2.48%) were less likely to receive PC compared to patients treated at a community cancer program (4.44%), P = .023. Those with private insurance (2.50%), were less likely to receive PC than those with no insurance (3.56%), P = .032. Participants who received treatment at a facility located in the South Atlantic (2.25%), East North Central (3.11%), West South Central (2.73%) or Pacific (1.36%), were less likely to receive PC than patients who received treatment at a New England facility (4.42%), P < .001, P = .031, P = .017, and P < .001, respectively. Those with tumors that were undifferentiated, anaplastic (3.52%) were more likely to receive PC than those with well-differentiated tumors (1.01%), P = .040.
Conclusions/Implications
PC is underutilized in patients with private insurance, received treatment at an academic/research program, had well-differentiated tumors, and were in the South Atlantic, East North Central, West South Central, and Pacific regions. By highlighting disparities that exist, our study can aid clinicians in addressing PC underutilization to help provide more comprehensive care for patients.
Study Purpose/Background
Malignant mixed Mullerian tumor (MMMT), known as carcinosarcoma of the uterus, is a rare tumor consisting of malignant epithelial and mesenchymal components. Palliative care (PC) has been shown to enhance quality of life and improve outcomes in patients with advanced or incurable cancer. Patients with MMMT may benefit from PC. The project’s objective is to describe disparities in PC utilization among MMMT patients using the National Cancer Database (NCDB).
Methods/Design
A total of 14,085 patients, diagnosed with MMMT, were identified utilizing the NCDB ICD-O-3 histology code 8950. Demographic factors (race, income, facility type, insurance, geographic location, grade, and Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score) were studied in relation to the receipt of PC using multivariate logistic regression.
Results
3.10% of the study cohort received PC (437/14085). Participants with a median income of ≥ $63,000 (2.74%) were less likely to receive PC than participants making < $38,000 (3.93%), P = .049. Participants treated at an academic/research program (2.48%) were less likely to receive PC compared to patients treated at a community cancer program (4.44%), P = .023. Those with private insurance (2.50%), were less likely to receive PC than those with no insurance (3.56%), P = .032. Participants who received treatment at a facility located in the South Atlantic (2.25%), East North Central (3.11%), West South Central (2.73%) or Pacific (1.36%), were less likely to receive PC than patients who received treatment at a New England facility (4.42%), P < .001, P = .031, P = .017, and P < .001, respectively. Those with tumors that were undifferentiated, anaplastic (3.52%) were more likely to receive PC than those with well-differentiated tumors (1.01%), P = .040.
Conclusions/Implications
PC is underutilized in patients with private insurance, received treatment at an academic/research program, had well-differentiated tumors, and were in the South Atlantic, East North Central, West South Central, and Pacific regions. By highlighting disparities that exist, our study can aid clinicians in addressing PC underutilization to help provide more comprehensive care for patients.
Complete Remission of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma after COVID-19 Vaccination
Clinical Presentation
A 58-year-old male was diagnosed 6 years ago with stage IV clear cell renal carcinoma (multiple lung nodules and mediastinal adenopathy). He was offered sunitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and achieved a partial response with stable disease. Five years later his scans showed worsening disease. Cabozantinib was offered but was poorly tolerated. He tried ipilimumab plus nivolumab but ipilimumab was dropped after 4 cycles due to diarrhea. His scans improved with 4 more cycles of nivolumab but he had to stop immunotherapy due to hypophysitis, diarrhea, and severe jaw pain. He received a COVID-19 booster vaccine and noticed profound fatigue and anorexia soon after. Over 8 weeks he lost 56 lbs (267 to 211 lb). Relapse was suspected but PET CT showed complete resolution of his lung nodules and multiple areas of adenopathy. Asymptomatic and in remission 6 months after vaccination.
Relevant Literature
Clear cell renal carcinoma is resistant to standard chemotherapy/radiation, which usually offers partial responses. Complete remissions are few. Low glycemic diets in animal models have anticancer activity. HIV causes B cell apoptosis. Coxsackievirus A21 oncolytic properties lyse myeloma and CD138+ plasma cells via intercellular adhesion molecule interaction. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID 19) proteins have oncolytic properties.
Intervention
The patient eliminated sugary food from his diet 6 years ago. Stopped bread 2 years ago. Sunitinib 37.5 mg daily × 5 years. Cabozantinib—poorly tolerated. Ipilimumab + nivolumab × 4 cycles followed by nivolumab × 4 cycles. Stopped treatment; immune side effects. COVID-19 booster.
Outcome
15 lb weight loss due to a low glycemic diet, which began since diagnosis. After 4 years he stopped eating bread. After COVID-19 vaccine had a rapid 56 lb. weight loss, fatigue, and nausea over 8 weeks. No evidence of disease. Asymptomatic, off therapy, weight is ideal (219 lb) 6 months after the vaccine.
Implications for Practice
Effects of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) on cancers remain unknown. A few case reports of cancer remissions after infections are emerging. This is the first case of complete remission after COVID-19 vaccination in a patient on immunotherapy/low glycemic diet. Research is needed to study the contribution of a COVID-19 inflammatory response.
Clinical Presentation
A 58-year-old male was diagnosed 6 years ago with stage IV clear cell renal carcinoma (multiple lung nodules and mediastinal adenopathy). He was offered sunitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and achieved a partial response with stable disease. Five years later his scans showed worsening disease. Cabozantinib was offered but was poorly tolerated. He tried ipilimumab plus nivolumab but ipilimumab was dropped after 4 cycles due to diarrhea. His scans improved with 4 more cycles of nivolumab but he had to stop immunotherapy due to hypophysitis, diarrhea, and severe jaw pain. He received a COVID-19 booster vaccine and noticed profound fatigue and anorexia soon after. Over 8 weeks he lost 56 lbs (267 to 211 lb). Relapse was suspected but PET CT showed complete resolution of his lung nodules and multiple areas of adenopathy. Asymptomatic and in remission 6 months after vaccination.
Relevant Literature
Clear cell renal carcinoma is resistant to standard chemotherapy/radiation, which usually offers partial responses. Complete remissions are few. Low glycemic diets in animal models have anticancer activity. HIV causes B cell apoptosis. Coxsackievirus A21 oncolytic properties lyse myeloma and CD138+ plasma cells via intercellular adhesion molecule interaction. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID 19) proteins have oncolytic properties.
Intervention
The patient eliminated sugary food from his diet 6 years ago. Stopped bread 2 years ago. Sunitinib 37.5 mg daily × 5 years. Cabozantinib—poorly tolerated. Ipilimumab + nivolumab × 4 cycles followed by nivolumab × 4 cycles. Stopped treatment; immune side effects. COVID-19 booster.
Outcome
15 lb weight loss due to a low glycemic diet, which began since diagnosis. After 4 years he stopped eating bread. After COVID-19 vaccine had a rapid 56 lb. weight loss, fatigue, and nausea over 8 weeks. No evidence of disease. Asymptomatic, off therapy, weight is ideal (219 lb) 6 months after the vaccine.
Implications for Practice
Effects of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) on cancers remain unknown. A few case reports of cancer remissions after infections are emerging. This is the first case of complete remission after COVID-19 vaccination in a patient on immunotherapy/low glycemic diet. Research is needed to study the contribution of a COVID-19 inflammatory response.
Clinical Presentation
A 58-year-old male was diagnosed 6 years ago with stage IV clear cell renal carcinoma (multiple lung nodules and mediastinal adenopathy). He was offered sunitinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and achieved a partial response with stable disease. Five years later his scans showed worsening disease. Cabozantinib was offered but was poorly tolerated. He tried ipilimumab plus nivolumab but ipilimumab was dropped after 4 cycles due to diarrhea. His scans improved with 4 more cycles of nivolumab but he had to stop immunotherapy due to hypophysitis, diarrhea, and severe jaw pain. He received a COVID-19 booster vaccine and noticed profound fatigue and anorexia soon after. Over 8 weeks he lost 56 lbs (267 to 211 lb). Relapse was suspected but PET CT showed complete resolution of his lung nodules and multiple areas of adenopathy. Asymptomatic and in remission 6 months after vaccination.
Relevant Literature
Clear cell renal carcinoma is resistant to standard chemotherapy/radiation, which usually offers partial responses. Complete remissions are few. Low glycemic diets in animal models have anticancer activity. HIV causes B cell apoptosis. Coxsackievirus A21 oncolytic properties lyse myeloma and CD138+ plasma cells via intercellular adhesion molecule interaction. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID 19) proteins have oncolytic properties.
Intervention
The patient eliminated sugary food from his diet 6 years ago. Stopped bread 2 years ago. Sunitinib 37.5 mg daily × 5 years. Cabozantinib—poorly tolerated. Ipilimumab + nivolumab × 4 cycles followed by nivolumab × 4 cycles. Stopped treatment; immune side effects. COVID-19 booster.
Outcome
15 lb weight loss due to a low glycemic diet, which began since diagnosis. After 4 years he stopped eating bread. After COVID-19 vaccine had a rapid 56 lb. weight loss, fatigue, and nausea over 8 weeks. No evidence of disease. Asymptomatic, off therapy, weight is ideal (219 lb) 6 months after the vaccine.
Implications for Practice
Effects of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) on cancers remain unknown. A few case reports of cancer remissions after infections are emerging. This is the first case of complete remission after COVID-19 vaccination in a patient on immunotherapy/low glycemic diet. Research is needed to study the contribution of a COVID-19 inflammatory response.
Neuropsychiatric symptoms after stroke
Many patients experience neuropsychiatric symptoms following stroke. There is tremendous variation in the type, severity, and timeline of these symptoms, which have the potential to significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Some symptoms occur as a direct result of ischemic injury to brain structures regulating behavior, executive function, perception, or affect. Other symptoms occur indirectly due to the patient’s often-difficult experiences with the health care system, disrupted routines, or altered poststroke functional abilities. Psychiatric symptoms are not as easily recognized as classic stroke symptoms (such as hemiparesis) and are frequently overlooked, especially in the acute phase. However, these symptoms can negatively influence patients’ interpersonal relationships, rehabilitation, and employment.
Patients and families may not realize certain symptoms are stroke-related and may not discuss them with their clinicians. It is important to ask about and recognize psychiatric symptoms in patients who have experienced a stroke so you can provide optimal education and treatment. In this article, we review the types of psychiatric symptoms associated with strokes in specific brain regions (Table1-10). We also describe symptoms that do not appear directly related to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct, including delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress.
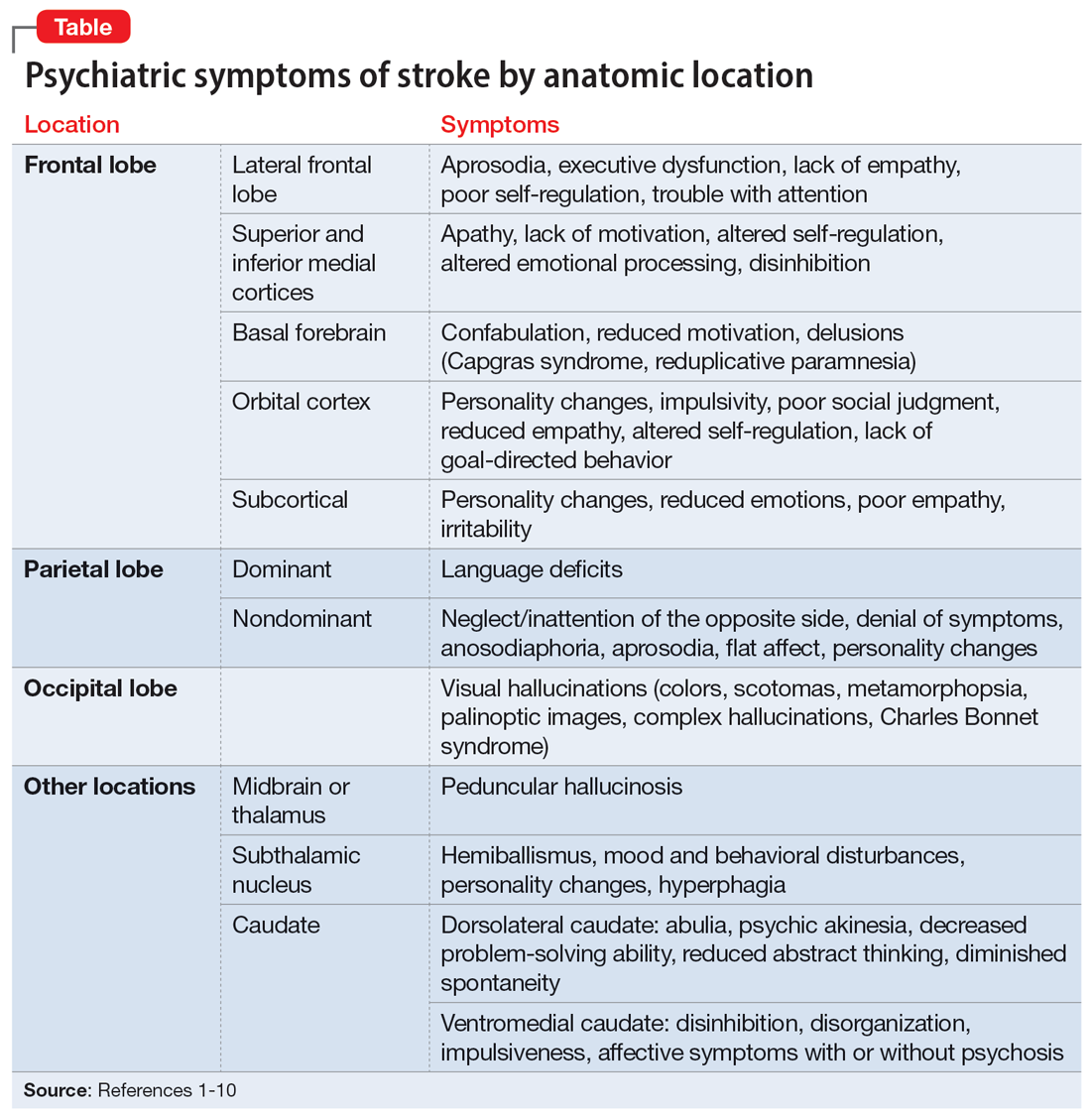
Symptoms associated with stroke in specific regions
Frontal lobe strokes
The frontal lobes are the largest lobes in the brain, and damage to areas within these lobes can cause behavioral and personality changes. Lesions in the lateral frontal cortex can cause aprosodia (difficulty expressing or comprehending variations in tone of voice), which can lead to communication errors. Lateral frontal cortex injury can cause executive dysfunction and a lack of empathy1 as well as trouble with attention, planning, and self-regulation that may affect daily functioning. Strokes affecting the superior and inferior mesial cortices may result in apathy, lack of motivation, altered self-regulation, altered emotional processing, and disinhibition. Patients who experience a basal forebrain stroke may exhibit confabulation, reduced motivation, and delusions such as Capgras syndrome (the belief that a person or place has been replaced by an exact copy) and reduplicative paramnesia (the belief that a place has been either moved, duplicated, or exists in 2 places simultaneously). Strokes involving the orbital cortex can be associated with personality changes, impulsivity, poor social judgment, reduced empathy, altered self-regulation, lack of goal-directed behavior, and environmental dependency.
Some strokes may occur primarily in the subcortical white matter within the frontal lobes. Symptoms may be due to a single stroke with sudden onset, or due to repeated ischemic events that accumulate over time, as seen with microvascular disease. In the case of microvascular disease, the onset of symptoms may be insidious and the course progressive. Infarcts in the subcortical area can also cause personality changes (though typically more subtle when compared to orbitofrontal strokes), reduced emotions, poor empathy, and irritability.1 Patients may lack insight into some of or all these symptoms following a frontal lobe infarct, which makes it critical to gather collateral information from the patient’s friends or family.
Parietal lobe strokes
Symptomatology from parietal strokes depends on whether the stroke affects the dominant or nondominant hemisphere. Dominant parietal lesions cause language deficits, and psychiatric symptoms may be difficult to elucidate due to the patient’s inability to communicate.2 On the other hand, patients with nondominant parietal stroke may have neglect of, or inattention to, the opposite (typically left) side.3 This often manifests as a reluctance to use the affected limb or limbs, in some cases despite a lack of true weakness or motor dysfunction. In addition, patients may also have visual and/or tactile inattention towards the affected side, despite a lack of gross visual or sensory impairment.2 In rare cases, a patient’s stroke may be misdiagnosed as a functional disorder due to the perceived unwillingness to use a neurologically intact limb. In severe cases, patients may not recognize an affected extremity as their own. Patients are also frequently unaware of deficits affecting their nondominant side and may argue with those attempting to explain their deficit. Anosodiaphoria—an abnormal lack of concern regarding their deficits—may also be observed. Additionally, aprosodia, flat affect, and personality changes may result from strokes affecting the nondominant hemisphere, which can impact the patient’s relationships and social functioning.3
Occipital lobe strokes
While negative or loss-of-function symptomatology is one of the hallmarks of stroke, occipital lobe infarcts can pose an exception. Although vision loss is the most common symptom with occipital lobe strokes, some patients experience visual hallucinations that may occur acutely or subacutely. In the acute phase, patients may report hallucinations of varied description,4 including poorly formed areas of color, scotomas, metamorphopsia (visual distortion in which straight lines appear curved), more complex and formed hallucinations and/or palinoptic images (images or brief scenes that continue to be perceived after looking away). These hallucinations, often referred to as release phenomena or release hallucinations, are thought to result from disinhibition of the visual cortex, which then fires spontaneously.
Hallucinations are associated with either infarction or hemorrhage in the posterior cerebral artery territory. In some cases, the hallucinations may take on a formed, complex appearance, and Charles Bonnet syndrome (visual hallucinations in the setting of vision loss, with insight into the hallucinations) has been identified in a small portion of patients.5
Continue to: The duration of these...
The duration of these hallucinations varies. Some patients describe very short periods of the disturbance, lasting minutes to hours and corresponding with the onset of their stroke. Others experience prolonged hallucinations, which frequently evolve into formed, complex images, lasting from days to months.6 In the setting of cortical stroke, patients may be at risk for seizures, which could manifest as visual hallucinations. It is essential to ensure that epileptic causes of hallucinations have been ruled out, because seizures may require treatment and other precautions.
Other stroke locations
Strokes in other locations also can result in psychiatric or behavioral symptoms. Acute stroke in the subcortical midbrain or thalamus may result in peduncular hallucinosis, a syndrome of vivid visual hallucinations.7 The midbrain (most commonly the reticular formation) is usually affected; however, certain lesions of the thalamus may also cause peduncular hallucinosis. This phenomenon is theorized to be due to an increase in serotonin activity relative to acetylcholine and is often accompanied by drowsiness.
The subthalamic nucleus is most frequently associated with disordered movement such as hemiballismus, but also causes disturbances in mood and behavior, including hyperphagia and personality changes.8 Irritability, aggressiveness, disinhibition, anxiety, and obscene speech may also be seen with lesions of the subthalamic nucleus.
Finally, the caudate nucleus may cause alterations in executive functioning and behavior.9 A stroke in the dorsolateral caudate may cause abulia and psychic akinesia, decreased problem-solving ability, reduced abstract thinking, and/or diminished spontaneity, whereas an infarct in the ventromedial region of the nucleus may cause disinhibition, disorganization, impulsiveness, and, in severe cases, affective symptoms with psychosis.10 Strokes in any of these areas are at risk for being misdiagnosed because patients may not have a hemiparesis, and isolated positive or psychiatric symptoms may not be recognized as stroke.
Symptoms not related to stroke location
Delirium and psychosis
Following a stroke, a patient may exhibit neuropsychiatric symptoms that do not appear to relate directly to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct. In the acute phase, factors such as older age and medical complications (including infection, metabolic derangement, and lack of sleep due to frequent neurologic checks) create a high risk of delirium.11 Differentiating delirium from alterations in mental status due to seizure, cerebral edema, or other medical complications is essential, and delirium precautions should be exercised to the greatest extent possible. Other neuropsychiatric symptoms may manifest following hospitalization.
Continue to: Poststroke psychosis...
Poststroke psychosis often presents subacutely. Among these patients, the most common psychosis is delusion disorder, followed by schizophrenia-like psychosis and mood disorder with psychotic features.12 Some evidence suggests antipsychotics may be highly effective for many of these patients.12 Poststroke psychosis does appear to correlate somewhat with nondominant hemisphere lesions, including the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and/or caudate nucleus. Because high mortality and poor functional outcomes have been associated with poststroke psychosis, early intervention is essential.
Depression
Depression is a common problem following stroke, affecting approximately 35% of stroke patients.13 In addition to impairing quality of life, depression negatively impacts rehabilitation and increases caregiver burden. There is significant variability regarding risk factors that increases the likelihood of poststroke depression; however, psychiatric history, dysphagia, and poor social support consistently correlate with a higher risk.14,15 Characteristics of a patient’s stroke, such as lesion volume and the ability to perform activities of daily living, are also risk factors. Identifying depression among patients who recently had a stroke is sometimes difficult due to a plethora of confounding factors. Patients may not communicate well due to aphasia, while strokes in other locations may result in an altered affect. Depending on the stroke location, patients may also suffer anosognosia (a lack of awareness of their deficits), which may impair their ability to learn and use adaptive strategies and equipment. An additional confounder is the significant overlap between depressive symptoms and those seen in the setting of a major medical event or hospitalization (decreased appetite, fatigue, etc). The prevalence of depression peaks approximately 3 to 6 months after stroke, with symptoms lasting 9 to 12 months on average, although many patients experience symptoms significantly longer.14 Because symptoms can begin within hours to days following a stroke, it is essential that both hospital and outpatient clinicians assess for depression when indicated. Patients with poststroke depression should receive prompt treatment because appropriate treatment correlates with improved rehabilitation, and most patients respond well to antidepressants.16 Early treatment reduces mortality and improves compliance with secondary stroke prevention measures, including pharmacotherapy.17
Anxiety and posttraumatic stress
Anxiety and anxiety-related disorders are additional potential complications following stroke that significantly influence patient outcomes and well-being. The abrupt, unexpected onset of stroke is often frightening to patients and families. The potential for life-altering deficits as well as intense, often invasive, interactions with the health care system does little to assuage patients’ fear. Stroke patients must contend with a change in neurologic function while processing their difficult experiences, and may develop profound fear of a recurrent stroke. As many as 22% of patients have an anxiety disorder 3 months after they have a stroke.18 Phobic disorder is the most prevalent subtype, followed by generalized anxiety disorder. Younger age and previous anxiety or depression place patients at greater risk of developing poststroke anxiety. Patients suffering from poststroke anxiety have a reduced quality of life, are more dependent, and show restricted participation in rehabilitation, all of which culminate in poorer outcomes.
Many patients describe their experiences surrounding their stroke as traumatic, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is increasingly acknowledged as a potential complication for patients with recent stroke.19 PTSD profoundly impacts patient quality of life. Interestingly, most patients who develop poststroke PTSD do not have a history of other psychiatric illness, and it is difficult to predict who may develop PTSD. Relatively little is known regarding optimal treatment strategies for poststroke PTSD, or the efficacy of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapeutic strategies to treat it.
Goals: Improve recovery and quality of life
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are common following a stroke and may manifest in a variety of ways. While some symptoms are a direct consequence of injury to a specific brain region, other symptoms may be a response to loss of independence, disability, experience with the medical system, or fear of recurrent stroke. The onset of psychiatric symptoms can be acute, beginning during hospitalization, or delayed. Understanding the association of psychiatric symptoms with the anatomical location of stroke may assist clinicians in identifying such symptoms. This knowledge informs conversations with patients and their caregivers, who may benefit from understanding that such symptoms are common after stroke. Furthermore, identifying psychiatric complications following stroke may affect rehabilitation. Additional investigation is necessary to find more effective treatment modalities and improve early intervention.
Continue to: Bottom Line
Bottom Line
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are frequently overlooked in patients with recent stroke. These symptoms include delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder, and can be the direct result of injury to neuroanatomical structures or a consequence of the patient’s experience. Prompt treatment can maximize stroke recovery and quality of life.
Related Resources
- Zhang S, Xu M, Liu ZJ, et al. Neuropsychiatric issues after stroke: clinical significance and therapeutic implications. World J Psychiatry. 2020;10(6):125-138. doi:10.5498/wjp. v10.i6.125
- Saha G, Chakraborty K, Pattojoshi A. Management of psychiatric disorders in patients with stroke and traumatic brain injury. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022;64(Suppl 2): S344-S354.
1. Eslinger PJ, Reichwein RK. Frontal lobe stroke syndromes. In: Caplan LR, van Gijn J, eds. Stroke Syndromes. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; 2012:232-241.
2. Critchley M, Russell WR, Zangwill OL. Discussion on parietal lobe syndromes. Proc R Soc Med. 1951;44(4):337-346.
3. Hier DB, Mondlock J, Caplan LR. Behavioral abnormalities after right hemisphere stroke. Neurology. 1983;33(3):337-344.
4. Brust JC, Behrens MM. “Release hallucinations” as the major symptom of posterior cerebral artery occlusion: a report of 2 cases. Ann Neurol. 1977;2(5):432-436.
5. Kumral E, Uluakay A, Donmez A. Complex visual hallucinations following stroke: epileptic origin or a deafferentiation phenomenon? Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis & Stroke. 2014;1(1):1005.
6. Lee JS, Ko KH, Oh JH, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome after occipital infarction. J Neurosonol Neuroimag. 2018;10(2):154-157.
7. Young JB. Peduncular hallucinosis. In: Aminoff MJ, Daroff RB, eds. Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2014:848.
8. Etemadifar M, Abtahi SH, Abtahi SM, et al. Hemiballismus, hyperphagia, and behavioral changes following subthalamic infarct. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:768580. doi:10.1155/2012/768580
9. Kumral E, Evyapan D, Balkir K. Acute caudate vascular lesions. Stroke. 1999;30(1):100-108.
10. Wang PY. Neurobehavioral changes following caudate infarct: a case report with literature review. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1991;47(3):199-203.
11. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-33.
12. Stangeland H, Orgeta V, Bell V. Poststroke psychosis: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(8):879-885.
13. Lenzi GL, Altieri M, Maestrini I. Post-stroke depression. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164(10):837-840.
14. Whyte EM, Mulsant BH. Post stroke depression: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and biological treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52(3):253-264.
15. Pritchard KT, Hreha KP, Hong I. Dysphagia associated with risk of depressive symptoms among stroke survivors after discharge from a cluster of inpatient rehabilitation facilities. Swallowing Rehabil. 2020;3(1):33-44.
16. Wiart L, Petit H, Joseph PA, et al. Fluoxetine in early poststroke depression: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2000;31(8):1829-1832.
17. Jorge RE, Robinson RG, Arndt S, et al. Mortality and poststroke depression: a placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(10):1823-1829.
18. Chun HY, Whiteley WN, Dennis MS, et al. Anxiety after stroke: the importance of subtyping. Stroke. 2018;49(3):556-564.
19. Garton AL, Sisti JA, Gupta VP, et al. Poststroke post-traumatic stress disorder: a review. Stroke. 2017;48(2):507-512.
Many patients experience neuropsychiatric symptoms following stroke. There is tremendous variation in the type, severity, and timeline of these symptoms, which have the potential to significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Some symptoms occur as a direct result of ischemic injury to brain structures regulating behavior, executive function, perception, or affect. Other symptoms occur indirectly due to the patient’s often-difficult experiences with the health care system, disrupted routines, or altered poststroke functional abilities. Psychiatric symptoms are not as easily recognized as classic stroke symptoms (such as hemiparesis) and are frequently overlooked, especially in the acute phase. However, these symptoms can negatively influence patients’ interpersonal relationships, rehabilitation, and employment.
Patients and families may not realize certain symptoms are stroke-related and may not discuss them with their clinicians. It is important to ask about and recognize psychiatric symptoms in patients who have experienced a stroke so you can provide optimal education and treatment. In this article, we review the types of psychiatric symptoms associated with strokes in specific brain regions (Table1-10). We also describe symptoms that do not appear directly related to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct, including delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress.

Symptoms associated with stroke in specific regions
Frontal lobe strokes
The frontal lobes are the largest lobes in the brain, and damage to areas within these lobes can cause behavioral and personality changes. Lesions in the lateral frontal cortex can cause aprosodia (difficulty expressing or comprehending variations in tone of voice), which can lead to communication errors. Lateral frontal cortex injury can cause executive dysfunction and a lack of empathy1 as well as trouble with attention, planning, and self-regulation that may affect daily functioning. Strokes affecting the superior and inferior mesial cortices may result in apathy, lack of motivation, altered self-regulation, altered emotional processing, and disinhibition. Patients who experience a basal forebrain stroke may exhibit confabulation, reduced motivation, and delusions such as Capgras syndrome (the belief that a person or place has been replaced by an exact copy) and reduplicative paramnesia (the belief that a place has been either moved, duplicated, or exists in 2 places simultaneously). Strokes involving the orbital cortex can be associated with personality changes, impulsivity, poor social judgment, reduced empathy, altered self-regulation, lack of goal-directed behavior, and environmental dependency.
Some strokes may occur primarily in the subcortical white matter within the frontal lobes. Symptoms may be due to a single stroke with sudden onset, or due to repeated ischemic events that accumulate over time, as seen with microvascular disease. In the case of microvascular disease, the onset of symptoms may be insidious and the course progressive. Infarcts in the subcortical area can also cause personality changes (though typically more subtle when compared to orbitofrontal strokes), reduced emotions, poor empathy, and irritability.1 Patients may lack insight into some of or all these symptoms following a frontal lobe infarct, which makes it critical to gather collateral information from the patient’s friends or family.
Parietal lobe strokes
Symptomatology from parietal strokes depends on whether the stroke affects the dominant or nondominant hemisphere. Dominant parietal lesions cause language deficits, and psychiatric symptoms may be difficult to elucidate due to the patient’s inability to communicate.2 On the other hand, patients with nondominant parietal stroke may have neglect of, or inattention to, the opposite (typically left) side.3 This often manifests as a reluctance to use the affected limb or limbs, in some cases despite a lack of true weakness or motor dysfunction. In addition, patients may also have visual and/or tactile inattention towards the affected side, despite a lack of gross visual or sensory impairment.2 In rare cases, a patient’s stroke may be misdiagnosed as a functional disorder due to the perceived unwillingness to use a neurologically intact limb. In severe cases, patients may not recognize an affected extremity as their own. Patients are also frequently unaware of deficits affecting their nondominant side and may argue with those attempting to explain their deficit. Anosodiaphoria—an abnormal lack of concern regarding their deficits—may also be observed. Additionally, aprosodia, flat affect, and personality changes may result from strokes affecting the nondominant hemisphere, which can impact the patient’s relationships and social functioning.3
Occipital lobe strokes
While negative or loss-of-function symptomatology is one of the hallmarks of stroke, occipital lobe infarcts can pose an exception. Although vision loss is the most common symptom with occipital lobe strokes, some patients experience visual hallucinations that may occur acutely or subacutely. In the acute phase, patients may report hallucinations of varied description,4 including poorly formed areas of color, scotomas, metamorphopsia (visual distortion in which straight lines appear curved), more complex and formed hallucinations and/or palinoptic images (images or brief scenes that continue to be perceived after looking away). These hallucinations, often referred to as release phenomena or release hallucinations, are thought to result from disinhibition of the visual cortex, which then fires spontaneously.
Hallucinations are associated with either infarction or hemorrhage in the posterior cerebral artery territory. In some cases, the hallucinations may take on a formed, complex appearance, and Charles Bonnet syndrome (visual hallucinations in the setting of vision loss, with insight into the hallucinations) has been identified in a small portion of patients.5
Continue to: The duration of these...
The duration of these hallucinations varies. Some patients describe very short periods of the disturbance, lasting minutes to hours and corresponding with the onset of their stroke. Others experience prolonged hallucinations, which frequently evolve into formed, complex images, lasting from days to months.6 In the setting of cortical stroke, patients may be at risk for seizures, which could manifest as visual hallucinations. It is essential to ensure that epileptic causes of hallucinations have been ruled out, because seizures may require treatment and other precautions.
Other stroke locations
Strokes in other locations also can result in psychiatric or behavioral symptoms. Acute stroke in the subcortical midbrain or thalamus may result in peduncular hallucinosis, a syndrome of vivid visual hallucinations.7 The midbrain (most commonly the reticular formation) is usually affected; however, certain lesions of the thalamus may also cause peduncular hallucinosis. This phenomenon is theorized to be due to an increase in serotonin activity relative to acetylcholine and is often accompanied by drowsiness.
The subthalamic nucleus is most frequently associated with disordered movement such as hemiballismus, but also causes disturbances in mood and behavior, including hyperphagia and personality changes.8 Irritability, aggressiveness, disinhibition, anxiety, and obscene speech may also be seen with lesions of the subthalamic nucleus.
Finally, the caudate nucleus may cause alterations in executive functioning and behavior.9 A stroke in the dorsolateral caudate may cause abulia and psychic akinesia, decreased problem-solving ability, reduced abstract thinking, and/or diminished spontaneity, whereas an infarct in the ventromedial region of the nucleus may cause disinhibition, disorganization, impulsiveness, and, in severe cases, affective symptoms with psychosis.10 Strokes in any of these areas are at risk for being misdiagnosed because patients may not have a hemiparesis, and isolated positive or psychiatric symptoms may not be recognized as stroke.
Symptoms not related to stroke location
Delirium and psychosis
Following a stroke, a patient may exhibit neuropsychiatric symptoms that do not appear to relate directly to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct. In the acute phase, factors such as older age and medical complications (including infection, metabolic derangement, and lack of sleep due to frequent neurologic checks) create a high risk of delirium.11 Differentiating delirium from alterations in mental status due to seizure, cerebral edema, or other medical complications is essential, and delirium precautions should be exercised to the greatest extent possible. Other neuropsychiatric symptoms may manifest following hospitalization.
Continue to: Poststroke psychosis...
Poststroke psychosis often presents subacutely. Among these patients, the most common psychosis is delusion disorder, followed by schizophrenia-like psychosis and mood disorder with psychotic features.12 Some evidence suggests antipsychotics may be highly effective for many of these patients.12 Poststroke psychosis does appear to correlate somewhat with nondominant hemisphere lesions, including the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and/or caudate nucleus. Because high mortality and poor functional outcomes have been associated with poststroke psychosis, early intervention is essential.
Depression
Depression is a common problem following stroke, affecting approximately 35% of stroke patients.13 In addition to impairing quality of life, depression negatively impacts rehabilitation and increases caregiver burden. There is significant variability regarding risk factors that increases the likelihood of poststroke depression; however, psychiatric history, dysphagia, and poor social support consistently correlate with a higher risk.14,15 Characteristics of a patient’s stroke, such as lesion volume and the ability to perform activities of daily living, are also risk factors. Identifying depression among patients who recently had a stroke is sometimes difficult due to a plethora of confounding factors. Patients may not communicate well due to aphasia, while strokes in other locations may result in an altered affect. Depending on the stroke location, patients may also suffer anosognosia (a lack of awareness of their deficits), which may impair their ability to learn and use adaptive strategies and equipment. An additional confounder is the significant overlap between depressive symptoms and those seen in the setting of a major medical event or hospitalization (decreased appetite, fatigue, etc). The prevalence of depression peaks approximately 3 to 6 months after stroke, with symptoms lasting 9 to 12 months on average, although many patients experience symptoms significantly longer.14 Because symptoms can begin within hours to days following a stroke, it is essential that both hospital and outpatient clinicians assess for depression when indicated. Patients with poststroke depression should receive prompt treatment because appropriate treatment correlates with improved rehabilitation, and most patients respond well to antidepressants.16 Early treatment reduces mortality and improves compliance with secondary stroke prevention measures, including pharmacotherapy.17
Anxiety and posttraumatic stress
Anxiety and anxiety-related disorders are additional potential complications following stroke that significantly influence patient outcomes and well-being. The abrupt, unexpected onset of stroke is often frightening to patients and families. The potential for life-altering deficits as well as intense, often invasive, interactions with the health care system does little to assuage patients’ fear. Stroke patients must contend with a change in neurologic function while processing their difficult experiences, and may develop profound fear of a recurrent stroke. As many as 22% of patients have an anxiety disorder 3 months after they have a stroke.18 Phobic disorder is the most prevalent subtype, followed by generalized anxiety disorder. Younger age and previous anxiety or depression place patients at greater risk of developing poststroke anxiety. Patients suffering from poststroke anxiety have a reduced quality of life, are more dependent, and show restricted participation in rehabilitation, all of which culminate in poorer outcomes.
Many patients describe their experiences surrounding their stroke as traumatic, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is increasingly acknowledged as a potential complication for patients with recent stroke.19 PTSD profoundly impacts patient quality of life. Interestingly, most patients who develop poststroke PTSD do not have a history of other psychiatric illness, and it is difficult to predict who may develop PTSD. Relatively little is known regarding optimal treatment strategies for poststroke PTSD, or the efficacy of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapeutic strategies to treat it.
Goals: Improve recovery and quality of life
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are common following a stroke and may manifest in a variety of ways. While some symptoms are a direct consequence of injury to a specific brain region, other symptoms may be a response to loss of independence, disability, experience with the medical system, or fear of recurrent stroke. The onset of psychiatric symptoms can be acute, beginning during hospitalization, or delayed. Understanding the association of psychiatric symptoms with the anatomical location of stroke may assist clinicians in identifying such symptoms. This knowledge informs conversations with patients and their caregivers, who may benefit from understanding that such symptoms are common after stroke. Furthermore, identifying psychiatric complications following stroke may affect rehabilitation. Additional investigation is necessary to find more effective treatment modalities and improve early intervention.
Continue to: Bottom Line
Bottom Line
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are frequently overlooked in patients with recent stroke. These symptoms include delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder, and can be the direct result of injury to neuroanatomical structures or a consequence of the patient’s experience. Prompt treatment can maximize stroke recovery and quality of life.
Related Resources
- Zhang S, Xu M, Liu ZJ, et al. Neuropsychiatric issues after stroke: clinical significance and therapeutic implications. World J Psychiatry. 2020;10(6):125-138. doi:10.5498/wjp. v10.i6.125
- Saha G, Chakraborty K, Pattojoshi A. Management of psychiatric disorders in patients with stroke and traumatic brain injury. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022;64(Suppl 2): S344-S354.
Many patients experience neuropsychiatric symptoms following stroke. There is tremendous variation in the type, severity, and timeline of these symptoms, which have the potential to significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Some symptoms occur as a direct result of ischemic injury to brain structures regulating behavior, executive function, perception, or affect. Other symptoms occur indirectly due to the patient’s often-difficult experiences with the health care system, disrupted routines, or altered poststroke functional abilities. Psychiatric symptoms are not as easily recognized as classic stroke symptoms (such as hemiparesis) and are frequently overlooked, especially in the acute phase. However, these symptoms can negatively influence patients’ interpersonal relationships, rehabilitation, and employment.
Patients and families may not realize certain symptoms are stroke-related and may not discuss them with their clinicians. It is important to ask about and recognize psychiatric symptoms in patients who have experienced a stroke so you can provide optimal education and treatment. In this article, we review the types of psychiatric symptoms associated with strokes in specific brain regions (Table1-10). We also describe symptoms that do not appear directly related to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct, including delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress.

Symptoms associated with stroke in specific regions
Frontal lobe strokes
The frontal lobes are the largest lobes in the brain, and damage to areas within these lobes can cause behavioral and personality changes. Lesions in the lateral frontal cortex can cause aprosodia (difficulty expressing or comprehending variations in tone of voice), which can lead to communication errors. Lateral frontal cortex injury can cause executive dysfunction and a lack of empathy1 as well as trouble with attention, planning, and self-regulation that may affect daily functioning. Strokes affecting the superior and inferior mesial cortices may result in apathy, lack of motivation, altered self-regulation, altered emotional processing, and disinhibition. Patients who experience a basal forebrain stroke may exhibit confabulation, reduced motivation, and delusions such as Capgras syndrome (the belief that a person or place has been replaced by an exact copy) and reduplicative paramnesia (the belief that a place has been either moved, duplicated, or exists in 2 places simultaneously). Strokes involving the orbital cortex can be associated with personality changes, impulsivity, poor social judgment, reduced empathy, altered self-regulation, lack of goal-directed behavior, and environmental dependency.
Some strokes may occur primarily in the subcortical white matter within the frontal lobes. Symptoms may be due to a single stroke with sudden onset, or due to repeated ischemic events that accumulate over time, as seen with microvascular disease. In the case of microvascular disease, the onset of symptoms may be insidious and the course progressive. Infarcts in the subcortical area can also cause personality changes (though typically more subtle when compared to orbitofrontal strokes), reduced emotions, poor empathy, and irritability.1 Patients may lack insight into some of or all these symptoms following a frontal lobe infarct, which makes it critical to gather collateral information from the patient’s friends or family.
Parietal lobe strokes
Symptomatology from parietal strokes depends on whether the stroke affects the dominant or nondominant hemisphere. Dominant parietal lesions cause language deficits, and psychiatric symptoms may be difficult to elucidate due to the patient’s inability to communicate.2 On the other hand, patients with nondominant parietal stroke may have neglect of, or inattention to, the opposite (typically left) side.3 This often manifests as a reluctance to use the affected limb or limbs, in some cases despite a lack of true weakness or motor dysfunction. In addition, patients may also have visual and/or tactile inattention towards the affected side, despite a lack of gross visual or sensory impairment.2 In rare cases, a patient’s stroke may be misdiagnosed as a functional disorder due to the perceived unwillingness to use a neurologically intact limb. In severe cases, patients may not recognize an affected extremity as their own. Patients are also frequently unaware of deficits affecting their nondominant side and may argue with those attempting to explain their deficit. Anosodiaphoria—an abnormal lack of concern regarding their deficits—may also be observed. Additionally, aprosodia, flat affect, and personality changes may result from strokes affecting the nondominant hemisphere, which can impact the patient’s relationships and social functioning.3
Occipital lobe strokes
While negative or loss-of-function symptomatology is one of the hallmarks of stroke, occipital lobe infarcts can pose an exception. Although vision loss is the most common symptom with occipital lobe strokes, some patients experience visual hallucinations that may occur acutely or subacutely. In the acute phase, patients may report hallucinations of varied description,4 including poorly formed areas of color, scotomas, metamorphopsia (visual distortion in which straight lines appear curved), more complex and formed hallucinations and/or palinoptic images (images or brief scenes that continue to be perceived after looking away). These hallucinations, often referred to as release phenomena or release hallucinations, are thought to result from disinhibition of the visual cortex, which then fires spontaneously.
Hallucinations are associated with either infarction or hemorrhage in the posterior cerebral artery territory. In some cases, the hallucinations may take on a formed, complex appearance, and Charles Bonnet syndrome (visual hallucinations in the setting of vision loss, with insight into the hallucinations) has been identified in a small portion of patients.5
Continue to: The duration of these...
The duration of these hallucinations varies. Some patients describe very short periods of the disturbance, lasting minutes to hours and corresponding with the onset of their stroke. Others experience prolonged hallucinations, which frequently evolve into formed, complex images, lasting from days to months.6 In the setting of cortical stroke, patients may be at risk for seizures, which could manifest as visual hallucinations. It is essential to ensure that epileptic causes of hallucinations have been ruled out, because seizures may require treatment and other precautions.
Other stroke locations
Strokes in other locations also can result in psychiatric or behavioral symptoms. Acute stroke in the subcortical midbrain or thalamus may result in peduncular hallucinosis, a syndrome of vivid visual hallucinations.7 The midbrain (most commonly the reticular formation) is usually affected; however, certain lesions of the thalamus may also cause peduncular hallucinosis. This phenomenon is theorized to be due to an increase in serotonin activity relative to acetylcholine and is often accompanied by drowsiness.
The subthalamic nucleus is most frequently associated with disordered movement such as hemiballismus, but also causes disturbances in mood and behavior, including hyperphagia and personality changes.8 Irritability, aggressiveness, disinhibition, anxiety, and obscene speech may also be seen with lesions of the subthalamic nucleus.
Finally, the caudate nucleus may cause alterations in executive functioning and behavior.9 A stroke in the dorsolateral caudate may cause abulia and psychic akinesia, decreased problem-solving ability, reduced abstract thinking, and/or diminished spontaneity, whereas an infarct in the ventromedial region of the nucleus may cause disinhibition, disorganization, impulsiveness, and, in severe cases, affective symptoms with psychosis.10 Strokes in any of these areas are at risk for being misdiagnosed because patients may not have a hemiparesis, and isolated positive or psychiatric symptoms may not be recognized as stroke.
Symptoms not related to stroke location
Delirium and psychosis
Following a stroke, a patient may exhibit neuropsychiatric symptoms that do not appear to relate directly to the anatomical structures affected by the infarct. In the acute phase, factors such as older age and medical complications (including infection, metabolic derangement, and lack of sleep due to frequent neurologic checks) create a high risk of delirium.11 Differentiating delirium from alterations in mental status due to seizure, cerebral edema, or other medical complications is essential, and delirium precautions should be exercised to the greatest extent possible. Other neuropsychiatric symptoms may manifest following hospitalization.
Continue to: Poststroke psychosis...
Poststroke psychosis often presents subacutely. Among these patients, the most common psychosis is delusion disorder, followed by schizophrenia-like psychosis and mood disorder with psychotic features.12 Some evidence suggests antipsychotics may be highly effective for many of these patients.12 Poststroke psychosis does appear to correlate somewhat with nondominant hemisphere lesions, including the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and/or caudate nucleus. Because high mortality and poor functional outcomes have been associated with poststroke psychosis, early intervention is essential.
Depression
Depression is a common problem following stroke, affecting approximately 35% of stroke patients.13 In addition to impairing quality of life, depression negatively impacts rehabilitation and increases caregiver burden. There is significant variability regarding risk factors that increases the likelihood of poststroke depression; however, psychiatric history, dysphagia, and poor social support consistently correlate with a higher risk.14,15 Characteristics of a patient’s stroke, such as lesion volume and the ability to perform activities of daily living, are also risk factors. Identifying depression among patients who recently had a stroke is sometimes difficult due to a plethora of confounding factors. Patients may not communicate well due to aphasia, while strokes in other locations may result in an altered affect. Depending on the stroke location, patients may also suffer anosognosia (a lack of awareness of their deficits), which may impair their ability to learn and use adaptive strategies and equipment. An additional confounder is the significant overlap between depressive symptoms and those seen in the setting of a major medical event or hospitalization (decreased appetite, fatigue, etc). The prevalence of depression peaks approximately 3 to 6 months after stroke, with symptoms lasting 9 to 12 months on average, although many patients experience symptoms significantly longer.14 Because symptoms can begin within hours to days following a stroke, it is essential that both hospital and outpatient clinicians assess for depression when indicated. Patients with poststroke depression should receive prompt treatment because appropriate treatment correlates with improved rehabilitation, and most patients respond well to antidepressants.16 Early treatment reduces mortality and improves compliance with secondary stroke prevention measures, including pharmacotherapy.17
Anxiety and posttraumatic stress
Anxiety and anxiety-related disorders are additional potential complications following stroke that significantly influence patient outcomes and well-being. The abrupt, unexpected onset of stroke is often frightening to patients and families. The potential for life-altering deficits as well as intense, often invasive, interactions with the health care system does little to assuage patients’ fear. Stroke patients must contend with a change in neurologic function while processing their difficult experiences, and may develop profound fear of a recurrent stroke. As many as 22% of patients have an anxiety disorder 3 months after they have a stroke.18 Phobic disorder is the most prevalent subtype, followed by generalized anxiety disorder. Younger age and previous anxiety or depression place patients at greater risk of developing poststroke anxiety. Patients suffering from poststroke anxiety have a reduced quality of life, are more dependent, and show restricted participation in rehabilitation, all of which culminate in poorer outcomes.
Many patients describe their experiences surrounding their stroke as traumatic, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is increasingly acknowledged as a potential complication for patients with recent stroke.19 PTSD profoundly impacts patient quality of life. Interestingly, most patients who develop poststroke PTSD do not have a history of other psychiatric illness, and it is difficult to predict who may develop PTSD. Relatively little is known regarding optimal treatment strategies for poststroke PTSD, or the efficacy of pharmacotherapy and psychotherapeutic strategies to treat it.
Goals: Improve recovery and quality of life
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are common following a stroke and may manifest in a variety of ways. While some symptoms are a direct consequence of injury to a specific brain region, other symptoms may be a response to loss of independence, disability, experience with the medical system, or fear of recurrent stroke. The onset of psychiatric symptoms can be acute, beginning during hospitalization, or delayed. Understanding the association of psychiatric symptoms with the anatomical location of stroke may assist clinicians in identifying such symptoms. This knowledge informs conversations with patients and their caregivers, who may benefit from understanding that such symptoms are common after stroke. Furthermore, identifying psychiatric complications following stroke may affect rehabilitation. Additional investigation is necessary to find more effective treatment modalities and improve early intervention.
Continue to: Bottom Line
Bottom Line
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are frequently overlooked in patients with recent stroke. These symptoms include delirium, psychosis, depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder, and can be the direct result of injury to neuroanatomical structures or a consequence of the patient’s experience. Prompt treatment can maximize stroke recovery and quality of life.
Related Resources
- Zhang S, Xu M, Liu ZJ, et al. Neuropsychiatric issues after stroke: clinical significance and therapeutic implications. World J Psychiatry. 2020;10(6):125-138. doi:10.5498/wjp. v10.i6.125
- Saha G, Chakraborty K, Pattojoshi A. Management of psychiatric disorders in patients with stroke and traumatic brain injury. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022;64(Suppl 2): S344-S354.
1. Eslinger PJ, Reichwein RK. Frontal lobe stroke syndromes. In: Caplan LR, van Gijn J, eds. Stroke Syndromes. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; 2012:232-241.
2. Critchley M, Russell WR, Zangwill OL. Discussion on parietal lobe syndromes. Proc R Soc Med. 1951;44(4):337-346.
3. Hier DB, Mondlock J, Caplan LR. Behavioral abnormalities after right hemisphere stroke. Neurology. 1983;33(3):337-344.
4. Brust JC, Behrens MM. “Release hallucinations” as the major symptom of posterior cerebral artery occlusion: a report of 2 cases. Ann Neurol. 1977;2(5):432-436.
5. Kumral E, Uluakay A, Donmez A. Complex visual hallucinations following stroke: epileptic origin or a deafferentiation phenomenon? Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis & Stroke. 2014;1(1):1005.
6. Lee JS, Ko KH, Oh JH, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome after occipital infarction. J Neurosonol Neuroimag. 2018;10(2):154-157.
7. Young JB. Peduncular hallucinosis. In: Aminoff MJ, Daroff RB, eds. Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2014:848.
8. Etemadifar M, Abtahi SH, Abtahi SM, et al. Hemiballismus, hyperphagia, and behavioral changes following subthalamic infarct. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:768580. doi:10.1155/2012/768580
9. Kumral E, Evyapan D, Balkir K. Acute caudate vascular lesions. Stroke. 1999;30(1):100-108.
10. Wang PY. Neurobehavioral changes following caudate infarct: a case report with literature review. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1991;47(3):199-203.
11. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-33.
12. Stangeland H, Orgeta V, Bell V. Poststroke psychosis: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(8):879-885.
13. Lenzi GL, Altieri M, Maestrini I. Post-stroke depression. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164(10):837-840.
14. Whyte EM, Mulsant BH. Post stroke depression: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and biological treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52(3):253-264.
15. Pritchard KT, Hreha KP, Hong I. Dysphagia associated with risk of depressive symptoms among stroke survivors after discharge from a cluster of inpatient rehabilitation facilities. Swallowing Rehabil. 2020;3(1):33-44.
16. Wiart L, Petit H, Joseph PA, et al. Fluoxetine in early poststroke depression: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2000;31(8):1829-1832.
17. Jorge RE, Robinson RG, Arndt S, et al. Mortality and poststroke depression: a placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(10):1823-1829.
18. Chun HY, Whiteley WN, Dennis MS, et al. Anxiety after stroke: the importance of subtyping. Stroke. 2018;49(3):556-564.
19. Garton AL, Sisti JA, Gupta VP, et al. Poststroke post-traumatic stress disorder: a review. Stroke. 2017;48(2):507-512.
1. Eslinger PJ, Reichwein RK. Frontal lobe stroke syndromes. In: Caplan LR, van Gijn J, eds. Stroke Syndromes. 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press; 2012:232-241.
2. Critchley M, Russell WR, Zangwill OL. Discussion on parietal lobe syndromes. Proc R Soc Med. 1951;44(4):337-346.
3. Hier DB, Mondlock J, Caplan LR. Behavioral abnormalities after right hemisphere stroke. Neurology. 1983;33(3):337-344.
4. Brust JC, Behrens MM. “Release hallucinations” as the major symptom of posterior cerebral artery occlusion: a report of 2 cases. Ann Neurol. 1977;2(5):432-436.
5. Kumral E, Uluakay A, Donmez A. Complex visual hallucinations following stroke: epileptic origin or a deafferentiation phenomenon? Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis & Stroke. 2014;1(1):1005.
6. Lee JS, Ko KH, Oh JH, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome after occipital infarction. J Neurosonol Neuroimag. 2018;10(2):154-157.
7. Young JB. Peduncular hallucinosis. In: Aminoff MJ, Daroff RB, eds. Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2014:848.
8. Etemadifar M, Abtahi SH, Abtahi SM, et al. Hemiballismus, hyperphagia, and behavioral changes following subthalamic infarct. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:768580. doi:10.1155/2012/768580
9. Kumral E, Evyapan D, Balkir K. Acute caudate vascular lesions. Stroke. 1999;30(1):100-108.
10. Wang PY. Neurobehavioral changes following caudate infarct: a case report with literature review. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1991;47(3):199-203.
11. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-33.
12. Stangeland H, Orgeta V, Bell V. Poststroke psychosis: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(8):879-885.
13. Lenzi GL, Altieri M, Maestrini I. Post-stroke depression. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164(10):837-840.
14. Whyte EM, Mulsant BH. Post stroke depression: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and biological treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;52(3):253-264.
15. Pritchard KT, Hreha KP, Hong I. Dysphagia associated with risk of depressive symptoms among stroke survivors after discharge from a cluster of inpatient rehabilitation facilities. Swallowing Rehabil. 2020;3(1):33-44.
16. Wiart L, Petit H, Joseph PA, et al. Fluoxetine in early poststroke depression: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Stroke. 2000;31(8):1829-1832.
17. Jorge RE, Robinson RG, Arndt S, et al. Mortality and poststroke depression: a placebo-controlled trial of antidepressants. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(10):1823-1829.
18. Chun HY, Whiteley WN, Dennis MS, et al. Anxiety after stroke: the importance of subtyping. Stroke. 2018;49(3):556-564.
19. Garton AL, Sisti JA, Gupta VP, et al. Poststroke post-traumatic stress disorder: a review. Stroke. 2017;48(2):507-512.
Laboratory monitoring for patients on buprenorphine: 10 questions
The opioid use disorder (OUD) epidemic is a major public health crisis in the United States.1 Naltrexone, methadone, and buprenorphine are first-line therapies for OUD and have high success rates.2 While studies have shown that naltrexone is effective, patients must achieve opioid detoxification and maintain 7 to 10 days of total abstinence to avoid a precipitated opioid withdrawal before it can be prescribed.3 Methadone does not require detoxification or a period of complete abstinence, but must be prescribed in special clinics and requires daily observed dosing for the first 90 days,4 though these requirements have been relaxed during the COVID-19 pandemic. In contrast, buprenorphine (with or without naloxone) can be used in office-based settings, which significantly improves the accessibility and availability of treatment for patients with OUD. Clinician knowledge and comfort prescribing buprenorphine are limiting factors to treatment.5 Increasing the number of clinicians proficient with buprenorphine management can improve access to effective treatment and recovery services, which is critical for patients with OUD.
Multiple resources are available for clinicians to learn how to prescribe buprenorphine, but clear guidance on laboratory testing for patients receiving buprenorphine is limited. To safely and effectively prescribe buprenorphine, clinicians need to understand its pharmacology (Box 16-9) and how laboratory testing influences treatment. In an effort to increase clinician knowledge of and proficiency with buprenorphine, this article answers 10 common questions about laboratory monitoring of patients receiving this medication.
Box 1
For patients with opioid use disorder, buprenorphine is indicated for opioid detoxification and maintenance. Oral formulations of buprenorphine (including tablets and buccal films) have long durations of action, and when dosed daily can prevent opioid withdrawal for at least 48 hours.6 The recommended formulation is a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, because this formulation is associated with a lower risk of misuse and diversion compared to formulations containing only buprenorphine.7 However, buprenorphine alone can be effective in patients who experience adverse effects from or are unable to tolerate the combination buprenorphine/naloxone formulation.7 Despite the addition of naloxone, buprenorphine prescriptions may still be misused and diverted, so close monitoring is necessary.
Buprenorphine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system (CYP) (primarily CYP3A4) to its active metabolite, norbuprenorphine, both of which are primarily excreted in feces.8 However, small quantities of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine are excreted in the urine,9 which makes urine specimen the best choice to monitor buprenorphine use for therapeutic purposes.
1. Why is laboratory monitoring important?
Proper laboratory monitoring discourages illicit substance use, encourages medication adherence, and influences treatment modifications. Patient self-reporting on medication compliance may be inaccurate or unreliable.10 Patients who relapse or use other illicit substances may also be reluctant to disclose their substance use.11
On the other hand, laboratory tests are objective markers of treatment outcome and adherence, and can verify a patient’s self-report.12 When used appropriately, laboratory monitoring can be therapeutic. It holds patients accountable, especially when used in conjunction with contingency management or other behavioral therapies.13 Laboratory monitoring is the most reliable method of determining if patients are abstaining from opioids and other illicit substances, or if the treatment plan requires revision.
2. Which tests should I order?
When initiating or maintaining a patient on buprenorphine, order a general urine drug screen (UDS), urine opioid screen (availability varies by institution), urine creatinine levels, urine buprenorphine/norbuprenorphine/naloxone/creatinine levels, urine alcohol metabolite levels, and a urine general toxicology test. It is also recommended to obtain a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) before starting buprenorphine,14,15 and to monitor CMP values at least once annually following treatment. Patients with a history of IV drug use or other high-risk factors should also be screened for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV.14,15
A general UDS can determine if opiates, amphetamines, cocaine, marijuana, or other common illicit substances are present to identify additional substance use. The proficiency of a general UDS may vary depending on the panels used at the respective institution. Some clinics use point-of-care UDS as part of their clinical management; these tests are inexpensive and provide immediate results.16 A basic UDS typically does not detect synthetic opioids due to the specificity of conventional immunoassays. As a result, specific tests for opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, fentanyl, and methadone should also be considered, depending on their availability. Though buprenorphine treatment may trigger a positive opiate or other opioid screen,17 buprenorphine adherence should be confirmed using several urine tests, including creatinine, buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and naloxone urine levels.
In addition to screening for illicit substances and buprenorphine adherence, it is important to also screen for alcohol. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is highly comorbid with OUD,18 and is associated with worse OUD treatment outcomes.19 Alcohol use may also affect liver function necessary for buprenorphine metabolism,8 so urine alcohol metabolites such as ethyl glucuronide and ethyl sulfate, serum transaminases, and gamma-glutamyl transferase should also be obtained.
Continue to: How frequently should patients be tested?
3. How frequently should patients be tested?
As part of the initial assessment, it is recommended to order CMP, UDS, and urine general toxicology.14 If indicated, specific laboratory tests such as specific opioid and alcohol metabolites screens can be ordered. After starting buprenorphine, the frequency of monitoring urine laboratory tests—including UDS, general drug toxicology, buprenorphine/norbuprenorphine/naloxone/creatinine, and alcohol and its metabolites—depends on a variety of factors, including a patient’s treatment response and stability as well as availability and cost of the tests. Ultimately, the frequency of laboratory monitoring should be determined on a patient-by-patient basis and clinicians should use their judgment.
The American Society of Addiction Medicine suggests testing more frequently earlier in the course of treatment (eg, weekly or biweekly), then spacing it out over time (eg, monthly or quarterly) as the patient’s recovery progresses.14,15 To conserve resources and reduce spending, some clinicians and guidelines recommend random monitoring as opposed to monitoring at every follow-up visit (eg, once out of every 3 to 5 visits, on average), which allows for longer intervals between testing while ensuring consistency with medication and abstinence from illicit substances.15,16 We suggest screening every 2 weeks for the first month, then spacing out to monthly and quarterly as patients demonstrate stability, with random screening as indicated. Monitoring of liver function should be done at least once annually.
4. How should urine buprenorphine and other results be interpreted?
There are several issues to consider when interpreting laboratory results. The clinician needs to know what to expect in the sample, and what approximate levels should be detected. To check treatment adherence, laboratory data should include stable urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels and negative urine screening for other illicit substances.14,15 While urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels have great interindividual variability due to genetic differences in hepatic metabolism, unusually high levels of buprenorphine (≥700 ng/mL) without norbuprenorphine suggests “urine spiking,” where patients put buprenorphine directly into their urine sample.20,21 Abnormally low or undetectable levels raise concern for medication nonadherence or diversion.
Though urine buprenorphine levels do not reliably correlate with dose, because there is typically not much intraindividual variability, patients should have relatively stable levels on each screen once a maintenance dose has been established.22 Furthermore, the buprenorphine-to-norbuprenorphine ratio (ie, “the metabolic ratio”) typically ranges from 1:2 to 1:4 across all individuals,20,21,23 regardless of dose or metabolic rate. Urine naloxone levels, which typically are included in commercial urine buprenorphine laboratory panels, also may aid in identifying tampered urine specimens when buprenorphine-to-norbuprenorphine ratios are abnormal or inconsistent with an individual’s prior ratio. Naloxone is typically (but not always) poorly absorbed and minimally detected in urine specimens.20 A high level of naloxone coupled with unusually high buprenorphine levels, particularly in the absence of norbuprenorphine in the urine, may indicate urine spiking.20,21,23
Urine creatinine is used to establish the reliability of the specimen. When urine creatinine concentration is <20 mg/dL, the concentration of most substances typically falls to subthreshold levels of detection.24 If a UDS is negative and the urine has a creatinine concentration <20 mg/dL, the patient should provide a new sample, because the urine was likely too diluted to detect any substances.
Continue to: The presence of alcohol...
The presence of alcohol metabolites can alert the clinician to recent alcohol use and possible AUD, which should be assessed and treated if indicated.
Liver enzymes should be normal or unchanged with short- and long-term buprenorphine use when taken as prescribed.25,26 However, acute liver injury may occur if patients inject buprenorphine intravenously, especially in those with underlying hepatitis C.25
5. What can cause a false negative result on UDS?
Laboratory monitoring may occasionally yield false negative drug screens. For urine buprenorphine levels, false negatives may occur in patients who are “rapid metabolizers,” infrequent or as-needed usage of the medication, patient mix-up, or laboratory error.27 For other substances, a false negative result may occur if the patient used the substance(s) outside the window of detection. The most common causes of false negative results, however, are overly diluted urine samples (eg, due to rapid water ingestion), or the use of an inappropriate test to measure a specific opioid or substance.27
Many laboratories use conventional immunoassays with morphine antibodies that react with various opioid substrates to determine the presence of a specific opioid. Some opioids—particularly synthetics such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, fentanyl, buprenorphine, and methadone—have poor cross-reactivity with the morphine antibody due to their distinct chemical structures, so standard immunoassays used to detect opioids may result in a false negative result.28 In such situations, a discussion with a clinical pathologist familiar with the laboratory detection method can help ensure proper testing. Additional tests for specific opioids should be ordered to more specifically target substances prone to false negative results.27
6. What can cause a false positive result on UDS?
The cross-reactivity of the morphine substrate may also result in a false positive result.28 Other over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medications that have cross-reactivity with the morphine antibody include dextromethorphan, verapamil, quinine, fluoroquinolones, and rifampin, which can normally be found in urine 2 to 3 days after consumption.17,27 Poppy seeds have long been known to result in positive opiate screens on urine testing, particularly when laboratories use lower cutoff values (eg, 300 ng/mL), so advise patients to avoid consuming poppy seeds.29
Continue to: For other drugs of abuse...
For other drugs of abuse, false positives are typically caused by cross-reactivity with other prescription or OTC medications. Numerous substances cross-react with amphetamines and produce false positive results on amphetamine immunoassays, including amantadine, bupropion, ephedrine, labetalol, phentermine, pseudoephedrine, ranitidine, selegiline, and trazodone.27 Sertraline and efavirenz are known to produce false positive results on benzodiazepine UDS, and ibuprofen, naproxen, and efavirenz can produce false positive results for cannabinoids.27
7. How do I communicate the results to patients?
Effectively communicating test results to patients is just as important as the results themselves. A trusting, therapeutic alliance between patient and clinician is highly predictive of successful treatment,30 and how the clinician communicates affects the strength of this collaboration. A principle of addiction treatment is the use of neutral language when discussing laboratory results.31,32 To avoid unintentional shaming or moral judgment, use words such as “positive” or “negative” rather than stigmatizing terms such as “clean” or “dirty.”33
Additionally, make it clear that laboratory findings are not used to punish patients, but rather to improve treatment.34 Reassuring the patient that a positive screen will not result in withdrawal of care encourages a working relationship.14 All patients who receive buprenorphine treatment should be informed that collecting a UDS is the standard of care used to monitor their progress. You might want to compare using UDS in patients with OUD to monitoring HbA1c levels in patients with diabetes as an example to demonstrate how laboratory values inform treatment.35,36
Before reporting the results, a helpful strategy to maintain the therapeutic alliance in the face of a positive UDS is to ask the patient what they expect their UDS to show. When the patient has been reassured that treatment will not be withdrawn due to a positive result, they may be more likely to fully disclose substance use. This allows them the opportunity to self-disclose rather than be “called out” by the clinician.35
8. What happens when a patient tests positive for drugs of abuse?
If a patient tests positive for opioids or other drugs of abuse, convey this information to them, ideally by asking them what they expect to see on laboratory findings. Patients may have “slip ups” or relapses, or use certain prescription medications for medical reasons with the intention of establishing abstinence. It is essential to convey laboratory findings in a nonjudgmental tone while maintaining a supportive stance with clear boundaries.
Continue to: Though addiction specialists...
Though addiction specialists often advise complete abstinence from all substances, including alcohol, cannabis, and tobacco, the harm-reduction model emphasizes “meeting patients where they are” in terms of continued substance use.37 If a patient can reduce their substance use or abstain from some substances while continuing others, these accomplishments should be acknowledged.
For patients who continue to test positive for illicit substances (>3 instances) without a clear explanation, schedule an appointment to re-educate them about buprenorphine treatment and reassess the patient’s treatment goals. Consider changing the current treatment plan, such as by having more frequent follow-ups, increasing the dose of the buprenorphine for patients whose cravings are not sufficiently suppressed, switching to another medication such as methadone or naltrexone, or referring the patient to a higher level of care, such as intensive outpatient or residential treatment.
9. What should I do if the results indicate abnormal levels of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and naloxone?
When urine buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, or naloxone levels appear low or the results indicate a likely “spiking,” clarify whether the sample tampering is due to poor adherence or diversion. Similar to dealing with a positive result for substances of abuse, ask the patient what they expect to find in their urine, and discuss the results in a nonjudgmental manner. Patients who admit to difficulty following their medication regimen may require additional psychoeducation and motivational interviewing to identify and address barriers. Strategies to improve adherence include setting an alarm, involving the family, using a pillbox, or simplifying the regimen.38 A long-acting injectable form of buprenorphine is also available.
If you suspect diversion, refer to your clinic’s policy and use other clinical management skills, such as increasing the frequency of visits, random pill counts, and supervised medication administration in the clinic.39 If diversion occurs repetitively and the patient is not appropriate for or benefiting from buprenorphine treatment, it may make sense to terminate treatment and consider other treatment options (such as methadone or residential treatment).39
10. What should I do if a patient disagrees with laboratory findings?
It is common for patients to disagree with laboratory results. Maintaining an attitude of neutrality and allowing the patient to speak and provide explanations is necessary to ensure they feel heard. Explanations patients frequently provide include passive exposure (“I was around someone who was using it”) or accidental ingestion, when a patient reports taking a medication they were not aware was a substance of concern. In a calm and nonjudgmental manner, provide education on what leads to a positive drug screen, including the possibility of false positive findings.
Continue to: Because a screening test...
Because a screening test has high sensitivity and low specificity, false positives may occur.17,27 Therefore, when a result is in dispute, the use of a high-specificity confirmatory test is often needed (many laboratories have reflex confirmatory testing). However, in the case of diluted urine (urine creatinine concentrations <20 mg/dL), patients should be told the findings are physiologically implausible, and a new urine sample should be obtained.24
Goals of laboratory monitoring
Laboratory monitoring, including UDS and urine buprenorphine levels, is a mainstay of treatment for patients with OUD. The increased use of telehealth has affected how laboratory testing is conducted (Box 240,41). The goal of laboratory testing is to influence treatment and improve patient outcomes. Clinical data such as clinician assessment, patient self-reporting, and collateral information provide essential details for patient management. However, laboratory monitoring is often the most reliable and objective source by which to influence treatment.
Box 2
While delivering therapy via telehealth has been shown to decrease the stigma that surrounds treatment, reduce no-show rates, increase retention in care, improve treatment access for patients who have difficulty commuting, and allow for continuity of outpatient treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic, there are also challenges.40,41 Inducing patients on buprenorphine via telehealth, as well as managing complex treatment cases or repeated failed urine drug screen tests, can be especially challenging. However, treatment standards should be followed as much as possible, and laboratory monitoring as clinically indicated should still be used to improve treatment outcomes.
If needed, patients may be directed to community labs for urine screening and should have results sent to their clinicians prior to the telehealth visit. Complex treatment cases (eg, repeat positive opioid screens, or negative urine buprenorphine screens with comorbid psychiatric conditions) should be handled on an individual basis and in-person appointments may be needed. Video assessment is always preferable to telephone. For patients who are unable to use video and have difficulty maintaining negative drug screens, an in-person visit should be requested.
An increased understanding of recommended laboratory monitoring practices may improve your comfort with OUD treatment and motivate more clinicians to offer buprenorphine, a life-saving and disease-modifying treatment for OUD. Doing so would increase access to OUD treatment for patients to reduce the individual and public health risks associated with untreated OUD.
Bottom Line
Laboratory monitoring, particularly urine drug screens and urine buprenorphine levels, is the most reliable source of information in the treatment of patients with opioid use disorder (OUD). An increased understanding of monitoring practices may improve a clinician’s willingness to offer buprenorphine as an option for therapy and their ability to properly treat patients with OUD.
Related Resources
- Li X, Moore S, Olson C. Urine drug tests: how to make the most of them. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(8):10-18,20.
- Moreno JL, Johnson JL, Peckham AM. Sublingual buprenorphine plus buprenorphine XR for opioid use disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(6):39-42,49. doi:10.12788/cp.0244
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Bupropion • Wellbutrin, Zyban
Efavirenz • Sustiva
Fentanyl • Actiq
Hydrocodone • Hysingla
Hydromorphone • Dilaudid
Methadone • Methadose
Naloxone • Evzio
Naltrexone • Vivitrol
Oxycodone • Oxycontin
Oxymorphone • Opana
Phentermine • Ionamin
Quinine • Qualaquin
Ranitidine • Zantac
Rifampin • Rifadin
Selegiline • Eldepryl
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Oleptro
Verapamil • Verelan
1. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: results from the 2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP19-5068, NSDUH Series H-54. May 2019. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/
2. Volkow ND, Frieden TR, Hyde PS, et al. Medication-assisted therapies—tackling the opioid-overdose epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2063-2066. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1402780
3. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32812-X
4. Sharma A, Kelly SM, Mitchell SG, et al. Update on barriers to pharmacotherapy for opioid use disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2017;19(6):35. doi:10.1007/s11920-017-0783-9
5. DeFlavio JR, Rolin SA, Nordstrom BR, et al. Analysis of barriers to adoption of buprenorphine maintenance therapy by family physicians. Rural Remote Health. 2015;15:3019. doi:10.22605/rrh3019
6. Kuhlman JJ Jr, Lalani S, Magluiolo J Jr, et al. Human pharmacokinetics of intravenous, sublingual, and buccal buprenorphine. J Anal Toxicol. 1996;20(6):369-378.
7. Fudala PJ, Bridge TP, Herbert S, et al. Office-based treatment of opiate addiction with a sublingual-tablet formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(10):949-958. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022164
8. Brown SM, Holtzman M, Kim T, et al. Buprenorphine metabolites, buprenorphine-3-glucuronide and norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide, are biologically active. Anesthesiology. 2011;115(6):1251-1260. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e318238fea0
9. Cone EJ, Gorodetzky CW, Yousefnejad D, et al. The metabolism and excretion of buprenorphine in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1984;12(5):577-581.
10. Stirratt MJ, Dunbar-Jacob J, Crane HM, et al. Self-report measures of medication adherence behavior: recommendations on optimal use. Transl Behav Med. 2015;5(4):470-482. doi:10.1007/s13142-015-0315-2
11. Del Boca FK, Noll JA. Truth or consequences: the validity of self-report data in health services research on addictions. Addiction. 2000;95 Suppl 3:S347-S360. doi:10.1080/09652140020004278
12. Preston KL, Silverman K, Schuster CR, et al. Comparison of self-reported drug use with quantitative and qualitative urinalysis for assessment of drug use in treatment studies. NIDA Res Monogr. 1997;167:130-145.
13. Knezevic NN, Khan OM, Beiranvand A, et al. Repeated quantitative urine toxicology analysis may improve chronic pain patient compliance with opioid therapy. Pain Physician. 2017;20(2S):S135-S145. doi:10.36076/ppj.2017.s145
14. Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. 2015;9(5):358-367.
15. The ASAM national practice guideline for the treatment of opioid use disorder: 2020 focused update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S Suppl 1):1-91. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000633
16. McDonell MG, Graves MC, West II, et al. Utility of point-of-care urine drug tests in the treatment of primary care patients with drug use disorders. J Addict Med. 2016;10(3):196-201. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000220
17. Algren DA, Christian MR. Buyer beware: pitfalls in toxicology laboratory testing. Mo Med. 2015;112(3):206-210.
18. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2010.05.008
19. Stapleton RD, Comiskey CM. Alcohol usage and associated treatment outcomes for opiate users entering treatment in Ireland. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;107(1):56-61. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.09.007
20. Warrington JS, Warrington GS, Francis-Fath S, et al. Urinary buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine and naloxone concentrations and ratios: review and potential clinical implications. J Addict Med. 2020;14(6):e344-e349. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000676
21. Donroe JH, Holt SR, O’Connor PG, et al. Interpreting quantitative urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels in office-based clinical practice. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:46-51. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.07.040
22. Bai SA, Xiang Q, Finn A. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of single- and multiple-dose buprenorphine buccal film in healthy volunteers. Clin Ther. 2016;38(2):358-369. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.12.016
23. Suzuki J, Zinser J, Issa M, et al. Quantitative testing of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine to identify urine sample spiking during office-based opioid treatment. Subst Abus. 2017;38(4):504-507. doi:10.1080/08897077.2017.1356796
24. Gowans EM, Fraser CG. Biological variation of serum and urine creatinine and creatinine clearance: ramifications for interpretation of results and patient care. Ann Clin Biochem. 1988;25( Pt 3):259-263. doi:10.1177/000456328802500312
25. Saxon AJ, Ling W, Hillhouse M, et al. Buprenorphine/naloxone and methadone effects on laboratory indices of liver health: a randomized trial. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013;128(1-2):71-76. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.08.002
26. Fareed A, Eilender P, Ketchen B, et al. Factors affecting noncompliance with buprenorphine maintenance treatment. J Addict Med. 2014;8(5):345-350. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000057
27. Moeller KE, Lee KC, Kissack JC. Urine drug screening: practical guide for clinicians. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83(1):66-76. doi:10.4065/83.1.66
28. Keary CJ, Wang Y, Moran JR, et al. Toxicologic testing for opiates: understanding false-positive and false-negative test results. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2012;14(4).PCC.12f01371 doi:10.4088/PCC.12f01371
29. Zebelman AM, Troyer BL, Randall GL, et al. Detection of morphine and codeine following consumption of poppy seeds. J Anal Toxicol. 1987;11(3):131-132. doi:10.1093/jat/11.3.131
30. Meier PS, Barrowclough C, Donmall MC. The role of the therapeutic alliance in the treatment of substance misuse: a critical review of the literature. Addiction. 2005;100(3):304-316. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00935.x
31. Kelly JF, Saitz R, Wakeman S. Language, substance use disorders, and policy: the need to reach consensus on an “addiction-ary.” Alcohol Treat Q. 2016;34(1):116-123. doi:10.1080/07347324.2016.1113103
32. Broyles LM, Binswanger IA, Jenkins JA, et al. Confronting inadvertent stigma and pejorative language in addiction scholarship: a recognition and response. Subst Abus. 2014;35(3):217-221. doi:10.1080/08897077.2014.930372
33. Kelly JF, Wakeman SE, Saitz R. Stop talking ‘dirty’: clinicians, language, and quality of care for the leading cause of preventable death in the United States. Am J Med. 2015;128(1):8-9. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.07.043
34. Jarvis M, Williams J, Hurford M, et al. Appropriate use of drug testing in clinical addiction medicine. J Addict Med. 2017;11(3):163-173. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000323
35. Martin SA, Chiodo LM, Bosse JD, et al. The next stage of buprenorphine care for opioid use disorder. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(9):628-635. doi:10.7326/M18-1652
36. Katz N, Fanciullo GJ. Role of urine toxicology testing in the management of chronic opioid therapy. Clin J Pain. 2002;18(4 Suppl):S76-S82.
37. Klein A. Harm reduction works: evidence and inclusion in drug policy and advocacy. Health Care Anal. 2020;28(4):404-414. doi:10.1007/s10728-020-00406-w
38. Patel MX, David AS. Medication adherence: predictive factors and enhancement strategies. Psychiatry. 2007;6(9):357-361. doi:10.1016/j.mppsy.2007.06.003
39. Lofwall MR, Walsh SL. A review of buprenorphine diversion and misuse: the current evidence base and experiences from around the world. J Addict Med. 2014;8(5):315-326. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000045
40. Wang L, Weiss J, Ryan EB, et al. Telemedicine increases access to buprenorphine initiation during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;124:108272. doi:10.1016/ j.jsat.2020.108272
41. Harris MTH, Lambert AM, Maschke AD, et al. “No home to take methadone to”: experiences with addiction services during the COVID-19 pandemic among survivors of opioid overdose in Boston. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2022;135:108655. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108655
The opioid use disorder (OUD) epidemic is a major public health crisis in the United States.1 Naltrexone, methadone, and buprenorphine are first-line therapies for OUD and have high success rates.2 While studies have shown that naltrexone is effective, patients must achieve opioid detoxification and maintain 7 to 10 days of total abstinence to avoid a precipitated opioid withdrawal before it can be prescribed.3 Methadone does not require detoxification or a period of complete abstinence, but must be prescribed in special clinics and requires daily observed dosing for the first 90 days,4 though these requirements have been relaxed during the COVID-19 pandemic. In contrast, buprenorphine (with or without naloxone) can be used in office-based settings, which significantly improves the accessibility and availability of treatment for patients with OUD. Clinician knowledge and comfort prescribing buprenorphine are limiting factors to treatment.5 Increasing the number of clinicians proficient with buprenorphine management can improve access to effective treatment and recovery services, which is critical for patients with OUD.
Multiple resources are available for clinicians to learn how to prescribe buprenorphine, but clear guidance on laboratory testing for patients receiving buprenorphine is limited. To safely and effectively prescribe buprenorphine, clinicians need to understand its pharmacology (Box 16-9) and how laboratory testing influences treatment. In an effort to increase clinician knowledge of and proficiency with buprenorphine, this article answers 10 common questions about laboratory monitoring of patients receiving this medication.
Box 1
For patients with opioid use disorder, buprenorphine is indicated for opioid detoxification and maintenance. Oral formulations of buprenorphine (including tablets and buccal films) have long durations of action, and when dosed daily can prevent opioid withdrawal for at least 48 hours.6 The recommended formulation is a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, because this formulation is associated with a lower risk of misuse and diversion compared to formulations containing only buprenorphine.7 However, buprenorphine alone can be effective in patients who experience adverse effects from or are unable to tolerate the combination buprenorphine/naloxone formulation.7 Despite the addition of naloxone, buprenorphine prescriptions may still be misused and diverted, so close monitoring is necessary.
Buprenorphine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system (CYP) (primarily CYP3A4) to its active metabolite, norbuprenorphine, both of which are primarily excreted in feces.8 However, small quantities of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine are excreted in the urine,9 which makes urine specimen the best choice to monitor buprenorphine use for therapeutic purposes.
1. Why is laboratory monitoring important?
Proper laboratory monitoring discourages illicit substance use, encourages medication adherence, and influences treatment modifications. Patient self-reporting on medication compliance may be inaccurate or unreliable.10 Patients who relapse or use other illicit substances may also be reluctant to disclose their substance use.11
On the other hand, laboratory tests are objective markers of treatment outcome and adherence, and can verify a patient’s self-report.12 When used appropriately, laboratory monitoring can be therapeutic. It holds patients accountable, especially when used in conjunction with contingency management or other behavioral therapies.13 Laboratory monitoring is the most reliable method of determining if patients are abstaining from opioids and other illicit substances, or if the treatment plan requires revision.
2. Which tests should I order?
When initiating or maintaining a patient on buprenorphine, order a general urine drug screen (UDS), urine opioid screen (availability varies by institution), urine creatinine levels, urine buprenorphine/norbuprenorphine/naloxone/creatinine levels, urine alcohol metabolite levels, and a urine general toxicology test. It is also recommended to obtain a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) before starting buprenorphine,14,15 and to monitor CMP values at least once annually following treatment. Patients with a history of IV drug use or other high-risk factors should also be screened for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV.14,15
A general UDS can determine if opiates, amphetamines, cocaine, marijuana, or other common illicit substances are present to identify additional substance use. The proficiency of a general UDS may vary depending on the panels used at the respective institution. Some clinics use point-of-care UDS as part of their clinical management; these tests are inexpensive and provide immediate results.16 A basic UDS typically does not detect synthetic opioids due to the specificity of conventional immunoassays. As a result, specific tests for opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, fentanyl, and methadone should also be considered, depending on their availability. Though buprenorphine treatment may trigger a positive opiate or other opioid screen,17 buprenorphine adherence should be confirmed using several urine tests, including creatinine, buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and naloxone urine levels.
In addition to screening for illicit substances and buprenorphine adherence, it is important to also screen for alcohol. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is highly comorbid with OUD,18 and is associated with worse OUD treatment outcomes.19 Alcohol use may also affect liver function necessary for buprenorphine metabolism,8 so urine alcohol metabolites such as ethyl glucuronide and ethyl sulfate, serum transaminases, and gamma-glutamyl transferase should also be obtained.
Continue to: How frequently should patients be tested?
3. How frequently should patients be tested?
As part of the initial assessment, it is recommended to order CMP, UDS, and urine general toxicology.14 If indicated, specific laboratory tests such as specific opioid and alcohol metabolites screens can be ordered. After starting buprenorphine, the frequency of monitoring urine laboratory tests—including UDS, general drug toxicology, buprenorphine/norbuprenorphine/naloxone/creatinine, and alcohol and its metabolites—depends on a variety of factors, including a patient’s treatment response and stability as well as availability and cost of the tests. Ultimately, the frequency of laboratory monitoring should be determined on a patient-by-patient basis and clinicians should use their judgment.
The American Society of Addiction Medicine suggests testing more frequently earlier in the course of treatment (eg, weekly or biweekly), then spacing it out over time (eg, monthly or quarterly) as the patient’s recovery progresses.14,15 To conserve resources and reduce spending, some clinicians and guidelines recommend random monitoring as opposed to monitoring at every follow-up visit (eg, once out of every 3 to 5 visits, on average), which allows for longer intervals between testing while ensuring consistency with medication and abstinence from illicit substances.15,16 We suggest screening every 2 weeks for the first month, then spacing out to monthly and quarterly as patients demonstrate stability, with random screening as indicated. Monitoring of liver function should be done at least once annually.
4. How should urine buprenorphine and other results be interpreted?
There are several issues to consider when interpreting laboratory results. The clinician needs to know what to expect in the sample, and what approximate levels should be detected. To check treatment adherence, laboratory data should include stable urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels and negative urine screening for other illicit substances.14,15 While urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels have great interindividual variability due to genetic differences in hepatic metabolism, unusually high levels of buprenorphine (≥700 ng/mL) without norbuprenorphine suggests “urine spiking,” where patients put buprenorphine directly into their urine sample.20,21 Abnormally low or undetectable levels raise concern for medication nonadherence or diversion.
Though urine buprenorphine levels do not reliably correlate with dose, because there is typically not much intraindividual variability, patients should have relatively stable levels on each screen once a maintenance dose has been established.22 Furthermore, the buprenorphine-to-norbuprenorphine ratio (ie, “the metabolic ratio”) typically ranges from 1:2 to 1:4 across all individuals,20,21,23 regardless of dose or metabolic rate. Urine naloxone levels, which typically are included in commercial urine buprenorphine laboratory panels, also may aid in identifying tampered urine specimens when buprenorphine-to-norbuprenorphine ratios are abnormal or inconsistent with an individual’s prior ratio. Naloxone is typically (but not always) poorly absorbed and minimally detected in urine specimens.20 A high level of naloxone coupled with unusually high buprenorphine levels, particularly in the absence of norbuprenorphine in the urine, may indicate urine spiking.20,21,23
Urine creatinine is used to establish the reliability of the specimen. When urine creatinine concentration is <20 mg/dL, the concentration of most substances typically falls to subthreshold levels of detection.24 If a UDS is negative and the urine has a creatinine concentration <20 mg/dL, the patient should provide a new sample, because the urine was likely too diluted to detect any substances.
Continue to: The presence of alcohol...
The presence of alcohol metabolites can alert the clinician to recent alcohol use and possible AUD, which should be assessed and treated if indicated.
Liver enzymes should be normal or unchanged with short- and long-term buprenorphine use when taken as prescribed.25,26 However, acute liver injury may occur if patients inject buprenorphine intravenously, especially in those with underlying hepatitis C.25
5. What can cause a false negative result on UDS?
Laboratory monitoring may occasionally yield false negative drug screens. For urine buprenorphine levels, false negatives may occur in patients who are “rapid metabolizers,” infrequent or as-needed usage of the medication, patient mix-up, or laboratory error.27 For other substances, a false negative result may occur if the patient used the substance(s) outside the window of detection. The most common causes of false negative results, however, are overly diluted urine samples (eg, due to rapid water ingestion), or the use of an inappropriate test to measure a specific opioid or substance.27
Many laboratories use conventional immunoassays with morphine antibodies that react with various opioid substrates to determine the presence of a specific opioid. Some opioids—particularly synthetics such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, fentanyl, buprenorphine, and methadone—have poor cross-reactivity with the morphine antibody due to their distinct chemical structures, so standard immunoassays used to detect opioids may result in a false negative result.28 In such situations, a discussion with a clinical pathologist familiar with the laboratory detection method can help ensure proper testing. Additional tests for specific opioids should be ordered to more specifically target substances prone to false negative results.27
6. What can cause a false positive result on UDS?
The cross-reactivity of the morphine substrate may also result in a false positive result.28 Other over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medications that have cross-reactivity with the morphine antibody include dextromethorphan, verapamil, quinine, fluoroquinolones, and rifampin, which can normally be found in urine 2 to 3 days after consumption.17,27 Poppy seeds have long been known to result in positive opiate screens on urine testing, particularly when laboratories use lower cutoff values (eg, 300 ng/mL), so advise patients to avoid consuming poppy seeds.29
Continue to: For other drugs of abuse...
For other drugs of abuse, false positives are typically caused by cross-reactivity with other prescription or OTC medications. Numerous substances cross-react with amphetamines and produce false positive results on amphetamine immunoassays, including amantadine, bupropion, ephedrine, labetalol, phentermine, pseudoephedrine, ranitidine, selegiline, and trazodone.27 Sertraline and efavirenz are known to produce false positive results on benzodiazepine UDS, and ibuprofen, naproxen, and efavirenz can produce false positive results for cannabinoids.27
7. How do I communicate the results to patients?
Effectively communicating test results to patients is just as important as the results themselves. A trusting, therapeutic alliance between patient and clinician is highly predictive of successful treatment,30 and how the clinician communicates affects the strength of this collaboration. A principle of addiction treatment is the use of neutral language when discussing laboratory results.31,32 To avoid unintentional shaming or moral judgment, use words such as “positive” or “negative” rather than stigmatizing terms such as “clean” or “dirty.”33
Additionally, make it clear that laboratory findings are not used to punish patients, but rather to improve treatment.34 Reassuring the patient that a positive screen will not result in withdrawal of care encourages a working relationship.14 All patients who receive buprenorphine treatment should be informed that collecting a UDS is the standard of care used to monitor their progress. You might want to compare using UDS in patients with OUD to monitoring HbA1c levels in patients with diabetes as an example to demonstrate how laboratory values inform treatment.35,36
Before reporting the results, a helpful strategy to maintain the therapeutic alliance in the face of a positive UDS is to ask the patient what they expect their UDS to show. When the patient has been reassured that treatment will not be withdrawn due to a positive result, they may be more likely to fully disclose substance use. This allows them the opportunity to self-disclose rather than be “called out” by the clinician.35
8. What happens when a patient tests positive for drugs of abuse?
If a patient tests positive for opioids or other drugs of abuse, convey this information to them, ideally by asking them what they expect to see on laboratory findings. Patients may have “slip ups” or relapses, or use certain prescription medications for medical reasons with the intention of establishing abstinence. It is essential to convey laboratory findings in a nonjudgmental tone while maintaining a supportive stance with clear boundaries.
Continue to: Though addiction specialists...
Though addiction specialists often advise complete abstinence from all substances, including alcohol, cannabis, and tobacco, the harm-reduction model emphasizes “meeting patients where they are” in terms of continued substance use.37 If a patient can reduce their substance use or abstain from some substances while continuing others, these accomplishments should be acknowledged.
For patients who continue to test positive for illicit substances (>3 instances) without a clear explanation, schedule an appointment to re-educate them about buprenorphine treatment and reassess the patient’s treatment goals. Consider changing the current treatment plan, such as by having more frequent follow-ups, increasing the dose of the buprenorphine for patients whose cravings are not sufficiently suppressed, switching to another medication such as methadone or naltrexone, or referring the patient to a higher level of care, such as intensive outpatient or residential treatment.
9. What should I do if the results indicate abnormal levels of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and naloxone?
When urine buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, or naloxone levels appear low or the results indicate a likely “spiking,” clarify whether the sample tampering is due to poor adherence or diversion. Similar to dealing with a positive result for substances of abuse, ask the patient what they expect to find in their urine, and discuss the results in a nonjudgmental manner. Patients who admit to difficulty following their medication regimen may require additional psychoeducation and motivational interviewing to identify and address barriers. Strategies to improve adherence include setting an alarm, involving the family, using a pillbox, or simplifying the regimen.38 A long-acting injectable form of buprenorphine is also available.
If you suspect diversion, refer to your clinic’s policy and use other clinical management skills, such as increasing the frequency of visits, random pill counts, and supervised medication administration in the clinic.39 If diversion occurs repetitively and the patient is not appropriate for or benefiting from buprenorphine treatment, it may make sense to terminate treatment and consider other treatment options (such as methadone or residential treatment).39
10. What should I do if a patient disagrees with laboratory findings?
It is common for patients to disagree with laboratory results. Maintaining an attitude of neutrality and allowing the patient to speak and provide explanations is necessary to ensure they feel heard. Explanations patients frequently provide include passive exposure (“I was around someone who was using it”) or accidental ingestion, when a patient reports taking a medication they were not aware was a substance of concern. In a calm and nonjudgmental manner, provide education on what leads to a positive drug screen, including the possibility of false positive findings.
Continue to: Because a screening test...
Because a screening test has high sensitivity and low specificity, false positives may occur.17,27 Therefore, when a result is in dispute, the use of a high-specificity confirmatory test is often needed (many laboratories have reflex confirmatory testing). However, in the case of diluted urine (urine creatinine concentrations <20 mg/dL), patients should be told the findings are physiologically implausible, and a new urine sample should be obtained.24
Goals of laboratory monitoring
Laboratory monitoring, including UDS and urine buprenorphine levels, is a mainstay of treatment for patients with OUD. The increased use of telehealth has affected how laboratory testing is conducted (Box 240,41). The goal of laboratory testing is to influence treatment and improve patient outcomes. Clinical data such as clinician assessment, patient self-reporting, and collateral information provide essential details for patient management. However, laboratory monitoring is often the most reliable and objective source by which to influence treatment.
Box 2
While delivering therapy via telehealth has been shown to decrease the stigma that surrounds treatment, reduce no-show rates, increase retention in care, improve treatment access for patients who have difficulty commuting, and allow for continuity of outpatient treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic, there are also challenges.40,41 Inducing patients on buprenorphine via telehealth, as well as managing complex treatment cases or repeated failed urine drug screen tests, can be especially challenging. However, treatment standards should be followed as much as possible, and laboratory monitoring as clinically indicated should still be used to improve treatment outcomes.
If needed, patients may be directed to community labs for urine screening and should have results sent to their clinicians prior to the telehealth visit. Complex treatment cases (eg, repeat positive opioid screens, or negative urine buprenorphine screens with comorbid psychiatric conditions) should be handled on an individual basis and in-person appointments may be needed. Video assessment is always preferable to telephone. For patients who are unable to use video and have difficulty maintaining negative drug screens, an in-person visit should be requested.
An increased understanding of recommended laboratory monitoring practices may improve your comfort with OUD treatment and motivate more clinicians to offer buprenorphine, a life-saving and disease-modifying treatment for OUD. Doing so would increase access to OUD treatment for patients to reduce the individual and public health risks associated with untreated OUD.
Bottom Line
Laboratory monitoring, particularly urine drug screens and urine buprenorphine levels, is the most reliable source of information in the treatment of patients with opioid use disorder (OUD). An increased understanding of monitoring practices may improve a clinician’s willingness to offer buprenorphine as an option for therapy and their ability to properly treat patients with OUD.
Related Resources
- Li X, Moore S, Olson C. Urine drug tests: how to make the most of them. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(8):10-18,20.
- Moreno JL, Johnson JL, Peckham AM. Sublingual buprenorphine plus buprenorphine XR for opioid use disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(6):39-42,49. doi:10.12788/cp.0244
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Bupropion • Wellbutrin, Zyban
Efavirenz • Sustiva
Fentanyl • Actiq
Hydrocodone • Hysingla
Hydromorphone • Dilaudid
Methadone • Methadose
Naloxone • Evzio
Naltrexone • Vivitrol
Oxycodone • Oxycontin
Oxymorphone • Opana
Phentermine • Ionamin
Quinine • Qualaquin
Ranitidine • Zantac
Rifampin • Rifadin
Selegiline • Eldepryl
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Oleptro
Verapamil • Verelan
The opioid use disorder (OUD) epidemic is a major public health crisis in the United States.1 Naltrexone, methadone, and buprenorphine are first-line therapies for OUD and have high success rates.2 While studies have shown that naltrexone is effective, patients must achieve opioid detoxification and maintain 7 to 10 days of total abstinence to avoid a precipitated opioid withdrawal before it can be prescribed.3 Methadone does not require detoxification or a period of complete abstinence, but must be prescribed in special clinics and requires daily observed dosing for the first 90 days,4 though these requirements have been relaxed during the COVID-19 pandemic. In contrast, buprenorphine (with or without naloxone) can be used in office-based settings, which significantly improves the accessibility and availability of treatment for patients with OUD. Clinician knowledge and comfort prescribing buprenorphine are limiting factors to treatment.5 Increasing the number of clinicians proficient with buprenorphine management can improve access to effective treatment and recovery services, which is critical for patients with OUD.
Multiple resources are available for clinicians to learn how to prescribe buprenorphine, but clear guidance on laboratory testing for patients receiving buprenorphine is limited. To safely and effectively prescribe buprenorphine, clinicians need to understand its pharmacology (Box 16-9) and how laboratory testing influences treatment. In an effort to increase clinician knowledge of and proficiency with buprenorphine, this article answers 10 common questions about laboratory monitoring of patients receiving this medication.
Box 1
For patients with opioid use disorder, buprenorphine is indicated for opioid detoxification and maintenance. Oral formulations of buprenorphine (including tablets and buccal films) have long durations of action, and when dosed daily can prevent opioid withdrawal for at least 48 hours.6 The recommended formulation is a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, because this formulation is associated with a lower risk of misuse and diversion compared to formulations containing only buprenorphine.7 However, buprenorphine alone can be effective in patients who experience adverse effects from or are unable to tolerate the combination buprenorphine/naloxone formulation.7 Despite the addition of naloxone, buprenorphine prescriptions may still be misused and diverted, so close monitoring is necessary.
Buprenorphine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system (CYP) (primarily CYP3A4) to its active metabolite, norbuprenorphine, both of which are primarily excreted in feces.8 However, small quantities of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine are excreted in the urine,9 which makes urine specimen the best choice to monitor buprenorphine use for therapeutic purposes.
1. Why is laboratory monitoring important?
Proper laboratory monitoring discourages illicit substance use, encourages medication adherence, and influences treatment modifications. Patient self-reporting on medication compliance may be inaccurate or unreliable.10 Patients who relapse or use other illicit substances may also be reluctant to disclose their substance use.11
On the other hand, laboratory tests are objective markers of treatment outcome and adherence, and can verify a patient’s self-report.12 When used appropriately, laboratory monitoring can be therapeutic. It holds patients accountable, especially when used in conjunction with contingency management or other behavioral therapies.13 Laboratory monitoring is the most reliable method of determining if patients are abstaining from opioids and other illicit substances, or if the treatment plan requires revision.
2. Which tests should I order?
When initiating or maintaining a patient on buprenorphine, order a general urine drug screen (UDS), urine opioid screen (availability varies by institution), urine creatinine levels, urine buprenorphine/norbuprenorphine/naloxone/creatinine levels, urine alcohol metabolite levels, and a urine general toxicology test. It is also recommended to obtain a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) before starting buprenorphine,14,15 and to monitor CMP values at least once annually following treatment. Patients with a history of IV drug use or other high-risk factors should also be screened for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV.14,15
A general UDS can determine if opiates, amphetamines, cocaine, marijuana, or other common illicit substances are present to identify additional substance use. The proficiency of a general UDS may vary depending on the panels used at the respective institution. Some clinics use point-of-care UDS as part of their clinical management; these tests are inexpensive and provide immediate results.16 A basic UDS typically does not detect synthetic opioids due to the specificity of conventional immunoassays. As a result, specific tests for opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, fentanyl, and methadone should also be considered, depending on their availability. Though buprenorphine treatment may trigger a positive opiate or other opioid screen,17 buprenorphine adherence should be confirmed using several urine tests, including creatinine, buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and naloxone urine levels.
In addition to screening for illicit substances and buprenorphine adherence, it is important to also screen for alcohol. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is highly comorbid with OUD,18 and is associated with worse OUD treatment outcomes.19 Alcohol use may also affect liver function necessary for buprenorphine metabolism,8 so urine alcohol metabolites such as ethyl glucuronide and ethyl sulfate, serum transaminases, and gamma-glutamyl transferase should also be obtained.
Continue to: How frequently should patients be tested?
3. How frequently should patients be tested?
As part of the initial assessment, it is recommended to order CMP, UDS, and urine general toxicology.14 If indicated, specific laboratory tests such as specific opioid and alcohol metabolites screens can be ordered. After starting buprenorphine, the frequency of monitoring urine laboratory tests—including UDS, general drug toxicology, buprenorphine/norbuprenorphine/naloxone/creatinine, and alcohol and its metabolites—depends on a variety of factors, including a patient’s treatment response and stability as well as availability and cost of the tests. Ultimately, the frequency of laboratory monitoring should be determined on a patient-by-patient basis and clinicians should use their judgment.
The American Society of Addiction Medicine suggests testing more frequently earlier in the course of treatment (eg, weekly or biweekly), then spacing it out over time (eg, monthly or quarterly) as the patient’s recovery progresses.14,15 To conserve resources and reduce spending, some clinicians and guidelines recommend random monitoring as opposed to monitoring at every follow-up visit (eg, once out of every 3 to 5 visits, on average), which allows for longer intervals between testing while ensuring consistency with medication and abstinence from illicit substances.15,16 We suggest screening every 2 weeks for the first month, then spacing out to monthly and quarterly as patients demonstrate stability, with random screening as indicated. Monitoring of liver function should be done at least once annually.
4. How should urine buprenorphine and other results be interpreted?
There are several issues to consider when interpreting laboratory results. The clinician needs to know what to expect in the sample, and what approximate levels should be detected. To check treatment adherence, laboratory data should include stable urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels and negative urine screening for other illicit substances.14,15 While urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels have great interindividual variability due to genetic differences in hepatic metabolism, unusually high levels of buprenorphine (≥700 ng/mL) without norbuprenorphine suggests “urine spiking,” where patients put buprenorphine directly into their urine sample.20,21 Abnormally low or undetectable levels raise concern for medication nonadherence or diversion.
Though urine buprenorphine levels do not reliably correlate with dose, because there is typically not much intraindividual variability, patients should have relatively stable levels on each screen once a maintenance dose has been established.22 Furthermore, the buprenorphine-to-norbuprenorphine ratio (ie, “the metabolic ratio”) typically ranges from 1:2 to 1:4 across all individuals,20,21,23 regardless of dose or metabolic rate. Urine naloxone levels, which typically are included in commercial urine buprenorphine laboratory panels, also may aid in identifying tampered urine specimens when buprenorphine-to-norbuprenorphine ratios are abnormal or inconsistent with an individual’s prior ratio. Naloxone is typically (but not always) poorly absorbed and minimally detected in urine specimens.20 A high level of naloxone coupled with unusually high buprenorphine levels, particularly in the absence of norbuprenorphine in the urine, may indicate urine spiking.20,21,23
Urine creatinine is used to establish the reliability of the specimen. When urine creatinine concentration is <20 mg/dL, the concentration of most substances typically falls to subthreshold levels of detection.24 If a UDS is negative and the urine has a creatinine concentration <20 mg/dL, the patient should provide a new sample, because the urine was likely too diluted to detect any substances.
Continue to: The presence of alcohol...
The presence of alcohol metabolites can alert the clinician to recent alcohol use and possible AUD, which should be assessed and treated if indicated.
Liver enzymes should be normal or unchanged with short- and long-term buprenorphine use when taken as prescribed.25,26 However, acute liver injury may occur if patients inject buprenorphine intravenously, especially in those with underlying hepatitis C.25
5. What can cause a false negative result on UDS?
Laboratory monitoring may occasionally yield false negative drug screens. For urine buprenorphine levels, false negatives may occur in patients who are “rapid metabolizers,” infrequent or as-needed usage of the medication, patient mix-up, or laboratory error.27 For other substances, a false negative result may occur if the patient used the substance(s) outside the window of detection. The most common causes of false negative results, however, are overly diluted urine samples (eg, due to rapid water ingestion), or the use of an inappropriate test to measure a specific opioid or substance.27
Many laboratories use conventional immunoassays with morphine antibodies that react with various opioid substrates to determine the presence of a specific opioid. Some opioids—particularly synthetics such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, fentanyl, buprenorphine, and methadone—have poor cross-reactivity with the morphine antibody due to their distinct chemical structures, so standard immunoassays used to detect opioids may result in a false negative result.28 In such situations, a discussion with a clinical pathologist familiar with the laboratory detection method can help ensure proper testing. Additional tests for specific opioids should be ordered to more specifically target substances prone to false negative results.27
6. What can cause a false positive result on UDS?
The cross-reactivity of the morphine substrate may also result in a false positive result.28 Other over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medications that have cross-reactivity with the morphine antibody include dextromethorphan, verapamil, quinine, fluoroquinolones, and rifampin, which can normally be found in urine 2 to 3 days after consumption.17,27 Poppy seeds have long been known to result in positive opiate screens on urine testing, particularly when laboratories use lower cutoff values (eg, 300 ng/mL), so advise patients to avoid consuming poppy seeds.29
Continue to: For other drugs of abuse...
For other drugs of abuse, false positives are typically caused by cross-reactivity with other prescription or OTC medications. Numerous substances cross-react with amphetamines and produce false positive results on amphetamine immunoassays, including amantadine, bupropion, ephedrine, labetalol, phentermine, pseudoephedrine, ranitidine, selegiline, and trazodone.27 Sertraline and efavirenz are known to produce false positive results on benzodiazepine UDS, and ibuprofen, naproxen, and efavirenz can produce false positive results for cannabinoids.27
7. How do I communicate the results to patients?
Effectively communicating test results to patients is just as important as the results themselves. A trusting, therapeutic alliance between patient and clinician is highly predictive of successful treatment,30 and how the clinician communicates affects the strength of this collaboration. A principle of addiction treatment is the use of neutral language when discussing laboratory results.31,32 To avoid unintentional shaming or moral judgment, use words such as “positive” or “negative” rather than stigmatizing terms such as “clean” or “dirty.”33
Additionally, make it clear that laboratory findings are not used to punish patients, but rather to improve treatment.34 Reassuring the patient that a positive screen will not result in withdrawal of care encourages a working relationship.14 All patients who receive buprenorphine treatment should be informed that collecting a UDS is the standard of care used to monitor their progress. You might want to compare using UDS in patients with OUD to monitoring HbA1c levels in patients with diabetes as an example to demonstrate how laboratory values inform treatment.35,36
Before reporting the results, a helpful strategy to maintain the therapeutic alliance in the face of a positive UDS is to ask the patient what they expect their UDS to show. When the patient has been reassured that treatment will not be withdrawn due to a positive result, they may be more likely to fully disclose substance use. This allows them the opportunity to self-disclose rather than be “called out” by the clinician.35
8. What happens when a patient tests positive for drugs of abuse?
If a patient tests positive for opioids or other drugs of abuse, convey this information to them, ideally by asking them what they expect to see on laboratory findings. Patients may have “slip ups” or relapses, or use certain prescription medications for medical reasons with the intention of establishing abstinence. It is essential to convey laboratory findings in a nonjudgmental tone while maintaining a supportive stance with clear boundaries.
Continue to: Though addiction specialists...
Though addiction specialists often advise complete abstinence from all substances, including alcohol, cannabis, and tobacco, the harm-reduction model emphasizes “meeting patients where they are” in terms of continued substance use.37 If a patient can reduce their substance use or abstain from some substances while continuing others, these accomplishments should be acknowledged.
For patients who continue to test positive for illicit substances (>3 instances) without a clear explanation, schedule an appointment to re-educate them about buprenorphine treatment and reassess the patient’s treatment goals. Consider changing the current treatment plan, such as by having more frequent follow-ups, increasing the dose of the buprenorphine for patients whose cravings are not sufficiently suppressed, switching to another medication such as methadone or naltrexone, or referring the patient to a higher level of care, such as intensive outpatient or residential treatment.
9. What should I do if the results indicate abnormal levels of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, and naloxone?
When urine buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine, or naloxone levels appear low or the results indicate a likely “spiking,” clarify whether the sample tampering is due to poor adherence or diversion. Similar to dealing with a positive result for substances of abuse, ask the patient what they expect to find in their urine, and discuss the results in a nonjudgmental manner. Patients who admit to difficulty following their medication regimen may require additional psychoeducation and motivational interviewing to identify and address barriers. Strategies to improve adherence include setting an alarm, involving the family, using a pillbox, or simplifying the regimen.38 A long-acting injectable form of buprenorphine is also available.
If you suspect diversion, refer to your clinic’s policy and use other clinical management skills, such as increasing the frequency of visits, random pill counts, and supervised medication administration in the clinic.39 If diversion occurs repetitively and the patient is not appropriate for or benefiting from buprenorphine treatment, it may make sense to terminate treatment and consider other treatment options (such as methadone or residential treatment).39
10. What should I do if a patient disagrees with laboratory findings?
It is common for patients to disagree with laboratory results. Maintaining an attitude of neutrality and allowing the patient to speak and provide explanations is necessary to ensure they feel heard. Explanations patients frequently provide include passive exposure (“I was around someone who was using it”) or accidental ingestion, when a patient reports taking a medication they were not aware was a substance of concern. In a calm and nonjudgmental manner, provide education on what leads to a positive drug screen, including the possibility of false positive findings.
Continue to: Because a screening test...
Because a screening test has high sensitivity and low specificity, false positives may occur.17,27 Therefore, when a result is in dispute, the use of a high-specificity confirmatory test is often needed (many laboratories have reflex confirmatory testing). However, in the case of diluted urine (urine creatinine concentrations <20 mg/dL), patients should be told the findings are physiologically implausible, and a new urine sample should be obtained.24
Goals of laboratory monitoring
Laboratory monitoring, including UDS and urine buprenorphine levels, is a mainstay of treatment for patients with OUD. The increased use of telehealth has affected how laboratory testing is conducted (Box 240,41). The goal of laboratory testing is to influence treatment and improve patient outcomes. Clinical data such as clinician assessment, patient self-reporting, and collateral information provide essential details for patient management. However, laboratory monitoring is often the most reliable and objective source by which to influence treatment.
Box 2
While delivering therapy via telehealth has been shown to decrease the stigma that surrounds treatment, reduce no-show rates, increase retention in care, improve treatment access for patients who have difficulty commuting, and allow for continuity of outpatient treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic, there are also challenges.40,41 Inducing patients on buprenorphine via telehealth, as well as managing complex treatment cases or repeated failed urine drug screen tests, can be especially challenging. However, treatment standards should be followed as much as possible, and laboratory monitoring as clinically indicated should still be used to improve treatment outcomes.
If needed, patients may be directed to community labs for urine screening and should have results sent to their clinicians prior to the telehealth visit. Complex treatment cases (eg, repeat positive opioid screens, or negative urine buprenorphine screens with comorbid psychiatric conditions) should be handled on an individual basis and in-person appointments may be needed. Video assessment is always preferable to telephone. For patients who are unable to use video and have difficulty maintaining negative drug screens, an in-person visit should be requested.
An increased understanding of recommended laboratory monitoring practices may improve your comfort with OUD treatment and motivate more clinicians to offer buprenorphine, a life-saving and disease-modifying treatment for OUD. Doing so would increase access to OUD treatment for patients to reduce the individual and public health risks associated with untreated OUD.
Bottom Line
Laboratory monitoring, particularly urine drug screens and urine buprenorphine levels, is the most reliable source of information in the treatment of patients with opioid use disorder (OUD). An increased understanding of monitoring practices may improve a clinician’s willingness to offer buprenorphine as an option for therapy and their ability to properly treat patients with OUD.
Related Resources
- Li X, Moore S, Olson C. Urine drug tests: how to make the most of them. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(8):10-18,20.
- Moreno JL, Johnson JL, Peckham AM. Sublingual buprenorphine plus buprenorphine XR for opioid use disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(6):39-42,49. doi:10.12788/cp.0244
Drug Brand Names
Amantadine • Gocovri
Buprenorphine • Subutex, Sublocade
Bupropion • Wellbutrin, Zyban
Efavirenz • Sustiva
Fentanyl • Actiq
Hydrocodone • Hysingla
Hydromorphone • Dilaudid
Methadone • Methadose
Naloxone • Evzio
Naltrexone • Vivitrol
Oxycodone • Oxycontin
Oxymorphone • Opana
Phentermine • Ionamin
Quinine • Qualaquin
Ranitidine • Zantac
Rifampin • Rifadin
Selegiline • Eldepryl
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Oleptro
Verapamil • Verelan
1. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: results from the 2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP19-5068, NSDUH Series H-54. May 2019. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/
2. Volkow ND, Frieden TR, Hyde PS, et al. Medication-assisted therapies—tackling the opioid-overdose epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2063-2066. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1402780
3. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32812-X
4. Sharma A, Kelly SM, Mitchell SG, et al. Update on barriers to pharmacotherapy for opioid use disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2017;19(6):35. doi:10.1007/s11920-017-0783-9
5. DeFlavio JR, Rolin SA, Nordstrom BR, et al. Analysis of barriers to adoption of buprenorphine maintenance therapy by family physicians. Rural Remote Health. 2015;15:3019. doi:10.22605/rrh3019
6. Kuhlman JJ Jr, Lalani S, Magluiolo J Jr, et al. Human pharmacokinetics of intravenous, sublingual, and buccal buprenorphine. J Anal Toxicol. 1996;20(6):369-378.
7. Fudala PJ, Bridge TP, Herbert S, et al. Office-based treatment of opiate addiction with a sublingual-tablet formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(10):949-958. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022164
8. Brown SM, Holtzman M, Kim T, et al. Buprenorphine metabolites, buprenorphine-3-glucuronide and norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide, are biologically active. Anesthesiology. 2011;115(6):1251-1260. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e318238fea0
9. Cone EJ, Gorodetzky CW, Yousefnejad D, et al. The metabolism and excretion of buprenorphine in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1984;12(5):577-581.
10. Stirratt MJ, Dunbar-Jacob J, Crane HM, et al. Self-report measures of medication adherence behavior: recommendations on optimal use. Transl Behav Med. 2015;5(4):470-482. doi:10.1007/s13142-015-0315-2
11. Del Boca FK, Noll JA. Truth or consequences: the validity of self-report data in health services research on addictions. Addiction. 2000;95 Suppl 3:S347-S360. doi:10.1080/09652140020004278
12. Preston KL, Silverman K, Schuster CR, et al. Comparison of self-reported drug use with quantitative and qualitative urinalysis for assessment of drug use in treatment studies. NIDA Res Monogr. 1997;167:130-145.
13. Knezevic NN, Khan OM, Beiranvand A, et al. Repeated quantitative urine toxicology analysis may improve chronic pain patient compliance with opioid therapy. Pain Physician. 2017;20(2S):S135-S145. doi:10.36076/ppj.2017.s145
14. Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. 2015;9(5):358-367.
15. The ASAM national practice guideline for the treatment of opioid use disorder: 2020 focused update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S Suppl 1):1-91. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000633
16. McDonell MG, Graves MC, West II, et al. Utility of point-of-care urine drug tests in the treatment of primary care patients with drug use disorders. J Addict Med. 2016;10(3):196-201. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000220
17. Algren DA, Christian MR. Buyer beware: pitfalls in toxicology laboratory testing. Mo Med. 2015;112(3):206-210.
18. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2010.05.008
19. Stapleton RD, Comiskey CM. Alcohol usage and associated treatment outcomes for opiate users entering treatment in Ireland. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;107(1):56-61. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.09.007
20. Warrington JS, Warrington GS, Francis-Fath S, et al. Urinary buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine and naloxone concentrations and ratios: review and potential clinical implications. J Addict Med. 2020;14(6):e344-e349. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000676
21. Donroe JH, Holt SR, O’Connor PG, et al. Interpreting quantitative urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels in office-based clinical practice. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:46-51. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.07.040
22. Bai SA, Xiang Q, Finn A. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of single- and multiple-dose buprenorphine buccal film in healthy volunteers. Clin Ther. 2016;38(2):358-369. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.12.016
23. Suzuki J, Zinser J, Issa M, et al. Quantitative testing of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine to identify urine sample spiking during office-based opioid treatment. Subst Abus. 2017;38(4):504-507. doi:10.1080/08897077.2017.1356796
24. Gowans EM, Fraser CG. Biological variation of serum and urine creatinine and creatinine clearance: ramifications for interpretation of results and patient care. Ann Clin Biochem. 1988;25( Pt 3):259-263. doi:10.1177/000456328802500312
25. Saxon AJ, Ling W, Hillhouse M, et al. Buprenorphine/naloxone and methadone effects on laboratory indices of liver health: a randomized trial. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013;128(1-2):71-76. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.08.002
26. Fareed A, Eilender P, Ketchen B, et al. Factors affecting noncompliance with buprenorphine maintenance treatment. J Addict Med. 2014;8(5):345-350. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000057
27. Moeller KE, Lee KC, Kissack JC. Urine drug screening: practical guide for clinicians. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83(1):66-76. doi:10.4065/83.1.66
28. Keary CJ, Wang Y, Moran JR, et al. Toxicologic testing for opiates: understanding false-positive and false-negative test results. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2012;14(4).PCC.12f01371 doi:10.4088/PCC.12f01371
29. Zebelman AM, Troyer BL, Randall GL, et al. Detection of morphine and codeine following consumption of poppy seeds. J Anal Toxicol. 1987;11(3):131-132. doi:10.1093/jat/11.3.131
30. Meier PS, Barrowclough C, Donmall MC. The role of the therapeutic alliance in the treatment of substance misuse: a critical review of the literature. Addiction. 2005;100(3):304-316. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00935.x
31. Kelly JF, Saitz R, Wakeman S. Language, substance use disorders, and policy: the need to reach consensus on an “addiction-ary.” Alcohol Treat Q. 2016;34(1):116-123. doi:10.1080/07347324.2016.1113103
32. Broyles LM, Binswanger IA, Jenkins JA, et al. Confronting inadvertent stigma and pejorative language in addiction scholarship: a recognition and response. Subst Abus. 2014;35(3):217-221. doi:10.1080/08897077.2014.930372
33. Kelly JF, Wakeman SE, Saitz R. Stop talking ‘dirty’: clinicians, language, and quality of care for the leading cause of preventable death in the United States. Am J Med. 2015;128(1):8-9. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.07.043
34. Jarvis M, Williams J, Hurford M, et al. Appropriate use of drug testing in clinical addiction medicine. J Addict Med. 2017;11(3):163-173. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000323
35. Martin SA, Chiodo LM, Bosse JD, et al. The next stage of buprenorphine care for opioid use disorder. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(9):628-635. doi:10.7326/M18-1652
36. Katz N, Fanciullo GJ. Role of urine toxicology testing in the management of chronic opioid therapy. Clin J Pain. 2002;18(4 Suppl):S76-S82.
37. Klein A. Harm reduction works: evidence and inclusion in drug policy and advocacy. Health Care Anal. 2020;28(4):404-414. doi:10.1007/s10728-020-00406-w
38. Patel MX, David AS. Medication adherence: predictive factors and enhancement strategies. Psychiatry. 2007;6(9):357-361. doi:10.1016/j.mppsy.2007.06.003
39. Lofwall MR, Walsh SL. A review of buprenorphine diversion and misuse: the current evidence base and experiences from around the world. J Addict Med. 2014;8(5):315-326. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000045
40. Wang L, Weiss J, Ryan EB, et al. Telemedicine increases access to buprenorphine initiation during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;124:108272. doi:10.1016/ j.jsat.2020.108272
41. Harris MTH, Lambert AM, Maschke AD, et al. “No home to take methadone to”: experiences with addiction services during the COVID-19 pandemic among survivors of opioid overdose in Boston. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2022;135:108655. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108655
1. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: results from the 2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health. HHS Publication PEP19-5068, NSDUH Series H-54. May 2019. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/
2. Volkow ND, Frieden TR, Hyde PS, et al. Medication-assisted therapies—tackling the opioid-overdose epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2063-2066. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1402780
3. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32812-X
4. Sharma A, Kelly SM, Mitchell SG, et al. Update on barriers to pharmacotherapy for opioid use disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2017;19(6):35. doi:10.1007/s11920-017-0783-9
5. DeFlavio JR, Rolin SA, Nordstrom BR, et al. Analysis of barriers to adoption of buprenorphine maintenance therapy by family physicians. Rural Remote Health. 2015;15:3019. doi:10.22605/rrh3019
6. Kuhlman JJ Jr, Lalani S, Magluiolo J Jr, et al. Human pharmacokinetics of intravenous, sublingual, and buccal buprenorphine. J Anal Toxicol. 1996;20(6):369-378.
7. Fudala PJ, Bridge TP, Herbert S, et al. Office-based treatment of opiate addiction with a sublingual-tablet formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(10):949-958. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022164
8. Brown SM, Holtzman M, Kim T, et al. Buprenorphine metabolites, buprenorphine-3-glucuronide and norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide, are biologically active. Anesthesiology. 2011;115(6):1251-1260. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e318238fea0
9. Cone EJ, Gorodetzky CW, Yousefnejad D, et al. The metabolism and excretion of buprenorphine in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1984;12(5):577-581.
10. Stirratt MJ, Dunbar-Jacob J, Crane HM, et al. Self-report measures of medication adherence behavior: recommendations on optimal use. Transl Behav Med. 2015;5(4):470-482. doi:10.1007/s13142-015-0315-2
11. Del Boca FK, Noll JA. Truth or consequences: the validity of self-report data in health services research on addictions. Addiction. 2000;95 Suppl 3:S347-S360. doi:10.1080/09652140020004278
12. Preston KL, Silverman K, Schuster CR, et al. Comparison of self-reported drug use with quantitative and qualitative urinalysis for assessment of drug use in treatment studies. NIDA Res Monogr. 1997;167:130-145.
13. Knezevic NN, Khan OM, Beiranvand A, et al. Repeated quantitative urine toxicology analysis may improve chronic pain patient compliance with opioid therapy. Pain Physician. 2017;20(2S):S135-S145. doi:10.36076/ppj.2017.s145
14. Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. 2015;9(5):358-367.
15. The ASAM national practice guideline for the treatment of opioid use disorder: 2020 focused update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S Suppl 1):1-91. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000633
16. McDonell MG, Graves MC, West II, et al. Utility of point-of-care urine drug tests in the treatment of primary care patients with drug use disorders. J Addict Med. 2016;10(3):196-201. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000220
17. Algren DA, Christian MR. Buyer beware: pitfalls in toxicology laboratory testing. Mo Med. 2015;112(3):206-210.
18. Hartzler B, Donovan DM, Huang Z. Comparison of opiate-primary treatment seekers with and without alcohol use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2010;39(2):114-123. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2010.05.008
19. Stapleton RD, Comiskey CM. Alcohol usage and associated treatment outcomes for opiate users entering treatment in Ireland. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;107(1):56-61. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.09.007
20. Warrington JS, Warrington GS, Francis-Fath S, et al. Urinary buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine and naloxone concentrations and ratios: review and potential clinical implications. J Addict Med. 2020;14(6):e344-e349. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000676
21. Donroe JH, Holt SR, O’Connor PG, et al. Interpreting quantitative urine buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine levels in office-based clinical practice. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:46-51. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.07.040
22. Bai SA, Xiang Q, Finn A. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of single- and multiple-dose buprenorphine buccal film in healthy volunteers. Clin Ther. 2016;38(2):358-369. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.12.016
23. Suzuki J, Zinser J, Issa M, et al. Quantitative testing of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine to identify urine sample spiking during office-based opioid treatment. Subst Abus. 2017;38(4):504-507. doi:10.1080/08897077.2017.1356796
24. Gowans EM, Fraser CG. Biological variation of serum and urine creatinine and creatinine clearance: ramifications for interpretation of results and patient care. Ann Clin Biochem. 1988;25( Pt 3):259-263. doi:10.1177/000456328802500312
25. Saxon AJ, Ling W, Hillhouse M, et al. Buprenorphine/naloxone and methadone effects on laboratory indices of liver health: a randomized trial. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013;128(1-2):71-76. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.08.002
26. Fareed A, Eilender P, Ketchen B, et al. Factors affecting noncompliance with buprenorphine maintenance treatment. J Addict Med. 2014;8(5):345-350. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000057
27. Moeller KE, Lee KC, Kissack JC. Urine drug screening: practical guide for clinicians. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83(1):66-76. doi:10.4065/83.1.66
28. Keary CJ, Wang Y, Moran JR, et al. Toxicologic testing for opiates: understanding false-positive and false-negative test results. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2012;14(4).PCC.12f01371 doi:10.4088/PCC.12f01371
29. Zebelman AM, Troyer BL, Randall GL, et al. Detection of morphine and codeine following consumption of poppy seeds. J Anal Toxicol. 1987;11(3):131-132. doi:10.1093/jat/11.3.131
30. Meier PS, Barrowclough C, Donmall MC. The role of the therapeutic alliance in the treatment of substance misuse: a critical review of the literature. Addiction. 2005;100(3):304-316. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00935.x
31. Kelly JF, Saitz R, Wakeman S. Language, substance use disorders, and policy: the need to reach consensus on an “addiction-ary.” Alcohol Treat Q. 2016;34(1):116-123. doi:10.1080/07347324.2016.1113103
32. Broyles LM, Binswanger IA, Jenkins JA, et al. Confronting inadvertent stigma and pejorative language in addiction scholarship: a recognition and response. Subst Abus. 2014;35(3):217-221. doi:10.1080/08897077.2014.930372
33. Kelly JF, Wakeman SE, Saitz R. Stop talking ‘dirty’: clinicians, language, and quality of care for the leading cause of preventable death in the United States. Am J Med. 2015;128(1):8-9. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.07.043
34. Jarvis M, Williams J, Hurford M, et al. Appropriate use of drug testing in clinical addiction medicine. J Addict Med. 2017;11(3):163-173. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000323
35. Martin SA, Chiodo LM, Bosse JD, et al. The next stage of buprenorphine care for opioid use disorder. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(9):628-635. doi:10.7326/M18-1652
36. Katz N, Fanciullo GJ. Role of urine toxicology testing in the management of chronic opioid therapy. Clin J Pain. 2002;18(4 Suppl):S76-S82.
37. Klein A. Harm reduction works: evidence and inclusion in drug policy and advocacy. Health Care Anal. 2020;28(4):404-414. doi:10.1007/s10728-020-00406-w
38. Patel MX, David AS. Medication adherence: predictive factors and enhancement strategies. Psychiatry. 2007;6(9):357-361. doi:10.1016/j.mppsy.2007.06.003
39. Lofwall MR, Walsh SL. A review of buprenorphine diversion and misuse: the current evidence base and experiences from around the world. J Addict Med. 2014;8(5):315-326. doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000045
40. Wang L, Weiss J, Ryan EB, et al. Telemedicine increases access to buprenorphine initiation during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2021;124:108272. doi:10.1016/ j.jsat.2020.108272
41. Harris MTH, Lambert AM, Maschke AD, et al. “No home to take methadone to”: experiences with addiction services during the COVID-19 pandemic among survivors of opioid overdose in Boston. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2022;135:108655. doi:10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108655
From neuroplasticity to psychoplasticity: Psilocybin may reverse personality disorders and political fanaticism
One of psychiatry’s long-standing dogmas is that personality disorders are enduring, unchangeable, and not amenable to treatment with potent psychotropics or intensive psychotherapy. I propose that this dogma may soon be shattered.
Several other dogmas in psychiatry have been demolished over the past several decades:
- that “insanity” is completely irreversible and requires lifetime institutionalization. The serendipitous discovery of chlorpromazine1 annihilated this centuries-old dogma
- that chronic, severe, refractory depression (with ongoing suicidal urges) that fails to improve with pharmacotherapy or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is hopeless and untreatable, until ketamine not only pulverized this dogma, but did it with lightning speed, dazzling us all2
- that dissociative agents such as ketamine are dangerous and condemnable drugs of abuse, until the therapeutic effect of ketamine slayed that dragon3
- that ECT “fries” the brain (as malevolently propagated by antipsychiatry cults), which was completely disproven by neuroimaging studies that show the hippocampus (which shrinks during depression) actually grows by >10% after a few ECT sessions4
- that psychotherapy is not a “real” treatment because talking cannot reverse a psychiatric brain disorder, until studies showed significant neuroplasticity with psychotherapy and decrease in inflammatory biomarkers with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)5
- that persons with refractory hallucinations and delusions are doomed to a life of disability, until clozapine torpedoed that pessimistic dogma6
- that hallucinogens/psychedelics are dangerous and should be banned, until a jarring paradigm shift occurred with the discovery of psilocybin’s transformative effects, and the remarkable therapeutic effects of its mystical trips.7
Psilocybin’s therapeutic effects
Psilocybin has already proved to have a strong and lasting effect on depression and promises to have therapeutic benefits for patients with substance use disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and anxiety.8 In addition, when the multiple psychological and neurobiological effects of psilocybin (and of other psychedelics) are examined, I see a very promising path to amelioration of severe personality disorders such as psychopathy, antisocial behavior, and narcissism. The mechanism(s) of action of psilocybin on the human brain are drastically different from any man-made psychotropic agent. As a psychiatric neuroscientist, I envision the neurologic impact of psilocybin to be conducive to a complete transformation of a patient’s view of themself, other people, and the meaning of life. It is reminiscent of religious conversion.
The psychological effects of psilocybin in humans have been described as follows:
- emotional breakthrough9
- increased psychological flexibility,10,11 a very cortical effect
- mystical experience,12 which results in sudden and significant changes in behavior and perception and includes the following dimensions: sacredness, noetic quality, deeply felt positive mood, ineffability, paradoxicality, and transcendence of time and space13
- oceanic boundlessness, feeling “one with the universe”14
- universal interconnectedness, insightfulness, blissful state, spiritual experience14
- ego dissolution,15 with loss of one’s personal identity
- increased neuroplasticity16
- changes in cognition and increase in insight.17
The neurobiological effects of psilocybin are mediated by serotonin 5HT2A agonism and include the following18:
- reduction in the activity of the medial prefrontal cortex, which regulates memory, attention, inhibitory control, and habit
- a decrease in the connectivity between the medial prefrontal cortex and the posterior cingulate cortex, which regulates memory and emotions
- reducing the default mode network, which is active during rest, stimulating internal thoughts and reminiscing about previous feelings and events, sometimes including ruminations. Psilocybin reverses those processes to thinking about others, not just the self, and becoming more open-minded about the world and other people. This can be therapeutic for depression, which is often associated with negative ruminations but also with entrenched habits (addictive behaviors), anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorders
- increased global functional connectivity among various brain networks, leading to stronger functional integration of behavior
- collapse of major cortical oscillatory rhythms such as alpha and others that perpetuate “prior” beliefs
- extensive neuroplasticity and recalibration of thought processes and decomposition of pathological beliefs, referred to as REBUS (relaxed beliefs under psychedelics).
The bottom line is psilocybin and other psychedelics can dramatically alter, reshape, and relax rigid beliefs and personality traits by decreasing “neuroticism” and increasing “extraversion,” insightfulness, openness, and possibly conscientiousness.19 Although no studies of psychedelics in psychopathic, antisocial, or narcissistic personality disorders have been conducted, it is very reasonable to speculate that psilocybin may reverse traits of these disorders such as callousness, lack of empathy, and pathological self-centeredness.
Going further, a preliminary report suggests psilocybin can modify political views by decreasing authoritarianism and increasing libertarianism.20,21 In the current political zeitgeist, could psychedelics such as psilocybin reduce or even eliminate political extremism and visceral hatred on all sides? It would be remarkable research to carry out to heal a politically divided populace.The dogma of untreatable personality disorders or hopelessly entrenched political extremism is on the chopping block, and psychedelics offer hope to splinter those beliefs by concurrently remodeling brain tissue (neuroplasticity) and rectifying the mindset (psychoplasticity).
1. Delay J, Deniker P. Neuroleptic effects of chlorpromazine in therapeutics of neuropsychiatry. J Clin Exp Psychopathol. 1955;16(2):104-112.
2. Walsh Z, Mollaahmetoglu OM, Rootman, J, et al. Ketamine for the treatment of mental health and substance use disorders: comprehensive systematic review. BJPsych Open. 2021;8(1):e19. doi:10.1192/bjo.2021.1061
3. Lener MS, Kadriu B, Zarate CA Jr. Ketamine and beyond: investigations into the potential of glutamatergic agents to treat depression. Drugs. 2017;77(4):381-401.
4. Ayers B, Leaver A, Woods RP, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
5. Cao B, Li R, Ding L, Xu J, et al. Does cognitive behaviour therapy affect peripheral inflammation of depression? A protocol for the systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2021;11(12):e048162. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048162
6. Wagner E, Siafis S, Fernando P, et al. Efficacy and safety of clozapine in psychotic disorders—a systematic quantitative meta-review. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11(1):487.
7. Daws RE, Timmermann C, Giribaldi B, et al. Increased global integration in the brain after psilocybin therapy for depression. Nat Med. 2022;28(4):844-851.
8. Pearson C, Siegel J, Gold JA. Psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for depression: emerging research on a psychedelic compound with a rich history. J Neurol Sci. 2022;434:120096. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2021.120096
9. Roseman L, Haijen E, Idialu-Ikato K, et al. Emotional breakthrough and psychedelics: validation of the Emotional Breakthrough Inventory. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(9):1076-1087.
10. Davis AK, Barrett FS, Griffiths RR. Psychological flexibility mediates the relations between acute psychedelic effects and subjective decreases in depression and anxiety. J Contextual Behav Sci. 2020;15:39-45.
11. Hayes SC, Luoma JB, Bond FW, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy: model, processes and outcomes. Behav Res Ther. 2006;44(1):1-25.
12. Ross S, Bossis A, Guss J, et al. Rapid and sustained symptom reduction following psilocybin treatment for anxiety and depression in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized controlled trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1165-1180.
13. Stace WT. Mysticism and Philosophy. Macmillan Pub Ltd; 1960:37.
14. Barrett FS, Griffiths RR. Classic hallucinogens and mystical experiences: phenomenology and neural correlates. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:393-430.
15. Nour MM, Evans L, Nutt D, et al. Ego-dissolution and psychedelics: validation of the Ego-Dissolution Inventory (EDI). Front Hum Neurosci. 2016;10:269. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2016.00269
16. Olson DE. The subjective effects of psychedelics may not be necessary for their enduring therapeutic effects. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020;4(2):563-567.
17. Carhart-Harris RL, Bolstridge M, Day CMJ, et al. Psilocybin with psychological support for treatment-resistant depression: six-month follow-up. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(2):399-408.
18. Carhart-Harris RL. How do psychedelics work? Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2019;32(1):16-21.
19. Erritzoe D, Roseman L, Nour MM, et al. Effects of psilocybin therapy on personality structure. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2018;138(5):368-378.
20. Lyons T, Carhart-Harris RL. Increased nature relatedness and decreased authoritarian political views after psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(7):811-819.
21. Nour MM, Evans L, Carhart-Harris RL. Psychedelics, personality and political perspectives. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2017;49(3):182-191.
One of psychiatry’s long-standing dogmas is that personality disorders are enduring, unchangeable, and not amenable to treatment with potent psychotropics or intensive psychotherapy. I propose that this dogma may soon be shattered.
Several other dogmas in psychiatry have been demolished over the past several decades:
- that “insanity” is completely irreversible and requires lifetime institutionalization. The serendipitous discovery of chlorpromazine1 annihilated this centuries-old dogma
- that chronic, severe, refractory depression (with ongoing suicidal urges) that fails to improve with pharmacotherapy or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is hopeless and untreatable, until ketamine not only pulverized this dogma, but did it with lightning speed, dazzling us all2
- that dissociative agents such as ketamine are dangerous and condemnable drugs of abuse, until the therapeutic effect of ketamine slayed that dragon3
- that ECT “fries” the brain (as malevolently propagated by antipsychiatry cults), which was completely disproven by neuroimaging studies that show the hippocampus (which shrinks during depression) actually grows by >10% after a few ECT sessions4
- that psychotherapy is not a “real” treatment because talking cannot reverse a psychiatric brain disorder, until studies showed significant neuroplasticity with psychotherapy and decrease in inflammatory biomarkers with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)5
- that persons with refractory hallucinations and delusions are doomed to a life of disability, until clozapine torpedoed that pessimistic dogma6
- that hallucinogens/psychedelics are dangerous and should be banned, until a jarring paradigm shift occurred with the discovery of psilocybin’s transformative effects, and the remarkable therapeutic effects of its mystical trips.7
Psilocybin’s therapeutic effects
Psilocybin has already proved to have a strong and lasting effect on depression and promises to have therapeutic benefits for patients with substance use disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and anxiety.8 In addition, when the multiple psychological and neurobiological effects of psilocybin (and of other psychedelics) are examined, I see a very promising path to amelioration of severe personality disorders such as psychopathy, antisocial behavior, and narcissism. The mechanism(s) of action of psilocybin on the human brain are drastically different from any man-made psychotropic agent. As a psychiatric neuroscientist, I envision the neurologic impact of psilocybin to be conducive to a complete transformation of a patient’s view of themself, other people, and the meaning of life. It is reminiscent of religious conversion.
The psychological effects of psilocybin in humans have been described as follows:
- emotional breakthrough9
- increased psychological flexibility,10,11 a very cortical effect
- mystical experience,12 which results in sudden and significant changes in behavior and perception and includes the following dimensions: sacredness, noetic quality, deeply felt positive mood, ineffability, paradoxicality, and transcendence of time and space13
- oceanic boundlessness, feeling “one with the universe”14
- universal interconnectedness, insightfulness, blissful state, spiritual experience14
- ego dissolution,15 with loss of one’s personal identity
- increased neuroplasticity16
- changes in cognition and increase in insight.17
The neurobiological effects of psilocybin are mediated by serotonin 5HT2A agonism and include the following18:
- reduction in the activity of the medial prefrontal cortex, which regulates memory, attention, inhibitory control, and habit
- a decrease in the connectivity between the medial prefrontal cortex and the posterior cingulate cortex, which regulates memory and emotions
- reducing the default mode network, which is active during rest, stimulating internal thoughts and reminiscing about previous feelings and events, sometimes including ruminations. Psilocybin reverses those processes to thinking about others, not just the self, and becoming more open-minded about the world and other people. This can be therapeutic for depression, which is often associated with negative ruminations but also with entrenched habits (addictive behaviors), anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorders
- increased global functional connectivity among various brain networks, leading to stronger functional integration of behavior
- collapse of major cortical oscillatory rhythms such as alpha and others that perpetuate “prior” beliefs
- extensive neuroplasticity and recalibration of thought processes and decomposition of pathological beliefs, referred to as REBUS (relaxed beliefs under psychedelics).
The bottom line is psilocybin and other psychedelics can dramatically alter, reshape, and relax rigid beliefs and personality traits by decreasing “neuroticism” and increasing “extraversion,” insightfulness, openness, and possibly conscientiousness.19 Although no studies of psychedelics in psychopathic, antisocial, or narcissistic personality disorders have been conducted, it is very reasonable to speculate that psilocybin may reverse traits of these disorders such as callousness, lack of empathy, and pathological self-centeredness.
Going further, a preliminary report suggests psilocybin can modify political views by decreasing authoritarianism and increasing libertarianism.20,21 In the current political zeitgeist, could psychedelics such as psilocybin reduce or even eliminate political extremism and visceral hatred on all sides? It would be remarkable research to carry out to heal a politically divided populace.The dogma of untreatable personality disorders or hopelessly entrenched political extremism is on the chopping block, and psychedelics offer hope to splinter those beliefs by concurrently remodeling brain tissue (neuroplasticity) and rectifying the mindset (psychoplasticity).
One of psychiatry’s long-standing dogmas is that personality disorders are enduring, unchangeable, and not amenable to treatment with potent psychotropics or intensive psychotherapy. I propose that this dogma may soon be shattered.
Several other dogmas in psychiatry have been demolished over the past several decades:
- that “insanity” is completely irreversible and requires lifetime institutionalization. The serendipitous discovery of chlorpromazine1 annihilated this centuries-old dogma
- that chronic, severe, refractory depression (with ongoing suicidal urges) that fails to improve with pharmacotherapy or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is hopeless and untreatable, until ketamine not only pulverized this dogma, but did it with lightning speed, dazzling us all2
- that dissociative agents such as ketamine are dangerous and condemnable drugs of abuse, until the therapeutic effect of ketamine slayed that dragon3
- that ECT “fries” the brain (as malevolently propagated by antipsychiatry cults), which was completely disproven by neuroimaging studies that show the hippocampus (which shrinks during depression) actually grows by >10% after a few ECT sessions4
- that psychotherapy is not a “real” treatment because talking cannot reverse a psychiatric brain disorder, until studies showed significant neuroplasticity with psychotherapy and decrease in inflammatory biomarkers with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)5
- that persons with refractory hallucinations and delusions are doomed to a life of disability, until clozapine torpedoed that pessimistic dogma6
- that hallucinogens/psychedelics are dangerous and should be banned, until a jarring paradigm shift occurred with the discovery of psilocybin’s transformative effects, and the remarkable therapeutic effects of its mystical trips.7
Psilocybin’s therapeutic effects
Psilocybin has already proved to have a strong and lasting effect on depression and promises to have therapeutic benefits for patients with substance use disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and anxiety.8 In addition, when the multiple psychological and neurobiological effects of psilocybin (and of other psychedelics) are examined, I see a very promising path to amelioration of severe personality disorders such as psychopathy, antisocial behavior, and narcissism. The mechanism(s) of action of psilocybin on the human brain are drastically different from any man-made psychotropic agent. As a psychiatric neuroscientist, I envision the neurologic impact of psilocybin to be conducive to a complete transformation of a patient’s view of themself, other people, and the meaning of life. It is reminiscent of religious conversion.
The psychological effects of psilocybin in humans have been described as follows:
- emotional breakthrough9
- increased psychological flexibility,10,11 a very cortical effect
- mystical experience,12 which results in sudden and significant changes in behavior and perception and includes the following dimensions: sacredness, noetic quality, deeply felt positive mood, ineffability, paradoxicality, and transcendence of time and space13
- oceanic boundlessness, feeling “one with the universe”14
- universal interconnectedness, insightfulness, blissful state, spiritual experience14
- ego dissolution,15 with loss of one’s personal identity
- increased neuroplasticity16
- changes in cognition and increase in insight.17
The neurobiological effects of psilocybin are mediated by serotonin 5HT2A agonism and include the following18:
- reduction in the activity of the medial prefrontal cortex, which regulates memory, attention, inhibitory control, and habit
- a decrease in the connectivity between the medial prefrontal cortex and the posterior cingulate cortex, which regulates memory and emotions
- reducing the default mode network, which is active during rest, stimulating internal thoughts and reminiscing about previous feelings and events, sometimes including ruminations. Psilocybin reverses those processes to thinking about others, not just the self, and becoming more open-minded about the world and other people. This can be therapeutic for depression, which is often associated with negative ruminations but also with entrenched habits (addictive behaviors), anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorders
- increased global functional connectivity among various brain networks, leading to stronger functional integration of behavior
- collapse of major cortical oscillatory rhythms such as alpha and others that perpetuate “prior” beliefs
- extensive neuroplasticity and recalibration of thought processes and decomposition of pathological beliefs, referred to as REBUS (relaxed beliefs under psychedelics).
The bottom line is psilocybin and other psychedelics can dramatically alter, reshape, and relax rigid beliefs and personality traits by decreasing “neuroticism” and increasing “extraversion,” insightfulness, openness, and possibly conscientiousness.19 Although no studies of psychedelics in psychopathic, antisocial, or narcissistic personality disorders have been conducted, it is very reasonable to speculate that psilocybin may reverse traits of these disorders such as callousness, lack of empathy, and pathological self-centeredness.
Going further, a preliminary report suggests psilocybin can modify political views by decreasing authoritarianism and increasing libertarianism.20,21 In the current political zeitgeist, could psychedelics such as psilocybin reduce or even eliminate political extremism and visceral hatred on all sides? It would be remarkable research to carry out to heal a politically divided populace.The dogma of untreatable personality disorders or hopelessly entrenched political extremism is on the chopping block, and psychedelics offer hope to splinter those beliefs by concurrently remodeling brain tissue (neuroplasticity) and rectifying the mindset (psychoplasticity).
1. Delay J, Deniker P. Neuroleptic effects of chlorpromazine in therapeutics of neuropsychiatry. J Clin Exp Psychopathol. 1955;16(2):104-112.
2. Walsh Z, Mollaahmetoglu OM, Rootman, J, et al. Ketamine for the treatment of mental health and substance use disorders: comprehensive systematic review. BJPsych Open. 2021;8(1):e19. doi:10.1192/bjo.2021.1061
3. Lener MS, Kadriu B, Zarate CA Jr. Ketamine and beyond: investigations into the potential of glutamatergic agents to treat depression. Drugs. 2017;77(4):381-401.
4. Ayers B, Leaver A, Woods RP, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
5. Cao B, Li R, Ding L, Xu J, et al. Does cognitive behaviour therapy affect peripheral inflammation of depression? A protocol for the systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2021;11(12):e048162. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048162
6. Wagner E, Siafis S, Fernando P, et al. Efficacy and safety of clozapine in psychotic disorders—a systematic quantitative meta-review. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11(1):487.
7. Daws RE, Timmermann C, Giribaldi B, et al. Increased global integration in the brain after psilocybin therapy for depression. Nat Med. 2022;28(4):844-851.
8. Pearson C, Siegel J, Gold JA. Psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for depression: emerging research on a psychedelic compound with a rich history. J Neurol Sci. 2022;434:120096. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2021.120096
9. Roseman L, Haijen E, Idialu-Ikato K, et al. Emotional breakthrough and psychedelics: validation of the Emotional Breakthrough Inventory. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(9):1076-1087.
10. Davis AK, Barrett FS, Griffiths RR. Psychological flexibility mediates the relations between acute psychedelic effects and subjective decreases in depression and anxiety. J Contextual Behav Sci. 2020;15:39-45.
11. Hayes SC, Luoma JB, Bond FW, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy: model, processes and outcomes. Behav Res Ther. 2006;44(1):1-25.
12. Ross S, Bossis A, Guss J, et al. Rapid and sustained symptom reduction following psilocybin treatment for anxiety and depression in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized controlled trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1165-1180.
13. Stace WT. Mysticism and Philosophy. Macmillan Pub Ltd; 1960:37.
14. Barrett FS, Griffiths RR. Classic hallucinogens and mystical experiences: phenomenology and neural correlates. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:393-430.
15. Nour MM, Evans L, Nutt D, et al. Ego-dissolution and psychedelics: validation of the Ego-Dissolution Inventory (EDI). Front Hum Neurosci. 2016;10:269. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2016.00269
16. Olson DE. The subjective effects of psychedelics may not be necessary for their enduring therapeutic effects. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020;4(2):563-567.
17. Carhart-Harris RL, Bolstridge M, Day CMJ, et al. Psilocybin with psychological support for treatment-resistant depression: six-month follow-up. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(2):399-408.
18. Carhart-Harris RL. How do psychedelics work? Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2019;32(1):16-21.
19. Erritzoe D, Roseman L, Nour MM, et al. Effects of psilocybin therapy on personality structure. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2018;138(5):368-378.
20. Lyons T, Carhart-Harris RL. Increased nature relatedness and decreased authoritarian political views after psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(7):811-819.
21. Nour MM, Evans L, Carhart-Harris RL. Psychedelics, personality and political perspectives. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2017;49(3):182-191.
1. Delay J, Deniker P. Neuroleptic effects of chlorpromazine in therapeutics of neuropsychiatry. J Clin Exp Psychopathol. 1955;16(2):104-112.
2. Walsh Z, Mollaahmetoglu OM, Rootman, J, et al. Ketamine for the treatment of mental health and substance use disorders: comprehensive systematic review. BJPsych Open. 2021;8(1):e19. doi:10.1192/bjo.2021.1061
3. Lener MS, Kadriu B, Zarate CA Jr. Ketamine and beyond: investigations into the potential of glutamatergic agents to treat depression. Drugs. 2017;77(4):381-401.
4. Ayers B, Leaver A, Woods RP, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(4):282-292.
5. Cao B, Li R, Ding L, Xu J, et al. Does cognitive behaviour therapy affect peripheral inflammation of depression? A protocol for the systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2021;11(12):e048162. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048162
6. Wagner E, Siafis S, Fernando P, et al. Efficacy and safety of clozapine in psychotic disorders—a systematic quantitative meta-review. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11(1):487.
7. Daws RE, Timmermann C, Giribaldi B, et al. Increased global integration in the brain after psilocybin therapy for depression. Nat Med. 2022;28(4):844-851.
8. Pearson C, Siegel J, Gold JA. Psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for depression: emerging research on a psychedelic compound with a rich history. J Neurol Sci. 2022;434:120096. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2021.120096
9. Roseman L, Haijen E, Idialu-Ikato K, et al. Emotional breakthrough and psychedelics: validation of the Emotional Breakthrough Inventory. J Psychopharmacol. 2019;33(9):1076-1087.
10. Davis AK, Barrett FS, Griffiths RR. Psychological flexibility mediates the relations between acute psychedelic effects and subjective decreases in depression and anxiety. J Contextual Behav Sci. 2020;15:39-45.
11. Hayes SC, Luoma JB, Bond FW, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy: model, processes and outcomes. Behav Res Ther. 2006;44(1):1-25.
12. Ross S, Bossis A, Guss J, et al. Rapid and sustained symptom reduction following psilocybin treatment for anxiety and depression in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized controlled trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1165-1180.
13. Stace WT. Mysticism and Philosophy. Macmillan Pub Ltd; 1960:37.
14. Barrett FS, Griffiths RR. Classic hallucinogens and mystical experiences: phenomenology and neural correlates. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:393-430.
15. Nour MM, Evans L, Nutt D, et al. Ego-dissolution and psychedelics: validation of the Ego-Dissolution Inventory (EDI). Front Hum Neurosci. 2016;10:269. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2016.00269
16. Olson DE. The subjective effects of psychedelics may not be necessary for their enduring therapeutic effects. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020;4(2):563-567.
17. Carhart-Harris RL, Bolstridge M, Day CMJ, et al. Psilocybin with psychological support for treatment-resistant depression: six-month follow-up. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(2):399-408.
18. Carhart-Harris RL. How do psychedelics work? Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2019;32(1):16-21.
19. Erritzoe D, Roseman L, Nour MM, et al. Effects of psilocybin therapy on personality structure. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2018;138(5):368-378.
20. Lyons T, Carhart-Harris RL. Increased nature relatedness and decreased authoritarian political views after psilocybin for treatment-resistant depression. J Psychopharmacol. 2018;32(7):811-819.
21. Nour MM, Evans L, Carhart-Harris RL. Psychedelics, personality and political perspectives. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2017;49(3):182-191.
More on neurotransmitters
The series “Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: A hypothesis” (Part 1:
The presentation of abnormal neurotransmission may occur along a continuum. For example, extreme dopamine deficiency can present as catatonia, moderate deficiency may present with inattention, normal activity permits adaptive functioning, and excitatory delirium and sudden death may be at the extreme end of dopaminergic excess.1
The amplitude, rate of change, and location of neurotransmitter dysfunction may determine which specialty takes the primary treatment role. Fatigue, pain, sleep difficulty, and emotional distress require clinicians to understand the whole patient, which is why health care professionals need cross training in psychiatry, and psychiatry recognizes multisystem pathology.
The recognition and treatment of substance use disorders requires an understanding of neurotransmitter symptoms, in terms of both acute drug effects and withdrawal. Fallows2 provides this information in an accessible chart. Discussions of neurotransmitters also have value in managing psychotropic medication withdrawal.3
Acetylcholine is another neurotransmitter of importance; it is essential to normal motor, cognitive, and emotional function. Extreme cholinergic deficiency or anticholinergic crisis has symptoms of pupillary dilation, psychosis, and delirium.4-6 The progressive decline seen in certain dementias is related in part to cholinergic deficit. Dominance of cholinergic activity is associated with depression and biomarkers such as increased rapid eye movement (REM) density, a measure of the frequency of rapid eye movements during REM sleep.7 Cholinergic excess or cholinergic crisis may present with symptoms of salivation, lacrimation, muscle weakness, delirium, or paralysis.8
The articles alluded to the interaction of neurotransmitter systems (eg, “dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression”). Isolating the effects of a single neurotransmitter is useful, but covariance of neurotransmitter activity also has diagnostic and treatment implications.9-11 Abnormalities in these interactions may be part of the causal process in fundamental cognitive functions.12 If endorphin suppression is insensitive to dopamine blockade, a relative endorphin excess may create symptoms. If acetylcholine changes are normally balanced by a relative increase in dopamine and norepinephrine, then a weak catecholamine response would fit the catecholamine-cholinergic balance hypothesis of depression. Neurotransmitter interactions are well worked out in the neurology of the basal ganglia but less clear in the frontal and limbic systems.13
Quantification has been applied in some areas of clinical care. Morphine equivalents are used to express opiate potency, and there are algorithms to summarize multiple medication effects on respiratory depression/overdose risk.14,15 Chlorpromazine equivalents were used to translate a range of antipsychotic potencies in the early days of antipsychotic treatment. Adverse effects and some treatment responses partially corresponded to the level of dopamine blockade, but not without noise. There is a wide range of variance as antipsychotic potency is assessed for clinical efficacy.16 We are still working on the array of medication potency and selectivity across neurotransmitter systems.17,18 For example, paroxetine is a potent serotonin reuptake blocker but less selective than citalopram, particularly antagonizing cholinergic muscarinic receptors.
The authors noted their hypothesis needs further elaboration and quantification as psychiatry moves from impressionistic practice to firmer science. Measurement of neurotransmitter activity is an area of intense research. Biomeasures have yet to add much value to the clinical practice of psychiatry, but we hope for progress. Functional neuroimaging with sophisticated algorithms is beginning to detail neocortical activity.19 CSF measurement of dopamine and serotonin metabolites seem to correlate with severe depression and suicidal behavior. Noninvasive, wearable technologies to measure galvanic skin response, oxygenation, and neurotransmitter metabolic products may add to neuro-transmitter-based assessment and treatment.
Neurotransmitters are one aspect of brain function. Other processes, such as hormonal neuromodulation20 and ion channels, may be over- or underactive. Channelopathies are of particular interest in cardiology and neurology but are also notable in pain and emotional disorders.21-26 Voltage-gated sodium channels are thought to be involved in general anesthesia.27 Adverse effects of some psychotropic medications are best understood as ion channel dysfunction.28 Using the strategy of this hypothesis applied to activation or inactivation of sodium, potassium, and calcium channels can guide useful diagnostic and treatment ideas for further study.
Mark C. Chandler, MD
Triangle Neuropsychiatry
Durham, North Carolina
Disclosures
The author reports no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in his letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
References
1. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
2. Fallows Z. MIT MedLinks. Accessed August 8, 2022. http://web.mit.edu/zakf/www/drugchart/drugchart11.html
3. Groot PC, van Os J. How user knowledge of psychotropic drug withdrawal resulted in the development of person-specific tapering medication. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320932452. doi:10.1177/2045125320932452
4. Picciotto MR, Higley MJ, Mineur YS. Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron. 2012;76(1):116-129.
5. Nair VP, Hunter JM. Anticholinesterases and anticholinergic drugs. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2004;4(5):164-168.
6. Dawson AH, Buckley NA. Pharmacological management of anticholinergic delirium--theory, evidence and practice. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;81(3):516-524.
7. Dulawa SC, Janowsky DS. Cholinergic regulation of mood: from basic and clinical studies to emerging therapeutics. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(5):694-709.
8. Adeyinka A, Kondamudi NP. Cholinergic Crisis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
9. El Mansari M, Guiard BP, Chernoloz O, et al. Relevance of norepinephrine-dopamine interactions in the treatment of major depressive disorder. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010;16(3):e1-e17.
10. Esposito E. Serotonin-dopamine interaction as a focus of novel antidepressant drugs. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7(2):177-185.
11. Kringelbach ML, Cruzat J, Cabral J, et al. Dynamic coupling of whole-brain neuronal and neurotransmitter systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(17):9566-9576.
12. Thiele A, Bellgrove MA. Neuromodulation of attention. Neuron. 2018;97(4):769-785.
13. Muñoz A, Lopez-Lopez A, Labandeira CM, et al. Interactions between the serotonergic and other neurotransmitter systems in the basal ganglia: role in Parkinson’s disease and adverse effects of L-DOPA. Front Neuroanat. 2020;14:26.
14. Nielsen S, Degenhardt L, Hoban B, et al. A synthesis of oral morphine equivalents (OME) for opioid utilisation studies. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016;25(6):733-737.
15. Lo-Ciganic WH, Huang JL, Zhang HH, et al. Evaluation of machine-learning algorithms for predicting opioid overdose risk among Medicare beneficiaries with opioid prescriptions. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(3):e190968. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.0968
16. Dewan MJ, Koss M. The clinical impact of reported variance in potency of antipsychotic agents. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1995;91(4):229-232.
17. Woods SW. Chlorpromazine equivalent doses for the newer atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64(6):663-667.
18. Hayasaka Y, Purgato M, Magni LR, et al. Dose equivalents of antidepressants: evidence-based recommendations from randomized controlled trials. J Affect Disord. 2015;180:179-184.
19. Hansen JY, Shafiei G, Markello RD, et al. Mapping neurotransmitter systems to the structural and functional organization of the human neocortex. bioRxiv. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.28.466336
20. Hwang WJ, Lee TY, Kim NS, et al. The role of estrogen receptors and their signaling across psychiatric disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):373.
21. Lawrence JH, Tomaselli GF, Marban E. Ion channels: structure and function. Heart Dis Stroke. 1993;2(1):75-80.
22. Fedele F, Severino P, Bruno N, et al. Role of ion channels in coronary microcirculation: a review of the literature. Future Cardiol. 2013;9(6):897-905.
23. Kumar P, Kumar D, Jha SK, et al. Ion channels in neurological disorders. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2016;103:97-136.
24. Quagliato LA, Nardi AE. The role of convergent ion channel pathways in microglial phenotypes: a systematic review of the implications for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):259.
25. Bianchi MT, Botzolakis EJ. Targeting ligand-gated ion channels in neurology and psychiatry: is pharmacological promiscuity an obstacle or an opportunity? BMC Pharmacol. 2010;10:3.
26. Imbrici P, Camerino DC, Tricarico D. Major channels involved in neuropsychiatric disorders and therapeutic perspectives. Front Genet. 2013;4:76.
27. Xiao J, Chen Z, Yu B. A potential mechanism of sodium channel mediating the general anesthesia induced by propofol. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:593050. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.593050
28. Kamei S, Sato N, Harayama Y, et al. Molecular analysis of potassium ion channel genes in sudden death cases among patients administered psychotropic drug therapy: are polymorphisms in LQT genes a potential risk factor? J Hum Genet. 2014;59(2):95-99.
The authors respond
Thank you for your thoughtful commentary. Our conceptual article was not designed to cover enough ground to be completely thorough. Everything you wrote adds to what we wanted to bring to the reader’s attention. The mechanisms of disease in psychiatry are numerous and still elusive, and the brain’s complexity is staggering. Our main goal was to point out possible correlations between specific symptoms and specific neurotransmitter activity. We had to oversimplify to make the article concise enough for publication. Neurotransmitter effects are based on their synthesis, storage, release, reuptake, and degradation. A receptor’s quantity and quality of function, inhibitors, inducers, and many other factors are involved in neurotransmitter performance. And, of course, there are additional fundamental neurotransmitters beyond the 6 we touched on. Our ability to sort through all of this is still rudimentary. You also reflect on the emerging methods to objectively measure neurotransmitter activity, which will eventually find their way to clinical practice and become invaluable. Still, we treat people, not tests or pictures, so diagnostic thinking based on clinical presentation will forever remain a cornerstone of dealing with individual patients.
We hope scientists and clinicians such as yourself will improve our concept and make it truly practical.
Dmitry M. Arbuck, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor of Psychiatry and Medicine
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, Indiana
President and Medical Director
Indiana Polyclinic
Carmel, Indiana
José Miguel Salmerón, MD
Professor
Department of Psychiatry
Universidad del Valle School of Medicine/Hospital
Universitario del Valle
Cali, Colombia
Disclosures
The authors report no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in their response, or with manufacturers of competing products.
The series “Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: A hypothesis” (Part 1:
The presentation of abnormal neurotransmission may occur along a continuum. For example, extreme dopamine deficiency can present as catatonia, moderate deficiency may present with inattention, normal activity permits adaptive functioning, and excitatory delirium and sudden death may be at the extreme end of dopaminergic excess.1
The amplitude, rate of change, and location of neurotransmitter dysfunction may determine which specialty takes the primary treatment role. Fatigue, pain, sleep difficulty, and emotional distress require clinicians to understand the whole patient, which is why health care professionals need cross training in psychiatry, and psychiatry recognizes multisystem pathology.
The recognition and treatment of substance use disorders requires an understanding of neurotransmitter symptoms, in terms of both acute drug effects and withdrawal. Fallows2 provides this information in an accessible chart. Discussions of neurotransmitters also have value in managing psychotropic medication withdrawal.3
Acetylcholine is another neurotransmitter of importance; it is essential to normal motor, cognitive, and emotional function. Extreme cholinergic deficiency or anticholinergic crisis has symptoms of pupillary dilation, psychosis, and delirium.4-6 The progressive decline seen in certain dementias is related in part to cholinergic deficit. Dominance of cholinergic activity is associated with depression and biomarkers such as increased rapid eye movement (REM) density, a measure of the frequency of rapid eye movements during REM sleep.7 Cholinergic excess or cholinergic crisis may present with symptoms of salivation, lacrimation, muscle weakness, delirium, or paralysis.8
The articles alluded to the interaction of neurotransmitter systems (eg, “dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression”). Isolating the effects of a single neurotransmitter is useful, but covariance of neurotransmitter activity also has diagnostic and treatment implications.9-11 Abnormalities in these interactions may be part of the causal process in fundamental cognitive functions.12 If endorphin suppression is insensitive to dopamine blockade, a relative endorphin excess may create symptoms. If acetylcholine changes are normally balanced by a relative increase in dopamine and norepinephrine, then a weak catecholamine response would fit the catecholamine-cholinergic balance hypothesis of depression. Neurotransmitter interactions are well worked out in the neurology of the basal ganglia but less clear in the frontal and limbic systems.13
Quantification has been applied in some areas of clinical care. Morphine equivalents are used to express opiate potency, and there are algorithms to summarize multiple medication effects on respiratory depression/overdose risk.14,15 Chlorpromazine equivalents were used to translate a range of antipsychotic potencies in the early days of antipsychotic treatment. Adverse effects and some treatment responses partially corresponded to the level of dopamine blockade, but not without noise. There is a wide range of variance as antipsychotic potency is assessed for clinical efficacy.16 We are still working on the array of medication potency and selectivity across neurotransmitter systems.17,18 For example, paroxetine is a potent serotonin reuptake blocker but less selective than citalopram, particularly antagonizing cholinergic muscarinic receptors.
The authors noted their hypothesis needs further elaboration and quantification as psychiatry moves from impressionistic practice to firmer science. Measurement of neurotransmitter activity is an area of intense research. Biomeasures have yet to add much value to the clinical practice of psychiatry, but we hope for progress. Functional neuroimaging with sophisticated algorithms is beginning to detail neocortical activity.19 CSF measurement of dopamine and serotonin metabolites seem to correlate with severe depression and suicidal behavior. Noninvasive, wearable technologies to measure galvanic skin response, oxygenation, and neurotransmitter metabolic products may add to neuro-transmitter-based assessment and treatment.
Neurotransmitters are one aspect of brain function. Other processes, such as hormonal neuromodulation20 and ion channels, may be over- or underactive. Channelopathies are of particular interest in cardiology and neurology but are also notable in pain and emotional disorders.21-26 Voltage-gated sodium channels are thought to be involved in general anesthesia.27 Adverse effects of some psychotropic medications are best understood as ion channel dysfunction.28 Using the strategy of this hypothesis applied to activation or inactivation of sodium, potassium, and calcium channels can guide useful diagnostic and treatment ideas for further study.
Mark C. Chandler, MD
Triangle Neuropsychiatry
Durham, North Carolina
Disclosures
The author reports no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in his letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
References
1. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
2. Fallows Z. MIT MedLinks. Accessed August 8, 2022. http://web.mit.edu/zakf/www/drugchart/drugchart11.html
3. Groot PC, van Os J. How user knowledge of psychotropic drug withdrawal resulted in the development of person-specific tapering medication. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320932452. doi:10.1177/2045125320932452
4. Picciotto MR, Higley MJ, Mineur YS. Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron. 2012;76(1):116-129.
5. Nair VP, Hunter JM. Anticholinesterases and anticholinergic drugs. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2004;4(5):164-168.
6. Dawson AH, Buckley NA. Pharmacological management of anticholinergic delirium--theory, evidence and practice. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;81(3):516-524.
7. Dulawa SC, Janowsky DS. Cholinergic regulation of mood: from basic and clinical studies to emerging therapeutics. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(5):694-709.
8. Adeyinka A, Kondamudi NP. Cholinergic Crisis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
9. El Mansari M, Guiard BP, Chernoloz O, et al. Relevance of norepinephrine-dopamine interactions in the treatment of major depressive disorder. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010;16(3):e1-e17.
10. Esposito E. Serotonin-dopamine interaction as a focus of novel antidepressant drugs. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7(2):177-185.
11. Kringelbach ML, Cruzat J, Cabral J, et al. Dynamic coupling of whole-brain neuronal and neurotransmitter systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(17):9566-9576.
12. Thiele A, Bellgrove MA. Neuromodulation of attention. Neuron. 2018;97(4):769-785.
13. Muñoz A, Lopez-Lopez A, Labandeira CM, et al. Interactions between the serotonergic and other neurotransmitter systems in the basal ganglia: role in Parkinson’s disease and adverse effects of L-DOPA. Front Neuroanat. 2020;14:26.
14. Nielsen S, Degenhardt L, Hoban B, et al. A synthesis of oral morphine equivalents (OME) for opioid utilisation studies. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016;25(6):733-737.
15. Lo-Ciganic WH, Huang JL, Zhang HH, et al. Evaluation of machine-learning algorithms for predicting opioid overdose risk among Medicare beneficiaries with opioid prescriptions. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(3):e190968. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.0968
16. Dewan MJ, Koss M. The clinical impact of reported variance in potency of antipsychotic agents. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1995;91(4):229-232.
17. Woods SW. Chlorpromazine equivalent doses for the newer atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64(6):663-667.
18. Hayasaka Y, Purgato M, Magni LR, et al. Dose equivalents of antidepressants: evidence-based recommendations from randomized controlled trials. J Affect Disord. 2015;180:179-184.
19. Hansen JY, Shafiei G, Markello RD, et al. Mapping neurotransmitter systems to the structural and functional organization of the human neocortex. bioRxiv. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.28.466336
20. Hwang WJ, Lee TY, Kim NS, et al. The role of estrogen receptors and their signaling across psychiatric disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):373.
21. Lawrence JH, Tomaselli GF, Marban E. Ion channels: structure and function. Heart Dis Stroke. 1993;2(1):75-80.
22. Fedele F, Severino P, Bruno N, et al. Role of ion channels in coronary microcirculation: a review of the literature. Future Cardiol. 2013;9(6):897-905.
23. Kumar P, Kumar D, Jha SK, et al. Ion channels in neurological disorders. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2016;103:97-136.
24. Quagliato LA, Nardi AE. The role of convergent ion channel pathways in microglial phenotypes: a systematic review of the implications for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):259.
25. Bianchi MT, Botzolakis EJ. Targeting ligand-gated ion channels in neurology and psychiatry: is pharmacological promiscuity an obstacle or an opportunity? BMC Pharmacol. 2010;10:3.
26. Imbrici P, Camerino DC, Tricarico D. Major channels involved in neuropsychiatric disorders and therapeutic perspectives. Front Genet. 2013;4:76.
27. Xiao J, Chen Z, Yu B. A potential mechanism of sodium channel mediating the general anesthesia induced by propofol. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:593050. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.593050
28. Kamei S, Sato N, Harayama Y, et al. Molecular analysis of potassium ion channel genes in sudden death cases among patients administered psychotropic drug therapy: are polymorphisms in LQT genes a potential risk factor? J Hum Genet. 2014;59(2):95-99.
The authors respond
Thank you for your thoughtful commentary. Our conceptual article was not designed to cover enough ground to be completely thorough. Everything you wrote adds to what we wanted to bring to the reader’s attention. The mechanisms of disease in psychiatry are numerous and still elusive, and the brain’s complexity is staggering. Our main goal was to point out possible correlations between specific symptoms and specific neurotransmitter activity. We had to oversimplify to make the article concise enough for publication. Neurotransmitter effects are based on their synthesis, storage, release, reuptake, and degradation. A receptor’s quantity and quality of function, inhibitors, inducers, and many other factors are involved in neurotransmitter performance. And, of course, there are additional fundamental neurotransmitters beyond the 6 we touched on. Our ability to sort through all of this is still rudimentary. You also reflect on the emerging methods to objectively measure neurotransmitter activity, which will eventually find their way to clinical practice and become invaluable. Still, we treat people, not tests or pictures, so diagnostic thinking based on clinical presentation will forever remain a cornerstone of dealing with individual patients.
We hope scientists and clinicians such as yourself will improve our concept and make it truly practical.
Dmitry M. Arbuck, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor of Psychiatry and Medicine
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, Indiana
President and Medical Director
Indiana Polyclinic
Carmel, Indiana
José Miguel Salmerón, MD
Professor
Department of Psychiatry
Universidad del Valle School of Medicine/Hospital
Universitario del Valle
Cali, Colombia
Disclosures
The authors report no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in their response, or with manufacturers of competing products.
The series “Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: A hypothesis” (Part 1:
The presentation of abnormal neurotransmission may occur along a continuum. For example, extreme dopamine deficiency can present as catatonia, moderate deficiency may present with inattention, normal activity permits adaptive functioning, and excitatory delirium and sudden death may be at the extreme end of dopaminergic excess.1
The amplitude, rate of change, and location of neurotransmitter dysfunction may determine which specialty takes the primary treatment role. Fatigue, pain, sleep difficulty, and emotional distress require clinicians to understand the whole patient, which is why health care professionals need cross training in psychiatry, and psychiatry recognizes multisystem pathology.
The recognition and treatment of substance use disorders requires an understanding of neurotransmitter symptoms, in terms of both acute drug effects and withdrawal. Fallows2 provides this information in an accessible chart. Discussions of neurotransmitters also have value in managing psychotropic medication withdrawal.3
Acetylcholine is another neurotransmitter of importance; it is essential to normal motor, cognitive, and emotional function. Extreme cholinergic deficiency or anticholinergic crisis has symptoms of pupillary dilation, psychosis, and delirium.4-6 The progressive decline seen in certain dementias is related in part to cholinergic deficit. Dominance of cholinergic activity is associated with depression and biomarkers such as increased rapid eye movement (REM) density, a measure of the frequency of rapid eye movements during REM sleep.7 Cholinergic excess or cholinergic crisis may present with symptoms of salivation, lacrimation, muscle weakness, delirium, or paralysis.8
The articles alluded to the interaction of neurotransmitter systems (eg, “dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression”). Isolating the effects of a single neurotransmitter is useful, but covariance of neurotransmitter activity also has diagnostic and treatment implications.9-11 Abnormalities in these interactions may be part of the causal process in fundamental cognitive functions.12 If endorphin suppression is insensitive to dopamine blockade, a relative endorphin excess may create symptoms. If acetylcholine changes are normally balanced by a relative increase in dopamine and norepinephrine, then a weak catecholamine response would fit the catecholamine-cholinergic balance hypothesis of depression. Neurotransmitter interactions are well worked out in the neurology of the basal ganglia but less clear in the frontal and limbic systems.13
Quantification has been applied in some areas of clinical care. Morphine equivalents are used to express opiate potency, and there are algorithms to summarize multiple medication effects on respiratory depression/overdose risk.14,15 Chlorpromazine equivalents were used to translate a range of antipsychotic potencies in the early days of antipsychotic treatment. Adverse effects and some treatment responses partially corresponded to the level of dopamine blockade, but not without noise. There is a wide range of variance as antipsychotic potency is assessed for clinical efficacy.16 We are still working on the array of medication potency and selectivity across neurotransmitter systems.17,18 For example, paroxetine is a potent serotonin reuptake blocker but less selective than citalopram, particularly antagonizing cholinergic muscarinic receptors.
The authors noted their hypothesis needs further elaboration and quantification as psychiatry moves from impressionistic practice to firmer science. Measurement of neurotransmitter activity is an area of intense research. Biomeasures have yet to add much value to the clinical practice of psychiatry, but we hope for progress. Functional neuroimaging with sophisticated algorithms is beginning to detail neocortical activity.19 CSF measurement of dopamine and serotonin metabolites seem to correlate with severe depression and suicidal behavior. Noninvasive, wearable technologies to measure galvanic skin response, oxygenation, and neurotransmitter metabolic products may add to neuro-transmitter-based assessment and treatment.
Neurotransmitters are one aspect of brain function. Other processes, such as hormonal neuromodulation20 and ion channels, may be over- or underactive. Channelopathies are of particular interest in cardiology and neurology but are also notable in pain and emotional disorders.21-26 Voltage-gated sodium channels are thought to be involved in general anesthesia.27 Adverse effects of some psychotropic medications are best understood as ion channel dysfunction.28 Using the strategy of this hypothesis applied to activation or inactivation of sodium, potassium, and calcium channels can guide useful diagnostic and treatment ideas for further study.
Mark C. Chandler, MD
Triangle Neuropsychiatry
Durham, North Carolina
Disclosures
The author reports no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in his letter, or with manufacturers of competing products.
References
1. Mash DC. Excited delirium and sudden death: a syndromal disorder at the extreme end of the neuropsychiatric continuum. Front Physiol. 2016;7:435.
2. Fallows Z. MIT MedLinks. Accessed August 8, 2022. http://web.mit.edu/zakf/www/drugchart/drugchart11.html
3. Groot PC, van Os J. How user knowledge of psychotropic drug withdrawal resulted in the development of person-specific tapering medication. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320932452. doi:10.1177/2045125320932452
4. Picciotto MR, Higley MJ, Mineur YS. Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron. 2012;76(1):116-129.
5. Nair VP, Hunter JM. Anticholinesterases and anticholinergic drugs. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain. 2004;4(5):164-168.
6. Dawson AH, Buckley NA. Pharmacological management of anticholinergic delirium--theory, evidence and practice. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;81(3):516-524.
7. Dulawa SC, Janowsky DS. Cholinergic regulation of mood: from basic and clinical studies to emerging therapeutics. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(5):694-709.
8. Adeyinka A, Kondamudi NP. Cholinergic Crisis. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
9. El Mansari M, Guiard BP, Chernoloz O, et al. Relevance of norepinephrine-dopamine interactions in the treatment of major depressive disorder. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010;16(3):e1-e17.
10. Esposito E. Serotonin-dopamine interaction as a focus of novel antidepressant drugs. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7(2):177-185.
11. Kringelbach ML, Cruzat J, Cabral J, et al. Dynamic coupling of whole-brain neuronal and neurotransmitter systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(17):9566-9576.
12. Thiele A, Bellgrove MA. Neuromodulation of attention. Neuron. 2018;97(4):769-785.
13. Muñoz A, Lopez-Lopez A, Labandeira CM, et al. Interactions between the serotonergic and other neurotransmitter systems in the basal ganglia: role in Parkinson’s disease and adverse effects of L-DOPA. Front Neuroanat. 2020;14:26.
14. Nielsen S, Degenhardt L, Hoban B, et al. A synthesis of oral morphine equivalents (OME) for opioid utilisation studies. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016;25(6):733-737.
15. Lo-Ciganic WH, Huang JL, Zhang HH, et al. Evaluation of machine-learning algorithms for predicting opioid overdose risk among Medicare beneficiaries with opioid prescriptions. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(3):e190968. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.0968
16. Dewan MJ, Koss M. The clinical impact of reported variance in potency of antipsychotic agents. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1995;91(4):229-232.
17. Woods SW. Chlorpromazine equivalent doses for the newer atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64(6):663-667.
18. Hayasaka Y, Purgato M, Magni LR, et al. Dose equivalents of antidepressants: evidence-based recommendations from randomized controlled trials. J Affect Disord. 2015;180:179-184.
19. Hansen JY, Shafiei G, Markello RD, et al. Mapping neurotransmitter systems to the structural and functional organization of the human neocortex. bioRxiv. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.28.466336
20. Hwang WJ, Lee TY, Kim NS, et al. The role of estrogen receptors and their signaling across psychiatric disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):373.
21. Lawrence JH, Tomaselli GF, Marban E. Ion channels: structure and function. Heart Dis Stroke. 1993;2(1):75-80.
22. Fedele F, Severino P, Bruno N, et al. Role of ion channels in coronary microcirculation: a review of the literature. Future Cardiol. 2013;9(6):897-905.
23. Kumar P, Kumar D, Jha SK, et al. Ion channels in neurological disorders. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2016;103:97-136.
24. Quagliato LA, Nardi AE. The role of convergent ion channel pathways in microglial phenotypes: a systematic review of the implications for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):259.
25. Bianchi MT, Botzolakis EJ. Targeting ligand-gated ion channels in neurology and psychiatry: is pharmacological promiscuity an obstacle or an opportunity? BMC Pharmacol. 2010;10:3.
26. Imbrici P, Camerino DC, Tricarico D. Major channels involved in neuropsychiatric disorders and therapeutic perspectives. Front Genet. 2013;4:76.
27. Xiao J, Chen Z, Yu B. A potential mechanism of sodium channel mediating the general anesthesia induced by propofol. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:593050. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.593050
28. Kamei S, Sato N, Harayama Y, et al. Molecular analysis of potassium ion channel genes in sudden death cases among patients administered psychotropic drug therapy: are polymorphisms in LQT genes a potential risk factor? J Hum Genet. 2014;59(2):95-99.
The authors respond
Thank you for your thoughtful commentary. Our conceptual article was not designed to cover enough ground to be completely thorough. Everything you wrote adds to what we wanted to bring to the reader’s attention. The mechanisms of disease in psychiatry are numerous and still elusive, and the brain’s complexity is staggering. Our main goal was to point out possible correlations between specific symptoms and specific neurotransmitter activity. We had to oversimplify to make the article concise enough for publication. Neurotransmitter effects are based on their synthesis, storage, release, reuptake, and degradation. A receptor’s quantity and quality of function, inhibitors, inducers, and many other factors are involved in neurotransmitter performance. And, of course, there are additional fundamental neurotransmitters beyond the 6 we touched on. Our ability to sort through all of this is still rudimentary. You also reflect on the emerging methods to objectively measure neurotransmitter activity, which will eventually find their way to clinical practice and become invaluable. Still, we treat people, not tests or pictures, so diagnostic thinking based on clinical presentation will forever remain a cornerstone of dealing with individual patients.
We hope scientists and clinicians such as yourself will improve our concept and make it truly practical.
Dmitry M. Arbuck, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor of Psychiatry and Medicine
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, Indiana
President and Medical Director
Indiana Polyclinic
Carmel, Indiana
José Miguel Salmerón, MD
Professor
Department of Psychiatry
Universidad del Valle School of Medicine/Hospital
Universitario del Valle
Cali, Colombia
Disclosures
The authors report no financial relationships with any companies whose products are mentioned in their response, or with manufacturers of competing products.
Drug-induced progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Rare but serious
Mr. P, age 67, presents to the clinic with vision changes and memory loss following a fall in his home due to limb weakness. Six years ago, his care team diagnosed him with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Mr. P’s current medication regimen includes methotrexate 20 mg once weekly and etanercept 50 mg once weekly, and he has been stable on this plan for 3 years. Mr. P also was recently diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD), but has not yet started treatment. Following a complete workup, an MRI of Mr. P’s brain revealed white matter demyelination. Due to these findings, he is scheduled for a brain biopsy, which confirms a diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
PML is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system caused by the John Cunningham virus (JCV), or JC polyomavirus, named for the first patient identified to have contracted the virus.1 Asymptomatic infection of JCV often occurs in childhood, and antibodies are found in ≤70% of healthy adults. In most individuals, JCV remains latent in the kidneys and lymphoid organs, but immunosuppression can cause it to reactivate.2
JCV infects oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and neurons, which results in white matter demyelination. Due to this demyelination, individuals can experience visual field defects, speech disturbances, ataxia, paresthesia, and cognitive impairments.2 Limb weakness presents in 60% of patients with PML, visual disturbances in 20%, and gait disturbances in 65%.3 Progression of these symptoms can lead to a more severe clinical presentation, including focal seizures in ≤10% of patients, and the mortality rate is 30% to 50%.3 Patients with comorbid HIV have a mortality rate ≤90%.2
Currently, there are no biomarkers that can identify PML in its early stages. A PML diagnosis is typically based on the patient’s clinical presentation, radiological imaging, and detection of JCV DNA. A brain biopsy is the gold standard for PML diagnosis.1
Interestingly, data suggest that glial cells harboring JCV in the brain express receptors for serotonin and dopamine.4 Researchers pinpointed 5HT2A receptors as JCV entry points into cells, and theorized that medications competing for binding, such as certain psychotropic agents, might decrease JCV entry. Cells lacking the 5HT2A receptor have shown immunity to JCV infection and the ability of cells to be infected was restored through transfection of 5HT2A receptors.4
Immunosuppressant medications can cause PML
PML was initially seen in individuals with conditions that cause immunosuppression, such as malignancies and HIV. However, “drug-induced PML” refers to cases in which drug-induced immunosuppression creates an environment that allows JCV to reactivate and disseminate back into the CNS.4 It is important to emphasize that drug-induced PML is a very rare effect of certain immunosuppressant medications. Medications that can weaken the immune system include glucocorticoids, monoclonal antibodies, alkylating agents, purine analogues, antimetabolites, and immunosuppressants (Table).1
These medications are used to treat conditions such as multiple sclerosis, RA, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus. Although drug-induced PML can result from the use of any of these agents, the highest incidence (1%) is found with natalizumab. Rates of incidence with other agents are either unknown or as low as .002%.1 Evidence suggests that the risk for PML increases with the duration of therapy.5
Continue to: Management
Management: Stop the offending agent, restore immune function
Specific pharmacologic treatments for PML are lacking. Management of drug-induced PML starts with discontinuing the offending agent. Restoring immune function has been found to be the most effective approach to treat PML.3 Restoration is possible through interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-7, and T-cell infusions. Other treatment options are theoretical and include the development of a JCV vaccine to stimulate host response, plasma exchange to remove the medication from the host, and antiviral therapy targeting JCV replication. Diclofenac, isotretinoin, and mefloquine can inhibit JCV replication.3
Based on the theory that JCV requires 5HT2A receptors for entry into cells, researchers have studied medications that block this receptor as a treatment for PML. The first-generation antipsychotic chlorpromazine did not show benefit when combined with cidofovir, a replication inhibitor.3 Antipsychotics agents such as ziprasidone and olanzapine have shown in vitro inhibition of JCV, while risperidone has mixed results, with 1 trial failing to find a difference on JCV in fetal glial cells.3 Second-generation antipsychotics may be the preferred option due to more potent antagonism of the 5HT2A receptors and fewer adverse effects compared to agents such as chlorpromazine.4 The antidepressant mirtazapine has shown to have promising results, with evidence indicating that earlier initiation is more beneficial.3 Overall, data involving the use of medications that act on the 5HT2A receptor are mixed. Recent data suggest that JCV might enter cells independent of 5HT2A receptors; however, more research in this area is needed.2
The best strategy for treating drug-induced PML has not yet been determined. While combination therapy is thought to be more successful than monotherapy, ultimately, it depends on the patient’s immune response. If a psychotropic medication is chosen as adjunct treatment for drug-induced PML, it is prudent to assess the patient’s entire clinical picture to determine the specific indication for therapy (ie, treating symptomatology or drug-induced PML).
CASE CONTINUED
Following diagnosis, Mr. P is provided supportive therapy, and his care team discontinues methotrexate and etanercept. Although data are mixed on the efficacy of medications that work on 5HT2A receptors, because Mr. P was recently diagnosed with MDD, he is started on mirtazapine 15 mg/d at night in an attempt to manage both MDD and PML. It is possible that his depressive symptoms developed as a result of drug-induced PML rather than major depressive disorder. Discontinuing methotrexate and etanercept stabilizes Mr. P’s PML symptoms but leads to an exacerbation of his RA symptoms. Mr. P is initiated on hyd
Related Resources
- Castle D, Robertson NP. Treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol. 2019;266(10):2587-2589. doi:10.1007/s00415-019-09501-y
Drug Brand Names
Abatacept • Orencia
Adalimumab • Humira
Alemtuzumab • Campath
Azathioprine • Azasan, Imuran
Basiliximab • Simulect
Belimumab • Benlysta
Bevacizumab • Avastin
Brentuximab vedotin • Adcetris
Cetuximab • Erbitux
Chlorpromazine • Thorazine, Largactil
Cidofovir • Vistide
Cladribine • Mavenclad
Cyclophosphamide • Cytoxan
Cyclosporine • Gengraf, Neoral
Dacarbazine • DTIC-Dome
Diclofenac • Cambia, Zorvolex
Dimethyl fumarate • Tecfidera
Etanercept • Enbrel
Fingolimod • Gilenya
Fludarabine • Fludara
Hydroxychloroquine • Plaquenil
Ibritumomab tiuxetan • Zevalin
Infliximab • Avsola, Inflectra
Isotretinoin • Absorica, Claravis
Mefloquine • Lariam
Methotrexate • Rheumatrex, Trexall
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Mitoxantrone • Novantrone
Muromonab-CD3 • Orthoclone OKT3
Mycophenolate mofetil • CellCept
Natalizumab • Tysabri
Nelarabine • Arranon
Obinutuzumab • Gazyva
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Risperidone • Risperdal
Tacrolimus • Prograf
Vincristine • Vincasar PFS
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Yukitake M. Drug-induced progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in multiple sclerosis: a comprehensive review. Clin Exp Neuroimmunol. 2018;9(1):37-47. doi:10.1111/cen3.12440
2. Alstadhaug KB, Myhr KM, Rinaldo CH. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2017;137(23-24):10.4045/tidsskr.16.1092. doi:10.4045/tidsskr.16.1092
3. Williamson EML, Berger JR. Diagnosis and treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with multiple sclerosis therapies. Neurotherapeutics. 2017;14(4):961-973. doi:10.1007/s13311-017-0570-7
4. Altschuler EL, Kast RE. The atypical antipsychotic agents ziprasidone, risperidone and olanzapine as treatment for and prophylaxis against progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Med Hypotheses. 2005;65(3):585-586.
5. Vinhas de Souza M, Keller-Stanislawski B, Blake K, et al. Drug-induced PML: a global agenda for a global challenge. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91(4):747-750. doi:10.1038/clpt.2012.4
Mr. P, age 67, presents to the clinic with vision changes and memory loss following a fall in his home due to limb weakness. Six years ago, his care team diagnosed him with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Mr. P’s current medication regimen includes methotrexate 20 mg once weekly and etanercept 50 mg once weekly, and he has been stable on this plan for 3 years. Mr. P also was recently diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD), but has not yet started treatment. Following a complete workup, an MRI of Mr. P’s brain revealed white matter demyelination. Due to these findings, he is scheduled for a brain biopsy, which confirms a diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
PML is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system caused by the John Cunningham virus (JCV), or JC polyomavirus, named for the first patient identified to have contracted the virus.1 Asymptomatic infection of JCV often occurs in childhood, and antibodies are found in ≤70% of healthy adults. In most individuals, JCV remains latent in the kidneys and lymphoid organs, but immunosuppression can cause it to reactivate.2
JCV infects oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and neurons, which results in white matter demyelination. Due to this demyelination, individuals can experience visual field defects, speech disturbances, ataxia, paresthesia, and cognitive impairments.2 Limb weakness presents in 60% of patients with PML, visual disturbances in 20%, and gait disturbances in 65%.3 Progression of these symptoms can lead to a more severe clinical presentation, including focal seizures in ≤10% of patients, and the mortality rate is 30% to 50%.3 Patients with comorbid HIV have a mortality rate ≤90%.2
Currently, there are no biomarkers that can identify PML in its early stages. A PML diagnosis is typically based on the patient’s clinical presentation, radiological imaging, and detection of JCV DNA. A brain biopsy is the gold standard for PML diagnosis.1
Interestingly, data suggest that glial cells harboring JCV in the brain express receptors for serotonin and dopamine.4 Researchers pinpointed 5HT2A receptors as JCV entry points into cells, and theorized that medications competing for binding, such as certain psychotropic agents, might decrease JCV entry. Cells lacking the 5HT2A receptor have shown immunity to JCV infection and the ability of cells to be infected was restored through transfection of 5HT2A receptors.4
Immunosuppressant medications can cause PML
PML was initially seen in individuals with conditions that cause immunosuppression, such as malignancies and HIV. However, “drug-induced PML” refers to cases in which drug-induced immunosuppression creates an environment that allows JCV to reactivate and disseminate back into the CNS.4 It is important to emphasize that drug-induced PML is a very rare effect of certain immunosuppressant medications. Medications that can weaken the immune system include glucocorticoids, monoclonal antibodies, alkylating agents, purine analogues, antimetabolites, and immunosuppressants (Table).1

These medications are used to treat conditions such as multiple sclerosis, RA, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus. Although drug-induced PML can result from the use of any of these agents, the highest incidence (1%) is found with natalizumab. Rates of incidence with other agents are either unknown or as low as .002%.1 Evidence suggests that the risk for PML increases with the duration of therapy.5
Continue to: Management
Management: Stop the offending agent, restore immune function
Specific pharmacologic treatments for PML are lacking. Management of drug-induced PML starts with discontinuing the offending agent. Restoring immune function has been found to be the most effective approach to treat PML.3 Restoration is possible through interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-7, and T-cell infusions. Other treatment options are theoretical and include the development of a JCV vaccine to stimulate host response, plasma exchange to remove the medication from the host, and antiviral therapy targeting JCV replication. Diclofenac, isotretinoin, and mefloquine can inhibit JCV replication.3
Based on the theory that JCV requires 5HT2A receptors for entry into cells, researchers have studied medications that block this receptor as a treatment for PML. The first-generation antipsychotic chlorpromazine did not show benefit when combined with cidofovir, a replication inhibitor.3 Antipsychotics agents such as ziprasidone and olanzapine have shown in vitro inhibition of JCV, while risperidone has mixed results, with 1 trial failing to find a difference on JCV in fetal glial cells.3 Second-generation antipsychotics may be the preferred option due to more potent antagonism of the 5HT2A receptors and fewer adverse effects compared to agents such as chlorpromazine.4 The antidepressant mirtazapine has shown to have promising results, with evidence indicating that earlier initiation is more beneficial.3 Overall, data involving the use of medications that act on the 5HT2A receptor are mixed. Recent data suggest that JCV might enter cells independent of 5HT2A receptors; however, more research in this area is needed.2
The best strategy for treating drug-induced PML has not yet been determined. While combination therapy is thought to be more successful than monotherapy, ultimately, it depends on the patient’s immune response. If a psychotropic medication is chosen as adjunct treatment for drug-induced PML, it is prudent to assess the patient’s entire clinical picture to determine the specific indication for therapy (ie, treating symptomatology or drug-induced PML).
CASE CONTINUED
Following diagnosis, Mr. P is provided supportive therapy, and his care team discontinues methotrexate and etanercept. Although data are mixed on the efficacy of medications that work on 5HT2A receptors, because Mr. P was recently diagnosed with MDD, he is started on mirtazapine 15 mg/d at night in an attempt to manage both MDD and PML. It is possible that his depressive symptoms developed as a result of drug-induced PML rather than major depressive disorder. Discontinuing methotrexate and etanercept stabilizes Mr. P’s PML symptoms but leads to an exacerbation of his RA symptoms. Mr. P is initiated on hyd
Related Resources
- Castle D, Robertson NP. Treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol. 2019;266(10):2587-2589. doi:10.1007/s00415-019-09501-y
Drug Brand Names
Abatacept • Orencia
Adalimumab • Humira
Alemtuzumab • Campath
Azathioprine • Azasan, Imuran
Basiliximab • Simulect
Belimumab • Benlysta
Bevacizumab • Avastin
Brentuximab vedotin • Adcetris
Cetuximab • Erbitux
Chlorpromazine • Thorazine, Largactil
Cidofovir • Vistide
Cladribine • Mavenclad
Cyclophosphamide • Cytoxan
Cyclosporine • Gengraf, Neoral
Dacarbazine • DTIC-Dome
Diclofenac • Cambia, Zorvolex
Dimethyl fumarate • Tecfidera
Etanercept • Enbrel
Fingolimod • Gilenya
Fludarabine • Fludara
Hydroxychloroquine • Plaquenil
Ibritumomab tiuxetan • Zevalin
Infliximab • Avsola, Inflectra
Isotretinoin • Absorica, Claravis
Mefloquine • Lariam
Methotrexate • Rheumatrex, Trexall
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Mitoxantrone • Novantrone
Muromonab-CD3 • Orthoclone OKT3
Mycophenolate mofetil • CellCept
Natalizumab • Tysabri
Nelarabine • Arranon
Obinutuzumab • Gazyva
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Risperidone • Risperdal
Tacrolimus • Prograf
Vincristine • Vincasar PFS
Ziprasidone • Geodon
Mr. P, age 67, presents to the clinic with vision changes and memory loss following a fall in his home due to limb weakness. Six years ago, his care team diagnosed him with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Mr. P’s current medication regimen includes methotrexate 20 mg once weekly and etanercept 50 mg once weekly, and he has been stable on this plan for 3 years. Mr. P also was recently diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD), but has not yet started treatment. Following a complete workup, an MRI of Mr. P’s brain revealed white matter demyelination. Due to these findings, he is scheduled for a brain biopsy, which confirms a diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
PML is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system caused by the John Cunningham virus (JCV), or JC polyomavirus, named for the first patient identified to have contracted the virus.1 Asymptomatic infection of JCV often occurs in childhood, and antibodies are found in ≤70% of healthy adults. In most individuals, JCV remains latent in the kidneys and lymphoid organs, but immunosuppression can cause it to reactivate.2
JCV infects oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and neurons, which results in white matter demyelination. Due to this demyelination, individuals can experience visual field defects, speech disturbances, ataxia, paresthesia, and cognitive impairments.2 Limb weakness presents in 60% of patients with PML, visual disturbances in 20%, and gait disturbances in 65%.3 Progression of these symptoms can lead to a more severe clinical presentation, including focal seizures in ≤10% of patients, and the mortality rate is 30% to 50%.3 Patients with comorbid HIV have a mortality rate ≤90%.2
Currently, there are no biomarkers that can identify PML in its early stages. A PML diagnosis is typically based on the patient’s clinical presentation, radiological imaging, and detection of JCV DNA. A brain biopsy is the gold standard for PML diagnosis.1
Interestingly, data suggest that glial cells harboring JCV in the brain express receptors for serotonin and dopamine.4 Researchers pinpointed 5HT2A receptors as JCV entry points into cells, and theorized that medications competing for binding, such as certain psychotropic agents, might decrease JCV entry. Cells lacking the 5HT2A receptor have shown immunity to JCV infection and the ability of cells to be infected was restored through transfection of 5HT2A receptors.4
Immunosuppressant medications can cause PML
PML was initially seen in individuals with conditions that cause immunosuppression, such as malignancies and HIV. However, “drug-induced PML” refers to cases in which drug-induced immunosuppression creates an environment that allows JCV to reactivate and disseminate back into the CNS.4 It is important to emphasize that drug-induced PML is a very rare effect of certain immunosuppressant medications. Medications that can weaken the immune system include glucocorticoids, monoclonal antibodies, alkylating agents, purine analogues, antimetabolites, and immunosuppressants (Table).1

These medications are used to treat conditions such as multiple sclerosis, RA, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus. Although drug-induced PML can result from the use of any of these agents, the highest incidence (1%) is found with natalizumab. Rates of incidence with other agents are either unknown or as low as .002%.1 Evidence suggests that the risk for PML increases with the duration of therapy.5
Continue to: Management
Management: Stop the offending agent, restore immune function
Specific pharmacologic treatments for PML are lacking. Management of drug-induced PML starts with discontinuing the offending agent. Restoring immune function has been found to be the most effective approach to treat PML.3 Restoration is possible through interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-7, and T-cell infusions. Other treatment options are theoretical and include the development of a JCV vaccine to stimulate host response, plasma exchange to remove the medication from the host, and antiviral therapy targeting JCV replication. Diclofenac, isotretinoin, and mefloquine can inhibit JCV replication.3
Based on the theory that JCV requires 5HT2A receptors for entry into cells, researchers have studied medications that block this receptor as a treatment for PML. The first-generation antipsychotic chlorpromazine did not show benefit when combined with cidofovir, a replication inhibitor.3 Antipsychotics agents such as ziprasidone and olanzapine have shown in vitro inhibition of JCV, while risperidone has mixed results, with 1 trial failing to find a difference on JCV in fetal glial cells.3 Second-generation antipsychotics may be the preferred option due to more potent antagonism of the 5HT2A receptors and fewer adverse effects compared to agents such as chlorpromazine.4 The antidepressant mirtazapine has shown to have promising results, with evidence indicating that earlier initiation is more beneficial.3 Overall, data involving the use of medications that act on the 5HT2A receptor are mixed. Recent data suggest that JCV might enter cells independent of 5HT2A receptors; however, more research in this area is needed.2
The best strategy for treating drug-induced PML has not yet been determined. While combination therapy is thought to be more successful than monotherapy, ultimately, it depends on the patient’s immune response. If a psychotropic medication is chosen as adjunct treatment for drug-induced PML, it is prudent to assess the patient’s entire clinical picture to determine the specific indication for therapy (ie, treating symptomatology or drug-induced PML).
CASE CONTINUED
Following diagnosis, Mr. P is provided supportive therapy, and his care team discontinues methotrexate and etanercept. Although data are mixed on the efficacy of medications that work on 5HT2A receptors, because Mr. P was recently diagnosed with MDD, he is started on mirtazapine 15 mg/d at night in an attempt to manage both MDD and PML. It is possible that his depressive symptoms developed as a result of drug-induced PML rather than major depressive disorder. Discontinuing methotrexate and etanercept stabilizes Mr. P’s PML symptoms but leads to an exacerbation of his RA symptoms. Mr. P is initiated on hyd
Related Resources
- Castle D, Robertson NP. Treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol. 2019;266(10):2587-2589. doi:10.1007/s00415-019-09501-y
Drug Brand Names
Abatacept • Orencia
Adalimumab • Humira
Alemtuzumab • Campath
Azathioprine • Azasan, Imuran
Basiliximab • Simulect
Belimumab • Benlysta
Bevacizumab • Avastin
Brentuximab vedotin • Adcetris
Cetuximab • Erbitux
Chlorpromazine • Thorazine, Largactil
Cidofovir • Vistide
Cladribine • Mavenclad
Cyclophosphamide • Cytoxan
Cyclosporine • Gengraf, Neoral
Dacarbazine • DTIC-Dome
Diclofenac • Cambia, Zorvolex
Dimethyl fumarate • Tecfidera
Etanercept • Enbrel
Fingolimod • Gilenya
Fludarabine • Fludara
Hydroxychloroquine • Plaquenil
Ibritumomab tiuxetan • Zevalin
Infliximab • Avsola, Inflectra
Isotretinoin • Absorica, Claravis
Mefloquine • Lariam
Methotrexate • Rheumatrex, Trexall
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Mitoxantrone • Novantrone
Muromonab-CD3 • Orthoclone OKT3
Mycophenolate mofetil • CellCept
Natalizumab • Tysabri
Nelarabine • Arranon
Obinutuzumab • Gazyva
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Risperidone • Risperdal
Tacrolimus • Prograf
Vincristine • Vincasar PFS
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Yukitake M. Drug-induced progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in multiple sclerosis: a comprehensive review. Clin Exp Neuroimmunol. 2018;9(1):37-47. doi:10.1111/cen3.12440
2. Alstadhaug KB, Myhr KM, Rinaldo CH. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2017;137(23-24):10.4045/tidsskr.16.1092. doi:10.4045/tidsskr.16.1092
3. Williamson EML, Berger JR. Diagnosis and treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with multiple sclerosis therapies. Neurotherapeutics. 2017;14(4):961-973. doi:10.1007/s13311-017-0570-7
4. Altschuler EL, Kast RE. The atypical antipsychotic agents ziprasidone, risperidone and olanzapine as treatment for and prophylaxis against progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Med Hypotheses. 2005;65(3):585-586.
5. Vinhas de Souza M, Keller-Stanislawski B, Blake K, et al. Drug-induced PML: a global agenda for a global challenge. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91(4):747-750. doi:10.1038/clpt.2012.4
1. Yukitake M. Drug-induced progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in multiple sclerosis: a comprehensive review. Clin Exp Neuroimmunol. 2018;9(1):37-47. doi:10.1111/cen3.12440
2. Alstadhaug KB, Myhr KM, Rinaldo CH. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2017;137(23-24):10.4045/tidsskr.16.1092. doi:10.4045/tidsskr.16.1092
3. Williamson EML, Berger JR. Diagnosis and treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with multiple sclerosis therapies. Neurotherapeutics. 2017;14(4):961-973. doi:10.1007/s13311-017-0570-7
4. Altschuler EL, Kast RE. The atypical antipsychotic agents ziprasidone, risperidone and olanzapine as treatment for and prophylaxis against progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Med Hypotheses. 2005;65(3):585-586.
5. Vinhas de Souza M, Keller-Stanislawski B, Blake K, et al. Drug-induced PML: a global agenda for a global challenge. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91(4):747-750. doi:10.1038/clpt.2012.4
Hold or not to hold: Navigating involuntary commitment
CASE Depressed and suicidal
Police arrive at the home of Mr. H, age 50, after his wife calls 911. She reports he has depression and she saw him in bed brandishing a firearm as if he wanted to hurt himself. Upon arrival, the officers enter the house and find Mr. H in bed without a firearm. Mr. H says little to the officers about the alleged events, but acknowledges he has depression and is willing to go the hospital for further evaluation. Neither his wife nor the officers locate a firearm in the home.
EVALUATION Emergency detention
In the emergency department (ED), Mr. H’s laboratory results and physical examination findings are normal. He acknowledges feeling depressed over the past 2 weeks. Though he cannot identify any precipitants, he says he has experienced anhedonia, lack of appetite, decreased energy, and changes in his sleep patterns. When asked about the day’s events concerning the firearm, Mr. H becomes guarded and does not give a clear answer regarding having thoughts of suicide.
The evaluating psychiatrist obtains collateral from Mr. H’s wife and reviews his medical records. There are no active prescriptions on file and the psychiatrist notices that last year there was a suicide attempt involving a firearm. Following that episode, Mr. H was hospitalized, treated with sertraline 50 mg/d, and discharged with a diagnosis of major depressive disorder. There was no legal or substance abuse history.
In the ED, the psychiatrist conducts a psychiatric evaluation, including a suicide risk assessment, and determines Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life. Mr. H’s psychiatrist explains there are 2 treatment options: to be admitted to the hospital or to be discharged. The psychiatrist recommends hospital admission to Mr. H for his safety and stabilization. Mr. H says he prefers to return home.
Because the psychiatrist believes Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life and there is no less restrictive setting for treatment, he implements an emergency detention. In Ohio, this allows Mr. H to be held in the hospital for no more than 3 court days in accordance with state law. Before Mr. H’s emergency detention periods ends, the psychiatrist will need to decide whether Mr. H can be safely discharged. If the psychiatrist determines that Mr. H still needs treatment, the court will be petitioned for a civil commitment hearing.
[polldaddy:11189291]
The author’s observations
In some cases, courts allow information a psychiatrist does not directly obtain from a patient to be admitted as testimony in a civil commitment hearing. However, some jurisdictions consider sources of information not obtained directly from the patient as hearsay and thus inadmissible.1 Though each source listed may provide credible information that could be presented at a hearing, the psychiatrist should discuss with the patient the information obtained from these sources to ensure it is admissable.2 A discussion with Mr. H about the factors that led to his hospital arrival will avoid the psychiatrist’s reliance on what another person has heard or seen when providing testimony. Even when a psychiatrist is not faced with an issue of admissibility, caution must be taken with third-party reports.3
TREATMENT Civil commitment hearing
Before the emergency detention period expires, Mr. H’s psychiatrist determines that he remains at imminent risk of self-harm. To continue hospitalization, the psychiatrist files a petition for civil commitment and testifies at the commitment hearing. He reports that Mr. H suffers from a substantial mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The psychiatrist also testifies that the least restrictive environment for treatment continues to be inpatient hospitalization, because Mr. H is still at imminent risk of harming himself.
Continue to: Following the psychiatrist's...
Following the psychiatrist’s testimony, the magistrate finds that Mr. H is a mentally ill person subject to hospitalization given his mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The magistrate orders that Mr. H be civilly committed to the hospital.
[polldaddy:11189293]
The author’s observations
The psychiatrist’s testimony mirrors the language regarding civil commitment in the Ohio Revised Code.4 Other elements considered for mental illness in Ohio are a substantial disorder of memory, thought, orientation, or perception that grossly impairs one’s capacity to recognize reality or meet the demands of life.4 The definition of what constitutes a mental disorder varies by state, but the burden of persuasion—the standard by which the court must be convinced—is generally uniform.5 In the 1979 case Addington v Texas, the United States Supreme Court concluded that in a civil commitment hearing, the minimum standard of proof for involuntary commitment must be clear and convincing evidence.6 Neither medical certainty nor substantial probability are burdens of persuasions.6 Instead, these terms may be presented in a forensic report when an examiner outlines their opinion. Table 1 and the Figure provide more detail on burdens of persuasion.
TREATMENT Civil commitment and patient rights
At a regularly scheduled treatment team meeting, the team informs Mr. H that he has been civilly committed for further treatment. Mr. H becomes upset and tells the team the decision is a complete violation of his rights. After a long rant, Mr. H walks out of the room, saying, “I did not even know when this hearing was.” A member of the treatment team becomes concerned that Mr. H may not have been notified of the hearing.
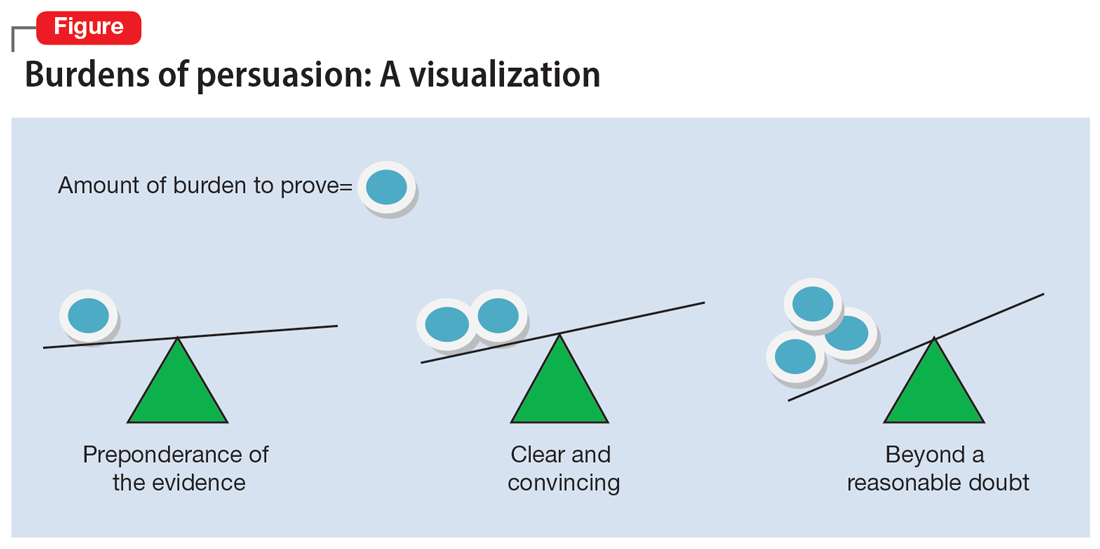
[polldaddy:11189294]
The author’s observations
It is not clear if Mr. H had been notified of his civil commitment hearing. If Mr. H had not been notified, his rights would have been compromised. Lessard v Schmidt (1972) outlined that individuals involved in a civil commitment hearing should be afforded the same rights as those involved in criminal proceedings.7 Mr. H should have been notified of his hearing and afforded the opportunity to have the assignment of counsel, the right to appear, the right to testify, the right to present witnesses and other evidence, and the right to confront witnesses.
Without notification of the hearing, the only right that would have remained intact for Mr. H would have been the assignment of counsel in his absence and without his knowledge. If Mr. H had been notified of the hearing and did not want to attend, yet still desired legal counsel, he could have waived his presence voluntarily after discussing this option with his attorney.8,9
Continue to: OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
During his 10-day stay, Mr. H is treated with sertraline 50 mg/d and engages in individual and group therapy. He shows noticeable improvement in his depressive symptoms and reports having no thoughts of suicide or self-harm. The treatment team determines it is appropriate to discharge him home (the firearm was never found) and involves his wife in safety planning and follow-up care. On the day of his discharge, Mr. H reflects on his treatment and civil commitment. He says, “I did not know a judge could order me to be hospitalized.”
[polldaddy:11189297]
The author’s observations
The physician’s decision to pursue civil commitment is best described by the legal doctrines of police powers and parens patriae. Other relevant ethical principles are described in Table 2.10

Though ethical principles may play a role in civil commitment, parens patriae and police powers is the answer with respect to the State.11Parens patriae is Latin for the “parent of the country” and grants the State the power to protect those residents who are most vulnerable. Police power is the authority of the State to enact and enforce rules that limit the rights of individuals for the greater good of ensuring health, safety, and welfare of all citizens.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists are entrusted with recognizing when a patient, due to mental illness, is a danger to themselves or others and in need of treatment. After an emergency detention period, if the patient remains a danger to themselves or others and does not want to voluntarily receive treatment, a court hearing is required. As an expert witness, the treating psychiatrist should know the factors of law in their jurisdiction that determine civil commitment.
Related Resources
- Extreme Risk Protection Orders. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. https://www.jhsph.edu/research/ centers-and-institutes/johns-hopkins-center-for-gun-violenceprevention-and-policy/research/extreme-risk-protectionorders/
- Gutheil TG. The Psychiatrist as Expert Witness. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2009.
- Landmark Cases 2014. American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. https://www.aapl.org/landmark-cases
Drug Brand Names
Sertraline • Zoloft
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for Civil Commitment. Oxford University Press; 2012.
2. Thatcher BT, Mossman D. Testifying for civil commitment: help unwilling patients get the treatment they need. Current Psychiatry. 2009;8(11):51-56.
3. Marett CP, Mossman D. What is your liability for involuntary commitment based on faulty information? Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(3):21-25,33.
4. Ohio Rev Code § 5122.01 (2018).
5. The Burden of Proof. University of Minnesota. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://open.lib.umn.edu/criminallaw/chapter/2-4-the-burden-of-proof/
6. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018.
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020.
8. Cook J. Good lawyering and bad role models: the role of respondent’s counsel in a civil commitment hearing. Georgetown Journal of Legal Ethics. 2000;14(1):179-195.
9. Ferris CE. The search for due process in civil commitment hearings: how procedural realities have altered substantive standards. Vanderbilt Law Rev. 2008;61(3):959-981.
10. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Civil Commitment and the Mental Health Care Continuum: Historical Trends and Principles for Law and Practice. 2019. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/resource/ebp/civil-commitment-mental-health-care-continuum-historical-trends-principles-law
11. Melton GB, Petrila J, Poythress NG, et al. Psychological Evaluations for the Courts: A Handbook for Mental Health Profession. 4th ed. Guilford Press; 2018.
CASE Depressed and suicidal
Police arrive at the home of Mr. H, age 50, after his wife calls 911. She reports he has depression and she saw him in bed brandishing a firearm as if he wanted to hurt himself. Upon arrival, the officers enter the house and find Mr. H in bed without a firearm. Mr. H says little to the officers about the alleged events, but acknowledges he has depression and is willing to go the hospital for further evaluation. Neither his wife nor the officers locate a firearm in the home.
EVALUATION Emergency detention
In the emergency department (ED), Mr. H’s laboratory results and physical examination findings are normal. He acknowledges feeling depressed over the past 2 weeks. Though he cannot identify any precipitants, he says he has experienced anhedonia, lack of appetite, decreased energy, and changes in his sleep patterns. When asked about the day’s events concerning the firearm, Mr. H becomes guarded and does not give a clear answer regarding having thoughts of suicide.
The evaluating psychiatrist obtains collateral from Mr. H’s wife and reviews his medical records. There are no active prescriptions on file and the psychiatrist notices that last year there was a suicide attempt involving a firearm. Following that episode, Mr. H was hospitalized, treated with sertraline 50 mg/d, and discharged with a diagnosis of major depressive disorder. There was no legal or substance abuse history.
In the ED, the psychiatrist conducts a psychiatric evaluation, including a suicide risk assessment, and determines Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life. Mr. H’s psychiatrist explains there are 2 treatment options: to be admitted to the hospital or to be discharged. The psychiatrist recommends hospital admission to Mr. H for his safety and stabilization. Mr. H says he prefers to return home.
Because the psychiatrist believes Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life and there is no less restrictive setting for treatment, he implements an emergency detention. In Ohio, this allows Mr. H to be held in the hospital for no more than 3 court days in accordance with state law. Before Mr. H’s emergency detention periods ends, the psychiatrist will need to decide whether Mr. H can be safely discharged. If the psychiatrist determines that Mr. H still needs treatment, the court will be petitioned for a civil commitment hearing.
[polldaddy:11189291]
The author’s observations
In some cases, courts allow information a psychiatrist does not directly obtain from a patient to be admitted as testimony in a civil commitment hearing. However, some jurisdictions consider sources of information not obtained directly from the patient as hearsay and thus inadmissible.1 Though each source listed may provide credible information that could be presented at a hearing, the psychiatrist should discuss with the patient the information obtained from these sources to ensure it is admissable.2 A discussion with Mr. H about the factors that led to his hospital arrival will avoid the psychiatrist’s reliance on what another person has heard or seen when providing testimony. Even when a psychiatrist is not faced with an issue of admissibility, caution must be taken with third-party reports.3
TREATMENT Civil commitment hearing
Before the emergency detention period expires, Mr. H’s psychiatrist determines that he remains at imminent risk of self-harm. To continue hospitalization, the psychiatrist files a petition for civil commitment and testifies at the commitment hearing. He reports that Mr. H suffers from a substantial mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The psychiatrist also testifies that the least restrictive environment for treatment continues to be inpatient hospitalization, because Mr. H is still at imminent risk of harming himself.
Continue to: Following the psychiatrist's...
Following the psychiatrist’s testimony, the magistrate finds that Mr. H is a mentally ill person subject to hospitalization given his mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The magistrate orders that Mr. H be civilly committed to the hospital.
[polldaddy:11189293]
The author’s observations
The psychiatrist’s testimony mirrors the language regarding civil commitment in the Ohio Revised Code.4 Other elements considered for mental illness in Ohio are a substantial disorder of memory, thought, orientation, or perception that grossly impairs one’s capacity to recognize reality or meet the demands of life.4 The definition of what constitutes a mental disorder varies by state, but the burden of persuasion—the standard by which the court must be convinced—is generally uniform.5 In the 1979 case Addington v Texas, the United States Supreme Court concluded that in a civil commitment hearing, the minimum standard of proof for involuntary commitment must be clear and convincing evidence.6 Neither medical certainty nor substantial probability are burdens of persuasions.6 Instead, these terms may be presented in a forensic report when an examiner outlines their opinion. Table 1 and the Figure provide more detail on burdens of persuasion.

TREATMENT Civil commitment and patient rights
At a regularly scheduled treatment team meeting, the team informs Mr. H that he has been civilly committed for further treatment. Mr. H becomes upset and tells the team the decision is a complete violation of his rights. After a long rant, Mr. H walks out of the room, saying, “I did not even know when this hearing was.” A member of the treatment team becomes concerned that Mr. H may not have been notified of the hearing.

[polldaddy:11189294]
The author’s observations
It is not clear if Mr. H had been notified of his civil commitment hearing. If Mr. H had not been notified, his rights would have been compromised. Lessard v Schmidt (1972) outlined that individuals involved in a civil commitment hearing should be afforded the same rights as those involved in criminal proceedings.7 Mr. H should have been notified of his hearing and afforded the opportunity to have the assignment of counsel, the right to appear, the right to testify, the right to present witnesses and other evidence, and the right to confront witnesses.
Without notification of the hearing, the only right that would have remained intact for Mr. H would have been the assignment of counsel in his absence and without his knowledge. If Mr. H had been notified of the hearing and did not want to attend, yet still desired legal counsel, he could have waived his presence voluntarily after discussing this option with his attorney.8,9
Continue to: OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
During his 10-day stay, Mr. H is treated with sertraline 50 mg/d and engages in individual and group therapy. He shows noticeable improvement in his depressive symptoms and reports having no thoughts of suicide or self-harm. The treatment team determines it is appropriate to discharge him home (the firearm was never found) and involves his wife in safety planning and follow-up care. On the day of his discharge, Mr. H reflects on his treatment and civil commitment. He says, “I did not know a judge could order me to be hospitalized.”
[polldaddy:11189297]
The author’s observations
The physician’s decision to pursue civil commitment is best described by the legal doctrines of police powers and parens patriae. Other relevant ethical principles are described in Table 2.10

Though ethical principles may play a role in civil commitment, parens patriae and police powers is the answer with respect to the State.11Parens patriae is Latin for the “parent of the country” and grants the State the power to protect those residents who are most vulnerable. Police power is the authority of the State to enact and enforce rules that limit the rights of individuals for the greater good of ensuring health, safety, and welfare of all citizens.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists are entrusted with recognizing when a patient, due to mental illness, is a danger to themselves or others and in need of treatment. After an emergency detention period, if the patient remains a danger to themselves or others and does not want to voluntarily receive treatment, a court hearing is required. As an expert witness, the treating psychiatrist should know the factors of law in their jurisdiction that determine civil commitment.
Related Resources
- Extreme Risk Protection Orders. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. https://www.jhsph.edu/research/ centers-and-institutes/johns-hopkins-center-for-gun-violenceprevention-and-policy/research/extreme-risk-protectionorders/
- Gutheil TG. The Psychiatrist as Expert Witness. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2009.
- Landmark Cases 2014. American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. https://www.aapl.org/landmark-cases
Drug Brand Names
Sertraline • Zoloft
CASE Depressed and suicidal
Police arrive at the home of Mr. H, age 50, after his wife calls 911. She reports he has depression and she saw him in bed brandishing a firearm as if he wanted to hurt himself. Upon arrival, the officers enter the house and find Mr. H in bed without a firearm. Mr. H says little to the officers about the alleged events, but acknowledges he has depression and is willing to go the hospital for further evaluation. Neither his wife nor the officers locate a firearm in the home.
EVALUATION Emergency detention
In the emergency department (ED), Mr. H’s laboratory results and physical examination findings are normal. He acknowledges feeling depressed over the past 2 weeks. Though he cannot identify any precipitants, he says he has experienced anhedonia, lack of appetite, decreased energy, and changes in his sleep patterns. When asked about the day’s events concerning the firearm, Mr. H becomes guarded and does not give a clear answer regarding having thoughts of suicide.
The evaluating psychiatrist obtains collateral from Mr. H’s wife and reviews his medical records. There are no active prescriptions on file and the psychiatrist notices that last year there was a suicide attempt involving a firearm. Following that episode, Mr. H was hospitalized, treated with sertraline 50 mg/d, and discharged with a diagnosis of major depressive disorder. There was no legal or substance abuse history.
In the ED, the psychiatrist conducts a psychiatric evaluation, including a suicide risk assessment, and determines Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life. Mr. H’s psychiatrist explains there are 2 treatment options: to be admitted to the hospital or to be discharged. The psychiatrist recommends hospital admission to Mr. H for his safety and stabilization. Mr. H says he prefers to return home.
Because the psychiatrist believes Mr. H is at imminent risk of ending his life and there is no less restrictive setting for treatment, he implements an emergency detention. In Ohio, this allows Mr. H to be held in the hospital for no more than 3 court days in accordance with state law. Before Mr. H’s emergency detention periods ends, the psychiatrist will need to decide whether Mr. H can be safely discharged. If the psychiatrist determines that Mr. H still needs treatment, the court will be petitioned for a civil commitment hearing.
[polldaddy:11189291]
The author’s observations
In some cases, courts allow information a psychiatrist does not directly obtain from a patient to be admitted as testimony in a civil commitment hearing. However, some jurisdictions consider sources of information not obtained directly from the patient as hearsay and thus inadmissible.1 Though each source listed may provide credible information that could be presented at a hearing, the psychiatrist should discuss with the patient the information obtained from these sources to ensure it is admissable.2 A discussion with Mr. H about the factors that led to his hospital arrival will avoid the psychiatrist’s reliance on what another person has heard or seen when providing testimony. Even when a psychiatrist is not faced with an issue of admissibility, caution must be taken with third-party reports.3
TREATMENT Civil commitment hearing
Before the emergency detention period expires, Mr. H’s psychiatrist determines that he remains at imminent risk of self-harm. To continue hospitalization, the psychiatrist files a petition for civil commitment and testifies at the commitment hearing. He reports that Mr. H suffers from a substantial mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The psychiatrist also testifies that the least restrictive environment for treatment continues to be inpatient hospitalization, because Mr. H is still at imminent risk of harming himself.
Continue to: Following the psychiatrist's...
Following the psychiatrist’s testimony, the magistrate finds that Mr. H is a mentally ill person subject to hospitalization given his mood disorder that grossly impairs his judgment and behavior. The magistrate orders that Mr. H be civilly committed to the hospital.
[polldaddy:11189293]
The author’s observations
The psychiatrist’s testimony mirrors the language regarding civil commitment in the Ohio Revised Code.4 Other elements considered for mental illness in Ohio are a substantial disorder of memory, thought, orientation, or perception that grossly impairs one’s capacity to recognize reality or meet the demands of life.4 The definition of what constitutes a mental disorder varies by state, but the burden of persuasion—the standard by which the court must be convinced—is generally uniform.5 In the 1979 case Addington v Texas, the United States Supreme Court concluded that in a civil commitment hearing, the minimum standard of proof for involuntary commitment must be clear and convincing evidence.6 Neither medical certainty nor substantial probability are burdens of persuasions.6 Instead, these terms may be presented in a forensic report when an examiner outlines their opinion. Table 1 and the Figure provide more detail on burdens of persuasion.

TREATMENT Civil commitment and patient rights
At a regularly scheduled treatment team meeting, the team informs Mr. H that he has been civilly committed for further treatment. Mr. H becomes upset and tells the team the decision is a complete violation of his rights. After a long rant, Mr. H walks out of the room, saying, “I did not even know when this hearing was.” A member of the treatment team becomes concerned that Mr. H may not have been notified of the hearing.

[polldaddy:11189294]
The author’s observations
It is not clear if Mr. H had been notified of his civil commitment hearing. If Mr. H had not been notified, his rights would have been compromised. Lessard v Schmidt (1972) outlined that individuals involved in a civil commitment hearing should be afforded the same rights as those involved in criminal proceedings.7 Mr. H should have been notified of his hearing and afforded the opportunity to have the assignment of counsel, the right to appear, the right to testify, the right to present witnesses and other evidence, and the right to confront witnesses.
Without notification of the hearing, the only right that would have remained intact for Mr. H would have been the assignment of counsel in his absence and without his knowledge. If Mr. H had been notified of the hearing and did not want to attend, yet still desired legal counsel, he could have waived his presence voluntarily after discussing this option with his attorney.8,9
Continue to: OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
OUTCOME Stabilization and discharge
During his 10-day stay, Mr. H is treated with sertraline 50 mg/d and engages in individual and group therapy. He shows noticeable improvement in his depressive symptoms and reports having no thoughts of suicide or self-harm. The treatment team determines it is appropriate to discharge him home (the firearm was never found) and involves his wife in safety planning and follow-up care. On the day of his discharge, Mr. H reflects on his treatment and civil commitment. He says, “I did not know a judge could order me to be hospitalized.”
[polldaddy:11189297]
The author’s observations
The physician’s decision to pursue civil commitment is best described by the legal doctrines of police powers and parens patriae. Other relevant ethical principles are described in Table 2.10

Though ethical principles may play a role in civil commitment, parens patriae and police powers is the answer with respect to the State.11Parens patriae is Latin for the “parent of the country” and grants the State the power to protect those residents who are most vulnerable. Police power is the authority of the State to enact and enforce rules that limit the rights of individuals for the greater good of ensuring health, safety, and welfare of all citizens.
Bottom Line
Psychiatrists are entrusted with recognizing when a patient, due to mental illness, is a danger to themselves or others and in need of treatment. After an emergency detention period, if the patient remains a danger to themselves or others and does not want to voluntarily receive treatment, a court hearing is required. As an expert witness, the treating psychiatrist should know the factors of law in their jurisdiction that determine civil commitment.
Related Resources
- Extreme Risk Protection Orders. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. https://www.jhsph.edu/research/ centers-and-institutes/johns-hopkins-center-for-gun-violenceprevention-and-policy/research/extreme-risk-protectionorders/
- Gutheil TG. The Psychiatrist as Expert Witness. 2nd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2009.
- Landmark Cases 2014. American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. https://www.aapl.org/landmark-cases
Drug Brand Names
Sertraline • Zoloft
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for Civil Commitment. Oxford University Press; 2012.
2. Thatcher BT, Mossman D. Testifying for civil commitment: help unwilling patients get the treatment they need. Current Psychiatry. 2009;8(11):51-56.
3. Marett CP, Mossman D. What is your liability for involuntary commitment based on faulty information? Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(3):21-25,33.
4. Ohio Rev Code § 5122.01 (2018).
5. The Burden of Proof. University of Minnesota. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://open.lib.umn.edu/criminallaw/chapter/2-4-the-burden-of-proof/
6. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018.
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020.
8. Cook J. Good lawyering and bad role models: the role of respondent’s counsel in a civil commitment hearing. Georgetown Journal of Legal Ethics. 2000;14(1):179-195.
9. Ferris CE. The search for due process in civil commitment hearings: how procedural realities have altered substantive standards. Vanderbilt Law Rev. 2008;61(3):959-981.
10. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Civil Commitment and the Mental Health Care Continuum: Historical Trends and Principles for Law and Practice. 2019. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/resource/ebp/civil-commitment-mental-health-care-continuum-historical-trends-principles-law
11. Melton GB, Petrila J, Poythress NG, et al. Psychological Evaluations for the Courts: A Handbook for Mental Health Profession. 4th ed. Guilford Press; 2018.
1. Pinals DA, Mossman D. Evaluation for Civil Commitment. Oxford University Press; 2012.
2. Thatcher BT, Mossman D. Testifying for civil commitment: help unwilling patients get the treatment they need. Current Psychiatry. 2009;8(11):51-56.
3. Marett CP, Mossman D. What is your liability for involuntary commitment based on faulty information? Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(3):21-25,33.
4. Ohio Rev Code § 5122.01 (2018).
5. The Burden of Proof. University of Minnesota. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://open.lib.umn.edu/criminallaw/chapter/2-4-the-burden-of-proof/
6. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2018.
7. Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Suicide Assessment and Management. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2020.
8. Cook J. Good lawyering and bad role models: the role of respondent’s counsel in a civil commitment hearing. Georgetown Journal of Legal Ethics. 2000;14(1):179-195.
9. Ferris CE. The search for due process in civil commitment hearings: how procedural realities have altered substantive standards. Vanderbilt Law Rev. 2008;61(3):959-981.
10. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Civil Commitment and the Mental Health Care Continuum: Historical Trends and Principles for Law and Practice. 2019. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://www.samhsa.gov/resource/ebp/civil-commitment-mental-health-care-continuum-historical-trends-principles-law
11. Melton GB, Petrila J, Poythress NG, et al. Psychological Evaluations for the Courts: A Handbook for Mental Health Profession. 4th ed. Guilford Press; 2018.
Preparing patients with serious mental illness for extreme HEAT
Climate change is causing intense heat waves that threaten human health across the globe.
A confluence of factors increases risk
Thermoregulatory dysfunction is thought to be intrinsic to patients with schizophrenia partly due to dysregulated dopaminergic neurotransmission.2 This is compounded by these patients’ higher burden of chronic medical comorbidities such as cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses, which together with psychotropic (ie, antipsychotics, antidepressants, lithium, benzodiazepines) and medical medications (ie, certain antihypertensives, diuretics, treatment for urinary incontinence) further disrupt the body’s cooling strategies and increase vulnerability to heat-related illnesses.1,3 Antipsychotics commonly prescribed to patients with SMI increase hyperthermia risk largely by 2 mechanisms: central and peripheral thermal dysregulation, and anticholinergic properties (ie, olanzapine, clozapine, chlorpromazine).2,3 Other anticholinergic medications prescribed to treat extrapyramidal symptoms (ie, diphenhydramine, benztropine, trihexyphenidyl), anxiety, depression, and insomnia (ie, paroxetine, trazodone, doxepin) further add insult to injury because they impair sweating, which decreases the body’s ability to eliminate heat through evaporation.2,3 Additionally, high temperature exacerbates psychiatric symptoms in patients with SMI, resulting in increased hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
How to keep patients safe
The acronym HEAT provides a framework that psychiatrists can use to highlight the importance of planning for heat waves in their institution and guiding discussions with individual patients about heat-related illnesses (Table 1).

Help the health care system where you work plan and prepare for heat waves. In-service training in mental health settings such as outpatient clinics, shelters, group homes, and residential programs can help staff identify patients at particular risk and reinforce key prevention messages.
Educate patients and their caregivers on strategies for preventing heat-related illness. Informational materials can be distributed in clinics, residential settings, and day programs. A 1-page downloadable pamphlet available at https://smiadviser.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SMI-Heat-Stroke-ver1.0-FINAL.pdf summarizes key prevention messages of staying hydrated, staying cool, and staying safe.
Assess personalized heat-related risks. Inquire about patients’ daily activities, access to air conditioning, and water intake. Minimize the use of anticholinergic medications. Identify who patients can turn to for assistance, especially for those who struggle with cognitive impairment and social isolation.
Teach patients, caregivers, and staff the signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat stroke and how to respond in such situations.
HEAT focuses psychiatric clinicians on preparing and protecting patients with SMI against dangerous heat waves. Clinicians can take a proactive leadership role in disseminating basic principles of heat-related illness prevention and heat-wave toolkits by using resources available from organizations such as the Climate Psychiatry Alliance (Table 2). They can also initiate advocacy efforts to raise awareness about the elevated risks of heat-related illnesses in this vulnerable population.

1. Schmeltz MT, Gamble JL. Risk characterization of hospitalizations for mental illness and/or behavioral disorders with concurrent heat-related illness. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186509. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186509
2. Lee CP, Chen PJ, Chang CM. Heat stroke during treatment with olanzapine, trihexyphenidyl, and trazodone in a patient with schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2015;27(6):380-385.
3. Bongers KS, Salahudeen MS, Peterson GM. Drug-associated non-pyrogenic hyperthermia: a narrative review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;76(1):9-16.
Climate change is causing intense heat waves that threaten human health across the globe.
A confluence of factors increases risk
Thermoregulatory dysfunction is thought to be intrinsic to patients with schizophrenia partly due to dysregulated dopaminergic neurotransmission.2 This is compounded by these patients’ higher burden of chronic medical comorbidities such as cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses, which together with psychotropic (ie, antipsychotics, antidepressants, lithium, benzodiazepines) and medical medications (ie, certain antihypertensives, diuretics, treatment for urinary incontinence) further disrupt the body’s cooling strategies and increase vulnerability to heat-related illnesses.1,3 Antipsychotics commonly prescribed to patients with SMI increase hyperthermia risk largely by 2 mechanisms: central and peripheral thermal dysregulation, and anticholinergic properties (ie, olanzapine, clozapine, chlorpromazine).2,3 Other anticholinergic medications prescribed to treat extrapyramidal symptoms (ie, diphenhydramine, benztropine, trihexyphenidyl), anxiety, depression, and insomnia (ie, paroxetine, trazodone, doxepin) further add insult to injury because they impair sweating, which decreases the body’s ability to eliminate heat through evaporation.2,3 Additionally, high temperature exacerbates psychiatric symptoms in patients with SMI, resulting in increased hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
How to keep patients safe
The acronym HEAT provides a framework that psychiatrists can use to highlight the importance of planning for heat waves in their institution and guiding discussions with individual patients about heat-related illnesses (Table 1).

Help the health care system where you work plan and prepare for heat waves. In-service training in mental health settings such as outpatient clinics, shelters, group homes, and residential programs can help staff identify patients at particular risk and reinforce key prevention messages.
Educate patients and their caregivers on strategies for preventing heat-related illness. Informational materials can be distributed in clinics, residential settings, and day programs. A 1-page downloadable pamphlet available at https://smiadviser.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SMI-Heat-Stroke-ver1.0-FINAL.pdf summarizes key prevention messages of staying hydrated, staying cool, and staying safe.
Assess personalized heat-related risks. Inquire about patients’ daily activities, access to air conditioning, and water intake. Minimize the use of anticholinergic medications. Identify who patients can turn to for assistance, especially for those who struggle with cognitive impairment and social isolation.
Teach patients, caregivers, and staff the signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat stroke and how to respond in such situations.
HEAT focuses psychiatric clinicians on preparing and protecting patients with SMI against dangerous heat waves. Clinicians can take a proactive leadership role in disseminating basic principles of heat-related illness prevention and heat-wave toolkits by using resources available from organizations such as the Climate Psychiatry Alliance (Table 2). They can also initiate advocacy efforts to raise awareness about the elevated risks of heat-related illnesses in this vulnerable population.

Climate change is causing intense heat waves that threaten human health across the globe.
A confluence of factors increases risk
Thermoregulatory dysfunction is thought to be intrinsic to patients with schizophrenia partly due to dysregulated dopaminergic neurotransmission.2 This is compounded by these patients’ higher burden of chronic medical comorbidities such as cardiovascular and respiratory illnesses, which together with psychotropic (ie, antipsychotics, antidepressants, lithium, benzodiazepines) and medical medications (ie, certain antihypertensives, diuretics, treatment for urinary incontinence) further disrupt the body’s cooling strategies and increase vulnerability to heat-related illnesses.1,3 Antipsychotics commonly prescribed to patients with SMI increase hyperthermia risk largely by 2 mechanisms: central and peripheral thermal dysregulation, and anticholinergic properties (ie, olanzapine, clozapine, chlorpromazine).2,3 Other anticholinergic medications prescribed to treat extrapyramidal symptoms (ie, diphenhydramine, benztropine, trihexyphenidyl), anxiety, depression, and insomnia (ie, paroxetine, trazodone, doxepin) further add insult to injury because they impair sweating, which decreases the body’s ability to eliminate heat through evaporation.2,3 Additionally, high temperature exacerbates psychiatric symptoms in patients with SMI, resulting in increased hospitalizations and emergency department visits.
How to keep patients safe
The acronym HEAT provides a framework that psychiatrists can use to highlight the importance of planning for heat waves in their institution and guiding discussions with individual patients about heat-related illnesses (Table 1).

Help the health care system where you work plan and prepare for heat waves. In-service training in mental health settings such as outpatient clinics, shelters, group homes, and residential programs can help staff identify patients at particular risk and reinforce key prevention messages.
Educate patients and their caregivers on strategies for preventing heat-related illness. Informational materials can be distributed in clinics, residential settings, and day programs. A 1-page downloadable pamphlet available at https://smiadviser.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/SMI-Heat-Stroke-ver1.0-FINAL.pdf summarizes key prevention messages of staying hydrated, staying cool, and staying safe.
Assess personalized heat-related risks. Inquire about patients’ daily activities, access to air conditioning, and water intake. Minimize the use of anticholinergic medications. Identify who patients can turn to for assistance, especially for those who struggle with cognitive impairment and social isolation.
Teach patients, caregivers, and staff the signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion and heat stroke and how to respond in such situations.
HEAT focuses psychiatric clinicians on preparing and protecting patients with SMI against dangerous heat waves. Clinicians can take a proactive leadership role in disseminating basic principles of heat-related illness prevention and heat-wave toolkits by using resources available from organizations such as the Climate Psychiatry Alliance (Table 2). They can also initiate advocacy efforts to raise awareness about the elevated risks of heat-related illnesses in this vulnerable population.

1. Schmeltz MT, Gamble JL. Risk characterization of hospitalizations for mental illness and/or behavioral disorders with concurrent heat-related illness. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186509. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186509
2. Lee CP, Chen PJ, Chang CM. Heat stroke during treatment with olanzapine, trihexyphenidyl, and trazodone in a patient with schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2015;27(6):380-385.
3. Bongers KS, Salahudeen MS, Peterson GM. Drug-associated non-pyrogenic hyperthermia: a narrative review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;76(1):9-16.
1. Schmeltz MT, Gamble JL. Risk characterization of hospitalizations for mental illness and/or behavioral disorders with concurrent heat-related illness. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186509. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186509
2. Lee CP, Chen PJ, Chang CM. Heat stroke during treatment with olanzapine, trihexyphenidyl, and trazodone in a patient with schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2015;27(6):380-385.
3. Bongers KS, Salahudeen MS, Peterson GM. Drug-associated non-pyrogenic hyperthermia: a narrative review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;76(1):9-16.
Lithium for bipolar disorder: Which patients will respond?
Though Cade discovered it 70 years ago, lithium is still considered the gold standard treatment for preventing manic and depressive phases of bipolar disorder (BD). In addition to its primary indication as a mood stabilizer, lithium has demonstrated efficacy as an augmenting medication for unipolar major depressive disorder.1 While lithium is a first-line agent for BD, it does not improve symptoms in every patient. In a 2004 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials of patients with BD, Geddes et al2 found lithium was more effective than placebo in preventing the recurrence of mania, with 60% in the lithium group remaining stable compared to 40% in the placebo group. Being able to predict which patients will respond to lithium is crucial to prevent unnecessary exposure to lithium, which can produce significant adverse effects, including somnolence, nausea, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism.2
Several studies have investigated various clinical factors that might predict which patients with BD will respond to lithium. In a review, Kleindienst et al3 highlighted 3 factors that predicted a positive response to lithium:
- fewer hospitalizations prior to treatment
- an episodic course characterized sequentially by mania, depression, and then euthymia
- a later age (>50) at onset of BD.
Recent studies and reviews have isolated additional positive predictors, including having a family history of BD and a shorter duration of illness before receiving lithium, as well as negative predictors, such as rapid cycling, a large number of previous hospitalizations, a depression/mania/euthymia pattern, mood-incongruent psychotic features, and the presence of residual symptoms between mood episodes.3,4
The Table provides a list of probable and possible positive and negative predictors for therapeutic response to lithium in patients with BD.3-6 While relevant, the factors listed as possible predictors may not carry as much influence on lithium responsivity as those categorized as probable predictors.
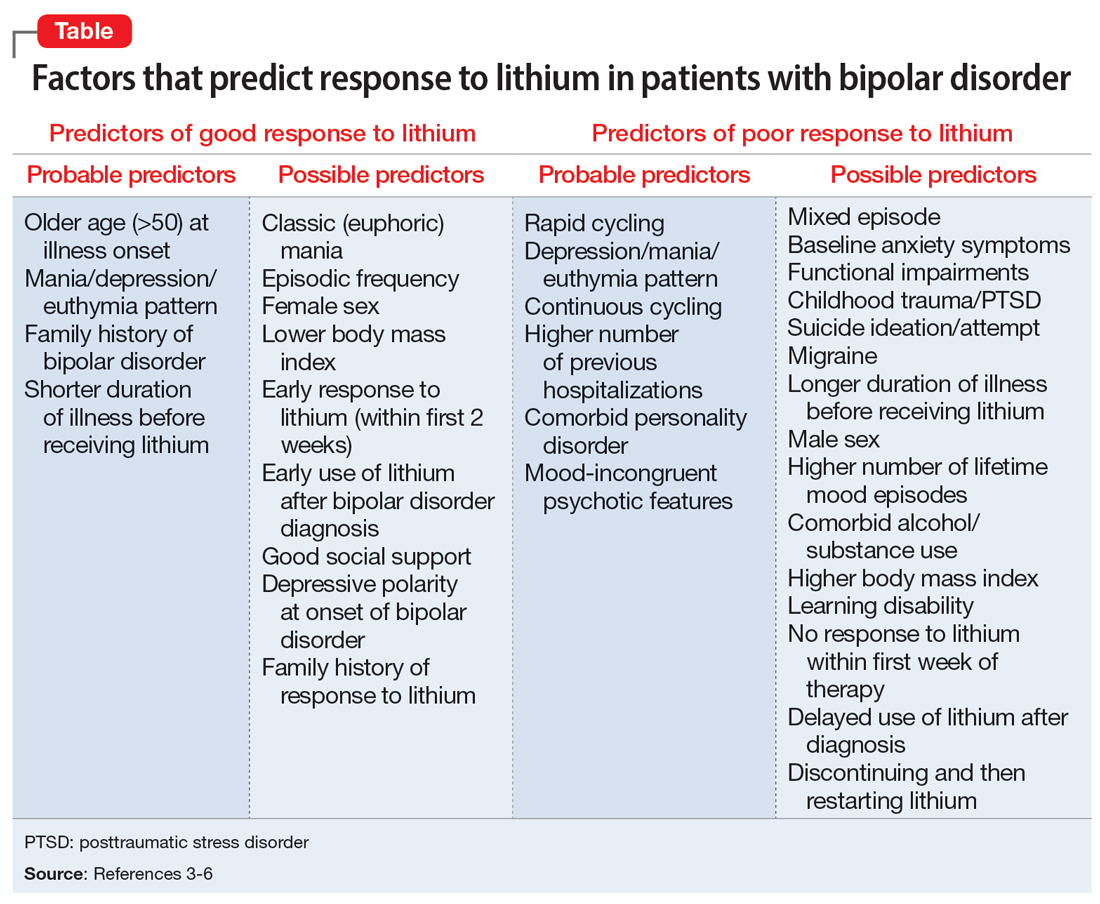
Because of heterogeneity among studies, clinicians should consider their patient’s presentation as a whole, rather than basing medication choice on independent factors. Ultimately, more studies are required to fully determine the most relevant clinical parameters for lithium response. Overall, however, it appears these clinical factors could be extremely useful to guide psychiatrists in the optimal use of lithium while caring for patients with BD.
1. Crossley NA, Bauer M. Acceleration and augmentation of antidepressants with lithium for depressive disorders: two meta-analyses of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(6):935-940.
2. Geddes JR, Burgess S, Hawton K, et al. Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;1m61(2):217-222.
3. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Which clinical factors predict response to prophylactic lithium? A systematic review for bipolar disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(5):404-417.
4. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Psychosocial and demographic factors associated with response to prophylactic lithium: a systematic review for bipolar disorders. Psychol Med. 2005;35(12):1685-1694.
5. Hui TP, Kandola A, Shen L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical predictors of lithium response in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2019;140(2):94-115.
6. Grillault Laroche D, Etain B, Severus E, et al. Socio-demographic and clinical predictors of outcome to long-term treatment with lithium in bipolar disorders: a systematic review of the contemporary literature and recommendations from the ISBD/IGSLI Task Force on treatment with lithium. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2020;8(1):40.
Though Cade discovered it 70 years ago, lithium is still considered the gold standard treatment for preventing manic and depressive phases of bipolar disorder (BD). In addition to its primary indication as a mood stabilizer, lithium has demonstrated efficacy as an augmenting medication for unipolar major depressive disorder.1 While lithium is a first-line agent for BD, it does not improve symptoms in every patient. In a 2004 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials of patients with BD, Geddes et al2 found lithium was more effective than placebo in preventing the recurrence of mania, with 60% in the lithium group remaining stable compared to 40% in the placebo group. Being able to predict which patients will respond to lithium is crucial to prevent unnecessary exposure to lithium, which can produce significant adverse effects, including somnolence, nausea, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism.2
Several studies have investigated various clinical factors that might predict which patients with BD will respond to lithium. In a review, Kleindienst et al3 highlighted 3 factors that predicted a positive response to lithium:
- fewer hospitalizations prior to treatment
- an episodic course characterized sequentially by mania, depression, and then euthymia
- a later age (>50) at onset of BD.
Recent studies and reviews have isolated additional positive predictors, including having a family history of BD and a shorter duration of illness before receiving lithium, as well as negative predictors, such as rapid cycling, a large number of previous hospitalizations, a depression/mania/euthymia pattern, mood-incongruent psychotic features, and the presence of residual symptoms between mood episodes.3,4
The Table provides a list of probable and possible positive and negative predictors for therapeutic response to lithium in patients with BD.3-6 While relevant, the factors listed as possible predictors may not carry as much influence on lithium responsivity as those categorized as probable predictors.

Because of heterogeneity among studies, clinicians should consider their patient’s presentation as a whole, rather than basing medication choice on independent factors. Ultimately, more studies are required to fully determine the most relevant clinical parameters for lithium response. Overall, however, it appears these clinical factors could be extremely useful to guide psychiatrists in the optimal use of lithium while caring for patients with BD.
Though Cade discovered it 70 years ago, lithium is still considered the gold standard treatment for preventing manic and depressive phases of bipolar disorder (BD). In addition to its primary indication as a mood stabilizer, lithium has demonstrated efficacy as an augmenting medication for unipolar major depressive disorder.1 While lithium is a first-line agent for BD, it does not improve symptoms in every patient. In a 2004 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials of patients with BD, Geddes et al2 found lithium was more effective than placebo in preventing the recurrence of mania, with 60% in the lithium group remaining stable compared to 40% in the placebo group. Being able to predict which patients will respond to lithium is crucial to prevent unnecessary exposure to lithium, which can produce significant adverse effects, including somnolence, nausea, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism.2
Several studies have investigated various clinical factors that might predict which patients with BD will respond to lithium. In a review, Kleindienst et al3 highlighted 3 factors that predicted a positive response to lithium:
- fewer hospitalizations prior to treatment
- an episodic course characterized sequentially by mania, depression, and then euthymia
- a later age (>50) at onset of BD.
Recent studies and reviews have isolated additional positive predictors, including having a family history of BD and a shorter duration of illness before receiving lithium, as well as negative predictors, such as rapid cycling, a large number of previous hospitalizations, a depression/mania/euthymia pattern, mood-incongruent psychotic features, and the presence of residual symptoms between mood episodes.3,4
The Table provides a list of probable and possible positive and negative predictors for therapeutic response to lithium in patients with BD.3-6 While relevant, the factors listed as possible predictors may not carry as much influence on lithium responsivity as those categorized as probable predictors.

Because of heterogeneity among studies, clinicians should consider their patient’s presentation as a whole, rather than basing medication choice on independent factors. Ultimately, more studies are required to fully determine the most relevant clinical parameters for lithium response. Overall, however, it appears these clinical factors could be extremely useful to guide psychiatrists in the optimal use of lithium while caring for patients with BD.
1. Crossley NA, Bauer M. Acceleration and augmentation of antidepressants with lithium for depressive disorders: two meta-analyses of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(6):935-940.
2. Geddes JR, Burgess S, Hawton K, et al. Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;1m61(2):217-222.
3. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Which clinical factors predict response to prophylactic lithium? A systematic review for bipolar disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(5):404-417.
4. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Psychosocial and demographic factors associated with response to prophylactic lithium: a systematic review for bipolar disorders. Psychol Med. 2005;35(12):1685-1694.
5. Hui TP, Kandola A, Shen L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical predictors of lithium response in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2019;140(2):94-115.
6. Grillault Laroche D, Etain B, Severus E, et al. Socio-demographic and clinical predictors of outcome to long-term treatment with lithium in bipolar disorders: a systematic review of the contemporary literature and recommendations from the ISBD/IGSLI Task Force on treatment with lithium. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2020;8(1):40.
1. Crossley NA, Bauer M. Acceleration and augmentation of antidepressants with lithium for depressive disorders: two meta-analyses of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(6):935-940.
2. Geddes JR, Burgess S, Hawton K, et al. Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;1m61(2):217-222.
3. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Which clinical factors predict response to prophylactic lithium? A systematic review for bipolar disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(5):404-417.
4. Kleindienst N, Engel RR, Greil W. Psychosocial and demographic factors associated with response to prophylactic lithium: a systematic review for bipolar disorders. Psychol Med. 2005;35(12):1685-1694.
5. Hui TP, Kandola A, Shen L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical predictors of lithium response in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2019;140(2):94-115.
6. Grillault Laroche D, Etain B, Severus E, et al. Socio-demographic and clinical predictors of outcome to long-term treatment with lithium in bipolar disorders: a systematic review of the contemporary literature and recommendations from the ISBD/IGSLI Task Force on treatment with lithium. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2020;8(1):40.