User login
Optimizing Narrowband UVB Phototherapy: Is It More Challenging for Your Older Patients?
Even with recent pharmacologic treatment advances, narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy remains a versatile, safe, and efficacious adjunctive or exclusive treatment for multiple dermatologic conditions, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
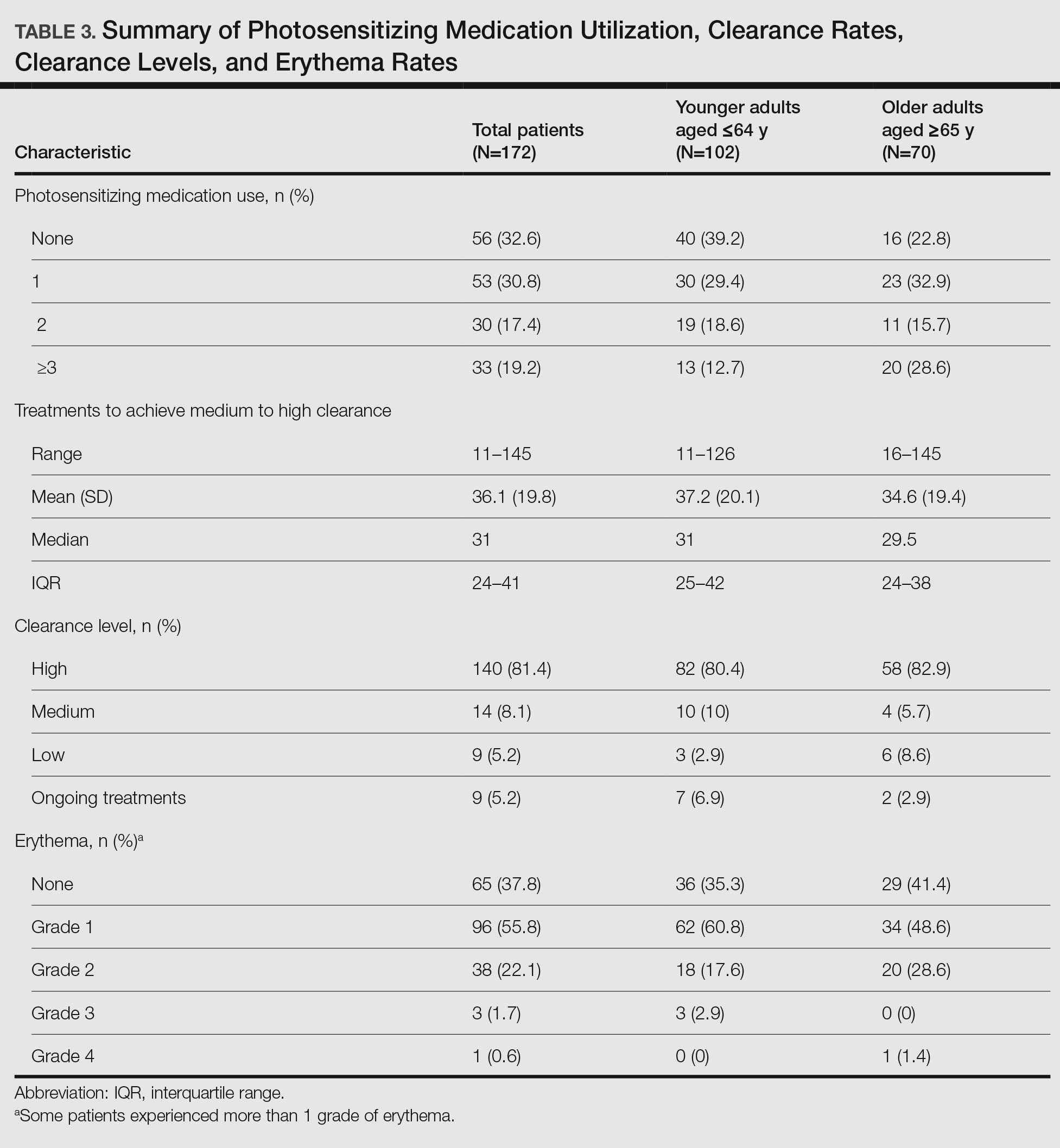
In a prior study, Matthews et al13 reported that 96% (50/52) of patients older than 65 years achieved medium to high levels of clearance with NB-UVB phototherapy. Nonetheless, 2 other findings in this study related to the number of treatments required to achieve clearance (ie, clearance rates) and erythema rates prompted further investigation. The first finding was higher-than-expected clearance rates. Older adults had a clearance rate with a mean of 33 treatments compared to prior studies featuring mean clearance rates of 20 to 28 treatments.7,8,14-16 This finding resembled a study in the United Kingdom17 with a median clearance rate in older adults of 30 treatments. In contrast, the median clearance rate from a study in Turkey18 was 42 treatments in older adults. We hypothesized that more photosensitizing medications used in older vs younger adults prompted more dose adjustments with NB-UVB phototherapy to avoid burning (ie, erythema) at baseline and throughout the treatment course. These dose adjustments may have increased the overall clearance rates. If true, we predicted that younger adults treated with the same protocol would have cleared more quickly, either because of age-related differences or because they likely had fewer comorbidities and therefore fewer medications.
The second finding from Matthews et al13 that warranted further investigation was a higher erythema rate compared to the older adult study from the United Kingdom.17 We hypothesized that potentially greater use of photosensitizing medications in the United States could explain the higher erythema rates. Although medication-induced photosensitivity is less likely with NB-UVB phototherapy than with UVA, certain medications can cause UVB photosensitivity, including thiazides, quinidine, calcium channel antagonists, phenothiazines, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.8,19,20 Therefore, photosensitizing medication use either at baseline or during a course of NB-UVB phototherapy could increase the risk for erythema. Age-related skin changes also have been considered as a
This retrospective study aimed to determine if NB-UVB phototherapy is equally effective in both older and younger adults treated with the same protocol; to examine the association between the use of photosensitizing medications and clearance rates in both older and younger adults; and to examine the association between the use of photosensitizing medications and erythema rates in older vs younger adults.
Methods
Study Design and Patients—This retrospective cohort study used billing records to identify patients who received NB-UVB phototherapy at 3 different clinical sites within a large US health care system in Washington (Group Health Cooperative, now Kaiser Permanente Washington), serving more than 600,000 patients between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2016. The institutional review board of Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute approved this study (IRB 1498087-4). Younger adults were classified as those 64 years or younger and older adults as those 65 years and older at the start of their phototherapy regimen. A power analysis determined that the optimal sample size for this study was 250 patients.
Individuals were excluded if they had fewer than 6 phototherapy treatments; a diagnosis of vitiligo, photosensitivity dermatitis, morphea, or pityriasis rubra pilaris; and/or treatment of the hands or feet only.
Phototherapy Protocol—Using a 48-lamp NB-UVB unit, trained phototherapy nurses provided all treatments following standardized treatment protocols13 based on previously published phototherapy guidelines.24 Nurses determined each patient’s disease clearance level using a 3-point clearance scale (high, medium, low).13 Each patient’s starting dose was determined based on the estimated MED for their skin phototype.
Statistical Analysis—Data were analyzed using Stata statistical software (StataCorp LLC). Univariate analyses were used to examine the data and identify outliers, bad values, and missing data, as well as to calculate descriptive statistics. Pearson χ2 and Fisher exact statistics were used to calculate differences in categorical variables. Linear multivariate regression models and logistic multivariate models were used to examine statistical relationships between variables. Statistical significance was defined as P≤.05.
Results
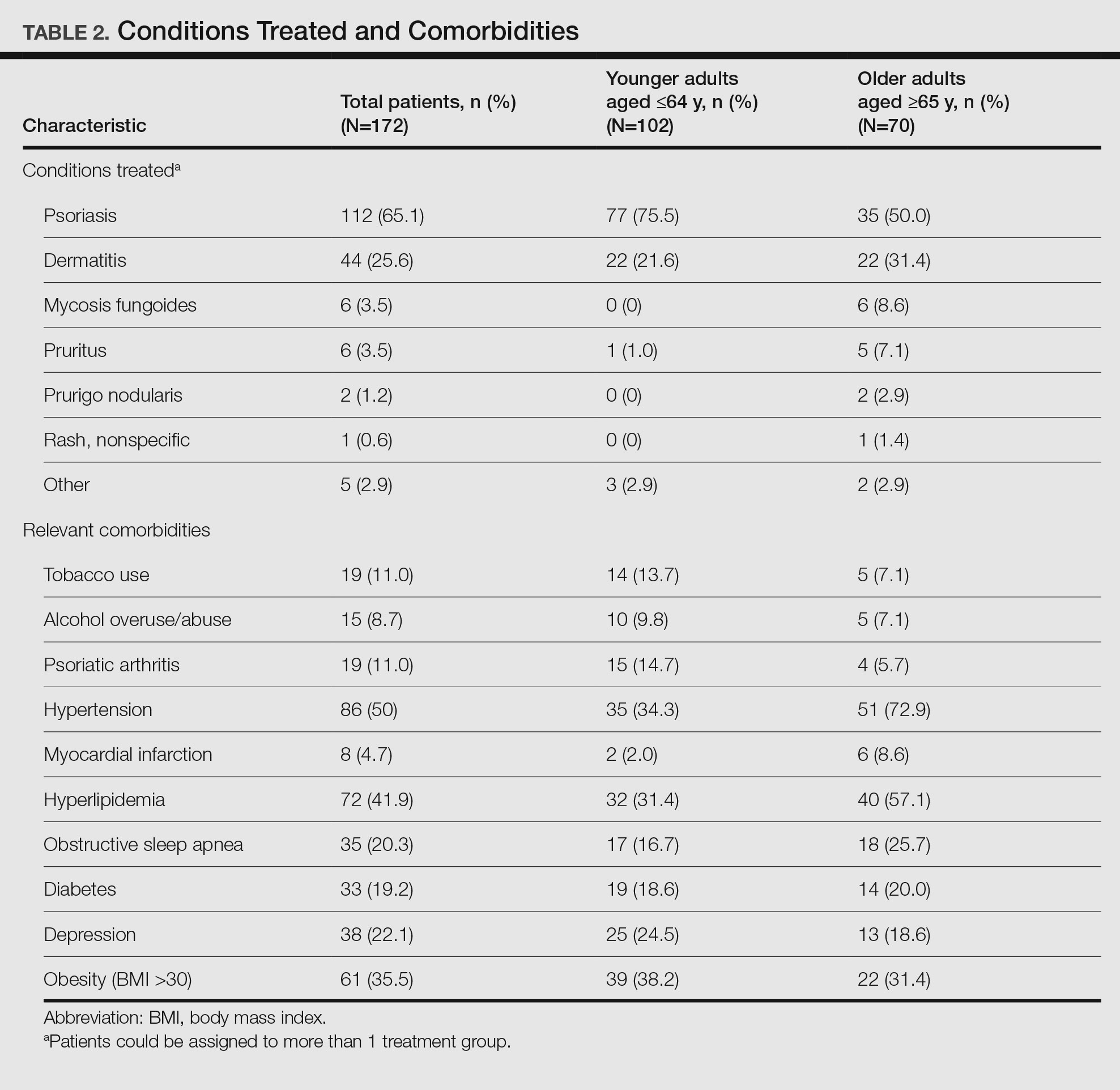
Patient Characteristics—Medical records were reviewed for 172 patients who received phototherapy between 2012 and 2016. Patients ranged in age from 23 to 91 years, with 102 patients 64 years and younger and 70 patients 65 years and older. Tables 1 and 2 outline the patient characteristics and conditions treated.

Phototherapy Effectiveness—
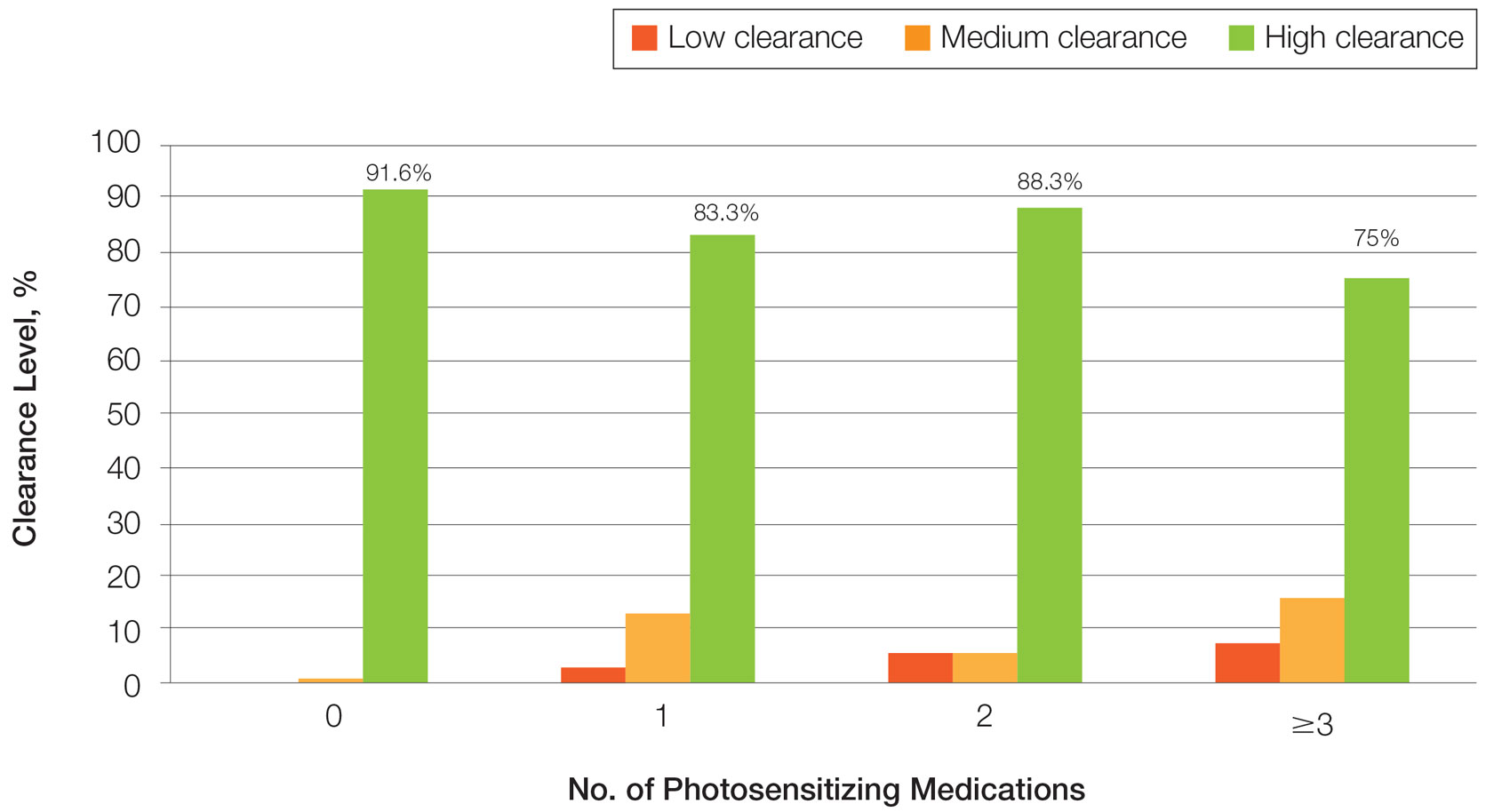
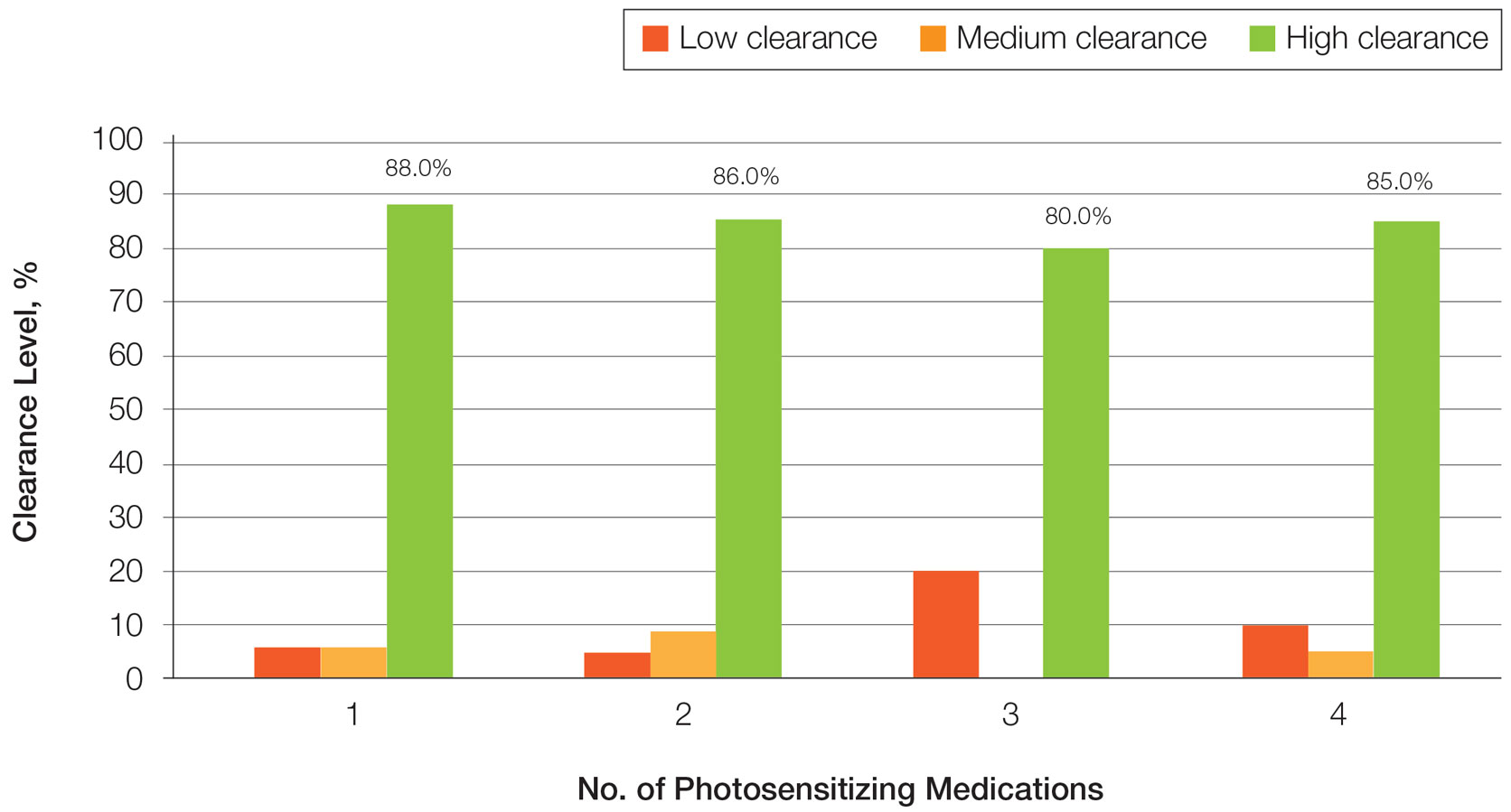
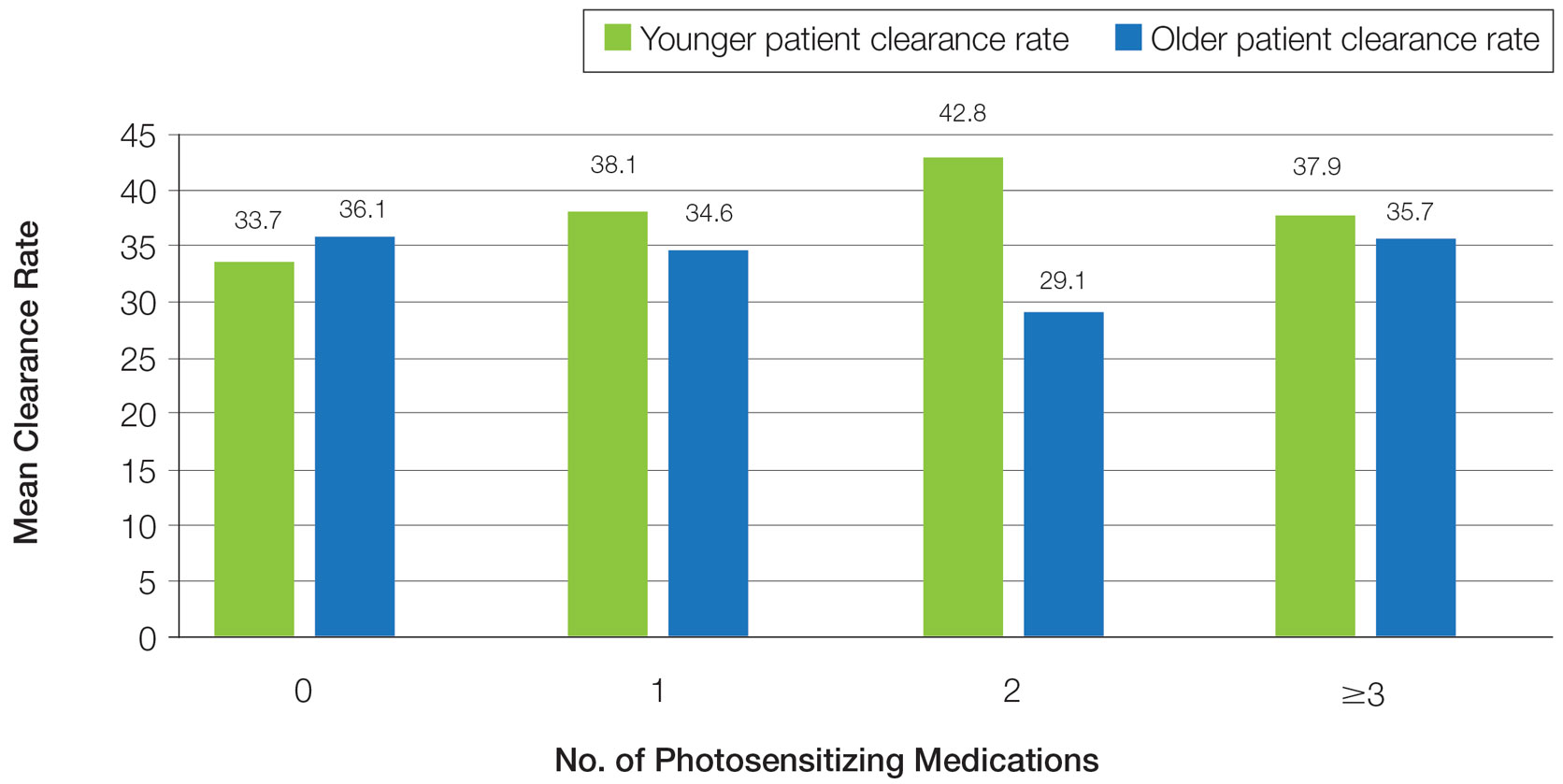
Photosensitizing Medications, Clearance Levels, and Clearance Rates—
Frequency of Treatments and Clearance Rates—Older adults more consistently completed the recommended frequency of treatments—3 times weekly—compared to younger adults (74.3% vs 58.5%). However, all patients who completed 3 treatments per week required a similar number of treatments to clear (older adults, mean [SD]: 35.7 [21.6]; younger adults, mean [SD]: 34.7 [19.0]; P=.85). Among patients completing 2 or fewer treatments per week, older adults required a mean (SD) of only 31 (9.0) treatments to clear vs 41.5 (21.3) treatments to clear for younger adults, but the difference was not statistically significant (P=.08). However, even those with suboptimal frequency ultimately achieved similar clearance levels.
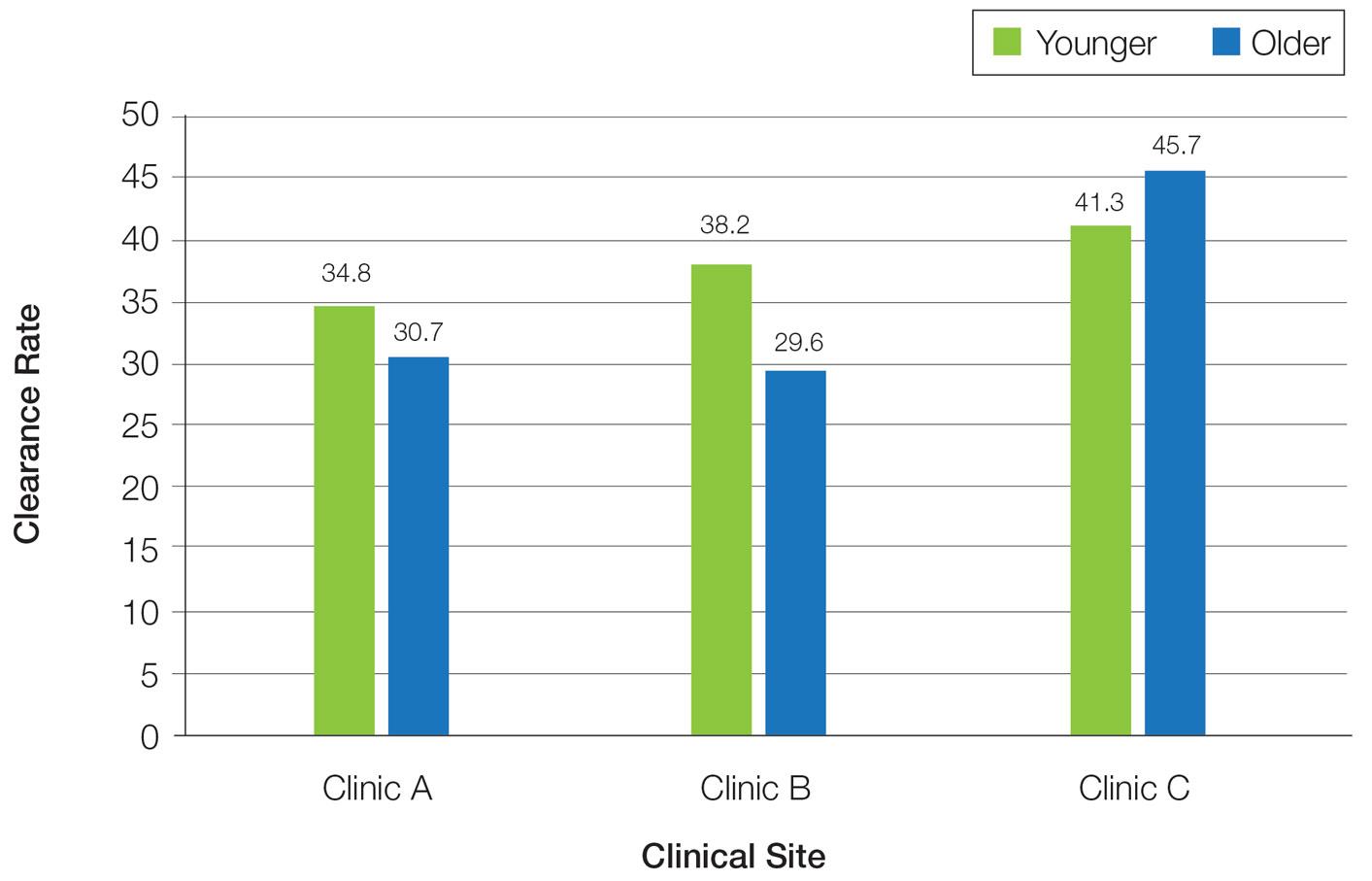
Photosensitizing Medications and Erythema Rates—
Overall, phototherapy nurses adjusted the starting dose according to the phototype-based protocol an average of 69% of the time for patients on medications with photosensitivity listed as a potential side effect. However, the frequency depended significantly on the clinic (clinic A, 24%; clinic B, 92%; clinic C, 87%)(P≤.001). Nurses across all clinics consistently decreased the treatment dose when patients reported starting new photosensitizing medications. Patients with adjusted starting doses had slightly but not significantly higher clearance rates compared to those without (mean, 37.8 vs 35.5; t(104)=0.58; P=.56).
Comment
Impact of Photosensitizing Medications on Clearance—Photosensitizing medications and treatment frequency were 2 factors that might explain the slower clearance rates in younger adults. In this study, both groups of patients used similar numbers of photosensitizing medications, but more older adults were taking 3 or more medications (Table 3). We found no statistically significant relationship between taking photosensitizing medications and either the clearance rates or the level of clearance achieved in either age group.
Impact of Treatment Frequency—Weekly treatment frequency also was examined. One prior study demonstrated that treatments 3 times weekly led to a faster clearance time and higher clearance levels compared with twice-weekly treatment.7 When patients completed treatments twice weekly, it took an average of 1.5 times more days to clear, which impacted cost and clinical resource availability. The patients ranged in age from 17 to 80 years, but outcomes in older patients were not described separately.7 Interestingly, our study seemed to find a difference between age groups when the impact of treatment frequency was examined. Older adults completed nearly 4 fewer mean treatments to clear when treating less often, with more than 80% achieving high levels of clearance, whereas the younger adults required almost 7 more treatments to clear when they came in less frequently, with approximately 80% achieving a high level of clearance. As a result, our study found that in both age groups, slowing the treatment frequency extended the treatment time to clearance—more for the younger adults than the older adults—but did not significantly change the percentage of individuals reaching full clearance in either group.
Erythema Rates—There was no association between photosensitizing medications and erythema rates except when patients were taking at least 3 medications. Most medications that listed photosensitivity as a possible side effect did not specify their relevant range of UV radiation; therefore, all such medications were examined during this analysis. Prior research has shown UVB range photosensitizing medications include thiazides, quinidine, calcium channel antagonists, phenothiazines, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.19 A sensitivity analysis that focused only on these medications found no association between them and any particular grade of erythema. However, patients taking 3 or more of any medications listing photosensitivity as a side effect had an increased risk for grade 2 erythema.
Erythema rates in this study were consistent with a 2013 systematic review that reported 57% of patients with asymptomatic grade 1 erythema.25 In the 2 other comparative older adult studies, erythema rates varied widely: 35% in a study from Turkey18compared to only1.89% in a study from the United Kingdom.17
The starting dose for NB-UVB may drive erythema rates. The current study’s protocols were based on an estimated MED that is subjectively determined by the dermatology provider’s assessment of the patient’s skin sensitivity via examination and questions to the patient about their response to environmental sun exposure (ie, burning and tanning)26 and is frequently used to determine the starting dose and subsequent dose escalation. Certain medications have been found to increase photosensitivity and erythema,20 which can change an individual’s MED. If photosensitizing medications are started prior to or during a course of NB-UVB without a pretreatment MED, they might increase the risk for erythema. This study did not identify specific erythema-inducing medications but did find that taking 3 or more photosensitizing medications was associated with increased episodes of grade 2 erythema. Similarly, Harrop et al8 found that patients who were taking photosensitizing medications were more likely to have grade 2 or higher erythema, despite baseline MED testing, which is an established safety mechanism to reduce the risk and severity of erythema.14,20,27 The authors of a recent study of older adults in Taiwan specifically recommended MED testing due to the unpredictable influence of polypharmacy on MED calculations in this population.28 Therefore, this study’s use of an estimated MED in older adults may have influenced the starting dose as well as the incidence and severity of erythemic events. Age-related skin changes likely are ruled out as a consideration for mild erythema by the similarity of grade 1 erythema rates in both older and younger adults. Other studies have identified differences between the age groups, where older patients experienced more intense erythema in the late phase of UVB treatments.22,23 This phenomenon could increase the risk for a grade 2 erythema, which may correspond with this study’s findings.
Other potential causes of erythema were ruled out during our study, including erythema related to missed treatments and shielding mishaps. Other factors, however, may impact the level of sensitivity each patient has to phototherapy, including genetics, epigenetics, and cumulative sun damage. With NB-UVB, near-erythemogenic doses are optimal to achieve effective treatments but require a delicate balance to achieve, which may be more problematic for older adults, especially those taking several medications.
Study Limitations—Our study design made it difficult to draw conclusions about rarer dermatologic conditions. Some patients received treatments over years that were not included in the study period. Finally, power calculations suggested that our actual sample size was too small, with approximately one-third of the required sample missing.
Practical Implications—The goals of phototherapy are to achieve a high level of disease clearance with the fewest number of treatments possible and minimal side effects.
The extra staff training and patient monitoring required for MED testing likely is to add value and preserve resources if faster clearance rates could be achieved and may warrant further investigation. Phototherapy centers require standardized treatment protocols, diligent well-trained staff, and program monitoring to ensure consistent care to all patients. This study highlighted the ongoing opportunity for health care organizations to conduct evidence-based practice inquiries to continually optimize care for their patients.
- Fernández-Guarino M, Aboin-Gonzalez S, Barchino L, et al. Treatment of moderate and severe adult chronic atopic dermatitis with narrow-band UVB and the combination of narrow-band UVB/UVA phototherapy. Dermatol Ther. 2016;29:19-23.
- Foerster J, Boswell K, West J, et al. Narrowband UVB treatment is highly effective and causes a strong reduction in the use of steroid and other creams in psoriasis patients in clinical practice. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181813.
- Gambichler T, Breuckmann F, Boms S, et al. Narrowband UVB phototherapy in skin conditions beyond psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:660-670.
- Ryu HH, Choe YS, Jo S, et al. Remission period in psoriasis after multiple cycles of narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy. J Dermatol. 2014;41:622-627.
- Schneider LA, Hinrichs R, Scharffetter-Kochanek K. Phototherapy and photochemotherapy. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:464-476.
- Tintle S, Shemer A, Suárez-Fariñas M, et al. Reversal of atopic dermatitis with narrow-band UVB phototherapy and biomarkers for therapeutic response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:583-593.e581-584.
- Cameron H, Dawe RS, Yule S, et al. A randomized, observer-blinded trial of twice vs. three times weekly narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy for chronic plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:973-978.
- Harrop G, Dawe RS, Ibbotson S. Are photosensitizing medications associated with increased risk of important erythemal reactions during ultraviolet B phototherapy? Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1184-1185.
- Torres AE, Lyons AB, Hamzavi IH, et al. Role of phototherapy in the era of biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:479-485.
- Bukvic´ć Mokos Z, Jovic´ A, Cˇeovic´ R, et al. Therapeutic challenges in the mature patient. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:128-139.
- Di Lernia V, Goldust M. An overview of the efficacy and safety of systemic treatments for psoriasis in the elderly. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018;18:897-903.
- Oliveira C, Torres T. More than skin deep: the systemic nature of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Dermatol. 2019;29:250-258.
- Matthews S, Pike K, Chien A. Phototherapy: safe and effective for challenging skin conditions in older adults. Cutis. 2021;108:E15-E21.
- Rodríguez-Granados MT, Estany-Gestal A, Pousa-Martínez M, et al. Is it useful to calculate minimal erythema dose before narrowband UV-B phototherapy? Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:852-858.
- Parlak N, Kundakci N, Parlak A, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy starting and incremental dose in patients with psoriasis: comparison of percentage dose and fixed dose protocols. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2015;31:90-97.
- Kleinpenning MM, Smits T, Boezeman J, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B therapy in psoriasis: randomized double-blind comparison of high-dose and low-dose irradiation regimens. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161:1351-1356.
- Powell JB, Gach JE. Phototherapy in the elderly. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:605-610.
- Bulur I, Erdogan HK, Aksu AE, et al. The efficacy and safety of phototherapy in geriatric patients: a retrospective study. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:33-38.
- Dawe RS, Ibbotson SH. Drug-induced photosensitivity. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:363-368, ix.
- Cameron H, Dawe RS. Photosensitizing drugs may lower the narrow-band ultraviolet B (TL-01) minimal erythema dose. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:389-390.
- Elmets CA, Lim HW, Stoff B, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology-National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:775-804.
- Gloor M, Scherotzke A. Age dependence of ultraviolet light-induced erythema following narrow-band UVB exposure. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2002;18:121-126.
- Cox NH, Diffey BL, Farr PM. The relationship between chronological age and the erythemal response to ultraviolet B radiation. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:315-319.
- Morrison W. Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy for Skin Disease. 2nd ed. Informa Healthcare; 2005.
- Almutawa F, Alnomair N, Wang Y, et al. Systematic review of UV-based therapy for psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:87-109.
- Trakatelli M, Bylaite-Bucinskiene M, Correia O, et al. Clinical assessment of skin phototypes: watch your words! Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:615-619.
- Kwon IH, Kwon HH, Na SJ, et al. Could colorimetric method replace the individual minimal erythemal dose (MED) measurements in determining the initial dose of narrow-band UVB treatment for psoriasis patients with skin phototype III-V? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:494-498.
- Chen WA, Chang CM. The minimal erythema dose of narrowband ultraviolet B in elderly Taiwanese [published online September 1, 2021]. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. doi:10.1111/phpp.12730
Even with recent pharmacologic treatment advances, narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy remains a versatile, safe, and efficacious adjunctive or exclusive treatment for multiple dermatologic conditions, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
In a prior study, Matthews et al13 reported that 96% (50/52) of patients older than 65 years achieved medium to high levels of clearance with NB-UVB phototherapy. Nonetheless, 2 other findings in this study related to the number of treatments required to achieve clearance (ie, clearance rates) and erythema rates prompted further investigation. The first finding was higher-than-expected clearance rates. Older adults had a clearance rate with a mean of 33 treatments compared to prior studies featuring mean clearance rates of 20 to 28 treatments.7,8,14-16 This finding resembled a study in the United Kingdom17 with a median clearance rate in older adults of 30 treatments. In contrast, the median clearance rate from a study in Turkey18 was 42 treatments in older adults. We hypothesized that more photosensitizing medications used in older vs younger adults prompted more dose adjustments with NB-UVB phototherapy to avoid burning (ie, erythema) at baseline and throughout the treatment course. These dose adjustments may have increased the overall clearance rates. If true, we predicted that younger adults treated with the same protocol would have cleared more quickly, either because of age-related differences or because they likely had fewer comorbidities and therefore fewer medications.
The second finding from Matthews et al13 that warranted further investigation was a higher erythema rate compared to the older adult study from the United Kingdom.17 We hypothesized that potentially greater use of photosensitizing medications in the United States could explain the higher erythema rates. Although medication-induced photosensitivity is less likely with NB-UVB phototherapy than with UVA, certain medications can cause UVB photosensitivity, including thiazides, quinidine, calcium channel antagonists, phenothiazines, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.8,19,20 Therefore, photosensitizing medication use either at baseline or during a course of NB-UVB phototherapy could increase the risk for erythema. Age-related skin changes also have been considered as a
This retrospective study aimed to determine if NB-UVB phototherapy is equally effective in both older and younger adults treated with the same protocol; to examine the association between the use of photosensitizing medications and clearance rates in both older and younger adults; and to examine the association between the use of photosensitizing medications and erythema rates in older vs younger adults.
Methods
Study Design and Patients—This retrospective cohort study used billing records to identify patients who received NB-UVB phototherapy at 3 different clinical sites within a large US health care system in Washington (Group Health Cooperative, now Kaiser Permanente Washington), serving more than 600,000 patients between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2016. The institutional review board of Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute approved this study (IRB 1498087-4). Younger adults were classified as those 64 years or younger and older adults as those 65 years and older at the start of their phototherapy regimen. A power analysis determined that the optimal sample size for this study was 250 patients.
Individuals were excluded if they had fewer than 6 phototherapy treatments; a diagnosis of vitiligo, photosensitivity dermatitis, morphea, or pityriasis rubra pilaris; and/or treatment of the hands or feet only.
Phototherapy Protocol—Using a 48-lamp NB-UVB unit, trained phototherapy nurses provided all treatments following standardized treatment protocols13 based on previously published phototherapy guidelines.24 Nurses determined each patient’s disease clearance level using a 3-point clearance scale (high, medium, low).13 Each patient’s starting dose was determined based on the estimated MED for their skin phototype.
Statistical Analysis—Data were analyzed using Stata statistical software (StataCorp LLC). Univariate analyses were used to examine the data and identify outliers, bad values, and missing data, as well as to calculate descriptive statistics. Pearson χ2 and Fisher exact statistics were used to calculate differences in categorical variables. Linear multivariate regression models and logistic multivariate models were used to examine statistical relationships between variables. Statistical significance was defined as P≤.05.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Medical records were reviewed for 172 patients who received phototherapy between 2012 and 2016. Patients ranged in age from 23 to 91 years, with 102 patients 64 years and younger and 70 patients 65 years and older. Tables 1 and 2 outline the patient characteristics and conditions treated.

Phototherapy Effectiveness—

Photosensitizing Medications, Clearance Levels, and Clearance Rates—

Frequency of Treatments and Clearance Rates—Older adults more consistently completed the recommended frequency of treatments—3 times weekly—compared to younger adults (74.3% vs 58.5%). However, all patients who completed 3 treatments per week required a similar number of treatments to clear (older adults, mean [SD]: 35.7 [21.6]; younger adults, mean [SD]: 34.7 [19.0]; P=.85). Among patients completing 2 or fewer treatments per week, older adults required a mean (SD) of only 31 (9.0) treatments to clear vs 41.5 (21.3) treatments to clear for younger adults, but the difference was not statistically significant (P=.08). However, even those with suboptimal frequency ultimately achieved similar clearance levels.


Photosensitizing Medications and Erythema Rates—

Overall, phototherapy nurses adjusted the starting dose according to the phototype-based protocol an average of 69% of the time for patients on medications with photosensitivity listed as a potential side effect. However, the frequency depended significantly on the clinic (clinic A, 24%; clinic B, 92%; clinic C, 87%)(P≤.001). Nurses across all clinics consistently decreased the treatment dose when patients reported starting new photosensitizing medications. Patients with adjusted starting doses had slightly but not significantly higher clearance rates compared to those without (mean, 37.8 vs 35.5; t(104)=0.58; P=.56).

Comment
Impact of Photosensitizing Medications on Clearance—Photosensitizing medications and treatment frequency were 2 factors that might explain the slower clearance rates in younger adults. In this study, both groups of patients used similar numbers of photosensitizing medications, but more older adults were taking 3 or more medications (Table 3). We found no statistically significant relationship between taking photosensitizing medications and either the clearance rates or the level of clearance achieved in either age group.
Impact of Treatment Frequency—Weekly treatment frequency also was examined. One prior study demonstrated that treatments 3 times weekly led to a faster clearance time and higher clearance levels compared with twice-weekly treatment.7 When patients completed treatments twice weekly, it took an average of 1.5 times more days to clear, which impacted cost and clinical resource availability. The patients ranged in age from 17 to 80 years, but outcomes in older patients were not described separately.7 Interestingly, our study seemed to find a difference between age groups when the impact of treatment frequency was examined. Older adults completed nearly 4 fewer mean treatments to clear when treating less often, with more than 80% achieving high levels of clearance, whereas the younger adults required almost 7 more treatments to clear when they came in less frequently, with approximately 80% achieving a high level of clearance. As a result, our study found that in both age groups, slowing the treatment frequency extended the treatment time to clearance—more for the younger adults than the older adults—but did not significantly change the percentage of individuals reaching full clearance in either group.
Erythema Rates—There was no association between photosensitizing medications and erythema rates except when patients were taking at least 3 medications. Most medications that listed photosensitivity as a possible side effect did not specify their relevant range of UV radiation; therefore, all such medications were examined during this analysis. Prior research has shown UVB range photosensitizing medications include thiazides, quinidine, calcium channel antagonists, phenothiazines, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.19 A sensitivity analysis that focused only on these medications found no association between them and any particular grade of erythema. However, patients taking 3 or more of any medications listing photosensitivity as a side effect had an increased risk for grade 2 erythema.
Erythema rates in this study were consistent with a 2013 systematic review that reported 57% of patients with asymptomatic grade 1 erythema.25 In the 2 other comparative older adult studies, erythema rates varied widely: 35% in a study from Turkey18compared to only1.89% in a study from the United Kingdom.17
The starting dose for NB-UVB may drive erythema rates. The current study’s protocols were based on an estimated MED that is subjectively determined by the dermatology provider’s assessment of the patient’s skin sensitivity via examination and questions to the patient about their response to environmental sun exposure (ie, burning and tanning)26 and is frequently used to determine the starting dose and subsequent dose escalation. Certain medications have been found to increase photosensitivity and erythema,20 which can change an individual’s MED. If photosensitizing medications are started prior to or during a course of NB-UVB without a pretreatment MED, they might increase the risk for erythema. This study did not identify specific erythema-inducing medications but did find that taking 3 or more photosensitizing medications was associated with increased episodes of grade 2 erythema. Similarly, Harrop et al8 found that patients who were taking photosensitizing medications were more likely to have grade 2 or higher erythema, despite baseline MED testing, which is an established safety mechanism to reduce the risk and severity of erythema.14,20,27 The authors of a recent study of older adults in Taiwan specifically recommended MED testing due to the unpredictable influence of polypharmacy on MED calculations in this population.28 Therefore, this study’s use of an estimated MED in older adults may have influenced the starting dose as well as the incidence and severity of erythemic events. Age-related skin changes likely are ruled out as a consideration for mild erythema by the similarity of grade 1 erythema rates in both older and younger adults. Other studies have identified differences between the age groups, where older patients experienced more intense erythema in the late phase of UVB treatments.22,23 This phenomenon could increase the risk for a grade 2 erythema, which may correspond with this study’s findings.
Other potential causes of erythema were ruled out during our study, including erythema related to missed treatments and shielding mishaps. Other factors, however, may impact the level of sensitivity each patient has to phototherapy, including genetics, epigenetics, and cumulative sun damage. With NB-UVB, near-erythemogenic doses are optimal to achieve effective treatments but require a delicate balance to achieve, which may be more problematic for older adults, especially those taking several medications.
Study Limitations—Our study design made it difficult to draw conclusions about rarer dermatologic conditions. Some patients received treatments over years that were not included in the study period. Finally, power calculations suggested that our actual sample size was too small, with approximately one-third of the required sample missing.
Practical Implications—The goals of phototherapy are to achieve a high level of disease clearance with the fewest number of treatments possible and minimal side effects.
The extra staff training and patient monitoring required for MED testing likely is to add value and preserve resources if faster clearance rates could be achieved and may warrant further investigation. Phototherapy centers require standardized treatment protocols, diligent well-trained staff, and program monitoring to ensure consistent care to all patients. This study highlighted the ongoing opportunity for health care organizations to conduct evidence-based practice inquiries to continually optimize care for their patients.
Even with recent pharmacologic treatment advances, narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy remains a versatile, safe, and efficacious adjunctive or exclusive treatment for multiple dermatologic conditions, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
In a prior study, Matthews et al13 reported that 96% (50/52) of patients older than 65 years achieved medium to high levels of clearance with NB-UVB phototherapy. Nonetheless, 2 other findings in this study related to the number of treatments required to achieve clearance (ie, clearance rates) and erythema rates prompted further investigation. The first finding was higher-than-expected clearance rates. Older adults had a clearance rate with a mean of 33 treatments compared to prior studies featuring mean clearance rates of 20 to 28 treatments.7,8,14-16 This finding resembled a study in the United Kingdom17 with a median clearance rate in older adults of 30 treatments. In contrast, the median clearance rate from a study in Turkey18 was 42 treatments in older adults. We hypothesized that more photosensitizing medications used in older vs younger adults prompted more dose adjustments with NB-UVB phototherapy to avoid burning (ie, erythema) at baseline and throughout the treatment course. These dose adjustments may have increased the overall clearance rates. If true, we predicted that younger adults treated with the same protocol would have cleared more quickly, either because of age-related differences or because they likely had fewer comorbidities and therefore fewer medications.
The second finding from Matthews et al13 that warranted further investigation was a higher erythema rate compared to the older adult study from the United Kingdom.17 We hypothesized that potentially greater use of photosensitizing medications in the United States could explain the higher erythema rates. Although medication-induced photosensitivity is less likely with NB-UVB phototherapy than with UVA, certain medications can cause UVB photosensitivity, including thiazides, quinidine, calcium channel antagonists, phenothiazines, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.8,19,20 Therefore, photosensitizing medication use either at baseline or during a course of NB-UVB phototherapy could increase the risk for erythema. Age-related skin changes also have been considered as a
This retrospective study aimed to determine if NB-UVB phototherapy is equally effective in both older and younger adults treated with the same protocol; to examine the association between the use of photosensitizing medications and clearance rates in both older and younger adults; and to examine the association between the use of photosensitizing medications and erythema rates in older vs younger adults.
Methods
Study Design and Patients—This retrospective cohort study used billing records to identify patients who received NB-UVB phototherapy at 3 different clinical sites within a large US health care system in Washington (Group Health Cooperative, now Kaiser Permanente Washington), serving more than 600,000 patients between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2016. The institutional review board of Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute approved this study (IRB 1498087-4). Younger adults were classified as those 64 years or younger and older adults as those 65 years and older at the start of their phototherapy regimen. A power analysis determined that the optimal sample size for this study was 250 patients.
Individuals were excluded if they had fewer than 6 phototherapy treatments; a diagnosis of vitiligo, photosensitivity dermatitis, morphea, or pityriasis rubra pilaris; and/or treatment of the hands or feet only.
Phototherapy Protocol—Using a 48-lamp NB-UVB unit, trained phototherapy nurses provided all treatments following standardized treatment protocols13 based on previously published phototherapy guidelines.24 Nurses determined each patient’s disease clearance level using a 3-point clearance scale (high, medium, low).13 Each patient’s starting dose was determined based on the estimated MED for their skin phototype.
Statistical Analysis—Data were analyzed using Stata statistical software (StataCorp LLC). Univariate analyses were used to examine the data and identify outliers, bad values, and missing data, as well as to calculate descriptive statistics. Pearson χ2 and Fisher exact statistics were used to calculate differences in categorical variables. Linear multivariate regression models and logistic multivariate models were used to examine statistical relationships between variables. Statistical significance was defined as P≤.05.
Results
Patient Characteristics—Medical records were reviewed for 172 patients who received phototherapy between 2012 and 2016. Patients ranged in age from 23 to 91 years, with 102 patients 64 years and younger and 70 patients 65 years and older. Tables 1 and 2 outline the patient characteristics and conditions treated.

Phototherapy Effectiveness—

Photosensitizing Medications, Clearance Levels, and Clearance Rates—

Frequency of Treatments and Clearance Rates—Older adults more consistently completed the recommended frequency of treatments—3 times weekly—compared to younger adults (74.3% vs 58.5%). However, all patients who completed 3 treatments per week required a similar number of treatments to clear (older adults, mean [SD]: 35.7 [21.6]; younger adults, mean [SD]: 34.7 [19.0]; P=.85). Among patients completing 2 or fewer treatments per week, older adults required a mean (SD) of only 31 (9.0) treatments to clear vs 41.5 (21.3) treatments to clear for younger adults, but the difference was not statistically significant (P=.08). However, even those with suboptimal frequency ultimately achieved similar clearance levels.


Photosensitizing Medications and Erythema Rates—

Overall, phototherapy nurses adjusted the starting dose according to the phototype-based protocol an average of 69% of the time for patients on medications with photosensitivity listed as a potential side effect. However, the frequency depended significantly on the clinic (clinic A, 24%; clinic B, 92%; clinic C, 87%)(P≤.001). Nurses across all clinics consistently decreased the treatment dose when patients reported starting new photosensitizing medications. Patients with adjusted starting doses had slightly but not significantly higher clearance rates compared to those without (mean, 37.8 vs 35.5; t(104)=0.58; P=.56).

Comment
Impact of Photosensitizing Medications on Clearance—Photosensitizing medications and treatment frequency were 2 factors that might explain the slower clearance rates in younger adults. In this study, both groups of patients used similar numbers of photosensitizing medications, but more older adults were taking 3 or more medications (Table 3). We found no statistically significant relationship between taking photosensitizing medications and either the clearance rates or the level of clearance achieved in either age group.
Impact of Treatment Frequency—Weekly treatment frequency also was examined. One prior study demonstrated that treatments 3 times weekly led to a faster clearance time and higher clearance levels compared with twice-weekly treatment.7 When patients completed treatments twice weekly, it took an average of 1.5 times more days to clear, which impacted cost and clinical resource availability. The patients ranged in age from 17 to 80 years, but outcomes in older patients were not described separately.7 Interestingly, our study seemed to find a difference between age groups when the impact of treatment frequency was examined. Older adults completed nearly 4 fewer mean treatments to clear when treating less often, with more than 80% achieving high levels of clearance, whereas the younger adults required almost 7 more treatments to clear when they came in less frequently, with approximately 80% achieving a high level of clearance. As a result, our study found that in both age groups, slowing the treatment frequency extended the treatment time to clearance—more for the younger adults than the older adults—but did not significantly change the percentage of individuals reaching full clearance in either group.
Erythema Rates—There was no association between photosensitizing medications and erythema rates except when patients were taking at least 3 medications. Most medications that listed photosensitivity as a possible side effect did not specify their relevant range of UV radiation; therefore, all such medications were examined during this analysis. Prior research has shown UVB range photosensitizing medications include thiazides, quinidine, calcium channel antagonists, phenothiazines, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.19 A sensitivity analysis that focused only on these medications found no association between them and any particular grade of erythema. However, patients taking 3 or more of any medications listing photosensitivity as a side effect had an increased risk for grade 2 erythema.
Erythema rates in this study were consistent with a 2013 systematic review that reported 57% of patients with asymptomatic grade 1 erythema.25 In the 2 other comparative older adult studies, erythema rates varied widely: 35% in a study from Turkey18compared to only1.89% in a study from the United Kingdom.17
The starting dose for NB-UVB may drive erythema rates. The current study’s protocols were based on an estimated MED that is subjectively determined by the dermatology provider’s assessment of the patient’s skin sensitivity via examination and questions to the patient about their response to environmental sun exposure (ie, burning and tanning)26 and is frequently used to determine the starting dose and subsequent dose escalation. Certain medications have been found to increase photosensitivity and erythema,20 which can change an individual’s MED. If photosensitizing medications are started prior to or during a course of NB-UVB without a pretreatment MED, they might increase the risk for erythema. This study did not identify specific erythema-inducing medications but did find that taking 3 or more photosensitizing medications was associated with increased episodes of grade 2 erythema. Similarly, Harrop et al8 found that patients who were taking photosensitizing medications were more likely to have grade 2 or higher erythema, despite baseline MED testing, which is an established safety mechanism to reduce the risk and severity of erythema.14,20,27 The authors of a recent study of older adults in Taiwan specifically recommended MED testing due to the unpredictable influence of polypharmacy on MED calculations in this population.28 Therefore, this study’s use of an estimated MED in older adults may have influenced the starting dose as well as the incidence and severity of erythemic events. Age-related skin changes likely are ruled out as a consideration for mild erythema by the similarity of grade 1 erythema rates in both older and younger adults. Other studies have identified differences between the age groups, where older patients experienced more intense erythema in the late phase of UVB treatments.22,23 This phenomenon could increase the risk for a grade 2 erythema, which may correspond with this study’s findings.
Other potential causes of erythema were ruled out during our study, including erythema related to missed treatments and shielding mishaps. Other factors, however, may impact the level of sensitivity each patient has to phototherapy, including genetics, epigenetics, and cumulative sun damage. With NB-UVB, near-erythemogenic doses are optimal to achieve effective treatments but require a delicate balance to achieve, which may be more problematic for older adults, especially those taking several medications.
Study Limitations—Our study design made it difficult to draw conclusions about rarer dermatologic conditions. Some patients received treatments over years that were not included in the study period. Finally, power calculations suggested that our actual sample size was too small, with approximately one-third of the required sample missing.
Practical Implications—The goals of phototherapy are to achieve a high level of disease clearance with the fewest number of treatments possible and minimal side effects.
The extra staff training and patient monitoring required for MED testing likely is to add value and preserve resources if faster clearance rates could be achieved and may warrant further investigation. Phototherapy centers require standardized treatment protocols, diligent well-trained staff, and program monitoring to ensure consistent care to all patients. This study highlighted the ongoing opportunity for health care organizations to conduct evidence-based practice inquiries to continually optimize care for their patients.
- Fernández-Guarino M, Aboin-Gonzalez S, Barchino L, et al. Treatment of moderate and severe adult chronic atopic dermatitis with narrow-band UVB and the combination of narrow-band UVB/UVA phototherapy. Dermatol Ther. 2016;29:19-23.
- Foerster J, Boswell K, West J, et al. Narrowband UVB treatment is highly effective and causes a strong reduction in the use of steroid and other creams in psoriasis patients in clinical practice. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181813.
- Gambichler T, Breuckmann F, Boms S, et al. Narrowband UVB phototherapy in skin conditions beyond psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:660-670.
- Ryu HH, Choe YS, Jo S, et al. Remission period in psoriasis after multiple cycles of narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy. J Dermatol. 2014;41:622-627.
- Schneider LA, Hinrichs R, Scharffetter-Kochanek K. Phototherapy and photochemotherapy. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:464-476.
- Tintle S, Shemer A, Suárez-Fariñas M, et al. Reversal of atopic dermatitis with narrow-band UVB phototherapy and biomarkers for therapeutic response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:583-593.e581-584.
- Cameron H, Dawe RS, Yule S, et al. A randomized, observer-blinded trial of twice vs. three times weekly narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy for chronic plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:973-978.
- Harrop G, Dawe RS, Ibbotson S. Are photosensitizing medications associated with increased risk of important erythemal reactions during ultraviolet B phototherapy? Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1184-1185.
- Torres AE, Lyons AB, Hamzavi IH, et al. Role of phototherapy in the era of biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:479-485.
- Bukvic´ć Mokos Z, Jovic´ A, Cˇeovic´ R, et al. Therapeutic challenges in the mature patient. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:128-139.
- Di Lernia V, Goldust M. An overview of the efficacy and safety of systemic treatments for psoriasis in the elderly. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018;18:897-903.
- Oliveira C, Torres T. More than skin deep: the systemic nature of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Dermatol. 2019;29:250-258.
- Matthews S, Pike K, Chien A. Phototherapy: safe and effective for challenging skin conditions in older adults. Cutis. 2021;108:E15-E21.
- Rodríguez-Granados MT, Estany-Gestal A, Pousa-Martínez M, et al. Is it useful to calculate minimal erythema dose before narrowband UV-B phototherapy? Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:852-858.
- Parlak N, Kundakci N, Parlak A, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy starting and incremental dose in patients with psoriasis: comparison of percentage dose and fixed dose protocols. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2015;31:90-97.
- Kleinpenning MM, Smits T, Boezeman J, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B therapy in psoriasis: randomized double-blind comparison of high-dose and low-dose irradiation regimens. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161:1351-1356.
- Powell JB, Gach JE. Phototherapy in the elderly. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:605-610.
- Bulur I, Erdogan HK, Aksu AE, et al. The efficacy and safety of phototherapy in geriatric patients: a retrospective study. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:33-38.
- Dawe RS, Ibbotson SH. Drug-induced photosensitivity. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:363-368, ix.
- Cameron H, Dawe RS. Photosensitizing drugs may lower the narrow-band ultraviolet B (TL-01) minimal erythema dose. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:389-390.
- Elmets CA, Lim HW, Stoff B, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology-National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:775-804.
- Gloor M, Scherotzke A. Age dependence of ultraviolet light-induced erythema following narrow-band UVB exposure. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2002;18:121-126.
- Cox NH, Diffey BL, Farr PM. The relationship between chronological age and the erythemal response to ultraviolet B radiation. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:315-319.
- Morrison W. Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy for Skin Disease. 2nd ed. Informa Healthcare; 2005.
- Almutawa F, Alnomair N, Wang Y, et al. Systematic review of UV-based therapy for psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:87-109.
- Trakatelli M, Bylaite-Bucinskiene M, Correia O, et al. Clinical assessment of skin phototypes: watch your words! Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:615-619.
- Kwon IH, Kwon HH, Na SJ, et al. Could colorimetric method replace the individual minimal erythemal dose (MED) measurements in determining the initial dose of narrow-band UVB treatment for psoriasis patients with skin phototype III-V? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:494-498.
- Chen WA, Chang CM. The minimal erythema dose of narrowband ultraviolet B in elderly Taiwanese [published online September 1, 2021]. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. doi:10.1111/phpp.12730
- Fernández-Guarino M, Aboin-Gonzalez S, Barchino L, et al. Treatment of moderate and severe adult chronic atopic dermatitis with narrow-band UVB and the combination of narrow-band UVB/UVA phototherapy. Dermatol Ther. 2016;29:19-23.
- Foerster J, Boswell K, West J, et al. Narrowband UVB treatment is highly effective and causes a strong reduction in the use of steroid and other creams in psoriasis patients in clinical practice. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181813.
- Gambichler T, Breuckmann F, Boms S, et al. Narrowband UVB phototherapy in skin conditions beyond psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:660-670.
- Ryu HH, Choe YS, Jo S, et al. Remission period in psoriasis after multiple cycles of narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy. J Dermatol. 2014;41:622-627.
- Schneider LA, Hinrichs R, Scharffetter-Kochanek K. Phototherapy and photochemotherapy. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:464-476.
- Tintle S, Shemer A, Suárez-Fariñas M, et al. Reversal of atopic dermatitis with narrow-band UVB phototherapy and biomarkers for therapeutic response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:583-593.e581-584.
- Cameron H, Dawe RS, Yule S, et al. A randomized, observer-blinded trial of twice vs. three times weekly narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy for chronic plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:973-978.
- Harrop G, Dawe RS, Ibbotson S. Are photosensitizing medications associated with increased risk of important erythemal reactions during ultraviolet B phototherapy? Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:1184-1185.
- Torres AE, Lyons AB, Hamzavi IH, et al. Role of phototherapy in the era of biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:479-485.
- Bukvic´ć Mokos Z, Jovic´ A, Cˇeovic´ R, et al. Therapeutic challenges in the mature patient. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:128-139.
- Di Lernia V, Goldust M. An overview of the efficacy and safety of systemic treatments for psoriasis in the elderly. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018;18:897-903.
- Oliveira C, Torres T. More than skin deep: the systemic nature of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Dermatol. 2019;29:250-258.
- Matthews S, Pike K, Chien A. Phototherapy: safe and effective for challenging skin conditions in older adults. Cutis. 2021;108:E15-E21.
- Rodríguez-Granados MT, Estany-Gestal A, Pousa-Martínez M, et al. Is it useful to calculate minimal erythema dose before narrowband UV-B phototherapy? Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017;108:852-858.
- Parlak N, Kundakci N, Parlak A, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy starting and incremental dose in patients with psoriasis: comparison of percentage dose and fixed dose protocols. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2015;31:90-97.
- Kleinpenning MM, Smits T, Boezeman J, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B therapy in psoriasis: randomized double-blind comparison of high-dose and low-dose irradiation regimens. Br J Dermatol. 2009;161:1351-1356.
- Powell JB, Gach JE. Phototherapy in the elderly. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:605-610.
- Bulur I, Erdogan HK, Aksu AE, et al. The efficacy and safety of phototherapy in geriatric patients: a retrospective study. An Bras Dermatol. 2018;93:33-38.
- Dawe RS, Ibbotson SH. Drug-induced photosensitivity. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:363-368, ix.
- Cameron H, Dawe RS. Photosensitizing drugs may lower the narrow-band ultraviolet B (TL-01) minimal erythema dose. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:389-390.
- Elmets CA, Lim HW, Stoff B, et al. Joint American Academy of Dermatology-National Psoriasis Foundation guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:775-804.
- Gloor M, Scherotzke A. Age dependence of ultraviolet light-induced erythema following narrow-band UVB exposure. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2002;18:121-126.
- Cox NH, Diffey BL, Farr PM. The relationship between chronological age and the erythemal response to ultraviolet B radiation. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:315-319.
- Morrison W. Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy for Skin Disease. 2nd ed. Informa Healthcare; 2005.
- Almutawa F, Alnomair N, Wang Y, et al. Systematic review of UV-based therapy for psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:87-109.
- Trakatelli M, Bylaite-Bucinskiene M, Correia O, et al. Clinical assessment of skin phototypes: watch your words! Eur J Dermatol. 2017;27:615-619.
- Kwon IH, Kwon HH, Na SJ, et al. Could colorimetric method replace the individual minimal erythemal dose (MED) measurements in determining the initial dose of narrow-band UVB treatment for psoriasis patients with skin phototype III-V? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:494-498.
- Chen WA, Chang CM. The minimal erythema dose of narrowband ultraviolet B in elderly Taiwanese [published online September 1, 2021]. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. doi:10.1111/phpp.12730
Practice Points
- Narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy remains a safe and efficacious nonpharmacologic treatment for dermatologic conditions in older and younger adults.
- Compared to younger adults, older adults using the same protocols need similar or even fewer treatments to achieve high levels of clearance.
- Individuals taking 3 or more photosensitizing medications, regardless of age, may be at higher risk for substantial erythema with NB-UVB phototherapy.
- Phototherapy program monitoring is important to ensure quality care and investigate opportunities for care optimization.
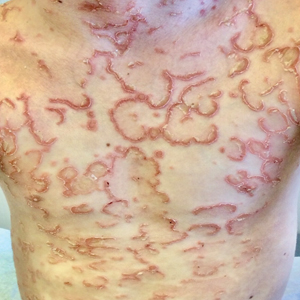
Polycyclic Scaly Eruption
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
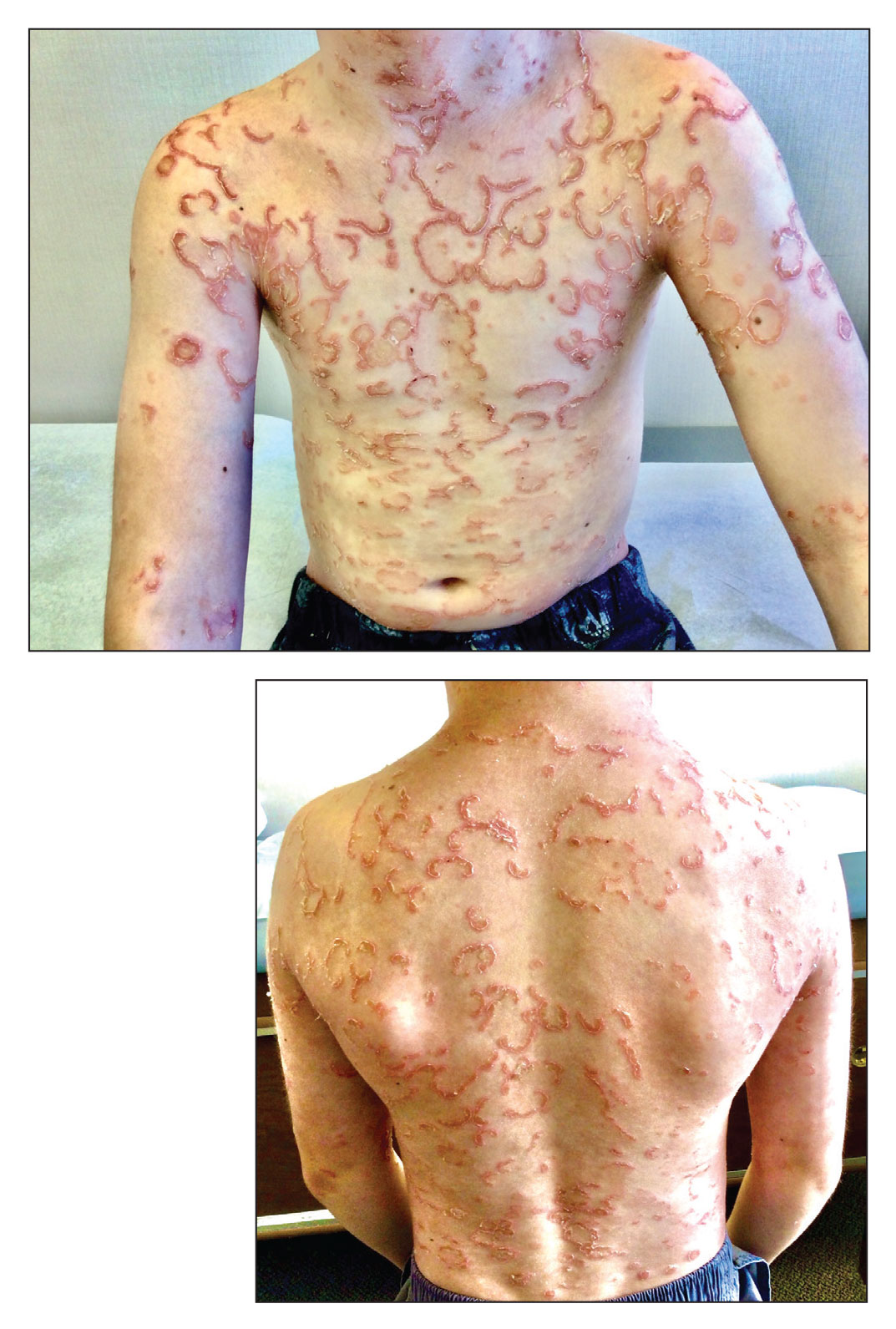
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
The Diagnosis: Netherton Syndrome
A punch biopsy from the right lower back supported the clinical diagnosis of ichthyosis linearis circumflexa. The patient underwent genetic testing and was found to have a heterozygous mutation in the serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5 gene, SPINK5, that was consistent with a diagnosis of Netherton syndrome.
Netherton syndrome is an autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by a triad of congenital ichthyosis, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopic diatheses.1,2 It affects approximately 1 in 200,000 live births2,3; however, it is considered by many to be underdiagnosed due to the variability in the clinical appearance. Therefore, the incidence of Netherton syndrome may actually be closer 1 in 50,000 live births.1 The manifestations of the disease are caused by a germline mutation in the SPINK5 gene, which encodes the serine protease inhibitor LEKTI.1,2 Dysfunctional LEKTI results in increased proteolytic activity of the lipid-processing enzymes in the stratum corneum, resulting in a disruption in the lipid bilayer.1 Dysfunctional LEKTI also results in a loss of the antiinflammatory and antimicrobial function of the stratum corneum. Clinical features of Netherton syndrome usually present at birth or shortly thereafter.1 Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or the continuous peeling of the skin, is a common presentation seen at birth and in the neonatal period.2 As the patient ages, the dermatologic manifestations evolve into serpiginous and circinate, erythematous plaques with a characteristic peripheral, double-edged scaling.1,2 This distinctive finding is termed ichthyosis linearis circumflexa and is pathognomonic for the syndrome.2 Lesions often affect the trunk and extremities and demonstrate an undulating course.1 Because eczematous and lichenified plaques in flexural areas as well as pruritus are common clinical features, this disease often is misdiagnosed as atopic dermatitis,1,3 as was the case in our patient.
Patients with Netherton syndrome can present with various hair abnormalities. Trichorrhexis invaginata, known as bamboo hair, is the intussusception of the hair shaft and is characteristic of the disease.3 It develops from a reduced number of disulfide bonds, which results in cortical softening.1 Trichorrhexis invaginata may not be present at birth and often improves with age.1,3 Other hair shaft abnormalities such as pili torti, trichorrhexis nodosa, and helical hair also may be observed in Netherton syndrome.1 Extracutaneous manifestations also are typical. There is immune dysregulation of memory B cells and natural killer cells, which manifests as frequent respiratory and skin infections as well as sepsis.1,2 Patients also may have increased levels of serum IgE and eosinophilia resulting in atopy and allergic reactions to various triggers such as foods.1 The neonatal period also may be complicated by dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, inability to regulate body temperature, and failure to thrive.1,3
When there is an extensive disruption of the skin barrier during the neonatal period, there may be severe electrolyte imbalances and thermoregulatory challenges necessitating treatment in the neonatal intensive care unit. Cutaneous disease can be treated with topical therapies with variable success.1 Topical therapies for symptom management include emollients, corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, calcipotriene, and retinoids; however, utmost caution must be employed with these therapies due to the increased risk for systemic absorption resulting from the disturbance of the skin barrier. When therapy with topical tacrolimus is implemented, monitoring of serum drug levels is required.1 Pruritus may be treated symptomatically with oral antihistamines. Intravenous immunoglobulin has been shown to decrease the frequency of infections and improve skin inflammation. Systemic retinoids have unpredictable effects and result in improvement of disease in some patients but exacerbation in others. Phototherapy with narrowband UVB, psoralen plus UVA, UVA1, and balneophototherapy also are effective treatments for cutaneous disease.1 Dupilumab has been shown to decrease pruritus, improve hair abnormalities, and improve skin disease, thereby demonstrating its effectiveness in treating the atopy and ichthyosis in Netherton syndrome.4
The differential diagnosis includes other figurate erythemas including erythema marginatum and erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Erythema marginatum is a cutaneous manifestation of acute rheumatic fever and is characterized by migratory polycyclic erythematous plaques without overlying scale, usually on the trunk and proximal extremities.5 Erythrokeratodermia variabilis is caused by heterozygous mutations in gap junction protein beta 3, GJB3, and gap junction protein beta 4, GJB4, and is characterized by transient geographic and erythematous patches and stable scaly plaques; however, double-edged scaling is not a feature.1 Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal-recessive disorder caused by mutations in the zinc transporter SLC39A4. Cutaneous manifestations occur after weaning from breast milk and are characterized by erythematous plaques with erosions, vesicles, and scaling, which characteristically occur in the perioral and perianal locations.6 Neonatal lupus is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Typical skin lesions are erythematous annular plaques with overlying scaling, which may be present at birth and have a predilection for the face and other sun-exposed areas. Lesions generally resolve after clearance of the pathogenic maternal antibodies.7
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
- Richard G, Ringpfeil F. Ichthyoses, erythrokeratodermas, and related disorders. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:888-923.
- Garza JI, Herz-Ruelas ME, Guerrero-González GA, et al. Netherton syndrome: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB129.
- Heymann W. Appending the appendages: new perspectives on Netherton syndrome and green nail syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:735-736.
- Murase C, Takeichi T, Taki T, et al. Successful dupilumab treatment for ichthyotic and atopic features of Netherton syndrome. J Dermatol Sci. 2021;102:126-129.
- España A. Figurate erythemas. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:320-331.
- Noguera-Morel L, McLeish Schaefer S, Hivnor C. Nutritional diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:793-809.
- Lee L, Werth V. Lupus erythematosus. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:662-680.
A 9-year-old boy presented to the dermatology clinic with a scaly eruption distributed throughout the body that had been present since birth. He had been diagnosed with atopic dermatitis by multiple dermatologists prior to the current presentation and had been treated with various topical steroids with minimal improvement. He had no family history of similar eruptions and no personal history of asthma or allergies. Physical examination revealed erythematous, serpiginous, polycyclic plaques with peripheral, double-edged scaling. Decreased hair density of the lateral eyebrows also was observed.
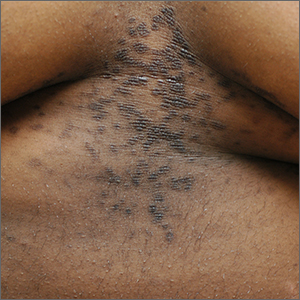
An asymptomatic rash
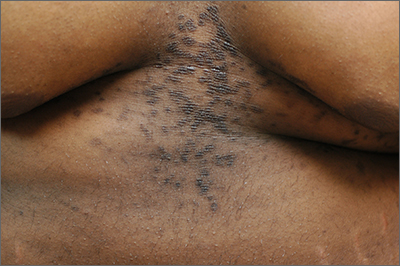
This patient was given a diagnosis of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (CRP) based on the clinical presentation.
CRP is characterized by centrally confluent and peripherally reticulated scaly brown plaques and papules that are cosmetically disfiguring.1 CRP is usually asymptomatic and primarily impacts young adults—especially teenagers.2,3 It affects both males and females and commonly occurs on the trunk.1-3 CRP is believed to be a disorder of keratinization. Malassezia furfur may induce CRP’s hyperproliferative epidermal changes, but systemic treatment that eliminates this organism does not clear CRP.3
A CRP diagnosis is made based on clinical presentation. The eruption usually begins as verrucous papules in the inframammary or epigastric region that enlarge to 4 to 5 mm in diameter and coalesce to form a confluent plaque with a peripheral reticulated pattern. CRP can extend over the back, chest, and abdomen to the neck, shoulders, and gluteal cleft. CRP does not affect the oral mucosa, and rarely involves flexural areas, which differentiates it from the similar looking acanthosis nigricans.2 Although most cases are asymptomatic, mild pruritus may occur.1,2
A skin biopsy is rarely necessary for making a CRP diagnosis, but histopathologic findings include papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, variable acanthosis, follicular plugging, and sparse dermal inflammation.1,3
Systemic antibiotics, most commonly minocycline 100 mg bid for 30 days or doxycycline 100 mg bid for 30 days, are safe and effective for CRP.1,4 Sometimes treatment is extended for as long as 6 months. Although CRP usually responds to minocycline or doxycycline, it is believed that this is the result of these drugs’ anti-inflammatory—rather than antibiotic—properties.1,2,4 Azithromycin is an effective alternative therapy.2,4 There is a high rate of recurrence of CRP in patients after systemic antibiotics are discontinued.2 Uniform responses to treatment and retreatment of flares have solidified the belief that antibiotics are an effective suppressive (if not curative) therapy despite a lack of randomized controlled trials.4
This patient was treated with minocycline 100 mg bid. After 1 month, the rash had improved by 70%. At 3 months, it was completely clear, and treatment was discontinued.
This case was adapted from: Sessums MT, Ward KMH, Brodell R. Cutaneous eruption on chest and back. J Fam Pract. 2014;63:467-468.
1. Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. A study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
2. Scheinfeld N. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a review of the literature. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:305-313. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200607050-00004
3. Tamraz H, Raffoul M, Kurban M, et al. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: clinical and histopathological study of 10 cases from Lebanon. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:e119-e123. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04328.x
4. Jang HS, Oh CK, Cha JH, et al. Six cases of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis alleviated by various antibiotics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:652-655. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.112577

This patient was given a diagnosis of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (CRP) based on the clinical presentation.
CRP is characterized by centrally confluent and peripherally reticulated scaly brown plaques and papules that are cosmetically disfiguring.1 CRP is usually asymptomatic and primarily impacts young adults—especially teenagers.2,3 It affects both males and females and commonly occurs on the trunk.1-3 CRP is believed to be a disorder of keratinization. Malassezia furfur may induce CRP’s hyperproliferative epidermal changes, but systemic treatment that eliminates this organism does not clear CRP.3
A CRP diagnosis is made based on clinical presentation. The eruption usually begins as verrucous papules in the inframammary or epigastric region that enlarge to 4 to 5 mm in diameter and coalesce to form a confluent plaque with a peripheral reticulated pattern. CRP can extend over the back, chest, and abdomen to the neck, shoulders, and gluteal cleft. CRP does not affect the oral mucosa, and rarely involves flexural areas, which differentiates it from the similar looking acanthosis nigricans.2 Although most cases are asymptomatic, mild pruritus may occur.1,2
A skin biopsy is rarely necessary for making a CRP diagnosis, but histopathologic findings include papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, variable acanthosis, follicular plugging, and sparse dermal inflammation.1,3
Systemic antibiotics, most commonly minocycline 100 mg bid for 30 days or doxycycline 100 mg bid for 30 days, are safe and effective for CRP.1,4 Sometimes treatment is extended for as long as 6 months. Although CRP usually responds to minocycline or doxycycline, it is believed that this is the result of these drugs’ anti-inflammatory—rather than antibiotic—properties.1,2,4 Azithromycin is an effective alternative therapy.2,4 There is a high rate of recurrence of CRP in patients after systemic antibiotics are discontinued.2 Uniform responses to treatment and retreatment of flares have solidified the belief that antibiotics are an effective suppressive (if not curative) therapy despite a lack of randomized controlled trials.4
This patient was treated with minocycline 100 mg bid. After 1 month, the rash had improved by 70%. At 3 months, it was completely clear, and treatment was discontinued.
This case was adapted from: Sessums MT, Ward KMH, Brodell R. Cutaneous eruption on chest and back. J Fam Pract. 2014;63:467-468.

This patient was given a diagnosis of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (CRP) based on the clinical presentation.
CRP is characterized by centrally confluent and peripherally reticulated scaly brown plaques and papules that are cosmetically disfiguring.1 CRP is usually asymptomatic and primarily impacts young adults—especially teenagers.2,3 It affects both males and females and commonly occurs on the trunk.1-3 CRP is believed to be a disorder of keratinization. Malassezia furfur may induce CRP’s hyperproliferative epidermal changes, but systemic treatment that eliminates this organism does not clear CRP.3
A CRP diagnosis is made based on clinical presentation. The eruption usually begins as verrucous papules in the inframammary or epigastric region that enlarge to 4 to 5 mm in diameter and coalesce to form a confluent plaque with a peripheral reticulated pattern. CRP can extend over the back, chest, and abdomen to the neck, shoulders, and gluteal cleft. CRP does not affect the oral mucosa, and rarely involves flexural areas, which differentiates it from the similar looking acanthosis nigricans.2 Although most cases are asymptomatic, mild pruritus may occur.1,2
A skin biopsy is rarely necessary for making a CRP diagnosis, but histopathologic findings include papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, variable acanthosis, follicular plugging, and sparse dermal inflammation.1,3
Systemic antibiotics, most commonly minocycline 100 mg bid for 30 days or doxycycline 100 mg bid for 30 days, are safe and effective for CRP.1,4 Sometimes treatment is extended for as long as 6 months. Although CRP usually responds to minocycline or doxycycline, it is believed that this is the result of these drugs’ anti-inflammatory—rather than antibiotic—properties.1,2,4 Azithromycin is an effective alternative therapy.2,4 There is a high rate of recurrence of CRP in patients after systemic antibiotics are discontinued.2 Uniform responses to treatment and retreatment of flares have solidified the belief that antibiotics are an effective suppressive (if not curative) therapy despite a lack of randomized controlled trials.4
This patient was treated with minocycline 100 mg bid. After 1 month, the rash had improved by 70%. At 3 months, it was completely clear, and treatment was discontinued.
This case was adapted from: Sessums MT, Ward KMH, Brodell R. Cutaneous eruption on chest and back. J Fam Pract. 2014;63:467-468.
1. Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. A study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
2. Scheinfeld N. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a review of the literature. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:305-313. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200607050-00004
3. Tamraz H, Raffoul M, Kurban M, et al. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: clinical and histopathological study of 10 cases from Lebanon. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:e119-e123. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04328.x
4. Jang HS, Oh CK, Cha JH, et al. Six cases of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis alleviated by various antibiotics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:652-655. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.112577
1. Davis MD, Weenig RH, Camilleri MJ. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (Gougerot-Carteaud syndrome): a minocycline-responsive dermatosis without evidence for yeast in pathogenesis. A study of 39 patients and a proposal of diagnostic criteria. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:287-293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06955.x
2. Scheinfeld N. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a review of the literature. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:305-313. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200607050-00004
3. Tamraz H, Raffoul M, Kurban M, et al. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: clinical and histopathological study of 10 cases from Lebanon. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:e119-e123. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04328.x
4. Jang HS, Oh CK, Cha JH, et al. Six cases of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis alleviated by various antibiotics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:652-655. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.112577
What barriers delay treatment in patients with hepatitis C?
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
Race, gender, and other factors are associated with lack of HCV Tx
A retrospective study (N = 894) assessed factors associated with direct-acting antiviral (DAA) initiation.1 Patients who were HCV+ with at least 1 clinical visit during the study period completed a survey of psychological, behavioral, and social life assessments. The final cohort (57% male; 64% ≥ 61 years old) was divided into patients who initiated DAA treatment (n = 690) and those who did not (n = 204).
In an adjusted multivariable analysis, factors associated with lower odds of DAA initiation included Black race (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.59 vs White race; 95% CI, 0.36-0.98); perceived difficulty accessing medical care (aOR = 0.48 vs no difficulty; 95% CI, 0.27-0.83); recent intravenous (IV) drug use (aOR = 0.11 vs no use; 95% CI, 0.02-0.54); alcohol use disorder (AUD; aOR = 0.58 vs no AUD; 95% CI, 0.38-0.90); severe depression (aOR = 0.42 vs no depression; 95% CI, 0.2-0.9); recent homelessness (aOR = 0.36 vs no homelessness; 95% CI, 0.14-0.94); and recent incarceration (aOR = 0.34 vs no incarceration; 95% CI, 0.12-0.94).1
A multicenter, observational prospective cohort study (N = 3075) evaluated receipt of HCV treatment for patients co-infected with HCV and HIV.2 The primary outcome was initiation of HCV treatment with DAAs; 1957 patients initiated therapy, while 1118 did not. Significant independent risk factors for noninitiation of treatment included age younger than 50 years, a history of IV drug use, and use of opioid substitution therapy (OST). Other factors included psychiatric comorbidity (odds ratio [OR] = 0.45; 95% CI, 0.27-0.75), incarceration (OR = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.43-0.87), and female gender (OR = 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98). In a multivariate analysis limited to those with a history of IV drug use, both use of OST (aOR = 0.55; 95% CI, 0.40-0.75) and recent IV drug use (aOR = 0.019; 95% CI, 0.004-0.087) were identified as factors with low odds of treatment implementation.2
A retrospective cohort study (N = 1024) of medical charts examined the barriers to treatment in adults with chronic HCV infection.3 Of the patient population, 208 were treated and 816 were untreated. Patients not receiving DAAs were associated with poor adherence to/loss to follow-up (n = 548; OR = 36.6; 95% CI, 19.6-68.4); significant psychiatric illness (n = 103; OR = 2.02; 95% CI, 1.13-3.71); and coinfection with HIV (n = 188; OR = 4.5; 95% CI, 2.5-8.2).3
A German multicenter retrospective case-control study (N = 793) identified factors in patient and physician decisions to initiate treatment for HCV.4 Patients were ≥ 18 years old, confirmed to be HCV+, and had visited their physician at least 1 time during the observation period. A total of 573 patients received treatment and 220 did not. Patients and clinicians of those who chose not to receive treatment completed a survey that collected reasons for not treating. The most prevalent reason for not initiating treatment was patient wish (42%). This was further delineated to reveal that 17.3% attributed their decision to fear of treatment and 13.2% to fear of adverse events. Other factors associated with nontreatment included IV drug use (aOR = 0.31; 95% CI, 0.16-0.62); HIV coinfection (aOR = 0.19; 95% CI, 0.09-0.40); and use of OST (aOR = 0.37; 95% CI, 0.21-0.68). Patient demographics associated with wish not to be treated included older age (20.2% of those ≥ 40 years old vs 6.4% of those < 40 years old; P = .03) and female gender (51.0% of females vs 35.2% of males; P = .019).4
An analysis of a French insurance database (N = 22,545) evaluated the incidence of HCV treatment with DAAs in patients who inject drugs (PWID) with a diagnosis of alcohol use disorder (AUD).5 All participants (78% male; median age, 49 years) were chronically HCV-infected and covered by national health insurance. Individuals were grouped by AUD status: untreated (n = 5176), treated (n = 3020), and no AUD (n = 14349). After multivariate adjustment, those with untreated AUD had lower uptake of DAAs than those who did not have AUD (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] = 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94) and those with treated AUD (aHR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.74-0.94). There were no differences between those with treated AUD and those who did not have AUD. Other factors associated with lower DAA uptake were access to care (aHR = 0.90; 95% CI, 0.83-0.98) and female gender (aHR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.76-0.9).5
A 2017 retrospective cohort study evaluated predictors and barriers to follow-up and treatment with DAAs among veterans who were HCV+.6 Patients (94% > 50 years old; 97% male; 48% white) had established HCV care within the US Department of Veterans Affairs system. Of those who followed up with at least 1 visit to an HCV specialty clinic (n = 47,165), 29% received DAAs. Factors associated with lack of treatment included race (Black vs White: OR = 0.77; 95% CI, 0.72-0.82; Hispanic vs White: OR = 0.88; 95% CI, 0.79-0.97); IV drug use (OR = 0.84; 95% CI, 0.80-0.88); AUD (OR = 0.73; 95% CI, 0.70-0.77); medical comorbidities (OR = 0.71; 95% CI, 0.66-0.77); and hepatocellular carcinoma (OR = 0.73; 95% CI, 0.65-0.83).6
Continue to: Providers identify similar barriers to treatment of HCV
Providers identify similar barriers to treatment of HCV
A 2017 prospective qualitative study (N = 24) from a Veterans Affairs health care system analyzed provider-perceived barriers to initiation of and adherence to HCV treatment.7 The analysis focused on differences by provider specialty. Primary care providers (PCPs; n = 12; 17% with > 40 patients with HCV) and hepatology providers (HPs; n = 12; 83% with > 40 patients with HCV) participated in a semi-structured telephone-based interview, providing their perceptions of patient-level barriers to HCV treatment. Eight patient-level barrier themes were identified; these are outlined in the TABLE7 along with data for both PCPs and HPs.
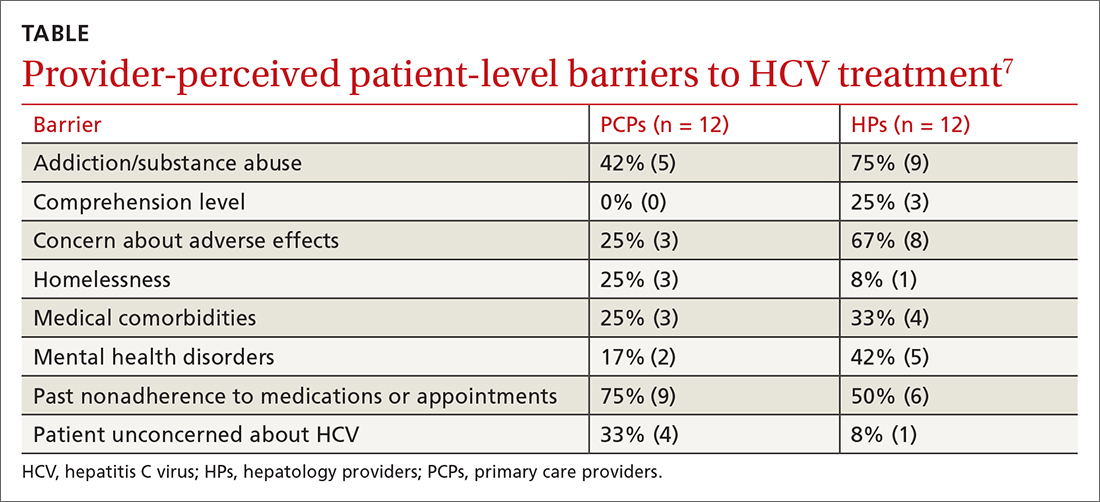
Editor’s takeaway
These 7 cohort studies show us the factors we consider and the reasons we give to not initiate HCV treatment. Some of the factors seem reasonable, but many do not. We might use this list to remind and challenge ourselves to work through barriers to provide the best possible treatment.
1. Spradling PR, Zhong Y, Moorman AC, et al. Psychosocial obstacles to hepatitis C treatment initiation among patients in care: a hitch in the cascade of cure. Hepatol Commun. 2021;5:400-411. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1632
2. Rivero-Juarez A, Tellez F, Castano-Carracedo M, et al. Parenteral drug use as the main barrier to hepatitis C treatment uptake in HIV-infected patients. HIV Medicine. 2019;20:359-367. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12715
3. Al-Khazraji A, Patel I, Saleh M, et al. Identifying barriers to the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection. Dig Dis. 2020;38:46-52. doi: 10.1159/000501821
4. Buggisch P, Heiken H, Mauss S, et al. Barriers to initiation of hepatitis C virus therapy in Germany: a retrospective, case-controlled study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:3p250833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250833
5. Barré T, Marcellin F, Di Beo V, et al. Untreated alcohol use disorder in people who inject drugs (PWID) in France: a major barrier to HCV treatment uptake (the ANRS-FANTASIO study). Addiction. 2019;115:573-582. doi: 10.1111/add.14820
6. Lin M, Kramer J, White D, et al. Barriers to hepatitis C treatment in the era of direct acting antiviral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:992-1000. doi: 10.1111/apt.14328
7. Rogal SS, McCarthy R, Reid A, et al. Primary care and hepatology provider-perceived barriers to and facilitators of hepatitis C treatment candidacy and adherence. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:1933-1943. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4608-9
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
Race, gender, and other factors are associated with lack of HCV Tx
A retrospective study (N = 894) assessed factors associated with direct-acting antiviral (DAA) initiation.1 Patients who were HCV+ with at least 1 clinical visit during the study period completed a survey of psychological, behavioral, and social life assessments. The final cohort (57% male; 64% ≥ 61 years old) was divided into patients who initiated DAA treatment (n = 690) and those who did not (n = 204).
In an adjusted multivariable analysis, factors associated with lower odds of DAA initiation included Black race (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.59 vs White race; 95% CI, 0.36-0.98); perceived difficulty accessing medical care (aOR = 0.48 vs no difficulty; 95% CI, 0.27-0.83); recent intravenous (IV) drug use (aOR = 0.11 vs no use; 95% CI, 0.02-0.54); alcohol use disorder (AUD; aOR = 0.58 vs no AUD; 95% CI, 0.38-0.90); severe depression (aOR = 0.42 vs no depression; 95% CI, 0.2-0.9); recent homelessness (aOR = 0.36 vs no homelessness; 95% CI, 0.14-0.94); and recent incarceration (aOR = 0.34 vs no incarceration; 95% CI, 0.12-0.94).1
A multicenter, observational prospective cohort study (N = 3075) evaluated receipt of HCV treatment for patients co-infected with HCV and HIV.2 The primary outcome was initiation of HCV treatment with DAAs; 1957 patients initiated therapy, while 1118 did not. Significant independent risk factors for noninitiation of treatment included age younger than 50 years, a history of IV drug use, and use of opioid substitution therapy (OST). Other factors included psychiatric comorbidity (odds ratio [OR] = 0.45; 95% CI, 0.27-0.75), incarceration (OR = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.43-0.87), and female gender (OR = 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98). In a multivariate analysis limited to those with a history of IV drug use, both use of OST (aOR = 0.55; 95% CI, 0.40-0.75) and recent IV drug use (aOR = 0.019; 95% CI, 0.004-0.087) were identified as factors with low odds of treatment implementation.2
A retrospective cohort study (N = 1024) of medical charts examined the barriers to treatment in adults with chronic HCV infection.3 Of the patient population, 208 were treated and 816 were untreated. Patients not receiving DAAs were associated with poor adherence to/loss to follow-up (n = 548; OR = 36.6; 95% CI, 19.6-68.4); significant psychiatric illness (n = 103; OR = 2.02; 95% CI, 1.13-3.71); and coinfection with HIV (n = 188; OR = 4.5; 95% CI, 2.5-8.2).3
A German multicenter retrospective case-control study (N = 793) identified factors in patient and physician decisions to initiate treatment for HCV.4 Patients were ≥ 18 years old, confirmed to be HCV+, and had visited their physician at least 1 time during the observation period. A total of 573 patients received treatment and 220 did not. Patients and clinicians of those who chose not to receive treatment completed a survey that collected reasons for not treating. The most prevalent reason for not initiating treatment was patient wish (42%). This was further delineated to reveal that 17.3% attributed their decision to fear of treatment and 13.2% to fear of adverse events. Other factors associated with nontreatment included IV drug use (aOR = 0.31; 95% CI, 0.16-0.62); HIV coinfection (aOR = 0.19; 95% CI, 0.09-0.40); and use of OST (aOR = 0.37; 95% CI, 0.21-0.68). Patient demographics associated with wish not to be treated included older age (20.2% of those ≥ 40 years old vs 6.4% of those < 40 years old; P = .03) and female gender (51.0% of females vs 35.2% of males; P = .019).4
An analysis of a French insurance database (N = 22,545) evaluated the incidence of HCV treatment with DAAs in patients who inject drugs (PWID) with a diagnosis of alcohol use disorder (AUD).5 All participants (78% male; median age, 49 years) were chronically HCV-infected and covered by national health insurance. Individuals were grouped by AUD status: untreated (n = 5176), treated (n = 3020), and no AUD (n = 14349). After multivariate adjustment, those with untreated AUD had lower uptake of DAAs than those who did not have AUD (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] = 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94) and those with treated AUD (aHR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.74-0.94). There were no differences between those with treated AUD and those who did not have AUD. Other factors associated with lower DAA uptake were access to care (aHR = 0.90; 95% CI, 0.83-0.98) and female gender (aHR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.76-0.9).5
A 2017 retrospective cohort study evaluated predictors and barriers to follow-up and treatment with DAAs among veterans who were HCV+.6 Patients (94% > 50 years old; 97% male; 48% white) had established HCV care within the US Department of Veterans Affairs system. Of those who followed up with at least 1 visit to an HCV specialty clinic (n = 47,165), 29% received DAAs. Factors associated with lack of treatment included race (Black vs White: OR = 0.77; 95% CI, 0.72-0.82; Hispanic vs White: OR = 0.88; 95% CI, 0.79-0.97); IV drug use (OR = 0.84; 95% CI, 0.80-0.88); AUD (OR = 0.73; 95% CI, 0.70-0.77); medical comorbidities (OR = 0.71; 95% CI, 0.66-0.77); and hepatocellular carcinoma (OR = 0.73; 95% CI, 0.65-0.83).6
Continue to: Providers identify similar barriers to treatment of HCV
Providers identify similar barriers to treatment of HCV
A 2017 prospective qualitative study (N = 24) from a Veterans Affairs health care system analyzed provider-perceived barriers to initiation of and adherence to HCV treatment.7 The analysis focused on differences by provider specialty. Primary care providers (PCPs; n = 12; 17% with > 40 patients with HCV) and hepatology providers (HPs; n = 12; 83% with > 40 patients with HCV) participated in a semi-structured telephone-based interview, providing their perceptions of patient-level barriers to HCV treatment. Eight patient-level barrier themes were identified; these are outlined in the TABLE7 along with data for both PCPs and HPs.

Editor’s takeaway
These 7 cohort studies show us the factors we consider and the reasons we give to not initiate HCV treatment. Some of the factors seem reasonable, but many do not. We might use this list to remind and challenge ourselves to work through barriers to provide the best possible treatment.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
Race, gender, and other factors are associated with lack of HCV Tx
A retrospective study (N = 894) assessed factors associated with direct-acting antiviral (DAA) initiation.1 Patients who were HCV+ with at least 1 clinical visit during the study period completed a survey of psychological, behavioral, and social life assessments. The final cohort (57% male; 64% ≥ 61 years old) was divided into patients who initiated DAA treatment (n = 690) and those who did not (n = 204).
In an adjusted multivariable analysis, factors associated with lower odds of DAA initiation included Black race (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 0.59 vs White race; 95% CI, 0.36-0.98); perceived difficulty accessing medical care (aOR = 0.48 vs no difficulty; 95% CI, 0.27-0.83); recent intravenous (IV) drug use (aOR = 0.11 vs no use; 95% CI, 0.02-0.54); alcohol use disorder (AUD; aOR = 0.58 vs no AUD; 95% CI, 0.38-0.90); severe depression (aOR = 0.42 vs no depression; 95% CI, 0.2-0.9); recent homelessness (aOR = 0.36 vs no homelessness; 95% CI, 0.14-0.94); and recent incarceration (aOR = 0.34 vs no incarceration; 95% CI, 0.12-0.94).1
A multicenter, observational prospective cohort study (N = 3075) evaluated receipt of HCV treatment for patients co-infected with HCV and HIV.2 The primary outcome was initiation of HCV treatment with DAAs; 1957 patients initiated therapy, while 1118 did not. Significant independent risk factors for noninitiation of treatment included age younger than 50 years, a history of IV drug use, and use of opioid substitution therapy (OST). Other factors included psychiatric comorbidity (odds ratio [OR] = 0.45; 95% CI, 0.27-0.75), incarceration (OR = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.43-0.87), and female gender (OR = 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.98). In a multivariate analysis limited to those with a history of IV drug use, both use of OST (aOR = 0.55; 95% CI, 0.40-0.75) and recent IV drug use (aOR = 0.019; 95% CI, 0.004-0.087) were identified as factors with low odds of treatment implementation.2
A retrospective cohort study (N = 1024) of medical charts examined the barriers to treatment in adults with chronic HCV infection.3 Of the patient population, 208 were treated and 816 were untreated. Patients not receiving DAAs were associated with poor adherence to/loss to follow-up (n = 548; OR = 36.6; 95% CI, 19.6-68.4); significant psychiatric illness (n = 103; OR = 2.02; 95% CI, 1.13-3.71); and coinfection with HIV (n = 188; OR = 4.5; 95% CI, 2.5-8.2).3
A German multicenter retrospective case-control study (N = 793) identified factors in patient and physician decisions to initiate treatment for HCV.4 Patients were ≥ 18 years old, confirmed to be HCV+, and had visited their physician at least 1 time during the observation period. A total of 573 patients received treatment and 220 did not. Patients and clinicians of those who chose not to receive treatment completed a survey that collected reasons for not treating. The most prevalent reason for not initiating treatment was patient wish (42%). This was further delineated to reveal that 17.3% attributed their decision to fear of treatment and 13.2% to fear of adverse events. Other factors associated with nontreatment included IV drug use (aOR = 0.31; 95% CI, 0.16-0.62); HIV coinfection (aOR = 0.19; 95% CI, 0.09-0.40); and use of OST (aOR = 0.37; 95% CI, 0.21-0.68). Patient demographics associated with wish not to be treated included older age (20.2% of those ≥ 40 years old vs 6.4% of those < 40 years old; P = .03) and female gender (51.0% of females vs 35.2% of males; P = .019).4
An analysis of a French insurance database (N = 22,545) evaluated the incidence of HCV treatment with DAAs in patients who inject drugs (PWID) with a diagnosis of alcohol use disorder (AUD).5 All participants (78% male; median age, 49 years) were chronically HCV-infected and covered by national health insurance. Individuals were grouped by AUD status: untreated (n = 5176), treated (n = 3020), and no AUD (n = 14349). After multivariate adjustment, those with untreated AUD had lower uptake of DAAs than those who did not have AUD (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] = 0.86; 95% CI, 0.78-0.94) and those with treated AUD (aHR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.74-0.94). There were no differences between those with treated AUD and those who did not have AUD. Other factors associated with lower DAA uptake were access to care (aHR = 0.90; 95% CI, 0.83-0.98) and female gender (aHR = 0.83; 95% CI, 0.76-0.9).5
A 2017 retrospective cohort study evaluated predictors and barriers to follow-up and treatment with DAAs among veterans who were HCV+.6 Patients (94% > 50 years old; 97% male; 48% white) had established HCV care within the US Department of Veterans Affairs system. Of those who followed up with at least 1 visit to an HCV specialty clinic (n = 47,165), 29% received DAAs. Factors associated with lack of treatment included race (Black vs White: OR = 0.77; 95% CI, 0.72-0.82; Hispanic vs White: OR = 0.88; 95% CI, 0.79-0.97); IV drug use (OR = 0.84; 95% CI, 0.80-0.88); AUD (OR = 0.73; 95% CI, 0.70-0.77); medical comorbidities (OR = 0.71; 95% CI, 0.66-0.77); and hepatocellular carcinoma (OR = 0.73; 95% CI, 0.65-0.83).6
Continue to: Providers identify similar barriers to treatment of HCV
Providers identify similar barriers to treatment of HCV
A 2017 prospective qualitative study (N = 24) from a Veterans Affairs health care system analyzed provider-perceived barriers to initiation of and adherence to HCV treatment.7 The analysis focused on differences by provider specialty. Primary care providers (PCPs; n = 12; 17% with > 40 patients with HCV) and hepatology providers (HPs; n = 12; 83% with > 40 patients with HCV) participated in a semi-structured telephone-based interview, providing their perceptions of patient-level barriers to HCV treatment. Eight patient-level barrier themes were identified; these are outlined in the TABLE7 along with data for both PCPs and HPs.

Editor’s takeaway
These 7 cohort studies show us the factors we consider and the reasons we give to not initiate HCV treatment. Some of the factors seem reasonable, but many do not. We might use this list to remind and challenge ourselves to work through barriers to provide the best possible treatment.
1. Spradling PR, Zhong Y, Moorman AC, et al. Psychosocial obstacles to hepatitis C treatment initiation among patients in care: a hitch in the cascade of cure. Hepatol Commun. 2021;5:400-411. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1632
2. Rivero-Juarez A, Tellez F, Castano-Carracedo M, et al. Parenteral drug use as the main barrier to hepatitis C treatment uptake in HIV-infected patients. HIV Medicine. 2019;20:359-367. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12715
3. Al-Khazraji A, Patel I, Saleh M, et al. Identifying barriers to the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection. Dig Dis. 2020;38:46-52. doi: 10.1159/000501821
4. Buggisch P, Heiken H, Mauss S, et al. Barriers to initiation of hepatitis C virus therapy in Germany: a retrospective, case-controlled study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:3p250833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250833
5. Barré T, Marcellin F, Di Beo V, et al. Untreated alcohol use disorder in people who inject drugs (PWID) in France: a major barrier to HCV treatment uptake (the ANRS-FANTASIO study). Addiction. 2019;115:573-582. doi: 10.1111/add.14820
6. Lin M, Kramer J, White D, et al. Barriers to hepatitis C treatment in the era of direct acting antiviral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:992-1000. doi: 10.1111/apt.14328
7. Rogal SS, McCarthy R, Reid A, et al. Primary care and hepatology provider-perceived barriers to and facilitators of hepatitis C treatment candidacy and adherence. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:1933-1943. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4608-9
1. Spradling PR, Zhong Y, Moorman AC, et al. Psychosocial obstacles to hepatitis C treatment initiation among patients in care: a hitch in the cascade of cure. Hepatol Commun. 2021;5:400-411. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1632
2. Rivero-Juarez A, Tellez F, Castano-Carracedo M, et al. Parenteral drug use as the main barrier to hepatitis C treatment uptake in HIV-infected patients. HIV Medicine. 2019;20:359-367. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12715
3. Al-Khazraji A, Patel I, Saleh M, et al. Identifying barriers to the treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection. Dig Dis. 2020;38:46-52. doi: 10.1159/000501821
4. Buggisch P, Heiken H, Mauss S, et al. Barriers to initiation of hepatitis C virus therapy in Germany: a retrospective, case-controlled study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:3p250833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250833
5. Barré T, Marcellin F, Di Beo V, et al. Untreated alcohol use disorder in people who inject drugs (PWID) in France: a major barrier to HCV treatment uptake (the ANRS-FANTASIO study). Addiction. 2019;115:573-582. doi: 10.1111/add.14820
6. Lin M, Kramer J, White D, et al. Barriers to hepatitis C treatment in the era of direct acting antiviral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46:992-1000. doi: 10.1111/apt.14328
7. Rogal SS, McCarthy R, Reid A, et al. Primary care and hepatology provider-perceived barriers to and facilitators of hepatitis C treatment candidacy and adherence. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:1933-1943. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4608-9
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
Multiple patient-specific and provider-perceived factors delay initiation of treatment in patients with hepatitis C. Patient-specific barriers to initiation of treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) include age, race, gender, economic status, insurance status, and comorbidities such as HIV coinfection, psychiatric illness, and other psychosocial factors.
Provider-perceived patient factors include substance abuse history, older age, psychiatric illness, medical comorbidities, treatment adverse effect risks, and factors that might limit adherence (eg, comprehension level).
Study limitations included problems with generalizability of the populations studied and variability in reporting or interpreting data associated with substance or alcohol use disorders
57-year-old man • type 2 diabetes • neuropathy • bilateral foot blisters • Dx?
THE CASE
A 57-year-old man with type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obesity presented to the emergency department (ED) for bilateral foot blisters, both of which appeared 1 day prior to evaluation. The patient’s history also included right-side Charcot foot diagnosed 4 years earlier and right foot osteomyelitis diagnosed 2 years prior. He had ongoing neuropathy in both feet but denied any significant pain.
The patient wore orthotics daily and he’d had new orthotics made 6 months prior; however, a recent COVID-19 diagnosis and prolonged hospital stay resulted in a 30-pound weight loss and decreased swelling in his ankles. He acquired new shoes 2 weeks prior to ED presentation.
Physical examination revealed large blisters along the medial aspect of the patient’s feet, with both hemorrhagic and serous fluid-filled bullae. The lesions were flaccid but intact, without drainage or surrounding erythema, warmth, or tenderness. The blister on the left foot measured 8 x 5 cm and extended from the great toe to mid-arch (FIGURE), while the one on the right foot measured 8 x 3 cm and extended from the great toe to the base of the proximal arch. Sensation was decreased in the bilateral first and second digits but unchanged from prior documented exams. Bilateral dorsalis pedis pulses were normal.
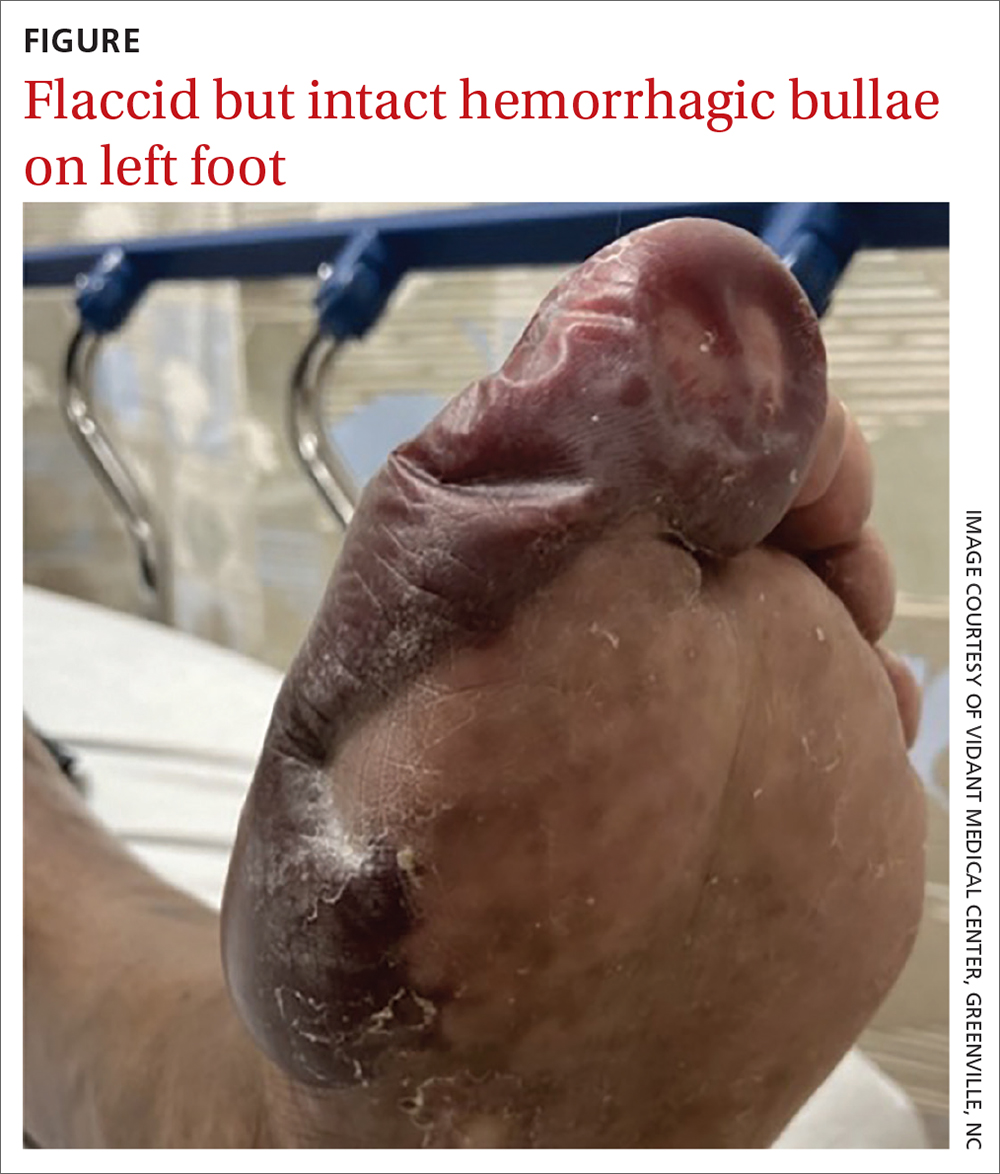
Work-up included imaging and lab work. The patient’s complete blood count was normal, as were his erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level. Radiographs of the right foot were normal, but those of the left foot were concerning, although inconclusive, for osteomyelitis. Further evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging of his left foot revealed a deformity of the first digit with some subchondral signal change that was thought to be posttraumatic or degenerative, but unlikely osteomyelitis.
THE DIAGNOSIS
Podiatry was consulted for blister management. Based on atraumatic history, rapid appearance, location of blisters, unremarkable lab work and imaging, and concurrent diabetes, the patient received a diagnosis of bilateral bullous diabeticorum (BD).
DISCUSSION
Roughly one-third of patients with diabetes will experience some cutaneous adverse effect because of the disease.1 Common iterations include acanthosis nigricans, rash, or even infection.2 BD is a rare bullous skin lesion that occurs in patients with diabetes; it has a reported annual incidence of 0.16% and may be underdiagnosed.1
Cases of BD have been described both in patients with longstanding diabetes and in those newly diagnosed, although the former group is more often affected.1 BD is reported more frequently in males than females, at a ratio of 2:1.1,3 Patients ages 17 to 80 years (average age, 55 years) have received a diagnosis of BD.1 Most affected patients will have a concomitant peripheral neuropathy and sometimes nephropathy or retinopathy.1
Continue to: The etiology of BD...
The etiology of BD is unclear but appears to be multifactorial. Hypotheses suggest that there’s a link to neuropathy/nephropathy, excessive exposure to ultraviolet light, or a vascular cause secondary to hyaline deposition in the capillary walls.4,5
What you’ll see at presentation
The typical manifestation of BD is the rapid appearance of tense blisters, which may occur overnight or even within hours.1 They are usually painless; common locations include the feet, distal legs, hands, and forearms.1,5 The bullae can be serous or hemorrhagic.1
Most notable in the patient’s history will be a lack of trauma or injury to the area.1 Although A1C values do not correlate with blister formation, patients with hypoglycemic episodes and highly varying blood glucose values seem to have higher rates of occurrence.1
Other sources of blistering must be ruled out
The diagnosis of BD is clinical and based on history, exam, and exclusion of other bullous diagnoses.6 A key clue in the history is the spontaneous and rapid onset without associated trauma in a patient with diabetes.6 Direct immunofluorescence, although nonspecific, can be helpful to rule out other disorders (such as porphyria cutanea tarda and bullous pemphigoid) if the history and exam are inconclusive. Direct and indirect immunofluorescence is typically negative in BD.4,6
The differential diagnosis includes other conditions that involve bullae—such as frictional bullae, bullous pemphigoid, and bullous systemic lupus erythematosus—as well as porphyria, erythema multiforme, insect bites, or even fixed drug eruption.2,7
Continue to: Porphyria
Porphyria tends to develop on the hands, whereas BD most commonly occurs on the feet.5
Erythema multiforme typically includes inflammatory skin changes.5
Trauma or fixed drug eruption as a cause of blistering lesions would be revealed during history taking.
Considerations for treatment and follow-up
Without treatment, blisters often self-resolve in 2 to 6 weeks, but there is high likelihood of recurrence.6,8 There is no consensus on treatment, although a typical course of action is to deroof the blister and examine the area to rule out infection.6 The wound is then covered with wet-to-dry gauze that is changed regularly. If there is suspicion for or signs of underlying infection, such as an ulcer or skin necrosis, antibiotics should be included in the treatment plan.7
Additional considerations. Patients will often need therapeutic footwear if the blisters are located on the feet. Given the higher prevalence of microvascular complications in patients with diabetes who develop BD, routine ophthalmologic examination and renal function testing to monitor for microalbuminuria are recommended.5
Our patient underwent bedside incision and drainage and was discharged home with appropriate wound care and follow-up.
THE TAKEAWAY
BD cases may be underdiagnosed in clinical practice, perhaps due to patients not seeking help for a seemingly nonthreatening condition or lack of clinician recognition that bullae are related to a patient’s diabetes status. Prompt recognition and proper wound care are important to prevent poor outcomes, such as ulceration or necrosis.
CORRESPONDENCE
Kathleen S. Kinderwater, MD, 101 Heart Drive, Greenville, NC 27834; [email protected]
1. Larsen K, Jensen T, Karlsmark T, et al. Incidence of bullosis diabeticorum—a controversial cause of chronic foot ulceration. Int Wound J. 2008;5:591-596. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2008.00476.x
2. Lipsky BA, Baker PD, Ahroni JH. Diabetic bullae: 12 cases of a purportedly rare cutaneous disorder. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:196-200. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00947.x
3. Gupta V, Gulati N, Bahl J, et al. Bullosis diabeticorum: rare presentation in a common disease. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2014;2014:862912.
4. Sonani H, Abdul Salim S, Garla VV, et al. Bullosis diabeticorum: a rare presentation with immunoglobulin G (IgG) deposition related vasculopathy. Case report and focused review. Am J Case Rep. 2018;19:52-56. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.905452
5. Chouk C, Litaiem N. Bullosis diabeticorum. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 5, 2021. Accessed July 14, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539872/
6. Chatterjee D, Radotra A, Radotra BD, et al. Bullous diabeticorum: a rare blistering manifestation of diabetes. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017;8:274-275. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_340_16
7. Kansal NK, Anuragi RP. Bullous lesions in diabetes mellitus: bullous diabeticorum (diabetic bulla). BMJ Case Rep. 2020;13:e238617. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238617
8. Bello F, Samaila OM, Lawal Y, et al. 2 cases of bullosis diabeticorum following long-distance journeys by road: a report of 2 cases. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2012;2012:367218. doi: 10.1155/2012/367218
THE CASE
A 57-year-old man with type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obesity presented to the emergency department (ED) for bilateral foot blisters, both of which appeared 1 day prior to evaluation. The patient’s history also included right-side Charcot foot diagnosed 4 years earlier and right foot osteomyelitis diagnosed 2 years prior. He had ongoing neuropathy in both feet but denied any significant pain.
The patient wore orthotics daily and he’d had new orthotics made 6 months prior; however, a recent COVID-19 diagnosis and prolonged hospital stay resulted in a 30-pound weight loss and decreased swelling in his ankles. He acquired new shoes 2 weeks prior to ED presentation.
Physical examination revealed large blisters along the medial aspect of the patient’s feet, with both hemorrhagic and serous fluid-filled bullae. The lesions were flaccid but intact, without drainage or surrounding erythema, warmth, or tenderness. The blister on the left foot measured 8 x 5 cm and extended from the great toe to mid-arch (FIGURE), while the one on the right foot measured 8 x 3 cm and extended from the great toe to the base of the proximal arch. Sensation was decreased in the bilateral first and second digits but unchanged from prior documented exams. Bilateral dorsalis pedis pulses were normal.

Work-up included imaging and lab work. The patient’s complete blood count was normal, as were his erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level. Radiographs of the right foot were normal, but those of the left foot were concerning, although inconclusive, for osteomyelitis. Further evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging of his left foot revealed a deformity of the first digit with some subchondral signal change that was thought to be posttraumatic or degenerative, but unlikely osteomyelitis.
THE DIAGNOSIS
Podiatry was consulted for blister management. Based on atraumatic history, rapid appearance, location of blisters, unremarkable lab work and imaging, and concurrent diabetes, the patient received a diagnosis of bilateral bullous diabeticorum (BD).
DISCUSSION
Roughly one-third of patients with diabetes will experience some cutaneous adverse effect because of the disease.1 Common iterations include acanthosis nigricans, rash, or even infection.2 BD is a rare bullous skin lesion that occurs in patients with diabetes; it has a reported annual incidence of 0.16% and may be underdiagnosed.1
Cases of BD have been described both in patients with longstanding diabetes and in those newly diagnosed, although the former group is more often affected.1 BD is reported more frequently in males than females, at a ratio of 2:1.1,3 Patients ages 17 to 80 years (average age, 55 years) have received a diagnosis of BD.1 Most affected patients will have a concomitant peripheral neuropathy and sometimes nephropathy or retinopathy.1
Continue to: The etiology of BD...
The etiology of BD is unclear but appears to be multifactorial. Hypotheses suggest that there’s a link to neuropathy/nephropathy, excessive exposure to ultraviolet light, or a vascular cause secondary to hyaline deposition in the capillary walls.4,5
What you’ll see at presentation
The typical manifestation of BD is the rapid appearance of tense blisters, which may occur overnight or even within hours.1 They are usually painless; common locations include the feet, distal legs, hands, and forearms.1,5 The bullae can be serous or hemorrhagic.1
Most notable in the patient’s history will be a lack of trauma or injury to the area.1 Although A1C values do not correlate with blister formation, patients with hypoglycemic episodes and highly varying blood glucose values seem to have higher rates of occurrence.1
Other sources of blistering must be ruled out
The diagnosis of BD is clinical and based on history, exam, and exclusion of other bullous diagnoses.6 A key clue in the history is the spontaneous and rapid onset without associated trauma in a patient with diabetes.6 Direct immunofluorescence, although nonspecific, can be helpful to rule out other disorders (such as porphyria cutanea tarda and bullous pemphigoid) if the history and exam are inconclusive. Direct and indirect immunofluorescence is typically negative in BD.4,6
The differential diagnosis includes other conditions that involve bullae—such as frictional bullae, bullous pemphigoid, and bullous systemic lupus erythematosus—as well as porphyria, erythema multiforme, insect bites, or even fixed drug eruption.2,7
Continue to: Porphyria
Porphyria tends to develop on the hands, whereas BD most commonly occurs on the feet.5
Erythema multiforme typically includes inflammatory skin changes.5
Trauma or fixed drug eruption as a cause of blistering lesions would be revealed during history taking.
Considerations for treatment and follow-up
Without treatment, blisters often self-resolve in 2 to 6 weeks, but there is high likelihood of recurrence.6,8 There is no consensus on treatment, although a typical course of action is to deroof the blister and examine the area to rule out infection.6 The wound is then covered with wet-to-dry gauze that is changed regularly. If there is suspicion for or signs of underlying infection, such as an ulcer or skin necrosis, antibiotics should be included in the treatment plan.7
Additional considerations. Patients will often need therapeutic footwear if the blisters are located on the feet. Given the higher prevalence of microvascular complications in patients with diabetes who develop BD, routine ophthalmologic examination and renal function testing to monitor for microalbuminuria are recommended.5
Our patient underwent bedside incision and drainage and was discharged home with appropriate wound care and follow-up.
THE TAKEAWAY
BD cases may be underdiagnosed in clinical practice, perhaps due to patients not seeking help for a seemingly nonthreatening condition or lack of clinician recognition that bullae are related to a patient’s diabetes status. Prompt recognition and proper wound care are important to prevent poor outcomes, such as ulceration or necrosis.
CORRESPONDENCE
Kathleen S. Kinderwater, MD, 101 Heart Drive, Greenville, NC 27834; [email protected]
THE CASE
A 57-year-old man with type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obesity presented to the emergency department (ED) for bilateral foot blisters, both of which appeared 1 day prior to evaluation. The patient’s history also included right-side Charcot foot diagnosed 4 years earlier and right foot osteomyelitis diagnosed 2 years prior. He had ongoing neuropathy in both feet but denied any significant pain.
The patient wore orthotics daily and he’d had new orthotics made 6 months prior; however, a recent COVID-19 diagnosis and prolonged hospital stay resulted in a 30-pound weight loss and decreased swelling in his ankles. He acquired new shoes 2 weeks prior to ED presentation.
Physical examination revealed large blisters along the medial aspect of the patient’s feet, with both hemorrhagic and serous fluid-filled bullae. The lesions were flaccid but intact, without drainage or surrounding erythema, warmth, or tenderness. The blister on the left foot measured 8 x 5 cm and extended from the great toe to mid-arch (FIGURE), while the one on the right foot measured 8 x 3 cm and extended from the great toe to the base of the proximal arch. Sensation was decreased in the bilateral first and second digits but unchanged from prior documented exams. Bilateral dorsalis pedis pulses were normal.

Work-up included imaging and lab work. The patient’s complete blood count was normal, as were his erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level. Radiographs of the right foot were normal, but those of the left foot were concerning, although inconclusive, for osteomyelitis. Further evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging of his left foot revealed a deformity of the first digit with some subchondral signal change that was thought to be posttraumatic or degenerative, but unlikely osteomyelitis.
THE DIAGNOSIS
Podiatry was consulted for blister management. Based on atraumatic history, rapid appearance, location of blisters, unremarkable lab work and imaging, and concurrent diabetes, the patient received a diagnosis of bilateral bullous diabeticorum (BD).
DISCUSSION
Roughly one-third of patients with diabetes will experience some cutaneous adverse effect because of the disease.1 Common iterations include acanthosis nigricans, rash, or even infection.2 BD is a rare bullous skin lesion that occurs in patients with diabetes; it has a reported annual incidence of 0.16% and may be underdiagnosed.1
Cases of BD have been described both in patients with longstanding diabetes and in those newly diagnosed, although the former group is more often affected.1 BD is reported more frequently in males than females, at a ratio of 2:1.1,3 Patients ages 17 to 80 years (average age, 55 years) have received a diagnosis of BD.1 Most affected patients will have a concomitant peripheral neuropathy and sometimes nephropathy or retinopathy.1
Continue to: The etiology of BD...
The etiology of BD is unclear but appears to be multifactorial. Hypotheses suggest that there’s a link to neuropathy/nephropathy, excessive exposure to ultraviolet light, or a vascular cause secondary to hyaline deposition in the capillary walls.4,5
What you’ll see at presentation
The typical manifestation of BD is the rapid appearance of tense blisters, which may occur overnight or even within hours.1 They are usually painless; common locations include the feet, distal legs, hands, and forearms.1,5 The bullae can be serous or hemorrhagic.1
Most notable in the patient’s history will be a lack of trauma or injury to the area.1 Although A1C values do not correlate with blister formation, patients with hypoglycemic episodes and highly varying blood glucose values seem to have higher rates of occurrence.1
Other sources of blistering must be ruled out
The diagnosis of BD is clinical and based on history, exam, and exclusion of other bullous diagnoses.6 A key clue in the history is the spontaneous and rapid onset without associated trauma in a patient with diabetes.6 Direct immunofluorescence, although nonspecific, can be helpful to rule out other disorders (such as porphyria cutanea tarda and bullous pemphigoid) if the history and exam are inconclusive. Direct and indirect immunofluorescence is typically negative in BD.4,6
The differential diagnosis includes other conditions that involve bullae—such as frictional bullae, bullous pemphigoid, and bullous systemic lupus erythematosus—as well as porphyria, erythema multiforme, insect bites, or even fixed drug eruption.2,7
Continue to: Porphyria
Porphyria tends to develop on the hands, whereas BD most commonly occurs on the feet.5
Erythema multiforme typically includes inflammatory skin changes.5
Trauma or fixed drug eruption as a cause of blistering lesions would be revealed during history taking.
Considerations for treatment and follow-up
Without treatment, blisters often self-resolve in 2 to 6 weeks, but there is high likelihood of recurrence.6,8 There is no consensus on treatment, although a typical course of action is to deroof the blister and examine the area to rule out infection.6 The wound is then covered with wet-to-dry gauze that is changed regularly. If there is suspicion for or signs of underlying infection, such as an ulcer or skin necrosis, antibiotics should be included in the treatment plan.7
Additional considerations. Patients will often need therapeutic footwear if the blisters are located on the feet. Given the higher prevalence of microvascular complications in patients with diabetes who develop BD, routine ophthalmologic examination and renal function testing to monitor for microalbuminuria are recommended.5
Our patient underwent bedside incision and drainage and was discharged home with appropriate wound care and follow-up.
THE TAKEAWAY
BD cases may be underdiagnosed in clinical practice, perhaps due to patients not seeking help for a seemingly nonthreatening condition or lack of clinician recognition that bullae are related to a patient’s diabetes status. Prompt recognition and proper wound care are important to prevent poor outcomes, such as ulceration or necrosis.
CORRESPONDENCE
Kathleen S. Kinderwater, MD, 101 Heart Drive, Greenville, NC 27834; [email protected]
1. Larsen K, Jensen T, Karlsmark T, et al. Incidence of bullosis diabeticorum—a controversial cause of chronic foot ulceration. Int Wound J. 2008;5:591-596. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2008.00476.x
2. Lipsky BA, Baker PD, Ahroni JH. Diabetic bullae: 12 cases of a purportedly rare cutaneous disorder. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:196-200. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00947.x
3. Gupta V, Gulati N, Bahl J, et al. Bullosis diabeticorum: rare presentation in a common disease. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2014;2014:862912.
4. Sonani H, Abdul Salim S, Garla VV, et al. Bullosis diabeticorum: a rare presentation with immunoglobulin G (IgG) deposition related vasculopathy. Case report and focused review. Am J Case Rep. 2018;19:52-56. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.905452
5. Chouk C, Litaiem N. Bullosis diabeticorum. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 5, 2021. Accessed July 14, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539872/
6. Chatterjee D, Radotra A, Radotra BD, et al. Bullous diabeticorum: a rare blistering manifestation of diabetes. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017;8:274-275. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_340_16
7. Kansal NK, Anuragi RP. Bullous lesions in diabetes mellitus: bullous diabeticorum (diabetic bulla). BMJ Case Rep. 2020;13:e238617. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238617
8. Bello F, Samaila OM, Lawal Y, et al. 2 cases of bullosis diabeticorum following long-distance journeys by road: a report of 2 cases. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2012;2012:367218. doi: 10.1155/2012/367218
1. Larsen K, Jensen T, Karlsmark T, et al. Incidence of bullosis diabeticorum—a controversial cause of chronic foot ulceration. Int Wound J. 2008;5:591-596. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2008.00476.x
2. Lipsky BA, Baker PD, Ahroni JH. Diabetic bullae: 12 cases of a purportedly rare cutaneous disorder. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:196-200. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.2000.00947.x
3. Gupta V, Gulati N, Bahl J, et al. Bullosis diabeticorum: rare presentation in a common disease. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2014;2014:862912.
4. Sonani H, Abdul Salim S, Garla VV, et al. Bullosis diabeticorum: a rare presentation with immunoglobulin G (IgG) deposition related vasculopathy. Case report and focused review. Am J Case Rep. 2018;19:52-56. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.905452
5. Chouk C, Litaiem N. Bullosis diabeticorum. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated June 5, 2021. Accessed July 14, 2022. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539872/
6. Chatterjee D, Radotra A, Radotra BD, et al. Bullous diabeticorum: a rare blistering manifestation of diabetes. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017;8:274-275. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_340_16
7. Kansal NK, Anuragi RP. Bullous lesions in diabetes mellitus: bullous diabeticorum (diabetic bulla). BMJ Case Rep. 2020;13:e238617. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238617
8. Bello F, Samaila OM, Lawal Y, et al. 2 cases of bullosis diabeticorum following long-distance journeys by road: a report of 2 cases. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2012;2012:367218. doi: 10.1155/2012/367218
COVID-19 therapy: What works? What doesn’t? And what’s on the horizon?
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has caused more than 1 million deaths in the United States and continues to be a major public health challenge. Cases can be asymptomatic, or symptoms can range from a mild respiratory tract infection to acute respiratory distress and multiorgan failure.
Three strategies can successfully contain the pandemic and its consequences:
- Public health measures, such as masking and social distancing
- Prophylactic vaccines to reduce transmission
- Safe and effective drugs for reducing morbidity and mortality among infected patients.
Optimal treatment strategies for patients in ambulatory and hospital settings continue to evolve as new studies are reported and new strains of the virus arise. Many medical and scientific organizations, including the National Institutes of Health (NIH) COVID-19 treatment panel,1 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA),2 World Health Organization (WHO),3 and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,4 provide recommendations for managing patients with COVID-19. Their guidance is based on the strongest research available and is updated intermittently; nevertheless, a plethora of new data emerges weekly and controversies surround several treatments.
In this article, we
We encourage clinicians, in planning treatment, to consider:
- The availability of medications (ie, use the COVID-19 Public Therapeutic Locatora)
- The local COVID-19 situation
- Patient factors and preferences
- Evolving evidence regarding new and existing treatments.
Most evidence about the treatment of COVID-19 comes from studies conducted when the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 was not the dominant variant, as it is today in the United States. As such, drugs authorized or approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat COVID-19 or used off-label for that purpose might not be as efficacious today as they were almost a year ago. Furthermore, many trials of potential therapies against new viral variants are ongoing; if your patient is interested in enrolling in a clinical trial of an investigational COVID-19 treatment, refer them to www.clinicaltrials.gov.
General managementof COVID-19
Patients with COVID-19 experience a range of illness severity—from asymptomatic to mild symptoms, such as fever and myalgia, to critical illness requiring intensive care (TABLE 11,2). Patients with COVID-19 should therefore be monitored for progression, remotely or in person, until full recovery is achieved. Key concepts of general management include:
Assess and monitor patients’ oxygenation status by pulse oximetry; identify those with low or declining oxygen saturation before further clinical deterioration.
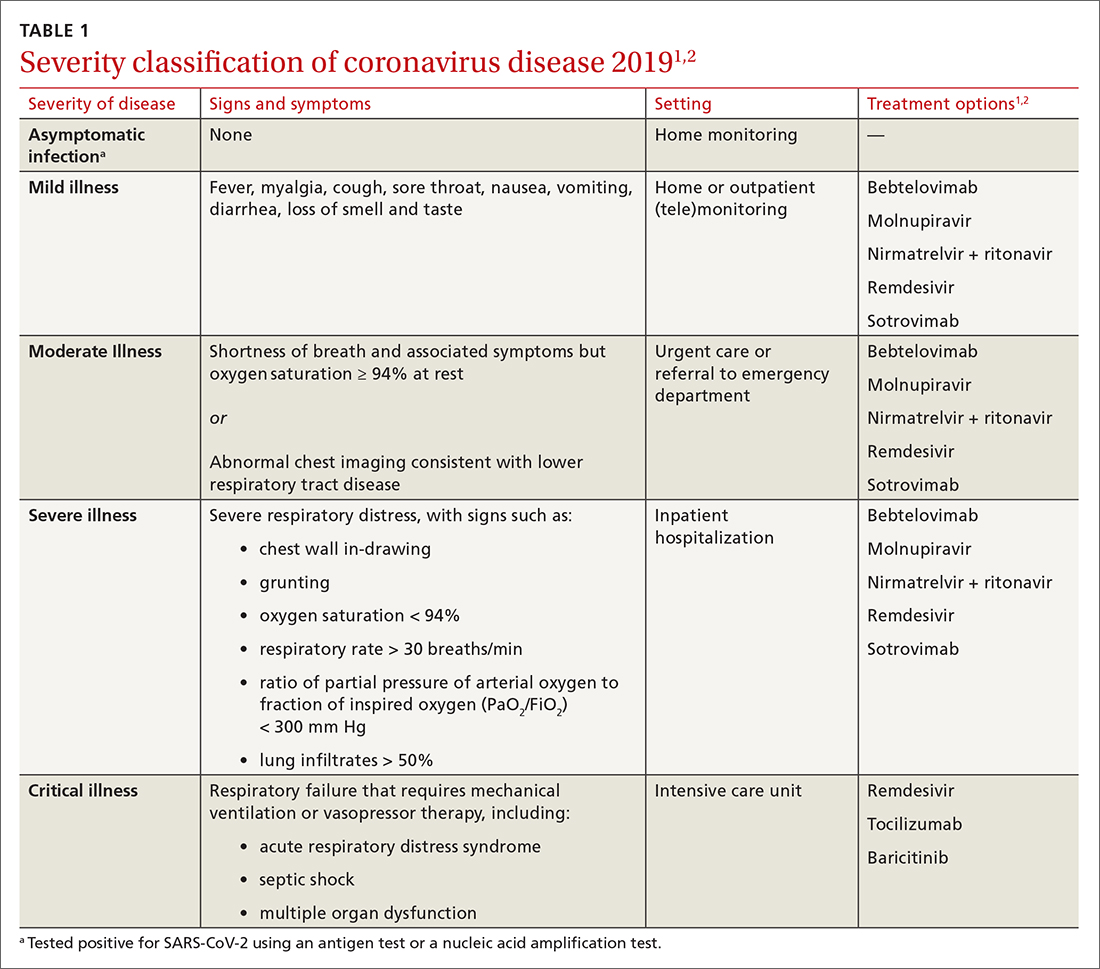
Continue to: Consider the patient's age and general health
Consider the patient’s age and general health. Patients are at higher risk of severe disease if they are > 65 years or have an underlying comorbidity.4
Emphasize self-isolation and supportive care, including rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve cough, reduce fever, and alleviate other symptoms.
Drugs: Few approved, some under study
The antiviral remdesivir is the only drug fully approved for clinical use by the FDA to treat COVID-19 in patients > 12 years.5,6
In addition, the FDA has issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for several monoclonal antibodies as prophylaxis and treatment: tixagevimab packaged with cilgavimab (Evusheld) is the first antibody combination for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against COVID-19; the separately packaged injectables are recommended for patients who have a history of severe allergy that prevents them from being vaccinated or those with moderate or severe immune-compromising disorders.7
In the pipeline. Several treatments are being tested in clinical trials to evaluate their effectiveness and safety in combating COVID-19, including:
- Antivirals, which prevent viruses from multiplying
- Immunomodulators, which reduce the body’s immune reaction to the virus
- Antibody therapies, which are manufactured antibodies against the virus
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, which reduce systemic inflammation and prevent organ dysfunction
- Cell therapies and gene therapies, which alter the expression of cells and genes.
Continue to: Outpatient treatment
Outpatient treatment
Several assessment tools that take into account patients’ age, respiratory status, and comorbidities are available for triage of patients infected with COVID-19.8
Most (> 80%) patients with COVID-19 have mild infection and are safely managed as outpatients or at home.9,10 For patients at high risk of severe disease, a few options are recommended for patients who do not require hospitalization or supplemental oxygen; guidelines on treatment of COVID-19 in outpatient settings that have been developed by various organizations are summarized in TABLE 2.7,11-25
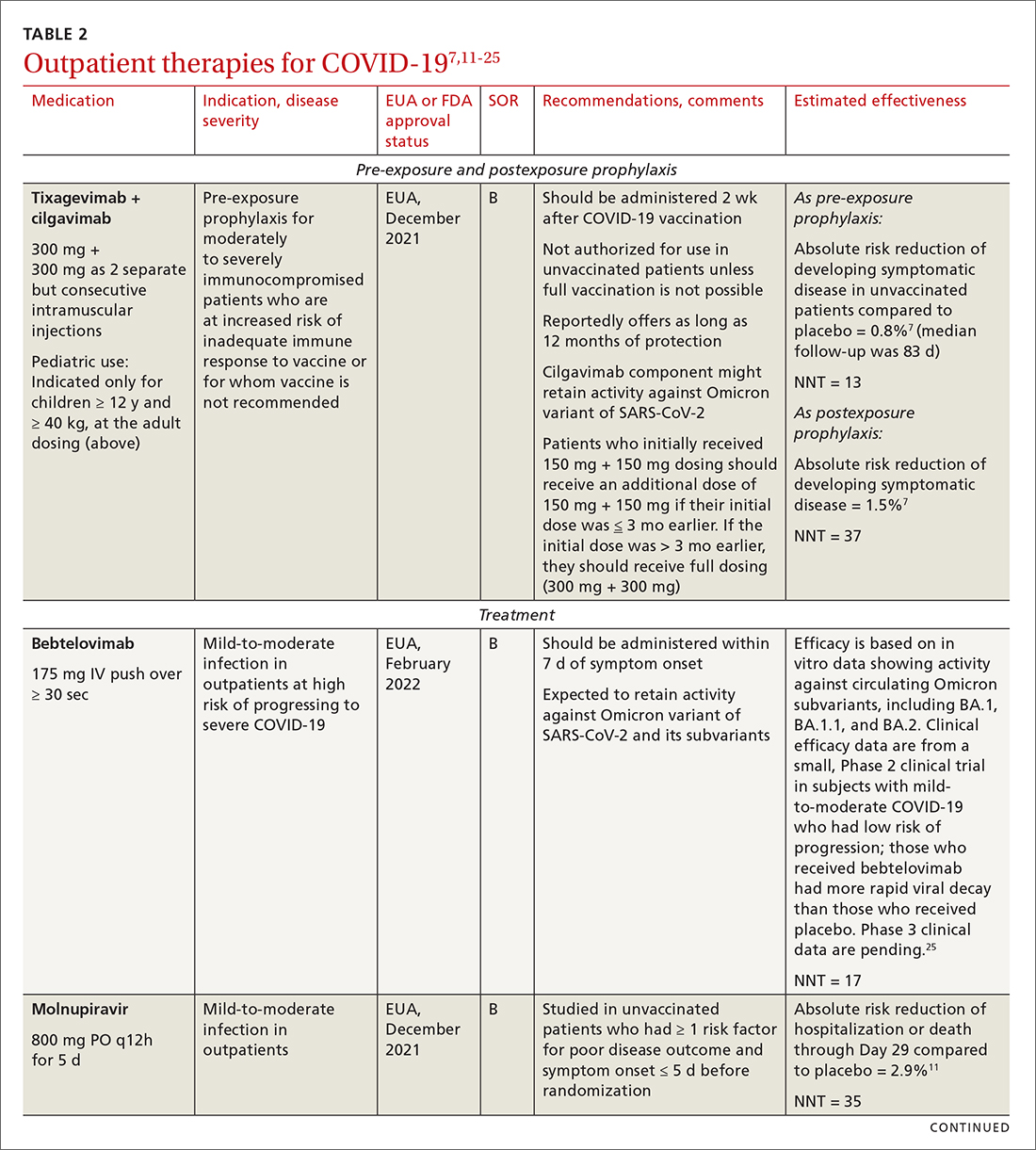
Antiviral drugs target different stages of the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle. They should be used early in the course of infection, particularly in patients at high risk of severe disease.
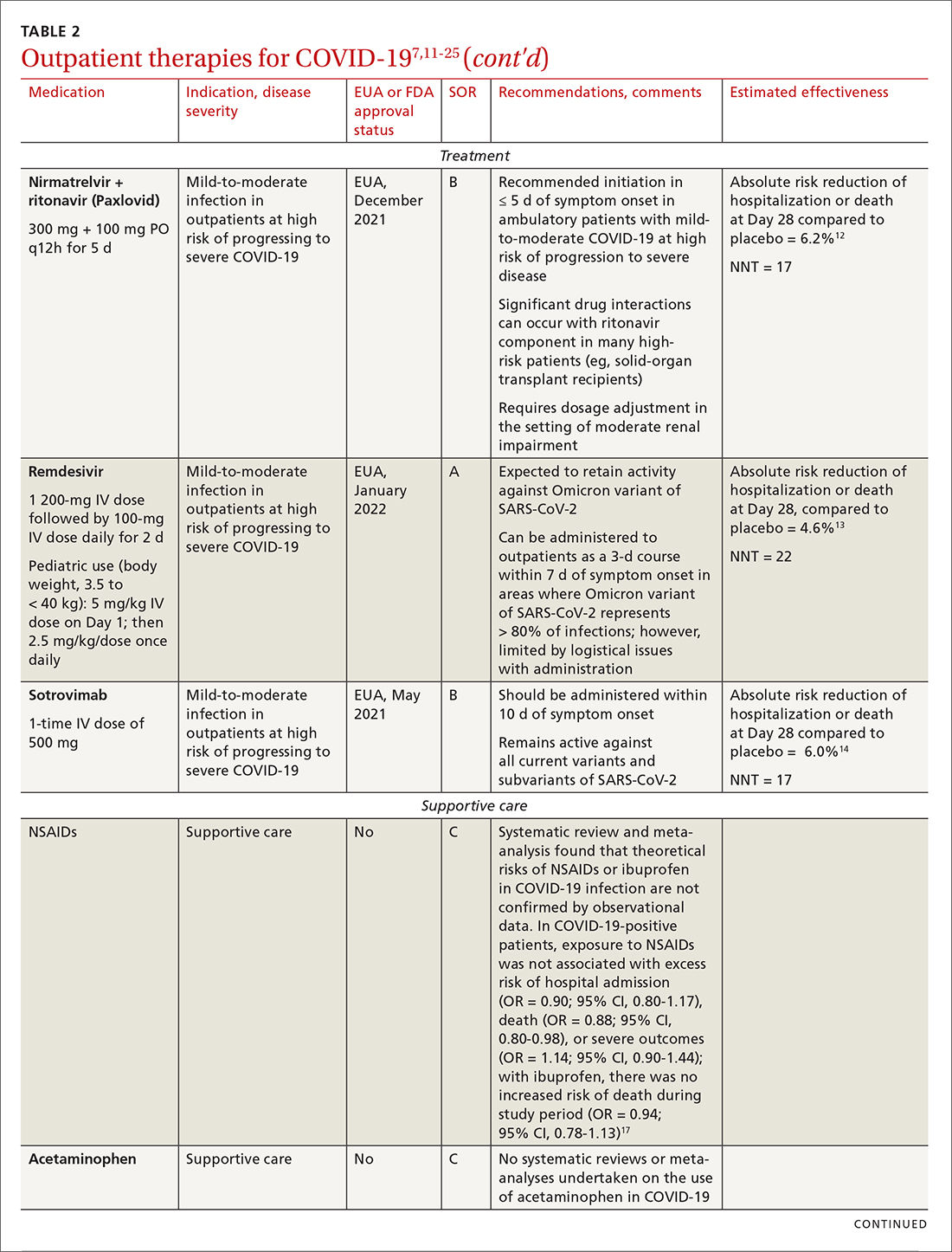
IDSA recommends antiviral therapy with molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir + ritonavir packaged together (Paxlovid), or remdesivir.11,12,26,27 Remdesivir requires intravenous (IV) infusion on 3 consecutive days, which can be difficult in some clinic settings.13,28 Nirmatrelvir + ritonavir should be initiated within 5 days after symptom onset. Overall, for most patients, nirmatrelvir + ritonavir is preferred because of oral dosing and higher efficacy in comparison to other antivirals. With nirmatrelvir + ritonavir, carefully consider drug–drug interactions and the need to adjust dosing in the presence of renal disease.28,29 There are no data on the efficacy of any combination treatments with these agents (other than co-packaged Paxlovid).
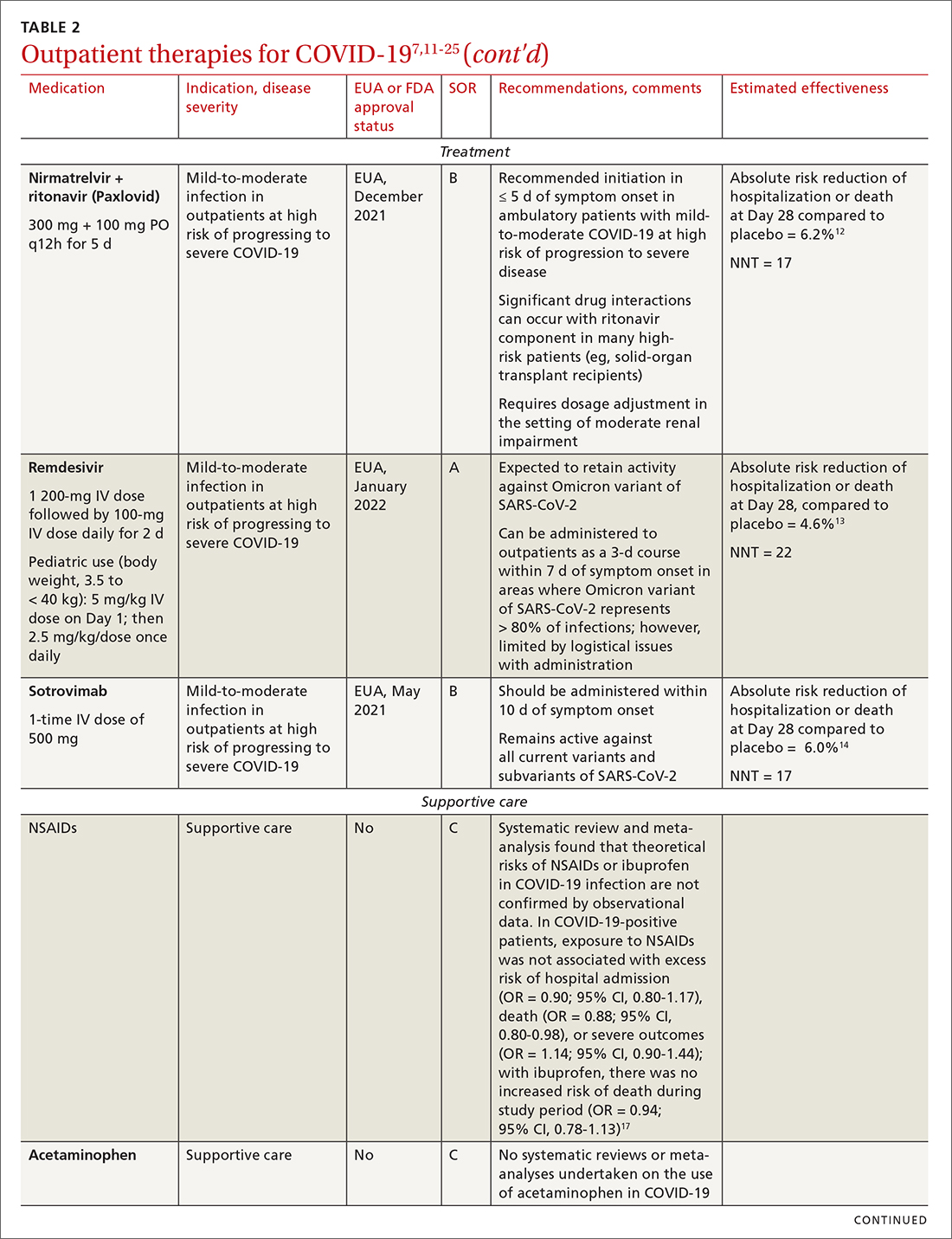
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 are given primarily intravenously. They bind to the viral spike protein, thus preventing SARS-CoV-2 from attaching to and entering cells. Bamlanivimab + etesevimab and bebtelovimab are available under an EUA for outpatient treatment.14b Treatment should be initiated as early as possible in the course of infection—ideally, within 7 to 10 days after onset of symptoms.
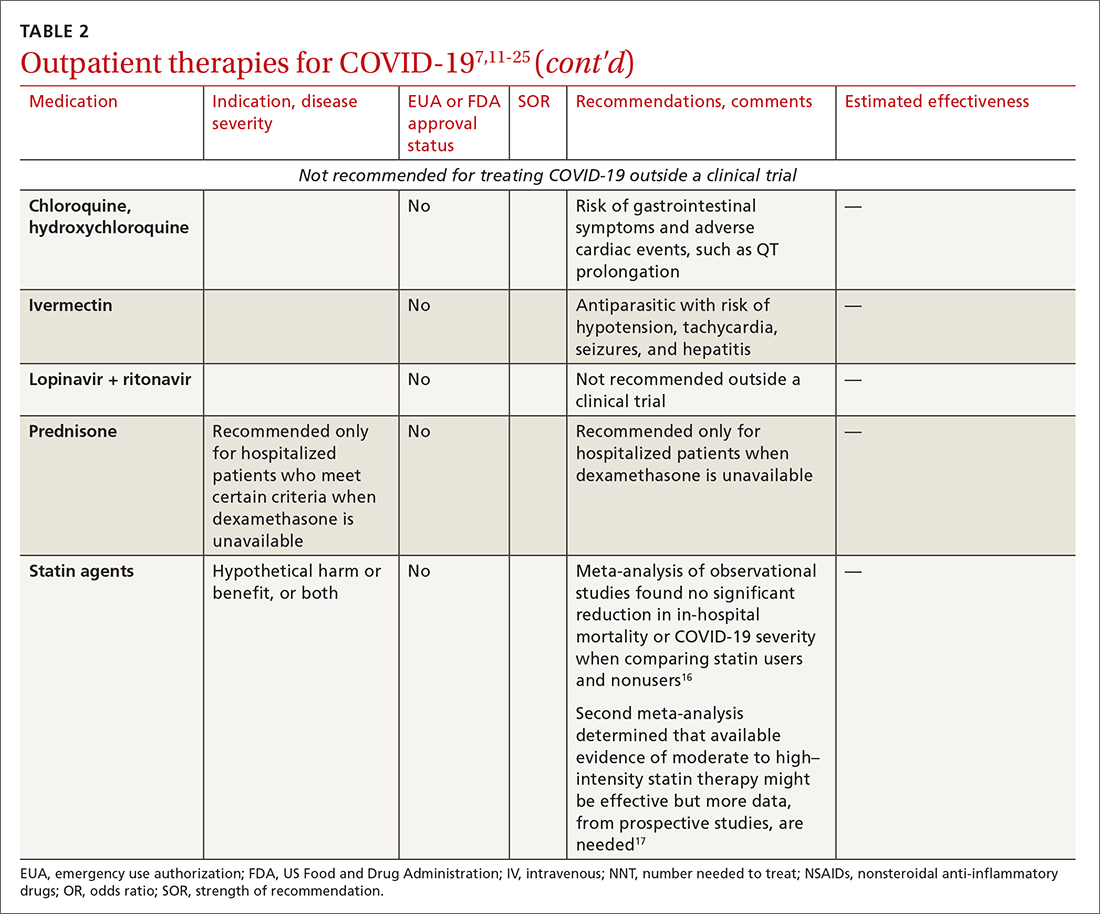
Continue to: Bebtelovimab was recently given...
Bebtelovimab was recently given an EUA. It is a next-generation antibody that neutralizes all currently known variants and is the most potent monoclonal antibody against the Omicron variant, including its BA.2 subvariant.31 However, data about its activity against the BA.2 subvariant are based on laboratory testing and have not been confirmed in clinical trials. Clinical data were similar for this agent alone and for its use in combination with other monoclonal antibodies, but those trials were conducted before the emergence of Omicron.
In your decision-making about the most appropriate therapy, consider (1) the requirement that monoclonal antibodies be administered parenterally and (2) the susceptibility of the locally predominating viral variant.
Other monoclonal antibody agents are in the investigative pipeline; however, data about them have been largely presented through press releases or selectively reported in applications to the FDA for EUA. For example, preliminary reports show cilgavimab coverage against the Omicron variant14; so far, cilgavimab is not approved for treatment but is used in combination with tixagevimab for PreP—reportedly providing as long as 12 months of protection for patients who are less likely to respond to a vaccine.32
Corticosteroids. Guidelines recommend against dexamethasone and other systemic corticosteroids in outpatient settings. For patients with moderate-to-severe symptoms but for whom hospitalization is not possible (eg, beds are unavailable), the NIH panel recommends dexamethasone, 6 mg/d, for the duration of supplemental oxygen, not to exceed 10 days of treatment.1
Patients who were recently discharged after COVID-19 hospitalization should not continue remdesivir, dexamethasone, or baricitinib at home, even if they still require supplemental oxygen.
Continue to: Some treatments should not be in your COVID-19 toolbox
Some treatments should not be in your COVID-19 toolbox
High-quality studies are lacking for several other potential COVID-19 treatments. Some of these drugs are under investigation, with unclear benefit and with the potential risk of toxicity—and therefore should not be prescribed or used outside a clinical trial. See “Treatments not recommended for COVID-19,” page E14. 1-4,15-19,33-41
SIDEBAR
Treatments not recommended for COVID-191-4,15-19,33-41
Fluvoxamine. A few studies suggest that the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluvoxamine reduces progression to severe disease; however, those studies have methodologic challenges.33 The drug is not FDA approved for treating COVID.33
Convalescent plasma, given to high-risk outpatients early in the course of disease, can reduce progression to severe disease,34,35 but it remains investigational for COVID-19 because trials have yielded mixed results.34-36
Ivermectin. The effect of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19 is unclear because high-quality studies do not exist and cases of ivermectin toxicity have occurred with incorrect administration.39
Hydroxychloroquine showed potential in a few observational studies, but randomized clinical trials have not shown any benefit.15
Azithromycin likewise showed potential in a few observational studies; randomized clinical trials have not shown any benefit, however.15
Statins. A few meta-analyses, based on observational studies, reported benefit from statins, but recent studies have shown that this class of drugs does not provide clinical benefit in alleviating COVID-19 symptoms.16,17,37
Inhaled corticosteroids. A systematic review reported no benefit or harm from using an inhaled corticosteroid.18 More recent studies show that the inhaled corticosteroid budesonide used in early COVID-19 might reduce the need for urgent care38 and, in patients who are at higher risk of COVID-19-related complications, shorten time to recovery.19
Vitamins and minerals. Limited observational studies suggest an association between vitamin and mineral deficiency (eg, vitamin C, zinc, and vitamin D) and risk of severe disease, but high-quality data about this finding do not exist.40,41
Casirivimab + imdevimab [REGEN-COV2]. This unapproved investigational combination treatment was granted an EUA in 2020 for postexposure prophylaxis. The EUA was withdrawn in January 2022 because of the limited efficacy of casirivimab + imdevimab against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
Postexposure prophylaxis. National guidelines1-4 recommend against postexposure prophylaxis with hydroxychloroquine, colchicine, inhaled corticosteroids, or azithromycin.
TABLE 27,11-25 and TABLE 326,42-46 provide additional information on treatments not recommended outside trials, or not recommended at all, for COVID-19.
Treatment during hospitalization
The NIH COVID-19 treatment panel recommends hospitalization for patients who have any of the following findings1:
- Oxygen saturation < 94% while breathing room air
- Respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min
- A ratio of partial pressure of arterial O2 to fraction of inspired O2 (PaO2/FiO2) < 300 mm Hg
- Lung infiltrates > 50%.
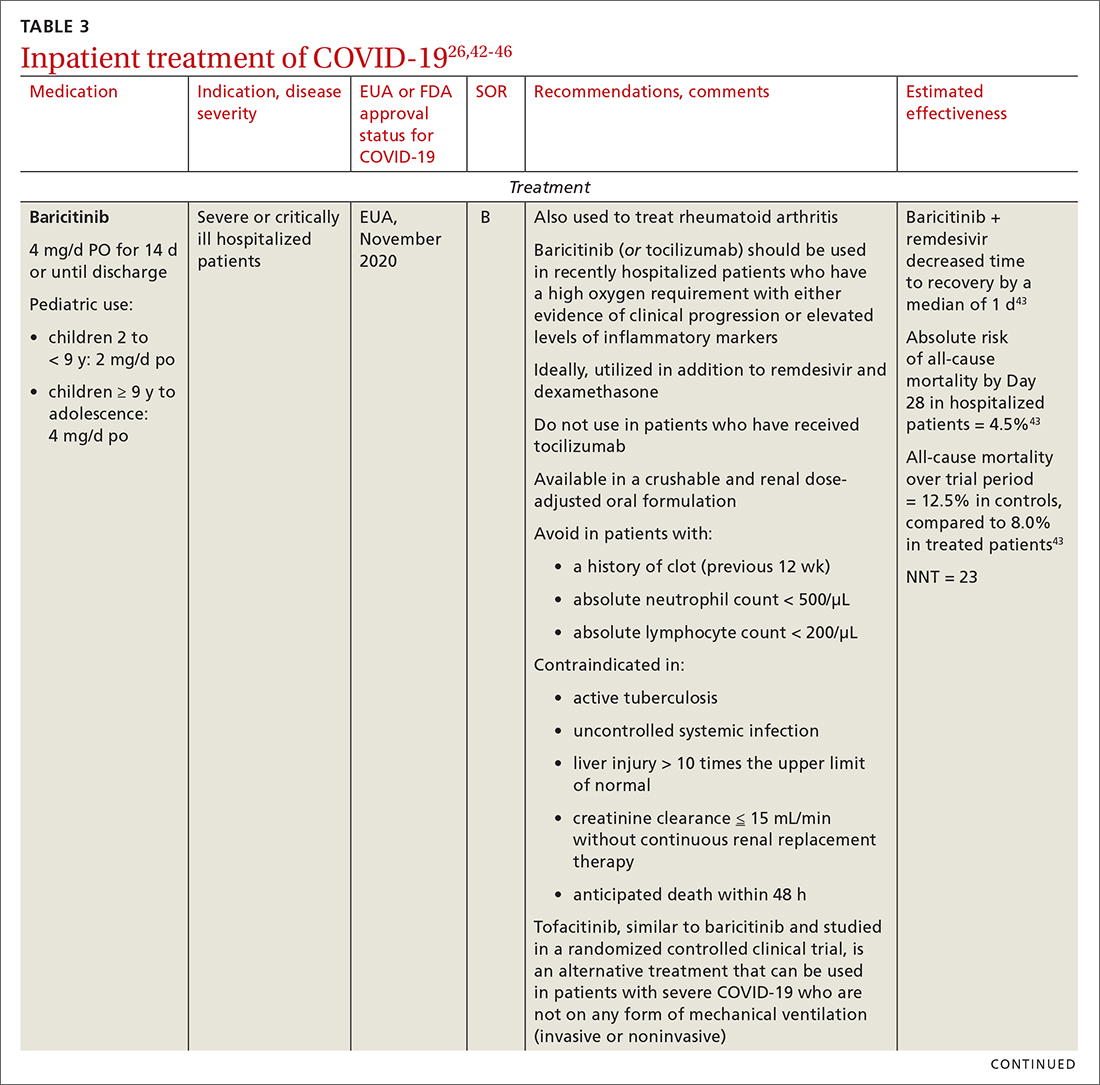
General guidance for the care of hospitalized patients:
- Treatments that target the virus have the greatest efficacy when given early in the course of disease.
- Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents help prevent tissue damage from a dysregulated immune system. (See TABLE 326,42-46)
- The NIH panel,1 IDSA,2 and WHO3 recommend against dexamethasone and other corticosteroids for hospitalized patients who do not require supplemental oxygen.
- Prone positioning distributes oxygen more evenly in the lungs and improves overall oxygenation, thus reducing the need for mechanical ventilation.
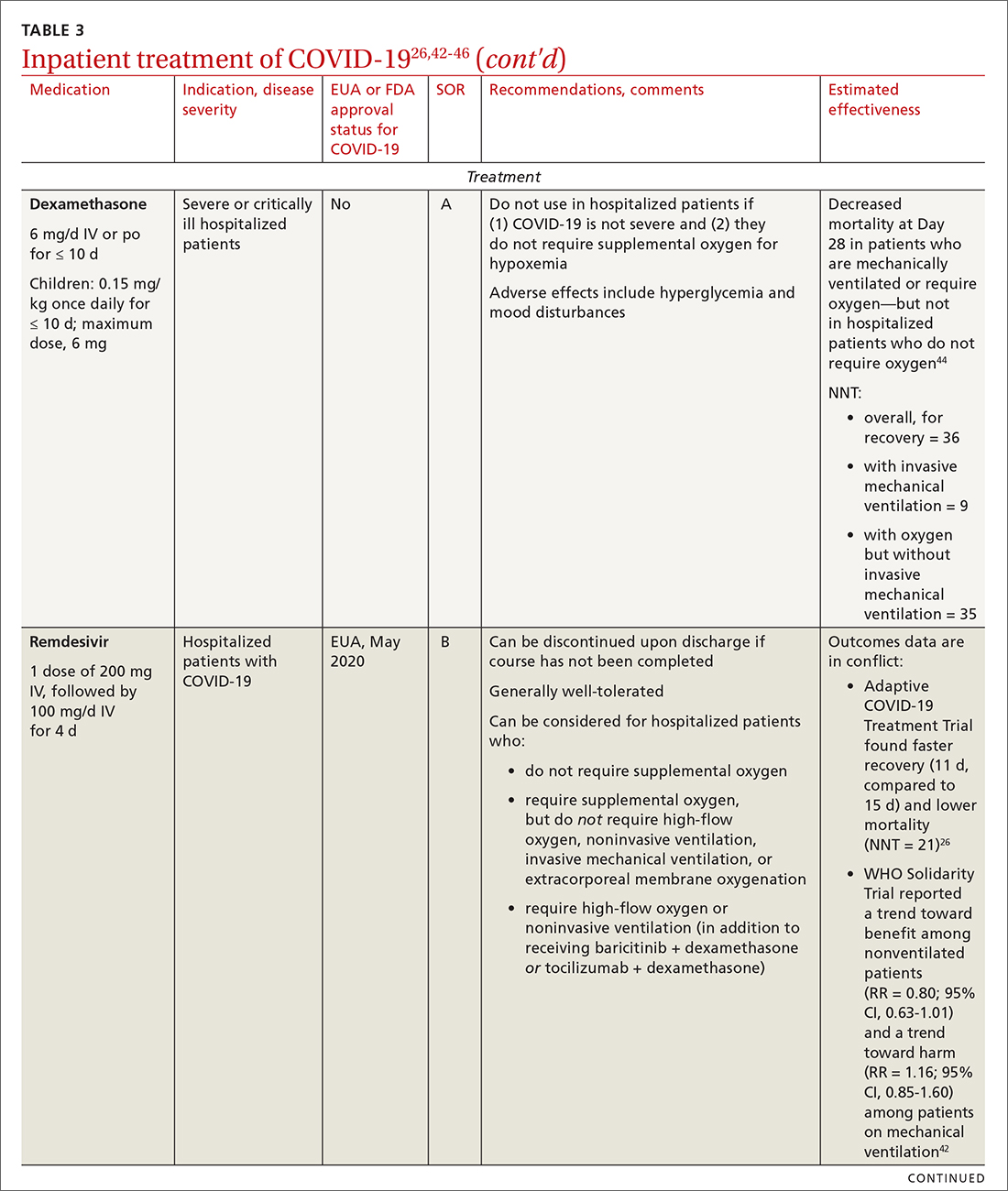
Remdesivir. Once a hospitalized patient does require supplemental oxygen, the NIH panel,1 IDSA,2 and WHO3 recommend remdesivir; however, remdesivir is not recommended in many other countries because WHO has noted its limited efficacy.42 Dexamethasone is recommended alone, or in combination with remdesivir for patients who require increasing supplemental oxygen and those on mechanical ventilation.
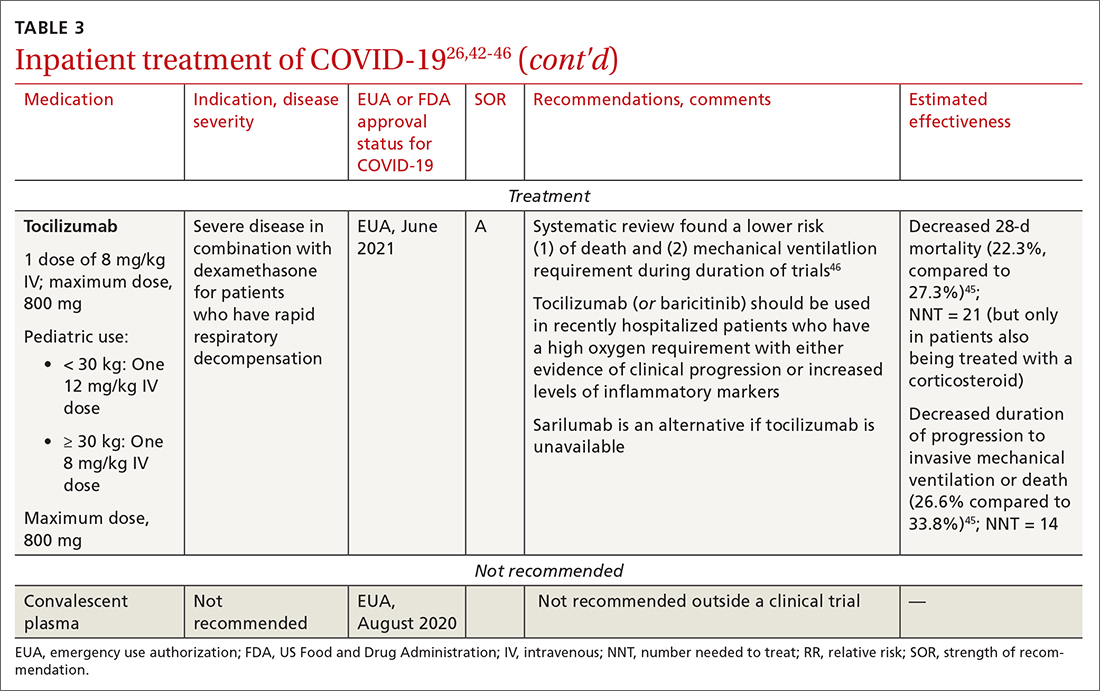
Baricitinib. For patients with rapidly increasing oxygen requirements, invasive mechanical ventilation, and systemic inflammation, baricitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, can be administered, in addition to dexamethasone, with or without remdesivir.47
Continue to: Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab. A monoclonal antibody and interleukin (IL)-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab is also recommended in addition to dexamethasone, with or without remdesivir.48 Tocilizumab should be given only in combination with dexamethasone.49 Patients should receive baricitinib or tocilizumab—not both. IDSA recommends tofacitinib, with a prophylactic dose of an anticoagulant, for patients who are hospitalized with severe COVID-19 but who are not on any form of ventilation.50
Care of special populations
Special patient populations often seek primary care. Although many questions remain regarding the appropriate care of these populations, it is useful to summarize existing evidence and recommendations from current guidelines.
Children. COVID-19 is generally milder in children than in adults; many infected children are asymptomatic. However, infants and children who have an underlying medical condition are at risk of severe disease, including multisystem inflammatory syndrome.51
The NIH panel recommends supportive care alone for most children with mild-to-moderate disease.1 Remdesivir is recommended for hospitalized children ≥ 12 years who weigh ≥ 40 kg, have risk factors for severe disease, and have an emergent or increasing need for supplemental oxygen. Dexamethasone is recommended for hospitalized children requiring high-flow oxygen, noninvasive ventilation, invasive mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Molnupiravir is not authorized for patients < 18 years because it can impede bone and cartilage growth.
There is insufficient evidence for or against the use of monoclonal antibody products for children with COVID-19 in an ambulatory setting. For hospitalized children, there is insufficient evidence for or against use of baricitinib and tocilizumab.
Continue to: Patients who are pregnant
Patients who are pregnant are at increased risk of severe COVID-19.52,53 The NIH states that, in general, treatment and vaccination of pregnant patients with COVID-19 should be the same as for nonpregnant patients.1
Pregnant subjects were excluded from several trials of COVID-19 treatments.54 Because Janus kinase inhibitors, such as baricitinib, are associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, they are not recommended in pregnant patients who are already at risk of thromboembolic complications. Molnupiravir is not recommended for pregnant patients because of its potential for teratogenic effects.
The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine states that there are no absolute contraindications to the use of monoclonal antibodies in appropriate pregnant patients with COVID-19.55 Remdesivir has no known fetal toxicity and is recommended as a treatment that can be offered to pregnant patients. Dexamethasone can also be administered to pregnant patients who require oxygen; however, if dexamethasone is also being used to accelerate fetal lung maturity, more frequent initial dosing is needed.
Older people. COVID-19 treatments for older patients are the same as for the general adult population. However, because older people are more likely to have impaired renal function, renal function should be monitored when an older patient is being treated with COVID-19 medications that are eliminated renally (eg, remdesivir, baricitinib). Furthermore, drug–drug interactions have been reported in older patients treated with nirmatrelvir + ritonavir, primarily because of the effects of ritonavir. Review all of a patient’s medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, when prescribing treatment for COVID-19, and adjust the dosage by following guidance in FDA-approved prescribing information—ideally, in consultation with a pharmacist.
Immunocompromised patients. The combination product tixagevimab + cilgavimab [Evusheld] is FDA approved for COVID-19 PrEP, under an EUA, in patients who are not infected with SARS-CoV-2 who have an immune-compromising condition, who are unlikely to mount an adequate immune response to the COVID-19 vaccine, or those in whom vaccination is not recommended because of their history of a severe adverse reaction to a COVID-19 vaccine or one of its components.7
Continue to: Summing up
Summing up
With a growing need for effective and readily available COVID-19 treatments, there are an unprecedented number of clinical trials in process. Besides antivirals, immunomodulators, and antibody therapies, some novel mechanisms being tested include Janus kinase inhibitors, IL-6-receptor blockers, and drugs that target adult respiratory distress syndrome and cytokine release.
Once larger trials are completed, we can expect stronger evidence of potential treatment options and of safety and efficacy in children, pregnant women, and vulnerable populations. During the pandemic, the FDA’s EUA program has brought emerging treatments rapidly to clinicians; nevertheless, high-quality evidence, with thorough peer review, remains critical to inform COVID-19 treatment guidelines.
a https://healthdata.gov/Health/COVID-19-PublicTherapeutic-Locator/rxn6-qnx8/data
b Sotrovimab was effective against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2—the dominant variant in early 2022— but is currently not FDA authorized in any region of the United States because of the prevalence of the Omicron BA.2 subvariant.30
CORRESPONDENCE
Ambar Kulshreshtha, MD, PhD, Department of Epidemiology, Emory Rollins School of Public Health, 4500 North Shallowford Road, Suite 134, Atlanta, GA 30338; [email protected]
1. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. National Institutes of Health. July 19, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov
2. IDSA guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Updated June 29, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/#toc-23
3. Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. World Health Organization. July 14, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1449398/retrieve
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical care considerations. Updated May 27, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html
5. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA approves first COVID-19 treatment for young children. Press release. US Food and Drug Administration. April 25, 2022. Accessed August 11, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-approves-first-covid-19-treatment-young-children
6. Know your treatment options for COVID-19. US Food and Drug Administration. Updated August 15, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-options-covid-19
7. Tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19. JAMA. 2022;327:384-385. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.24931
8. Judson TJ, Odisho AY, Neinstein AB, et al. Rapid design and implementation of an integrated patient self-triage and self-scheduling tool for COVID-19. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27:860-866. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa051
9. Gandhi RT, Lynch JB, Del Rio C. Mild or moderate Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1757-1766. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp2009249
10. Greenhalgh T, Koh GCH, Car J. Covid-19: a remote assessment in primary care. BMJ. 2020;368:m1182. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1182
11. Jayk Bernal A, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, et al; . Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:509-520. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
12. Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al; . Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1397-1408. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
13. Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE, Paredes R, et al; . Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:305-315. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
14. Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, et al; . Early treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1941-1950. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107934
15. Skipper CP, Pastick KA, Engen NW, et al. Hydroxychloroquine in nonhospitalized adults with early COVID-19: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:623-631. doi: 10.7326/M20-4207
16. Scheen AJ. Statins and clinical outcomes with COVID-19: meta-analyses of observational studies. Diabetes Metab. 2021;47:101220. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101220
17. Kow CS, Hasan SS. Meta-analysis of effect of statins in patients with COVID-19. Am J Cardiol. 2020;134:153-155. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.08.004
18. Halpin DMG, Singh D, Hadfield RM. Inhaled corticosteroids and COVID-19: a systematic review and clinical perspective. Eur Respir J. 2020;55:2001009. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01009-2020
19. Yu L-M, Bafadhel M, Dorward J, et al; . Inhaled budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial. Lancet. 2021;398:843-855. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01744-X
20. Siemieniuk RA, Bartoszko JJ, JP, et al. Antibody and cellular therapies for treatment of covid-19: a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;374:n2231. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n2231
21. Siemieniuk RA, Bartoszko JJ, Zeraatkar D, et al. Drug treatments for covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;370:m2980. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2980
22. Agarwal A, Rochwerg B, Lamontagne F, et al. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ. 2020;370:m3379. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3379
23. Goldstein KM, Ghadimi K, Mystakelis H, et al. Risk of transmitting coronavirus disease 2019 during nebulizer treatment: a systematic review. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2021;34:155-170. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2020.1659
24. Schultze A, Walker AJ, MacKenna B, et al; . Risk of COVID-19-related death among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma prescribed inhaled corticosteroids: an observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:1106-1120. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30415-X
25. What are the safety and efficacy results of bebtelovimab from BLAZE-4? Lilly USA. January 12, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.lillymedical.com/en-us/answers/what-are-the-safety-and-efficacy-results-of-bebtelovimab-from-blaze-4-159290
26. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al; . Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1813-1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
27. Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, et al. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1787-1799. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
28. Gandhi RT, Malani PN, Del Rio C. COVID-19 therapeutics for nonhospitalized patients. JAMA. 2022;327:617-618. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0335
29. Wen W, Chen C, Tang J, et al. Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2022;54:516-523. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2034936
30. Planas D, Saunders N, Maes P, et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature. 2022:602:671-675. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z
31. Emergency use authorization (EUA) for bebtelovimab (LY-CoV1404): Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) review. US Food and Drug Administration. Updated February 11, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.fda.gov/media/156396/download
32. Bartoszko JJ, Siemieniuk RAC, Kum E, et al. Prophylaxis against covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;373:n949. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n949
33. Reis G, Dos Santos Moreira-Silva EA, Silva DCM, et al; TOGETHER Investigators. Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2022;10:e42-e51. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
34. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2049-2059. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7
35. Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, et al; . A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:619-629. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
36. Joyner MJ, Carter RE, Senefeld JW, et al. Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1015-1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031893
37. Ayeh SK, Abbey EJ, Khalifa BAA, et al. Statins use and COVID-19 outcomes in hospitalized patients. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0256899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256899
38. Ramakrishnan S, Nicolau DV Jr, Langford B, et al. Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9:763-772. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0
39. Temple C, Hoang R, Hendrickson RG. Toxic effects from ivermectin use associated with prevention and treatment of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2197-2198. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2114907
40. Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, et al. Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e210369. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
41. Adams KK, Baker WL, Sobieraj DM. Myth busters: dietary supplements and COVID-19. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54:820-826. doi: 10.1177/1060028020928052
42. Pan H, Peto R, Henao-Restrepo A-M, et al. Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19—interim WHO Solidarity trial results. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:497-511. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
43. Kalil AC, Patterson TF, Mehta AK, et al; . Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:795-807. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031994
44. ; Sterne JAC, Murthy S, Diaz JV, et al. Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2020;324:1330-1341. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17023
45. ; Shankar-Hari M, Vale CL, Godolphin PJ, et al. Association between administration of IL-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2021;326:499-518. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.11330
46. Wei QW, Lin H, Wei R-G, et al. Tocilizumab treatment for COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021;10:71. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00857-w
47. Zhang X, Shang L, Fan G, et al. The efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors for patients with COVID-19: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:800492. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.800492
48. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021;397:1637-1645. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0
49. Gordon AC, Mouncey PR, Al-Beidh F, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1491-1502. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100433
50. Guimaraes PO, Quirk D, Furtado RH, et al; . Tofacitinib in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:406-415. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2101643
51. Feldstein LR, Rose EB, Horwitz SM, et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in U.S. children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:334-346. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021680
52. Allotey J, Stallings E, Bonet M, et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;370:m3320. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3320
53. Villar J, Ariff S, Gunier RB, et al. Maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality among pregnant women with and without COVID-19 infection: the INTERCOVID multinational cohort study. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175:817-826. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1050
54. Jorgensen SCJ, Davis MR, Lapinsky SE. A review of remdesivir for COVID-19 in pregnancy and lactation. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021;77:24-30. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab311
55. Management considerations for pregnant patients with COVID-19. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Accessed July 21, 2022. https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn.smfm.org/media/2336/SMFM_COVID_Management_of_COVID_pos_preg_patients_4-30-20_final.pdf
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has caused more than 1 million deaths in the United States and continues to be a major public health challenge. Cases can be asymptomatic, or symptoms can range from a mild respiratory tract infection to acute respiratory distress and multiorgan failure.
Three strategies can successfully contain the pandemic and its consequences:
- Public health measures, such as masking and social distancing
- Prophylactic vaccines to reduce transmission
- Safe and effective drugs for reducing morbidity and mortality among infected patients.
Optimal treatment strategies for patients in ambulatory and hospital settings continue to evolve as new studies are reported and new strains of the virus arise. Many medical and scientific organizations, including the National Institutes of Health (NIH) COVID-19 treatment panel,1 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA),2 World Health Organization (WHO),3 and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,4 provide recommendations for managing patients with COVID-19. Their guidance is based on the strongest research available and is updated intermittently; nevertheless, a plethora of new data emerges weekly and controversies surround several treatments.
In this article, we
We encourage clinicians, in planning treatment, to consider:
- The availability of medications (ie, use the COVID-19 Public Therapeutic Locatora)
- The local COVID-19 situation
- Patient factors and preferences
- Evolving evidence regarding new and existing treatments.
Most evidence about the treatment of COVID-19 comes from studies conducted when the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 was not the dominant variant, as it is today in the United States. As such, drugs authorized or approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat COVID-19 or used off-label for that purpose might not be as efficacious today as they were almost a year ago. Furthermore, many trials of potential therapies against new viral variants are ongoing; if your patient is interested in enrolling in a clinical trial of an investigational COVID-19 treatment, refer them to www.clinicaltrials.gov.
General managementof COVID-19
Patients with COVID-19 experience a range of illness severity—from asymptomatic to mild symptoms, such as fever and myalgia, to critical illness requiring intensive care (TABLE 11,2). Patients with COVID-19 should therefore be monitored for progression, remotely or in person, until full recovery is achieved. Key concepts of general management include:
Assess and monitor patients’ oxygenation status by pulse oximetry; identify those with low or declining oxygen saturation before further clinical deterioration.

Continue to: Consider the patient's age and general health
Consider the patient’s age and general health. Patients are at higher risk of severe disease if they are > 65 years or have an underlying comorbidity.4
Emphasize self-isolation and supportive care, including rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve cough, reduce fever, and alleviate other symptoms.
Drugs: Few approved, some under study
The antiviral remdesivir is the only drug fully approved for clinical use by the FDA to treat COVID-19 in patients > 12 years.5,6
In addition, the FDA has issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for several monoclonal antibodies as prophylaxis and treatment: tixagevimab packaged with cilgavimab (Evusheld) is the first antibody combination for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against COVID-19; the separately packaged injectables are recommended for patients who have a history of severe allergy that prevents them from being vaccinated or those with moderate or severe immune-compromising disorders.7
In the pipeline. Several treatments are being tested in clinical trials to evaluate their effectiveness and safety in combating COVID-19, including:
- Antivirals, which prevent viruses from multiplying
- Immunomodulators, which reduce the body’s immune reaction to the virus
- Antibody therapies, which are manufactured antibodies against the virus
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, which reduce systemic inflammation and prevent organ dysfunction
- Cell therapies and gene therapies, which alter the expression of cells and genes.
Continue to: Outpatient treatment
Outpatient treatment
Several assessment tools that take into account patients’ age, respiratory status, and comorbidities are available for triage of patients infected with COVID-19.8
Most (> 80%) patients with COVID-19 have mild infection and are safely managed as outpatients or at home.9,10 For patients at high risk of severe disease, a few options are recommended for patients who do not require hospitalization or supplemental oxygen; guidelines on treatment of COVID-19 in outpatient settings that have been developed by various organizations are summarized in TABLE 2.7,11-25

Antiviral drugs target different stages of the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle. They should be used early in the course of infection, particularly in patients at high risk of severe disease.

IDSA recommends antiviral therapy with molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir + ritonavir packaged together (Paxlovid), or remdesivir.11,12,26,27 Remdesivir requires intravenous (IV) infusion on 3 consecutive days, which can be difficult in some clinic settings.13,28 Nirmatrelvir + ritonavir should be initiated within 5 days after symptom onset. Overall, for most patients, nirmatrelvir + ritonavir is preferred because of oral dosing and higher efficacy in comparison to other antivirals. With nirmatrelvir + ritonavir, carefully consider drug–drug interactions and the need to adjust dosing in the presence of renal disease.28,29 There are no data on the efficacy of any combination treatments with these agents (other than co-packaged Paxlovid).

Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 are given primarily intravenously. They bind to the viral spike protein, thus preventing SARS-CoV-2 from attaching to and entering cells. Bamlanivimab + etesevimab and bebtelovimab are available under an EUA for outpatient treatment.14b Treatment should be initiated as early as possible in the course of infection—ideally, within 7 to 10 days after onset of symptoms.

Continue to: Bebtelovimab was recently given...
Bebtelovimab was recently given an EUA. It is a next-generation antibody that neutralizes all currently known variants and is the most potent monoclonal antibody against the Omicron variant, including its BA.2 subvariant.31 However, data about its activity against the BA.2 subvariant are based on laboratory testing and have not been confirmed in clinical trials. Clinical data were similar for this agent alone and for its use in combination with other monoclonal antibodies, but those trials were conducted before the emergence of Omicron.
In your decision-making about the most appropriate therapy, consider (1) the requirement that monoclonal antibodies be administered parenterally and (2) the susceptibility of the locally predominating viral variant.
Other monoclonal antibody agents are in the investigative pipeline; however, data about them have been largely presented through press releases or selectively reported in applications to the FDA for EUA. For example, preliminary reports show cilgavimab coverage against the Omicron variant14; so far, cilgavimab is not approved for treatment but is used in combination with tixagevimab for PreP—reportedly providing as long as 12 months of protection for patients who are less likely to respond to a vaccine.32
Corticosteroids. Guidelines recommend against dexamethasone and other systemic corticosteroids in outpatient settings. For patients with moderate-to-severe symptoms but for whom hospitalization is not possible (eg, beds are unavailable), the NIH panel recommends dexamethasone, 6 mg/d, for the duration of supplemental oxygen, not to exceed 10 days of treatment.1
Patients who were recently discharged after COVID-19 hospitalization should not continue remdesivir, dexamethasone, or baricitinib at home, even if they still require supplemental oxygen.
Continue to: Some treatments should not be in your COVID-19 toolbox
Some treatments should not be in your COVID-19 toolbox
High-quality studies are lacking for several other potential COVID-19 treatments. Some of these drugs are under investigation, with unclear benefit and with the potential risk of toxicity—and therefore should not be prescribed or used outside a clinical trial. See “Treatments not recommended for COVID-19,” page E14. 1-4,15-19,33-41
SIDEBAR
Treatments not recommended for COVID-191-4,15-19,33-41
Fluvoxamine. A few studies suggest that the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluvoxamine reduces progression to severe disease; however, those studies have methodologic challenges.33 The drug is not FDA approved for treating COVID.33
Convalescent plasma, given to high-risk outpatients early in the course of disease, can reduce progression to severe disease,34,35 but it remains investigational for COVID-19 because trials have yielded mixed results.34-36
Ivermectin. The effect of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19 is unclear because high-quality studies do not exist and cases of ivermectin toxicity have occurred with incorrect administration.39
Hydroxychloroquine showed potential in a few observational studies, but randomized clinical trials have not shown any benefit.15
Azithromycin likewise showed potential in a few observational studies; randomized clinical trials have not shown any benefit, however.15
Statins. A few meta-analyses, based on observational studies, reported benefit from statins, but recent studies have shown that this class of drugs does not provide clinical benefit in alleviating COVID-19 symptoms.16,17,37
Inhaled corticosteroids. A systematic review reported no benefit or harm from using an inhaled corticosteroid.18 More recent studies show that the inhaled corticosteroid budesonide used in early COVID-19 might reduce the need for urgent care38 and, in patients who are at higher risk of COVID-19-related complications, shorten time to recovery.19
Vitamins and minerals. Limited observational studies suggest an association between vitamin and mineral deficiency (eg, vitamin C, zinc, and vitamin D) and risk of severe disease, but high-quality data about this finding do not exist.40,41
Casirivimab + imdevimab [REGEN-COV2]. This unapproved investigational combination treatment was granted an EUA in 2020 for postexposure prophylaxis. The EUA was withdrawn in January 2022 because of the limited efficacy of casirivimab + imdevimab against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
Postexposure prophylaxis. National guidelines1-4 recommend against postexposure prophylaxis with hydroxychloroquine, colchicine, inhaled corticosteroids, or azithromycin.
TABLE 27,11-25 and TABLE 326,42-46 provide additional information on treatments not recommended outside trials, or not recommended at all, for COVID-19.
Treatment during hospitalization
The NIH COVID-19 treatment panel recommends hospitalization for patients who have any of the following findings1:
- Oxygen saturation < 94% while breathing room air
- Respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min
- A ratio of partial pressure of arterial O2 to fraction of inspired O2 (PaO2/FiO2) < 300 mm Hg
- Lung infiltrates > 50%.

General guidance for the care of hospitalized patients:
- Treatments that target the virus have the greatest efficacy when given early in the course of disease.
- Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents help prevent tissue damage from a dysregulated immune system. (See TABLE 326,42-46)
- The NIH panel,1 IDSA,2 and WHO3 recommend against dexamethasone and other corticosteroids for hospitalized patients who do not require supplemental oxygen.
- Prone positioning distributes oxygen more evenly in the lungs and improves overall oxygenation, thus reducing the need for mechanical ventilation.

Remdesivir. Once a hospitalized patient does require supplemental oxygen, the NIH panel,1 IDSA,2 and WHO3 recommend remdesivir; however, remdesivir is not recommended in many other countries because WHO has noted its limited efficacy.42 Dexamethasone is recommended alone, or in combination with remdesivir for patients who require increasing supplemental oxygen and those on mechanical ventilation.

Baricitinib. For patients with rapidly increasing oxygen requirements, invasive mechanical ventilation, and systemic inflammation, baricitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, can be administered, in addition to dexamethasone, with or without remdesivir.47
Continue to: Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab. A monoclonal antibody and interleukin (IL)-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab is also recommended in addition to dexamethasone, with or without remdesivir.48 Tocilizumab should be given only in combination with dexamethasone.49 Patients should receive baricitinib or tocilizumab—not both. IDSA recommends tofacitinib, with a prophylactic dose of an anticoagulant, for patients who are hospitalized with severe COVID-19 but who are not on any form of ventilation.50
Care of special populations
Special patient populations often seek primary care. Although many questions remain regarding the appropriate care of these populations, it is useful to summarize existing evidence and recommendations from current guidelines.
Children. COVID-19 is generally milder in children than in adults; many infected children are asymptomatic. However, infants and children who have an underlying medical condition are at risk of severe disease, including multisystem inflammatory syndrome.51
The NIH panel recommends supportive care alone for most children with mild-to-moderate disease.1 Remdesivir is recommended for hospitalized children ≥ 12 years who weigh ≥ 40 kg, have risk factors for severe disease, and have an emergent or increasing need for supplemental oxygen. Dexamethasone is recommended for hospitalized children requiring high-flow oxygen, noninvasive ventilation, invasive mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Molnupiravir is not authorized for patients < 18 years because it can impede bone and cartilage growth.
There is insufficient evidence for or against the use of monoclonal antibody products for children with COVID-19 in an ambulatory setting. For hospitalized children, there is insufficient evidence for or against use of baricitinib and tocilizumab.
Continue to: Patients who are pregnant
Patients who are pregnant are at increased risk of severe COVID-19.52,53 The NIH states that, in general, treatment and vaccination of pregnant patients with COVID-19 should be the same as for nonpregnant patients.1
Pregnant subjects were excluded from several trials of COVID-19 treatments.54 Because Janus kinase inhibitors, such as baricitinib, are associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, they are not recommended in pregnant patients who are already at risk of thromboembolic complications. Molnupiravir is not recommended for pregnant patients because of its potential for teratogenic effects.
The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine states that there are no absolute contraindications to the use of monoclonal antibodies in appropriate pregnant patients with COVID-19.55 Remdesivir has no known fetal toxicity and is recommended as a treatment that can be offered to pregnant patients. Dexamethasone can also be administered to pregnant patients who require oxygen; however, if dexamethasone is also being used to accelerate fetal lung maturity, more frequent initial dosing is needed.
Older people. COVID-19 treatments for older patients are the same as for the general adult population. However, because older people are more likely to have impaired renal function, renal function should be monitored when an older patient is being treated with COVID-19 medications that are eliminated renally (eg, remdesivir, baricitinib). Furthermore, drug–drug interactions have been reported in older patients treated with nirmatrelvir + ritonavir, primarily because of the effects of ritonavir. Review all of a patient’s medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, when prescribing treatment for COVID-19, and adjust the dosage by following guidance in FDA-approved prescribing information—ideally, in consultation with a pharmacist.
Immunocompromised patients. The combination product tixagevimab + cilgavimab [Evusheld] is FDA approved for COVID-19 PrEP, under an EUA, in patients who are not infected with SARS-CoV-2 who have an immune-compromising condition, who are unlikely to mount an adequate immune response to the COVID-19 vaccine, or those in whom vaccination is not recommended because of their history of a severe adverse reaction to a COVID-19 vaccine or one of its components.7
Continue to: Summing up
Summing up
With a growing need for effective and readily available COVID-19 treatments, there are an unprecedented number of clinical trials in process. Besides antivirals, immunomodulators, and antibody therapies, some novel mechanisms being tested include Janus kinase inhibitors, IL-6-receptor blockers, and drugs that target adult respiratory distress syndrome and cytokine release.
Once larger trials are completed, we can expect stronger evidence of potential treatment options and of safety and efficacy in children, pregnant women, and vulnerable populations. During the pandemic, the FDA’s EUA program has brought emerging treatments rapidly to clinicians; nevertheless, high-quality evidence, with thorough peer review, remains critical to inform COVID-19 treatment guidelines.
a https://healthdata.gov/Health/COVID-19-PublicTherapeutic-Locator/rxn6-qnx8/data
b Sotrovimab was effective against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2—the dominant variant in early 2022— but is currently not FDA authorized in any region of the United States because of the prevalence of the Omicron BA.2 subvariant.30
CORRESPONDENCE
Ambar Kulshreshtha, MD, PhD, Department of Epidemiology, Emory Rollins School of Public Health, 4500 North Shallowford Road, Suite 134, Atlanta, GA 30338; [email protected]
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has caused more than 1 million deaths in the United States and continues to be a major public health challenge. Cases can be asymptomatic, or symptoms can range from a mild respiratory tract infection to acute respiratory distress and multiorgan failure.
Three strategies can successfully contain the pandemic and its consequences:
- Public health measures, such as masking and social distancing
- Prophylactic vaccines to reduce transmission
- Safe and effective drugs for reducing morbidity and mortality among infected patients.
Optimal treatment strategies for patients in ambulatory and hospital settings continue to evolve as new studies are reported and new strains of the virus arise. Many medical and scientific organizations, including the National Institutes of Health (NIH) COVID-19 treatment panel,1 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA),2 World Health Organization (WHO),3 and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,4 provide recommendations for managing patients with COVID-19. Their guidance is based on the strongest research available and is updated intermittently; nevertheless, a plethora of new data emerges weekly and controversies surround several treatments.
In this article, we
We encourage clinicians, in planning treatment, to consider:
- The availability of medications (ie, use the COVID-19 Public Therapeutic Locatora)
- The local COVID-19 situation
- Patient factors and preferences
- Evolving evidence regarding new and existing treatments.
Most evidence about the treatment of COVID-19 comes from studies conducted when the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 was not the dominant variant, as it is today in the United States. As such, drugs authorized or approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat COVID-19 or used off-label for that purpose might not be as efficacious today as they were almost a year ago. Furthermore, many trials of potential therapies against new viral variants are ongoing; if your patient is interested in enrolling in a clinical trial of an investigational COVID-19 treatment, refer them to www.clinicaltrials.gov.
General managementof COVID-19
Patients with COVID-19 experience a range of illness severity—from asymptomatic to mild symptoms, such as fever and myalgia, to critical illness requiring intensive care (TABLE 11,2). Patients with COVID-19 should therefore be monitored for progression, remotely or in person, until full recovery is achieved. Key concepts of general management include:
Assess and monitor patients’ oxygenation status by pulse oximetry; identify those with low or declining oxygen saturation before further clinical deterioration.

Continue to: Consider the patient's age and general health
Consider the patient’s age and general health. Patients are at higher risk of severe disease if they are > 65 years or have an underlying comorbidity.4
Emphasize self-isolation and supportive care, including rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve cough, reduce fever, and alleviate other symptoms.
Drugs: Few approved, some under study
The antiviral remdesivir is the only drug fully approved for clinical use by the FDA to treat COVID-19 in patients > 12 years.5,6
In addition, the FDA has issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for several monoclonal antibodies as prophylaxis and treatment: tixagevimab packaged with cilgavimab (Evusheld) is the first antibody combination for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against COVID-19; the separately packaged injectables are recommended for patients who have a history of severe allergy that prevents them from being vaccinated or those with moderate or severe immune-compromising disorders.7
In the pipeline. Several treatments are being tested in clinical trials to evaluate their effectiveness and safety in combating COVID-19, including:
- Antivirals, which prevent viruses from multiplying
- Immunomodulators, which reduce the body’s immune reaction to the virus
- Antibody therapies, which are manufactured antibodies against the virus
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, which reduce systemic inflammation and prevent organ dysfunction
- Cell therapies and gene therapies, which alter the expression of cells and genes.
Continue to: Outpatient treatment
Outpatient treatment
Several assessment tools that take into account patients’ age, respiratory status, and comorbidities are available for triage of patients infected with COVID-19.8
Most (> 80%) patients with COVID-19 have mild infection and are safely managed as outpatients or at home.9,10 For patients at high risk of severe disease, a few options are recommended for patients who do not require hospitalization or supplemental oxygen; guidelines on treatment of COVID-19 in outpatient settings that have been developed by various organizations are summarized in TABLE 2.7,11-25

Antiviral drugs target different stages of the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle. They should be used early in the course of infection, particularly in patients at high risk of severe disease.

IDSA recommends antiviral therapy with molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir + ritonavir packaged together (Paxlovid), or remdesivir.11,12,26,27 Remdesivir requires intravenous (IV) infusion on 3 consecutive days, which can be difficult in some clinic settings.13,28 Nirmatrelvir + ritonavir should be initiated within 5 days after symptom onset. Overall, for most patients, nirmatrelvir + ritonavir is preferred because of oral dosing and higher efficacy in comparison to other antivirals. With nirmatrelvir + ritonavir, carefully consider drug–drug interactions and the need to adjust dosing in the presence of renal disease.28,29 There are no data on the efficacy of any combination treatments with these agents (other than co-packaged Paxlovid).

Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 are given primarily intravenously. They bind to the viral spike protein, thus preventing SARS-CoV-2 from attaching to and entering cells. Bamlanivimab + etesevimab and bebtelovimab are available under an EUA for outpatient treatment.14b Treatment should be initiated as early as possible in the course of infection—ideally, within 7 to 10 days after onset of symptoms.

Continue to: Bebtelovimab was recently given...
Bebtelovimab was recently given an EUA. It is a next-generation antibody that neutralizes all currently known variants and is the most potent monoclonal antibody against the Omicron variant, including its BA.2 subvariant.31 However, data about its activity against the BA.2 subvariant are based on laboratory testing and have not been confirmed in clinical trials. Clinical data were similar for this agent alone and for its use in combination with other monoclonal antibodies, but those trials were conducted before the emergence of Omicron.
In your decision-making about the most appropriate therapy, consider (1) the requirement that monoclonal antibodies be administered parenterally and (2) the susceptibility of the locally predominating viral variant.
Other monoclonal antibody agents are in the investigative pipeline; however, data about them have been largely presented through press releases or selectively reported in applications to the FDA for EUA. For example, preliminary reports show cilgavimab coverage against the Omicron variant14; so far, cilgavimab is not approved for treatment but is used in combination with tixagevimab for PreP—reportedly providing as long as 12 months of protection for patients who are less likely to respond to a vaccine.32
Corticosteroids. Guidelines recommend against dexamethasone and other systemic corticosteroids in outpatient settings. For patients with moderate-to-severe symptoms but for whom hospitalization is not possible (eg, beds are unavailable), the NIH panel recommends dexamethasone, 6 mg/d, for the duration of supplemental oxygen, not to exceed 10 days of treatment.1
Patients who were recently discharged after COVID-19 hospitalization should not continue remdesivir, dexamethasone, or baricitinib at home, even if they still require supplemental oxygen.
Continue to: Some treatments should not be in your COVID-19 toolbox
Some treatments should not be in your COVID-19 toolbox
High-quality studies are lacking for several other potential COVID-19 treatments. Some of these drugs are under investigation, with unclear benefit and with the potential risk of toxicity—and therefore should not be prescribed or used outside a clinical trial. See “Treatments not recommended for COVID-19,” page E14. 1-4,15-19,33-41
SIDEBAR
Treatments not recommended for COVID-191-4,15-19,33-41
Fluvoxamine. A few studies suggest that the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluvoxamine reduces progression to severe disease; however, those studies have methodologic challenges.33 The drug is not FDA approved for treating COVID.33
Convalescent plasma, given to high-risk outpatients early in the course of disease, can reduce progression to severe disease,34,35 but it remains investigational for COVID-19 because trials have yielded mixed results.34-36
Ivermectin. The effect of ivermectin in patients with COVID-19 is unclear because high-quality studies do not exist and cases of ivermectin toxicity have occurred with incorrect administration.39
Hydroxychloroquine showed potential in a few observational studies, but randomized clinical trials have not shown any benefit.15
Azithromycin likewise showed potential in a few observational studies; randomized clinical trials have not shown any benefit, however.15
Statins. A few meta-analyses, based on observational studies, reported benefit from statins, but recent studies have shown that this class of drugs does not provide clinical benefit in alleviating COVID-19 symptoms.16,17,37
Inhaled corticosteroids. A systematic review reported no benefit or harm from using an inhaled corticosteroid.18 More recent studies show that the inhaled corticosteroid budesonide used in early COVID-19 might reduce the need for urgent care38 and, in patients who are at higher risk of COVID-19-related complications, shorten time to recovery.19
Vitamins and minerals. Limited observational studies suggest an association between vitamin and mineral deficiency (eg, vitamin C, zinc, and vitamin D) and risk of severe disease, but high-quality data about this finding do not exist.40,41
Casirivimab + imdevimab [REGEN-COV2]. This unapproved investigational combination treatment was granted an EUA in 2020 for postexposure prophylaxis. The EUA was withdrawn in January 2022 because of the limited efficacy of casirivimab + imdevimab against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2.
Postexposure prophylaxis. National guidelines1-4 recommend against postexposure prophylaxis with hydroxychloroquine, colchicine, inhaled corticosteroids, or azithromycin.
TABLE 27,11-25 and TABLE 326,42-46 provide additional information on treatments not recommended outside trials, or not recommended at all, for COVID-19.
Treatment during hospitalization
The NIH COVID-19 treatment panel recommends hospitalization for patients who have any of the following findings1:
- Oxygen saturation < 94% while breathing room air
- Respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min
- A ratio of partial pressure of arterial O2 to fraction of inspired O2 (PaO2/FiO2) < 300 mm Hg
- Lung infiltrates > 50%.

General guidance for the care of hospitalized patients:
- Treatments that target the virus have the greatest efficacy when given early in the course of disease.
- Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents help prevent tissue damage from a dysregulated immune system. (See TABLE 326,42-46)
- The NIH panel,1 IDSA,2 and WHO3 recommend against dexamethasone and other corticosteroids for hospitalized patients who do not require supplemental oxygen.
- Prone positioning distributes oxygen more evenly in the lungs and improves overall oxygenation, thus reducing the need for mechanical ventilation.

Remdesivir. Once a hospitalized patient does require supplemental oxygen, the NIH panel,1 IDSA,2 and WHO3 recommend remdesivir; however, remdesivir is not recommended in many other countries because WHO has noted its limited efficacy.42 Dexamethasone is recommended alone, or in combination with remdesivir for patients who require increasing supplemental oxygen and those on mechanical ventilation.

Baricitinib. For patients with rapidly increasing oxygen requirements, invasive mechanical ventilation, and systemic inflammation, baricitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, can be administered, in addition to dexamethasone, with or without remdesivir.47
Continue to: Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab. A monoclonal antibody and interleukin (IL)-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab is also recommended in addition to dexamethasone, with or without remdesivir.48 Tocilizumab should be given only in combination with dexamethasone.49 Patients should receive baricitinib or tocilizumab—not both. IDSA recommends tofacitinib, with a prophylactic dose of an anticoagulant, for patients who are hospitalized with severe COVID-19 but who are not on any form of ventilation.50
Care of special populations
Special patient populations often seek primary care. Although many questions remain regarding the appropriate care of these populations, it is useful to summarize existing evidence and recommendations from current guidelines.
Children. COVID-19 is generally milder in children than in adults; many infected children are asymptomatic. However, infants and children who have an underlying medical condition are at risk of severe disease, including multisystem inflammatory syndrome.51
The NIH panel recommends supportive care alone for most children with mild-to-moderate disease.1 Remdesivir is recommended for hospitalized children ≥ 12 years who weigh ≥ 40 kg, have risk factors for severe disease, and have an emergent or increasing need for supplemental oxygen. Dexamethasone is recommended for hospitalized children requiring high-flow oxygen, noninvasive ventilation, invasive mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Molnupiravir is not authorized for patients < 18 years because it can impede bone and cartilage growth.
There is insufficient evidence for or against the use of monoclonal antibody products for children with COVID-19 in an ambulatory setting. For hospitalized children, there is insufficient evidence for or against use of baricitinib and tocilizumab.
Continue to: Patients who are pregnant
Patients who are pregnant are at increased risk of severe COVID-19.52,53 The NIH states that, in general, treatment and vaccination of pregnant patients with COVID-19 should be the same as for nonpregnant patients.1
Pregnant subjects were excluded from several trials of COVID-19 treatments.54 Because Janus kinase inhibitors, such as baricitinib, are associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, they are not recommended in pregnant patients who are already at risk of thromboembolic complications. Molnupiravir is not recommended for pregnant patients because of its potential for teratogenic effects.
The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine states that there are no absolute contraindications to the use of monoclonal antibodies in appropriate pregnant patients with COVID-19.55 Remdesivir has no known fetal toxicity and is recommended as a treatment that can be offered to pregnant patients. Dexamethasone can also be administered to pregnant patients who require oxygen; however, if dexamethasone is also being used to accelerate fetal lung maturity, more frequent initial dosing is needed.
Older people. COVID-19 treatments for older patients are the same as for the general adult population. However, because older people are more likely to have impaired renal function, renal function should be monitored when an older patient is being treated with COVID-19 medications that are eliminated renally (eg, remdesivir, baricitinib). Furthermore, drug–drug interactions have been reported in older patients treated with nirmatrelvir + ritonavir, primarily because of the effects of ritonavir. Review all of a patient’s medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, when prescribing treatment for COVID-19, and adjust the dosage by following guidance in FDA-approved prescribing information—ideally, in consultation with a pharmacist.
Immunocompromised patients. The combination product tixagevimab + cilgavimab [Evusheld] is FDA approved for COVID-19 PrEP, under an EUA, in patients who are not infected with SARS-CoV-2 who have an immune-compromising condition, who are unlikely to mount an adequate immune response to the COVID-19 vaccine, or those in whom vaccination is not recommended because of their history of a severe adverse reaction to a COVID-19 vaccine or one of its components.7
Continue to: Summing up
Summing up
With a growing need for effective and readily available COVID-19 treatments, there are an unprecedented number of clinical trials in process. Besides antivirals, immunomodulators, and antibody therapies, some novel mechanisms being tested include Janus kinase inhibitors, IL-6-receptor blockers, and drugs that target adult respiratory distress syndrome and cytokine release.
Once larger trials are completed, we can expect stronger evidence of potential treatment options and of safety and efficacy in children, pregnant women, and vulnerable populations. During the pandemic, the FDA’s EUA program has brought emerging treatments rapidly to clinicians; nevertheless, high-quality evidence, with thorough peer review, remains critical to inform COVID-19 treatment guidelines.
a https://healthdata.gov/Health/COVID-19-PublicTherapeutic-Locator/rxn6-qnx8/data
b Sotrovimab was effective against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2—the dominant variant in early 2022— but is currently not FDA authorized in any region of the United States because of the prevalence of the Omicron BA.2 subvariant.30
CORRESPONDENCE
Ambar Kulshreshtha, MD, PhD, Department of Epidemiology, Emory Rollins School of Public Health, 4500 North Shallowford Road, Suite 134, Atlanta, GA 30338; [email protected]
1. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. National Institutes of Health. July 19, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov
2. IDSA guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Updated June 29, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/#toc-23
3. Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. World Health Organization. July 14, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1449398/retrieve
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical care considerations. Updated May 27, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html
5. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA approves first COVID-19 treatment for young children. Press release. US Food and Drug Administration. April 25, 2022. Accessed August 11, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-approves-first-covid-19-treatment-young-children
6. Know your treatment options for COVID-19. US Food and Drug Administration. Updated August 15, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-options-covid-19
7. Tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19. JAMA. 2022;327:384-385. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.24931
8. Judson TJ, Odisho AY, Neinstein AB, et al. Rapid design and implementation of an integrated patient self-triage and self-scheduling tool for COVID-19. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27:860-866. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa051
9. Gandhi RT, Lynch JB, Del Rio C. Mild or moderate Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1757-1766. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp2009249
10. Greenhalgh T, Koh GCH, Car J. Covid-19: a remote assessment in primary care. BMJ. 2020;368:m1182. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1182
11. Jayk Bernal A, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, et al; . Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:509-520. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
12. Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al; . Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1397-1408. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
13. Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE, Paredes R, et al; . Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:305-315. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
14. Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, et al; . Early treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1941-1950. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107934
15. Skipper CP, Pastick KA, Engen NW, et al. Hydroxychloroquine in nonhospitalized adults with early COVID-19: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:623-631. doi: 10.7326/M20-4207
16. Scheen AJ. Statins and clinical outcomes with COVID-19: meta-analyses of observational studies. Diabetes Metab. 2021;47:101220. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101220
17. Kow CS, Hasan SS. Meta-analysis of effect of statins in patients with COVID-19. Am J Cardiol. 2020;134:153-155. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.08.004
18. Halpin DMG, Singh D, Hadfield RM. Inhaled corticosteroids and COVID-19: a systematic review and clinical perspective. Eur Respir J. 2020;55:2001009. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01009-2020
19. Yu L-M, Bafadhel M, Dorward J, et al; . Inhaled budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial. Lancet. 2021;398:843-855. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01744-X
20. Siemieniuk RA, Bartoszko JJ, JP, et al. Antibody and cellular therapies for treatment of covid-19: a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;374:n2231. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n2231
21. Siemieniuk RA, Bartoszko JJ, Zeraatkar D, et al. Drug treatments for covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;370:m2980. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2980
22. Agarwal A, Rochwerg B, Lamontagne F, et al. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ. 2020;370:m3379. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3379
23. Goldstein KM, Ghadimi K, Mystakelis H, et al. Risk of transmitting coronavirus disease 2019 during nebulizer treatment: a systematic review. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2021;34:155-170. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2020.1659
24. Schultze A, Walker AJ, MacKenna B, et al; . Risk of COVID-19-related death among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma prescribed inhaled corticosteroids: an observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:1106-1120. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30415-X
25. What are the safety and efficacy results of bebtelovimab from BLAZE-4? Lilly USA. January 12, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.lillymedical.com/en-us/answers/what-are-the-safety-and-efficacy-results-of-bebtelovimab-from-blaze-4-159290
26. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al; . Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1813-1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
27. Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, et al. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1787-1799. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
28. Gandhi RT, Malani PN, Del Rio C. COVID-19 therapeutics for nonhospitalized patients. JAMA. 2022;327:617-618. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0335
29. Wen W, Chen C, Tang J, et al. Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2022;54:516-523. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2034936
30. Planas D, Saunders N, Maes P, et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature. 2022:602:671-675. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z
31. Emergency use authorization (EUA) for bebtelovimab (LY-CoV1404): Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) review. US Food and Drug Administration. Updated February 11, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.fda.gov/media/156396/download
32. Bartoszko JJ, Siemieniuk RAC, Kum E, et al. Prophylaxis against covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;373:n949. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n949
33. Reis G, Dos Santos Moreira-Silva EA, Silva DCM, et al; TOGETHER Investigators. Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2022;10:e42-e51. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
34. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2049-2059. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7
35. Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, et al; . A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:619-629. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
36. Joyner MJ, Carter RE, Senefeld JW, et al. Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1015-1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031893
37. Ayeh SK, Abbey EJ, Khalifa BAA, et al. Statins use and COVID-19 outcomes in hospitalized patients. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0256899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256899
38. Ramakrishnan S, Nicolau DV Jr, Langford B, et al. Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9:763-772. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0
39. Temple C, Hoang R, Hendrickson RG. Toxic effects from ivermectin use associated with prevention and treatment of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2197-2198. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2114907
40. Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, et al. Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e210369. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
41. Adams KK, Baker WL, Sobieraj DM. Myth busters: dietary supplements and COVID-19. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54:820-826. doi: 10.1177/1060028020928052
42. Pan H, Peto R, Henao-Restrepo A-M, et al. Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19—interim WHO Solidarity trial results. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:497-511. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
43. Kalil AC, Patterson TF, Mehta AK, et al; . Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:795-807. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031994
44. ; Sterne JAC, Murthy S, Diaz JV, et al. Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2020;324:1330-1341. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17023
45. ; Shankar-Hari M, Vale CL, Godolphin PJ, et al. Association between administration of IL-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2021;326:499-518. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.11330
46. Wei QW, Lin H, Wei R-G, et al. Tocilizumab treatment for COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021;10:71. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00857-w
47. Zhang X, Shang L, Fan G, et al. The efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors for patients with COVID-19: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:800492. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.800492
48. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021;397:1637-1645. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0
49. Gordon AC, Mouncey PR, Al-Beidh F, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1491-1502. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100433
50. Guimaraes PO, Quirk D, Furtado RH, et al; . Tofacitinib in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:406-415. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2101643
51. Feldstein LR, Rose EB, Horwitz SM, et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in U.S. children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:334-346. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021680
52. Allotey J, Stallings E, Bonet M, et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;370:m3320. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3320
53. Villar J, Ariff S, Gunier RB, et al. Maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality among pregnant women with and without COVID-19 infection: the INTERCOVID multinational cohort study. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175:817-826. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1050
54. Jorgensen SCJ, Davis MR, Lapinsky SE. A review of remdesivir for COVID-19 in pregnancy and lactation. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021;77:24-30. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab311
55. Management considerations for pregnant patients with COVID-19. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Accessed July 21, 2022. https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn.smfm.org/media/2336/SMFM_COVID_Management_of_COVID_pos_preg_patients_4-30-20_final.pdf
1. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. National Institutes of Health. July 19, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov
2. IDSA guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. Infectious Diseases Society of America. Updated June 29, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/#toc-23
3. Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline. World Health Organization. July 14, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1449398/retrieve
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical care considerations. Updated May 27, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html
5. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA approves first COVID-19 treatment for young children. Press release. US Food and Drug Administration. April 25, 2022. Accessed August 11, 2020. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-approves-first-covid-19-treatment-young-children
6. Know your treatment options for COVID-19. US Food and Drug Administration. Updated August 15, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-options-covid-19
7. Tixagevimab and cilgavimab (Evusheld) for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19. JAMA. 2022;327:384-385. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.24931
8. Judson TJ, Odisho AY, Neinstein AB, et al. Rapid design and implementation of an integrated patient self-triage and self-scheduling tool for COVID-19. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27:860-866. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa051
9. Gandhi RT, Lynch JB, Del Rio C. Mild or moderate Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1757-1766. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp2009249
10. Greenhalgh T, Koh GCH, Car J. Covid-19: a remote assessment in primary care. BMJ. 2020;368:m1182. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1182
11. Jayk Bernal A, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, et al; . Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:509-520. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
12. Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al; . Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:1397-1408. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
13. Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE, Paredes R, et al; . Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:305-315. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
14. Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, et al; . Early treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1941-1950. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107934
15. Skipper CP, Pastick KA, Engen NW, et al. Hydroxychloroquine in nonhospitalized adults with early COVID-19: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2020;173:623-631. doi: 10.7326/M20-4207
16. Scheen AJ. Statins and clinical outcomes with COVID-19: meta-analyses of observational studies. Diabetes Metab. 2021;47:101220. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2020.101220
17. Kow CS, Hasan SS. Meta-analysis of effect of statins in patients with COVID-19. Am J Cardiol. 2020;134:153-155. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.08.004
18. Halpin DMG, Singh D, Hadfield RM. Inhaled corticosteroids and COVID-19: a systematic review and clinical perspective. Eur Respir J. 2020;55:2001009. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01009-2020
19. Yu L-M, Bafadhel M, Dorward J, et al; . Inhaled budesonide for COVID-19 in people at high risk of complications in the community in the UK (PRINCIPLE): a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial. Lancet. 2021;398:843-855. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01744-X
20. Siemieniuk RA, Bartoszko JJ, JP, et al. Antibody and cellular therapies for treatment of covid-19: a living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;374:n2231. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n2231
21. Siemieniuk RA, Bartoszko JJ, Zeraatkar D, et al. Drug treatments for covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;370:m2980. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2980
22. Agarwal A, Rochwerg B, Lamontagne F, et al. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ. 2020;370:m3379. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3379
23. Goldstein KM, Ghadimi K, Mystakelis H, et al. Risk of transmitting coronavirus disease 2019 during nebulizer treatment: a systematic review. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2021;34:155-170. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2020.1659
24. Schultze A, Walker AJ, MacKenna B, et al; . Risk of COVID-19-related death among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma prescribed inhaled corticosteroids: an observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:1106-1120. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30415-X
25. What are the safety and efficacy results of bebtelovimab from BLAZE-4? Lilly USA. January 12, 2022. Accessed August 17, 2022. www.lillymedical.com/en-us/answers/what-are-the-safety-and-efficacy-results-of-bebtelovimab-from-blaze-4-159290
26. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al; . Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1813-1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
27. Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, et al. A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1787-1799. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
28. Gandhi RT, Malani PN, Del Rio C. COVID-19 therapeutics for nonhospitalized patients. JAMA. 2022;327:617-618. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0335
29. Wen W, Chen C, Tang J, et al. Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2022;54:516-523. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2034936
30. Planas D, Saunders N, Maes P, et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature. 2022:602:671-675. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z
31. Emergency use authorization (EUA) for bebtelovimab (LY-CoV1404): Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) review. US Food and Drug Administration. Updated February 11, 2022. Accessed July 21, 2022. www.fda.gov/media/156396/download
32. Bartoszko JJ, Siemieniuk RAC, Kum E, et al. Prophylaxis against covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;373:n949. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n949
33. Reis G, Dos Santos Moreira-Silva EA, Silva DCM, et al; TOGETHER Investigators. Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2022;10:e42-e51. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
34. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2049-2059. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7
35. Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, et al; . A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:619-629. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
36. Joyner MJ, Carter RE, Senefeld JW, et al. Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1015-1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031893
37. Ayeh SK, Abbey EJ, Khalifa BAA, et al. Statins use and COVID-19 outcomes in hospitalized patients. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0256899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256899
38. Ramakrishnan S, Nicolau DV Jr, Langford B, et al. Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9:763-772. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0
39. Temple C, Hoang R, Hendrickson RG. Toxic effects from ivermectin use associated with prevention and treatment of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2197-2198. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2114907
40. Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, et al. Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e210369. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
41. Adams KK, Baker WL, Sobieraj DM. Myth busters: dietary supplements and COVID-19. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54:820-826. doi: 10.1177/1060028020928052
42. Pan H, Peto R, Henao-Restrepo A-M, et al. Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19—interim WHO Solidarity trial results. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:497-511. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
43. Kalil AC, Patterson TF, Mehta AK, et al; . Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:795-807. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2031994
44. ; Sterne JAC, Murthy S, Diaz JV, et al. Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2020;324:1330-1341. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17023
45. ; Shankar-Hari M, Vale CL, Godolphin PJ, et al. Association between administration of IL-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2021;326:499-518. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.11330
46. Wei QW, Lin H, Wei R-G, et al. Tocilizumab treatment for COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021;10:71. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00857-w
47. Zhang X, Shang L, Fan G, et al. The efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors for patients with COVID-19: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:800492. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.800492
48. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021;397:1637-1645. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0
49. Gordon AC, Mouncey PR, Al-Beidh F, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1491-1502. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100433
50. Guimaraes PO, Quirk D, Furtado RH, et al; . Tofacitinib in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:406-415. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2101643
51. Feldstein LR, Rose EB, Horwitz SM, et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in U.S. children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:334-346. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021680
52. Allotey J, Stallings E, Bonet M, et al. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;370:m3320. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m3320
53. Villar J, Ariff S, Gunier RB, et al. Maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality among pregnant women with and without COVID-19 infection: the INTERCOVID multinational cohort study. JAMA Pediatr. 2021;175:817-826. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1050
54. Jorgensen SCJ, Davis MR, Lapinsky SE. A review of remdesivir for COVID-19 in pregnancy and lactation. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021;77:24-30. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab311
55. Management considerations for pregnant patients with COVID-19. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Accessed July 21, 2022. https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn.smfm.org/media/2336/SMFM_COVID_Management_of_COVID_pos_preg_patients_4-30-20_final.pdf
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Use antivirals (eg, molnupiravir, nirmatrelvir packaged with ritonavir [Paxlovid], and remdesivir) and monoclonal antibody agents (eg, bebtelovimab) effective against the circulating Omicron variant, to treat symptoms of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 illness. C
› Treat severely ill hospitalized COVID-19 patients who require supplemental oxygen with dexamethasone, alone or in combination with remdesivir, to produce better outcomes. B
› Consider administering baricitinib or tocilizumab, in addition to dexamethasone with or without remdesivir, to COVID-19 patients with rapidly increasing oxygen requirements. B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Intimate partner violence: Opening the door to a safer future
THE CASE
Louise T* is a 42-year-old woman who presented to her family medicine office for a routine annual visit. During the exam, her physician noticed bruises on Ms. T’s arms and back. Upon further inquiry, Ms. T reported that she and her husband had argued the night before the appointment. With some hesitancy, she went on to say that this was not the first time this had happened. She said that she and her husband had been arguing frequently for several years and that 6 months earlier, when he lost his job, he began hitting and pushing her.
●
*The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity.
Intimate partner violence (IPV) includes physical, sexual, or psychological aggression or stalking perpetrated by a current or former relationship partner.1 IPV affects more than 12 million men and women living in the United States each year.2 According to a national survey of IPV, approximately one-third (35.6%) of women and one-quarter (28.5%) of men living in the United States experience rape, physical violence, or stalking by an intimate partner during their lifetime.2 Lifetime exposure to psychological IPV is even more prevalent, affecting nearly half of women and men (48.4% and 48.8%, respectively).2
Lifetime prevalence of any form of IPV is higher among women who identify as bisexual (59.8%) and lesbian (46.3%) compared with those who identify as heterosexual (37.2%); rates are comparable among men who identify as heterosexual (31.9%), bisexual (35.3%), and gay (35.1%).3 Preliminary data suggest that IPV may have increased in frequency and severity during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in the context of mandated shelter-in-place and stay-at-home orders.4-6
IPV is associated with numerous negative health consequences. They include fear and concern for safety, mental health disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and physical health problems including physical injury, chronic pain, sleep disturbance, and frequent headaches.2 IPV is also associated with a greater number of missed days from school and work and increased utilization of legal, health care, and housing services.2,7 The overall annual cost of IPV against women is estimated at $5.8 billion, with health care costs accounting for approximately $4.1 billion.7 Family physicians can play an important role in curbing the devastating effects of IPV by screening patients and providing resources when needed.
Facilitate disclosure using screening tools and protocol
In Ms. T’s case, evidence of violence was clearly visible. However, not all instances of IPV leave physical marks. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all women of childbearing age be screened for IPV, whether or not they exhibit signs of violence.8 While the USPSTF has only published recommendations regarding screening women for IPV, there has been a recent push to screen all patients given that men also experience high rates of IPV.9
Utilize a brief screening tool. Directly ask patients about IPV; this can help reduce stigma, facilitate disclosure, and initiate the process of connecting patients to potentially lifesaving resources. The USPSTF lists several brief screening measures that can be used in primary care settings to assess exposure to IPV (TABLE 18,10-17). The brevity of these screening tools makes them well suited for busy physicians; cutoff scores facilitate the rapid identification of positive screens. While the USPSTF has not made specific recommendations regarding a screening interval, many studies examining the utility of these measures have reported on annual screenings.8 While there is limited evidence that brief screening alone leads to reductions in IPV,8 discussing IPV in a supportive and empathic manner and connecting patients to resources, such as supportive counseling, does have an important benefit: It can reduce symptoms of depression.18
Continue to: Screen patients in private; this protocol can help
Screen patients in private; this protocol can help. Given the sensitive nature of IPV and the potential danger some patients may be facing, it is important to screen patients in a safe and supportive environment.19,20 Screening should be conducted by the primary care clinician, ideally when a trusting relationship already has been formed. Screen patients only when they are alone in a private room; avoid screening in public spaces such as clinic waiting rooms or in the vicinity of the patient’s partner or children older than age 2 years.19,20
To provide all patients with an opportunity for private and safe IPV screening, clinics are encouraged to develop a clinic-wide policy whereby patients are routinely escorted to the exam room alone for the first portion of their visit, after which any accompanying individuals may be invited to join.21 Clinic staff can inform patients and accompanying individuals of this policy when they first arrive. Once in the exam room, and before the screening process begins, clearly state reporting requirements to ensure that patients can make an informed decision about whether to disclose IPV.19
Set a receptive tone. The manner in which clinicians discuss IPV with their patients is just as important as the setting. Demonstrating sensitivity and genuine concern for the patient’s safety and well-being may increase the patient’s comfort level throughout the screening process and may facilitate disclosures of IPV.19,22 When screening patients for IPV, sit face to face rather than standing over them, maintain warm and open body language, and speak in a soft tone of voice.22
Patients may feel more comfortable if you ask screening questions in a straightforward, nonjudgmental manner, as this helps to normalize the screening experience. We also recommend using behaviorally specific language (eg, “Do arguments [with your partner] ever result in hitting, kicking, or pushing?”16 or “How often does your partner scream or curse at you?”),13 as some patients who have experienced IPV will not label their experiences as “abuse” or “violence.” Not every patient who experiences IPV will be ready to disclose these events; however, maintaining a positive and supportive relationship during routine IPV screening and throughout the remainder of the medical visit may help facilitate future disclosures if, and when, a patient is ready to seek support.19
CRITICAL INTERVENTION ELEMENTS: EMPATHY AND SAFETY
A physician’s response to an IPV disclosure can have a lasting impact on the patient. We encourage family physicians to respond to IPV disclosures with empathy. Maintain eye contact and warm body language, validate the patient’s experiences (“I am sorry this happened to you,” “that must have been terrifying”), tell the patient that the violence was not their fault, and thank the patient for disclosing.23
Continue to: Assess patient safety
Assess patient safety. Another critical component of intervention is to assess the patient’s safety and engage in safety planning. If the patient agrees to this next step, you may wish to provide a warm handoff to a trained social worker, nurse, or psychologist in the clinic who can spend more time covering this information with the patient. Some key components of a safety assessment include determining whether the violence or threat of violence is ongoing and identifying who lives in the home (eg, the partner, children, and any pets). You and the patient can also discuss red flags that would indicate elevated risk. You should discuss red flags that are unique to the patient’s relationship as well as common factors that have been found to heighten risk for IPV (eg, partner engaging in heavy alcohol use).1
With the patient’s permission, collaboratively construct a safety plan that details how the patient can stay safe on a daily basis and how to safely leave should a dangerous situation arise (TABLE 29,24). The interactive safety planning tool available on the National Domestic Violence Hotline’s website can be a valuable resource (www.thehotline.org/plan-for-safety/).24 Finally, if a patient is experiencing mental health concerns associated with IPV (eg, PTSD, depression, substance misuse, suicidal ideation), consider a referral to a domestic violence counseling center or mental health provider.
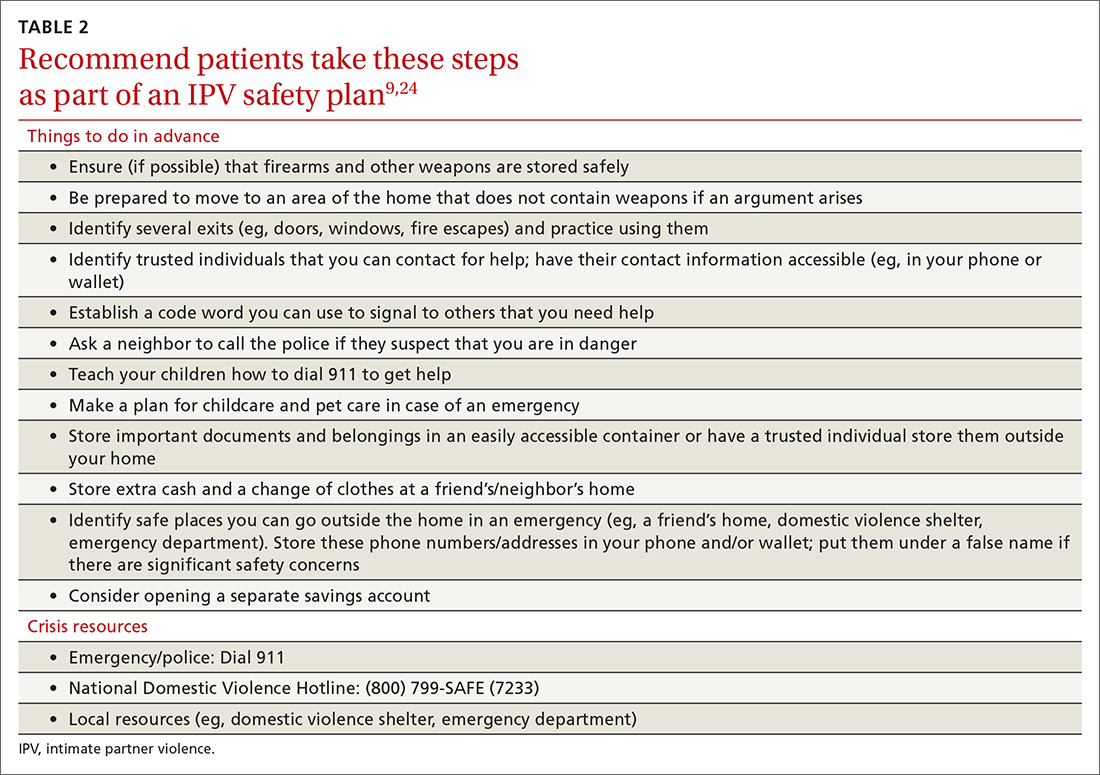
Move at the patient’s pace. Even if patients are willing to disclose IPV, they will differ in their readiness to discuss psychoeducation, safety planning, and referrals. Similarly, even if a patient is experiencing severe violence, they may not be ready to leave the relationship. Thus, it’s important to ask the patient for permission before initiating each successive step of the follow-up intervention. You and the patient may wish to schedule additional appointments to discuss this information at a pace the patient finds appropriate.
You may need to spend some time helping the patient recognize the severity of their situation and to feel empowered to take action. In addition, offer information and resources to all patients, even those who do not disclose IPV. Some patients may want to receive this information even if they do not feel comfortable sharing their experiences during the appointment.20 You can also inform patients that they are welcome to bring up issues related to IPV at any future appointments in order to leave the door open to future disclosures.
THE CASE
The physician determined that Ms. T had been experiencing physical and psychological IPV in her current relationship. After responding empathically and obtaining the patient’s consent, the physician provided a warm handoff to the psychologist in the clinic. With Ms. T’s permission, the psychologist provided psychoeducation about IPV, and they discussed Ms. T’s current situation and risk level. They determined that Ms. T was at risk for subsequent episodes of IPV and they collaborated on a safety plan, making sure to discuss contact information for local and national crisis resources.
Continue to: Ms. T saved the phone number...
Ms. T saved the phone number for her local domestic violence shelter in her phone under a false name in case her husband looked through her phone. She said she planned to work on several safety plan items when her husband was away from the house and it was safe to do so. For example, she planned to identify additional ways to exit the house in an emergency and she was going to put together a bag with a change of clothes and some money and drop it off at a trusted friend’s house.
Ms. T and the psychologist agreed to follow up with an office visit in 1 week to discuss any additional safety concerns and to determine whether Ms. T could benefit from a referral to domestic violence counseling services or mental health treatment. The psychologist provided a summary of the topics she and Ms. T had discussed to the physician. The physician scheduled a follow-up appointment with Ms. T in 3 weeks to assess her current safety, troubleshoot any difficulties in implementing her safety plan, and offer additional resources, as needed.
CORRESPONDENCE
Andrea Massa, PhD, 125 Doughty Street, Suite 300, Charleston, SC 29403; [email protected]
1. CDC. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. Preventing intimate partner violence. 2021. Accessed June 27, 2022. www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/intimatepartnerviolence/fastfact.html
2. CDC. Black MC, Basile KC, Breiding MJ, et al. The National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey: 2010 Summary Report. Accessed June 27, 2022. www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/pdf/nisvs_executive_summary-a.pdf
3. Chen J, Walters ML, Gilbert LK, et al. Sexual violence, stalking, and intimate partner violence by sexual orientation, United States. Psychol Violence. 2020;10:110-119. doi:10.1037/vio0000252
4. Kofman YB, Garfin DR. Home is not always a haven: the domestic violence crisis amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol Trauma. 2020;12:S199-S201. doi:10.1037/tra0000866
5. Lyons M, Brewer G. Experiences of intimate partner violence during lockdown and the COVID-19 pandemic. J Fam Violence. 2021:1-9. doi:10.1007/s10896-021-00260-x
6. Parrott DJ, Halmos MB, Stappenbeck CA, et al. Intimate partner aggression during the COVID-19 pandemic: associations with stress and heavy drinking. Psychol Violence. 2021;12:95-103. doi:10.1037/vio0000395
7. CDC. National Center for Injury Prevention and
8. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for intimate partner violence, elder abuse, and abuse of vulnerable adults: US Preventive Services Task Force final recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;320:1678-1687. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.14741
9. Sprunger JG, Schumacher JA, Coffey SF, et al. It’s time to start asking all patients about intimate partner violence. J Fam Pract. 2019;68:152-161.
10. Chan CC, Chan YC, Au A, et al. Reliability and validity of the “Extended - Hurt, Insult, Threaten, Scream” (E-HITS) screening tool in detecting intimate partner violence in hospital emergency departments in Hong Kong. Hong Kong J Emerg Med. 2010;17:109-117. doi:10.1177/102490791001700202
11. Iverson KM, King MW, Gerber MR, et al. Accuracy of an intimate partner violence screening tool for female VHA patients: a replication and extension. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28:79-82. doi:10.1002/jts.21985
12. Sohal H, Eldridge S, Feder G. The sensitivity and specificity of four questions (HARK) to identify intimate partner violence: a diagnostic accuracy study in general practice. BMC Fam Pract. 2007;8:49. doi:10.1186/1471-2296-8-49
13. Sherin KM, Sinacore JM, Li X, et al. HITS: a short domestic violence screening tool for use in a family practice setting. Fam Med. 1998;30:508-512.
14. Rabin RF, Jennings JM, Campbell JC, et al. Intimate partner violence screening tools: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med. 2009;36:439-445.e4. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2009.01.024
15. Feldhaus KM, Koziol-McLain J, Amsbury HL, et al. Accuracy of 3 brief screening questions for detecting partner violence in the emergency department. JAMA. 1997;277:1357-1361. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540410035027
16. Brown JB, Lent B, Schmidt G, et al. Application of the Woman Abuse Screening Tool (WAST) and WAST-short in the family practice setting. J Fam Pract. 2000;49:896-903.
17. Wathen CN, Jamieson E, MacMillan HL, MVAWRG. Who is identified by screening for intimate partner violence? Womens Health Issues. 2008;18:423-432. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2008.08.003
18. Hegarty K, O’Doherty L, Taft A, et al. Screening and counselling in the primary care setting for women who have experienced intimate partner violence (WEAVE): a cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2013;382:249-258. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60052-5
19. Correa NP, Cain CM, Bertenthal M, et al. Women’s experiences of being screened for intimate partner violence in the health care setting. Nurs Womens Health. 2020;24:185-196. doi:10.1016/j.nwh.2020.04.002
20. Chang JC, Decker MR, Moracco KE, et al. Asking about intimate partner violence: advice from female survivors to health care providers. Patient Educ Couns. 2005;59:141-147. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2004.10.008
21. Paterno MT, Draughon JE. Screening for intimate partner violence. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2016;61:370-375. doi:10.1111/jmwh.12443
22. Iverson KM, Huang K, Wells SY, et al. Women veterans’ preferences for intimate partner violence screening and response procedures within the Veterans Health Administration. Res Nurs Health. 2014;37:302-311. doi:10.1002/nur.21602
23. National Sexual Violence Research Center. Assessing patients for sexual violence: A guide for health care providers. 2011. Accessed June 28, 2022. www.nsvrc.org/publications/assessing-patients-sexual-violence-guide-health-care-providers
24. National Domestic Violence Hotline. Interactive guide to safety planning. Accessed August 22, 2022. https://www.thehotline.org/plan-for-safety/create-a-safety-plan/
THE CASE
Louise T* is a 42-year-old woman who presented to her family medicine office for a routine annual visit. During the exam, her physician noticed bruises on Ms. T’s arms and back. Upon further inquiry, Ms. T reported that she and her husband had argued the night before the appointment. With some hesitancy, she went on to say that this was not the first time this had happened. She said that she and her husband had been arguing frequently for several years and that 6 months earlier, when he lost his job, he began hitting and pushing her.
●
*The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity.
Intimate partner violence (IPV) includes physical, sexual, or psychological aggression or stalking perpetrated by a current or former relationship partner.1 IPV affects more than 12 million men and women living in the United States each year.2 According to a national survey of IPV, approximately one-third (35.6%) of women and one-quarter (28.5%) of men living in the United States experience rape, physical violence, or stalking by an intimate partner during their lifetime.2 Lifetime exposure to psychological IPV is even more prevalent, affecting nearly half of women and men (48.4% and 48.8%, respectively).2
Lifetime prevalence of any form of IPV is higher among women who identify as bisexual (59.8%) and lesbian (46.3%) compared with those who identify as heterosexual (37.2%); rates are comparable among men who identify as heterosexual (31.9%), bisexual (35.3%), and gay (35.1%).3 Preliminary data suggest that IPV may have increased in frequency and severity during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in the context of mandated shelter-in-place and stay-at-home orders.4-6
IPV is associated with numerous negative health consequences. They include fear and concern for safety, mental health disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and physical health problems including physical injury, chronic pain, sleep disturbance, and frequent headaches.2 IPV is also associated with a greater number of missed days from school and work and increased utilization of legal, health care, and housing services.2,7 The overall annual cost of IPV against women is estimated at $5.8 billion, with health care costs accounting for approximately $4.1 billion.7 Family physicians can play an important role in curbing the devastating effects of IPV by screening patients and providing resources when needed.
Facilitate disclosure using screening tools and protocol
In Ms. T’s case, evidence of violence was clearly visible. However, not all instances of IPV leave physical marks. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all women of childbearing age be screened for IPV, whether or not they exhibit signs of violence.8 While the USPSTF has only published recommendations regarding screening women for IPV, there has been a recent push to screen all patients given that men also experience high rates of IPV.9
Utilize a brief screening tool. Directly ask patients about IPV; this can help reduce stigma, facilitate disclosure, and initiate the process of connecting patients to potentially lifesaving resources. The USPSTF lists several brief screening measures that can be used in primary care settings to assess exposure to IPV (TABLE 18,10-17). The brevity of these screening tools makes them well suited for busy physicians; cutoff scores facilitate the rapid identification of positive screens. While the USPSTF has not made specific recommendations regarding a screening interval, many studies examining the utility of these measures have reported on annual screenings.8 While there is limited evidence that brief screening alone leads to reductions in IPV,8 discussing IPV in a supportive and empathic manner and connecting patients to resources, such as supportive counseling, does have an important benefit: It can reduce symptoms of depression.18

Continue to: Screen patients in private; this protocol can help
Screen patients in private; this protocol can help. Given the sensitive nature of IPV and the potential danger some patients may be facing, it is important to screen patients in a safe and supportive environment.19,20 Screening should be conducted by the primary care clinician, ideally when a trusting relationship already has been formed. Screen patients only when they are alone in a private room; avoid screening in public spaces such as clinic waiting rooms or in the vicinity of the patient’s partner or children older than age 2 years.19,20
To provide all patients with an opportunity for private and safe IPV screening, clinics are encouraged to develop a clinic-wide policy whereby patients are routinely escorted to the exam room alone for the first portion of their visit, after which any accompanying individuals may be invited to join.21 Clinic staff can inform patients and accompanying individuals of this policy when they first arrive. Once in the exam room, and before the screening process begins, clearly state reporting requirements to ensure that patients can make an informed decision about whether to disclose IPV.19
Set a receptive tone. The manner in which clinicians discuss IPV with their patients is just as important as the setting. Demonstrating sensitivity and genuine concern for the patient’s safety and well-being may increase the patient’s comfort level throughout the screening process and may facilitate disclosures of IPV.19,22 When screening patients for IPV, sit face to face rather than standing over them, maintain warm and open body language, and speak in a soft tone of voice.22
Patients may feel more comfortable if you ask screening questions in a straightforward, nonjudgmental manner, as this helps to normalize the screening experience. We also recommend using behaviorally specific language (eg, “Do arguments [with your partner] ever result in hitting, kicking, or pushing?”16 or “How often does your partner scream or curse at you?”),13 as some patients who have experienced IPV will not label their experiences as “abuse” or “violence.” Not every patient who experiences IPV will be ready to disclose these events; however, maintaining a positive and supportive relationship during routine IPV screening and throughout the remainder of the medical visit may help facilitate future disclosures if, and when, a patient is ready to seek support.19
CRITICAL INTERVENTION ELEMENTS: EMPATHY AND SAFETY
A physician’s response to an IPV disclosure can have a lasting impact on the patient. We encourage family physicians to respond to IPV disclosures with empathy. Maintain eye contact and warm body language, validate the patient’s experiences (“I am sorry this happened to you,” “that must have been terrifying”), tell the patient that the violence was not their fault, and thank the patient for disclosing.23
Continue to: Assess patient safety
Assess patient safety. Another critical component of intervention is to assess the patient’s safety and engage in safety planning. If the patient agrees to this next step, you may wish to provide a warm handoff to a trained social worker, nurse, or psychologist in the clinic who can spend more time covering this information with the patient. Some key components of a safety assessment include determining whether the violence or threat of violence is ongoing and identifying who lives in the home (eg, the partner, children, and any pets). You and the patient can also discuss red flags that would indicate elevated risk. You should discuss red flags that are unique to the patient’s relationship as well as common factors that have been found to heighten risk for IPV (eg, partner engaging in heavy alcohol use).1
With the patient’s permission, collaboratively construct a safety plan that details how the patient can stay safe on a daily basis and how to safely leave should a dangerous situation arise (TABLE 29,24). The interactive safety planning tool available on the National Domestic Violence Hotline’s website can be a valuable resource (www.thehotline.org/plan-for-safety/).24 Finally, if a patient is experiencing mental health concerns associated with IPV (eg, PTSD, depression, substance misuse, suicidal ideation), consider a referral to a domestic violence counseling center or mental health provider.

Move at the patient’s pace. Even if patients are willing to disclose IPV, they will differ in their readiness to discuss psychoeducation, safety planning, and referrals. Similarly, even if a patient is experiencing severe violence, they may not be ready to leave the relationship. Thus, it’s important to ask the patient for permission before initiating each successive step of the follow-up intervention. You and the patient may wish to schedule additional appointments to discuss this information at a pace the patient finds appropriate.
You may need to spend some time helping the patient recognize the severity of their situation and to feel empowered to take action. In addition, offer information and resources to all patients, even those who do not disclose IPV. Some patients may want to receive this information even if they do not feel comfortable sharing their experiences during the appointment.20 You can also inform patients that they are welcome to bring up issues related to IPV at any future appointments in order to leave the door open to future disclosures.
THE CASE
The physician determined that Ms. T had been experiencing physical and psychological IPV in her current relationship. After responding empathically and obtaining the patient’s consent, the physician provided a warm handoff to the psychologist in the clinic. With Ms. T’s permission, the psychologist provided psychoeducation about IPV, and they discussed Ms. T’s current situation and risk level. They determined that Ms. T was at risk for subsequent episodes of IPV and they collaborated on a safety plan, making sure to discuss contact information for local and national crisis resources.
Continue to: Ms. T saved the phone number...
Ms. T saved the phone number for her local domestic violence shelter in her phone under a false name in case her husband looked through her phone. She said she planned to work on several safety plan items when her husband was away from the house and it was safe to do so. For example, she planned to identify additional ways to exit the house in an emergency and she was going to put together a bag with a change of clothes and some money and drop it off at a trusted friend’s house.
Ms. T and the psychologist agreed to follow up with an office visit in 1 week to discuss any additional safety concerns and to determine whether Ms. T could benefit from a referral to domestic violence counseling services or mental health treatment. The psychologist provided a summary of the topics she and Ms. T had discussed to the physician. The physician scheduled a follow-up appointment with Ms. T in 3 weeks to assess her current safety, troubleshoot any difficulties in implementing her safety plan, and offer additional resources, as needed.
CORRESPONDENCE
Andrea Massa, PhD, 125 Doughty Street, Suite 300, Charleston, SC 29403; [email protected]
THE CASE
Louise T* is a 42-year-old woman who presented to her family medicine office for a routine annual visit. During the exam, her physician noticed bruises on Ms. T’s arms and back. Upon further inquiry, Ms. T reported that she and her husband had argued the night before the appointment. With some hesitancy, she went on to say that this was not the first time this had happened. She said that she and her husband had been arguing frequently for several years and that 6 months earlier, when he lost his job, he began hitting and pushing her.
●
*The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity.
Intimate partner violence (IPV) includes physical, sexual, or psychological aggression or stalking perpetrated by a current or former relationship partner.1 IPV affects more than 12 million men and women living in the United States each year.2 According to a national survey of IPV, approximately one-third (35.6%) of women and one-quarter (28.5%) of men living in the United States experience rape, physical violence, or stalking by an intimate partner during their lifetime.2 Lifetime exposure to psychological IPV is even more prevalent, affecting nearly half of women and men (48.4% and 48.8%, respectively).2
Lifetime prevalence of any form of IPV is higher among women who identify as bisexual (59.8%) and lesbian (46.3%) compared with those who identify as heterosexual (37.2%); rates are comparable among men who identify as heterosexual (31.9%), bisexual (35.3%), and gay (35.1%).3 Preliminary data suggest that IPV may have increased in frequency and severity during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in the context of mandated shelter-in-place and stay-at-home orders.4-6
IPV is associated with numerous negative health consequences. They include fear and concern for safety, mental health disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and physical health problems including physical injury, chronic pain, sleep disturbance, and frequent headaches.2 IPV is also associated with a greater number of missed days from school and work and increased utilization of legal, health care, and housing services.2,7 The overall annual cost of IPV against women is estimated at $5.8 billion, with health care costs accounting for approximately $4.1 billion.7 Family physicians can play an important role in curbing the devastating effects of IPV by screening patients and providing resources when needed.
Facilitate disclosure using screening tools and protocol
In Ms. T’s case, evidence of violence was clearly visible. However, not all instances of IPV leave physical marks. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all women of childbearing age be screened for IPV, whether or not they exhibit signs of violence.8 While the USPSTF has only published recommendations regarding screening women for IPV, there has been a recent push to screen all patients given that men also experience high rates of IPV.9
Utilize a brief screening tool. Directly ask patients about IPV; this can help reduce stigma, facilitate disclosure, and initiate the process of connecting patients to potentially lifesaving resources. The USPSTF lists several brief screening measures that can be used in primary care settings to assess exposure to IPV (TABLE 18,10-17). The brevity of these screening tools makes them well suited for busy physicians; cutoff scores facilitate the rapid identification of positive screens. While the USPSTF has not made specific recommendations regarding a screening interval, many studies examining the utility of these measures have reported on annual screenings.8 While there is limited evidence that brief screening alone leads to reductions in IPV,8 discussing IPV in a supportive and empathic manner and connecting patients to resources, such as supportive counseling, does have an important benefit: It can reduce symptoms of depression.18

Continue to: Screen patients in private; this protocol can help
Screen patients in private; this protocol can help. Given the sensitive nature of IPV and the potential danger some patients may be facing, it is important to screen patients in a safe and supportive environment.19,20 Screening should be conducted by the primary care clinician, ideally when a trusting relationship already has been formed. Screen patients only when they are alone in a private room; avoid screening in public spaces such as clinic waiting rooms or in the vicinity of the patient’s partner or children older than age 2 years.19,20
To provide all patients with an opportunity for private and safe IPV screening, clinics are encouraged to develop a clinic-wide policy whereby patients are routinely escorted to the exam room alone for the first portion of their visit, after which any accompanying individuals may be invited to join.21 Clinic staff can inform patients and accompanying individuals of this policy when they first arrive. Once in the exam room, and before the screening process begins, clearly state reporting requirements to ensure that patients can make an informed decision about whether to disclose IPV.19
Set a receptive tone. The manner in which clinicians discuss IPV with their patients is just as important as the setting. Demonstrating sensitivity and genuine concern for the patient’s safety and well-being may increase the patient’s comfort level throughout the screening process and may facilitate disclosures of IPV.19,22 When screening patients for IPV, sit face to face rather than standing over them, maintain warm and open body language, and speak in a soft tone of voice.22
Patients may feel more comfortable if you ask screening questions in a straightforward, nonjudgmental manner, as this helps to normalize the screening experience. We also recommend using behaviorally specific language (eg, “Do arguments [with your partner] ever result in hitting, kicking, or pushing?”16 or “How often does your partner scream or curse at you?”),13 as some patients who have experienced IPV will not label their experiences as “abuse” or “violence.” Not every patient who experiences IPV will be ready to disclose these events; however, maintaining a positive and supportive relationship during routine IPV screening and throughout the remainder of the medical visit may help facilitate future disclosures if, and when, a patient is ready to seek support.19
CRITICAL INTERVENTION ELEMENTS: EMPATHY AND SAFETY
A physician’s response to an IPV disclosure can have a lasting impact on the patient. We encourage family physicians to respond to IPV disclosures with empathy. Maintain eye contact and warm body language, validate the patient’s experiences (“I am sorry this happened to you,” “that must have been terrifying”), tell the patient that the violence was not their fault, and thank the patient for disclosing.23
Continue to: Assess patient safety
Assess patient safety. Another critical component of intervention is to assess the patient’s safety and engage in safety planning. If the patient agrees to this next step, you may wish to provide a warm handoff to a trained social worker, nurse, or psychologist in the clinic who can spend more time covering this information with the patient. Some key components of a safety assessment include determining whether the violence or threat of violence is ongoing and identifying who lives in the home (eg, the partner, children, and any pets). You and the patient can also discuss red flags that would indicate elevated risk. You should discuss red flags that are unique to the patient’s relationship as well as common factors that have been found to heighten risk for IPV (eg, partner engaging in heavy alcohol use).1
With the patient’s permission, collaboratively construct a safety plan that details how the patient can stay safe on a daily basis and how to safely leave should a dangerous situation arise (TABLE 29,24). The interactive safety planning tool available on the National Domestic Violence Hotline’s website can be a valuable resource (www.thehotline.org/plan-for-safety/).24 Finally, if a patient is experiencing mental health concerns associated with IPV (eg, PTSD, depression, substance misuse, suicidal ideation), consider a referral to a domestic violence counseling center or mental health provider.

Move at the patient’s pace. Even if patients are willing to disclose IPV, they will differ in their readiness to discuss psychoeducation, safety planning, and referrals. Similarly, even if a patient is experiencing severe violence, they may not be ready to leave the relationship. Thus, it’s important to ask the patient for permission before initiating each successive step of the follow-up intervention. You and the patient may wish to schedule additional appointments to discuss this information at a pace the patient finds appropriate.
You may need to spend some time helping the patient recognize the severity of their situation and to feel empowered to take action. In addition, offer information and resources to all patients, even those who do not disclose IPV. Some patients may want to receive this information even if they do not feel comfortable sharing their experiences during the appointment.20 You can also inform patients that they are welcome to bring up issues related to IPV at any future appointments in order to leave the door open to future disclosures.
THE CASE
The physician determined that Ms. T had been experiencing physical and psychological IPV in her current relationship. After responding empathically and obtaining the patient’s consent, the physician provided a warm handoff to the psychologist in the clinic. With Ms. T’s permission, the psychologist provided psychoeducation about IPV, and they discussed Ms. T’s current situation and risk level. They determined that Ms. T was at risk for subsequent episodes of IPV and they collaborated on a safety plan, making sure to discuss contact information for local and national crisis resources.
Continue to: Ms. T saved the phone number...
Ms. T saved the phone number for her local domestic violence shelter in her phone under a false name in case her husband looked through her phone. She said she planned to work on several safety plan items when her husband was away from the house and it was safe to do so. For example, she planned to identify additional ways to exit the house in an emergency and she was going to put together a bag with a change of clothes and some money and drop it off at a trusted friend’s house.
Ms. T and the psychologist agreed to follow up with an office visit in 1 week to discuss any additional safety concerns and to determine whether Ms. T could benefit from a referral to domestic violence counseling services or mental health treatment. The psychologist provided a summary of the topics she and Ms. T had discussed to the physician. The physician scheduled a follow-up appointment with Ms. T in 3 weeks to assess her current safety, troubleshoot any difficulties in implementing her safety plan, and offer additional resources, as needed.
CORRESPONDENCE
Andrea Massa, PhD, 125 Doughty Street, Suite 300, Charleston, SC 29403; [email protected]
1. CDC. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. Preventing intimate partner violence. 2021. Accessed June 27, 2022. www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/intimatepartnerviolence/fastfact.html
2. CDC. Black MC, Basile KC, Breiding MJ, et al. The National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey: 2010 Summary Report. Accessed June 27, 2022. www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/pdf/nisvs_executive_summary-a.pdf
3. Chen J, Walters ML, Gilbert LK, et al. Sexual violence, stalking, and intimate partner violence by sexual orientation, United States. Psychol Violence. 2020;10:110-119. doi:10.1037/vio0000252
4. Kofman YB, Garfin DR. Home is not always a haven: the domestic violence crisis amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol Trauma. 2020;12:S199-S201. doi:10.1037/tra0000866
5. Lyons M, Brewer G. Experiences of intimate partner violence during lockdown and the COVID-19 pandemic. J Fam Violence. 2021:1-9. doi:10.1007/s10896-021-00260-x
6. Parrott DJ, Halmos MB, Stappenbeck CA, et al. Intimate partner aggression during the COVID-19 pandemic: associations with stress and heavy drinking. Psychol Violence. 2021;12:95-103. doi:10.1037/vio0000395
7. CDC. National Center for Injury Prevention and
8. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for intimate partner violence, elder abuse, and abuse of vulnerable adults: US Preventive Services Task Force final recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;320:1678-1687. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.14741
9. Sprunger JG, Schumacher JA, Coffey SF, et al. It’s time to start asking all patients about intimate partner violence. J Fam Pract. 2019;68:152-161.
10. Chan CC, Chan YC, Au A, et al. Reliability and validity of the “Extended - Hurt, Insult, Threaten, Scream” (E-HITS) screening tool in detecting intimate partner violence in hospital emergency departments in Hong Kong. Hong Kong J Emerg Med. 2010;17:109-117. doi:10.1177/102490791001700202
11. Iverson KM, King MW, Gerber MR, et al. Accuracy of an intimate partner violence screening tool for female VHA patients: a replication and extension. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28:79-82. doi:10.1002/jts.21985
12. Sohal H, Eldridge S, Feder G. The sensitivity and specificity of four questions (HARK) to identify intimate partner violence: a diagnostic accuracy study in general practice. BMC Fam Pract. 2007;8:49. doi:10.1186/1471-2296-8-49
13. Sherin KM, Sinacore JM, Li X, et al. HITS: a short domestic violence screening tool for use in a family practice setting. Fam Med. 1998;30:508-512.
14. Rabin RF, Jennings JM, Campbell JC, et al. Intimate partner violence screening tools: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med. 2009;36:439-445.e4. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2009.01.024
15. Feldhaus KM, Koziol-McLain J, Amsbury HL, et al. Accuracy of 3 brief screening questions for detecting partner violence in the emergency department. JAMA. 1997;277:1357-1361. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540410035027
16. Brown JB, Lent B, Schmidt G, et al. Application of the Woman Abuse Screening Tool (WAST) and WAST-short in the family practice setting. J Fam Pract. 2000;49:896-903.
17. Wathen CN, Jamieson E, MacMillan HL, MVAWRG. Who is identified by screening for intimate partner violence? Womens Health Issues. 2008;18:423-432. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2008.08.003
18. Hegarty K, O’Doherty L, Taft A, et al. Screening and counselling in the primary care setting for women who have experienced intimate partner violence (WEAVE): a cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2013;382:249-258. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60052-5
19. Correa NP, Cain CM, Bertenthal M, et al. Women’s experiences of being screened for intimate partner violence in the health care setting. Nurs Womens Health. 2020;24:185-196. doi:10.1016/j.nwh.2020.04.002
20. Chang JC, Decker MR, Moracco KE, et al. Asking about intimate partner violence: advice from female survivors to health care providers. Patient Educ Couns. 2005;59:141-147. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2004.10.008
21. Paterno MT, Draughon JE. Screening for intimate partner violence. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2016;61:370-375. doi:10.1111/jmwh.12443
22. Iverson KM, Huang K, Wells SY, et al. Women veterans’ preferences for intimate partner violence screening and response procedures within the Veterans Health Administration. Res Nurs Health. 2014;37:302-311. doi:10.1002/nur.21602
23. National Sexual Violence Research Center. Assessing patients for sexual violence: A guide for health care providers. 2011. Accessed June 28, 2022. www.nsvrc.org/publications/assessing-patients-sexual-violence-guide-health-care-providers
24. National Domestic Violence Hotline. Interactive guide to safety planning. Accessed August 22, 2022. https://www.thehotline.org/plan-for-safety/create-a-safety-plan/
1. CDC. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. Preventing intimate partner violence. 2021. Accessed June 27, 2022. www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/intimatepartnerviolence/fastfact.html
2. CDC. Black MC, Basile KC, Breiding MJ, et al. The National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey: 2010 Summary Report. Accessed June 27, 2022. www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/pdf/nisvs_executive_summary-a.pdf
3. Chen J, Walters ML, Gilbert LK, et al. Sexual violence, stalking, and intimate partner violence by sexual orientation, United States. Psychol Violence. 2020;10:110-119. doi:10.1037/vio0000252
4. Kofman YB, Garfin DR. Home is not always a haven: the domestic violence crisis amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol Trauma. 2020;12:S199-S201. doi:10.1037/tra0000866
5. Lyons M, Brewer G. Experiences of intimate partner violence during lockdown and the COVID-19 pandemic. J Fam Violence. 2021:1-9. doi:10.1007/s10896-021-00260-x
6. Parrott DJ, Halmos MB, Stappenbeck CA, et al. Intimate partner aggression during the COVID-19 pandemic: associations with stress and heavy drinking. Psychol Violence. 2021;12:95-103. doi:10.1037/vio0000395
7. CDC. National Center for Injury Prevention and
8. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for intimate partner violence, elder abuse, and abuse of vulnerable adults: US Preventive Services Task Force final recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;320:1678-1687. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.14741
9. Sprunger JG, Schumacher JA, Coffey SF, et al. It’s time to start asking all patients about intimate partner violence. J Fam Pract. 2019;68:152-161.
10. Chan CC, Chan YC, Au A, et al. Reliability and validity of the “Extended - Hurt, Insult, Threaten, Scream” (E-HITS) screening tool in detecting intimate partner violence in hospital emergency departments in Hong Kong. Hong Kong J Emerg Med. 2010;17:109-117. doi:10.1177/102490791001700202
11. Iverson KM, King MW, Gerber MR, et al. Accuracy of an intimate partner violence screening tool for female VHA patients: a replication and extension. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28:79-82. doi:10.1002/jts.21985
12. Sohal H, Eldridge S, Feder G. The sensitivity and specificity of four questions (HARK) to identify intimate partner violence: a diagnostic accuracy study in general practice. BMC Fam Pract. 2007;8:49. doi:10.1186/1471-2296-8-49
13. Sherin KM, Sinacore JM, Li X, et al. HITS: a short domestic violence screening tool for use in a family practice setting. Fam Med. 1998;30:508-512.
14. Rabin RF, Jennings JM, Campbell JC, et al. Intimate partner violence screening tools: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med. 2009;36:439-445.e4. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2009.01.024
15. Feldhaus KM, Koziol-McLain J, Amsbury HL, et al. Accuracy of 3 brief screening questions for detecting partner violence in the emergency department. JAMA. 1997;277:1357-1361. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540410035027
16. Brown JB, Lent B, Schmidt G, et al. Application of the Woman Abuse Screening Tool (WAST) and WAST-short in the family practice setting. J Fam Pract. 2000;49:896-903.
17. Wathen CN, Jamieson E, MacMillan HL, MVAWRG. Who is identified by screening for intimate partner violence? Womens Health Issues. 2008;18:423-432. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2008.08.003
18. Hegarty K, O’Doherty L, Taft A, et al. Screening and counselling in the primary care setting for women who have experienced intimate partner violence (WEAVE): a cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2013;382:249-258. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60052-5
19. Correa NP, Cain CM, Bertenthal M, et al. Women’s experiences of being screened for intimate partner violence in the health care setting. Nurs Womens Health. 2020;24:185-196. doi:10.1016/j.nwh.2020.04.002
20. Chang JC, Decker MR, Moracco KE, et al. Asking about intimate partner violence: advice from female survivors to health care providers. Patient Educ Couns. 2005;59:141-147. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2004.10.008
21. Paterno MT, Draughon JE. Screening for intimate partner violence. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2016;61:370-375. doi:10.1111/jmwh.12443
22. Iverson KM, Huang K, Wells SY, et al. Women veterans’ preferences for intimate partner violence screening and response procedures within the Veterans Health Administration. Res Nurs Health. 2014;37:302-311. doi:10.1002/nur.21602
23. National Sexual Violence Research Center. Assessing patients for sexual violence: A guide for health care providers. 2011. Accessed June 28, 2022. www.nsvrc.org/publications/assessing-patients-sexual-violence-guide-health-care-providers
24. National Domestic Violence Hotline. Interactive guide to safety planning. Accessed August 22, 2022. https://www.thehotline.org/plan-for-safety/create-a-safety-plan/
New Research Supports a Changing Approach to Peripheral Artery Disease
SAN DIEGO–A cardiologist/vascular medicine specialist urged hematologist and oncologists within the US Department of Veterans Affairs system to think beyond the guidelines–at least until they’re updated–when they consider how to treat peripheral artery disease (PAD).
The 2016 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines for PAD care are due for an update and don’t reflect recent positive research into the role that the blood thinner rivaroxaban can play in certain patients, said Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, of the University of Michigan Health System, in a presentation here at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO).
Recent research has “really got us excited about the potential for this drug in this particular patient population,” Barnes said, although he cautioned that it’s most appropriate for patients at highest risk of PAD.
Research has found that patients with PAD are more likely to develop cancer, apparently because of common risk factors, and there’s discussion about whether they should undergo special screening. Cancer treatment may also boost the risk of PAD, according to a 2021 US study that tracked 248 patients with both breast cancer and PAD. “Of all patients, 48% were on statins and 54% were on antiplatelet therapies,” the study found, although the 2016 guidelines recommend both (statins for all patients with PAD, antiplatelets for those with symptoms).
In his presentation, Barnes noted that the 2016 guidelines specifically recommend aspirin (75-325 mg daily) or clopidogrel (75 mg) in patients with symptomatic PAD. Treatment is especially important, he said, because the risk of cardiovascular mortality in PAD is high. A 2020 study found that 9.1% of 13,885 patients died over a median 30-month follow-up.
The good news about treatment Brand said, came in a 2020 industry-funded study of patients with PAD who had undergone revascularization. Various outcomes such as amputation, heart attack, and death from cardiovascular causes—the primary efficacy outcome—were less common in subjects who took 2.5 mg twice daily of rivaroxaban plus aspirin or placebo plus aspirin (hazard ratio, 0.85, 95% CI, 0.76-0.96; P = .009).
So who should go on rivaroxaban? As Brand noted, a 2019 study found that patients with no high-risk features didn’t benefit much in terms of risk of vascular events, but those with high-risk features did. In higher-risk patients, the study found, “rivaroxaban and aspirin prevented 33 serious vascular events, whereas in lower-risk patients, rivaroxaban and aspirin treatment led to the avoidance of 10 events per 1,000 patients treated for 30 months.”
Per the study, patients at higher risk are those with heart failure, at least 2 vascular beds affected, renal insufficiency, or diabetes.
Brand supports the use of rivaroxaban in these patients. However, he cautioned colleagues not to switch out the drug with apixaban, another blood thinner. “These are not interchangeable,” he said. “You do need to stick with rivaroxaban. And you do need to remember that you’re going to use 2.5 milligrams twice a day—very different than many of the other ways we are using rivaroxaban.”
Brand discloses consulting fees (Pfizer/Bristol-Myers Squib, Janssen, Acelis Connected Health, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular), grant funding (Boston Scientific) and board of directors service (Anticoagulation Forum).
SAN DIEGO–A cardiologist/vascular medicine specialist urged hematologist and oncologists within the US Department of Veterans Affairs system to think beyond the guidelines–at least until they’re updated–when they consider how to treat peripheral artery disease (PAD).
The 2016 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines for PAD care are due for an update and don’t reflect recent positive research into the role that the blood thinner rivaroxaban can play in certain patients, said Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, of the University of Michigan Health System, in a presentation here at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO).
Recent research has “really got us excited about the potential for this drug in this particular patient population,” Barnes said, although he cautioned that it’s most appropriate for patients at highest risk of PAD.
Research has found that patients with PAD are more likely to develop cancer, apparently because of common risk factors, and there’s discussion about whether they should undergo special screening. Cancer treatment may also boost the risk of PAD, according to a 2021 US study that tracked 248 patients with both breast cancer and PAD. “Of all patients, 48% were on statins and 54% were on antiplatelet therapies,” the study found, although the 2016 guidelines recommend both (statins for all patients with PAD, antiplatelets for those with symptoms).
In his presentation, Barnes noted that the 2016 guidelines specifically recommend aspirin (75-325 mg daily) or clopidogrel (75 mg) in patients with symptomatic PAD. Treatment is especially important, he said, because the risk of cardiovascular mortality in PAD is high. A 2020 study found that 9.1% of 13,885 patients died over a median 30-month follow-up.
The good news about treatment Brand said, came in a 2020 industry-funded study of patients with PAD who had undergone revascularization. Various outcomes such as amputation, heart attack, and death from cardiovascular causes—the primary efficacy outcome—were less common in subjects who took 2.5 mg twice daily of rivaroxaban plus aspirin or placebo plus aspirin (hazard ratio, 0.85, 95% CI, 0.76-0.96; P = .009).
So who should go on rivaroxaban? As Brand noted, a 2019 study found that patients with no high-risk features didn’t benefit much in terms of risk of vascular events, but those with high-risk features did. In higher-risk patients, the study found, “rivaroxaban and aspirin prevented 33 serious vascular events, whereas in lower-risk patients, rivaroxaban and aspirin treatment led to the avoidance of 10 events per 1,000 patients treated for 30 months.”
Per the study, patients at higher risk are those with heart failure, at least 2 vascular beds affected, renal insufficiency, or diabetes.
Brand supports the use of rivaroxaban in these patients. However, he cautioned colleagues not to switch out the drug with apixaban, another blood thinner. “These are not interchangeable,” he said. “You do need to stick with rivaroxaban. And you do need to remember that you’re going to use 2.5 milligrams twice a day—very different than many of the other ways we are using rivaroxaban.”
Brand discloses consulting fees (Pfizer/Bristol-Myers Squib, Janssen, Acelis Connected Health, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular), grant funding (Boston Scientific) and board of directors service (Anticoagulation Forum).
SAN DIEGO–A cardiologist/vascular medicine specialist urged hematologist and oncologists within the US Department of Veterans Affairs system to think beyond the guidelines–at least until they’re updated–when they consider how to treat peripheral artery disease (PAD).
The 2016 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines for PAD care are due for an update and don’t reflect recent positive research into the role that the blood thinner rivaroxaban can play in certain patients, said Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, of the University of Michigan Health System, in a presentation here at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO).
Recent research has “really got us excited about the potential for this drug in this particular patient population,” Barnes said, although he cautioned that it’s most appropriate for patients at highest risk of PAD.
Research has found that patients with PAD are more likely to develop cancer, apparently because of common risk factors, and there’s discussion about whether they should undergo special screening. Cancer treatment may also boost the risk of PAD, according to a 2021 US study that tracked 248 patients with both breast cancer and PAD. “Of all patients, 48% were on statins and 54% were on antiplatelet therapies,” the study found, although the 2016 guidelines recommend both (statins for all patients with PAD, antiplatelets for those with symptoms).
In his presentation, Barnes noted that the 2016 guidelines specifically recommend aspirin (75-325 mg daily) or clopidogrel (75 mg) in patients with symptomatic PAD. Treatment is especially important, he said, because the risk of cardiovascular mortality in PAD is high. A 2020 study found that 9.1% of 13,885 patients died over a median 30-month follow-up.
The good news about treatment Brand said, came in a 2020 industry-funded study of patients with PAD who had undergone revascularization. Various outcomes such as amputation, heart attack, and death from cardiovascular causes—the primary efficacy outcome—were less common in subjects who took 2.5 mg twice daily of rivaroxaban plus aspirin or placebo plus aspirin (hazard ratio, 0.85, 95% CI, 0.76-0.96; P = .009).
So who should go on rivaroxaban? As Brand noted, a 2019 study found that patients with no high-risk features didn’t benefit much in terms of risk of vascular events, but those with high-risk features did. In higher-risk patients, the study found, “rivaroxaban and aspirin prevented 33 serious vascular events, whereas in lower-risk patients, rivaroxaban and aspirin treatment led to the avoidance of 10 events per 1,000 patients treated for 30 months.”
Per the study, patients at higher risk are those with heart failure, at least 2 vascular beds affected, renal insufficiency, or diabetes.
Brand supports the use of rivaroxaban in these patients. However, he cautioned colleagues not to switch out the drug with apixaban, another blood thinner. “These are not interchangeable,” he said. “You do need to stick with rivaroxaban. And you do need to remember that you’re going to use 2.5 milligrams twice a day—very different than many of the other ways we are using rivaroxaban.”
Brand discloses consulting fees (Pfizer/Bristol-Myers Squib, Janssen, Acelis Connected Health, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular), grant funding (Boston Scientific) and board of directors service (Anticoagulation Forum).