User login
Psychotropic medications for chronic pain
The opioid crisis presents a need to consider alternative options for treating chronic pain. There is significant overlap in neuroanatomical circuits that process pain, emotions, and motivation. Neurotransmitters modulated by psychotropic medications are also involved in regulating the pain pathways.1,2 In light of this, psychotropics can be considered for treating chronic pain in certain patients. The Table1-3 outlines various uses and adverse effects of select psychotropic medications used to treat pain, as well as their psychiatric uses.
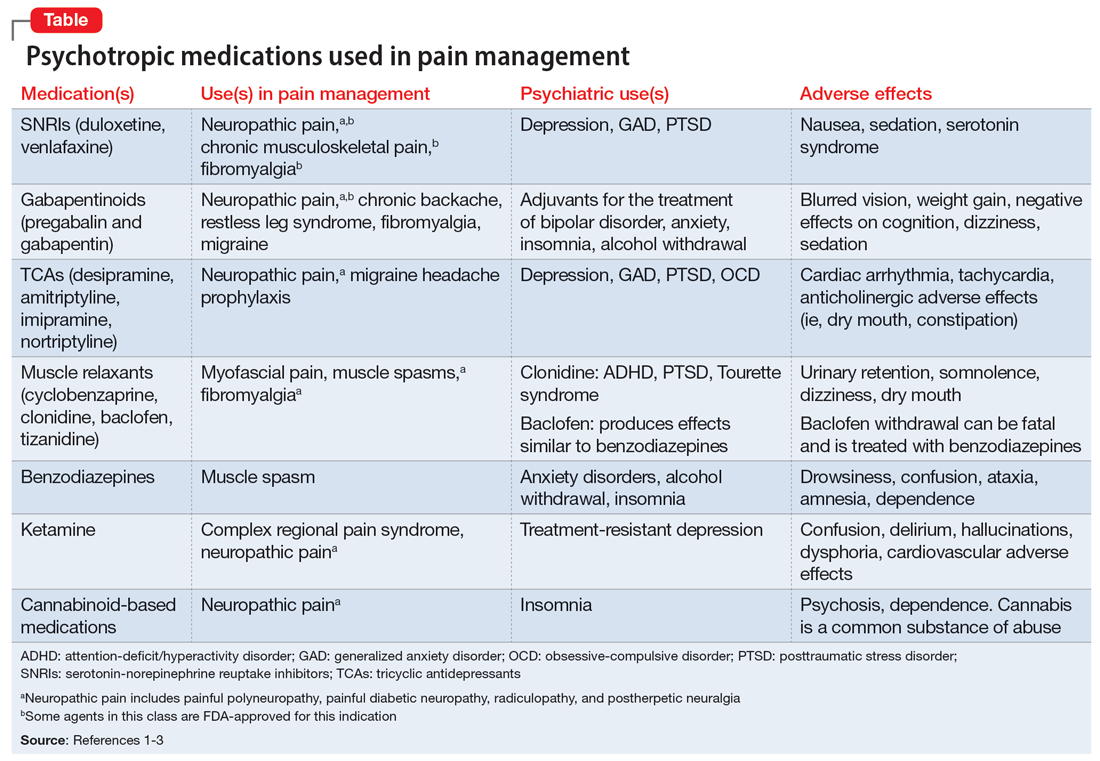
In addition to its psychiatric indications, the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor duloxetine is FDA-approved for treating fibromyalgia and diabetic neuropathic pain. It is often prescribed in the treatment of multiple pain disorders. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) have the largest effect size in the treatment of neuropathic pain.2 Cyclobenzaprine is a TCA used to treat muscle spasms. Gabapentinoids (alpha-2 delta-1 calcium channel inhibition) are FDA-approved for treating postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia, and diabetic neuropathy.1,2
Ketamine is an anesthetic with analgesic and antidepressant properties used as an IV infusion to manage several pain disorders.2 The alpha-2 adrenergic agonists tizanidine and clonidine are muscle relaxants2; the latter is used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and Tourette syndrome. Benzodiazepines (GABA-A agonists) are used for short-term treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, and muscle spasms.1,2 Baclofen (GABA-B receptor agonist) is used to treat spasticity.2 Medical cannabis (tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol) is also gaining popularity for treating chronic pain and insomnia.1-3
1. Sutherland AM, Nicholls J, Bao J, et al. Overlaps in pharmacology for the treatment of chronic pain and mental health disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018;87(Pt B):290-297.
2. Bajwa ZH, Wootton RJ, Warfield CA. Principles and Practice of Pain Medicine. 3rd ed. McGraw Hill; 2016.
3. McDonagh MS, Selph SS, Buckley DI, et al. Nonopioid Pharmacologic Treatments for Chronic Pain. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 228. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2020. doi:10.23970/AHRQEPCCER228
The opioid crisis presents a need to consider alternative options for treating chronic pain. There is significant overlap in neuroanatomical circuits that process pain, emotions, and motivation. Neurotransmitters modulated by psychotropic medications are also involved in regulating the pain pathways.1,2 In light of this, psychotropics can be considered for treating chronic pain in certain patients. The Table1-3 outlines various uses and adverse effects of select psychotropic medications used to treat pain, as well as their psychiatric uses.

In addition to its psychiatric indications, the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor duloxetine is FDA-approved for treating fibromyalgia and diabetic neuropathic pain. It is often prescribed in the treatment of multiple pain disorders. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) have the largest effect size in the treatment of neuropathic pain.2 Cyclobenzaprine is a TCA used to treat muscle spasms. Gabapentinoids (alpha-2 delta-1 calcium channel inhibition) are FDA-approved for treating postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia, and diabetic neuropathy.1,2
Ketamine is an anesthetic with analgesic and antidepressant properties used as an IV infusion to manage several pain disorders.2 The alpha-2 adrenergic agonists tizanidine and clonidine are muscle relaxants2; the latter is used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and Tourette syndrome. Benzodiazepines (GABA-A agonists) are used for short-term treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, and muscle spasms.1,2 Baclofen (GABA-B receptor agonist) is used to treat spasticity.2 Medical cannabis (tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol) is also gaining popularity for treating chronic pain and insomnia.1-3
The opioid crisis presents a need to consider alternative options for treating chronic pain. There is significant overlap in neuroanatomical circuits that process pain, emotions, and motivation. Neurotransmitters modulated by psychotropic medications are also involved in regulating the pain pathways.1,2 In light of this, psychotropics can be considered for treating chronic pain in certain patients. The Table1-3 outlines various uses and adverse effects of select psychotropic medications used to treat pain, as well as their psychiatric uses.

In addition to its psychiatric indications, the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor duloxetine is FDA-approved for treating fibromyalgia and diabetic neuropathic pain. It is often prescribed in the treatment of multiple pain disorders. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) have the largest effect size in the treatment of neuropathic pain.2 Cyclobenzaprine is a TCA used to treat muscle spasms. Gabapentinoids (alpha-2 delta-1 calcium channel inhibition) are FDA-approved for treating postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia, and diabetic neuropathy.1,2
Ketamine is an anesthetic with analgesic and antidepressant properties used as an IV infusion to manage several pain disorders.2 The alpha-2 adrenergic agonists tizanidine and clonidine are muscle relaxants2; the latter is used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and Tourette syndrome. Benzodiazepines (GABA-A agonists) are used for short-term treatment of anxiety disorders, insomnia, and muscle spasms.1,2 Baclofen (GABA-B receptor agonist) is used to treat spasticity.2 Medical cannabis (tetrahydrocannabinol/cannabidiol) is also gaining popularity for treating chronic pain and insomnia.1-3
1. Sutherland AM, Nicholls J, Bao J, et al. Overlaps in pharmacology for the treatment of chronic pain and mental health disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018;87(Pt B):290-297.
2. Bajwa ZH, Wootton RJ, Warfield CA. Principles and Practice of Pain Medicine. 3rd ed. McGraw Hill; 2016.
3. McDonagh MS, Selph SS, Buckley DI, et al. Nonopioid Pharmacologic Treatments for Chronic Pain. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 228. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2020. doi:10.23970/AHRQEPCCER228
1. Sutherland AM, Nicholls J, Bao J, et al. Overlaps in pharmacology for the treatment of chronic pain and mental health disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018;87(Pt B):290-297.
2. Bajwa ZH, Wootton RJ, Warfield CA. Principles and Practice of Pain Medicine. 3rd ed. McGraw Hill; 2016.
3. McDonagh MS, Selph SS, Buckley DI, et al. Nonopioid Pharmacologic Treatments for Chronic Pain. Comparative Effectiveness Review No. 228. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2020. doi:10.23970/AHRQEPCCER228
The light at the end of the tunnel: Reflecting on a 7-year training journey
Throughout my training, a common refrain from more senior colleagues was that training “goes by quickly.” At the risk of sounding cliché, and even after a 7-year journey spanning psychiatry and preventive medicine residencies as well as a consultation-liaison psychiatry fellowship, I agree without reservations that it does indeed go quickly. In the waning days of my training, reflection and nostalgia have become commonplace, as one might expect after such a meaningful pursuit. In sharing my reflections, I hope others progressing through training will also reflect on elements that added meaning to their experience and how they might improve the journey for future trainees.
Residency is a team sport
One realization that quickly struck me was that residency is a team sport, and finding supportive communities is essential to survival. Other residents, colleagues, and mentors played integral roles in making my experience rewarding. Training might be considered a shared traumatic experience, but having peers to commiserate with at each step has been among its greatest rewards. Residency automatically provided a cohort of colleagues who shared and validated my experiences. Additionally, having mentors who have been through it themselves and find ways to improve the training experience made mine superlative. Mentors assisted me in tailoring my training and developing interests that I could integrate into my future practice. The interpersonal connections I made were critical in helping me survive and thrive during training.
See one, do one, teach one
Residency and fellowship programs might be considered “see one, do one, teach one”1 at large scale. Since their inception, these programs—designed to develop junior physicians—have been inherently educational in nature. The structure is elegant, allowing trainees to continue learning while incrementally gaining more autonomy and teaching responsibility.2 Naively, I did not understand that implicit within my education was an expectation to become an educator and hone my teaching skills. Initially, being a newly minted resident receiving brand-new 3rd-year medical students charged me with apprehension. Thoughts I internalized, such as “these students probably know more than me” or “how can I be responsible for patients and students simultaneously,” may have resulted from a paucity of instruction about teaching available during medical school.3,4 I quickly found, though, that teaching was among the most rewarding facets of training. Helping other learners grow became one of my passions and added to my experience.
Iron sharpens iron
Although my experience was enjoyable, I would be remiss without also considering accompanying trials and tribulations. Seemingly interminable night shifts, sleep deprivation, lack of autonomy, and system inefficiencies frustrated me. Eventually, these frustrations seemed less bothersome. These challenges likely had not vanished with time, but perhaps my capacity to tolerate distress improved—likely corresponding with increasing skill and confidence. These challenges allowed me to hone my clinical decision-making abilities while under duress. My struggles and frustrations were not unique but perhaps lessons themselves.
Residency is not meant to be easy. The crucible of residency taught me that I had resilience to draw upon during challenging times. “Iron sharpens iron,” as the adage goes, and I believe adversity ultimately helped me become a better psychiatrist.
Self-reflection is part of completing training
Reminders that my journey is at an end are everywhere. Seeing notes written by past residents or fellows reminds me that soon I too will merely be a name in the chart to future trainees. Perhaps this line of thought is unfair, reducing my training experience to notes I signed—whereas my training experience was defined by connections made with colleagues and mentors, opportunities to teach junior learners, and confidence gained by overcoming adversity.
While becoming an attending psychiatrist fills me with trepidation, fear need not be an inherent aspect of new beginnings. Reflection has been a powerful practice, allowing me to realize what made my experience so meaningful, and that training is meant to be process-oriented rather than outcome-oriented. My reflection has underscored the realization that challenges are inherent in training, although not without purpose. I believe these struggles were meant to allow me to build meaningful relationships with colleagues, discover joy in teaching, and build resiliency.
The purpose of residencies and fellowships should be to produce clinically excellent psychiatrists, but I feel the journey was as important as the destination. Psychiatrists likely understand this better than most, as we were trained to thoughtfully approach the process of termination with patients.5 While the conclusion of our training journeys may seem unceremonious or anticlimactic, the termination process should include self-reflection on meaningful facets of training. For me, this reflection has itself been invaluable, while also making me hopeful to contribute value to the training journeys of future psychiatrists.
1. Gorrindo T, Beresin EV. Is “See one, do one, teach one” dead? Implications for the professionalization of medical educators in the twenty-first century. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(6):613-614. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0424-8
2. Wright Jr. JR, Schachar NS. Necessity is the mother of invention: William Stewart Halsted’s addiction and its influence on the development of residency training in North America. Can J Surg. 2020;63(1):E13-E19. doi:10.1503/cjs.003319
3. Dandavino M, Snell L, Wiseman J. Why medical students should learn how to teach. Med Teach. 2007;29(6):558-565. doi:10.1080/01421590701477449
4. Liu AC, Liu M, Dannaway J, et al. Are Australian medical students being taught to teach? Clin Teach. 2017;14(5):330-335. doi:10.1111/tct.12591
5. Vasquez MJ, Bingham RP, Barnett JE. Psychotherapy termination: clinical and ethical responsibilities. J Clin Psychol. 2008;64(5):653-665. doi:10.1002/jclp.20478
Throughout my training, a common refrain from more senior colleagues was that training “goes by quickly.” At the risk of sounding cliché, and even after a 7-year journey spanning psychiatry and preventive medicine residencies as well as a consultation-liaison psychiatry fellowship, I agree without reservations that it does indeed go quickly. In the waning days of my training, reflection and nostalgia have become commonplace, as one might expect after such a meaningful pursuit. In sharing my reflections, I hope others progressing through training will also reflect on elements that added meaning to their experience and how they might improve the journey for future trainees.
Residency is a team sport
One realization that quickly struck me was that residency is a team sport, and finding supportive communities is essential to survival. Other residents, colleagues, and mentors played integral roles in making my experience rewarding. Training might be considered a shared traumatic experience, but having peers to commiserate with at each step has been among its greatest rewards. Residency automatically provided a cohort of colleagues who shared and validated my experiences. Additionally, having mentors who have been through it themselves and find ways to improve the training experience made mine superlative. Mentors assisted me in tailoring my training and developing interests that I could integrate into my future practice. The interpersonal connections I made were critical in helping me survive and thrive during training.
See one, do one, teach one
Residency and fellowship programs might be considered “see one, do one, teach one”1 at large scale. Since their inception, these programs—designed to develop junior physicians—have been inherently educational in nature. The structure is elegant, allowing trainees to continue learning while incrementally gaining more autonomy and teaching responsibility.2 Naively, I did not understand that implicit within my education was an expectation to become an educator and hone my teaching skills. Initially, being a newly minted resident receiving brand-new 3rd-year medical students charged me with apprehension. Thoughts I internalized, such as “these students probably know more than me” or “how can I be responsible for patients and students simultaneously,” may have resulted from a paucity of instruction about teaching available during medical school.3,4 I quickly found, though, that teaching was among the most rewarding facets of training. Helping other learners grow became one of my passions and added to my experience.
Iron sharpens iron
Although my experience was enjoyable, I would be remiss without also considering accompanying trials and tribulations. Seemingly interminable night shifts, sleep deprivation, lack of autonomy, and system inefficiencies frustrated me. Eventually, these frustrations seemed less bothersome. These challenges likely had not vanished with time, but perhaps my capacity to tolerate distress improved—likely corresponding with increasing skill and confidence. These challenges allowed me to hone my clinical decision-making abilities while under duress. My struggles and frustrations were not unique but perhaps lessons themselves.
Residency is not meant to be easy. The crucible of residency taught me that I had resilience to draw upon during challenging times. “Iron sharpens iron,” as the adage goes, and I believe adversity ultimately helped me become a better psychiatrist.
Self-reflection is part of completing training
Reminders that my journey is at an end are everywhere. Seeing notes written by past residents or fellows reminds me that soon I too will merely be a name in the chart to future trainees. Perhaps this line of thought is unfair, reducing my training experience to notes I signed—whereas my training experience was defined by connections made with colleagues and mentors, opportunities to teach junior learners, and confidence gained by overcoming adversity.
While becoming an attending psychiatrist fills me with trepidation, fear need not be an inherent aspect of new beginnings. Reflection has been a powerful practice, allowing me to realize what made my experience so meaningful, and that training is meant to be process-oriented rather than outcome-oriented. My reflection has underscored the realization that challenges are inherent in training, although not without purpose. I believe these struggles were meant to allow me to build meaningful relationships with colleagues, discover joy in teaching, and build resiliency.
The purpose of residencies and fellowships should be to produce clinically excellent psychiatrists, but I feel the journey was as important as the destination. Psychiatrists likely understand this better than most, as we were trained to thoughtfully approach the process of termination with patients.5 While the conclusion of our training journeys may seem unceremonious or anticlimactic, the termination process should include self-reflection on meaningful facets of training. For me, this reflection has itself been invaluable, while also making me hopeful to contribute value to the training journeys of future psychiatrists.
Throughout my training, a common refrain from more senior colleagues was that training “goes by quickly.” At the risk of sounding cliché, and even after a 7-year journey spanning psychiatry and preventive medicine residencies as well as a consultation-liaison psychiatry fellowship, I agree without reservations that it does indeed go quickly. In the waning days of my training, reflection and nostalgia have become commonplace, as one might expect after such a meaningful pursuit. In sharing my reflections, I hope others progressing through training will also reflect on elements that added meaning to their experience and how they might improve the journey for future trainees.
Residency is a team sport
One realization that quickly struck me was that residency is a team sport, and finding supportive communities is essential to survival. Other residents, colleagues, and mentors played integral roles in making my experience rewarding. Training might be considered a shared traumatic experience, but having peers to commiserate with at each step has been among its greatest rewards. Residency automatically provided a cohort of colleagues who shared and validated my experiences. Additionally, having mentors who have been through it themselves and find ways to improve the training experience made mine superlative. Mentors assisted me in tailoring my training and developing interests that I could integrate into my future practice. The interpersonal connections I made were critical in helping me survive and thrive during training.
See one, do one, teach one
Residency and fellowship programs might be considered “see one, do one, teach one”1 at large scale. Since their inception, these programs—designed to develop junior physicians—have been inherently educational in nature. The structure is elegant, allowing trainees to continue learning while incrementally gaining more autonomy and teaching responsibility.2 Naively, I did not understand that implicit within my education was an expectation to become an educator and hone my teaching skills. Initially, being a newly minted resident receiving brand-new 3rd-year medical students charged me with apprehension. Thoughts I internalized, such as “these students probably know more than me” or “how can I be responsible for patients and students simultaneously,” may have resulted from a paucity of instruction about teaching available during medical school.3,4 I quickly found, though, that teaching was among the most rewarding facets of training. Helping other learners grow became one of my passions and added to my experience.
Iron sharpens iron
Although my experience was enjoyable, I would be remiss without also considering accompanying trials and tribulations. Seemingly interminable night shifts, sleep deprivation, lack of autonomy, and system inefficiencies frustrated me. Eventually, these frustrations seemed less bothersome. These challenges likely had not vanished with time, but perhaps my capacity to tolerate distress improved—likely corresponding with increasing skill and confidence. These challenges allowed me to hone my clinical decision-making abilities while under duress. My struggles and frustrations were not unique but perhaps lessons themselves.
Residency is not meant to be easy. The crucible of residency taught me that I had resilience to draw upon during challenging times. “Iron sharpens iron,” as the adage goes, and I believe adversity ultimately helped me become a better psychiatrist.
Self-reflection is part of completing training
Reminders that my journey is at an end are everywhere. Seeing notes written by past residents or fellows reminds me that soon I too will merely be a name in the chart to future trainees. Perhaps this line of thought is unfair, reducing my training experience to notes I signed—whereas my training experience was defined by connections made with colleagues and mentors, opportunities to teach junior learners, and confidence gained by overcoming adversity.
While becoming an attending psychiatrist fills me with trepidation, fear need not be an inherent aspect of new beginnings. Reflection has been a powerful practice, allowing me to realize what made my experience so meaningful, and that training is meant to be process-oriented rather than outcome-oriented. My reflection has underscored the realization that challenges are inherent in training, although not without purpose. I believe these struggles were meant to allow me to build meaningful relationships with colleagues, discover joy in teaching, and build resiliency.
The purpose of residencies and fellowships should be to produce clinically excellent psychiatrists, but I feel the journey was as important as the destination. Psychiatrists likely understand this better than most, as we were trained to thoughtfully approach the process of termination with patients.5 While the conclusion of our training journeys may seem unceremonious or anticlimactic, the termination process should include self-reflection on meaningful facets of training. For me, this reflection has itself been invaluable, while also making me hopeful to contribute value to the training journeys of future psychiatrists.
1. Gorrindo T, Beresin EV. Is “See one, do one, teach one” dead? Implications for the professionalization of medical educators in the twenty-first century. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(6):613-614. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0424-8
2. Wright Jr. JR, Schachar NS. Necessity is the mother of invention: William Stewart Halsted’s addiction and its influence on the development of residency training in North America. Can J Surg. 2020;63(1):E13-E19. doi:10.1503/cjs.003319
3. Dandavino M, Snell L, Wiseman J. Why medical students should learn how to teach. Med Teach. 2007;29(6):558-565. doi:10.1080/01421590701477449
4. Liu AC, Liu M, Dannaway J, et al. Are Australian medical students being taught to teach? Clin Teach. 2017;14(5):330-335. doi:10.1111/tct.12591
5. Vasquez MJ, Bingham RP, Barnett JE. Psychotherapy termination: clinical and ethical responsibilities. J Clin Psychol. 2008;64(5):653-665. doi:10.1002/jclp.20478
1. Gorrindo T, Beresin EV. Is “See one, do one, teach one” dead? Implications for the professionalization of medical educators in the twenty-first century. Acad Psychiatry. 2015;39(6):613-614. doi:10.1007/s40596-015-0424-8
2. Wright Jr. JR, Schachar NS. Necessity is the mother of invention: William Stewart Halsted’s addiction and its influence on the development of residency training in North America. Can J Surg. 2020;63(1):E13-E19. doi:10.1503/cjs.003319
3. Dandavino M, Snell L, Wiseman J. Why medical students should learn how to teach. Med Teach. 2007;29(6):558-565. doi:10.1080/01421590701477449
4. Liu AC, Liu M, Dannaway J, et al. Are Australian medical students being taught to teach? Clin Teach. 2017;14(5):330-335. doi:10.1111/tct.12591
5. Vasquez MJ, Bingham RP, Barnett JE. Psychotherapy termination: clinical and ethical responsibilities. J Clin Psychol. 2008;64(5):653-665. doi:10.1002/jclp.20478
Lamotrigine for bipolar depression?
In reading Dr. Nasrallah's August 2022 editorial (“Reversing depression: A plethora of therapeutic strategies and mechanisms,”
Dr. Nasrallah responds
Thanks for your message. Lamotrigine is not FDA-approved for bipolar or unipolar depression, either as monotherapy or as an adjunctive therapy. It has never been approved for mania, either (no efficacy at all). Its only FDA-approved psychiatric indication is maintenance therapy after a patient with bipolar I disorder emerges from mania with the help of one of the antimanic drugs. Yet many clinicians may perceive lamotrigine as useful for bipolar depression because more than 20 years ago the manufacturer sponsored several small studies (not FDA trials). Two studies that showed efficacy were published, but 4 other studies that failed to show efficacy were not published. As a result, many clinicians got the false impression that lamotrigine is an effective antidepressant. I hope this explains why lamotrigine was not included in the list of antidepressants in my editorial.
In reading Dr. Nasrallah's August 2022 editorial (“Reversing depression: A plethora of therapeutic strategies and mechanisms,”
Dr. Nasrallah responds
Thanks for your message. Lamotrigine is not FDA-approved for bipolar or unipolar depression, either as monotherapy or as an adjunctive therapy. It has never been approved for mania, either (no efficacy at all). Its only FDA-approved psychiatric indication is maintenance therapy after a patient with bipolar I disorder emerges from mania with the help of one of the antimanic drugs. Yet many clinicians may perceive lamotrigine as useful for bipolar depression because more than 20 years ago the manufacturer sponsored several small studies (not FDA trials). Two studies that showed efficacy were published, but 4 other studies that failed to show efficacy were not published. As a result, many clinicians got the false impression that lamotrigine is an effective antidepressant. I hope this explains why lamotrigine was not included in the list of antidepressants in my editorial.
In reading Dr. Nasrallah's August 2022 editorial (“Reversing depression: A plethora of therapeutic strategies and mechanisms,”
Dr. Nasrallah responds
Thanks for your message. Lamotrigine is not FDA-approved for bipolar or unipolar depression, either as monotherapy or as an adjunctive therapy. It has never been approved for mania, either (no efficacy at all). Its only FDA-approved psychiatric indication is maintenance therapy after a patient with bipolar I disorder emerges from mania with the help of one of the antimanic drugs. Yet many clinicians may perceive lamotrigine as useful for bipolar depression because more than 20 years ago the manufacturer sponsored several small studies (not FDA trials). Two studies that showed efficacy were published, but 4 other studies that failed to show efficacy were not published. As a result, many clinicians got the false impression that lamotrigine is an effective antidepressant. I hope this explains why lamotrigine was not included in the list of antidepressants in my editorial.
Treatment of HER2-Low Breast Cancer
Can you talk about the evolution and treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-low breast cancer?
Dr. Abdou: Until recently, HER2 status had been defined as a positive or negative result, but this convention has evolved, and now a newly defined population with low levels of HER2 expression has been identified. This HER2-low population accounts for about 55% of all breast cancers. Previously, low HER2 expression levels were considered HER2-negative in clinical practice because HER2-targeted therapies had been considered ineffective in this setting. Patients with HER2-low disease therefore had limited targeted treatment options after progression on their primary therapy.
Now, new studies and clinical trials have opened the door to effective treatments for this cohort of patients. The clinical trial DESTINY-Breast04, which was presented at ASCO 2022, led to the first FDA approval in August 2022 of a targeted therapy option for patients with HER2-low breast cancer subtypes, reclassifying this cohort as a new targetable subset in breast cancer.
DESTINY-Breast04 was the first randomized clinical trial to show that targeting HER2 provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients with HER2-low metastatic breast cancer, not only patients with HER2-positive disease. The phase 3 study enrolled about 557 patients with hormone receptor (HR)-negative or -positive breast cancer and centrally confirmed HER2-low expression who were previously treated with 1 or 2 prior lines of chemotherapy. Patients were randomized to receive either the antibody–drug conjugate trastuzumab deruxtecan or physician’s choice of standard chemotherapy. The risk of disease progression was about 50% lower and the risk of death was about 36% lower with trastuzumab deruxtecan compared with chemotherapy.1
These impressive and practice-changing results opened the door to a new treatment option for a substantial group of patients with HER2-low disease and significantly expanded the population of patients who can benefit from HER2-targeted therapy.
What molecular characteristics do you take into consideration to help determine whether patients are eligible for these targeted treatment options?
Dr. Abdou: As we said earlier, HER2 status should no longer be recorded as a binary result of either HER2-positive or HER2-negative. It is important to start routinely testing for the level of HER2 expression in the tumor. Obtaining these levels is done through commonly used immunohistochemical (IHC) assays that allow direct visualization of the HER2 protein. Breast tumors considered to be HER2-low are classified as IHC1+ or as IHC2+ with in situ hybridization or FISH-negative status.
HER2-low breast cancer consists of a heterogeneous group of breast cancers, most of which are HR-positive tumors, whereas about 20% are HR-negative tumors. While these tumors may have distinct molecular profiles leading to clinicopathological and prognostic differences within these groups—HR-positive tumors represent more luminal subtypes and HR-negative tumors tend to be predominantly basal-like subtypes—these distinctions do not necessarily affect patient eligibility for targeted therapy. The benefit of trastuzumab deruxtecan was seen in both subgroups, although the HR-positive population was much more well represented in the DESTINY-Breast04 study.
Other than the HER2 expression status, I also take into consideration the presence of clinical comorbidities, particularly pulmonary comorbidities or prior lung injuries. Trastuzumab deruxtecan can cause a potentially serious type of lung toxicity called interstitial lung disease (ILD). In DESTINY-Breast04, ILD developed in about 12% of patients in the trastuzumab deruxtecan group, with 3 deaths as a result.
Therefore, it’s important for us to carefully select these patients and closely monitor them while they’re on treatment.
What is next in the treatment of HER2-low breast cancer, and what would you like to see in the future?
Dr. Abdou: The exciting new field of HER2-low breast cancer has really opened the door to novel studies and clinical trials, several of which are exploring the role of antibody–drug conjugates in patients with metastatic HER2-low disease and others that are studying early-stage HER2-low breast cancer. In early-stage HER2-low breast cancer, we may potentially see an even greater benefit with these drugs because the disease has not yet developed resistance to therapy. Other studies are examining the role of combination therapy in metastatic breast cancer, such as antibody–drug conjugates in combination with immunotherapy and other targeted agents. I look forward to results from those studies.
Also, importantly, as we start using these therapies more widely, I would like to see more accurate and sensitive ways of assessing the HER2 expression status. The current IHC assay, although widely available, fails to identify many women who have HER2 expression in their tumors. I think more sensitive tests may be able to identify even more women who can benefit from these targeted therapies.
1. Modi S, Jacot W, Yamashita T, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-low advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(1):9-20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2203690
Can you talk about the evolution and treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-low breast cancer?
Dr. Abdou: Until recently, HER2 status had been defined as a positive or negative result, but this convention has evolved, and now a newly defined population with low levels of HER2 expression has been identified. This HER2-low population accounts for about 55% of all breast cancers. Previously, low HER2 expression levels were considered HER2-negative in clinical practice because HER2-targeted therapies had been considered ineffective in this setting. Patients with HER2-low disease therefore had limited targeted treatment options after progression on their primary therapy.
Now, new studies and clinical trials have opened the door to effective treatments for this cohort of patients. The clinical trial DESTINY-Breast04, which was presented at ASCO 2022, led to the first FDA approval in August 2022 of a targeted therapy option for patients with HER2-low breast cancer subtypes, reclassifying this cohort as a new targetable subset in breast cancer.
DESTINY-Breast04 was the first randomized clinical trial to show that targeting HER2 provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients with HER2-low metastatic breast cancer, not only patients with HER2-positive disease. The phase 3 study enrolled about 557 patients with hormone receptor (HR)-negative or -positive breast cancer and centrally confirmed HER2-low expression who were previously treated with 1 or 2 prior lines of chemotherapy. Patients were randomized to receive either the antibody–drug conjugate trastuzumab deruxtecan or physician’s choice of standard chemotherapy. The risk of disease progression was about 50% lower and the risk of death was about 36% lower with trastuzumab deruxtecan compared with chemotherapy.1
These impressive and practice-changing results opened the door to a new treatment option for a substantial group of patients with HER2-low disease and significantly expanded the population of patients who can benefit from HER2-targeted therapy.
What molecular characteristics do you take into consideration to help determine whether patients are eligible for these targeted treatment options?
Dr. Abdou: As we said earlier, HER2 status should no longer be recorded as a binary result of either HER2-positive or HER2-negative. It is important to start routinely testing for the level of HER2 expression in the tumor. Obtaining these levels is done through commonly used immunohistochemical (IHC) assays that allow direct visualization of the HER2 protein. Breast tumors considered to be HER2-low are classified as IHC1+ or as IHC2+ with in situ hybridization or FISH-negative status.
HER2-low breast cancer consists of a heterogeneous group of breast cancers, most of which are HR-positive tumors, whereas about 20% are HR-negative tumors. While these tumors may have distinct molecular profiles leading to clinicopathological and prognostic differences within these groups—HR-positive tumors represent more luminal subtypes and HR-negative tumors tend to be predominantly basal-like subtypes—these distinctions do not necessarily affect patient eligibility for targeted therapy. The benefit of trastuzumab deruxtecan was seen in both subgroups, although the HR-positive population was much more well represented in the DESTINY-Breast04 study.
Other than the HER2 expression status, I also take into consideration the presence of clinical comorbidities, particularly pulmonary comorbidities or prior lung injuries. Trastuzumab deruxtecan can cause a potentially serious type of lung toxicity called interstitial lung disease (ILD). In DESTINY-Breast04, ILD developed in about 12% of patients in the trastuzumab deruxtecan group, with 3 deaths as a result.
Therefore, it’s important for us to carefully select these patients and closely monitor them while they’re on treatment.
What is next in the treatment of HER2-low breast cancer, and what would you like to see in the future?
Dr. Abdou: The exciting new field of HER2-low breast cancer has really opened the door to novel studies and clinical trials, several of which are exploring the role of antibody–drug conjugates in patients with metastatic HER2-low disease and others that are studying early-stage HER2-low breast cancer. In early-stage HER2-low breast cancer, we may potentially see an even greater benefit with these drugs because the disease has not yet developed resistance to therapy. Other studies are examining the role of combination therapy in metastatic breast cancer, such as antibody–drug conjugates in combination with immunotherapy and other targeted agents. I look forward to results from those studies.
Also, importantly, as we start using these therapies more widely, I would like to see more accurate and sensitive ways of assessing the HER2 expression status. The current IHC assay, although widely available, fails to identify many women who have HER2 expression in their tumors. I think more sensitive tests may be able to identify even more women who can benefit from these targeted therapies.
Can you talk about the evolution and treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-low breast cancer?
Dr. Abdou: Until recently, HER2 status had been defined as a positive or negative result, but this convention has evolved, and now a newly defined population with low levels of HER2 expression has been identified. This HER2-low population accounts for about 55% of all breast cancers. Previously, low HER2 expression levels were considered HER2-negative in clinical practice because HER2-targeted therapies had been considered ineffective in this setting. Patients with HER2-low disease therefore had limited targeted treatment options after progression on their primary therapy.
Now, new studies and clinical trials have opened the door to effective treatments for this cohort of patients. The clinical trial DESTINY-Breast04, which was presented at ASCO 2022, led to the first FDA approval in August 2022 of a targeted therapy option for patients with HER2-low breast cancer subtypes, reclassifying this cohort as a new targetable subset in breast cancer.
DESTINY-Breast04 was the first randomized clinical trial to show that targeting HER2 provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients with HER2-low metastatic breast cancer, not only patients with HER2-positive disease. The phase 3 study enrolled about 557 patients with hormone receptor (HR)-negative or -positive breast cancer and centrally confirmed HER2-low expression who were previously treated with 1 or 2 prior lines of chemotherapy. Patients were randomized to receive either the antibody–drug conjugate trastuzumab deruxtecan or physician’s choice of standard chemotherapy. The risk of disease progression was about 50% lower and the risk of death was about 36% lower with trastuzumab deruxtecan compared with chemotherapy.1
These impressive and practice-changing results opened the door to a new treatment option for a substantial group of patients with HER2-low disease and significantly expanded the population of patients who can benefit from HER2-targeted therapy.
What molecular characteristics do you take into consideration to help determine whether patients are eligible for these targeted treatment options?
Dr. Abdou: As we said earlier, HER2 status should no longer be recorded as a binary result of either HER2-positive or HER2-negative. It is important to start routinely testing for the level of HER2 expression in the tumor. Obtaining these levels is done through commonly used immunohistochemical (IHC) assays that allow direct visualization of the HER2 protein. Breast tumors considered to be HER2-low are classified as IHC1+ or as IHC2+ with in situ hybridization or FISH-negative status.
HER2-low breast cancer consists of a heterogeneous group of breast cancers, most of which are HR-positive tumors, whereas about 20% are HR-negative tumors. While these tumors may have distinct molecular profiles leading to clinicopathological and prognostic differences within these groups—HR-positive tumors represent more luminal subtypes and HR-negative tumors tend to be predominantly basal-like subtypes—these distinctions do not necessarily affect patient eligibility for targeted therapy. The benefit of trastuzumab deruxtecan was seen in both subgroups, although the HR-positive population was much more well represented in the DESTINY-Breast04 study.
Other than the HER2 expression status, I also take into consideration the presence of clinical comorbidities, particularly pulmonary comorbidities or prior lung injuries. Trastuzumab deruxtecan can cause a potentially serious type of lung toxicity called interstitial lung disease (ILD). In DESTINY-Breast04, ILD developed in about 12% of patients in the trastuzumab deruxtecan group, with 3 deaths as a result.
Therefore, it’s important for us to carefully select these patients and closely monitor them while they’re on treatment.
What is next in the treatment of HER2-low breast cancer, and what would you like to see in the future?
Dr. Abdou: The exciting new field of HER2-low breast cancer has really opened the door to novel studies and clinical trials, several of which are exploring the role of antibody–drug conjugates in patients with metastatic HER2-low disease and others that are studying early-stage HER2-low breast cancer. In early-stage HER2-low breast cancer, we may potentially see an even greater benefit with these drugs because the disease has not yet developed resistance to therapy. Other studies are examining the role of combination therapy in metastatic breast cancer, such as antibody–drug conjugates in combination with immunotherapy and other targeted agents. I look forward to results from those studies.
Also, importantly, as we start using these therapies more widely, I would like to see more accurate and sensitive ways of assessing the HER2 expression status. The current IHC assay, although widely available, fails to identify many women who have HER2 expression in their tumors. I think more sensitive tests may be able to identify even more women who can benefit from these targeted therapies.
1. Modi S, Jacot W, Yamashita T, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-low advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(1):9-20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2203690
1. Modi S, Jacot W, Yamashita T, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-low advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(1):9-20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2203690
Commentary: Alternate considerations in treating IBS, November 2022
Acupuncture is a very popular treatment strategy in some areas of the world and is extensively applied in Chinese practice. Though this is a regularly applied treatment, a direct comparison with first-line antispasmodics has not been previously completed. The study by Shi and colleagues sought to compare the treatment of IBS using an adjusted indirect treatment comparison meta-analysis. This study proves that cimetropium was the most effective for relieving abdominal pain, whereas drotaverine, acupuncture, and pinaverium remained superior to the placebo. That being said, acupuncture was shown to be superior in relieving global IBS symptoms and caused fewer side effects than did antispasmodics. This shows that acupuncture may have a role in the treatment algorithm for IBS even outside of China, where it is used broadly.
The study by Formica and colleagues provides new insights on the etiology and pathogenesis of IBS. These insights include the positive correlation between disgust sensitivity and IBS quality of life (QOL) scores. The relationship between IBS and the emotional intensity of the experience of disgust is discussed throughout this study and more severe IBS-QOL scores were linked to those with high levels of disgust sensitivity. This study had gender limitations because of the low number of male participants, so these correlations were patterned mostly in female participants.
Acupuncture is a very popular treatment strategy in some areas of the world and is extensively applied in Chinese practice. Though this is a regularly applied treatment, a direct comparison with first-line antispasmodics has not been previously completed. The study by Shi and colleagues sought to compare the treatment of IBS using an adjusted indirect treatment comparison meta-analysis. This study proves that cimetropium was the most effective for relieving abdominal pain, whereas drotaverine, acupuncture, and pinaverium remained superior to the placebo. That being said, acupuncture was shown to be superior in relieving global IBS symptoms and caused fewer side effects than did antispasmodics. This shows that acupuncture may have a role in the treatment algorithm for IBS even outside of China, where it is used broadly.
The study by Formica and colleagues provides new insights on the etiology and pathogenesis of IBS. These insights include the positive correlation between disgust sensitivity and IBS quality of life (QOL) scores. The relationship between IBS and the emotional intensity of the experience of disgust is discussed throughout this study and more severe IBS-QOL scores were linked to those with high levels of disgust sensitivity. This study had gender limitations because of the low number of male participants, so these correlations were patterned mostly in female participants.
Acupuncture is a very popular treatment strategy in some areas of the world and is extensively applied in Chinese practice. Though this is a regularly applied treatment, a direct comparison with first-line antispasmodics has not been previously completed. The study by Shi and colleagues sought to compare the treatment of IBS using an adjusted indirect treatment comparison meta-analysis. This study proves that cimetropium was the most effective for relieving abdominal pain, whereas drotaverine, acupuncture, and pinaverium remained superior to the placebo. That being said, acupuncture was shown to be superior in relieving global IBS symptoms and caused fewer side effects than did antispasmodics. This shows that acupuncture may have a role in the treatment algorithm for IBS even outside of China, where it is used broadly.
The study by Formica and colleagues provides new insights on the etiology and pathogenesis of IBS. These insights include the positive correlation between disgust sensitivity and IBS quality of life (QOL) scores. The relationship between IBS and the emotional intensity of the experience of disgust is discussed throughout this study and more severe IBS-QOL scores were linked to those with high levels of disgust sensitivity. This study had gender limitations because of the low number of male participants, so these correlations were patterned mostly in female participants.
Commentary: Multifocal Hepatocellular Carcinoma, November 2022
Orimo and colleagues addressed the use of liver resection in patients with more than one HCC in the liver. Patients with no or Child-Pugh A/B cirrhosis were included in this single-center retrospective study of 1088 patients who underwent hepatectomy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage 0 (n = 88), A (n = 750), or B (n = 250) HCC, with stages A and B subcategorized into A1 (single nodule 2-5 cm or ≤ 3 nodules ≤ 3 cm), A2 (single nodule 5-10 cm), A3 (single nodule ≥ 10 cm), B1 (2-3 nodules > 3 cm), and B2 (≥ 4 nodules). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rates for stage 0, A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2 patients were 70.4%, 74.2%, 63.8%, 47.7%, 47.5%, and 31.9%, respectively (P < .0001). Significant differences in overall survival (OS) were found between stages A1 and A2 (P = .0118), A2 and A3 (P = .0013), and B1 and B2 (P = .0050), but not between stages A3 and B1 (P = .4742). In stage B1 patients, Child-Pugh B cirrhosis was the only independent prognostic factor for OS. The authors concluded that hepatectomy is beneficial in patients with three or fewer hepatocellular carcinomas and either no or Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, with the long-term results being comparable to those in patients who underwent a resection of a single HCC. Therefore, resection of up to three HCC is safe and should be considered in clinically appropriate patients.
Many patients with multifocal HCC are not eligible for liver-directed therapies. The standard of care for first-line systemic therapy is the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab, as reported in the IMbrave150 clinical trial. Fulgenzi and colleagues published the results of a multicenter prospective observational study, AB-Real, that included 433 patients who received atezolizumab and bevacizumab in routine clinical practice. The investigators confirmed the efficacy of the combination and found that portal vein tumor thrombosis and worse albumin-bilirubin grade were independent prognostic factors for poor OS and were associated with an increased risk for hemorrhagic events. In addition, the authors reported that the overall response rate (ORR) predicted better outcomes, including longer OS. Therefore, atezolizumab and bevacizumab remains a safe and effective first-line treatment for many patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, Finn and colleagues reported the results of an open-label, noncomparative cohort of the REACH-2 study of ramucirumab in 47 patients with advanced HCC and an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level ≥ 400 ng/mL. These patients had previously received one to two lines of systemic therapy, excluding sorafenib or chemotherapy. Lenvatinib was the most common prior systemic therapy (n = 20; 43%). Others included immune checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) monotherapies (n = 11), CPI/antiangiogenic therapy (n = 14), or dual CPI therapy (n = 5). The ORR was 10.6% (95% CI 1.8-19.5) and disease control rate was 46.8% (95% CI 32.5-61.1), with a median duration of response of 8.3 months [95% CI 2.4 to not reached). The grade 3 or more adverse event rate was 57%, with hypertension (11%) being the most common, allowing the authors to conclude that ramucirumab offers clinically significant efficacy with no new safety signals in this setting. Therefore, ramucirumab remains as a safe and effective later-line treatment option for patients with unresectable HCC and an AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL.
Orimo and colleagues addressed the use of liver resection in patients with more than one HCC in the liver. Patients with no or Child-Pugh A/B cirrhosis were included in this single-center retrospective study of 1088 patients who underwent hepatectomy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage 0 (n = 88), A (n = 750), or B (n = 250) HCC, with stages A and B subcategorized into A1 (single nodule 2-5 cm or ≤ 3 nodules ≤ 3 cm), A2 (single nodule 5-10 cm), A3 (single nodule ≥ 10 cm), B1 (2-3 nodules > 3 cm), and B2 (≥ 4 nodules). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rates for stage 0, A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2 patients were 70.4%, 74.2%, 63.8%, 47.7%, 47.5%, and 31.9%, respectively (P < .0001). Significant differences in overall survival (OS) were found between stages A1 and A2 (P = .0118), A2 and A3 (P = .0013), and B1 and B2 (P = .0050), but not between stages A3 and B1 (P = .4742). In stage B1 patients, Child-Pugh B cirrhosis was the only independent prognostic factor for OS. The authors concluded that hepatectomy is beneficial in patients with three or fewer hepatocellular carcinomas and either no or Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, with the long-term results being comparable to those in patients who underwent a resection of a single HCC. Therefore, resection of up to three HCC is safe and should be considered in clinically appropriate patients.
Many patients with multifocal HCC are not eligible for liver-directed therapies. The standard of care for first-line systemic therapy is the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab, as reported in the IMbrave150 clinical trial. Fulgenzi and colleagues published the results of a multicenter prospective observational study, AB-Real, that included 433 patients who received atezolizumab and bevacizumab in routine clinical practice. The investigators confirmed the efficacy of the combination and found that portal vein tumor thrombosis and worse albumin-bilirubin grade were independent prognostic factors for poor OS and were associated with an increased risk for hemorrhagic events. In addition, the authors reported that the overall response rate (ORR) predicted better outcomes, including longer OS. Therefore, atezolizumab and bevacizumab remains a safe and effective first-line treatment for many patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, Finn and colleagues reported the results of an open-label, noncomparative cohort of the REACH-2 study of ramucirumab in 47 patients with advanced HCC and an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level ≥ 400 ng/mL. These patients had previously received one to two lines of systemic therapy, excluding sorafenib or chemotherapy. Lenvatinib was the most common prior systemic therapy (n = 20; 43%). Others included immune checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) monotherapies (n = 11), CPI/antiangiogenic therapy (n = 14), or dual CPI therapy (n = 5). The ORR was 10.6% (95% CI 1.8-19.5) and disease control rate was 46.8% (95% CI 32.5-61.1), with a median duration of response of 8.3 months [95% CI 2.4 to not reached). The grade 3 or more adverse event rate was 57%, with hypertension (11%) being the most common, allowing the authors to conclude that ramucirumab offers clinically significant efficacy with no new safety signals in this setting. Therefore, ramucirumab remains as a safe and effective later-line treatment option for patients with unresectable HCC and an AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL.
Orimo and colleagues addressed the use of liver resection in patients with more than one HCC in the liver. Patients with no or Child-Pugh A/B cirrhosis were included in this single-center retrospective study of 1088 patients who underwent hepatectomy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage 0 (n = 88), A (n = 750), or B (n = 250) HCC, with stages A and B subcategorized into A1 (single nodule 2-5 cm or ≤ 3 nodules ≤ 3 cm), A2 (single nodule 5-10 cm), A3 (single nodule ≥ 10 cm), B1 (2-3 nodules > 3 cm), and B2 (≥ 4 nodules). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rates for stage 0, A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2 patients were 70.4%, 74.2%, 63.8%, 47.7%, 47.5%, and 31.9%, respectively (P < .0001). Significant differences in overall survival (OS) were found between stages A1 and A2 (P = .0118), A2 and A3 (P = .0013), and B1 and B2 (P = .0050), but not between stages A3 and B1 (P = .4742). In stage B1 patients, Child-Pugh B cirrhosis was the only independent prognostic factor for OS. The authors concluded that hepatectomy is beneficial in patients with three or fewer hepatocellular carcinomas and either no or Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, with the long-term results being comparable to those in patients who underwent a resection of a single HCC. Therefore, resection of up to three HCC is safe and should be considered in clinically appropriate patients.
Many patients with multifocal HCC are not eligible for liver-directed therapies. The standard of care for first-line systemic therapy is the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab, as reported in the IMbrave150 clinical trial. Fulgenzi and colleagues published the results of a multicenter prospective observational study, AB-Real, that included 433 patients who received atezolizumab and bevacizumab in routine clinical practice. The investigators confirmed the efficacy of the combination and found that portal vein tumor thrombosis and worse albumin-bilirubin grade were independent prognostic factors for poor OS and were associated with an increased risk for hemorrhagic events. In addition, the authors reported that the overall response rate (ORR) predicted better outcomes, including longer OS. Therefore, atezolizumab and bevacizumab remains a safe and effective first-line treatment for many patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, Finn and colleagues reported the results of an open-label, noncomparative cohort of the REACH-2 study of ramucirumab in 47 patients with advanced HCC and an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level ≥ 400 ng/mL. These patients had previously received one to two lines of systemic therapy, excluding sorafenib or chemotherapy. Lenvatinib was the most common prior systemic therapy (n = 20; 43%). Others included immune checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) monotherapies (n = 11), CPI/antiangiogenic therapy (n = 14), or dual CPI therapy (n = 5). The ORR was 10.6% (95% CI 1.8-19.5) and disease control rate was 46.8% (95% CI 32.5-61.1), with a median duration of response of 8.3 months [95% CI 2.4 to not reached). The grade 3 or more adverse event rate was 57%, with hypertension (11%) being the most common, allowing the authors to conclude that ramucirumab offers clinically significant efficacy with no new safety signals in this setting. Therefore, ramucirumab remains as a safe and effective later-line treatment option for patients with unresectable HCC and an AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL.
Commentary: Multifocal Hepatocellular Carcinoma, November 2022
Orimo and colleagues addressed the use of liver resection in patients with more than one HCC in the liver. Patients with no or Child-Pugh A/B cirrhosis were included in this single-center retrospective study of 1088 patients who underwent hepatectomy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage 0 (n = 88), A (n = 750), or B (n = 250) HCC, with stages A and B subcategorized into A1 (single nodule 2-5 cm or ≤ 3 nodules ≤ 3 cm), A2 (single nodule 5-10 cm), A3 (single nodule ≥ 10 cm), B1 (2-3 nodules > 3 cm), and B2 (≥ 4 nodules). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rates for stage 0, A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2 patients were 70.4%, 74.2%, 63.8%, 47.7%, 47.5%, and 31.9%, respectively (P < .0001). Significant differences in overall survival (OS) were found between stages A1 and A2 (P = .0118), A2 and A3 (P = .0013), and B1 and B2 (P = .0050), but not between stages A3 and B1 (P = .4742). In stage B1 patients, Child-Pugh B cirrhosis was the only independent prognostic factor for OS. The authors concluded that hepatectomy is beneficial in patients with three or fewer hepatocellular carcinomas and either no or Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, with the long-term results being comparable to those in patients who underwent a resection of a single HCC. Therefore, resection of up to three HCC is safe and should be considered in clinically appropriate patients.
Many patients with multifocal HCC are not eligible for liver-directed therapies. The standard of care for first-line systemic therapy is the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab, as reported in the IMbrave150 clinical trial. Fulgenzi and colleagues published the results of a multicenter prospective observational study, AB-Real, that included 433 patients who received atezolizumab and bevacizumab in routine clinical practice. The investigators confirmed the efficacy of the combination and found that portal vein tumor thrombosis and worse albumin-bilirubin grade were independent prognostic factors for poor OS and were associated with an increased risk for hemorrhagic events. In addition, the authors reported that the overall response rate (ORR) predicted better outcomes, including longer OS. Therefore, atezolizumab and bevacizumab remains a safe and effective first-line treatment for many patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, Finn and colleagues reported the results of an open-label, noncomparative cohort of the REACH-2 study of ramucirumab in 47 patients with advanced HCC and an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level ≥ 400 ng/mL. These patients had previously received one to two lines of systemic therapy, excluding sorafenib or chemotherapy. Lenvatinib was the most common prior systemic therapy (n = 20; 43%). Others included immune checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) monotherapies (n = 11), CPI/antiangiogenic therapy (n = 14), or dual CPI therapy (n = 5). The ORR was 10.6% (95% CI 1.8-19.5) and disease control rate was 46.8% (95% CI 32.5-61.1), with a median duration of response of 8.3 months (95% CI 2.4 to not reached). The grade 3 or more adverse event rate was 57%, with hypertension (11%) being the most common, allowing the authors to conclude that ramucirumab offers clinically significant efficacy with no new safety signals in this setting. Therefore, ramucirumab remains as a safe and effective later-line treatment option for patients with unresectable HCC and an AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL.
Orimo and colleagues addressed the use of liver resection in patients with more than one HCC in the liver. Patients with no or Child-Pugh A/B cirrhosis were included in this single-center retrospective study of 1088 patients who underwent hepatectomy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage 0 (n = 88), A (n = 750), or B (n = 250) HCC, with stages A and B subcategorized into A1 (single nodule 2-5 cm or ≤ 3 nodules ≤ 3 cm), A2 (single nodule 5-10 cm), A3 (single nodule ≥ 10 cm), B1 (2-3 nodules > 3 cm), and B2 (≥ 4 nodules). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rates for stage 0, A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2 patients were 70.4%, 74.2%, 63.8%, 47.7%, 47.5%, and 31.9%, respectively (P < .0001). Significant differences in overall survival (OS) were found between stages A1 and A2 (P = .0118), A2 and A3 (P = .0013), and B1 and B2 (P = .0050), but not between stages A3 and B1 (P = .4742). In stage B1 patients, Child-Pugh B cirrhosis was the only independent prognostic factor for OS. The authors concluded that hepatectomy is beneficial in patients with three or fewer hepatocellular carcinomas and either no or Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, with the long-term results being comparable to those in patients who underwent a resection of a single HCC. Therefore, resection of up to three HCC is safe and should be considered in clinically appropriate patients.
Many patients with multifocal HCC are not eligible for liver-directed therapies. The standard of care for first-line systemic therapy is the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab, as reported in the IMbrave150 clinical trial. Fulgenzi and colleagues published the results of a multicenter prospective observational study, AB-Real, that included 433 patients who received atezolizumab and bevacizumab in routine clinical practice. The investigators confirmed the efficacy of the combination and found that portal vein tumor thrombosis and worse albumin-bilirubin grade were independent prognostic factors for poor OS and were associated with an increased risk for hemorrhagic events. In addition, the authors reported that the overall response rate (ORR) predicted better outcomes, including longer OS. Therefore, atezolizumab and bevacizumab remains a safe and effective first-line treatment for many patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, Finn and colleagues reported the results of an open-label, noncomparative cohort of the REACH-2 study of ramucirumab in 47 patients with advanced HCC and an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level ≥ 400 ng/mL. These patients had previously received one to two lines of systemic therapy, excluding sorafenib or chemotherapy. Lenvatinib was the most common prior systemic therapy (n = 20; 43%). Others included immune checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) monotherapies (n = 11), CPI/antiangiogenic therapy (n = 14), or dual CPI therapy (n = 5). The ORR was 10.6% (95% CI 1.8-19.5) and disease control rate was 46.8% (95% CI 32.5-61.1), with a median duration of response of 8.3 months (95% CI 2.4 to not reached). The grade 3 or more adverse event rate was 57%, with hypertension (11%) being the most common, allowing the authors to conclude that ramucirumab offers clinically significant efficacy with no new safety signals in this setting. Therefore, ramucirumab remains as a safe and effective later-line treatment option for patients with unresectable HCC and an AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL.
Orimo and colleagues addressed the use of liver resection in patients with more than one HCC in the liver. Patients with no or Child-Pugh A/B cirrhosis were included in this single-center retrospective study of 1088 patients who underwent hepatectomy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage 0 (n = 88), A (n = 750), or B (n = 250) HCC, with stages A and B subcategorized into A1 (single nodule 2-5 cm or ≤ 3 nodules ≤ 3 cm), A2 (single nodule 5-10 cm), A3 (single nodule ≥ 10 cm), B1 (2-3 nodules > 3 cm), and B2 (≥ 4 nodules). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rates for stage 0, A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2 patients were 70.4%, 74.2%, 63.8%, 47.7%, 47.5%, and 31.9%, respectively (P < .0001). Significant differences in overall survival (OS) were found between stages A1 and A2 (P = .0118), A2 and A3 (P = .0013), and B1 and B2 (P = .0050), but not between stages A3 and B1 (P = .4742). In stage B1 patients, Child-Pugh B cirrhosis was the only independent prognostic factor for OS. The authors concluded that hepatectomy is beneficial in patients with three or fewer hepatocellular carcinomas and either no or Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, with the long-term results being comparable to those in patients who underwent a resection of a single HCC. Therefore, resection of up to three HCC is safe and should be considered in clinically appropriate patients.
Many patients with multifocal HCC are not eligible for liver-directed therapies. The standard of care for first-line systemic therapy is the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab, as reported in the IMbrave150 clinical trial. Fulgenzi and colleagues published the results of a multicenter prospective observational study, AB-Real, that included 433 patients who received atezolizumab and bevacizumab in routine clinical practice. The investigators confirmed the efficacy of the combination and found that portal vein tumor thrombosis and worse albumin-bilirubin grade were independent prognostic factors for poor OS and were associated with an increased risk for hemorrhagic events. In addition, the authors reported that the overall response rate (ORR) predicted better outcomes, including longer OS. Therefore, atezolizumab and bevacizumab remains a safe and effective first-line treatment for many patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, Finn and colleagues reported the results of an open-label, noncomparative cohort of the REACH-2 study of ramucirumab in 47 patients with advanced HCC and an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level ≥ 400 ng/mL. These patients had previously received one to two lines of systemic therapy, excluding sorafenib or chemotherapy. Lenvatinib was the most common prior systemic therapy (n = 20; 43%). Others included immune checkpoint inhibitor (CPI) monotherapies (n = 11), CPI/antiangiogenic therapy (n = 14), or dual CPI therapy (n = 5). The ORR was 10.6% (95% CI 1.8-19.5) and disease control rate was 46.8% (95% CI 32.5-61.1), with a median duration of response of 8.3 months (95% CI 2.4 to not reached). The grade 3 or more adverse event rate was 57%, with hypertension (11%) being the most common, allowing the authors to conclude that ramucirumab offers clinically significant efficacy with no new safety signals in this setting. Therefore, ramucirumab remains as a safe and effective later-line treatment option for patients with unresectable HCC and an AFP ≥ 400 ng/mL.
Legal and malpractice risks when taking call
Taking call is one of the more challenging - and annoying - aspects of the job for many physicians. Calls may wake them up in the middle of the night and can interfere with their at-home activities. In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report, 37% of respondents said they have from 1 to 5 hours of call per month; 19% said they have 6 to 10 hours; and 12% have 11 hours or more.
“Even if you don’t have to come in to the ED, you can get calls in the middle of the night, and you may get paid very little, if anything,” said Robert Bitterman MD, JD, an emergency physician and attorney in Harbor Springs, Mich.
And responding to the calls is not optional. Dr. Bitterman said
On-call activities are regulated by the federal Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA). Dr. Bitterman said it’s rare for the federal government to prosecute on-call physicians for violating EMTALA. Instead, it’s more likely that the hospital will be fined for EMTALA violations committed by on-call physicians.
However, the hospital passes the on-call obligation on to individual physicians through medical staff bylaws. Physicians who violate the bylaws may have their privileges restricted or removed, Dr. Bitterman said. Physicians could also be sued for malpractice, even if they never treated the patient, he added.
After-hours call duty in physicians’ practices
A very different type of call duty is having to respond to calls from one’s own patients after regular hours. Unlike doctors on ED call, who usually deal with patients they have never met, these physicians deal with their established patients or those of a colleague in their practice.
Courts have established that physicians have to provide an answering service or other means for their patients to contact them after hours, and the doctor must respond to these calls in a timely manner.
In a 2015 Louisiana ruling, a cardiologist was found liable for malpractice because he didn’t respond to an after-hours call from his patient. The patient tried several times to contact the cardiologist but got no reply.
Physicians may also be responsible if their answering service does not send critical messages to them immediately, if it fails to make appropriate documentation, or if it sends inaccurate data to the doctor.
Cases when on-call doctors didn’t respond
The Office of the Inspector General (OIG) of the U.S. Health and Human Services Administration oversees federal EMTALA violations and regularly reports them.
In 2018, the OIG fined a hospital in Waterloo, Iowa, $90,000 when an on-call cardiologist failed to implant a pacemaker for an ED patient. According to the OIG’s report, the patient arrived at the hospital with heart problems. Reached by phone, the cardiologist directed the ED physician to begin transcutaneous pacing but asked that the patient be transferred to another hospital for placement of the pacemaker. The patient died after transfer.
The OIG found that the original cardiologist could have placed the pacemaker, but, as often happens, it only fined the hospital, not the on-call physician for the EMTALA violation.
EMTALA requires that hospitals provide on-call specialists to assist emergency physicians with care of patients who arrive in the ED. In specialties for which there are few doctors to choose from, the on-call specialist may be on duty every third night and every third weekend. This can be daunting, especially for specialists who’ve had a grueling day of work.
Occasionally, on-call physicians, fearful they could make a medical error, request that the patient be transferred to another hospital for treatment. This is what a neurosurgeon who was on call at a Topeka, Kan., hospital did in 2001. Transferred to another hospital, the patient underwent an operation but lost sensation in his lower extremities. The patient sued the on-call neurosurgeon for negligence.
During the trial, the on-call neurosurgeon testified that he was “feeling run-down because he had been an on-call physician every third night for more than 10 years.” He also said this was the first time he had refused to see a patient because of fatigue, and he had decided that the patient “would be better off at a trauma center that had a trauma team and a fresher surgeon.”
The neurosurgeon successfully defended the malpractice suit, but Dr. Bitterman said he might have lost had there not been some unusual circumstances in the case. The court ruled that the hospital had not clearly defined the duties of on-call physicians, and the lawsuit didn’t cite the neurosurgeon’s EMTALA duty.
On-call duties defined by EMTALA
EMTALA sets the overall rules for on-call duties, which each hospital is expected to fine-tune on the basis of its own particular circumstances. Here are some of those rules, issued by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and the OIG.
Only an individual physician can be on call. The hospital’s on-call schedule cannot name a physician practice.
Call applies to all ED patients. Physicians cannot limit their on-call responsibilities to their own patients, to patients in their insurance network, or to paying patients.
There may be some gaps in the call schedule. The OIG is not specific as to how many gaps are allowed, said Nick Healey, an attorney in Cheyenne, Wyo., who has written about on-call duties. Among other things, adequate coverage depends on the number of available physicians and the demand for their services. Mr. Healey added that states may require more extensive availability of on-call physicians at high-level trauma centers.
Hospitals must have made arrangements for transfer. Whenever there is a gap in the schedule, hospitals need to have a designated hospital to send the patient to. Hospitals that unnecessarily transfer patients will be penalized.
The ED physician calls the shots. The emergency physician handling the case decides if the on-call doctor has to come in and treat the patient firsthand.
The on-call physician may delegate the work to others. On-call physicians may designate a nurse practitioner or physician assistant, but the on-call physician is ultimately responsible. The ED doctor may require the physician to come in anyway, according to Todd B. Taylor, MD, an emergency physician in Phoenix, who has written about on-call duties. Dr. Bitterman noted that the physician may designate a colleague to take their call, but the substitute has to have privileges at the hospital.
Physicians may do their own work while on call. Physicians can perform elective surgery while on call, provided they have made arrangements if they then become unavailable for duty, Dr. Taylor said. He added that physicians can also have simultaneous call at other hospitals, provided they make arrangements.
The hospital fine-tunes call obligations
The hospital is expected to further define the federal rules. For instance, the CMS says physicians should respond to calls within a “reasonable period of time” and requires hospitals to specify response times, which may be 15-30 minutes for responding to phone calls and traveling to the ED, Dr. Bitterman said.
The CMS says older physicians can be exempted from call. The hospital determines the age at which physicians can be exempted. “Hospitals typically exempt physicians over age 65 or 70, or when they have certain medical conditions,” said Lowell Brown, a Los Angeles attorney who deals with on-call duties.
The hospital also sets the call schedule, which may result in uncovered periods in specialties in which there are few physicians to draw from, according to Mr. Healey. He said many hospitals still use a simple rule of thumb, even though it has been dismissed by the CMS. Under this so-called “rule of three,” hospitals that have three doctors or fewer in a specialty do not have to provide constant call coverage.
On-call rules are part of the medical staff bylaws, and they have to be approved by the medical staff. This may require delicate negotiations between the staff’s leadership and administrators, Dr. Bitterman said.
It is often up to the emergency physician on duty to enforce the hospital’s on-call rules, Dr. Taylor said. “If the ED physician is having trouble, he or she may contact the on-call physician’s department chairman or, if necessary, the chief of the medical staff and ask that person to deal with the physician,” Dr. Taylor said.
The ED physician has to determine whether the patient needs to be transferred to another hospital. Dr. Taylor said the ED physician must fill out a transfer form and obtain consent from the receiving hospital.
If a patient has to be transferred because an on-call physician failed to appear, the originating hospital has to report this to the CMS, and the physician and the hospital can be cited for an inappropriate transfer and fined, Mr. Brown said. “The possibility of being identified in this way should be a powerful incentive to accept call duty,” he added.
Malpractice exposure of on-call physicians
When on-call doctors provide medical advice regarding an ED patient, that advice may be subject to malpractice litigation, Dr. Taylor said. “Even if you only give the ED doctor advice over the phone, that may establish a patient-physician relationship and a duty that patient can cite in a malpractice case,” he noted.
Refusing to take call may also be grounds for a malpractice lawsuit, Dr. Bitterman said. Refusing to see a patient would not be considered medical negligence, he continued, because no medical decision is made. Rather, it involves general negligence, which occurs when physicians fail to carry out duties expected of them.
Dr. Bitterman cited a 2006 malpractice judgment in which an on-call neurosurgeon in Missouri was found to be generally negligent. The neurosurgeon had arranged for a colleague in his practice to take his call, but the colleague did not have privileges at the hospital.
A patient with a brain bleed came in and the substitute was on duty. The patient had to be transferred to another hospital, where the patient died. The court ordered that the on-call doctor and the originating hospital had to split a fine of $400,800.
On-call physicians can be charged with abandonment
Dr. Bitterman said that if on-call physicians do not provide expected follow-up treatment for an ED patient, they could be charged with abandonment, which is a matter of state law and involves filing a malpractice lawsuit.
Abandonment involves unilaterally terminating the patient relationship without providing notice. There must be an established relationship, which, in the case of call, is formed when the doctor comes to the ED to examine or admit the patient, Dr. Bitterman said. He added that the on-call doctor’s obligation applies only to the medical condition the patient came in for.
Even when an on-call doctor does not see a patient, a relationship can be established if the hospital requires its on-call doctors to make follow-up visits for ED patients, Dr. Taylor said. At some hospitals, he said, on-call doctors have blanket agreements to provide follow-up care in return for not having to arrive in the middle of the night during the ED visit.
Dr. Taylor gave an example of the on-call doctor’s obligation: “The ED doctor puts a splint on the patient’s ankle fracture, and the orthopedic surgeon on call agrees to follow up with the patient within the next few days. If the orthopedic surgeon refuses to follow up without making a reasonable accommodation, it may become an issue of patient abandonment.”
Now everyone has a good grasp of the rules
Fifteen years ago, many doctors were in open revolt against on-call duties, but they are more accepting now and understand the rules better, Mr. Healey said.
“Many hospitals have begun paying some specialists for call and designating hospitalists and surgicalists to do at least some of the work that used to be expected of on-call doctors,” he said.
According to Dr. Taylor, today’s on-call doctors often have less to do than in the past. “For example,” he said, “the hospitalist may admit an orthopedic patient at night, and then the orthopedic surgeon does the operation the next day. We’ve had EMTALA for 36 years now, and hospitals and doctors know how call works.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Taking call is one of the more challenging - and annoying - aspects of the job for many physicians. Calls may wake them up in the middle of the night and can interfere with their at-home activities. In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report, 37% of respondents said they have from 1 to 5 hours of call per month; 19% said they have 6 to 10 hours; and 12% have 11 hours or more.
“Even if you don’t have to come in to the ED, you can get calls in the middle of the night, and you may get paid very little, if anything,” said Robert Bitterman MD, JD, an emergency physician and attorney in Harbor Springs, Mich.
And responding to the calls is not optional. Dr. Bitterman said
On-call activities are regulated by the federal Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA). Dr. Bitterman said it’s rare for the federal government to prosecute on-call physicians for violating EMTALA. Instead, it’s more likely that the hospital will be fined for EMTALA violations committed by on-call physicians.
However, the hospital passes the on-call obligation on to individual physicians through medical staff bylaws. Physicians who violate the bylaws may have their privileges restricted or removed, Dr. Bitterman said. Physicians could also be sued for malpractice, even if they never treated the patient, he added.
After-hours call duty in physicians’ practices
A very different type of call duty is having to respond to calls from one’s own patients after regular hours. Unlike doctors on ED call, who usually deal with patients they have never met, these physicians deal with their established patients or those of a colleague in their practice.
Courts have established that physicians have to provide an answering service or other means for their patients to contact them after hours, and the doctor must respond to these calls in a timely manner.
In a 2015 Louisiana ruling, a cardiologist was found liable for malpractice because he didn’t respond to an after-hours call from his patient. The patient tried several times to contact the cardiologist but got no reply.
Physicians may also be responsible if their answering service does not send critical messages to them immediately, if it fails to make appropriate documentation, or if it sends inaccurate data to the doctor.
Cases when on-call doctors didn’t respond
The Office of the Inspector General (OIG) of the U.S. Health and Human Services Administration oversees federal EMTALA violations and regularly reports them.
In 2018, the OIG fined a hospital in Waterloo, Iowa, $90,000 when an on-call cardiologist failed to implant a pacemaker for an ED patient. According to the OIG’s report, the patient arrived at the hospital with heart problems. Reached by phone, the cardiologist directed the ED physician to begin transcutaneous pacing but asked that the patient be transferred to another hospital for placement of the pacemaker. The patient died after transfer.
The OIG found that the original cardiologist could have placed the pacemaker, but, as often happens, it only fined the hospital, not the on-call physician for the EMTALA violation.
EMTALA requires that hospitals provide on-call specialists to assist emergency physicians with care of patients who arrive in the ED. In specialties for which there are few doctors to choose from, the on-call specialist may be on duty every third night and every third weekend. This can be daunting, especially for specialists who’ve had a grueling day of work.
Occasionally, on-call physicians, fearful they could make a medical error, request that the patient be transferred to another hospital for treatment. This is what a neurosurgeon who was on call at a Topeka, Kan., hospital did in 2001. Transferred to another hospital, the patient underwent an operation but lost sensation in his lower extremities. The patient sued the on-call neurosurgeon for negligence.
During the trial, the on-call neurosurgeon testified that he was “feeling run-down because he had been an on-call physician every third night for more than 10 years.” He also said this was the first time he had refused to see a patient because of fatigue, and he had decided that the patient “would be better off at a trauma center that had a trauma team and a fresher surgeon.”
The neurosurgeon successfully defended the malpractice suit, but Dr. Bitterman said he might have lost had there not been some unusual circumstances in the case. The court ruled that the hospital had not clearly defined the duties of on-call physicians, and the lawsuit didn’t cite the neurosurgeon’s EMTALA duty.
On-call duties defined by EMTALA
EMTALA sets the overall rules for on-call duties, which each hospital is expected to fine-tune on the basis of its own particular circumstances. Here are some of those rules, issued by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and the OIG.
Only an individual physician can be on call. The hospital’s on-call schedule cannot name a physician practice.
Call applies to all ED patients. Physicians cannot limit their on-call responsibilities to their own patients, to patients in their insurance network, or to paying patients.
There may be some gaps in the call schedule. The OIG is not specific as to how many gaps are allowed, said Nick Healey, an attorney in Cheyenne, Wyo., who has written about on-call duties. Among other things, adequate coverage depends on the number of available physicians and the demand for their services. Mr. Healey added that states may require more extensive availability of on-call physicians at high-level trauma centers.
Hospitals must have made arrangements for transfer. Whenever there is a gap in the schedule, hospitals need to have a designated hospital to send the patient to. Hospitals that unnecessarily transfer patients will be penalized.
The ED physician calls the shots. The emergency physician handling the case decides if the on-call doctor has to come in and treat the patient firsthand.
The on-call physician may delegate the work to others. On-call physicians may designate a nurse practitioner or physician assistant, but the on-call physician is ultimately responsible. The ED doctor may require the physician to come in anyway, according to Todd B. Taylor, MD, an emergency physician in Phoenix, who has written about on-call duties. Dr. Bitterman noted that the physician may designate a colleague to take their call, but the substitute has to have privileges at the hospital.
Physicians may do their own work while on call. Physicians can perform elective surgery while on call, provided they have made arrangements if they then become unavailable for duty, Dr. Taylor said. He added that physicians can also have simultaneous call at other hospitals, provided they make arrangements.
The hospital fine-tunes call obligations
The hospital is expected to further define the federal rules. For instance, the CMS says physicians should respond to calls within a “reasonable period of time” and requires hospitals to specify response times, which may be 15-30 minutes for responding to phone calls and traveling to the ED, Dr. Bitterman said.
The CMS says older physicians can be exempted from call. The hospital determines the age at which physicians can be exempted. “Hospitals typically exempt physicians over age 65 or 70, or when they have certain medical conditions,” said Lowell Brown, a Los Angeles attorney who deals with on-call duties.
The hospital also sets the call schedule, which may result in uncovered periods in specialties in which there are few physicians to draw from, according to Mr. Healey. He said many hospitals still use a simple rule of thumb, even though it has been dismissed by the CMS. Under this so-called “rule of three,” hospitals that have three doctors or fewer in a specialty do not have to provide constant call coverage.
On-call rules are part of the medical staff bylaws, and they have to be approved by the medical staff. This may require delicate negotiations between the staff’s leadership and administrators, Dr. Bitterman said.
It is often up to the emergency physician on duty to enforce the hospital’s on-call rules, Dr. Taylor said. “If the ED physician is having trouble, he or she may contact the on-call physician’s department chairman or, if necessary, the chief of the medical staff and ask that person to deal with the physician,” Dr. Taylor said.
The ED physician has to determine whether the patient needs to be transferred to another hospital. Dr. Taylor said the ED physician must fill out a transfer form and obtain consent from the receiving hospital.
If a patient has to be transferred because an on-call physician failed to appear, the originating hospital has to report this to the CMS, and the physician and the hospital can be cited for an inappropriate transfer and fined, Mr. Brown said. “The possibility of being identified in this way should be a powerful incentive to accept call duty,” he added.
Malpractice exposure of on-call physicians
When on-call doctors provide medical advice regarding an ED patient, that advice may be subject to malpractice litigation, Dr. Taylor said. “Even if you only give the ED doctor advice over the phone, that may establish a patient-physician relationship and a duty that patient can cite in a malpractice case,” he noted.
Refusing to take call may also be grounds for a malpractice lawsuit, Dr. Bitterman said. Refusing to see a patient would not be considered medical negligence, he continued, because no medical decision is made. Rather, it involves general negligence, which occurs when physicians fail to carry out duties expected of them.
Dr. Bitterman cited a 2006 malpractice judgment in which an on-call neurosurgeon in Missouri was found to be generally negligent. The neurosurgeon had arranged for a colleague in his practice to take his call, but the colleague did not have privileges at the hospital.
A patient with a brain bleed came in and the substitute was on duty. The patient had to be transferred to another hospital, where the patient died. The court ordered that the on-call doctor and the originating hospital had to split a fine of $400,800.
On-call physicians can be charged with abandonment
Dr. Bitterman said that if on-call physicians do not provide expected follow-up treatment for an ED patient, they could be charged with abandonment, which is a matter of state law and involves filing a malpractice lawsuit.
Abandonment involves unilaterally terminating the patient relationship without providing notice. There must be an established relationship, which, in the case of call, is formed when the doctor comes to the ED to examine or admit the patient, Dr. Bitterman said. He added that the on-call doctor’s obligation applies only to the medical condition the patient came in for.
Even when an on-call doctor does not see a patient, a relationship can be established if the hospital requires its on-call doctors to make follow-up visits for ED patients, Dr. Taylor said. At some hospitals, he said, on-call doctors have blanket agreements to provide follow-up care in return for not having to arrive in the middle of the night during the ED visit.
Dr. Taylor gave an example of the on-call doctor’s obligation: “The ED doctor puts a splint on the patient’s ankle fracture, and the orthopedic surgeon on call agrees to follow up with the patient within the next few days. If the orthopedic surgeon refuses to follow up without making a reasonable accommodation, it may become an issue of patient abandonment.”
Now everyone has a good grasp of the rules
Fifteen years ago, many doctors were in open revolt against on-call duties, but they are more accepting now and understand the rules better, Mr. Healey said.
“Many hospitals have begun paying some specialists for call and designating hospitalists and surgicalists to do at least some of the work that used to be expected of on-call doctors,” he said.
According to Dr. Taylor, today’s on-call doctors often have less to do than in the past. “For example,” he said, “the hospitalist may admit an orthopedic patient at night, and then the orthopedic surgeon does the operation the next day. We’ve had EMTALA for 36 years now, and hospitals and doctors know how call works.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Taking call is one of the more challenging - and annoying - aspects of the job for many physicians. Calls may wake them up in the middle of the night and can interfere with their at-home activities. In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report, 37% of respondents said they have from 1 to 5 hours of call per month; 19% said they have 6 to 10 hours; and 12% have 11 hours or more.
“Even if you don’t have to come in to the ED, you can get calls in the middle of the night, and you may get paid very little, if anything,” said Robert Bitterman MD, JD, an emergency physician and attorney in Harbor Springs, Mich.
And responding to the calls is not optional. Dr. Bitterman said
On-call activities are regulated by the federal Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA). Dr. Bitterman said it’s rare for the federal government to prosecute on-call physicians for violating EMTALA. Instead, it’s more likely that the hospital will be fined for EMTALA violations committed by on-call physicians.
However, the hospital passes the on-call obligation on to individual physicians through medical staff bylaws. Physicians who violate the bylaws may have their privileges restricted or removed, Dr. Bitterman said. Physicians could also be sued for malpractice, even if they never treated the patient, he added.
After-hours call duty in physicians’ practices
A very different type of call duty is having to respond to calls from one’s own patients after regular hours. Unlike doctors on ED call, who usually deal with patients they have never met, these physicians deal with their established patients or those of a colleague in their practice.
Courts have established that physicians have to provide an answering service or other means for their patients to contact them after hours, and the doctor must respond to these calls in a timely manner.
In a 2015 Louisiana ruling, a cardiologist was found liable for malpractice because he didn’t respond to an after-hours call from his patient. The patient tried several times to contact the cardiologist but got no reply.
Physicians may also be responsible if their answering service does not send critical messages to them immediately, if it fails to make appropriate documentation, or if it sends inaccurate data to the doctor.
Cases when on-call doctors didn’t respond
The Office of the Inspector General (OIG) of the U.S. Health and Human Services Administration oversees federal EMTALA violations and regularly reports them.
In 2018, the OIG fined a hospital in Waterloo, Iowa, $90,000 when an on-call cardiologist failed to implant a pacemaker for an ED patient. According to the OIG’s report, the patient arrived at the hospital with heart problems. Reached by phone, the cardiologist directed the ED physician to begin transcutaneous pacing but asked that the patient be transferred to another hospital for placement of the pacemaker. The patient died after transfer.
The OIG found that the original cardiologist could have placed the pacemaker, but, as often happens, it only fined the hospital, not the on-call physician for the EMTALA violation.
EMTALA requires that hospitals provide on-call specialists to assist emergency physicians with care of patients who arrive in the ED. In specialties for which there are few doctors to choose from, the on-call specialist may be on duty every third night and every third weekend. This can be daunting, especially for specialists who’ve had a grueling day of work.
Occasionally, on-call physicians, fearful they could make a medical error, request that the patient be transferred to another hospital for treatment. This is what a neurosurgeon who was on call at a Topeka, Kan., hospital did in 2001. Transferred to another hospital, the patient underwent an operation but lost sensation in his lower extremities. The patient sued the on-call neurosurgeon for negligence.
During the trial, the on-call neurosurgeon testified that he was “feeling run-down because he had been an on-call physician every third night for more than 10 years.” He also said this was the first time he had refused to see a patient because of fatigue, and he had decided that the patient “would be better off at a trauma center that had a trauma team and a fresher surgeon.”
The neurosurgeon successfully defended the malpractice suit, but Dr. Bitterman said he might have lost had there not been some unusual circumstances in the case. The court ruled that the hospital had not clearly defined the duties of on-call physicians, and the lawsuit didn’t cite the neurosurgeon’s EMTALA duty.
On-call duties defined by EMTALA
EMTALA sets the overall rules for on-call duties, which each hospital is expected to fine-tune on the basis of its own particular circumstances. Here are some of those rules, issued by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and the OIG.
Only an individual physician can be on call. The hospital’s on-call schedule cannot name a physician practice.
Call applies to all ED patients. Physicians cannot limit their on-call responsibilities to their own patients, to patients in their insurance network, or to paying patients.
There may be some gaps in the call schedule. The OIG is not specific as to how many gaps are allowed, said Nick Healey, an attorney in Cheyenne, Wyo., who has written about on-call duties. Among other things, adequate coverage depends on the number of available physicians and the demand for their services. Mr. Healey added that states may require more extensive availability of on-call physicians at high-level trauma centers.
Hospitals must have made arrangements for transfer. Whenever there is a gap in the schedule, hospitals need to have a designated hospital to send the patient to. Hospitals that unnecessarily transfer patients will be penalized.
The ED physician calls the shots. The emergency physician handling the case decides if the on-call doctor has to come in and treat the patient firsthand.
The on-call physician may delegate the work to others. On-call physicians may designate a nurse practitioner or physician assistant, but the on-call physician is ultimately responsible. The ED doctor may require the physician to come in anyway, according to Todd B. Taylor, MD, an emergency physician in Phoenix, who has written about on-call duties. Dr. Bitterman noted that the physician may designate a colleague to take their call, but the substitute has to have privileges at the hospital.
Physicians may do their own work while on call. Physicians can perform elective surgery while on call, provided they have made arrangements if they then become unavailable for duty, Dr. Taylor said. He added that physicians can also have simultaneous call at other hospitals, provided they make arrangements.
The hospital fine-tunes call obligations
The hospital is expected to further define the federal rules. For instance, the CMS says physicians should respond to calls within a “reasonable period of time” and requires hospitals to specify response times, which may be 15-30 minutes for responding to phone calls and traveling to the ED, Dr. Bitterman said.
The CMS says older physicians can be exempted from call. The hospital determines the age at which physicians can be exempted. “Hospitals typically exempt physicians over age 65 or 70, or when they have certain medical conditions,” said Lowell Brown, a Los Angeles attorney who deals with on-call duties.
The hospital also sets the call schedule, which may result in uncovered periods in specialties in which there are few physicians to draw from, according to Mr. Healey. He said many hospitals still use a simple rule of thumb, even though it has been dismissed by the CMS. Under this so-called “rule of three,” hospitals that have three doctors or fewer in a specialty do not have to provide constant call coverage.
On-call rules are part of the medical staff bylaws, and they have to be approved by the medical staff. This may require delicate negotiations between the staff’s leadership and administrators, Dr. Bitterman said.
It is often up to the emergency physician on duty to enforce the hospital’s on-call rules, Dr. Taylor said. “If the ED physician is having trouble, he or she may contact the on-call physician’s department chairman or, if necessary, the chief of the medical staff and ask that person to deal with the physician,” Dr. Taylor said.
The ED physician has to determine whether the patient needs to be transferred to another hospital. Dr. Taylor said the ED physician must fill out a transfer form and obtain consent from the receiving hospital.
If a patient has to be transferred because an on-call physician failed to appear, the originating hospital has to report this to the CMS, and the physician and the hospital can be cited for an inappropriate transfer and fined, Mr. Brown said. “The possibility of being identified in this way should be a powerful incentive to accept call duty,” he added.
Malpractice exposure of on-call physicians
When on-call doctors provide medical advice regarding an ED patient, that advice may be subject to malpractice litigation, Dr. Taylor said. “Even if you only give the ED doctor advice over the phone, that may establish a patient-physician relationship and a duty that patient can cite in a malpractice case,” he noted.
Refusing to take call may also be grounds for a malpractice lawsuit, Dr. Bitterman said. Refusing to see a patient would not be considered medical negligence, he continued, because no medical decision is made. Rather, it involves general negligence, which occurs when physicians fail to carry out duties expected of them.
Dr. Bitterman cited a 2006 malpractice judgment in which an on-call neurosurgeon in Missouri was found to be generally negligent. The neurosurgeon had arranged for a colleague in his practice to take his call, but the colleague did not have privileges at the hospital.
A patient with a brain bleed came in and the substitute was on duty. The patient had to be transferred to another hospital, where the patient died. The court ordered that the on-call doctor and the originating hospital had to split a fine of $400,800.
On-call physicians can be charged with abandonment
Dr. Bitterman said that if on-call physicians do not provide expected follow-up treatment for an ED patient, they could be charged with abandonment, which is a matter of state law and involves filing a malpractice lawsuit.
Abandonment involves unilaterally terminating the patient relationship without providing notice. There must be an established relationship, which, in the case of call, is formed when the doctor comes to the ED to examine or admit the patient, Dr. Bitterman said. He added that the on-call doctor’s obligation applies only to the medical condition the patient came in for.
Even when an on-call doctor does not see a patient, a relationship can be established if the hospital requires its on-call doctors to make follow-up visits for ED patients, Dr. Taylor said. At some hospitals, he said, on-call doctors have blanket agreements to provide follow-up care in return for not having to arrive in the middle of the night during the ED visit.
Dr. Taylor gave an example of the on-call doctor’s obligation: “The ED doctor puts a splint on the patient’s ankle fracture, and the orthopedic surgeon on call agrees to follow up with the patient within the next few days. If the orthopedic surgeon refuses to follow up without making a reasonable accommodation, it may become an issue of patient abandonment.”
Now everyone has a good grasp of the rules
Fifteen years ago, many doctors were in open revolt against on-call duties, but they are more accepting now and understand the rules better, Mr. Healey said.
“Many hospitals have begun paying some specialists for call and designating hospitalists and surgicalists to do at least some of the work that used to be expected of on-call doctors,” he said.
According to Dr. Taylor, today’s on-call doctors often have less to do than in the past. “For example,” he said, “the hospitalist may admit an orthopedic patient at night, and then the orthopedic surgeon does the operation the next day. We’ve had EMTALA for 36 years now, and hospitals and doctors know how call works.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Syphilis screening: Who and when
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) published updated recommendations on screening for syphilis on September 27.1 The Task Force continues to recommend screening for all adolescents and adults who are at increased risk for infection. (As part of previous recommendations, the USPSTF also advocates screening all pregnant women for syphilis early in their pregnancy to prevent congenital syphilis.2)
Who is at increased risk? Men who have sex with men (MSM), those with HIV or other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), those who use illicit drugs, and those with a history of incarceration, sex work, or military service are considered to be at increased risk for syphilis. Additionally, since state and local health departments collect and publish STI incidence data, it’s important to stay up to date on how common syphilis is in one’s community and tailor screening practices accordingly.
Men account for more than 80% of all primary and secondary syphilis infections, and MSM account for 53% of cases in men.3 The highest rates of syphilis are in men ages 25-29 years and 30-34 years (58.1 and 55.7 cases per 100,000, respectively).3
Why screening is important. Primary and secondary syphilis rates have increased steadily from an all-time low of 2.1 per 100,000 in 2000 to 12.7 per 100,000 in 2020.4 There were 171,074 cases reported in 2021.5
If not detected and treated, syphilis will progress from the primary and secondary stages to a latent form. About one-third of those with latent syphilis will develop tertiary syphilis, which can affect every organ system and cause multiple neurologic disorders.
How to screen. Syphilis screening typically involves a 2-step process. The first test that should be performed is a Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) or rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. This is followed by a treponemal antibody test if the initial test is positive. While the VDRL and RPR tests have high sensitivity, many other conditions can cause a false-positive result, necessitating confirmation with the more specific antibody test.
As far as frequency, the Task Force suggests screening annually for those at continued risk and more frequently (every 3 or 6 months) for those at highest risk.
Treatment for primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis (< 1 year’s duration) is a single intramuscular (IM) injection of benzathine penicillin, 2.4 million units. For late latent syphilis or syphilis of unknown duration, treatment is benzathine penicillin, 2.4 million units, administered in 3 weekly IM doses.
Treatment for those with penicillin allergies depends on the stage of syphilis and whether or not the patient is pregnant. Refer to the STD treatment guidelines for guidance.6
The CDC recommends presumptive treatment for anyone who has had sexual contact in the past 90 days with a person who’s been given a diagnosis of primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis.6
And finally, remember that all STIs are reportable to your local health department, which can assist with contract tracing and treatment follow-up.
1. USPSTF. Syphilis infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults: Screening. Final recommendation statement. September 27, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/syphilis-infection-nonpregnant-adults-adolescents-screening
2. USPSTF. Syphilis infection in pregnant women: screening. Final recommendation statement. September 4, 2018. Accessed October 25, 2022. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/syphilis-infection-in-pregnancy-screening
3. CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020: syphilis. Updated August 22, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/figures/2020-STD-Surveillance-Syphilis.pptx
4. CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020. Table 1: Sexually transmitted diseases—reported cases and rates of reported cases, United States, 1941-2020. Updated April 12, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/tables/1.htm
5. CDC. Preliminary 2021 STD surveillance data. Updated September 1, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2021/default.htm
6. Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recommend Rep. 2021;70:1-187.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) published updated recommendations on screening for syphilis on September 27.1 The Task Force continues to recommend screening for all adolescents and adults who are at increased risk for infection. (As part of previous recommendations, the USPSTF also advocates screening all pregnant women for syphilis early in their pregnancy to prevent congenital syphilis.2)
Who is at increased risk? Men who have sex with men (MSM), those with HIV or other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), those who use illicit drugs, and those with a history of incarceration, sex work, or military service are considered to be at increased risk for syphilis. Additionally, since state and local health departments collect and publish STI incidence data, it’s important to stay up to date on how common syphilis is in one’s community and tailor screening practices accordingly.
Men account for more than 80% of all primary and secondary syphilis infections, and MSM account for 53% of cases in men.3 The highest rates of syphilis are in men ages 25-29 years and 30-34 years (58.1 and 55.7 cases per 100,000, respectively).3
Why screening is important. Primary and secondary syphilis rates have increased steadily from an all-time low of 2.1 per 100,000 in 2000 to 12.7 per 100,000 in 2020.4 There were 171,074 cases reported in 2021.5
If not detected and treated, syphilis will progress from the primary and secondary stages to a latent form. About one-third of those with latent syphilis will develop tertiary syphilis, which can affect every organ system and cause multiple neurologic disorders.
How to screen. Syphilis screening typically involves a 2-step process. The first test that should be performed is a Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) or rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. This is followed by a treponemal antibody test if the initial test is positive. While the VDRL and RPR tests have high sensitivity, many other conditions can cause a false-positive result, necessitating confirmation with the more specific antibody test.
As far as frequency, the Task Force suggests screening annually for those at continued risk and more frequently (every 3 or 6 months) for those at highest risk.
Treatment for primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis (< 1 year’s duration) is a single intramuscular (IM) injection of benzathine penicillin, 2.4 million units. For late latent syphilis or syphilis of unknown duration, treatment is benzathine penicillin, 2.4 million units, administered in 3 weekly IM doses.
Treatment for those with penicillin allergies depends on the stage of syphilis and whether or not the patient is pregnant. Refer to the STD treatment guidelines for guidance.6
The CDC recommends presumptive treatment for anyone who has had sexual contact in the past 90 days with a person who’s been given a diagnosis of primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis.6
And finally, remember that all STIs are reportable to your local health department, which can assist with contract tracing and treatment follow-up.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) published updated recommendations on screening for syphilis on September 27.1 The Task Force continues to recommend screening for all adolescents and adults who are at increased risk for infection. (As part of previous recommendations, the USPSTF also advocates screening all pregnant women for syphilis early in their pregnancy to prevent congenital syphilis.2)
Who is at increased risk? Men who have sex with men (MSM), those with HIV or other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), those who use illicit drugs, and those with a history of incarceration, sex work, or military service are considered to be at increased risk for syphilis. Additionally, since state and local health departments collect and publish STI incidence data, it’s important to stay up to date on how common syphilis is in one’s community and tailor screening practices accordingly.
Men account for more than 80% of all primary and secondary syphilis infections, and MSM account for 53% of cases in men.3 The highest rates of syphilis are in men ages 25-29 years and 30-34 years (58.1 and 55.7 cases per 100,000, respectively).3
Why screening is important. Primary and secondary syphilis rates have increased steadily from an all-time low of 2.1 per 100,000 in 2000 to 12.7 per 100,000 in 2020.4 There were 171,074 cases reported in 2021.5
If not detected and treated, syphilis will progress from the primary and secondary stages to a latent form. About one-third of those with latent syphilis will develop tertiary syphilis, which can affect every organ system and cause multiple neurologic disorders.
How to screen. Syphilis screening typically involves a 2-step process. The first test that should be performed is a Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) or rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test. This is followed by a treponemal antibody test if the initial test is positive. While the VDRL and RPR tests have high sensitivity, many other conditions can cause a false-positive result, necessitating confirmation with the more specific antibody test.
As far as frequency, the Task Force suggests screening annually for those at continued risk and more frequently (every 3 or 6 months) for those at highest risk.
Treatment for primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis (< 1 year’s duration) is a single intramuscular (IM) injection of benzathine penicillin, 2.4 million units. For late latent syphilis or syphilis of unknown duration, treatment is benzathine penicillin, 2.4 million units, administered in 3 weekly IM doses.
Treatment for those with penicillin allergies depends on the stage of syphilis and whether or not the patient is pregnant. Refer to the STD treatment guidelines for guidance.6
The CDC recommends presumptive treatment for anyone who has had sexual contact in the past 90 days with a person who’s been given a diagnosis of primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis.6
And finally, remember that all STIs are reportable to your local health department, which can assist with contract tracing and treatment follow-up.
1. USPSTF. Syphilis infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults: Screening. Final recommendation statement. September 27, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/syphilis-infection-nonpregnant-adults-adolescents-screening
2. USPSTF. Syphilis infection in pregnant women: screening. Final recommendation statement. September 4, 2018. Accessed October 25, 2022. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/syphilis-infection-in-pregnancy-screening
3. CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020: syphilis. Updated August 22, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/figures/2020-STD-Surveillance-Syphilis.pptx
4. CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020. Table 1: Sexually transmitted diseases—reported cases and rates of reported cases, United States, 1941-2020. Updated April 12, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/tables/1.htm
5. CDC. Preliminary 2021 STD surveillance data. Updated September 1, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2021/default.htm
6. Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recommend Rep. 2021;70:1-187.
1. USPSTF. Syphilis infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults: Screening. Final recommendation statement. September 27, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/syphilis-infection-nonpregnant-adults-adolescents-screening
2. USPSTF. Syphilis infection in pregnant women: screening. Final recommendation statement. September 4, 2018. Accessed October 25, 2022. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/syphilis-infection-in-pregnancy-screening
3. CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020: syphilis. Updated August 22, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/figures/2020-STD-Surveillance-Syphilis.pptx
4. CDC. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2020. Table 1: Sexually transmitted diseases—reported cases and rates of reported cases, United States, 1941-2020. Updated April 12, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2020/tables/1.htm
5. CDC. Preliminary 2021 STD surveillance data. Updated September 1, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2022. www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2021/default.htm
6. Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recommend Rep. 2021;70:1-187.