User login
Topical prebiotics and postbiotics effective and well tolerated in mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: A topical formulation containing a mixture of prebiotics and postbiotics was effective and well tolerated in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: After 15 weeks, the SCORing AD index (−59.2%; P < .001) and the PRURISCORE (−64.1%; P < .001) reduced significantly, with 68.0% of patients reporting the tolerability of the drug as “very good” or “excellent.”
Study details: Findings are from a study including 396 patients with mild or moderate AD who received a topical formulation containing a mixture of prebiotics and postbiotics.
Disclosures: This work was supported by the Istituto Ganassini di Ricerche Biochimiche, Italy. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gelmetti C et al. Topical prebiotics/postbiotics and PRURISCORE validation in atopic dermatitis. International study of 396 patients. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 (Oct 17). Doi: 10.1080/09546634.2022.2131703
Key clinical point: A topical formulation containing a mixture of prebiotics and postbiotics was effective and well tolerated in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: After 15 weeks, the SCORing AD index (−59.2%; P < .001) and the PRURISCORE (−64.1%; P < .001) reduced significantly, with 68.0% of patients reporting the tolerability of the drug as “very good” or “excellent.”
Study details: Findings are from a study including 396 patients with mild or moderate AD who received a topical formulation containing a mixture of prebiotics and postbiotics.
Disclosures: This work was supported by the Istituto Ganassini di Ricerche Biochimiche, Italy. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gelmetti C et al. Topical prebiotics/postbiotics and PRURISCORE validation in atopic dermatitis. International study of 396 patients. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 (Oct 17). Doi: 10.1080/09546634.2022.2131703
Key clinical point: A topical formulation containing a mixture of prebiotics and postbiotics was effective and well tolerated in patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: After 15 weeks, the SCORing AD index (−59.2%; P < .001) and the PRURISCORE (−64.1%; P < .001) reduced significantly, with 68.0% of patients reporting the tolerability of the drug as “very good” or “excellent.”
Study details: Findings are from a study including 396 patients with mild or moderate AD who received a topical formulation containing a mixture of prebiotics and postbiotics.
Disclosures: This work was supported by the Istituto Ganassini di Ricerche Biochimiche, Italy. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gelmetti C et al. Topical prebiotics/postbiotics and PRURISCORE validation in atopic dermatitis. International study of 396 patients. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022 (Oct 17). Doi: 10.1080/09546634.2022.2131703
Atopic dermatitis patients with good clinical response or conjunctivitis may opt for longer dupilumab dosing interval
Key clinical point: A longer dupilumab dosing interval might be a good treatment option for patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) who have achieved good clinical response (GCR) or report treatment-related conjunctivitis with a previous dupilumab treatment (600 mg followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks).
Major finding: In the GCR group, the mean Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was 28.22, which reduced significantly to 0.44 among patients receiving dupilumab once every 3 weeks (Q3W) and to 0.19 among patients receiving dupilumab once every 4 weeks (Q4W) after >60 weeks (both P < .0001). EASI improved after 18 weeks in the treatment-resistant conjunctivitis group (P < .0001).
Study details: Findings are retrospectively collected data of 59 adult patients with AD who implemented Q3W (84.75%) or Q4W (15.25%) dupilumab dosing interval due to GCR or conjunctivitis.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared serving as speakers, investigators, consultants, or advisory board members, or receiving personal fees from several sources.
Source: Patruno C et al. Dupilumab dose spacing after initial successful treatment or adverse events in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: A retrospective analysis. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 13). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15933
Key clinical point: A longer dupilumab dosing interval might be a good treatment option for patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) who have achieved good clinical response (GCR) or report treatment-related conjunctivitis with a previous dupilumab treatment (600 mg followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks).
Major finding: In the GCR group, the mean Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was 28.22, which reduced significantly to 0.44 among patients receiving dupilumab once every 3 weeks (Q3W) and to 0.19 among patients receiving dupilumab once every 4 weeks (Q4W) after >60 weeks (both P < .0001). EASI improved after 18 weeks in the treatment-resistant conjunctivitis group (P < .0001).
Study details: Findings are retrospectively collected data of 59 adult patients with AD who implemented Q3W (84.75%) or Q4W (15.25%) dupilumab dosing interval due to GCR or conjunctivitis.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared serving as speakers, investigators, consultants, or advisory board members, or receiving personal fees from several sources.
Source: Patruno C et al. Dupilumab dose spacing after initial successful treatment or adverse events in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: A retrospective analysis. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 13). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15933
Key clinical point: A longer dupilumab dosing interval might be a good treatment option for patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) who have achieved good clinical response (GCR) or report treatment-related conjunctivitis with a previous dupilumab treatment (600 mg followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks).
Major finding: In the GCR group, the mean Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was 28.22, which reduced significantly to 0.44 among patients receiving dupilumab once every 3 weeks (Q3W) and to 0.19 among patients receiving dupilumab once every 4 weeks (Q4W) after >60 weeks (both P < .0001). EASI improved after 18 weeks in the treatment-resistant conjunctivitis group (P < .0001).
Study details: Findings are retrospectively collected data of 59 adult patients with AD who implemented Q3W (84.75%) or Q4W (15.25%) dupilumab dosing interval due to GCR or conjunctivitis.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared serving as speakers, investigators, consultants, or advisory board members, or receiving personal fees from several sources.
Source: Patruno C et al. Dupilumab dose spacing after initial successful treatment or adverse events in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: A retrospective analysis. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 13). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15933
Long-term efficacy of baricitinib in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: Baricitinib demonstrated long-term (52 weeks) efficacy in reducing disease severity in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: At week 52, >45% of patients achieved ≥75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), with a mean improvement of 56.8 points in the total EASI score.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3, BREEZE-AD5 study including 146 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were assigned to receive 2 mg baricitinib, of which 98 patients participated in the open-label extension, BREEZE-AD6 study.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company, under license from Incyte Corporation. Five authors declared being employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly, and the other authors reported ties with several sources, including Eli Lily.
Source: Simpson E et al. Baricitinib 2 mg for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in North America: Long-term efficacy and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15954
Key clinical point: Baricitinib demonstrated long-term (52 weeks) efficacy in reducing disease severity in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: At week 52, >45% of patients achieved ≥75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), with a mean improvement of 56.8 points in the total EASI score.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3, BREEZE-AD5 study including 146 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were assigned to receive 2 mg baricitinib, of which 98 patients participated in the open-label extension, BREEZE-AD6 study.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company, under license from Incyte Corporation. Five authors declared being employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly, and the other authors reported ties with several sources, including Eli Lily.
Source: Simpson E et al. Baricitinib 2 mg for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in North America: Long-term efficacy and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15954
Key clinical point: Baricitinib demonstrated long-term (52 weeks) efficacy in reducing disease severity in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: At week 52, >45% of patients achieved ≥75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), with a mean improvement of 56.8 points in the total EASI score.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3, BREEZE-AD5 study including 146 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were assigned to receive 2 mg baricitinib, of which 98 patients participated in the open-label extension, BREEZE-AD6 study.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company, under license from Incyte Corporation. Five authors declared being employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly, and the other authors reported ties with several sources, including Eli Lily.
Source: Simpson E et al. Baricitinib 2 mg for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in North America: Long-term efficacy and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15954
Long-term efficacy of baricitinib in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
Key clinical point: Baricitinib demonstrated long-term (52 weeks) efficacy in reducing disease severity in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: At week 52, >45% of patients achieved ≥75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), with a mean improvement of 56.8 points in the total EASI score.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3, BREEZE-AD5 study including 146 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were assigned to receive 2 mg baricitinib, of which 98 patients participated in the open-label extension, BREEZE-AD6 study.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company, under license from Incyte Corporation. Five authors declared being employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly, and the other authors reported ties with several sources, including Eli Lily.
Source: Simpson E et al. Baricitinib 2 mg for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in North America: Long-term efficacy and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15954
Key clinical point: Baricitinib demonstrated long-term (52 weeks) efficacy in reducing disease severity in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: At week 52, >45% of patients achieved ≥75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), with a mean improvement of 56.8 points in the total EASI score.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3, BREEZE-AD5 study including 146 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were assigned to receive 2 mg baricitinib, of which 98 patients participated in the open-label extension, BREEZE-AD6 study.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company, under license from Incyte Corporation. Five authors declared being employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly, and the other authors reported ties with several sources, including Eli Lily.
Source: Simpson E et al. Baricitinib 2 mg for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in North America: Long-term efficacy and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15954
Key clinical point: Baricitinib demonstrated long-term (52 weeks) efficacy in reducing disease severity in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD).
Major finding: At week 52, >45% of patients achieved ≥75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), with a mean improvement of 56.8 points in the total EASI score.
Study details: Findings are from the phase 3, BREEZE-AD5 study including 146 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who were assigned to receive 2 mg baricitinib, of which 98 patients participated in the open-label extension, BREEZE-AD6 study.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Eli Lilly and Company, under license from Incyte Corporation. Five authors declared being employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly, and the other authors reported ties with several sources, including Eli Lily.
Source: Simpson E et al. Baricitinib 2 mg for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in North America: Long-term efficacy and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Ther. 2022 (Oct 21). Doi: 10.1111/dth.15954
Moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: No increased infection risk with long-term dupilumab use
Key clinical point: In patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD), continuous long-term dupilumab treatment was not associated with an increased risk for overall systemic/cutaneous infections.
Major finding: At 4 years, the overall infection rate was 71.27 number of patients with ≥1 event per 100 patient-years (nP/100 PY), with most infections being mild to moderate in severity, and only a very small number of infections resulted in treatment discontinuation (0.34 nP/100 PY). The rate of total skin infections decreased from 28.10 to 11.48 nP/100 PY from week 16 to year 4.
Study details: Findings are from the analysis of the LIBERTY AD OLE study including 2677 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received dupilumab, of which 13.1% completed treatment up to week 204.
Disclosures: This research was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Three authors declared being employees or holding stock options in Sanofi. The other authors reported ties with several sources, including Regeneron and Sanofi.
Source: Blauvelt A et al. No increased risk of overall infection in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated for up to 4 years with dupilumab. Adv Ther. 2022 (Nov 1). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02322-y
Key clinical point: In patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD), continuous long-term dupilumab treatment was not associated with an increased risk for overall systemic/cutaneous infections.
Major finding: At 4 years, the overall infection rate was 71.27 number of patients with ≥1 event per 100 patient-years (nP/100 PY), with most infections being mild to moderate in severity, and only a very small number of infections resulted in treatment discontinuation (0.34 nP/100 PY). The rate of total skin infections decreased from 28.10 to 11.48 nP/100 PY from week 16 to year 4.
Study details: Findings are from the analysis of the LIBERTY AD OLE study including 2677 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received dupilumab, of which 13.1% completed treatment up to week 204.
Disclosures: This research was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Three authors declared being employees or holding stock options in Sanofi. The other authors reported ties with several sources, including Regeneron and Sanofi.
Source: Blauvelt A et al. No increased risk of overall infection in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated for up to 4 years with dupilumab. Adv Ther. 2022 (Nov 1). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02322-y
Key clinical point: In patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD), continuous long-term dupilumab treatment was not associated with an increased risk for overall systemic/cutaneous infections.
Major finding: At 4 years, the overall infection rate was 71.27 number of patients with ≥1 event per 100 patient-years (nP/100 PY), with most infections being mild to moderate in severity, and only a very small number of infections resulted in treatment discontinuation (0.34 nP/100 PY). The rate of total skin infections decreased from 28.10 to 11.48 nP/100 PY from week 16 to year 4.
Study details: Findings are from the analysis of the LIBERTY AD OLE study including 2677 patients with moderate-to-severe AD who received dupilumab, of which 13.1% completed treatment up to week 204.
Disclosures: This research was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Three authors declared being employees or holding stock options in Sanofi. The other authors reported ties with several sources, including Regeneron and Sanofi.
Source: Blauvelt A et al. No increased risk of overall infection in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis treated for up to 4 years with dupilumab. Adv Ther. 2022 (Nov 1). Doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02322-y
Exposure to wildfire air pollution increases atopic dermatitis risk in older adults
Key clinical point: Air pollution due to a wildfire increased the rate of clinic visits for atopic dermatitis (AD), especially at a 0-week lag, in adults aged ≥65 years.
Major finding: In adults aged ≥65 years, the adjusted rate of clinic visits for AD during a week with a wildfire was 1.4 (95% CI 1.1-1.9) times the rate during weeks without wildfire and every 1-unit increase in the mean weekly smoke plume density score increased the rate of clinic visits for AD by 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6) times.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of outpatient dermatology visits for AD (5529 visits) and itch (1319 visits).
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. Dr. Grimes declared receiving grants from the University of California, San Francisco.
Source: Fadadu RP et al. Association of exposure to wildfire air pollution with exacerbations of atopic dermatitis and itch among older adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2238594 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38594
Key clinical point: Air pollution due to a wildfire increased the rate of clinic visits for atopic dermatitis (AD), especially at a 0-week lag, in adults aged ≥65 years.
Major finding: In adults aged ≥65 years, the adjusted rate of clinic visits for AD during a week with a wildfire was 1.4 (95% CI 1.1-1.9) times the rate during weeks without wildfire and every 1-unit increase in the mean weekly smoke plume density score increased the rate of clinic visits for AD by 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6) times.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of outpatient dermatology visits for AD (5529 visits) and itch (1319 visits).
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. Dr. Grimes declared receiving grants from the University of California, San Francisco.
Source: Fadadu RP et al. Association of exposure to wildfire air pollution with exacerbations of atopic dermatitis and itch among older adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2238594 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38594
Key clinical point: Air pollution due to a wildfire increased the rate of clinic visits for atopic dermatitis (AD), especially at a 0-week lag, in adults aged ≥65 years.
Major finding: In adults aged ≥65 years, the adjusted rate of clinic visits for AD during a week with a wildfire was 1.4 (95% CI 1.1-1.9) times the rate during weeks without wildfire and every 1-unit increase in the mean weekly smoke plume density score increased the rate of clinic visits for AD by 1.3 (95% CI 1.1-1.6) times.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of outpatient dermatology visits for AD (5529 visits) and itch (1319 visits).
Disclosures: This study did not report the source of funding. Dr. Grimes declared receiving grants from the University of California, San Francisco.
Source: Fadadu RP et al. Association of exposure to wildfire air pollution with exacerbations of atopic dermatitis and itch among older adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2238594 (Oct 26). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38594
Atopic dermatitis: Dupilumab serum levels not associated with treatment response or adverse effects
Key clinical point: In patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), serum dupilumab levels at week 16 were not associated with treatment response or adverse effects due to dupilumab during the first year of treatment.
Major finding: Serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks were not associated with the prediction of treatment response at 52 weeks (≥90% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index; odds ratio [OR] 0.96; P = .34) or adverse events during the first year of treatment (OR 1.01; P = .83).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective clinical cohort study including 295 patients with AD who started dupilumab and had treatment week 16 serum samples available.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and other sources. The authors declared receiving consulting fees, speaking fees, investigator fees, or research funding from several sources.
Source: Spekhorst LS et al. Association of serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks with treatment response and adverse effects in patients with atopic dermatitis: A prospective clinical cohort study from the BioDay registry. JAMA Dermatol. 2022 (Nov 2). Doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.4639
Key clinical point: In patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), serum dupilumab levels at week 16 were not associated with treatment response or adverse effects due to dupilumab during the first year of treatment.
Major finding: Serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks were not associated with the prediction of treatment response at 52 weeks (≥90% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index; odds ratio [OR] 0.96; P = .34) or adverse events during the first year of treatment (OR 1.01; P = .83).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective clinical cohort study including 295 patients with AD who started dupilumab and had treatment week 16 serum samples available.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and other sources. The authors declared receiving consulting fees, speaking fees, investigator fees, or research funding from several sources.
Source: Spekhorst LS et al. Association of serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks with treatment response and adverse effects in patients with atopic dermatitis: A prospective clinical cohort study from the BioDay registry. JAMA Dermatol. 2022 (Nov 2). Doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.4639
Key clinical point: In patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), serum dupilumab levels at week 16 were not associated with treatment response or adverse effects due to dupilumab during the first year of treatment.
Major finding: Serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks were not associated with the prediction of treatment response at 52 weeks (≥90% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index; odds ratio [OR] 0.96; P = .34) or adverse events during the first year of treatment (OR 1.01; P = .83).
Study details: Findings are from a prospective clinical cohort study including 295 patients with AD who started dupilumab and had treatment week 16 serum samples available.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and other sources. The authors declared receiving consulting fees, speaking fees, investigator fees, or research funding from several sources.
Source: Spekhorst LS et al. Association of serum dupilumab levels at 16 weeks with treatment response and adverse effects in patients with atopic dermatitis: A prospective clinical cohort study from the BioDay registry. JAMA Dermatol. 2022 (Nov 2). Doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.4639
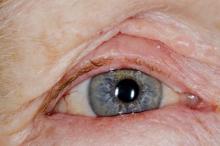
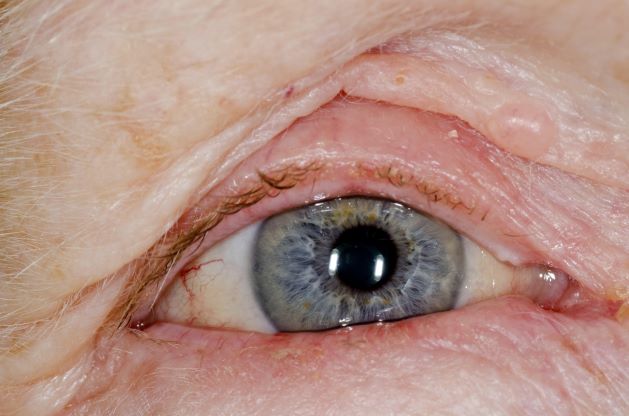
Red swollen eyelids
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's symptoms are consistent with a diagnosis of blepharitis.
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelids that is frequently associated with bacterial colonization of the eyelid. Anatomically, it can be categorized as anterior blepharitis or posterior blepharitis. Anterior blepharitis refers to inflammation primarily positioned around the skin, eyelashes, and lash follicles and is usually further divided into staphylococcal and seborrheic variants. Posterior blepharitis involves the meibomian gland orifices, meibomian glands, tarsal plate, and blepharo-conjunctival junction.
Blepharitis can be acute or chronic. It is frequently associated with systemic diseases, such as rosacea, atopy, and seborrheic dermatitis, as well as ocular diseases, such as dry eye syndromes, chalazion, trichiasis, ectropion and entropion, infectious or other inflammatory conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Moreover, high rates of blepharitis have been reported in patients treated with dupilumab for atopic dermatitis.
Eye irritation, itching, erythema of the lids, flaking of the lid margins, and/or changes in the eyelashes are common presenting symptoms in patients with blepharitis. Other symptoms may include:
• Burning
• Watering
• Foreign-body sensation
• Crusting and mattering of the lashes and medial canthus
• Red lids
• Red eyes
• Photophobia
• Pain
• Decreased vision
• Visual fluctuations
• Heat, cold, alcohol, and spicy-food intolerance
The differential diagnosis for blepharitis includes bacterial keratitis, which is a serious ocular disorder that can lead to vision loss if not properly treated. Bacterial keratitis progresses rapidly and can result in corneal destruction within 24-48 hours with some particularly virulent bacteria. Patients with bacterial keratitis typically report rapid onset of pain, photophobia, and decreased vision.
Ocular rosacea should also be considered in the differential diagnosis of blepharitis, and the two conditions can co-occur. Patients with ocular rosacea may experience facial symptoms (eg, recurrent flushing episodes, persistent and/or recurrent midfacial erythema, papular and pustular lesions) in addition to ocular symptoms, which can range from minor irritation, foreign-body sensation, and blurry vision to severe ocular surface disruption and inflammatory keratitis.
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva, whereas blepharitis involves inflammation of the eyelids only. Other conditions to consider in the diagnosis of blepharitis can be found here.
Given the unprecedented efficacy seen in clinical trials, dupilumab is emerging as a first-line therapeutic for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. However, clinicians should be alert to ocular complications among their patients with atopic dermatitis who are being treated with dupilumab. In some patients, this may be because of preexisting meibomian gland disease and ocular surface disease. After a diagnosis of ocular complications, the continued use of dupilumab should be jointly evaluated by the ophthalmologist and dermatologist or allergist on the basis of the ocular risk vs systemic benefit. Treatment for blepharitis typically includes strict eyelid hygiene and topical antibiotic ointment; oral antibiotics can be beneficial for refractory disease.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 71-year-old woman was referred for an ophthalmologic examination by her dermatologist. The patient reports recent onset of red, swollen eyelids; ocular itching; and a burning sensation. Prior medical history includes severe atopic dermatitis, type 2 diabetes, and osteoarthritis. Current medications include metformin 1000 mg/d, celecoxib 200 mg/d, and clobetasol propionate 0.05% cream twice daily. The patient began receiving subcutaneous dupilumab 300 mg/once every 2 weeks about 6 weeks earlier.
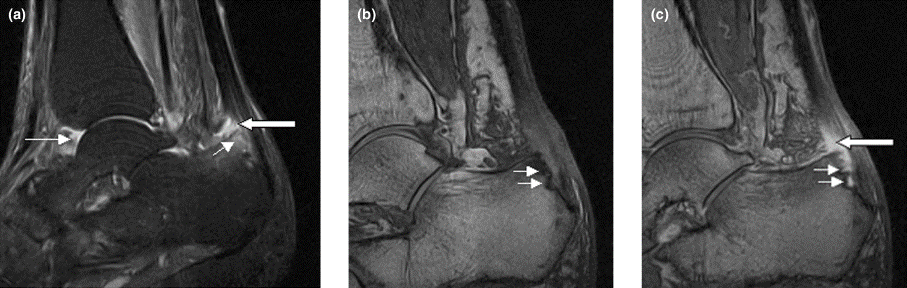
Right ankle pain and swelling
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of psoriatic enthesitis.
Enthesitis is a hallmark manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis are estimated to be affected by PsA, which belongs to the spondyloarthritis (SpA) family of inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
An enthesis is an attachment site of ligaments, tendons, and joint capsules to bone and is a key inflammatory target in SpA. It is a complex structure that dissipates biomechanical stress to preserve homeostasis. Entheses are anatomically and functionally integrated with bursa, fibrocartilage, and synovium in a synovial entheseal complex; biomechanical stress in this area may trigger inflammation. Enthesitis is an early manifestation of PsA that has been associated with radiographic peripheral/axial joint damage and severe disease, as well as reduced quality of life.
Enthesitis can be difficult to diagnose in clinical practice. Symptoms include tenderness, soreness, and pain at entheses on palpation, often without overt clinical evidence of inflammation. In contrast, dactylitis, another hallmark manifestation of PsA, can be recognized by swelling of an entire digit that is different from adjacent digits. Fibromyalgia frequently coexists with enthesitis, and it can be difficult to distinguish the two given the anatomic overlap between the tender points of fibromyalgia and many entheseal sites. Long-lasting morning stiffness and a sustained response to a course of steroids is more suggestive of enthesitis, whereas a higher number of somatoform symptoms is more suggestive of fibromyalgia.
Enthesitis is included in the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) as a hallmark of PsA. While it can be diagnosed clinically, imaging studies may be required, particularly in patients in whom symptoms may be difficult to discern. Evidence of enthesitis by conventional radiography includes bone cortex irregularities, erosions, entheseal soft tissue calcifications, and new bone formation; however, entheseal bone changes detected with conventional radiography appear relatively late in the disease process. Ultrasound is highly sensitive for assessing inflammation and can detect various features of enthesitis, such as increased thickness of tendon insertion, hypoechogenicity, erosions, enthesophytes, and subclinical enthesitis in people with PsA. MRI has the advantage of identifying perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema. Fat-suppressed MRI with or without gadolinium enhancement is a highly sensitive method for visualizing active enthesitis and can identify perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema.
Delayed treatment of PsA can result in irreversible joint damage and reduced quality of life; thus, patients with psoriasis should be closely monitored for early signs of its development, such as enthesitis. A thorough evaluation of the key clinical features of PsA (psoriasis, arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and spondylitis), including evaluation of severity of each feature and impact on physical function and quality of life, is encouraged at each clinical encounter. Because patients may not understand the link between psoriasis and joint pain, specific probing questions can be helpful. Screening questionnaires to detect early signs and symptoms of PsA are available, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST), Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation (PASE) questionnaire, and Toronto Psoriatic Arthritis Screening (ToPAS) questionnaire. These and many others may be used to help dermatologists detect early signs and symptoms of PsA. Although these questionnaires all have limitations in sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PsA, their use can still improve early diagnosis.
The treatment of PsA focuses on achieving the least amount of disease activity and inflammation possible; optimizing functional status, quality of life, and well-being; and preventing structural damage. Treatment decisions are based on the specific domains affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections are first-line treatments for enthesitis. Early use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF) (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, infliximab, and golimumab) is recommended. Alternative biologic disease-modifying agents are indicated when these TNF inhibitors provide an inadequate response. They include ustekinumab (dual interleukin [IL]-12 and IL-23 inhibitor), secukinumab (IL-17A inhibitor), and apremilast (phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor) and may be considered for patients with predominantly entheseal manifestations of PsA or dactylitis. Biological disease-modifying agents approved for PsA that have shown efficacy for enthesitis include ixekizumab (which targets IL-17A), abatacept (a T-cell inhibitor), guselkumab (monoclonal antibody), and ustekinumab (monoclonal antibody). Tofacitinib and upadacitinib, both oral Janus kinase inhibitors, may also be considered.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of psoriatic enthesitis.
Enthesitis is a hallmark manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis are estimated to be affected by PsA, which belongs to the spondyloarthritis (SpA) family of inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
An enthesis is an attachment site of ligaments, tendons, and joint capsules to bone and is a key inflammatory target in SpA. It is a complex structure that dissipates biomechanical stress to preserve homeostasis. Entheses are anatomically and functionally integrated with bursa, fibrocartilage, and synovium in a synovial entheseal complex; biomechanical stress in this area may trigger inflammation. Enthesitis is an early manifestation of PsA that has been associated with radiographic peripheral/axial joint damage and severe disease, as well as reduced quality of life.
Enthesitis can be difficult to diagnose in clinical practice. Symptoms include tenderness, soreness, and pain at entheses on palpation, often without overt clinical evidence of inflammation. In contrast, dactylitis, another hallmark manifestation of PsA, can be recognized by swelling of an entire digit that is different from adjacent digits. Fibromyalgia frequently coexists with enthesitis, and it can be difficult to distinguish the two given the anatomic overlap between the tender points of fibromyalgia and many entheseal sites. Long-lasting morning stiffness and a sustained response to a course of steroids is more suggestive of enthesitis, whereas a higher number of somatoform symptoms is more suggestive of fibromyalgia.
Enthesitis is included in the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) as a hallmark of PsA. While it can be diagnosed clinically, imaging studies may be required, particularly in patients in whom symptoms may be difficult to discern. Evidence of enthesitis by conventional radiography includes bone cortex irregularities, erosions, entheseal soft tissue calcifications, and new bone formation; however, entheseal bone changes detected with conventional radiography appear relatively late in the disease process. Ultrasound is highly sensitive for assessing inflammation and can detect various features of enthesitis, such as increased thickness of tendon insertion, hypoechogenicity, erosions, enthesophytes, and subclinical enthesitis in people with PsA. MRI has the advantage of identifying perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema. Fat-suppressed MRI with or without gadolinium enhancement is a highly sensitive method for visualizing active enthesitis and can identify perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema.
Delayed treatment of PsA can result in irreversible joint damage and reduced quality of life; thus, patients with psoriasis should be closely monitored for early signs of its development, such as enthesitis. A thorough evaluation of the key clinical features of PsA (psoriasis, arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and spondylitis), including evaluation of severity of each feature and impact on physical function and quality of life, is encouraged at each clinical encounter. Because patients may not understand the link between psoriasis and joint pain, specific probing questions can be helpful. Screening questionnaires to detect early signs and symptoms of PsA are available, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST), Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation (PASE) questionnaire, and Toronto Psoriatic Arthritis Screening (ToPAS) questionnaire. These and many others may be used to help dermatologists detect early signs and symptoms of PsA. Although these questionnaires all have limitations in sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PsA, their use can still improve early diagnosis.
The treatment of PsA focuses on achieving the least amount of disease activity and inflammation possible; optimizing functional status, quality of life, and well-being; and preventing structural damage. Treatment decisions are based on the specific domains affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections are first-line treatments for enthesitis. Early use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF) (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, infliximab, and golimumab) is recommended. Alternative biologic disease-modifying agents are indicated when these TNF inhibitors provide an inadequate response. They include ustekinumab (dual interleukin [IL]-12 and IL-23 inhibitor), secukinumab (IL-17A inhibitor), and apremilast (phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor) and may be considered for patients with predominantly entheseal manifestations of PsA or dactylitis. Biological disease-modifying agents approved for PsA that have shown efficacy for enthesitis include ixekizumab (which targets IL-17A), abatacept (a T-cell inhibitor), guselkumab (monoclonal antibody), and ustekinumab (monoclonal antibody). Tofacitinib and upadacitinib, both oral Janus kinase inhibitors, may also be considered.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's findings are consistent with a diagnosis of psoriatic enthesitis.
Enthesitis is a hallmark manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Approximately 30% of patients with psoriasis are estimated to be affected by PsA, which belongs to the spondyloarthritis (SpA) family of inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
An enthesis is an attachment site of ligaments, tendons, and joint capsules to bone and is a key inflammatory target in SpA. It is a complex structure that dissipates biomechanical stress to preserve homeostasis. Entheses are anatomically and functionally integrated with bursa, fibrocartilage, and synovium in a synovial entheseal complex; biomechanical stress in this area may trigger inflammation. Enthesitis is an early manifestation of PsA that has been associated with radiographic peripheral/axial joint damage and severe disease, as well as reduced quality of life.
Enthesitis can be difficult to diagnose in clinical practice. Symptoms include tenderness, soreness, and pain at entheses on palpation, often without overt clinical evidence of inflammation. In contrast, dactylitis, another hallmark manifestation of PsA, can be recognized by swelling of an entire digit that is different from adjacent digits. Fibromyalgia frequently coexists with enthesitis, and it can be difficult to distinguish the two given the anatomic overlap between the tender points of fibromyalgia and many entheseal sites. Long-lasting morning stiffness and a sustained response to a course of steroids is more suggestive of enthesitis, whereas a higher number of somatoform symptoms is more suggestive of fibromyalgia.
Enthesitis is included in the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) as a hallmark of PsA. While it can be diagnosed clinically, imaging studies may be required, particularly in patients in whom symptoms may be difficult to discern. Evidence of enthesitis by conventional radiography includes bone cortex irregularities, erosions, entheseal soft tissue calcifications, and new bone formation; however, entheseal bone changes detected with conventional radiography appear relatively late in the disease process. Ultrasound is highly sensitive for assessing inflammation and can detect various features of enthesitis, such as increased thickness of tendon insertion, hypoechogenicity, erosions, enthesophytes, and subclinical enthesitis in people with PsA. MRI has the advantage of identifying perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema. Fat-suppressed MRI with or without gadolinium enhancement is a highly sensitive method for visualizing active enthesitis and can identify perientheseal inflammation with adjacent bone marrow edema.
Delayed treatment of PsA can result in irreversible joint damage and reduced quality of life; thus, patients with psoriasis should be closely monitored for early signs of its development, such as enthesitis. A thorough evaluation of the key clinical features of PsA (psoriasis, arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and spondylitis), including evaluation of severity of each feature and impact on physical function and quality of life, is encouraged at each clinical encounter. Because patients may not understand the link between psoriasis and joint pain, specific probing questions can be helpful. Screening questionnaires to detect early signs and symptoms of PsA are available, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST), Psoriatic Arthritis Screening and Evaluation (PASE) questionnaire, and Toronto Psoriatic Arthritis Screening (ToPAS) questionnaire. These and many others may be used to help dermatologists detect early signs and symptoms of PsA. Although these questionnaires all have limitations in sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of PsA, their use can still improve early diagnosis.
The treatment of PsA focuses on achieving the least amount of disease activity and inflammation possible; optimizing functional status, quality of life, and well-being; and preventing structural damage. Treatment decisions are based on the specific domains affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroid injections are first-line treatments for enthesitis. Early use of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF) (adalimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept, infliximab, and golimumab) is recommended. Alternative biologic disease-modifying agents are indicated when these TNF inhibitors provide an inadequate response. They include ustekinumab (dual interleukin [IL]-12 and IL-23 inhibitor), secukinumab (IL-17A inhibitor), and apremilast (phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor) and may be considered for patients with predominantly entheseal manifestations of PsA or dactylitis. Biological disease-modifying agents approved for PsA that have shown efficacy for enthesitis include ixekizumab (which targets IL-17A), abatacept (a T-cell inhibitor), guselkumab (monoclonal antibody), and ustekinumab (monoclonal antibody). Tofacitinib and upadacitinib, both oral Janus kinase inhibitors, may also be considered.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 42-year-old woman with a 20-year history of plaque psoriasis presents with complaints of a 3-month history of pain, tenderness, and swelling in her right ankle and foot, of unknown origin. Physical examination reveals active psoriasis, with a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of 6.7 and psoriatic nail dystrophy, including onycholysis, pitting, and hyperkeratosis. Tenderness and swelling are noted at the back of the heel. The patient denies any other complaints. Laboratory tests are normal, including negative rheumatoid factor and antinuclear factor. MRI reveals soft tissue and bone marrow edema below the Achilles insertion.
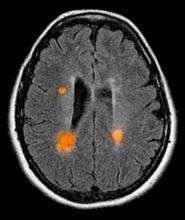
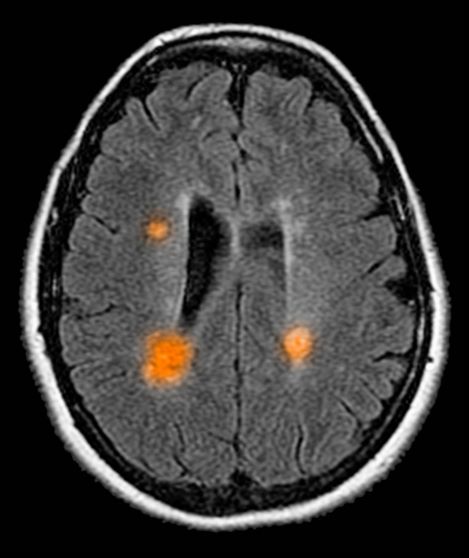
Decline in ambulatory function
Based on this patient's history and presentation, the likely diagnosis is primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). PPMS represents around 10% of MS cases and tends to develop about a decade later than relapsing MS. Unlike other forms of MS, this phenotype progresses steadily instead of in an episodic fashion like relapsing forms of MS. Most patients with PPMS present with gait difficulty because lesions often develop on the spinal cord. While relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is much more common among women than men, men with MS are more likely to have the progressive form.
Although this patient's MRI ultimately points to multiple sclerosis, his functional deficits may initially suggest other conditions in the differential diagnosis. Brainstem gliomas typically manifest in unsteady gait, weakness, double vision, difficulty swallowing, dysarthria, headache, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. Transverse myelitis often presents with rapid-onset weakness, sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. Musculoskeletal and neurologic symptoms are common in Lyme disease. B12 deficiency can present with worsening weakness and a sensory ataxia that can present as balance difficulties, but it would not cause focal lesions on the MRI, nor would it present with bladder symptoms. In addition, the patient's steady decline in function rules out RRMS.
PPMS is diagnosed with confirmation of gradual change in functional ability (often ambulation) over time without remission or relapse. These criteria include 1 full year of worsening neurologic function without asymptomatic periods as well as two of these signs of disease: brain lesion, two or more spinal cord lesions, and oligoclonal bands or elevated Immunoglobulin G index. These timing-specific criteria can delay diagnosis, as seen here.
Ocrelizumab is the only FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy (DMT) proven to alter disease progression in ambulatory patients with PPMS. American Academy of Neurology guidelines recommend ocrelizumab for patients with PPMS who are likely to benefit from this therapy. While it is thought that DMTs are more effective at targeting inflammation in RRMS than nerve degeneration in PPMS, these agents may show benefit for patients with active PPMS (relapse and/or evidence of new MRI activity) rather than inactive disease. A recent PPMS study concluded that among patients with relapse or disease activity, DMTs were associated with a significant reduction of long-term disability risk. Together with immunomodulatory therapy, rehabilitation can help manage symptoms.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on this patient's history and presentation, the likely diagnosis is primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). PPMS represents around 10% of MS cases and tends to develop about a decade later than relapsing MS. Unlike other forms of MS, this phenotype progresses steadily instead of in an episodic fashion like relapsing forms of MS. Most patients with PPMS present with gait difficulty because lesions often develop on the spinal cord. While relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is much more common among women than men, men with MS are more likely to have the progressive form.
Although this patient's MRI ultimately points to multiple sclerosis, his functional deficits may initially suggest other conditions in the differential diagnosis. Brainstem gliomas typically manifest in unsteady gait, weakness, double vision, difficulty swallowing, dysarthria, headache, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. Transverse myelitis often presents with rapid-onset weakness, sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. Musculoskeletal and neurologic symptoms are common in Lyme disease. B12 deficiency can present with worsening weakness and a sensory ataxia that can present as balance difficulties, but it would not cause focal lesions on the MRI, nor would it present with bladder symptoms. In addition, the patient's steady decline in function rules out RRMS.
PPMS is diagnosed with confirmation of gradual change in functional ability (often ambulation) over time without remission or relapse. These criteria include 1 full year of worsening neurologic function without asymptomatic periods as well as two of these signs of disease: brain lesion, two or more spinal cord lesions, and oligoclonal bands or elevated Immunoglobulin G index. These timing-specific criteria can delay diagnosis, as seen here.
Ocrelizumab is the only FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy (DMT) proven to alter disease progression in ambulatory patients with PPMS. American Academy of Neurology guidelines recommend ocrelizumab for patients with PPMS who are likely to benefit from this therapy. While it is thought that DMTs are more effective at targeting inflammation in RRMS than nerve degeneration in PPMS, these agents may show benefit for patients with active PPMS (relapse and/or evidence of new MRI activity) rather than inactive disease. A recent PPMS study concluded that among patients with relapse or disease activity, DMTs were associated with a significant reduction of long-term disability risk. Together with immunomodulatory therapy, rehabilitation can help manage symptoms.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on this patient's history and presentation, the likely diagnosis is primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS). PPMS represents around 10% of MS cases and tends to develop about a decade later than relapsing MS. Unlike other forms of MS, this phenotype progresses steadily instead of in an episodic fashion like relapsing forms of MS. Most patients with PPMS present with gait difficulty because lesions often develop on the spinal cord. While relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is much more common among women than men, men with MS are more likely to have the progressive form.
Although this patient's MRI ultimately points to multiple sclerosis, his functional deficits may initially suggest other conditions in the differential diagnosis. Brainstem gliomas typically manifest in unsteady gait, weakness, double vision, difficulty swallowing, dysarthria, headache, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. Transverse myelitis often presents with rapid-onset weakness, sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. Musculoskeletal and neurologic symptoms are common in Lyme disease. B12 deficiency can present with worsening weakness and a sensory ataxia that can present as balance difficulties, but it would not cause focal lesions on the MRI, nor would it present with bladder symptoms. In addition, the patient's steady decline in function rules out RRMS.
PPMS is diagnosed with confirmation of gradual change in functional ability (often ambulation) over time without remission or relapse. These criteria include 1 full year of worsening neurologic function without asymptomatic periods as well as two of these signs of disease: brain lesion, two or more spinal cord lesions, and oligoclonal bands or elevated Immunoglobulin G index. These timing-specific criteria can delay diagnosis, as seen here.
Ocrelizumab is the only FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy (DMT) proven to alter disease progression in ambulatory patients with PPMS. American Academy of Neurology guidelines recommend ocrelizumab for patients with PPMS who are likely to benefit from this therapy. While it is thought that DMTs are more effective at targeting inflammation in RRMS than nerve degeneration in PPMS, these agents may show benefit for patients with active PPMS (relapse and/or evidence of new MRI activity) rather than inactive disease. A recent PPMS study concluded that among patients with relapse or disease activity, DMTs were associated with a significant reduction of long-term disability risk. Together with immunomodulatory therapy, rehabilitation can help manage symptoms.
Krupa Pandey, MD, Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Department of Neurology & Neuroscience Institute, Hackensack University Medical Center; Neurologist, Department of Neurology, Hackensack Meridian Health, Hackensack, NJ.
Krupa Pandey, MD, has serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Biogen; Alexion; Genentech; Sanofi-Genzyme.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 59-year-old man presents with worsening decline in ambulatory function and worsening bladder function. He reports "difficulty getting around" for the past year and a half, which he theorized might be because of arthritis, aging, or many years of biking. He presented to his primary care physician 2 months ago and was referred to rheumatology. His height is 5 ft 11 in and his weight is 166 lb (BMI 23.1). The patient subsequently reported a decreased attention span to the rheumatologist. He has no other significant medical or surgical history, though his brother has psoriatic arthritis. MRI shows multiple brain lesions without gadolinium enhancement and multiple spinal cord lesions.