User login
Highlights in Diabetes and Metabolism From ASN 2022
Dr Carol Wysham, of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Spokane, reports on key studies looking at glucose-lowering therapies in adults with type 2 diabetes, as presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Dr Wysham first highlights a real-world study evaluating the long-term use of empagliflozin compared with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The researchers used the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) slope as their predictive value for clinical kidney benefit. They found that long-term use of empagliflozin was associated with less impairment of kidney function than DPP-4 inhibitors.
Next, Dr Wysham discusses a study testing the safety of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with both chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Researchers found that in this patient population undergoing routine care, use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with an increased risk for nonvertebral fractures, lower-limb amputations, and genital infections.
Next, Dr Wysham examines a report pooling data from the SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6 studies to determine whether semaglutide improves the eGFR slope. Researchers found that across the A1c and blood pressure subgroups, semaglutide reduced eGFR compared with placebo.
Finally, Dr Wysham discusses an analysis using data from the Framingham Heart Study to determine whether a demonstrable link could be established between kidney disease and mild cognitive impairment. Researchers reported that patients with albuminuria had an increased risk for brain infarctions.
--
Carol Wysham, MD, Clinical Professor of Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine; Clinical Endocrinologist, Rockwood Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology, MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Washington
Carol Wysham, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Endocrine Society; MultiCare Health Systems
Received research grant from: Allergan; Abbott; Corcept; Eli Lilly; Mylan; Novo Nordisk; Regeneron
Dr Carol Wysham, of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Spokane, reports on key studies looking at glucose-lowering therapies in adults with type 2 diabetes, as presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Dr Wysham first highlights a real-world study evaluating the long-term use of empagliflozin compared with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The researchers used the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) slope as their predictive value for clinical kidney benefit. They found that long-term use of empagliflozin was associated with less impairment of kidney function than DPP-4 inhibitors.
Next, Dr Wysham discusses a study testing the safety of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with both chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Researchers found that in this patient population undergoing routine care, use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with an increased risk for nonvertebral fractures, lower-limb amputations, and genital infections.
Next, Dr Wysham examines a report pooling data from the SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6 studies to determine whether semaglutide improves the eGFR slope. Researchers found that across the A1c and blood pressure subgroups, semaglutide reduced eGFR compared with placebo.
Finally, Dr Wysham discusses an analysis using data from the Framingham Heart Study to determine whether a demonstrable link could be established between kidney disease and mild cognitive impairment. Researchers reported that patients with albuminuria had an increased risk for brain infarctions.
--
Carol Wysham, MD, Clinical Professor of Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine; Clinical Endocrinologist, Rockwood Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology, MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Washington
Carol Wysham, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Endocrine Society; MultiCare Health Systems
Received research grant from: Allergan; Abbott; Corcept; Eli Lilly; Mylan; Novo Nordisk; Regeneron
Dr Carol Wysham, of the University of Washington School of Medicine in Spokane, reports on key studies looking at glucose-lowering therapies in adults with type 2 diabetes, as presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
Dr Wysham first highlights a real-world study evaluating the long-term use of empagliflozin compared with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. The researchers used the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) slope as their predictive value for clinical kidney benefit. They found that long-term use of empagliflozin was associated with less impairment of kidney function than DPP-4 inhibitors.
Next, Dr Wysham discusses a study testing the safety of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with both chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Researchers found that in this patient population undergoing routine care, use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with an increased risk for nonvertebral fractures, lower-limb amputations, and genital infections.
Next, Dr Wysham examines a report pooling data from the SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6 studies to determine whether semaglutide improves the eGFR slope. Researchers found that across the A1c and blood pressure subgroups, semaglutide reduced eGFR compared with placebo.
Finally, Dr Wysham discusses an analysis using data from the Framingham Heart Study to determine whether a demonstrable link could be established between kidney disease and mild cognitive impairment. Researchers reported that patients with albuminuria had an increased risk for brain infarctions.
--
Carol Wysham, MD, Clinical Professor of Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine; Clinical Endocrinologist, Rockwood Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology, MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Washington
Carol Wysham, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Endocrine Society; MultiCare Health Systems
Received research grant from: Allergan; Abbott; Corcept; Eli Lilly; Mylan; Novo Nordisk; Regeneron

Product update: HPV assay
BD ONCLARITYTM HPV ASSAY
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://womens-health-solutions.bd.com/
BD ONCLARITYTM HPV ASSAY
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://womens-health-solutions.bd.com/
BD ONCLARITYTM HPV ASSAY
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://womens-health-solutions.bd.com/
Commentary: Evaluating colonoscopy in CRC, December 2022
As usual, several provocative additions to the colorectal cancer literature were published last month, but I will review only one today: the NordICC trial. This trial evaluated the use of screening colonoscopy to reduce the incidence of colorectal cancer, death from colorectal cancer, and all-cause mortality.
We have long accepted that colonoscopy is the gold standard for detection of colorectal cancer, but until the publication of this study there has never been a prospective, randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of the test. Nearly 85,000 men and women from Nordic nations were randomly assigned to receive an invitation for either screening colonoscopy or usual care (ie, no colonoscopy). In the intention-to-screen analysis, colonoscopy reduced the risk for colorectal cancer over a period of 10 years by 18% (relative risk [RR] 0.82; 95% CI 0.70-0.93). However, the reduction in risk for death from colorectal cancer failed to reach statistical significance (RR 0.90; 95% CI 0.64-1.16).
These results were especially disappointing because sigmoidoscopy, a test that evaluates only the rectum and left colon, has been shown in multiple studies to reduce risk for colorectal cancer death and all-cause mortality. It is difficult for me to think of a biologically plausible explanation for colonoscopy to be less effective than sigmoidoscopy in the prevention of cause-specific and all-cause death. However, potential explanations are hidden in the study data. Most glaringly, only 42% of the colonoscopy invitees received a colonoscopy as compared with a much larger percentage of patients (58%-87%) in the sigmoidoscopy trials. While this might be an important real-world data point, it is far less than the estimated 60% of patients in the United States who adhere to the recommendation for screening colonoscopy from ages 45 to 55. Additionally, the study had only 10 years of follow-up. It is possible that this is just not long enough for the benefits of screening colonoscopy to be fully realized. Finally, 29% of endoscopists had an adenoma detection below the recommended threshold of 25%, suggesting that poor colonoscopic technique may have played a role in the limited efficacy of colonoscopy found in the study.
Regardless of what we think of these results, the study was generally well designed and, therefore, very important. Studies like this give us critical information that we, as a nation, need to determine how best to allot our limited healthcare resources. While this study does not change my perception of the efficacy of colonoscopy, it makes me think twice about its societal utility.
As usual, several provocative additions to the colorectal cancer literature were published last month, but I will review only one today: the NordICC trial. This trial evaluated the use of screening colonoscopy to reduce the incidence of colorectal cancer, death from colorectal cancer, and all-cause mortality.
We have long accepted that colonoscopy is the gold standard for detection of colorectal cancer, but until the publication of this study there has never been a prospective, randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of the test. Nearly 85,000 men and women from Nordic nations were randomly assigned to receive an invitation for either screening colonoscopy or usual care (ie, no colonoscopy). In the intention-to-screen analysis, colonoscopy reduced the risk for colorectal cancer over a period of 10 years by 18% (relative risk [RR] 0.82; 95% CI 0.70-0.93). However, the reduction in risk for death from colorectal cancer failed to reach statistical significance (RR 0.90; 95% CI 0.64-1.16).
These results were especially disappointing because sigmoidoscopy, a test that evaluates only the rectum and left colon, has been shown in multiple studies to reduce risk for colorectal cancer death and all-cause mortality. It is difficult for me to think of a biologically plausible explanation for colonoscopy to be less effective than sigmoidoscopy in the prevention of cause-specific and all-cause death. However, potential explanations are hidden in the study data. Most glaringly, only 42% of the colonoscopy invitees received a colonoscopy as compared with a much larger percentage of patients (58%-87%) in the sigmoidoscopy trials. While this might be an important real-world data point, it is far less than the estimated 60% of patients in the United States who adhere to the recommendation for screening colonoscopy from ages 45 to 55. Additionally, the study had only 10 years of follow-up. It is possible that this is just not long enough for the benefits of screening colonoscopy to be fully realized. Finally, 29% of endoscopists had an adenoma detection below the recommended threshold of 25%, suggesting that poor colonoscopic technique may have played a role in the limited efficacy of colonoscopy found in the study.
Regardless of what we think of these results, the study was generally well designed and, therefore, very important. Studies like this give us critical information that we, as a nation, need to determine how best to allot our limited healthcare resources. While this study does not change my perception of the efficacy of colonoscopy, it makes me think twice about its societal utility.
As usual, several provocative additions to the colorectal cancer literature were published last month, but I will review only one today: the NordICC trial. This trial evaluated the use of screening colonoscopy to reduce the incidence of colorectal cancer, death from colorectal cancer, and all-cause mortality.
We have long accepted that colonoscopy is the gold standard for detection of colorectal cancer, but until the publication of this study there has never been a prospective, randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of the test. Nearly 85,000 men and women from Nordic nations were randomly assigned to receive an invitation for either screening colonoscopy or usual care (ie, no colonoscopy). In the intention-to-screen analysis, colonoscopy reduced the risk for colorectal cancer over a period of 10 years by 18% (relative risk [RR] 0.82; 95% CI 0.70-0.93). However, the reduction in risk for death from colorectal cancer failed to reach statistical significance (RR 0.90; 95% CI 0.64-1.16).
These results were especially disappointing because sigmoidoscopy, a test that evaluates only the rectum and left colon, has been shown in multiple studies to reduce risk for colorectal cancer death and all-cause mortality. It is difficult for me to think of a biologically plausible explanation for colonoscopy to be less effective than sigmoidoscopy in the prevention of cause-specific and all-cause death. However, potential explanations are hidden in the study data. Most glaringly, only 42% of the colonoscopy invitees received a colonoscopy as compared with a much larger percentage of patients (58%-87%) in the sigmoidoscopy trials. While this might be an important real-world data point, it is far less than the estimated 60% of patients in the United States who adhere to the recommendation for screening colonoscopy from ages 45 to 55. Additionally, the study had only 10 years of follow-up. It is possible that this is just not long enough for the benefits of screening colonoscopy to be fully realized. Finally, 29% of endoscopists had an adenoma detection below the recommended threshold of 25%, suggesting that poor colonoscopic technique may have played a role in the limited efficacy of colonoscopy found in the study.
Regardless of what we think of these results, the study was generally well designed and, therefore, very important. Studies like this give us critical information that we, as a nation, need to determine how best to allot our limited healthcare resources. While this study does not change my perception of the efficacy of colonoscopy, it makes me think twice about its societal utility.
Clinical Implications of Partial Response to Antidepressants
Only about one third of patients with major depressive disorder achieve full remission with antidepressant therapy. Another third are considered nonresponders, and the remaining one third are partial responders. The latter group of patients are those who have seen some improvement but have not achieved full remission.
Dr Michael Thase at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, discusses the symptomatic burden and risk for relapse faced by partial responders, who present a significant treatment challenge.
Dr Thase explores the therapeutic options available when a first-choice treatment option proves incompletely effective. In addition to medication optimization, adjunctive treatment and alternative approaches are considered.
--
Michael E. Thase, MD, Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Mood and Anxiety Disorders Treatment and Research Program, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Michael E. Thase, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as an advisor or consultant for: Acadia, Inc; Akili, Inc;
Alkermes PLC; Allergan, Inc; Axsome Therapeutics, Inc; BioHaven, Inc; Bocemtium Consulting, SL; Boehringer Ingelheim International; CatalYm GmbH; Clexio Biosciences; Gerson Lehrman Group, Inc; H Lundbeck, A/S; Jazz Pharmaceuticals; Janssen; Johnson & Johnson; Luye Pharma Group, Ltd; Merck & Company, Inc; Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Company, Ltd; Pfizer, Inc; Sage Pharmaceuicals; Seelos Pharmaceuticals; Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd
Receive research funding from: Acadia, Inc; Allergan, Inc; AssureRx; Axsome Therapeutics, Inc; BioHaven, Inc; Intracellular, Inc; Johnson & Johnson; Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Company, Ltd; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd
Receive royalties from: American Psychiatric Foundation; Guilford Publications; Herald House; Kluwer-Wolters; W W Norton & Company, Inc
Only about one third of patients with major depressive disorder achieve full remission with antidepressant therapy. Another third are considered nonresponders, and the remaining one third are partial responders. The latter group of patients are those who have seen some improvement but have not achieved full remission.
Dr Michael Thase at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, discusses the symptomatic burden and risk for relapse faced by partial responders, who present a significant treatment challenge.
Dr Thase explores the therapeutic options available when a first-choice treatment option proves incompletely effective. In addition to medication optimization, adjunctive treatment and alternative approaches are considered.
--
Michael E. Thase, MD, Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Mood and Anxiety Disorders Treatment and Research Program, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Michael E. Thase, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as an advisor or consultant for: Acadia, Inc; Akili, Inc;
Alkermes PLC; Allergan, Inc; Axsome Therapeutics, Inc; BioHaven, Inc; Bocemtium Consulting, SL; Boehringer Ingelheim International; CatalYm GmbH; Clexio Biosciences; Gerson Lehrman Group, Inc; H Lundbeck, A/S; Jazz Pharmaceuticals; Janssen; Johnson & Johnson; Luye Pharma Group, Ltd; Merck & Company, Inc; Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Company, Ltd; Pfizer, Inc; Sage Pharmaceuicals; Seelos Pharmaceuticals; Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd
Receive research funding from: Acadia, Inc; Allergan, Inc; AssureRx; Axsome Therapeutics, Inc; BioHaven, Inc; Intracellular, Inc; Johnson & Johnson; Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Company, Ltd; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd
Receive royalties from: American Psychiatric Foundation; Guilford Publications; Herald House; Kluwer-Wolters; W W Norton & Company, Inc
Only about one third of patients with major depressive disorder achieve full remission with antidepressant therapy. Another third are considered nonresponders, and the remaining one third are partial responders. The latter group of patients are those who have seen some improvement but have not achieved full remission.
Dr Michael Thase at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, discusses the symptomatic burden and risk for relapse faced by partial responders, who present a significant treatment challenge.
Dr Thase explores the therapeutic options available when a first-choice treatment option proves incompletely effective. In addition to medication optimization, adjunctive treatment and alternative approaches are considered.
--
Michael E. Thase, MD, Professor, Department of Psychiatry, Mood and Anxiety Disorders Treatment and Research Program, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Michael E. Thase, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as an advisor or consultant for: Acadia, Inc; Akili, Inc;
Alkermes PLC; Allergan, Inc; Axsome Therapeutics, Inc; BioHaven, Inc; Bocemtium Consulting, SL; Boehringer Ingelheim International; CatalYm GmbH; Clexio Biosciences; Gerson Lehrman Group, Inc; H Lundbeck, A/S; Jazz Pharmaceuticals; Janssen; Johnson & Johnson; Luye Pharma Group, Ltd; Merck & Company, Inc; Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Company, Ltd; Pfizer, Inc; Sage Pharmaceuicals; Seelos Pharmaceuticals; Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd
Receive research funding from: Acadia, Inc; Allergan, Inc; AssureRx; Axsome Therapeutics, Inc; BioHaven, Inc; Intracellular, Inc; Johnson & Johnson; Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Company, Ltd; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd
Receive royalties from: American Psychiatric Foundation; Guilford Publications; Herald House; Kluwer-Wolters; W W Norton & Company, Inc

Therapeutic Considerations in Adults With Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by recurrent boils, abscesses, and nodules that can progress to narrow channels that form under the skin. An estimated 1%-4% of the US population has the condition, and women are affected more commonly than men.
Treatment of HS is challenging and the pathogenesis is still under investigation. Many believe that the disease involves follicular occlusion that leads to perifollicular cyst development followed by ruptures of the cyst contents. Many drug classes, including antibiotics and topical therapies, as well as lifestyle modifications, have been used to successfully treat mild to moderate HS. Management of moderate to severe HS has been less successful, however.
Dr Jennifer Hsiao, from the University of Southern California, highlights the various approaches to HS treatment, including medical, procedural, and emerging options.
--
Jennifer Hsiao, MD, Associate Professor, Physician, Department of Dermatology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
Jennifer Hsiao, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Novartis; UCB
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AbbVie
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by recurrent boils, abscesses, and nodules that can progress to narrow channels that form under the skin. An estimated 1%-4% of the US population has the condition, and women are affected more commonly than men.
Treatment of HS is challenging and the pathogenesis is still under investigation. Many believe that the disease involves follicular occlusion that leads to perifollicular cyst development followed by ruptures of the cyst contents. Many drug classes, including antibiotics and topical therapies, as well as lifestyle modifications, have been used to successfully treat mild to moderate HS. Management of moderate to severe HS has been less successful, however.
Dr Jennifer Hsiao, from the University of Southern California, highlights the various approaches to HS treatment, including medical, procedural, and emerging options.
--
Jennifer Hsiao, MD, Associate Professor, Physician, Department of Dermatology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
Jennifer Hsiao, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Novartis; UCB
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AbbVie
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by recurrent boils, abscesses, and nodules that can progress to narrow channels that form under the skin. An estimated 1%-4% of the US population has the condition, and women are affected more commonly than men.
Treatment of HS is challenging and the pathogenesis is still under investigation. Many believe that the disease involves follicular occlusion that leads to perifollicular cyst development followed by ruptures of the cyst contents. Many drug classes, including antibiotics and topical therapies, as well as lifestyle modifications, have been used to successfully treat mild to moderate HS. Management of moderate to severe HS has been less successful, however.
Dr Jennifer Hsiao, from the University of Southern California, highlights the various approaches to HS treatment, including medical, procedural, and emerging options.
--
Jennifer Hsiao, MD, Associate Professor, Physician, Department of Dermatology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
Jennifer Hsiao, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Novartis; UCB
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AbbVie

Novel and Emerging Treatments for Adult ADHD: The Path From Inception to Implementation
Lupus Nephritis Highlights From ASN Kidney Week 2022
Dr Gregg Silverman of New York University Langone Medical Center highlights four key studies on lupus nephritis (LN) presented at ASN Kidney Week 2022.
First, he focuses on a follow-up study of voclosporin after the successful phase 3 trial of the medication. According to the study, persistent proteinuria increases risk for comorbidities in lupus nephritis and rapid reductions in protein are predictive of improved long-term renal health. Voclosporin may be beneficial in limiting the negative long-term effects of proteinuria for patients with LN.
Next, Dr Silverman discusses a study that investigates the safety and tolerability of a first-in-class selective proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of LN. Use of this type of proteasome may improve autoimmunity for these patients.
The third abstract he discusses is a study of an investigational agent, VIB 4920, that was first explored over 20 years ago and that may have activity in LN.
Finally, Dr Silverman examines a phase 2b study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of telitacicept vs placebo in combination with standard therapy in patients with lupus. Early results were encouraging, but more mature results are needed.
--
Highlights in lupus nephritis (LN) from ASN Kidney Week 2022 focus on results on voclosporin, repurposing of telitacicept, promising agent VIB 4920, and other novel treatments for patients with LN.
Gregg J. Silverman, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr Gregg Silverman of New York University Langone Medical Center highlights four key studies on lupus nephritis (LN) presented at ASN Kidney Week 2022.
First, he focuses on a follow-up study of voclosporin after the successful phase 3 trial of the medication. According to the study, persistent proteinuria increases risk for comorbidities in lupus nephritis and rapid reductions in protein are predictive of improved long-term renal health. Voclosporin may be beneficial in limiting the negative long-term effects of proteinuria for patients with LN.
Next, Dr Silverman discusses a study that investigates the safety and tolerability of a first-in-class selective proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of LN. Use of this type of proteasome may improve autoimmunity for these patients.
The third abstract he discusses is a study of an investigational agent, VIB 4920, that was first explored over 20 years ago and that may have activity in LN.
Finally, Dr Silverman examines a phase 2b study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of telitacicept vs placebo in combination with standard therapy in patients with lupus. Early results were encouraging, but more mature results are needed.
--
Highlights in lupus nephritis (LN) from ASN Kidney Week 2022 focus on results on voclosporin, repurposing of telitacicept, promising agent VIB 4920, and other novel treatments for patients with LN.
Gregg J. Silverman, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr Gregg Silverman of New York University Langone Medical Center highlights four key studies on lupus nephritis (LN) presented at ASN Kidney Week 2022.
First, he focuses on a follow-up study of voclosporin after the successful phase 3 trial of the medication. According to the study, persistent proteinuria increases risk for comorbidities in lupus nephritis and rapid reductions in protein are predictive of improved long-term renal health. Voclosporin may be beneficial in limiting the negative long-term effects of proteinuria for patients with LN.
Next, Dr Silverman discusses a study that investigates the safety and tolerability of a first-in-class selective proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of LN. Use of this type of proteasome may improve autoimmunity for these patients.
The third abstract he discusses is a study of an investigational agent, VIB 4920, that was first explored over 20 years ago and that may have activity in LN.
Finally, Dr Silverman examines a phase 2b study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of telitacicept vs placebo in combination with standard therapy in patients with lupus. Early results were encouraging, but more mature results are needed.
--
Highlights in lupus nephritis (LN) from ASN Kidney Week 2022 focus on results on voclosporin, repurposing of telitacicept, promising agent VIB 4920, and other novel treatments for patients with LN.
Gregg J. Silverman, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.

Meet the JCOM Author with Dr. Barkoudah: Neurosurgery Operating Room Efficiency During the COVID-19 Era
Surgical management of early pregnancy loss
CASE Concern for surgical management after repeat miscarriage
A 34-year-old woman (G3P0030) with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss was recently diagnosed with a 7-week missed abortion. After her second miscarriage, she had an evaluation for recurrent pregnancy loss which was unremarkable. Both prior miscarriages were managed with dilation & curettage (D&C), but cytogenetic testing of the tissue did not yield a result in either case. The karyotype from the first pregnancy resulted as 46, XX but was confirmed to be due to maternal cell contamination, and the karyotype from the second pregnancy resulted in cell culture failure. The patient is interested in surgical management for her current missed abortion to help with tissue collection for cytogenetic testing, she but is concerned about her risk of intrauterine adhesions with repeated uterine instrumentation given 2 prior D&Cs, one of which was complicated by retained products of conception.
How do you approach the surgical management of this patient with recurrent pregnancy loss?
Approximately 1 in every 8 recognized pregnancies results in miscarriage. The risk of loss is lowest in women with no history of miscarriage (11%), and increases by about 10% for each additional miscarriage, reaching 42% in women with 3 or more previous losses. The population prevalence of women who have had 1 miscarriage is 11%, 2 miscarriages is 2%, and 3 or more is <1%.1 While 90% of miscarriages occur in the first trimester, their etiology can be quite varied.2 A woman’s age is the most strongly associated risk factor, with both very young (<20 years) and older age (>35 years) groups at highest risk. This association is largely attributed to an age-related increase in embryonic chromosomal aneuploidies, of which trisomies, particularly trisomy 16, are the most common.3 Maternal anatomic anomalies such as leiomyomas, intrauterine adhesions, Müllerian anomalies, and adenomyosis have been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage in addition to several lifestyle and environmental factor exposures.1
Regardless of the etiology, women with recurrent miscarriage are exposed to the potential for iatrogenic harm from the management of their pregnancy loss, including intrauterine adhesions and retained products, which may negatively impact future reproductive attempts. The management of patients with recurrent miscarriages demands special attention to reduce the risk of iatrogenic harm, maximize diagnostic evaluation of the products of conception, and improve future reproductive outcomes.
Management strategies
First trimester pregnancy loss may be managed expectantly, medically, or surgically. Approximately 76% of women who opt for expectant management will successfully pass pregnancy tissue, but for 1 out of every 6 women it may take longer than 14 days.4 For patients who prefer to expedite this process, medication abortion is a highly effective and safe option. According to Schreiber and colleagues, a combination of mifepristone and misoprostol together resulted in expulsion in approximately 91% of 148 patients, although 9% still required surgical intervention for incomplete passage of tissue.5 Both expectant management and medical management strategies are associated with the potential for retained products of conception requiring subsequent instrumentation as well as tissue that is often unsuitable or contaminated for cytogenetic analysis.
The most definitive treatment option is surgical management via manual or electric vacuum aspiration or curettage, with efficacy approaching 99.6% in some series.6 While highly effective, even ultrasound-guided evacuation carries with it procedure-related risks that are of particular consequence for patients of reproductive age, including adhesion formation and retained products of conception.
In 1997, Goldenberg and colleagues reported on the use of hysteroscopy for the management of retained products of conception as a strategy to minimize trauma to the uterus and maximize excision of retained tissue, both of which reduce potential for adhesion formation.7 Based on these data, several groups have extended the use of hysteroscopic resection for retained tissue to upfront evacuation following pregnancy loss, in lieu of D&C.8,9 This approach allows for the direct visualization of the focal removal of the implanted pregnancy tissue, which can:
- decrease the risk of intrauterine adhesion formation
- decrease the risk of retained products of conception
- allow for directed tissue sampling to improve the accuracy of cytogenetic testing
- allow for detection of embryo anatomic anomalies that often go undetected on traditional cytogenetic analysis.
For the remainder of this article, we will discuss the advantages of hysteroscopic management of a missed abortion in greater detail.
Continue to: Hysteroscopic management...
Hysteroscopic management
Like aspiration or curettage, hysteroscopic management may be offered once the diagnosis of fetal demise is confirmed on ultrasonography. The procedure may be accomplished in the office setting or in the operative room with either morcellation or resectoscopic instruments. Morcellation allows for improved visibility during the procedure given the ability of continuous suction to manage tissue fragments in the surgical field, while resectoscopic instruments offer the added benefit of electrosurgery should bleeding that is unresponsive to increased distention pressure be encountered. Use of the cold loop of the resectoscope to accomplish evacuation is advocated to avoid the thermal damage to the endometrium with electrosurgery. Regardless of the chosen instrument, there are several potential benefits for a hysteroscopic approach over the traditional ultrasound-guided or blind D&C.
Reducing risk of iatrogenic harm
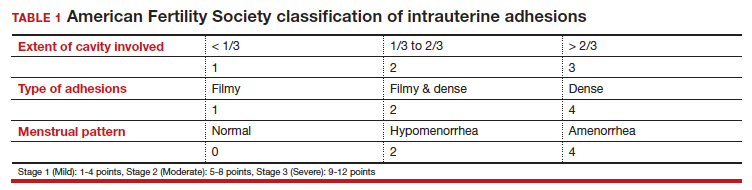
Intrauterine adhesions form secondary to trauma to the endometrial basalis layer, where a population of adult progenitor stem cells continuously work to regenerate the overlying functionalis layer. Once damaged, adhesions may form and range from thin, filmy adhesions to dense, cavity obliterating bands of scar tissue (FIGURE). The degree of severity and location of the adhesions account for the variable presentation that range from menstrual abnormalities to infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss. While several classification systems exist for scoring severity of adhesions, the American Fertility Society (now American Society for Reproductive Medicine) Classification system from 1988 is still commonly utilized (TABLE 1).
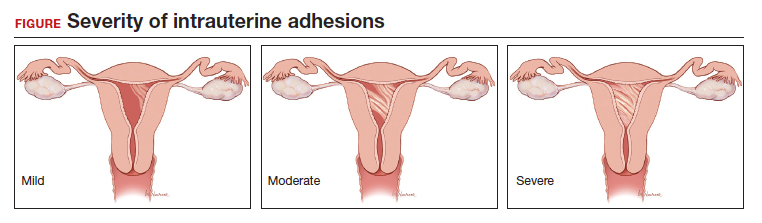
Intrauterine adhesions from D&C after pregnancy loss are not uncommon. A 2014 meta-analysis of 10 prospective studies including 912 women reported a pooled prevalence for intrauterine adhesions of 19.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.8–27.5) on hysteroscopic evaluation within 12 months following curettage.10 Once formed, these adhesions are associated with long-term impairment in reproductive outcomes, regardless of if they were treated or not. In a long-term follow-up study of women with and without adhesions after recurrent D&C for miscarriage, women with treated adhesions reported lower live birth rates, longer time to pregnancy, higher rates of preterm birth and higher rates of peripartum complications compared with those without adhesions.11
Compared with curettage, hysteroscopy affords the surgeon complete visualization of the uterine cavity and tissue to be resected. This, in turn, minimizes trauma to the surrounding uterine cavity, minimizes the potential for post-procedural adhesion formation and their associated sequelae, and maximizes complete resection of tissue. Those treated with D&C appear to be significantly more likely to have adhesions than those treated via a hysteroscopic approach (30% vs 13%).12
Retained products of conception. Classically, a “gritty” sensation of the endometrium following evacuation of the uterus with a sharp curette has been used to indicate complete removal of tissue. The evolution from a nonvisualized procedure to ultrasound-guided vacuum aspiration of 1st trimester pregnancy tissue has been associated with a decreased risk of procedural complications and retained products of conception.13 However, even with intraoperative imaging, the risk of retained products of conception remains because it can be difficult to distinguish a small blood clot from retained pregnancy tissue on ultrasonography.
Retained pregnancy tissue can result in abnormal or heavy bleeding, require additional medical or surgical intervention, and is associated with endometrial inflammation and infection. Approximately 1 in every 4 women undergoing hysteroscopic resection of retained products are found to have evidence of endometritis in the resected tissue.14 This number is even higher in women with a diagnosis of recurrent pregnancy loss (62%).15
These complications from retained products of conception can be avoided with the hysteroscopic approach due to the direct visualization of the tissue removal. This benefit may be particularly beneficial in patients with known abnormal uterine cavities, such as those with Müllerian anomalies, uterine leiomyomas, preexisting adhesions, and history of placenta accreta spectrum disorder.
Continue to: Maximizing diagnostic yield...
Maximizing diagnostic yield
Many patients prefer surgical management of a missed abortion not for the procedural advantages, but to assist with tissue collection for cytogenetic testing of the pregnancy tissue. Given that embryonic chromosomal aneuploidy is implicated in 70% of miscarriages prior to 20 weeks’ gestation, genetic evaluation of the products of conception is commonly performed to identify a potential cause for the miscarriage.16 G-band karyotype is the most commonly performed genetic evaluation. Karyotype requires culturing of pregnancy tissue for 7-14 days to produce metaphase cells that are then chemically treated to arrest them at their maximally contracted stage. Cytogenetic evaluation is often curtailed when nonviable cells from products of conception fail to culture due to either time elapsed from diagnosis to demise or damage from tissue handling. Careful, directly observed tissue handling via a hysteroscopic approach may alleviate culture failure secondary to tissue damage.
Another concern with cultures of products of conception is the potential for maternal cell contamination. Early studies from the 1970s noted a significant skew toward 46, XX karyotype results in miscarried tissue as compared with 46, XY results. It was not until microsatellite analysis technology was available that it was determined that the result was due to analysis of maternal cells instead of products of conception.17 A 2014 study by Levy and colleagues and another by Lathi and colleagues that utilized single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) microarray found that maternal cell contamination affected 22% of all miscarriage samples analyzed and over half of karyotypes with a 46, XX result.18,19
Traditional “blind” suction and curettage may inadvertently collect maternal endometrial tissue and contaminate the culture of fetal cells, limiting the validity of karyotype for products of conception.20 The hysteroscopic approach may provide a higher diagnostic yield for karyotype analysis of fetal tissue by the nature of targeted tissue sampling under direct visualization, minimizing maternal cell contamination. One retrospective study by Cholkeri-Singh and colleagues evaluated rates of fetal chromosome detection without maternal contamination in a total of 264 patients undergoing either suction curettage or hysteroscopic resection. They found that fetal chromosomal detection without contamination was significantly higher in the hysteroscopy group compared with the suction curettage group (88.5 vs 64.8%, P< .001).21 Additionally, biopsies of tissue under direct visualization may enable the diagnosis of a true placental mosaicism and the study of the individual karyotype of each embryo in dizygotic twin missed abortions.
Finally, a hysteroscopic approach may afford the opportunity to also perform morphologic evaluation of the intact early fetus furthering the diagnostic utility of the procedure. With hysteroscopy, the gestational sac is identified and carefully entered, allowing for complete visualization of the early fetus and assessment of anatomic malformations that may provide insight into the pregnancy loss (ie, embryoscopy). In one series of 272 patients with missed abortions, while nearly 75% of conceptuses had abnormal karyotypes, 18% were found to have gross morphologic defects with a normal karyotype.22
Bottom line
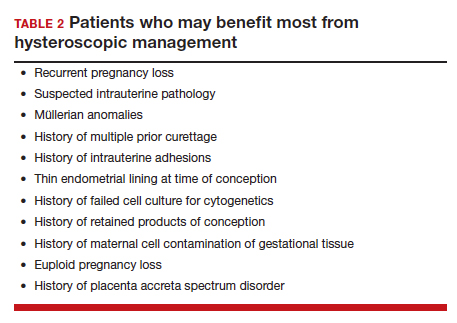
When faced with a patient with an early pregnancy loss, physicians should consider the decreased iatrogenic risks and improved diagnostic yield when deciding between D&C versus hysteroscopy for surgical management. There are certain patients with pre-existing risk factors that may stand to benefit the most (TABLE 2). Much like the opening case, those at risk for intrauterine adhesions, retained products of conception, or in whom a successful and accurate cytogenetic analysis is essential are the most likely to benefit from a hysteroscopic approach. The hysteroscopic approach also affords concurrent diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology, such as leiomyomas and uterine septum, which are encountered approximately 12.5% of the time after one miscarriage and 29.4% of the time in patients with a history of more than one miscarriage.10 In the appropriately counseled patient and clinical setting, clinicians could also perform definitive surgical management during the same hysteroscopy. Finally, evaluation of the morphology of the demised fetus may provide additional information for patient counseling in those with euploid pregnancy losses.
CASE Resolved
Ultimately, our patient underwent complete hysteroscopic resection of the pregnancy tissue, which confirmed both a morphologically abnormal fetus and a 45, X karyotype of the products of conception. ●
- Quenby S, Gallos ID, Dhillon-Smith RK, et al. Miscarriage matters: the epidemiological, physical, psychological, and economic costs of early pregnancy loss. Lancet. 2021;397:1658-1667.
- Kolte AM, Westergaard D, Lidegaard Ø, et al. Chance of live birth: a nationwide, registry-based cohort study. Hum Reprod Oxf Engl. 2021;36:1065-1073.
- Magnus MC, Wilcox AJ, Morken N-H, et al. Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: prospective register-based study. BMJ. 2019;364:869.
- Luise C, Jermy K, May C, et al. Outcome of expectant management of spontaneous first trimester miscarriage: observational study. BMJ. 2002;324:873-875.
- Schreiber CA, Creinin MD, Atrio J, et al. Mifepristone pretreatment for the medical management of early pregnancy loss. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2161-2170.
- Ireland LD, Gatter M, Chen AY. Medical compared with surgical abortion for effective pregnancy termination in the first trimester. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:22-28.
- Goldenberg M, Schiff E, Achiron R, et al. Managing residual trophoblastic tissue. Hysteroscopy for directing curettage. J Reprod Med. 1997;42:26-28.
- Weinberg S, Pansky M, Burshtein I, et al. A pilot study of guided conservative hysteroscopic evacuation of early miscarriage. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28:1860-1867.
- Young S, Miller CE. Hysteroscopic resection for management of early pregnancy loss: a case report and literature review. FS Rep. 2022;3:163-167.
- Hooker AB, Lemmers M, Thurkow AL, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of intrauterine adhesions after miscarriage: prevalence, risk factors and long-term reproductive outcome. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20:262-278.
- Hooker AB, de Leeuw RA, Twisk JWR, et al. Reproductive performance of women with and without intrauterine adhesions following recurrent dilatation and curettage for miscarriage: long-term follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Hum Reprod. 2021;36:70-81.
- Hooker AB, Aydin H, Brölmann HAM, et al. Longterm complications and reproductive outcome after the management of retained products of conception: a systematic review. Fertil Steril. 2016;105:156-164.e1-e2.
- Debby A, Malinger G, Harow E, et al. Transvaginal ultrasound after first-trimester uterine evacuation reduces the incidence of retained products of conception. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006;27:61-64.
- Elder S, Bortoletto P, Romanski PA, et al. Chronic endometritis in women with suspected retained products of conception and their reproductive outcomes. Am J Reprod Immunol N Y N 1989. 2021;86:e13410.
- McQueen DB, Maniar KP, Hutchinson A, et al. Retained pregnancy tissue after miscarriage is associated with high rate of chronic endometritis. J Obstet Gynaecol J Inst Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;1-5.
- Soler A, Morales C, Mademont-Soler I, et al. Overview of chromosome abnormalities in first trimester miscarriages: a series of 1,011 consecutive chorionic villi sample karyotypes. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2017;152:81-89.
- Jarrett KL, Michaelis RC, Phelan MC, et al. Microsatellite analysis reveals a high incidence of maternal cell contamination in 46, XX products of conception consisting of villi or a combination of villi and membranous material. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185:198-203.
- Levy B, Sigurjonsson S, Pettersen B, et al. Genomic imbalance in products of conception: single-nucleotide polymorphism chromosomal microarray analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124:202-209.
- Lathi RB, Gustin SLF, Keller J, et al. Reliability of 46, XX results on miscarriage specimens: a review of 1,222 first-trimester miscarriage specimens. Fertil Steril. 2014;101:178-182.
- Chung JPW, Li Y, Law TSM, et al. Ultrasound-guided manual vacuum aspiration is an optimal method for obtaining products of conception from early pregnancy loss for cytogenetic testing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2022;147:106226.
- Cholkeri-Singh A, Zamfirova I, Miller CE. Increased fetal chromosome detection with the use of operative hysteroscopy during evacuation of products of conception for diagnosed miscarriage. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:160-165.
- Philipp T, Philipp K, Reiner A, et al. Embryoscopic and cytogenetic analysis of 233 missed abortions: factors involved in the pathogenesis of developmental defects of early failed pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:1724-1732.
CASE Concern for surgical management after repeat miscarriage
A 34-year-old woman (G3P0030) with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss was recently diagnosed with a 7-week missed abortion. After her second miscarriage, she had an evaluation for recurrent pregnancy loss which was unremarkable. Both prior miscarriages were managed with dilation & curettage (D&C), but cytogenetic testing of the tissue did not yield a result in either case. The karyotype from the first pregnancy resulted as 46, XX but was confirmed to be due to maternal cell contamination, and the karyotype from the second pregnancy resulted in cell culture failure. The patient is interested in surgical management for her current missed abortion to help with tissue collection for cytogenetic testing, she but is concerned about her risk of intrauterine adhesions with repeated uterine instrumentation given 2 prior D&Cs, one of which was complicated by retained products of conception.
How do you approach the surgical management of this patient with recurrent pregnancy loss?
Approximately 1 in every 8 recognized pregnancies results in miscarriage. The risk of loss is lowest in women with no history of miscarriage (11%), and increases by about 10% for each additional miscarriage, reaching 42% in women with 3 or more previous losses. The population prevalence of women who have had 1 miscarriage is 11%, 2 miscarriages is 2%, and 3 or more is <1%.1 While 90% of miscarriages occur in the first trimester, their etiology can be quite varied.2 A woman’s age is the most strongly associated risk factor, with both very young (<20 years) and older age (>35 years) groups at highest risk. This association is largely attributed to an age-related increase in embryonic chromosomal aneuploidies, of which trisomies, particularly trisomy 16, are the most common.3 Maternal anatomic anomalies such as leiomyomas, intrauterine adhesions, Müllerian anomalies, and adenomyosis have been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage in addition to several lifestyle and environmental factor exposures.1
Regardless of the etiology, women with recurrent miscarriage are exposed to the potential for iatrogenic harm from the management of their pregnancy loss, including intrauterine adhesions and retained products, which may negatively impact future reproductive attempts. The management of patients with recurrent miscarriages demands special attention to reduce the risk of iatrogenic harm, maximize diagnostic evaluation of the products of conception, and improve future reproductive outcomes.
Management strategies
First trimester pregnancy loss may be managed expectantly, medically, or surgically. Approximately 76% of women who opt for expectant management will successfully pass pregnancy tissue, but for 1 out of every 6 women it may take longer than 14 days.4 For patients who prefer to expedite this process, medication abortion is a highly effective and safe option. According to Schreiber and colleagues, a combination of mifepristone and misoprostol together resulted in expulsion in approximately 91% of 148 patients, although 9% still required surgical intervention for incomplete passage of tissue.5 Both expectant management and medical management strategies are associated with the potential for retained products of conception requiring subsequent instrumentation as well as tissue that is often unsuitable or contaminated for cytogenetic analysis.
The most definitive treatment option is surgical management via manual or electric vacuum aspiration or curettage, with efficacy approaching 99.6% in some series.6 While highly effective, even ultrasound-guided evacuation carries with it procedure-related risks that are of particular consequence for patients of reproductive age, including adhesion formation and retained products of conception.
In 1997, Goldenberg and colleagues reported on the use of hysteroscopy for the management of retained products of conception as a strategy to minimize trauma to the uterus and maximize excision of retained tissue, both of which reduce potential for adhesion formation.7 Based on these data, several groups have extended the use of hysteroscopic resection for retained tissue to upfront evacuation following pregnancy loss, in lieu of D&C.8,9 This approach allows for the direct visualization of the focal removal of the implanted pregnancy tissue, which can:
- decrease the risk of intrauterine adhesion formation
- decrease the risk of retained products of conception
- allow for directed tissue sampling to improve the accuracy of cytogenetic testing
- allow for detection of embryo anatomic anomalies that often go undetected on traditional cytogenetic analysis.
For the remainder of this article, we will discuss the advantages of hysteroscopic management of a missed abortion in greater detail.
Continue to: Hysteroscopic management...
Hysteroscopic management
Like aspiration or curettage, hysteroscopic management may be offered once the diagnosis of fetal demise is confirmed on ultrasonography. The procedure may be accomplished in the office setting or in the operative room with either morcellation or resectoscopic instruments. Morcellation allows for improved visibility during the procedure given the ability of continuous suction to manage tissue fragments in the surgical field, while resectoscopic instruments offer the added benefit of electrosurgery should bleeding that is unresponsive to increased distention pressure be encountered. Use of the cold loop of the resectoscope to accomplish evacuation is advocated to avoid the thermal damage to the endometrium with electrosurgery. Regardless of the chosen instrument, there are several potential benefits for a hysteroscopic approach over the traditional ultrasound-guided or blind D&C.
Reducing risk of iatrogenic harm
Intrauterine adhesions form secondary to trauma to the endometrial basalis layer, where a population of adult progenitor stem cells continuously work to regenerate the overlying functionalis layer. Once damaged, adhesions may form and range from thin, filmy adhesions to dense, cavity obliterating bands of scar tissue (FIGURE). The degree of severity and location of the adhesions account for the variable presentation that range from menstrual abnormalities to infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss. While several classification systems exist for scoring severity of adhesions, the American Fertility Society (now American Society for Reproductive Medicine) Classification system from 1988 is still commonly utilized (TABLE 1).


Intrauterine adhesions from D&C after pregnancy loss are not uncommon. A 2014 meta-analysis of 10 prospective studies including 912 women reported a pooled prevalence for intrauterine adhesions of 19.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.8–27.5) on hysteroscopic evaluation within 12 months following curettage.10 Once formed, these adhesions are associated with long-term impairment in reproductive outcomes, regardless of if they were treated or not. In a long-term follow-up study of women with and without adhesions after recurrent D&C for miscarriage, women with treated adhesions reported lower live birth rates, longer time to pregnancy, higher rates of preterm birth and higher rates of peripartum complications compared with those without adhesions.11
Compared with curettage, hysteroscopy affords the surgeon complete visualization of the uterine cavity and tissue to be resected. This, in turn, minimizes trauma to the surrounding uterine cavity, minimizes the potential for post-procedural adhesion formation and their associated sequelae, and maximizes complete resection of tissue. Those treated with D&C appear to be significantly more likely to have adhesions than those treated via a hysteroscopic approach (30% vs 13%).12
Retained products of conception. Classically, a “gritty” sensation of the endometrium following evacuation of the uterus with a sharp curette has been used to indicate complete removal of tissue. The evolution from a nonvisualized procedure to ultrasound-guided vacuum aspiration of 1st trimester pregnancy tissue has been associated with a decreased risk of procedural complications and retained products of conception.13 However, even with intraoperative imaging, the risk of retained products of conception remains because it can be difficult to distinguish a small blood clot from retained pregnancy tissue on ultrasonography.
Retained pregnancy tissue can result in abnormal or heavy bleeding, require additional medical or surgical intervention, and is associated with endometrial inflammation and infection. Approximately 1 in every 4 women undergoing hysteroscopic resection of retained products are found to have evidence of endometritis in the resected tissue.14 This number is even higher in women with a diagnosis of recurrent pregnancy loss (62%).15
These complications from retained products of conception can be avoided with the hysteroscopic approach due to the direct visualization of the tissue removal. This benefit may be particularly beneficial in patients with known abnormal uterine cavities, such as those with Müllerian anomalies, uterine leiomyomas, preexisting adhesions, and history of placenta accreta spectrum disorder.
Continue to: Maximizing diagnostic yield...
Maximizing diagnostic yield
Many patients prefer surgical management of a missed abortion not for the procedural advantages, but to assist with tissue collection for cytogenetic testing of the pregnancy tissue. Given that embryonic chromosomal aneuploidy is implicated in 70% of miscarriages prior to 20 weeks’ gestation, genetic evaluation of the products of conception is commonly performed to identify a potential cause for the miscarriage.16 G-band karyotype is the most commonly performed genetic evaluation. Karyotype requires culturing of pregnancy tissue for 7-14 days to produce metaphase cells that are then chemically treated to arrest them at their maximally contracted stage. Cytogenetic evaluation is often curtailed when nonviable cells from products of conception fail to culture due to either time elapsed from diagnosis to demise or damage from tissue handling. Careful, directly observed tissue handling via a hysteroscopic approach may alleviate culture failure secondary to tissue damage.
Another concern with cultures of products of conception is the potential for maternal cell contamination. Early studies from the 1970s noted a significant skew toward 46, XX karyotype results in miscarried tissue as compared with 46, XY results. It was not until microsatellite analysis technology was available that it was determined that the result was due to analysis of maternal cells instead of products of conception.17 A 2014 study by Levy and colleagues and another by Lathi and colleagues that utilized single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) microarray found that maternal cell contamination affected 22% of all miscarriage samples analyzed and over half of karyotypes with a 46, XX result.18,19
Traditional “blind” suction and curettage may inadvertently collect maternal endometrial tissue and contaminate the culture of fetal cells, limiting the validity of karyotype for products of conception.20 The hysteroscopic approach may provide a higher diagnostic yield for karyotype analysis of fetal tissue by the nature of targeted tissue sampling under direct visualization, minimizing maternal cell contamination. One retrospective study by Cholkeri-Singh and colleagues evaluated rates of fetal chromosome detection without maternal contamination in a total of 264 patients undergoing either suction curettage or hysteroscopic resection. They found that fetal chromosomal detection without contamination was significantly higher in the hysteroscopy group compared with the suction curettage group (88.5 vs 64.8%, P< .001).21 Additionally, biopsies of tissue under direct visualization may enable the diagnosis of a true placental mosaicism and the study of the individual karyotype of each embryo in dizygotic twin missed abortions.
Finally, a hysteroscopic approach may afford the opportunity to also perform morphologic evaluation of the intact early fetus furthering the diagnostic utility of the procedure. With hysteroscopy, the gestational sac is identified and carefully entered, allowing for complete visualization of the early fetus and assessment of anatomic malformations that may provide insight into the pregnancy loss (ie, embryoscopy). In one series of 272 patients with missed abortions, while nearly 75% of conceptuses had abnormal karyotypes, 18% were found to have gross morphologic defects with a normal karyotype.22
Bottom line
When faced with a patient with an early pregnancy loss, physicians should consider the decreased iatrogenic risks and improved diagnostic yield when deciding between D&C versus hysteroscopy for surgical management. There are certain patients with pre-existing risk factors that may stand to benefit the most (TABLE 2). Much like the opening case, those at risk for intrauterine adhesions, retained products of conception, or in whom a successful and accurate cytogenetic analysis is essential are the most likely to benefit from a hysteroscopic approach. The hysteroscopic approach also affords concurrent diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology, such as leiomyomas and uterine septum, which are encountered approximately 12.5% of the time after one miscarriage and 29.4% of the time in patients with a history of more than one miscarriage.10 In the appropriately counseled patient and clinical setting, clinicians could also perform definitive surgical management during the same hysteroscopy. Finally, evaluation of the morphology of the demised fetus may provide additional information for patient counseling in those with euploid pregnancy losses.

CASE Resolved
Ultimately, our patient underwent complete hysteroscopic resection of the pregnancy tissue, which confirmed both a morphologically abnormal fetus and a 45, X karyotype of the products of conception. ●
CASE Concern for surgical management after repeat miscarriage
A 34-year-old woman (G3P0030) with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss was recently diagnosed with a 7-week missed abortion. After her second miscarriage, she had an evaluation for recurrent pregnancy loss which was unremarkable. Both prior miscarriages were managed with dilation & curettage (D&C), but cytogenetic testing of the tissue did not yield a result in either case. The karyotype from the first pregnancy resulted as 46, XX but was confirmed to be due to maternal cell contamination, and the karyotype from the second pregnancy resulted in cell culture failure. The patient is interested in surgical management for her current missed abortion to help with tissue collection for cytogenetic testing, she but is concerned about her risk of intrauterine adhesions with repeated uterine instrumentation given 2 prior D&Cs, one of which was complicated by retained products of conception.
How do you approach the surgical management of this patient with recurrent pregnancy loss?
Approximately 1 in every 8 recognized pregnancies results in miscarriage. The risk of loss is lowest in women with no history of miscarriage (11%), and increases by about 10% for each additional miscarriage, reaching 42% in women with 3 or more previous losses. The population prevalence of women who have had 1 miscarriage is 11%, 2 miscarriages is 2%, and 3 or more is <1%.1 While 90% of miscarriages occur in the first trimester, their etiology can be quite varied.2 A woman’s age is the most strongly associated risk factor, with both very young (<20 years) and older age (>35 years) groups at highest risk. This association is largely attributed to an age-related increase in embryonic chromosomal aneuploidies, of which trisomies, particularly trisomy 16, are the most common.3 Maternal anatomic anomalies such as leiomyomas, intrauterine adhesions, Müllerian anomalies, and adenomyosis have been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage in addition to several lifestyle and environmental factor exposures.1
Regardless of the etiology, women with recurrent miscarriage are exposed to the potential for iatrogenic harm from the management of their pregnancy loss, including intrauterine adhesions and retained products, which may negatively impact future reproductive attempts. The management of patients with recurrent miscarriages demands special attention to reduce the risk of iatrogenic harm, maximize diagnostic evaluation of the products of conception, and improve future reproductive outcomes.
Management strategies
First trimester pregnancy loss may be managed expectantly, medically, or surgically. Approximately 76% of women who opt for expectant management will successfully pass pregnancy tissue, but for 1 out of every 6 women it may take longer than 14 days.4 For patients who prefer to expedite this process, medication abortion is a highly effective and safe option. According to Schreiber and colleagues, a combination of mifepristone and misoprostol together resulted in expulsion in approximately 91% of 148 patients, although 9% still required surgical intervention for incomplete passage of tissue.5 Both expectant management and medical management strategies are associated with the potential for retained products of conception requiring subsequent instrumentation as well as tissue that is often unsuitable or contaminated for cytogenetic analysis.
The most definitive treatment option is surgical management via manual or electric vacuum aspiration or curettage, with efficacy approaching 99.6% in some series.6 While highly effective, even ultrasound-guided evacuation carries with it procedure-related risks that are of particular consequence for patients of reproductive age, including adhesion formation and retained products of conception.
In 1997, Goldenberg and colleagues reported on the use of hysteroscopy for the management of retained products of conception as a strategy to minimize trauma to the uterus and maximize excision of retained tissue, both of which reduce potential for adhesion formation.7 Based on these data, several groups have extended the use of hysteroscopic resection for retained tissue to upfront evacuation following pregnancy loss, in lieu of D&C.8,9 This approach allows for the direct visualization of the focal removal of the implanted pregnancy tissue, which can:
- decrease the risk of intrauterine adhesion formation
- decrease the risk of retained products of conception
- allow for directed tissue sampling to improve the accuracy of cytogenetic testing
- allow for detection of embryo anatomic anomalies that often go undetected on traditional cytogenetic analysis.
For the remainder of this article, we will discuss the advantages of hysteroscopic management of a missed abortion in greater detail.
Continue to: Hysteroscopic management...
Hysteroscopic management
Like aspiration or curettage, hysteroscopic management may be offered once the diagnosis of fetal demise is confirmed on ultrasonography. The procedure may be accomplished in the office setting or in the operative room with either morcellation or resectoscopic instruments. Morcellation allows for improved visibility during the procedure given the ability of continuous suction to manage tissue fragments in the surgical field, while resectoscopic instruments offer the added benefit of electrosurgery should bleeding that is unresponsive to increased distention pressure be encountered. Use of the cold loop of the resectoscope to accomplish evacuation is advocated to avoid the thermal damage to the endometrium with electrosurgery. Regardless of the chosen instrument, there are several potential benefits for a hysteroscopic approach over the traditional ultrasound-guided or blind D&C.
Reducing risk of iatrogenic harm
Intrauterine adhesions form secondary to trauma to the endometrial basalis layer, where a population of adult progenitor stem cells continuously work to regenerate the overlying functionalis layer. Once damaged, adhesions may form and range from thin, filmy adhesions to dense, cavity obliterating bands of scar tissue (FIGURE). The degree of severity and location of the adhesions account for the variable presentation that range from menstrual abnormalities to infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss. While several classification systems exist for scoring severity of adhesions, the American Fertility Society (now American Society for Reproductive Medicine) Classification system from 1988 is still commonly utilized (TABLE 1).


Intrauterine adhesions from D&C after pregnancy loss are not uncommon. A 2014 meta-analysis of 10 prospective studies including 912 women reported a pooled prevalence for intrauterine adhesions of 19.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.8–27.5) on hysteroscopic evaluation within 12 months following curettage.10 Once formed, these adhesions are associated with long-term impairment in reproductive outcomes, regardless of if they were treated or not. In a long-term follow-up study of women with and without adhesions after recurrent D&C for miscarriage, women with treated adhesions reported lower live birth rates, longer time to pregnancy, higher rates of preterm birth and higher rates of peripartum complications compared with those without adhesions.11
Compared with curettage, hysteroscopy affords the surgeon complete visualization of the uterine cavity and tissue to be resected. This, in turn, minimizes trauma to the surrounding uterine cavity, minimizes the potential for post-procedural adhesion formation and their associated sequelae, and maximizes complete resection of tissue. Those treated with D&C appear to be significantly more likely to have adhesions than those treated via a hysteroscopic approach (30% vs 13%).12
Retained products of conception. Classically, a “gritty” sensation of the endometrium following evacuation of the uterus with a sharp curette has been used to indicate complete removal of tissue. The evolution from a nonvisualized procedure to ultrasound-guided vacuum aspiration of 1st trimester pregnancy tissue has been associated with a decreased risk of procedural complications and retained products of conception.13 However, even with intraoperative imaging, the risk of retained products of conception remains because it can be difficult to distinguish a small blood clot from retained pregnancy tissue on ultrasonography.
Retained pregnancy tissue can result in abnormal or heavy bleeding, require additional medical or surgical intervention, and is associated with endometrial inflammation and infection. Approximately 1 in every 4 women undergoing hysteroscopic resection of retained products are found to have evidence of endometritis in the resected tissue.14 This number is even higher in women with a diagnosis of recurrent pregnancy loss (62%).15
These complications from retained products of conception can be avoided with the hysteroscopic approach due to the direct visualization of the tissue removal. This benefit may be particularly beneficial in patients with known abnormal uterine cavities, such as those with Müllerian anomalies, uterine leiomyomas, preexisting adhesions, and history of placenta accreta spectrum disorder.
Continue to: Maximizing diagnostic yield...
Maximizing diagnostic yield
Many patients prefer surgical management of a missed abortion not for the procedural advantages, but to assist with tissue collection for cytogenetic testing of the pregnancy tissue. Given that embryonic chromosomal aneuploidy is implicated in 70% of miscarriages prior to 20 weeks’ gestation, genetic evaluation of the products of conception is commonly performed to identify a potential cause for the miscarriage.16 G-band karyotype is the most commonly performed genetic evaluation. Karyotype requires culturing of pregnancy tissue for 7-14 days to produce metaphase cells that are then chemically treated to arrest them at their maximally contracted stage. Cytogenetic evaluation is often curtailed when nonviable cells from products of conception fail to culture due to either time elapsed from diagnosis to demise or damage from tissue handling. Careful, directly observed tissue handling via a hysteroscopic approach may alleviate culture failure secondary to tissue damage.
Another concern with cultures of products of conception is the potential for maternal cell contamination. Early studies from the 1970s noted a significant skew toward 46, XX karyotype results in miscarried tissue as compared with 46, XY results. It was not until microsatellite analysis technology was available that it was determined that the result was due to analysis of maternal cells instead of products of conception.17 A 2014 study by Levy and colleagues and another by Lathi and colleagues that utilized single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) microarray found that maternal cell contamination affected 22% of all miscarriage samples analyzed and over half of karyotypes with a 46, XX result.18,19
Traditional “blind” suction and curettage may inadvertently collect maternal endometrial tissue and contaminate the culture of fetal cells, limiting the validity of karyotype for products of conception.20 The hysteroscopic approach may provide a higher diagnostic yield for karyotype analysis of fetal tissue by the nature of targeted tissue sampling under direct visualization, minimizing maternal cell contamination. One retrospective study by Cholkeri-Singh and colleagues evaluated rates of fetal chromosome detection without maternal contamination in a total of 264 patients undergoing either suction curettage or hysteroscopic resection. They found that fetal chromosomal detection without contamination was significantly higher in the hysteroscopy group compared with the suction curettage group (88.5 vs 64.8%, P< .001).21 Additionally, biopsies of tissue under direct visualization may enable the diagnosis of a true placental mosaicism and the study of the individual karyotype of each embryo in dizygotic twin missed abortions.
Finally, a hysteroscopic approach may afford the opportunity to also perform morphologic evaluation of the intact early fetus furthering the diagnostic utility of the procedure. With hysteroscopy, the gestational sac is identified and carefully entered, allowing for complete visualization of the early fetus and assessment of anatomic malformations that may provide insight into the pregnancy loss (ie, embryoscopy). In one series of 272 patients with missed abortions, while nearly 75% of conceptuses had abnormal karyotypes, 18% were found to have gross morphologic defects with a normal karyotype.22
Bottom line
When faced with a patient with an early pregnancy loss, physicians should consider the decreased iatrogenic risks and improved diagnostic yield when deciding between D&C versus hysteroscopy for surgical management. There are certain patients with pre-existing risk factors that may stand to benefit the most (TABLE 2). Much like the opening case, those at risk for intrauterine adhesions, retained products of conception, or in whom a successful and accurate cytogenetic analysis is essential are the most likely to benefit from a hysteroscopic approach. The hysteroscopic approach also affords concurrent diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine pathology, such as leiomyomas and uterine septum, which are encountered approximately 12.5% of the time after one miscarriage and 29.4% of the time in patients with a history of more than one miscarriage.10 In the appropriately counseled patient and clinical setting, clinicians could also perform definitive surgical management during the same hysteroscopy. Finally, evaluation of the morphology of the demised fetus may provide additional information for patient counseling in those with euploid pregnancy losses.

CASE Resolved
Ultimately, our patient underwent complete hysteroscopic resection of the pregnancy tissue, which confirmed both a morphologically abnormal fetus and a 45, X karyotype of the products of conception. ●
- Quenby S, Gallos ID, Dhillon-Smith RK, et al. Miscarriage matters: the epidemiological, physical, psychological, and economic costs of early pregnancy loss. Lancet. 2021;397:1658-1667.
- Kolte AM, Westergaard D, Lidegaard Ø, et al. Chance of live birth: a nationwide, registry-based cohort study. Hum Reprod Oxf Engl. 2021;36:1065-1073.
- Magnus MC, Wilcox AJ, Morken N-H, et al. Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: prospective register-based study. BMJ. 2019;364:869.
- Luise C, Jermy K, May C, et al. Outcome of expectant management of spontaneous first trimester miscarriage: observational study. BMJ. 2002;324:873-875.
- Schreiber CA, Creinin MD, Atrio J, et al. Mifepristone pretreatment for the medical management of early pregnancy loss. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2161-2170.
- Ireland LD, Gatter M, Chen AY. Medical compared with surgical abortion for effective pregnancy termination in the first trimester. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:22-28.
- Goldenberg M, Schiff E, Achiron R, et al. Managing residual trophoblastic tissue. Hysteroscopy for directing curettage. J Reprod Med. 1997;42:26-28.
- Weinberg S, Pansky M, Burshtein I, et al. A pilot study of guided conservative hysteroscopic evacuation of early miscarriage. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28:1860-1867.
- Young S, Miller CE. Hysteroscopic resection for management of early pregnancy loss: a case report and literature review. FS Rep. 2022;3:163-167.
- Hooker AB, Lemmers M, Thurkow AL, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of intrauterine adhesions after miscarriage: prevalence, risk factors and long-term reproductive outcome. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20:262-278.
- Hooker AB, de Leeuw RA, Twisk JWR, et al. Reproductive performance of women with and without intrauterine adhesions following recurrent dilatation and curettage for miscarriage: long-term follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Hum Reprod. 2021;36:70-81.
- Hooker AB, Aydin H, Brölmann HAM, et al. Longterm complications and reproductive outcome after the management of retained products of conception: a systematic review. Fertil Steril. 2016;105:156-164.e1-e2.
- Debby A, Malinger G, Harow E, et al. Transvaginal ultrasound after first-trimester uterine evacuation reduces the incidence of retained products of conception. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006;27:61-64.
- Elder S, Bortoletto P, Romanski PA, et al. Chronic endometritis in women with suspected retained products of conception and their reproductive outcomes. Am J Reprod Immunol N Y N 1989. 2021;86:e13410.
- McQueen DB, Maniar KP, Hutchinson A, et al. Retained pregnancy tissue after miscarriage is associated with high rate of chronic endometritis. J Obstet Gynaecol J Inst Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;1-5.
- Soler A, Morales C, Mademont-Soler I, et al. Overview of chromosome abnormalities in first trimester miscarriages: a series of 1,011 consecutive chorionic villi sample karyotypes. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2017;152:81-89.
- Jarrett KL, Michaelis RC, Phelan MC, et al. Microsatellite analysis reveals a high incidence of maternal cell contamination in 46, XX products of conception consisting of villi or a combination of villi and membranous material. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185:198-203.
- Levy B, Sigurjonsson S, Pettersen B, et al. Genomic imbalance in products of conception: single-nucleotide polymorphism chromosomal microarray analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124:202-209.
- Lathi RB, Gustin SLF, Keller J, et al. Reliability of 46, XX results on miscarriage specimens: a review of 1,222 first-trimester miscarriage specimens. Fertil Steril. 2014;101:178-182.
- Chung JPW, Li Y, Law TSM, et al. Ultrasound-guided manual vacuum aspiration is an optimal method for obtaining products of conception from early pregnancy loss for cytogenetic testing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2022;147:106226.
- Cholkeri-Singh A, Zamfirova I, Miller CE. Increased fetal chromosome detection with the use of operative hysteroscopy during evacuation of products of conception for diagnosed miscarriage. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:160-165.
- Philipp T, Philipp K, Reiner A, et al. Embryoscopic and cytogenetic analysis of 233 missed abortions: factors involved in the pathogenesis of developmental defects of early failed pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:1724-1732.
- Quenby S, Gallos ID, Dhillon-Smith RK, et al. Miscarriage matters: the epidemiological, physical, psychological, and economic costs of early pregnancy loss. Lancet. 2021;397:1658-1667.
- Kolte AM, Westergaard D, Lidegaard Ø, et al. Chance of live birth: a nationwide, registry-based cohort study. Hum Reprod Oxf Engl. 2021;36:1065-1073.
- Magnus MC, Wilcox AJ, Morken N-H, et al. Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: prospective register-based study. BMJ. 2019;364:869.
- Luise C, Jermy K, May C, et al. Outcome of expectant management of spontaneous first trimester miscarriage: observational study. BMJ. 2002;324:873-875.
- Schreiber CA, Creinin MD, Atrio J, et al. Mifepristone pretreatment for the medical management of early pregnancy loss. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2161-2170.
- Ireland LD, Gatter M, Chen AY. Medical compared with surgical abortion for effective pregnancy termination in the first trimester. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:22-28.
- Goldenberg M, Schiff E, Achiron R, et al. Managing residual trophoblastic tissue. Hysteroscopy for directing curettage. J Reprod Med. 1997;42:26-28.
- Weinberg S, Pansky M, Burshtein I, et al. A pilot study of guided conservative hysteroscopic evacuation of early miscarriage. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2021;28:1860-1867.
- Young S, Miller CE. Hysteroscopic resection for management of early pregnancy loss: a case report and literature review. FS Rep. 2022;3:163-167.
- Hooker AB, Lemmers M, Thurkow AL, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of intrauterine adhesions after miscarriage: prevalence, risk factors and long-term reproductive outcome. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20:262-278.
- Hooker AB, de Leeuw RA, Twisk JWR, et al. Reproductive performance of women with and without intrauterine adhesions following recurrent dilatation and curettage for miscarriage: long-term follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Hum Reprod. 2021;36:70-81.
- Hooker AB, Aydin H, Brölmann HAM, et al. Longterm complications and reproductive outcome after the management of retained products of conception: a systematic review. Fertil Steril. 2016;105:156-164.e1-e2.
- Debby A, Malinger G, Harow E, et al. Transvaginal ultrasound after first-trimester uterine evacuation reduces the incidence of retained products of conception. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006;27:61-64.
- Elder S, Bortoletto P, Romanski PA, et al. Chronic endometritis in women with suspected retained products of conception and their reproductive outcomes. Am J Reprod Immunol N Y N 1989. 2021;86:e13410.
- McQueen DB, Maniar KP, Hutchinson A, et al. Retained pregnancy tissue after miscarriage is associated with high rate of chronic endometritis. J Obstet Gynaecol J Inst Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;1-5.
- Soler A, Morales C, Mademont-Soler I, et al. Overview of chromosome abnormalities in first trimester miscarriages: a series of 1,011 consecutive chorionic villi sample karyotypes. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2017;152:81-89.
- Jarrett KL, Michaelis RC, Phelan MC, et al. Microsatellite analysis reveals a high incidence of maternal cell contamination in 46, XX products of conception consisting of villi or a combination of villi and membranous material. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185:198-203.
- Levy B, Sigurjonsson S, Pettersen B, et al. Genomic imbalance in products of conception: single-nucleotide polymorphism chromosomal microarray analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124:202-209.
- Lathi RB, Gustin SLF, Keller J, et al. Reliability of 46, XX results on miscarriage specimens: a review of 1,222 first-trimester miscarriage specimens. Fertil Steril. 2014;101:178-182.
- Chung JPW, Li Y, Law TSM, et al. Ultrasound-guided manual vacuum aspiration is an optimal method for obtaining products of conception from early pregnancy loss for cytogenetic testing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2022;147:106226.
- Cholkeri-Singh A, Zamfirova I, Miller CE. Increased fetal chromosome detection with the use of operative hysteroscopy during evacuation of products of conception for diagnosed miscarriage. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020;27:160-165.
- Philipp T, Philipp K, Reiner A, et al. Embryoscopic and cytogenetic analysis of 233 missed abortions: factors involved in the pathogenesis of developmental defects of early failed pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:1724-1732.
Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Middle Ear
To the Editor:
An 82-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for a total-body skin examination due to a recently diagnosed primary melanoma of the left middle ear. He reported pain of the left ear and water behind the left eardrum of 1 year’s duration. An otorhinolaryngologist performed surgery due to the severe mastoiditis. A biopsy of the contents of the left middle ear revealed malignant melanoma. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography revealed the mass was mainly located in the anterior aspect of the left middle ear with suspicion of tumor extension into the bony portion of the eustachian tube. No other disease was present. Prior to presentation to dermatology, gross excision of the left middle ear with removal of additional melanoma was confirmed by biopsy, and further analysis revealed v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene (BRAF) was not detected while cellular proto-oncogene receptor kinase (KIT) mutation was detected on exon 13p (K642E).
The patient had no family history of melanoma. He never smoked and did not have contact with hazardous material. Initial examination at our clinic revealed no other suspicious pigmented lesions. After additional negative workup by the oncologist, the patient was presented to the tumor board, and postoperative radiotherapy was recommended to improve local control. Eight months after the patient’s initial diagnosis of the primary middle ear melanoma, a computed tomography–guided right lung biopsy showed metastatic melanoma. After various treatment modalities were discussed with the patient and his family, he was started on pembrolizumab. After 6 months on pembrolizumab, the patient developed autoimmune pneumonitis and pembrolizumab was discontinued. The patient elected to discontinue treatment and died 6 months later.
Malignant melanoma with primary involvement of the middle ear and mastoid mucosa rarely has been reported.1-3 Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa is difficult to diagnose clinically. Difficulty and delay in diagnosis occur because of the location and frequent lack of pathognomonic symptoms of the disease.2 A comprehensive literature review by Maxwell et al3 in 2018 of the 10 reported primary middle ear mucosal melanomas found that patients most commonly presented with otorrhea, aural fullness, and hearing loss. Less common symptoms included otalgia, tinnitus, and facial weakness. Clinical examination revealed patients presented with serous otitis and/or a visible mass within the middle ear or external auditory canal. These melanomas demonstrated particularly poor outcomes, with 70% mortality, 20% local recurrence, and 50% distant metastasis. Distant metastases that occurred with primary middle ear mucosal melanoma include lung, liver, intraparotid, abdomen, and cutaneous metastasis.3
The specific pathophysiologic factors underlying the development of primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa are not known.2 The middle ear and its components develop from the first and second pharyngeal arches.4 Melanocyte precursors from the neural crest migrate during the seventh or eighth week of embryogenesis. These precursors migrate to the epidermis, various mucosal epithelial, hair follicles, dermis, retina, uveal tract, leptomeninges, inner ear, and other tissues.5 The ossicles of the middle ear develop from the neural crest6 and remain in the mesenchyme until the eighth month, when the surrounding tissue dissolves.4 Cutaneous melanomas arise from the malignant transformation of melanocytes in the skin of neural crest lineage. Noncutaneous melanomas are hypothesized to arise from melanoblasts migrating to noncutaneous organs after neural crest cells undergo an epithelial-mesenchymal translation.7
Melanoma 5-year survival rates vary based on the melanoma disease stage: 98% for stage 1, 90% for stage 2, 70% for stage 3, and 10% for stage 4. Although early-stage disease mainly is treated with surgery, advanced and unresectable disease is managed with different therapeutic options, including BRAF inhibitors such as vemurafenib, dabrafenib mesylate, and encorafenib; immune checkpoint inhibitors such as ipilimumab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab; and oncolytic virus such as talimogene laherparepvec.8,9
Ninety percent of melanomas are of cutaneous origin. Extracutaneous melanomas may be derived from the uvea, leptomeninges, mucous membranes, and gastrointestinal tract.10 Mucosal melanomas are rare and represent only approximately 1% of all melanomas.11 In order of frequency, primary mucosal melanomas include the head and neck, anorectal region, vulvovaginal region, and urinary tract. UV radiation exposure is an important risk factor for cutaneous melanoma but has not been associated with the development of mucosal melanoma.7 In 2019, Altieri et al11 analyzed 1824 cases of mucosal melanoma and found that anatomic site influences survival because mucosal melanomas in the most occult anatomic sites—spinal/central nervous system, lung and pleura, liver, and pancreas—have the worst prognosis, likely because they have already metastasized by the time they are diagnosed. Due to their occult anatomic location and lack of early presenting signs and symptoms, mucosal melanomas are difficult to diagnose at an early stage, resulting in a poorer prognosis compared with cutaneous melanomas. The most important prognostic indicator for cutaneous melanomas of tumor thickness (ie, Breslow depth) provides less prognostic value for patients with mucosal melanoma. Limitations also include the lack of a standardized staging system for mucosal melanoma, but Altieri et al11 found that poorer survival in patients with mucosal melanoma was observed in relation to stage based on the clinical and pathologic tumor-node-metastasis staging system of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. An aggregate 5-year survival estimate of patients diagnosed with mucosal melanoma is 28%, underscoring that mucosal melanoma is an aggressive melanoma that carries a poor prognosis and warrants a more aggressive treatment approach at the time of diagnosis.11
Common treatment of primary middle ear mucosal melanoma involves a multimodality therapy including surgical oncological resection for most patients. Currently, radiation is in use for adjuvant treatment and definitive therapy in unresectable tumors or patients who are poor surgical candidates. Malignant melanoma traditionally was considered radioresistant, yet considerable variability in responsiveness has been observed both within and between tumors. Although there are no defined indications for adjuvant therapy, it is often administered in advanced or recurrent cases and those with positive or close margins. Chemotherapy generally is reserved for patients with systemic disease. The chemotherapeutic agents that have been used in the treatment of patients with melanoma of the middle ear include the alkylating agents dacarbazine, cisplatin, nimustine, paclitaxel, and temozolomide. Also, chemotherapeutic agents that have been reported in the treatment of melanoma of the middle ear include tamoxifen, the selective estrogen receptor inhibitor, and interferon. Most recently, programed cell death protein 1 inhibitors pembrolizumab and nivolumab have been used in the treatment of middle ear melanoma. Outcomes remain poor with a high rate of mortality. Novel immunotherapeutic agents combined with adjuvant radiotherapy have been proposed to improve disease control and survival rates.3
Data on systemic therapies for mucosal melanomas are limited due to the rarity of the disease. Even with the development of novel therapies, outcomes remain poor for mucosal melanomas, and additional treatment strategies are needed. Although proto-oncogene BRAF mutations occur in 50% to 70% of cutaneous melanomas, these mutations are rare in mucosal melanomas.3 In mucosal melanomas, activating mutations of the cell receptor KIT are identified more frequently.7 Alterations in proto-oncogene KIT have been found in acral, mucosal, and cutaneous melanoma. KIT mutations were found on exons 11 and 13.12 Variability in the biology of KIT is suggested. Treatment of melanomas with the KIT mutations with tyrosine inhibitors imatinib and nilotinib have shown variable benefits.10 In a 2019 study of 44 patients with mucosal melanoma, Moya-Plana et al13 found that in cases of unresectable and/or metastatic disease, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab had a better benefit-risk ratio than immune treatment with ipilimumab, a cytotoxic T-cell lymphocyte-associated protein 4 inhibitor.
Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear is unusual and difficult to diagnose clinically. These melanomas have a poor prognosis and can have distant metastasis including cutaneous metastasis. We present this case to emphasize the need to be aware that melanoma can arise in the middle ear.
- Ozturk O, Baglam T, Uneri C, et al. Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa: a case report. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2006;16:83-86.
- Idris IA, Daud KM, Yusof Z, et al. Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa: a case report. Egypt J ENT Allied Sci. 2017;18:307-309.
- Maxwell AK, Takeda H, Gubbels SP. Primary middle ear mucosal melanoma: case report and comprehensive literature review of 21 cases of primary middle ear and eustachian tube melanoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2018;127:856-863.
- Sadler TW. Ear. In: Sadler TW, ed. Langman’s Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012:324-325.
- Jakubovic HR, Akerman AB. Structure and function of skin: development, morphology and physiology. In: Moschella SL, Hurley HJ, eds. Dermatology. Vol 1. WB Saunders Co; 1985:22-23.
- Sadler TW. The axial skeleton. In: Sadler TW, ed. Langman’s Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012:133-137.
- Tacastacas JD, Bray J, Cohen YK, et al. Update on primary mucosal melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:366-375.
- Abdutaali R, Alkhattib NS, Oh M, et al. Economic evaluation of talimogene laherparepvec plus ipilimumab combination therapy vs ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with advanced unresectable melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:22-28.
- Skudalski L, Waldeman R, Kerr PE, et al. Melanoma: an update on systemic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:515-524.
- Heymann WR. A step toward demystifying melanomas of unknown primary sites. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:208-209.
- Altieri L, Eguchi M, Peng DH, et al. Predictors of mucosal melanoma survival in a population-based setting. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:136-142.
- Volpe VO, Klufas DM, Hegde U, et al. The new paradigm of systemic therapies for metastatic melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:356-368.
- Moya-Plana A, Herrera Gomez RG, Rossoni C, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of immunotherapy for non-resectable mucosal melanoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:1171-1178.
To the Editor:
An 82-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for a total-body skin examination due to a recently diagnosed primary melanoma of the left middle ear. He reported pain of the left ear and water behind the left eardrum of 1 year’s duration. An otorhinolaryngologist performed surgery due to the severe mastoiditis. A biopsy of the contents of the left middle ear revealed malignant melanoma. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography revealed the mass was mainly located in the anterior aspect of the left middle ear with suspicion of tumor extension into the bony portion of the eustachian tube. No other disease was present. Prior to presentation to dermatology, gross excision of the left middle ear with removal of additional melanoma was confirmed by biopsy, and further analysis revealed v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene (BRAF) was not detected while cellular proto-oncogene receptor kinase (KIT) mutation was detected on exon 13p (K642E).
The patient had no family history of melanoma. He never smoked and did not have contact with hazardous material. Initial examination at our clinic revealed no other suspicious pigmented lesions. After additional negative workup by the oncologist, the patient was presented to the tumor board, and postoperative radiotherapy was recommended to improve local control. Eight months after the patient’s initial diagnosis of the primary middle ear melanoma, a computed tomography–guided right lung biopsy showed metastatic melanoma. After various treatment modalities were discussed with the patient and his family, he was started on pembrolizumab. After 6 months on pembrolizumab, the patient developed autoimmune pneumonitis and pembrolizumab was discontinued. The patient elected to discontinue treatment and died 6 months later.
Malignant melanoma with primary involvement of the middle ear and mastoid mucosa rarely has been reported.1-3 Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa is difficult to diagnose clinically. Difficulty and delay in diagnosis occur because of the location and frequent lack of pathognomonic symptoms of the disease.2 A comprehensive literature review by Maxwell et al3 in 2018 of the 10 reported primary middle ear mucosal melanomas found that patients most commonly presented with otorrhea, aural fullness, and hearing loss. Less common symptoms included otalgia, tinnitus, and facial weakness. Clinical examination revealed patients presented with serous otitis and/or a visible mass within the middle ear or external auditory canal. These melanomas demonstrated particularly poor outcomes, with 70% mortality, 20% local recurrence, and 50% distant metastasis. Distant metastases that occurred with primary middle ear mucosal melanoma include lung, liver, intraparotid, abdomen, and cutaneous metastasis.3
The specific pathophysiologic factors underlying the development of primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa are not known.2 The middle ear and its components develop from the first and second pharyngeal arches.4 Melanocyte precursors from the neural crest migrate during the seventh or eighth week of embryogenesis. These precursors migrate to the epidermis, various mucosal epithelial, hair follicles, dermis, retina, uveal tract, leptomeninges, inner ear, and other tissues.5 The ossicles of the middle ear develop from the neural crest6 and remain in the mesenchyme until the eighth month, when the surrounding tissue dissolves.4 Cutaneous melanomas arise from the malignant transformation of melanocytes in the skin of neural crest lineage. Noncutaneous melanomas are hypothesized to arise from melanoblasts migrating to noncutaneous organs after neural crest cells undergo an epithelial-mesenchymal translation.7
Melanoma 5-year survival rates vary based on the melanoma disease stage: 98% for stage 1, 90% for stage 2, 70% for stage 3, and 10% for stage 4. Although early-stage disease mainly is treated with surgery, advanced and unresectable disease is managed with different therapeutic options, including BRAF inhibitors such as vemurafenib, dabrafenib mesylate, and encorafenib; immune checkpoint inhibitors such as ipilimumab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab; and oncolytic virus such as talimogene laherparepvec.8,9
Ninety percent of melanomas are of cutaneous origin. Extracutaneous melanomas may be derived from the uvea, leptomeninges, mucous membranes, and gastrointestinal tract.10 Mucosal melanomas are rare and represent only approximately 1% of all melanomas.11 In order of frequency, primary mucosal melanomas include the head and neck, anorectal region, vulvovaginal region, and urinary tract. UV radiation exposure is an important risk factor for cutaneous melanoma but has not been associated with the development of mucosal melanoma.7 In 2019, Altieri et al11 analyzed 1824 cases of mucosal melanoma and found that anatomic site influences survival because mucosal melanomas in the most occult anatomic sites—spinal/central nervous system, lung and pleura, liver, and pancreas—have the worst prognosis, likely because they have already metastasized by the time they are diagnosed. Due to their occult anatomic location and lack of early presenting signs and symptoms, mucosal melanomas are difficult to diagnose at an early stage, resulting in a poorer prognosis compared with cutaneous melanomas. The most important prognostic indicator for cutaneous melanomas of tumor thickness (ie, Breslow depth) provides less prognostic value for patients with mucosal melanoma. Limitations also include the lack of a standardized staging system for mucosal melanoma, but Altieri et al11 found that poorer survival in patients with mucosal melanoma was observed in relation to stage based on the clinical and pathologic tumor-node-metastasis staging system of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. An aggregate 5-year survival estimate of patients diagnosed with mucosal melanoma is 28%, underscoring that mucosal melanoma is an aggressive melanoma that carries a poor prognosis and warrants a more aggressive treatment approach at the time of diagnosis.11
Common treatment of primary middle ear mucosal melanoma involves a multimodality therapy including surgical oncological resection for most patients. Currently, radiation is in use for adjuvant treatment and definitive therapy in unresectable tumors or patients who are poor surgical candidates. Malignant melanoma traditionally was considered radioresistant, yet considerable variability in responsiveness has been observed both within and between tumors. Although there are no defined indications for adjuvant therapy, it is often administered in advanced or recurrent cases and those with positive or close margins. Chemotherapy generally is reserved for patients with systemic disease. The chemotherapeutic agents that have been used in the treatment of patients with melanoma of the middle ear include the alkylating agents dacarbazine, cisplatin, nimustine, paclitaxel, and temozolomide. Also, chemotherapeutic agents that have been reported in the treatment of melanoma of the middle ear include tamoxifen, the selective estrogen receptor inhibitor, and interferon. Most recently, programed cell death protein 1 inhibitors pembrolizumab and nivolumab have been used in the treatment of middle ear melanoma. Outcomes remain poor with a high rate of mortality. Novel immunotherapeutic agents combined with adjuvant radiotherapy have been proposed to improve disease control and survival rates.3
Data on systemic therapies for mucosal melanomas are limited due to the rarity of the disease. Even with the development of novel therapies, outcomes remain poor for mucosal melanomas, and additional treatment strategies are needed. Although proto-oncogene BRAF mutations occur in 50% to 70% of cutaneous melanomas, these mutations are rare in mucosal melanomas.3 In mucosal melanomas, activating mutations of the cell receptor KIT are identified more frequently.7 Alterations in proto-oncogene KIT have been found in acral, mucosal, and cutaneous melanoma. KIT mutations were found on exons 11 and 13.12 Variability in the biology of KIT is suggested. Treatment of melanomas with the KIT mutations with tyrosine inhibitors imatinib and nilotinib have shown variable benefits.10 In a 2019 study of 44 patients with mucosal melanoma, Moya-Plana et al13 found that in cases of unresectable and/or metastatic disease, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab had a better benefit-risk ratio than immune treatment with ipilimumab, a cytotoxic T-cell lymphocyte-associated protein 4 inhibitor.
Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear is unusual and difficult to diagnose clinically. These melanomas have a poor prognosis and can have distant metastasis including cutaneous metastasis. We present this case to emphasize the need to be aware that melanoma can arise in the middle ear.
To the Editor:
An 82-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for a total-body skin examination due to a recently diagnosed primary melanoma of the left middle ear. He reported pain of the left ear and water behind the left eardrum of 1 year’s duration. An otorhinolaryngologist performed surgery due to the severe mastoiditis. A biopsy of the contents of the left middle ear revealed malignant melanoma. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography revealed the mass was mainly located in the anterior aspect of the left middle ear with suspicion of tumor extension into the bony portion of the eustachian tube. No other disease was present. Prior to presentation to dermatology, gross excision of the left middle ear with removal of additional melanoma was confirmed by biopsy, and further analysis revealed v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene (BRAF) was not detected while cellular proto-oncogene receptor kinase (KIT) mutation was detected on exon 13p (K642E).
The patient had no family history of melanoma. He never smoked and did not have contact with hazardous material. Initial examination at our clinic revealed no other suspicious pigmented lesions. After additional negative workup by the oncologist, the patient was presented to the tumor board, and postoperative radiotherapy was recommended to improve local control. Eight months after the patient’s initial diagnosis of the primary middle ear melanoma, a computed tomography–guided right lung biopsy showed metastatic melanoma. After various treatment modalities were discussed with the patient and his family, he was started on pembrolizumab. After 6 months on pembrolizumab, the patient developed autoimmune pneumonitis and pembrolizumab was discontinued. The patient elected to discontinue treatment and died 6 months later.
Malignant melanoma with primary involvement of the middle ear and mastoid mucosa rarely has been reported.1-3 Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa is difficult to diagnose clinically. Difficulty and delay in diagnosis occur because of the location and frequent lack of pathognomonic symptoms of the disease.2 A comprehensive literature review by Maxwell et al3 in 2018 of the 10 reported primary middle ear mucosal melanomas found that patients most commonly presented with otorrhea, aural fullness, and hearing loss. Less common symptoms included otalgia, tinnitus, and facial weakness. Clinical examination revealed patients presented with serous otitis and/or a visible mass within the middle ear or external auditory canal. These melanomas demonstrated particularly poor outcomes, with 70% mortality, 20% local recurrence, and 50% distant metastasis. Distant metastases that occurred with primary middle ear mucosal melanoma include lung, liver, intraparotid, abdomen, and cutaneous metastasis.3
The specific pathophysiologic factors underlying the development of primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa are not known.2 The middle ear and its components develop from the first and second pharyngeal arches.4 Melanocyte precursors from the neural crest migrate during the seventh or eighth week of embryogenesis. These precursors migrate to the epidermis, various mucosal epithelial, hair follicles, dermis, retina, uveal tract, leptomeninges, inner ear, and other tissues.5 The ossicles of the middle ear develop from the neural crest6 and remain in the mesenchyme until the eighth month, when the surrounding tissue dissolves.4 Cutaneous melanomas arise from the malignant transformation of melanocytes in the skin of neural crest lineage. Noncutaneous melanomas are hypothesized to arise from melanoblasts migrating to noncutaneous organs after neural crest cells undergo an epithelial-mesenchymal translation.7
Melanoma 5-year survival rates vary based on the melanoma disease stage: 98% for stage 1, 90% for stage 2, 70% for stage 3, and 10% for stage 4. Although early-stage disease mainly is treated with surgery, advanced and unresectable disease is managed with different therapeutic options, including BRAF inhibitors such as vemurafenib, dabrafenib mesylate, and encorafenib; immune checkpoint inhibitors such as ipilimumab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab; and oncolytic virus such as talimogene laherparepvec.8,9
Ninety percent of melanomas are of cutaneous origin. Extracutaneous melanomas may be derived from the uvea, leptomeninges, mucous membranes, and gastrointestinal tract.10 Mucosal melanomas are rare and represent only approximately 1% of all melanomas.11 In order of frequency, primary mucosal melanomas include the head and neck, anorectal region, vulvovaginal region, and urinary tract. UV radiation exposure is an important risk factor for cutaneous melanoma but has not been associated with the development of mucosal melanoma.7 In 2019, Altieri et al11 analyzed 1824 cases of mucosal melanoma and found that anatomic site influences survival because mucosal melanomas in the most occult anatomic sites—spinal/central nervous system, lung and pleura, liver, and pancreas—have the worst prognosis, likely because they have already metastasized by the time they are diagnosed. Due to their occult anatomic location and lack of early presenting signs and symptoms, mucosal melanomas are difficult to diagnose at an early stage, resulting in a poorer prognosis compared with cutaneous melanomas. The most important prognostic indicator for cutaneous melanomas of tumor thickness (ie, Breslow depth) provides less prognostic value for patients with mucosal melanoma. Limitations also include the lack of a standardized staging system for mucosal melanoma, but Altieri et al11 found that poorer survival in patients with mucosal melanoma was observed in relation to stage based on the clinical and pathologic tumor-node-metastasis staging system of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. An aggregate 5-year survival estimate of patients diagnosed with mucosal melanoma is 28%, underscoring that mucosal melanoma is an aggressive melanoma that carries a poor prognosis and warrants a more aggressive treatment approach at the time of diagnosis.11
Common treatment of primary middle ear mucosal melanoma involves a multimodality therapy including surgical oncological resection for most patients. Currently, radiation is in use for adjuvant treatment and definitive therapy in unresectable tumors or patients who are poor surgical candidates. Malignant melanoma traditionally was considered radioresistant, yet considerable variability in responsiveness has been observed both within and between tumors. Although there are no defined indications for adjuvant therapy, it is often administered in advanced or recurrent cases and those with positive or close margins. Chemotherapy generally is reserved for patients with systemic disease. The chemotherapeutic agents that have been used in the treatment of patients with melanoma of the middle ear include the alkylating agents dacarbazine, cisplatin, nimustine, paclitaxel, and temozolomide. Also, chemotherapeutic agents that have been reported in the treatment of melanoma of the middle ear include tamoxifen, the selective estrogen receptor inhibitor, and interferon. Most recently, programed cell death protein 1 inhibitors pembrolizumab and nivolumab have been used in the treatment of middle ear melanoma. Outcomes remain poor with a high rate of mortality. Novel immunotherapeutic agents combined with adjuvant radiotherapy have been proposed to improve disease control and survival rates.3
Data on systemic therapies for mucosal melanomas are limited due to the rarity of the disease. Even with the development of novel therapies, outcomes remain poor for mucosal melanomas, and additional treatment strategies are needed. Although proto-oncogene BRAF mutations occur in 50% to 70% of cutaneous melanomas, these mutations are rare in mucosal melanomas.3 In mucosal melanomas, activating mutations of the cell receptor KIT are identified more frequently.7 Alterations in proto-oncogene KIT have been found in acral, mucosal, and cutaneous melanoma. KIT mutations were found on exons 11 and 13.12 Variability in the biology of KIT is suggested. Treatment of melanomas with the KIT mutations with tyrosine inhibitors imatinib and nilotinib have shown variable benefits.10 In a 2019 study of 44 patients with mucosal melanoma, Moya-Plana et al13 found that in cases of unresectable and/or metastatic disease, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab had a better benefit-risk ratio than immune treatment with ipilimumab, a cytotoxic T-cell lymphocyte-associated protein 4 inhibitor.
Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear is unusual and difficult to diagnose clinically. These melanomas have a poor prognosis and can have distant metastasis including cutaneous metastasis. We present this case to emphasize the need to be aware that melanoma can arise in the middle ear.
- Ozturk O, Baglam T, Uneri C, et al. Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa: a case report. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2006;16:83-86.
- Idris IA, Daud KM, Yusof Z, et al. Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa: a case report. Egypt J ENT Allied Sci. 2017;18:307-309.
- Maxwell AK, Takeda H, Gubbels SP. Primary middle ear mucosal melanoma: case report and comprehensive literature review of 21 cases of primary middle ear and eustachian tube melanoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2018;127:856-863.
- Sadler TW. Ear. In: Sadler TW, ed. Langman’s Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012:324-325.
- Jakubovic HR, Akerman AB. Structure and function of skin: development, morphology and physiology. In: Moschella SL, Hurley HJ, eds. Dermatology. Vol 1. WB Saunders Co; 1985:22-23.
- Sadler TW. The axial skeleton. In: Sadler TW, ed. Langman’s Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012:133-137.
- Tacastacas JD, Bray J, Cohen YK, et al. Update on primary mucosal melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:366-375.
- Abdutaali R, Alkhattib NS, Oh M, et al. Economic evaluation of talimogene laherparepvec plus ipilimumab combination therapy vs ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with advanced unresectable melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:22-28.
- Skudalski L, Waldeman R, Kerr PE, et al. Melanoma: an update on systemic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:515-524.
- Heymann WR. A step toward demystifying melanomas of unknown primary sites. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:208-209.
- Altieri L, Eguchi M, Peng DH, et al. Predictors of mucosal melanoma survival in a population-based setting. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:136-142.
- Volpe VO, Klufas DM, Hegde U, et al. The new paradigm of systemic therapies for metastatic melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:356-368.
- Moya-Plana A, Herrera Gomez RG, Rossoni C, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of immunotherapy for non-resectable mucosal melanoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:1171-1178.
- Ozturk O, Baglam T, Uneri C, et al. Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa: a case report. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2006;16:83-86.
- Idris IA, Daud KM, Yusof Z, et al. Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear mucosa: a case report. Egypt J ENT Allied Sci. 2017;18:307-309.
- Maxwell AK, Takeda H, Gubbels SP. Primary middle ear mucosal melanoma: case report and comprehensive literature review of 21 cases of primary middle ear and eustachian tube melanoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2018;127:856-863.
- Sadler TW. Ear. In: Sadler TW, ed. Langman’s Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012:324-325.
- Jakubovic HR, Akerman AB. Structure and function of skin: development, morphology and physiology. In: Moschella SL, Hurley HJ, eds. Dermatology. Vol 1. WB Saunders Co; 1985:22-23.
- Sadler TW. The axial skeleton. In: Sadler TW, ed. Langman’s Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012:133-137.
- Tacastacas JD, Bray J, Cohen YK, et al. Update on primary mucosal melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:366-375.
- Abdutaali R, Alkhattib NS, Oh M, et al. Economic evaluation of talimogene laherparepvec plus ipilimumab combination therapy vs ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with advanced unresectable melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:22-28.
- Skudalski L, Waldeman R, Kerr PE, et al. Melanoma: an update on systemic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:515-524.
- Heymann WR. A step toward demystifying melanomas of unknown primary sites. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:208-209.
- Altieri L, Eguchi M, Peng DH, et al. Predictors of mucosal melanoma survival in a population-based setting. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:136-142.
- Volpe VO, Klufas DM, Hegde U, et al. The new paradigm of systemic therapies for metastatic melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:356-368.
- Moya-Plana A, Herrera Gomez RG, Rossoni C, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of immunotherapy for non-resectable mucosal melanoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:1171-1178.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Primary malignant melanoma of the middle ear is rare and has poor prognosis.
- Distant metastasis, including cutaneous metastasis, results from primary middle ear melanoma.