User login
Rapidly Growing Nodule Within a Previously Radiated Area of the Scalp
The Diagnosis: Pseudoangiomatous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
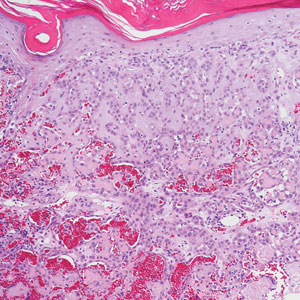
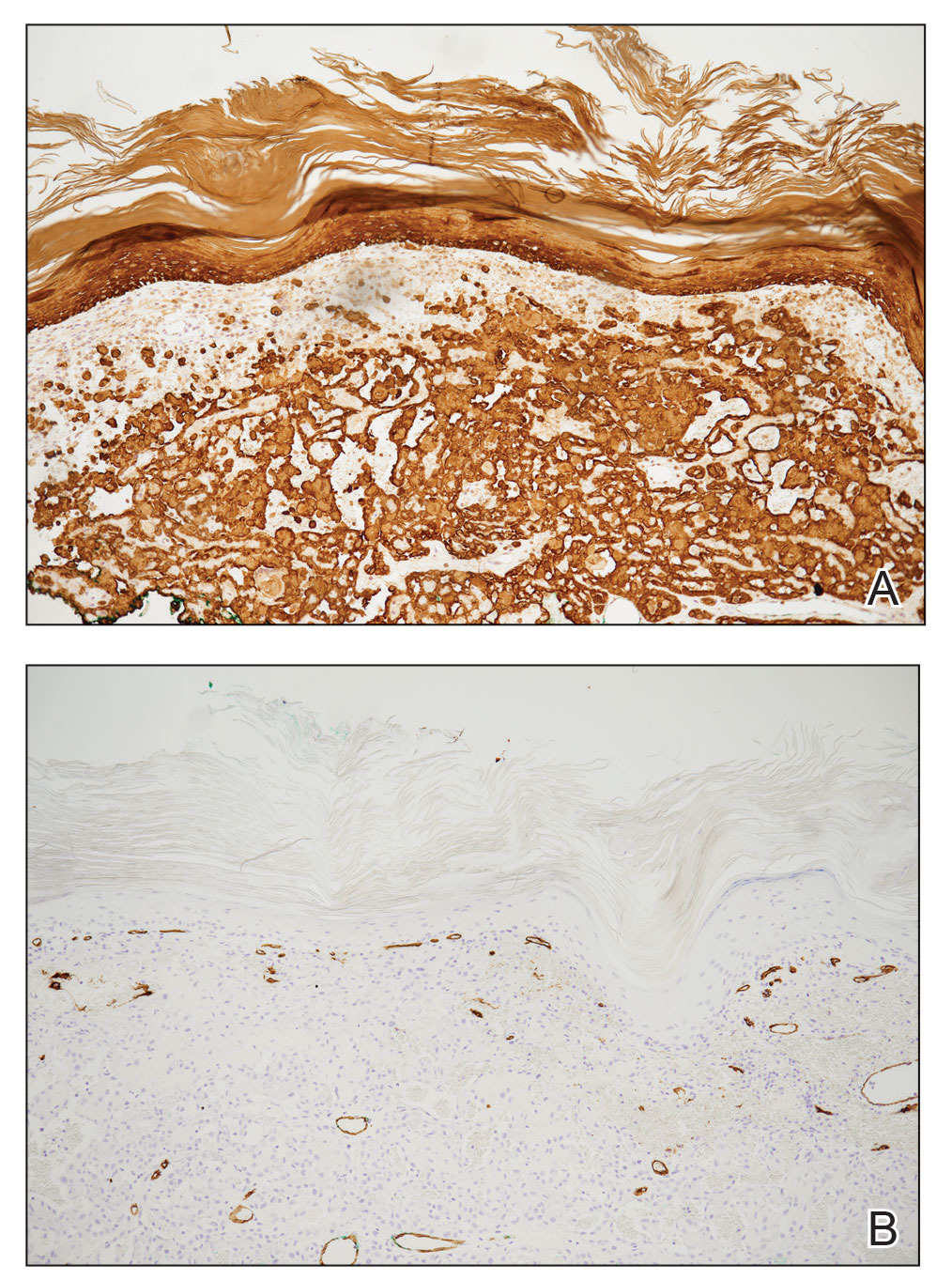
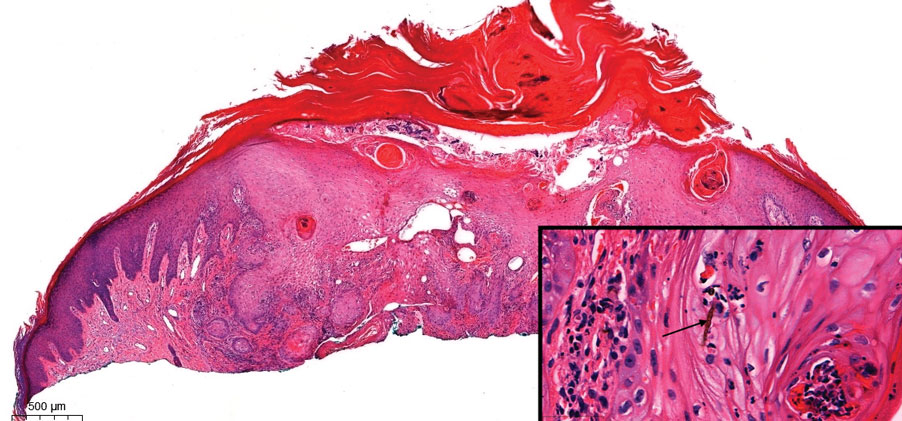
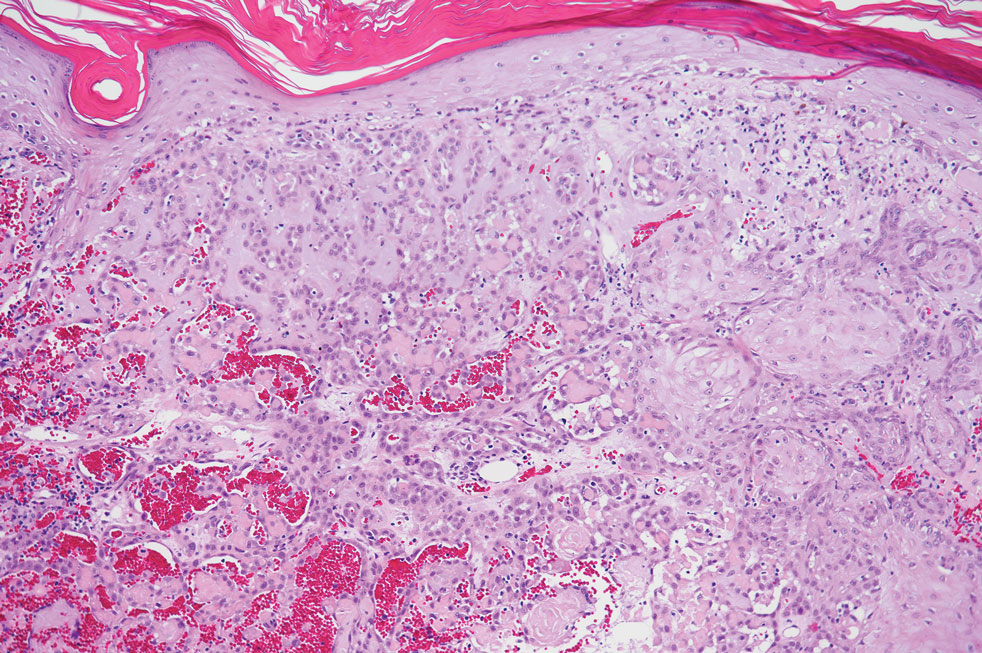
Pseudoangiomatous squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC), a variant of acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), is a rare epithelial neoplasm that can mimic angiosarcoma.1 Clinically, PSCC presents as a white-gray ulcer or nodular pink tumor on sun-exposed areas, typically on the head and neck. Due to its increased potential for metastasis, this variant of SCC is considered particularly aggressive. Histologically, PSCC shows nests of acantholytic atypical keratinocytes arranged in anastomosing arrays that form pseudovascular or pseudoglandular structures.2 Acantholytic spaces frequently are filled with erythrocytes. Immunohistochemically, PSCC tumor cells express classic squamous markers such as cytokeratin (CK) 5 and p63 but not vascular markers such as CD31, CD34, and von Willebrand factor.3 In our patient, histopathology of the lesion revealed invasive nests, lobules, and interconnected columns of well-differentiated squamous tumor cells that emanated from the base of the epidermis. The tumor exhibited acantholysis forming ectatic and slitlike spaces, some of which contained erythrocytes. The neoplastic cells, including those lining pseudovascular spaces, positively stained for CK5 (Figure 1A) and nuclear p63 but lacked reactivity to CD31 (Figure 1B) and CD34, corroborating squamous and not vascular differentiation. Current treatment guidelines include Mohs micrographic surgery, excisional surgery, or radiation.4 Our patient’s lesion was completely removed by Mohs micrographic surgery. Three months later, there was no evidence of recurrence.
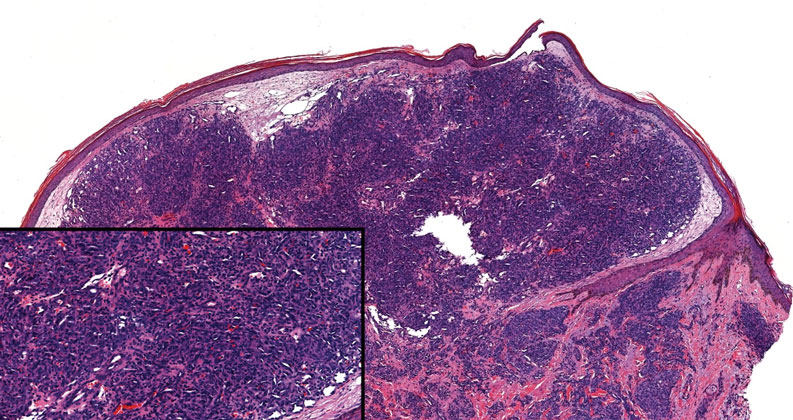
Angiosarcoma is an aggressive neoplasm associated with a poor prognosis and 5-year survival rate of 30% to 40%. The etiology of angiosarcoma still is unclear, but identified risk factors include prior radiation therapy, lymphedema (Stewart-Treves syndrome), and genetic predisposition.5 In the skin, angiosarcoma often occurs in the head and neck region, accounting for 60% of cutaneous cases.5,6 Early in the disease, most patients present with a bruiselike lesion on the scalp or forehead, often delaying the diagnosis.6 As the cancer progresses, tissue infiltration, edema, and hemorrhage contribute to the formation of violaceous nodules, which eventually prompt for biopsy. Angiosarcoma spans a broad histologic spectrum depending on the cytology of malignant cells (eg, spindle, small round, epithelioid) and their capacity for vasoformation. Welldifferentiated angiosarcoma shows retiform slitlike spaces in between collagen bundles that are lined by hyperchromatic hobnailing endothelial cells (Figure 2).7 Epithelioid angiosarcoma can be mistaken for SCC.8 Immunohistochemically, angiosarcoma stains positively for CD31, CD34, ETS-related gene 1, D2-40, and factor VIII.9 In our patient, the neoplasm was negative for vascular markers CD31 and CD34.
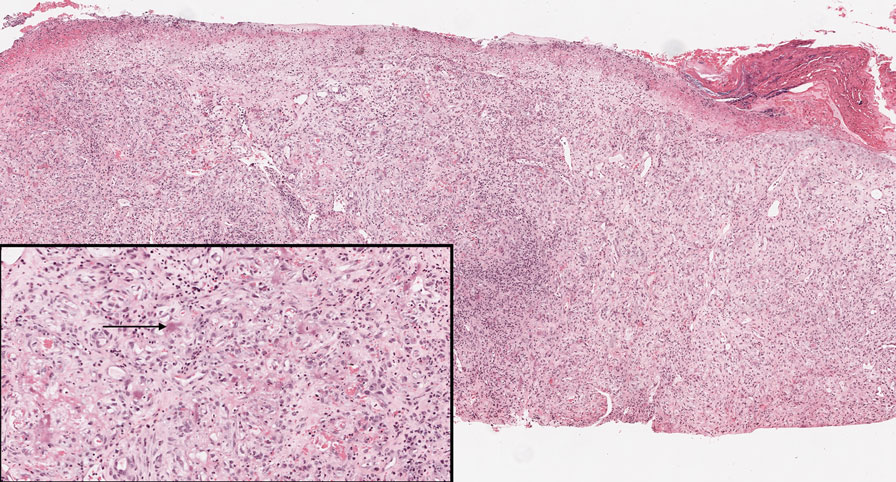
Bacillary angiomatosis (BA), caused by Bartonella henselae, is a rare disease that first was identified in HIV patients with diminished CD4+ T-cell counts. In the skin, BA often manifests as centrally ulcerated, single or clustered, reddish-purple nodules.10 Histologically, it is characterized by highly vascularized, histiocyterich infiltrates with admixed neutrophils and plasma cells (Figure 3). Capillaries often proliferate in a lobular fashion.11 Atypical cytology with areas of necrosis may mimic angiosarcoma.12 The pathognomonic feature of BA is the presence of enlarged histiocytes with pink-purplish cytoplasm corresponding to intracytoplasmic aggregates of bacteria, which can be revealed by Warthin-Starry or Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver staining. Immunohistochemically, proliferative benign capillaries are highlighted by CD34 and CD31, and histiocytes are decorated by CD68.12 This diagnosis was excluded based on the patient’s history, clinical presentation, and positive staining for CK5 and p63.
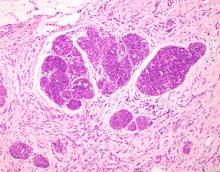
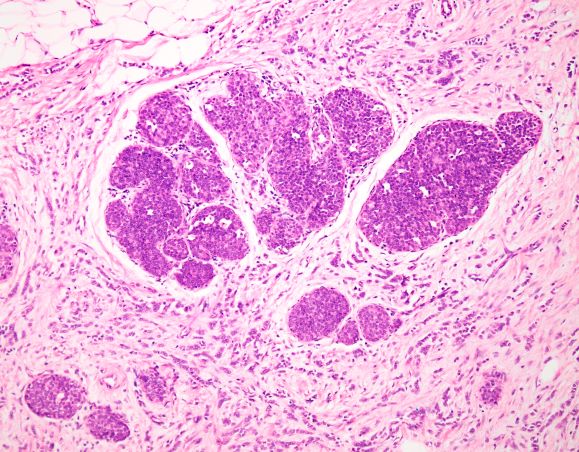
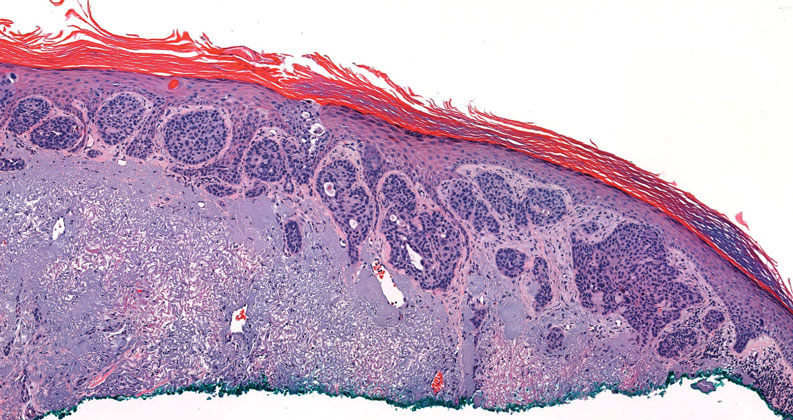
Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma is an exceedingly rare subtype of eccrine carcinoma that mimics SCC both clinically and histologically.13 It most often occurs on the head and neck of elderly patients. This neoplasm can look similar to SCC and its variants, including PSCC. Histologically, squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma exhibits a biphasic growth pattern.14 Well-differentiated squamous dysplasia transitions to carcinoma with eccrine duct formation as the tumor percolates deep into the dermis (Figure 4). As a result, superficial skin biopsies often lead to an incorrect diagnosis.15 Unlike SCC, the risk for locoregional and widespread metastasis is elevated. Identifying ducts in the deep aspect of the tumor is critical, thus immunohistochemical staining for carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen is paramount for the diagnosis.15 Pseudoangiomatous SCC will stain negative for carcinoembryonic antigen, as was the case in our patient.
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is a benign histologic reaction that can result from trauma, chronic inflammation (ie, pyoderma gangrenosum), tattoo placement, underlying neoplasia or fungal infection, or a spider bite reaction.14,15 It most commonly is seen as a well-demarcated nodule or plaque associated with scaling or crusting. Papules vary in size from less than 1 cm to several centimeters. Histologically, it is defined by an acanthotic proliferation of the adnexal epithelium and epidermis (Figure 5).16,17 Irregular strands, cords, and nests of squamoid cells can extend into the dermis.18 It can closely mimic SCC, but there are a few key differences. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia will not display atypical mitotic figures or atypical nuclei and will never invade lymphatics or vascular systems.19 Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia shows identical histology to well-differentiated SCC, and thus clinicopathologic correlation and mindful histologic evaluation are crucial. The presence of an increased influx of neutrophils and histiocytes should prompt for microbial stains or deeper sectioning. A superficial biopsy should be followed by a deep biopsy. In our patient, microorganismal stains were negative.
- Kiyohara T, Miyamoto M, Shijimaya T, et al. Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma: a review of the published work and reassessment of prognosis. J Dermatol. 2018;45:1448-1451.
- Nagore E, Sánchez-Motilla JM, Pérez-Vallés A, et al. Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:206-208.
- Han X, Lin X, Shao X. Pseudovascular adenoid squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: a case report and literature review. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020;13:1086-1089.
- Singh S, Bisht N, Purkayastha A, et al. Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma of the scalp in an elderly patient treated with radical radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Pract. 2018;5:165-168.
- Cao J, Wang J, He C, et al. Angiosarcoma: a review of diagnosis and current treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9:2303-2313.
- Buehler D, Rice SR, Moody JS, et al. Angiosarcoma outcomes and prognostic factors: a 25-year single institution experience. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37:473-479.
- Ronen S, Ivan D, Torres-Cabala CA, et al. Post‐radiation vascular lesions of the breast. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:52-58.
- Shilpa K, Leelavathy B, Gorur D, et al. Early-onset epithelioid angiosarcoma: diagnostic enigma, a rare case report. Indian J Dermatopathol Diagn Dermatol. 2019;6:36-38.
- Gaballah AH, Jensen CT, Palmquist S, et al. Angiosarcoma: clinical and imaging features from head to toe [published online May 4, 2017]. Br J Radiol. 2017;90:20170039. doi:10.1259/bjr.20170039
- Hoffman CF, Papadopoulos D, Palmer DM, et al. A case report of bacillary angiomatosis in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Cutis. 2002;69:175-178.
- Biwer E, Uerlich M, Wimheuer R, et al. Bacillary angiomatosis: an important differential diagnosis in patients with HIV. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:110.
- Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN. Bacillary angiomatosis. In: Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN, eds. Diagnostic Pathology: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2018:58-63.
- van der Horst MP, Garcia-Herrera A, Markiewicz D, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of 30 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40:755-760.
- Mckissack S, Wohltmann W, Dalton S, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: an aggressive mimicker of squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:140-143.
- Wollina U. Pyoderma gangrenosum—a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:19
- Chow P, Goddard L, Greenway H, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: the Scripps experience. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1115-1117.
- Zayour M, Lazova R. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia: a review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:112-122; quiz 123-126.
- Lynch JM. Understanding pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. Pathol Case Rev. 2004;9:36-45.
- Goel R, Wallace ML. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia secondary to cutaneous aspergillus. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:224-226.
The Diagnosis: Pseudoangiomatous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Pseudoangiomatous squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC), a variant of acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), is a rare epithelial neoplasm that can mimic angiosarcoma.1 Clinically, PSCC presents as a white-gray ulcer or nodular pink tumor on sun-exposed areas, typically on the head and neck. Due to its increased potential for metastasis, this variant of SCC is considered particularly aggressive. Histologically, PSCC shows nests of acantholytic atypical keratinocytes arranged in anastomosing arrays that form pseudovascular or pseudoglandular structures.2 Acantholytic spaces frequently are filled with erythrocytes. Immunohistochemically, PSCC tumor cells express classic squamous markers such as cytokeratin (CK) 5 and p63 but not vascular markers such as CD31, CD34, and von Willebrand factor.3 In our patient, histopathology of the lesion revealed invasive nests, lobules, and interconnected columns of well-differentiated squamous tumor cells that emanated from the base of the epidermis. The tumor exhibited acantholysis forming ectatic and slitlike spaces, some of which contained erythrocytes. The neoplastic cells, including those lining pseudovascular spaces, positively stained for CK5 (Figure 1A) and nuclear p63 but lacked reactivity to CD31 (Figure 1B) and CD34, corroborating squamous and not vascular differentiation. Current treatment guidelines include Mohs micrographic surgery, excisional surgery, or radiation.4 Our patient’s lesion was completely removed by Mohs micrographic surgery. Three months later, there was no evidence of recurrence.

Angiosarcoma is an aggressive neoplasm associated with a poor prognosis and 5-year survival rate of 30% to 40%. The etiology of angiosarcoma still is unclear, but identified risk factors include prior radiation therapy, lymphedema (Stewart-Treves syndrome), and genetic predisposition.5 In the skin, angiosarcoma often occurs in the head and neck region, accounting for 60% of cutaneous cases.5,6 Early in the disease, most patients present with a bruiselike lesion on the scalp or forehead, often delaying the diagnosis.6 As the cancer progresses, tissue infiltration, edema, and hemorrhage contribute to the formation of violaceous nodules, which eventually prompt for biopsy. Angiosarcoma spans a broad histologic spectrum depending on the cytology of malignant cells (eg, spindle, small round, epithelioid) and their capacity for vasoformation. Welldifferentiated angiosarcoma shows retiform slitlike spaces in between collagen bundles that are lined by hyperchromatic hobnailing endothelial cells (Figure 2).7 Epithelioid angiosarcoma can be mistaken for SCC.8 Immunohistochemically, angiosarcoma stains positively for CD31, CD34, ETS-related gene 1, D2-40, and factor VIII.9 In our patient, the neoplasm was negative for vascular markers CD31 and CD34.

Bacillary angiomatosis (BA), caused by Bartonella henselae, is a rare disease that first was identified in HIV patients with diminished CD4+ T-cell counts. In the skin, BA often manifests as centrally ulcerated, single or clustered, reddish-purple nodules.10 Histologically, it is characterized by highly vascularized, histiocyterich infiltrates with admixed neutrophils and plasma cells (Figure 3). Capillaries often proliferate in a lobular fashion.11 Atypical cytology with areas of necrosis may mimic angiosarcoma.12 The pathognomonic feature of BA is the presence of enlarged histiocytes with pink-purplish cytoplasm corresponding to intracytoplasmic aggregates of bacteria, which can be revealed by Warthin-Starry or Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver staining. Immunohistochemically, proliferative benign capillaries are highlighted by CD34 and CD31, and histiocytes are decorated by CD68.12 This diagnosis was excluded based on the patient’s history, clinical presentation, and positive staining for CK5 and p63.

Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma is an exceedingly rare subtype of eccrine carcinoma that mimics SCC both clinically and histologically.13 It most often occurs on the head and neck of elderly patients. This neoplasm can look similar to SCC and its variants, including PSCC. Histologically, squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma exhibits a biphasic growth pattern.14 Well-differentiated squamous dysplasia transitions to carcinoma with eccrine duct formation as the tumor percolates deep into the dermis (Figure 4). As a result, superficial skin biopsies often lead to an incorrect diagnosis.15 Unlike SCC, the risk for locoregional and widespread metastasis is elevated. Identifying ducts in the deep aspect of the tumor is critical, thus immunohistochemical staining for carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen is paramount for the diagnosis.15 Pseudoangiomatous SCC will stain negative for carcinoembryonic antigen, as was the case in our patient.

Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is a benign histologic reaction that can result from trauma, chronic inflammation (ie, pyoderma gangrenosum), tattoo placement, underlying neoplasia or fungal infection, or a spider bite reaction.14,15 It most commonly is seen as a well-demarcated nodule or plaque associated with scaling or crusting. Papules vary in size from less than 1 cm to several centimeters. Histologically, it is defined by an acanthotic proliferation of the adnexal epithelium and epidermis (Figure 5).16,17 Irregular strands, cords, and nests of squamoid cells can extend into the dermis.18 It can closely mimic SCC, but there are a few key differences. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia will not display atypical mitotic figures or atypical nuclei and will never invade lymphatics or vascular systems.19 Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia shows identical histology to well-differentiated SCC, and thus clinicopathologic correlation and mindful histologic evaluation are crucial. The presence of an increased influx of neutrophils and histiocytes should prompt for microbial stains or deeper sectioning. A superficial biopsy should be followed by a deep biopsy. In our patient, microorganismal stains were negative.

The Diagnosis: Pseudoangiomatous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Pseudoangiomatous squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC), a variant of acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), is a rare epithelial neoplasm that can mimic angiosarcoma.1 Clinically, PSCC presents as a white-gray ulcer or nodular pink tumor on sun-exposed areas, typically on the head and neck. Due to its increased potential for metastasis, this variant of SCC is considered particularly aggressive. Histologically, PSCC shows nests of acantholytic atypical keratinocytes arranged in anastomosing arrays that form pseudovascular or pseudoglandular structures.2 Acantholytic spaces frequently are filled with erythrocytes. Immunohistochemically, PSCC tumor cells express classic squamous markers such as cytokeratin (CK) 5 and p63 but not vascular markers such as CD31, CD34, and von Willebrand factor.3 In our patient, histopathology of the lesion revealed invasive nests, lobules, and interconnected columns of well-differentiated squamous tumor cells that emanated from the base of the epidermis. The tumor exhibited acantholysis forming ectatic and slitlike spaces, some of which contained erythrocytes. The neoplastic cells, including those lining pseudovascular spaces, positively stained for CK5 (Figure 1A) and nuclear p63 but lacked reactivity to CD31 (Figure 1B) and CD34, corroborating squamous and not vascular differentiation. Current treatment guidelines include Mohs micrographic surgery, excisional surgery, or radiation.4 Our patient’s lesion was completely removed by Mohs micrographic surgery. Three months later, there was no evidence of recurrence.

Angiosarcoma is an aggressive neoplasm associated with a poor prognosis and 5-year survival rate of 30% to 40%. The etiology of angiosarcoma still is unclear, but identified risk factors include prior radiation therapy, lymphedema (Stewart-Treves syndrome), and genetic predisposition.5 In the skin, angiosarcoma often occurs in the head and neck region, accounting for 60% of cutaneous cases.5,6 Early in the disease, most patients present with a bruiselike lesion on the scalp or forehead, often delaying the diagnosis.6 As the cancer progresses, tissue infiltration, edema, and hemorrhage contribute to the formation of violaceous nodules, which eventually prompt for biopsy. Angiosarcoma spans a broad histologic spectrum depending on the cytology of malignant cells (eg, spindle, small round, epithelioid) and their capacity for vasoformation. Welldifferentiated angiosarcoma shows retiform slitlike spaces in between collagen bundles that are lined by hyperchromatic hobnailing endothelial cells (Figure 2).7 Epithelioid angiosarcoma can be mistaken for SCC.8 Immunohistochemically, angiosarcoma stains positively for CD31, CD34, ETS-related gene 1, D2-40, and factor VIII.9 In our patient, the neoplasm was negative for vascular markers CD31 and CD34.

Bacillary angiomatosis (BA), caused by Bartonella henselae, is a rare disease that first was identified in HIV patients with diminished CD4+ T-cell counts. In the skin, BA often manifests as centrally ulcerated, single or clustered, reddish-purple nodules.10 Histologically, it is characterized by highly vascularized, histiocyterich infiltrates with admixed neutrophils and plasma cells (Figure 3). Capillaries often proliferate in a lobular fashion.11 Atypical cytology with areas of necrosis may mimic angiosarcoma.12 The pathognomonic feature of BA is the presence of enlarged histiocytes with pink-purplish cytoplasm corresponding to intracytoplasmic aggregates of bacteria, which can be revealed by Warthin-Starry or Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver staining. Immunohistochemically, proliferative benign capillaries are highlighted by CD34 and CD31, and histiocytes are decorated by CD68.12 This diagnosis was excluded based on the patient’s history, clinical presentation, and positive staining for CK5 and p63.

Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma is an exceedingly rare subtype of eccrine carcinoma that mimics SCC both clinically and histologically.13 It most often occurs on the head and neck of elderly patients. This neoplasm can look similar to SCC and its variants, including PSCC. Histologically, squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma exhibits a biphasic growth pattern.14 Well-differentiated squamous dysplasia transitions to carcinoma with eccrine duct formation as the tumor percolates deep into the dermis (Figure 4). As a result, superficial skin biopsies often lead to an incorrect diagnosis.15 Unlike SCC, the risk for locoregional and widespread metastasis is elevated. Identifying ducts in the deep aspect of the tumor is critical, thus immunohistochemical staining for carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen is paramount for the diagnosis.15 Pseudoangiomatous SCC will stain negative for carcinoembryonic antigen, as was the case in our patient.

Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is a benign histologic reaction that can result from trauma, chronic inflammation (ie, pyoderma gangrenosum), tattoo placement, underlying neoplasia or fungal infection, or a spider bite reaction.14,15 It most commonly is seen as a well-demarcated nodule or plaque associated with scaling or crusting. Papules vary in size from less than 1 cm to several centimeters. Histologically, it is defined by an acanthotic proliferation of the adnexal epithelium and epidermis (Figure 5).16,17 Irregular strands, cords, and nests of squamoid cells can extend into the dermis.18 It can closely mimic SCC, but there are a few key differences. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia will not display atypical mitotic figures or atypical nuclei and will never invade lymphatics or vascular systems.19 Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia shows identical histology to well-differentiated SCC, and thus clinicopathologic correlation and mindful histologic evaluation are crucial. The presence of an increased influx of neutrophils and histiocytes should prompt for microbial stains or deeper sectioning. A superficial biopsy should be followed by a deep biopsy. In our patient, microorganismal stains were negative.

- Kiyohara T, Miyamoto M, Shijimaya T, et al. Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma: a review of the published work and reassessment of prognosis. J Dermatol. 2018;45:1448-1451.
- Nagore E, Sánchez-Motilla JM, Pérez-Vallés A, et al. Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:206-208.
- Han X, Lin X, Shao X. Pseudovascular adenoid squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: a case report and literature review. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020;13:1086-1089.
- Singh S, Bisht N, Purkayastha A, et al. Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma of the scalp in an elderly patient treated with radical radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Pract. 2018;5:165-168.
- Cao J, Wang J, He C, et al. Angiosarcoma: a review of diagnosis and current treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9:2303-2313.
- Buehler D, Rice SR, Moody JS, et al. Angiosarcoma outcomes and prognostic factors: a 25-year single institution experience. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37:473-479.
- Ronen S, Ivan D, Torres-Cabala CA, et al. Post‐radiation vascular lesions of the breast. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:52-58.
- Shilpa K, Leelavathy B, Gorur D, et al. Early-onset epithelioid angiosarcoma: diagnostic enigma, a rare case report. Indian J Dermatopathol Diagn Dermatol. 2019;6:36-38.
- Gaballah AH, Jensen CT, Palmquist S, et al. Angiosarcoma: clinical and imaging features from head to toe [published online May 4, 2017]. Br J Radiol. 2017;90:20170039. doi:10.1259/bjr.20170039
- Hoffman CF, Papadopoulos D, Palmer DM, et al. A case report of bacillary angiomatosis in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Cutis. 2002;69:175-178.
- Biwer E, Uerlich M, Wimheuer R, et al. Bacillary angiomatosis: an important differential diagnosis in patients with HIV. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:110.
- Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN. Bacillary angiomatosis. In: Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN, eds. Diagnostic Pathology: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2018:58-63.
- van der Horst MP, Garcia-Herrera A, Markiewicz D, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of 30 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40:755-760.
- Mckissack S, Wohltmann W, Dalton S, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: an aggressive mimicker of squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:140-143.
- Wollina U. Pyoderma gangrenosum—a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:19
- Chow P, Goddard L, Greenway H, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: the Scripps experience. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1115-1117.
- Zayour M, Lazova R. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia: a review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:112-122; quiz 123-126.
- Lynch JM. Understanding pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. Pathol Case Rev. 2004;9:36-45.
- Goel R, Wallace ML. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia secondary to cutaneous aspergillus. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:224-226.
- Kiyohara T, Miyamoto M, Shijimaya T, et al. Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma: a review of the published work and reassessment of prognosis. J Dermatol. 2018;45:1448-1451.
- Nagore E, Sánchez-Motilla JM, Pérez-Vallés A, et al. Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2000;25:206-208.
- Han X, Lin X, Shao X. Pseudovascular adenoid squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: a case report and literature review. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020;13:1086-1089.
- Singh S, Bisht N, Purkayastha A, et al. Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma of the scalp in an elderly patient treated with radical radiotherapy. J Cancer Res Pract. 2018;5:165-168.
- Cao J, Wang J, He C, et al. Angiosarcoma: a review of diagnosis and current treatment. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9:2303-2313.
- Buehler D, Rice SR, Moody JS, et al. Angiosarcoma outcomes and prognostic factors: a 25-year single institution experience. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37:473-479.
- Ronen S, Ivan D, Torres-Cabala CA, et al. Post‐radiation vascular lesions of the breast. J Cutan Pathol. 2019;46:52-58.
- Shilpa K, Leelavathy B, Gorur D, et al. Early-onset epithelioid angiosarcoma: diagnostic enigma, a rare case report. Indian J Dermatopathol Diagn Dermatol. 2019;6:36-38.
- Gaballah AH, Jensen CT, Palmquist S, et al. Angiosarcoma: clinical and imaging features from head to toe [published online May 4, 2017]. Br J Radiol. 2017;90:20170039. doi:10.1259/bjr.20170039
- Hoffman CF, Papadopoulos D, Palmer DM, et al. A case report of bacillary angiomatosis in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Cutis. 2002;69:175-178.
- Biwer E, Uerlich M, Wimheuer R, et al. Bacillary angiomatosis: an important differential diagnosis in patients with HIV. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:110.
- Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN. Bacillary angiomatosis. In: Medeiros LJ, Miranda RN, eds. Diagnostic Pathology: Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2018:58-63.
- van der Horst MP, Garcia-Herrera A, Markiewicz D, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of 30 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40:755-760.
- Mckissack S, Wohltmann W, Dalton S, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: an aggressive mimicker of squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:140-143.
- Wollina U. Pyoderma gangrenosum—a review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:19
- Chow P, Goddard L, Greenway H, et al. Squamoid eccrine ductal carcinoma: the Scripps experience. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:1115-1117.
- Zayour M, Lazova R. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia: a review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:112-122; quiz 123-126.
- Lynch JM. Understanding pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. Pathol Case Rev. 2004;9:36-45.
- Goel R, Wallace ML. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia secondary to cutaneous aspergillus. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:224-226.
An 84-year-old man with a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer presented to our clinic with a 1.6×1.5-cm exophytic lesion on the left posterior parietal scalp. The lesion nearly doubled in size over the last 4 months. The patient received radiation therapy in this area for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma 7 years prior to presentation. A shave biopsy was performed.
Rituximab Treatment and Improvement of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Pemphigus
Pemphigus is a group of autoimmune blistering diseases characterized by the development of painful and flaccid blisters on the skin and/or mucous membranes. Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) and pemphigus foliaceus (PF) are 2 major subtypes and can be distinguished by the location of blister formation or the specificity of autoantibodies directed against different desmogleins.1,2 Although rare, pemphigus is considered a serious and life-threatening condition with a great impact on quality of life (QOL) due to disease symptoms (eg, painful lesions, physical appearance of skin lesions) as well as treatment complications (eg, adverse drug effects, cost of treatment).3-6 Moreover, the physical and psychological effects can lead to marked functional morbidity and work-related disability during patients’ productive years.7 Therefore, affected individuals usually have a remarkably compromised health-related quality of life (HRQOL).8 Effective treatments may considerably improve the QOL of patients with pemphigus.6
Despite the available treatment options, finding the best regimen for pemphigus remains a challenge. Corticosteroids are assumed to be the main treatment, though they have considerable side effects.9,10 Adjuvant therapies are used to suppress or modulate immune responses, leading to remission with the least possible need for corticosteroids. Finding an optimal steroid-sparing agent has been the aim of research, and biologic agents seem to be the best option.8 Rituximab (RTX), an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has shown great promise in several studies of its clinical efficacy and has become a first-line treatment in new guidelines.11-14 Rituximab treatment has been associated with notable improvement in physician-assessed outcome measures with a favorable safety profile in patients with pemphigus.11-15 However, it is important to assess response to treatment from a patient’s perspective through the use of outcome-assessment measures that encompass patient-reported outcomes to reflect the complete patient experience and establish the overall impact of RTX as well as its likelihood of acceptance by patients with pemphigus.
In our study, we compared clinical outcomes and HRQOL through the use of disease-specific measures as well as comprehensive generic health status measures among patients with PV and PF who received RTX treatment 3 months earlier and those who received RTX in the last 2 weeks. The clinical relevance of the patient-reported outcomes is discussed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Design
We conducted a single-center cross-sectional study of 96 patients with pemphigus aged 18 to 65 years of either sex who were willing to participate in this study. Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of PV or PF who received RTX 3 months earlier or in the last 2 weeks were enrolled in the study. Patients were identified using Dermatry.ir, an archiving software that contains patients’ medical data. Exclusion criteria included lack of sufficient knowledge of the concepts of the questionnaires as well as age younger than 16 years. The study was conducted from October 2019 to April 2020 by the Autoimmune Bullous Disease Research Center at Razi Hospital in Tehran, Iran, which is the main dermatology-specific center and teaching hospital of Iran. The study protocol was approved by the relevant ethics committee.
Patients were categorized into 2 groups: (1) those who received RTX 3 months earlier (3M group); and (2) those who received RTX in the last 2 weeks (R group).
After an explanation of the study to participants, informed written consent was signed by each patient, and their personal data (eg, age, sex, education, marital status, smoking status), as well as clinical data (eg, type of pemphigus, duration of disease, site of onset, prednisolone dosage, presence of Nikolsky sign, anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values, Pemphigus Disease Area Index [PDAI] score, RTX treatment protocol); any known comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or morbid obesity; and any chronic pulmonary, cardiac, endocrinologic, renal, or hepatic condition, were collected and recorded in a predefined Case Record.
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
The effect of RTX on QOL in patients with pemphigus was assessed using 2 HRQOL instruments: (1) a general health status indicator, the 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36), and (2) a validated, Persian version of a dermatology-specific questionnaire, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). The questionnaires were completed by each patient or by an assistant if needed.
The SF-36 is a widely used 36-item questionnaire measuring functional health and well-being across 8 domains—mental health, pain, physical function, role emotional, role physical, social functioning, vitality, and general health perception—with scores for each ranging from 0 to 100. The physical component scores (PCSs) and mental component scores (MCSs) were derived from these 8 subscales, each ranging from 0 to 400, with higher scores indicating better health status.6
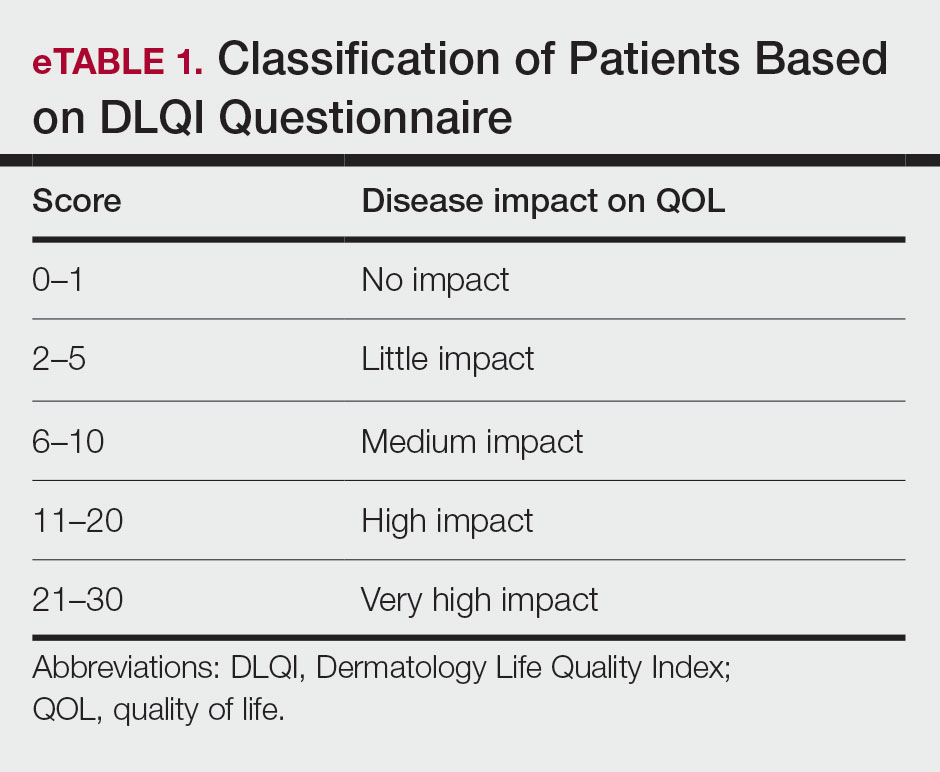
The DLQI, one of the most frequently used QOL measures in dermatology, contains 10 questions, each referring to the prior week and classified in the following 6 subscales: symptoms and feelings, daily activities, leisure, personal relationships, work and school, and treatment.16 The total score ranges from 0 (no impact) to 30 (very high impact), with a higher score indicating a lower QOL (eTable 1). The minimal clinically important difference (MCD) for the DLQI was considered to be 2- to 5-point changes in prior studies.17,18 In this study, we used an MCD of a 5-point change or more between study groups.
Moreover, the patient general assessment (PGA) of disease severity was identified using a 3-point scale (1=mild, 2=moderate, 3=severe).
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics version 23. P≤.05 was considered significant. Mean and SD were calculated for descriptive data. The t test, Fisher exact test, analysis of variance, multiple regression analysis, and logistic regression analysis were used to identify the relationship between variables.
RESULTS
Patient Characteristics
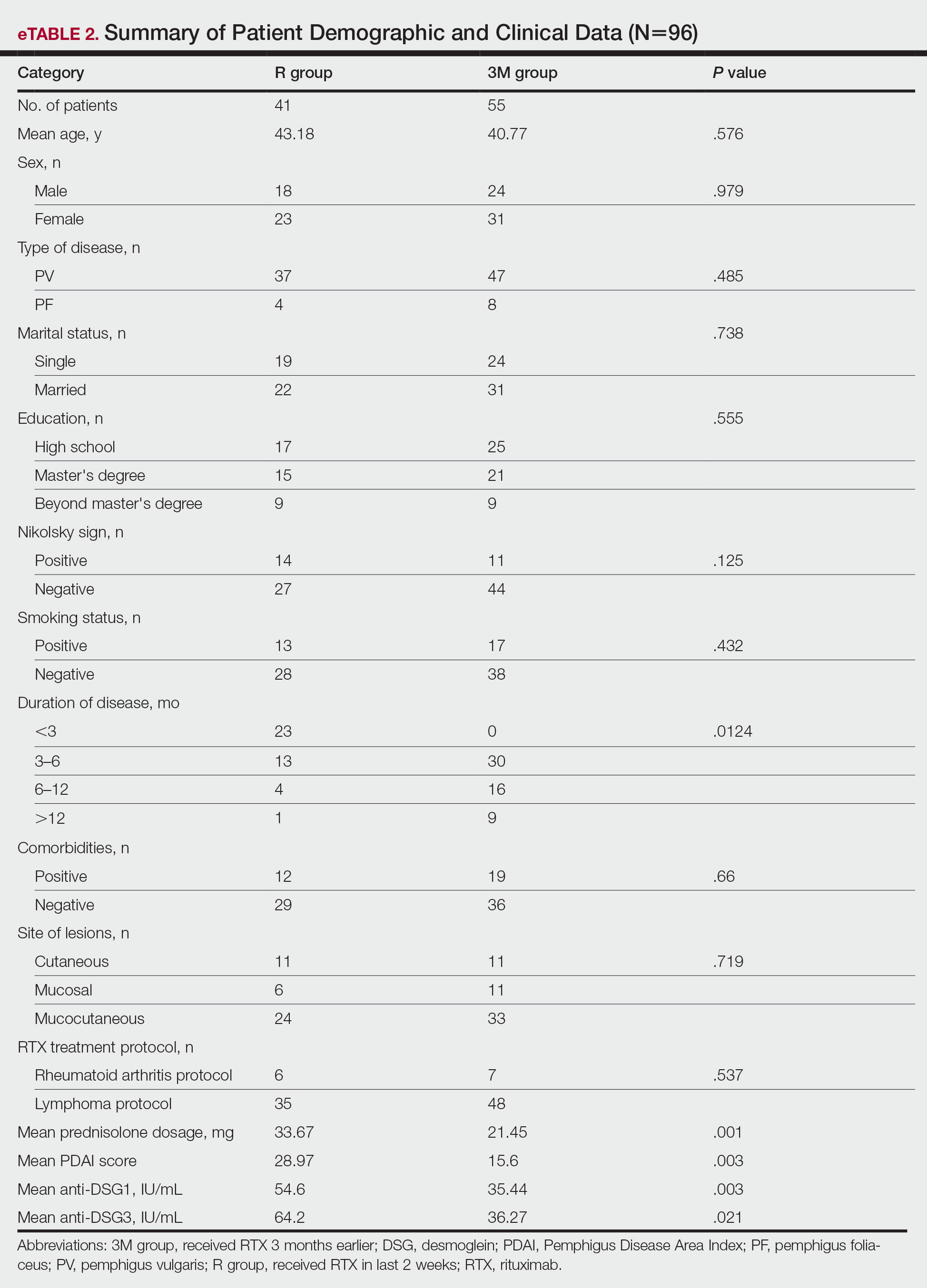
A total of 96 patients were enrolled in this study. The mean (SD) age of participants was 41.42 (15.1) years (range, 18–58 years). Of 96 patients whose data were included, 55 (57.29%) patients had received RTX 3 months earlier (3M group) and 41 (42.71%) received RTX in the last 2 weeks (R group). A summary of study patient characteristics in each group is provided in eTable 2. There was no significant difference between the 2 groups in terms of age, sex, type of pemphigus, marital status, education, positive Nikolsky sign, smoking status, existence of comorbidities, site of lesions, and RTX treatment protocol. However, a significant difference was found for duration of disease (P=.0124) and mean prednisolone dosage (P=.001) as well as severity of disease measured by PDAI score (P=.003) and anti-DSG1 (P=.003) and anti-DSG3 (P=.021) values.
Patient-Reported Outcomes
Physical and mental component scores are summarized in eTable 3. Generally, SF-36 scores were improved with RTX treatment in all dimensions except for mental health, though these differences were not statistically significant, with the greatest mean improvement in the role physical index (75.45 in the 3M group vs 53.04 in the R group; P=.009). Mean SF-36 PCS and MCS scores were higher in the 3M group vs the R group, though the difference in MCS score did not reach the level of significance (eTable 3).
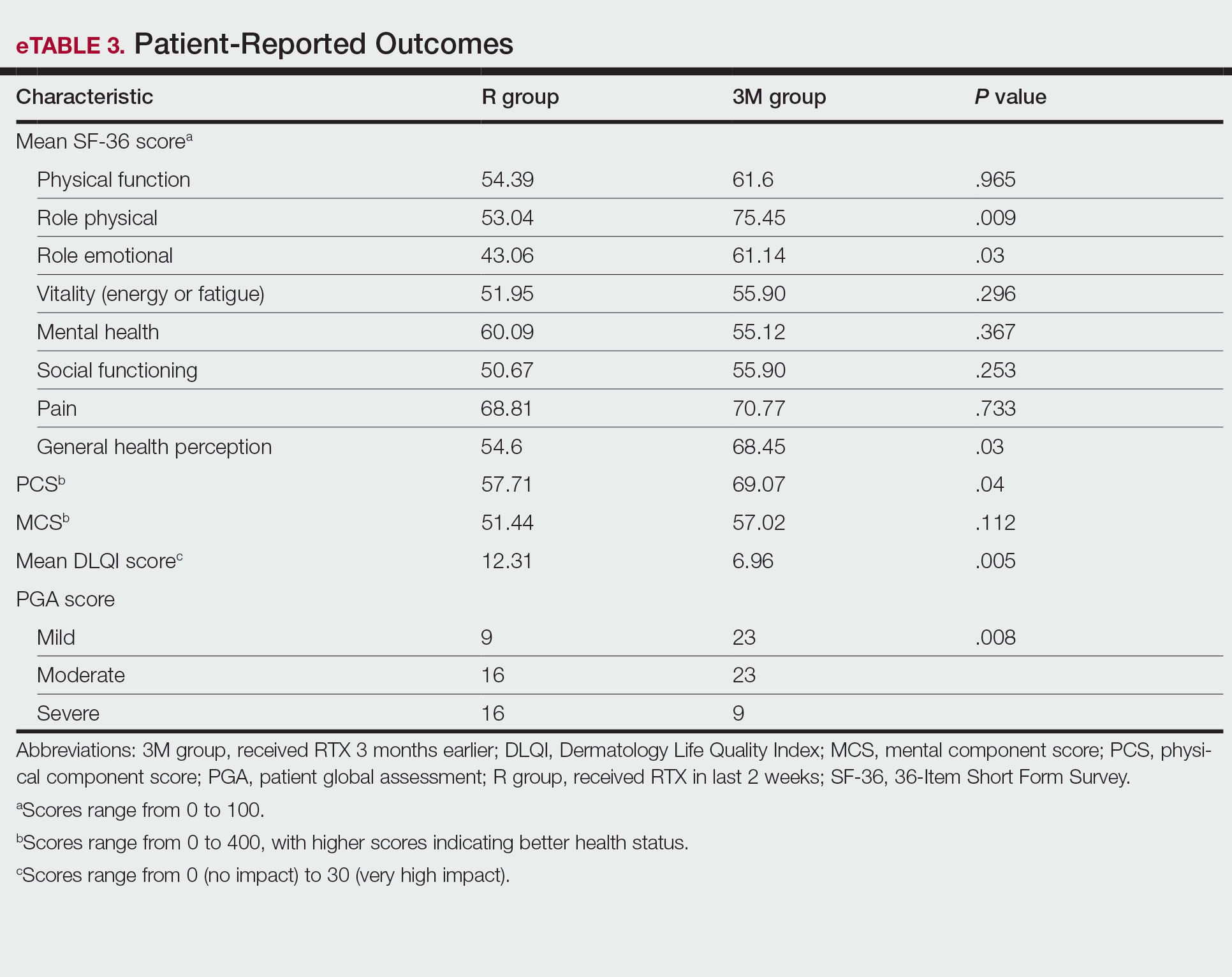
Mean DLQI scores in the R and 3M groups were 12.31 and 6.96, respectively, indicating a considerable burden on HRQOL in both groups. However, a statistically significant difference between these values was seen that also was clinically meaningful, indicating a significant improvement of QOL in patients receiving RTX 3 months earlier (P=.005)(eTable 3).
The PGA scores indicated that patients in the 3M group were significantly more likely to report less severe disease vs the R group (P=.008)(eTable 3).
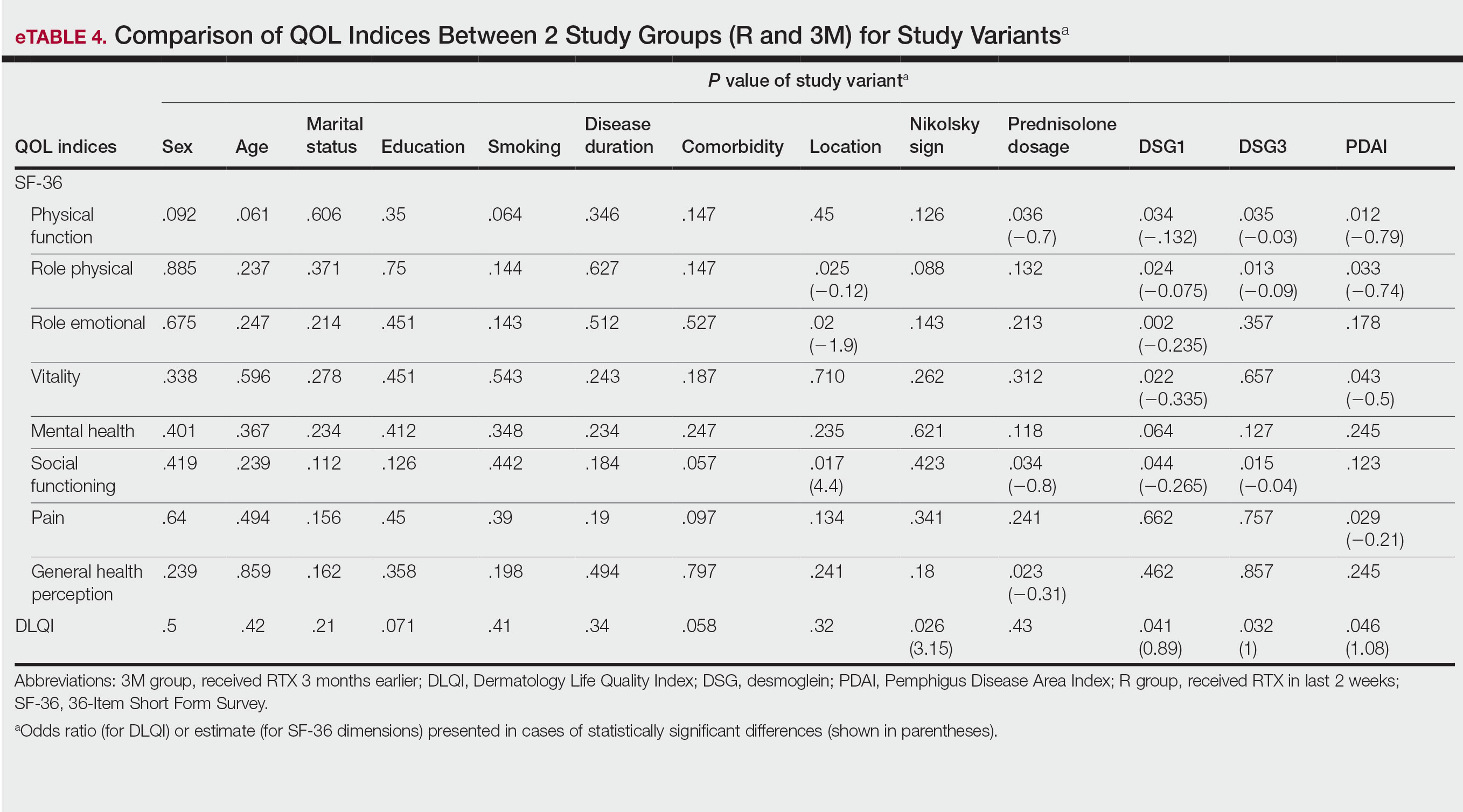
Multivariate Analysis—Effect of the patient characteristics and some disease features on indices of QOL was evaluated using the multiple linear regression model. eTable 4 shows the P values of those analyses.
COMMENT
Pemphigus is a chronic disabling disease with notable QOL impairment due to disease burden as well as the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive agents during the disease course. To study the effect of RTX on QOL of patients with pemphigus, we compared 2 sets of patients. Prior studies have shown that clinically significant effects of RTX take 4 to 12 weeks to appear.19,20 Therefore, we selected patients who received RTX 3 months earlier to measure their HRQOL indices and compare them with patients who had received RTX in the last 2 weeks as a control group to investigate the effect of RTX intrinsically, as this was the focus of this study.
In our study, one of the research tools was the DLQI. Healthy patients typically have an average score of 0.5.21 The mean DLQI score of the patients in R group was 12.31, which was similar to prior analysis8 and reflects a substantial burden of disease comparable to atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.21,22 In patients in the 3M group, the mean DLQI score was lower than the R group (6.96 vs 12.31), indicating a significant (P=.005) and clinically meaningful improvement in QOL of patients due to the dramatic therapeutic effect of RTX. However, this score indicated a moderate effect on HRQOL, even in the context of clinical improvement due to RTX treatment, which may reflect that the short duration of treatment in the 3M group was a limitation of this study. Although the 12-week treatment duration was comparable with other studies19,20 and major differences in objective measures of treatment efficacy were found in PDAI as well as anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values, longer treatment duration may be needed for a more comprehensive assessment of the benefit of RTX on HRQOL indices in patients with pemphigus.
Based on results of the SF-36 questionnaire, PCS and MCS scores were not substantially impaired in the R group considering the fact that a mean score of 50 has been articulated as a normative value for all scales.23 These data demonstrated the importance of using a dermatologic-specific instrument such as the DLQI instead of a general questionnaire to assess QOL in patients with pemphigus. However, better indices were reported with RTX treatment in the 3 SF-36 domains—role physical (P=.009), role emotional (P=.03), and general health perception (P=.03)—with the role physical showing the greatest magnitude of mean change (75.45 in the 3M group vs 53.04 in the R group). Notably, PCS was impaired to a greater extent than MCS in patients in the R group and showed a greater magnitude of improvement after 3 months of treatment. These results could be explained by the fact that MCS can be largely changed in diseases with a direct effect on the central nervous system.23
Our results also revealed that the dose of corticosteroid correlated to HRQOL of patients with pemphigus who recently received RTX therapy. Indeed, it is more likely that patients on lower-dose prednisolone have a higher QOL, especially on physical function and social function dimensions of SF-36. This finding is highly expectable by less severe disease due to RTX treatment and also lower potential dose-dependent adverse effects of long-term steroid therapy.
One of the most striking findings of this study was the correlation of location of lesions to QOL indices. We found that the mucocutaneous phenotype was significantly correlated to greater improvement in role emotional, role physical, and social functioning scores due to RTX treatment compared with cutaneous or mucosal types (P=.02, P=.025, and P=.017, respectively). Although mucosal involvement of the disease can be the most burdensome feature because of its large impact on essential activities such as eating and speaking, cutaneous lesions with unpleasant appearance and undesirable symptoms may have a similar impact on QOL. Therefore, having both mucosal and cutaneous lesions causes a worsened QOL and decreased treatment efficacy vs having only one area involved. This may explain the greater improvement in some QOL indices with RTX treatment.
Limitations—Given the cross-sectional design of this study in which patients were observed at a single time point during their treatment course, it is not possible to establish a clear cause-effect relationship between variables. Moreover, we did not evaluate the impact of RTX or prednisolone adverse effects on QOL. Therefore, further prospective studies with longer treatment durations may help to validate our findings. In addition, MCDs for DLQI and SF-36 in pemphigus need to be determined and validated in future studies.
CONCLUSION
The results of our study demonstrated that patients with pemphigus may benefit from taking RTX, not only in terms of clinical improvement of their disease measured by objective indices such as PDAI and anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values but also in several domains that are important to patients, including physical and mental health status (SF-36), HRQOL (DLQI), and overall disease severity (PGA). Rituximab administration in patients with pemphigus can lead to rapid and significant improvement in HRQOL as well as patient- and physician-assessed measures. Its favorable safety profile along with its impact on patients’ daily lives and mental health makes RTX a suitable treatment option for patients with pemphigus. Moreover, we recommend taking QOL indices into account while evaluating the efficacy of new medications to improve our insight into the patient experience and provide better patient adherence to treatment, which is an important issue for optimal control of chronic disorders.
- Hammers CM, Stanley JR. Mechanisms of disease: pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Ann Rev Pathol. 2016;11:175-197.
- Kasperkiewicz M, Ellebrecht CT, Takahashi H, et al. Pemphigus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17026.
- Mayrshofer F, Hertl M, Sinkgraven R, et al. Significant decrease in quality of life in patients with pemphigus vulgaris, result from the German Bullous Skin Disease (BSD) Study Group. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2005;3:431-435.
- Terrab Z, Benckikhi H, Maaroufi A, et al. Quality of life and pemphigus. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2005;132:321-328.
- Tabolli S, Mozzetta A, Antinone V, et al. The health impact of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus assessed using the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form health survey questionnaire. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:1029-1034.
- Paradisi A, Sampogna F, Di Pietro, C, et al. Quality-of-life assessment in patients with pemphigus using a minimum set of evaluation tools. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:261-269.
- Heelan K, Hitzig SL, Knowles S, et al. Loss of work productivity and quality of life in patients with autoimmune bullous dermatoses. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015;19:546-554.
- Ghodsi SZ, Chams-Davatchi C, Daneshpazhooh M, et al. Quality of life and psychological status of patients with pemphigus vulgaris using Dermatology Life Quality Index and General Health Questionnaires. J Dermatol. 2012;39:141-144.
- Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:2343.
- Mohammad-Javad N, Parvaneh H, Maryam G, et al. Randomized trial of tacrolimus 0.1% ointment versus triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% paste in the treatment of oral pemphigus vulgaris. Iranian J Dermatol. 2012;15:42-46.
- Lunardon L, Tsai KJ, Propert KJ, et al. Adjuvant rituximab therapy of pemphigus: a single-center experience with 31 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:1031-1036.
- Colliou N, Picard D, Caillot F, et al. Long-term remissions of severe pemphigus after rituximab therapy are associated with prolonged failure of desmoglein B cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:175ra30.
- Heelan K, Al-Mohammedi F, Smith MJ, et al. Durable remission of pemphigus with a fixed-dose rituximab protocol. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:703-708.
- Joly P, Maho-Vaillant M, Prost-Squarcioni C, et al. First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux3): a prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2031-2040
- Aryanian Z, Balighi K, Daneshpazhooh M, et al. Rituximab exhibits a better safety profile when used as a first line of treatment for pemphigus vulgaris: a retrospective study. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;96:107755.
- Aghai S, Sodaifi M, Jafari P, et al. DLQI scores in vitiligo: reliability and validity of the Persian version. BMC Dermatol. 2004;4:8.
- Schünemann HJ, Akl EA, Guyatt GH. Interpreting the results of patient reported outcome measures in clinical trials: the clinician’s perspective. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2006;4:62.
- Quality of life questionnaires. Cardiff University website. Accessed December 16, 2022. http://sites.cardiff.ac.uk/dermatology/quality-oflife/dermatology-quality-of-life-index-dlqi/dlqi-instructions-foruse-and-scoring/
- Kanwar AJ, Tsuruta D, Vinay K, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab treatment in Indian pemphigus patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E17-E23.
- Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Cosnes A, et al. First-line treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with a combination of rituximab and high-potency topical corticosteroids. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:200-203.
- Finlay AY, Khan GK. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1994;19:210-216.
- Aghaei S, Moradi A, Ardekani GS. Impact of psoriasis on quality of life in Iran. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:220.
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). 1. conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473-483.
Pemphigus is a group of autoimmune blistering diseases characterized by the development of painful and flaccid blisters on the skin and/or mucous membranes. Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) and pemphigus foliaceus (PF) are 2 major subtypes and can be distinguished by the location of blister formation or the specificity of autoantibodies directed against different desmogleins.1,2 Although rare, pemphigus is considered a serious and life-threatening condition with a great impact on quality of life (QOL) due to disease symptoms (eg, painful lesions, physical appearance of skin lesions) as well as treatment complications (eg, adverse drug effects, cost of treatment).3-6 Moreover, the physical and psychological effects can lead to marked functional morbidity and work-related disability during patients’ productive years.7 Therefore, affected individuals usually have a remarkably compromised health-related quality of life (HRQOL).8 Effective treatments may considerably improve the QOL of patients with pemphigus.6
Despite the available treatment options, finding the best regimen for pemphigus remains a challenge. Corticosteroids are assumed to be the main treatment, though they have considerable side effects.9,10 Adjuvant therapies are used to suppress or modulate immune responses, leading to remission with the least possible need for corticosteroids. Finding an optimal steroid-sparing agent has been the aim of research, and biologic agents seem to be the best option.8 Rituximab (RTX), an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has shown great promise in several studies of its clinical efficacy and has become a first-line treatment in new guidelines.11-14 Rituximab treatment has been associated with notable improvement in physician-assessed outcome measures with a favorable safety profile in patients with pemphigus.11-15 However, it is important to assess response to treatment from a patient’s perspective through the use of outcome-assessment measures that encompass patient-reported outcomes to reflect the complete patient experience and establish the overall impact of RTX as well as its likelihood of acceptance by patients with pemphigus.
In our study, we compared clinical outcomes and HRQOL through the use of disease-specific measures as well as comprehensive generic health status measures among patients with PV and PF who received RTX treatment 3 months earlier and those who received RTX in the last 2 weeks. The clinical relevance of the patient-reported outcomes is discussed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Design
We conducted a single-center cross-sectional study of 96 patients with pemphigus aged 18 to 65 years of either sex who were willing to participate in this study. Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of PV or PF who received RTX 3 months earlier or in the last 2 weeks were enrolled in the study. Patients were identified using Dermatry.ir, an archiving software that contains patients’ medical data. Exclusion criteria included lack of sufficient knowledge of the concepts of the questionnaires as well as age younger than 16 years. The study was conducted from October 2019 to April 2020 by the Autoimmune Bullous Disease Research Center at Razi Hospital in Tehran, Iran, which is the main dermatology-specific center and teaching hospital of Iran. The study protocol was approved by the relevant ethics committee.
Patients were categorized into 2 groups: (1) those who received RTX 3 months earlier (3M group); and (2) those who received RTX in the last 2 weeks (R group).
After an explanation of the study to participants, informed written consent was signed by each patient, and their personal data (eg, age, sex, education, marital status, smoking status), as well as clinical data (eg, type of pemphigus, duration of disease, site of onset, prednisolone dosage, presence of Nikolsky sign, anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values, Pemphigus Disease Area Index [PDAI] score, RTX treatment protocol); any known comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or morbid obesity; and any chronic pulmonary, cardiac, endocrinologic, renal, or hepatic condition, were collected and recorded in a predefined Case Record.
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
The effect of RTX on QOL in patients with pemphigus was assessed using 2 HRQOL instruments: (1) a general health status indicator, the 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36), and (2) a validated, Persian version of a dermatology-specific questionnaire, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). The questionnaires were completed by each patient or by an assistant if needed.
The SF-36 is a widely used 36-item questionnaire measuring functional health and well-being across 8 domains—mental health, pain, physical function, role emotional, role physical, social functioning, vitality, and general health perception—with scores for each ranging from 0 to 100. The physical component scores (PCSs) and mental component scores (MCSs) were derived from these 8 subscales, each ranging from 0 to 400, with higher scores indicating better health status.6
The DLQI, one of the most frequently used QOL measures in dermatology, contains 10 questions, each referring to the prior week and classified in the following 6 subscales: symptoms and feelings, daily activities, leisure, personal relationships, work and school, and treatment.16 The total score ranges from 0 (no impact) to 30 (very high impact), with a higher score indicating a lower QOL (eTable 1). The minimal clinically important difference (MCD) for the DLQI was considered to be 2- to 5-point changes in prior studies.17,18 In this study, we used an MCD of a 5-point change or more between study groups.

Moreover, the patient general assessment (PGA) of disease severity was identified using a 3-point scale (1=mild, 2=moderate, 3=severe).
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics version 23. P≤.05 was considered significant. Mean and SD were calculated for descriptive data. The t test, Fisher exact test, analysis of variance, multiple regression analysis, and logistic regression analysis were used to identify the relationship between variables.
RESULTS
Patient Characteristics
A total of 96 patients were enrolled in this study. The mean (SD) age of participants was 41.42 (15.1) years (range, 18–58 years). Of 96 patients whose data were included, 55 (57.29%) patients had received RTX 3 months earlier (3M group) and 41 (42.71%) received RTX in the last 2 weeks (R group). A summary of study patient characteristics in each group is provided in eTable 2. There was no significant difference between the 2 groups in terms of age, sex, type of pemphigus, marital status, education, positive Nikolsky sign, smoking status, existence of comorbidities, site of lesions, and RTX treatment protocol. However, a significant difference was found for duration of disease (P=.0124) and mean prednisolone dosage (P=.001) as well as severity of disease measured by PDAI score (P=.003) and anti-DSG1 (P=.003) and anti-DSG3 (P=.021) values.

Patient-Reported Outcomes
Physical and mental component scores are summarized in eTable 3. Generally, SF-36 scores were improved with RTX treatment in all dimensions except for mental health, though these differences were not statistically significant, with the greatest mean improvement in the role physical index (75.45 in the 3M group vs 53.04 in the R group; P=.009). Mean SF-36 PCS and MCS scores were higher in the 3M group vs the R group, though the difference in MCS score did not reach the level of significance (eTable 3).

Mean DLQI scores in the R and 3M groups were 12.31 and 6.96, respectively, indicating a considerable burden on HRQOL in both groups. However, a statistically significant difference between these values was seen that also was clinically meaningful, indicating a significant improvement of QOL in patients receiving RTX 3 months earlier (P=.005)(eTable 3).
The PGA scores indicated that patients in the 3M group were significantly more likely to report less severe disease vs the R group (P=.008)(eTable 3).
Multivariate Analysis—Effect of the patient characteristics and some disease features on indices of QOL was evaluated using the multiple linear regression model. eTable 4 shows the P values of those analyses.

COMMENT
Pemphigus is a chronic disabling disease with notable QOL impairment due to disease burden as well as the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive agents during the disease course. To study the effect of RTX on QOL of patients with pemphigus, we compared 2 sets of patients. Prior studies have shown that clinically significant effects of RTX take 4 to 12 weeks to appear.19,20 Therefore, we selected patients who received RTX 3 months earlier to measure their HRQOL indices and compare them with patients who had received RTX in the last 2 weeks as a control group to investigate the effect of RTX intrinsically, as this was the focus of this study.
In our study, one of the research tools was the DLQI. Healthy patients typically have an average score of 0.5.21 The mean DLQI score of the patients in R group was 12.31, which was similar to prior analysis8 and reflects a substantial burden of disease comparable to atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.21,22 In patients in the 3M group, the mean DLQI score was lower than the R group (6.96 vs 12.31), indicating a significant (P=.005) and clinically meaningful improvement in QOL of patients due to the dramatic therapeutic effect of RTX. However, this score indicated a moderate effect on HRQOL, even in the context of clinical improvement due to RTX treatment, which may reflect that the short duration of treatment in the 3M group was a limitation of this study. Although the 12-week treatment duration was comparable with other studies19,20 and major differences in objective measures of treatment efficacy were found in PDAI as well as anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values, longer treatment duration may be needed for a more comprehensive assessment of the benefit of RTX on HRQOL indices in patients with pemphigus.
Based on results of the SF-36 questionnaire, PCS and MCS scores were not substantially impaired in the R group considering the fact that a mean score of 50 has been articulated as a normative value for all scales.23 These data demonstrated the importance of using a dermatologic-specific instrument such as the DLQI instead of a general questionnaire to assess QOL in patients with pemphigus. However, better indices were reported with RTX treatment in the 3 SF-36 domains—role physical (P=.009), role emotional (P=.03), and general health perception (P=.03)—with the role physical showing the greatest magnitude of mean change (75.45 in the 3M group vs 53.04 in the R group). Notably, PCS was impaired to a greater extent than MCS in patients in the R group and showed a greater magnitude of improvement after 3 months of treatment. These results could be explained by the fact that MCS can be largely changed in diseases with a direct effect on the central nervous system.23
Our results also revealed that the dose of corticosteroid correlated to HRQOL of patients with pemphigus who recently received RTX therapy. Indeed, it is more likely that patients on lower-dose prednisolone have a higher QOL, especially on physical function and social function dimensions of SF-36. This finding is highly expectable by less severe disease due to RTX treatment and also lower potential dose-dependent adverse effects of long-term steroid therapy.
One of the most striking findings of this study was the correlation of location of lesions to QOL indices. We found that the mucocutaneous phenotype was significantly correlated to greater improvement in role emotional, role physical, and social functioning scores due to RTX treatment compared with cutaneous or mucosal types (P=.02, P=.025, and P=.017, respectively). Although mucosal involvement of the disease can be the most burdensome feature because of its large impact on essential activities such as eating and speaking, cutaneous lesions with unpleasant appearance and undesirable symptoms may have a similar impact on QOL. Therefore, having both mucosal and cutaneous lesions causes a worsened QOL and decreased treatment efficacy vs having only one area involved. This may explain the greater improvement in some QOL indices with RTX treatment.
Limitations—Given the cross-sectional design of this study in which patients were observed at a single time point during their treatment course, it is not possible to establish a clear cause-effect relationship between variables. Moreover, we did not evaluate the impact of RTX or prednisolone adverse effects on QOL. Therefore, further prospective studies with longer treatment durations may help to validate our findings. In addition, MCDs for DLQI and SF-36 in pemphigus need to be determined and validated in future studies.
CONCLUSION
The results of our study demonstrated that patients with pemphigus may benefit from taking RTX, not only in terms of clinical improvement of their disease measured by objective indices such as PDAI and anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values but also in several domains that are important to patients, including physical and mental health status (SF-36), HRQOL (DLQI), and overall disease severity (PGA). Rituximab administration in patients with pemphigus can lead to rapid and significant improvement in HRQOL as well as patient- and physician-assessed measures. Its favorable safety profile along with its impact on patients’ daily lives and mental health makes RTX a suitable treatment option for patients with pemphigus. Moreover, we recommend taking QOL indices into account while evaluating the efficacy of new medications to improve our insight into the patient experience and provide better patient adherence to treatment, which is an important issue for optimal control of chronic disorders.
Pemphigus is a group of autoimmune blistering diseases characterized by the development of painful and flaccid blisters on the skin and/or mucous membranes. Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) and pemphigus foliaceus (PF) are 2 major subtypes and can be distinguished by the location of blister formation or the specificity of autoantibodies directed against different desmogleins.1,2 Although rare, pemphigus is considered a serious and life-threatening condition with a great impact on quality of life (QOL) due to disease symptoms (eg, painful lesions, physical appearance of skin lesions) as well as treatment complications (eg, adverse drug effects, cost of treatment).3-6 Moreover, the physical and psychological effects can lead to marked functional morbidity and work-related disability during patients’ productive years.7 Therefore, affected individuals usually have a remarkably compromised health-related quality of life (HRQOL).8 Effective treatments may considerably improve the QOL of patients with pemphigus.6
Despite the available treatment options, finding the best regimen for pemphigus remains a challenge. Corticosteroids are assumed to be the main treatment, though they have considerable side effects.9,10 Adjuvant therapies are used to suppress or modulate immune responses, leading to remission with the least possible need for corticosteroids. Finding an optimal steroid-sparing agent has been the aim of research, and biologic agents seem to be the best option.8 Rituximab (RTX), an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has shown great promise in several studies of its clinical efficacy and has become a first-line treatment in new guidelines.11-14 Rituximab treatment has been associated with notable improvement in physician-assessed outcome measures with a favorable safety profile in patients with pemphigus.11-15 However, it is important to assess response to treatment from a patient’s perspective through the use of outcome-assessment measures that encompass patient-reported outcomes to reflect the complete patient experience and establish the overall impact of RTX as well as its likelihood of acceptance by patients with pemphigus.
In our study, we compared clinical outcomes and HRQOL through the use of disease-specific measures as well as comprehensive generic health status measures among patients with PV and PF who received RTX treatment 3 months earlier and those who received RTX in the last 2 weeks. The clinical relevance of the patient-reported outcomes is discussed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Design
We conducted a single-center cross-sectional study of 96 patients with pemphigus aged 18 to 65 years of either sex who were willing to participate in this study. Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of PV or PF who received RTX 3 months earlier or in the last 2 weeks were enrolled in the study. Patients were identified using Dermatry.ir, an archiving software that contains patients’ medical data. Exclusion criteria included lack of sufficient knowledge of the concepts of the questionnaires as well as age younger than 16 years. The study was conducted from October 2019 to April 2020 by the Autoimmune Bullous Disease Research Center at Razi Hospital in Tehran, Iran, which is the main dermatology-specific center and teaching hospital of Iran. The study protocol was approved by the relevant ethics committee.
Patients were categorized into 2 groups: (1) those who received RTX 3 months earlier (3M group); and (2) those who received RTX in the last 2 weeks (R group).
After an explanation of the study to participants, informed written consent was signed by each patient, and their personal data (eg, age, sex, education, marital status, smoking status), as well as clinical data (eg, type of pemphigus, duration of disease, site of onset, prednisolone dosage, presence of Nikolsky sign, anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values, Pemphigus Disease Area Index [PDAI] score, RTX treatment protocol); any known comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or morbid obesity; and any chronic pulmonary, cardiac, endocrinologic, renal, or hepatic condition, were collected and recorded in a predefined Case Record.
Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
The effect of RTX on QOL in patients with pemphigus was assessed using 2 HRQOL instruments: (1) a general health status indicator, the 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36), and (2) a validated, Persian version of a dermatology-specific questionnaire, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). The questionnaires were completed by each patient or by an assistant if needed.
The SF-36 is a widely used 36-item questionnaire measuring functional health and well-being across 8 domains—mental health, pain, physical function, role emotional, role physical, social functioning, vitality, and general health perception—with scores for each ranging from 0 to 100. The physical component scores (PCSs) and mental component scores (MCSs) were derived from these 8 subscales, each ranging from 0 to 400, with higher scores indicating better health status.6
The DLQI, one of the most frequently used QOL measures in dermatology, contains 10 questions, each referring to the prior week and classified in the following 6 subscales: symptoms and feelings, daily activities, leisure, personal relationships, work and school, and treatment.16 The total score ranges from 0 (no impact) to 30 (very high impact), with a higher score indicating a lower QOL (eTable 1). The minimal clinically important difference (MCD) for the DLQI was considered to be 2- to 5-point changes in prior studies.17,18 In this study, we used an MCD of a 5-point change or more between study groups.

Moreover, the patient general assessment (PGA) of disease severity was identified using a 3-point scale (1=mild, 2=moderate, 3=severe).
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics version 23. P≤.05 was considered significant. Mean and SD were calculated for descriptive data. The t test, Fisher exact test, analysis of variance, multiple regression analysis, and logistic regression analysis were used to identify the relationship between variables.
RESULTS
Patient Characteristics
A total of 96 patients were enrolled in this study. The mean (SD) age of participants was 41.42 (15.1) years (range, 18–58 years). Of 96 patients whose data were included, 55 (57.29%) patients had received RTX 3 months earlier (3M group) and 41 (42.71%) received RTX in the last 2 weeks (R group). A summary of study patient characteristics in each group is provided in eTable 2. There was no significant difference between the 2 groups in terms of age, sex, type of pemphigus, marital status, education, positive Nikolsky sign, smoking status, existence of comorbidities, site of lesions, and RTX treatment protocol. However, a significant difference was found for duration of disease (P=.0124) and mean prednisolone dosage (P=.001) as well as severity of disease measured by PDAI score (P=.003) and anti-DSG1 (P=.003) and anti-DSG3 (P=.021) values.

Patient-Reported Outcomes
Physical and mental component scores are summarized in eTable 3. Generally, SF-36 scores were improved with RTX treatment in all dimensions except for mental health, though these differences were not statistically significant, with the greatest mean improvement in the role physical index (75.45 in the 3M group vs 53.04 in the R group; P=.009). Mean SF-36 PCS and MCS scores were higher in the 3M group vs the R group, though the difference in MCS score did not reach the level of significance (eTable 3).

Mean DLQI scores in the R and 3M groups were 12.31 and 6.96, respectively, indicating a considerable burden on HRQOL in both groups. However, a statistically significant difference between these values was seen that also was clinically meaningful, indicating a significant improvement of QOL in patients receiving RTX 3 months earlier (P=.005)(eTable 3).
The PGA scores indicated that patients in the 3M group were significantly more likely to report less severe disease vs the R group (P=.008)(eTable 3).
Multivariate Analysis—Effect of the patient characteristics and some disease features on indices of QOL was evaluated using the multiple linear regression model. eTable 4 shows the P values of those analyses.

COMMENT
Pemphigus is a chronic disabling disease with notable QOL impairment due to disease burden as well as the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive agents during the disease course. To study the effect of RTX on QOL of patients with pemphigus, we compared 2 sets of patients. Prior studies have shown that clinically significant effects of RTX take 4 to 12 weeks to appear.19,20 Therefore, we selected patients who received RTX 3 months earlier to measure their HRQOL indices and compare them with patients who had received RTX in the last 2 weeks as a control group to investigate the effect of RTX intrinsically, as this was the focus of this study.
In our study, one of the research tools was the DLQI. Healthy patients typically have an average score of 0.5.21 The mean DLQI score of the patients in R group was 12.31, which was similar to prior analysis8 and reflects a substantial burden of disease comparable to atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.21,22 In patients in the 3M group, the mean DLQI score was lower than the R group (6.96 vs 12.31), indicating a significant (P=.005) and clinically meaningful improvement in QOL of patients due to the dramatic therapeutic effect of RTX. However, this score indicated a moderate effect on HRQOL, even in the context of clinical improvement due to RTX treatment, which may reflect that the short duration of treatment in the 3M group was a limitation of this study. Although the 12-week treatment duration was comparable with other studies19,20 and major differences in objective measures of treatment efficacy were found in PDAI as well as anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values, longer treatment duration may be needed for a more comprehensive assessment of the benefit of RTX on HRQOL indices in patients with pemphigus.
Based on results of the SF-36 questionnaire, PCS and MCS scores were not substantially impaired in the R group considering the fact that a mean score of 50 has been articulated as a normative value for all scales.23 These data demonstrated the importance of using a dermatologic-specific instrument such as the DLQI instead of a general questionnaire to assess QOL in patients with pemphigus. However, better indices were reported with RTX treatment in the 3 SF-36 domains—role physical (P=.009), role emotional (P=.03), and general health perception (P=.03)—with the role physical showing the greatest magnitude of mean change (75.45 in the 3M group vs 53.04 in the R group). Notably, PCS was impaired to a greater extent than MCS in patients in the R group and showed a greater magnitude of improvement after 3 months of treatment. These results could be explained by the fact that MCS can be largely changed in diseases with a direct effect on the central nervous system.23
Our results also revealed that the dose of corticosteroid correlated to HRQOL of patients with pemphigus who recently received RTX therapy. Indeed, it is more likely that patients on lower-dose prednisolone have a higher QOL, especially on physical function and social function dimensions of SF-36. This finding is highly expectable by less severe disease due to RTX treatment and also lower potential dose-dependent adverse effects of long-term steroid therapy.
One of the most striking findings of this study was the correlation of location of lesions to QOL indices. We found that the mucocutaneous phenotype was significantly correlated to greater improvement in role emotional, role physical, and social functioning scores due to RTX treatment compared with cutaneous or mucosal types (P=.02, P=.025, and P=.017, respectively). Although mucosal involvement of the disease can be the most burdensome feature because of its large impact on essential activities such as eating and speaking, cutaneous lesions with unpleasant appearance and undesirable symptoms may have a similar impact on QOL. Therefore, having both mucosal and cutaneous lesions causes a worsened QOL and decreased treatment efficacy vs having only one area involved. This may explain the greater improvement in some QOL indices with RTX treatment.
Limitations—Given the cross-sectional design of this study in which patients were observed at a single time point during their treatment course, it is not possible to establish a clear cause-effect relationship between variables. Moreover, we did not evaluate the impact of RTX or prednisolone adverse effects on QOL. Therefore, further prospective studies with longer treatment durations may help to validate our findings. In addition, MCDs for DLQI and SF-36 in pemphigus need to be determined and validated in future studies.
CONCLUSION
The results of our study demonstrated that patients with pemphigus may benefit from taking RTX, not only in terms of clinical improvement of their disease measured by objective indices such as PDAI and anti-DSG1 and anti-DSG3 values but also in several domains that are important to patients, including physical and mental health status (SF-36), HRQOL (DLQI), and overall disease severity (PGA). Rituximab administration in patients with pemphigus can lead to rapid and significant improvement in HRQOL as well as patient- and physician-assessed measures. Its favorable safety profile along with its impact on patients’ daily lives and mental health makes RTX a suitable treatment option for patients with pemphigus. Moreover, we recommend taking QOL indices into account while evaluating the efficacy of new medications to improve our insight into the patient experience and provide better patient adherence to treatment, which is an important issue for optimal control of chronic disorders.
- Hammers CM, Stanley JR. Mechanisms of disease: pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Ann Rev Pathol. 2016;11:175-197.
- Kasperkiewicz M, Ellebrecht CT, Takahashi H, et al. Pemphigus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17026.
- Mayrshofer F, Hertl M, Sinkgraven R, et al. Significant decrease in quality of life in patients with pemphigus vulgaris, result from the German Bullous Skin Disease (BSD) Study Group. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2005;3:431-435.
- Terrab Z, Benckikhi H, Maaroufi A, et al. Quality of life and pemphigus. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2005;132:321-328.
- Tabolli S, Mozzetta A, Antinone V, et al. The health impact of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus assessed using the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form health survey questionnaire. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:1029-1034.
- Paradisi A, Sampogna F, Di Pietro, C, et al. Quality-of-life assessment in patients with pemphigus using a minimum set of evaluation tools. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:261-269.
- Heelan K, Hitzig SL, Knowles S, et al. Loss of work productivity and quality of life in patients with autoimmune bullous dermatoses. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015;19:546-554.
- Ghodsi SZ, Chams-Davatchi C, Daneshpazhooh M, et al. Quality of life and psychological status of patients with pemphigus vulgaris using Dermatology Life Quality Index and General Health Questionnaires. J Dermatol. 2012;39:141-144.
- Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:2343.
- Mohammad-Javad N, Parvaneh H, Maryam G, et al. Randomized trial of tacrolimus 0.1% ointment versus triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% paste in the treatment of oral pemphigus vulgaris. Iranian J Dermatol. 2012;15:42-46.
- Lunardon L, Tsai KJ, Propert KJ, et al. Adjuvant rituximab therapy of pemphigus: a single-center experience with 31 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:1031-1036.
- Colliou N, Picard D, Caillot F, et al. Long-term remissions of severe pemphigus after rituximab therapy are associated with prolonged failure of desmoglein B cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:175ra30.
- Heelan K, Al-Mohammedi F, Smith MJ, et al. Durable remission of pemphigus with a fixed-dose rituximab protocol. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:703-708.
- Joly P, Maho-Vaillant M, Prost-Squarcioni C, et al. First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux3): a prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2031-2040
- Aryanian Z, Balighi K, Daneshpazhooh M, et al. Rituximab exhibits a better safety profile when used as a first line of treatment for pemphigus vulgaris: a retrospective study. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;96:107755.
- Aghai S, Sodaifi M, Jafari P, et al. DLQI scores in vitiligo: reliability and validity of the Persian version. BMC Dermatol. 2004;4:8.
- Schünemann HJ, Akl EA, Guyatt GH. Interpreting the results of patient reported outcome measures in clinical trials: the clinician’s perspective. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2006;4:62.
- Quality of life questionnaires. Cardiff University website. Accessed December 16, 2022. http://sites.cardiff.ac.uk/dermatology/quality-oflife/dermatology-quality-of-life-index-dlqi/dlqi-instructions-foruse-and-scoring/
- Kanwar AJ, Tsuruta D, Vinay K, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab treatment in Indian pemphigus patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E17-E23.
- Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Cosnes A, et al. First-line treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with a combination of rituximab and high-potency topical corticosteroids. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:200-203.
- Finlay AY, Khan GK. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1994;19:210-216.
- Aghaei S, Moradi A, Ardekani GS. Impact of psoriasis on quality of life in Iran. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:220.
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). 1. conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473-483.
- Hammers CM, Stanley JR. Mechanisms of disease: pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Ann Rev Pathol. 2016;11:175-197.
- Kasperkiewicz M, Ellebrecht CT, Takahashi H, et al. Pemphigus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17026.
- Mayrshofer F, Hertl M, Sinkgraven R, et al. Significant decrease in quality of life in patients with pemphigus vulgaris, result from the German Bullous Skin Disease (BSD) Study Group. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2005;3:431-435.
- Terrab Z, Benckikhi H, Maaroufi A, et al. Quality of life and pemphigus. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2005;132:321-328.
- Tabolli S, Mozzetta A, Antinone V, et al. The health impact of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus assessed using the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form health survey questionnaire. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:1029-1034.
- Paradisi A, Sampogna F, Di Pietro, C, et al. Quality-of-life assessment in patients with pemphigus using a minimum set of evaluation tools. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:261-269.
- Heelan K, Hitzig SL, Knowles S, et al. Loss of work productivity and quality of life in patients with autoimmune bullous dermatoses. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015;19:546-554.
- Ghodsi SZ, Chams-Davatchi C, Daneshpazhooh M, et al. Quality of life and psychological status of patients with pemphigus vulgaris using Dermatology Life Quality Index and General Health Questionnaires. J Dermatol. 2012;39:141-144.
- Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:2343.
- Mohammad-Javad N, Parvaneh H, Maryam G, et al. Randomized trial of tacrolimus 0.1% ointment versus triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% paste in the treatment of oral pemphigus vulgaris. Iranian J Dermatol. 2012;15:42-46.
- Lunardon L, Tsai KJ, Propert KJ, et al. Adjuvant rituximab therapy of pemphigus: a single-center experience with 31 patients. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:1031-1036.
- Colliou N, Picard D, Caillot F, et al. Long-term remissions of severe pemphigus after rituximab therapy are associated with prolonged failure of desmoglein B cell response. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:175ra30.
- Heelan K, Al-Mohammedi F, Smith MJ, et al. Durable remission of pemphigus with a fixed-dose rituximab protocol. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:703-708.
- Joly P, Maho-Vaillant M, Prost-Squarcioni C, et al. First-line rituximab combined with short-term prednisone versus prednisone alone for the treatment of pemphigus (Ritux3): a prospective, multicentre, parallel-group, open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2031-2040
- Aryanian Z, Balighi K, Daneshpazhooh M, et al. Rituximab exhibits a better safety profile when used as a first line of treatment for pemphigus vulgaris: a retrospective study. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;96:107755.
- Aghai S, Sodaifi M, Jafari P, et al. DLQI scores in vitiligo: reliability and validity of the Persian version. BMC Dermatol. 2004;4:8.
- Schünemann HJ, Akl EA, Guyatt GH. Interpreting the results of patient reported outcome measures in clinical trials: the clinician’s perspective. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2006;4:62.
- Quality of life questionnaires. Cardiff University website. Accessed December 16, 2022. http://sites.cardiff.ac.uk/dermatology/quality-oflife/dermatology-quality-of-life-index-dlqi/dlqi-instructions-foruse-and-scoring/
- Kanwar AJ, Tsuruta D, Vinay K, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab treatment in Indian pemphigus patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:E17-E23.
- Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Valeyrie-Allanore L, Cosnes A, et al. First-line treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with a combination of rituximab and high-potency topical corticosteroids. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:200-203.
- Finlay AY, Khan GK. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1994;19:210-216.
- Aghaei S, Moradi A, Ardekani GS. Impact of psoriasis on quality of life in Iran. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:220.
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). 1. conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473-483.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Pemphigus is an autoimmune blistering disease that can negatively affect patients’ lives.
- Assessing the impact of treatment from a patient’s perspective using outcome assessment measures is important and relevant in trials of new pemphigus treatments including rituximab.
- Rituximab administration in pemphigus patients led to rapid and notable improvement in health-related quality of life and patient-assessed measures.
Cutaneous Manifestations in Hereditary Alpha Tryptasemia
Hereditary alpha tryptasemia (HaT), an autosomal-dominant disorder of tryptase overproduction, was first described in 2014 by Lyons et al.1 It has been associated with multiple dermatologic, allergic, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, neuropsychiatric, respiratory, autonomic, and connective tissue abnormalities. These multisystem concerns may include cutaneous flushing, chronic pruritus, urticaria, GI tract symptoms, arthralgia, and autonomic dysfunction.2 The diverse symptoms and the recent discovery of HaT make recognition of this disorder challenging. Currently, it also is believed that HaT is associated with an elevated risk for anaphylaxis and is a biomarker for severe symptoms in disorders with increased mast cell burden such as mastocytosis.3-5
Given the potential cutaneous manifestations and the fact that dermatologic symptoms may be the initial presentation of HaT, awareness and recognition of this condition by dermatologists are essential for diagnosis and treatment. This review summarizes the cutaneous presentations consistent with HaT and discusses various conditions that share overlapping dermatologic symptoms with HaT.
Background on HaT
Mast cells are known to secrete several vasoactive mediators including tryptase and histamine when activated by foreign substances, similar to IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions. In their baseline state, mast cells continuously secrete immature forms of tryptases called protryptases.6 These protryptases come in 2 forms: α and β. Although mature tryptase is acutely elevatedin anaphylaxis, persistently elevated total serum tryptase levels frequently are regarded as indicative of a systemic mast cell disorder such as systemic mastocytosis (SM).3 Despite the wide-ranging phenotype of HaT, all individuals with the disorder have an elevated basal serum tryptase level (>8 ng/mL). Hereditary alpha tryptasemia has been identified as another possible cause of persistently elevated levels.2,6
Genetics and Epidemiology of HaT—The humantryptase locus at chromosome 16p13.3 is composed of 4 paralog genes: TPSG1, TPSB2, TPSAB1, and TPSD1.4 Only TPSAB1 encodes for α-tryptase, while both TPSB2 and TPSAB1 encode for β-tryptase.4 Hereditary alpha tryptasemia is an autosomal-dominant disorder resulting from a copy number increase in the α-tryptase encoding sequence within the TPSAB1 gene. Despite the wide-ranging phenotype of HaT, all individuals identified with the disorder have a basal serum tryptase level greater than 8 ng/mL, with mean (SD) levels of 15 (5) ng/mL and 24 (6) ng/mL with gene duplication and triplication, respectively (reference range, 0–11.4 ng/mL).2,6 Hereditary alpha tryptasemia likely is common and largely undiagnosed, with a recently estimated prevalence of 5% in the United Kingdom7 and 5.6% in a cohort of 125 individuals from Italy, Slovenia, and the United States.5
Implications of Increased α-tryptase Levels—After an inciting stimulus, the active portions of α-protryptase and β-protryptase are secreted as tetramers by activated mast cells via degranulation. In vitro, β-tryptase homotetramers have been found to play a role in anaphylaxis, while α-homotetramers are nearly inactive.8,9 Recently, however, it has been discovered that α2β2 tetramers also can form and do so in a higher ratio in individuals with increased α-tryptase–encoding gene copies, such as those with HaT.8 These heterotetramers exhibit unique properties compared with the homotetramers and may stimulate epidermal growth factor–like module-containing mucinlike hormone receptor 2 and protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2). Epidermal growth factor–like module-containing mucinlike hormone receptor 2 activation likely contributes to vibratory urticaria in patients, while activation of PAR2 may have a range of clinical effects, including worsening asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, pruritus, and the exacerbation of dermal inflammation and hyperalgesia.8,10 Thus, α- and β-tryptase tetramers can be considered mediators that may influence the severity of disorders in which mast cells are naturally prevalent and likely contribute to the phenotype of those with HaT.7 Furthermore, these characteristics have been shown to potentially increase in severity with increasing tryptase levels and with increased TPSAB1 duplications.1,2 In contrast, more than 25% of the population is deficient in α-tryptase without known deleterious effects.5
Cutaneous Manifestations of HaT
A case series reported by Lyons et al1 in 2014 detailed persistent elevated basal serum tryptase levels in 9 families with an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance. In this cohort, 31 of 33 (94%) affected individuals had a history of atopic dermatitis (AD), and 26 of 33 (79%) affected individuals reported symptoms consistent with mast cell degranulation, including urticaria; flushing; and/or crampy abdominal pain unprovoked or triggered by heat, exercise, vibration, stress, certain foods, or minor physical stimulation.1 A later report by Lyons et al2 in 2016 identified the TPSAB1 α-tryptase–encoding sequence copy number increase as the causative entity for HaT by examining a group of 96 patients from 35 families with frequent recurrent cutaneous flushing and pruritus, sometimes associated with urticaria and sleep disruption. Flushing and pruritus were found in 45% (33/73) of those with a TPSAB1 duplication and 80% (12/15) of those with a triplication (P=.022), suggesting a gene dose effect regarding α-tryptase encoding sequence copy number and these symptoms.2
A 2019 study further explored the clinical finding of urticaria in patients with HaT by specifically examining if vibration-induced urticaria was affected by TPSAB1 gene dosage.8 A cohort of 56 volunteers—35 healthy and 21 with HaT—underwent tryptase genotyping and cutaneous vibratory challenge. The presence of TPSAB1 was significantly correlated with induction of vibration-induced urticaria (P<.01), as the severity and prevalence of the urticarial response increased along with α- and β-tryptase gene ratios.8
Urticaria and angioedema also were seen in 51% (36/70) of patients in a cohort of HaT patients in the United Kingdom, in which 41% (29/70) also had skin flushing. In contrast to prior studies, these manifestations were not more common in patients with gene triplications or quintuplications than those with duplications.7 In another recent retrospective evaluation conducted at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts)(N=101), 80% of patients aged 4 to 85 years with confirmed diagnoses of HaT had skin manifestations such as urticaria, flushing, and pruritus.4
HaT and Mast Cell Activation Syndrome—In 2019, a Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report outlined recommendations for diagnosing and treating primary mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), a disorder in which mast cells seem to be more easily activated. Mast cell activation syndrome is defined as a primary clinical condition in which there are episodic signs and symptoms of systemic anaphylaxis (Table) concurrently affecting at least 2 organ systems, resulting from secreted mast cell mediators.9,11 The 2019 report also touched on clinical criteria that lack precision for diagnosing MCAS yet are in use, including dermographism and several types of rashes.9 Episode triggers frequent in MCAS include hot water, alcohol, stress, exercise, infection, hormonal changes, and physical stimuli.
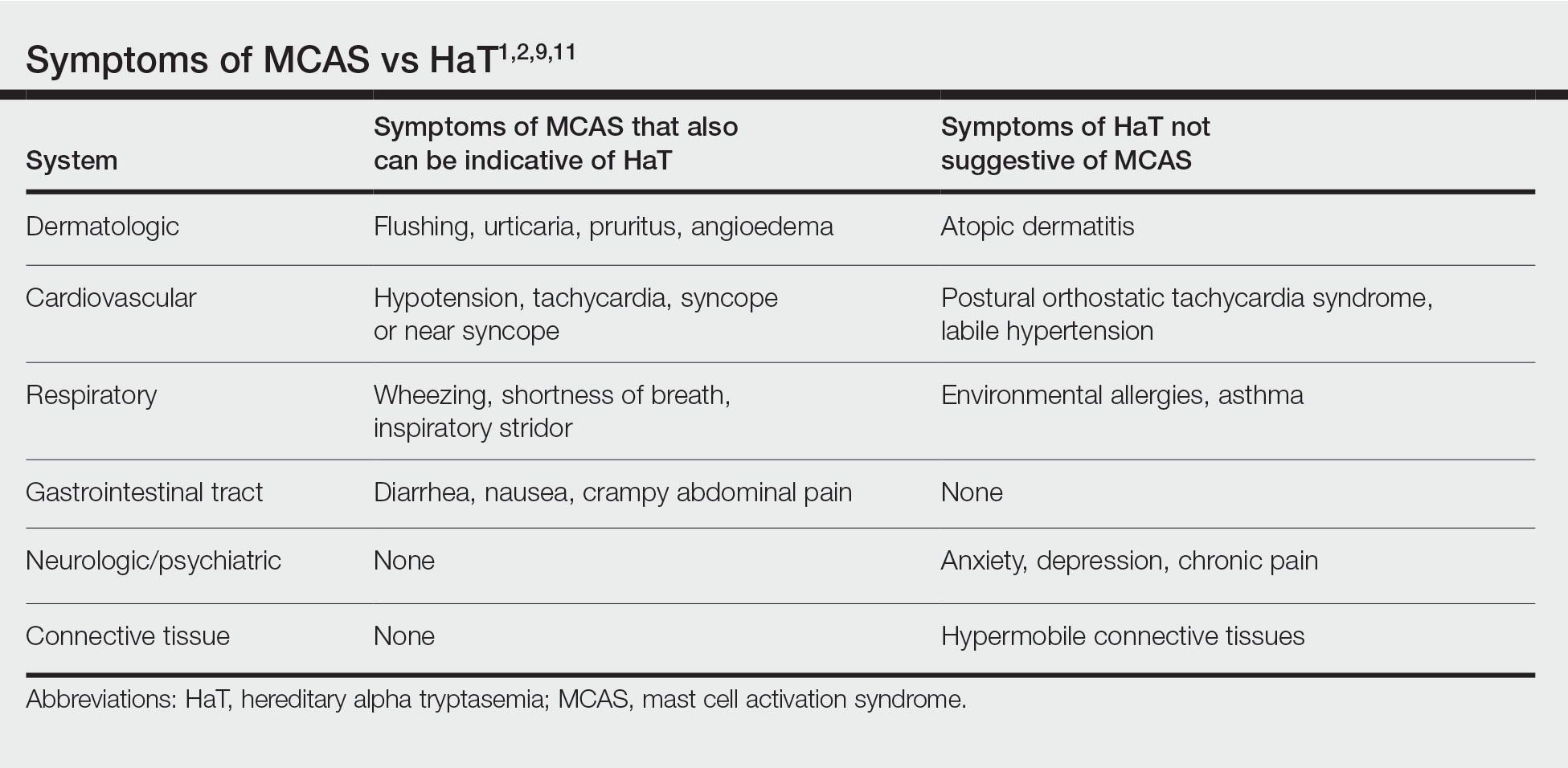
Hereditary alpha tryptasemia has been suggested to be a risk factor for MCAS, which also can be associated with SM and clonal MCAS.9 Patients with MCAS should be tested for increased α-tryptase gene copy number given the overlap in symptoms, the likely predisposition of those with HaT to develop MCAS, and the fact that these patients could be at an increased risk for anaphylaxis.4,7,9,11 However, the clinical phenotype for HaT includes allergic disorders affecting the skin as well as neuropsychiatric and connective tissue abnormalities that are distinctive from MCAS. Although HaT may be considered a heritable risk factor for MCAS, MCAS is only 1 potential phenotype associated with HaT.9
Implications of HaT
Hereditary alpha tryptasemia should be considered in all patients with basal tryptase levels greater than 8 ng/mL. Cutaneous symptoms are among the most common presentations for individuals with HaT and can include AD, chronic or episodic urticaria, pruritus, flushing, and angioedema. However, HaT is unique because of the coupling of these common dermatologic findings with other abnormalities, including abdominal pain and diarrhea, hypermobile joints, and autonomic dysfunction. Patients with HaT also may manifest psychiatric concerns of anxiety, depression, and chronic pain, all of which have been linked to this disorder.
It is unclear in HaT if the presence of extra-allelic copies of tryptase in an individual is directly pathogenic. The effects of increased basal tryptase and α2β2 tetramers have been shown to likely be responsible for some of the clinical features in these individuals but also may magnify other individual underlying disease(s) or diathesis in which mast cells are naturally abundant.8 In the skin, this increased mast cell activation and subsequent histamine release frequently are visible as dermatographia and urticaria. However, mast cell numbers also are known to be increased in both psoriatic and AD skin lesions,12 thus severe presentation of these diseases in conjunction with the other symptoms associated with mast cell activation should prompt suspicion for HaT.
Effects of HaT on Other Cutaneous Disease—Given the increase of mast cells in AD skin lesions and fact that 94% of patients in the 2014 Lyons et al1 study cited a history of AD, HaT may be a risk factor in the development of AD. Interestingly, in addition to the increased mast cells in AD lesions, PAR2+ nerve fibers also are increased in AD lesions and have been implicated in the nonhistaminergic pruritus experienced by patients with AD.12 Thus, given the proposed propensity for α2β2 tetramers to activate PAR2, it is possible this mechanism may contribute to severe pruritus in individuals with AD and concurrent HaT, as those with HaT express increased α2β2 tetramers. However, no study to date has directly compared AD symptoms in patients with concurrent HaT vs patients without it. Further research is needed on how HaT impacts other allergic and inflammatory skin diseases such as AD and psoriasis, but one may reasonably consider HaT when treating chronic inflammatory skin diseases refractory to typical interventions and/or severe presentations. Although HaT is an autosomal-dominant disorder, it is not detected by standard whole exome sequencing or microarrays. A commercial test is available, utilizing a buccal swab to test for TPSAB1 copy number.
HaT and Mast Cell Disorders—When evaluating someone with suspected HaT, it is important to screen for other symptoms of mast cell activation. For instance, in the GI tract increased mast cell activation results in activation of motor neurons and nociceptors and increases secretion and peristalsis with consequent bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.10 Likewise, tryptase also has neuromodulatory effects that amplify the perception of pain and are likely responsible for the feelings of hyperalgesia reported in patients with HaT.13
There is substantial overlap in the clinical pictures of HaT and MCAS, and HaT is considered a heritable risk factor for MCAS. Consequently, any patient undergoing workup for MCAS also should be tested for HaT. Although HaT is associated with consistently elevated tryptase, MCAS is episodic in nature, and an increase in tryptase levels of at least 20% plus 2 ng/mL from baseline only in the presence of other symptoms reflective of mast cell activation (Table) is a prerequisite for diagnosis.9 Chronic signs and symptoms of atopy, chronic urticaria, and severe asthma are not indicative of MCAS but are frequently seen in HaT.
Another cause of persistently elevated tryptase levels is SM. Systemic mastocytosis is defined by aberrant clonal mast cell expansion and systemic involvement11 and can cause persistent symptoms, unlike MCAS alone. However, SM also can be associated with MCAS.9 Notably, a baseline serum tryptase level greater than 20 ng/mL—much higher than the threshold of greater than 8 ng/mL for suspicion of HaT—is seen in 75% of SM cases and is part of the minor diagnostic criteria for the disease.9,11 However, the 2016 study identifying increased TPSAB1 α-tryptase–encoding sequences as the causative entity for HaT by Lyons et al2 found the average (SD) basal serum tryptase level in individuals with α-tryptase–encoding sequence duplications to be 15 (5) ng/mL and 24 (6) ng/mL in those with triplications. Thus, there likely is no threshold for elevated baseline tryptase levels that would indicate SM over HaT as a more likely diagnosis. However, SM will present with new persistently elevated tryptase levels, whereas the elevation in HaT is believed to be lifelong.5 Also in contrast to HaT, SM can present with liver, spleen, and lymph node involvement; bone sclerosis; and cytopenia.11,14
Mastocytosis is much rarer than HaT, with an estimated prevalence of 9 cases per 100,000 individuals in the United States.11 Although HaT diagnostic testing is noninvasive, SM requires a bone marrow biopsy for definitive diagnosis. Given the likely much higher prevalence of HaT than SM and the patient burden of a bone marrow biopsy, HaT should be considered before proceeding with a bone marrow biopsy to evaluate for SM when a patient presents with persistent systemic symptoms of mast cell activation and elevated baseline tryptase levels. Furthermore, it also would be prudent to test for HaT in patients with known SM, as a cohort study by Lyons et al5 indicated that HaT is likely more common in those with SM (12.2% [10/82] of cohort with known SM vs 5.3% of 398 controls), and patients with concurrent SM and HaT were at a higher risk for severe anaphylaxis (RR=9.5; P=.007).
Studies thus far surrounding HaT have not evaluated timing of initial symptom onset or age of initial presentation for HaT. Furthermore, there is no guarantee that those with increased TPSAB1 copy number will be symptomatic, as there have been reports of asymptomatic individuals with HaT who had basal serum levels greater than 8 ng/mL.7 As research into HaT continues and larger cohorts are evaluated, questions surrounding timing of symptom onset and various factors that may make someone more likely to display a particular phenotype will be answered.
Treatment—Long-term prognosis for individuals with HaT is largely unknown. Unfortunately, there are limited data to support a single effective treatment strategy for managing HaT, and treatment has varied based on predominant symptoms. For cutaneous and GI tract symptoms, trials of maximal H1 and H2 antihistamines twice daily have been recommended.4 Omalizumab was reported to improve chronic urticaria in 3 of 3 patients, showing potential promise as a treatment.4 Mast cell stabilizers, such as oral cromolyn, have been used for severe GI symptoms, while some patients also have reported improvement with oral ketotifen.6 Other medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants, clemastine fumarate, and gabapentin, have been beneficial anecdotally.6 Given the lack of harmful effects seen in individuals who are α-tryptase deficient, α-tryptase inhibition is an intriguing target for future therapies.
Conclusion
Patients who present with a constellation of dermatologic, allergic, GI tract, neuropsychiatric, respiratory, autonomic, and connective tissue abnormalities consistent with HaT may receive a prompt diagnosis if the association is recognized. The full relationship between HaT and other chronic dermatologic disorders is still unknown. Ultimately, heightened interest and research into HaT will lead to more treatment options available for affected patients.
1. Lyons JJ, Sun G, Stone KD, et al. Mendelian inheritance of elevated serum tryptase associated with atopy and connective tissue abnormalities. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1471-1474.
2. Lyons JJ, Yu X, Hughes JD, et al. Elevated basal serum tryptase identifies a multisystem disorder associated with increased TPSAB1 copy number. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1564-1569.
3. Schwartz L. Diagnostic value of tryptase in anaphylaxis and mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006;6:451-463.
4. Giannetti MP, Weller E, Bormans C, et al. Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia in 101 patients with mast cell activation–related symptomatology including anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;126:655-660.
5. Lyons JJ, Chovanec J, O’Connell MP, et al. Heritable risk for severe anaphylaxis associated with increased α-tryptase–encoding germline copy number at TPSAB1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;147:622-632.
6. Lyons JJ. Hereditary alpha tryptasemia: genotyping and associated clinical features. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2018;38:483-495.
7. Robey RC, Wilcock A, Bonin H, et al. Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia: UK prevalence and variability in disease expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8:3549-3556.
8. Le QT, Lyons JJ, Naranjo AN, et al. Impact of naturally forming human α/β-tryptase heterotetramers in the pathogenesis of hereditary α-tryptasemia. J Exp Med. 2019;216:2348-2361.
9. Weiler CR, Austen KF, Akin C, et al. AAAAI Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report: mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) diagnosis and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144:883-896.
10. Ramsay DB, Stephen S, Borum M, et al. Mast cells in gastrointestinal disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2010;6:772-777.
11. Giannetti A, Filice E, Caffarelli C, et al. Mast cell activation disorders. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57:124.
12. Siiskonen H, Harvima I. Mast cells and sensory nerves contribute to neurogenic inflammation and pruritus in chronic skin inflammation. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:422.
13. Varrassi G, Fusco M, Skaper SD, et al. A pharmacological rationale to reduce the incidence of opioid induced tolerance and hyperalgesia: a review. Pain Ther. 2018;7:59-75.
14. Núñez E, Moreno-Borque R, García-Montero A, et al. Serum tryptase monitoring in indolent systemic mastocytosis: association with disease features and patient outcome. PLoS One. 2013;8:E76116.
Hereditary alpha tryptasemia (HaT), an autosomal-dominant disorder of tryptase overproduction, was first described in 2014 by Lyons et al.1 It has been associated with multiple dermatologic, allergic, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, neuropsychiatric, respiratory, autonomic, and connective tissue abnormalities. These multisystem concerns may include cutaneous flushing, chronic pruritus, urticaria, GI tract symptoms, arthralgia, and autonomic dysfunction.2 The diverse symptoms and the recent discovery of HaT make recognition of this disorder challenging. Currently, it also is believed that HaT is associated with an elevated risk for anaphylaxis and is a biomarker for severe symptoms in disorders with increased mast cell burden such as mastocytosis.3-5
Given the potential cutaneous manifestations and the fact that dermatologic symptoms may be the initial presentation of HaT, awareness and recognition of this condition by dermatologists are essential for diagnosis and treatment. This review summarizes the cutaneous presentations consistent with HaT and discusses various conditions that share overlapping dermatologic symptoms with HaT.
Background on HaT
Mast cells are known to secrete several vasoactive mediators including tryptase and histamine when activated by foreign substances, similar to IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions. In their baseline state, mast cells continuously secrete immature forms of tryptases called protryptases.6 These protryptases come in 2 forms: α and β. Although mature tryptase is acutely elevatedin anaphylaxis, persistently elevated total serum tryptase levels frequently are regarded as indicative of a systemic mast cell disorder such as systemic mastocytosis (SM).3 Despite the wide-ranging phenotype of HaT, all individuals with the disorder have an elevated basal serum tryptase level (>8 ng/mL). Hereditary alpha tryptasemia has been identified as another possible cause of persistently elevated levels.2,6
Genetics and Epidemiology of HaT—The humantryptase locus at chromosome 16p13.3 is composed of 4 paralog genes: TPSG1, TPSB2, TPSAB1, and TPSD1.4 Only TPSAB1 encodes for α-tryptase, while both TPSB2 and TPSAB1 encode for β-tryptase.4 Hereditary alpha tryptasemia is an autosomal-dominant disorder resulting from a copy number increase in the α-tryptase encoding sequence within the TPSAB1 gene. Despite the wide-ranging phenotype of HaT, all individuals identified with the disorder have a basal serum tryptase level greater than 8 ng/mL, with mean (SD) levels of 15 (5) ng/mL and 24 (6) ng/mL with gene duplication and triplication, respectively (reference range, 0–11.4 ng/mL).2,6 Hereditary alpha tryptasemia likely is common and largely undiagnosed, with a recently estimated prevalence of 5% in the United Kingdom7 and 5.6% in a cohort of 125 individuals from Italy, Slovenia, and the United States.5
Implications of Increased α-tryptase Levels—After an inciting stimulus, the active portions of α-protryptase and β-protryptase are secreted as tetramers by activated mast cells via degranulation. In vitro, β-tryptase homotetramers have been found to play a role in anaphylaxis, while α-homotetramers are nearly inactive.8,9 Recently, however, it has been discovered that α2β2 tetramers also can form and do so in a higher ratio in individuals with increased α-tryptase–encoding gene copies, such as those with HaT.8 These heterotetramers exhibit unique properties compared with the homotetramers and may stimulate epidermal growth factor–like module-containing mucinlike hormone receptor 2 and protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2). Epidermal growth factor–like module-containing mucinlike hormone receptor 2 activation likely contributes to vibratory urticaria in patients, while activation of PAR2 may have a range of clinical effects, including worsening asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, pruritus, and the exacerbation of dermal inflammation and hyperalgesia.8,10 Thus, α- and β-tryptase tetramers can be considered mediators that may influence the severity of disorders in which mast cells are naturally prevalent and likely contribute to the phenotype of those with HaT.7 Furthermore, these characteristics have been shown to potentially increase in severity with increasing tryptase levels and with increased TPSAB1 duplications.1,2 In contrast, more than 25% of the population is deficient in α-tryptase without known deleterious effects.5
Cutaneous Manifestations of HaT
A case series reported by Lyons et al1 in 2014 detailed persistent elevated basal serum tryptase levels in 9 families with an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance. In this cohort, 31 of 33 (94%) affected individuals had a history of atopic dermatitis (AD), and 26 of 33 (79%) affected individuals reported symptoms consistent with mast cell degranulation, including urticaria; flushing; and/or crampy abdominal pain unprovoked or triggered by heat, exercise, vibration, stress, certain foods, or minor physical stimulation.1 A later report by Lyons et al2 in 2016 identified the TPSAB1 α-tryptase–encoding sequence copy number increase as the causative entity for HaT by examining a group of 96 patients from 35 families with frequent recurrent cutaneous flushing and pruritus, sometimes associated with urticaria and sleep disruption. Flushing and pruritus were found in 45% (33/73) of those with a TPSAB1 duplication and 80% (12/15) of those with a triplication (P=.022), suggesting a gene dose effect regarding α-tryptase encoding sequence copy number and these symptoms.2
A 2019 study further explored the clinical finding of urticaria in patients with HaT by specifically examining if vibration-induced urticaria was affected by TPSAB1 gene dosage.8 A cohort of 56 volunteers—35 healthy and 21 with HaT—underwent tryptase genotyping and cutaneous vibratory challenge. The presence of TPSAB1 was significantly correlated with induction of vibration-induced urticaria (P<.01), as the severity and prevalence of the urticarial response increased along with α- and β-tryptase gene ratios.8
Urticaria and angioedema also were seen in 51% (36/70) of patients in a cohort of HaT patients in the United Kingdom, in which 41% (29/70) also had skin flushing. In contrast to prior studies, these manifestations were not more common in patients with gene triplications or quintuplications than those with duplications.7 In another recent retrospective evaluation conducted at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts)(N=101), 80% of patients aged 4 to 85 years with confirmed diagnoses of HaT had skin manifestations such as urticaria, flushing, and pruritus.4
HaT and Mast Cell Activation Syndrome—In 2019, a Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report outlined recommendations for diagnosing and treating primary mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), a disorder in which mast cells seem to be more easily activated. Mast cell activation syndrome is defined as a primary clinical condition in which there are episodic signs and symptoms of systemic anaphylaxis (Table) concurrently affecting at least 2 organ systems, resulting from secreted mast cell mediators.9,11 The 2019 report also touched on clinical criteria that lack precision for diagnosing MCAS yet are in use, including dermographism and several types of rashes.9 Episode triggers frequent in MCAS include hot water, alcohol, stress, exercise, infection, hormonal changes, and physical stimuli.

Hereditary alpha tryptasemia has been suggested to be a risk factor for MCAS, which also can be associated with SM and clonal MCAS.9 Patients with MCAS should be tested for increased α-tryptase gene copy number given the overlap in symptoms, the likely predisposition of those with HaT to develop MCAS, and the fact that these patients could be at an increased risk for anaphylaxis.4,7,9,11 However, the clinical phenotype for HaT includes allergic disorders affecting the skin as well as neuropsychiatric and connective tissue abnormalities that are distinctive from MCAS. Although HaT may be considered a heritable risk factor for MCAS, MCAS is only 1 potential phenotype associated with HaT.9
Implications of HaT
Hereditary alpha tryptasemia should be considered in all patients with basal tryptase levels greater than 8 ng/mL. Cutaneous symptoms are among the most common presentations for individuals with HaT and can include AD, chronic or episodic urticaria, pruritus, flushing, and angioedema. However, HaT is unique because of the coupling of these common dermatologic findings with other abnormalities, including abdominal pain and diarrhea, hypermobile joints, and autonomic dysfunction. Patients with HaT also may manifest psychiatric concerns of anxiety, depression, and chronic pain, all of which have been linked to this disorder.
It is unclear in HaT if the presence of extra-allelic copies of tryptase in an individual is directly pathogenic. The effects of increased basal tryptase and α2β2 tetramers have been shown to likely be responsible for some of the clinical features in these individuals but also may magnify other individual underlying disease(s) or diathesis in which mast cells are naturally abundant.8 In the skin, this increased mast cell activation and subsequent histamine release frequently are visible as dermatographia and urticaria. However, mast cell numbers also are known to be increased in both psoriatic and AD skin lesions,12 thus severe presentation of these diseases in conjunction with the other symptoms associated with mast cell activation should prompt suspicion for HaT.
Effects of HaT on Other Cutaneous Disease—Given the increase of mast cells in AD skin lesions and fact that 94% of patients in the 2014 Lyons et al1 study cited a history of AD, HaT may be a risk factor in the development of AD. Interestingly, in addition to the increased mast cells in AD lesions, PAR2+ nerve fibers also are increased in AD lesions and have been implicated in the nonhistaminergic pruritus experienced by patients with AD.12 Thus, given the proposed propensity for α2β2 tetramers to activate PAR2, it is possible this mechanism may contribute to severe pruritus in individuals with AD and concurrent HaT, as those with HaT express increased α2β2 tetramers. However, no study to date has directly compared AD symptoms in patients with concurrent HaT vs patients without it. Further research is needed on how HaT impacts other allergic and inflammatory skin diseases such as AD and psoriasis, but one may reasonably consider HaT when treating chronic inflammatory skin diseases refractory to typical interventions and/or severe presentations. Although HaT is an autosomal-dominant disorder, it is not detected by standard whole exome sequencing or microarrays. A commercial test is available, utilizing a buccal swab to test for TPSAB1 copy number.
HaT and Mast Cell Disorders—When evaluating someone with suspected HaT, it is important to screen for other symptoms of mast cell activation. For instance, in the GI tract increased mast cell activation results in activation of motor neurons and nociceptors and increases secretion and peristalsis with consequent bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.10 Likewise, tryptase also has neuromodulatory effects that amplify the perception of pain and are likely responsible for the feelings of hyperalgesia reported in patients with HaT.13
There is substantial overlap in the clinical pictures of HaT and MCAS, and HaT is considered a heritable risk factor for MCAS. Consequently, any patient undergoing workup for MCAS also should be tested for HaT. Although HaT is associated with consistently elevated tryptase, MCAS is episodic in nature, and an increase in tryptase levels of at least 20% plus 2 ng/mL from baseline only in the presence of other symptoms reflective of mast cell activation (Table) is a prerequisite for diagnosis.9 Chronic signs and symptoms of atopy, chronic urticaria, and severe asthma are not indicative of MCAS but are frequently seen in HaT.
Another cause of persistently elevated tryptase levels is SM. Systemic mastocytosis is defined by aberrant clonal mast cell expansion and systemic involvement11 and can cause persistent symptoms, unlike MCAS alone. However, SM also can be associated with MCAS.9 Notably, a baseline serum tryptase level greater than 20 ng/mL—much higher than the threshold of greater than 8 ng/mL for suspicion of HaT—is seen in 75% of SM cases and is part of the minor diagnostic criteria for the disease.9,11 However, the 2016 study identifying increased TPSAB1 α-tryptase–encoding sequences as the causative entity for HaT by Lyons et al2 found the average (SD) basal serum tryptase level in individuals with α-tryptase–encoding sequence duplications to be 15 (5) ng/mL and 24 (6) ng/mL in those with triplications. Thus, there likely is no threshold for elevated baseline tryptase levels that would indicate SM over HaT as a more likely diagnosis. However, SM will present with new persistently elevated tryptase levels, whereas the elevation in HaT is believed to be lifelong.5 Also in contrast to HaT, SM can present with liver, spleen, and lymph node involvement; bone sclerosis; and cytopenia.11,14
Mastocytosis is much rarer than HaT, with an estimated prevalence of 9 cases per 100,000 individuals in the United States.11 Although HaT diagnostic testing is noninvasive, SM requires a bone marrow biopsy for definitive diagnosis. Given the likely much higher prevalence of HaT than SM and the patient burden of a bone marrow biopsy, HaT should be considered before proceeding with a bone marrow biopsy to evaluate for SM when a patient presents with persistent systemic symptoms of mast cell activation and elevated baseline tryptase levels. Furthermore, it also would be prudent to test for HaT in patients with known SM, as a cohort study by Lyons et al5 indicated that HaT is likely more common in those with SM (12.2% [10/82] of cohort with known SM vs 5.3% of 398 controls), and patients with concurrent SM and HaT were at a higher risk for severe anaphylaxis (RR=9.5; P=.007).
Studies thus far surrounding HaT have not evaluated timing of initial symptom onset or age of initial presentation for HaT. Furthermore, there is no guarantee that those with increased TPSAB1 copy number will be symptomatic, as there have been reports of asymptomatic individuals with HaT who had basal serum levels greater than 8 ng/mL.7 As research into HaT continues and larger cohorts are evaluated, questions surrounding timing of symptom onset and various factors that may make someone more likely to display a particular phenotype will be answered.
Treatment—Long-term prognosis for individuals with HaT is largely unknown. Unfortunately, there are limited data to support a single effective treatment strategy for managing HaT, and treatment has varied based on predominant symptoms. For cutaneous and GI tract symptoms, trials of maximal H1 and H2 antihistamines twice daily have been recommended.4 Omalizumab was reported to improve chronic urticaria in 3 of 3 patients, showing potential promise as a treatment.4 Mast cell stabilizers, such as oral cromolyn, have been used for severe GI symptoms, while some patients also have reported improvement with oral ketotifen.6 Other medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants, clemastine fumarate, and gabapentin, have been beneficial anecdotally.6 Given the lack of harmful effects seen in individuals who are α-tryptase deficient, α-tryptase inhibition is an intriguing target for future therapies.
Conclusion
Patients who present with a constellation of dermatologic, allergic, GI tract, neuropsychiatric, respiratory, autonomic, and connective tissue abnormalities consistent with HaT may receive a prompt diagnosis if the association is recognized. The full relationship between HaT and other chronic dermatologic disorders is still unknown. Ultimately, heightened interest and research into HaT will lead to more treatment options available for affected patients.
Hereditary alpha tryptasemia (HaT), an autosomal-dominant disorder of tryptase overproduction, was first described in 2014 by Lyons et al.1 It has been associated with multiple dermatologic, allergic, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, neuropsychiatric, respiratory, autonomic, and connective tissue abnormalities. These multisystem concerns may include cutaneous flushing, chronic pruritus, urticaria, GI tract symptoms, arthralgia, and autonomic dysfunction.2 The diverse symptoms and the recent discovery of HaT make recognition of this disorder challenging. Currently, it also is believed that HaT is associated with an elevated risk for anaphylaxis and is a biomarker for severe symptoms in disorders with increased mast cell burden such as mastocytosis.3-5
Given the potential cutaneous manifestations and the fact that dermatologic symptoms may be the initial presentation of HaT, awareness and recognition of this condition by dermatologists are essential for diagnosis and treatment. This review summarizes the cutaneous presentations consistent with HaT and discusses various conditions that share overlapping dermatologic symptoms with HaT.
Background on HaT
Mast cells are known to secrete several vasoactive mediators including tryptase and histamine when activated by foreign substances, similar to IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions. In their baseline state, mast cells continuously secrete immature forms of tryptases called protryptases.6 These protryptases come in 2 forms: α and β. Although mature tryptase is acutely elevatedin anaphylaxis, persistently elevated total serum tryptase levels frequently are regarded as indicative of a systemic mast cell disorder such as systemic mastocytosis (SM).3 Despite the wide-ranging phenotype of HaT, all individuals with the disorder have an elevated basal serum tryptase level (>8 ng/mL). Hereditary alpha tryptasemia has been identified as another possible cause of persistently elevated levels.2,6
Genetics and Epidemiology of HaT—The humantryptase locus at chromosome 16p13.3 is composed of 4 paralog genes: TPSG1, TPSB2, TPSAB1, and TPSD1.4 Only TPSAB1 encodes for α-tryptase, while both TPSB2 and TPSAB1 encode for β-tryptase.4 Hereditary alpha tryptasemia is an autosomal-dominant disorder resulting from a copy number increase in the α-tryptase encoding sequence within the TPSAB1 gene. Despite the wide-ranging phenotype of HaT, all individuals identified with the disorder have a basal serum tryptase level greater than 8 ng/mL, with mean (SD) levels of 15 (5) ng/mL and 24 (6) ng/mL with gene duplication and triplication, respectively (reference range, 0–11.4 ng/mL).2,6 Hereditary alpha tryptasemia likely is common and largely undiagnosed, with a recently estimated prevalence of 5% in the United Kingdom7 and 5.6% in a cohort of 125 individuals from Italy, Slovenia, and the United States.5
Implications of Increased α-tryptase Levels—After an inciting stimulus, the active portions of α-protryptase and β-protryptase are secreted as tetramers by activated mast cells via degranulation. In vitro, β-tryptase homotetramers have been found to play a role in anaphylaxis, while α-homotetramers are nearly inactive.8,9 Recently, however, it has been discovered that α2β2 tetramers also can form and do so in a higher ratio in individuals with increased α-tryptase–encoding gene copies, such as those with HaT.8 These heterotetramers exhibit unique properties compared with the homotetramers and may stimulate epidermal growth factor–like module-containing mucinlike hormone receptor 2 and protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2). Epidermal growth factor–like module-containing mucinlike hormone receptor 2 activation likely contributes to vibratory urticaria in patients, while activation of PAR2 may have a range of clinical effects, including worsening asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, pruritus, and the exacerbation of dermal inflammation and hyperalgesia.8,10 Thus, α- and β-tryptase tetramers can be considered mediators that may influence the severity of disorders in which mast cells are naturally prevalent and likely contribute to the phenotype of those with HaT.7 Furthermore, these characteristics have been shown to potentially increase in severity with increasing tryptase levels and with increased TPSAB1 duplications.1,2 In contrast, more than 25% of the population is deficient in α-tryptase without known deleterious effects.5
Cutaneous Manifestations of HaT
A case series reported by Lyons et al1 in 2014 detailed persistent elevated basal serum tryptase levels in 9 families with an autosomal-dominant pattern of inheritance. In this cohort, 31 of 33 (94%) affected individuals had a history of atopic dermatitis (AD), and 26 of 33 (79%) affected individuals reported symptoms consistent with mast cell degranulation, including urticaria; flushing; and/or crampy abdominal pain unprovoked or triggered by heat, exercise, vibration, stress, certain foods, or minor physical stimulation.1 A later report by Lyons et al2 in 2016 identified the TPSAB1 α-tryptase–encoding sequence copy number increase as the causative entity for HaT by examining a group of 96 patients from 35 families with frequent recurrent cutaneous flushing and pruritus, sometimes associated with urticaria and sleep disruption. Flushing and pruritus were found in 45% (33/73) of those with a TPSAB1 duplication and 80% (12/15) of those with a triplication (P=.022), suggesting a gene dose effect regarding α-tryptase encoding sequence copy number and these symptoms.2
A 2019 study further explored the clinical finding of urticaria in patients with HaT by specifically examining if vibration-induced urticaria was affected by TPSAB1 gene dosage.8 A cohort of 56 volunteers—35 healthy and 21 with HaT—underwent tryptase genotyping and cutaneous vibratory challenge. The presence of TPSAB1 was significantly correlated with induction of vibration-induced urticaria (P<.01), as the severity and prevalence of the urticarial response increased along with α- and β-tryptase gene ratios.8
Urticaria and angioedema also were seen in 51% (36/70) of patients in a cohort of HaT patients in the United Kingdom, in which 41% (29/70) also had skin flushing. In contrast to prior studies, these manifestations were not more common in patients with gene triplications or quintuplications than those with duplications.7 In another recent retrospective evaluation conducted at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts)(N=101), 80% of patients aged 4 to 85 years with confirmed diagnoses of HaT had skin manifestations such as urticaria, flushing, and pruritus.4
HaT and Mast Cell Activation Syndrome—In 2019, a Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report outlined recommendations for diagnosing and treating primary mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), a disorder in which mast cells seem to be more easily activated. Mast cell activation syndrome is defined as a primary clinical condition in which there are episodic signs and symptoms of systemic anaphylaxis (Table) concurrently affecting at least 2 organ systems, resulting from secreted mast cell mediators.9,11 The 2019 report also touched on clinical criteria that lack precision for diagnosing MCAS yet are in use, including dermographism and several types of rashes.9 Episode triggers frequent in MCAS include hot water, alcohol, stress, exercise, infection, hormonal changes, and physical stimuli.

Hereditary alpha tryptasemia has been suggested to be a risk factor for MCAS, which also can be associated with SM and clonal MCAS.9 Patients with MCAS should be tested for increased α-tryptase gene copy number given the overlap in symptoms, the likely predisposition of those with HaT to develop MCAS, and the fact that these patients could be at an increased risk for anaphylaxis.4,7,9,11 However, the clinical phenotype for HaT includes allergic disorders affecting the skin as well as neuropsychiatric and connective tissue abnormalities that are distinctive from MCAS. Although HaT may be considered a heritable risk factor for MCAS, MCAS is only 1 potential phenotype associated with HaT.9
Implications of HaT
Hereditary alpha tryptasemia should be considered in all patients with basal tryptase levels greater than 8 ng/mL. Cutaneous symptoms are among the most common presentations for individuals with HaT and can include AD, chronic or episodic urticaria, pruritus, flushing, and angioedema. However, HaT is unique because of the coupling of these common dermatologic findings with other abnormalities, including abdominal pain and diarrhea, hypermobile joints, and autonomic dysfunction. Patients with HaT also may manifest psychiatric concerns of anxiety, depression, and chronic pain, all of which have been linked to this disorder.
It is unclear in HaT if the presence of extra-allelic copies of tryptase in an individual is directly pathogenic. The effects of increased basal tryptase and α2β2 tetramers have been shown to likely be responsible for some of the clinical features in these individuals but also may magnify other individual underlying disease(s) or diathesis in which mast cells are naturally abundant.8 In the skin, this increased mast cell activation and subsequent histamine release frequently are visible as dermatographia and urticaria. However, mast cell numbers also are known to be increased in both psoriatic and AD skin lesions,12 thus severe presentation of these diseases in conjunction with the other symptoms associated with mast cell activation should prompt suspicion for HaT.
Effects of HaT on Other Cutaneous Disease—Given the increase of mast cells in AD skin lesions and fact that 94% of patients in the 2014 Lyons et al1 study cited a history of AD, HaT may be a risk factor in the development of AD. Interestingly, in addition to the increased mast cells in AD lesions, PAR2+ nerve fibers also are increased in AD lesions and have been implicated in the nonhistaminergic pruritus experienced by patients with AD.12 Thus, given the proposed propensity for α2β2 tetramers to activate PAR2, it is possible this mechanism may contribute to severe pruritus in individuals with AD and concurrent HaT, as those with HaT express increased α2β2 tetramers. However, no study to date has directly compared AD symptoms in patients with concurrent HaT vs patients without it. Further research is needed on how HaT impacts other allergic and inflammatory skin diseases such as AD and psoriasis, but one may reasonably consider HaT when treating chronic inflammatory skin diseases refractory to typical interventions and/or severe presentations. Although HaT is an autosomal-dominant disorder, it is not detected by standard whole exome sequencing or microarrays. A commercial test is available, utilizing a buccal swab to test for TPSAB1 copy number.
HaT and Mast Cell Disorders—When evaluating someone with suspected HaT, it is important to screen for other symptoms of mast cell activation. For instance, in the GI tract increased mast cell activation results in activation of motor neurons and nociceptors and increases secretion and peristalsis with consequent bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.10 Likewise, tryptase also has neuromodulatory effects that amplify the perception of pain and are likely responsible for the feelings of hyperalgesia reported in patients with HaT.13
There is substantial overlap in the clinical pictures of HaT and MCAS, and HaT is considered a heritable risk factor for MCAS. Consequently, any patient undergoing workup for MCAS also should be tested for HaT. Although HaT is associated with consistently elevated tryptase, MCAS is episodic in nature, and an increase in tryptase levels of at least 20% plus 2 ng/mL from baseline only in the presence of other symptoms reflective of mast cell activation (Table) is a prerequisite for diagnosis.9 Chronic signs and symptoms of atopy, chronic urticaria, and severe asthma are not indicative of MCAS but are frequently seen in HaT.
Another cause of persistently elevated tryptase levels is SM. Systemic mastocytosis is defined by aberrant clonal mast cell expansion and systemic involvement11 and can cause persistent symptoms, unlike MCAS alone. However, SM also can be associated with MCAS.9 Notably, a baseline serum tryptase level greater than 20 ng/mL—much higher than the threshold of greater than 8 ng/mL for suspicion of HaT—is seen in 75% of SM cases and is part of the minor diagnostic criteria for the disease.9,11 However, the 2016 study identifying increased TPSAB1 α-tryptase–encoding sequences as the causative entity for HaT by Lyons et al2 found the average (SD) basal serum tryptase level in individuals with α-tryptase–encoding sequence duplications to be 15 (5) ng/mL and 24 (6) ng/mL in those with triplications. Thus, there likely is no threshold for elevated baseline tryptase levels that would indicate SM over HaT as a more likely diagnosis. However, SM will present with new persistently elevated tryptase levels, whereas the elevation in HaT is believed to be lifelong.5 Also in contrast to HaT, SM can present with liver, spleen, and lymph node involvement; bone sclerosis; and cytopenia.11,14
Mastocytosis is much rarer than HaT, with an estimated prevalence of 9 cases per 100,000 individuals in the United States.11 Although HaT diagnostic testing is noninvasive, SM requires a bone marrow biopsy for definitive diagnosis. Given the likely much higher prevalence of HaT than SM and the patient burden of a bone marrow biopsy, HaT should be considered before proceeding with a bone marrow biopsy to evaluate for SM when a patient presents with persistent systemic symptoms of mast cell activation and elevated baseline tryptase levels. Furthermore, it also would be prudent to test for HaT in patients with known SM, as a cohort study by Lyons et al5 indicated that HaT is likely more common in those with SM (12.2% [10/82] of cohort with known SM vs 5.3% of 398 controls), and patients with concurrent SM and HaT were at a higher risk for severe anaphylaxis (RR=9.5; P=.007).
Studies thus far surrounding HaT have not evaluated timing of initial symptom onset or age of initial presentation for HaT. Furthermore, there is no guarantee that those with increased TPSAB1 copy number will be symptomatic, as there have been reports of asymptomatic individuals with HaT who had basal serum levels greater than 8 ng/mL.7 As research into HaT continues and larger cohorts are evaluated, questions surrounding timing of symptom onset and various factors that may make someone more likely to display a particular phenotype will be answered.
Treatment—Long-term prognosis for individuals with HaT is largely unknown. Unfortunately, there are limited data to support a single effective treatment strategy for managing HaT, and treatment has varied based on predominant symptoms. For cutaneous and GI tract symptoms, trials of maximal H1 and H2 antihistamines twice daily have been recommended.4 Omalizumab was reported to improve chronic urticaria in 3 of 3 patients, showing potential promise as a treatment.4 Mast cell stabilizers, such as oral cromolyn, have been used for severe GI symptoms, while some patients also have reported improvement with oral ketotifen.6 Other medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants, clemastine fumarate, and gabapentin, have been beneficial anecdotally.6 Given the lack of harmful effects seen in individuals who are α-tryptase deficient, α-tryptase inhibition is an intriguing target for future therapies.
Conclusion
Patients who present with a constellation of dermatologic, allergic, GI tract, neuropsychiatric, respiratory, autonomic, and connective tissue abnormalities consistent with HaT may receive a prompt diagnosis if the association is recognized. The full relationship between HaT and other chronic dermatologic disorders is still unknown. Ultimately, heightened interest and research into HaT will lead to more treatment options available for affected patients.
1. Lyons JJ, Sun G, Stone KD, et al. Mendelian inheritance of elevated serum tryptase associated with atopy and connective tissue abnormalities. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1471-1474.
2. Lyons JJ, Yu X, Hughes JD, et al. Elevated basal serum tryptase identifies a multisystem disorder associated with increased TPSAB1 copy number. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1564-1569.
3. Schwartz L. Diagnostic value of tryptase in anaphylaxis and mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006;6:451-463.
4. Giannetti MP, Weller E, Bormans C, et al. Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia in 101 patients with mast cell activation–related symptomatology including anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;126:655-660.
5. Lyons JJ, Chovanec J, O’Connell MP, et al. Heritable risk for severe anaphylaxis associated with increased α-tryptase–encoding germline copy number at TPSAB1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;147:622-632.
6. Lyons JJ. Hereditary alpha tryptasemia: genotyping and associated clinical features. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2018;38:483-495.
7. Robey RC, Wilcock A, Bonin H, et al. Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia: UK prevalence and variability in disease expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8:3549-3556.
8. Le QT, Lyons JJ, Naranjo AN, et al. Impact of naturally forming human α/β-tryptase heterotetramers in the pathogenesis of hereditary α-tryptasemia. J Exp Med. 2019;216:2348-2361.
9. Weiler CR, Austen KF, Akin C, et al. AAAAI Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report: mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) diagnosis and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144:883-896.
10. Ramsay DB, Stephen S, Borum M, et al. Mast cells in gastrointestinal disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2010;6:772-777.
11. Giannetti A, Filice E, Caffarelli C, et al. Mast cell activation disorders. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57:124.
12. Siiskonen H, Harvima I. Mast cells and sensory nerves contribute to neurogenic inflammation and pruritus in chronic skin inflammation. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:422.
13. Varrassi G, Fusco M, Skaper SD, et al. A pharmacological rationale to reduce the incidence of opioid induced tolerance and hyperalgesia: a review. Pain Ther. 2018;7:59-75.
14. Núñez E, Moreno-Borque R, García-Montero A, et al. Serum tryptase monitoring in indolent systemic mastocytosis: association with disease features and patient outcome. PLoS One. 2013;8:E76116.
1. Lyons JJ, Sun G, Stone KD, et al. Mendelian inheritance of elevated serum tryptase associated with atopy and connective tissue abnormalities. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1471-1474.
2. Lyons JJ, Yu X, Hughes JD, et al. Elevated basal serum tryptase identifies a multisystem disorder associated with increased TPSAB1 copy number. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1564-1569.
3. Schwartz L. Diagnostic value of tryptase in anaphylaxis and mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2006;6:451-463.
4. Giannetti MP, Weller E, Bormans C, et al. Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia in 101 patients with mast cell activation–related symptomatology including anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;126:655-660.
5. Lyons JJ, Chovanec J, O’Connell MP, et al. Heritable risk for severe anaphylaxis associated with increased α-tryptase–encoding germline copy number at TPSAB1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;147:622-632.
6. Lyons JJ. Hereditary alpha tryptasemia: genotyping and associated clinical features. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2018;38:483-495.
7. Robey RC, Wilcock A, Bonin H, et al. Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia: UK prevalence and variability in disease expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8:3549-3556.
8. Le QT, Lyons JJ, Naranjo AN, et al. Impact of naturally forming human α/β-tryptase heterotetramers in the pathogenesis of hereditary α-tryptasemia. J Exp Med. 2019;216:2348-2361.
9. Weiler CR, Austen KF, Akin C, et al. AAAAI Mast Cell Disorders Committee Work Group Report: mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) diagnosis and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144:883-896.
10. Ramsay DB, Stephen S, Borum M, et al. Mast cells in gastrointestinal disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2010;6:772-777.
11. Giannetti A, Filice E, Caffarelli C, et al. Mast cell activation disorders. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57:124.
12. Siiskonen H, Harvima I. Mast cells and sensory nerves contribute to neurogenic inflammation and pruritus in chronic skin inflammation. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:422.
13. Varrassi G, Fusco M, Skaper SD, et al. A pharmacological rationale to reduce the incidence of opioid induced tolerance and hyperalgesia: a review. Pain Ther. 2018;7:59-75.
14. Núñez E, Moreno-Borque R, García-Montero A, et al. Serum tryptase monitoring in indolent systemic mastocytosis: association with disease features and patient outcome. PLoS One. 2013;8:E76116.
Practice Points
- Chronic or episodic urticaria, flushing, and pruritus are the most consistent cutaneous abnormalities associated with hereditary alpha tryptasemia (HaT), but HaT also may augment symptoms of other underlying inflammatory skin disorders, such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
- Individuals with episodic dermatologic manifestations indicative of mast cell activation accompanied by symptoms affecting 1 or more organ systems should be evaluated for mast cell activation syndrome as well as HaT.
Hyperpigmented Papules on the Tongue of a Child
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
The Diagnosis: Pigmented Fungiform Papillae of the Tongue
Our patient’s hyperpigmentation was confined to the fungiform papillae, leading to a diagnosis of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue (PFPT). A biopsy was not performed, and reassurance was provided regarding the benign nature of this finding, which did not require treatment.
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a benign, nonprogressive, asymptomatic pigmentary condition that is most common among patients with skin of color and typically develops within the second or third decade of life.1,2 The pathogenesis is unclear, but activation of subepithelial melanophages without evidence of inflammation has been implicated.2 Although no standard treatment exists, cosmetic improvement with the use of the Q-switched ruby laser has been reported.3,4 Clinically, PFPT presents as asymptomatic hyperpigmentation confined to the fungiform papillae along the anterior and lateral portions of the tongue.1,2
Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue typically is an isolated finding but rarely can be associated with hyperpigmentation of the nails (as in our patient) or gingiva.2 Three different clinical patterns of presentation have been described: (1) a single well-circumscribed collection of pigmented fungiform papillae, (2) few scattered pigmented fungiform papillae admixed with many nonpigmented fungiform papillae, or (3) pigmentation of all fungiform papillae on the dorsal aspect of the tongue.2,5,6 Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue is a clinical diagnosis based on visual recognition. Dermoscopic examination revealing a cobblestonelike or rose petal–like pattern may be helpful in diagnosing PFPT.2,5-7 Although not typically recommended in the evaluation of PFPT, a biopsy will reveal papillary structures with hyperpigmentation of basilar keratinocytes as well as melanophages in the lamina propria.8 The latter finding suggests a transient inflammatory process despite the hallmark absence of inflammation.5 Melanocytic neoplasia and exogenous granules of pigment typically are not seen.8
Other conditions that may present with dark-colored macules or papules on the tongue should be considered in the evaluation of a patient with these clinical findings. Black hairy tongue (BHT), or lingua villosa nigra, is a benign finding due to filiform papillae hypertrophy on the dorsum of the tongue.9 Food particle debris caught in BHT can lead to porphyrin production by chromogenic bacteria and fungi. These porphyrins result in discoloration ranging from brown-black to yellow and green occurring anteriorly to the circumvallate papillae while usually sparing the tip and lateral sides of the tongue. Dermoscopy can show thin discolored fibers with a hairy appearance. Although normal filiform papillae are less than 1-mm long, 3-mm long papillae are considered diagnostic of BHT.9 Treatment includes effective oral hygiene and desquamation measures, which can lead to complete resolution.10
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is a rare genodermatosis that is characterized by focal hyperpigmentation and multiple gastrointestinal mucosal hamartomatous polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome should be suspected in a patient with discrete, 1- to 5-mm, brown to black macules on the perioral or periocular skin, tongue, genitals, palms, soles, and buccal mucosa with a history of abdominal symptoms.11,12
Addison disease, or primary adrenal insufficiency, may present with brown hyperpigmentation on chronically sun-exposed areas; regions of friction or pressure; surrounding scar tissue; and mucosal surfaces such as the tongue, inner surface of the lip, and buccal and gingival mucosa.13 Addison disease is differentiated from PFPT by a more generalized hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production as well as the presence of systemic symptoms related to hypocortisolism. The pigmentation seen on the buccal mucosa in Addison disease is patchy and diffuse, and histology reveals basal melanin hyperpigmentation with superficial dermal melanophages.13
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited disorder featuring telangiectasia and generally appears in the third decade of life.14 Telangiectases classically are 1 to 3 mm in diameter with or without slight elevation. Dermoscopic findings include small red clots, lacunae, and serpentine or linear vessels arranged in a radial conformation surrounding a homogenous pink center.15 These telangiectases typically occur on the skin or mucosa, particularly the face, lips, tongue, nail beds, and nasal mucosa; however, any organ can be affected with arteriovenous malformations. Recurrent epistaxis occurs in more than half of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.14 Histopathology reveals dilated vessels and lacunae near the dermoepidermal junction displacing the epidermis and papillary dermis.15 It is distinguished from PFPT by the vascular nature of the lesions and by the presence of other characteristic symptoms such as recurrent epistaxis and visceral arteriovenous malformations.
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
- Romiti R, Molina De Medeiros L. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:398-399. doi:10.1111/j .1525-1470.2010.01183.x
- Chessa MA, Patrizi A, Sechi A, et al. Pigmented fungiform lingual papillae: dermoscopic and clinical features. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:935-939. doi:10.1111/jdv.14809
- Rice SM, Lal K. Successful treatment of pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue with Q-switched ruby laser. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:368-369. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003371
- Mizawa M, Makino T, Furukawa F, et al. Efficacy of Q-switched ruby laser treatment for pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2022;49:E133-E134. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16270
- Holzwanger JM, Rudolph RI, Heaton CL. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a common variant of oral pigmentation. Int J Dermatol. 1974;13:403-408. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974. tb05073.x
- Mukamal LV, Ormiga P, Ramos-E-Silva M. Dermoscopy of the pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue. J Dermatol. 2012;39:397-399. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01328.x
- Surboyo MDC, Santosh ABR, Hariyani N, et al. Clinical utility of dermoscopy on diagnosing pigmented papillary fungiform papillae of the tongue: a systematic review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2021;11:618-623. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2021.09.008
- Chamseddin B, Vandergriff T. Pigmented fungiform papillae of the tongue: a clinical and histologic description [published online September 15, 2019]. Dermatol Online J. 2019;25:13030/qt8674c519.
- Jayasree P, Kaliyadan F, Ashique KT. Black hairy tongue. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:573. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5314
- Schlager E, St Claire C, Ashack K, et al. Black hairy tongue: predisposing factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:563-569. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0268-y
- Sandru F, Petca A, Dumitrascu MC, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: skin manifestations and endocrine anomalies (review). Exp Ther Med. 2021;22:1387. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10823
- Shah KR, Boland CR, Patel M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:189.e1-210. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.10.037
- Lee K, Lian C, Vaidya A, et al. Oral mucosal hyperpigmentation. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:993-995. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.08.013
- Haitjema T, Westermann CJ, Overtoom TT, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease): new insights in pathogenesis, complications, and treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:714-719.
- Tokoro S, Namiki T, Ugajin T, et al. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber’s disease): detailed assessment of skin lesions by dermoscopy and ultrasound. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:E224-E226. doi:10.1111/ijd.14578
A 9-year-old Black boy presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of dark spots on the tongue. The family first noted these spots 5 months prior and reported that they remained stable during that time. The patient’s medical history was notable for autism spectrum disorder and multiple food allergies. His family history was negative for similar oral pigmentation or other pigmentary anomalies. A review of systems was positive only for selective eating and rare nosebleeds. Physical examination revealed numerous dark brown, pinpoint papules across the dorsal aspect of the tongue. No hyperpigmentation of the buccal mucosae, lips, palms, or soles was identified. Several light brown streaks were present on the fingernails and toenails, consistent with longitudinal melanonychia. A prior complete blood cell count was within reference range.
Commentary: Interstitial Lung Disease, Onset Time, and RA, January 2023
Though rheumatoid arthritis (RA)–associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) is a feared complication that can significantly affect morbidity and mortality, the role of methotrexate in treatment and its possible contribution to ILD is yet unknown. Kim and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis of a series of 170 patients with RA-ILD to try to identify risk factors and protective factors for mortality and decline of lung function. Previously known risk factors included older age, smoking, and seropositivity for cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP). In this series, patients who had exposure to methotrexate after a diagnosis of RA-ILD were found to have less progression of decline in lung function and decreased mortality compared with those who did not, which is a finding that warrants further examination. On the other hand, there was a suggestion that sulfasalazine use is associated with increased mortality, though this finding was not borne out in multivariate analysis.
A different group of authors also examined the association with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD) with ILD progression in a prospective analysis of 143 patients in the multicenter Korean RA-ILD cohort. Patients were classified regarding exposure to methotrexate, leflunomide, or tacrolimus as well as biologic DMARD and glucocorticoid exposure, with a primary outcome of ILD progression based on pulmonary function tests or mortality. The study did not detect any difference in time to ILD progression with methotrexate exposure, though it is not clear that the study would be able to detect a protective effect as was possible in the prior study. However, patients who were exposed to leflunomide had a shorter time to ILD progression than did those who were not, though this did not persist in multivariate analysis, and tacrolimus exposure had a statistically insignificant impact on ILD progression. Because the study is small, other associations which could affect use of leflunomide in these patients were not examined, though prior studies have suggested an association with leflunomide in ILD progression in patients with existing RA-ILD.
Li and colleagues addressed the characteristics and prognosis of late-onset RA (LORA) in people 60 years or older compared with younger-onset RA (YORA) in a prospective cohort study using a Canadian RA registry. Patients in the registry were enrolled early in the course of their illness and clinical characteristics as well as time to Disease Activity Score (DAS28) remission were analyzed. Of note, YORA and LORA patients had similar times to remission but were on less aggressive medication regimens, such as conventional DMARD without biologic DMARD or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. In this registry, a smaller percentage of LORA patients compared with YORA patients were seropositive, which, given the enrollment of patients early in their disease course, may affect the use of biologic DMARD and JAK inhibitors.
Finally, the issue of noninflammatory pain contributing to disease activity and quality of life in RA has received increased scrutiny recently. Choy and colleagues studied disproportionate articular pain (DP) and its response to sarilumab, adalimumab, or placebo in a post hoc analysis of data from prior randomized clinical trials. DP was defined as a tender joint count that exceeded swollen joint count by seven and was present in about 20% of patients in the three randomized clinical trials examined. In these studies, DP was reduced in patients treated with sarilumab compared with placebo or adalimumab. Although this finding is exciting in raising the possibility of an immunologic explanation for DP via interleukin 6 (IL-6), the results should be considered carefully in the context of this post hoc analysis, especially before considering sarilumab or other IL-6 inhibitors as viable treatment options for DP in RA.
Though rheumatoid arthritis (RA)–associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) is a feared complication that can significantly affect morbidity and mortality, the role of methotrexate in treatment and its possible contribution to ILD is yet unknown. Kim and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis of a series of 170 patients with RA-ILD to try to identify risk factors and protective factors for mortality and decline of lung function. Previously known risk factors included older age, smoking, and seropositivity for cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP). In this series, patients who had exposure to methotrexate after a diagnosis of RA-ILD were found to have less progression of decline in lung function and decreased mortality compared with those who did not, which is a finding that warrants further examination. On the other hand, there was a suggestion that sulfasalazine use is associated with increased mortality, though this finding was not borne out in multivariate analysis.
A different group of authors also examined the association with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD) with ILD progression in a prospective analysis of 143 patients in the multicenter Korean RA-ILD cohort. Patients were classified regarding exposure to methotrexate, leflunomide, or tacrolimus as well as biologic DMARD and glucocorticoid exposure, with a primary outcome of ILD progression based on pulmonary function tests or mortality. The study did not detect any difference in time to ILD progression with methotrexate exposure, though it is not clear that the study would be able to detect a protective effect as was possible in the prior study. However, patients who were exposed to leflunomide had a shorter time to ILD progression than did those who were not, though this did not persist in multivariate analysis, and tacrolimus exposure had a statistically insignificant impact on ILD progression. Because the study is small, other associations which could affect use of leflunomide in these patients were not examined, though prior studies have suggested an association with leflunomide in ILD progression in patients with existing RA-ILD.
Li and colleagues addressed the characteristics and prognosis of late-onset RA (LORA) in people 60 years or older compared with younger-onset RA (YORA) in a prospective cohort study using a Canadian RA registry. Patients in the registry were enrolled early in the course of their illness and clinical characteristics as well as time to Disease Activity Score (DAS28) remission were analyzed. Of note, YORA and LORA patients had similar times to remission but were on less aggressive medication regimens, such as conventional DMARD without biologic DMARD or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. In this registry, a smaller percentage of LORA patients compared with YORA patients were seropositive, which, given the enrollment of patients early in their disease course, may affect the use of biologic DMARD and JAK inhibitors.
Finally, the issue of noninflammatory pain contributing to disease activity and quality of life in RA has received increased scrutiny recently. Choy and colleagues studied disproportionate articular pain (DP) and its response to sarilumab, adalimumab, or placebo in a post hoc analysis of data from prior randomized clinical trials. DP was defined as a tender joint count that exceeded swollen joint count by seven and was present in about 20% of patients in the three randomized clinical trials examined. In these studies, DP was reduced in patients treated with sarilumab compared with placebo or adalimumab. Although this finding is exciting in raising the possibility of an immunologic explanation for DP via interleukin 6 (IL-6), the results should be considered carefully in the context of this post hoc analysis, especially before considering sarilumab or other IL-6 inhibitors as viable treatment options for DP in RA.
Though rheumatoid arthritis (RA)–associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) is a feared complication that can significantly affect morbidity and mortality, the role of methotrexate in treatment and its possible contribution to ILD is yet unknown. Kim and colleagues performed a retrospective analysis of a series of 170 patients with RA-ILD to try to identify risk factors and protective factors for mortality and decline of lung function. Previously known risk factors included older age, smoking, and seropositivity for cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP). In this series, patients who had exposure to methotrexate after a diagnosis of RA-ILD were found to have less progression of decline in lung function and decreased mortality compared with those who did not, which is a finding that warrants further examination. On the other hand, there was a suggestion that sulfasalazine use is associated with increased mortality, though this finding was not borne out in multivariate analysis.
A different group of authors also examined the association with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD) with ILD progression in a prospective analysis of 143 patients in the multicenter Korean RA-ILD cohort. Patients were classified regarding exposure to methotrexate, leflunomide, or tacrolimus as well as biologic DMARD and glucocorticoid exposure, with a primary outcome of ILD progression based on pulmonary function tests or mortality. The study did not detect any difference in time to ILD progression with methotrexate exposure, though it is not clear that the study would be able to detect a protective effect as was possible in the prior study. However, patients who were exposed to leflunomide had a shorter time to ILD progression than did those who were not, though this did not persist in multivariate analysis, and tacrolimus exposure had a statistically insignificant impact on ILD progression. Because the study is small, other associations which could affect use of leflunomide in these patients were not examined, though prior studies have suggested an association with leflunomide in ILD progression in patients with existing RA-ILD.
Li and colleagues addressed the characteristics and prognosis of late-onset RA (LORA) in people 60 years or older compared with younger-onset RA (YORA) in a prospective cohort study using a Canadian RA registry. Patients in the registry were enrolled early in the course of their illness and clinical characteristics as well as time to Disease Activity Score (DAS28) remission were analyzed. Of note, YORA and LORA patients had similar times to remission but were on less aggressive medication regimens, such as conventional DMARD without biologic DMARD or Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. In this registry, a smaller percentage of LORA patients compared with YORA patients were seropositive, which, given the enrollment of patients early in their disease course, may affect the use of biologic DMARD and JAK inhibitors.
Finally, the issue of noninflammatory pain contributing to disease activity and quality of life in RA has received increased scrutiny recently. Choy and colleagues studied disproportionate articular pain (DP) and its response to sarilumab, adalimumab, or placebo in a post hoc analysis of data from prior randomized clinical trials. DP was defined as a tender joint count that exceeded swollen joint count by seven and was present in about 20% of patients in the three randomized clinical trials examined. In these studies, DP was reduced in patients treated with sarilumab compared with placebo or adalimumab. Although this finding is exciting in raising the possibility of an immunologic explanation for DP via interleukin 6 (IL-6), the results should be considered carefully in the context of this post hoc analysis, especially before considering sarilumab or other IL-6 inhibitors as viable treatment options for DP in RA.
ObGyns united in a divided post-Dobbs America
While many anticipated the fall of Roe v Wade after the leaked Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) decision in the Dobbs v Jackson case, few may have fully comprehended the myriad of ways this ruling would create a national health care crisis overnight. Since the ruling, abortion has been banned, or a 6-week gestational age limit has been implemented, in a total of 13 states, all within the South
The 2022 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Annual Clinical and Scientific Meeting, held shortly after the leaked SCOTUS opinion, was unlike most others. ACOG staff appropriately recognized the vastly different ways this ruling would affect patients and providers alike, simply based on the states in which they reside. ACOG staff organized the large group of attendees according to self-identified status (ie, whether they worked in states with protected, restricted, or threatened access to abortion care). Since this is such a vast topic, attendees also were asked to identify an area upon which to focus, such as the provision of health care, advocacy, or education. As a clinician practicing in Massachusetts, Dr. Bradley found herself meeting with an ACOG leader from California as they brainstormed how to best help our own communities. In conversing with attendees from other parts of the country, it became apparent the challenges others would be facing elsewhere were far more substantive than those we would be facing in “blue states.” After the Dobbs ruling, those predictions became harsh realities.
As we begin to see and hear reports of the devastating consequences of this ruling in “red states,” those of us in protected states have been struggling to try and ascertain how to help. Many of us have worked with our own legislatures to further enshrine protections for our patients and clinicians. New York and Massachusetts exemplify these efforts.6,7 These legislative efforts have included liability protections for patients and their clinicians who care for those who travel from restricted to protected states. Others involve codifying the principles of Roe and clarifying existing law to improve access. An online fundraiser organized by physicians to assist Dr. Bernard with her legal costs as she faces politically motivated investigation by Indiana state authorities has raised more than $260,000.8 Many expressed the potential legal and medical peril for examiners and examinees if the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology held in-person oral examinations in Texas as previously scheduled.9 An online petition to change the format to virtual had 728 signatories, and the format was changed back to virtual.10
The implications on medical schools, residencies, and fellowships cannot be overstated. The Dobbs ruling almost immediately affected nearly half of the training programs, which is particularly problematic given the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirement that all ObGyn residents have access to abortion training.11 Other programs already are starting to try to meet this vast training need. The University of California San Francisco started offering training to physicians from Texas who were affected by the strict restrictions that predated Dobbs in the SB8 legislation, which turned ordinary citizens into vigilantes.12
ACOG has created an online resource (https://www.acog.org/advocacy/abortion-is-essential) with a number of different sections regarding clinical care, education and training, advocacy at the state level, and how to use effective language when talking about abortion in our communities. Planned Parenthood also suggests a myriad of ways those directly and indirectly affected could get involved:
- Donate to the National Network of Abortion Funds. This fund (https://secure.actblue.com/donate/fundabortionnow) facilitates care for those without the financial means to obtain it, supporting travel, lodging, and child care.
- Share #AbortionAccess posts on social media. These stories are a powerful reminder of the incredibly harmful impact this legislation can have on our patients.
- Donate to the If When How’s Legal Repro Defense Fund (https:/www.ifwhenhow.org/), which helps cover legal costs for those facing state persecution related to reproductive health care.
- Volunteer to help protect abortion health care at the state level.
- Engage with members of Congress in their home districts. (https://www.congress.gov/members/find-your-member)
- Contact the Planned Parenthood Local Engagement Team to facilitate your group, business, or organization’s involvement.
- Partner. Facilitate your organization and other companies to partner with Planned Parenthood and sign up for Bans off our Bodies (https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSdrmxwMcwNXJ8I NE8S2gYjDDXuT76ws_Fr7CLm3 qbtR8dcZHw/viewform).
- Record your perspective about abortion (https://www.together.plannedparenthood.org/articles/6-share-abortion-story), whether it’s having had one, supported someone who had one, or advocated for others to have access to the procedure.13
ACOG also outlines several ways those of us in protected states could help shape the landscape in other communities in addition to advocating for state medical society resolutions, writing op-eds and letters to the editor, and utilizing ACOG’s social media graphics.14 In recognition of the often sensitive, polarizing nature of these discussions, ACOG is offering a workshop entitled “Building Evidence-Based Skills for Effective Conversations about Abortion.”15
Abortion traditionally was a policy issue other medical organizations shied away from developing official policy on and speaking out in support of, but recognizing the devastating scope of the public health crisis, 75 medical professional organizations recently released a strongly worded joint statement noting, “As leading medical and health care organizations dedicated to patient care and public health, we condemn this and all interference in the patient–clinician relationship.”16 Clinicians could work to expand this list to include all aspects of organized medicine. Initiatives to get out the vote may be helpful in vulnerable states, as well.
Clinicians in protected states are not necessarily directly affected in our daily interactions with patients, but we stand in solidarity with those who are. We must remain united as a profession as different state legislatures seek to divide us. We must support those who are struggling every day. Our colleagues and fellow citizens deserve nothing less. ●
- Tracking the states where abortion is now banned. New York Times. November 23, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2022/us/abortion-laws-roe-v-wade.html. Accessed November 28, 2022.
- Stanton A. ‘She’s 10’: child rape victims abortion denial spreads outrage on Twitter. Newsweek. July 2, 2022. https://www.newsweek.com/shes-10-child-rape-victims-abortion-denial-sparks-outrage-twitter-1721248. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Judge-Golden C, Flink-Bochacki R. The burden of abortion restrictions and conservative diagnostic guidelines on patient-centered care for early pregnancy loss. Obstet Gynecol 2021;138:467071.
- Nambiar A, Patel S, Santiago-Munoz P, et al. Maternal morbidity and fetal outcomes among pregnant women at 22 weeks’ gestation or less with complications in 2 Texas hospitals after legislation on abortion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227:648-650.e1. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.06.060.
- Winter J. The Dobbs decision has unleashed legal chaos for doctors and patients. The New Yorker. July 2, 2022. https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/the-dobbs-decision-has-unleashed-legal-chaos-for-doctors-and-patients. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Lynch B, Mallow M, Bodde K, et al. Addressing a crisis in abortion access: a case study in advocacy. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:110-114.
- Evans M, Bradley T, Ireland L, et al. How the fall of Roe could change abortion care in Mass. Cognoscenti. July 26, 2022. https://www.wbur.org/cognoscenti/2022/07/26/dobbs-roe-abortion-massachusetts-megan-l-evans-erin-t-bradley-luu-ireland-chloe-zera. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Spocchia G. Over $200k raised for doctor who performed abortion on 10-year-old rape victim. Independent. July 18, 2022. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/fundriaser-ohio-abortion-doctor-rape-b2125621.html. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- ABOG petition: convert to online examination to protect OBGYN providers. Change.org website. https://www.change.org/p/abog-petition?original_footer_petition_id=33459909&algorithm=promoted&source_location=petition_footer&grid_position=8&pt=AVBldGl0aW9uAHgWBQIAAAAAYs65vIyhbUxhZGM0MWVhZg%3D%3D. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- D’Ambrosio A. Ob/Gyn board certification exam stays virtual in light of Dobbs. MedPageToday. July 15, 2022. https://www.medpagetoday.com/special-reports/features/99758. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Weiner S. How the repeal of Roe v. Wade will affect training in abortion and reproductive health. AAMC News. June 24, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/news-insights/how-repeal-roe-v-wade-will-affect-training-abortion-and-reproductive-health. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Anderson N. The fall of Roe scrambles abortion training for university hospitals. The Washington Post. June 30, 2022. https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2022/06/30/abortion-training-upheaval-dobbs/. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Bans off our bodies. Planned Parenthood website. https://www.plannedparenthoodaction.org/rightfully-ours/bans-off-our-bodies. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Shape the public discourse. ACOG website. https://www.acog.org/advocacy/abortion-is-essential/connect-in-your-community. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Building evidence-based skills for effective conversations about abortion. ACOG website. https://www.acog.org/programs/impact/activities-initiatives/building-evidence-based-skills-for-effective-conversations-about-abortion. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. More than 75 health care organizations release joint statement in opposition to legislative interference. ACOG website. Published July 7, 2022. https://www.acog.org/news/news-releases/2022/07/more-than-75-health-care-organizations-release-joint-statement-in-opposition-to-legislative-interference. Accessed November 6, 2022.
While many anticipated the fall of Roe v Wade after the leaked Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) decision in the Dobbs v Jackson case, few may have fully comprehended the myriad of ways this ruling would create a national health care crisis overnight. Since the ruling, abortion has been banned, or a 6-week gestational age limit has been implemented, in a total of 13 states, all within the South
The 2022 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Annual Clinical and Scientific Meeting, held shortly after the leaked SCOTUS opinion, was unlike most others. ACOG staff appropriately recognized the vastly different ways this ruling would affect patients and providers alike, simply based on the states in which they reside. ACOG staff organized the large group of attendees according to self-identified status (ie, whether they worked in states with protected, restricted, or threatened access to abortion care). Since this is such a vast topic, attendees also were asked to identify an area upon which to focus, such as the provision of health care, advocacy, or education. As a clinician practicing in Massachusetts, Dr. Bradley found herself meeting with an ACOG leader from California as they brainstormed how to best help our own communities. In conversing with attendees from other parts of the country, it became apparent the challenges others would be facing elsewhere were far more substantive than those we would be facing in “blue states.” After the Dobbs ruling, those predictions became harsh realities.
As we begin to see and hear reports of the devastating consequences of this ruling in “red states,” those of us in protected states have been struggling to try and ascertain how to help. Many of us have worked with our own legislatures to further enshrine protections for our patients and clinicians. New York and Massachusetts exemplify these efforts.6,7 These legislative efforts have included liability protections for patients and their clinicians who care for those who travel from restricted to protected states. Others involve codifying the principles of Roe and clarifying existing law to improve access. An online fundraiser organized by physicians to assist Dr. Bernard with her legal costs as she faces politically motivated investigation by Indiana state authorities has raised more than $260,000.8 Many expressed the potential legal and medical peril for examiners and examinees if the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology held in-person oral examinations in Texas as previously scheduled.9 An online petition to change the format to virtual had 728 signatories, and the format was changed back to virtual.10
The implications on medical schools, residencies, and fellowships cannot be overstated. The Dobbs ruling almost immediately affected nearly half of the training programs, which is particularly problematic given the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirement that all ObGyn residents have access to abortion training.11 Other programs already are starting to try to meet this vast training need. The University of California San Francisco started offering training to physicians from Texas who were affected by the strict restrictions that predated Dobbs in the SB8 legislation, which turned ordinary citizens into vigilantes.12
ACOG has created an online resource (https://www.acog.org/advocacy/abortion-is-essential) with a number of different sections regarding clinical care, education and training, advocacy at the state level, and how to use effective language when talking about abortion in our communities. Planned Parenthood also suggests a myriad of ways those directly and indirectly affected could get involved:
- Donate to the National Network of Abortion Funds. This fund (https://secure.actblue.com/donate/fundabortionnow) facilitates care for those without the financial means to obtain it, supporting travel, lodging, and child care.
- Share #AbortionAccess posts on social media. These stories are a powerful reminder of the incredibly harmful impact this legislation can have on our patients.
- Donate to the If When How’s Legal Repro Defense Fund (https:/www.ifwhenhow.org/), which helps cover legal costs for those facing state persecution related to reproductive health care.
- Volunteer to help protect abortion health care at the state level.
- Engage with members of Congress in their home districts. (https://www.congress.gov/members/find-your-member)
- Contact the Planned Parenthood Local Engagement Team to facilitate your group, business, or organization’s involvement.
- Partner. Facilitate your organization and other companies to partner with Planned Parenthood and sign up for Bans off our Bodies (https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSdrmxwMcwNXJ8I NE8S2gYjDDXuT76ws_Fr7CLm3 qbtR8dcZHw/viewform).
- Record your perspective about abortion (https://www.together.plannedparenthood.org/articles/6-share-abortion-story), whether it’s having had one, supported someone who had one, or advocated for others to have access to the procedure.13
ACOG also outlines several ways those of us in protected states could help shape the landscape in other communities in addition to advocating for state medical society resolutions, writing op-eds and letters to the editor, and utilizing ACOG’s social media graphics.14 In recognition of the often sensitive, polarizing nature of these discussions, ACOG is offering a workshop entitled “Building Evidence-Based Skills for Effective Conversations about Abortion.”15
Abortion traditionally was a policy issue other medical organizations shied away from developing official policy on and speaking out in support of, but recognizing the devastating scope of the public health crisis, 75 medical professional organizations recently released a strongly worded joint statement noting, “As leading medical and health care organizations dedicated to patient care and public health, we condemn this and all interference in the patient–clinician relationship.”16 Clinicians could work to expand this list to include all aspects of organized medicine. Initiatives to get out the vote may be helpful in vulnerable states, as well.
Clinicians in protected states are not necessarily directly affected in our daily interactions with patients, but we stand in solidarity with those who are. We must remain united as a profession as different state legislatures seek to divide us. We must support those who are struggling every day. Our colleagues and fellow citizens deserve nothing less. ●
While many anticipated the fall of Roe v Wade after the leaked Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) decision in the Dobbs v Jackson case, few may have fully comprehended the myriad of ways this ruling would create a national health care crisis overnight. Since the ruling, abortion has been banned, or a 6-week gestational age limit has been implemented, in a total of 13 states, all within the South
The 2022 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Annual Clinical and Scientific Meeting, held shortly after the leaked SCOTUS opinion, was unlike most others. ACOG staff appropriately recognized the vastly different ways this ruling would affect patients and providers alike, simply based on the states in which they reside. ACOG staff organized the large group of attendees according to self-identified status (ie, whether they worked in states with protected, restricted, or threatened access to abortion care). Since this is such a vast topic, attendees also were asked to identify an area upon which to focus, such as the provision of health care, advocacy, or education. As a clinician practicing in Massachusetts, Dr. Bradley found herself meeting with an ACOG leader from California as they brainstormed how to best help our own communities. In conversing with attendees from other parts of the country, it became apparent the challenges others would be facing elsewhere were far more substantive than those we would be facing in “blue states.” After the Dobbs ruling, those predictions became harsh realities.
As we begin to see and hear reports of the devastating consequences of this ruling in “red states,” those of us in protected states have been struggling to try and ascertain how to help. Many of us have worked with our own legislatures to further enshrine protections for our patients and clinicians. New York and Massachusetts exemplify these efforts.6,7 These legislative efforts have included liability protections for patients and their clinicians who care for those who travel from restricted to protected states. Others involve codifying the principles of Roe and clarifying existing law to improve access. An online fundraiser organized by physicians to assist Dr. Bernard with her legal costs as she faces politically motivated investigation by Indiana state authorities has raised more than $260,000.8 Many expressed the potential legal and medical peril for examiners and examinees if the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology held in-person oral examinations in Texas as previously scheduled.9 An online petition to change the format to virtual had 728 signatories, and the format was changed back to virtual.10
The implications on medical schools, residencies, and fellowships cannot be overstated. The Dobbs ruling almost immediately affected nearly half of the training programs, which is particularly problematic given the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirement that all ObGyn residents have access to abortion training.11 Other programs already are starting to try to meet this vast training need. The University of California San Francisco started offering training to physicians from Texas who were affected by the strict restrictions that predated Dobbs in the SB8 legislation, which turned ordinary citizens into vigilantes.12
ACOG has created an online resource (https://www.acog.org/advocacy/abortion-is-essential) with a number of different sections regarding clinical care, education and training, advocacy at the state level, and how to use effective language when talking about abortion in our communities. Planned Parenthood also suggests a myriad of ways those directly and indirectly affected could get involved:
- Donate to the National Network of Abortion Funds. This fund (https://secure.actblue.com/donate/fundabortionnow) facilitates care for those without the financial means to obtain it, supporting travel, lodging, and child care.
- Share #AbortionAccess posts on social media. These stories are a powerful reminder of the incredibly harmful impact this legislation can have on our patients.
- Donate to the If When How’s Legal Repro Defense Fund (https:/www.ifwhenhow.org/), which helps cover legal costs for those facing state persecution related to reproductive health care.
- Volunteer to help protect abortion health care at the state level.
- Engage with members of Congress in their home districts. (https://www.congress.gov/members/find-your-member)
- Contact the Planned Parenthood Local Engagement Team to facilitate your group, business, or organization’s involvement.
- Partner. Facilitate your organization and other companies to partner with Planned Parenthood and sign up for Bans off our Bodies (https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSdrmxwMcwNXJ8I NE8S2gYjDDXuT76ws_Fr7CLm3 qbtR8dcZHw/viewform).
- Record your perspective about abortion (https://www.together.plannedparenthood.org/articles/6-share-abortion-story), whether it’s having had one, supported someone who had one, or advocated for others to have access to the procedure.13
ACOG also outlines several ways those of us in protected states could help shape the landscape in other communities in addition to advocating for state medical society resolutions, writing op-eds and letters to the editor, and utilizing ACOG’s social media graphics.14 In recognition of the often sensitive, polarizing nature of these discussions, ACOG is offering a workshop entitled “Building Evidence-Based Skills for Effective Conversations about Abortion.”15
Abortion traditionally was a policy issue other medical organizations shied away from developing official policy on and speaking out in support of, but recognizing the devastating scope of the public health crisis, 75 medical professional organizations recently released a strongly worded joint statement noting, “As leading medical and health care organizations dedicated to patient care and public health, we condemn this and all interference in the patient–clinician relationship.”16 Clinicians could work to expand this list to include all aspects of organized medicine. Initiatives to get out the vote may be helpful in vulnerable states, as well.
Clinicians in protected states are not necessarily directly affected in our daily interactions with patients, but we stand in solidarity with those who are. We must remain united as a profession as different state legislatures seek to divide us. We must support those who are struggling every day. Our colleagues and fellow citizens deserve nothing less. ●
- Tracking the states where abortion is now banned. New York Times. November 23, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2022/us/abortion-laws-roe-v-wade.html. Accessed November 28, 2022.
- Stanton A. ‘She’s 10’: child rape victims abortion denial spreads outrage on Twitter. Newsweek. July 2, 2022. https://www.newsweek.com/shes-10-child-rape-victims-abortion-denial-sparks-outrage-twitter-1721248. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Judge-Golden C, Flink-Bochacki R. The burden of abortion restrictions and conservative diagnostic guidelines on patient-centered care for early pregnancy loss. Obstet Gynecol 2021;138:467071.
- Nambiar A, Patel S, Santiago-Munoz P, et al. Maternal morbidity and fetal outcomes among pregnant women at 22 weeks’ gestation or less with complications in 2 Texas hospitals after legislation on abortion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227:648-650.e1. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.06.060.
- Winter J. The Dobbs decision has unleashed legal chaos for doctors and patients. The New Yorker. July 2, 2022. https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/the-dobbs-decision-has-unleashed-legal-chaos-for-doctors-and-patients. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Lynch B, Mallow M, Bodde K, et al. Addressing a crisis in abortion access: a case study in advocacy. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:110-114.
- Evans M, Bradley T, Ireland L, et al. How the fall of Roe could change abortion care in Mass. Cognoscenti. July 26, 2022. https://www.wbur.org/cognoscenti/2022/07/26/dobbs-roe-abortion-massachusetts-megan-l-evans-erin-t-bradley-luu-ireland-chloe-zera. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Spocchia G. Over $200k raised for doctor who performed abortion on 10-year-old rape victim. Independent. July 18, 2022. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/fundriaser-ohio-abortion-doctor-rape-b2125621.html. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- ABOG petition: convert to online examination to protect OBGYN providers. Change.org website. https://www.change.org/p/abog-petition?original_footer_petition_id=33459909&algorithm=promoted&source_location=petition_footer&grid_position=8&pt=AVBldGl0aW9uAHgWBQIAAAAAYs65vIyhbUxhZGM0MWVhZg%3D%3D. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- D’Ambrosio A. Ob/Gyn board certification exam stays virtual in light of Dobbs. MedPageToday. July 15, 2022. https://www.medpagetoday.com/special-reports/features/99758. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Weiner S. How the repeal of Roe v. Wade will affect training in abortion and reproductive health. AAMC News. June 24, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/news-insights/how-repeal-roe-v-wade-will-affect-training-abortion-and-reproductive-health. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Anderson N. The fall of Roe scrambles abortion training for university hospitals. The Washington Post. June 30, 2022. https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2022/06/30/abortion-training-upheaval-dobbs/. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Bans off our bodies. Planned Parenthood website. https://www.plannedparenthoodaction.org/rightfully-ours/bans-off-our-bodies. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Shape the public discourse. ACOG website. https://www.acog.org/advocacy/abortion-is-essential/connect-in-your-community. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Building evidence-based skills for effective conversations about abortion. ACOG website. https://www.acog.org/programs/impact/activities-initiatives/building-evidence-based-skills-for-effective-conversations-about-abortion. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. More than 75 health care organizations release joint statement in opposition to legislative interference. ACOG website. Published July 7, 2022. https://www.acog.org/news/news-releases/2022/07/more-than-75-health-care-organizations-release-joint-statement-in-opposition-to-legislative-interference. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Tracking the states where abortion is now banned. New York Times. November 23, 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2022/us/abortion-laws-roe-v-wade.html. Accessed November 28, 2022.
- Stanton A. ‘She’s 10’: child rape victims abortion denial spreads outrage on Twitter. Newsweek. July 2, 2022. https://www.newsweek.com/shes-10-child-rape-victims-abortion-denial-sparks-outrage-twitter-1721248. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Judge-Golden C, Flink-Bochacki R. The burden of abortion restrictions and conservative diagnostic guidelines on patient-centered care for early pregnancy loss. Obstet Gynecol 2021;138:467071.
- Nambiar A, Patel S, Santiago-Munoz P, et al. Maternal morbidity and fetal outcomes among pregnant women at 22 weeks’ gestation or less with complications in 2 Texas hospitals after legislation on abortion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022;227:648-650.e1. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2022.06.060.
- Winter J. The Dobbs decision has unleashed legal chaos for doctors and patients. The New Yorker. July 2, 2022. https://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/the-dobbs-decision-has-unleashed-legal-chaos-for-doctors-and-patients. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Lynch B, Mallow M, Bodde K, et al. Addressing a crisis in abortion access: a case study in advocacy. Obstet Gynecol. 2022;140:110-114.
- Evans M, Bradley T, Ireland L, et al. How the fall of Roe could change abortion care in Mass. Cognoscenti. July 26, 2022. https://www.wbur.org/cognoscenti/2022/07/26/dobbs-roe-abortion-massachusetts-megan-l-evans-erin-t-bradley-luu-ireland-chloe-zera. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Spocchia G. Over $200k raised for doctor who performed abortion on 10-year-old rape victim. Independent. July 18, 2022. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/americas/fundriaser-ohio-abortion-doctor-rape-b2125621.html. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- ABOG petition: convert to online examination to protect OBGYN providers. Change.org website. https://www.change.org/p/abog-petition?original_footer_petition_id=33459909&algorithm=promoted&source_location=petition_footer&grid_position=8&pt=AVBldGl0aW9uAHgWBQIAAAAAYs65vIyhbUxhZGM0MWVhZg%3D%3D. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- D’Ambrosio A. Ob/Gyn board certification exam stays virtual in light of Dobbs. MedPageToday. July 15, 2022. https://www.medpagetoday.com/special-reports/features/99758. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Weiner S. How the repeal of Roe v. Wade will affect training in abortion and reproductive health. AAMC News. June 24, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/news-insights/how-repeal-roe-v-wade-will-affect-training-abortion-and-reproductive-health. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Anderson N. The fall of Roe scrambles abortion training for university hospitals. The Washington Post. June 30, 2022. https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2022/06/30/abortion-training-upheaval-dobbs/. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- Bans off our bodies. Planned Parenthood website. https://www.plannedparenthoodaction.org/rightfully-ours/bans-off-our-bodies. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Shape the public discourse. ACOG website. https://www.acog.org/advocacy/abortion-is-essential/connect-in-your-community. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Building evidence-based skills for effective conversations about abortion. ACOG website. https://www.acog.org/programs/impact/activities-initiatives/building-evidence-based-skills-for-effective-conversations-about-abortion. Accessed November 6, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. More than 75 health care organizations release joint statement in opposition to legislative interference. ACOG website. Published July 7, 2022. https://www.acog.org/news/news-releases/2022/07/more-than-75-health-care-organizations-release-joint-statement-in-opposition-to-legislative-interference. Accessed November 6, 2022.
Home births in the United States, 2019—2021
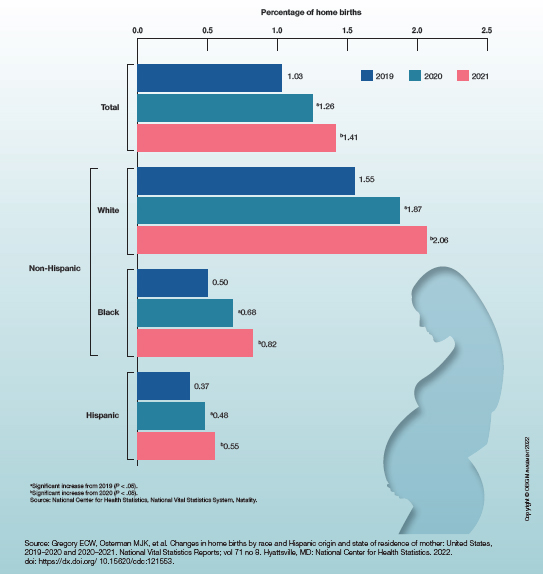


Unintentional weight loss
This patient's clinical presentation is consistent with a diagnosis of metastatic invasive lobular carcinoma, with nodal involvement.
Breast cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide. In Western countries, 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer at some point in their lives. Various histologic subtypes with specific clinical characteristics exist. Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is the second most common subtype, accounting for an estimated 10%-15% of breast cancers. Over the past two decades, a significant increase has been observed in the incidence of ILC, particularly among postmenopausal women. Improved diagnostic techniques and the use of hormone replacement therapy may account for this increased incidence. White women have the highest incidence of ILC; however, compared with White women and women of other races, Black women experience the worst 5-year overall survival from ILC.
ILC arises in the mammary ducts (lobules) of the breast. Women with ILC are typically slightly older than women with invasive breast cancer of no special type at diagnosis (mean age 63.4 vs 59.5 years, respectively). Risk factors for ILC may include early menarche, use of progesterone-based hormone replacement therapy, late age at first live birth, and alcohol consumption.
In most cases, ILC does not form a discrete palpable mass until it has reached an advanced stage, making it more difficult to detect through physical examination or imaging. Patients often present with a large tumor and with nodal involvement. A slight thickening of the nipple, an exudative scab on the skin, or other changes in the skin, such as flushing or swelling, may be seen in patients presenting with advanced disease. Additionally, ILC tumors are often bilateral and multifocal.
ILC is predominantly a histopathologic diagnosis based on standard hematoxylin and eosin staining. Histologically, ILC is characterized by a proliferation of small cells that lack cohesion. These cells are often dispersed individually through a fibrous connective tissue; alternatively, they may be organized in single-file linear cords invading the stroma. A concentric pattern around normal ducts is often seen in the infiltrating cords. There is usually little host reaction of the background architecture. Round or notched ovoid nuclei are seen in the neoplastic cells, along with a thin rim of cytoplasm. Occasionally, an intracytoplasmic lumen is present and may harbor a central mucoid inclusion. Very few or no mitoses are seen.
Several variants of ILC exist, all of which lack cell-to-cell cohesion. These include:
• Solid type
• Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma
• Tubulo-lobular variant
• Alveolar variant
• Mixed type
Complete loss of E-cadherin expression occurs in most ILCs, which can help to differentiate it from invasive ductal cancers or ductal carcinomas in situ. Diffuse cortical thickening without hilar mass effect is often seen in nodal metastases associated with ILC.
Most classic ILCs are estrogen receptor– and progesterone receptor–positive. Conversely, HER2 overexpression and amplification rarely occurs in ILC.
Late relapses more than 10 years after remission may occur. In addition to frequent bone and liver metastasis, ILC is associated with metastatic spread to unusual sites, including the peritoneum, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, leptomeninges, skin, orbit, and ovaries.
Mastectomy is often indicated in ILC. In the neoadjuvant setting, ILC is associated with low pathologic complete response rates. Endocrine therapy in the neoadjuvant setting is an emerging approach for some patients with ILC. According to 2022 National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, adjuvant chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy or endocrine therapy alone should be considered for pre- and postmenopausal patients with ILC.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's clinical presentation is consistent with a diagnosis of metastatic invasive lobular carcinoma, with nodal involvement.
Breast cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide. In Western countries, 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer at some point in their lives. Various histologic subtypes with specific clinical characteristics exist. Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is the second most common subtype, accounting for an estimated 10%-15% of breast cancers. Over the past two decades, a significant increase has been observed in the incidence of ILC, particularly among postmenopausal women. Improved diagnostic techniques and the use of hormone replacement therapy may account for this increased incidence. White women have the highest incidence of ILC; however, compared with White women and women of other races, Black women experience the worst 5-year overall survival from ILC.
ILC arises in the mammary ducts (lobules) of the breast. Women with ILC are typically slightly older than women with invasive breast cancer of no special type at diagnosis (mean age 63.4 vs 59.5 years, respectively). Risk factors for ILC may include early menarche, use of progesterone-based hormone replacement therapy, late age at first live birth, and alcohol consumption.
In most cases, ILC does not form a discrete palpable mass until it has reached an advanced stage, making it more difficult to detect through physical examination or imaging. Patients often present with a large tumor and with nodal involvement. A slight thickening of the nipple, an exudative scab on the skin, or other changes in the skin, such as flushing or swelling, may be seen in patients presenting with advanced disease. Additionally, ILC tumors are often bilateral and multifocal.
ILC is predominantly a histopathologic diagnosis based on standard hematoxylin and eosin staining. Histologically, ILC is characterized by a proliferation of small cells that lack cohesion. These cells are often dispersed individually through a fibrous connective tissue; alternatively, they may be organized in single-file linear cords invading the stroma. A concentric pattern around normal ducts is often seen in the infiltrating cords. There is usually little host reaction of the background architecture. Round or notched ovoid nuclei are seen in the neoplastic cells, along with a thin rim of cytoplasm. Occasionally, an intracytoplasmic lumen is present and may harbor a central mucoid inclusion. Very few or no mitoses are seen.
Several variants of ILC exist, all of which lack cell-to-cell cohesion. These include:
• Solid type
• Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma
• Tubulo-lobular variant
• Alveolar variant
• Mixed type
Complete loss of E-cadherin expression occurs in most ILCs, which can help to differentiate it from invasive ductal cancers or ductal carcinomas in situ. Diffuse cortical thickening without hilar mass effect is often seen in nodal metastases associated with ILC.
Most classic ILCs are estrogen receptor– and progesterone receptor–positive. Conversely, HER2 overexpression and amplification rarely occurs in ILC.
Late relapses more than 10 years after remission may occur. In addition to frequent bone and liver metastasis, ILC is associated with metastatic spread to unusual sites, including the peritoneum, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, leptomeninges, skin, orbit, and ovaries.
Mastectomy is often indicated in ILC. In the neoadjuvant setting, ILC is associated with low pathologic complete response rates. Endocrine therapy in the neoadjuvant setting is an emerging approach for some patients with ILC. According to 2022 National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, adjuvant chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy or endocrine therapy alone should be considered for pre- and postmenopausal patients with ILC.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's clinical presentation is consistent with a diagnosis of metastatic invasive lobular carcinoma, with nodal involvement.
Breast cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide. In Western countries, 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer at some point in their lives. Various histologic subtypes with specific clinical characteristics exist. Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is the second most common subtype, accounting for an estimated 10%-15% of breast cancers. Over the past two decades, a significant increase has been observed in the incidence of ILC, particularly among postmenopausal women. Improved diagnostic techniques and the use of hormone replacement therapy may account for this increased incidence. White women have the highest incidence of ILC; however, compared with White women and women of other races, Black women experience the worst 5-year overall survival from ILC.
ILC arises in the mammary ducts (lobules) of the breast. Women with ILC are typically slightly older than women with invasive breast cancer of no special type at diagnosis (mean age 63.4 vs 59.5 years, respectively). Risk factors for ILC may include early menarche, use of progesterone-based hormone replacement therapy, late age at first live birth, and alcohol consumption.
In most cases, ILC does not form a discrete palpable mass until it has reached an advanced stage, making it more difficult to detect through physical examination or imaging. Patients often present with a large tumor and with nodal involvement. A slight thickening of the nipple, an exudative scab on the skin, or other changes in the skin, such as flushing or swelling, may be seen in patients presenting with advanced disease. Additionally, ILC tumors are often bilateral and multifocal.
ILC is predominantly a histopathologic diagnosis based on standard hematoxylin and eosin staining. Histologically, ILC is characterized by a proliferation of small cells that lack cohesion. These cells are often dispersed individually through a fibrous connective tissue; alternatively, they may be organized in single-file linear cords invading the stroma. A concentric pattern around normal ducts is often seen in the infiltrating cords. There is usually little host reaction of the background architecture. Round or notched ovoid nuclei are seen in the neoplastic cells, along with a thin rim of cytoplasm. Occasionally, an intracytoplasmic lumen is present and may harbor a central mucoid inclusion. Very few or no mitoses are seen.
Several variants of ILC exist, all of which lack cell-to-cell cohesion. These include:
• Solid type
• Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma
• Tubulo-lobular variant
• Alveolar variant
• Mixed type
Complete loss of E-cadherin expression occurs in most ILCs, which can help to differentiate it from invasive ductal cancers or ductal carcinomas in situ. Diffuse cortical thickening without hilar mass effect is often seen in nodal metastases associated with ILC.
Most classic ILCs are estrogen receptor– and progesterone receptor–positive. Conversely, HER2 overexpression and amplification rarely occurs in ILC.
Late relapses more than 10 years after remission may occur. In addition to frequent bone and liver metastasis, ILC is associated with metastatic spread to unusual sites, including the peritoneum, gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, leptomeninges, skin, orbit, and ovaries.
Mastectomy is often indicated in ILC. In the neoadjuvant setting, ILC is associated with low pathologic complete response rates. Endocrine therapy in the neoadjuvant setting is an emerging approach for some patients with ILC. According to 2022 National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, adjuvant chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy or endocrine therapy alone should be considered for pre- and postmenopausal patients with ILC.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 47-year-old woman presented for her annual gynecologic examination. Her current height and weight were 5 ft 4 in and 133 lb. This reflected a 9-lb weight loss since the previous visit. At completion of the height and weight intake by a nurse, the patient reported being surprised by this unintentional weight loss. Her previous medical history was unremarkable except for an advanced maternal age pregnancy 5 years earlier and dental implant surgery approximately 1 month earlier. The patient believed that her weight loss was related to her diminished appetite and transient difficulty chewing following her dental surgery. Laboratory findings were all within normal ranges except for a hemoglobin level of 9.4 g/dL. Physical examination revealed a palpable mass in the right upper outer quadrant of the right breast with slight thickening of the nipple and a right axillary mass. The patient's last bilateral screening mammogram 3 months earlier did not reveal any suspicious masses or lesions.
An ultrasound-guided biopsy of the right breast and axillary lymph node was performed. Histopathologic findings included small tumor cells without cohesion arranged in single files, loss of the long arm of chromosome 16, and a complete loss of E-cadherin expression on immunohistochemistry. Additionally, the tumor was estrogen receptor–positive/progesterone receptor–positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative (ER+/PR+/HER2-).
Botanical Briefs: Daffodils (Narcissus Species)
Contact dermatitis is a common problem in the floral bulb industry and is considered an occupational disease. Daffodils (Narcissus species)(Figure) are thought to be the most common cause of irritant contact dermatitis among florists.1
Clinical Importance
Picking daffodils can start as early as October, when the flowers are still closed. The picker’s hand slides down the stem to snap the stalk at the base. This potentially traumatic maneuver to the web of the fingers leads to abrasions, which are irritated by the sap and cause granulomatous sores and paronychia. An experienced picker can pick 20,000 flowers a day, leading to extensive contact with sap.2
Eczematous or granulomatous rash on the arms also is seen as the sap irritates the wrist and forearm. The pickers often hold the flowers until a bunch of 10 has been collected. The 10 flowers are held together by a rubber band and stacked along the arm, the chin, and the axilla, causing the rash to extend to those areas. Sap also can be transferred by the hand to other parts of the body, such as the face. In men, sap can be transferred to the genitalia as the men urinate in the field.
Narcissus also can cause poisoning if ingested by humans or animals. Researchers who analyzed calls made to the New Zealand Natural Poisons Centre between 2003 and 2010 determined that daffodil was the 11th most common call for plant-related poisoning.3
Although the severity of plant poisoning often is low due to the small amount of plant material usually consumed, more severe poisoning can occur when the plant is eaten for medicinal purposes or mistaken for an edible plant.3 Vomiting, respiratory symptoms, abdominal pain, diarrhea, trembling, and convulsions can occur when daffodils are ingested. Death has been reported due to ingestion of the bulbs.4
In February 2010, 10 children aged 10 and 11 years and their 22-year-old guide presented to an emergency department in Israel after ingesting Narcissus bulbs, which were mistakenly believed to be the bulbs of onions.4 Eight children and the guide vomited. One child and the guide reported abdominal pain. All were discharged in stable condition after 4 hours of observation.4
Clinical Manifestations
Daffodil rash or lily rash was first described in 1910.5 The typical rash presents as dryness, fissures, scaling, and erythema of the fingertips, hands, and forearms, often with subungual hyperkeratosis. Vesicles and pustules may be seen. The rash may extend to other areas of the body, including the face.6
Prevention and Treatment
Use of protective gloves and clothing to avoid contact with the plant is recommended.2 Treatment includes stopping contact with the irritant, eye irrigation, and supportive measures (airway, breathing, and circulation). Activated charcoal can be helpful if used within 1 hour after ingestion but is contraindicated in vomiting patients.4
Identifying Features
The genus Narcissus is in the family Amaryllidaceae and contains ornamental plants, including daffodil (trumpet Narcissus, Narcissus pseudonarcissus), jonquil (Narcissus jonquilla), and poet’s narcissus (Narcissus poeticus). Most species are perennial; the plant emerges from a bulb in spring. Leaves originate from the base of the plant and range from 5-cm to 1.2-meters long, depending on the species. The flowers span a range of shapes and colors—from a trumpet (the daffodil) to a ringlike cup (poet’s Narcissus) and in yellow, white, and pink.7
Distribution and Plant Facts
Distribution—There are approximately 80 to 100 wild Narcissus species, which are found in southwestern Europe, North Africa, the Balkan Peninsula, Italy, and France. There are more than 27,000 Narcissus cultivars registered in the International Daffodil Register.8
Plant Facts—The daffodil is the national flower of Wales. It also is often used to depict hope and joy and is the symbol of cancer charities in many countries.9
The name Narcissus is believed to have originated from Greek mythology. A handsome youth, Narcissus, fell in love with his own reflection, for which the gods punished him by turning him into a flower.10
Another theory states that Narcissus is derived from the Greek word narkao (to benumb) due to its narcotic properties. When an open wound is subjected to an extract of the bulb, numbness of the entire nervous system is said to occur as well as paralysis of the heart. This narcotic effect led Socrates to refer to the Narcissus plant as the “chaplet of the infernal gods.”11
Narcissus is an important flower in various ethnic rituals. The Greeks often planted daffodils near tombs. In Muslim culture, white is believed to be the symbol of good and purity; Narcissus was one of the most common white-flowered plants found in Muslim graveyards.12
Medicinal Qualities and Uses—Narcissus species have been used as medicinal plants for a variety of ailments. For example, Narcissus tazetta contains flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tannins, cardiac glycosides, oil, steroids, terpenoids, and anthraquinones that contribute to its antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antimalarial, anticancer, antioxidant, dermatologic, cardiovascular, immunomodulatory, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory effects.13 In a study, chloroform extracts from N tazetta bulbs were found to be more active than doxorubicin against hepatocellular and colon cancer cell lines.14
More than 500 alkaloids have been isolated from the Narcissus genus.15 In 2001, the US Food and Drug Administration approved one of the alkaloids, galantamine, for the treatment of mild to moderate stages of Alzheimer disease.16 Galantamine selectively and reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme believed responsible for neurodegeneration seen in Alzheimer disease. Plants are the main source of galantamine, despite the ability of pharmaceutical companies to synthesize the compound. Galantamine hydrobromide is sold by prescription (Razadyne [Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc]); generic formulations approved by the US Food and Drug Administration have been produced by more than 15 pharmaceutical companies.17,18
Irritant and Allergen
Sap found in the bulbs and hollow stems of Narcissus contains calcium oxalate crystals, or raphides. The minute, needle-shaped calcium oxalate crystals are believed to be a waste product of cellular metabolism.19 When the plant structure is compromised by pickers snapping the stalk, the sharp crystals penetrate the skin to cause an irritant contact dermatitis.
Relevant Research—A study used electron microscopy to characterize the structure of raphides from various plants,2 though not from Narcissus species; the structure of each raphide was then compared to the degree of irritation it produced. The researchers concluded that more elongated crystals (those containing barbs) produce a greater degree of irritation. Narcissus species are known to cause varying degrees of skin irritation: For example, N tazetta rarely causes skin irritation, whereas N pseudonarcissi (daffodil) tends to cause remarkably more skin irritation.2
Allergic reactions to and strong toxicity from Narcissus species are not well understood. In a study, only 2 alkaloids—homolycorine and masonin—produced a weakly positive reaction in patch tests on sensitized guinea pigs, which correlates with the finding of a different study, in which only 2 of 12 patients whose findings were examined over 14 years had a positive patch test for Narcissus.20,21
However, IgE-mediated allergies indicative of an allergic response to Narcissus have been reported. A study isolated an allergenic protein, narcin, from bulbs of N tazetta. Narcin is a 13-kDa protein with potent allergenic effects capable of inducing production of proinflammatory cytokines and increasing IgE levels in mononuclear cells in peripheral blood.22
More research is required to find and understand the compounds responsible for causing an allergic reaction to Narcissus.
- Modi GM, Doherty CB, Katta R, et al. Irritant contact dermatitis from plants. Dermatitis. 2009;20:63-78. doi:10.2310/6620.2009.08051
- Julian CG, Bowers PW. The nature and distribution of daffodil pickers’ rash. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:259-262. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb02461.x
- Slaughter RJ, Beasley DMG, Lambie BS, et al. Poisonous plants in New Zealand: a review of those that are most commonly enquired about to the National Poisons Centre. N Z Med J. 2012;125:87-118.
- Hussein A, Yassin A. Poisoning following ingestion of Narcissus tazetta bulbs by schoolchildren. Isr Med Assoc J. 2014;16:125-126.
- Hanks GR, ed. Narcissus and Daffodil: The Genus Narcissus. CRC Press; 2002. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203219355
- McGovern TW. Botanical briefs: daffodils—Narcissus L. Cutis. 2000;65:130-132.
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Narcissus. Encyclopedia Britannica. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/narcissus-plant
- M, A, D, et al. Alkaloids from Narcissus poeticus cv. Pink Parasol of various structural types and their biological activity. Arch Pharm Res. 2018;41:208-218. doi:10.1007/s12272-017-1000-4
- Crampton L. Beautiful daffodils: plant facts, toxicity, and a symbol of hope. Owlcation. April 19, 2022. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://owlcation.com/stem/Daffodils-Beautiful-Flowers-and-a-Symbol-of-Hope
- Rademaker M. Daffodil. DermNet. Published 1999. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/daffodil
- Grieve M. Narcissus. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/n/narcis01.html
- Dafni A, Lev E, Beckmann S, et al. Ritual plants of Muslim graveyards in northern Israel. J Ethnobiolog Ethnomed. 2006;2:38. doi:10.1186/1746-4269-2-38
- Al-Snafi AE. Constituents and pharmacology of Narcissus tazetta. IOSR J Pharm. 2020;10:44-53.
- Shawky E, Abou-Donia AH, Darwish FA, et al. In vitro cytotoxicity of some Narcissus plants extracts. Nat Prod Res. 2015;29:363-365. doi:10.1080/14786419.2014.942302
- Havlasov J, M, Siatka T, et al. Chemical composition of bioactive alkaloid extracts from some Narcissus species and varieties and their biological activity. Nat Prod Commun. 2014;9:1151-1155.
- Pigni NB, S, V, et al. Alkaloids from Narcissus serotinus. J Nat Prod. 2012;75:1643-1647. doi:10.1021/np3003595
- Razadyne. Prescribing information. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2013. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021169Orig1s032,021224Orig1s030,021615Orig1s023lbl.pdf
- Takos AM, Rook F. Towards a molecular understanding of the biosynthesis of amaryllidaceae alkaloids in support of their expanding medical use. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:11713-11741. doi:10.3390/ijms140611713
- Evans FJ, Schmidt RJ. Plants and plant products that induce contact dermatitis. Planta Med. 1980;38:289-316. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1074883
- Gude M, Hausen BM, Heitsch H, et al. An investigation of the irritant and allergenic properties of daffodils (Narcissus pseudonarcissus L., Amaryllidaceae). a review of daffodil dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1988;19:1-10.
- Lamminpää A, Estlander T, Jolanki R, et al. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis caused by decorative plants. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;34:330-335.
- Sinha M, Singh A, Shokeen A, et al. Evidence of a novel allergenic protein Narcin in the bulbs of Narcissus tazetta. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;4:95-101.
Contact dermatitis is a common problem in the floral bulb industry and is considered an occupational disease. Daffodils (Narcissus species)(Figure) are thought to be the most common cause of irritant contact dermatitis among florists.1
Clinical Importance
Picking daffodils can start as early as October, when the flowers are still closed. The picker’s hand slides down the stem to snap the stalk at the base. This potentially traumatic maneuver to the web of the fingers leads to abrasions, which are irritated by the sap and cause granulomatous sores and paronychia. An experienced picker can pick 20,000 flowers a day, leading to extensive contact with sap.2
Eczematous or granulomatous rash on the arms also is seen as the sap irritates the wrist and forearm. The pickers often hold the flowers until a bunch of 10 has been collected. The 10 flowers are held together by a rubber band and stacked along the arm, the chin, and the axilla, causing the rash to extend to those areas. Sap also can be transferred by the hand to other parts of the body, such as the face. In men, sap can be transferred to the genitalia as the men urinate in the field.
Narcissus also can cause poisoning if ingested by humans or animals. Researchers who analyzed calls made to the New Zealand Natural Poisons Centre between 2003 and 2010 determined that daffodil was the 11th most common call for plant-related poisoning.3
Although the severity of plant poisoning often is low due to the small amount of plant material usually consumed, more severe poisoning can occur when the plant is eaten for medicinal purposes or mistaken for an edible plant.3 Vomiting, respiratory symptoms, abdominal pain, diarrhea, trembling, and convulsions can occur when daffodils are ingested. Death has been reported due to ingestion of the bulbs.4
In February 2010, 10 children aged 10 and 11 years and their 22-year-old guide presented to an emergency department in Israel after ingesting Narcissus bulbs, which were mistakenly believed to be the bulbs of onions.4 Eight children and the guide vomited. One child and the guide reported abdominal pain. All were discharged in stable condition after 4 hours of observation.4
Clinical Manifestations
Daffodil rash or lily rash was first described in 1910.5 The typical rash presents as dryness, fissures, scaling, and erythema of the fingertips, hands, and forearms, often with subungual hyperkeratosis. Vesicles and pustules may be seen. The rash may extend to other areas of the body, including the face.6
Prevention and Treatment
Use of protective gloves and clothing to avoid contact with the plant is recommended.2 Treatment includes stopping contact with the irritant, eye irrigation, and supportive measures (airway, breathing, and circulation). Activated charcoal can be helpful if used within 1 hour after ingestion but is contraindicated in vomiting patients.4
Identifying Features
The genus Narcissus is in the family Amaryllidaceae and contains ornamental plants, including daffodil (trumpet Narcissus, Narcissus pseudonarcissus), jonquil (Narcissus jonquilla), and poet’s narcissus (Narcissus poeticus). Most species are perennial; the plant emerges from a bulb in spring. Leaves originate from the base of the plant and range from 5-cm to 1.2-meters long, depending on the species. The flowers span a range of shapes and colors—from a trumpet (the daffodil) to a ringlike cup (poet’s Narcissus) and in yellow, white, and pink.7
Distribution and Plant Facts
Distribution—There are approximately 80 to 100 wild Narcissus species, which are found in southwestern Europe, North Africa, the Balkan Peninsula, Italy, and France. There are more than 27,000 Narcissus cultivars registered in the International Daffodil Register.8
Plant Facts—The daffodil is the national flower of Wales. It also is often used to depict hope and joy and is the symbol of cancer charities in many countries.9
The name Narcissus is believed to have originated from Greek mythology. A handsome youth, Narcissus, fell in love with his own reflection, for which the gods punished him by turning him into a flower.10
Another theory states that Narcissus is derived from the Greek word narkao (to benumb) due to its narcotic properties. When an open wound is subjected to an extract of the bulb, numbness of the entire nervous system is said to occur as well as paralysis of the heart. This narcotic effect led Socrates to refer to the Narcissus plant as the “chaplet of the infernal gods.”11
Narcissus is an important flower in various ethnic rituals. The Greeks often planted daffodils near tombs. In Muslim culture, white is believed to be the symbol of good and purity; Narcissus was one of the most common white-flowered plants found in Muslim graveyards.12
Medicinal Qualities and Uses—Narcissus species have been used as medicinal plants for a variety of ailments. For example, Narcissus tazetta contains flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tannins, cardiac glycosides, oil, steroids, terpenoids, and anthraquinones that contribute to its antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antimalarial, anticancer, antioxidant, dermatologic, cardiovascular, immunomodulatory, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory effects.13 In a study, chloroform extracts from N tazetta bulbs were found to be more active than doxorubicin against hepatocellular and colon cancer cell lines.14
More than 500 alkaloids have been isolated from the Narcissus genus.15 In 2001, the US Food and Drug Administration approved one of the alkaloids, galantamine, for the treatment of mild to moderate stages of Alzheimer disease.16 Galantamine selectively and reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme believed responsible for neurodegeneration seen in Alzheimer disease. Plants are the main source of galantamine, despite the ability of pharmaceutical companies to synthesize the compound. Galantamine hydrobromide is sold by prescription (Razadyne [Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc]); generic formulations approved by the US Food and Drug Administration have been produced by more than 15 pharmaceutical companies.17,18
Irritant and Allergen
Sap found in the bulbs and hollow stems of Narcissus contains calcium oxalate crystals, or raphides. The minute, needle-shaped calcium oxalate crystals are believed to be a waste product of cellular metabolism.19 When the plant structure is compromised by pickers snapping the stalk, the sharp crystals penetrate the skin to cause an irritant contact dermatitis.
Relevant Research—A study used electron microscopy to characterize the structure of raphides from various plants,2 though not from Narcissus species; the structure of each raphide was then compared to the degree of irritation it produced. The researchers concluded that more elongated crystals (those containing barbs) produce a greater degree of irritation. Narcissus species are known to cause varying degrees of skin irritation: For example, N tazetta rarely causes skin irritation, whereas N pseudonarcissi (daffodil) tends to cause remarkably more skin irritation.2
Allergic reactions to and strong toxicity from Narcissus species are not well understood. In a study, only 2 alkaloids—homolycorine and masonin—produced a weakly positive reaction in patch tests on sensitized guinea pigs, which correlates with the finding of a different study, in which only 2 of 12 patients whose findings were examined over 14 years had a positive patch test for Narcissus.20,21
However, IgE-mediated allergies indicative of an allergic response to Narcissus have been reported. A study isolated an allergenic protein, narcin, from bulbs of N tazetta. Narcin is a 13-kDa protein with potent allergenic effects capable of inducing production of proinflammatory cytokines and increasing IgE levels in mononuclear cells in peripheral blood.22
More research is required to find and understand the compounds responsible for causing an allergic reaction to Narcissus.
Contact dermatitis is a common problem in the floral bulb industry and is considered an occupational disease. Daffodils (Narcissus species)(Figure) are thought to be the most common cause of irritant contact dermatitis among florists.1
Clinical Importance
Picking daffodils can start as early as October, when the flowers are still closed. The picker’s hand slides down the stem to snap the stalk at the base. This potentially traumatic maneuver to the web of the fingers leads to abrasions, which are irritated by the sap and cause granulomatous sores and paronychia. An experienced picker can pick 20,000 flowers a day, leading to extensive contact with sap.2
Eczematous or granulomatous rash on the arms also is seen as the sap irritates the wrist and forearm. The pickers often hold the flowers until a bunch of 10 has been collected. The 10 flowers are held together by a rubber band and stacked along the arm, the chin, and the axilla, causing the rash to extend to those areas. Sap also can be transferred by the hand to other parts of the body, such as the face. In men, sap can be transferred to the genitalia as the men urinate in the field.
Narcissus also can cause poisoning if ingested by humans or animals. Researchers who analyzed calls made to the New Zealand Natural Poisons Centre between 2003 and 2010 determined that daffodil was the 11th most common call for plant-related poisoning.3
Although the severity of plant poisoning often is low due to the small amount of plant material usually consumed, more severe poisoning can occur when the plant is eaten for medicinal purposes or mistaken for an edible plant.3 Vomiting, respiratory symptoms, abdominal pain, diarrhea, trembling, and convulsions can occur when daffodils are ingested. Death has been reported due to ingestion of the bulbs.4
In February 2010, 10 children aged 10 and 11 years and their 22-year-old guide presented to an emergency department in Israel after ingesting Narcissus bulbs, which were mistakenly believed to be the bulbs of onions.4 Eight children and the guide vomited. One child and the guide reported abdominal pain. All were discharged in stable condition after 4 hours of observation.4
Clinical Manifestations
Daffodil rash or lily rash was first described in 1910.5 The typical rash presents as dryness, fissures, scaling, and erythema of the fingertips, hands, and forearms, often with subungual hyperkeratosis. Vesicles and pustules may be seen. The rash may extend to other areas of the body, including the face.6
Prevention and Treatment
Use of protective gloves and clothing to avoid contact with the plant is recommended.2 Treatment includes stopping contact with the irritant, eye irrigation, and supportive measures (airway, breathing, and circulation). Activated charcoal can be helpful if used within 1 hour after ingestion but is contraindicated in vomiting patients.4
Identifying Features
The genus Narcissus is in the family Amaryllidaceae and contains ornamental plants, including daffodil (trumpet Narcissus, Narcissus pseudonarcissus), jonquil (Narcissus jonquilla), and poet’s narcissus (Narcissus poeticus). Most species are perennial; the plant emerges from a bulb in spring. Leaves originate from the base of the plant and range from 5-cm to 1.2-meters long, depending on the species. The flowers span a range of shapes and colors—from a trumpet (the daffodil) to a ringlike cup (poet’s Narcissus) and in yellow, white, and pink.7
Distribution and Plant Facts
Distribution—There are approximately 80 to 100 wild Narcissus species, which are found in southwestern Europe, North Africa, the Balkan Peninsula, Italy, and France. There are more than 27,000 Narcissus cultivars registered in the International Daffodil Register.8
Plant Facts—The daffodil is the national flower of Wales. It also is often used to depict hope and joy and is the symbol of cancer charities in many countries.9
The name Narcissus is believed to have originated from Greek mythology. A handsome youth, Narcissus, fell in love with his own reflection, for which the gods punished him by turning him into a flower.10
Another theory states that Narcissus is derived from the Greek word narkao (to benumb) due to its narcotic properties. When an open wound is subjected to an extract of the bulb, numbness of the entire nervous system is said to occur as well as paralysis of the heart. This narcotic effect led Socrates to refer to the Narcissus plant as the “chaplet of the infernal gods.”11
Narcissus is an important flower in various ethnic rituals. The Greeks often planted daffodils near tombs. In Muslim culture, white is believed to be the symbol of good and purity; Narcissus was one of the most common white-flowered plants found in Muslim graveyards.12
Medicinal Qualities and Uses—Narcissus species have been used as medicinal plants for a variety of ailments. For example, Narcissus tazetta contains flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tannins, cardiac glycosides, oil, steroids, terpenoids, and anthraquinones that contribute to its antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antimalarial, anticancer, antioxidant, dermatologic, cardiovascular, immunomodulatory, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory effects.13 In a study, chloroform extracts from N tazetta bulbs were found to be more active than doxorubicin against hepatocellular and colon cancer cell lines.14
More than 500 alkaloids have been isolated from the Narcissus genus.15 In 2001, the US Food and Drug Administration approved one of the alkaloids, galantamine, for the treatment of mild to moderate stages of Alzheimer disease.16 Galantamine selectively and reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme believed responsible for neurodegeneration seen in Alzheimer disease. Plants are the main source of galantamine, despite the ability of pharmaceutical companies to synthesize the compound. Galantamine hydrobromide is sold by prescription (Razadyne [Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc]); generic formulations approved by the US Food and Drug Administration have been produced by more than 15 pharmaceutical companies.17,18
Irritant and Allergen
Sap found in the bulbs and hollow stems of Narcissus contains calcium oxalate crystals, or raphides. The minute, needle-shaped calcium oxalate crystals are believed to be a waste product of cellular metabolism.19 When the plant structure is compromised by pickers snapping the stalk, the sharp crystals penetrate the skin to cause an irritant contact dermatitis.
Relevant Research—A study used electron microscopy to characterize the structure of raphides from various plants,2 though not from Narcissus species; the structure of each raphide was then compared to the degree of irritation it produced. The researchers concluded that more elongated crystals (those containing barbs) produce a greater degree of irritation. Narcissus species are known to cause varying degrees of skin irritation: For example, N tazetta rarely causes skin irritation, whereas N pseudonarcissi (daffodil) tends to cause remarkably more skin irritation.2
Allergic reactions to and strong toxicity from Narcissus species are not well understood. In a study, only 2 alkaloids—homolycorine and masonin—produced a weakly positive reaction in patch tests on sensitized guinea pigs, which correlates with the finding of a different study, in which only 2 of 12 patients whose findings were examined over 14 years had a positive patch test for Narcissus.20,21
However, IgE-mediated allergies indicative of an allergic response to Narcissus have been reported. A study isolated an allergenic protein, narcin, from bulbs of N tazetta. Narcin is a 13-kDa protein with potent allergenic effects capable of inducing production of proinflammatory cytokines and increasing IgE levels in mononuclear cells in peripheral blood.22
More research is required to find and understand the compounds responsible for causing an allergic reaction to Narcissus.
- Modi GM, Doherty CB, Katta R, et al. Irritant contact dermatitis from plants. Dermatitis. 2009;20:63-78. doi:10.2310/6620.2009.08051
- Julian CG, Bowers PW. The nature and distribution of daffodil pickers’ rash. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:259-262. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb02461.x
- Slaughter RJ, Beasley DMG, Lambie BS, et al. Poisonous plants in New Zealand: a review of those that are most commonly enquired about to the National Poisons Centre. N Z Med J. 2012;125:87-118.
- Hussein A, Yassin A. Poisoning following ingestion of Narcissus tazetta bulbs by schoolchildren. Isr Med Assoc J. 2014;16:125-126.
- Hanks GR, ed. Narcissus and Daffodil: The Genus Narcissus. CRC Press; 2002. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203219355
- McGovern TW. Botanical briefs: daffodils—Narcissus L. Cutis. 2000;65:130-132.
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Narcissus. Encyclopedia Britannica. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/narcissus-plant
- M, A, D, et al. Alkaloids from Narcissus poeticus cv. Pink Parasol of various structural types and their biological activity. Arch Pharm Res. 2018;41:208-218. doi:10.1007/s12272-017-1000-4
- Crampton L. Beautiful daffodils: plant facts, toxicity, and a symbol of hope. Owlcation. April 19, 2022. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://owlcation.com/stem/Daffodils-Beautiful-Flowers-and-a-Symbol-of-Hope
- Rademaker M. Daffodil. DermNet. Published 1999. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/daffodil
- Grieve M. Narcissus. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/n/narcis01.html
- Dafni A, Lev E, Beckmann S, et al. Ritual plants of Muslim graveyards in northern Israel. J Ethnobiolog Ethnomed. 2006;2:38. doi:10.1186/1746-4269-2-38
- Al-Snafi AE. Constituents and pharmacology of Narcissus tazetta. IOSR J Pharm. 2020;10:44-53.
- Shawky E, Abou-Donia AH, Darwish FA, et al. In vitro cytotoxicity of some Narcissus plants extracts. Nat Prod Res. 2015;29:363-365. doi:10.1080/14786419.2014.942302
- Havlasov J, M, Siatka T, et al. Chemical composition of bioactive alkaloid extracts from some Narcissus species and varieties and their biological activity. Nat Prod Commun. 2014;9:1151-1155.
- Pigni NB, S, V, et al. Alkaloids from Narcissus serotinus. J Nat Prod. 2012;75:1643-1647. doi:10.1021/np3003595
- Razadyne. Prescribing information. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2013. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021169Orig1s032,021224Orig1s030,021615Orig1s023lbl.pdf
- Takos AM, Rook F. Towards a molecular understanding of the biosynthesis of amaryllidaceae alkaloids in support of their expanding medical use. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:11713-11741. doi:10.3390/ijms140611713
- Evans FJ, Schmidt RJ. Plants and plant products that induce contact dermatitis. Planta Med. 1980;38:289-316. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1074883
- Gude M, Hausen BM, Heitsch H, et al. An investigation of the irritant and allergenic properties of daffodils (Narcissus pseudonarcissus L., Amaryllidaceae). a review of daffodil dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1988;19:1-10.
- Lamminpää A, Estlander T, Jolanki R, et al. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis caused by decorative plants. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;34:330-335.
- Sinha M, Singh A, Shokeen A, et al. Evidence of a novel allergenic protein Narcin in the bulbs of Narcissus tazetta. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;4:95-101.
- Modi GM, Doherty CB, Katta R, et al. Irritant contact dermatitis from plants. Dermatitis. 2009;20:63-78. doi:10.2310/6620.2009.08051
- Julian CG, Bowers PW. The nature and distribution of daffodil pickers’ rash. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:259-262. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb02461.x
- Slaughter RJ, Beasley DMG, Lambie BS, et al. Poisonous plants in New Zealand: a review of those that are most commonly enquired about to the National Poisons Centre. N Z Med J. 2012;125:87-118.
- Hussein A, Yassin A. Poisoning following ingestion of Narcissus tazetta bulbs by schoolchildren. Isr Med Assoc J. 2014;16:125-126.
- Hanks GR, ed. Narcissus and Daffodil: The Genus Narcissus. CRC Press; 2002. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203219355
- McGovern TW. Botanical briefs: daffodils—Narcissus L. Cutis. 2000;65:130-132.
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Narcissus. Encyclopedia Britannica. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/narcissus-plant
- M, A, D, et al. Alkaloids from Narcissus poeticus cv. Pink Parasol of various structural types and their biological activity. Arch Pharm Res. 2018;41:208-218. doi:10.1007/s12272-017-1000-4
- Crampton L. Beautiful daffodils: plant facts, toxicity, and a symbol of hope. Owlcation. April 19, 2022. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://owlcation.com/stem/Daffodils-Beautiful-Flowers-and-a-Symbol-of-Hope
- Rademaker M. Daffodil. DermNet. Published 1999. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/daffodil
- Grieve M. Narcissus. Accessed December 13, 2022. https://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/n/narcis01.html
- Dafni A, Lev E, Beckmann S, et al. Ritual plants of Muslim graveyards in northern Israel. J Ethnobiolog Ethnomed. 2006;2:38. doi:10.1186/1746-4269-2-38
- Al-Snafi AE. Constituents and pharmacology of Narcissus tazetta. IOSR J Pharm. 2020;10:44-53.
- Shawky E, Abou-Donia AH, Darwish FA, et al. In vitro cytotoxicity of some Narcissus plants extracts. Nat Prod Res. 2015;29:363-365. doi:10.1080/14786419.2014.942302
- Havlasov J, M, Siatka T, et al. Chemical composition of bioactive alkaloid extracts from some Narcissus species and varieties and their biological activity. Nat Prod Commun. 2014;9:1151-1155.
- Pigni NB, S, V, et al. Alkaloids from Narcissus serotinus. J Nat Prod. 2012;75:1643-1647. doi:10.1021/np3003595
- Razadyne. Prescribing information. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2013. Accessed December 19, 2022. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/021169Orig1s032,021224Orig1s030,021615Orig1s023lbl.pdf
- Takos AM, Rook F. Towards a molecular understanding of the biosynthesis of amaryllidaceae alkaloids in support of their expanding medical use. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:11713-11741. doi:10.3390/ijms140611713
- Evans FJ, Schmidt RJ. Plants and plant products that induce contact dermatitis. Planta Med. 1980;38:289-316. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1074883
- Gude M, Hausen BM, Heitsch H, et al. An investigation of the irritant and allergenic properties of daffodils (Narcissus pseudonarcissus L., Amaryllidaceae). a review of daffodil dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1988;19:1-10.
- Lamminpää A, Estlander T, Jolanki R, et al. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis caused by decorative plants. Contact Dermatitis. 1996;34:330-335.
- Sinha M, Singh A, Shokeen A, et al. Evidence of a novel allergenic protein Narcin in the bulbs of Narcissus tazetta. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;4:95-101.
Practice Points
- Narcissus species are thought to be the most common cause of irritant contact dermatitis among florists.
- Use of protective gloves and clothing to prevent Narcissus-induced contact dermatitis is recommended.