User login
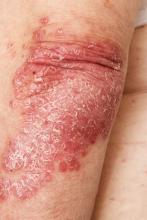
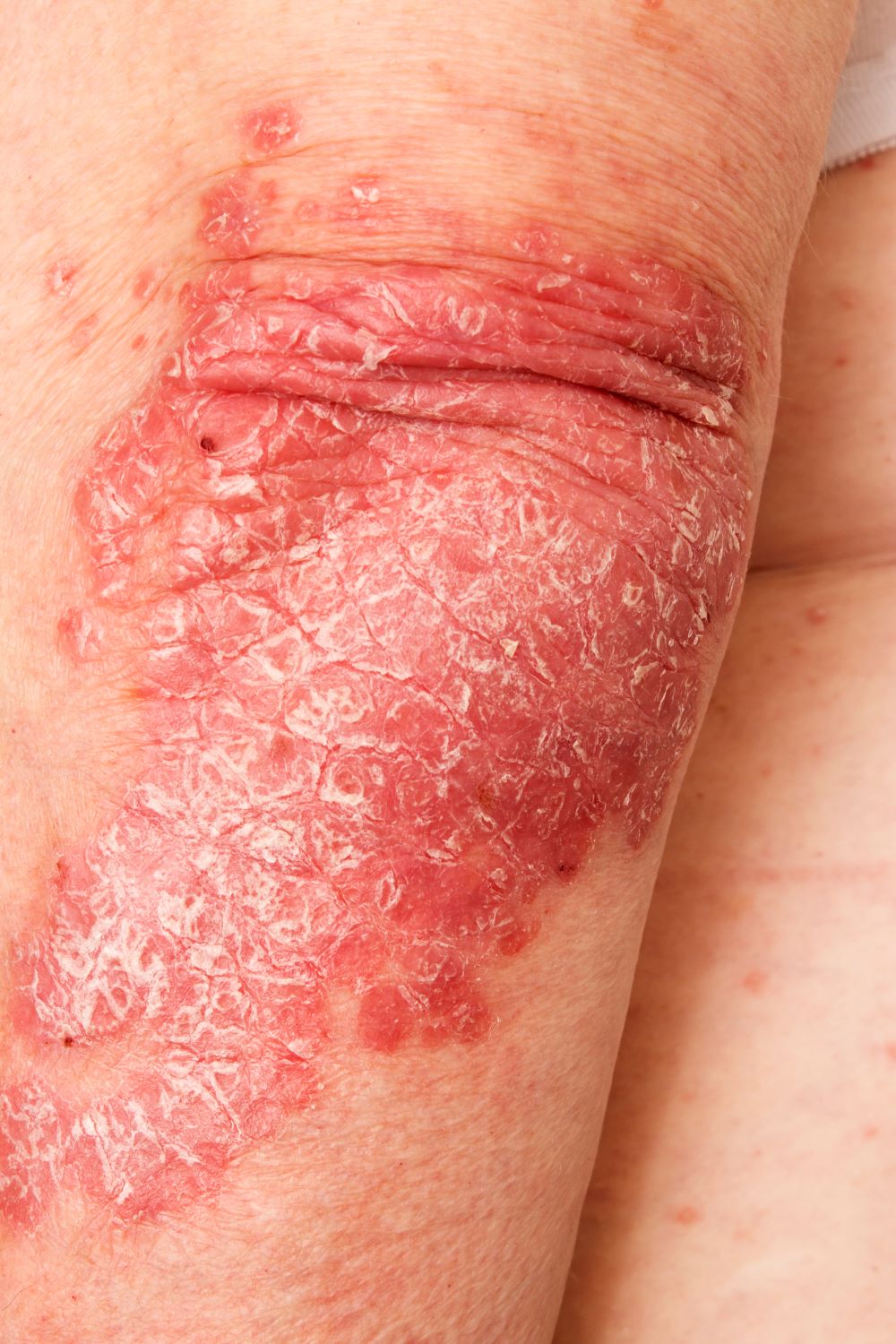
Intensely pruritic rash
The history and findings in this case are consistent with atopic dermatitis (AD).
AD is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects more than 200 million people worldwide, including as many as 30% of children and 10% of adults. Although it is more common in children (and may persist into adulthood), approximately 1 in 4 adults with AD have adult-onset disease.
The etiology of AD is complex and includes both genetic and environmental factors, including a weakened skin barrier, immune dysregulation, and abnormalities of the skin microbiome. AD is a member of the atopic triad (ie, AD, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and asthma), which may commence concurrently or in succession in what is referred to as the "atopic march."
The presentation of adult-onset AD may differ from that seen in children. For example, the most commonly reported body regions affected in adult-onset AD are the hands, eyelids, neck, and flexural surfaces of the upper limbs. In contrast, childhood-onset AD is less specific to body regions other than flexural areas. Xerosis is a prominent feature, and lichenification may be present. Some patients may have a rippled, brown macular ring around the neck, simulating the pigmentations seen in macular amyloid but due instead to postinflammatory melanin deposition. Pruritus is the most common and bothersome symptom associated with AD; patients may also experience anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.
Diminished quality of life, reduced productivity at work and school, and increased healthcare costs (hospitalizations, emergency visits, outpatient visits, and medications) have all been reported in patients with AD. Triggers for flare-ups vary among individuals; commonly reported triggers include physical or emotional stress, changes in temperature or humidity, sweating, allergens, and irritants.
AD is typically diagnosed clinically given the characteristic distribution of lesions in various age groups (infancy, childhood, and adult). Associated findings such as keratosis pilaris may help to facilitate the diagnosis. No biomarker for the diagnosis of AD has been found and laboratory testing is rarely necessary. However, a swab of infected skin may help to isolate a specific involved organism (eg, Staphylococcus or Streptococcus) and antibiotic sensitivity. Allergy and radioallergosorbent testing are not necessary to make the diagnosis. A swab for viral polymerase chain reaction may be beneficial to help identify superinfection with herpes simplex virus and identify a diagnosis of eczema herpeticum. Testing for serum IgE level can also be helpful for supporting the diagnosis of AD.
The management of AD includes trigger avoidance, daily skin care with application of emollients, anti-inflammatory therapy, and other complementary modalities. For mild or moderate AD, first-line treatment consists of topical anti-inflammatory ointments and creams, including topical corticosteroids, which are available in a broad range of potencies. Other topical medications include topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for patients aged ≥ 2 years), which may be particularly appropriate when there is concern for adverse events secondary to corticosteroid use; topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor (crisaborole ointment for patients aged ≥ 3 months); and topical Janus kinase inhibitor (ruxolitinib cream for patients aged ≥ 12 years).
For patients with moderate to severe AD, or for those who are refractory to topical medications, treatment may include biologic therapy (dupilumab and tralokinumab for patients aged ≥ 6 months and ≥ 18 years, respectively), oral Janus kinase inhibitors (upadacitinib and abrocitinib for patients ages ≥ 12 and ≥ 18 years, respectively), phototherapy (commonly narrow-band ultraviolet light type B treatment), and oral immunomodulators (including methotrexate, mycophenolate, and azathioprine). Combination therapy may be required for the long-term management of more severe AD.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are consistent with atopic dermatitis (AD).
AD is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects more than 200 million people worldwide, including as many as 30% of children and 10% of adults. Although it is more common in children (and may persist into adulthood), approximately 1 in 4 adults with AD have adult-onset disease.
The etiology of AD is complex and includes both genetic and environmental factors, including a weakened skin barrier, immune dysregulation, and abnormalities of the skin microbiome. AD is a member of the atopic triad (ie, AD, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and asthma), which may commence concurrently or in succession in what is referred to as the "atopic march."
The presentation of adult-onset AD may differ from that seen in children. For example, the most commonly reported body regions affected in adult-onset AD are the hands, eyelids, neck, and flexural surfaces of the upper limbs. In contrast, childhood-onset AD is less specific to body regions other than flexural areas. Xerosis is a prominent feature, and lichenification may be present. Some patients may have a rippled, brown macular ring around the neck, simulating the pigmentations seen in macular amyloid but due instead to postinflammatory melanin deposition. Pruritus is the most common and bothersome symptom associated with AD; patients may also experience anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.
Diminished quality of life, reduced productivity at work and school, and increased healthcare costs (hospitalizations, emergency visits, outpatient visits, and medications) have all been reported in patients with AD. Triggers for flare-ups vary among individuals; commonly reported triggers include physical or emotional stress, changes in temperature or humidity, sweating, allergens, and irritants.
AD is typically diagnosed clinically given the characteristic distribution of lesions in various age groups (infancy, childhood, and adult). Associated findings such as keratosis pilaris may help to facilitate the diagnosis. No biomarker for the diagnosis of AD has been found and laboratory testing is rarely necessary. However, a swab of infected skin may help to isolate a specific involved organism (eg, Staphylococcus or Streptococcus) and antibiotic sensitivity. Allergy and radioallergosorbent testing are not necessary to make the diagnosis. A swab for viral polymerase chain reaction may be beneficial to help identify superinfection with herpes simplex virus and identify a diagnosis of eczema herpeticum. Testing for serum IgE level can also be helpful for supporting the diagnosis of AD.
The management of AD includes trigger avoidance, daily skin care with application of emollients, anti-inflammatory therapy, and other complementary modalities. For mild or moderate AD, first-line treatment consists of topical anti-inflammatory ointments and creams, including topical corticosteroids, which are available in a broad range of potencies. Other topical medications include topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for patients aged ≥ 2 years), which may be particularly appropriate when there is concern for adverse events secondary to corticosteroid use; topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor (crisaborole ointment for patients aged ≥ 3 months); and topical Janus kinase inhibitor (ruxolitinib cream for patients aged ≥ 12 years).
For patients with moderate to severe AD, or for those who are refractory to topical medications, treatment may include biologic therapy (dupilumab and tralokinumab for patients aged ≥ 6 months and ≥ 18 years, respectively), oral Janus kinase inhibitors (upadacitinib and abrocitinib for patients ages ≥ 12 and ≥ 18 years, respectively), phototherapy (commonly narrow-band ultraviolet light type B treatment), and oral immunomodulators (including methotrexate, mycophenolate, and azathioprine). Combination therapy may be required for the long-term management of more severe AD.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are consistent with atopic dermatitis (AD).
AD is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects more than 200 million people worldwide, including as many as 30% of children and 10% of adults. Although it is more common in children (and may persist into adulthood), approximately 1 in 4 adults with AD have adult-onset disease.
The etiology of AD is complex and includes both genetic and environmental factors, including a weakened skin barrier, immune dysregulation, and abnormalities of the skin microbiome. AD is a member of the atopic triad (ie, AD, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and asthma), which may commence concurrently or in succession in what is referred to as the "atopic march."
The presentation of adult-onset AD may differ from that seen in children. For example, the most commonly reported body regions affected in adult-onset AD are the hands, eyelids, neck, and flexural surfaces of the upper limbs. In contrast, childhood-onset AD is less specific to body regions other than flexural areas. Xerosis is a prominent feature, and lichenification may be present. Some patients may have a rippled, brown macular ring around the neck, simulating the pigmentations seen in macular amyloid but due instead to postinflammatory melanin deposition. Pruritus is the most common and bothersome symptom associated with AD; patients may also experience anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances.
Diminished quality of life, reduced productivity at work and school, and increased healthcare costs (hospitalizations, emergency visits, outpatient visits, and medications) have all been reported in patients with AD. Triggers for flare-ups vary among individuals; commonly reported triggers include physical or emotional stress, changes in temperature or humidity, sweating, allergens, and irritants.
AD is typically diagnosed clinically given the characteristic distribution of lesions in various age groups (infancy, childhood, and adult). Associated findings such as keratosis pilaris may help to facilitate the diagnosis. No biomarker for the diagnosis of AD has been found and laboratory testing is rarely necessary. However, a swab of infected skin may help to isolate a specific involved organism (eg, Staphylococcus or Streptococcus) and antibiotic sensitivity. Allergy and radioallergosorbent testing are not necessary to make the diagnosis. A swab for viral polymerase chain reaction may be beneficial to help identify superinfection with herpes simplex virus and identify a diagnosis of eczema herpeticum. Testing for serum IgE level can also be helpful for supporting the diagnosis of AD.
The management of AD includes trigger avoidance, daily skin care with application of emollients, anti-inflammatory therapy, and other complementary modalities. For mild or moderate AD, first-line treatment consists of topical anti-inflammatory ointments and creams, including topical corticosteroids, which are available in a broad range of potencies. Other topical medications include topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus for patients aged ≥ 2 years), which may be particularly appropriate when there is concern for adverse events secondary to corticosteroid use; topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor (crisaborole ointment for patients aged ≥ 3 months); and topical Janus kinase inhibitor (ruxolitinib cream for patients aged ≥ 12 years).
For patients with moderate to severe AD, or for those who are refractory to topical medications, treatment may include biologic therapy (dupilumab and tralokinumab for patients aged ≥ 6 months and ≥ 18 years, respectively), oral Janus kinase inhibitors (upadacitinib and abrocitinib for patients ages ≥ 12 and ≥ 18 years, respectively), phototherapy (commonly narrow-band ultraviolet light type B treatment), and oral immunomodulators (including methotrexate, mycophenolate, and azathioprine). Combination therapy may be required for the long-term management of more severe AD.
William D. James, MD, Professor, Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Disclosure: William D. James, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Elsevier.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 52-year-old woman presents with complaints of an itchy rash on her arms, legs, neck, and eyelids. She reports having flares with a similar eruption on her arms and legs over the past 2 years, but on previous occasions she was able to manage it with topical emollients. Over the past 6 months, however, it has worsened both in intensity and spread. She describes the rash as intensely pruritic, and now that it has become more visible, she reports feeling embarrassed by it at work and during social outings. The itch is also disrupting her sleep. The patient states that she is undergoing an extremely stressful period in her life because of her parents' declining health and a recent separation from her husband.
Approximately 3 months ago, she visited her primary care provider, who diagnosed her with an allergic rash and prescribed a course of an oral glucocorticoid. Initially, she thought the treatment worked, but the rash soon recurred after she finished her treatment.
Physical examination reveals scaly, crusted hyperpigmented lesions involving the arms, flexural areas of the elbows and knees, neck, and eyelids. Lichenification and xerosis are observed. There is no evidence of conjunctivitis or scalp involvement. The turbinates are not inflamed. Complete blood count findings are within normal range. The patient is 5 ft 3 in and weighs 125 lb (BMI 22.1) and is a nonsmoker.
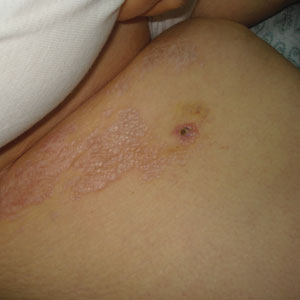
Porcelain White, Crinkled, Violaceous Patches on the Inner Thighs
The Diagnosis: Extragenital Lichen Sclerosus et Atrophicus
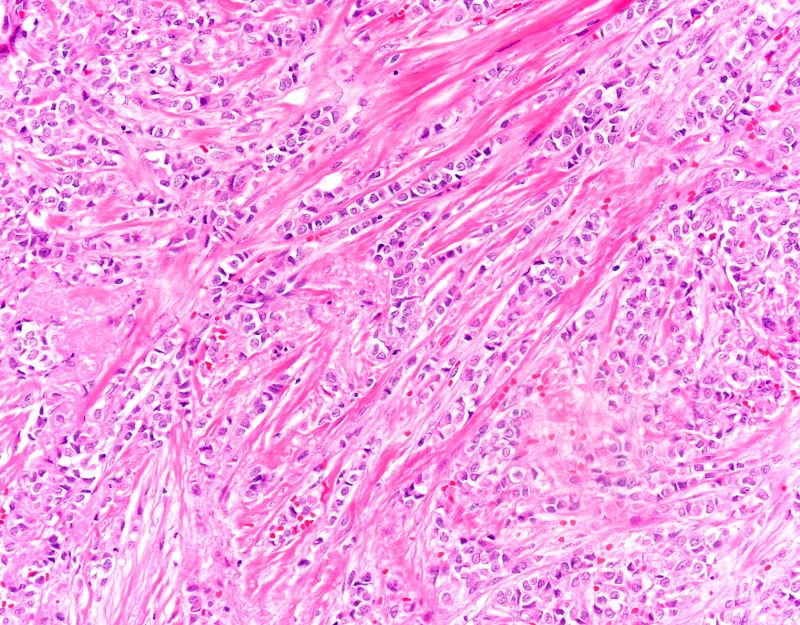
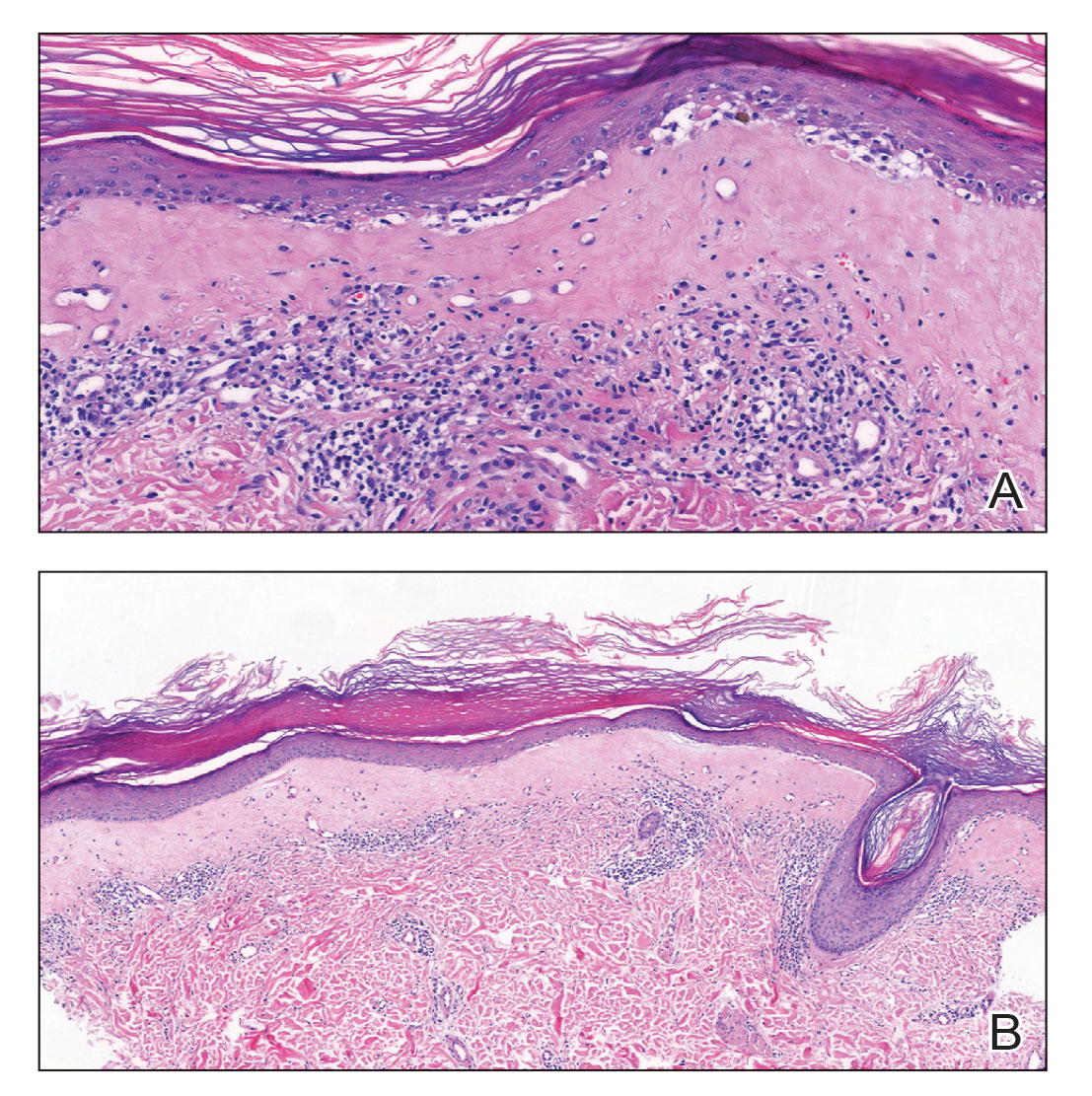
A punch biopsy of the lesion revealed epidermal hyperkeratosis, atrophy, follicular plugs with basal vacuolar degeneration, and homogenous dense fibrosis in the papillary dermis with a dense lymphocytic infiltrate beneath the fibrosis (Figure 1). Dermoscopic examination was remarkable for a distinctive rainbow pattern. Clinical, histopathologic, and dermoscopic findings led to the diagnosis of extragenital lichen sclerosus et atrophicus (LSEA). A potent corticosteroid cream was prescribed twice daily for 2 months, after which the lesions completely resolved. At 2-year follow-up, a relapse was not observed (Figure 2).
Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus is an inflammatory dermatosis that clinically presents as atrophic or hypertrophic plaques that may show pigmentation changes with anogenital and extragenital involvement. It is common among females and predominantly occurs in prepubescent girls and postmenopausal women. The exact etiology is unclear; however, it is hypothesized to occur secondary to autoimmunity with an underlying genetic predisposition. Local trauma, hormonal influences, and infections are other suspected etiologic factors. Genital lesions often lead to itching, pain, and dyspareunia, whereas extragenital lesions predominantly are asymptomatic. When symptomatic, itching usually is the main concern. Unlike genital LSEA, extragenital lesions are not associated with squamous cell carcinoma development. Reported dermoscopic features of LSEA are white structureless areas with scaling, comedolike openings, follicular plugs, white shiny streaks, blue-gray peppering, pigment network, and red-purple globules.1 In our case, the dermoscopic finding of a rainbow pattern in LSEA is rare.2 Although the mechanism behind this appearance unclear, it can be the result of the birefringence effect—local variations in refractive index—influenced by the direction of structures within the dermis such as collagen. In this case, there was diffuse and dense homogenous fibrosis in the superficial dermis that corresponded to dermoscopic white polygonal clods.

Extragenital LSEA commonly is located on the neck, shoulders, wrists, and upper trunk and manifests clinically as whitish papules coalescing into scarlike plaques. Of all patients who have LSEA, 20% have extragenital lesions, and most of these lesions are seen in patients who also have genital LSEA. Approximately 6% of all LSEA patients have extragenital LSEA without genital involvement.3
For experienced dermatologists, clinical symptoms and lesion characteristics usually are sufficient for diagnosis; however, a differential diagnosis of atypical lesions and isolated extragenital presentations such as morphea, lichen simplex chronicus, lichen planus, and vitiligo requires the correlation of clinical findings with histopathology and dermoscopy. Morphea, known as localized scleroderma, is an idiopathic inflammatory skin disease with sclerotic changes. It manifests as inflammatory plaques that vary in color from red to purple. If there is moderate sclerosis in the center of this plaque, the color progressively fades to white, leaving a purplish ring around the edges. Dermoscopic features of morphea are reported as areas of erythema; red-focused vessels of linear, irregular, or dotted morphology; white fibrotic beams; and pigmentary structures.2 Lichen simplex chronicus is characterized by single or multiple dry and patchy skin lesions that are intensely pruritic. It commonly occurs on the neck, scalp, extremities, genital areas, and buttocks. Scratching the lesions leads to scarring, thickening of the skin, and increased frequency of itching. Histopathology of lichen simplex chronicus most frequently demonstrates a thickening of the epidermis and papillary dermis, irregularly elongated rete ridges, and fibroplasia with stellate or multinucleated fibroblasts completed by perivascular lymphocytic inflammation.4 Lichen planus presents with pruritic, polygonal, purple papules and/or plaques that can present in a variety of clinical forms, including atrophic and hypertrophic lichen planus.5 Lichen planus was an unlikely diagnosis for our patient due to the presence of patchy scarlike lesions and dermoscopic features that are well described in patients with LSEA. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus presents with hypopigmented and/or hyperpigmented patches and plaques, distinguishing itself from vitiligo, which has flat lesions.
Topical steroids are the first-line therapeutic agents in the treatment of LSEA.6 Despite frequent use in this setting, common side effects such as localized scarring and atrophic degenerations have led to debate about their use. In our patient, the lesions resolved almost completely in 2 months, and no relapse was observed in the following 2 years. In the setting of topical steroid resistance, topical calcineurin inhibitors, UVA/UVB phototherapy, and topical tacrolimus can be used for treatment.6
The diagnosis of isolated extragenital LSEA may be a clinical challenge and generally requires further workup. When evaluating extragenital lesions, dermatologists should keep in mind extragenital LSEA as a differential diagnosis in the presence of a dermoscopic rainbow pattern arranged over white polygonal clods.
- Wang Y-K, Hao J-C, Liu J, et al. Dermoscopic features of morphea and extragenital lichen sclerosus in Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133:2109-2111.
- Errichetti E, Lallas A, Apalla Z, et al. Dermoscopy of morphea and cutaneous lichen sclerosus: clinicopathological correlation study and comparative analysis. Dermatology. 2017;233:462-470.
- Wallace HJ. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus. Trans St Johns Hosp Dermatol Soc. 1971;57:9-30.
- Balan R, Grigoras¸ A, Popovici D, et al. The histopathological landscape of the major psoriasiform dermatoses. Arch Clin Cases. 2021;6:59-68.
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149.
- Kirtschig G, Becker K, Günthert A, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline on (anogenital) lichen sclerosus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:E1-E43.
The Diagnosis: Extragenital Lichen Sclerosus et Atrophicus
A punch biopsy of the lesion revealed epidermal hyperkeratosis, atrophy, follicular plugs with basal vacuolar degeneration, and homogenous dense fibrosis in the papillary dermis with a dense lymphocytic infiltrate beneath the fibrosis (Figure 1). Dermoscopic examination was remarkable for a distinctive rainbow pattern. Clinical, histopathologic, and dermoscopic findings led to the diagnosis of extragenital lichen sclerosus et atrophicus (LSEA). A potent corticosteroid cream was prescribed twice daily for 2 months, after which the lesions completely resolved. At 2-year follow-up, a relapse was not observed (Figure 2).

Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus is an inflammatory dermatosis that clinically presents as atrophic or hypertrophic plaques that may show pigmentation changes with anogenital and extragenital involvement. It is common among females and predominantly occurs in prepubescent girls and postmenopausal women. The exact etiology is unclear; however, it is hypothesized to occur secondary to autoimmunity with an underlying genetic predisposition. Local trauma, hormonal influences, and infections are other suspected etiologic factors. Genital lesions often lead to itching, pain, and dyspareunia, whereas extragenital lesions predominantly are asymptomatic. When symptomatic, itching usually is the main concern. Unlike genital LSEA, extragenital lesions are not associated with squamous cell carcinoma development. Reported dermoscopic features of LSEA are white structureless areas with scaling, comedolike openings, follicular plugs, white shiny streaks, blue-gray peppering, pigment network, and red-purple globules.1 In our case, the dermoscopic finding of a rainbow pattern in LSEA is rare.2 Although the mechanism behind this appearance unclear, it can be the result of the birefringence effect—local variations in refractive index—influenced by the direction of structures within the dermis such as collagen. In this case, there was diffuse and dense homogenous fibrosis in the superficial dermis that corresponded to dermoscopic white polygonal clods.

Extragenital LSEA commonly is located on the neck, shoulders, wrists, and upper trunk and manifests clinically as whitish papules coalescing into scarlike plaques. Of all patients who have LSEA, 20% have extragenital lesions, and most of these lesions are seen in patients who also have genital LSEA. Approximately 6% of all LSEA patients have extragenital LSEA without genital involvement.3
For experienced dermatologists, clinical symptoms and lesion characteristics usually are sufficient for diagnosis; however, a differential diagnosis of atypical lesions and isolated extragenital presentations such as morphea, lichen simplex chronicus, lichen planus, and vitiligo requires the correlation of clinical findings with histopathology and dermoscopy. Morphea, known as localized scleroderma, is an idiopathic inflammatory skin disease with sclerotic changes. It manifests as inflammatory plaques that vary in color from red to purple. If there is moderate sclerosis in the center of this plaque, the color progressively fades to white, leaving a purplish ring around the edges. Dermoscopic features of morphea are reported as areas of erythema; red-focused vessels of linear, irregular, or dotted morphology; white fibrotic beams; and pigmentary structures.2 Lichen simplex chronicus is characterized by single or multiple dry and patchy skin lesions that are intensely pruritic. It commonly occurs on the neck, scalp, extremities, genital areas, and buttocks. Scratching the lesions leads to scarring, thickening of the skin, and increased frequency of itching. Histopathology of lichen simplex chronicus most frequently demonstrates a thickening of the epidermis and papillary dermis, irregularly elongated rete ridges, and fibroplasia with stellate or multinucleated fibroblasts completed by perivascular lymphocytic inflammation.4 Lichen planus presents with pruritic, polygonal, purple papules and/or plaques that can present in a variety of clinical forms, including atrophic and hypertrophic lichen planus.5 Lichen planus was an unlikely diagnosis for our patient due to the presence of patchy scarlike lesions and dermoscopic features that are well described in patients with LSEA. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus presents with hypopigmented and/or hyperpigmented patches and plaques, distinguishing itself from vitiligo, which has flat lesions.
Topical steroids are the first-line therapeutic agents in the treatment of LSEA.6 Despite frequent use in this setting, common side effects such as localized scarring and atrophic degenerations have led to debate about their use. In our patient, the lesions resolved almost completely in 2 months, and no relapse was observed in the following 2 years. In the setting of topical steroid resistance, topical calcineurin inhibitors, UVA/UVB phototherapy, and topical tacrolimus can be used for treatment.6
The diagnosis of isolated extragenital LSEA may be a clinical challenge and generally requires further workup. When evaluating extragenital lesions, dermatologists should keep in mind extragenital LSEA as a differential diagnosis in the presence of a dermoscopic rainbow pattern arranged over white polygonal clods.
The Diagnosis: Extragenital Lichen Sclerosus et Atrophicus
A punch biopsy of the lesion revealed epidermal hyperkeratosis, atrophy, follicular plugs with basal vacuolar degeneration, and homogenous dense fibrosis in the papillary dermis with a dense lymphocytic infiltrate beneath the fibrosis (Figure 1). Dermoscopic examination was remarkable for a distinctive rainbow pattern. Clinical, histopathologic, and dermoscopic findings led to the diagnosis of extragenital lichen sclerosus et atrophicus (LSEA). A potent corticosteroid cream was prescribed twice daily for 2 months, after which the lesions completely resolved. At 2-year follow-up, a relapse was not observed (Figure 2).

Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus is an inflammatory dermatosis that clinically presents as atrophic or hypertrophic plaques that may show pigmentation changes with anogenital and extragenital involvement. It is common among females and predominantly occurs in prepubescent girls and postmenopausal women. The exact etiology is unclear; however, it is hypothesized to occur secondary to autoimmunity with an underlying genetic predisposition. Local trauma, hormonal influences, and infections are other suspected etiologic factors. Genital lesions often lead to itching, pain, and dyspareunia, whereas extragenital lesions predominantly are asymptomatic. When symptomatic, itching usually is the main concern. Unlike genital LSEA, extragenital lesions are not associated with squamous cell carcinoma development. Reported dermoscopic features of LSEA are white structureless areas with scaling, comedolike openings, follicular plugs, white shiny streaks, blue-gray peppering, pigment network, and red-purple globules.1 In our case, the dermoscopic finding of a rainbow pattern in LSEA is rare.2 Although the mechanism behind this appearance unclear, it can be the result of the birefringence effect—local variations in refractive index—influenced by the direction of structures within the dermis such as collagen. In this case, there was diffuse and dense homogenous fibrosis in the superficial dermis that corresponded to dermoscopic white polygonal clods.

Extragenital LSEA commonly is located on the neck, shoulders, wrists, and upper trunk and manifests clinically as whitish papules coalescing into scarlike plaques. Of all patients who have LSEA, 20% have extragenital lesions, and most of these lesions are seen in patients who also have genital LSEA. Approximately 6% of all LSEA patients have extragenital LSEA without genital involvement.3
For experienced dermatologists, clinical symptoms and lesion characteristics usually are sufficient for diagnosis; however, a differential diagnosis of atypical lesions and isolated extragenital presentations such as morphea, lichen simplex chronicus, lichen planus, and vitiligo requires the correlation of clinical findings with histopathology and dermoscopy. Morphea, known as localized scleroderma, is an idiopathic inflammatory skin disease with sclerotic changes. It manifests as inflammatory plaques that vary in color from red to purple. If there is moderate sclerosis in the center of this plaque, the color progressively fades to white, leaving a purplish ring around the edges. Dermoscopic features of morphea are reported as areas of erythema; red-focused vessels of linear, irregular, or dotted morphology; white fibrotic beams; and pigmentary structures.2 Lichen simplex chronicus is characterized by single or multiple dry and patchy skin lesions that are intensely pruritic. It commonly occurs on the neck, scalp, extremities, genital areas, and buttocks. Scratching the lesions leads to scarring, thickening of the skin, and increased frequency of itching. Histopathology of lichen simplex chronicus most frequently demonstrates a thickening of the epidermis and papillary dermis, irregularly elongated rete ridges, and fibroplasia with stellate or multinucleated fibroblasts completed by perivascular lymphocytic inflammation.4 Lichen planus presents with pruritic, polygonal, purple papules and/or plaques that can present in a variety of clinical forms, including atrophic and hypertrophic lichen planus.5 Lichen planus was an unlikely diagnosis for our patient due to the presence of patchy scarlike lesions and dermoscopic features that are well described in patients with LSEA. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus presents with hypopigmented and/or hyperpigmented patches and plaques, distinguishing itself from vitiligo, which has flat lesions.
Topical steroids are the first-line therapeutic agents in the treatment of LSEA.6 Despite frequent use in this setting, common side effects such as localized scarring and atrophic degenerations have led to debate about their use. In our patient, the lesions resolved almost completely in 2 months, and no relapse was observed in the following 2 years. In the setting of topical steroid resistance, topical calcineurin inhibitors, UVA/UVB phototherapy, and topical tacrolimus can be used for treatment.6
The diagnosis of isolated extragenital LSEA may be a clinical challenge and generally requires further workup. When evaluating extragenital lesions, dermatologists should keep in mind extragenital LSEA as a differential diagnosis in the presence of a dermoscopic rainbow pattern arranged over white polygonal clods.
- Wang Y-K, Hao J-C, Liu J, et al. Dermoscopic features of morphea and extragenital lichen sclerosus in Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133:2109-2111.
- Errichetti E, Lallas A, Apalla Z, et al. Dermoscopy of morphea and cutaneous lichen sclerosus: clinicopathological correlation study and comparative analysis. Dermatology. 2017;233:462-470.
- Wallace HJ. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus. Trans St Johns Hosp Dermatol Soc. 1971;57:9-30.
- Balan R, Grigoras¸ A, Popovici D, et al. The histopathological landscape of the major psoriasiform dermatoses. Arch Clin Cases. 2021;6:59-68.
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149.
- Kirtschig G, Becker K, Günthert A, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline on (anogenital) lichen sclerosus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:E1-E43.
- Wang Y-K, Hao J-C, Liu J, et al. Dermoscopic features of morphea and extragenital lichen sclerosus in Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133:2109-2111.
- Errichetti E, Lallas A, Apalla Z, et al. Dermoscopy of morphea and cutaneous lichen sclerosus: clinicopathological correlation study and comparative analysis. Dermatology. 2017;233:462-470.
- Wallace HJ. Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus. Trans St Johns Hosp Dermatol Soc. 1971;57:9-30.
- Balan R, Grigoras¸ A, Popovici D, et al. The histopathological landscape of the major psoriasiform dermatoses. Arch Clin Cases. 2021;6:59-68.
- Weston G, Payette M. Update on lichen planus and its clinical variants. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2015;1:140-149.
- Kirtschig G, Becker K, Günthert A, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline on (anogenital) lichen sclerosus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:E1-E43.
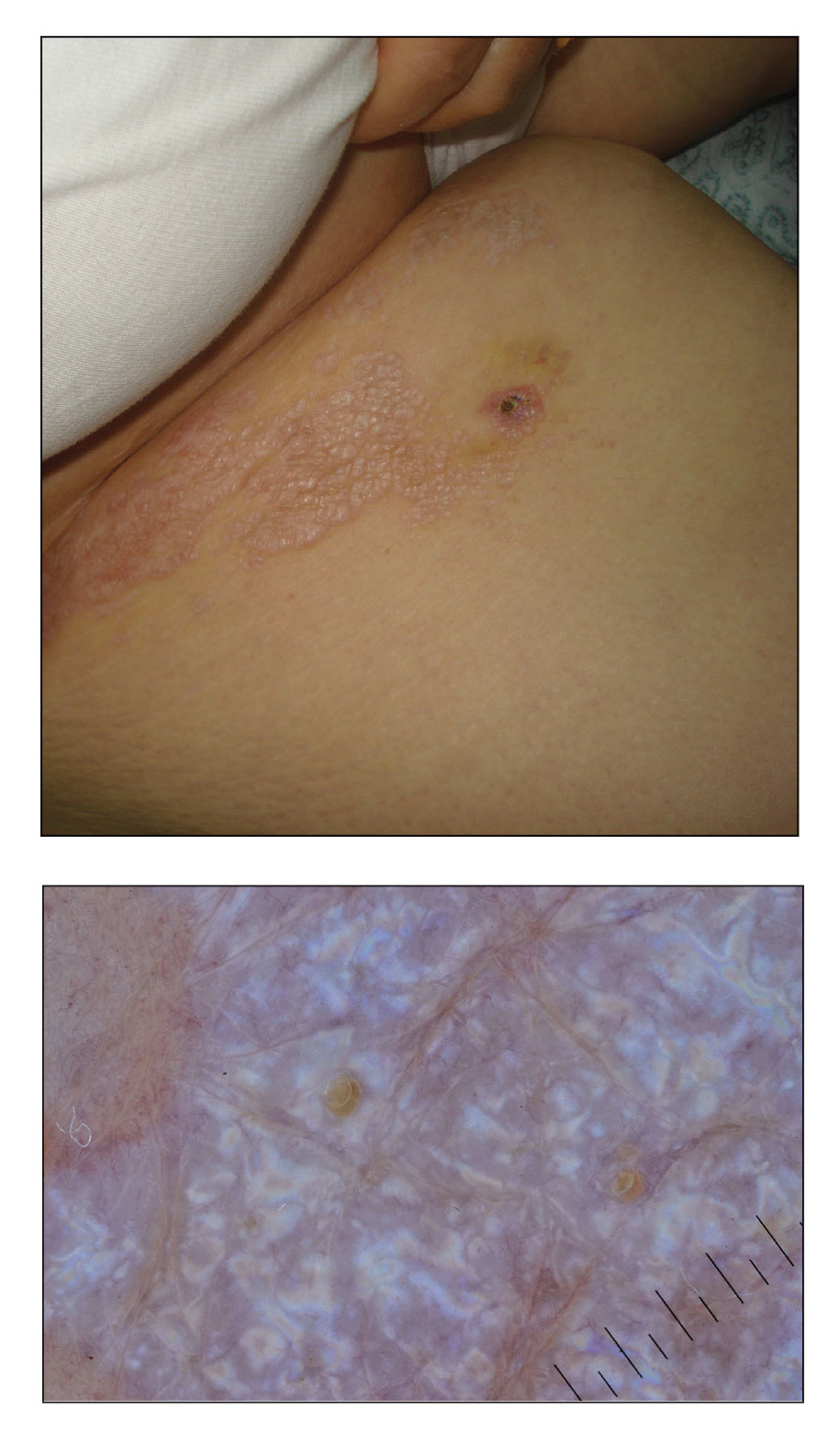
A 50-year-old woman presented with multiple pruritic lesions on the right inner thigh of 2 years’ duration. Physical examination revealed porcelain white, crinkled, violaceous patches extending from the right inner thigh to the inguinal fold (top). Dermoscopic examination revealed follicular plugs, white structureless areas, white lines, and a rainbow pattern arranged over white polygonal clods on polarized mode (bottom).
Effects of Multiple Sclerosis Disease-Modifying Therapies on the Immune System
In recent years, many disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) have been approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). DMTs are not a cure for MS, but they have been proven to alter the course of the disease, reduce relapses, slow its progression, and alleviate symptoms. DMTs function by surpressing immune activity. This, in turn, diminishes the intensity of the inflammatory attack responsible for driving this disorder.
Dr Lauren Krupp, a neurologist at NYU Langone Health in New York, NY, presents an overview of the mechanisms of action (MOA) for the various DMTs and their effects on the immune system, including the potential to increase risk for infection and alter response to vaccination.
Dr Krupp notes that DMTs can be administered orally, by injection, and by infusion, depending on the drug prescribed. She further explains that because there are now more DMT options, it is important to understand how best to tailor therapy decisions to individual patients.
--
Lauren Krupp, MD, Professor, Department of Neurology, NYU Grossman School of Medicine; Director, NYU Langone Comprehensive Care Center, Deaprtment of Neurology, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY
Lauren Krupp, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Novartis; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb
Received research grant from: Biogen; Novartis
In recent years, many disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) have been approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). DMTs are not a cure for MS, but they have been proven to alter the course of the disease, reduce relapses, slow its progression, and alleviate symptoms. DMTs function by surpressing immune activity. This, in turn, diminishes the intensity of the inflammatory attack responsible for driving this disorder.
Dr Lauren Krupp, a neurologist at NYU Langone Health in New York, NY, presents an overview of the mechanisms of action (MOA) for the various DMTs and their effects on the immune system, including the potential to increase risk for infection and alter response to vaccination.
Dr Krupp notes that DMTs can be administered orally, by injection, and by infusion, depending on the drug prescribed. She further explains that because there are now more DMT options, it is important to understand how best to tailor therapy decisions to individual patients.
--
Lauren Krupp, MD, Professor, Department of Neurology, NYU Grossman School of Medicine; Director, NYU Langone Comprehensive Care Center, Deaprtment of Neurology, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY
Lauren Krupp, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Novartis; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb
Received research grant from: Biogen; Novartis
In recent years, many disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) have been approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). DMTs are not a cure for MS, but they have been proven to alter the course of the disease, reduce relapses, slow its progression, and alleviate symptoms. DMTs function by surpressing immune activity. This, in turn, diminishes the intensity of the inflammatory attack responsible for driving this disorder.
Dr Lauren Krupp, a neurologist at NYU Langone Health in New York, NY, presents an overview of the mechanisms of action (MOA) for the various DMTs and their effects on the immune system, including the potential to increase risk for infection and alter response to vaccination.
Dr Krupp notes that DMTs can be administered orally, by injection, and by infusion, depending on the drug prescribed. She further explains that because there are now more DMT options, it is important to understand how best to tailor therapy decisions to individual patients.
--
Lauren Krupp, MD, Professor, Department of Neurology, NYU Grossman School of Medicine; Director, NYU Langone Comprehensive Care Center, Deaprtment of Neurology, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY
Lauren Krupp, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Novartis; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb
Received research grant from: Biogen; Novartis

Severe Asthma: Multidisciplinary Assessment and Management Including Biologic Therapy
Distinguishing severe asthma from asthma that is difficult to control can present a clinical challenge, especially in primary care settings. Patients with severe asthma often benefit from multidisciplinary assessment and management.
In this panel ReCAP, experts in allergy, pulmonary disease, and primary care discuss the difference between severe and difficult-to-control asthma and the clinical importance of this distinction. They then outline optimal management of severe asthma using conventional therapies and the six biologics that are now available.
According to the panelists, patients with asthma that is difficult to control may have comorbidities that have not been addressed and may contribute to their respiratory symptoms. In patients with severe asthma, comorbidities have typically been addressed and patients are adherent to prescribed therapies; their disease worsens if therapy is stepped down. This definition follows the 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines.
The experts discuss how tests administered in primary care and specialty settings can distinguish between eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic phenotypes. In patients who continue to have symptoms despite maximized conventional therapies, biologics targeting specific inflammatory pathways may come into play.
--
Richard Barbers, MD, Professor of Medicine, KECK Medical Center of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
Richard Barbers, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Kraft, MD, Murray M. Rosenberg Professor of Medicine, System Chair, Department of Medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; System Chair, Department of Medicine, Respiratory Institute at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY
Monica Kraft, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a consultant for: Sanofi; Regeneron; AstraZeneca; Chiesi
Serve(d) as Co-founder for: CMO; RaeSedo, Inc
Received research grant from: National Institutes of Health; American Lung Association
Have a 5% or greater equity interest in: RaeSedo, Inc (start-up in preclinical development of therapeutics)
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: UptoDate, section editor; received > $250 and < $5k from consultant activities above
Louis J. Papa, MD, Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of Medicine, Primary Care, University of Rochester Medical Center; Director of Professional Licensing and Credentialing Navigation, Olsan Medical Group, Rochester, New York
Louis J. Papa, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Lifetime Healthcare Cos
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Lifetime Healthcare Cos
Distinguishing severe asthma from asthma that is difficult to control can present a clinical challenge, especially in primary care settings. Patients with severe asthma often benefit from multidisciplinary assessment and management.
In this panel ReCAP, experts in allergy, pulmonary disease, and primary care discuss the difference between severe and difficult-to-control asthma and the clinical importance of this distinction. They then outline optimal management of severe asthma using conventional therapies and the six biologics that are now available.
According to the panelists, patients with asthma that is difficult to control may have comorbidities that have not been addressed and may contribute to their respiratory symptoms. In patients with severe asthma, comorbidities have typically been addressed and patients are adherent to prescribed therapies; their disease worsens if therapy is stepped down. This definition follows the 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines.
The experts discuss how tests administered in primary care and specialty settings can distinguish between eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic phenotypes. In patients who continue to have symptoms despite maximized conventional therapies, biologics targeting specific inflammatory pathways may come into play.
--
Richard Barbers, MD, Professor of Medicine, KECK Medical Center of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
Richard Barbers, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Kraft, MD, Murray M. Rosenberg Professor of Medicine, System Chair, Department of Medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; System Chair, Department of Medicine, Respiratory Institute at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY
Monica Kraft, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a consultant for: Sanofi; Regeneron; AstraZeneca; Chiesi
Serve(d) as Co-founder for: CMO; RaeSedo, Inc
Received research grant from: National Institutes of Health; American Lung Association
Have a 5% or greater equity interest in: RaeSedo, Inc (start-up in preclinical development of therapeutics)
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: UptoDate, section editor; received > $250 and < $5k from consultant activities above
Louis J. Papa, MD, Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of Medicine, Primary Care, University of Rochester Medical Center; Director of Professional Licensing and Credentialing Navigation, Olsan Medical Group, Rochester, New York
Louis J. Papa, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Lifetime Healthcare Cos
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Lifetime Healthcare Cos
Distinguishing severe asthma from asthma that is difficult to control can present a clinical challenge, especially in primary care settings. Patients with severe asthma often benefit from multidisciplinary assessment and management.
In this panel ReCAP, experts in allergy, pulmonary disease, and primary care discuss the difference between severe and difficult-to-control asthma and the clinical importance of this distinction. They then outline optimal management of severe asthma using conventional therapies and the six biologics that are now available.
According to the panelists, patients with asthma that is difficult to control may have comorbidities that have not been addressed and may contribute to their respiratory symptoms. In patients with severe asthma, comorbidities have typically been addressed and patients are adherent to prescribed therapies; their disease worsens if therapy is stepped down. This definition follows the 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines.
The experts discuss how tests administered in primary care and specialty settings can distinguish between eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic phenotypes. In patients who continue to have symptoms despite maximized conventional therapies, biologics targeting specific inflammatory pathways may come into play.
--
Richard Barbers, MD, Professor of Medicine, KECK Medical Center of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
Richard Barbers, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Monica Kraft, MD, Murray M. Rosenberg Professor of Medicine, System Chair, Department of Medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; System Chair, Department of Medicine, Respiratory Institute at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY
Monica Kraft, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a consultant for: Sanofi; Regeneron; AstraZeneca; Chiesi
Serve(d) as Co-founder for: CMO; RaeSedo, Inc
Received research grant from: National Institutes of Health; American Lung Association
Have a 5% or greater equity interest in: RaeSedo, Inc (start-up in preclinical development of therapeutics)
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: UptoDate, section editor; received > $250 and < $5k from consultant activities above
Louis J. Papa, MD, Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of Medicine, Primary Care, University of Rochester Medical Center; Director of Professional Licensing and Credentialing Navigation, Olsan Medical Group, Rochester, New York
Louis J. Papa, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Lifetime Healthcare Cos
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Lifetime Healthcare Cos

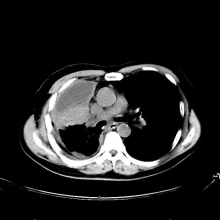
Cough and hemoptysis
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of combined small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Globally, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality, accounting for an estimated 2 million new diagnoses and 1.76 million deaths per year. It consists of two major subtypes: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and SCLC. SCLC is unique in its presentation, imaging appearances, treatment, and prognosis. SCLC accounts for approximately 15% of all lung cancers and is associated with an exceptionally high proliferative rate, strong predilection for early metastasis, and poor prognosis.
There are two subtypes of SCLC: oat cell carcinoma and combined SCLC. Combined SCLC is defined as SCLC with non-small cell components, such as squamous cell or adenocarcinoma. Men are affected more frequently than are women. Most presenting patients are older than 70 years and are either a current or former smoker. Patients frequently have multiple cardiovascular or pulmonary comorbidities.
In most cases, patients experience rapid onset of symptoms, normally beginning 8-12 weeks before presentation. Signs and symptoms vary depending on the location and bulk of the primary tumor, but may include cough, wheezing, and hemoptysis as well as weight loss, debility, and other signs of metastatic disease. Local intrathoracic tumor growth can affect the superior vena cava (leading to superior vena cava syndrome), chest wall, or esophagus. Neurologic problems, recurrent nerve pain, fatigue, and anorexia may result from extrapulmonary metastasis. Nearly 60% of patients present with metastatic disease, most commonly in the brain, liver, adrenal glands, bone, and bone marrow. If left untreated, SCLC tumors progress rapidly, with a median survival of 2-4 months.
All patients with SCLC require a thorough staging workup to evaluate the extent of disease because stage plays a central role in treatment selection. The initial imaging workup includes plain film radiography and contrast-enhanced CT of the chest and upper abdomen, brain MRI, and PET-CT. Laboratory studies to evaluate for the presence of neoplastic syndromes include complete blood count, electrolytes, calcium, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and creatinine. Biopsy is usually obtained via CT-guided biopsy or transbronchial biopsy, though this can vary depending on the location of the tumor.
According to 2023 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), most patients with limited-stage SCLC are not eligible for surgery or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR). Surgery is only recommended for select patients with stage I–IIA SCLC (about 5% of patients). Concurrent chemoradiation or SABR is recommended for patients with limited stage I-IIA (T1-2,N0) SCLC who are ineligible for or do not want to pursue surgical resection. The majority of patients with SCLC have extensive-stage disease, and treatment with systemic therapy alone (with or without palliative radiotherapy) is recommended. Preferred cytotoxic and immunotherapeutic agents can be found in the NCCN guidelines.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of combined small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Globally, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality, accounting for an estimated 2 million new diagnoses and 1.76 million deaths per year. It consists of two major subtypes: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and SCLC. SCLC is unique in its presentation, imaging appearances, treatment, and prognosis. SCLC accounts for approximately 15% of all lung cancers and is associated with an exceptionally high proliferative rate, strong predilection for early metastasis, and poor prognosis.
There are two subtypes of SCLC: oat cell carcinoma and combined SCLC. Combined SCLC is defined as SCLC with non-small cell components, such as squamous cell or adenocarcinoma. Men are affected more frequently than are women. Most presenting patients are older than 70 years and are either a current or former smoker. Patients frequently have multiple cardiovascular or pulmonary comorbidities.
In most cases, patients experience rapid onset of symptoms, normally beginning 8-12 weeks before presentation. Signs and symptoms vary depending on the location and bulk of the primary tumor, but may include cough, wheezing, and hemoptysis as well as weight loss, debility, and other signs of metastatic disease. Local intrathoracic tumor growth can affect the superior vena cava (leading to superior vena cava syndrome), chest wall, or esophagus. Neurologic problems, recurrent nerve pain, fatigue, and anorexia may result from extrapulmonary metastasis. Nearly 60% of patients present with metastatic disease, most commonly in the brain, liver, adrenal glands, bone, and bone marrow. If left untreated, SCLC tumors progress rapidly, with a median survival of 2-4 months.
All patients with SCLC require a thorough staging workup to evaluate the extent of disease because stage plays a central role in treatment selection. The initial imaging workup includes plain film radiography and contrast-enhanced CT of the chest and upper abdomen, brain MRI, and PET-CT. Laboratory studies to evaluate for the presence of neoplastic syndromes include complete blood count, electrolytes, calcium, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and creatinine. Biopsy is usually obtained via CT-guided biopsy or transbronchial biopsy, though this can vary depending on the location of the tumor.
According to 2023 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), most patients with limited-stage SCLC are not eligible for surgery or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR). Surgery is only recommended for select patients with stage I–IIA SCLC (about 5% of patients). Concurrent chemoradiation or SABR is recommended for patients with limited stage I-IIA (T1-2,N0) SCLC who are ineligible for or do not want to pursue surgical resection. The majority of patients with SCLC have extensive-stage disease, and treatment with systemic therapy alone (with or without palliative radiotherapy) is recommended. Preferred cytotoxic and immunotherapeutic agents can be found in the NCCN guidelines.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of combined small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Globally, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality, accounting for an estimated 2 million new diagnoses and 1.76 million deaths per year. It consists of two major subtypes: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and SCLC. SCLC is unique in its presentation, imaging appearances, treatment, and prognosis. SCLC accounts for approximately 15% of all lung cancers and is associated with an exceptionally high proliferative rate, strong predilection for early metastasis, and poor prognosis.
There are two subtypes of SCLC: oat cell carcinoma and combined SCLC. Combined SCLC is defined as SCLC with non-small cell components, such as squamous cell or adenocarcinoma. Men are affected more frequently than are women. Most presenting patients are older than 70 years and are either a current or former smoker. Patients frequently have multiple cardiovascular or pulmonary comorbidities.
In most cases, patients experience rapid onset of symptoms, normally beginning 8-12 weeks before presentation. Signs and symptoms vary depending on the location and bulk of the primary tumor, but may include cough, wheezing, and hemoptysis as well as weight loss, debility, and other signs of metastatic disease. Local intrathoracic tumor growth can affect the superior vena cava (leading to superior vena cava syndrome), chest wall, or esophagus. Neurologic problems, recurrent nerve pain, fatigue, and anorexia may result from extrapulmonary metastasis. Nearly 60% of patients present with metastatic disease, most commonly in the brain, liver, adrenal glands, bone, and bone marrow. If left untreated, SCLC tumors progress rapidly, with a median survival of 2-4 months.
All patients with SCLC require a thorough staging workup to evaluate the extent of disease because stage plays a central role in treatment selection. The initial imaging workup includes plain film radiography and contrast-enhanced CT of the chest and upper abdomen, brain MRI, and PET-CT. Laboratory studies to evaluate for the presence of neoplastic syndromes include complete blood count, electrolytes, calcium, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and creatinine. Biopsy is usually obtained via CT-guided biopsy or transbronchial biopsy, though this can vary depending on the location of the tumor.
According to 2023 guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), most patients with limited-stage SCLC are not eligible for surgery or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR). Surgery is only recommended for select patients with stage I–IIA SCLC (about 5% of patients). Concurrent chemoradiation or SABR is recommended for patients with limited stage I-IIA (T1-2,N0) SCLC who are ineligible for or do not want to pursue surgical resection. The majority of patients with SCLC have extensive-stage disease, and treatment with systemic therapy alone (with or without palliative radiotherapy) is recommended. Preferred cytotoxic and immunotherapeutic agents can be found in the NCCN guidelines.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 74-year-old man presents to the emergency department with reports of cough, hemoptysis, and unintentional weight loss of approximately 8 weeks' duration. The patient has a 35-year history of smoking (35 pack years). The patient's vital signs include temperature of 98.4 °F, BP of 135/80 mm Hg, and pulse oximeter reading of 94%. Physical examination reveals rales over the left side of the chest and decreased breath sounds in bilateral bases of the lungs. The patient appears cachexic. He is 6 ft 2 in and weighs 163 lb.
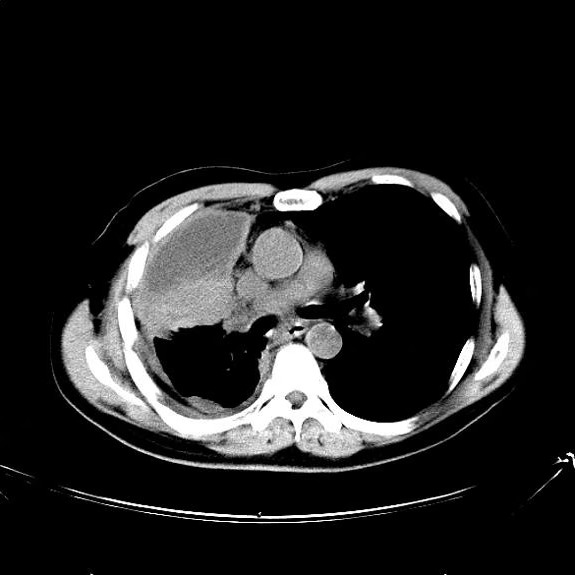
A chest radiograph reveals a mass in the right lung field. A subsequent CT of the chest reveals multiple pulmonary nodules and extensive mediastinal nodal metastases. Histopathology reveals small, uniform, poorly differentiated necrotic cancers and adenocarcinoma with papillary and acinar features.
Forgetfulness and confusion
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of late-onset familial AD (onset after age 65 years).
AD is a common neurodegenerative disease associated with progressive impairment of behavioral and cognitive functions, including memory, comprehension, language, attention, reasoning, and judgment. In 2020, 5.8 million Americans were living with AD. By 2050, this number is projected to increase to 13.9 million people, or almost 3.3% of the US population. Globally, 152 million people are projected to have AD and other dementias by 2050. The worldwide increase in incidence and prevalence of AD is at least partially explained by an aging population and increased life expectancy.
The cause of AD remains unclear, but there is substantial evidence that AD is a highly heritable disorder. Familial AD is characterized by having more than one member in more than one generation with AD. The autosomal-dominant form of AD is linked to mutations in three genes: AAP on chromosome 21, PSEN1 on chromosome 14, and PSEN2 on chromosome 1. APP mutations may cause increased generation and aggregation of beta-amyloid peptide, whereas PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations result in aggregation of beta-amyloid by interfering with the processing of gamma-secretase.
APOE is another genetic marker that increases the risk for AD. Isoform e4 of the APOE gene (located on chromosome 19) has been associated with more sporadic and familial forms of AD that present after age 65 years. Approximately 50% of individuals carrying one APOEe4 develop AD, and 90% of individuals who have two alleles develop AD. Variants in the gene for the sortilin receptor, SORT1, have also been found in familial and sporadic forms of AD.
The cognitive and behavioral impairment associated with AD significantly affects a patient's social and occupational functioning. Insidiously progressive memory loss is a characteristic symptoms seen in patients presenting with AD. As the disease advances over the course of several years, other areas of cognition are impaired. Patients may develop language disorders (eg, anomic aphasia or anomia) and impairment in visuospatial skills and executive functions. A slow progression of behavioral changes may also occur in individuals with AD.
Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of AD (eg, insidious onset of cognitive impairment, clear history of worsening symptoms) have been developed and are often used to diagnose patients. In addition, biomarker evidence may help to increase the diagnostic certainty. Several cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers have shown excellent diagnostic ability by identifying tau pathology and cerebral amyloid-beta for AD.
Neuroimaging is becoming increasingly important for identifying the underlying causes of cognitive impairment. Currently, MRI is considered the preferred neuroimaging modality for AD because it allows for accurate measurement of the three-dimensional volume of brain structures, particularly the size of the hippocampus and related regions. CT can be used when MRI is not available or is contraindicated, such as in a patient with a pacemaker. PET is another noninvasive method for depicting tau pathology deposition and distribution in patients with cognitive impairment. In 2020, US Food and Drug Administration approved the first tau PET tracer, 18F-flortaucipir, which marked a significant achievement to improve AD diagnosis.
At present, the only therapies available for AD are symptomatic therapies. Cholinesterase inhibitors and a partial N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist are the standard medical treatments for AD. Antiamyloid therapies are also available for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. These include aducanumab, a first-in-class amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2021, and lecanemab, another amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2023. Both aducanumab and lecanemab are recommended for the treatment of patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which the safety and efficacy of these newer agents were demonstrated in clinical trials.
Secondary symptoms of AD, such as depression, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, delusions, and/or sleep disorders, can be treated with psychotropic agents. Behavioral interventions including patient-centered approaches and caregiver training can also be helpful for managing the cognitive and behavioral manifestations of AD, often in combination with pharmacologic interventions (eg, anxiolytics for anxiety and agitation, neuroleptics for delusions or hallucinations, and antidepressants or mood stabilizers for mood disorders). Regular physical activity and exercise may also play a role in delaying AD progression and possibly conferring a protective effect on brain health.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, Professor of Neurology, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood; Director, Clinical Neurophysiology Lab, Department of Neurology, Hines VA Hospital, Hines, IL.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of late-onset familial AD (onset after age 65 years).
AD is a common neurodegenerative disease associated with progressive impairment of behavioral and cognitive functions, including memory, comprehension, language, attention, reasoning, and judgment. In 2020, 5.8 million Americans were living with AD. By 2050, this number is projected to increase to 13.9 million people, or almost 3.3% of the US population. Globally, 152 million people are projected to have AD and other dementias by 2050. The worldwide increase in incidence and prevalence of AD is at least partially explained by an aging population and increased life expectancy.
The cause of AD remains unclear, but there is substantial evidence that AD is a highly heritable disorder. Familial AD is characterized by having more than one member in more than one generation with AD. The autosomal-dominant form of AD is linked to mutations in three genes: AAP on chromosome 21, PSEN1 on chromosome 14, and PSEN2 on chromosome 1. APP mutations may cause increased generation and aggregation of beta-amyloid peptide, whereas PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations result in aggregation of beta-amyloid by interfering with the processing of gamma-secretase.
APOE is another genetic marker that increases the risk for AD. Isoform e4 of the APOE gene (located on chromosome 19) has been associated with more sporadic and familial forms of AD that present after age 65 years. Approximately 50% of individuals carrying one APOEe4 develop AD, and 90% of individuals who have two alleles develop AD. Variants in the gene for the sortilin receptor, SORT1, have also been found in familial and sporadic forms of AD.
The cognitive and behavioral impairment associated with AD significantly affects a patient's social and occupational functioning. Insidiously progressive memory loss is a characteristic symptoms seen in patients presenting with AD. As the disease advances over the course of several years, other areas of cognition are impaired. Patients may develop language disorders (eg, anomic aphasia or anomia) and impairment in visuospatial skills and executive functions. A slow progression of behavioral changes may also occur in individuals with AD.
Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of AD (eg, insidious onset of cognitive impairment, clear history of worsening symptoms) have been developed and are often used to diagnose patients. In addition, biomarker evidence may help to increase the diagnostic certainty. Several cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers have shown excellent diagnostic ability by identifying tau pathology and cerebral amyloid-beta for AD.
Neuroimaging is becoming increasingly important for identifying the underlying causes of cognitive impairment. Currently, MRI is considered the preferred neuroimaging modality for AD because it allows for accurate measurement of the three-dimensional volume of brain structures, particularly the size of the hippocampus and related regions. CT can be used when MRI is not available or is contraindicated, such as in a patient with a pacemaker. PET is another noninvasive method for depicting tau pathology deposition and distribution in patients with cognitive impairment. In 2020, US Food and Drug Administration approved the first tau PET tracer, 18F-flortaucipir, which marked a significant achievement to improve AD diagnosis.
At present, the only therapies available for AD are symptomatic therapies. Cholinesterase inhibitors and a partial N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist are the standard medical treatments for AD. Antiamyloid therapies are also available for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. These include aducanumab, a first-in-class amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2021, and lecanemab, another amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2023. Both aducanumab and lecanemab are recommended for the treatment of patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which the safety and efficacy of these newer agents were demonstrated in clinical trials.
Secondary symptoms of AD, such as depression, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, delusions, and/or sleep disorders, can be treated with psychotropic agents. Behavioral interventions including patient-centered approaches and caregiver training can also be helpful for managing the cognitive and behavioral manifestations of AD, often in combination with pharmacologic interventions (eg, anxiolytics for anxiety and agitation, neuroleptics for delusions or hallucinations, and antidepressants or mood stabilizers for mood disorders). Regular physical activity and exercise may also play a role in delaying AD progression and possibly conferring a protective effect on brain health.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, Professor of Neurology, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood; Director, Clinical Neurophysiology Lab, Department of Neurology, Hines VA Hospital, Hines, IL.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of late-onset familial AD (onset after age 65 years).
AD is a common neurodegenerative disease associated with progressive impairment of behavioral and cognitive functions, including memory, comprehension, language, attention, reasoning, and judgment. In 2020, 5.8 million Americans were living with AD. By 2050, this number is projected to increase to 13.9 million people, or almost 3.3% of the US population. Globally, 152 million people are projected to have AD and other dementias by 2050. The worldwide increase in incidence and prevalence of AD is at least partially explained by an aging population and increased life expectancy.
The cause of AD remains unclear, but there is substantial evidence that AD is a highly heritable disorder. Familial AD is characterized by having more than one member in more than one generation with AD. The autosomal-dominant form of AD is linked to mutations in three genes: AAP on chromosome 21, PSEN1 on chromosome 14, and PSEN2 on chromosome 1. APP mutations may cause increased generation and aggregation of beta-amyloid peptide, whereas PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations result in aggregation of beta-amyloid by interfering with the processing of gamma-secretase.
APOE is another genetic marker that increases the risk for AD. Isoform e4 of the APOE gene (located on chromosome 19) has been associated with more sporadic and familial forms of AD that present after age 65 years. Approximately 50% of individuals carrying one APOEe4 develop AD, and 90% of individuals who have two alleles develop AD. Variants in the gene for the sortilin receptor, SORT1, have also been found in familial and sporadic forms of AD.
The cognitive and behavioral impairment associated with AD significantly affects a patient's social and occupational functioning. Insidiously progressive memory loss is a characteristic symptoms seen in patients presenting with AD. As the disease advances over the course of several years, other areas of cognition are impaired. Patients may develop language disorders (eg, anomic aphasia or anomia) and impairment in visuospatial skills and executive functions. A slow progression of behavioral changes may also occur in individuals with AD.
Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of AD (eg, insidious onset of cognitive impairment, clear history of worsening symptoms) have been developed and are often used to diagnose patients. In addition, biomarker evidence may help to increase the diagnostic certainty. Several cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers have shown excellent diagnostic ability by identifying tau pathology and cerebral amyloid-beta for AD.
Neuroimaging is becoming increasingly important for identifying the underlying causes of cognitive impairment. Currently, MRI is considered the preferred neuroimaging modality for AD because it allows for accurate measurement of the three-dimensional volume of brain structures, particularly the size of the hippocampus and related regions. CT can be used when MRI is not available or is contraindicated, such as in a patient with a pacemaker. PET is another noninvasive method for depicting tau pathology deposition and distribution in patients with cognitive impairment. In 2020, US Food and Drug Administration approved the first tau PET tracer, 18F-flortaucipir, which marked a significant achievement to improve AD diagnosis.
At present, the only therapies available for AD are symptomatic therapies. Cholinesterase inhibitors and a partial N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist are the standard medical treatments for AD. Antiamyloid therapies are also available for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. These include aducanumab, a first-in-class amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2021, and lecanemab, another amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2023. Both aducanumab and lecanemab are recommended for the treatment of patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which the safety and efficacy of these newer agents were demonstrated in clinical trials.
Secondary symptoms of AD, such as depression, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, delusions, and/or sleep disorders, can be treated with psychotropic agents. Behavioral interventions including patient-centered approaches and caregiver training can also be helpful for managing the cognitive and behavioral manifestations of AD, often in combination with pharmacologic interventions (eg, anxiolytics for anxiety and agitation, neuroleptics for delusions or hallucinations, and antidepressants or mood stabilizers for mood disorders). Regular physical activity and exercise may also play a role in delaying AD progression and possibly conferring a protective effect on brain health.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, Professor of Neurology, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood; Director, Clinical Neurophysiology Lab, Department of Neurology, Hines VA Hospital, Hines, IL.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 72-year-old woman presents with a 12-month history of short-term memory loss. The patient is accompanied by her husband, who states her symptoms have become increasingly frequent and severe. The patient can no longer drive familiar routes after becoming lost on several occasions. She frequently misplaces items; recently, she placed her husband's car keys in the refrigerator. The patient admits to increasing bouts of forgetfulness and confusion and states that she has been feeling very down. She has not been able to watch her grandchildren over the past few months, which makes her feel sad and old. She also reports trouble sleeping at night due to generalized anxiety.
The patient's past medical history is significant for hypertension and dyslipidemia. There is no history of neurotoxic exposure, head injuries, strokes, or seizures. Her family history is positive for dementia. Her older brother was diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease (AD) at age 68 years, and her mother died from AD at age 82 years. Current medications include rosuvastatin 20 mg/d and lisinopril 20 mg/d. The patient's current height and weight are 5 ft 5 in and 163 lb, respectively (BMI is 27.1).
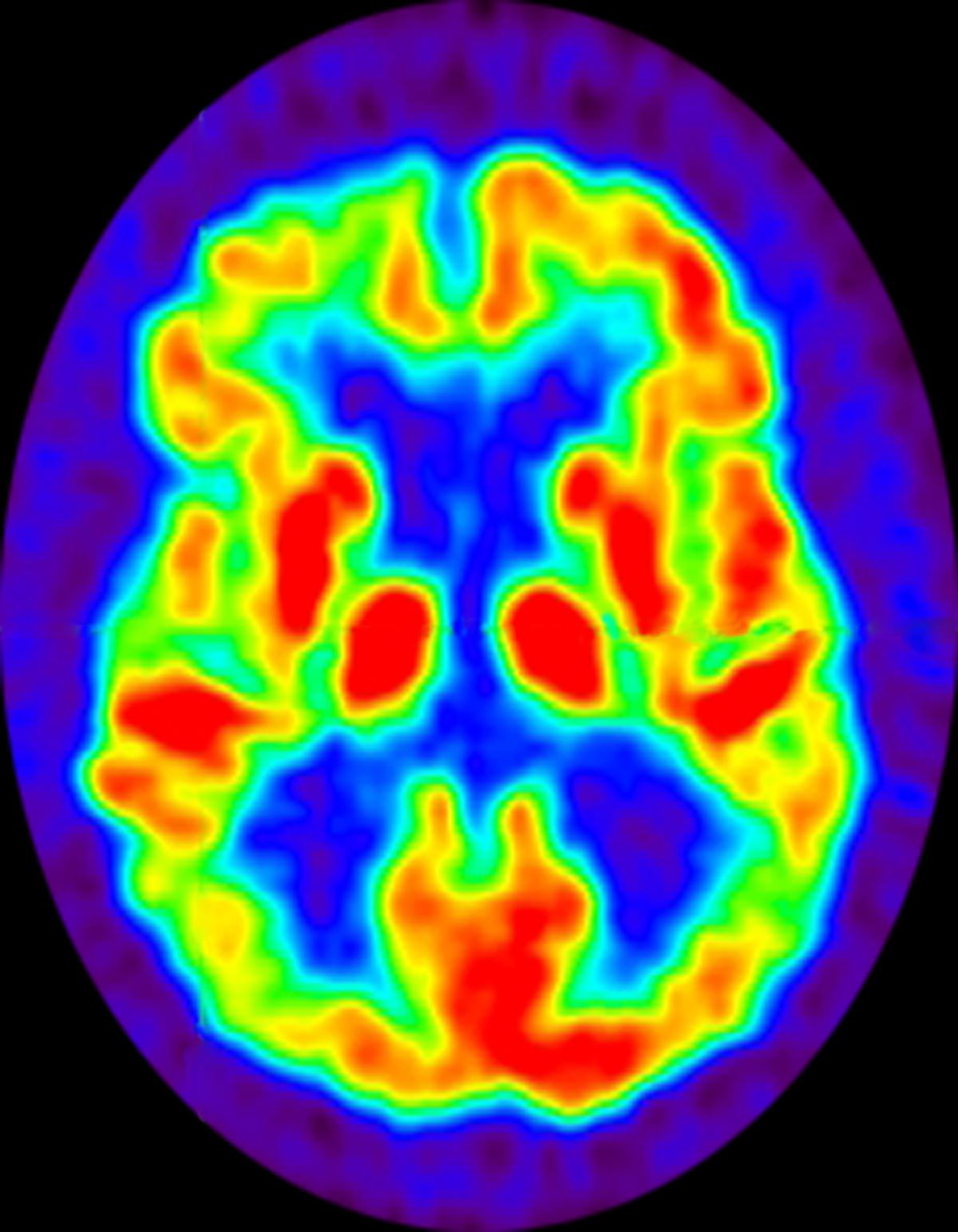
No abnormalities are noted on physical examination; the patient's blood pressure, pulse oximetry, and heart rate are within normal ranges. Laboratory tests are within normal ranges. The patient scores 18 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment test. The patient's clinician orders a brain fluorodeoxyglucose-PET, which reveals areas of decreased glucose metabolism involving the posterior cingulate cortex, precuneus, inferior parietal lobule, and middle temporal gyrus.
Gender and racial biases in Press Ganey patient satisfaction surveys

Patient satisfaction questionnaires were developed in the 1980s as part of the movement to better understand the patient’s experience and their perspective of the quality of care. In 1985, the Press Ganey survey—now the most widely used method to assess patient satisfaction—was developed by 2 professors in anthropology and sociology-statistics at Notre Dame. Initially intended for inpatient admissions, the survey was validated based on a few thousand survey results.1 Given the strong interest in improving patient satisfaction at the time, it became widely adopted and quickly expanded into outpatient encounters and ambulatory surgery settings.
Although other surveys have been developed,2 the Press Ganey survey is the most commonly used assessment tool for patient satisfaction metrics in the United States, with approximately 50% of all hospitals and more than 41,000 health care organizations using its services.3,4 The survey consists of 6 domains related to satisfaction with:
1. the care provider
2. the nurse or assistant
3. personal issues
4. overall assessment
5. access
6. moving through the visit.
Survey items are scored using a 5-point Likert scale, with scores ranging from “very poor” (a score of 1) to “very good” (a score of 5). According to the company, because this format is balanced and parallel (unlike a “poor” to “excellent” format), responses can be quantified and used statistically without violating methodologic assumptions. Also, variability in patients’ responses with this format allows for the identification of opportunities to improve, unlike “yes/no” response formats.1 There are limitations to this design, however, which can impact data quality,5 as we will see.
Adoption of the survey as we move toward value-based care
More recently, patients’ satisfaction with their health care has received increased attention as we move to a patient-centered care model and as health care reimbursement models shift toward value-based care. Current trends in health care policy statements include the importance of raising the standard of care and shifting from a “fee-for-service” to a “pay-for-performance” reimbursement model.7,8 As a result, hospitals are establishing systems to measure “performance” that are not nationally standardized or extensively studied with objective measures. The changing standard of health care expectations in the United States is a topic of much public debate.9 And as expectations and new standards are defined, the impact of implementing novel measures of performance should be evaluated prior to widespread adoption and utilization.
Patient satisfaction also has been identified as a driver for hospital finances through loyalty, described as the “likelihood to return to that system for future medical services.”10,11 This measure has contributed to policy changes that reinforce prioritization of patient satisfaction. For example, the Affordable Care Act tied Medicare reimbursement and patient satisfaction together in the Hospital Value-Based Purchasing Program. This program uses measures of clinical processes, efficiency, outcomes, and patient experiences to calculate a total score that results in hospital reimbursement and incentives,12 which creates a direct pathway from patient experience to reimbursement—underscoring hospitals’ desire for ongoing assessment of patient satisfaction.
In 2005, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the Agency for Health care Research and Quality developed the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Health care Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey in response to criticisms of the Press Ganey survey. The HCAHPS survey consists of 27 questions with 3 broad goals19:
- to produce data about patients’ perspectives of care that allow for objective and meaningful comparisons of hospitals
- to publicly report survey results and create new incentives for hospitals to improve quality of care
- to produce public reports that enhance accountability by increasing transparency.
One difference with the HCAHPS is that it measures frequency, or how often a service was performed (“never”, “sometimes”, “usually”, “always”), whereas Press Ganey measures satisfaction. It also only surveys inpatients and does not address outpatient encounters. Despite the differences, it is a widely used patient satisfaction survey and is subject to similar issues and biases as the Press Ganey survey.
Continue to: Gender, race, and age bias...
Gender, race, and age bias
Although the rationale behind gathering patient input is important, recent data suggest that patient satisfaction surveys are subject to inherent biases.6,13,14 These biases tend to negatively impact women and non-White physicians, adding to the systemic discrimination against women and physicians of color that already exists in health care.
In a single-site retrospective study performed in 2018 by Rogo-Gupta et al, female gynecologists were found to be 47% less likely to receive top patient satisfaction scores than their male counterparts owing to their gender alone, suggesting that gender bias may impact the results of patient satisfaction questionnaires.13 The authors encouraged that the results of patient satisfaction surveys be interpreted with great caution until the impact on female physicians is better understood.
A multi-center study by the same group (Rogo-Gupta et al) assessed the same construct across 5 different geographically diverse institutions.15 This study confirmed that female gynecologists were less likely to receive a top satisfaction score from their patients (19% lower odds when compared with male gynecologists). They also studied the effects of other patient demographics, including age, race/ethnicity, and race concordance. Older patients (aged ≥63 years) had an over-3-fold increase in odds of providing a top satisfaction score than younger patients. Additionally, Asian physicians had significantly lower odds of receiving a top satisfaction score when compared with White physicians, while Asian patients had significantly lower odds of providing a top satisfaction score when compared with White patients. Lastly, in most cases, when underrepresented-in-medicine patients saw an underrepresented-in-medicine physician (race concordance), there was a significant increase in odds of receiving a top satisfaction score. Asian race concordance, however, actually resulted in a lower likelihood of receiving a top satisfaction score.15
Literature from other specialties supports these findings. These results are consistent with emerging data from other medical specialties that also suggest that Press Ganey survey data are subject to inherent biases. For example, data from emergency medicine literature have shown discrepancies between patient satisfaction for providers at tertiary inner-city institutions versus those in affluent suburban populations,16 and that worse mortality is actually correlated with better patient satisfaction scores, and vice versa.17
Another study by Sotto-Santiago in 2019 assessed patient satisfaction scores in multiple specialties at a single institution where quality-related financial incentives were offered based on this metric. They found a significant difference in patient satisfaction scores between underrepresented and White physicians, which suggests a potential bias among patients and institutional practices—ultimately leading to pay inequities through differences in financial incentives.18
Percentile differences reveal small gaps in satisfaction ratings
When examining the difference between raw Press Ganey patient satisfaction data and the percentiles associated with these scores, an interesting finding arises. Looking at the 2023 multicenter study by Rogo-Gupta et al, the difference in the top raw scores between male and female gynecologists appears to be small (3.3%).15 However, in 2020, the difference in top scores separating the top (75th) and bottom (25th) percentile quartiles of physicians was also small, at only 6.9%.
Considering the percentiles, if a provider who scores in the 25th percentile is compared with a colleague who scores in the 75th percentile, they may think the reported satisfaction score differences were quite large. This may potentially invoke feelings of decreased self-worth, negatively impact their professional identity or overall well-being, and they may seek (or be told to seek) improvement opportunities. Now imagine the provider in question realizes the difference between the 25th percentile and 75th percentile is actually only 6.9%. This information may completely change how the results are interpreted and acted upon by administrators. This is further changed with the understanding that 3.3% of the difference may be due to gender alone, narrowing the gap even further. Providers would become understandably frustrated if measures of success such as reimbursement, financial bonus or incentives, promotion, or advancement are linked to these results. It violates the value of fairness and does not offer an equitable starting point.
Evolution of the data distribution. Another consideration, as noted by Robert C. Lloyd, PhD, one of the statisticians who helped develop the percentile statistical analysis mapping in 1985, is that it was based on a classic bell-shaped distribution of patient satisfaction survey scores.19 Because hospitals, medical groups, and physicians have been working these past 20 years to achieve higher Press Ganey scores, the data no longer have a bell-shaped distribution. Rather, there are significant clusters of raw scores at the high end with a very narrow response range. When these data are mapped to the percentile spectrum, they are highly inaccurate.19
Impact of sample size. According to Press Ganey, a minimum of 30 survey responses collected over the designated time period is necessary to draw meaningful conclusions of the data for a specific individual, program, or hospital. Despite this requirement to achieve statistical significance, Sullivan and DeLucia found that the firm often provides comparative data about hospital departments and individual physicians based on a smaller sample size that may create an unacceptably large margin of error.20 Sullivan, for example, said his department may only have 8 to 10 Press Ganey survey responses per month and yet still receives monthly reports from the company analyzing the data. Because of the small sample size, 1 month his department ranked in the 1st percentile and 2 months later it ranked in the 99th percentile.20
The effect of a high ceiling rate. A psychometrics report for the Press Ganey survey is available from the vendor that provides vague assessments of reliability and validity based on 2,762 surveys from 12 practices across 10 states. This report describes a 12-question version of the survey with “no problems encountered” with missingness and response variability. The report further states that the Press Ganey survey demonstrates construct, convergent, divergent, and predictive validities, and high reliability; however, these data are not made available.1
In response to this report, Presson et al analyzed more than 34,000 surveys from one institution to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Press Ganey survey.21 Overall, the survey demonstrated suitable psychometric properties for most metrics. However, Presson et al noted a significantly high ceiling rate of 29.3% for the total score, which ranged from 55.4% to 84.1% across items.21 (Ceiling rates are considered substantial if they occur more than 20% of the time.) Ultimately, a high ceiling rate reduces the power to discriminate between patients who have high satisfaction (everyone is “happy”) with those who are just slightly less than happy, but not dissatisfied. This data quality metric can impact the reliability and validity of a survey—and substantial ceiling rates can notably impact percentile rankings of scores within an institution, offering a possible explanation for the small percentage change between the top and bottom percentiles.
Continue to: Other issues with surveys...
Other issues with surveys
In addition to the limitations associated with percentile groupings, survey data are always subject to nonresponse bias, and small sample size can lead to nonsignificant results. Skewed responses also can make it difficult to identify true outlying providers who may need remediation or may be offering a superior patient experience. Satisfaction surveys also lack an assessment of objective data and instead assess how patients perceive and feel, which introduces subjectivity to the results.
Additionally, focusing on improving patient experience ratings can incentivize unnecessary or inappropriate care (ie, overprescribing of narcotics, prescribing antibiotics when not indicated, or ordering testing that may not change management). Some physicians even state that they are not getting the type of feedback that they are asking for and that the survey is not asking the right questions to elicit patient input that is meaningful to their practice. Lastly, the incorporation of trainees and advanced practice providers in the patient care experience leads to the assessment of an alternative provider being included in the ultimate score and may not be representative of that physician.
Patients’ perception and survey results. In some circumstances, the patient’s understanding of their medical situation may affect their responses. Some may argue that patients may mistake a physician’s confidence for competence, when in reality these two entities are mutually exclusive. In a randomized controlled trial, researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine and Columbia University Medical Center surveyed inner-city women with newly diagnosed and surgically treated early-stage breast cancer for their perceived quality of care and the process of getting care, including referrals, test results, and treatments. They compared the responses with patient records to determine the actual quality of care. Of the 374 women who received treatment for early-stage breast cancer, 55% said they received “excellent care,” but most—88%—actually got care that was in line with the best current treatment guidelines. Interestingly, the study found African American women were less likely to report excellent care than White or Hispanic women, less likely to trust their doctor, and more likely to say they experienced bias during the process. However, there was no difference in actual quality of care received in any group.22
You can’t improve what you can’t control. Ultimately, while many providers think patient satisfaction survey results may help inform some aspects of their practice, they cannot improve what they cannot control. For example, the multicenter study by Rogo-Gupta et al found that older patients (≥63 years) have more than a 3-fold increase in odds of giving a top satisfaction score than younger patients (≤33 years), independent of other aspects of the care experience.15 Additionally, they found that older physicians (≥56 years) had a significant increase in odds of receiving a top satisfaction score when compared with physicians who were younger than 55 years old.15 Given that physicians clearly cannot control their own age or the age of their patients, the negative impacts of these biases need to be addressed and remedied at a systems level.
Why might these biases exist?
While we cannot completely understand all of the possible explanations for these biases, it is important to emphasize the long-standing prejudice and discrimination against women and people of color in our society and how this has impacted our behavior. While strides have been made, there clearly still seems to be a difference between what we say and how our biases impact our behavior. Women are still tougher on women in professional evaluations in other fields as well23; it is not unique to medicine. While workplace improvements are slowly changing, women still face inequities. The more research we publish to describe it, the more we hope the conversation continues, allowing us to reduce the impact of bias on our sense of self-worth and identity related to our careers, narrow the pay gap, and see women advance at the same rate as male counterparts. Considerable transformation is crucial to prevent further workforce attrition.
With regard to the lower scores provided by Asian patients, studies suggest that cultural response bias, rather than true differences in quality of care, may account for these discrepancies. Previous literature has found that Asian patients are more likely to select midpoints, rather than extremes, when completing Likert-type studies24 and are not more likely to change medical providers than other race/ethnicities, indicating that lower ratings may not necessarily imply greater dissatisfaction with care.25
Far-reaching effects on finances, income, well-being, job satisfaction, etc.
Depending on how the results are distributed and used, the effects of patient satisfaction surveys can extend well beyond the original intentions. At some institutions, income for physicians is directly tied to their Press Ganey satisfaction scores, which could have profound implications for female and Asian physicians,13,15 who would be paid less—resulting in a wider pay gap than already exists.18
When negative and not constructive, patient evaluations can contribute to physician burnout and a loss of productive members of the workforce.26 This is especially important in obstetrics and gynecology, where physicians are most likely to experience burnout due to multiple factors such as high-risk medical conditions, pressures of the electronic medical record (EMR), the medicolegal environment, and difficulty balancing patient expectations for autonomy with professional judgement.27 Burnout also disproportionately affects women and younger physicians, which is especially concerning given that, in 2017, approximately one-third of practicing obstetrician/gynecologists were women, while that same year more than 80% of trainees matching into the field were women.28 In one survey sent to members of a prominent medical society, 20% of the medical professionals who responded said they have had their employment threatened by low patient satisfaction scores, 78% reported that patient satisfaction surveys moderately or severely affected their job satisfaction, and 28% stated they had considered quitting their job or leaving the medical profession.29Another related effect is the association between malpractice proceedings and a lack of satisfaction with perceived quality of physician-patient communication.30 This may be an important determinant of malpractice lawsuits, and ensuring high patient satisfaction may be a form of defensive medicine.
Continue to: Controlling the narrative for the future: Proposed strategies...
Controlling the narrative for the future: Proposed strategies
The rapid, widespread adoption of the Press Ganey survey across specialties, clinical care settings, and geographic areas may have been largely due to the ease and operational benefits for hospitals rather than after rigorous study and validation. For example, repeated use of a specific measurement tool may facilitate comparison across areas within a hospital but also across institutions, which can help assess performance at a national level. Hospitals also may have a financial incentive to work with a single third-party or vendor instead of using multiple options across multiple vendors. However, the impact of adoption of novel measures of performance should be evaluated prior to widespread adoption and utilization.
A similar example of an emergence of a technological advancement that has changed the field of medicine and how we provide care is the EMR. Epic is now the most commonly used medical record system and holds the market share of the industry, covering 78% of patients in the United States.31 While there are certainly many potential benefits of a common EMR, such as ease of information sharing and standardization of formatting, opportunities are identified in real time and require product adjustment. For example, modifications have been made to accurately represent gender outside of the previously used dichotomous options. Diagnoses such as cervical cancer screening can now be used even if the patient gender is listed as male.
Similarly, the Press Ganey and other patient satisfaction questionnaires should be evaluated and modified to address existing societal biases. The World Health Organization estimates that it will take 300 years to fix gender inequality,32 but we have an opportunity now to control the narrative and improve patient feedback.
Future research avenues
Ultimately, there is a need to further explore currently available methods of evaluating clinical encounters to better understand the inherent biases and limitations. We hope this review will encourage other physicians to examine their specialties and hospitals and require similar analyses from vendors of such satisfaction rating products prior to using them. At the very least, health systems should be willing to partner with vendors and physicians on an ongoing basis to better understand the biases involved in these survey results and make modifications as needed. Patients also obtain information from and contribute to self-reported, publicly available websites; therefore, additional exploration into a nationalized standard for assessing patient satisfaction also may serve as an opportunity to standardize the information patients evaluate.33 Further assessment of the potential financial and emotional impact of using the currently available patient-reported surveys on female physicians, Asian physicians, young physicians, and physicians who see young patients is needed. It is time to put pressure on a broken patient satisfaction system and improve on a national level to avoid undue negative consequences on our physicians. Use of patient satisfaction survey data should be limited until we all understand and account for the biases that are evident. ●
- Appeal to the Press Ganey corporation with the results of recent data and other studies to ensure they are aware of the biases that exist in their product
- Appeal to hospital-level administration to refrain from using Press Ganey scores as a tool to dictate reimbursement; instead rely on other more objective measures of performance (such as publications, presentations, research accomplishments, patient and surgical outcomes, promotion, committees, national leadership roles, etc)
- Apply a “corrective factor” or “adjustment factor” to eliminate the baseline discrepancy between scores for men and women
- Consider moving to an alternative survey methodology
- Provide patient education to define “performance” (ie, frame what a patient can expect from a provider such as being on time, courteous, and empathetic; caution against asking patients to assess competence and knowledge)
- Outpatient Services (OU) Survey Psychometrics Report. Published online 2019.
- Zusman EE. HCAHPS replaces Press Ganey Survey as quality measure for patient hospital experience. Neurosurgery. 2012;71:N21-N24. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000417536.07871.ed
- Press Ganey. Company. Accessed April 20, 2023. www.pressganey. com/company/
- Press, Ganey--first year of patient satisfaction measurement. Hosp Guest Relations Rep. 1986;1:4-5.
- DeCastellarnau A. A classification of response scale characteristics that affect data quality: a literature review. Qual Quant. 2018;52:15231559. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0533-4
- Tyser AR, Abtahi AM, McFadden M, et al. Evidence of non-response bias in the Press-Ganey patient satisfaction survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:350. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1595-z
- Duseja R, Durham M, Schreiber M. CMS quality measure development. JAMA. 2020;324:1213-1214. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12070
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. National Academies Press; 2001. doi: 10.17226/10027
- Parmet WE. Health: policy or law? A population-based analysis of the Supreme Court’s ACA cases. J Health Polit Policy Law. 2016;41:10611081. doi: 10.1215/03616878-3665949
- Richter JP, Muhlestein DB. Patient experience and hospital profitability: is there a link? Health Care Manage Rev. 2017;42:247-257. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000105
- Huang C-H, Wu H-H, Lee Y-C, et al. What role does patient gratitude play in the relationship between relationship quality and patient loyalty? Inquiry. 2019;56:46958019868324. doi: 10.1177/0046958019868324
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), HHS. Medicare program; hospital inpatient value-based purchasing program. Final rule. Fed Regist. 2011;76:26490-26547.
- Rogo-Gupta LJ, Haunschild C, Altamirano J, et al. Physician gender is associated with Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores in outpatient gynecology. Womens Health Issues. 2018;28:281-285. doi: 10.1016 /j.whi.2018.01.001
- DeLoughery EP. Physician race and specialty influence Press Ganey survey results. Neth J Med. 2019;77:366-369.
- Homewood L, Altamirano J, Fassiotto M, et al. Women gynecologists receive lower Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores in a multicenter cross-sectional study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;228:S801. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.12.025
- Sharp B, Johnson J, Hamedani AG, et al. What are we measuring? Evaluating physician-specific satisfaction scores between emergency departments. West J Emerg Med. 2019;20:454-459. doi: 10.5811 /westjem.2019.4.41040
- Mosley M. Viewpoint: Press Ganey is a worthless tool for the ED. Emerg Med News. 2019;41:3-4. doi: 10.1097/01.EEM.0000616512.68475.69
- Sotto-Santiago S, Slaven JE, Rohr-Kirchgraber T. (Dis)Incentivizing patient satisfaction metrics: the unintended consequences of institutional bias. Health Equity. 2019;3:13-18. doi: 10.1089/heq.2018.0065
- Lloyd RC. Quality Health Care: A Guide to Developing and Using Indicators. 2nd ed. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2019. Accessed April 23, 2023. www.jblearning.com/catalog/productdetails /9781284023077
- 2+2=7? Seven things you may not know about Press Ganey statistics. Emergency Physicians Monthly. Accessed April 23, 2023. epmonthly. com/article/227-seven-things-you-may-not-know-about-pressgainey-statistics/
- Presson AP, Zhang C, Abtahi AM, et al. Psychometric properties of the Press Ganey® Outpatient Medical Practice Survey. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15:32. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0610-3
- Bickell NA, Neuman J, Fei K, et al. Quality of breast cancer care: perception versus practice. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1791-1795. doi: 10.1200 /JCO.2011.38.7605
- Strauss K. Women in the workplace: are women tougher on other women? Forbes. July 18, 2016. Accessed April 27, 2023. www.forbes. com/sites/karstenstrauss/2016/07/18/women-in-the-workplace -are-women-tougher-on-other-women/
- Lee JW, Jones PS, Mineyama Y, et al. Cultural differences in responses to a Likert scale. Res Nurs Health. 2002;25:295-306. doi: 10.1002 /nur.10041
- Saha S, Hickam DH. Explaining low ratings of patient satisfaction among Asian-Americans. Am J Med Qual. 2003;18:256-264. doi: 10.1177/106286060301800606
- Halbesleben JRB, Rathert C. Linking physician burnout and patient outcomes: exploring the dyadic relationship between physicians and patients. Health Care Manage Rev. 2008;33:29-39. doi: 10.1097/01. HMR.0000304493.87898.72
- Bradford L, Glaser G. Addressing physician burnout and ensuring high-quality care of the physician workforce. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137:3-11. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004197
- Boyle P. Nation’s physician workforce evolves: more women, a bit older, and toward different specialties. AAMCNEWS. February 2, 2021. Accessed April 20, 2023. www.aamc.org/news-insights/nations-physician-workforce-evolves-more-women-bit-older-and-towarddifferent-specialties
- Zgierska A, Rabago D, Miller MM. Impact of patient satisfaction ratings on physicians and clinical care. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:437-446. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S59077
- Yeh J, Nagel EE. Patient satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology: individualized patient-centered communication. Clin Med Insights Womens Health. 2010;3:23. doi: 10.4137/CMWH.S5870
- Epic. About us. Accessed April 19, 2023. www.epic.com/about
- United Nations. Without investment, gender equality will take nearly 300 years: UN report. September 7, 2022. Accessed April 19, 2023. news.un.org/en/story/2022/09/1126171
- Ryan T, Specht J, Smith S, et al. Does the Press Ganey Survey correlate to online health grades for a major academic otolaryngology department? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;155:411-415. doi: 10.1177/0194599816652386

Patient satisfaction questionnaires were developed in the 1980s as part of the movement to better understand the patient’s experience and their perspective of the quality of care. In 1985, the Press Ganey survey—now the most widely used method to assess patient satisfaction—was developed by 2 professors in anthropology and sociology-statistics at Notre Dame. Initially intended for inpatient admissions, the survey was validated based on a few thousand survey results.1 Given the strong interest in improving patient satisfaction at the time, it became widely adopted and quickly expanded into outpatient encounters and ambulatory surgery settings.
Although other surveys have been developed,2 the Press Ganey survey is the most commonly used assessment tool for patient satisfaction metrics in the United States, with approximately 50% of all hospitals and more than 41,000 health care organizations using its services.3,4 The survey consists of 6 domains related to satisfaction with:
1. the care provider
2. the nurse or assistant
3. personal issues
4. overall assessment
5. access
6. moving through the visit.
Survey items are scored using a 5-point Likert scale, with scores ranging from “very poor” (a score of 1) to “very good” (a score of 5). According to the company, because this format is balanced and parallel (unlike a “poor” to “excellent” format), responses can be quantified and used statistically without violating methodologic assumptions. Also, variability in patients’ responses with this format allows for the identification of opportunities to improve, unlike “yes/no” response formats.1 There are limitations to this design, however, which can impact data quality,5 as we will see.
Adoption of the survey as we move toward value-based care
More recently, patients’ satisfaction with their health care has received increased attention as we move to a patient-centered care model and as health care reimbursement models shift toward value-based care. Current trends in health care policy statements include the importance of raising the standard of care and shifting from a “fee-for-service” to a “pay-for-performance” reimbursement model.7,8 As a result, hospitals are establishing systems to measure “performance” that are not nationally standardized or extensively studied with objective measures. The changing standard of health care expectations in the United States is a topic of much public debate.9 And as expectations and new standards are defined, the impact of implementing novel measures of performance should be evaluated prior to widespread adoption and utilization.
Patient satisfaction also has been identified as a driver for hospital finances through loyalty, described as the “likelihood to return to that system for future medical services.”10,11 This measure has contributed to policy changes that reinforce prioritization of patient satisfaction. For example, the Affordable Care Act tied Medicare reimbursement and patient satisfaction together in the Hospital Value-Based Purchasing Program. This program uses measures of clinical processes, efficiency, outcomes, and patient experiences to calculate a total score that results in hospital reimbursement and incentives,12 which creates a direct pathway from patient experience to reimbursement—underscoring hospitals’ desire for ongoing assessment of patient satisfaction.
In 2005, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the Agency for Health care Research and Quality developed the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Health care Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey in response to criticisms of the Press Ganey survey. The HCAHPS survey consists of 27 questions with 3 broad goals19:
- to produce data about patients’ perspectives of care that allow for objective and meaningful comparisons of hospitals
- to publicly report survey results and create new incentives for hospitals to improve quality of care
- to produce public reports that enhance accountability by increasing transparency.
One difference with the HCAHPS is that it measures frequency, or how often a service was performed (“never”, “sometimes”, “usually”, “always”), whereas Press Ganey measures satisfaction. It also only surveys inpatients and does not address outpatient encounters. Despite the differences, it is a widely used patient satisfaction survey and is subject to similar issues and biases as the Press Ganey survey.
Continue to: Gender, race, and age bias...
Gender, race, and age bias
Although the rationale behind gathering patient input is important, recent data suggest that patient satisfaction surveys are subject to inherent biases.6,13,14 These biases tend to negatively impact women and non-White physicians, adding to the systemic discrimination against women and physicians of color that already exists in health care.
In a single-site retrospective study performed in 2018 by Rogo-Gupta et al, female gynecologists were found to be 47% less likely to receive top patient satisfaction scores than their male counterparts owing to their gender alone, suggesting that gender bias may impact the results of patient satisfaction questionnaires.13 The authors encouraged that the results of patient satisfaction surveys be interpreted with great caution until the impact on female physicians is better understood.
A multi-center study by the same group (Rogo-Gupta et al) assessed the same construct across 5 different geographically diverse institutions.15 This study confirmed that female gynecologists were less likely to receive a top satisfaction score from their patients (19% lower odds when compared with male gynecologists). They also studied the effects of other patient demographics, including age, race/ethnicity, and race concordance. Older patients (aged ≥63 years) had an over-3-fold increase in odds of providing a top satisfaction score than younger patients. Additionally, Asian physicians had significantly lower odds of receiving a top satisfaction score when compared with White physicians, while Asian patients had significantly lower odds of providing a top satisfaction score when compared with White patients. Lastly, in most cases, when underrepresented-in-medicine patients saw an underrepresented-in-medicine physician (race concordance), there was a significant increase in odds of receiving a top satisfaction score. Asian race concordance, however, actually resulted in a lower likelihood of receiving a top satisfaction score.15
Literature from other specialties supports these findings. These results are consistent with emerging data from other medical specialties that also suggest that Press Ganey survey data are subject to inherent biases. For example, data from emergency medicine literature have shown discrepancies between patient satisfaction for providers at tertiary inner-city institutions versus those in affluent suburban populations,16 and that worse mortality is actually correlated with better patient satisfaction scores, and vice versa.17
Another study by Sotto-Santiago in 2019 assessed patient satisfaction scores in multiple specialties at a single institution where quality-related financial incentives were offered based on this metric. They found a significant difference in patient satisfaction scores between underrepresented and White physicians, which suggests a potential bias among patients and institutional practices—ultimately leading to pay inequities through differences in financial incentives.18
Percentile differences reveal small gaps in satisfaction ratings
When examining the difference between raw Press Ganey patient satisfaction data and the percentiles associated with these scores, an interesting finding arises. Looking at the 2023 multicenter study by Rogo-Gupta et al, the difference in the top raw scores between male and female gynecologists appears to be small (3.3%).15 However, in 2020, the difference in top scores separating the top (75th) and bottom (25th) percentile quartiles of physicians was also small, at only 6.9%.
Considering the percentiles, if a provider who scores in the 25th percentile is compared with a colleague who scores in the 75th percentile, they may think the reported satisfaction score differences were quite large. This may potentially invoke feelings of decreased self-worth, negatively impact their professional identity or overall well-being, and they may seek (or be told to seek) improvement opportunities. Now imagine the provider in question realizes the difference between the 25th percentile and 75th percentile is actually only 6.9%. This information may completely change how the results are interpreted and acted upon by administrators. This is further changed with the understanding that 3.3% of the difference may be due to gender alone, narrowing the gap even further. Providers would become understandably frustrated if measures of success such as reimbursement, financial bonus or incentives, promotion, or advancement are linked to these results. It violates the value of fairness and does not offer an equitable starting point.
Evolution of the data distribution. Another consideration, as noted by Robert C. Lloyd, PhD, one of the statisticians who helped develop the percentile statistical analysis mapping in 1985, is that it was based on a classic bell-shaped distribution of patient satisfaction survey scores.19 Because hospitals, medical groups, and physicians have been working these past 20 years to achieve higher Press Ganey scores, the data no longer have a bell-shaped distribution. Rather, there are significant clusters of raw scores at the high end with a very narrow response range. When these data are mapped to the percentile spectrum, they are highly inaccurate.19
Impact of sample size. According to Press Ganey, a minimum of 30 survey responses collected over the designated time period is necessary to draw meaningful conclusions of the data for a specific individual, program, or hospital. Despite this requirement to achieve statistical significance, Sullivan and DeLucia found that the firm often provides comparative data about hospital departments and individual physicians based on a smaller sample size that may create an unacceptably large margin of error.20 Sullivan, for example, said his department may only have 8 to 10 Press Ganey survey responses per month and yet still receives monthly reports from the company analyzing the data. Because of the small sample size, 1 month his department ranked in the 1st percentile and 2 months later it ranked in the 99th percentile.20
The effect of a high ceiling rate. A psychometrics report for the Press Ganey survey is available from the vendor that provides vague assessments of reliability and validity based on 2,762 surveys from 12 practices across 10 states. This report describes a 12-question version of the survey with “no problems encountered” with missingness and response variability. The report further states that the Press Ganey survey demonstrates construct, convergent, divergent, and predictive validities, and high reliability; however, these data are not made available.1
In response to this report, Presson et al analyzed more than 34,000 surveys from one institution to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Press Ganey survey.21 Overall, the survey demonstrated suitable psychometric properties for most metrics. However, Presson et al noted a significantly high ceiling rate of 29.3% for the total score, which ranged from 55.4% to 84.1% across items.21 (Ceiling rates are considered substantial if they occur more than 20% of the time.) Ultimately, a high ceiling rate reduces the power to discriminate between patients who have high satisfaction (everyone is “happy”) with those who are just slightly less than happy, but not dissatisfied. This data quality metric can impact the reliability and validity of a survey—and substantial ceiling rates can notably impact percentile rankings of scores within an institution, offering a possible explanation for the small percentage change between the top and bottom percentiles.
Continue to: Other issues with surveys...
Other issues with surveys
In addition to the limitations associated with percentile groupings, survey data are always subject to nonresponse bias, and small sample size can lead to nonsignificant results. Skewed responses also can make it difficult to identify true outlying providers who may need remediation or may be offering a superior patient experience. Satisfaction surveys also lack an assessment of objective data and instead assess how patients perceive and feel, which introduces subjectivity to the results.
Additionally, focusing on improving patient experience ratings can incentivize unnecessary or inappropriate care (ie, overprescribing of narcotics, prescribing antibiotics when not indicated, or ordering testing that may not change management). Some physicians even state that they are not getting the type of feedback that they are asking for and that the survey is not asking the right questions to elicit patient input that is meaningful to their practice. Lastly, the incorporation of trainees and advanced practice providers in the patient care experience leads to the assessment of an alternative provider being included in the ultimate score and may not be representative of that physician.
Patients’ perception and survey results. In some circumstances, the patient’s understanding of their medical situation may affect their responses. Some may argue that patients may mistake a physician’s confidence for competence, when in reality these two entities are mutually exclusive. In a randomized controlled trial, researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine and Columbia University Medical Center surveyed inner-city women with newly diagnosed and surgically treated early-stage breast cancer for their perceived quality of care and the process of getting care, including referrals, test results, and treatments. They compared the responses with patient records to determine the actual quality of care. Of the 374 women who received treatment for early-stage breast cancer, 55% said they received “excellent care,” but most—88%—actually got care that was in line with the best current treatment guidelines. Interestingly, the study found African American women were less likely to report excellent care than White or Hispanic women, less likely to trust their doctor, and more likely to say they experienced bias during the process. However, there was no difference in actual quality of care received in any group.22
You can’t improve what you can’t control. Ultimately, while many providers think patient satisfaction survey results may help inform some aspects of their practice, they cannot improve what they cannot control. For example, the multicenter study by Rogo-Gupta et al found that older patients (≥63 years) have more than a 3-fold increase in odds of giving a top satisfaction score than younger patients (≤33 years), independent of other aspects of the care experience.15 Additionally, they found that older physicians (≥56 years) had a significant increase in odds of receiving a top satisfaction score when compared with physicians who were younger than 55 years old.15 Given that physicians clearly cannot control their own age or the age of their patients, the negative impacts of these biases need to be addressed and remedied at a systems level.
Why might these biases exist?
While we cannot completely understand all of the possible explanations for these biases, it is important to emphasize the long-standing prejudice and discrimination against women and people of color in our society and how this has impacted our behavior. While strides have been made, there clearly still seems to be a difference between what we say and how our biases impact our behavior. Women are still tougher on women in professional evaluations in other fields as well23; it is not unique to medicine. While workplace improvements are slowly changing, women still face inequities. The more research we publish to describe it, the more we hope the conversation continues, allowing us to reduce the impact of bias on our sense of self-worth and identity related to our careers, narrow the pay gap, and see women advance at the same rate as male counterparts. Considerable transformation is crucial to prevent further workforce attrition.
With regard to the lower scores provided by Asian patients, studies suggest that cultural response bias, rather than true differences in quality of care, may account for these discrepancies. Previous literature has found that Asian patients are more likely to select midpoints, rather than extremes, when completing Likert-type studies24 and are not more likely to change medical providers than other race/ethnicities, indicating that lower ratings may not necessarily imply greater dissatisfaction with care.25
Far-reaching effects on finances, income, well-being, job satisfaction, etc.
Depending on how the results are distributed and used, the effects of patient satisfaction surveys can extend well beyond the original intentions. At some institutions, income for physicians is directly tied to their Press Ganey satisfaction scores, which could have profound implications for female and Asian physicians,13,15 who would be paid less—resulting in a wider pay gap than already exists.18
When negative and not constructive, patient evaluations can contribute to physician burnout and a loss of productive members of the workforce.26 This is especially important in obstetrics and gynecology, where physicians are most likely to experience burnout due to multiple factors such as high-risk medical conditions, pressures of the electronic medical record (EMR), the medicolegal environment, and difficulty balancing patient expectations for autonomy with professional judgement.27 Burnout also disproportionately affects women and younger physicians, which is especially concerning given that, in 2017, approximately one-third of practicing obstetrician/gynecologists were women, while that same year more than 80% of trainees matching into the field were women.28 In one survey sent to members of a prominent medical society, 20% of the medical professionals who responded said they have had their employment threatened by low patient satisfaction scores, 78% reported that patient satisfaction surveys moderately or severely affected their job satisfaction, and 28% stated they had considered quitting their job or leaving the medical profession.29Another related effect is the association between malpractice proceedings and a lack of satisfaction with perceived quality of physician-patient communication.30 This may be an important determinant of malpractice lawsuits, and ensuring high patient satisfaction may be a form of defensive medicine.
Continue to: Controlling the narrative for the future: Proposed strategies...
Controlling the narrative for the future: Proposed strategies
The rapid, widespread adoption of the Press Ganey survey across specialties, clinical care settings, and geographic areas may have been largely due to the ease and operational benefits for hospitals rather than after rigorous study and validation. For example, repeated use of a specific measurement tool may facilitate comparison across areas within a hospital but also across institutions, which can help assess performance at a national level. Hospitals also may have a financial incentive to work with a single third-party or vendor instead of using multiple options across multiple vendors. However, the impact of adoption of novel measures of performance should be evaluated prior to widespread adoption and utilization.
A similar example of an emergence of a technological advancement that has changed the field of medicine and how we provide care is the EMR. Epic is now the most commonly used medical record system and holds the market share of the industry, covering 78% of patients in the United States.31 While there are certainly many potential benefits of a common EMR, such as ease of information sharing and standardization of formatting, opportunities are identified in real time and require product adjustment. For example, modifications have been made to accurately represent gender outside of the previously used dichotomous options. Diagnoses such as cervical cancer screening can now be used even if the patient gender is listed as male.
Similarly, the Press Ganey and other patient satisfaction questionnaires should be evaluated and modified to address existing societal biases. The World Health Organization estimates that it will take 300 years to fix gender inequality,32 but we have an opportunity now to control the narrative and improve patient feedback.
Future research avenues
Ultimately, there is a need to further explore currently available methods of evaluating clinical encounters to better understand the inherent biases and limitations. We hope this review will encourage other physicians to examine their specialties and hospitals and require similar analyses from vendors of such satisfaction rating products prior to using them. At the very least, health systems should be willing to partner with vendors and physicians on an ongoing basis to better understand the biases involved in these survey results and make modifications as needed. Patients also obtain information from and contribute to self-reported, publicly available websites; therefore, additional exploration into a nationalized standard for assessing patient satisfaction also may serve as an opportunity to standardize the information patients evaluate.33 Further assessment of the potential financial and emotional impact of using the currently available patient-reported surveys on female physicians, Asian physicians, young physicians, and physicians who see young patients is needed. It is time to put pressure on a broken patient satisfaction system and improve on a national level to avoid undue negative consequences on our physicians. Use of patient satisfaction survey data should be limited until we all understand and account for the biases that are evident. ●
- Appeal to the Press Ganey corporation with the results of recent data and other studies to ensure they are aware of the biases that exist in their product
- Appeal to hospital-level administration to refrain from using Press Ganey scores as a tool to dictate reimbursement; instead rely on other more objective measures of performance (such as publications, presentations, research accomplishments, patient and surgical outcomes, promotion, committees, national leadership roles, etc)
- Apply a “corrective factor” or “adjustment factor” to eliminate the baseline discrepancy between scores for men and women
- Consider moving to an alternative survey methodology
- Provide patient education to define “performance” (ie, frame what a patient can expect from a provider such as being on time, courteous, and empathetic; caution against asking patients to assess competence and knowledge)

Patient satisfaction questionnaires were developed in the 1980s as part of the movement to better understand the patient’s experience and their perspective of the quality of care. In 1985, the Press Ganey survey—now the most widely used method to assess patient satisfaction—was developed by 2 professors in anthropology and sociology-statistics at Notre Dame. Initially intended for inpatient admissions, the survey was validated based on a few thousand survey results.1 Given the strong interest in improving patient satisfaction at the time, it became widely adopted and quickly expanded into outpatient encounters and ambulatory surgery settings.
Although other surveys have been developed,2 the Press Ganey survey is the most commonly used assessment tool for patient satisfaction metrics in the United States, with approximately 50% of all hospitals and more than 41,000 health care organizations using its services.3,4 The survey consists of 6 domains related to satisfaction with:
1. the care provider
2. the nurse or assistant
3. personal issues
4. overall assessment
5. access
6. moving through the visit.
Survey items are scored using a 5-point Likert scale, with scores ranging from “very poor” (a score of 1) to “very good” (a score of 5). According to the company, because this format is balanced and parallel (unlike a “poor” to “excellent” format), responses can be quantified and used statistically without violating methodologic assumptions. Also, variability in patients’ responses with this format allows for the identification of opportunities to improve, unlike “yes/no” response formats.1 There are limitations to this design, however, which can impact data quality,5 as we will see.
Adoption of the survey as we move toward value-based care
More recently, patients’ satisfaction with their health care has received increased attention as we move to a patient-centered care model and as health care reimbursement models shift toward value-based care. Current trends in health care policy statements include the importance of raising the standard of care and shifting from a “fee-for-service” to a “pay-for-performance” reimbursement model.7,8 As a result, hospitals are establishing systems to measure “performance” that are not nationally standardized or extensively studied with objective measures. The changing standard of health care expectations in the United States is a topic of much public debate.9 And as expectations and new standards are defined, the impact of implementing novel measures of performance should be evaluated prior to widespread adoption and utilization.
Patient satisfaction also has been identified as a driver for hospital finances through loyalty, described as the “likelihood to return to that system for future medical services.”10,11 This measure has contributed to policy changes that reinforce prioritization of patient satisfaction. For example, the Affordable Care Act tied Medicare reimbursement and patient satisfaction together in the Hospital Value-Based Purchasing Program. This program uses measures of clinical processes, efficiency, outcomes, and patient experiences to calculate a total score that results in hospital reimbursement and incentives,12 which creates a direct pathway from patient experience to reimbursement—underscoring hospitals’ desire for ongoing assessment of patient satisfaction.
In 2005, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the Agency for Health care Research and Quality developed the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Health care Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey in response to criticisms of the Press Ganey survey. The HCAHPS survey consists of 27 questions with 3 broad goals19:
- to produce data about patients’ perspectives of care that allow for objective and meaningful comparisons of hospitals
- to publicly report survey results and create new incentives for hospitals to improve quality of care
- to produce public reports that enhance accountability by increasing transparency.
One difference with the HCAHPS is that it measures frequency, or how often a service was performed (“never”, “sometimes”, “usually”, “always”), whereas Press Ganey measures satisfaction. It also only surveys inpatients and does not address outpatient encounters. Despite the differences, it is a widely used patient satisfaction survey and is subject to similar issues and biases as the Press Ganey survey.
Continue to: Gender, race, and age bias...
Gender, race, and age bias
Although the rationale behind gathering patient input is important, recent data suggest that patient satisfaction surveys are subject to inherent biases.6,13,14 These biases tend to negatively impact women and non-White physicians, adding to the systemic discrimination against women and physicians of color that already exists in health care.
In a single-site retrospective study performed in 2018 by Rogo-Gupta et al, female gynecologists were found to be 47% less likely to receive top patient satisfaction scores than their male counterparts owing to their gender alone, suggesting that gender bias may impact the results of patient satisfaction questionnaires.13 The authors encouraged that the results of patient satisfaction surveys be interpreted with great caution until the impact on female physicians is better understood.
A multi-center study by the same group (Rogo-Gupta et al) assessed the same construct across 5 different geographically diverse institutions.15 This study confirmed that female gynecologists were less likely to receive a top satisfaction score from their patients (19% lower odds when compared with male gynecologists). They also studied the effects of other patient demographics, including age, race/ethnicity, and race concordance. Older patients (aged ≥63 years) had an over-3-fold increase in odds of providing a top satisfaction score than younger patients. Additionally, Asian physicians had significantly lower odds of receiving a top satisfaction score when compared with White physicians, while Asian patients had significantly lower odds of providing a top satisfaction score when compared with White patients. Lastly, in most cases, when underrepresented-in-medicine patients saw an underrepresented-in-medicine physician (race concordance), there was a significant increase in odds of receiving a top satisfaction score. Asian race concordance, however, actually resulted in a lower likelihood of receiving a top satisfaction score.15
Literature from other specialties supports these findings. These results are consistent with emerging data from other medical specialties that also suggest that Press Ganey survey data are subject to inherent biases. For example, data from emergency medicine literature have shown discrepancies between patient satisfaction for providers at tertiary inner-city institutions versus those in affluent suburban populations,16 and that worse mortality is actually correlated with better patient satisfaction scores, and vice versa.17
Another study by Sotto-Santiago in 2019 assessed patient satisfaction scores in multiple specialties at a single institution where quality-related financial incentives were offered based on this metric. They found a significant difference in patient satisfaction scores between underrepresented and White physicians, which suggests a potential bias among patients and institutional practices—ultimately leading to pay inequities through differences in financial incentives.18
Percentile differences reveal small gaps in satisfaction ratings
When examining the difference between raw Press Ganey patient satisfaction data and the percentiles associated with these scores, an interesting finding arises. Looking at the 2023 multicenter study by Rogo-Gupta et al, the difference in the top raw scores between male and female gynecologists appears to be small (3.3%).15 However, in 2020, the difference in top scores separating the top (75th) and bottom (25th) percentile quartiles of physicians was also small, at only 6.9%.
Considering the percentiles, if a provider who scores in the 25th percentile is compared with a colleague who scores in the 75th percentile, they may think the reported satisfaction score differences were quite large. This may potentially invoke feelings of decreased self-worth, negatively impact their professional identity or overall well-being, and they may seek (or be told to seek) improvement opportunities. Now imagine the provider in question realizes the difference between the 25th percentile and 75th percentile is actually only 6.9%. This information may completely change how the results are interpreted and acted upon by administrators. This is further changed with the understanding that 3.3% of the difference may be due to gender alone, narrowing the gap even further. Providers would become understandably frustrated if measures of success such as reimbursement, financial bonus or incentives, promotion, or advancement are linked to these results. It violates the value of fairness and does not offer an equitable starting point.
Evolution of the data distribution. Another consideration, as noted by Robert C. Lloyd, PhD, one of the statisticians who helped develop the percentile statistical analysis mapping in 1985, is that it was based on a classic bell-shaped distribution of patient satisfaction survey scores.19 Because hospitals, medical groups, and physicians have been working these past 20 years to achieve higher Press Ganey scores, the data no longer have a bell-shaped distribution. Rather, there are significant clusters of raw scores at the high end with a very narrow response range. When these data are mapped to the percentile spectrum, they are highly inaccurate.19
Impact of sample size. According to Press Ganey, a minimum of 30 survey responses collected over the designated time period is necessary to draw meaningful conclusions of the data for a specific individual, program, or hospital. Despite this requirement to achieve statistical significance, Sullivan and DeLucia found that the firm often provides comparative data about hospital departments and individual physicians based on a smaller sample size that may create an unacceptably large margin of error.20 Sullivan, for example, said his department may only have 8 to 10 Press Ganey survey responses per month and yet still receives monthly reports from the company analyzing the data. Because of the small sample size, 1 month his department ranked in the 1st percentile and 2 months later it ranked in the 99th percentile.20
The effect of a high ceiling rate. A psychometrics report for the Press Ganey survey is available from the vendor that provides vague assessments of reliability and validity based on 2,762 surveys from 12 practices across 10 states. This report describes a 12-question version of the survey with “no problems encountered” with missingness and response variability. The report further states that the Press Ganey survey demonstrates construct, convergent, divergent, and predictive validities, and high reliability; however, these data are not made available.1
In response to this report, Presson et al analyzed more than 34,000 surveys from one institution to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Press Ganey survey.21 Overall, the survey demonstrated suitable psychometric properties for most metrics. However, Presson et al noted a significantly high ceiling rate of 29.3% for the total score, which ranged from 55.4% to 84.1% across items.21 (Ceiling rates are considered substantial if they occur more than 20% of the time.) Ultimately, a high ceiling rate reduces the power to discriminate between patients who have high satisfaction (everyone is “happy”) with those who are just slightly less than happy, but not dissatisfied. This data quality metric can impact the reliability and validity of a survey—and substantial ceiling rates can notably impact percentile rankings of scores within an institution, offering a possible explanation for the small percentage change between the top and bottom percentiles.
Continue to: Other issues with surveys...
Other issues with surveys
In addition to the limitations associated with percentile groupings, survey data are always subject to nonresponse bias, and small sample size can lead to nonsignificant results. Skewed responses also can make it difficult to identify true outlying providers who may need remediation or may be offering a superior patient experience. Satisfaction surveys also lack an assessment of objective data and instead assess how patients perceive and feel, which introduces subjectivity to the results.
Additionally, focusing on improving patient experience ratings can incentivize unnecessary or inappropriate care (ie, overprescribing of narcotics, prescribing antibiotics when not indicated, or ordering testing that may not change management). Some physicians even state that they are not getting the type of feedback that they are asking for and that the survey is not asking the right questions to elicit patient input that is meaningful to their practice. Lastly, the incorporation of trainees and advanced practice providers in the patient care experience leads to the assessment of an alternative provider being included in the ultimate score and may not be representative of that physician.
Patients’ perception and survey results. In some circumstances, the patient’s understanding of their medical situation may affect their responses. Some may argue that patients may mistake a physician’s confidence for competence, when in reality these two entities are mutually exclusive. In a randomized controlled trial, researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine and Columbia University Medical Center surveyed inner-city women with newly diagnosed and surgically treated early-stage breast cancer for their perceived quality of care and the process of getting care, including referrals, test results, and treatments. They compared the responses with patient records to determine the actual quality of care. Of the 374 women who received treatment for early-stage breast cancer, 55% said they received “excellent care,” but most—88%—actually got care that was in line with the best current treatment guidelines. Interestingly, the study found African American women were less likely to report excellent care than White or Hispanic women, less likely to trust their doctor, and more likely to say they experienced bias during the process. However, there was no difference in actual quality of care received in any group.22
You can’t improve what you can’t control. Ultimately, while many providers think patient satisfaction survey results may help inform some aspects of their practice, they cannot improve what they cannot control. For example, the multicenter study by Rogo-Gupta et al found that older patients (≥63 years) have more than a 3-fold increase in odds of giving a top satisfaction score than younger patients (≤33 years), independent of other aspects of the care experience.15 Additionally, they found that older physicians (≥56 years) had a significant increase in odds of receiving a top satisfaction score when compared with physicians who were younger than 55 years old.15 Given that physicians clearly cannot control their own age or the age of their patients, the negative impacts of these biases need to be addressed and remedied at a systems level.
Why might these biases exist?
While we cannot completely understand all of the possible explanations for these biases, it is important to emphasize the long-standing prejudice and discrimination against women and people of color in our society and how this has impacted our behavior. While strides have been made, there clearly still seems to be a difference between what we say and how our biases impact our behavior. Women are still tougher on women in professional evaluations in other fields as well23; it is not unique to medicine. While workplace improvements are slowly changing, women still face inequities. The more research we publish to describe it, the more we hope the conversation continues, allowing us to reduce the impact of bias on our sense of self-worth and identity related to our careers, narrow the pay gap, and see women advance at the same rate as male counterparts. Considerable transformation is crucial to prevent further workforce attrition.
With regard to the lower scores provided by Asian patients, studies suggest that cultural response bias, rather than true differences in quality of care, may account for these discrepancies. Previous literature has found that Asian patients are more likely to select midpoints, rather than extremes, when completing Likert-type studies24 and are not more likely to change medical providers than other race/ethnicities, indicating that lower ratings may not necessarily imply greater dissatisfaction with care.25
Far-reaching effects on finances, income, well-being, job satisfaction, etc.
Depending on how the results are distributed and used, the effects of patient satisfaction surveys can extend well beyond the original intentions. At some institutions, income for physicians is directly tied to their Press Ganey satisfaction scores, which could have profound implications for female and Asian physicians,13,15 who would be paid less—resulting in a wider pay gap than already exists.18
When negative and not constructive, patient evaluations can contribute to physician burnout and a loss of productive members of the workforce.26 This is especially important in obstetrics and gynecology, where physicians are most likely to experience burnout due to multiple factors such as high-risk medical conditions, pressures of the electronic medical record (EMR), the medicolegal environment, and difficulty balancing patient expectations for autonomy with professional judgement.27 Burnout also disproportionately affects women and younger physicians, which is especially concerning given that, in 2017, approximately one-third of practicing obstetrician/gynecologists were women, while that same year more than 80% of trainees matching into the field were women.28 In one survey sent to members of a prominent medical society, 20% of the medical professionals who responded said they have had their employment threatened by low patient satisfaction scores, 78% reported that patient satisfaction surveys moderately or severely affected their job satisfaction, and 28% stated they had considered quitting their job or leaving the medical profession.29Another related effect is the association between malpractice proceedings and a lack of satisfaction with perceived quality of physician-patient communication.30 This may be an important determinant of malpractice lawsuits, and ensuring high patient satisfaction may be a form of defensive medicine.
Continue to: Controlling the narrative for the future: Proposed strategies...
Controlling the narrative for the future: Proposed strategies
The rapid, widespread adoption of the Press Ganey survey across specialties, clinical care settings, and geographic areas may have been largely due to the ease and operational benefits for hospitals rather than after rigorous study and validation. For example, repeated use of a specific measurement tool may facilitate comparison across areas within a hospital but also across institutions, which can help assess performance at a national level. Hospitals also may have a financial incentive to work with a single third-party or vendor instead of using multiple options across multiple vendors. However, the impact of adoption of novel measures of performance should be evaluated prior to widespread adoption and utilization.
A similar example of an emergence of a technological advancement that has changed the field of medicine and how we provide care is the EMR. Epic is now the most commonly used medical record system and holds the market share of the industry, covering 78% of patients in the United States.31 While there are certainly many potential benefits of a common EMR, such as ease of information sharing and standardization of formatting, opportunities are identified in real time and require product adjustment. For example, modifications have been made to accurately represent gender outside of the previously used dichotomous options. Diagnoses such as cervical cancer screening can now be used even if the patient gender is listed as male.
Similarly, the Press Ganey and other patient satisfaction questionnaires should be evaluated and modified to address existing societal biases. The World Health Organization estimates that it will take 300 years to fix gender inequality,32 but we have an opportunity now to control the narrative and improve patient feedback.
Future research avenues
Ultimately, there is a need to further explore currently available methods of evaluating clinical encounters to better understand the inherent biases and limitations. We hope this review will encourage other physicians to examine their specialties and hospitals and require similar analyses from vendors of such satisfaction rating products prior to using them. At the very least, health systems should be willing to partner with vendors and physicians on an ongoing basis to better understand the biases involved in these survey results and make modifications as needed. Patients also obtain information from and contribute to self-reported, publicly available websites; therefore, additional exploration into a nationalized standard for assessing patient satisfaction also may serve as an opportunity to standardize the information patients evaluate.33 Further assessment of the potential financial and emotional impact of using the currently available patient-reported surveys on female physicians, Asian physicians, young physicians, and physicians who see young patients is needed. It is time to put pressure on a broken patient satisfaction system and improve on a national level to avoid undue negative consequences on our physicians. Use of patient satisfaction survey data should be limited until we all understand and account for the biases that are evident. ●
- Appeal to the Press Ganey corporation with the results of recent data and other studies to ensure they are aware of the biases that exist in their product
- Appeal to hospital-level administration to refrain from using Press Ganey scores as a tool to dictate reimbursement; instead rely on other more objective measures of performance (such as publications, presentations, research accomplishments, patient and surgical outcomes, promotion, committees, national leadership roles, etc)
- Apply a “corrective factor” or “adjustment factor” to eliminate the baseline discrepancy between scores for men and women
- Consider moving to an alternative survey methodology
- Provide patient education to define “performance” (ie, frame what a patient can expect from a provider such as being on time, courteous, and empathetic; caution against asking patients to assess competence and knowledge)
- Outpatient Services (OU) Survey Psychometrics Report. Published online 2019.
- Zusman EE. HCAHPS replaces Press Ganey Survey as quality measure for patient hospital experience. Neurosurgery. 2012;71:N21-N24. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000417536.07871.ed
- Press Ganey. Company. Accessed April 20, 2023. www.pressganey. com/company/
- Press, Ganey--first year of patient satisfaction measurement. Hosp Guest Relations Rep. 1986;1:4-5.
- DeCastellarnau A. A classification of response scale characteristics that affect data quality: a literature review. Qual Quant. 2018;52:15231559. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0533-4
- Tyser AR, Abtahi AM, McFadden M, et al. Evidence of non-response bias in the Press-Ganey patient satisfaction survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:350. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1595-z
- Duseja R, Durham M, Schreiber M. CMS quality measure development. JAMA. 2020;324:1213-1214. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12070
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. National Academies Press; 2001. doi: 10.17226/10027
- Parmet WE. Health: policy or law? A population-based analysis of the Supreme Court’s ACA cases. J Health Polit Policy Law. 2016;41:10611081. doi: 10.1215/03616878-3665949
- Richter JP, Muhlestein DB. Patient experience and hospital profitability: is there a link? Health Care Manage Rev. 2017;42:247-257. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000105
- Huang C-H, Wu H-H, Lee Y-C, et al. What role does patient gratitude play in the relationship between relationship quality and patient loyalty? Inquiry. 2019;56:46958019868324. doi: 10.1177/0046958019868324
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), HHS. Medicare program; hospital inpatient value-based purchasing program. Final rule. Fed Regist. 2011;76:26490-26547.
- Rogo-Gupta LJ, Haunschild C, Altamirano J, et al. Physician gender is associated with Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores in outpatient gynecology. Womens Health Issues. 2018;28:281-285. doi: 10.1016 /j.whi.2018.01.001
- DeLoughery EP. Physician race and specialty influence Press Ganey survey results. Neth J Med. 2019;77:366-369.
- Homewood L, Altamirano J, Fassiotto M, et al. Women gynecologists receive lower Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores in a multicenter cross-sectional study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;228:S801. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.12.025
- Sharp B, Johnson J, Hamedani AG, et al. What are we measuring? Evaluating physician-specific satisfaction scores between emergency departments. West J Emerg Med. 2019;20:454-459. doi: 10.5811 /westjem.2019.4.41040
- Mosley M. Viewpoint: Press Ganey is a worthless tool for the ED. Emerg Med News. 2019;41:3-4. doi: 10.1097/01.EEM.0000616512.68475.69
- Sotto-Santiago S, Slaven JE, Rohr-Kirchgraber T. (Dis)Incentivizing patient satisfaction metrics: the unintended consequences of institutional bias. Health Equity. 2019;3:13-18. doi: 10.1089/heq.2018.0065
- Lloyd RC. Quality Health Care: A Guide to Developing and Using Indicators. 2nd ed. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2019. Accessed April 23, 2023. www.jblearning.com/catalog/productdetails /9781284023077
- 2+2=7? Seven things you may not know about Press Ganey statistics. Emergency Physicians Monthly. Accessed April 23, 2023. epmonthly. com/article/227-seven-things-you-may-not-know-about-pressgainey-statistics/
- Presson AP, Zhang C, Abtahi AM, et al. Psychometric properties of the Press Ganey® Outpatient Medical Practice Survey. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15:32. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0610-3
- Bickell NA, Neuman J, Fei K, et al. Quality of breast cancer care: perception versus practice. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1791-1795. doi: 10.1200 /JCO.2011.38.7605
- Strauss K. Women in the workplace: are women tougher on other women? Forbes. July 18, 2016. Accessed April 27, 2023. www.forbes. com/sites/karstenstrauss/2016/07/18/women-in-the-workplace -are-women-tougher-on-other-women/
- Lee JW, Jones PS, Mineyama Y, et al. Cultural differences in responses to a Likert scale. Res Nurs Health. 2002;25:295-306. doi: 10.1002 /nur.10041
- Saha S, Hickam DH. Explaining low ratings of patient satisfaction among Asian-Americans. Am J Med Qual. 2003;18:256-264. doi: 10.1177/106286060301800606
- Halbesleben JRB, Rathert C. Linking physician burnout and patient outcomes: exploring the dyadic relationship between physicians and patients. Health Care Manage Rev. 2008;33:29-39. doi: 10.1097/01. HMR.0000304493.87898.72
- Bradford L, Glaser G. Addressing physician burnout and ensuring high-quality care of the physician workforce. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137:3-11. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004197
- Boyle P. Nation’s physician workforce evolves: more women, a bit older, and toward different specialties. AAMCNEWS. February 2, 2021. Accessed April 20, 2023. www.aamc.org/news-insights/nations-physician-workforce-evolves-more-women-bit-older-and-towarddifferent-specialties
- Zgierska A, Rabago D, Miller MM. Impact of patient satisfaction ratings on physicians and clinical care. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:437-446. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S59077
- Yeh J, Nagel EE. Patient satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology: individualized patient-centered communication. Clin Med Insights Womens Health. 2010;3:23. doi: 10.4137/CMWH.S5870
- Epic. About us. Accessed April 19, 2023. www.epic.com/about
- United Nations. Without investment, gender equality will take nearly 300 years: UN report. September 7, 2022. Accessed April 19, 2023. news.un.org/en/story/2022/09/1126171
- Ryan T, Specht J, Smith S, et al. Does the Press Ganey Survey correlate to online health grades for a major academic otolaryngology department? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;155:411-415. doi: 10.1177/0194599816652386
- Outpatient Services (OU) Survey Psychometrics Report. Published online 2019.
- Zusman EE. HCAHPS replaces Press Ganey Survey as quality measure for patient hospital experience. Neurosurgery. 2012;71:N21-N24. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000417536.07871.ed
- Press Ganey. Company. Accessed April 20, 2023. www.pressganey. com/company/
- Press, Ganey--first year of patient satisfaction measurement. Hosp Guest Relations Rep. 1986;1:4-5.
- DeCastellarnau A. A classification of response scale characteristics that affect data quality: a literature review. Qual Quant. 2018;52:15231559. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0533-4
- Tyser AR, Abtahi AM, McFadden M, et al. Evidence of non-response bias in the Press-Ganey patient satisfaction survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:350. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1595-z
- Duseja R, Durham M, Schreiber M. CMS quality measure development. JAMA. 2020;324:1213-1214. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12070
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. National Academies Press; 2001. doi: 10.17226/10027
- Parmet WE. Health: policy or law? A population-based analysis of the Supreme Court’s ACA cases. J Health Polit Policy Law. 2016;41:10611081. doi: 10.1215/03616878-3665949
- Richter JP, Muhlestein DB. Patient experience and hospital profitability: is there a link? Health Care Manage Rev. 2017;42:247-257. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000105
- Huang C-H, Wu H-H, Lee Y-C, et al. What role does patient gratitude play in the relationship between relationship quality and patient loyalty? Inquiry. 2019;56:46958019868324. doi: 10.1177/0046958019868324
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), HHS. Medicare program; hospital inpatient value-based purchasing program. Final rule. Fed Regist. 2011;76:26490-26547.
- Rogo-Gupta LJ, Haunschild C, Altamirano J, et al. Physician gender is associated with Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores in outpatient gynecology. Womens Health Issues. 2018;28:281-285. doi: 10.1016 /j.whi.2018.01.001
- DeLoughery EP. Physician race and specialty influence Press Ganey survey results. Neth J Med. 2019;77:366-369.
- Homewood L, Altamirano J, Fassiotto M, et al. Women gynecologists receive lower Press Ganey patient satisfaction scores in a multicenter cross-sectional study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;228:S801. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.12.025
- Sharp B, Johnson J, Hamedani AG, et al. What are we measuring? Evaluating physician-specific satisfaction scores between emergency departments. West J Emerg Med. 2019;20:454-459. doi: 10.5811 /westjem.2019.4.41040
- Mosley M. Viewpoint: Press Ganey is a worthless tool for the ED. Emerg Med News. 2019;41:3-4. doi: 10.1097/01.EEM.0000616512.68475.69
- Sotto-Santiago S, Slaven JE, Rohr-Kirchgraber T. (Dis)Incentivizing patient satisfaction metrics: the unintended consequences of institutional bias. Health Equity. 2019;3:13-18. doi: 10.1089/heq.2018.0065
- Lloyd RC. Quality Health Care: A Guide to Developing and Using Indicators. 2nd ed. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2019. Accessed April 23, 2023. www.jblearning.com/catalog/productdetails /9781284023077
- 2+2=7? Seven things you may not know about Press Ganey statistics. Emergency Physicians Monthly. Accessed April 23, 2023. epmonthly. com/article/227-seven-things-you-may-not-know-about-pressgainey-statistics/
- Presson AP, Zhang C, Abtahi AM, et al. Psychometric properties of the Press Ganey® Outpatient Medical Practice Survey. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15:32. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0610-3
- Bickell NA, Neuman J, Fei K, et al. Quality of breast cancer care: perception versus practice. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1791-1795. doi: 10.1200 /JCO.2011.38.7605
- Strauss K. Women in the workplace: are women tougher on other women? Forbes. July 18, 2016. Accessed April 27, 2023. www.forbes. com/sites/karstenstrauss/2016/07/18/women-in-the-workplace -are-women-tougher-on-other-women/
- Lee JW, Jones PS, Mineyama Y, et al. Cultural differences in responses to a Likert scale. Res Nurs Health. 2002;25:295-306. doi: 10.1002 /nur.10041
- Saha S, Hickam DH. Explaining low ratings of patient satisfaction among Asian-Americans. Am J Med Qual. 2003;18:256-264. doi: 10.1177/106286060301800606
- Halbesleben JRB, Rathert C. Linking physician burnout and patient outcomes: exploring the dyadic relationship between physicians and patients. Health Care Manage Rev. 2008;33:29-39. doi: 10.1097/01. HMR.0000304493.87898.72
- Bradford L, Glaser G. Addressing physician burnout and ensuring high-quality care of the physician workforce. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;137:3-11. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004197
- Boyle P. Nation’s physician workforce evolves: more women, a bit older, and toward different specialties. AAMCNEWS. February 2, 2021. Accessed April 20, 2023. www.aamc.org/news-insights/nations-physician-workforce-evolves-more-women-bit-older-and-towarddifferent-specialties
- Zgierska A, Rabago D, Miller MM. Impact of patient satisfaction ratings on physicians and clinical care. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:437-446. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S59077
- Yeh J, Nagel EE. Patient satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology: individualized patient-centered communication. Clin Med Insights Womens Health. 2010;3:23. doi: 10.4137/CMWH.S5870
- Epic. About us. Accessed April 19, 2023. www.epic.com/about
- United Nations. Without investment, gender equality will take nearly 300 years: UN report. September 7, 2022. Accessed April 19, 2023. news.un.org/en/story/2022/09/1126171
- Ryan T, Specht J, Smith S, et al. Does the Press Ganey Survey correlate to online health grades for a major academic otolaryngology department? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;155:411-415. doi: 10.1177/0194599816652386
2023 Update on menopause
This year’s menopause Update highlights a highly effective nonhormonal medication that recently received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of bothersome menopausal vasomotor symptoms. In addition, the Update provides guidance regarding how ObGyns should respond when an endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes.
Breakthrough in women’s health: A new nonhormone therapy for vasomotor symptoms
Johnson KA, Martin N, Nappi RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant in moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a phase 3 RCT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad058. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad058.
Lederman S, Ottery FD, Cano A, et al. Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2023;401:1091-1102. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00085-5.
A new oral nonestrogen-containing medication for relief of moderate to severe hot flashes, fezolinetant (Veozah) 45 mg daily, has been approved by the FDA and was expected to be available by the end of May 2023. Fezolinetant is a selective neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor antagonistthat offers a targeted nonhormonal approach to menopausal vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and it is the first in its class to make it to market.
The decline in estrogen at menopause appears to result in increased signaling at kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in the thermoregulatory center within the hypothalamus with resultant increases in hot flashes.1,2 Fezolinetant works by binding to and blocking the activities of the NK3 receptor.3-5
Key study findings
Selective NK3 receptor antagonists, including fezolinetant, effectively reduce the frequency and severity of VMS comparable to that of hormone therapy (HT). Two phase 3 clinical trials, Skylight 1 and 2, confirmed the efficacy and safety of fezolinetant 45 mg in treating VMS,6,7 and an additional 52-week placebo-controlled study, Skylight 4, confirmed long-term safety.8 Onset of action occurs within a week. Reported adverse events occurred in 1% to 2% of healthy menopausal women participating in clinical trials; these included headaches, abdominal pain, diarrhea, insomnia, back pain, hot flushes, and reversible elevated hepatic transaminase levels.6-9
The published phase 2 trials9 and the international randomized controlled trial (RCT) 12-week studies, Skylight 1 and 2,6,7 found that once-daily 30-mg and 45-mg doses of fezolinetant significantly reduced VMS frequency and severity at 12 weeks among women aged 40 to 60 years who reported an average of 7 moderate to severe VMS/day; the reduction in reported VMS was sustained at 40 weeks. Phase 3 data from Skylight 1 and 2 demonstrated fezolinetant’s efficacy in reducing the frequency and severity of VMS and provided information on the safety profile of fezolinetant compared with placebo over 12 weeks and a noncontrolled extension for an additional 40 weeks.6,7
Oral fezolinetant was associated with improved quality of life, including reduced VMS-related interference with daily life.10 Johnson and colleagues, reporting for Skylight 2, found VMS frequency and severity improvement by week 1, which achieved statistical significance at weeks 4 and 12, with this improvement maintained through week 52.6 A 64.3% reduction in mean daily VMS from baseline was seen at 12 weeks for fezolinetant 45 mg compared with a 45.4% reduction for placebo. VMS severity significantly decreased compared with placebo at 4 and 12 weeks.6
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events were infrequent, reported by 2%, 1%, and 0% of those receiving fezolinetant 30 mg, fezolinetant 45 mg, and placebo.6 Increases in levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were noted and were described as asymptomatic, isolated, intermittent, or transient, and these levels returned to baseline during treatment or after discontinuation.6
Of the 5 participants taking fezolinetant in Skyline 1 with ALT or AST levels greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal in the 12-week randomized trial, levels returned to normal range while continuing treatment in 2 participants, with treatment interruption in 2, and with discontinuation in 1. No new safety signals were seen in the 40-week extension trial.6
Fezolinetant offers a much-needed effective and safe selective nonhormone NK3 receptor antagonist therapy that reduces the frequency and severity of menopausal VMS and has been shown to be safe through 52 weeks of treatment.
To read more about how fezolinetant specifically targets the hormone receptor that triggers hot flashes as well as on prescribing hormone therapy for women with menopausal symptoms, see “Focus on menopause: Q&A with Jan Shifren, MD, and Genevieve NealPerry, MD, PhD,” in the December 2022 issue of OBG Management at https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/article/260380/menopause
Continue to: Endometrial and bone safety...
Endometrial and bone safety
Results from Skylight 4, a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, 52-week safety study, provided additional evidence that confirmed the longer-term safety of fezolinetant over a 52-week treatment period.8
Endometrial safety was assessed in postmenopausal women with normal baseline endometrium (n = 599).8 For fezolinetant 45 mg, 1 of 203 participants had endometrial hyperplasia (EH) (0.5%; upper limit of one-sided 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.3%); no cases of EH were noted in the placebo (0 of 186) or fezolinetant 30-mg (0 of 210) groups. The incidence of EH or malignancy in fezolinetant-treated participants was within prespecified limits, as assessed by blinded, centrally read endometrial biopsies. Endometrial malignancy occurred in 1 of 210 in the fezolinetant 30-mg group (0.5%; 95% CI, 2.2%) with no cases in the other groups, thus meeting FDA requirements for endometrial safety.8
In addition, no significant differences were noted in change from baseline endometrial thickness on transvaginal ultrasonography between fezolinetant-treated and placebo groups. Likewise, no loss of bone density was found on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans or trabecular bone scores.8
Liver safety
Although no cases of severe liver injury were noted, elevations in serum transaminase concentrations greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal were observed in the clinical trials. In Skylight 4, liver enzyme elevations more than 3 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 6 of 583 participants taking placebo, 8 of 590 taking fezolinetant 30 mg, and 12 of 589 taking fezolinetant 45 mg.8
The prescribing information for fezolinetant includes a warning for elevated hepatic transaminases: Fezolinetant should not be started if baseline serum transaminase concentration is equal to or exceeds 2 times the upper limit of normal. Liver tests should be obtained at baseline and repeated every 3 months for the first 9 months and then if symptoms suggest liver injury.11,12
Unmet need for nonhormone treatment of VMS
Vasomotor symptoms affect up to 80% of women, with approximately 25% bothersome enough to warrant treatment. Vasomotor symptoms persist for a median of 7 years, with duration and severity differing by race and ethnicity. Black, Hispanic, and possibly Native American women experience the highest burden of VMS.2 Although VMS, including hot flashes, night sweats, and mood and sleep disturbances, often are considered an annoyance to those with mild symptoms, moderate to severe VMS impact women’s lives, including functioning at home or work, affecting relationships, and decreasing perceived quality of life, and they have been associated with workplace absenteeism and increased health care costs, both direct from medical care and testing and indirect costs from lost work.13-15
Women with 7 or more daily moderate to severe VMS (defined as with sweating or affecting function) reported interference with sleep (94%), concentration (84%), mood (85%), energy (77%), and sexual activity (61%).16 Moderately to severely bothersome VMS have been associated with impaired psychological and general well-being, affecting work performance.17 Based on a Mayo Clinic workplace survey, Faubion and colleagues estimated an annual loss of $1.8 billion in the United States for menopause-related missed work and a $28 billion loss when medical expenses were added.15
Menopausal HT has been the primary treatment for VMS and has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes, with additional benefits on sleep, mood, fatigue, bone loss and reduction of fracture, and genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), and with potential improvement in cardiovascular health with decreased type 2 diabetes.18,19 For healthy women with early menopause and no contraindications, HT has been recommended until at least the age of natural menopause, as observational data suggest that HT prevents osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative changes, and sexual dysfunction for these women.19,20 Similarly, for healthy women younger than age 60 or within 10 years of menopause, initiating HT has been shown to be safe and effective in treating bothersome VMS and preventing osteoporotic fractures and genitourinary changes.19,21
Most systemic HT formulations are inexpensive (for example, available as generics), with multiple dosing and formulations available for use alone or combined as oral, transdermal, or vaginal therapies. Despite the fear that arose for clinicians and women from the initial 2002 findings of the Women’s Health Initiative regarding increased risk of breast cancer, stroke, venous thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, and dementia, major medical societies agree that when initiated at or soon after menopause, HT is a safe and effective therapy to relieve VMS, protect against bone loss, and treat genitourinary changes.19,21
Many women, however, cannot take HT, including those with estrogen-sensitive cancers, such as breast or uterine cancers; prior cardiovascular disease, stroke, or venous thrombotic events; severe endometriosis; or migraine headaches with visual auras.2 In addition, many symptomatic menopausal women without health contraindications choose not to take HT.2 Until now, the only FDA-approved VMS nonhormone therapy has been a low-dose 7.5-mg paroxetine salt. Unfortunately, this formulation, along with the off-label use of other antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors), gabapentinoids, oxybutynin, and clonidine, are substantially less effective than HT in treating moderate to severe VMS.
Bottom line
A substantial unmet need remains for effective therapy for moderate to severe VMS for women who cannot or choose not to take menopausal HT to relieve VMS.2,16 Effective, safe nonhormone treatment options such as the new NK3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant will address this clinically important need.
One concern is that the cost of developing and bringing to market the first of a new type of medication will be passed on to consumers, which may put it out of the price range for the many women who need it. However, the development and FDA approval of fezolinetant as the first NK3 receptor antagonist to treat menopausal VMS is potentially a practice changer. It provides a novel, effective, and safe FDA-approved nonhormonal treatment for menopausal women with moderate to severe VMS, particularly for women who cannot or will not take hormone therapy.
Continue to: When endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes, how should we respond?...
When endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes, how should we respond?
Abraham C. Proliferative endometrium in menopause: to treat or not to treat? Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:265-267. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005054.
The following case represents a common scenario for ObGyns.
CASE Patient with proliferative endometrial changes
A menopausal patient with a body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2 presents with uterine bleeding. She does not use systemic menopausal hormone therapy. Endometrial biopsy indicates proliferative changes.
When endometrial biopsy performed for bleeding reveals proliferative changes in menopausal women, we traditionally have responded by reassuring the patient that the findings are benign and advising that she should let us know if future spotting or bleeding occurs.
However, a recent review by Abraham published in Obstetrics and Gynecology details the implications of proliferative endometrial changes in menopausal patients, advising that treatment, as well as monitoring, may be appropriate.22
Endometrial changes and what they suggest
In premenopausal women, proliferative endometrial changes are physiologic and result from ovarian estrogen production early in each cycle, during what is called the proliferative (referring to the endometrium) or follicular (referring to the dominant follicle that synthesizes estrogen) phase. In menopausal women who are not using HT, however, proliferative endometrial changes, with orderly uniform glands seen on histologic evaluation, reflect aromatization of androgens by adipose and other tissues into estrogen.
The next step on the continuum to hyperplasia (benign or atypical) after proliferative endometrium is disordered proliferative endometrium. At this stage, histologic evaluation reveals scattered cystic and dilated glands that have a normal gland-to-stroma ratio with a low gland density overall and without any atypia. Randomly distributed glands may have tubal metaplasia or fibrin thrombi associated with microinfarcts, often presenting with irregular bleeding. This is a noncancerous change that occurs with excess estrogen (endogenous or exogenous).23
Progestins reverse endometrial hyperplasia by activating progesterone receptors, which leads to stromal decidualization with thinning of the endometrium. They have a pronounced effect on the histologic appearance of the endometrium. By contrast, endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN, previously known as endometrial hyperplasiawith atypia) shows underlying molecular mutations and histologic alterations and represents a sharp transition to true neoplasia, which greatly increases the risk of endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma.24
For decades, we have been aware that if women diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia are not treated with progestational therapy, their future risk of endometrial cancer is elevated. More recently, we also recognize that menopausal women found to have proliferative endometrial changes, if not treated, have an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
In a retrospective cohort study of almost 300 menopausal women who were not treated after endometrial biopsy revealed proliferative changes, investigators followed participants for an average of 11 years.25 These women had a mean BMI of 34 kg/m2. During follow-up, almost 12% of these women were diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. This incidence of endometrial neoplasia was some 4 times higher than for women initially found to have atrophic endometrial changes.25
Progestin treatment
Oral progestin therapy with follow-up endometrial biopsy constitutes traditional management for endometrial hyperplasia. Such therapy minimizes the likelihood that hyperplasia will progress to endometrial cancer.
We now recognize that the convenience, as well as the high endometrial progestin levels achieved, with levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices (LNG-IUDs) have advantages over oral progestin therapy in treating endometrial hyperplasia. Indeed, a recent US report found that among women with EIN managed medically, use of progestin-releasing IUDs has grown from 7.7% in 2008 to 35.6% in 2020.26
Although both oral and intrauterine progestin are highly effective in treating simple hyperplasia, progestin IUDs are substantially more effective than oral progestins in treating EIN.27 Progestin concentrations in the endometrium have been shown to be 100-fold higher after LNG-IUD placement compared with oral progestin use.22 In addition, adverse effects, including bloating, unpleasant mood changes, and increased appetite, are more common with oral than intrauterine progestin therapy.28
Unfortunately, data from randomized trials addressing progestational treatment of proliferative endometrium in menopausal women are not available to support the treatment of proliferative endometrium with either oral progestins or the LNG-IUD.22
Role of ultrasonography
Another concern is relying on a finding of thin endometrial thickness on vaginal ultrasonography. In a simulated retrospective cohort study, use of transvaginal ultrasonography to determine the appropriateness of a biopsy was found not to be sufficiently accurate or racially equitable with regard to Black women.29 In simulated data, transvaginal ultrasonography missed almost 5 times more cases of endometrial cancer among Black women compared with White women due to higher fibroid prevalence and nonendometrioid histologic type malignancies in Black women.29
Assessing risk
If proliferative endometrium is found, Abraham suggests assessing risk using22:
- age
- comorbidities (including obesity)
- endometrial echo thickness on vaginal ultrasonography.
Consider the patient’s risk and tolerance of recurrent bleeding as well as her tolerance for progestational adverse effects if medical therapy is chosen. Discussion about next steps should include reviewing the histologic findings with the patient and discussing the difference in risk of progression to endometrial cancer of a finding of proliferative endometrium compared with a histologic finding of endometrial hyperplasia.
Using this patient-centered approach, observation over time with follow-up endometrial biopsies remains a management option. Although some women may tolerate micronized progesterone over synthetic progestins, there is concern that it may be less effective in suppressing the endometrium than synthetic progestins.30 Accordingly, synthetic progestins represent first-line options in this setting.
In her review, Abraham suggests that when endometrial biopsy reveals proliferative changes in a menopausal woman, we should initiate progestin treatment and perform surveillance endometrial sampling every 3 to 6 months. If such sampling reveals benign but not proliferative endometrium, progestin therapy can be stopped and endometrial biopsy repeated if bleeding recurs.22 ●
ObGyns may choose to adopt Abraham’s approach or to hold off on progestin therapy while performing follow-up endometrial sampling. Either way, the take-home message is that the finding of proliferative endometrial changes on biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding requires proactive management.
- Modi M, Dhillo WS. Neurokinin 3 receptor antagonism: a novel treatment for menopausal hot flushes. Neuroendocrinology. 2019;109:242-248. doi:10.1159/000495889
- Pinkerton JV, Redick DL, Homewood LN, et al. Neurokinin receptor antagonist, fezolinetant, for treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad209. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad209
- Rance NE, Dacks PA, Mittelman-Smith MA, et al. Modulation of body temperature and LH secretion by hypothalamic KNDy (kisspeptin, neurokinin B and dynorphin) neurons: a novel hypothesis on the mechanism of hot flushes. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2013;34:211-227. doi:10.1016 /j.yfrne.2013.07.003
- Mittelman-Smith MA, Williams H, Krajewski-Hall SJ, et al. Role for kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in cutaneous vasodilatation and the estrogen modulation of body temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:1984619851. doi:10.1073/pnas.1211517109
- Astellas Pharma. Astellas’ Veozah (fezolinetant) approved by US FDA for treatment of vasomotor symptoms due to menopause. May 12, 2023. PR Newswire. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/astellas-veozah-fezolinetant-approved-by-us-fda-for -treatment-of-vasomotor-symptoms-due-to-menopause -301823639.html
- Johnson KA, Martin N, Nappi RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant in moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a phase 3 RCT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad058. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad058
- Lederman S, Ottery FD, Cano A, et al. Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2023;401:1091-1102. doi:10.1016 /S0140-6736(23)00085-5
- Neal-Perry G, Cano A, Lederman S, et al. Safety of fezolinetant for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:737-747. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005114
- Depypere H, Timmerman D, Donders G, et al. Treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms with fezolinetant, a neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist: a phase 2a trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:5893-5905. doi: 10.1210/jc .2019-00677
- Santoro N, Waldbaum A, Lederman S, et al. Effect of the neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant on patientreported outcomes in postmenopausal women with vasomotor symptoms: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-ranging study (VESTA). Menopause. 2020;27:1350-1356. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001621
- FDA approves novel drug to treat moderate to severe hot flashes caused by menopause. May 12, 2023. US Food and Drug Administration. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www .fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves -novel-drug-treat-moderate-severe-hot-flashes-caused -menopause
- Veozah. Prescribing information. Astellas; 2023. Accessed May 16, 2023. https://www.astellas.com/us/system/files /veozah_uspi.pdf
- Pinkerton JV. Money talks: untreated hot flashes cost women, the workplace, and society. Menopause. 2015;22:254-255. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000427
- Sarrel P, Portman D, Lefebvre P, et al. Incremental direct and indirect costs of untreated vasomotor symptoms. Menopause. 2015;22(3):260-266. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000320
- Faubion SS, Enders F, Hedges MS, et al. Impact of menopause symptoms on women in the workplace. Mayo Clin Proc. 2023;98:833-845. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2023.02.025
- Williams RE, Levine KB, Kalilani L, et al. Menopause- specific questionnaire assessment in US populationbased study shows negative impact on health-related quality of life. Maturitas. 2009;62:153-159. doi:10.1016 /j.maturitas.2008.12.006
- Gartoulla P, Bell RJ, Worsley R, et al. Moderate-severely bothersome vasomotor symptoms are associated with lowered psychological general wellbeing in women at midlife. Maturitas. 2015;81:487-492. doi:10.1016 /j.maturitas.2015.06.004
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1514242
- 2022 Hormone Therapy Position Statement of the North American Menopause Society Advisory Panel. The 2022 hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2022;29:767-794. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000002028
- Kaunitz AM, Kapoor E, Faubion S. Treatment of women after bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy performed prior to natural menopause. JAMA. 2021;12;326:1429-1430. doi:10.1001 /jama.2021.3305
- Pinkerton JV. Hormone therapy for postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:446-455. doi:10.1056 /NEJMcp1714787
- Abraham C. Proliferative endometrium in menopause: to treat or not to treat? Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:265-267. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005054
- Chandra V, Kim JJ, Benbrook DM, et al. Therapeutic options for management of endometrial hyperplasia. J Gynecol Oncol. 2016;27:e8. doi:10.3802/jgo.2016.27.e8
- Owings RA, Quick CM. Endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:484-491. doi:10.5858 /arpa.2012-0709-RA
- Rotenberg O, Doulaveris G, Fridman D, et al. Long-term outcome of postmenopausal women with proliferative endometrium on endometrial sampling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:896.e1-896.e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.045
- Suzuki Y, Chen L, Hou JY, et al. Systemic progestins and progestin-releasing intrauterine device therapy for premenopausal patients with endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:979-987. doi:10.1097 /AOG.0000000000005124
- Mandelbaum RS, Ciccone MA, Nusbaum DJ, et al. Progestin therapy for obese women with complex atypical hyperplasia: levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device vs systemic therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:103.e1-103.e13. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2019.12.273
- Liu S, Kciuk O, Frank M, et al. Progestins of today and tomorrow. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2022;34:344-350. doi:10.1097 /GCO.0000000000000819
- Doll KM, Romano SS, Marsh EE, et al. Estimated performance of transvaginal ultrasonography for evaluation of postmenopausal bleeding in a simulated cohort of black and white women in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:1158-1165. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1700
- Gompel A. Progesterone and endometrial cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;69:95-107. doi:10.1016 /j.bpobgyn.2020.05.003
This year’s menopause Update highlights a highly effective nonhormonal medication that recently received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of bothersome menopausal vasomotor symptoms. In addition, the Update provides guidance regarding how ObGyns should respond when an endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes.
Breakthrough in women’s health: A new nonhormone therapy for vasomotor symptoms
Johnson KA, Martin N, Nappi RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant in moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a phase 3 RCT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad058. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad058.
Lederman S, Ottery FD, Cano A, et al. Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2023;401:1091-1102. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00085-5.
A new oral nonestrogen-containing medication for relief of moderate to severe hot flashes, fezolinetant (Veozah) 45 mg daily, has been approved by the FDA and was expected to be available by the end of May 2023. Fezolinetant is a selective neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor antagonistthat offers a targeted nonhormonal approach to menopausal vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and it is the first in its class to make it to market.
The decline in estrogen at menopause appears to result in increased signaling at kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in the thermoregulatory center within the hypothalamus with resultant increases in hot flashes.1,2 Fezolinetant works by binding to and blocking the activities of the NK3 receptor.3-5
Key study findings
Selective NK3 receptor antagonists, including fezolinetant, effectively reduce the frequency and severity of VMS comparable to that of hormone therapy (HT). Two phase 3 clinical trials, Skylight 1 and 2, confirmed the efficacy and safety of fezolinetant 45 mg in treating VMS,6,7 and an additional 52-week placebo-controlled study, Skylight 4, confirmed long-term safety.8 Onset of action occurs within a week. Reported adverse events occurred in 1% to 2% of healthy menopausal women participating in clinical trials; these included headaches, abdominal pain, diarrhea, insomnia, back pain, hot flushes, and reversible elevated hepatic transaminase levels.6-9
The published phase 2 trials9 and the international randomized controlled trial (RCT) 12-week studies, Skylight 1 and 2,6,7 found that once-daily 30-mg and 45-mg doses of fezolinetant significantly reduced VMS frequency and severity at 12 weeks among women aged 40 to 60 years who reported an average of 7 moderate to severe VMS/day; the reduction in reported VMS was sustained at 40 weeks. Phase 3 data from Skylight 1 and 2 demonstrated fezolinetant’s efficacy in reducing the frequency and severity of VMS and provided information on the safety profile of fezolinetant compared with placebo over 12 weeks and a noncontrolled extension for an additional 40 weeks.6,7
Oral fezolinetant was associated with improved quality of life, including reduced VMS-related interference with daily life.10 Johnson and colleagues, reporting for Skylight 2, found VMS frequency and severity improvement by week 1, which achieved statistical significance at weeks 4 and 12, with this improvement maintained through week 52.6 A 64.3% reduction in mean daily VMS from baseline was seen at 12 weeks for fezolinetant 45 mg compared with a 45.4% reduction for placebo. VMS severity significantly decreased compared with placebo at 4 and 12 weeks.6
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events were infrequent, reported by 2%, 1%, and 0% of those receiving fezolinetant 30 mg, fezolinetant 45 mg, and placebo.6 Increases in levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were noted and were described as asymptomatic, isolated, intermittent, or transient, and these levels returned to baseline during treatment or after discontinuation.6
Of the 5 participants taking fezolinetant in Skyline 1 with ALT or AST levels greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal in the 12-week randomized trial, levels returned to normal range while continuing treatment in 2 participants, with treatment interruption in 2, and with discontinuation in 1. No new safety signals were seen in the 40-week extension trial.6
Fezolinetant offers a much-needed effective and safe selective nonhormone NK3 receptor antagonist therapy that reduces the frequency and severity of menopausal VMS and has been shown to be safe through 52 weeks of treatment.
To read more about how fezolinetant specifically targets the hormone receptor that triggers hot flashes as well as on prescribing hormone therapy for women with menopausal symptoms, see “Focus on menopause: Q&A with Jan Shifren, MD, and Genevieve NealPerry, MD, PhD,” in the December 2022 issue of OBG Management at https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/article/260380/menopause
Continue to: Endometrial and bone safety...
Endometrial and bone safety
Results from Skylight 4, a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, 52-week safety study, provided additional evidence that confirmed the longer-term safety of fezolinetant over a 52-week treatment period.8
Endometrial safety was assessed in postmenopausal women with normal baseline endometrium (n = 599).8 For fezolinetant 45 mg, 1 of 203 participants had endometrial hyperplasia (EH) (0.5%; upper limit of one-sided 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.3%); no cases of EH were noted in the placebo (0 of 186) or fezolinetant 30-mg (0 of 210) groups. The incidence of EH or malignancy in fezolinetant-treated participants was within prespecified limits, as assessed by blinded, centrally read endometrial biopsies. Endometrial malignancy occurred in 1 of 210 in the fezolinetant 30-mg group (0.5%; 95% CI, 2.2%) with no cases in the other groups, thus meeting FDA requirements for endometrial safety.8
In addition, no significant differences were noted in change from baseline endometrial thickness on transvaginal ultrasonography between fezolinetant-treated and placebo groups. Likewise, no loss of bone density was found on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans or trabecular bone scores.8
Liver safety
Although no cases of severe liver injury were noted, elevations in serum transaminase concentrations greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal were observed in the clinical trials. In Skylight 4, liver enzyme elevations more than 3 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 6 of 583 participants taking placebo, 8 of 590 taking fezolinetant 30 mg, and 12 of 589 taking fezolinetant 45 mg.8
The prescribing information for fezolinetant includes a warning for elevated hepatic transaminases: Fezolinetant should not be started if baseline serum transaminase concentration is equal to or exceeds 2 times the upper limit of normal. Liver tests should be obtained at baseline and repeated every 3 months for the first 9 months and then if symptoms suggest liver injury.11,12
Unmet need for nonhormone treatment of VMS
Vasomotor symptoms affect up to 80% of women, with approximately 25% bothersome enough to warrant treatment. Vasomotor symptoms persist for a median of 7 years, with duration and severity differing by race and ethnicity. Black, Hispanic, and possibly Native American women experience the highest burden of VMS.2 Although VMS, including hot flashes, night sweats, and mood and sleep disturbances, often are considered an annoyance to those with mild symptoms, moderate to severe VMS impact women’s lives, including functioning at home or work, affecting relationships, and decreasing perceived quality of life, and they have been associated with workplace absenteeism and increased health care costs, both direct from medical care and testing and indirect costs from lost work.13-15
Women with 7 or more daily moderate to severe VMS (defined as with sweating or affecting function) reported interference with sleep (94%), concentration (84%), mood (85%), energy (77%), and sexual activity (61%).16 Moderately to severely bothersome VMS have been associated with impaired psychological and general well-being, affecting work performance.17 Based on a Mayo Clinic workplace survey, Faubion and colleagues estimated an annual loss of $1.8 billion in the United States for menopause-related missed work and a $28 billion loss when medical expenses were added.15
Menopausal HT has been the primary treatment for VMS and has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes, with additional benefits on sleep, mood, fatigue, bone loss and reduction of fracture, and genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), and with potential improvement in cardiovascular health with decreased type 2 diabetes.18,19 For healthy women with early menopause and no contraindications, HT has been recommended until at least the age of natural menopause, as observational data suggest that HT prevents osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative changes, and sexual dysfunction for these women.19,20 Similarly, for healthy women younger than age 60 or within 10 years of menopause, initiating HT has been shown to be safe and effective in treating bothersome VMS and preventing osteoporotic fractures and genitourinary changes.19,21
Most systemic HT formulations are inexpensive (for example, available as generics), with multiple dosing and formulations available for use alone or combined as oral, transdermal, or vaginal therapies. Despite the fear that arose for clinicians and women from the initial 2002 findings of the Women’s Health Initiative regarding increased risk of breast cancer, stroke, venous thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, and dementia, major medical societies agree that when initiated at or soon after menopause, HT is a safe and effective therapy to relieve VMS, protect against bone loss, and treat genitourinary changes.19,21
Many women, however, cannot take HT, including those with estrogen-sensitive cancers, such as breast or uterine cancers; prior cardiovascular disease, stroke, or venous thrombotic events; severe endometriosis; or migraine headaches with visual auras.2 In addition, many symptomatic menopausal women without health contraindications choose not to take HT.2 Until now, the only FDA-approved VMS nonhormone therapy has been a low-dose 7.5-mg paroxetine salt. Unfortunately, this formulation, along with the off-label use of other antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors), gabapentinoids, oxybutynin, and clonidine, are substantially less effective than HT in treating moderate to severe VMS.
Bottom line
A substantial unmet need remains for effective therapy for moderate to severe VMS for women who cannot or choose not to take menopausal HT to relieve VMS.2,16 Effective, safe nonhormone treatment options such as the new NK3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant will address this clinically important need.
One concern is that the cost of developing and bringing to market the first of a new type of medication will be passed on to consumers, which may put it out of the price range for the many women who need it. However, the development and FDA approval of fezolinetant as the first NK3 receptor antagonist to treat menopausal VMS is potentially a practice changer. It provides a novel, effective, and safe FDA-approved nonhormonal treatment for menopausal women with moderate to severe VMS, particularly for women who cannot or will not take hormone therapy.
Continue to: When endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes, how should we respond?...
When endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes, how should we respond?
Abraham C. Proliferative endometrium in menopause: to treat or not to treat? Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:265-267. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005054.
The following case represents a common scenario for ObGyns.
CASE Patient with proliferative endometrial changes
A menopausal patient with a body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2 presents with uterine bleeding. She does not use systemic menopausal hormone therapy. Endometrial biopsy indicates proliferative changes.
When endometrial biopsy performed for bleeding reveals proliferative changes in menopausal women, we traditionally have responded by reassuring the patient that the findings are benign and advising that she should let us know if future spotting or bleeding occurs.
However, a recent review by Abraham published in Obstetrics and Gynecology details the implications of proliferative endometrial changes in menopausal patients, advising that treatment, as well as monitoring, may be appropriate.22
Endometrial changes and what they suggest
In premenopausal women, proliferative endometrial changes are physiologic and result from ovarian estrogen production early in each cycle, during what is called the proliferative (referring to the endometrium) or follicular (referring to the dominant follicle that synthesizes estrogen) phase. In menopausal women who are not using HT, however, proliferative endometrial changes, with orderly uniform glands seen on histologic evaluation, reflect aromatization of androgens by adipose and other tissues into estrogen.
The next step on the continuum to hyperplasia (benign or atypical) after proliferative endometrium is disordered proliferative endometrium. At this stage, histologic evaluation reveals scattered cystic and dilated glands that have a normal gland-to-stroma ratio with a low gland density overall and without any atypia. Randomly distributed glands may have tubal metaplasia or fibrin thrombi associated with microinfarcts, often presenting with irregular bleeding. This is a noncancerous change that occurs with excess estrogen (endogenous or exogenous).23
Progestins reverse endometrial hyperplasia by activating progesterone receptors, which leads to stromal decidualization with thinning of the endometrium. They have a pronounced effect on the histologic appearance of the endometrium. By contrast, endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN, previously known as endometrial hyperplasiawith atypia) shows underlying molecular mutations and histologic alterations and represents a sharp transition to true neoplasia, which greatly increases the risk of endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma.24
For decades, we have been aware that if women diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia are not treated with progestational therapy, their future risk of endometrial cancer is elevated. More recently, we also recognize that menopausal women found to have proliferative endometrial changes, if not treated, have an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
In a retrospective cohort study of almost 300 menopausal women who were not treated after endometrial biopsy revealed proliferative changes, investigators followed participants for an average of 11 years.25 These women had a mean BMI of 34 kg/m2. During follow-up, almost 12% of these women were diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. This incidence of endometrial neoplasia was some 4 times higher than for women initially found to have atrophic endometrial changes.25
Progestin treatment
Oral progestin therapy with follow-up endometrial biopsy constitutes traditional management for endometrial hyperplasia. Such therapy minimizes the likelihood that hyperplasia will progress to endometrial cancer.
We now recognize that the convenience, as well as the high endometrial progestin levels achieved, with levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices (LNG-IUDs) have advantages over oral progestin therapy in treating endometrial hyperplasia. Indeed, a recent US report found that among women with EIN managed medically, use of progestin-releasing IUDs has grown from 7.7% in 2008 to 35.6% in 2020.26
Although both oral and intrauterine progestin are highly effective in treating simple hyperplasia, progestin IUDs are substantially more effective than oral progestins in treating EIN.27 Progestin concentrations in the endometrium have been shown to be 100-fold higher after LNG-IUD placement compared with oral progestin use.22 In addition, adverse effects, including bloating, unpleasant mood changes, and increased appetite, are more common with oral than intrauterine progestin therapy.28
Unfortunately, data from randomized trials addressing progestational treatment of proliferative endometrium in menopausal women are not available to support the treatment of proliferative endometrium with either oral progestins or the LNG-IUD.22
Role of ultrasonography
Another concern is relying on a finding of thin endometrial thickness on vaginal ultrasonography. In a simulated retrospective cohort study, use of transvaginal ultrasonography to determine the appropriateness of a biopsy was found not to be sufficiently accurate or racially equitable with regard to Black women.29 In simulated data, transvaginal ultrasonography missed almost 5 times more cases of endometrial cancer among Black women compared with White women due to higher fibroid prevalence and nonendometrioid histologic type malignancies in Black women.29
Assessing risk
If proliferative endometrium is found, Abraham suggests assessing risk using22:
- age
- comorbidities (including obesity)
- endometrial echo thickness on vaginal ultrasonography.
Consider the patient’s risk and tolerance of recurrent bleeding as well as her tolerance for progestational adverse effects if medical therapy is chosen. Discussion about next steps should include reviewing the histologic findings with the patient and discussing the difference in risk of progression to endometrial cancer of a finding of proliferative endometrium compared with a histologic finding of endometrial hyperplasia.
Using this patient-centered approach, observation over time with follow-up endometrial biopsies remains a management option. Although some women may tolerate micronized progesterone over synthetic progestins, there is concern that it may be less effective in suppressing the endometrium than synthetic progestins.30 Accordingly, synthetic progestins represent first-line options in this setting.
In her review, Abraham suggests that when endometrial biopsy reveals proliferative changes in a menopausal woman, we should initiate progestin treatment and perform surveillance endometrial sampling every 3 to 6 months. If such sampling reveals benign but not proliferative endometrium, progestin therapy can be stopped and endometrial biopsy repeated if bleeding recurs.22 ●
ObGyns may choose to adopt Abraham’s approach or to hold off on progestin therapy while performing follow-up endometrial sampling. Either way, the take-home message is that the finding of proliferative endometrial changes on biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding requires proactive management.
This year’s menopause Update highlights a highly effective nonhormonal medication that recently received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of bothersome menopausal vasomotor symptoms. In addition, the Update provides guidance regarding how ObGyns should respond when an endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes.
Breakthrough in women’s health: A new nonhormone therapy for vasomotor symptoms
Johnson KA, Martin N, Nappi RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant in moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a phase 3 RCT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad058. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad058.
Lederman S, Ottery FD, Cano A, et al. Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2023;401:1091-1102. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00085-5.
A new oral nonestrogen-containing medication for relief of moderate to severe hot flashes, fezolinetant (Veozah) 45 mg daily, has been approved by the FDA and was expected to be available by the end of May 2023. Fezolinetant is a selective neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor antagonistthat offers a targeted nonhormonal approach to menopausal vasomotor symptoms (VMS), and it is the first in its class to make it to market.
The decline in estrogen at menopause appears to result in increased signaling at kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in the thermoregulatory center within the hypothalamus with resultant increases in hot flashes.1,2 Fezolinetant works by binding to and blocking the activities of the NK3 receptor.3-5
Key study findings
Selective NK3 receptor antagonists, including fezolinetant, effectively reduce the frequency and severity of VMS comparable to that of hormone therapy (HT). Two phase 3 clinical trials, Skylight 1 and 2, confirmed the efficacy and safety of fezolinetant 45 mg in treating VMS,6,7 and an additional 52-week placebo-controlled study, Skylight 4, confirmed long-term safety.8 Onset of action occurs within a week. Reported adverse events occurred in 1% to 2% of healthy menopausal women participating in clinical trials; these included headaches, abdominal pain, diarrhea, insomnia, back pain, hot flushes, and reversible elevated hepatic transaminase levels.6-9
The published phase 2 trials9 and the international randomized controlled trial (RCT) 12-week studies, Skylight 1 and 2,6,7 found that once-daily 30-mg and 45-mg doses of fezolinetant significantly reduced VMS frequency and severity at 12 weeks among women aged 40 to 60 years who reported an average of 7 moderate to severe VMS/day; the reduction in reported VMS was sustained at 40 weeks. Phase 3 data from Skylight 1 and 2 demonstrated fezolinetant’s efficacy in reducing the frequency and severity of VMS and provided information on the safety profile of fezolinetant compared with placebo over 12 weeks and a noncontrolled extension for an additional 40 weeks.6,7
Oral fezolinetant was associated with improved quality of life, including reduced VMS-related interference with daily life.10 Johnson and colleagues, reporting for Skylight 2, found VMS frequency and severity improvement by week 1, which achieved statistical significance at weeks 4 and 12, with this improvement maintained through week 52.6 A 64.3% reduction in mean daily VMS from baseline was seen at 12 weeks for fezolinetant 45 mg compared with a 45.4% reduction for placebo. VMS severity significantly decreased compared with placebo at 4 and 12 weeks.6
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events were infrequent, reported by 2%, 1%, and 0% of those receiving fezolinetant 30 mg, fezolinetant 45 mg, and placebo.6 Increases in levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were noted and were described as asymptomatic, isolated, intermittent, or transient, and these levels returned to baseline during treatment or after discontinuation.6
Of the 5 participants taking fezolinetant in Skyline 1 with ALT or AST levels greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal in the 12-week randomized trial, levels returned to normal range while continuing treatment in 2 participants, with treatment interruption in 2, and with discontinuation in 1. No new safety signals were seen in the 40-week extension trial.6
Fezolinetant offers a much-needed effective and safe selective nonhormone NK3 receptor antagonist therapy that reduces the frequency and severity of menopausal VMS and has been shown to be safe through 52 weeks of treatment.
To read more about how fezolinetant specifically targets the hormone receptor that triggers hot flashes as well as on prescribing hormone therapy for women with menopausal symptoms, see “Focus on menopause: Q&A with Jan Shifren, MD, and Genevieve NealPerry, MD, PhD,” in the December 2022 issue of OBG Management at https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/article/260380/menopause
Continue to: Endometrial and bone safety...
Endometrial and bone safety
Results from Skylight 4, a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, 52-week safety study, provided additional evidence that confirmed the longer-term safety of fezolinetant over a 52-week treatment period.8
Endometrial safety was assessed in postmenopausal women with normal baseline endometrium (n = 599).8 For fezolinetant 45 mg, 1 of 203 participants had endometrial hyperplasia (EH) (0.5%; upper limit of one-sided 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.3%); no cases of EH were noted in the placebo (0 of 186) or fezolinetant 30-mg (0 of 210) groups. The incidence of EH or malignancy in fezolinetant-treated participants was within prespecified limits, as assessed by blinded, centrally read endometrial biopsies. Endometrial malignancy occurred in 1 of 210 in the fezolinetant 30-mg group (0.5%; 95% CI, 2.2%) with no cases in the other groups, thus meeting FDA requirements for endometrial safety.8
In addition, no significant differences were noted in change from baseline endometrial thickness on transvaginal ultrasonography between fezolinetant-treated and placebo groups. Likewise, no loss of bone density was found on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans or trabecular bone scores.8
Liver safety
Although no cases of severe liver injury were noted, elevations in serum transaminase concentrations greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal were observed in the clinical trials. In Skylight 4, liver enzyme elevations more than 3 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 6 of 583 participants taking placebo, 8 of 590 taking fezolinetant 30 mg, and 12 of 589 taking fezolinetant 45 mg.8
The prescribing information for fezolinetant includes a warning for elevated hepatic transaminases: Fezolinetant should not be started if baseline serum transaminase concentration is equal to or exceeds 2 times the upper limit of normal. Liver tests should be obtained at baseline and repeated every 3 months for the first 9 months and then if symptoms suggest liver injury.11,12
Unmet need for nonhormone treatment of VMS
Vasomotor symptoms affect up to 80% of women, with approximately 25% bothersome enough to warrant treatment. Vasomotor symptoms persist for a median of 7 years, with duration and severity differing by race and ethnicity. Black, Hispanic, and possibly Native American women experience the highest burden of VMS.2 Although VMS, including hot flashes, night sweats, and mood and sleep disturbances, often are considered an annoyance to those with mild symptoms, moderate to severe VMS impact women’s lives, including functioning at home or work, affecting relationships, and decreasing perceived quality of life, and they have been associated with workplace absenteeism and increased health care costs, both direct from medical care and testing and indirect costs from lost work.13-15
Women with 7 or more daily moderate to severe VMS (defined as with sweating or affecting function) reported interference with sleep (94%), concentration (84%), mood (85%), energy (77%), and sexual activity (61%).16 Moderately to severely bothersome VMS have been associated with impaired psychological and general well-being, affecting work performance.17 Based on a Mayo Clinic workplace survey, Faubion and colleagues estimated an annual loss of $1.8 billion in the United States for menopause-related missed work and a $28 billion loss when medical expenses were added.15
Menopausal HT has been the primary treatment for VMS and has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes, with additional benefits on sleep, mood, fatigue, bone loss and reduction of fracture, and genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), and with potential improvement in cardiovascular health with decreased type 2 diabetes.18,19 For healthy women with early menopause and no contraindications, HT has been recommended until at least the age of natural menopause, as observational data suggest that HT prevents osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative changes, and sexual dysfunction for these women.19,20 Similarly, for healthy women younger than age 60 or within 10 years of menopause, initiating HT has been shown to be safe and effective in treating bothersome VMS and preventing osteoporotic fractures and genitourinary changes.19,21
Most systemic HT formulations are inexpensive (for example, available as generics), with multiple dosing and formulations available for use alone or combined as oral, transdermal, or vaginal therapies. Despite the fear that arose for clinicians and women from the initial 2002 findings of the Women’s Health Initiative regarding increased risk of breast cancer, stroke, venous thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, and dementia, major medical societies agree that when initiated at or soon after menopause, HT is a safe and effective therapy to relieve VMS, protect against bone loss, and treat genitourinary changes.19,21
Many women, however, cannot take HT, including those with estrogen-sensitive cancers, such as breast or uterine cancers; prior cardiovascular disease, stroke, or venous thrombotic events; severe endometriosis; or migraine headaches with visual auras.2 In addition, many symptomatic menopausal women without health contraindications choose not to take HT.2 Until now, the only FDA-approved VMS nonhormone therapy has been a low-dose 7.5-mg paroxetine salt. Unfortunately, this formulation, along with the off-label use of other antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors), gabapentinoids, oxybutynin, and clonidine, are substantially less effective than HT in treating moderate to severe VMS.
Bottom line
A substantial unmet need remains for effective therapy for moderate to severe VMS for women who cannot or choose not to take menopausal HT to relieve VMS.2,16 Effective, safe nonhormone treatment options such as the new NK3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant will address this clinically important need.
One concern is that the cost of developing and bringing to market the first of a new type of medication will be passed on to consumers, which may put it out of the price range for the many women who need it. However, the development and FDA approval of fezolinetant as the first NK3 receptor antagonist to treat menopausal VMS is potentially a practice changer. It provides a novel, effective, and safe FDA-approved nonhormonal treatment for menopausal women with moderate to severe VMS, particularly for women who cannot or will not take hormone therapy.
Continue to: When endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes, how should we respond?...
When endometrial biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding reveals proliferative changes, how should we respond?
Abraham C. Proliferative endometrium in menopause: to treat or not to treat? Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:265-267. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005054.
The following case represents a common scenario for ObGyns.
CASE Patient with proliferative endometrial changes
A menopausal patient with a body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2 presents with uterine bleeding. She does not use systemic menopausal hormone therapy. Endometrial biopsy indicates proliferative changes.
When endometrial biopsy performed for bleeding reveals proliferative changes in menopausal women, we traditionally have responded by reassuring the patient that the findings are benign and advising that she should let us know if future spotting or bleeding occurs.
However, a recent review by Abraham published in Obstetrics and Gynecology details the implications of proliferative endometrial changes in menopausal patients, advising that treatment, as well as monitoring, may be appropriate.22
Endometrial changes and what they suggest
In premenopausal women, proliferative endometrial changes are physiologic and result from ovarian estrogen production early in each cycle, during what is called the proliferative (referring to the endometrium) or follicular (referring to the dominant follicle that synthesizes estrogen) phase. In menopausal women who are not using HT, however, proliferative endometrial changes, with orderly uniform glands seen on histologic evaluation, reflect aromatization of androgens by adipose and other tissues into estrogen.
The next step on the continuum to hyperplasia (benign or atypical) after proliferative endometrium is disordered proliferative endometrium. At this stage, histologic evaluation reveals scattered cystic and dilated glands that have a normal gland-to-stroma ratio with a low gland density overall and without any atypia. Randomly distributed glands may have tubal metaplasia or fibrin thrombi associated with microinfarcts, often presenting with irregular bleeding. This is a noncancerous change that occurs with excess estrogen (endogenous or exogenous).23
Progestins reverse endometrial hyperplasia by activating progesterone receptors, which leads to stromal decidualization with thinning of the endometrium. They have a pronounced effect on the histologic appearance of the endometrium. By contrast, endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN, previously known as endometrial hyperplasiawith atypia) shows underlying molecular mutations and histologic alterations and represents a sharp transition to true neoplasia, which greatly increases the risk of endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma.24
For decades, we have been aware that if women diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia are not treated with progestational therapy, their future risk of endometrial cancer is elevated. More recently, we also recognize that menopausal women found to have proliferative endometrial changes, if not treated, have an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
In a retrospective cohort study of almost 300 menopausal women who were not treated after endometrial biopsy revealed proliferative changes, investigators followed participants for an average of 11 years.25 These women had a mean BMI of 34 kg/m2. During follow-up, almost 12% of these women were diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. This incidence of endometrial neoplasia was some 4 times higher than for women initially found to have atrophic endometrial changes.25
Progestin treatment
Oral progestin therapy with follow-up endometrial biopsy constitutes traditional management for endometrial hyperplasia. Such therapy minimizes the likelihood that hyperplasia will progress to endometrial cancer.
We now recognize that the convenience, as well as the high endometrial progestin levels achieved, with levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices (LNG-IUDs) have advantages over oral progestin therapy in treating endometrial hyperplasia. Indeed, a recent US report found that among women with EIN managed medically, use of progestin-releasing IUDs has grown from 7.7% in 2008 to 35.6% in 2020.26
Although both oral and intrauterine progestin are highly effective in treating simple hyperplasia, progestin IUDs are substantially more effective than oral progestins in treating EIN.27 Progestin concentrations in the endometrium have been shown to be 100-fold higher after LNG-IUD placement compared with oral progestin use.22 In addition, adverse effects, including bloating, unpleasant mood changes, and increased appetite, are more common with oral than intrauterine progestin therapy.28
Unfortunately, data from randomized trials addressing progestational treatment of proliferative endometrium in menopausal women are not available to support the treatment of proliferative endometrium with either oral progestins or the LNG-IUD.22
Role of ultrasonography
Another concern is relying on a finding of thin endometrial thickness on vaginal ultrasonography. In a simulated retrospective cohort study, use of transvaginal ultrasonography to determine the appropriateness of a biopsy was found not to be sufficiently accurate or racially equitable with regard to Black women.29 In simulated data, transvaginal ultrasonography missed almost 5 times more cases of endometrial cancer among Black women compared with White women due to higher fibroid prevalence and nonendometrioid histologic type malignancies in Black women.29
Assessing risk
If proliferative endometrium is found, Abraham suggests assessing risk using22:
- age
- comorbidities (including obesity)
- endometrial echo thickness on vaginal ultrasonography.
Consider the patient’s risk and tolerance of recurrent bleeding as well as her tolerance for progestational adverse effects if medical therapy is chosen. Discussion about next steps should include reviewing the histologic findings with the patient and discussing the difference in risk of progression to endometrial cancer of a finding of proliferative endometrium compared with a histologic finding of endometrial hyperplasia.
Using this patient-centered approach, observation over time with follow-up endometrial biopsies remains a management option. Although some women may tolerate micronized progesterone over synthetic progestins, there is concern that it may be less effective in suppressing the endometrium than synthetic progestins.30 Accordingly, synthetic progestins represent first-line options in this setting.
In her review, Abraham suggests that when endometrial biopsy reveals proliferative changes in a menopausal woman, we should initiate progestin treatment and perform surveillance endometrial sampling every 3 to 6 months. If such sampling reveals benign but not proliferative endometrium, progestin therapy can be stopped and endometrial biopsy repeated if bleeding recurs.22 ●
ObGyns may choose to adopt Abraham’s approach or to hold off on progestin therapy while performing follow-up endometrial sampling. Either way, the take-home message is that the finding of proliferative endometrial changes on biopsy for postmenopausal bleeding requires proactive management.
- Modi M, Dhillo WS. Neurokinin 3 receptor antagonism: a novel treatment for menopausal hot flushes. Neuroendocrinology. 2019;109:242-248. doi:10.1159/000495889
- Pinkerton JV, Redick DL, Homewood LN, et al. Neurokinin receptor antagonist, fezolinetant, for treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad209. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad209
- Rance NE, Dacks PA, Mittelman-Smith MA, et al. Modulation of body temperature and LH secretion by hypothalamic KNDy (kisspeptin, neurokinin B and dynorphin) neurons: a novel hypothesis on the mechanism of hot flushes. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2013;34:211-227. doi:10.1016 /j.yfrne.2013.07.003
- Mittelman-Smith MA, Williams H, Krajewski-Hall SJ, et al. Role for kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in cutaneous vasodilatation and the estrogen modulation of body temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:1984619851. doi:10.1073/pnas.1211517109
- Astellas Pharma. Astellas’ Veozah (fezolinetant) approved by US FDA for treatment of vasomotor symptoms due to menopause. May 12, 2023. PR Newswire. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/astellas-veozah-fezolinetant-approved-by-us-fda-for -treatment-of-vasomotor-symptoms-due-to-menopause -301823639.html
- Johnson KA, Martin N, Nappi RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant in moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a phase 3 RCT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad058. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad058
- Lederman S, Ottery FD, Cano A, et al. Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2023;401:1091-1102. doi:10.1016 /S0140-6736(23)00085-5
- Neal-Perry G, Cano A, Lederman S, et al. Safety of fezolinetant for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:737-747. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005114
- Depypere H, Timmerman D, Donders G, et al. Treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms with fezolinetant, a neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist: a phase 2a trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:5893-5905. doi: 10.1210/jc .2019-00677
- Santoro N, Waldbaum A, Lederman S, et al. Effect of the neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant on patientreported outcomes in postmenopausal women with vasomotor symptoms: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-ranging study (VESTA). Menopause. 2020;27:1350-1356. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001621
- FDA approves novel drug to treat moderate to severe hot flashes caused by menopause. May 12, 2023. US Food and Drug Administration. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www .fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves -novel-drug-treat-moderate-severe-hot-flashes-caused -menopause
- Veozah. Prescribing information. Astellas; 2023. Accessed May 16, 2023. https://www.astellas.com/us/system/files /veozah_uspi.pdf
- Pinkerton JV. Money talks: untreated hot flashes cost women, the workplace, and society. Menopause. 2015;22:254-255. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000427
- Sarrel P, Portman D, Lefebvre P, et al. Incremental direct and indirect costs of untreated vasomotor symptoms. Menopause. 2015;22(3):260-266. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000320
- Faubion SS, Enders F, Hedges MS, et al. Impact of menopause symptoms on women in the workplace. Mayo Clin Proc. 2023;98:833-845. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2023.02.025
- Williams RE, Levine KB, Kalilani L, et al. Menopause- specific questionnaire assessment in US populationbased study shows negative impact on health-related quality of life. Maturitas. 2009;62:153-159. doi:10.1016 /j.maturitas.2008.12.006
- Gartoulla P, Bell RJ, Worsley R, et al. Moderate-severely bothersome vasomotor symptoms are associated with lowered psychological general wellbeing in women at midlife. Maturitas. 2015;81:487-492. doi:10.1016 /j.maturitas.2015.06.004
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1514242
- 2022 Hormone Therapy Position Statement of the North American Menopause Society Advisory Panel. The 2022 hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2022;29:767-794. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000002028
- Kaunitz AM, Kapoor E, Faubion S. Treatment of women after bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy performed prior to natural menopause. JAMA. 2021;12;326:1429-1430. doi:10.1001 /jama.2021.3305
- Pinkerton JV. Hormone therapy for postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:446-455. doi:10.1056 /NEJMcp1714787
- Abraham C. Proliferative endometrium in menopause: to treat or not to treat? Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:265-267. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005054
- Chandra V, Kim JJ, Benbrook DM, et al. Therapeutic options for management of endometrial hyperplasia. J Gynecol Oncol. 2016;27:e8. doi:10.3802/jgo.2016.27.e8
- Owings RA, Quick CM. Endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:484-491. doi:10.5858 /arpa.2012-0709-RA
- Rotenberg O, Doulaveris G, Fridman D, et al. Long-term outcome of postmenopausal women with proliferative endometrium on endometrial sampling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:896.e1-896.e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.045
- Suzuki Y, Chen L, Hou JY, et al. Systemic progestins and progestin-releasing intrauterine device therapy for premenopausal patients with endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:979-987. doi:10.1097 /AOG.0000000000005124
- Mandelbaum RS, Ciccone MA, Nusbaum DJ, et al. Progestin therapy for obese women with complex atypical hyperplasia: levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device vs systemic therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:103.e1-103.e13. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2019.12.273
- Liu S, Kciuk O, Frank M, et al. Progestins of today and tomorrow. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2022;34:344-350. doi:10.1097 /GCO.0000000000000819
- Doll KM, Romano SS, Marsh EE, et al. Estimated performance of transvaginal ultrasonography for evaluation of postmenopausal bleeding in a simulated cohort of black and white women in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:1158-1165. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1700
- Gompel A. Progesterone and endometrial cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;69:95-107. doi:10.1016 /j.bpobgyn.2020.05.003
- Modi M, Dhillo WS. Neurokinin 3 receptor antagonism: a novel treatment for menopausal hot flushes. Neuroendocrinology. 2019;109:242-248. doi:10.1159/000495889
- Pinkerton JV, Redick DL, Homewood LN, et al. Neurokinin receptor antagonist, fezolinetant, for treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad209. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad209
- Rance NE, Dacks PA, Mittelman-Smith MA, et al. Modulation of body temperature and LH secretion by hypothalamic KNDy (kisspeptin, neurokinin B and dynorphin) neurons: a novel hypothesis on the mechanism of hot flushes. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2013;34:211-227. doi:10.1016 /j.yfrne.2013.07.003
- Mittelman-Smith MA, Williams H, Krajewski-Hall SJ, et al. Role for kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in cutaneous vasodilatation and the estrogen modulation of body temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:1984619851. doi:10.1073/pnas.1211517109
- Astellas Pharma. Astellas’ Veozah (fezolinetant) approved by US FDA for treatment of vasomotor symptoms due to menopause. May 12, 2023. PR Newswire. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/astellas-veozah-fezolinetant-approved-by-us-fda-for -treatment-of-vasomotor-symptoms-due-to-menopause -301823639.html
- Johnson KA, Martin N, Nappi RE, et al. Efficacy and safety of fezolinetant in moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a phase 3 RCT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;dgad058. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgad058
- Lederman S, Ottery FD, Cano A, et al. Fezolinetant for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (SKYLIGHT 1): a phase 3 randomised controlled study. Lancet. 2023;401:1091-1102. doi:10.1016 /S0140-6736(23)00085-5
- Neal-Perry G, Cano A, Lederman S, et al. Safety of fezolinetant for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:737-747. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005114
- Depypere H, Timmerman D, Donders G, et al. Treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms with fezolinetant, a neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist: a phase 2a trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:5893-5905. doi: 10.1210/jc .2019-00677
- Santoro N, Waldbaum A, Lederman S, et al. Effect of the neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist fezolinetant on patientreported outcomes in postmenopausal women with vasomotor symptoms: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-ranging study (VESTA). Menopause. 2020;27:1350-1356. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001621
- FDA approves novel drug to treat moderate to severe hot flashes caused by menopause. May 12, 2023. US Food and Drug Administration. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www .fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves -novel-drug-treat-moderate-severe-hot-flashes-caused -menopause
- Veozah. Prescribing information. Astellas; 2023. Accessed May 16, 2023. https://www.astellas.com/us/system/files /veozah_uspi.pdf
- Pinkerton JV. Money talks: untreated hot flashes cost women, the workplace, and society. Menopause. 2015;22:254-255. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000427
- Sarrel P, Portman D, Lefebvre P, et al. Incremental direct and indirect costs of untreated vasomotor symptoms. Menopause. 2015;22(3):260-266. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000000320
- Faubion SS, Enders F, Hedges MS, et al. Impact of menopause symptoms on women in the workplace. Mayo Clin Proc. 2023;98:833-845. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2023.02.025
- Williams RE, Levine KB, Kalilani L, et al. Menopause- specific questionnaire assessment in US populationbased study shows negative impact on health-related quality of life. Maturitas. 2009;62:153-159. doi:10.1016 /j.maturitas.2008.12.006
- Gartoulla P, Bell RJ, Worsley R, et al. Moderate-severely bothersome vasomotor symptoms are associated with lowered psychological general wellbeing in women at midlife. Maturitas. 2015;81:487-492. doi:10.1016 /j.maturitas.2015.06.004
- Manson JE, Kaunitz AM. Menopause management—getting clinical care back on track. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:803-806. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1514242
- 2022 Hormone Therapy Position Statement of the North American Menopause Society Advisory Panel. The 2022 hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2022;29:767-794. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000002028
- Kaunitz AM, Kapoor E, Faubion S. Treatment of women after bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy performed prior to natural menopause. JAMA. 2021;12;326:1429-1430. doi:10.1001 /jama.2021.3305
- Pinkerton JV. Hormone therapy for postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:446-455. doi:10.1056 /NEJMcp1714787
- Abraham C. Proliferative endometrium in menopause: to treat or not to treat? Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:265-267. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005054
- Chandra V, Kim JJ, Benbrook DM, et al. Therapeutic options for management of endometrial hyperplasia. J Gynecol Oncol. 2016;27:e8. doi:10.3802/jgo.2016.27.e8
- Owings RA, Quick CM. Endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:484-491. doi:10.5858 /arpa.2012-0709-RA
- Rotenberg O, Doulaveris G, Fridman D, et al. Long-term outcome of postmenopausal women with proliferative endometrium on endometrial sampling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:896.e1-896.e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.045
- Suzuki Y, Chen L, Hou JY, et al. Systemic progestins and progestin-releasing intrauterine device therapy for premenopausal patients with endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:979-987. doi:10.1097 /AOG.0000000000005124
- Mandelbaum RS, Ciccone MA, Nusbaum DJ, et al. Progestin therapy for obese women with complex atypical hyperplasia: levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device vs systemic therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:103.e1-103.e13. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2019.12.273
- Liu S, Kciuk O, Frank M, et al. Progestins of today and tomorrow. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2022;34:344-350. doi:10.1097 /GCO.0000000000000819
- Doll KM, Romano SS, Marsh EE, et al. Estimated performance of transvaginal ultrasonography for evaluation of postmenopausal bleeding in a simulated cohort of black and white women in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:1158-1165. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1700
- Gompel A. Progesterone and endometrial cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;69:95-107. doi:10.1016 /j.bpobgyn.2020.05.003
Postmenopausal screening mammogram
The findings in this case are suggestive of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC).
Globally, breast cancer remains the most common life-threatening cancer diagnosed and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. In the United States, approximately 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer were diagnosed in 2022 and 43,250 deaths were attributed to breast cancer in the same year. Worldwide, approximately 2.3 million new diagnoses and 685,000 breast cancer-related deaths were reported in 2020.
ILC is one of the leading histologic types of invasive carcinoma, second in incidence only to invasive carcinoma of no special type. ILC accounts for 5%-15% of all invasive breast cancers, and its incidence has been steadily increasing — particularly among postmenopausal women — over the past two decades. ILC has distinct molecular and histopathologic features, including the loss of cell-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, resulting in small, discohesive cells proliferating in single-file strands; positivity for both the estrogen and progesterone receptor; and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negativity.
The diagnosis of ILC can be challenging, as it is difficult to detect both on physical examination and with standard imaging techniques. Patients are often diagnosed with late-stage disease, characterized by large tumors and lymph node involvement. The signs of ILC are often vague, such as skin thickening or dimpling. In addition, measuring the extent of ILC can be challenging, as traditional screening methods (eg, mammography and ultrasonography) have a low sensitivity for detecting ILC compared with other invasive breast tumors. This difficulty is usually ascribed to the diffuse infiltrative growth pattern of ILC. MRI has a greater sensitivity for detecting ILC.
Risk factors for the development of ILC have been identified and include:
• Alcohol consumption
• Use of combined hormone replacement therapy
• Early menarche (menarche before the age of 12 years)
• Late-onset menopause (menopause after the age of 55 years)
• Nulliparity/low parity (defined by World Health Organization as fewer than five pregnancies with gestation periods of ≥ 20 weeks)
• Late age at birth (> 30 years)
• Family history (eg, hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome)
• Genetics (eg, CDH1 mutations)
Treatment protocols for ILC align with those used in other breast cancer subtypes and typically involve a multidisciplinary approach comprising surgery, radiotherapy, and systemic therapies. Cancers that are deemed resectable will typically be managed surgically upfront, although some patients may require neoadjuvant therapy to reduce tumor burden and facilitate surgical intervention. Breast-conserving surgery using a wide local excision can frequently be performed; however, in up to 65% of cases, a second surgery will be required (re-excision or mastectomy). Axillary lymph node status is a crucial factor in the prognosis of all breast cancers and affects surgical planning. Sentinel node biopsy is the standard method of assessing the axilla.
Systemic therapy is an integral part of the multidisciplinary approach to treating breast cancer and usually involves the use of chemotherapy. However, because of the unique molecular biology of ILC, treatment response to chemotherapy is often poor, resulting in lower rates of complete pathologic response and higher rates of mastectomy. Conversely, ILC has been shown to respond well to endocrine therapy, making it the optimal treatment choice. Novel therapeutic approaches are under investigation.
Detailed guidance on the treatment of ILC is available from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The findings in this case are suggestive of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC).
Globally, breast cancer remains the most common life-threatening cancer diagnosed and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. In the United States, approximately 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer were diagnosed in 2022 and 43,250 deaths were attributed to breast cancer in the same year. Worldwide, approximately 2.3 million new diagnoses and 685,000 breast cancer-related deaths were reported in 2020.
ILC is one of the leading histologic types of invasive carcinoma, second in incidence only to invasive carcinoma of no special type. ILC accounts for 5%-15% of all invasive breast cancers, and its incidence has been steadily increasing — particularly among postmenopausal women — over the past two decades. ILC has distinct molecular and histopathologic features, including the loss of cell-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, resulting in small, discohesive cells proliferating in single-file strands; positivity for both the estrogen and progesterone receptor; and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negativity.
The diagnosis of ILC can be challenging, as it is difficult to detect both on physical examination and with standard imaging techniques. Patients are often diagnosed with late-stage disease, characterized by large tumors and lymph node involvement. The signs of ILC are often vague, such as skin thickening or dimpling. In addition, measuring the extent of ILC can be challenging, as traditional screening methods (eg, mammography and ultrasonography) have a low sensitivity for detecting ILC compared with other invasive breast tumors. This difficulty is usually ascribed to the diffuse infiltrative growth pattern of ILC. MRI has a greater sensitivity for detecting ILC.
Risk factors for the development of ILC have been identified and include:
• Alcohol consumption
• Use of combined hormone replacement therapy
• Early menarche (menarche before the age of 12 years)
• Late-onset menopause (menopause after the age of 55 years)
• Nulliparity/low parity (defined by World Health Organization as fewer than five pregnancies with gestation periods of ≥ 20 weeks)
• Late age at birth (> 30 years)
• Family history (eg, hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome)
• Genetics (eg, CDH1 mutations)
Treatment protocols for ILC align with those used in other breast cancer subtypes and typically involve a multidisciplinary approach comprising surgery, radiotherapy, and systemic therapies. Cancers that are deemed resectable will typically be managed surgically upfront, although some patients may require neoadjuvant therapy to reduce tumor burden and facilitate surgical intervention. Breast-conserving surgery using a wide local excision can frequently be performed; however, in up to 65% of cases, a second surgery will be required (re-excision or mastectomy). Axillary lymph node status is a crucial factor in the prognosis of all breast cancers and affects surgical planning. Sentinel node biopsy is the standard method of assessing the axilla.
Systemic therapy is an integral part of the multidisciplinary approach to treating breast cancer and usually involves the use of chemotherapy. However, because of the unique molecular biology of ILC, treatment response to chemotherapy is often poor, resulting in lower rates of complete pathologic response and higher rates of mastectomy. Conversely, ILC has been shown to respond well to endocrine therapy, making it the optimal treatment choice. Novel therapeutic approaches are under investigation.
Detailed guidance on the treatment of ILC is available from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The findings in this case are suggestive of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC).
Globally, breast cancer remains the most common life-threatening cancer diagnosed and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women. In the United States, approximately 287,850 new cases of invasive breast cancer were diagnosed in 2022 and 43,250 deaths were attributed to breast cancer in the same year. Worldwide, approximately 2.3 million new diagnoses and 685,000 breast cancer-related deaths were reported in 2020.
ILC is one of the leading histologic types of invasive carcinoma, second in incidence only to invasive carcinoma of no special type. ILC accounts for 5%-15% of all invasive breast cancers, and its incidence has been steadily increasing — particularly among postmenopausal women — over the past two decades. ILC has distinct molecular and histopathologic features, including the loss of cell-cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, resulting in small, discohesive cells proliferating in single-file strands; positivity for both the estrogen and progesterone receptor; and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negativity.
The diagnosis of ILC can be challenging, as it is difficult to detect both on physical examination and with standard imaging techniques. Patients are often diagnosed with late-stage disease, characterized by large tumors and lymph node involvement. The signs of ILC are often vague, such as skin thickening or dimpling. In addition, measuring the extent of ILC can be challenging, as traditional screening methods (eg, mammography and ultrasonography) have a low sensitivity for detecting ILC compared with other invasive breast tumors. This difficulty is usually ascribed to the diffuse infiltrative growth pattern of ILC. MRI has a greater sensitivity for detecting ILC.
Risk factors for the development of ILC have been identified and include:
• Alcohol consumption
• Use of combined hormone replacement therapy
• Early menarche (menarche before the age of 12 years)
• Late-onset menopause (menopause after the age of 55 years)
• Nulliparity/low parity (defined by World Health Organization as fewer than five pregnancies with gestation periods of ≥ 20 weeks)
• Late age at birth (> 30 years)
• Family history (eg, hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome)
• Genetics (eg, CDH1 mutations)
Treatment protocols for ILC align with those used in other breast cancer subtypes and typically involve a multidisciplinary approach comprising surgery, radiotherapy, and systemic therapies. Cancers that are deemed resectable will typically be managed surgically upfront, although some patients may require neoadjuvant therapy to reduce tumor burden and facilitate surgical intervention. Breast-conserving surgery using a wide local excision can frequently be performed; however, in up to 65% of cases, a second surgery will be required (re-excision or mastectomy). Axillary lymph node status is a crucial factor in the prognosis of all breast cancers and affects surgical planning. Sentinel node biopsy is the standard method of assessing the axilla.
Systemic therapy is an integral part of the multidisciplinary approach to treating breast cancer and usually involves the use of chemotherapy. However, because of the unique molecular biology of ILC, treatment response to chemotherapy is often poor, resulting in lower rates of complete pathologic response and higher rates of mastectomy. Conversely, ILC has been shown to respond well to endocrine therapy, making it the optimal treatment choice. Novel therapeutic approaches are under investigation.
Detailed guidance on the treatment of ILC is available from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, Assistant Member, Department of Breast Oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL.
Avan J. Armaghani, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 58-year-old postmenopausal woman presents for screening mammography. The patient's last mammogram was 18 months ago and showed dense breast tissue with no abnormalities. The patient states that she has no breast symptoms. She is 5 ft 3 in and weighs 196 lb (BMI 34.7). Her previous medical history is unremarkable. There is a family history of breast cancer (two maternal cousins) and colon cancer (paternal grandmother). Bilateral mammography reveals an irregular mass that is approximately 2.4 cm and calcifications in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. Physical examination reveals no palpable abnormalities. The patient undergoes a stereotactic breast biopsy. Pathology findings include malignant monomorphic cells that form loosely dispersed linear columns encircling the mammary ducts and infiltrating breast tissue and fat.