User login
Researchers find drug target in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma
Preclinical research indicates that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective in treating anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Researchers found evidence to suggest that TYK2 “is highly expressed in all cases of human ALCL.”
The team also discovered that TYK2 inhibition induces apoptosis in human ALCL cells, and it delays tumor onset, and prolongs survival in a mouse model of ALCL.
Olaf Merkel, PhD, of the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, and his colleagues detailed these findings in Leukemia.
The researchers said their analyses suggest TYK2 is expressed in all types of ALCL, regardless of ALK status, and TYK2 mediates the same anti-apoptotic response across ALCLs.
“Therefore, we could consider TYK2 signaling as the Achilles’ heel of ALCL, as, in all patients we have analyzed, the tumor cells relied on this activity to support the essential survival signal,” Dr. Merkel said in a statement.
He and his colleagues found that disrupting TYK2 – either via gene knockdown or with small-molecule TYK2 inhibitors – induced apoptosis in human ALCL cells in vitro.
In a mouse model of NPM-ALK-induced lymphoma, Tyk2 deletion slowed the rate of tumor growth and significantly prolonged survival. The median survival was 53.3 weeks in mice with Tyk2 deletion and 16.0 weeks in control mice (P less than .0001).
Additional experiments in human ALCL cell lines showed that “TYK2 is activated by autocrine production of IL-10 and IL-22 and by interaction with specific receptors expressed by the cells,” the researchers said.
They also found that “activated TYK2 leads to STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation, activated expression of MCL1, and aberrant ALCL cell survival.”
Taking these findings together, the researchers concluded that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective for treating ALCL.
“We are looking forward to TYK2 inhibitors becoming available,” said study coauthor Lukas Kenner, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna. “[I]n the more rare lymphomas, we urgently need better therapies.”
The researchers received grant funding from various organizations but reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Prutsch N et al. Leukemia. 2018 Aug 21. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0239-1.
Preclinical research indicates that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective in treating anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Researchers found evidence to suggest that TYK2 “is highly expressed in all cases of human ALCL.”
The team also discovered that TYK2 inhibition induces apoptosis in human ALCL cells, and it delays tumor onset, and prolongs survival in a mouse model of ALCL.
Olaf Merkel, PhD, of the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, and his colleagues detailed these findings in Leukemia.
The researchers said their analyses suggest TYK2 is expressed in all types of ALCL, regardless of ALK status, and TYK2 mediates the same anti-apoptotic response across ALCLs.
“Therefore, we could consider TYK2 signaling as the Achilles’ heel of ALCL, as, in all patients we have analyzed, the tumor cells relied on this activity to support the essential survival signal,” Dr. Merkel said in a statement.
He and his colleagues found that disrupting TYK2 – either via gene knockdown or with small-molecule TYK2 inhibitors – induced apoptosis in human ALCL cells in vitro.
In a mouse model of NPM-ALK-induced lymphoma, Tyk2 deletion slowed the rate of tumor growth and significantly prolonged survival. The median survival was 53.3 weeks in mice with Tyk2 deletion and 16.0 weeks in control mice (P less than .0001).
Additional experiments in human ALCL cell lines showed that “TYK2 is activated by autocrine production of IL-10 and IL-22 and by interaction with specific receptors expressed by the cells,” the researchers said.
They also found that “activated TYK2 leads to STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation, activated expression of MCL1, and aberrant ALCL cell survival.”
Taking these findings together, the researchers concluded that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective for treating ALCL.
“We are looking forward to TYK2 inhibitors becoming available,” said study coauthor Lukas Kenner, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna. “[I]n the more rare lymphomas, we urgently need better therapies.”
The researchers received grant funding from various organizations but reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Prutsch N et al. Leukemia. 2018 Aug 21. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0239-1.
Preclinical research indicates that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective in treating anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Researchers found evidence to suggest that TYK2 “is highly expressed in all cases of human ALCL.”
The team also discovered that TYK2 inhibition induces apoptosis in human ALCL cells, and it delays tumor onset, and prolongs survival in a mouse model of ALCL.
Olaf Merkel, PhD, of the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, and his colleagues detailed these findings in Leukemia.
The researchers said their analyses suggest TYK2 is expressed in all types of ALCL, regardless of ALK status, and TYK2 mediates the same anti-apoptotic response across ALCLs.
“Therefore, we could consider TYK2 signaling as the Achilles’ heel of ALCL, as, in all patients we have analyzed, the tumor cells relied on this activity to support the essential survival signal,” Dr. Merkel said in a statement.
He and his colleagues found that disrupting TYK2 – either via gene knockdown or with small-molecule TYK2 inhibitors – induced apoptosis in human ALCL cells in vitro.
In a mouse model of NPM-ALK-induced lymphoma, Tyk2 deletion slowed the rate of tumor growth and significantly prolonged survival. The median survival was 53.3 weeks in mice with Tyk2 deletion and 16.0 weeks in control mice (P less than .0001).
Additional experiments in human ALCL cell lines showed that “TYK2 is activated by autocrine production of IL-10 and IL-22 and by interaction with specific receptors expressed by the cells,” the researchers said.
They also found that “activated TYK2 leads to STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation, activated expression of MCL1, and aberrant ALCL cell survival.”
Taking these findings together, the researchers concluded that TYK2 inhibitors could be effective for treating ALCL.
“We are looking forward to TYK2 inhibitors becoming available,” said study coauthor Lukas Kenner, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna. “[I]n the more rare lymphomas, we urgently need better therapies.”
The researchers received grant funding from various organizations but reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Prutsch N et al. Leukemia. 2018 Aug 21. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0239-1.
FROM LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: TYK2 was expressed in all types of ALCL studied and mediated the same anti-apoptotic response across ALCLs.
Study details: A preclinical study of mouse and human ALCL cell lines.
Disclosures: The researchers received grant funding from various organizations but reported having no conflicts of interest.
Source: Prutsch N et al. Leukemia. 2018 Aug 21. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0239-1.
CPI-613 receives orphan designation for PTCL
The Food and Drug Administration has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Rafael Pharmaceuticals is developing CPI-613 as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
CPI-613 is currently under investigation in combination with bendamustine in a phase 1 study of patients with relapsed or refractory T-cell lymphoma or classical Hodgkin lymphoma, according to the press release from the company.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2016 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
CPI-613 was given at escalating doses starting at 2,000 mg/m2 over 2 hours on days 1-4 as well as on days 8, 11, 15, and 18. Bendamustine was infused at 90 mg/m2 on days 4 and 5 of each 4-week treatment cycle. The treatment cycles were repeated for up to six cycles. There was no intrapatient dose escalation.
The ASH presentation included safety data on eight patients. The most common grade 3 or higher toxicities – lymphopenia and neutropenia – occurred in four patients.
A patient dosed at 2,750 mg/m2 had a dose-limiting toxicity of grade 3 acute kidney injury and grade 4 lactic acidosis. Because of this, the study protocol was amended to discontinue dose escalation at doses of 2,750 mg/m2 or higher and to expand the 2,500 mg/m2 cohort.
Six patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the overall response rate was 83% (5/6).
There were three complete responses in patients with PTCL not otherwise specified, a partial response in a patient with mycosis fungoides, and a partial response in a patient with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma.
One patient with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia experienced progressive disease.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the United States.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Rafael Pharmaceuticals is developing CPI-613 as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
CPI-613 is currently under investigation in combination with bendamustine in a phase 1 study of patients with relapsed or refractory T-cell lymphoma or classical Hodgkin lymphoma, according to the press release from the company.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2016 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
CPI-613 was given at escalating doses starting at 2,000 mg/m2 over 2 hours on days 1-4 as well as on days 8, 11, 15, and 18. Bendamustine was infused at 90 mg/m2 on days 4 and 5 of each 4-week treatment cycle. The treatment cycles were repeated for up to six cycles. There was no intrapatient dose escalation.
The ASH presentation included safety data on eight patients. The most common grade 3 or higher toxicities – lymphopenia and neutropenia – occurred in four patients.
A patient dosed at 2,750 mg/m2 had a dose-limiting toxicity of grade 3 acute kidney injury and grade 4 lactic acidosis. Because of this, the study protocol was amended to discontinue dose escalation at doses of 2,750 mg/m2 or higher and to expand the 2,500 mg/m2 cohort.
Six patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the overall response rate was 83% (5/6).
There were three complete responses in patients with PTCL not otherwise specified, a partial response in a patient with mycosis fungoides, and a partial response in a patient with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma.
One patient with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia experienced progressive disease.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the United States.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted orphan drug designation to CPI-613 for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
CPI-613 is a novel lipoic acid analogue that inhibits multiple enzyme targets within the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Rafael Pharmaceuticals is developing CPI-613 as a treatment for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors.
CPI-613 is currently under investigation in combination with bendamustine in a phase 1 study of patients with relapsed or refractory T-cell lymphoma or classical Hodgkin lymphoma, according to the press release from the company.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2016 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
CPI-613 was given at escalating doses starting at 2,000 mg/m2 over 2 hours on days 1-4 as well as on days 8, 11, 15, and 18. Bendamustine was infused at 90 mg/m2 on days 4 and 5 of each 4-week treatment cycle. The treatment cycles were repeated for up to six cycles. There was no intrapatient dose escalation.
The ASH presentation included safety data on eight patients. The most common grade 3 or higher toxicities – lymphopenia and neutropenia – occurred in four patients.
A patient dosed at 2,750 mg/m2 had a dose-limiting toxicity of grade 3 acute kidney injury and grade 4 lactic acidosis. Because of this, the study protocol was amended to discontinue dose escalation at doses of 2,750 mg/m2 or higher and to expand the 2,500 mg/m2 cohort.
Six patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the overall response rate was 83% (5/6).
There were three complete responses in patients with PTCL not otherwise specified, a partial response in a patient with mycosis fungoides, and a partial response in a patient with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma.
One patient with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia experienced progressive disease.
The FDA grants orphan designation to products intended to treat, diagnose, or prevent diseases/disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the United States.
The designation provides incentives for sponsors to develop products for rare diseases. This may include tax credits toward the cost of clinical trials, prescription drug user fee waivers, and 7 years of market exclusivity if the product is approved.
Make The Diagnosis - September 2018
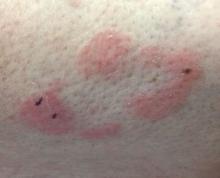
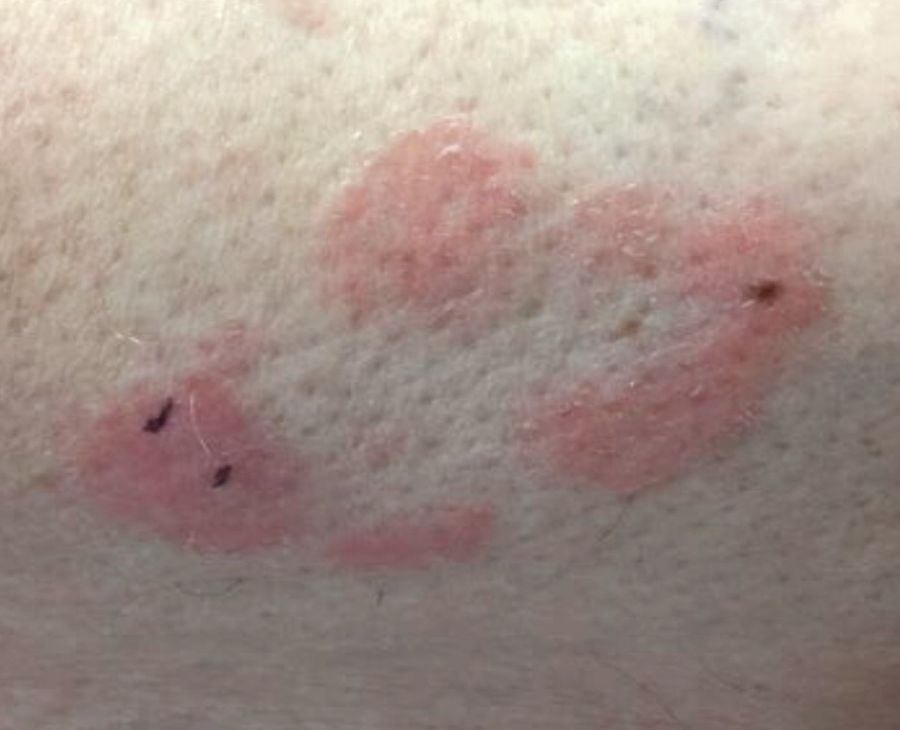
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Some have postulated an infectious agent as the cause. Atopic dermatitis may confer an increased risk because of the chronic stimulation of T cells. Males are more commonly affected than females by a 2:1 ratio. A worse prognosis is associated with advanced age. Children and adolescents may be affected as well.
With mycosis fungoides, there are three main types of skin lesions: patch, plaque, and tumor. Patients will progress from patch to plaque to tumor stage in classic MF. Often, lesions begin as scaly, erythematous patches that resemble eczema. Because of the nonspecific nature of early lesions, the median duration from the onset of skin lesions to the diagnosis of MF is 4-6 years. Patch stage lesions may be pruritic or asymptomatic. Commonly, they present in non–sun-exposed areas, such as the buttocks. Annular, infiltrated, red-brown or violaceous plaques can develop, which represent malignant T-cell infiltration. Many patients never progress past the plaque stage. Tumor stage MF is more aggressive, with nodules that may undergo necrosis and ulceration.
The leukemic form of MF is Sézary syndrome. Patients present with pruritic erythroderma and lymphadenopathy. Nail dystrophy, scaling of palms and soles, and alopecia may be present. A peripheral blood smear reveals Sézary cells, which are large, hyperconvoluted lymphocytes. The count of Sézary cells is usually greater than 1000 cells/mm3.
Histology of early lesions may not be diagnostic for CTCL. Often, biopsies will be read as eczematous or psoriasiform for years before the diagnosis of MF is made. Classically, epidermotropism (single-cell exocytosis of lymphocytes into the epidermis) is present. Advanced stages may show a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes in the dermis. Groups of lymphocytes in the epidermis form Pautrier’s microabscesses. Mycosis cells may exhibit cerebriform nuclei. Neoplastic cells in MF are CD3+, CD4+, CD45RO+, CD8–. Tissue can be sent for T-cell gene rearrangement polymerase chain reaction. The presence of monoclonal T-cell gene receptor rearrangements can aid in the diagnosis of MF.
Treatment includes topical steroids, mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard) or bexarotene gel, PUVA therapy, and narrow-band UVB light for limited and/or patch disease. Localized radiotherapy can be used for more resistant lesions. Topical therapies are preferred in the early stages in MF. Systemic treatments for patients who do not respond to local therapy, or in more advanced disease include methotrexate, interferon-alpha, oral bexarotene, denileukin diftitox, and combination chemotherapy. Photopheresis is reserved for erythrodermic disease.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
New regimens for youth with T-cell malignancies yield best outcomes yet
A set of novel chemotherapy regimens yield excellent outcomes—the best yet—among pediatric and young adult patients with T-cell malignancies, finds a phase 3 randomized controlled trial conducted by the Children’s Oncology Group (ALL0434).
“Despite very intense and complex chemotherapy, 20% of children and adolescents enrolled in Children’s Oncology Group T-cell leukemia trials between 2000 and 2005 did not survive. New drugs were needed to improve survival rates for T-cell malignancies,” lead study author Kimberly P. Dunsmore, MD, a professor at Virginia Tech, Roanoke, said in a press briefing leading up to the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The ALL0434 trial tested the addition of methotrexate (Trexall) and/or nelarabine (Arranon), a T cell–specific drug known to be efficacious in relapsed disease, to standard chemotherapy, with tailoring of the regimen to recurrence risk. Analyses were based on 1,545 patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) or T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LL).
Results for all patients with T-ALL showed that, with addition of either or both drugs, more than 90% were alive at 4 years and more than 80% were leukemia free. Adding nelarabine to standard chemotherapy improved disease-free survival among the subset having intermediate- or high-risk disease, and the best outcomes were seen with addition of both nelarabine and an escalating dose of methotrexate.
Although patients with T-LL did not see benefit from addition of nelarabine, they still had an 85% rate of overall survival at 4 years.
“ALL0434 is the largest trial for children and young adults with T-cell malignancy ever conducted. It has the best-ever survival data,” Dr. Dunsmore commented.
“Our next steps will be to examine what implications and benefits may accrue when using nelarabine in protocols without cranial irradiation. This is to decrease long-term neurologic side effects, and we think it may be possible since nelarabine also reduces CNS relapses,” she said.
“This trial highlights how effective our pediatric and young adult oncologists are at accruing: This is a rare disease, and they were able to put more than 1,500 patients on trial with this rare disease over the course of time,” commented ASCO President Bruce E. Johnson, MD, FASCO.
The new combination regimens are noteworthy in that they improved survival by an absolute 10% without minimal increase in toxicity, he maintained.
“This is part of the paradigm where nelarabine had been approved [by the FDA] for relapsed or recurrent disease, and in this particular setting, it has been moved upfront, closer to the initial treatment, improving the outcomes for those patients,” elaborated Dr. Johnson, who is also a professor of medicine at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and a leader of the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center Lung Cancer Program, both in Boston.
Study details
The ALL0434 trial enrolled patients aged 1-30 years with newly diagnosed T-ALL or T-LL. After induction chemotherapy, all patients received standard chemotherapy, the Children’s Oncology Group augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster regimen (N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1663-71), and depending on recurrence risk, cranial irradiation.
In addition to that regimen, they were randomly assigned to four arms, according to methotrexate dosing (high dose with leucovorin rescue in the inpatient setting vs. escalating dose in the outpatient setting) and nelarabine therapy (receipt vs. nonreceipt).
Among patients with T-ALL, those with low-risk disease were ineligible for nelarabine and did not receive cranial irradiation, whereas those with intermediate- and high-risk disease were randomized to all four arms, Dr. Dunsmore explained. In addition, those who did not achieve remission on induction chemotherapy were nonrandomly assigned to the high-dose methotrexate plus nelarabine arm.
Patients with T-LL were ineligible for high-dose methotrexate and were randomized to escalating-dose methotrexate with or without nelarabine.
Among all patients with T-ALL, the 4-year rate of overall survival was 90.2%, and the 4-year rate of disease-free survival was 84.1%, Dr. Dunsmore reported.
Disease-free survival was better with escalating-dose methotrexate than with high-dose methotrexate (89.8% vs. 78%).
Addition of nelarabine for patients with T-ALL having intermediate- or high-risk disease improved disease-free survival, from 83% without the drug to 88% with the drug (P = .0450), and reduced the rate of CNS relapse. Disease-free survival was highest, at 91%, among those who received both escalating-dose methotrexate and nelarabine.
Among the patients who did not achieve remission from induction chemotherapy, the 4-year rate of overall survival was 54%. “This is important because it’s more than double the past survival rates,” Dr. Dunsmore noted.
Patients with T-LL fared similarly well whether they received nelarabine or not; fully 85% overall were still alive at 4 years.
In terms of adverse effects of nelarabine therapy, the rate of peripheral neuropathy (motor or sensory), one of the more problematic adverse effects of the drug, was 8% in the trial population overall and did not exceed 9% in any treatment arm, she reported.
Dr. Dunsmore disclosed that an immediate family member is an employee of and has a leadership role with TypeZero Technologies; that she receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Novo Nordisk; and that an immediate family member receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Tandem Diabetes Care. The study received funding from the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program within the National Cancer Institute/National Institutes of Health and received support from the St. Baldrick’s Foundation.
SOURCE: Dunsmore KP et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 10500.
A set of novel chemotherapy regimens yield excellent outcomes—the best yet—among pediatric and young adult patients with T-cell malignancies, finds a phase 3 randomized controlled trial conducted by the Children’s Oncology Group (ALL0434).
“Despite very intense and complex chemotherapy, 20% of children and adolescents enrolled in Children’s Oncology Group T-cell leukemia trials between 2000 and 2005 did not survive. New drugs were needed to improve survival rates for T-cell malignancies,” lead study author Kimberly P. Dunsmore, MD, a professor at Virginia Tech, Roanoke, said in a press briefing leading up to the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The ALL0434 trial tested the addition of methotrexate (Trexall) and/or nelarabine (Arranon), a T cell–specific drug known to be efficacious in relapsed disease, to standard chemotherapy, with tailoring of the regimen to recurrence risk. Analyses were based on 1,545 patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) or T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LL).
Results for all patients with T-ALL showed that, with addition of either or both drugs, more than 90% were alive at 4 years and more than 80% were leukemia free. Adding nelarabine to standard chemotherapy improved disease-free survival among the subset having intermediate- or high-risk disease, and the best outcomes were seen with addition of both nelarabine and an escalating dose of methotrexate.
Although patients with T-LL did not see benefit from addition of nelarabine, they still had an 85% rate of overall survival at 4 years.
“ALL0434 is the largest trial for children and young adults with T-cell malignancy ever conducted. It has the best-ever survival data,” Dr. Dunsmore commented.
“Our next steps will be to examine what implications and benefits may accrue when using nelarabine in protocols without cranial irradiation. This is to decrease long-term neurologic side effects, and we think it may be possible since nelarabine also reduces CNS relapses,” she said.
“This trial highlights how effective our pediatric and young adult oncologists are at accruing: This is a rare disease, and they were able to put more than 1,500 patients on trial with this rare disease over the course of time,” commented ASCO President Bruce E. Johnson, MD, FASCO.
The new combination regimens are noteworthy in that they improved survival by an absolute 10% without minimal increase in toxicity, he maintained.
“This is part of the paradigm where nelarabine had been approved [by the FDA] for relapsed or recurrent disease, and in this particular setting, it has been moved upfront, closer to the initial treatment, improving the outcomes for those patients,” elaborated Dr. Johnson, who is also a professor of medicine at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and a leader of the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center Lung Cancer Program, both in Boston.
Study details
The ALL0434 trial enrolled patients aged 1-30 years with newly diagnosed T-ALL or T-LL. After induction chemotherapy, all patients received standard chemotherapy, the Children’s Oncology Group augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster regimen (N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1663-71), and depending on recurrence risk, cranial irradiation.
In addition to that regimen, they were randomly assigned to four arms, according to methotrexate dosing (high dose with leucovorin rescue in the inpatient setting vs. escalating dose in the outpatient setting) and nelarabine therapy (receipt vs. nonreceipt).
Among patients with T-ALL, those with low-risk disease were ineligible for nelarabine and did not receive cranial irradiation, whereas those with intermediate- and high-risk disease were randomized to all four arms, Dr. Dunsmore explained. In addition, those who did not achieve remission on induction chemotherapy were nonrandomly assigned to the high-dose methotrexate plus nelarabine arm.
Patients with T-LL were ineligible for high-dose methotrexate and were randomized to escalating-dose methotrexate with or without nelarabine.
Among all patients with T-ALL, the 4-year rate of overall survival was 90.2%, and the 4-year rate of disease-free survival was 84.1%, Dr. Dunsmore reported.
Disease-free survival was better with escalating-dose methotrexate than with high-dose methotrexate (89.8% vs. 78%).
Addition of nelarabine for patients with T-ALL having intermediate- or high-risk disease improved disease-free survival, from 83% without the drug to 88% with the drug (P = .0450), and reduced the rate of CNS relapse. Disease-free survival was highest, at 91%, among those who received both escalating-dose methotrexate and nelarabine.
Among the patients who did not achieve remission from induction chemotherapy, the 4-year rate of overall survival was 54%. “This is important because it’s more than double the past survival rates,” Dr. Dunsmore noted.
Patients with T-LL fared similarly well whether they received nelarabine or not; fully 85% overall were still alive at 4 years.
In terms of adverse effects of nelarabine therapy, the rate of peripheral neuropathy (motor or sensory), one of the more problematic adverse effects of the drug, was 8% in the trial population overall and did not exceed 9% in any treatment arm, she reported.
Dr. Dunsmore disclosed that an immediate family member is an employee of and has a leadership role with TypeZero Technologies; that she receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Novo Nordisk; and that an immediate family member receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Tandem Diabetes Care. The study received funding from the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program within the National Cancer Institute/National Institutes of Health and received support from the St. Baldrick’s Foundation.
SOURCE: Dunsmore KP et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 10500.
A set of novel chemotherapy regimens yield excellent outcomes—the best yet—among pediatric and young adult patients with T-cell malignancies, finds a phase 3 randomized controlled trial conducted by the Children’s Oncology Group (ALL0434).
“Despite very intense and complex chemotherapy, 20% of children and adolescents enrolled in Children’s Oncology Group T-cell leukemia trials between 2000 and 2005 did not survive. New drugs were needed to improve survival rates for T-cell malignancies,” lead study author Kimberly P. Dunsmore, MD, a professor at Virginia Tech, Roanoke, said in a press briefing leading up to the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The ALL0434 trial tested the addition of methotrexate (Trexall) and/or nelarabine (Arranon), a T cell–specific drug known to be efficacious in relapsed disease, to standard chemotherapy, with tailoring of the regimen to recurrence risk. Analyses were based on 1,545 patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) or T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LL).
Results for all patients with T-ALL showed that, with addition of either or both drugs, more than 90% were alive at 4 years and more than 80% were leukemia free. Adding nelarabine to standard chemotherapy improved disease-free survival among the subset having intermediate- or high-risk disease, and the best outcomes were seen with addition of both nelarabine and an escalating dose of methotrexate.
Although patients with T-LL did not see benefit from addition of nelarabine, they still had an 85% rate of overall survival at 4 years.
“ALL0434 is the largest trial for children and young adults with T-cell malignancy ever conducted. It has the best-ever survival data,” Dr. Dunsmore commented.
“Our next steps will be to examine what implications and benefits may accrue when using nelarabine in protocols without cranial irradiation. This is to decrease long-term neurologic side effects, and we think it may be possible since nelarabine also reduces CNS relapses,” she said.
“This trial highlights how effective our pediatric and young adult oncologists are at accruing: This is a rare disease, and they were able to put more than 1,500 patients on trial with this rare disease over the course of time,” commented ASCO President Bruce E. Johnson, MD, FASCO.
The new combination regimens are noteworthy in that they improved survival by an absolute 10% without minimal increase in toxicity, he maintained.
“This is part of the paradigm where nelarabine had been approved [by the FDA] for relapsed or recurrent disease, and in this particular setting, it has been moved upfront, closer to the initial treatment, improving the outcomes for those patients,” elaborated Dr. Johnson, who is also a professor of medicine at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and a leader of the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center Lung Cancer Program, both in Boston.
Study details
The ALL0434 trial enrolled patients aged 1-30 years with newly diagnosed T-ALL or T-LL. After induction chemotherapy, all patients received standard chemotherapy, the Children’s Oncology Group augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster regimen (N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1663-71), and depending on recurrence risk, cranial irradiation.
In addition to that regimen, they were randomly assigned to four arms, according to methotrexate dosing (high dose with leucovorin rescue in the inpatient setting vs. escalating dose in the outpatient setting) and nelarabine therapy (receipt vs. nonreceipt).
Among patients with T-ALL, those with low-risk disease were ineligible for nelarabine and did not receive cranial irradiation, whereas those with intermediate- and high-risk disease were randomized to all four arms, Dr. Dunsmore explained. In addition, those who did not achieve remission on induction chemotherapy were nonrandomly assigned to the high-dose methotrexate plus nelarabine arm.
Patients with T-LL were ineligible for high-dose methotrexate and were randomized to escalating-dose methotrexate with or without nelarabine.
Among all patients with T-ALL, the 4-year rate of overall survival was 90.2%, and the 4-year rate of disease-free survival was 84.1%, Dr. Dunsmore reported.
Disease-free survival was better with escalating-dose methotrexate than with high-dose methotrexate (89.8% vs. 78%).
Addition of nelarabine for patients with T-ALL having intermediate- or high-risk disease improved disease-free survival, from 83% without the drug to 88% with the drug (P = .0450), and reduced the rate of CNS relapse. Disease-free survival was highest, at 91%, among those who received both escalating-dose methotrexate and nelarabine.
Among the patients who did not achieve remission from induction chemotherapy, the 4-year rate of overall survival was 54%. “This is important because it’s more than double the past survival rates,” Dr. Dunsmore noted.
Patients with T-LL fared similarly well whether they received nelarabine or not; fully 85% overall were still alive at 4 years.
In terms of adverse effects of nelarabine therapy, the rate of peripheral neuropathy (motor or sensory), one of the more problematic adverse effects of the drug, was 8% in the trial population overall and did not exceed 9% in any treatment arm, she reported.
Dr. Dunsmore disclosed that an immediate family member is an employee of and has a leadership role with TypeZero Technologies; that she receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Novo Nordisk; and that an immediate family member receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Tandem Diabetes Care. The study received funding from the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program within the National Cancer Institute/National Institutes of Health and received support from the St. Baldrick’s Foundation.
SOURCE: Dunsmore KP et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 10500.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients with T-ALL had a 4-year rate of overall survival of 90.2% and disease-free survival of 84.1%; patients with T-LL had a 4-year rate of overall survival of 85%.
Study details: Phase 3 randomized controlled trial among 1,545 youth with T-ALL or T-LL testing various regimens of methotrexate and/or nelarabine with standard chemotherapy (ALL0434).
Disclosures: Dr. Dunsmore disclosed that an immediate family member is an employee of and has a leadership role with TypeZero; that she receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Novo Nordisk; and that an immediate family member receives travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Tandem Diabetes Care. The study received funding from the Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program within the National Cancer Institute/National Institutes of Health and received support from the St. Baldrick’s Foundation.
Source: Dunsmore KP et al. ASCO 2018, Abstract 10500.
FDA places partial hold on trials after secondary lymphoma
The drugmaker after a pediatric patient developed a secondary T-cell lymphoma.
The Food and Drug Administration had issued a partial clinical hold in April on new enrollment of any patients with genetically defined solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. Patients already enrolled who have not had disease progression can continue to receive tazemetostat.
Tazemetostat is a first-in-class EZH2 inhibitor being studied as monotherapy in phase 1 and 2 trials for certain molecularly defined solid tumors, follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, mesothelioma, and in combination studies of DLBCL and non–small cell lung cancer.
Epizyme is currently working to update informed consent, the investigator’s brochure, and study protocols, the company said in a statement.
The drugmaker after a pediatric patient developed a secondary T-cell lymphoma.
The Food and Drug Administration had issued a partial clinical hold in April on new enrollment of any patients with genetically defined solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. Patients already enrolled who have not had disease progression can continue to receive tazemetostat.
Tazemetostat is a first-in-class EZH2 inhibitor being studied as monotherapy in phase 1 and 2 trials for certain molecularly defined solid tumors, follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, mesothelioma, and in combination studies of DLBCL and non–small cell lung cancer.
Epizyme is currently working to update informed consent, the investigator’s brochure, and study protocols, the company said in a statement.
The drugmaker after a pediatric patient developed a secondary T-cell lymphoma.
The Food and Drug Administration had issued a partial clinical hold in April on new enrollment of any patients with genetically defined solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. Patients already enrolled who have not had disease progression can continue to receive tazemetostat.
Tazemetostat is a first-in-class EZH2 inhibitor being studied as monotherapy in phase 1 and 2 trials for certain molecularly defined solid tumors, follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, mesothelioma, and in combination studies of DLBCL and non–small cell lung cancer.
Epizyme is currently working to update informed consent, the investigator’s brochure, and study protocols, the company said in a statement.
VIDEO: How to prepare PTCL patients for transplant
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – according to Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“If you’re really trying to go to transplant, you want a complete remission or close to it. So that’s often been combination chemotherapy. But I think what we’re learning is, when some of the newer agents are combined, we’re seeing higher complete response rates. And we’re doing a better job at picking subtype specific approaches,” Dr. Horwitz said in a video interview at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Horwitz also explored the role for reduced-intensity regimens in older patients, the use of radiation conditioning, and which new agents look most promising in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Dr. Horwitz had previously disclosed financial relationships with Celgene, Forty Seven, Huya Bioscience International, Infinity, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Millennium, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Horwitz SM. TCLF 2018.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – according to Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“If you’re really trying to go to transplant, you want a complete remission or close to it. So that’s often been combination chemotherapy. But I think what we’re learning is, when some of the newer agents are combined, we’re seeing higher complete response rates. And we’re doing a better job at picking subtype specific approaches,” Dr. Horwitz said in a video interview at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Horwitz also explored the role for reduced-intensity regimens in older patients, the use of radiation conditioning, and which new agents look most promising in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Dr. Horwitz had previously disclosed financial relationships with Celgene, Forty Seven, Huya Bioscience International, Infinity, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Millennium, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Horwitz SM. TCLF 2018.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – according to Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“If you’re really trying to go to transplant, you want a complete remission or close to it. So that’s often been combination chemotherapy. But I think what we’re learning is, when some of the newer agents are combined, we’re seeing higher complete response rates. And we’re doing a better job at picking subtype specific approaches,” Dr. Horwitz said in a video interview at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Horwitz also explored the role for reduced-intensity regimens in older patients, the use of radiation conditioning, and which new agents look most promising in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Dr. Horwitz had previously disclosed financial relationships with Celgene, Forty Seven, Huya Bioscience International, Infinity, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Millennium, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Horwitz SM. TCLF 2018.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2018
FDA updates breast implant–associated lymphoma cases, risk
(BIA-ALCL), including nine deaths.
This figure includes all medical device reports received by the agency between 2011 and September 2017. The FDA recently provided an update on ALCL linked to breast implants and an estimate of lifetime risk of developing ALCL.
Based on available medical literature, the lifetime risk of developing BIA-ALCL for patients with textured breast implants ranges from 1 in 3,817 to 1 in 30,000, according to the update.
Of the 272 reports with data on surface type, 242 were textured implants and 30 were smooth implants. In addition, 413 reports include information on the implant fill type: 234 used silicone gel and 179 were saline filled.
“The FDA has been closely tracking the relationship between breast implants and a rare type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma since we first identified this possible association. We’ve been working to gather additional information to better characterize and quantify the risk so that patients and providers can have more informed discussions about breast implants,” said Binita Ashar, MD, director of the division of surgical devices in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “As part of that effort, we are working to update and enhance the information we have on this association, including updating the total number of known cases of BIA-ALCL and the lifetime risk of developing BIA-ALCL as reported in medical literature.”
The possible association between breast implants and the development of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) was first identified in 2011. At that time, there were not enough cases of to determine what factors increased a patient’s risk of developing the disease. As more information became available, the World Health Organization designated BIA-ALCL as a T-cell lymphoma that can develop following breast implants.
(BIA-ALCL), including nine deaths.
This figure includes all medical device reports received by the agency between 2011 and September 2017. The FDA recently provided an update on ALCL linked to breast implants and an estimate of lifetime risk of developing ALCL.
Based on available medical literature, the lifetime risk of developing BIA-ALCL for patients with textured breast implants ranges from 1 in 3,817 to 1 in 30,000, according to the update.
Of the 272 reports with data on surface type, 242 were textured implants and 30 were smooth implants. In addition, 413 reports include information on the implant fill type: 234 used silicone gel and 179 were saline filled.
“The FDA has been closely tracking the relationship between breast implants and a rare type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma since we first identified this possible association. We’ve been working to gather additional information to better characterize and quantify the risk so that patients and providers can have more informed discussions about breast implants,” said Binita Ashar, MD, director of the division of surgical devices in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “As part of that effort, we are working to update and enhance the information we have on this association, including updating the total number of known cases of BIA-ALCL and the lifetime risk of developing BIA-ALCL as reported in medical literature.”
The possible association between breast implants and the development of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) was first identified in 2011. At that time, there were not enough cases of to determine what factors increased a patient’s risk of developing the disease. As more information became available, the World Health Organization designated BIA-ALCL as a T-cell lymphoma that can develop following breast implants.
(BIA-ALCL), including nine deaths.
This figure includes all medical device reports received by the agency between 2011 and September 2017. The FDA recently provided an update on ALCL linked to breast implants and an estimate of lifetime risk of developing ALCL.
Based on available medical literature, the lifetime risk of developing BIA-ALCL for patients with textured breast implants ranges from 1 in 3,817 to 1 in 30,000, according to the update.
Of the 272 reports with data on surface type, 242 were textured implants and 30 were smooth implants. In addition, 413 reports include information on the implant fill type: 234 used silicone gel and 179 were saline filled.
“The FDA has been closely tracking the relationship between breast implants and a rare type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma since we first identified this possible association. We’ve been working to gather additional information to better characterize and quantify the risk so that patients and providers can have more informed discussions about breast implants,” said Binita Ashar, MD, director of the division of surgical devices in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “As part of that effort, we are working to update and enhance the information we have on this association, including updating the total number of known cases of BIA-ALCL and the lifetime risk of developing BIA-ALCL as reported in medical literature.”
The possible association between breast implants and the development of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) was first identified in 2011. At that time, there were not enough cases of to determine what factors increased a patient’s risk of developing the disease. As more information became available, the World Health Organization designated BIA-ALCL as a T-cell lymphoma that can develop following breast implants.
The Long and Winding Road: PTCL 10 Years from Now

Release Date: March 20, 2018
Expiration Date: March 19, 2019
Note: This activity is no longer available for credit
Agenda
New targeted agents for PTCL
(Duration: 20 minutes)
Pier Luigi Zinzani, MD, PhD
Bologna University
Institute of Hematology “Seragnoli”
Bologna, Italy
Recently approved therapies for PTCL in Asia:
What have we learned from the US experience?
(Duration: 18 minutes)
Won Seog Kim, MD, PhD
Samsung Medical Center
Seoul, Republic of Korea
Novel combination therapies:
Where are we now and where are we going?
(Duration: 23 minutes)
Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD
Columbia University Medical Center
The New York Presbyterian Hospital
New York, NY USA
Provided by:

Original activity supported by an educational grant from:
Spectrum Pharmaceuticals
Learning Objectives
At the conclusion of this educational activity, the healthcare team will be better able to:
- Discuss the treatment and management of peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- Appraise how U.S. T-cell lymphoma treatment experience can impact practice in Asia
- Summarize the importance of combination therapy in peripheral T-cell lymphoma
Target Audience
Hematologists, oncologists, and other clinicians and scientists with an interest in T-cell lymphoma
Statement of Need
Peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCL) are rare, heterogeneous and aggressive neoplasms that are associated with a poor prognosis. In addition, with current therapies, up to 70% of patients undergo relapse or develop refractory disease. Recent evidence has indicated an increase in the incidence of PTCLs and hence current challenges including pathobiology, clinical management, new drug testing as well as clinical trial accrual, need to be addressed. This activity will provide the healthcare team with the ideal foundation to facilitate progress in PTCL treatment and management.
Won Seog Kim, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Samsung Medical Center
Seoul, Republic of Korea
Disclosure: Consulting fees: Celltrion; Contracted research: Takeda; Kyowa-Kirin; J & J; Merck; Donga; Novartis; Celltrion
Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Columbia University Medical Center
The New York Presbyterian Hospital
New York, NY USA
Disclosure: Contracted research: Celgene; Merck; Spectrum; Agensys
Pier Luigi Zinzani, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Bologna University
Institute of Hematology “Seragnoli”
Bologna, Italy
Disclosure: Speakers Bureau: Janssen; Merck; Servier; Gilead; Verastem; BMS; Sandoz; Mundipharma
Permissions
Won Seog Kim presentation
Slide 4: Frequency of T and NK-cell lymphomas in Asia
Park S, Ko YH. Peripheral T cell lymphoma in Asia. Int J Hematol 2014;99:227-239. Reprinted with permission of the Japanese Society of Hematology.
Slide 29: Off-label use: 100mg of pembrolizumab, HK, Singapore, Korea
Republished with permission of the American Society of Hematology, from Kwong YL, et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing L-asparaginase. Blood. 2017;129(17):2437-2442; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Owen A. O’Connor presentation
Slide 12: Schematic of study design, patient disposition, and thrombocytopenia as a function of schedule & dose
Republished with permission of American Society of Hematology, from Amengual JE…O’Connor OA. A phase 1 study of romidepsin and pralatrexate reveals marked activity in relapsed and refractory T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018;131:397-407; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Slide 13: Summary of response rates across study population for patients treated with romidepsin and pralatrexate
Same as slide above.
Slide 14: Pharmacokinetic parameters for pralatrexate and romidepsin in the study population
Same as slide above.
Slide 15: PFS and OS as a function of treatment in study population
Same as slide above.
Slide 19: The combination of HoME and HDAC inhibitor synergistically produces apoptosis across panel of T-cell lymphomas: tCTCL H9
Marchi E . . . O’Connor OA.The combination of hypomethylating agents and histone deacetylase inhibitors produce marked synergy in preclinical models of T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2015; 171:215-226.
Slide 20: Supervised hierarchial clustering based on GEP
Same as slide above.
Slide 27: Panobinostat plus bortezomib in PTCL
Reprinted from Lancet Haematol, Tan D, et al. Panobinostat in combination with bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: an open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. 2015; 2(8):e326-e333, with permission from Elsevier.
Pier Luigi Zinzani presentation
Slides 4, 11: New agents in T-cell lymphomas (2), Belinostat (2)
O’Connor OA, et al. Belinostat in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: Results of the pivotal phase II BELIEF (CLN-19) study. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 2492-2499. Reprinted with permission. © 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 5, 8, 10, 12, 18, 20: Pralatrexate (1), Romidepsin (1), Belinostat (1), Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (1), Brentuximab vedotin – CD30+ peripheral T-cell lymphoma (1), Off-label compounds in peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Reprinted from Cancer Treat Rev, volume 60, Broccoli A, Argnani L, Zinzani PL. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas: Focusing on novel agents in relapsed and refractory disease, pp 120-129, © 2017, with permission from Elsevier.
Slides 6, 7: Pralatrexate (2) and Pralatrexate (3)
O’Connor OA, et al. Pralatrexate in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: results from the pivotal PROPEL study. J Clin Oncol, 2011; 29: 1182-1189. Reprinted with permission. © 2011 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slide 9: Romidepsin (2)
Coiffier B, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 631-636. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 13, 14: Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (2), Brentulximab vedotin — Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (3)
Pro B, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2190-2196. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 16, 17: Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (5), Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (6)
Broccoli A, et al. Italian real-life experience with brentuximab vedotin: results of a large observational study of 40 cases of relapsed/refractory systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2017; 102: 1931-1935. Obtained from the Haematologica Journal website http://www.haematologica.org
Slide 19: Brentuximab vedotin –CD30+ peripheral T-cell lymphomas (2)
Horwitz SM, et al. Blood 2014; 123: 3095-3100. Permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Slide 21: Gemcitabine in peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Zinzani PL, et al. Ann Oncol 2010; 21: 860-863. European Society of Medical Oncology licensee.
Slide 23: Lenalidomide in T-cell lymphomas (2)
Reprinted from Morschhauser F, et al. A phase 2, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of single-agent lenalidomide (Revlimid) in subjects with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the EXPECT trial. Eur J Cancer 2013, with permission from Elsevier.
Slides 24, 25: Bendamustine in T-cell lymphomas (1), Bendamustine in T-cell lymphomas (2)
Damaj G, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 31: 104-110. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
The content and views presented in this educational activity are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Hemedicus, the supporter, or Frontline Medical Communications. This material is prepared based upon a review of multiple sources of information, but it is not exhaustive of the subject matter. Therefore, healthcare professionals and other individuals should review and consider other publications and materials on the subject matter before relying solely upon the information contained within this educational activity.

Release Date: March 20, 2018
Expiration Date: March 19, 2019
Note: This activity is no longer available for credit
Agenda
New targeted agents for PTCL
(Duration: 20 minutes)
Pier Luigi Zinzani, MD, PhD
Bologna University
Institute of Hematology “Seragnoli”
Bologna, Italy
Recently approved therapies for PTCL in Asia:
What have we learned from the US experience?
(Duration: 18 minutes)
Won Seog Kim, MD, PhD
Samsung Medical Center
Seoul, Republic of Korea
Novel combination therapies:
Where are we now and where are we going?
(Duration: 23 minutes)
Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD
Columbia University Medical Center
The New York Presbyterian Hospital
New York, NY USA
Provided by:

Original activity supported by an educational grant from:
Spectrum Pharmaceuticals
Learning Objectives
At the conclusion of this educational activity, the healthcare team will be better able to:
- Discuss the treatment and management of peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- Appraise how U.S. T-cell lymphoma treatment experience can impact practice in Asia
- Summarize the importance of combination therapy in peripheral T-cell lymphoma
Target Audience
Hematologists, oncologists, and other clinicians and scientists with an interest in T-cell lymphoma
Statement of Need
Peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCL) are rare, heterogeneous and aggressive neoplasms that are associated with a poor prognosis. In addition, with current therapies, up to 70% of patients undergo relapse or develop refractory disease. Recent evidence has indicated an increase in the incidence of PTCLs and hence current challenges including pathobiology, clinical management, new drug testing as well as clinical trial accrual, need to be addressed. This activity will provide the healthcare team with the ideal foundation to facilitate progress in PTCL treatment and management.
Won Seog Kim, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Samsung Medical Center
Seoul, Republic of Korea
Disclosure: Consulting fees: Celltrion; Contracted research: Takeda; Kyowa-Kirin; J & J; Merck; Donga; Novartis; Celltrion
Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Columbia University Medical Center
The New York Presbyterian Hospital
New York, NY USA
Disclosure: Contracted research: Celgene; Merck; Spectrum; Agensys
Pier Luigi Zinzani, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Bologna University
Institute of Hematology “Seragnoli”
Bologna, Italy
Disclosure: Speakers Bureau: Janssen; Merck; Servier; Gilead; Verastem; BMS; Sandoz; Mundipharma
Permissions
Won Seog Kim presentation
Slide 4: Frequency of T and NK-cell lymphomas in Asia
Park S, Ko YH. Peripheral T cell lymphoma in Asia. Int J Hematol 2014;99:227-239. Reprinted with permission of the Japanese Society of Hematology.
Slide 29: Off-label use: 100mg of pembrolizumab, HK, Singapore, Korea
Republished with permission of the American Society of Hematology, from Kwong YL, et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing L-asparaginase. Blood. 2017;129(17):2437-2442; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Owen A. O’Connor presentation
Slide 12: Schematic of study design, patient disposition, and thrombocytopenia as a function of schedule & dose
Republished with permission of American Society of Hematology, from Amengual JE…O’Connor OA. A phase 1 study of romidepsin and pralatrexate reveals marked activity in relapsed and refractory T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018;131:397-407; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Slide 13: Summary of response rates across study population for patients treated with romidepsin and pralatrexate
Same as slide above.
Slide 14: Pharmacokinetic parameters for pralatrexate and romidepsin in the study population
Same as slide above.
Slide 15: PFS and OS as a function of treatment in study population
Same as slide above.
Slide 19: The combination of HoME and HDAC inhibitor synergistically produces apoptosis across panel of T-cell lymphomas: tCTCL H9
Marchi E . . . O’Connor OA.The combination of hypomethylating agents and histone deacetylase inhibitors produce marked synergy in preclinical models of T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2015; 171:215-226.
Slide 20: Supervised hierarchial clustering based on GEP
Same as slide above.
Slide 27: Panobinostat plus bortezomib in PTCL
Reprinted from Lancet Haematol, Tan D, et al. Panobinostat in combination with bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: an open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. 2015; 2(8):e326-e333, with permission from Elsevier.
Pier Luigi Zinzani presentation
Slides 4, 11: New agents in T-cell lymphomas (2), Belinostat (2)
O’Connor OA, et al. Belinostat in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: Results of the pivotal phase II BELIEF (CLN-19) study. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 2492-2499. Reprinted with permission. © 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 5, 8, 10, 12, 18, 20: Pralatrexate (1), Romidepsin (1), Belinostat (1), Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (1), Brentuximab vedotin – CD30+ peripheral T-cell lymphoma (1), Off-label compounds in peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Reprinted from Cancer Treat Rev, volume 60, Broccoli A, Argnani L, Zinzani PL. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas: Focusing on novel agents in relapsed and refractory disease, pp 120-129, © 2017, with permission from Elsevier.
Slides 6, 7: Pralatrexate (2) and Pralatrexate (3)
O’Connor OA, et al. Pralatrexate in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: results from the pivotal PROPEL study. J Clin Oncol, 2011; 29: 1182-1189. Reprinted with permission. © 2011 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slide 9: Romidepsin (2)
Coiffier B, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 631-636. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 13, 14: Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (2), Brentulximab vedotin — Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (3)
Pro B, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2190-2196. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 16, 17: Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (5), Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (6)
Broccoli A, et al. Italian real-life experience with brentuximab vedotin: results of a large observational study of 40 cases of relapsed/refractory systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2017; 102: 1931-1935. Obtained from the Haematologica Journal website http://www.haematologica.org
Slide 19: Brentuximab vedotin –CD30+ peripheral T-cell lymphomas (2)
Horwitz SM, et al. Blood 2014; 123: 3095-3100. Permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Slide 21: Gemcitabine in peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Zinzani PL, et al. Ann Oncol 2010; 21: 860-863. European Society of Medical Oncology licensee.
Slide 23: Lenalidomide in T-cell lymphomas (2)
Reprinted from Morschhauser F, et al. A phase 2, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of single-agent lenalidomide (Revlimid) in subjects with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the EXPECT trial. Eur J Cancer 2013, with permission from Elsevier.
Slides 24, 25: Bendamustine in T-cell lymphomas (1), Bendamustine in T-cell lymphomas (2)
Damaj G, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 31: 104-110. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
The content and views presented in this educational activity are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Hemedicus, the supporter, or Frontline Medical Communications. This material is prepared based upon a review of multiple sources of information, but it is not exhaustive of the subject matter. Therefore, healthcare professionals and other individuals should review and consider other publications and materials on the subject matter before relying solely upon the information contained within this educational activity.

Release Date: March 20, 2018
Expiration Date: March 19, 2019
Note: This activity is no longer available for credit
Agenda
New targeted agents for PTCL
(Duration: 20 minutes)
Pier Luigi Zinzani, MD, PhD
Bologna University
Institute of Hematology “Seragnoli”
Bologna, Italy
Recently approved therapies for PTCL in Asia:
What have we learned from the US experience?
(Duration: 18 minutes)
Won Seog Kim, MD, PhD
Samsung Medical Center
Seoul, Republic of Korea
Novel combination therapies:
Where are we now and where are we going?
(Duration: 23 minutes)
Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD
Columbia University Medical Center
The New York Presbyterian Hospital
New York, NY USA
Provided by:

Original activity supported by an educational grant from:
Spectrum Pharmaceuticals
Learning Objectives
At the conclusion of this educational activity, the healthcare team will be better able to:
- Discuss the treatment and management of peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- Appraise how U.S. T-cell lymphoma treatment experience can impact practice in Asia
- Summarize the importance of combination therapy in peripheral T-cell lymphoma
Target Audience
Hematologists, oncologists, and other clinicians and scientists with an interest in T-cell lymphoma
Statement of Need
Peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCL) are rare, heterogeneous and aggressive neoplasms that are associated with a poor prognosis. In addition, with current therapies, up to 70% of patients undergo relapse or develop refractory disease. Recent evidence has indicated an increase in the incidence of PTCLs and hence current challenges including pathobiology, clinical management, new drug testing as well as clinical trial accrual, need to be addressed. This activity will provide the healthcare team with the ideal foundation to facilitate progress in PTCL treatment and management.
Won Seog Kim, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Samsung Medical Center
Seoul, Republic of Korea
Disclosure: Consulting fees: Celltrion; Contracted research: Takeda; Kyowa-Kirin; J & J; Merck; Donga; Novartis; Celltrion
Owen A. O’Connor, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Columbia University Medical Center
The New York Presbyterian Hospital
New York, NY USA
Disclosure: Contracted research: Celgene; Merck; Spectrum; Agensys
Pier Luigi Zinzani, MD, PhD (Presenter)
Bologna University
Institute of Hematology “Seragnoli”
Bologna, Italy
Disclosure: Speakers Bureau: Janssen; Merck; Servier; Gilead; Verastem; BMS; Sandoz; Mundipharma
Permissions
Won Seog Kim presentation
Slide 4: Frequency of T and NK-cell lymphomas in Asia
Park S, Ko YH. Peripheral T cell lymphoma in Asia. Int J Hematol 2014;99:227-239. Reprinted with permission of the Japanese Society of Hematology.
Slide 29: Off-label use: 100mg of pembrolizumab, HK, Singapore, Korea
Republished with permission of the American Society of Hematology, from Kwong YL, et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing L-asparaginase. Blood. 2017;129(17):2437-2442; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Owen A. O’Connor presentation
Slide 12: Schematic of study design, patient disposition, and thrombocytopenia as a function of schedule & dose
Republished with permission of American Society of Hematology, from Amengual JE…O’Connor OA. A phase 1 study of romidepsin and pralatrexate reveals marked activity in relapsed and refractory T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018;131:397-407; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Slide 13: Summary of response rates across study population for patients treated with romidepsin and pralatrexate
Same as slide above.
Slide 14: Pharmacokinetic parameters for pralatrexate and romidepsin in the study population
Same as slide above.
Slide 15: PFS and OS as a function of treatment in study population
Same as slide above.
Slide 19: The combination of HoME and HDAC inhibitor synergistically produces apoptosis across panel of T-cell lymphomas: tCTCL H9
Marchi E . . . O’Connor OA.The combination of hypomethylating agents and histone deacetylase inhibitors produce marked synergy in preclinical models of T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2015; 171:215-226.
Slide 20: Supervised hierarchial clustering based on GEP
Same as slide above.
Slide 27: Panobinostat plus bortezomib in PTCL
Reprinted from Lancet Haematol, Tan D, et al. Panobinostat in combination with bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: an open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. 2015; 2(8):e326-e333, with permission from Elsevier.
Pier Luigi Zinzani presentation
Slides 4, 11: New agents in T-cell lymphomas (2), Belinostat (2)
O’Connor OA, et al. Belinostat in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: Results of the pivotal phase II BELIEF (CLN-19) study. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 2492-2499. Reprinted with permission. © 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 5, 8, 10, 12, 18, 20: Pralatrexate (1), Romidepsin (1), Belinostat (1), Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (1), Brentuximab vedotin – CD30+ peripheral T-cell lymphoma (1), Off-label compounds in peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Reprinted from Cancer Treat Rev, volume 60, Broccoli A, Argnani L, Zinzani PL. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas: Focusing on novel agents in relapsed and refractory disease, pp 120-129, © 2017, with permission from Elsevier.
Slides 6, 7: Pralatrexate (2) and Pralatrexate (3)
O’Connor OA, et al. Pralatrexate in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: results from the pivotal PROPEL study. J Clin Oncol, 2011; 29: 1182-1189. Reprinted with permission. © 2011 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slide 9: Romidepsin (2)
Coiffier B, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 631-636. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 13, 14: Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (2), Brentulximab vedotin — Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (3)
Pro B, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2190-2196. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Slides 16, 17: Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (5), Brentuximab vedotin – Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (6)
Broccoli A, et al. Italian real-life experience with brentuximab vedotin: results of a large observational study of 40 cases of relapsed/refractory systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2017; 102: 1931-1935. Obtained from the Haematologica Journal website http://www.haematologica.org
Slide 19: Brentuximab vedotin –CD30+ peripheral T-cell lymphomas (2)
Horwitz SM, et al. Blood 2014; 123: 3095-3100. Permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.
Slide 21: Gemcitabine in peripheral T-cell lymphomas
Zinzani PL, et al. Ann Oncol 2010; 21: 860-863. European Society of Medical Oncology licensee.
Slide 23: Lenalidomide in T-cell lymphomas (2)
Reprinted from Morschhauser F, et al. A phase 2, multicentre, single-arm, open-label study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of single-agent lenalidomide (Revlimid) in subjects with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the EXPECT trial. Eur J Cancer 2013, with permission from Elsevier.
Slides 24, 25: Bendamustine in T-cell lymphomas (1), Bendamustine in T-cell lymphomas (2)
Damaj G, et al. J Clin Oncol 2012; 31: 104-110. Reprinted with permission. © 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
The content and views presented in this educational activity are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Hemedicus, the supporter, or Frontline Medical Communications. This material is prepared based upon a review of multiple sources of information, but it is not exhaustive of the subject matter. Therefore, healthcare professionals and other individuals should review and consider other publications and materials on the subject matter before relying solely upon the information contained within this educational activity.
Best options for treating relapsed/refractory PTCL
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – When patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) experience relapse, consider an allogeneic stem cell transplant or clinical trial, investigators advised.
Patients with relapsed PTCL have generally dismal outcomes, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 3.7 months and a median overall survival (OS) of just 6.5 months, according to one study (J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jun 1;31[16]:1970-6).
“Clearly the problem with most of the relapsed PTCL [cases] is that they don’t achieve a good response to salvage therapy. If they do, then they have much better chance of doing well,” she said at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
She outlined her center’s approach for treating patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL, following a case presentation by Royal Marsden fellow Matthew Cross, MD.
Complex disease, multiple therapies
The patient was a 71-year-old woman who in 2007 had a diagnosis of asymptomatic stage 4A follicular lymphoma managed with observation; in 2010, she was diagnosed with a CD30-positive PTCL not otherwise specified with ongoing low-level bone marrow involvement with follicular lymphoma.
She initially was treated elsewhere with R-CHOP chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone plus rituximab) and had a response after four cycles; however, she had progression with new intra-abdominal nodal sites by the sixth cycle and then was started on two cycles of ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin), but she had further progression by May 2011 and opted to forgo additional treatment.
By July 2011, however, she became highly symptomatic with new pruritic rashes on her legs, abdominal pain, and distention. She was referred to the Royal Marsden Hospital, where she was eventually diagnosed with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) with an Epstein-Barr virus–negative clonal large B-cell proliferation in her bone marrow.
She was treated with gemcitabine plus methylprednisolone and prophylactic intrathecal methotrexate and had an “excellent clinical and radiological response,” Dr. Cross said.
A subsequent bone marrow biopsy showed marked hypocellularity but no evidence of either T-cell of B-cell lymphomas.
An autologous stem cell transplant was planned, but two attempts at harvesting peripheral blood stem cells – including one with plerixafor (Mozobil) – failed, and a PET scan within 3 months showed signs of early progression.
In April 2012, the patient was started on romidepsin (Istodax) and had a 1-year remission. But in April 2013, a repeat biopsy again showed CD30-positive AITL. Based on the CD30 positivity, the patient was started on brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) in May 2013. She was observed to have progression in inguinal nodes in January 2014; she was treated with local radiotherapy and continued on brentuximab but had further progression in June 2014. At that time, she had additional gemcitabine-based combination chemotherapy and had stable disease for 10 months.
In March 2015, she received lenalidomide for further progression but could not tolerate the drug. She died in September 2015, 5 years after diagnosis and 4.5 years after frontline therapy failed.
Therapeutic rationale
Dr. Dearden walked through the choices that she, along with Dr. Cross and their colleagues, made in treating the patient. They chose gemcitabine-based regimens for salvage therapy because of the drug’s efficacy across various forms on non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma, she said.
However, a randomized, phase 3, noninferiority trial in the United Kingdom comparing GEM-P (gemcitabine, cisplatin, and methylprednisolone) with CHOP for first-line therapy of PTCL was halted at the interim analysis because GEM-P had not meet the primary endpoint, she said. Results of that trial have not been published to date.
“Clearly, if it’s the patients who do well, often it’s because they achieve a good enough remission to be able to proceed to some sort of consolidation therapy with autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplants, and I think auto-graft is probably accepted for the younger, fitter patients with relapsed chemo-sensitive disease,” she said.
Three-year survival rates for autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation range from 36% to 58% and are better than those seen with chemotherapy alone, she said.
“The problem of course is that not many patients receive the planned auto-graft, even if that’s the intention, either because of failure to respond to salvage regimen or early disease progression, which happens before the transplant is able to take place,” she said,
A reasonable alternative for patients with relapsed/refractory PTCL is allogeneic transplantation, as shown in a 2008 study.
Among 77 patients – 57 of whom had received myeloablative conditioning, 31 of whom were in complete remission, and 26 of whom had partial response at the time of transplants – the 5-year treatment-related mortality rate was 33%. However, the 5-year event-free and overall survival rates were 53% and 57%, respectively. Patients with AITL had especially good outcomes (J Clin Oncol. 2008 May 10;26[14]:2264-71).
“In an ideal world, if our patient had been a suitable candidate for an allo-transplant, it’s what we would have tried to undertake,” Dr. Dearden said.
Dr. Dearden recommended that all patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL be considered for clinical trials. For fit patients in first relapse, combination platinum-based chemotherapy followed by autologous or allogeneic transplant may be effective.
For patients not eligible for transplant or with chemotherapy-refractory disease, she recommended trying the following monotherapy approaches: pralatrexate for patients with PTCL not otherwise specified, histone deacetylase inhibitors or 5-azacytidine for AITL, brentuximab vedotin for anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and pembrolizumab for natural killer/T-cell lymphomas.
Although two lines of intensive chemotherapy had failed the case patient within 6 months of diagnosis, she still survived for 5 years with sequential monotherapies, Dr. Dearden noted.
“I use to say to her, ‘You just need to stay one drug ahead of your disease.’ And she was well, she had a very good quality of life for a period of time, and if you can deliver a treatment that is effective for a patient, it will extend their survival,” Dr. Dearden said.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization. Dr. Dearden has consulted for MedImmune, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Gilead Sciences, and Roche, and has received honoraria from Janssen and Gilead. Dr. Cross reported no having no financial disclosures.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – When patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) experience relapse, consider an allogeneic stem cell transplant or clinical trial, investigators advised.
Patients with relapsed PTCL have generally dismal outcomes, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 3.7 months and a median overall survival (OS) of just 6.5 months, according to one study (J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jun 1;31[16]:1970-6).
“Clearly the problem with most of the relapsed PTCL [cases] is that they don’t achieve a good response to salvage therapy. If they do, then they have much better chance of doing well,” she said at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
She outlined her center’s approach for treating patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL, following a case presentation by Royal Marsden fellow Matthew Cross, MD.
Complex disease, multiple therapies
The patient was a 71-year-old woman who in 2007 had a diagnosis of asymptomatic stage 4A follicular lymphoma managed with observation; in 2010, she was diagnosed with a CD30-positive PTCL not otherwise specified with ongoing low-level bone marrow involvement with follicular lymphoma.
She initially was treated elsewhere with R-CHOP chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone plus rituximab) and had a response after four cycles; however, she had progression with new intra-abdominal nodal sites by the sixth cycle and then was started on two cycles of ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin), but she had further progression by May 2011 and opted to forgo additional treatment.
By July 2011, however, she became highly symptomatic with new pruritic rashes on her legs, abdominal pain, and distention. She was referred to the Royal Marsden Hospital, where she was eventually diagnosed with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) with an Epstein-Barr virus–negative clonal large B-cell proliferation in her bone marrow.
She was treated with gemcitabine plus methylprednisolone and prophylactic intrathecal methotrexate and had an “excellent clinical and radiological response,” Dr. Cross said.
A subsequent bone marrow biopsy showed marked hypocellularity but no evidence of either T-cell of B-cell lymphomas.
An autologous stem cell transplant was planned, but two attempts at harvesting peripheral blood stem cells – including one with plerixafor (Mozobil) – failed, and a PET scan within 3 months showed signs of early progression.
In April 2012, the patient was started on romidepsin (Istodax) and had a 1-year remission. But in April 2013, a repeat biopsy again showed CD30-positive AITL. Based on the CD30 positivity, the patient was started on brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) in May 2013. She was observed to have progression in inguinal nodes in January 2014; she was treated with local radiotherapy and continued on brentuximab but had further progression in June 2014. At that time, she had additional gemcitabine-based combination chemotherapy and had stable disease for 10 months.
In March 2015, she received lenalidomide for further progression but could not tolerate the drug. She died in September 2015, 5 years after diagnosis and 4.5 years after frontline therapy failed.
Therapeutic rationale
Dr. Dearden walked through the choices that she, along with Dr. Cross and their colleagues, made in treating the patient. They chose gemcitabine-based regimens for salvage therapy because of the drug’s efficacy across various forms on non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma, she said.
However, a randomized, phase 3, noninferiority trial in the United Kingdom comparing GEM-P (gemcitabine, cisplatin, and methylprednisolone) with CHOP for first-line therapy of PTCL was halted at the interim analysis because GEM-P had not meet the primary endpoint, she said. Results of that trial have not been published to date.
“Clearly, if it’s the patients who do well, often it’s because they achieve a good enough remission to be able to proceed to some sort of consolidation therapy with autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplants, and I think auto-graft is probably accepted for the younger, fitter patients with relapsed chemo-sensitive disease,” she said.
Three-year survival rates for autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation range from 36% to 58% and are better than those seen with chemotherapy alone, she said.
“The problem of course is that not many patients receive the planned auto-graft, even if that’s the intention, either because of failure to respond to salvage regimen or early disease progression, which happens before the transplant is able to take place,” she said,
A reasonable alternative for patients with relapsed/refractory PTCL is allogeneic transplantation, as shown in a 2008 study.
Among 77 patients – 57 of whom had received myeloablative conditioning, 31 of whom were in complete remission, and 26 of whom had partial response at the time of transplants – the 5-year treatment-related mortality rate was 33%. However, the 5-year event-free and overall survival rates were 53% and 57%, respectively. Patients with AITL had especially good outcomes (J Clin Oncol. 2008 May 10;26[14]:2264-71).
“In an ideal world, if our patient had been a suitable candidate for an allo-transplant, it’s what we would have tried to undertake,” Dr. Dearden said.
Dr. Dearden recommended that all patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL be considered for clinical trials. For fit patients in first relapse, combination platinum-based chemotherapy followed by autologous or allogeneic transplant may be effective.
For patients not eligible for transplant or with chemotherapy-refractory disease, she recommended trying the following monotherapy approaches: pralatrexate for patients with PTCL not otherwise specified, histone deacetylase inhibitors or 5-azacytidine for AITL, brentuximab vedotin for anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and pembrolizumab for natural killer/T-cell lymphomas.
Although two lines of intensive chemotherapy had failed the case patient within 6 months of diagnosis, she still survived for 5 years with sequential monotherapies, Dr. Dearden noted.
“I use to say to her, ‘You just need to stay one drug ahead of your disease.’ And she was well, she had a very good quality of life for a period of time, and if you can deliver a treatment that is effective for a patient, it will extend their survival,” Dr. Dearden said.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization. Dr. Dearden has consulted for MedImmune, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Gilead Sciences, and Roche, and has received honoraria from Janssen and Gilead. Dr. Cross reported no having no financial disclosures.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – When patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) experience relapse, consider an allogeneic stem cell transplant or clinical trial, investigators advised.
Patients with relapsed PTCL have generally dismal outcomes, with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 3.7 months and a median overall survival (OS) of just 6.5 months, according to one study (J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jun 1;31[16]:1970-6).
“Clearly the problem with most of the relapsed PTCL [cases] is that they don’t achieve a good response to salvage therapy. If they do, then they have much better chance of doing well,” she said at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
She outlined her center’s approach for treating patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL, following a case presentation by Royal Marsden fellow Matthew Cross, MD.
Complex disease, multiple therapies
The patient was a 71-year-old woman who in 2007 had a diagnosis of asymptomatic stage 4A follicular lymphoma managed with observation; in 2010, she was diagnosed with a CD30-positive PTCL not otherwise specified with ongoing low-level bone marrow involvement with follicular lymphoma.
She initially was treated elsewhere with R-CHOP chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone plus rituximab) and had a response after four cycles; however, she had progression with new intra-abdominal nodal sites by the sixth cycle and then was started on two cycles of ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin), but she had further progression by May 2011 and opted to forgo additional treatment.
By July 2011, however, she became highly symptomatic with new pruritic rashes on her legs, abdominal pain, and distention. She was referred to the Royal Marsden Hospital, where she was eventually diagnosed with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) with an Epstein-Barr virus–negative clonal large B-cell proliferation in her bone marrow.
She was treated with gemcitabine plus methylprednisolone and prophylactic intrathecal methotrexate and had an “excellent clinical and radiological response,” Dr. Cross said.
A subsequent bone marrow biopsy showed marked hypocellularity but no evidence of either T-cell of B-cell lymphomas.
An autologous stem cell transplant was planned, but two attempts at harvesting peripheral blood stem cells – including one with plerixafor (Mozobil) – failed, and a PET scan within 3 months showed signs of early progression.
In April 2012, the patient was started on romidepsin (Istodax) and had a 1-year remission. But in April 2013, a repeat biopsy again showed CD30-positive AITL. Based on the CD30 positivity, the patient was started on brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) in May 2013. She was observed to have progression in inguinal nodes in January 2014; she was treated with local radiotherapy and continued on brentuximab but had further progression in June 2014. At that time, she had additional gemcitabine-based combination chemotherapy and had stable disease for 10 months.
In March 2015, she received lenalidomide for further progression but could not tolerate the drug. She died in September 2015, 5 years after diagnosis and 4.5 years after frontline therapy failed.
Therapeutic rationale
Dr. Dearden walked through the choices that she, along with Dr. Cross and their colleagues, made in treating the patient. They chose gemcitabine-based regimens for salvage therapy because of the drug’s efficacy across various forms on non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma, she said.
However, a randomized, phase 3, noninferiority trial in the United Kingdom comparing GEM-P (gemcitabine, cisplatin, and methylprednisolone) with CHOP for first-line therapy of PTCL was halted at the interim analysis because GEM-P had not meet the primary endpoint, she said. Results of that trial have not been published to date.
“Clearly, if it’s the patients who do well, often it’s because they achieve a good enough remission to be able to proceed to some sort of consolidation therapy with autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplants, and I think auto-graft is probably accepted for the younger, fitter patients with relapsed chemo-sensitive disease,” she said.
Three-year survival rates for autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation range from 36% to 58% and are better than those seen with chemotherapy alone, she said.
“The problem of course is that not many patients receive the planned auto-graft, even if that’s the intention, either because of failure to respond to salvage regimen or early disease progression, which happens before the transplant is able to take place,” she said,
A reasonable alternative for patients with relapsed/refractory PTCL is allogeneic transplantation, as shown in a 2008 study.
Among 77 patients – 57 of whom had received myeloablative conditioning, 31 of whom were in complete remission, and 26 of whom had partial response at the time of transplants – the 5-year treatment-related mortality rate was 33%. However, the 5-year event-free and overall survival rates were 53% and 57%, respectively. Patients with AITL had especially good outcomes (J Clin Oncol. 2008 May 10;26[14]:2264-71).
“In an ideal world, if our patient had been a suitable candidate for an allo-transplant, it’s what we would have tried to undertake,” Dr. Dearden said.
Dr. Dearden recommended that all patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL be considered for clinical trials. For fit patients in first relapse, combination platinum-based chemotherapy followed by autologous or allogeneic transplant may be effective.
For patients not eligible for transplant or with chemotherapy-refractory disease, she recommended trying the following monotherapy approaches: pralatrexate for patients with PTCL not otherwise specified, histone deacetylase inhibitors or 5-azacytidine for AITL, brentuximab vedotin for anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and pembrolizumab for natural killer/T-cell lymphomas.
Although two lines of intensive chemotherapy had failed the case patient within 6 months of diagnosis, she still survived for 5 years with sequential monotherapies, Dr. Dearden noted.
“I use to say to her, ‘You just need to stay one drug ahead of your disease.’ And she was well, she had a very good quality of life for a period of time, and if you can deliver a treatment that is effective for a patient, it will extend their survival,” Dr. Dearden said.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization. Dr. Dearden has consulted for MedImmune, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Gilead Sciences, and Roche, and has received honoraria from Janssen and Gilead. Dr. Cross reported no having no financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM TCLF 2018
Mycosis fungoides increases risk for second cancers
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Patients with mycosis fungoides are at increased risk for developing other cancers and should be screened for second primary and hematologic malignancies, results of a cancer registry survey suggest.
A study of data on 6,196 patients included in 18 population-based cancer registries comprising the SEER-18 (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 18) database who were diagnosed and followed from 2000 to 2014 showed that 514 (8.3%) developed second cancers, compared with the 70.8 secondary malignancies that would be expected in the general population. This difference translated into a standardized incidence ratio (SIR) of 7.3, reported Amrita Goyal, MD, and Aleksandr Lazaryan, MD, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Patients with MF have a 500% greater risk for developing a second solid malignancy and a 2700% greater likelihood of developing a second hematologic malignancy, she said.
The investigators hypothesized that MF predisposes patients to second malignancies because of its immunocompromising effects.
Dr. Goyal said that, although the SEER data set does not include information on disease stage for all patients, when they looked at a separate cohort of 173 University of Minnesota patients with MF, they saw that patients with higher-stage MF were significantly more likely to develop secondary malignancies than patients with lower-stage disease.
The investigators looked at the actual and expected cancer incidence rates for the SEER-18 population sample, and used data on age, sex, race, and calendar year to generate incidence estimates for the general population.
They found that 514 patients in the SEER-18 population developed a total of 170 second primary hematologic malignancies, for a SIR of 27.4, compared with the general population. The most common hematologic cancers were Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR 69.8) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR 46.5), and other second hematologic malignancies included multiple myeloma (SIR 4.5), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SIR 9.1). and acute leukemias (SIR 8.1).
The most frequently occurring second solid tumors included cancers of the nose, nasal cavity, and middle ear (SIR 30.4); thyroid (SIR 16.1); brain (SIR 15.1); and breast (SIR 8.0).
Other solid tumors with an approximately 400%-500% higher incidence included cancers of the prostate, bladder, colon, and kidneys.
Dr. Goyal and Dr. Lazaryan recommend development of targeted cancer screening strategies for patients with MF.
The study was funded in part by an American Society of Hematology HONORS grant. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Goyal A et al. TCLF 2018 Abstract EP18_2.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Patients with mycosis fungoides are at increased risk for developing other cancers and should be screened for second primary and hematologic malignancies, results of a cancer registry survey suggest.
A study of data on 6,196 patients included in 18 population-based cancer registries comprising the SEER-18 (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 18) database who were diagnosed and followed from 2000 to 2014 showed that 514 (8.3%) developed second cancers, compared with the 70.8 secondary malignancies that would be expected in the general population. This difference translated into a standardized incidence ratio (SIR) of 7.3, reported Amrita Goyal, MD, and Aleksandr Lazaryan, MD, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Patients with MF have a 500% greater risk for developing a second solid malignancy and a 2700% greater likelihood of developing a second hematologic malignancy, she said.
The investigators hypothesized that MF predisposes patients to second malignancies because of its immunocompromising effects.
Dr. Goyal said that, although the SEER data set does not include information on disease stage for all patients, when they looked at a separate cohort of 173 University of Minnesota patients with MF, they saw that patients with higher-stage MF were significantly more likely to develop secondary malignancies than patients with lower-stage disease.
The investigators looked at the actual and expected cancer incidence rates for the SEER-18 population sample, and used data on age, sex, race, and calendar year to generate incidence estimates for the general population.
They found that 514 patients in the SEER-18 population developed a total of 170 second primary hematologic malignancies, for a SIR of 27.4, compared with the general population. The most common hematologic cancers were Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR 69.8) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR 46.5), and other second hematologic malignancies included multiple myeloma (SIR 4.5), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SIR 9.1). and acute leukemias (SIR 8.1).
The most frequently occurring second solid tumors included cancers of the nose, nasal cavity, and middle ear (SIR 30.4); thyroid (SIR 16.1); brain (SIR 15.1); and breast (SIR 8.0).
Other solid tumors with an approximately 400%-500% higher incidence included cancers of the prostate, bladder, colon, and kidneys.
Dr. Goyal and Dr. Lazaryan recommend development of targeted cancer screening strategies for patients with MF.
The study was funded in part by an American Society of Hematology HONORS grant. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Goyal A et al. TCLF 2018 Abstract EP18_2.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Patients with mycosis fungoides are at increased risk for developing other cancers and should be screened for second primary and hematologic malignancies, results of a cancer registry survey suggest.
A study of data on 6,196 patients included in 18 population-based cancer registries comprising the SEER-18 (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 18) database who were diagnosed and followed from 2000 to 2014 showed that 514 (8.3%) developed second cancers, compared with the 70.8 secondary malignancies that would be expected in the general population. This difference translated into a standardized incidence ratio (SIR) of 7.3, reported Amrita Goyal, MD, and Aleksandr Lazaryan, MD, PhD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Patients with MF have a 500% greater risk for developing a second solid malignancy and a 2700% greater likelihood of developing a second hematologic malignancy, she said.
The investigators hypothesized that MF predisposes patients to second malignancies because of its immunocompromising effects.
Dr. Goyal said that, although the SEER data set does not include information on disease stage for all patients, when they looked at a separate cohort of 173 University of Minnesota patients with MF, they saw that patients with higher-stage MF were significantly more likely to develop secondary malignancies than patients with lower-stage disease.
The investigators looked at the actual and expected cancer incidence rates for the SEER-18 population sample, and used data on age, sex, race, and calendar year to generate incidence estimates for the general population.
They found that 514 patients in the SEER-18 population developed a total of 170 second primary hematologic malignancies, for a SIR of 27.4, compared with the general population. The most common hematologic cancers were Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR 69.8) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR 46.5), and other second hematologic malignancies included multiple myeloma (SIR 4.5), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SIR 9.1). and acute leukemias (SIR 8.1).
The most frequently occurring second solid tumors included cancers of the nose, nasal cavity, and middle ear (SIR 30.4); thyroid (SIR 16.1); brain (SIR 15.1); and breast (SIR 8.0).
Other solid tumors with an approximately 400%-500% higher incidence included cancers of the prostate, bladder, colon, and kidneys.
Dr. Goyal and Dr. Lazaryan recommend development of targeted cancer screening strategies for patients with MF.
The study was funded in part by an American Society of Hematology HONORS grant. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Goyal A et al. TCLF 2018 Abstract EP18_2.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients with MF have a 730% greater likelihood of developing a second primary hematologic malignancy.
Study details: A retrospective review of data on 6,196 patients in the SEER-18 database.
Disclosures: The study was funded in part by an American Society of Hematology HONORS grant. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
Source: Goyal A et al. TCLF 2018 Abstract EP18_2.