User login
Most rheumatology drugs don’t increase COVID-19 hospitalization risk
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vast majority of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases who contract COVID-19 recover from the virus, regardless of which medication they receive for their rheumatic condition, new international research suggests.
“These results provide, for the first time, information about the outcome of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases,” said study investigator Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, from University College London. “They should provide some reassurance to patients and healthcare providers.”
Machado and his colleagues looked at 600 COVID-19 patients from 40 countries, and found that those taking TNF inhibitors for their rheumatic disease were less likely to be hospitalized for COVID-19. However, treatment with more than 10 mg of prednisone daily — considered a moderate to high dose — was associated with a higher probability of hospitalization.
In addition, hospitalization was not associated with biologics; JAK inhibitors; conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as methotrexate; antimalarials, such as hydroxychloroquine; or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) — either alone or in combination with other biologics, such as TNF-alpha inhibitors.
The findings were presented at the virtual European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 2020 Congress and were published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
“Initially, there was a huge concern that these drugs could affect the outcome of patients getting COVID-19, but what this is showing is that probably these drugs do not increase their risk of severe outcome,” Machado, who is chair of the EULAR standing committee on epidemiology and health services research, told Medscape Medical News.
As of June 1, 1061 patients from 28 participating countries had been entered into the EULAR COVID-19 database, which was launched as part of the international Global Rheumatology Alliance registry. Patient data are categorized by factors such as top rheumatology diagnosis, comorbidities, top-five COVID-19 symptoms, and DMARD therapy at the time of virus infection. Anonymized data will be shared with an international register based in the United States.
Machado’s team combined data from the EULAR and Global Rheumatology Alliance COVID-19 registries from March 24 to April 20. They looked at patient factors — such as age, sex, smoking status, rheumatic diagnosis, comorbidities, and rheumatic therapies — to examine the association of rheumatic therapies with hospitalization rates and COVID-19 disease course.
Of the 277 patients (46%) in the study cohort who required hospitalization, 55 (9%) died. But this finding shouldn’t be viewed as the true rate of hospitalization or death in patients with rheumatic disease and COVID-19, said Gerd Burmester, MD, from Charité–University Medicine Berlin.
“There’s tremendous bias in terms of more serious cases of COVID-19 being reported to the registries,” he explained, “because the mild cases won’t even show up at their rheumatologist’s office.”
“This can skew the idea that COVID-19 is much more dangerous to rheumatic patients than to the regular population,” Burmester told Medscape Medical News. “It scares the patients, obviously, but we believe this is not justified.”
It’s still unclear whether rituximab use raises the risk for severe COVID-19, he said. “It appears to be the only biologic for which the jury is still out,” he said.
“Anti-TNFs and anti-IL-6 drugs may even be beneficial, although we don’t have robust data,” he added.
The study can only highlight associations between rheumatic drugs and COVID-19 outcomes. “We cannot say there is a causal relationship between the findings,” Machado said.
Longer-term data, when available, should illuminate “more granular” aspects of COVID-19 outcomes in rheumatic patients, including their risks of requiring ventilation or developing a cytokine storm, he noted.
Burmester and Machado agree that research needs to continue as the pandemic rages on. But so far, “there are no data suggesting that, if you’re on a targeted, dedicated immunomodulator, your risk is higher to have a worse course of COVID-19 than the general population,” Burmester said.
“We simply didn’t know that when the pandemic started, and some patients even discontinued their drugs out of this fear,” he added. “It’s more reassuring than we originally thought.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Working group proposes MRI definitions of structural lesions indicative of axial spondyloarthritis
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that showed a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease.
“There is a lack of consensus as to what defines a structural lesion on MRI of the sacroiliac joint [SIJ] typical of axial spondyloarthritis. Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies. The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
Making a definitive diagnosis of axSpA can be difficult because MRI can show a variety of SIJ abnormalities in healthy people as well as those with axSpA, said Dr. Maksymowych, chief medical officer of CARE Arthritis and professor in rheumatology at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, said in an interview prior to his presentation at the e-congress. “People who evaluate MRI scans are looking for clues as to what types of lesions they can be confident are indicative of axSpA.”
That started a process by the ASAS MRI group to evaluate scans from the landmark ASAS Classification Cohort study (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1550-8). “But,” said Dr. Maksymowych, “the MRI scans from that study were never evaluated.” So that work was handed off to the working group, whose 25 members included 7 expert image readers who evaluated the MRI scans.
The group adopted a standardized approach for evaluating MRIs of the SIJ in 148 cases, dividing each SIJ into quadrants and then evaluating consecutive MRI slices. The readers first documented whether they observed a definite structural lesion on the scan, which they then used as an external reference standard. They then analyzed which lesion, and in how many SIJ quadrants or slices, best reflected this external standard.
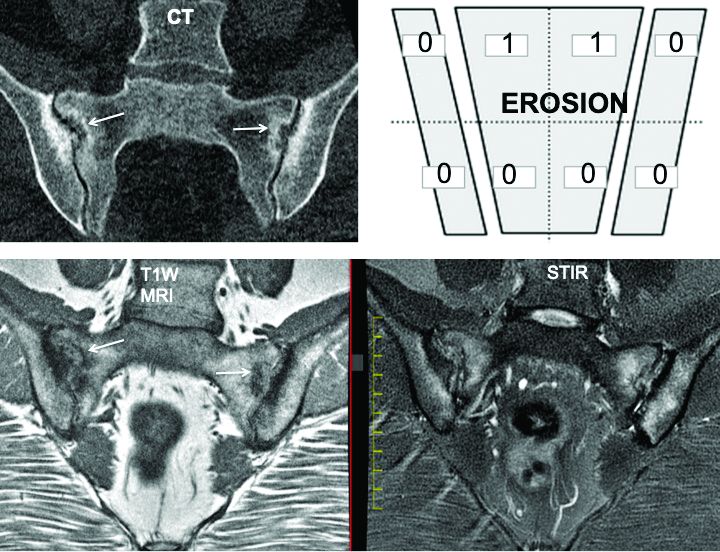
The investigators defined an erosion as “a defect in subchondral bone associated with full-thickness loss of a dark appearance of the subchondral cortex at its expected location, with loss of signal on a T1-weighted, non–fat-suppressed sequence, compared with the normal bright appearance of adjacent bone marrow.” They defined a fat lesion or fat metaplasia as a “bright signal seen on a T1-weighted, non–fat-suppressed sequence that is brighter than normal bone marrow which meets the following requirements: It is homogeneously bright, located in a typical anatomical area (specifically subchondral bone), and has a sharply defined border along its nonarticular border with normal bone marrow.”
An erosion in one quadrant isn’t sufficient to define a scan as positive for a definite structural lesion, said Dr. Maksymowych; but an erosion in three quadrants or in two or more consecutive slices meets the group’s designation of a definite structural lesion. “This showed over a 95% specificity for being associated with a definite structural lesion as defined by a majority of the seven experts,” he said.
The group also determined that a fat lesion typical of axSpA has a homogeneous white appearance on T1-weighted scans with a sharply defined border. The group also determined that such a fat lesion with at least 1-cm horizontal depth from the joint margin in at least one SIJ quadrant is strongly indicative of axSpA.
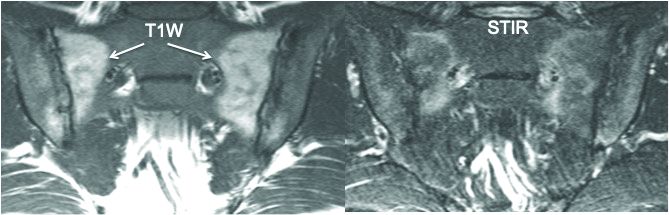
“So we now have definitions for two structural lesions, erosion and fat lesions, that reflect what a majority of experts consider to be a definite structural lesion according to at least 95% specificity,” he said. Sensitivity values were 90% for erosion in three quadrants and 83% for erosions in two or more consecutive slices. and 59% for a fat lesion with at least 1-cm horizontal depth from the joint margin in at least one SIJ quadrant.
The second part of the analysis evaluated the predictive capacity of these lesion definitions for a rheumatologic diagnosis of axSpA at 4.4 years of follow-up. “These lesions predicted SpA with over 95% positive predictive value,” he said. “In other words, if you see them at baseline they’re going to predict SpA with high certainty at follow-up after 4.4 years.”
Three aspects of this study design are unique, Dr. Maksymowych noted. First is the high number of expert MRI readers who evaluated the scans. “There aren’t really too many studies I can think of that used more than two or three expert MRI readers,” he said.
Second is the way in which the study “very precisely and in a very standardized way” applied all the consensus-based ASAS definitions of structural SIJ lesions. “In the past, a variety of ways were used to define these lesions,” he said. “A good example would be the different ways in which erosions have been defined.”
The third novel aspect of the study is that the expert readers’ assessment of what constitutes a definite structural lesion was used as an external reference standard. For example, the study calculated sensitivity and specificity for numbers of SIJ quadrants and consecutive slices with erosion, sclerosis, and fat lesions where a majority of readers agreed on the presence of a structural lesion typical of axSpA with high confidence (3 or greater on a scale of 1-4). “The reason this was put in place is because we recognize sometimes lesions are very subtle and you can’t be certain that they’re reflecting SpA,” he said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, and UCB.
Maksymowych WP et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020;79[suppl 1]:53. Abstract OP0079.
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that showed a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease.
“There is a lack of consensus as to what defines a structural lesion on MRI of the sacroiliac joint [SIJ] typical of axial spondyloarthritis. Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies. The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
Making a definitive diagnosis of axSpA can be difficult because MRI can show a variety of SIJ abnormalities in healthy people as well as those with axSpA, said Dr. Maksymowych, chief medical officer of CARE Arthritis and professor in rheumatology at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, said in an interview prior to his presentation at the e-congress. “People who evaluate MRI scans are looking for clues as to what types of lesions they can be confident are indicative of axSpA.”
That started a process by the ASAS MRI group to evaluate scans from the landmark ASAS Classification Cohort study (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1550-8). “But,” said Dr. Maksymowych, “the MRI scans from that study were never evaluated.” So that work was handed off to the working group, whose 25 members included 7 expert image readers who evaluated the MRI scans.
The group adopted a standardized approach for evaluating MRIs of the SIJ in 148 cases, dividing each SIJ into quadrants and then evaluating consecutive MRI slices. The readers first documented whether they observed a definite structural lesion on the scan, which they then used as an external reference standard. They then analyzed which lesion, and in how many SIJ quadrants or slices, best reflected this external standard.

The investigators defined an erosion as “a defect in subchondral bone associated with full-thickness loss of a dark appearance of the subchondral cortex at its expected location, with loss of signal on a T1-weighted, non–fat-suppressed sequence, compared with the normal bright appearance of adjacent bone marrow.” They defined a fat lesion or fat metaplasia as a “bright signal seen on a T1-weighted, non–fat-suppressed sequence that is brighter than normal bone marrow which meets the following requirements: It is homogeneously bright, located in a typical anatomical area (specifically subchondral bone), and has a sharply defined border along its nonarticular border with normal bone marrow.”
An erosion in one quadrant isn’t sufficient to define a scan as positive for a definite structural lesion, said Dr. Maksymowych; but an erosion in three quadrants or in two or more consecutive slices meets the group’s designation of a definite structural lesion. “This showed over a 95% specificity for being associated with a definite structural lesion as defined by a majority of the seven experts,” he said.
The group also determined that a fat lesion typical of axSpA has a homogeneous white appearance on T1-weighted scans with a sharply defined border. The group also determined that such a fat lesion with at least 1-cm horizontal depth from the joint margin in at least one SIJ quadrant is strongly indicative of axSpA.

“So we now have definitions for two structural lesions, erosion and fat lesions, that reflect what a majority of experts consider to be a definite structural lesion according to at least 95% specificity,” he said. Sensitivity values were 90% for erosion in three quadrants and 83% for erosions in two or more consecutive slices. and 59% for a fat lesion with at least 1-cm horizontal depth from the joint margin in at least one SIJ quadrant.
The second part of the analysis evaluated the predictive capacity of these lesion definitions for a rheumatologic diagnosis of axSpA at 4.4 years of follow-up. “These lesions predicted SpA with over 95% positive predictive value,” he said. “In other words, if you see them at baseline they’re going to predict SpA with high certainty at follow-up after 4.4 years.”
Three aspects of this study design are unique, Dr. Maksymowych noted. First is the high number of expert MRI readers who evaluated the scans. “There aren’t really too many studies I can think of that used more than two or three expert MRI readers,” he said.
Second is the way in which the study “very precisely and in a very standardized way” applied all the consensus-based ASAS definitions of structural SIJ lesions. “In the past, a variety of ways were used to define these lesions,” he said. “A good example would be the different ways in which erosions have been defined.”
The third novel aspect of the study is that the expert readers’ assessment of what constitutes a definite structural lesion was used as an external reference standard. For example, the study calculated sensitivity and specificity for numbers of SIJ quadrants and consecutive slices with erosion, sclerosis, and fat lesions where a majority of readers agreed on the presence of a structural lesion typical of axSpA with high confidence (3 or greater on a scale of 1-4). “The reason this was put in place is because we recognize sometimes lesions are very subtle and you can’t be certain that they’re reflecting SpA,” he said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, and UCB.
Maksymowych WP et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020;79[suppl 1]:53. Abstract OP0079.
What constitutes a structural lesion of the sacroiliac joints on MRI that’s indicative of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has long been a matter of conjecture, but the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Working Group has developed new definitions that showed a high degree of specificity in identifying such lesions in the disease.
“There is a lack of consensus as to what defines a structural lesion on MRI of the sacroiliac joint [SIJ] typical of axial spondyloarthritis. Previous studies have described structural lesions in different ways, precluding meaningful comparisons between studies. The ASAS MRI group has generated updated consensus lesion definitions that describe each of the MRI lesions in the sacroiliac joint. These definitions have been validated by seven expert readers from the ASAS MRI group on MRI images from the ASAS classification cohort,” Walter P. Maksymowych, MD, said at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
Making a definitive diagnosis of axSpA can be difficult because MRI can show a variety of SIJ abnormalities in healthy people as well as those with axSpA, said Dr. Maksymowych, chief medical officer of CARE Arthritis and professor in rheumatology at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, said in an interview prior to his presentation at the e-congress. “People who evaluate MRI scans are looking for clues as to what types of lesions they can be confident are indicative of axSpA.”
That started a process by the ASAS MRI group to evaluate scans from the landmark ASAS Classification Cohort study (Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1550-8). “But,” said Dr. Maksymowych, “the MRI scans from that study were never evaluated.” So that work was handed off to the working group, whose 25 members included 7 expert image readers who evaluated the MRI scans.
The group adopted a standardized approach for evaluating MRIs of the SIJ in 148 cases, dividing each SIJ into quadrants and then evaluating consecutive MRI slices. The readers first documented whether they observed a definite structural lesion on the scan, which they then used as an external reference standard. They then analyzed which lesion, and in how many SIJ quadrants or slices, best reflected this external standard.

The investigators defined an erosion as “a defect in subchondral bone associated with full-thickness loss of a dark appearance of the subchondral cortex at its expected location, with loss of signal on a T1-weighted, non–fat-suppressed sequence, compared with the normal bright appearance of adjacent bone marrow.” They defined a fat lesion or fat metaplasia as a “bright signal seen on a T1-weighted, non–fat-suppressed sequence that is brighter than normal bone marrow which meets the following requirements: It is homogeneously bright, located in a typical anatomical area (specifically subchondral bone), and has a sharply defined border along its nonarticular border with normal bone marrow.”
An erosion in one quadrant isn’t sufficient to define a scan as positive for a definite structural lesion, said Dr. Maksymowych; but an erosion in three quadrants or in two or more consecutive slices meets the group’s designation of a definite structural lesion. “This showed over a 95% specificity for being associated with a definite structural lesion as defined by a majority of the seven experts,” he said.
The group also determined that a fat lesion typical of axSpA has a homogeneous white appearance on T1-weighted scans with a sharply defined border. The group also determined that such a fat lesion with at least 1-cm horizontal depth from the joint margin in at least one SIJ quadrant is strongly indicative of axSpA.

“So we now have definitions for two structural lesions, erosion and fat lesions, that reflect what a majority of experts consider to be a definite structural lesion according to at least 95% specificity,” he said. Sensitivity values were 90% for erosion in three quadrants and 83% for erosions in two or more consecutive slices. and 59% for a fat lesion with at least 1-cm horizontal depth from the joint margin in at least one SIJ quadrant.
The second part of the analysis evaluated the predictive capacity of these lesion definitions for a rheumatologic diagnosis of axSpA at 4.4 years of follow-up. “These lesions predicted SpA with over 95% positive predictive value,” he said. “In other words, if you see them at baseline they’re going to predict SpA with high certainty at follow-up after 4.4 years.”
Three aspects of this study design are unique, Dr. Maksymowych noted. First is the high number of expert MRI readers who evaluated the scans. “There aren’t really too many studies I can think of that used more than two or three expert MRI readers,” he said.
Second is the way in which the study “very precisely and in a very standardized way” applied all the consensus-based ASAS definitions of structural SIJ lesions. “In the past, a variety of ways were used to define these lesions,” he said. “A good example would be the different ways in which erosions have been defined.”
The third novel aspect of the study is that the expert readers’ assessment of what constitutes a definite structural lesion was used as an external reference standard. For example, the study calculated sensitivity and specificity for numbers of SIJ quadrants and consecutive slices with erosion, sclerosis, and fat lesions where a majority of readers agreed on the presence of a structural lesion typical of axSpA with high confidence (3 or greater on a scale of 1-4). “The reason this was put in place is because we recognize sometimes lesions are very subtle and you can’t be certain that they’re reflecting SpA,” he said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, and UCB.
Maksymowych WP et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020;79[suppl 1]:53. Abstract OP0079.
FROM EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS
FDA approves ixekizumab for nonradiographic axSpA
The Food and Drug Administration has extended approval of ixekizumab (Taltz) to the treatment of nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA), according to a press release from its manufacturer, Eli Lilly. Specifically, this supplemental biologics license application refers to nr-axSpA with objective signs of inflammation.
The monoclonal interleukin-17A antagonist has three other indications, including ankylosing spondylitis in adults, psoriatic arthritis in adults, and plaque psoriasis in adults and children aged 6 years and older. It is the first IL-17A antagonist to receive FDA approval for nr-axSpA.
Approval for this indication was based on the phase 3, randomized, double-blind COAST-X trial, which put 96 nr-axSpA patients on 80-mg injections of ixekizumab every 4 weeks and 105 on placebo. After 52 weeks, ixekizumab was superior on the trial’s primary endpoint: 30% of patients had achieved a 40% improvement in Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society response criteria (ASAS 40), compared with 13% of patients on placebo (P = .0045).
Warnings and precautions for ixekizumab include considering potentially increased risk of infection and inflammatory bowel disease, as well as evaluating patients for tuberculosis before treatment. The most common adverse reactions (≥1%) are injection-site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and tinea infections. The safety profile for ixekizumab among nr-axSpA patients is mostly consistent with that seen among patients receiving it for other indications, according to Lilly. The full prescribing information is available on Lilly’s website.
The Food and Drug Administration has extended approval of ixekizumab (Taltz) to the treatment of nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA), according to a press release from its manufacturer, Eli Lilly. Specifically, this supplemental biologics license application refers to nr-axSpA with objective signs of inflammation.
The monoclonal interleukin-17A antagonist has three other indications, including ankylosing spondylitis in adults, psoriatic arthritis in adults, and plaque psoriasis in adults and children aged 6 years and older. It is the first IL-17A antagonist to receive FDA approval for nr-axSpA.
Approval for this indication was based on the phase 3, randomized, double-blind COAST-X trial, which put 96 nr-axSpA patients on 80-mg injections of ixekizumab every 4 weeks and 105 on placebo. After 52 weeks, ixekizumab was superior on the trial’s primary endpoint: 30% of patients had achieved a 40% improvement in Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society response criteria (ASAS 40), compared with 13% of patients on placebo (P = .0045).
Warnings and precautions for ixekizumab include considering potentially increased risk of infection and inflammatory bowel disease, as well as evaluating patients for tuberculosis before treatment. The most common adverse reactions (≥1%) are injection-site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and tinea infections. The safety profile for ixekizumab among nr-axSpA patients is mostly consistent with that seen among patients receiving it for other indications, according to Lilly. The full prescribing information is available on Lilly’s website.
The Food and Drug Administration has extended approval of ixekizumab (Taltz) to the treatment of nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA), according to a press release from its manufacturer, Eli Lilly. Specifically, this supplemental biologics license application refers to nr-axSpA with objective signs of inflammation.
The monoclonal interleukin-17A antagonist has three other indications, including ankylosing spondylitis in adults, psoriatic arthritis in adults, and plaque psoriasis in adults and children aged 6 years and older. It is the first IL-17A antagonist to receive FDA approval for nr-axSpA.
Approval for this indication was based on the phase 3, randomized, double-blind COAST-X trial, which put 96 nr-axSpA patients on 80-mg injections of ixekizumab every 4 weeks and 105 on placebo. After 52 weeks, ixekizumab was superior on the trial’s primary endpoint: 30% of patients had achieved a 40% improvement in Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society response criteria (ASAS 40), compared with 13% of patients on placebo (P = .0045).
Warnings and precautions for ixekizumab include considering potentially increased risk of infection and inflammatory bowel disease, as well as evaluating patients for tuberculosis before treatment. The most common adverse reactions (≥1%) are injection-site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, nausea, and tinea infections. The safety profile for ixekizumab among nr-axSpA patients is mostly consistent with that seen among patients receiving it for other indications, according to Lilly. The full prescribing information is available on Lilly’s website.
Nonpharmacologic ankylosing spondylitis recommendations not followed
Nonpharmacologic recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis aren’t often followed by rheumatologists in the Boston-based Partners Healthcare system, and probably elsewhere, according to a review presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN).
The American College of Rheumatology, Spondylitis Association of America, and SPARTAN released joint guidelines for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in 2016. Nonpharmacologic recommendations for AS included regular disease activity monitoring using a validated measure and C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate; physical therapy (PT) or home back exercises; and screening for osteoporosis with dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning.
However, “the extent to which these recommendations are followed in clinical practice is unknown,” said lead investigator Akash Patel, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, in Boston.
To find out, the team reviewed electronic records for 304 AS patients who had 564 rheumatology clinic visits with Brigham and Women’s and other Partners Healthcare physicians from July 1, 2016, to June 30, 2019.
Records documented DXA scans in less than 20% of visits. PT was documented in only 9% of visits, and home back exercise in just 7%. Inflammatory marker measurement was documented in about half of visits, and disease activity was measured in only 17%.
Comparing the first year of the study – right after the recommendations came out – to the third year, the team found just an 8% increase in disease activity documentation, and about a 3% increase in documentation of PT and back exercises.
In short, the recommendations “were performed at low frequencies in this study population,” Mr. Patel said at the meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
It’s unclear what’s going on. Perhaps some physicians disagree with the 2016 advice – the regular monitoring of disease activity, after all, was a conditional recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Other times, physicians might not have had enough time to talk about exercise or draw blood for AS biomarkers. Maybe they didn’t bring up PT when they knew their patients couldn’t afford the out-of-pocket cost.
Whatever the case, future iterations of the guidelines should include advice on how to implement them. “We believe that including some sort of strategy for rheumatologists may help increase compliance,” Mr. Patel said.
A member of the online viewing audience suggested that the problem may be widespread in rheumatology. "I think if we did this at my institution,” for example, “it would also look abysmal. I think we all just suck at this,” the attendee said.*
Mr. Patel and his team presented the results to Brigham and Women’s rheumatologists in February 2020, but it’s too early to tell if it made a difference.
It was a typical AS cohort. Almost three-quarters of the subjects were men; the average age was 50 years old; and the diagnosis was made by imaging. The majority of patients were HLA-B27 positive, and over one-third had a history of uveitis.
The study’s funding source and disclosures – if any – weren’t reported.
*Correction, 6/3/2020: A previous version of this story misattributed this quote.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. SPARTAN 2020 abstract session May 15.
Nonpharmacologic recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis aren’t often followed by rheumatologists in the Boston-based Partners Healthcare system, and probably elsewhere, according to a review presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN).
The American College of Rheumatology, Spondylitis Association of America, and SPARTAN released joint guidelines for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in 2016. Nonpharmacologic recommendations for AS included regular disease activity monitoring using a validated measure and C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate; physical therapy (PT) or home back exercises; and screening for osteoporosis with dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning.
However, “the extent to which these recommendations are followed in clinical practice is unknown,” said lead investigator Akash Patel, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, in Boston.
To find out, the team reviewed electronic records for 304 AS patients who had 564 rheumatology clinic visits with Brigham and Women’s and other Partners Healthcare physicians from July 1, 2016, to June 30, 2019.
Records documented DXA scans in less than 20% of visits. PT was documented in only 9% of visits, and home back exercise in just 7%. Inflammatory marker measurement was documented in about half of visits, and disease activity was measured in only 17%.
Comparing the first year of the study – right after the recommendations came out – to the third year, the team found just an 8% increase in disease activity documentation, and about a 3% increase in documentation of PT and back exercises.
In short, the recommendations “were performed at low frequencies in this study population,” Mr. Patel said at the meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
It’s unclear what’s going on. Perhaps some physicians disagree with the 2016 advice – the regular monitoring of disease activity, after all, was a conditional recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Other times, physicians might not have had enough time to talk about exercise or draw blood for AS biomarkers. Maybe they didn’t bring up PT when they knew their patients couldn’t afford the out-of-pocket cost.
Whatever the case, future iterations of the guidelines should include advice on how to implement them. “We believe that including some sort of strategy for rheumatologists may help increase compliance,” Mr. Patel said.
A member of the online viewing audience suggested that the problem may be widespread in rheumatology. "I think if we did this at my institution,” for example, “it would also look abysmal. I think we all just suck at this,” the attendee said.*
Mr. Patel and his team presented the results to Brigham and Women’s rheumatologists in February 2020, but it’s too early to tell if it made a difference.
It was a typical AS cohort. Almost three-quarters of the subjects were men; the average age was 50 years old; and the diagnosis was made by imaging. The majority of patients were HLA-B27 positive, and over one-third had a history of uveitis.
The study’s funding source and disclosures – if any – weren’t reported.
*Correction, 6/3/2020: A previous version of this story misattributed this quote.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. SPARTAN 2020 abstract session May 15.
Nonpharmacologic recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis aren’t often followed by rheumatologists in the Boston-based Partners Healthcare system, and probably elsewhere, according to a review presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN).
The American College of Rheumatology, Spondylitis Association of America, and SPARTAN released joint guidelines for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis in 2016. Nonpharmacologic recommendations for AS included regular disease activity monitoring using a validated measure and C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate; physical therapy (PT) or home back exercises; and screening for osteoporosis with dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanning.
However, “the extent to which these recommendations are followed in clinical practice is unknown,” said lead investigator Akash Patel, of the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Division of Rheumatology, Immunology, and Allergy, in Boston.
To find out, the team reviewed electronic records for 304 AS patients who had 564 rheumatology clinic visits with Brigham and Women’s and other Partners Healthcare physicians from July 1, 2016, to June 30, 2019.
Records documented DXA scans in less than 20% of visits. PT was documented in only 9% of visits, and home back exercise in just 7%. Inflammatory marker measurement was documented in about half of visits, and disease activity was measured in only 17%.
Comparing the first year of the study – right after the recommendations came out – to the third year, the team found just an 8% increase in disease activity documentation, and about a 3% increase in documentation of PT and back exercises.
In short, the recommendations “were performed at low frequencies in this study population,” Mr. Patel said at the meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
It’s unclear what’s going on. Perhaps some physicians disagree with the 2016 advice – the regular monitoring of disease activity, after all, was a conditional recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Other times, physicians might not have had enough time to talk about exercise or draw blood for AS biomarkers. Maybe they didn’t bring up PT when they knew their patients couldn’t afford the out-of-pocket cost.
Whatever the case, future iterations of the guidelines should include advice on how to implement them. “We believe that including some sort of strategy for rheumatologists may help increase compliance,” Mr. Patel said.
A member of the online viewing audience suggested that the problem may be widespread in rheumatology. "I think if we did this at my institution,” for example, “it would also look abysmal. I think we all just suck at this,” the attendee said.*
Mr. Patel and his team presented the results to Brigham and Women’s rheumatologists in February 2020, but it’s too early to tell if it made a difference.
It was a typical AS cohort. Almost three-quarters of the subjects were men; the average age was 50 years old; and the diagnosis was made by imaging. The majority of patients were HLA-B27 positive, and over one-third had a history of uveitis.
The study’s funding source and disclosures – if any – weren’t reported.
*Correction, 6/3/2020: A previous version of this story misattributed this quote.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. SPARTAN 2020 abstract session May 15.
FROM SPARTAN 2020
Inflammatory back pain likely underrecognized in primary care
according to a review of 239 charts there by rheumatologists and rheumatology fellows.
In more than two-thirds of cases, the reviewers were unable to determine if patients had inflammatory back pain or not based on what was documented. When symptoms relevant to inflammation – such as improvement with movement – were documented, it wasn’t clear if providers were actually trying to solicit a history of inflammation or if they simply recorded what patients volunteered.
Spondyloarthritis was listed in the differential of just five charts (2%), and only eight (3.3%) documented considering a rheumatology referral.
It raises the possibility that, in at least some cases, an opportunity to diagnose and treat spondyloarthritis early was missed. It’s a known problem in the literature; previous studies report a delay of 2-10 years before ankylosing spondylitis diagnosis.
“In our primary care practice, there appears to be poor awareness of inflammatory back pain [that] could lead to diagnostic delay,” said senior investigator and rheumatologist Steven Vlad, MD, PhD, an assistant professor at Tufts. Primary care providers are usually the first to see back pain patients, but they “did not seem to be screening for” inflammation, he said.
Dr. Vlad presented the study results at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network. The meeting was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The findings suggest that a reminder to check for inflammation might be in order. Dr. Vlad and his colleagues have since held educational sessions, and plan to do more, with the idea of repeating the study in a year or 2 to see if the sessions made a difference.
“People take away what they learn as residents. We probably need to focus on resident education if we really want to make a dent in this,” he said.
The generalizability of the single-center results is unclear, and it’s possible at least in some cases that providers asked the right questions but did not document them in the chart. Even so, the issue “deserves future study in other populations,” Dr. Vlad said.
The subjects all had a diagnostic code for low back pain and were seen by Tuft’s primary care at least twice 3 or more months apart, which indicated chronic pain. Chart reviews included clinical notes, labs, imaging studies, and consultation reports. “We looked for specific documentation that primary care physicians had been asking questions related to inflammatory back pain,” Dr. Vlad explained.
Overall, 128 charts (53.6%) documented some feature of inflammatory low back pain. Insidious onset was the most common, but morning stiffness, a cardinal sign, was the least common, noted in only five charts (2%). About 30% of the subjects had a lumbar spine x-ray, which was the most common imaging study, followed by lumbar spine MRI. Only a handful had imaging of the sacroiliac joints.
In 111 charts (46.4%), there was no documentation that primary care providers had looked for inflammatory features or asked questions about them.
Patients were seen from Jan. 2016 to May 2018. The average age in the study was 37.6 years, and two-thirds of the subjects were women.
Funding source and disclosures weren’t reported.
according to a review of 239 charts there by rheumatologists and rheumatology fellows.
In more than two-thirds of cases, the reviewers were unable to determine if patients had inflammatory back pain or not based on what was documented. When symptoms relevant to inflammation – such as improvement with movement – were documented, it wasn’t clear if providers were actually trying to solicit a history of inflammation or if they simply recorded what patients volunteered.
Spondyloarthritis was listed in the differential of just five charts (2%), and only eight (3.3%) documented considering a rheumatology referral.
It raises the possibility that, in at least some cases, an opportunity to diagnose and treat spondyloarthritis early was missed. It’s a known problem in the literature; previous studies report a delay of 2-10 years before ankylosing spondylitis diagnosis.
“In our primary care practice, there appears to be poor awareness of inflammatory back pain [that] could lead to diagnostic delay,” said senior investigator and rheumatologist Steven Vlad, MD, PhD, an assistant professor at Tufts. Primary care providers are usually the first to see back pain patients, but they “did not seem to be screening for” inflammation, he said.
Dr. Vlad presented the study results at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network. The meeting was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The findings suggest that a reminder to check for inflammation might be in order. Dr. Vlad and his colleagues have since held educational sessions, and plan to do more, with the idea of repeating the study in a year or 2 to see if the sessions made a difference.
“People take away what they learn as residents. We probably need to focus on resident education if we really want to make a dent in this,” he said.
The generalizability of the single-center results is unclear, and it’s possible at least in some cases that providers asked the right questions but did not document them in the chart. Even so, the issue “deserves future study in other populations,” Dr. Vlad said.
The subjects all had a diagnostic code for low back pain and were seen by Tuft’s primary care at least twice 3 or more months apart, which indicated chronic pain. Chart reviews included clinical notes, labs, imaging studies, and consultation reports. “We looked for specific documentation that primary care physicians had been asking questions related to inflammatory back pain,” Dr. Vlad explained.
Overall, 128 charts (53.6%) documented some feature of inflammatory low back pain. Insidious onset was the most common, but morning stiffness, a cardinal sign, was the least common, noted in only five charts (2%). About 30% of the subjects had a lumbar spine x-ray, which was the most common imaging study, followed by lumbar spine MRI. Only a handful had imaging of the sacroiliac joints.
In 111 charts (46.4%), there was no documentation that primary care providers had looked for inflammatory features or asked questions about them.
Patients were seen from Jan. 2016 to May 2018. The average age in the study was 37.6 years, and two-thirds of the subjects were women.
Funding source and disclosures weren’t reported.
according to a review of 239 charts there by rheumatologists and rheumatology fellows.
In more than two-thirds of cases, the reviewers were unable to determine if patients had inflammatory back pain or not based on what was documented. When symptoms relevant to inflammation – such as improvement with movement – were documented, it wasn’t clear if providers were actually trying to solicit a history of inflammation or if they simply recorded what patients volunteered.
Spondyloarthritis was listed in the differential of just five charts (2%), and only eight (3.3%) documented considering a rheumatology referral.
It raises the possibility that, in at least some cases, an opportunity to diagnose and treat spondyloarthritis early was missed. It’s a known problem in the literature; previous studies report a delay of 2-10 years before ankylosing spondylitis diagnosis.
“In our primary care practice, there appears to be poor awareness of inflammatory back pain [that] could lead to diagnostic delay,” said senior investigator and rheumatologist Steven Vlad, MD, PhD, an assistant professor at Tufts. Primary care providers are usually the first to see back pain patients, but they “did not seem to be screening for” inflammation, he said.
Dr. Vlad presented the study results at the virtual annual meeting of the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network. The meeting was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The findings suggest that a reminder to check for inflammation might be in order. Dr. Vlad and his colleagues have since held educational sessions, and plan to do more, with the idea of repeating the study in a year or 2 to see if the sessions made a difference.
“People take away what they learn as residents. We probably need to focus on resident education if we really want to make a dent in this,” he said.
The generalizability of the single-center results is unclear, and it’s possible at least in some cases that providers asked the right questions but did not document them in the chart. Even so, the issue “deserves future study in other populations,” Dr. Vlad said.
The subjects all had a diagnostic code for low back pain and were seen by Tuft’s primary care at least twice 3 or more months apart, which indicated chronic pain. Chart reviews included clinical notes, labs, imaging studies, and consultation reports. “We looked for specific documentation that primary care physicians had been asking questions related to inflammatory back pain,” Dr. Vlad explained.
Overall, 128 charts (53.6%) documented some feature of inflammatory low back pain. Insidious onset was the most common, but morning stiffness, a cardinal sign, was the least common, noted in only five charts (2%). About 30% of the subjects had a lumbar spine x-ray, which was the most common imaging study, followed by lumbar spine MRI. Only a handful had imaging of the sacroiliac joints.
In 111 charts (46.4%), there was no documentation that primary care providers had looked for inflammatory features or asked questions about them.
Patients were seen from Jan. 2016 to May 2018. The average age in the study was 37.6 years, and two-thirds of the subjects were women.
Funding source and disclosures weren’t reported.
REPORTING FROM SPARTAN 2020
TNF inhibitors may dampen COVID-19 severity
Patients on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for their rheumatic disease when they became infected with COVID-19 were markedly less likely to subsequently require hospitalization, according to intriguing early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry.
On the other hand, those registry patients who were on 10 mg of prednisone or more daily when they got infected were more than twice as likely to be hospitalized than were those who were not on corticosteroids, even after controlling for the severity of their rheumatic disease and other potential confounders, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, reported at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
“We saw a signal with moderate to high-dose steroids. I think it’s something we’re going to have to keep an eye out on as more data come in,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
The global registry launched on March 24, 2020, and was quickly embraced by rheumatologists from around the world. By May 12, the registry included more than 1,300 patients with a range of rheumatic diseases, all with confirmed COVID-19 infection as a requisite for enrollment; the cases were submitted by more than 300 rheumatologists in 40 countries. The registry is supported by the ACR and European League Against Rheumatism.
Dr. Yazdany, a member of the registry steering committee, described the project’s two main goals: To learn the outcomes of COVID-19–infected patients with various rheumatic diseases and to make inferences regarding the impact of the immunosuppressive and antimalarial medications widely prescribed by rheumatologists.
She presented soon-to-be-published data on the characteristics and disposition of the first 600 patients, 46% of whom were hospitalized and 9% died. A caveat regarding the registry, she noted, is that these are observational data and thus potentially subject to unrecognized confounders. Also, the registry population is skewed toward the sicker end of the COVID-19 disease spectrum because while all participants have confirmed infection, testing for the infection has been notoriously uneven. Many people are infected asymptomatically and thus may not undergo testing even where readily available.
Early key findings from registry
The risk factors for more severe infection resulting in hospitalization in patients with rheumatic diseases are by and large the same drivers described in the general population: older age and comorbid conditions including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and lung disease. Notably, however, patients on the equivalent of 10 mg/day of prednisone or more were at a 105% increased risk for hospitalization, compared with those not on corticosteroids after adjustment for age, comorbid conditions, and rheumatic disease severity.
Patients on a background tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor had an adjusted 60% reduction in risk of hospitalization. This apparent protective effect against more severe COVID-19 disease is mechanistically plausible: In animal studies, being on a TNF inhibitor has been associated with less severe infection following exposure to influenza virus, Dr. Yazdany observed.
COVID-infected patients on any biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug had a 54% decreased risk of hospitalization. However, in this early analysis, the study was sufficiently powered only to specifically assess the impact of TNF inhibitors, since those agents were by far the most commonly used biologics. As the registry grows, it will be possible to analyze the impact of other antirheumatic medications.
Being on hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization.
The only rheumatic disease diagnosis with an odds of hospitalization significantly different from that of RA patients was systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Lupus patients were at 80% increased risk of hospitalization. Although this was a statistically significant difference, Dr. Yazdany cautioned against making too much of it because of the strong potential for unmeasured confounding. In particular, lupus patients as a group are known to rate on the lower end of measures of social determinants of health, a status that is an established major risk factor for COVID-19 disease.
“A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” she said.
Being on background NSAIDs at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with increased risk of hospitalization; in fact, NSAID users were 36% less likely to be hospitalized for their COVID-19 disease, although this difference didn’t reach statistical significance.
Dr. Yazdany urged her fellow rheumatologists to enter their cases on the registry website: rheum-covid.org. There they can also join the registry mailing list and receive weekly updates.
Other recent insights on COVID-19 in rheumatology
An as-yet unpublished U.K. observational study involving electronic health record data on 17 million people included 885,000 individuals with RA, SLE, or psoriasis. After extensive statistical controlling for the known risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, including a measure of socioeconomic deprivation, the group with one of these autoimmune diseases had an adjusted, statistically significant 23% increased risk of hospital death because of COVID-19 infection.
“This is the largest study of its kind to date. There’s potential for unmeasured confounding and selection bias here due to who gets tested. We’ll have to see where this study lands, but I think it does suggest there’s a slightly higher mortality risk in COVID-infected patients with rheumatic disease,” according to Dr. Yazdany.
On the other hand, there have been at least eight recently published patient surveys and case series of patients with rheumatic diseases in areas of the world hardest hit by the pandemic, and they paint a consistent picture.
“What we’ve learned from these studies was the infection rate was generally in the ballpark of people in the region. It doesn’t seem like there’s a dramatically higher infection rate in people with rheumatic disease in these surveys. The hospitalized rheumatology patients had many of the familiar comorbidities. This is the first glance at how likely people are to become infected and how they fared, and I think overall the data have been quite reassuring,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly and receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Patients on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for their rheumatic disease when they became infected with COVID-19 were markedly less likely to subsequently require hospitalization, according to intriguing early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry.
On the other hand, those registry patients who were on 10 mg of prednisone or more daily when they got infected were more than twice as likely to be hospitalized than were those who were not on corticosteroids, even after controlling for the severity of their rheumatic disease and other potential confounders, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, reported at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
“We saw a signal with moderate to high-dose steroids. I think it’s something we’re going to have to keep an eye out on as more data come in,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
The global registry launched on March 24, 2020, and was quickly embraced by rheumatologists from around the world. By May 12, the registry included more than 1,300 patients with a range of rheumatic diseases, all with confirmed COVID-19 infection as a requisite for enrollment; the cases were submitted by more than 300 rheumatologists in 40 countries. The registry is supported by the ACR and European League Against Rheumatism.
Dr. Yazdany, a member of the registry steering committee, described the project’s two main goals: To learn the outcomes of COVID-19–infected patients with various rheumatic diseases and to make inferences regarding the impact of the immunosuppressive and antimalarial medications widely prescribed by rheumatologists.
She presented soon-to-be-published data on the characteristics and disposition of the first 600 patients, 46% of whom were hospitalized and 9% died. A caveat regarding the registry, she noted, is that these are observational data and thus potentially subject to unrecognized confounders. Also, the registry population is skewed toward the sicker end of the COVID-19 disease spectrum because while all participants have confirmed infection, testing for the infection has been notoriously uneven. Many people are infected asymptomatically and thus may not undergo testing even where readily available.
Early key findings from registry
The risk factors for more severe infection resulting in hospitalization in patients with rheumatic diseases are by and large the same drivers described in the general population: older age and comorbid conditions including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and lung disease. Notably, however, patients on the equivalent of 10 mg/day of prednisone or more were at a 105% increased risk for hospitalization, compared with those not on corticosteroids after adjustment for age, comorbid conditions, and rheumatic disease severity.
Patients on a background tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor had an adjusted 60% reduction in risk of hospitalization. This apparent protective effect against more severe COVID-19 disease is mechanistically plausible: In animal studies, being on a TNF inhibitor has been associated with less severe infection following exposure to influenza virus, Dr. Yazdany observed.
COVID-infected patients on any biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug had a 54% decreased risk of hospitalization. However, in this early analysis, the study was sufficiently powered only to specifically assess the impact of TNF inhibitors, since those agents were by far the most commonly used biologics. As the registry grows, it will be possible to analyze the impact of other antirheumatic medications.
Being on hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization.
The only rheumatic disease diagnosis with an odds of hospitalization significantly different from that of RA patients was systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Lupus patients were at 80% increased risk of hospitalization. Although this was a statistically significant difference, Dr. Yazdany cautioned against making too much of it because of the strong potential for unmeasured confounding. In particular, lupus patients as a group are known to rate on the lower end of measures of social determinants of health, a status that is an established major risk factor for COVID-19 disease.
“A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” she said.
Being on background NSAIDs at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with increased risk of hospitalization; in fact, NSAID users were 36% less likely to be hospitalized for their COVID-19 disease, although this difference didn’t reach statistical significance.
Dr. Yazdany urged her fellow rheumatologists to enter their cases on the registry website: rheum-covid.org. There they can also join the registry mailing list and receive weekly updates.
Other recent insights on COVID-19 in rheumatology
An as-yet unpublished U.K. observational study involving electronic health record data on 17 million people included 885,000 individuals with RA, SLE, or psoriasis. After extensive statistical controlling for the known risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, including a measure of socioeconomic deprivation, the group with one of these autoimmune diseases had an adjusted, statistically significant 23% increased risk of hospital death because of COVID-19 infection.
“This is the largest study of its kind to date. There’s potential for unmeasured confounding and selection bias here due to who gets tested. We’ll have to see where this study lands, but I think it does suggest there’s a slightly higher mortality risk in COVID-infected patients with rheumatic disease,” according to Dr. Yazdany.
On the other hand, there have been at least eight recently published patient surveys and case series of patients with rheumatic diseases in areas of the world hardest hit by the pandemic, and they paint a consistent picture.
“What we’ve learned from these studies was the infection rate was generally in the ballpark of people in the region. It doesn’t seem like there’s a dramatically higher infection rate in people with rheumatic disease in these surveys. The hospitalized rheumatology patients had many of the familiar comorbidities. This is the first glance at how likely people are to become infected and how they fared, and I think overall the data have been quite reassuring,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly and receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Patients on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for their rheumatic disease when they became infected with COVID-19 were markedly less likely to subsequently require hospitalization, according to intriguing early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry.
On the other hand, those registry patients who were on 10 mg of prednisone or more daily when they got infected were more than twice as likely to be hospitalized than were those who were not on corticosteroids, even after controlling for the severity of their rheumatic disease and other potential confounders, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, reported at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
“We saw a signal with moderate to high-dose steroids. I think it’s something we’re going to have to keep an eye out on as more data come in,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
The global registry launched on March 24, 2020, and was quickly embraced by rheumatologists from around the world. By May 12, the registry included more than 1,300 patients with a range of rheumatic diseases, all with confirmed COVID-19 infection as a requisite for enrollment; the cases were submitted by more than 300 rheumatologists in 40 countries. The registry is supported by the ACR and European League Against Rheumatism.
Dr. Yazdany, a member of the registry steering committee, described the project’s two main goals: To learn the outcomes of COVID-19–infected patients with various rheumatic diseases and to make inferences regarding the impact of the immunosuppressive and antimalarial medications widely prescribed by rheumatologists.
She presented soon-to-be-published data on the characteristics and disposition of the first 600 patients, 46% of whom were hospitalized and 9% died. A caveat regarding the registry, she noted, is that these are observational data and thus potentially subject to unrecognized confounders. Also, the registry population is skewed toward the sicker end of the COVID-19 disease spectrum because while all participants have confirmed infection, testing for the infection has been notoriously uneven. Many people are infected asymptomatically and thus may not undergo testing even where readily available.
Early key findings from registry
The risk factors for more severe infection resulting in hospitalization in patients with rheumatic diseases are by and large the same drivers described in the general population: older age and comorbid conditions including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and lung disease. Notably, however, patients on the equivalent of 10 mg/day of prednisone or more were at a 105% increased risk for hospitalization, compared with those not on corticosteroids after adjustment for age, comorbid conditions, and rheumatic disease severity.
Patients on a background tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor had an adjusted 60% reduction in risk of hospitalization. This apparent protective effect against more severe COVID-19 disease is mechanistically plausible: In animal studies, being on a TNF inhibitor has been associated with less severe infection following exposure to influenza virus, Dr. Yazdany observed.
COVID-infected patients on any biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug had a 54% decreased risk of hospitalization. However, in this early analysis, the study was sufficiently powered only to specifically assess the impact of TNF inhibitors, since those agents were by far the most commonly used biologics. As the registry grows, it will be possible to analyze the impact of other antirheumatic medications.
Being on hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization.
The only rheumatic disease diagnosis with an odds of hospitalization significantly different from that of RA patients was systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Lupus patients were at 80% increased risk of hospitalization. Although this was a statistically significant difference, Dr. Yazdany cautioned against making too much of it because of the strong potential for unmeasured confounding. In particular, lupus patients as a group are known to rate on the lower end of measures of social determinants of health, a status that is an established major risk factor for COVID-19 disease.
“A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” she said.
Being on background NSAIDs at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with increased risk of hospitalization; in fact, NSAID users were 36% less likely to be hospitalized for their COVID-19 disease, although this difference didn’t reach statistical significance.
Dr. Yazdany urged her fellow rheumatologists to enter their cases on the registry website: rheum-covid.org. There they can also join the registry mailing list and receive weekly updates.
Other recent insights on COVID-19 in rheumatology
An as-yet unpublished U.K. observational study involving electronic health record data on 17 million people included 885,000 individuals with RA, SLE, or psoriasis. After extensive statistical controlling for the known risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, including a measure of socioeconomic deprivation, the group with one of these autoimmune diseases had an adjusted, statistically significant 23% increased risk of hospital death because of COVID-19 infection.
“This is the largest study of its kind to date. There’s potential for unmeasured confounding and selection bias here due to who gets tested. We’ll have to see where this study lands, but I think it does suggest there’s a slightly higher mortality risk in COVID-infected patients with rheumatic disease,” according to Dr. Yazdany.
On the other hand, there have been at least eight recently published patient surveys and case series of patients with rheumatic diseases in areas of the world hardest hit by the pandemic, and they paint a consistent picture.
“What we’ve learned from these studies was the infection rate was generally in the ballpark of people in the region. It doesn’t seem like there’s a dramatically higher infection rate in people with rheumatic disease in these surveys. The hospitalized rheumatology patients had many of the familiar comorbidities. This is the first glance at how likely people are to become infected and how they fared, and I think overall the data have been quite reassuring,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly and receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
REPORTING FROM SOTA 2020
Advice on treating rheumatic diseases from a COVID-19 epicenter
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose an unprecedented challenge to health care systems worldwide. In addition to the direct impact of the disease itself, there is a growing concern related to ensuring adequate health care utilization and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations, such as those with chronic illness.
Emanuel et al. have advocated a framework of fair allocation of resources, led by the principles of equity, maximizing benefits, and prioritizing the vulnerable. In these uncertain times, patients with rheumatic diseases represent a vulnerable population whose health and wellness are particularly threatened, not only by the risk of COVID-19, but also by reduced access to usual medical care (e.g., in-person clinic visits), potential treatment interruptions (e.g., planned infusion therapies), and the ongoing shortage of hydroxychloroquine, to name a few.
As rheumatologists, we are now tasked with the development of best practices for caring for patients with rheumatic conditions in this uncertain, evolving, and nearly data-free landscape. We also must maintain an active role as advocates for our patients to help them navigate this pandemic. Herein, we discuss our approach to caring for patients with rheumatic diseases within our practice in New York City, an epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Communication with patients
Maintaining an open line of communication with our patients (by phone, patient portal, telemedicine, and so on) has become more essential than ever. It is through these communications that we best understand our patients’ concerns and provide support and personalized treatment decisions. The most common questions we have received during recent weeks are:
- Should I stop my medication to lower my risk for infection?
- Are my current symptoms caused by coronavirus, and what should I do next?
- Where can I fill my hydroxychloroquine prescription?
The American College of Rheumatology has deployed a number of task forces aimed at advocating for rheumatologists and patients with rheumatic diseases and is doing an exemplary job guiding us. For patients, several other organizations (e.g., CreakyJoints, Arthritis Foundation, Lupus Research Alliance, Vasculitis Foundation, and Scleroderma Foundation) are also providing accurate information regarding hygiene practices, social distancing, management of medications, and other guidance related to specific rheumatic diseases. In line with ACR recommendations, we encourage a personalized, shared decision-making process with each of our patients.
Patients with rheumatic disease at risk for COVID-19 infection
First, for rheumatology patients who have no COVID-19 symptoms, our management approach is individualized. For patients who are able to maintain social distancing, we have not routinely stopped immunosuppressive medications, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents. However, we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing immunosuppressive therapy during this time with all of our patients.
In certain cases of stable, non–life-threatening disease, we may consider spacing or temporarily interrupting immunosuppressive therapy, using individualized, shared decision making. Yet, it is important to recognize that, for some patients, achieving adequate disease control can require a substantial amount of time.
Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that disease flares requiring steroid therapy may increase the risk for infection even more, keeping in mind that, in some rheumatic diseases, high disease activity itself can increase infection risk. We advise patients who are continuing therapy to maintain at least a 1-month supply of their medications.
Decisions regarding infusions in the hospital and outpatient settings are similarly made on an individual basis, weighing the risk for virus exposure against that of disease flare. The more limited availability of appropriately distanced infusion chairs in some already overburdened systems must be considered in this discussion. We agree with the ACR, whose infusion guidance recommends that “possible changes might include temporary interruption of therapy, temporary initiation of a bridge therapy such as a less potent anti-inflammatory or immune-modulating agent, or temporary change to an alternative therapy.”
We also reinforce recommended behaviors for preventing infection, including social distancing, frequent handwashing, and avoiding touching one’s face.
Patients with rheumatic disease and confirmed or suspected COVID-19 infection
With the worldwide spread of COVID-19, patients with rheumatic diseases will undoubtedly be among those exposed and infected. Though current data are limited, within a cohort from China, 1% had an autoimmune disease. Testing recommendations to confirm COVID-19 and decision guidelines for outpatient versus inpatient management are evolving, and we consult the most up-to-date, local information regarding testing as individual potential cases arise.
For patients who develop COVID-19 and are currently taking DMARDs and biologics, we recommend that they discontinue these medications, with the exception of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). HCQ may be continued because its mechanism is not expected to worsen infection, and it plays a key role in the management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In addition, in vitro antiviral effects have been reported and there is growing interest for its use in the management of COVID-19. However, there are conflicting data and methodological concerns about the nonrandomized human studies that suggest a benefit of HCQ against COVID-19.
The decision regarding management of glucocorticoids in the setting of new COVID-19 infection is challenging and should be individualized. At present, expert panels recommend against the use of glucocorticoids among individuals with COVID-19 who do not have acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, adrenal insufficiency must be considered among patients with COVID-19 who are treated with chronic glucocorticoids. Again, these decisions should be made on an individual, case-by-case basis.
Implications of a hydroxychloroquine shortage
The use of HCQ in rheumatology is supported by years of research. Particularly in SLE, HCQ has been shown to reduce disease activity and damage and to improve survival. Furthermore, for pregnant patients with SLE, numerous studies have demonstrated the safety and benefit of HCQ for both the mother and fetus; thus, it is strongly recommended. By contrast, despite the growing interest for HCQ in patients with COVID-19, the evidence is inconclusive and limited.
The ACR suggests that decisions regarding HCQ dose reductions to extend individual patients supplies should be tailored to each patient’s need and risk in the unfortunate setting of medication shortages. Even in patients with stable SLE, however, disease flares at 6 months are more common among individuals who discontinue HCQ. Of note, these flares may incorporate novel and severe disease manifestations.
Unfortunately, other therapeutic options for SLE are associated with more adverse effects (including increased susceptibility to infection) or are largely unavailable (e.g., quinacrine). Thus, we strive to continue standard dosing of HCQ for patients who are currently flaring or recently flared, and we make shared, individualized decisions for those patients with stable disease as the HCQ shortage evolves.
Future research on COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
While we might expect that an underlying rheumatic disease and associated treatments may predispose individuals to developing COVID-19, current data do not indicate which, if any, rheumatic diseases and associated therapies convey the greatest risk.
To address this uncertainty, the rheumatology community created the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, an international effort to initiate and maintain a deidentified patient registry for individuals with rheumatic disease who develop COVID-19. These efforts will allow us to gain essential insights regarding which patient demographics, underlying diseases, and medications are most common among patients who develop COVID-19.
This alliance encourages rheumatologists and those caring for patients with rheumatic diseases to report their patient cases to this registry. As we are confronted with making management decisions with a scarcity of supporting data, efforts like these will improve our ability to make individualized treatment recommendations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented us all with unprecedented challenges. As rheumatologists, it is our duty to lead our patients through this uncharted territory with close communication, information, advocacy, and personalized treatment decisions. Each of these is central to the management of rheumatology patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
With the growing interest in immunomodulatory therapies for the complications of this infection, we have the unique opportunity to share our expertise, recommendations, and caution with our colleagues. As clinicians and scientists, we must advocate for data collection and studies that will allow us to develop novel, data-driven disease management approaches while providing the best care possible for our patients.
Stephen Paget, MD, is physician in chief emeritus for the Center for Rheumatology at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York. Kimberly Showalter, MD, is a third-year rheumatology fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery. Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, is a third-year rheumatology and 1-year vasculitis fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose an unprecedented challenge to health care systems worldwide. In addition to the direct impact of the disease itself, there is a growing concern related to ensuring adequate health care utilization and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations, such as those with chronic illness.
Emanuel et al. have advocated a framework of fair allocation of resources, led by the principles of equity, maximizing benefits, and prioritizing the vulnerable. In these uncertain times, patients with rheumatic diseases represent a vulnerable population whose health and wellness are particularly threatened, not only by the risk of COVID-19, but also by reduced access to usual medical care (e.g., in-person clinic visits), potential treatment interruptions (e.g., planned infusion therapies), and the ongoing shortage of hydroxychloroquine, to name a few.
As rheumatologists, we are now tasked with the development of best practices for caring for patients with rheumatic conditions in this uncertain, evolving, and nearly data-free landscape. We also must maintain an active role as advocates for our patients to help them navigate this pandemic. Herein, we discuss our approach to caring for patients with rheumatic diseases within our practice in New York City, an epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Communication with patients
Maintaining an open line of communication with our patients (by phone, patient portal, telemedicine, and so on) has become more essential than ever. It is through these communications that we best understand our patients’ concerns and provide support and personalized treatment decisions. The most common questions we have received during recent weeks are:
- Should I stop my medication to lower my risk for infection?
- Are my current symptoms caused by coronavirus, and what should I do next?
- Where can I fill my hydroxychloroquine prescription?
The American College of Rheumatology has deployed a number of task forces aimed at advocating for rheumatologists and patients with rheumatic diseases and is doing an exemplary job guiding us. For patients, several other organizations (e.g., CreakyJoints, Arthritis Foundation, Lupus Research Alliance, Vasculitis Foundation, and Scleroderma Foundation) are also providing accurate information regarding hygiene practices, social distancing, management of medications, and other guidance related to specific rheumatic diseases. In line with ACR recommendations, we encourage a personalized, shared decision-making process with each of our patients.
Patients with rheumatic disease at risk for COVID-19 infection
First, for rheumatology patients who have no COVID-19 symptoms, our management approach is individualized. For patients who are able to maintain social distancing, we have not routinely stopped immunosuppressive medications, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents. However, we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing immunosuppressive therapy during this time with all of our patients.
In certain cases of stable, non–life-threatening disease, we may consider spacing or temporarily interrupting immunosuppressive therapy, using individualized, shared decision making. Yet, it is important to recognize that, for some patients, achieving adequate disease control can require a substantial amount of time.
Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that disease flares requiring steroid therapy may increase the risk for infection even more, keeping in mind that, in some rheumatic diseases, high disease activity itself can increase infection risk. We advise patients who are continuing therapy to maintain at least a 1-month supply of their medications.
Decisions regarding infusions in the hospital and outpatient settings are similarly made on an individual basis, weighing the risk for virus exposure against that of disease flare. The more limited availability of appropriately distanced infusion chairs in some already overburdened systems must be considered in this discussion. We agree with the ACR, whose infusion guidance recommends that “possible changes might include temporary interruption of therapy, temporary initiation of a bridge therapy such as a less potent anti-inflammatory or immune-modulating agent, or temporary change to an alternative therapy.”
We also reinforce recommended behaviors for preventing infection, including social distancing, frequent handwashing, and avoiding touching one’s face.
Patients with rheumatic disease and confirmed or suspected COVID-19 infection
With the worldwide spread of COVID-19, patients with rheumatic diseases will undoubtedly be among those exposed and infected. Though current data are limited, within a cohort from China, 1% had an autoimmune disease. Testing recommendations to confirm COVID-19 and decision guidelines for outpatient versus inpatient management are evolving, and we consult the most up-to-date, local information regarding testing as individual potential cases arise.
For patients who develop COVID-19 and are currently taking DMARDs and biologics, we recommend that they discontinue these medications, with the exception of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). HCQ may be continued because its mechanism is not expected to worsen infection, and it plays a key role in the management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In addition, in vitro antiviral effects have been reported and there is growing interest for its use in the management of COVID-19. However, there are conflicting data and methodological concerns about the nonrandomized human studies that suggest a benefit of HCQ against COVID-19.
The decision regarding management of glucocorticoids in the setting of new COVID-19 infection is challenging and should be individualized. At present, expert panels recommend against the use of glucocorticoids among individuals with COVID-19 who do not have acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, adrenal insufficiency must be considered among patients with COVID-19 who are treated with chronic glucocorticoids. Again, these decisions should be made on an individual, case-by-case basis.
Implications of a hydroxychloroquine shortage
The use of HCQ in rheumatology is supported by years of research. Particularly in SLE, HCQ has been shown to reduce disease activity and damage and to improve survival. Furthermore, for pregnant patients with SLE, numerous studies have demonstrated the safety and benefit of HCQ for both the mother and fetus; thus, it is strongly recommended. By contrast, despite the growing interest for HCQ in patients with COVID-19, the evidence is inconclusive and limited.
The ACR suggests that decisions regarding HCQ dose reductions to extend individual patients supplies should be tailored to each patient’s need and risk in the unfortunate setting of medication shortages. Even in patients with stable SLE, however, disease flares at 6 months are more common among individuals who discontinue HCQ. Of note, these flares may incorporate novel and severe disease manifestations.
Unfortunately, other therapeutic options for SLE are associated with more adverse effects (including increased susceptibility to infection) or are largely unavailable (e.g., quinacrine). Thus, we strive to continue standard dosing of HCQ for patients who are currently flaring or recently flared, and we make shared, individualized decisions for those patients with stable disease as the HCQ shortage evolves.
Future research on COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
While we might expect that an underlying rheumatic disease and associated treatments may predispose individuals to developing COVID-19, current data do not indicate which, if any, rheumatic diseases and associated therapies convey the greatest risk.
To address this uncertainty, the rheumatology community created the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, an international effort to initiate and maintain a deidentified patient registry for individuals with rheumatic disease who develop COVID-19. These efforts will allow us to gain essential insights regarding which patient demographics, underlying diseases, and medications are most common among patients who develop COVID-19.
This alliance encourages rheumatologists and those caring for patients with rheumatic diseases to report their patient cases to this registry. As we are confronted with making management decisions with a scarcity of supporting data, efforts like these will improve our ability to make individualized treatment recommendations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented us all with unprecedented challenges. As rheumatologists, it is our duty to lead our patients through this uncharted territory with close communication, information, advocacy, and personalized treatment decisions. Each of these is central to the management of rheumatology patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
With the growing interest in immunomodulatory therapies for the complications of this infection, we have the unique opportunity to share our expertise, recommendations, and caution with our colleagues. As clinicians and scientists, we must advocate for data collection and studies that will allow us to develop novel, data-driven disease management approaches while providing the best care possible for our patients.
Stephen Paget, MD, is physician in chief emeritus for the Center for Rheumatology at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York. Kimberly Showalter, MD, is a third-year rheumatology fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery. Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, is a third-year rheumatology and 1-year vasculitis fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to pose an unprecedented challenge to health care systems worldwide. In addition to the direct impact of the disease itself, there is a growing concern related to ensuring adequate health care utilization and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations, such as those with chronic illness.
Emanuel et al. have advocated a framework of fair allocation of resources, led by the principles of equity, maximizing benefits, and prioritizing the vulnerable. In these uncertain times, patients with rheumatic diseases represent a vulnerable population whose health and wellness are particularly threatened, not only by the risk of COVID-19, but also by reduced access to usual medical care (e.g., in-person clinic visits), potential treatment interruptions (e.g., planned infusion therapies), and the ongoing shortage of hydroxychloroquine, to name a few.
As rheumatologists, we are now tasked with the development of best practices for caring for patients with rheumatic conditions in this uncertain, evolving, and nearly data-free landscape. We also must maintain an active role as advocates for our patients to help them navigate this pandemic. Herein, we discuss our approach to caring for patients with rheumatic diseases within our practice in New York City, an epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Communication with patients
Maintaining an open line of communication with our patients (by phone, patient portal, telemedicine, and so on) has become more essential than ever. It is through these communications that we best understand our patients’ concerns and provide support and personalized treatment decisions. The most common questions we have received during recent weeks are:
- Should I stop my medication to lower my risk for infection?
- Are my current symptoms caused by coronavirus, and what should I do next?
- Where can I fill my hydroxychloroquine prescription?
The American College of Rheumatology has deployed a number of task forces aimed at advocating for rheumatologists and patients with rheumatic diseases and is doing an exemplary job guiding us. For patients, several other organizations (e.g., CreakyJoints, Arthritis Foundation, Lupus Research Alliance, Vasculitis Foundation, and Scleroderma Foundation) are also providing accurate information regarding hygiene practices, social distancing, management of medications, and other guidance related to specific rheumatic diseases. In line with ACR recommendations, we encourage a personalized, shared decision-making process with each of our patients.
Patients with rheumatic disease at risk for COVID-19 infection
First, for rheumatology patients who have no COVID-19 symptoms, our management approach is individualized. For patients who are able to maintain social distancing, we have not routinely stopped immunosuppressive medications, including disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents. However, we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing immunosuppressive therapy during this time with all of our patients.
In certain cases of stable, non–life-threatening disease, we may consider spacing or temporarily interrupting immunosuppressive therapy, using individualized, shared decision making. Yet, it is important to recognize that, for some patients, achieving adequate disease control can require a substantial amount of time.
Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that disease flares requiring steroid therapy may increase the risk for infection even more, keeping in mind that, in some rheumatic diseases, high disease activity itself can increase infection risk. We advise patients who are continuing therapy to maintain at least a 1-month supply of their medications.
Decisions regarding infusions in the hospital and outpatient settings are similarly made on an individual basis, weighing the risk for virus exposure against that of disease flare. The more limited availability of appropriately distanced infusion chairs in some already overburdened systems must be considered in this discussion. We agree with the ACR, whose infusion guidance recommends that “possible changes might include temporary interruption of therapy, temporary initiation of a bridge therapy such as a less potent anti-inflammatory or immune-modulating agent, or temporary change to an alternative therapy.”
We also reinforce recommended behaviors for preventing infection, including social distancing, frequent handwashing, and avoiding touching one’s face.
Patients with rheumatic disease and confirmed or suspected COVID-19 infection
With the worldwide spread of COVID-19, patients with rheumatic diseases will undoubtedly be among those exposed and infected. Though current data are limited, within a cohort from China, 1% had an autoimmune disease. Testing recommendations to confirm COVID-19 and decision guidelines for outpatient versus inpatient management are evolving, and we consult the most up-to-date, local information regarding testing as individual potential cases arise.
For patients who develop COVID-19 and are currently taking DMARDs and biologics, we recommend that they discontinue these medications, with the exception of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). HCQ may be continued because its mechanism is not expected to worsen infection, and it plays a key role in the management of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In addition, in vitro antiviral effects have been reported and there is growing interest for its use in the management of COVID-19. However, there are conflicting data and methodological concerns about the nonrandomized human studies that suggest a benefit of HCQ against COVID-19.
The decision regarding management of glucocorticoids in the setting of new COVID-19 infection is challenging and should be individualized. At present, expert panels recommend against the use of glucocorticoids among individuals with COVID-19 who do not have acute respiratory distress syndrome. However, adrenal insufficiency must be considered among patients with COVID-19 who are treated with chronic glucocorticoids. Again, these decisions should be made on an individual, case-by-case basis.
Implications of a hydroxychloroquine shortage
The use of HCQ in rheumatology is supported by years of research. Particularly in SLE, HCQ has been shown to reduce disease activity and damage and to improve survival. Furthermore, for pregnant patients with SLE, numerous studies have demonstrated the safety and benefit of HCQ for both the mother and fetus; thus, it is strongly recommended. By contrast, despite the growing interest for HCQ in patients with COVID-19, the evidence is inconclusive and limited.
The ACR suggests that decisions regarding HCQ dose reductions to extend individual patients supplies should be tailored to each patient’s need and risk in the unfortunate setting of medication shortages. Even in patients with stable SLE, however, disease flares at 6 months are more common among individuals who discontinue HCQ. Of note, these flares may incorporate novel and severe disease manifestations.
Unfortunately, other therapeutic options for SLE are associated with more adverse effects (including increased susceptibility to infection) or are largely unavailable (e.g., quinacrine). Thus, we strive to continue standard dosing of HCQ for patients who are currently flaring or recently flared, and we make shared, individualized decisions for those patients with stable disease as the HCQ shortage evolves.
Future research on COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
While we might expect that an underlying rheumatic disease and associated treatments may predispose individuals to developing COVID-19, current data do not indicate which, if any, rheumatic diseases and associated therapies convey the greatest risk.
To address this uncertainty, the rheumatology community created the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, an international effort to initiate and maintain a deidentified patient registry for individuals with rheumatic disease who develop COVID-19. These efforts will allow us to gain essential insights regarding which patient demographics, underlying diseases, and medications are most common among patients who develop COVID-19.
This alliance encourages rheumatologists and those caring for patients with rheumatic diseases to report their patient cases to this registry. As we are confronted with making management decisions with a scarcity of supporting data, efforts like these will improve our ability to make individualized treatment recommendations.
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented us all with unprecedented challenges. As rheumatologists, it is our duty to lead our patients through this uncharted territory with close communication, information, advocacy, and personalized treatment decisions. Each of these is central to the management of rheumatology patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
With the growing interest in immunomodulatory therapies for the complications of this infection, we have the unique opportunity to share our expertise, recommendations, and caution with our colleagues. As clinicians and scientists, we must advocate for data collection and studies that will allow us to develop novel, data-driven disease management approaches while providing the best care possible for our patients.
Stephen Paget, MD, is physician in chief emeritus for the Center for Rheumatology at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York. Kimberly Showalter, MD, is a third-year rheumatology fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery. Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, is a third-year rheumatology and 1-year vasculitis fellow at Hospital for Special Surgery.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ACR gives guidance on rheumatic disease management during pandemic
When COVID-19 is suspected or confirmed in a patient with a rheumatic disease, treatment with hydroxychloroquine may be continued, but other treatments may need to be stopped or held temporarily, according to new guidance issued by the American College of Rheumatology.
That includes disease-modifying treatment with antirheumatic drugs such as sulfasalazine, methotrexate, leflunomide, and the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as immunosuppressants and non-interleukin (IL)-6 biologics, and this is regardless of how severe the COVID-19 illness is. NSAIDs should also be stopped if there are respiratory symptoms.
The advice is slightly less drastic if someone with stable rheumatic disease has probably been exposed to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or are asymptomatic. In those patients, DMARDs may be continued, although there is uncertainty over whether there is a need to temporarily stop methotrexate or leflunomide. Interruption of immunosuppressive, non–IL-6, and JAK inhibitor treatment is advised pending a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result, assuming the patient’s rheumatic disease is stable.
Impetus for ACR COVID-19 guidance
“One of the earliest challenges for rheumatologists during the COVID-19 pandemic was determining how to advise our patients who were taking immunosuppressive medications and were concerned as to whether or not to discontinue their therapy,” ACR President Ellen Gravallese, MD, said in an interview about the ACR Clinical Guidance Document, which is published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“A second challenge was keeping our patients safe from exposure to the virus, while still seeing those patients in person who required office visits,” added Dr. Gravallese, who is chief of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
She continued: “The ACR Clinical Guidance Document was prepared in order to assist rheumatologists with decisions as to how to handle current medications during different phases of a patient’s exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.”
But with very little evidence available on how to manage COVID-19 patients generally, let alone specifically in those with rheumatic diseases, “it became evident that any recommendations made would need to be done in a thoughtful and organized manner, evaluating the evidence that was available and obtaining the advice of experts in infectious disease, epidemiology, and in the use of biologic and nonbiologic agents for rheumatic disease,” she said.
As such, the ACR convened a task force of 10 rheumatologists and 4 infectious disease specialists from North America to look at how best to manage patients with rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our charge was to develop a guidance document for the care of adult rheumatic disease patients in the context of COVID-19 and not per se to provide guidance for the treatment of COVID-19,” explained task force member and the corresponding author for the guidance, Ted R. Mikuls, MD, MSPH, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Dr. Mikuls, who was speaking at a virtual town hall meeting hosted by the ACR on May 6, noted that the guidance was obviously based on the best consensus of the available data and as such represented a “living document” that “would change and be added to” as necessary.
General recommendations for adult rheumatic disease management
In terms of general recommendations for the management of adult rheumatic disease patients, Dr. Mikuls said that six statements had been made “specific to risk assessment, prevention of infection, and best practices related to glucocorticoid use and the use of ACE [angiotensin-converting enzyme] inhibitors and ARBs [angiotensin II receptor blockers] during the pandemic.”
For example, general advice is to counsel patients to keep up general preventive measures such as social distancing and regular hand washing, reducing the number of in-person health care visits, and undertaking other means to try to prevent potential SARS-CoV-2 exposure. As for general treatment advice, glucocorticoids should be used at their lowest doses possible and should not be abruptly stopped, and antihypertensive treatment should be used as indicated.
Additional guidance statements include those that address the treatment of patients with stable rheumatic disease in the absence of infection or known exposure to SARS-CoV-2, with guidance specific to the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and those with newly diagnosed or active rheumatic disease.
SLE and inflammatory arthritis recommendations
“There are several sections within the guidance document that address the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during this pandemic,” Dr. Gravallese pointed out. “In general, it is recommended that lupus patients who are currently taking hydroxychloroquine can remain on the therapy prior to and during infection and that newly diagnosed patients with lupus can be placed on this medication at full dose. It is recommended that pregnant patients with lupus remain on therapy with this drug.”
She also observed that, for the treatment of active inflammatory arthritis, “the recommendations were written to address specific medications that could be used in this setting. In general, the task force recommendations were guided by the importance of controlling inflammation prior to exposure to the virus, even during this pandemic.
Guidance raises questions
During the ACR’s town hall meeting, the task force answered several questions raised by the guidance, such as the reasoning behind recommending that the use of traditional DMARDs be discontinued in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Dr. Mikuls observed: “Maybe if you just read the guidance statements it isn’t terribly intuitive.” There was a lot of discussion about whether or not conventional DMARDs were immunosuppressive, and even though they may not have such effects, it was decided to err on the side of caution.
“I think the task force felt that, with a COVID-19–positive patient, there is a concern of potentially confusing adverse effects related to medicines or conflate those with problems from the infection,” he said. Although rare, examples of those issues could be drug-induced hypersensitivity, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, or gastrointestinal side effects of hepatitis, all of which have been described in COVID-19. “Not only could it cause confusion, but it could maybe worsen those sequalae of COVID-19,” he said.
“I think the other part of this answer was that the panel really felt that the risk in terms of the flaring of the underlying rheumatic disease was likely to be pretty low given the finite time frame you’d be taking about – usually a time frame of 2-3 weeks you’d be holding the agent – so I think that is really why the task force ended up with that recommendation.”
Similarly, for the JAK inhibitors, the decision was to err on the side of caution when COVID-19 was suspected or confirmed. “Not so much because of the risk of thromboembolic disease, but concerns over immunosuppression that these drugs carry with them and also the fact the JAK inhibitors are probably inhibitors of type 1 interferons, which play a significant role in viral immunity and could potentially have a negative impact,” said Stanley Cohen, MD, who practices rheumatology in the Dallas area.
“On the flipside, there is interest in some of the JAK inhibitors as a potential treatment for COVID-19,” Dr. Cohen said, referring to anecdotal evidence for baricitinib (Olumiant).
Michael Weinblatt, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, addressed the recent concern over the use of NSAIDs by the public.
“There’s been a lot in the lay press that NSAIDs – because of the effects on receptors in the lung – could lead to deleterious outcomes in patients with COVID and there’s very little data to support this.
“We did recommend that NSAIDs be held in the hospitalized patient and that wasn’t because of the COVID-19 issue, it really was just medical practice, and we didn’t want to confound the care of these really sick patients with potential toxicities from NSAIDs. But as far as routine rheumatological care in your outpatients, we did not recommend that nonsteroidals be stopped if they were tolerated.”
One part of the guidance that might already need revision is the recommendation on the continued use of hydroxychloroquine in patients who develop COVID-19.
“Our guidance document says it’s OK; we were all in very strong agreement to continue hydroxychloroquine in our patients with COVID-19 because at that point, just a couple of weeks ago, we thought it was part of the potential treatment,” Karen Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said during the town hall meeting.
“Now the pendulum has swung the other way, and we’re worried about maybe we shouldn’t be continuing it because COVID-19 patients will be getting many other medications,” Dr. Costenbader said, and these may affect the QT-interval. “They will not be getting azithromycin because the pendulum swung the other way on that one too, but definitely on many other medications when they are sick.”
Potentially, she added, “if the rheumatic disease is under good control the inpatient physicians could decide whether they should continue [hydroxychloroquine] or not. If the COVID-19 is a mild disease, I would say we probably could continue in accordance with what we put in the document, but we will have to revisit this as well.”
Guidance is a ‘living document’
“We will be providing updates to the Clinical Guidance Document as the need arises,” Dr. Gravallese emphasized. While the general recommendations are unlikely to change very much, “the task force will be interested in seeing the results of all new data, but the results of randomized, clinical trials will be particularly important as they become available,” she said. In particular, randomized, controlled trials of glucocorticoids and IL-6 receptor blockade for use in COVID-19 will be of great importance.
“In this initial document, we could not take on all of the medical scenarios our members will face. For example, we could not take on recommendations for the pediatric population as this group of patients has a very different response than adults to the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Dr. Gravallese acknowledged. The plan is to provide guidance for that group of patients soon.
In addition, the ACR Executive Committee has appointed a Practice and Advocacy Task Force that will “address issues rheumatologists face on the practice side, including advice regarding how to effectively use telemedicine, address the frequency and safety of infusions, determine urgent versus nonurgent issues that would or would not require face-to-face visits, and help with financial challenges.”
The American College of Rheumatology supported the guidance-development process. Dr. Mikuls, Dr. Weinblatt, Dr. Cohen, and Dr. Costenbader each disclosed research support or consultancies with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Gravallese had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mikuls TR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1002/art.41301.
When COVID-19 is suspected or confirmed in a patient with a rheumatic disease, treatment with hydroxychloroquine may be continued, but other treatments may need to be stopped or held temporarily, according to new guidance issued by the American College of Rheumatology.
That includes disease-modifying treatment with antirheumatic drugs such as sulfasalazine, methotrexate, leflunomide, and the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as immunosuppressants and non-interleukin (IL)-6 biologics, and this is regardless of how severe the COVID-19 illness is. NSAIDs should also be stopped if there are respiratory symptoms.
The advice is slightly less drastic if someone with stable rheumatic disease has probably been exposed to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or are asymptomatic. In those patients, DMARDs may be continued, although there is uncertainty over whether there is a need to temporarily stop methotrexate or leflunomide. Interruption of immunosuppressive, non–IL-6, and JAK inhibitor treatment is advised pending a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result, assuming the patient’s rheumatic disease is stable.
Impetus for ACR COVID-19 guidance
“One of the earliest challenges for rheumatologists during the COVID-19 pandemic was determining how to advise our patients who were taking immunosuppressive medications and were concerned as to whether or not to discontinue their therapy,” ACR President Ellen Gravallese, MD, said in an interview about the ACR Clinical Guidance Document, which is published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“A second challenge was keeping our patients safe from exposure to the virus, while still seeing those patients in person who required office visits,” added Dr. Gravallese, who is chief of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
She continued: “The ACR Clinical Guidance Document was prepared in order to assist rheumatologists with decisions as to how to handle current medications during different phases of a patient’s exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.”
But with very little evidence available on how to manage COVID-19 patients generally, let alone specifically in those with rheumatic diseases, “it became evident that any recommendations made would need to be done in a thoughtful and organized manner, evaluating the evidence that was available and obtaining the advice of experts in infectious disease, epidemiology, and in the use of biologic and nonbiologic agents for rheumatic disease,” she said.
As such, the ACR convened a task force of 10 rheumatologists and 4 infectious disease specialists from North America to look at how best to manage patients with rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our charge was to develop a guidance document for the care of adult rheumatic disease patients in the context of COVID-19 and not per se to provide guidance for the treatment of COVID-19,” explained task force member and the corresponding author for the guidance, Ted R. Mikuls, MD, MSPH, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Dr. Mikuls, who was speaking at a virtual town hall meeting hosted by the ACR on May 6, noted that the guidance was obviously based on the best consensus of the available data and as such represented a “living document” that “would change and be added to” as necessary.
General recommendations for adult rheumatic disease management
In terms of general recommendations for the management of adult rheumatic disease patients, Dr. Mikuls said that six statements had been made “specific to risk assessment, prevention of infection, and best practices related to glucocorticoid use and the use of ACE [angiotensin-converting enzyme] inhibitors and ARBs [angiotensin II receptor blockers] during the pandemic.”
For example, general advice is to counsel patients to keep up general preventive measures such as social distancing and regular hand washing, reducing the number of in-person health care visits, and undertaking other means to try to prevent potential SARS-CoV-2 exposure. As for general treatment advice, glucocorticoids should be used at their lowest doses possible and should not be abruptly stopped, and antihypertensive treatment should be used as indicated.
Additional guidance statements include those that address the treatment of patients with stable rheumatic disease in the absence of infection or known exposure to SARS-CoV-2, with guidance specific to the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and those with newly diagnosed or active rheumatic disease.
SLE and inflammatory arthritis recommendations
“There are several sections within the guidance document that address the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during this pandemic,” Dr. Gravallese pointed out. “In general, it is recommended that lupus patients who are currently taking hydroxychloroquine can remain on the therapy prior to and during infection and that newly diagnosed patients with lupus can be placed on this medication at full dose. It is recommended that pregnant patients with lupus remain on therapy with this drug.”
She also observed that, for the treatment of active inflammatory arthritis, “the recommendations were written to address specific medications that could be used in this setting. In general, the task force recommendations were guided by the importance of controlling inflammation prior to exposure to the virus, even during this pandemic.
Guidance raises questions
During the ACR’s town hall meeting, the task force answered several questions raised by the guidance, such as the reasoning behind recommending that the use of traditional DMARDs be discontinued in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Dr. Mikuls observed: “Maybe if you just read the guidance statements it isn’t terribly intuitive.” There was a lot of discussion about whether or not conventional DMARDs were immunosuppressive, and even though they may not have such effects, it was decided to err on the side of caution.
“I think the task force felt that, with a COVID-19–positive patient, there is a concern of potentially confusing adverse effects related to medicines or conflate those with problems from the infection,” he said. Although rare, examples of those issues could be drug-induced hypersensitivity, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, or gastrointestinal side effects of hepatitis, all of which have been described in COVID-19. “Not only could it cause confusion, but it could maybe worsen those sequalae of COVID-19,” he said.
“I think the other part of this answer was that the panel really felt that the risk in terms of the flaring of the underlying rheumatic disease was likely to be pretty low given the finite time frame you’d be taking about – usually a time frame of 2-3 weeks you’d be holding the agent – so I think that is really why the task force ended up with that recommendation.”
Similarly, for the JAK inhibitors, the decision was to err on the side of caution when COVID-19 was suspected or confirmed. “Not so much because of the risk of thromboembolic disease, but concerns over immunosuppression that these drugs carry with them and also the fact the JAK inhibitors are probably inhibitors of type 1 interferons, which play a significant role in viral immunity and could potentially have a negative impact,” said Stanley Cohen, MD, who practices rheumatology in the Dallas area.
“On the flipside, there is interest in some of the JAK inhibitors as a potential treatment for COVID-19,” Dr. Cohen said, referring to anecdotal evidence for baricitinib (Olumiant).
Michael Weinblatt, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, addressed the recent concern over the use of NSAIDs by the public.
“There’s been a lot in the lay press that NSAIDs – because of the effects on receptors in the lung – could lead to deleterious outcomes in patients with COVID and there’s very little data to support this.
“We did recommend that NSAIDs be held in the hospitalized patient and that wasn’t because of the COVID-19 issue, it really was just medical practice, and we didn’t want to confound the care of these really sick patients with potential toxicities from NSAIDs. But as far as routine rheumatological care in your outpatients, we did not recommend that nonsteroidals be stopped if they were tolerated.”
One part of the guidance that might already need revision is the recommendation on the continued use of hydroxychloroquine in patients who develop COVID-19.
“Our guidance document says it’s OK; we were all in very strong agreement to continue hydroxychloroquine in our patients with COVID-19 because at that point, just a couple of weeks ago, we thought it was part of the potential treatment,” Karen Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said during the town hall meeting.
“Now the pendulum has swung the other way, and we’re worried about maybe we shouldn’t be continuing it because COVID-19 patients will be getting many other medications,” Dr. Costenbader said, and these may affect the QT-interval. “They will not be getting azithromycin because the pendulum swung the other way on that one too, but definitely on many other medications when they are sick.”
Potentially, she added, “if the rheumatic disease is under good control the inpatient physicians could decide whether they should continue [hydroxychloroquine] or not. If the COVID-19 is a mild disease, I would say we probably could continue in accordance with what we put in the document, but we will have to revisit this as well.”
Guidance is a ‘living document’
“We will be providing updates to the Clinical Guidance Document as the need arises,” Dr. Gravallese emphasized. While the general recommendations are unlikely to change very much, “the task force will be interested in seeing the results of all new data, but the results of randomized, clinical trials will be particularly important as they become available,” she said. In particular, randomized, controlled trials of glucocorticoids and IL-6 receptor blockade for use in COVID-19 will be of great importance.
“In this initial document, we could not take on all of the medical scenarios our members will face. For example, we could not take on recommendations for the pediatric population as this group of patients has a very different response than adults to the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Dr. Gravallese acknowledged. The plan is to provide guidance for that group of patients soon.
In addition, the ACR Executive Committee has appointed a Practice and Advocacy Task Force that will “address issues rheumatologists face on the practice side, including advice regarding how to effectively use telemedicine, address the frequency and safety of infusions, determine urgent versus nonurgent issues that would or would not require face-to-face visits, and help with financial challenges.”
The American College of Rheumatology supported the guidance-development process. Dr. Mikuls, Dr. Weinblatt, Dr. Cohen, and Dr. Costenbader each disclosed research support or consultancies with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Gravallese had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mikuls TR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1002/art.41301.
When COVID-19 is suspected or confirmed in a patient with a rheumatic disease, treatment with hydroxychloroquine may be continued, but other treatments may need to be stopped or held temporarily, according to new guidance issued by the American College of Rheumatology.
That includes disease-modifying treatment with antirheumatic drugs such as sulfasalazine, methotrexate, leflunomide, and the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as immunosuppressants and non-interleukin (IL)-6 biologics, and this is regardless of how severe the COVID-19 illness is. NSAIDs should also be stopped if there are respiratory symptoms.
The advice is slightly less drastic if someone with stable rheumatic disease has probably been exposed to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or are asymptomatic. In those patients, DMARDs may be continued, although there is uncertainty over whether there is a need to temporarily stop methotrexate or leflunomide. Interruption of immunosuppressive, non–IL-6, and JAK inhibitor treatment is advised pending a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result, assuming the patient’s rheumatic disease is stable.
Impetus for ACR COVID-19 guidance
“One of the earliest challenges for rheumatologists during the COVID-19 pandemic was determining how to advise our patients who were taking immunosuppressive medications and were concerned as to whether or not to discontinue their therapy,” ACR President Ellen Gravallese, MD, said in an interview about the ACR Clinical Guidance Document, which is published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“A second challenge was keeping our patients safe from exposure to the virus, while still seeing those patients in person who required office visits,” added Dr. Gravallese, who is chief of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
She continued: “The ACR Clinical Guidance Document was prepared in order to assist rheumatologists with decisions as to how to handle current medications during different phases of a patient’s exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.”
But with very little evidence available on how to manage COVID-19 patients generally, let alone specifically in those with rheumatic diseases, “it became evident that any recommendations made would need to be done in a thoughtful and organized manner, evaluating the evidence that was available and obtaining the advice of experts in infectious disease, epidemiology, and in the use of biologic and nonbiologic agents for rheumatic disease,” she said.
As such, the ACR convened a task force of 10 rheumatologists and 4 infectious disease specialists from North America to look at how best to manage patients with rheumatic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Our charge was to develop a guidance document for the care of adult rheumatic disease patients in the context of COVID-19 and not per se to provide guidance for the treatment of COVID-19,” explained task force member and the corresponding author for the guidance, Ted R. Mikuls, MD, MSPH, of the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Dr. Mikuls, who was speaking at a virtual town hall meeting hosted by the ACR on May 6, noted that the guidance was obviously based on the best consensus of the available data and as such represented a “living document” that “would change and be added to” as necessary.
General recommendations for adult rheumatic disease management
In terms of general recommendations for the management of adult rheumatic disease patients, Dr. Mikuls said that six statements had been made “specific to risk assessment, prevention of infection, and best practices related to glucocorticoid use and the use of ACE [angiotensin-converting enzyme] inhibitors and ARBs [angiotensin II receptor blockers] during the pandemic.”
For example, general advice is to counsel patients to keep up general preventive measures such as social distancing and regular hand washing, reducing the number of in-person health care visits, and undertaking other means to try to prevent potential SARS-CoV-2 exposure. As for general treatment advice, glucocorticoids should be used at their lowest doses possible and should not be abruptly stopped, and antihypertensive treatment should be used as indicated.
Additional guidance statements include those that address the treatment of patients with stable rheumatic disease in the absence of infection or known exposure to SARS-CoV-2, with guidance specific to the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and those with newly diagnosed or active rheumatic disease.
SLE and inflammatory arthritis recommendations
“There are several sections within the guidance document that address the treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during this pandemic,” Dr. Gravallese pointed out. “In general, it is recommended that lupus patients who are currently taking hydroxychloroquine can remain on the therapy prior to and during infection and that newly diagnosed patients with lupus can be placed on this medication at full dose. It is recommended that pregnant patients with lupus remain on therapy with this drug.”
She also observed that, for the treatment of active inflammatory arthritis, “the recommendations were written to address specific medications that could be used in this setting. In general, the task force recommendations were guided by the importance of controlling inflammation prior to exposure to the virus, even during this pandemic.
Guidance raises questions
During the ACR’s town hall meeting, the task force answered several questions raised by the guidance, such as the reasoning behind recommending that the use of traditional DMARDs be discontinued in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Dr. Mikuls observed: “Maybe if you just read the guidance statements it isn’t terribly intuitive.” There was a lot of discussion about whether or not conventional DMARDs were immunosuppressive, and even though they may not have such effects, it was decided to err on the side of caution.
“I think the task force felt that, with a COVID-19–positive patient, there is a concern of potentially confusing adverse effects related to medicines or conflate those with problems from the infection,” he said. Although rare, examples of those issues could be drug-induced hypersensitivity, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, or gastrointestinal side effects of hepatitis, all of which have been described in COVID-19. “Not only could it cause confusion, but it could maybe worsen those sequalae of COVID-19,” he said.
“I think the other part of this answer was that the panel really felt that the risk in terms of the flaring of the underlying rheumatic disease was likely to be pretty low given the finite time frame you’d be taking about – usually a time frame of 2-3 weeks you’d be holding the agent – so I think that is really why the task force ended up with that recommendation.”
Similarly, for the JAK inhibitors, the decision was to err on the side of caution when COVID-19 was suspected or confirmed. “Not so much because of the risk of thromboembolic disease, but concerns over immunosuppression that these drugs carry with them and also the fact the JAK inhibitors are probably inhibitors of type 1 interferons, which play a significant role in viral immunity and could potentially have a negative impact,” said Stanley Cohen, MD, who practices rheumatology in the Dallas area.
“On the flipside, there is interest in some of the JAK inhibitors as a potential treatment for COVID-19,” Dr. Cohen said, referring to anecdotal evidence for baricitinib (Olumiant).
Michael Weinblatt, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, addressed the recent concern over the use of NSAIDs by the public.
“There’s been a lot in the lay press that NSAIDs – because of the effects on receptors in the lung – could lead to deleterious outcomes in patients with COVID and there’s very little data to support this.
“We did recommend that NSAIDs be held in the hospitalized patient and that wasn’t because of the COVID-19 issue, it really was just medical practice, and we didn’t want to confound the care of these really sick patients with potential toxicities from NSAIDs. But as far as routine rheumatological care in your outpatients, we did not recommend that nonsteroidals be stopped if they were tolerated.”
One part of the guidance that might already need revision is the recommendation on the continued use of hydroxychloroquine in patients who develop COVID-19.
“Our guidance document says it’s OK; we were all in very strong agreement to continue hydroxychloroquine in our patients with COVID-19 because at that point, just a couple of weeks ago, we thought it was part of the potential treatment,” Karen Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said during the town hall meeting.
“Now the pendulum has swung the other way, and we’re worried about maybe we shouldn’t be continuing it because COVID-19 patients will be getting many other medications,” Dr. Costenbader said, and these may affect the QT-interval. “They will not be getting azithromycin because the pendulum swung the other way on that one too, but definitely on many other medications when they are sick.”
Potentially, she added, “if the rheumatic disease is under good control the inpatient physicians could decide whether they should continue [hydroxychloroquine] or not. If the COVID-19 is a mild disease, I would say we probably could continue in accordance with what we put in the document, but we will have to revisit this as well.”
Guidance is a ‘living document’
“We will be providing updates to the Clinical Guidance Document as the need arises,” Dr. Gravallese emphasized. While the general recommendations are unlikely to change very much, “the task force will be interested in seeing the results of all new data, but the results of randomized, clinical trials will be particularly important as they become available,” she said. In particular, randomized, controlled trials of glucocorticoids and IL-6 receptor blockade for use in COVID-19 will be of great importance.
“In this initial document, we could not take on all of the medical scenarios our members will face. For example, we could not take on recommendations for the pediatric population as this group of patients has a very different response than adults to the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Dr. Gravallese acknowledged. The plan is to provide guidance for that group of patients soon.
In addition, the ACR Executive Committee has appointed a Practice and Advocacy Task Force that will “address issues rheumatologists face on the practice side, including advice regarding how to effectively use telemedicine, address the frequency and safety of infusions, determine urgent versus nonurgent issues that would or would not require face-to-face visits, and help with financial challenges.”
The American College of Rheumatology supported the guidance-development process. Dr. Mikuls, Dr. Weinblatt, Dr. Cohen, and Dr. Costenbader each disclosed research support or consultancies with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Gravallese had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Mikuls TR et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1002/art.41301.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Case series suggests biologics, JAK inhibitors safe during pandemic
Use of biologics and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors was not associated with worse outcomes in 86 people with inflammatory diseases who contracted COVID-19, according to a case series from New York University Langone Health.
“We are not seeing worse outcomes with overall use of either. It’s reassuring” that the data support continued use during the pandemic, said rheumatologist and senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, an associate professor at New York University.
There have been concerns among rheumatologists, gastroenterologists, and dermatologists that underlying inflammatory diseases and the agents used to treat them would impact outcomes in COVID-19.
Dr. Scher and colleagues, including lead author and rheumatologist Rebecca Haberman, MD, wanted to address the issue, so they reviewed the experience in their own health system of patients with inflammatory diseases – most commonly psoriatic arthritis, RA, and Crohn’s disease – who were assessed for COVID-19 from March 3 to April 3.
Fever, cough, and shortness of breath were the most common symptoms. The infection was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction in 59 (69%) and highly suspected in 27.
A total of 62 patients (72%) were on JAK inhibitors or biologics at baseline, including 38 (44%) on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Overall, 14 patients (16%) were hospitalized with COVID-19, which is consistent the 26% hospitalization rate among the general population in New York City.
Baseline biologic and JAK inhibitor use was actually lower among hospitalized patients than among those who weren’t hospitalized (50% vs. 76%), and the hospitalization rate was only 11% among 62 subjects who had been on the agents long term, more than a year among most.
Hospitalized patients tended to be slightly older (mean, 50 vs. 46 years) with a higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. They also had a higher prevalence of RA (43% vs. 19%), methotrexate use (43% vs. 15%), and use of hydroxychloroquine (21% vs. 7%) and oral glucocorticoids (29% vs. 6%).
It’s unknown what to make of those findings for now, Dr. Scher said. The study didn’t address differences in the severity of the underlying inflammatory illness, but a new and significantly larger case series is in the works that will analyze that and other potential confounders.
Dr. Scher noted that he’s particularly interested in drilling down further on the higher prevalence of RA and methotrexate in hospitalized patients. “We want to understand those signals better. All of this needs further validation,” he said.
Of the 14 hospitalized patients, 11 (79%) were discharged after a mean of 5.6 days. One died in the ED, and two remained hospitalized as of April 3, including one in the ICU.
The investigators are contributing to COVID-19 registries for inflammatory disease patients. The registries are tending to report higher hospitalization rates, but Dr. Scher noted they might be biased towards more severe cases, among other issues.
As for the current situation in New York City, he said that the “last week in March and first 3 in April were indescribable in terms of admissions, intubations, and deaths. Over the last week or so, it has calmed down significantly.”
There was no external funding. Dr. Haberman reported ties to Janssen, and Dr. Scher reported ties to Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and other companies.
SOURCE: Haberman R et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009567.
Use of biologics and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors was not associated with worse outcomes in 86 people with inflammatory diseases who contracted COVID-19, according to a case series from New York University Langone Health.
“We are not seeing worse outcomes with overall use of either. It’s reassuring” that the data support continued use during the pandemic, said rheumatologist and senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, an associate professor at New York University.
There have been concerns among rheumatologists, gastroenterologists, and dermatologists that underlying inflammatory diseases and the agents used to treat them would impact outcomes in COVID-19.
Dr. Scher and colleagues, including lead author and rheumatologist Rebecca Haberman, MD, wanted to address the issue, so they reviewed the experience in their own health system of patients with inflammatory diseases – most commonly psoriatic arthritis, RA, and Crohn’s disease – who were assessed for COVID-19 from March 3 to April 3.
Fever, cough, and shortness of breath were the most common symptoms. The infection was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction in 59 (69%) and highly suspected in 27.
A total of 62 patients (72%) were on JAK inhibitors or biologics at baseline, including 38 (44%) on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Overall, 14 patients (16%) were hospitalized with COVID-19, which is consistent the 26% hospitalization rate among the general population in New York City.
Baseline biologic and JAK inhibitor use was actually lower among hospitalized patients than among those who weren’t hospitalized (50% vs. 76%), and the hospitalization rate was only 11% among 62 subjects who had been on the agents long term, more than a year among most.
Hospitalized patients tended to be slightly older (mean, 50 vs. 46 years) with a higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. They also had a higher prevalence of RA (43% vs. 19%), methotrexate use (43% vs. 15%), and use of hydroxychloroquine (21% vs. 7%) and oral glucocorticoids (29% vs. 6%).
It’s unknown what to make of those findings for now, Dr. Scher said. The study didn’t address differences in the severity of the underlying inflammatory illness, but a new and significantly larger case series is in the works that will analyze that and other potential confounders.
Dr. Scher noted that he’s particularly interested in drilling down further on the higher prevalence of RA and methotrexate in hospitalized patients. “We want to understand those signals better. All of this needs further validation,” he said.
Of the 14 hospitalized patients, 11 (79%) were discharged after a mean of 5.6 days. One died in the ED, and two remained hospitalized as of April 3, including one in the ICU.
The investigators are contributing to COVID-19 registries for inflammatory disease patients. The registries are tending to report higher hospitalization rates, but Dr. Scher noted they might be biased towards more severe cases, among other issues.
As for the current situation in New York City, he said that the “last week in March and first 3 in April were indescribable in terms of admissions, intubations, and deaths. Over the last week or so, it has calmed down significantly.”
There was no external funding. Dr. Haberman reported ties to Janssen, and Dr. Scher reported ties to Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and other companies.
SOURCE: Haberman R et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009567.
Use of biologics and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors was not associated with worse outcomes in 86 people with inflammatory diseases who contracted COVID-19, according to a case series from New York University Langone Health.
“We are not seeing worse outcomes with overall use of either. It’s reassuring” that the data support continued use during the pandemic, said rheumatologist and senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, an associate professor at New York University.
There have been concerns among rheumatologists, gastroenterologists, and dermatologists that underlying inflammatory diseases and the agents used to treat them would impact outcomes in COVID-19.
Dr. Scher and colleagues, including lead author and rheumatologist Rebecca Haberman, MD, wanted to address the issue, so they reviewed the experience in their own health system of patients with inflammatory diseases – most commonly psoriatic arthritis, RA, and Crohn’s disease – who were assessed for COVID-19 from March 3 to April 3.
Fever, cough, and shortness of breath were the most common symptoms. The infection was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction in 59 (69%) and highly suspected in 27.
A total of 62 patients (72%) were on JAK inhibitors or biologics at baseline, including 38 (44%) on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Overall, 14 patients (16%) were hospitalized with COVID-19, which is consistent the 26% hospitalization rate among the general population in New York City.
Baseline biologic and JAK inhibitor use was actually lower among hospitalized patients than among those who weren’t hospitalized (50% vs. 76%), and the hospitalization rate was only 11% among 62 subjects who had been on the agents long term, more than a year among most.
Hospitalized patients tended to be slightly older (mean, 50 vs. 46 years) with a higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. They also had a higher prevalence of RA (43% vs. 19%), methotrexate use (43% vs. 15%), and use of hydroxychloroquine (21% vs. 7%) and oral glucocorticoids (29% vs. 6%).
It’s unknown what to make of those findings for now, Dr. Scher said. The study didn’t address differences in the severity of the underlying inflammatory illness, but a new and significantly larger case series is in the works that will analyze that and other potential confounders.
Dr. Scher noted that he’s particularly interested in drilling down further on the higher prevalence of RA and methotrexate in hospitalized patients. “We want to understand those signals better. All of this needs further validation,” he said.
Of the 14 hospitalized patients, 11 (79%) were discharged after a mean of 5.6 days. One died in the ED, and two remained hospitalized as of April 3, including one in the ICU.
The investigators are contributing to COVID-19 registries for inflammatory disease patients. The registries are tending to report higher hospitalization rates, but Dr. Scher noted they might be biased towards more severe cases, among other issues.
As for the current situation in New York City, he said that the “last week in March and first 3 in April were indescribable in terms of admissions, intubations, and deaths. Over the last week or so, it has calmed down significantly.”
There was no external funding. Dr. Haberman reported ties to Janssen, and Dr. Scher reported ties to Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and other companies.
SOURCE: Haberman R et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009567.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Sacroiliac bone marrow edema on MRI may be common postpartum
A “strikingly high number” of women have bone marrow edema on MRI of the sacroiliac joints postpartum, according to a prospective study of 35 patients published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. Postpartum sacroiliac bone marrow edema decreases over time. Its occurrence may be associated with a shorter duration of labor and a lack of epidural anesthesia, the researchers wrote.
Sacroiliac bone marrow edema in postpartum women “persists mainly in subjects older than 30 years,” noted Thomas Renson, MD, of Ghent (Belgium) University Hospital and colleagues. “When suspecting AxSpA [axial spondyloarthritis], our data indicate the need to wait at least 6 months to perform an MRI [of the sacroiliac joints] in postpartum women and, if positive, repeat the MRI after 12 months.”
Sacroiliac bone marrow edema is a hallmark of axSpA. However, recent studies of young, active people without the disease have found a high prevalence of bone marrow edema meeting the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis. Researchers have reported sacroiliac bone marrow edema in women during pregnancy and after childbirth, but prior studies have not assessed the trajectory of sacroiliac bone marrow edema after delivery, Dr. Renson and his colleagues said.
To study this question, the researchers recruited 35 subjects from the department of obstetrics at Ghent University Hospital. All participants were aged 18-45 years and had an uncomplicated, vaginal childbirth. The investigators excluded patients with a diagnosis of spondyloarthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, severe scoliosis, treatment with anti–tumor necrosis factor-alpha agents, any contraindication for MRI, childbirth through cesarean section, or pregnancy with more than one fetus.
Researchers performed a baseline MRI within 10 days of when patients gave birth and another MRI after 6 months. If the second MRI fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis, another MRI was performed at 12 months. Bone marrow edema was scored using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) method.
In all, 77% of the patients had sacroiliac bone marrow edema on MRI an average of 5 days postpartum, and 60% fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI. After 6 months, 46% had bone marrow edema on MRI, and 15% had a positive MRI according to the ASAS definition. After 12 months, MRI was positive in 12% of the subjects. There was a high prevalence of bone marrow edema “even in subjects without back pain,” the researchers said.
“Four subjects would have fulfilled the ASAS classification criteria if there was a suspicion of axSpA: Three fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis and had inflammatory back pain, [and] one had chronic back pain, a positive MRI, and skin psoriasis,” the researchers wrote.
Misdiagnosis of axSpA based on MRI findings entails risks, the authors noted. NSAIDs may be less effective in patients who do not have axSpA, and patients may be “subsequently more likely to receive ineffective biological therapy, which has significant potential side effects and encompasses high socioeconomic costs,” the investigators said.
The study was supported by an ASAS research grant. The authors declared having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Renson T et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Apr 16. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217095.
A “strikingly high number” of women have bone marrow edema on MRI of the sacroiliac joints postpartum, according to a prospective study of 35 patients published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. Postpartum sacroiliac bone marrow edema decreases over time. Its occurrence may be associated with a shorter duration of labor and a lack of epidural anesthesia, the researchers wrote.
Sacroiliac bone marrow edema in postpartum women “persists mainly in subjects older than 30 years,” noted Thomas Renson, MD, of Ghent (Belgium) University Hospital and colleagues. “When suspecting AxSpA [axial spondyloarthritis], our data indicate the need to wait at least 6 months to perform an MRI [of the sacroiliac joints] in postpartum women and, if positive, repeat the MRI after 12 months.”
Sacroiliac bone marrow edema is a hallmark of axSpA. However, recent studies of young, active people without the disease have found a high prevalence of bone marrow edema meeting the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis. Researchers have reported sacroiliac bone marrow edema in women during pregnancy and after childbirth, but prior studies have not assessed the trajectory of sacroiliac bone marrow edema after delivery, Dr. Renson and his colleagues said.
To study this question, the researchers recruited 35 subjects from the department of obstetrics at Ghent University Hospital. All participants were aged 18-45 years and had an uncomplicated, vaginal childbirth. The investigators excluded patients with a diagnosis of spondyloarthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, severe scoliosis, treatment with anti–tumor necrosis factor-alpha agents, any contraindication for MRI, childbirth through cesarean section, or pregnancy with more than one fetus.
Researchers performed a baseline MRI within 10 days of when patients gave birth and another MRI after 6 months. If the second MRI fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis, another MRI was performed at 12 months. Bone marrow edema was scored using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) method.
In all, 77% of the patients had sacroiliac bone marrow edema on MRI an average of 5 days postpartum, and 60% fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI. After 6 months, 46% had bone marrow edema on MRI, and 15% had a positive MRI according to the ASAS definition. After 12 months, MRI was positive in 12% of the subjects. There was a high prevalence of bone marrow edema “even in subjects without back pain,” the researchers said.
“Four subjects would have fulfilled the ASAS classification criteria if there was a suspicion of axSpA: Three fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis and had inflammatory back pain, [and] one had chronic back pain, a positive MRI, and skin psoriasis,” the researchers wrote.
Misdiagnosis of axSpA based on MRI findings entails risks, the authors noted. NSAIDs may be less effective in patients who do not have axSpA, and patients may be “subsequently more likely to receive ineffective biological therapy, which has significant potential side effects and encompasses high socioeconomic costs,” the investigators said.
The study was supported by an ASAS research grant. The authors declared having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Renson T et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Apr 16. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217095.
A “strikingly high number” of women have bone marrow edema on MRI of the sacroiliac joints postpartum, according to a prospective study of 35 patients published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. Postpartum sacroiliac bone marrow edema decreases over time. Its occurrence may be associated with a shorter duration of labor and a lack of epidural anesthesia, the researchers wrote.
Sacroiliac bone marrow edema in postpartum women “persists mainly in subjects older than 30 years,” noted Thomas Renson, MD, of Ghent (Belgium) University Hospital and colleagues. “When suspecting AxSpA [axial spondyloarthritis], our data indicate the need to wait at least 6 months to perform an MRI [of the sacroiliac joints] in postpartum women and, if positive, repeat the MRI after 12 months.”
Sacroiliac bone marrow edema is a hallmark of axSpA. However, recent studies of young, active people without the disease have found a high prevalence of bone marrow edema meeting the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis. Researchers have reported sacroiliac bone marrow edema in women during pregnancy and after childbirth, but prior studies have not assessed the trajectory of sacroiliac bone marrow edema after delivery, Dr. Renson and his colleagues said.
To study this question, the researchers recruited 35 subjects from the department of obstetrics at Ghent University Hospital. All participants were aged 18-45 years and had an uncomplicated, vaginal childbirth. The investigators excluded patients with a diagnosis of spondyloarthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, severe scoliosis, treatment with anti–tumor necrosis factor-alpha agents, any contraindication for MRI, childbirth through cesarean section, or pregnancy with more than one fetus.
Researchers performed a baseline MRI within 10 days of when patients gave birth and another MRI after 6 months. If the second MRI fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis, another MRI was performed at 12 months. Bone marrow edema was scored using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) method.
In all, 77% of the patients had sacroiliac bone marrow edema on MRI an average of 5 days postpartum, and 60% fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI. After 6 months, 46% had bone marrow edema on MRI, and 15% had a positive MRI according to the ASAS definition. After 12 months, MRI was positive in 12% of the subjects. There was a high prevalence of bone marrow edema “even in subjects without back pain,” the researchers said.
“Four subjects would have fulfilled the ASAS classification criteria if there was a suspicion of axSpA: Three fulfilled the ASAS definition of a positive MRI for sacroiliitis and had inflammatory back pain, [and] one had chronic back pain, a positive MRI, and skin psoriasis,” the researchers wrote.
Misdiagnosis of axSpA based on MRI findings entails risks, the authors noted. NSAIDs may be less effective in patients who do not have axSpA, and patients may be “subsequently more likely to receive ineffective biological therapy, which has significant potential side effects and encompasses high socioeconomic costs,” the investigators said.
The study was supported by an ASAS research grant. The authors declared having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Renson T et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Apr 16. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217095.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES