User login
Food as Medicine: Diet’s Role in Parkinson’s Disease
For 15 years, John Duda, MD, national director of the VA Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education and Clinical Centers, has urged his patients to “keep waiting” for effective treatments to manage both motor and nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
However, Duda, who also serves as director of the Brain Wellness Clinic at the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, recognized the persistent lack of effective drugs to address these symptoms. This prompted him to consider what other evidence-based strategies he could use to support his patients.
“I recognized that nutritional approaches within a broader program that includes medication review, stress management, social connections, adequate sleep, and physical exercise could make a real difference,” he said.
Observational studies have shown an inverse association between dietary patterns and Parkinson’s disease risk, age of onset, symptom severity, and mortality rates — particularly with the Mediterranean diet (MeDi) and the MIND diet, which combines elements of MeDi and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. Although randomized controlled trials are still limited, the epidemiologic evidence supporting dietary interventions is “compelling,” said Duda.
For example, a cross-sectional study comparing 167 participants with Parkinson’s disease vs 119 controls showed that later age of Parkinson’s disease onset correlated with adherence to the MIND diet in women, with a difference of up to 17.4 years (P < .001) between low and high dietary tertiles.
The MeDi was correlated with later onset in men, with differences of up to 8.4 years (P = .002). As previously reported, a healthy diet emphasizing vegetables, fruits, nuts, and grains was inversely associated with prodromal features of Parkinson’s disease, including constipation, excessive daytime sleepiness, and depression. In addition, lower rates of Parkinson’s disease have been shown in populations following vegetarian and vegan dietary patterns.
Does Parkinson’s disease Start in the Gut?
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by decreased short-chain fatty acid–producing bacteria and increased pro-inflammatory species linked to intestinal inflammation and alpha-synuclein aggregation. “There are reasons to believe that a-synuclein accumulation may start in the gut,” Duda noted.
Numerous studies implicate gut microbiome dysbiosis as a pathogenic mechanism in Parkinson’s disease, with gastrointestinal symptoms often predating motor symptoms. Dysbiosis might result in a pro-inflammatory state potentially linked to the recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms. Fecal microbiota transplant may restore a healthier gut environment and beneficially affect Parkinson’s disease symptoms, he said.
Some of the benefits conferred by the MeDi and other healthy diets may be mediated by improving the gut microbiome. Duda cited a study that showed that a 14-day ovo-lacto vegetarian diet intervention and a daily fecal enema for 8 days improved not only the microbiome but also Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale—part III scores.
Duda also reviewed the role of dietary interventions in addressing common Parkinson’s disease symptoms, such as orthostatic hypotension. He recommended that Parkinson’s disease patients with this condition should avoid eating large meals, increase dietary salt intake, increase fluid intake, and decrease alcohol intake.
Malnutrition affects close to 25% of those with Parkinson’s disease, which is partially attributable to diminished olfaction. Because the experience of taste is largely driven by a sense of smell, patients may be less interested in eating. Duda recommended increasing herbs, spices, and other flavors in food. High caloric–density foods, including nuts, nut butters, and seeds, can boost weight, he said. However, he added, any patient with significant weight loss should consult a nutritionist.
Constipation is one of the most debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, affecting up to 66% of patients. Duda advised increasing fluid intake, exercise, and dietary fiber and use of stool softeners and laxatives. The MeDi may reduce symptoms of constipation and have a beneficial effect on gut microbiota.
Coffee may be helpful for sleepiness in Parkinson’s disease and may also confer neuroprotective, motor, and cognitive benefits. As an adjuvant treatment, caffeine may alter levodopa pharmacokinetics, reduce dyskinesia, improve gait in patients with freezing and may even reduce the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, with a maximum benefit reached at approximately three cups of coffee daily.
Problematic Foods
There is also a growing body of evidence regarding the deleterious effects of ultraprocessed foods (UPFs), Duda said. He noted that a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of 28 studies showed that higher UPF intake was significantly associated with an enhanced risk for Parkinson’s disease (relative risk, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.21-2.02). As previously reported, UPFs have been tied to a host of adverse neurologic outcomes, including cognitive decline and stroke.
Although protein is a necessary nutrient, incorporating it into the diet of Parkinson’s disease patients taking levodopa is complicated. Levodopa, a large neutral amino acid (LNAA), competes with other LNAAs for transport to the brain from the small intestine, Duda explained.
“Some people notice that carbidopa-levodopa doesn’t work as well if taken with a high-protein meal.” He recommended taking carbidopa-levodopa 30 minutes before or 60 minutes after meals.
Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief mission officer of the American Parkinson’s Disease Association, said that patients with Parkinson’s disease might want to avoid eating protein during the day, concentrating instead on carbohydrates and vegetables and saving the protein for the evening, which is closer to bedtime. Some evidence also supports the use of protein redistribution diets to enhance the clinical response to levodopa and reduce motor fluctuations.
What About Supplements?
It’s “hard to prove that one specific supplement can be protective against Parkinson’s disease because diet consists of many different components and the whole diet may be worth more than the sum of its parts,” Gilbert said. The evidence for individual supplements “isn’t robust enough to say they prevent or treat Parkinson’s disease.”
Research on the role of specific nutrients in Parkinson’s disease is conflicting, with no clear evidence supporting or refuting their benefits. For example, a study that followed participants for about 30 years showed no link between reduced Parkinson’s disease risk and vitamin B or folate intake.
On the other hand, there is research suggesting that certain vitamins may help reduce Parkinson’s disease risk, although these nutrients do not operate in isolation. For instance, one recent study showed a connection between vitamins C and E and reduced Parkinson’s disease risk, but factors such as body mass index and coffee consumption appeared to influence the strength of this association.
Consuming polyunsaturated fatty acids along with reducing saturated fatty acid intake has been tied to a reduced risk for Parkinson’s disease.
Additionally, certain foods may offer protective effects, including green and black tea, with consumption of three or more cups per day associated with a delay in motor symptom onset by 7.7 years. Foods high in nicotine content, such as those from the Solanaceae family — including peppers, tomatoes, tomato juice, and potatoes — have also been linked to potential protective benefits.
Diets rich in antioxidants, including carotenoids, lutein, and vitamins E and C, have been robustly linked to a reduced risk for parkinsonism and progression of parkinsonian symptoms in older adults.
Increasing the intake of dietary flavonoids, particularly tea, berry fruits, apples, red wine, and oranges or orange juice, can reduce Parkinson’s disease risk. One study showed that male participants in the highest quintile of total flavonoid consumption had a 40% lower Parkinson’s disease risk compared with those in the lowest quintile. Another study showed that flavonoid-rich foods were also associated with a lower risk for death in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Food as Medicine
Although recent research shows that the drug development pipeline for Parkinson’s disease is robust, with a wide variety of approaches being developed and evaluated in phase 1 and 2, investigators note that only a limited number of disease-modifying treatments are transitioning to phase 3.
Duda noted that phytochemicals incorporated into the diet might target some of the same mechanisms that are targets of these drugs in development.
“Flavonoids have been shown to stabilize alpha-synuclein in vitro,” he said. “Caffeine, curcumin, resveratrol, and eliminating meat and dairy inhibit mTOR [mammalian target of rapamycin], and mTOR inhibition results in increased autophagy that may help clear alpha-synuclein. Genestein, an isoflavone in soybeans, protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting microglia activation. Flavonoids inhibit inflammation by inhibiting release of NO [nitric oxide] and pro-inflammatory cytokines,” he noted.
Ongoing studies of dietary interventions for Parkinson’s disease are exploring various areas, including the potential role of the ketogenic diet in protecting the gut microbiome, optimizing protein intake for muscle preservation and sleep, the effects of psyllium and wheat bran on weight and constipation, and the impact of a gluten-free diet.
Practical Tips for Healthy Eating
Gilbert emphasized that there are no medications or interventions currently available that can delay a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis by up to 17 years, as some dietary patterns have been shown to do, and she noted that it’s not possible to replicate the MeDi diet in a pill. However, she recommended a practical approach to eating that includes a diet low in ultraprocessed foods and high in beneficial nutrients. She encouraged people to shop for “real food” and enjoy a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
Duda acknowledged that motivating patients to follow a healthy diet can be difficult. As a result, the focus often shifts to making small adjustments and modifications. For example, he suggested that instead of pairing meat with French fries, people could opt for vegetables or add greens to their meals. Similarly, instead of having eggs and bacon for breakfast, they might choose oatmeal.
Preparing whole-food, plant-based meals may take more time than patients are accustomed to, so Duda suggests that, if possible, patients involve loved ones in both the meal preparation and the meal itself. He explained that a healthy meal can become an opportunity for bonding and that the key is educating them about new meal-related concepts.
Duda reported no relevant financial relationships with the pharmaceutical or food industries. He has received compensation from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine for his lecture delivered at the conference and research grant support from the VA, the National Institutes of Health, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and the Department of Defense unrelated to this topic. Gilbert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For 15 years, John Duda, MD, national director of the VA Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education and Clinical Centers, has urged his patients to “keep waiting” for effective treatments to manage both motor and nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
However, Duda, who also serves as director of the Brain Wellness Clinic at the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, recognized the persistent lack of effective drugs to address these symptoms. This prompted him to consider what other evidence-based strategies he could use to support his patients.
“I recognized that nutritional approaches within a broader program that includes medication review, stress management, social connections, adequate sleep, and physical exercise could make a real difference,” he said.
Observational studies have shown an inverse association between dietary patterns and Parkinson’s disease risk, age of onset, symptom severity, and mortality rates — particularly with the Mediterranean diet (MeDi) and the MIND diet, which combines elements of MeDi and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. Although randomized controlled trials are still limited, the epidemiologic evidence supporting dietary interventions is “compelling,” said Duda.
For example, a cross-sectional study comparing 167 participants with Parkinson’s disease vs 119 controls showed that later age of Parkinson’s disease onset correlated with adherence to the MIND diet in women, with a difference of up to 17.4 years (P < .001) between low and high dietary tertiles.
The MeDi was correlated with later onset in men, with differences of up to 8.4 years (P = .002). As previously reported, a healthy diet emphasizing vegetables, fruits, nuts, and grains was inversely associated with prodromal features of Parkinson’s disease, including constipation, excessive daytime sleepiness, and depression. In addition, lower rates of Parkinson’s disease have been shown in populations following vegetarian and vegan dietary patterns.
Does Parkinson’s disease Start in the Gut?
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by decreased short-chain fatty acid–producing bacteria and increased pro-inflammatory species linked to intestinal inflammation and alpha-synuclein aggregation. “There are reasons to believe that a-synuclein accumulation may start in the gut,” Duda noted.
Numerous studies implicate gut microbiome dysbiosis as a pathogenic mechanism in Parkinson’s disease, with gastrointestinal symptoms often predating motor symptoms. Dysbiosis might result in a pro-inflammatory state potentially linked to the recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms. Fecal microbiota transplant may restore a healthier gut environment and beneficially affect Parkinson’s disease symptoms, he said.
Some of the benefits conferred by the MeDi and other healthy diets may be mediated by improving the gut microbiome. Duda cited a study that showed that a 14-day ovo-lacto vegetarian diet intervention and a daily fecal enema for 8 days improved not only the microbiome but also Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale—part III scores.
Duda also reviewed the role of dietary interventions in addressing common Parkinson’s disease symptoms, such as orthostatic hypotension. He recommended that Parkinson’s disease patients with this condition should avoid eating large meals, increase dietary salt intake, increase fluid intake, and decrease alcohol intake.
Malnutrition affects close to 25% of those with Parkinson’s disease, which is partially attributable to diminished olfaction. Because the experience of taste is largely driven by a sense of smell, patients may be less interested in eating. Duda recommended increasing herbs, spices, and other flavors in food. High caloric–density foods, including nuts, nut butters, and seeds, can boost weight, he said. However, he added, any patient with significant weight loss should consult a nutritionist.
Constipation is one of the most debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, affecting up to 66% of patients. Duda advised increasing fluid intake, exercise, and dietary fiber and use of stool softeners and laxatives. The MeDi may reduce symptoms of constipation and have a beneficial effect on gut microbiota.
Coffee may be helpful for sleepiness in Parkinson’s disease and may also confer neuroprotective, motor, and cognitive benefits. As an adjuvant treatment, caffeine may alter levodopa pharmacokinetics, reduce dyskinesia, improve gait in patients with freezing and may even reduce the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, with a maximum benefit reached at approximately three cups of coffee daily.
Problematic Foods
There is also a growing body of evidence regarding the deleterious effects of ultraprocessed foods (UPFs), Duda said. He noted that a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of 28 studies showed that higher UPF intake was significantly associated with an enhanced risk for Parkinson’s disease (relative risk, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.21-2.02). As previously reported, UPFs have been tied to a host of adverse neurologic outcomes, including cognitive decline and stroke.
Although protein is a necessary nutrient, incorporating it into the diet of Parkinson’s disease patients taking levodopa is complicated. Levodopa, a large neutral amino acid (LNAA), competes with other LNAAs for transport to the brain from the small intestine, Duda explained.
“Some people notice that carbidopa-levodopa doesn’t work as well if taken with a high-protein meal.” He recommended taking carbidopa-levodopa 30 minutes before or 60 minutes after meals.
Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief mission officer of the American Parkinson’s Disease Association, said that patients with Parkinson’s disease might want to avoid eating protein during the day, concentrating instead on carbohydrates and vegetables and saving the protein for the evening, which is closer to bedtime. Some evidence also supports the use of protein redistribution diets to enhance the clinical response to levodopa and reduce motor fluctuations.
What About Supplements?
It’s “hard to prove that one specific supplement can be protective against Parkinson’s disease because diet consists of many different components and the whole diet may be worth more than the sum of its parts,” Gilbert said. The evidence for individual supplements “isn’t robust enough to say they prevent or treat Parkinson’s disease.”
Research on the role of specific nutrients in Parkinson’s disease is conflicting, with no clear evidence supporting or refuting their benefits. For example, a study that followed participants for about 30 years showed no link between reduced Parkinson’s disease risk and vitamin B or folate intake.
On the other hand, there is research suggesting that certain vitamins may help reduce Parkinson’s disease risk, although these nutrients do not operate in isolation. For instance, one recent study showed a connection between vitamins C and E and reduced Parkinson’s disease risk, but factors such as body mass index and coffee consumption appeared to influence the strength of this association.
Consuming polyunsaturated fatty acids along with reducing saturated fatty acid intake has been tied to a reduced risk for Parkinson’s disease.
Additionally, certain foods may offer protective effects, including green and black tea, with consumption of three or more cups per day associated with a delay in motor symptom onset by 7.7 years. Foods high in nicotine content, such as those from the Solanaceae family — including peppers, tomatoes, tomato juice, and potatoes — have also been linked to potential protective benefits.
Diets rich in antioxidants, including carotenoids, lutein, and vitamins E and C, have been robustly linked to a reduced risk for parkinsonism and progression of parkinsonian symptoms in older adults.
Increasing the intake of dietary flavonoids, particularly tea, berry fruits, apples, red wine, and oranges or orange juice, can reduce Parkinson’s disease risk. One study showed that male participants in the highest quintile of total flavonoid consumption had a 40% lower Parkinson’s disease risk compared with those in the lowest quintile. Another study showed that flavonoid-rich foods were also associated with a lower risk for death in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Food as Medicine
Although recent research shows that the drug development pipeline for Parkinson’s disease is robust, with a wide variety of approaches being developed and evaluated in phase 1 and 2, investigators note that only a limited number of disease-modifying treatments are transitioning to phase 3.
Duda noted that phytochemicals incorporated into the diet might target some of the same mechanisms that are targets of these drugs in development.
“Flavonoids have been shown to stabilize alpha-synuclein in vitro,” he said. “Caffeine, curcumin, resveratrol, and eliminating meat and dairy inhibit mTOR [mammalian target of rapamycin], and mTOR inhibition results in increased autophagy that may help clear alpha-synuclein. Genestein, an isoflavone in soybeans, protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting microglia activation. Flavonoids inhibit inflammation by inhibiting release of NO [nitric oxide] and pro-inflammatory cytokines,” he noted.
Ongoing studies of dietary interventions for Parkinson’s disease are exploring various areas, including the potential role of the ketogenic diet in protecting the gut microbiome, optimizing protein intake for muscle preservation and sleep, the effects of psyllium and wheat bran on weight and constipation, and the impact of a gluten-free diet.
Practical Tips for Healthy Eating
Gilbert emphasized that there are no medications or interventions currently available that can delay a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis by up to 17 years, as some dietary patterns have been shown to do, and she noted that it’s not possible to replicate the MeDi diet in a pill. However, she recommended a practical approach to eating that includes a diet low in ultraprocessed foods and high in beneficial nutrients. She encouraged people to shop for “real food” and enjoy a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
Duda acknowledged that motivating patients to follow a healthy diet can be difficult. As a result, the focus often shifts to making small adjustments and modifications. For example, he suggested that instead of pairing meat with French fries, people could opt for vegetables or add greens to their meals. Similarly, instead of having eggs and bacon for breakfast, they might choose oatmeal.
Preparing whole-food, plant-based meals may take more time than patients are accustomed to, so Duda suggests that, if possible, patients involve loved ones in both the meal preparation and the meal itself. He explained that a healthy meal can become an opportunity for bonding and that the key is educating them about new meal-related concepts.
Duda reported no relevant financial relationships with the pharmaceutical or food industries. He has received compensation from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine for his lecture delivered at the conference and research grant support from the VA, the National Institutes of Health, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and the Department of Defense unrelated to this topic. Gilbert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For 15 years, John Duda, MD, national director of the VA Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education and Clinical Centers, has urged his patients to “keep waiting” for effective treatments to manage both motor and nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
However, Duda, who also serves as director of the Brain Wellness Clinic at the Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, recognized the persistent lack of effective drugs to address these symptoms. This prompted him to consider what other evidence-based strategies he could use to support his patients.
“I recognized that nutritional approaches within a broader program that includes medication review, stress management, social connections, adequate sleep, and physical exercise could make a real difference,” he said.
Observational studies have shown an inverse association between dietary patterns and Parkinson’s disease risk, age of onset, symptom severity, and mortality rates — particularly with the Mediterranean diet (MeDi) and the MIND diet, which combines elements of MeDi and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. Although randomized controlled trials are still limited, the epidemiologic evidence supporting dietary interventions is “compelling,” said Duda.
For example, a cross-sectional study comparing 167 participants with Parkinson’s disease vs 119 controls showed that later age of Parkinson’s disease onset correlated with adherence to the MIND diet in women, with a difference of up to 17.4 years (P < .001) between low and high dietary tertiles.
The MeDi was correlated with later onset in men, with differences of up to 8.4 years (P = .002). As previously reported, a healthy diet emphasizing vegetables, fruits, nuts, and grains was inversely associated with prodromal features of Parkinson’s disease, including constipation, excessive daytime sleepiness, and depression. In addition, lower rates of Parkinson’s disease have been shown in populations following vegetarian and vegan dietary patterns.
Does Parkinson’s disease Start in the Gut?
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by decreased short-chain fatty acid–producing bacteria and increased pro-inflammatory species linked to intestinal inflammation and alpha-synuclein aggregation. “There are reasons to believe that a-synuclein accumulation may start in the gut,” Duda noted.
Numerous studies implicate gut microbiome dysbiosis as a pathogenic mechanism in Parkinson’s disease, with gastrointestinal symptoms often predating motor symptoms. Dysbiosis might result in a pro-inflammatory state potentially linked to the recurrent gastrointestinal symptoms. Fecal microbiota transplant may restore a healthier gut environment and beneficially affect Parkinson’s disease symptoms, he said.
Some of the benefits conferred by the MeDi and other healthy diets may be mediated by improving the gut microbiome. Duda cited a study that showed that a 14-day ovo-lacto vegetarian diet intervention and a daily fecal enema for 8 days improved not only the microbiome but also Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale—part III scores.
Duda also reviewed the role of dietary interventions in addressing common Parkinson’s disease symptoms, such as orthostatic hypotension. He recommended that Parkinson’s disease patients with this condition should avoid eating large meals, increase dietary salt intake, increase fluid intake, and decrease alcohol intake.
Malnutrition affects close to 25% of those with Parkinson’s disease, which is partially attributable to diminished olfaction. Because the experience of taste is largely driven by a sense of smell, patients may be less interested in eating. Duda recommended increasing herbs, spices, and other flavors in food. High caloric–density foods, including nuts, nut butters, and seeds, can boost weight, he said. However, he added, any patient with significant weight loss should consult a nutritionist.
Constipation is one of the most debilitating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, affecting up to 66% of patients. Duda advised increasing fluid intake, exercise, and dietary fiber and use of stool softeners and laxatives. The MeDi may reduce symptoms of constipation and have a beneficial effect on gut microbiota.
Coffee may be helpful for sleepiness in Parkinson’s disease and may also confer neuroprotective, motor, and cognitive benefits. As an adjuvant treatment, caffeine may alter levodopa pharmacokinetics, reduce dyskinesia, improve gait in patients with freezing and may even reduce the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, with a maximum benefit reached at approximately three cups of coffee daily.
Problematic Foods
There is also a growing body of evidence regarding the deleterious effects of ultraprocessed foods (UPFs), Duda said. He noted that a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of 28 studies showed that higher UPF intake was significantly associated with an enhanced risk for Parkinson’s disease (relative risk, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.21-2.02). As previously reported, UPFs have been tied to a host of adverse neurologic outcomes, including cognitive decline and stroke.
Although protein is a necessary nutrient, incorporating it into the diet of Parkinson’s disease patients taking levodopa is complicated. Levodopa, a large neutral amino acid (LNAA), competes with other LNAAs for transport to the brain from the small intestine, Duda explained.
“Some people notice that carbidopa-levodopa doesn’t work as well if taken with a high-protein meal.” He recommended taking carbidopa-levodopa 30 minutes before or 60 minutes after meals.
Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief mission officer of the American Parkinson’s Disease Association, said that patients with Parkinson’s disease might want to avoid eating protein during the day, concentrating instead on carbohydrates and vegetables and saving the protein for the evening, which is closer to bedtime. Some evidence also supports the use of protein redistribution diets to enhance the clinical response to levodopa and reduce motor fluctuations.
What About Supplements?
It’s “hard to prove that one specific supplement can be protective against Parkinson’s disease because diet consists of many different components and the whole diet may be worth more than the sum of its parts,” Gilbert said. The evidence for individual supplements “isn’t robust enough to say they prevent or treat Parkinson’s disease.”
Research on the role of specific nutrients in Parkinson’s disease is conflicting, with no clear evidence supporting or refuting their benefits. For example, a study that followed participants for about 30 years showed no link between reduced Parkinson’s disease risk and vitamin B or folate intake.
On the other hand, there is research suggesting that certain vitamins may help reduce Parkinson’s disease risk, although these nutrients do not operate in isolation. For instance, one recent study showed a connection between vitamins C and E and reduced Parkinson’s disease risk, but factors such as body mass index and coffee consumption appeared to influence the strength of this association.
Consuming polyunsaturated fatty acids along with reducing saturated fatty acid intake has been tied to a reduced risk for Parkinson’s disease.
Additionally, certain foods may offer protective effects, including green and black tea, with consumption of three or more cups per day associated with a delay in motor symptom onset by 7.7 years. Foods high in nicotine content, such as those from the Solanaceae family — including peppers, tomatoes, tomato juice, and potatoes — have also been linked to potential protective benefits.
Diets rich in antioxidants, including carotenoids, lutein, and vitamins E and C, have been robustly linked to a reduced risk for parkinsonism and progression of parkinsonian symptoms in older adults.
Increasing the intake of dietary flavonoids, particularly tea, berry fruits, apples, red wine, and oranges or orange juice, can reduce Parkinson’s disease risk. One study showed that male participants in the highest quintile of total flavonoid consumption had a 40% lower Parkinson’s disease risk compared with those in the lowest quintile. Another study showed that flavonoid-rich foods were also associated with a lower risk for death in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Food as Medicine
Although recent research shows that the drug development pipeline for Parkinson’s disease is robust, with a wide variety of approaches being developed and evaluated in phase 1 and 2, investigators note that only a limited number of disease-modifying treatments are transitioning to phase 3.
Duda noted that phytochemicals incorporated into the diet might target some of the same mechanisms that are targets of these drugs in development.
“Flavonoids have been shown to stabilize alpha-synuclein in vitro,” he said. “Caffeine, curcumin, resveratrol, and eliminating meat and dairy inhibit mTOR [mammalian target of rapamycin], and mTOR inhibition results in increased autophagy that may help clear alpha-synuclein. Genestein, an isoflavone in soybeans, protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting microglia activation. Flavonoids inhibit inflammation by inhibiting release of NO [nitric oxide] and pro-inflammatory cytokines,” he noted.
Ongoing studies of dietary interventions for Parkinson’s disease are exploring various areas, including the potential role of the ketogenic diet in protecting the gut microbiome, optimizing protein intake for muscle preservation and sleep, the effects of psyllium and wheat bran on weight and constipation, and the impact of a gluten-free diet.
Practical Tips for Healthy Eating
Gilbert emphasized that there are no medications or interventions currently available that can delay a Parkinson’s disease diagnosis by up to 17 years, as some dietary patterns have been shown to do, and she noted that it’s not possible to replicate the MeDi diet in a pill. However, she recommended a practical approach to eating that includes a diet low in ultraprocessed foods and high in beneficial nutrients. She encouraged people to shop for “real food” and enjoy a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables.
Duda acknowledged that motivating patients to follow a healthy diet can be difficult. As a result, the focus often shifts to making small adjustments and modifications. For example, he suggested that instead of pairing meat with French fries, people could opt for vegetables or add greens to their meals. Similarly, instead of having eggs and bacon for breakfast, they might choose oatmeal.
Preparing whole-food, plant-based meals may take more time than patients are accustomed to, so Duda suggests that, if possible, patients involve loved ones in both the meal preparation and the meal itself. He explained that a healthy meal can become an opportunity for bonding and that the key is educating them about new meal-related concepts.
Duda reported no relevant financial relationships with the pharmaceutical or food industries. He has received compensation from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine for his lecture delivered at the conference and research grant support from the VA, the National Institutes of Health, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and the Department of Defense unrelated to this topic. Gilbert reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Strange Untold Story of How Science Solved Narcolepsy
It was 1996, and Masashi Yanagisawa was on the brink of his next discovery.
The Japanese scientist had arrived at the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas 5 years earlier, setting up his own lab at age 31. After earning his medical degree, he’d gained notoriety as a PhD student when he discovered endothelin, the body’s most potent vasoconstrictor.
Yanagisawa was about to prove this wasn’t a first-timer’s fluke.
His focus was G-protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), cell surface receptors that respond to a range of molecules and a popular target for drug discovery. The Human Genome Project had just revealed a slew of newly discovered receptors, or “orphan” GPCRs, and identifying an activating molecule could yield a new drug. (That vasoconstrictor endothelin was one such success story, leading to four new drug approvals in the United States over the past quarter century.)
Yanagisawa and his team created 50 cell lines, each expressing one orphan receptor. They applied animal tissue to every line, along with a calcium-sensitive dye. If the cells glowed under the microscope, they had a hit.
“He was basically doing an elaborate fishing expedition,” said Jon Willie, MD, PhD, an associate professor of neurosurgery at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, who would later join Yanagisawa’s team.
It wasn’t long before the neon-green fluorescence signaled a match. After isolating the activating molecule, the scientists realized they were dealing with two neuropeptides.
No one had ever seen these proteins before. And no one knew their discovery would set off a decades-long journey that would finally solve a century-old medical mystery — and may even fix one of the biggest health crises of our time, as revealed by research published earlier in 2024. It’s a story of strange coincidences, serendipitous discoveries, and quirky details. Most of all, it’s a fascinating example of how basic science can revolutionize medicine — and how true breakthroughs happen over time and in real time.
But That’s Basic Science for You
Most basic science studies — the early, foundational research that provides the building blocks for science that follows — don’t lead to medical breakthroughs. But some do, often in surprising ways.
Also called curiosity-driven research, basic science aims to fill knowledge gaps to keep science moving, even if the trajectory isn’t always clear.
“The people working on the basic research that led to discoveries that transformed the modern world had no idea at the time,” said Isobel Ronai, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in life sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts. “Often, these stories can only be seen in hindsight,” sometimes decades later.
Case in point: For molecular biology techniques — things like DNA sequencing and gene targeting — the lag between basic science and breakthrough is, on average, 23 years. While many of the resulting techniques have received Nobel Prizes, few of the foundational discoveries have been awarded such accolades.
“The scientific glory is more often associated with the downstream applications,” said Ronai. “The importance of basic research can get lost. But it is the foundation for any future application, such as drug development.”
As funding is increasingly funneled toward applied research, basic science can require a certain persistence. What this under-appreciation can obscure is the pathway to discovery — which is often as compelling as the end result, full of unpredictable twists, turns, and even interpersonal intrigue.
And then there’s the fascinating — and definitely complicated — phenomenon of multiple independent discoveries.
As in: What happens when two independent teams discover the same thing at the same time?
Back to Yanagisawa’s Lab ...
... where he and his team learned a few things about those new neuropeptides. Rat brain studies pinpointed the lateral hypothalamus as the peptides’ area of activity — a region often called the brain’s feeding center.
“If you destroy that part of the brain, animals lose appetite,” said Yanagisawa. So these peptides must control feeding, the scientists thought.
Sure enough, injecting the proteins into rat brains led the rodents to start eating.
Satisfied, the team named them “orexin-A” and “orexin-B,” for the Greek word “orexis,” meaning appetite. The brain receptors became “orexin-1” and “orexin-2.” The team prepared to publish its findings in Cell.
But another group beat them to it.
Introducing the ‘Hypocretins’
In early January 1998, a team of Scripps Research Institute scientists, led by J. Gregor Sutcliffe, PhD, released a paper in the journal PNAS. They described a gene encoding for the precursor to two neuropeptides
As the peptides were in the hypothalamus and structurally like secretin (a gut hormone), they called them “hypocretins.” The hypocretin peptides excited neurons in the hypothalamus, and later that year, the scientists discovered that the neurons’ branches extended, tentacle-like, throughout the brain. “Many of the connected areas were involved in sleep-wake control,” said Thomas Kilduff, PhD, who joined the Sutcliffe lab just weeks before the hypocretin discovery. At the time, however, the significance of this finding was not yet clear.
Weeks later, in February 1998, Yanagisawa’s paper came out.
Somehow, two groups, over 1000 miles apart, had stumbled on the same neuropeptides at the same time.
“I first heard about [Yanagisawa’s] paper on NBC Nightly News,” recalls Kilduff. “I was skiing in the mountains, so I had to wait until Monday to get back to the lab to see what the paper was all about.”
He realized that Yanagisawa’s orexin was his lab’s hypocretin, although the study didn’t mention another team’s discovery.
“There may have been accusations. But as far as I know, it’s because [Yanagisawa] didn’t know [about the other paper],” said Willie. “This was not something he produced in 2 months. This was clearly years of work.”
‘Multiple Discovery’ Happens More Often Than You Think
In the mid-20th century, sociologist Robert Merton described the phenomenon of “multiple discovery,” where many scientific discoveries or inventions are made independently at roughly the same time.
“This happens much more frequently in scientific research than people suppose,” said David Pendlebury, head of research analysis at Clarivate’s Institute for Scientific Information, the analytics company’s research arm. (Last year, Pendlebury flagged the hypocretin/orexin discovery for Clarivate’s prestigious Citations Laureates award, an honor that aims to predict, often successfully, who will go on to win the Nobel Prize.)
“People have this idea of the lone researcher making a brilliant discovery,” Pendlebury said. “But more and more, teams find things at the same time.”
While this can — and does — lead to squabbling about who deserves credit, the desire to be first can also be highly motivating, said Mike Schneider, PhD, an assistant professor of philosophy at the University of Missouri, Columbia, who studies the social dynamics of science, potentially leading to faster scientific advancement.
The downside? If two groups produce the same or similar results, but one publishes first, scientific journals tend to reject the second, citing a lack of novelty.
Yet duplicating research is a key step in confirming the validity of a discovery.
That’s why, in 2018, the journal PLOS Biology created a provision for “scooped” scientists, allowing them to submit their paper within 6 months of the first as a complementary finding. Instead of viewing this as redundancy, the editors believe it adds robustness to the research.
‘What the Heck Is This Mouse Doing?’
Even though he’d been scooped, Yanagisawa forged on to the next challenge: Confirming whether orexin regulated feeding.
He began breeding mice missing the orexin gene. His team expected these “knockout” mice to eat less, resulting in a thinner body than other rodents. To the contrary, “they were on average fatter,” said Willie. “They were eating less but weighed more, indicating a slower metabolism.”
The researchers were befuddled. “We were really disappointed, almost desperate about what to do,” said Yanagisawa.
As nocturnal animals eat more at night, he decided they should study the mice after dark. One of his students, Richard Chemelli, MD, bought an infrared video camera from Radio Shack, filming the first 4 hours of the mice’s active period for several nights.
After watching the footage, “Rick called me and said, ‘Let’s get into the lab,’ ” said Willie. “It was four of us on a Saturday looking at these videos, saying, ‘What the heck is this mouse doing?’ ”
While exploring their habitat, the knockout mice would randomly fall over, pop back up after a minute or so, and resume normal activity. This happened over and over — and the scientists were unsure why.
They began monitoring the mice’s brains during these episodes — and made a startling discovery.
The mice weren’t having seizures. They were shifting directly into REM sleep, bypassing the non-REM stage, then quickly toggling back to wake mode.
“That’s when we knew these animals had something akin to narcolepsy,” said Willie.
The team recruited Thomas Scammell, MD, a Harvard neurologist, to investigate whether modafinil — an anti-narcoleptic drug without a clear mechanism — affected orexin neurons.
Two hours after injecting the mice with the medication, the scientists sacrificed them and stained their brains. Remarkably, the number of neurons showing orexin activity had increased ninefold. It seemed modafinil worked by activating the orexin system.
These findings had the potential to crack open the science of narcolepsy, one of the most mysterious sleep disorders.
Unless, of course, another team did it first.
The Mystery of Narcolepsy
Yet another multiple discovery, narcolepsy was first described by two scientists — one in Germany, the other in France — within a short span in the late 1800s.
It would be more than a hundred years before anyone understood the disorder’s cause, even though it affects about 1 in 2000 people.
“Patients were often labeled as lazy and malingerers,” said Kilduff, “since they were sleepy all the time and had this weird motor behavior called cataplexy” or the sudden loss of muscle tone.
In the early 1970s, William Dement, MD, PhD — “the father of sleep medicine” — was searching for a narcoleptic cat to study. He couldn’t find a feline, but several colleagues mentioned dogs with narcolepsy-like symptoms.
Dement, who died in 2020, had found his newest research subjects.
In 1973, he started a narcoleptic dog colony at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California. At first, he focused on poodles and beagles. After discovering their narcolepsy wasn’t genetic, he pivoted to dobermans and labradors. Their narcolepsy was inherited, so he could breed them to populate the colony.
Although human narcolepsy is rarely genetic, it’s otherwise a lot like the version in these dogs.
Both involve daytime sleepiness, “pathological” bouts of REM sleep, and the loss of muscle tone in response to emotions, often positive ones.
The researchers hoped the canines could unlock a treatment for human narcolepsy. They began laying out a path of dog kibble, then injecting the dogs with drugs such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. They wanted to see what might help them stay awake as they excitedly chowed down.
Kilduff also started a molecular genetics program, trying to identify the genetic defect behind canine narcolepsy. But after a parvovirus outbreak, Kilduff resigned from the project, drained from the strain of seeing so many dogs die.
A decade after his departure from the dog colony, his work would dramatically intersect with that of his successor, Emmanuel Mignot, MD, PhD.
“I thought I had closed the narcolepsy chapter in my life forever,” said Kilduff. “Then in 1998, we described this novel neuropeptide, hypocretin, that turned out to be the key to understanding the disorder.”
Narcoleptic Dogs in California, Mutant Mice in Texas
It was modafinil — the same anti-narcoleptic drug Yanagisawa’s team studied — that brought Emmanuel Mignot to the United States. After training as a pharmacologist in France, his home country sent him to Stanford to study the drug, which was discovered by French scientists, as his required military service.
As Kilduff’s replacement at the dog colony, his goal was to figure out how modafinil worked, hoping to attract a US company to develop the drug.
The plan succeeded. Modafinil became Provigil, a billion-dollar narcolepsy drug, and Mignot became “completely fascinated” with the disorder.
“I realized quickly that there was no way we’d find the cause of narcolepsy by finding the mode of action of this drug,” Mignot said. “Most likely, the drug was acting downstream, not at the cause of the disorder.”
To discover the answer, he needed to become a geneticist. And so began his 11-year odyssey to find the cause of canine narcolepsy.
After mapping the dog genome, Mignot set out to find the smallest stretch of chromosome that the narcoleptic animals had in common. “For a very long time, we were stuck with a relatively large region [of DNA],” he recalls. “It was a no man’s land.”
Within that region was the gene for the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor — the same receptor that Yanagisawa had identified in his first orexin paper. Mignot didn’t immediately pursue that gene as a possibility — even though his students suggested it. Why?
“The decision was simply: Should we lose time to test a possible candidate [gene] among many?” Mignot said.
As Mignot studied dog DNA in California, Yanagisawa was creating mutant mice in Texas. Unbeknownst to either scientist, their work was about to converge.
What Happened Next Is Somewhat Disputed
After diagnosing his mice with narcolepsy, Yanagisawa opted not to share this finding with Mignot, though he knew about Mignot’s interest in the condition. Instead, he asked a colleague to find out how far along Mignot was in his genetics research.
According to Yanagisawa, his colleague didn’t realize how quickly DNA sequencing could happen once a target gene was identified. At a sleep meeting, “he showed Emmanuel all of our raw data. Almost accidentally, he disclosed our findings,” he said. “It was a shock for me.”
Unsure whether he was part of the orexin group, Mignot decided not to reveal that he’d identified the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor gene as the faulty one in his narcoleptic dogs.
Although he didn’t share this finding, Mignot said he did offer to speak with the lead researcher to see if their findings were the same. If they were, they could jointly submit their articles. But Mignot never heard back.
Meanwhile, back at his lab, Mignot buckled down. While he wasn’t convinced the mouse data proved anything, it did give him the motivation to move faster.
Within weeks, he submitted his findings to Cell, revealing a mutation in the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor gene as the cause of canine narcolepsy. According to Yanagisawa, the journal’s editor invited him to peer-review the paper, tipping him off to its existence.
“I told him I had a conflict of interest,” said Yanagisawa. “And then we scrambled to finish our manuscript. We wrote up the paper within almost 5 days.”
For a moment, it seemed both papers would be published together in Cell. Instead, on August 6, 1999, Mignot’s study was splashed solo across the journal’s cover.
“At the time, our team was pissed off, but looking back, what else could Emmanuel have done?” said Willie, who was part of Yanagisawa’s team. “The grant he’d been working on for years was at risk. He had it within his power to do the final experiments. Of course he was going to finish.”
Two weeks later, Yanagisawa’s findings followed, also in Cell.
His paper proposed knockout mice as a model for human narcolepsy and orexin as a key regulator of the sleep/wake cycle. With orexin-activated neurons branching into other areas of the brain, the peptide seemed to promote wakefulness by synchronizing several arousal neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine.
“If you don’t have orexin, each of those systems can still function, but they’re not as coordinated,” said Willie. “If you have narcolepsy, you’re capable of wakefulness, and you’re capable of sleep. What you can’t do is prevent inappropriately switching between states.”
Together, the two papers painted a clear picture: Narcolepsy was the result of a dysfunction in the hypocretin/orexin system.
After more than a century, the cause of narcolepsy was starting to come into focus.
“This was blockbuster,” said Willie.
By itself, either finding — one in dogs, one in mice — might have been met with skepticism. But in combination, they offered indisputable evidence about narcolepsy’s cause.
The Human Brains in Your Fridge Hold Secrets
Jerome Siegel had been searching for the cause of human narcolepsy for years. A PhD and professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, he had managed to acquire four human narcoleptic brains. As laughter is often the trigger for the sudden shift to REM sleep in humans, he focused on the amygdala, an area linked to emotion.
“I looked in the amygdala and didn’t see anything,” he said. “So the brains stayed in my refrigerator for probably 10 years.”
Then he was invited to review Yanagisawa’s study in Cell. The lightbulb clicked on: Maybe the hypothalamus — not the amygdala — was the area of abnormality. He and his team dug out the decade-old brains.
When they stained the brains, the massive loss of hypocretin-activated neurons was hard to miss: On average, the narcoleptic brains had only about 7000 of the cells versus 70,000 in the average human brain. The scientists also noticed scar tissue in the hypothalamus, indicating that the neurons had at some point died, rather than being absent from birth.
What Siegel didn’t know: Mignot had also acquired a handful of human narcoleptic brains.
Already, he had coauthored a study showing that hypocretin/orexin was undetectable in the cerebrospinal fluid of the majority of the people with narcolepsy his team tested. It seemed clear that the hypocretin/orexin system was flawed — or even broken — in people with the condition.
“It looked like the cause of narcolepsy in humans was indeed this lack of orexin in the brain,” he said. “That was the hypothesis immediately. To me, this is when we established that narcolepsy in humans was due to a lack of orexin. The next thing was to check that the cells were missing.”
Now he could do exactly that.
As expected, Mignot’s team observed a dramatic loss of hypocretin/orexin cells in the narcoleptic brains. They also noticed that a different cell type in the hypothalamus was unaffected. This implied the damage was specific to the hypocretin-activated cells and supported a hunch they already had: That the deficit was the result not of a genetic defect but of an autoimmune attack. (It’s a hypothesis Mignot has spent the last 15 years proving.)
It wasn’t until a gathering in Hawaii, in late August 2000, that the two realized the overlap of their work.
To celebrate his team’s finding, Mignot had invited a group of researchers to Big Island. With his paper scheduled for publication on September 1, he felt comfortable presenting his findings to his guests, which included Siegel.
Until then, “I didn’t know what he had found, and he didn’t know what I had found, which basically was the same thing,” said Siegel.
In yet another strange twist, the two papers were published just weeks apart, simultaneously revealing that human narcoleptics have a depleted supply of the neurons that bind to hypocretin/orexin. The cause of the disorder was at last a certainty.
“Even if I was first, what does it matter? In the end, you need confirmation,” said Mignot. “You need multiple people to make sure that it’s true. It’s good science when things like this happen.”
How All of This Changed Medicine
Since these groundbreaking discoveries, the diagnosis of narcolepsy has become much simpler. Lab tests can now easily measure hypocretin in cerebrospinal fluid, providing a definitive diagnosis.
But the development of narcolepsy treatments has lagged — even though hypocretin/orexin replacement therapy is the obvious answer.
“Almost 25 years have elapsed, and there’s no such therapeutic on the market,” said Kilduff, who now works for SRI International, a non-profit research and development institute.
That’s partly because agonists — drugs that bind to receptors in the brain — are challenging to create, as this requires mimicking the activating molecule’s structure, like copying the grooves of an intricate key.
Antagonists, by comparison, are easier to develop. These act as a gate, blocking access to the receptors. As a result, drugs that promote sleep by thwarting hypocretin/orexin have emerged more quickly, providing a flurry of new options for people with insomnia. The first, suvorexant, was launched in 2014. Two others followed in recent years.
Researchers are hopeful a hypocretin/orexin agonist is on the horizon.
“This is a very hot area of drug development,” said Kilduff. “It’s just a matter of who’s going to get the drug to market first.”
One More Hypocretin/Orexin Surprise — and It Could Be The Biggest
Several years ago, Siegel’s lab received what was supposed to be a healthy human brain — one they could use as a comparison for narcoleptic brains. But researcher Thomas Thannickal, PhD, lead author of the UCLA study linking hypocretin loss to human narcolepsy, noticed something strange: This brain had significantly more hypocretin neurons than average.
Was this due to a seizure? A traumatic death? Siegel called the brain bank to request the donor’s records. He was told they were missing.
Years later, Siegel happened to be visiting the brain bank for another project and found himself in a room adjacent to the medical records. “Nobody was there,” he said, “so I just opened a drawer.”
Shuffling through the brain bank’s files, Siegel found the medical records he’d been told were lost. In the file was a note from the donor, explaining that he was a former heroin addict.
“I almost fell out of my chair,” said Siegel. “I realized this guy’s heroin addiction likely had something to do with his very unusual brain.”
Obviously, opioids affected the orexin system. But how?
“It’s when people are happy that this peptide is released,” said Siegel. “The hypocretin system is not just related to alertness. It’s related to pleasure.”
As Yanagisawa observed early on, hypocretin/orexin does indeed play a role in eating — just not the one he initially thought. The peptides prompted pleasure seeking. So the rodents ate.
In 2018, after acquiring five more brains, Siegel’s group published a study in Translational Medicine showing 54% more detectable hypocretin neurons in the brains of heroin addicts than in those of control individuals.
In 2022, another breakthrough: His team showed that morphine significantly altered the pathways of hypocretin neurons in mice, sending their axons into brain regions associated with addiction. Then, when they removed the mice’s hypocretin neurons and discontinued their daily morphine dose, the rodents showed no symptoms of opioid withdrawal.
This fits the connection with narcolepsy: Among the standard treatments for the condition are amphetamines and other stimulants, which all have addictive potential. Yet, “narcoleptics never abuse these drugs,” Siegel said. “They seem to be uniquely resistant to addiction.”
This could powerfully change the way opioids are administered.
“If you prevent the hypocretin response to opioids, you may be able to prevent opioid addiction,” said Siegel. In other words, blocking the hypocretin system with a drug like those used to treat insomnia may allow patients to experience the pain-relieving benefits of opioids — without the risk for addiction.
His team is currently investigating treatments targeting the hypocretin/orexin system for opioid addiction.
In a study published in July, they found that mice who received suvorexant — the drug for insomnia — didn’t anticipate their daily dose of opioids the way other rodents did. This suggests the medication prevented addiction, without diminishing the pain-relieving effect of opioids.
If it translates to humans, this discovery could potentially save millions of lives.
“I think it’s just us working on this,” said Siegel.
But with hypocretin/orexin, you never know.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It was 1996, and Masashi Yanagisawa was on the brink of his next discovery.
The Japanese scientist had arrived at the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas 5 years earlier, setting up his own lab at age 31. After earning his medical degree, he’d gained notoriety as a PhD student when he discovered endothelin, the body’s most potent vasoconstrictor.
Yanagisawa was about to prove this wasn’t a first-timer’s fluke.
His focus was G-protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), cell surface receptors that respond to a range of molecules and a popular target for drug discovery. The Human Genome Project had just revealed a slew of newly discovered receptors, or “orphan” GPCRs, and identifying an activating molecule could yield a new drug. (That vasoconstrictor endothelin was one such success story, leading to four new drug approvals in the United States over the past quarter century.)
Yanagisawa and his team created 50 cell lines, each expressing one orphan receptor. They applied animal tissue to every line, along with a calcium-sensitive dye. If the cells glowed under the microscope, they had a hit.
“He was basically doing an elaborate fishing expedition,” said Jon Willie, MD, PhD, an associate professor of neurosurgery at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, who would later join Yanagisawa’s team.
It wasn’t long before the neon-green fluorescence signaled a match. After isolating the activating molecule, the scientists realized they were dealing with two neuropeptides.
No one had ever seen these proteins before. And no one knew their discovery would set off a decades-long journey that would finally solve a century-old medical mystery — and may even fix one of the biggest health crises of our time, as revealed by research published earlier in 2024. It’s a story of strange coincidences, serendipitous discoveries, and quirky details. Most of all, it’s a fascinating example of how basic science can revolutionize medicine — and how true breakthroughs happen over time and in real time.
But That’s Basic Science for You
Most basic science studies — the early, foundational research that provides the building blocks for science that follows — don’t lead to medical breakthroughs. But some do, often in surprising ways.
Also called curiosity-driven research, basic science aims to fill knowledge gaps to keep science moving, even if the trajectory isn’t always clear.
“The people working on the basic research that led to discoveries that transformed the modern world had no idea at the time,” said Isobel Ronai, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in life sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts. “Often, these stories can only be seen in hindsight,” sometimes decades later.
Case in point: For molecular biology techniques — things like DNA sequencing and gene targeting — the lag between basic science and breakthrough is, on average, 23 years. While many of the resulting techniques have received Nobel Prizes, few of the foundational discoveries have been awarded such accolades.
“The scientific glory is more often associated with the downstream applications,” said Ronai. “The importance of basic research can get lost. But it is the foundation for any future application, such as drug development.”
As funding is increasingly funneled toward applied research, basic science can require a certain persistence. What this under-appreciation can obscure is the pathway to discovery — which is often as compelling as the end result, full of unpredictable twists, turns, and even interpersonal intrigue.
And then there’s the fascinating — and definitely complicated — phenomenon of multiple independent discoveries.
As in: What happens when two independent teams discover the same thing at the same time?
Back to Yanagisawa’s Lab ...
... where he and his team learned a few things about those new neuropeptides. Rat brain studies pinpointed the lateral hypothalamus as the peptides’ area of activity — a region often called the brain’s feeding center.
“If you destroy that part of the brain, animals lose appetite,” said Yanagisawa. So these peptides must control feeding, the scientists thought.
Sure enough, injecting the proteins into rat brains led the rodents to start eating.
Satisfied, the team named them “orexin-A” and “orexin-B,” for the Greek word “orexis,” meaning appetite. The brain receptors became “orexin-1” and “orexin-2.” The team prepared to publish its findings in Cell.
But another group beat them to it.
Introducing the ‘Hypocretins’
In early January 1998, a team of Scripps Research Institute scientists, led by J. Gregor Sutcliffe, PhD, released a paper in the journal PNAS. They described a gene encoding for the precursor to two neuropeptides
As the peptides were in the hypothalamus and structurally like secretin (a gut hormone), they called them “hypocretins.” The hypocretin peptides excited neurons in the hypothalamus, and later that year, the scientists discovered that the neurons’ branches extended, tentacle-like, throughout the brain. “Many of the connected areas were involved in sleep-wake control,” said Thomas Kilduff, PhD, who joined the Sutcliffe lab just weeks before the hypocretin discovery. At the time, however, the significance of this finding was not yet clear.
Weeks later, in February 1998, Yanagisawa’s paper came out.
Somehow, two groups, over 1000 miles apart, had stumbled on the same neuropeptides at the same time.
“I first heard about [Yanagisawa’s] paper on NBC Nightly News,” recalls Kilduff. “I was skiing in the mountains, so I had to wait until Monday to get back to the lab to see what the paper was all about.”
He realized that Yanagisawa’s orexin was his lab’s hypocretin, although the study didn’t mention another team’s discovery.
“There may have been accusations. But as far as I know, it’s because [Yanagisawa] didn’t know [about the other paper],” said Willie. “This was not something he produced in 2 months. This was clearly years of work.”
‘Multiple Discovery’ Happens More Often Than You Think
In the mid-20th century, sociologist Robert Merton described the phenomenon of “multiple discovery,” where many scientific discoveries or inventions are made independently at roughly the same time.
“This happens much more frequently in scientific research than people suppose,” said David Pendlebury, head of research analysis at Clarivate’s Institute for Scientific Information, the analytics company’s research arm. (Last year, Pendlebury flagged the hypocretin/orexin discovery for Clarivate’s prestigious Citations Laureates award, an honor that aims to predict, often successfully, who will go on to win the Nobel Prize.)
“People have this idea of the lone researcher making a brilliant discovery,” Pendlebury said. “But more and more, teams find things at the same time.”
While this can — and does — lead to squabbling about who deserves credit, the desire to be first can also be highly motivating, said Mike Schneider, PhD, an assistant professor of philosophy at the University of Missouri, Columbia, who studies the social dynamics of science, potentially leading to faster scientific advancement.
The downside? If two groups produce the same or similar results, but one publishes first, scientific journals tend to reject the second, citing a lack of novelty.
Yet duplicating research is a key step in confirming the validity of a discovery.
That’s why, in 2018, the journal PLOS Biology created a provision for “scooped” scientists, allowing them to submit their paper within 6 months of the first as a complementary finding. Instead of viewing this as redundancy, the editors believe it adds robustness to the research.
‘What the Heck Is This Mouse Doing?’
Even though he’d been scooped, Yanagisawa forged on to the next challenge: Confirming whether orexin regulated feeding.
He began breeding mice missing the orexin gene. His team expected these “knockout” mice to eat less, resulting in a thinner body than other rodents. To the contrary, “they were on average fatter,” said Willie. “They were eating less but weighed more, indicating a slower metabolism.”
The researchers were befuddled. “We were really disappointed, almost desperate about what to do,” said Yanagisawa.
As nocturnal animals eat more at night, he decided they should study the mice after dark. One of his students, Richard Chemelli, MD, bought an infrared video camera from Radio Shack, filming the first 4 hours of the mice’s active period for several nights.
After watching the footage, “Rick called me and said, ‘Let’s get into the lab,’ ” said Willie. “It was four of us on a Saturday looking at these videos, saying, ‘What the heck is this mouse doing?’ ”
While exploring their habitat, the knockout mice would randomly fall over, pop back up after a minute or so, and resume normal activity. This happened over and over — and the scientists were unsure why.
They began monitoring the mice’s brains during these episodes — and made a startling discovery.
The mice weren’t having seizures. They were shifting directly into REM sleep, bypassing the non-REM stage, then quickly toggling back to wake mode.
“That’s when we knew these animals had something akin to narcolepsy,” said Willie.
The team recruited Thomas Scammell, MD, a Harvard neurologist, to investigate whether modafinil — an anti-narcoleptic drug without a clear mechanism — affected orexin neurons.
Two hours after injecting the mice with the medication, the scientists sacrificed them and stained their brains. Remarkably, the number of neurons showing orexin activity had increased ninefold. It seemed modafinil worked by activating the orexin system.
These findings had the potential to crack open the science of narcolepsy, one of the most mysterious sleep disorders.
Unless, of course, another team did it first.
The Mystery of Narcolepsy
Yet another multiple discovery, narcolepsy was first described by two scientists — one in Germany, the other in France — within a short span in the late 1800s.
It would be more than a hundred years before anyone understood the disorder’s cause, even though it affects about 1 in 2000 people.
“Patients were often labeled as lazy and malingerers,” said Kilduff, “since they were sleepy all the time and had this weird motor behavior called cataplexy” or the sudden loss of muscle tone.
In the early 1970s, William Dement, MD, PhD — “the father of sleep medicine” — was searching for a narcoleptic cat to study. He couldn’t find a feline, but several colleagues mentioned dogs with narcolepsy-like symptoms.
Dement, who died in 2020, had found his newest research subjects.
In 1973, he started a narcoleptic dog colony at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California. At first, he focused on poodles and beagles. After discovering their narcolepsy wasn’t genetic, he pivoted to dobermans and labradors. Their narcolepsy was inherited, so he could breed them to populate the colony.
Although human narcolepsy is rarely genetic, it’s otherwise a lot like the version in these dogs.
Both involve daytime sleepiness, “pathological” bouts of REM sleep, and the loss of muscle tone in response to emotions, often positive ones.
The researchers hoped the canines could unlock a treatment for human narcolepsy. They began laying out a path of dog kibble, then injecting the dogs with drugs such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. They wanted to see what might help them stay awake as they excitedly chowed down.
Kilduff also started a molecular genetics program, trying to identify the genetic defect behind canine narcolepsy. But after a parvovirus outbreak, Kilduff resigned from the project, drained from the strain of seeing so many dogs die.
A decade after his departure from the dog colony, his work would dramatically intersect with that of his successor, Emmanuel Mignot, MD, PhD.
“I thought I had closed the narcolepsy chapter in my life forever,” said Kilduff. “Then in 1998, we described this novel neuropeptide, hypocretin, that turned out to be the key to understanding the disorder.”
Narcoleptic Dogs in California, Mutant Mice in Texas
It was modafinil — the same anti-narcoleptic drug Yanagisawa’s team studied — that brought Emmanuel Mignot to the United States. After training as a pharmacologist in France, his home country sent him to Stanford to study the drug, which was discovered by French scientists, as his required military service.
As Kilduff’s replacement at the dog colony, his goal was to figure out how modafinil worked, hoping to attract a US company to develop the drug.
The plan succeeded. Modafinil became Provigil, a billion-dollar narcolepsy drug, and Mignot became “completely fascinated” with the disorder.
“I realized quickly that there was no way we’d find the cause of narcolepsy by finding the mode of action of this drug,” Mignot said. “Most likely, the drug was acting downstream, not at the cause of the disorder.”
To discover the answer, he needed to become a geneticist. And so began his 11-year odyssey to find the cause of canine narcolepsy.
After mapping the dog genome, Mignot set out to find the smallest stretch of chromosome that the narcoleptic animals had in common. “For a very long time, we were stuck with a relatively large region [of DNA],” he recalls. “It was a no man’s land.”
Within that region was the gene for the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor — the same receptor that Yanagisawa had identified in his first orexin paper. Mignot didn’t immediately pursue that gene as a possibility — even though his students suggested it. Why?
“The decision was simply: Should we lose time to test a possible candidate [gene] among many?” Mignot said.
As Mignot studied dog DNA in California, Yanagisawa was creating mutant mice in Texas. Unbeknownst to either scientist, their work was about to converge.
What Happened Next Is Somewhat Disputed
After diagnosing his mice with narcolepsy, Yanagisawa opted not to share this finding with Mignot, though he knew about Mignot’s interest in the condition. Instead, he asked a colleague to find out how far along Mignot was in his genetics research.
According to Yanagisawa, his colleague didn’t realize how quickly DNA sequencing could happen once a target gene was identified. At a sleep meeting, “he showed Emmanuel all of our raw data. Almost accidentally, he disclosed our findings,” he said. “It was a shock for me.”
Unsure whether he was part of the orexin group, Mignot decided not to reveal that he’d identified the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor gene as the faulty one in his narcoleptic dogs.
Although he didn’t share this finding, Mignot said he did offer to speak with the lead researcher to see if their findings were the same. If they were, they could jointly submit their articles. But Mignot never heard back.
Meanwhile, back at his lab, Mignot buckled down. While he wasn’t convinced the mouse data proved anything, it did give him the motivation to move faster.
Within weeks, he submitted his findings to Cell, revealing a mutation in the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor gene as the cause of canine narcolepsy. According to Yanagisawa, the journal’s editor invited him to peer-review the paper, tipping him off to its existence.
“I told him I had a conflict of interest,” said Yanagisawa. “And then we scrambled to finish our manuscript. We wrote up the paper within almost 5 days.”
For a moment, it seemed both papers would be published together in Cell. Instead, on August 6, 1999, Mignot’s study was splashed solo across the journal’s cover.
“At the time, our team was pissed off, but looking back, what else could Emmanuel have done?” said Willie, who was part of Yanagisawa’s team. “The grant he’d been working on for years was at risk. He had it within his power to do the final experiments. Of course he was going to finish.”
Two weeks later, Yanagisawa’s findings followed, also in Cell.
His paper proposed knockout mice as a model for human narcolepsy and orexin as a key regulator of the sleep/wake cycle. With orexin-activated neurons branching into other areas of the brain, the peptide seemed to promote wakefulness by synchronizing several arousal neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine.
“If you don’t have orexin, each of those systems can still function, but they’re not as coordinated,” said Willie. “If you have narcolepsy, you’re capable of wakefulness, and you’re capable of sleep. What you can’t do is prevent inappropriately switching between states.”
Together, the two papers painted a clear picture: Narcolepsy was the result of a dysfunction in the hypocretin/orexin system.
After more than a century, the cause of narcolepsy was starting to come into focus.
“This was blockbuster,” said Willie.
By itself, either finding — one in dogs, one in mice — might have been met with skepticism. But in combination, they offered indisputable evidence about narcolepsy’s cause.
The Human Brains in Your Fridge Hold Secrets
Jerome Siegel had been searching for the cause of human narcolepsy for years. A PhD and professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, he had managed to acquire four human narcoleptic brains. As laughter is often the trigger for the sudden shift to REM sleep in humans, he focused on the amygdala, an area linked to emotion.
“I looked in the amygdala and didn’t see anything,” he said. “So the brains stayed in my refrigerator for probably 10 years.”
Then he was invited to review Yanagisawa’s study in Cell. The lightbulb clicked on: Maybe the hypothalamus — not the amygdala — was the area of abnormality. He and his team dug out the decade-old brains.
When they stained the brains, the massive loss of hypocretin-activated neurons was hard to miss: On average, the narcoleptic brains had only about 7000 of the cells versus 70,000 in the average human brain. The scientists also noticed scar tissue in the hypothalamus, indicating that the neurons had at some point died, rather than being absent from birth.
What Siegel didn’t know: Mignot had also acquired a handful of human narcoleptic brains.
Already, he had coauthored a study showing that hypocretin/orexin was undetectable in the cerebrospinal fluid of the majority of the people with narcolepsy his team tested. It seemed clear that the hypocretin/orexin system was flawed — or even broken — in people with the condition.
“It looked like the cause of narcolepsy in humans was indeed this lack of orexin in the brain,” he said. “That was the hypothesis immediately. To me, this is when we established that narcolepsy in humans was due to a lack of orexin. The next thing was to check that the cells were missing.”
Now he could do exactly that.
As expected, Mignot’s team observed a dramatic loss of hypocretin/orexin cells in the narcoleptic brains. They also noticed that a different cell type in the hypothalamus was unaffected. This implied the damage was specific to the hypocretin-activated cells and supported a hunch they already had: That the deficit was the result not of a genetic defect but of an autoimmune attack. (It’s a hypothesis Mignot has spent the last 15 years proving.)
It wasn’t until a gathering in Hawaii, in late August 2000, that the two realized the overlap of their work.
To celebrate his team’s finding, Mignot had invited a group of researchers to Big Island. With his paper scheduled for publication on September 1, he felt comfortable presenting his findings to his guests, which included Siegel.
Until then, “I didn’t know what he had found, and he didn’t know what I had found, which basically was the same thing,” said Siegel.
In yet another strange twist, the two papers were published just weeks apart, simultaneously revealing that human narcoleptics have a depleted supply of the neurons that bind to hypocretin/orexin. The cause of the disorder was at last a certainty.
“Even if I was first, what does it matter? In the end, you need confirmation,” said Mignot. “You need multiple people to make sure that it’s true. It’s good science when things like this happen.”
How All of This Changed Medicine
Since these groundbreaking discoveries, the diagnosis of narcolepsy has become much simpler. Lab tests can now easily measure hypocretin in cerebrospinal fluid, providing a definitive diagnosis.
But the development of narcolepsy treatments has lagged — even though hypocretin/orexin replacement therapy is the obvious answer.
“Almost 25 years have elapsed, and there’s no such therapeutic on the market,” said Kilduff, who now works for SRI International, a non-profit research and development institute.
That’s partly because agonists — drugs that bind to receptors in the brain — are challenging to create, as this requires mimicking the activating molecule’s structure, like copying the grooves of an intricate key.
Antagonists, by comparison, are easier to develop. These act as a gate, blocking access to the receptors. As a result, drugs that promote sleep by thwarting hypocretin/orexin have emerged more quickly, providing a flurry of new options for people with insomnia. The first, suvorexant, was launched in 2014. Two others followed in recent years.
Researchers are hopeful a hypocretin/orexin agonist is on the horizon.
“This is a very hot area of drug development,” said Kilduff. “It’s just a matter of who’s going to get the drug to market first.”
One More Hypocretin/Orexin Surprise — and It Could Be The Biggest
Several years ago, Siegel’s lab received what was supposed to be a healthy human brain — one they could use as a comparison for narcoleptic brains. But researcher Thomas Thannickal, PhD, lead author of the UCLA study linking hypocretin loss to human narcolepsy, noticed something strange: This brain had significantly more hypocretin neurons than average.
Was this due to a seizure? A traumatic death? Siegel called the brain bank to request the donor’s records. He was told they were missing.
Years later, Siegel happened to be visiting the brain bank for another project and found himself in a room adjacent to the medical records. “Nobody was there,” he said, “so I just opened a drawer.”
Shuffling through the brain bank’s files, Siegel found the medical records he’d been told were lost. In the file was a note from the donor, explaining that he was a former heroin addict.
“I almost fell out of my chair,” said Siegel. “I realized this guy’s heroin addiction likely had something to do with his very unusual brain.”
Obviously, opioids affected the orexin system. But how?
“It’s when people are happy that this peptide is released,” said Siegel. “The hypocretin system is not just related to alertness. It’s related to pleasure.”
As Yanagisawa observed early on, hypocretin/orexin does indeed play a role in eating — just not the one he initially thought. The peptides prompted pleasure seeking. So the rodents ate.
In 2018, after acquiring five more brains, Siegel’s group published a study in Translational Medicine showing 54% more detectable hypocretin neurons in the brains of heroin addicts than in those of control individuals.
In 2022, another breakthrough: His team showed that morphine significantly altered the pathways of hypocretin neurons in mice, sending their axons into brain regions associated with addiction. Then, when they removed the mice’s hypocretin neurons and discontinued their daily morphine dose, the rodents showed no symptoms of opioid withdrawal.
This fits the connection with narcolepsy: Among the standard treatments for the condition are amphetamines and other stimulants, which all have addictive potential. Yet, “narcoleptics never abuse these drugs,” Siegel said. “They seem to be uniquely resistant to addiction.”
This could powerfully change the way opioids are administered.
“If you prevent the hypocretin response to opioids, you may be able to prevent opioid addiction,” said Siegel. In other words, blocking the hypocretin system with a drug like those used to treat insomnia may allow patients to experience the pain-relieving benefits of opioids — without the risk for addiction.
His team is currently investigating treatments targeting the hypocretin/orexin system for opioid addiction.
In a study published in July, they found that mice who received suvorexant — the drug for insomnia — didn’t anticipate their daily dose of opioids the way other rodents did. This suggests the medication prevented addiction, without diminishing the pain-relieving effect of opioids.
If it translates to humans, this discovery could potentially save millions of lives.
“I think it’s just us working on this,” said Siegel.
But with hypocretin/orexin, you never know.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It was 1996, and Masashi Yanagisawa was on the brink of his next discovery.
The Japanese scientist had arrived at the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas 5 years earlier, setting up his own lab at age 31. After earning his medical degree, he’d gained notoriety as a PhD student when he discovered endothelin, the body’s most potent vasoconstrictor.
Yanagisawa was about to prove this wasn’t a first-timer’s fluke.
His focus was G-protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), cell surface receptors that respond to a range of molecules and a popular target for drug discovery. The Human Genome Project had just revealed a slew of newly discovered receptors, or “orphan” GPCRs, and identifying an activating molecule could yield a new drug. (That vasoconstrictor endothelin was one such success story, leading to four new drug approvals in the United States over the past quarter century.)
Yanagisawa and his team created 50 cell lines, each expressing one orphan receptor. They applied animal tissue to every line, along with a calcium-sensitive dye. If the cells glowed under the microscope, they had a hit.
“He was basically doing an elaborate fishing expedition,” said Jon Willie, MD, PhD, an associate professor of neurosurgery at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, who would later join Yanagisawa’s team.
It wasn’t long before the neon-green fluorescence signaled a match. After isolating the activating molecule, the scientists realized they were dealing with two neuropeptides.
No one had ever seen these proteins before. And no one knew their discovery would set off a decades-long journey that would finally solve a century-old medical mystery — and may even fix one of the biggest health crises of our time, as revealed by research published earlier in 2024. It’s a story of strange coincidences, serendipitous discoveries, and quirky details. Most of all, it’s a fascinating example of how basic science can revolutionize medicine — and how true breakthroughs happen over time and in real time.
But That’s Basic Science for You
Most basic science studies — the early, foundational research that provides the building blocks for science that follows — don’t lead to medical breakthroughs. But some do, often in surprising ways.
Also called curiosity-driven research, basic science aims to fill knowledge gaps to keep science moving, even if the trajectory isn’t always clear.
“The people working on the basic research that led to discoveries that transformed the modern world had no idea at the time,” said Isobel Ronai, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in life sciences at Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts. “Often, these stories can only be seen in hindsight,” sometimes decades later.
Case in point: For molecular biology techniques — things like DNA sequencing and gene targeting — the lag between basic science and breakthrough is, on average, 23 years. While many of the resulting techniques have received Nobel Prizes, few of the foundational discoveries have been awarded such accolades.
“The scientific glory is more often associated with the downstream applications,” said Ronai. “The importance of basic research can get lost. But it is the foundation for any future application, such as drug development.”
As funding is increasingly funneled toward applied research, basic science can require a certain persistence. What this under-appreciation can obscure is the pathway to discovery — which is often as compelling as the end result, full of unpredictable twists, turns, and even interpersonal intrigue.
And then there’s the fascinating — and definitely complicated — phenomenon of multiple independent discoveries.
As in: What happens when two independent teams discover the same thing at the same time?
Back to Yanagisawa’s Lab ...
... where he and his team learned a few things about those new neuropeptides. Rat brain studies pinpointed the lateral hypothalamus as the peptides’ area of activity — a region often called the brain’s feeding center.
“If you destroy that part of the brain, animals lose appetite,” said Yanagisawa. So these peptides must control feeding, the scientists thought.
Sure enough, injecting the proteins into rat brains led the rodents to start eating.
Satisfied, the team named them “orexin-A” and “orexin-B,” for the Greek word “orexis,” meaning appetite. The brain receptors became “orexin-1” and “orexin-2.” The team prepared to publish its findings in Cell.
But another group beat them to it.
Introducing the ‘Hypocretins’
In early January 1998, a team of Scripps Research Institute scientists, led by J. Gregor Sutcliffe, PhD, released a paper in the journal PNAS. They described a gene encoding for the precursor to two neuropeptides
As the peptides were in the hypothalamus and structurally like secretin (a gut hormone), they called them “hypocretins.” The hypocretin peptides excited neurons in the hypothalamus, and later that year, the scientists discovered that the neurons’ branches extended, tentacle-like, throughout the brain. “Many of the connected areas were involved in sleep-wake control,” said Thomas Kilduff, PhD, who joined the Sutcliffe lab just weeks before the hypocretin discovery. At the time, however, the significance of this finding was not yet clear.
Weeks later, in February 1998, Yanagisawa’s paper came out.
Somehow, two groups, over 1000 miles apart, had stumbled on the same neuropeptides at the same time.
“I first heard about [Yanagisawa’s] paper on NBC Nightly News,” recalls Kilduff. “I was skiing in the mountains, so I had to wait until Monday to get back to the lab to see what the paper was all about.”
He realized that Yanagisawa’s orexin was his lab’s hypocretin, although the study didn’t mention another team’s discovery.
“There may have been accusations. But as far as I know, it’s because [Yanagisawa] didn’t know [about the other paper],” said Willie. “This was not something he produced in 2 months. This was clearly years of work.”
‘Multiple Discovery’ Happens More Often Than You Think
In the mid-20th century, sociologist Robert Merton described the phenomenon of “multiple discovery,” where many scientific discoveries or inventions are made independently at roughly the same time.
“This happens much more frequently in scientific research than people suppose,” said David Pendlebury, head of research analysis at Clarivate’s Institute for Scientific Information, the analytics company’s research arm. (Last year, Pendlebury flagged the hypocretin/orexin discovery for Clarivate’s prestigious Citations Laureates award, an honor that aims to predict, often successfully, who will go on to win the Nobel Prize.)
“People have this idea of the lone researcher making a brilliant discovery,” Pendlebury said. “But more and more, teams find things at the same time.”
While this can — and does — lead to squabbling about who deserves credit, the desire to be first can also be highly motivating, said Mike Schneider, PhD, an assistant professor of philosophy at the University of Missouri, Columbia, who studies the social dynamics of science, potentially leading to faster scientific advancement.
The downside? If two groups produce the same or similar results, but one publishes first, scientific journals tend to reject the second, citing a lack of novelty.
Yet duplicating research is a key step in confirming the validity of a discovery.
That’s why, in 2018, the journal PLOS Biology created a provision for “scooped” scientists, allowing them to submit their paper within 6 months of the first as a complementary finding. Instead of viewing this as redundancy, the editors believe it adds robustness to the research.
‘What the Heck Is This Mouse Doing?’
Even though he’d been scooped, Yanagisawa forged on to the next challenge: Confirming whether orexin regulated feeding.
He began breeding mice missing the orexin gene. His team expected these “knockout” mice to eat less, resulting in a thinner body than other rodents. To the contrary, “they were on average fatter,” said Willie. “They were eating less but weighed more, indicating a slower metabolism.”
The researchers were befuddled. “We were really disappointed, almost desperate about what to do,” said Yanagisawa.
As nocturnal animals eat more at night, he decided they should study the mice after dark. One of his students, Richard Chemelli, MD, bought an infrared video camera from Radio Shack, filming the first 4 hours of the mice’s active period for several nights.
After watching the footage, “Rick called me and said, ‘Let’s get into the lab,’ ” said Willie. “It was four of us on a Saturday looking at these videos, saying, ‘What the heck is this mouse doing?’ ”
While exploring their habitat, the knockout mice would randomly fall over, pop back up after a minute or so, and resume normal activity. This happened over and over — and the scientists were unsure why.
They began monitoring the mice’s brains during these episodes — and made a startling discovery.
The mice weren’t having seizures. They were shifting directly into REM sleep, bypassing the non-REM stage, then quickly toggling back to wake mode.
“That’s when we knew these animals had something akin to narcolepsy,” said Willie.
The team recruited Thomas Scammell, MD, a Harvard neurologist, to investigate whether modafinil — an anti-narcoleptic drug without a clear mechanism — affected orexin neurons.
Two hours after injecting the mice with the medication, the scientists sacrificed them and stained their brains. Remarkably, the number of neurons showing orexin activity had increased ninefold. It seemed modafinil worked by activating the orexin system.
These findings had the potential to crack open the science of narcolepsy, one of the most mysterious sleep disorders.
Unless, of course, another team did it first.
The Mystery of Narcolepsy
Yet another multiple discovery, narcolepsy was first described by two scientists — one in Germany, the other in France — within a short span in the late 1800s.
It would be more than a hundred years before anyone understood the disorder’s cause, even though it affects about 1 in 2000 people.
“Patients were often labeled as lazy and malingerers,” said Kilduff, “since they were sleepy all the time and had this weird motor behavior called cataplexy” or the sudden loss of muscle tone.
In the early 1970s, William Dement, MD, PhD — “the father of sleep medicine” — was searching for a narcoleptic cat to study. He couldn’t find a feline, but several colleagues mentioned dogs with narcolepsy-like symptoms.
Dement, who died in 2020, had found his newest research subjects.
In 1973, he started a narcoleptic dog colony at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California. At first, he focused on poodles and beagles. After discovering their narcolepsy wasn’t genetic, he pivoted to dobermans and labradors. Their narcolepsy was inherited, so he could breed them to populate the colony.
Although human narcolepsy is rarely genetic, it’s otherwise a lot like the version in these dogs.
Both involve daytime sleepiness, “pathological” bouts of REM sleep, and the loss of muscle tone in response to emotions, often positive ones.
The researchers hoped the canines could unlock a treatment for human narcolepsy. They began laying out a path of dog kibble, then injecting the dogs with drugs such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. They wanted to see what might help them stay awake as they excitedly chowed down.
Kilduff also started a molecular genetics program, trying to identify the genetic defect behind canine narcolepsy. But after a parvovirus outbreak, Kilduff resigned from the project, drained from the strain of seeing so many dogs die.
A decade after his departure from the dog colony, his work would dramatically intersect with that of his successor, Emmanuel Mignot, MD, PhD.
“I thought I had closed the narcolepsy chapter in my life forever,” said Kilduff. “Then in 1998, we described this novel neuropeptide, hypocretin, that turned out to be the key to understanding the disorder.”
Narcoleptic Dogs in California, Mutant Mice in Texas
It was modafinil — the same anti-narcoleptic drug Yanagisawa’s team studied — that brought Emmanuel Mignot to the United States. After training as a pharmacologist in France, his home country sent him to Stanford to study the drug, which was discovered by French scientists, as his required military service.
As Kilduff’s replacement at the dog colony, his goal was to figure out how modafinil worked, hoping to attract a US company to develop the drug.
The plan succeeded. Modafinil became Provigil, a billion-dollar narcolepsy drug, and Mignot became “completely fascinated” with the disorder.
“I realized quickly that there was no way we’d find the cause of narcolepsy by finding the mode of action of this drug,” Mignot said. “Most likely, the drug was acting downstream, not at the cause of the disorder.”
To discover the answer, he needed to become a geneticist. And so began his 11-year odyssey to find the cause of canine narcolepsy.
After mapping the dog genome, Mignot set out to find the smallest stretch of chromosome that the narcoleptic animals had in common. “For a very long time, we were stuck with a relatively large region [of DNA],” he recalls. “It was a no man’s land.”
Within that region was the gene for the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor — the same receptor that Yanagisawa had identified in his first orexin paper. Mignot didn’t immediately pursue that gene as a possibility — even though his students suggested it. Why?
“The decision was simply: Should we lose time to test a possible candidate [gene] among many?” Mignot said.
As Mignot studied dog DNA in California, Yanagisawa was creating mutant mice in Texas. Unbeknownst to either scientist, their work was about to converge.
What Happened Next Is Somewhat Disputed
After diagnosing his mice with narcolepsy, Yanagisawa opted not to share this finding with Mignot, though he knew about Mignot’s interest in the condition. Instead, he asked a colleague to find out how far along Mignot was in his genetics research.
According to Yanagisawa, his colleague didn’t realize how quickly DNA sequencing could happen once a target gene was identified. At a sleep meeting, “he showed Emmanuel all of our raw data. Almost accidentally, he disclosed our findings,” he said. “It was a shock for me.”
Unsure whether he was part of the orexin group, Mignot decided not to reveal that he’d identified the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor gene as the faulty one in his narcoleptic dogs.
Although he didn’t share this finding, Mignot said he did offer to speak with the lead researcher to see if their findings were the same. If they were, they could jointly submit their articles. But Mignot never heard back.
Meanwhile, back at his lab, Mignot buckled down. While he wasn’t convinced the mouse data proved anything, it did give him the motivation to move faster.
Within weeks, he submitted his findings to Cell, revealing a mutation in the hypocretin/orexin-2 receptor gene as the cause of canine narcolepsy. According to Yanagisawa, the journal’s editor invited him to peer-review the paper, tipping him off to its existence.
“I told him I had a conflict of interest,” said Yanagisawa. “And then we scrambled to finish our manuscript. We wrote up the paper within almost 5 days.”
For a moment, it seemed both papers would be published together in Cell. Instead, on August 6, 1999, Mignot’s study was splashed solo across the journal’s cover.
“At the time, our team was pissed off, but looking back, what else could Emmanuel have done?” said Willie, who was part of Yanagisawa’s team. “The grant he’d been working on for years was at risk. He had it within his power to do the final experiments. Of course he was going to finish.”
Two weeks later, Yanagisawa’s findings followed, also in Cell.
His paper proposed knockout mice as a model for human narcolepsy and orexin as a key regulator of the sleep/wake cycle. With orexin-activated neurons branching into other areas of the brain, the peptide seemed to promote wakefulness by synchronizing several arousal neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and histamine.
“If you don’t have orexin, each of those systems can still function, but they’re not as coordinated,” said Willie. “If you have narcolepsy, you’re capable of wakefulness, and you’re capable of sleep. What you can’t do is prevent inappropriately switching between states.”
Together, the two papers painted a clear picture: Narcolepsy was the result of a dysfunction in the hypocretin/orexin system.
After more than a century, the cause of narcolepsy was starting to come into focus.
“This was blockbuster,” said Willie.
By itself, either finding — one in dogs, one in mice — might have been met with skepticism. But in combination, they offered indisputable evidence about narcolepsy’s cause.
The Human Brains in Your Fridge Hold Secrets
Jerome Siegel had been searching for the cause of human narcolepsy for years. A PhD and professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, he had managed to acquire four human narcoleptic brains. As laughter is often the trigger for the sudden shift to REM sleep in humans, he focused on the amygdala, an area linked to emotion.
“I looked in the amygdala and didn’t see anything,” he said. “So the brains stayed in my refrigerator for probably 10 years.”
Then he was invited to review Yanagisawa’s study in Cell. The lightbulb clicked on: Maybe the hypothalamus — not the amygdala — was the area of abnormality. He and his team dug out the decade-old brains.
When they stained the brains, the massive loss of hypocretin-activated neurons was hard to miss: On average, the narcoleptic brains had only about 7000 of the cells versus 70,000 in the average human brain. The scientists also noticed scar tissue in the hypothalamus, indicating that the neurons had at some point died, rather than being absent from birth.
What Siegel didn’t know: Mignot had also acquired a handful of human narcoleptic brains.
Already, he had coauthored a study showing that hypocretin/orexin was undetectable in the cerebrospinal fluid of the majority of the people with narcolepsy his team tested. It seemed clear that the hypocretin/orexin system was flawed — or even broken — in people with the condition.
“It looked like the cause of narcolepsy in humans was indeed this lack of orexin in the brain,” he said. “That was the hypothesis immediately. To me, this is when we established that narcolepsy in humans was due to a lack of orexin. The next thing was to check that the cells were missing.”
Now he could do exactly that.
As expected, Mignot’s team observed a dramatic loss of hypocretin/orexin cells in the narcoleptic brains. They also noticed that a different cell type in the hypothalamus was unaffected. This implied the damage was specific to the hypocretin-activated cells and supported a hunch they already had: That the deficit was the result not of a genetic defect but of an autoimmune attack. (It’s a hypothesis Mignot has spent the last 15 years proving.)
It wasn’t until a gathering in Hawaii, in late August 2000, that the two realized the overlap of their work.
To celebrate his team’s finding, Mignot had invited a group of researchers to Big Island. With his paper scheduled for publication on September 1, he felt comfortable presenting his findings to his guests, which included Siegel.
Until then, “I didn’t know what he had found, and he didn’t know what I had found, which basically was the same thing,” said Siegel.
In yet another strange twist, the two papers were published just weeks apart, simultaneously revealing that human narcoleptics have a depleted supply of the neurons that bind to hypocretin/orexin. The cause of the disorder was at last a certainty.
“Even if I was first, what does it matter? In the end, you need confirmation,” said Mignot. “You need multiple people to make sure that it’s true. It’s good science when things like this happen.”
How All of This Changed Medicine
Since these groundbreaking discoveries, the diagnosis of narcolepsy has become much simpler. Lab tests can now easily measure hypocretin in cerebrospinal fluid, providing a definitive diagnosis.
But the development of narcolepsy treatments has lagged — even though hypocretin/orexin replacement therapy is the obvious answer.
“Almost 25 years have elapsed, and there’s no such therapeutic on the market,” said Kilduff, who now works for SRI International, a non-profit research and development institute.
That’s partly because agonists — drugs that bind to receptors in the brain — are challenging to create, as this requires mimicking the activating molecule’s structure, like copying the grooves of an intricate key.
Antagonists, by comparison, are easier to develop. These act as a gate, blocking access to the receptors. As a result, drugs that promote sleep by thwarting hypocretin/orexin have emerged more quickly, providing a flurry of new options for people with insomnia. The first, suvorexant, was launched in 2014. Two others followed in recent years.
Researchers are hopeful a hypocretin/orexin agonist is on the horizon.
“This is a very hot area of drug development,” said Kilduff. “It’s just a matter of who’s going to get the drug to market first.”
One More Hypocretin/Orexin Surprise — and It Could Be The Biggest
Several years ago, Siegel’s lab received what was supposed to be a healthy human brain — one they could use as a comparison for narcoleptic brains. But researcher Thomas Thannickal, PhD, lead author of the UCLA study linking hypocretin loss to human narcolepsy, noticed something strange: This brain had significantly more hypocretin neurons than average.
Was this due to a seizure? A traumatic death? Siegel called the brain bank to request the donor’s records. He was told they were missing.
Years later, Siegel happened to be visiting the brain bank for another project and found himself in a room adjacent to the medical records. “Nobody was there,” he said, “so I just opened a drawer.”
Shuffling through the brain bank’s files, Siegel found the medical records he’d been told were lost. In the file was a note from the donor, explaining that he was a former heroin addict.
“I almost fell out of my chair,” said Siegel. “I realized this guy’s heroin addiction likely had something to do with his very unusual brain.”
Obviously, opioids affected the orexin system. But how?
“It’s when people are happy that this peptide is released,” said Siegel. “The hypocretin system is not just related to alertness. It’s related to pleasure.”
As Yanagisawa observed early on, hypocretin/orexin does indeed play a role in eating — just not the one he initially thought. The peptides prompted pleasure seeking. So the rodents ate.
In 2018, after acquiring five more brains, Siegel’s group published a study in Translational Medicine showing 54% more detectable hypocretin neurons in the brains of heroin addicts than in those of control individuals.
In 2022, another breakthrough: His team showed that morphine significantly altered the pathways of hypocretin neurons in mice, sending their axons into brain regions associated with addiction. Then, when they removed the mice’s hypocretin neurons and discontinued their daily morphine dose, the rodents showed no symptoms of opioid withdrawal.
This fits the connection with narcolepsy: Among the standard treatments for the condition are amphetamines and other stimulants, which all have addictive potential. Yet, “narcoleptics never abuse these drugs,” Siegel said. “They seem to be uniquely resistant to addiction.”
This could powerfully change the way opioids are administered.
“If you prevent the hypocretin response to opioids, you may be able to prevent opioid addiction,” said Siegel. In other words, blocking the hypocretin system with a drug like those used to treat insomnia may allow patients to experience the pain-relieving benefits of opioids — without the risk for addiction.
His team is currently investigating treatments targeting the hypocretin/orexin system for opioid addiction.
In a study published in July, they found that mice who received suvorexant — the drug for insomnia — didn’t anticipate their daily dose of opioids the way other rodents did. This suggests the medication prevented addiction, without diminishing the pain-relieving effect of opioids.
If it translates to humans, this discovery could potentially save millions of lives.
“I think it’s just us working on this,” said Siegel.
But with hypocretin/orexin, you never know.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Mortality Not Higher for Patients With Autoimmune Disease on Checkpoint Inhibitors
WASHINGTON — Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy does not increase mortality in people with preexisting autoimmune diseases, new research has found.
Results from a large database analysis of patients with and without autoimmune diseases suggest it is safe to treat them with ICI if they develop a cancer for which it is indicated, Greg Challener, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Rheumatology and Allergy Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the American College of Rheumatology 2024 Annual Meeting.
“One message is that, when rheumatologists are asked by oncologists about patients with rheumatoid arthritis or vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases and whether it’s safe to treat them with immune checkpoint inhibitors, this result provides some evidence that it probably is safe…. Checkpoint inhibitors are really incredible drugs, and they’ve improved mortality for a lot of cancers, particularly melanoma, and so I think there should be a pretty high threshold for us to say a patient shouldn’t receive them because of an autoimmune condition,” he told this news organization.
Another implication, Challener said, is that people with autoimmune diseases shouldn’t routinely be excluded from clinical trials of ICIs. Currently they are excluded because of concerns about exacerbation of underlying autoimmunity, possible interference between the ICI and the immunosuppressive drugs used to treat the autoimmune condition, and a theoretical risk for serious adverse events.
“Clinical trials are continuing to exclude these patients, and they paint with a very broad brush anyone with underlying autoimmunity ... I’m hoping that that changes. I don’t think there’s a great evidence base to support that practice, and it’s unfortunate that patients with underlying autoimmune diseases are excluded from important studies,” Challener said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, told this news organization that he agrees the data are generally reassuring. “If one of our patients gets cancer and their oncologist wants to use a checkpoint inhibitor, we’d obviously still monitor them for complications, but we wouldn’t automatically assume the combination of a checkpoint inhibitor and autoimmune disease would increase their mortality.”
No Difference in Mortality for Those With and Without Autoimmune Disease
Challener and colleagues used administrative health data from the TriNetX Diamond network of 92 US healthcare sites with 212 million patients. All patients included in the study were receiving anti-programmed death protein 1/programmed death ligand 1 to treat malignancies involving the skin, lung/bronchus, digestive organs, or urinary tract. The study population also had at least one rheumatologic, gastrointestinal, neurologic, dermatologic, or endocrine autoimmune disease.
Propensity score matching between those with and without autoimmune disease was performed for about 100 covariates. Prior to the matching, the autoimmune disease group had significantly higher rates of cardiovascular and other comorbidities. The matching yielded 23,714 individuals with autoimmune disease and the same number without who had similar demographics and comorbidity rates, as well as malignancy type, alcohol/tobacco use, and medication use.
At a median follow-up of 250 days, the risk for mortality prior to propensity matching was 40.0% in the autoimmune disease group and 38.1% for those without, a significant difference with hazard ratio 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.10). But after the matching, the difference was no longer significant: 39.8% vs 40.2%, respectively (0.97, 0.94-1.00).
The Kaplan-Meier curves for survival probability for those with or without autoimmune disease were nearly superimposed, showing no difference up to 1600 days. An analysis of just the patients with rheumatic diseases yielded similar results, Challener said.
Some Caveats About the Data
Jeffries, who is also an associate professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and the Oklahoma VA, said he would like to see additional data on outcomes, both for the autoimmune conditions and the cancers. Challener said there are plans to look at other hard endpoints such as myocardial infarction and end-stage renal disease, but that the database is limited.
Both Challener and Jeffries also cautioned that the reassurance may not apply to patients with active disease.
“One thing this research doesn’t address is whether active autoimmune disease might have a different outcome compared to more kind of quiet disease…. If you have a patient who has extremely active rheumatoid arthritis or extremely active giant cell arthritis, for instance, I think that could be more challenging. I would be frightened to put a patient with really active GCA on pembrolizumab or say that it’s safe without their disease being controlled. But for someone who has well-controlled disease or minimally active disease, this is very reassuring,” Challener told this news organization.
“I think this may also be important in that it’s a good argument to tell the drug companies to include autoimmune patients in these trials so we can get better data,” Jeffries said.
Challener and Jeffries had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy does not increase mortality in people with preexisting autoimmune diseases, new research has found.
Results from a large database analysis of patients with and without autoimmune diseases suggest it is safe to treat them with ICI if they develop a cancer for which it is indicated, Greg Challener, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Rheumatology and Allergy Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the American College of Rheumatology 2024 Annual Meeting.
“One message is that, when rheumatologists are asked by oncologists about patients with rheumatoid arthritis or vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases and whether it’s safe to treat them with immune checkpoint inhibitors, this result provides some evidence that it probably is safe…. Checkpoint inhibitors are really incredible drugs, and they’ve improved mortality for a lot of cancers, particularly melanoma, and so I think there should be a pretty high threshold for us to say a patient shouldn’t receive them because of an autoimmune condition,” he told this news organization.
Another implication, Challener said, is that people with autoimmune diseases shouldn’t routinely be excluded from clinical trials of ICIs. Currently they are excluded because of concerns about exacerbation of underlying autoimmunity, possible interference between the ICI and the immunosuppressive drugs used to treat the autoimmune condition, and a theoretical risk for serious adverse events.
“Clinical trials are continuing to exclude these patients, and they paint with a very broad brush anyone with underlying autoimmunity ... I’m hoping that that changes. I don’t think there’s a great evidence base to support that practice, and it’s unfortunate that patients with underlying autoimmune diseases are excluded from important studies,” Challener said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, told this news organization that he agrees the data are generally reassuring. “If one of our patients gets cancer and their oncologist wants to use a checkpoint inhibitor, we’d obviously still monitor them for complications, but we wouldn’t automatically assume the combination of a checkpoint inhibitor and autoimmune disease would increase their mortality.”
No Difference in Mortality for Those With and Without Autoimmune Disease
Challener and colleagues used administrative health data from the TriNetX Diamond network of 92 US healthcare sites with 212 million patients. All patients included in the study were receiving anti-programmed death protein 1/programmed death ligand 1 to treat malignancies involving the skin, lung/bronchus, digestive organs, or urinary tract. The study population also had at least one rheumatologic, gastrointestinal, neurologic, dermatologic, or endocrine autoimmune disease.
Propensity score matching between those with and without autoimmune disease was performed for about 100 covariates. Prior to the matching, the autoimmune disease group had significantly higher rates of cardiovascular and other comorbidities. The matching yielded 23,714 individuals with autoimmune disease and the same number without who had similar demographics and comorbidity rates, as well as malignancy type, alcohol/tobacco use, and medication use.
At a median follow-up of 250 days, the risk for mortality prior to propensity matching was 40.0% in the autoimmune disease group and 38.1% for those without, a significant difference with hazard ratio 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.10). But after the matching, the difference was no longer significant: 39.8% vs 40.2%, respectively (0.97, 0.94-1.00).
The Kaplan-Meier curves for survival probability for those with or without autoimmune disease were nearly superimposed, showing no difference up to 1600 days. An analysis of just the patients with rheumatic diseases yielded similar results, Challener said.
Some Caveats About the Data
Jeffries, who is also an associate professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and the Oklahoma VA, said he would like to see additional data on outcomes, both for the autoimmune conditions and the cancers. Challener said there are plans to look at other hard endpoints such as myocardial infarction and end-stage renal disease, but that the database is limited.
Both Challener and Jeffries also cautioned that the reassurance may not apply to patients with active disease.
“One thing this research doesn’t address is whether active autoimmune disease might have a different outcome compared to more kind of quiet disease…. If you have a patient who has extremely active rheumatoid arthritis or extremely active giant cell arthritis, for instance, I think that could be more challenging. I would be frightened to put a patient with really active GCA on pembrolizumab or say that it’s safe without their disease being controlled. But for someone who has well-controlled disease or minimally active disease, this is very reassuring,” Challener told this news organization.
“I think this may also be important in that it’s a good argument to tell the drug companies to include autoimmune patients in these trials so we can get better data,” Jeffries said.
Challener and Jeffries had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy does not increase mortality in people with preexisting autoimmune diseases, new research has found.
Results from a large database analysis of patients with and without autoimmune diseases suggest it is safe to treat them with ICI if they develop a cancer for which it is indicated, Greg Challener, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Rheumatology and Allergy Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said at the American College of Rheumatology 2024 Annual Meeting.
“One message is that, when rheumatologists are asked by oncologists about patients with rheumatoid arthritis or vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases and whether it’s safe to treat them with immune checkpoint inhibitors, this result provides some evidence that it probably is safe…. Checkpoint inhibitors are really incredible drugs, and they’ve improved mortality for a lot of cancers, particularly melanoma, and so I think there should be a pretty high threshold for us to say a patient shouldn’t receive them because of an autoimmune condition,” he told this news organization.
Another implication, Challener said, is that people with autoimmune diseases shouldn’t routinely be excluded from clinical trials of ICIs. Currently they are excluded because of concerns about exacerbation of underlying autoimmunity, possible interference between the ICI and the immunosuppressive drugs used to treat the autoimmune condition, and a theoretical risk for serious adverse events.
“Clinical trials are continuing to exclude these patients, and they paint with a very broad brush anyone with underlying autoimmunity ... I’m hoping that that changes. I don’t think there’s a great evidence base to support that practice, and it’s unfortunate that patients with underlying autoimmune diseases are excluded from important studies,” Challener said.
Asked to comment, session moderator Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, told this news organization that he agrees the data are generally reassuring. “If one of our patients gets cancer and their oncologist wants to use a checkpoint inhibitor, we’d obviously still monitor them for complications, but we wouldn’t automatically assume the combination of a checkpoint inhibitor and autoimmune disease would increase their mortality.”
No Difference in Mortality for Those With and Without Autoimmune Disease
Challener and colleagues used administrative health data from the TriNetX Diamond network of 92 US healthcare sites with 212 million patients. All patients included in the study were receiving anti-programmed death protein 1/programmed death ligand 1 to treat malignancies involving the skin, lung/bronchus, digestive organs, or urinary tract. The study population also had at least one rheumatologic, gastrointestinal, neurologic, dermatologic, or endocrine autoimmune disease.
Propensity score matching between those with and without autoimmune disease was performed for about 100 covariates. Prior to the matching, the autoimmune disease group had significantly higher rates of cardiovascular and other comorbidities. The matching yielded 23,714 individuals with autoimmune disease and the same number without who had similar demographics and comorbidity rates, as well as malignancy type, alcohol/tobacco use, and medication use.
At a median follow-up of 250 days, the risk for mortality prior to propensity matching was 40.0% in the autoimmune disease group and 38.1% for those without, a significant difference with hazard ratio 1.07 (95% CI, 1.05-1.10). But after the matching, the difference was no longer significant: 39.8% vs 40.2%, respectively (0.97, 0.94-1.00).
The Kaplan-Meier curves for survival probability for those with or without autoimmune disease were nearly superimposed, showing no difference up to 1600 days. An analysis of just the patients with rheumatic diseases yielded similar results, Challener said.
Some Caveats About the Data
Jeffries, who is also an associate professor of medicine at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, and the Oklahoma VA, said he would like to see additional data on outcomes, both for the autoimmune conditions and the cancers. Challener said there are plans to look at other hard endpoints such as myocardial infarction and end-stage renal disease, but that the database is limited.
Both Challener and Jeffries also cautioned that the reassurance may not apply to patients with active disease.
“One thing this research doesn’t address is whether active autoimmune disease might have a different outcome compared to more kind of quiet disease…. If you have a patient who has extremely active rheumatoid arthritis or extremely active giant cell arthritis, for instance, I think that could be more challenging. I would be frightened to put a patient with really active GCA on pembrolizumab or say that it’s safe without their disease being controlled. But for someone who has well-controlled disease or minimally active disease, this is very reassuring,” Challener told this news organization.
“I think this may also be important in that it’s a good argument to tell the drug companies to include autoimmune patients in these trials so we can get better data,” Jeffries said.
Challener and Jeffries had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Two Brain Stim Methods Better Than One for Depression?
TOPLINE:
a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a double-blind, sham-controlled randomized clinical trial from 2021 to 2023 at three hospitals in China with 240 participants with MDD (mean age, 32.5 years; 58% women).
- Participants received active tDCS + active rTMS, sham tDCS + active rTMS, active tDCS + sham rTMS, or sham tDCS + sham rTMS with treatments administered five times per week for 2 weeks.
- tDCS was administered in 20-minute sessions using a 2-mA direct current stimulator, whereas rTMS involved 1600 pulses of 10-Hz stimulation targeting the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Sham treatments used a pseudostimulation coil and only emitted sound.
- The primary outcome was change in the 24-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-24) total score from baseline to week 2.
- Secondary outcomes included HDRS-24 total score change at week 4, remission rate (HDRS-24 total score ≤ 9), response rate (≥ 50% reduction in HDRS-24 total score), and adverse events.
TAKEAWAY:
- The active tDCS + active rTMS group demonstrated the greatest reduction in mean HDRS-24 score (18.33 ± 5.39) at week 2 compared with sham tDCS + active rTMS, active tDCS + sham rTMS, and sham tDCS + sham rTMS (P < .001).
- Response rates at week 2 were notably higher in the active tDCS + active rTMS group (85%) than in the active tDCS + sham rTMS (30%) and sham tDCS + sham rTMS groups (32%).
- The remission rate at week 4 reached 83% in the active tDCS + active rTMS group, which was significantly higher than the remission rates with the other interventions (P < .001).
- The treatments were well tolerated, with no serious adverse events, seizures, or manic symptoms reported across all intervention groups.
IN PRACTICE:
This trial “was the first to evaluate the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of combining tDCS and rTMS in treating depression. Future studies should focus on investigating the mechanism of this synergistic effect and improving the stimulation parameters to optimize the therapeutic effect,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Dongsheng Zhou, MD, Ningbo Kangning Hospital, Ningbo, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The brief treatment duration involving 10 sessions may have been insufficient for tDCS and rTMS to demonstrate their full antidepressant potential. The inability to regulate participants’ antidepressant medications throughout the study period presented another limitation. Additionally, the lack of stratified randomization and adjustment for center effects may have introduced variability in the results.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received support from multiple grants, including from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, Basic Public Welfare Research Project of Zhejiang Province, Ningbo Medical and Health Brand Discipline, Ningbo Clinical Medical Research Centre for Mental Health, Ningbo Top Medical and Health Research Program, and the Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan Project. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a double-blind, sham-controlled randomized clinical trial from 2021 to 2023 at three hospitals in China with 240 participants with MDD (mean age, 32.5 years; 58% women).
- Participants received active tDCS + active rTMS, sham tDCS + active rTMS, active tDCS + sham rTMS, or sham tDCS + sham rTMS with treatments administered five times per week for 2 weeks.
- tDCS was administered in 20-minute sessions using a 2-mA direct current stimulator, whereas rTMS involved 1600 pulses of 10-Hz stimulation targeting the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Sham treatments used a pseudostimulation coil and only emitted sound.
- The primary outcome was change in the 24-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-24) total score from baseline to week 2.
- Secondary outcomes included HDRS-24 total score change at week 4, remission rate (HDRS-24 total score ≤ 9), response rate (≥ 50% reduction in HDRS-24 total score), and adverse events.
TAKEAWAY:
- The active tDCS + active rTMS group demonstrated the greatest reduction in mean HDRS-24 score (18.33 ± 5.39) at week 2 compared with sham tDCS + active rTMS, active tDCS + sham rTMS, and sham tDCS + sham rTMS (P < .001).
- Response rates at week 2 were notably higher in the active tDCS + active rTMS group (85%) than in the active tDCS + sham rTMS (30%) and sham tDCS + sham rTMS groups (32%).
- The remission rate at week 4 reached 83% in the active tDCS + active rTMS group, which was significantly higher than the remission rates with the other interventions (P < .001).
- The treatments were well tolerated, with no serious adverse events, seizures, or manic symptoms reported across all intervention groups.
IN PRACTICE:
This trial “was the first to evaluate the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of combining tDCS and rTMS in treating depression. Future studies should focus on investigating the mechanism of this synergistic effect and improving the stimulation parameters to optimize the therapeutic effect,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Dongsheng Zhou, MD, Ningbo Kangning Hospital, Ningbo, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The brief treatment duration involving 10 sessions may have been insufficient for tDCS and rTMS to demonstrate their full antidepressant potential. The inability to regulate participants’ antidepressant medications throughout the study period presented another limitation. Additionally, the lack of stratified randomization and adjustment for center effects may have introduced variability in the results.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received support from multiple grants, including from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, Basic Public Welfare Research Project of Zhejiang Province, Ningbo Medical and Health Brand Discipline, Ningbo Clinical Medical Research Centre for Mental Health, Ningbo Top Medical and Health Research Program, and the Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan Project. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a double-blind, sham-controlled randomized clinical trial from 2021 to 2023 at three hospitals in China with 240 participants with MDD (mean age, 32.5 years; 58% women).
- Participants received active tDCS + active rTMS, sham tDCS + active rTMS, active tDCS + sham rTMS, or sham tDCS + sham rTMS with treatments administered five times per week for 2 weeks.
- tDCS was administered in 20-minute sessions using a 2-mA direct current stimulator, whereas rTMS involved 1600 pulses of 10-Hz stimulation targeting the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Sham treatments used a pseudostimulation coil and only emitted sound.
- The primary outcome was change in the 24-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-24) total score from baseline to week 2.
- Secondary outcomes included HDRS-24 total score change at week 4, remission rate (HDRS-24 total score ≤ 9), response rate (≥ 50% reduction in HDRS-24 total score), and adverse events.
TAKEAWAY:
- The active tDCS + active rTMS group demonstrated the greatest reduction in mean HDRS-24 score (18.33 ± 5.39) at week 2 compared with sham tDCS + active rTMS, active tDCS + sham rTMS, and sham tDCS + sham rTMS (P < .001).
- Response rates at week 2 were notably higher in the active tDCS + active rTMS group (85%) than in the active tDCS + sham rTMS (30%) and sham tDCS + sham rTMS groups (32%).
- The remission rate at week 4 reached 83% in the active tDCS + active rTMS group, which was significantly higher than the remission rates with the other interventions (P < .001).
- The treatments were well tolerated, with no serious adverse events, seizures, or manic symptoms reported across all intervention groups.
IN PRACTICE:
This trial “was the first to evaluate the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of combining tDCS and rTMS in treating depression. Future studies should focus on investigating the mechanism of this synergistic effect and improving the stimulation parameters to optimize the therapeutic effect,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Dongsheng Zhou, MD, Ningbo Kangning Hospital, Ningbo, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The brief treatment duration involving 10 sessions may have been insufficient for tDCS and rTMS to demonstrate their full antidepressant potential. The inability to regulate participants’ antidepressant medications throughout the study period presented another limitation. Additionally, the lack of stratified randomization and adjustment for center effects may have introduced variability in the results.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received support from multiple grants, including from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, Basic Public Welfare Research Project of Zhejiang Province, Ningbo Medical and Health Brand Discipline, Ningbo Clinical Medical Research Centre for Mental Health, Ningbo Top Medical and Health Research Program, and the Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan Project. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Daytime Sleepiness May Flag Predementia Risk
TOPLINE:
a new study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers included 445 older adults without dementia (mean age, 76 years; 57% women).
- Sleep components were assessed, and participants were classified as poor or good sleepers using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire.
- The primary outcome was incidence of MCR syndrome.
- The mean follow-up duration was 2.9 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 36 participants developed MCR syndrome.
- Poor sleepers had a higher risk for incident MCR syndrome, compared with good sleepers, after adjustment for age, sex, and educational level (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.6; 95% CI, 1.3-5.0; P < .05). However, this association was no longer significant after further adjustment for depressive symptoms.
- Sleep-related daytime dysfunction, defined as excessive sleepiness and lower enthusiasm for activities, was the only sleep component linked to a significant risk for MCR syndrome in fully adjusted models (aHR, 3.3; 95% CI, 1.5-7.4; P < .05).
- Prevalent MCR syndrome was not significantly associated with poor sleep quality (odds ratio, 1.1), suggesting that the relationship is unidirectional.
IN PRACTICE:
“Establishing the relationship between sleep dysfunction and MCR [syndrome] risk is important because early intervention may offer the best hope for preventing dementia,” the investigators wrote.
“Our findings emphasize the need for screening for sleep issues. There’s potential that people could get help with their sleep issues and prevent cognitive decline later in life,” lead author Victoire Leroy, MD, PhD, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, added in a press release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the lack of objective sleep measurements and potential recall bias in self-reported sleep complaints, particularly among participants with cognitive issues. In addition, the relatively short follow-up period may have resulted in a lower number of incident MCR syndrome cases. The sample population was also predominantly White (80%), which may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging. No conflicts of interest were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
a new study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers included 445 older adults without dementia (mean age, 76 years; 57% women).
- Sleep components were assessed, and participants were classified as poor or good sleepers using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire.
- The primary outcome was incidence of MCR syndrome.
- The mean follow-up duration was 2.9 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 36 participants developed MCR syndrome.
- Poor sleepers had a higher risk for incident MCR syndrome, compared with good sleepers, after adjustment for age, sex, and educational level (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.6; 95% CI, 1.3-5.0; P < .05). However, this association was no longer significant after further adjustment for depressive symptoms.
- Sleep-related daytime dysfunction, defined as excessive sleepiness and lower enthusiasm for activities, was the only sleep component linked to a significant risk for MCR syndrome in fully adjusted models (aHR, 3.3; 95% CI, 1.5-7.4; P < .05).
- Prevalent MCR syndrome was not significantly associated with poor sleep quality (odds ratio, 1.1), suggesting that the relationship is unidirectional.
IN PRACTICE:
“Establishing the relationship between sleep dysfunction and MCR [syndrome] risk is important because early intervention may offer the best hope for preventing dementia,” the investigators wrote.
“Our findings emphasize the need for screening for sleep issues. There’s potential that people could get help with their sleep issues and prevent cognitive decline later in life,” lead author Victoire Leroy, MD, PhD, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, added in a press release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the lack of objective sleep measurements and potential recall bias in self-reported sleep complaints, particularly among participants with cognitive issues. In addition, the relatively short follow-up period may have resulted in a lower number of incident MCR syndrome cases. The sample population was also predominantly White (80%), which may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging. No conflicts of interest were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
a new study shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers included 445 older adults without dementia (mean age, 76 years; 57% women).
- Sleep components were assessed, and participants were classified as poor or good sleepers using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire.
- The primary outcome was incidence of MCR syndrome.
- The mean follow-up duration was 2.9 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- During the study period, 36 participants developed MCR syndrome.
- Poor sleepers had a higher risk for incident MCR syndrome, compared with good sleepers, after adjustment for age, sex, and educational level (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.6; 95% CI, 1.3-5.0; P < .05). However, this association was no longer significant after further adjustment for depressive symptoms.
- Sleep-related daytime dysfunction, defined as excessive sleepiness and lower enthusiasm for activities, was the only sleep component linked to a significant risk for MCR syndrome in fully adjusted models (aHR, 3.3; 95% CI, 1.5-7.4; P < .05).
- Prevalent MCR syndrome was not significantly associated with poor sleep quality (odds ratio, 1.1), suggesting that the relationship is unidirectional.
IN PRACTICE:
“Establishing the relationship between sleep dysfunction and MCR [syndrome] risk is important because early intervention may offer the best hope for preventing dementia,” the investigators wrote.
“Our findings emphasize the need for screening for sleep issues. There’s potential that people could get help with their sleep issues and prevent cognitive decline later in life,” lead author Victoire Leroy, MD, PhD, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, added in a press release.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in Neurology.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the lack of objective sleep measurements and potential recall bias in self-reported sleep complaints, particularly among participants with cognitive issues. In addition, the relatively short follow-up period may have resulted in a lower number of incident MCR syndrome cases. The sample population was also predominantly White (80%), which may have limited the generalizability of the findings to other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging. No conflicts of interest were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Impact and Recovery of VHA Epilepsy Care Services During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic affected diverse workplaces globally, leading to temporary and permanent changes across the health care landscape. Included among the impacted areas of care were epilepsy and electroencephalogram (EEG) clinicians and services. Surveys among epilepsy specialists and neurophysiologists conducted at the onset of the pandemic to evaluate working conditions include analyses from the American Epilepsy Society (AES), the National Association of Epilepsy Centers (NAEC), the International League Against Epilepsy, and an Italian national survey.1-4 These investigations revealed reductions in epilepsy monitoring unit (EMU) admissions (23% decline), epilepsy surgery (6% decline), inpatient EEG (22% of respondents reported decline), and patients having difficulty accessing epilepsy professionals (28% of respondents reported decline) or obtaining medications (20% of respondents reported decline).1-3
While such research provided evidence for changes to epilepsy care in 2020, there are limited data on subsequent adaptations during the pandemic. These studies did not incorporate data on the spread of COVID-19 or administrative workload numbers to analyze service delivery beyond self reports. This study aimed to address this gap in the literature by highlighting results from longitudinal national surveys conducted at the Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE), a specialty care service within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), which annually serves > 9 million veterans.5 The ECoE represents epileptologists and neurophysiologists across the United States at the 17 primary facilities that were established at the time of this survey (2 ECoEs have been added since survey completion) in 4 geographical regions and for which other regional facilities refer patients for diagnostic services or specialty care.6
National surveys were conducted among the ECoE directors regarding adaptations made from May 2020 to June 2022 to provide a comprehensive account of limitations they experienced and how adjustments have been made to improve patient care. Survey responses were compared to administrative workload numbers and COVID-19 spread data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to provide a comprehensive analysis of performance during the pandemic.
METHODS
Data were collected as part of a quality improvement initiative by the VHA ECoE; institutional review board approval was not required. An 18-item survey covering 5 broad domains was sent to ECoE directors 4 separate times to accumulate data from 4 time periods: May to June 2020 (T1); December 2020 to February 2021 (T2); July to August 2021 (T3); and June to July 2022 (T4). These periods correspond to the following phases of the pandemic: T1, onset of pandemic; T2, vaccine availability; T3, Delta variant predominant; T4, Omicron variant predominant.
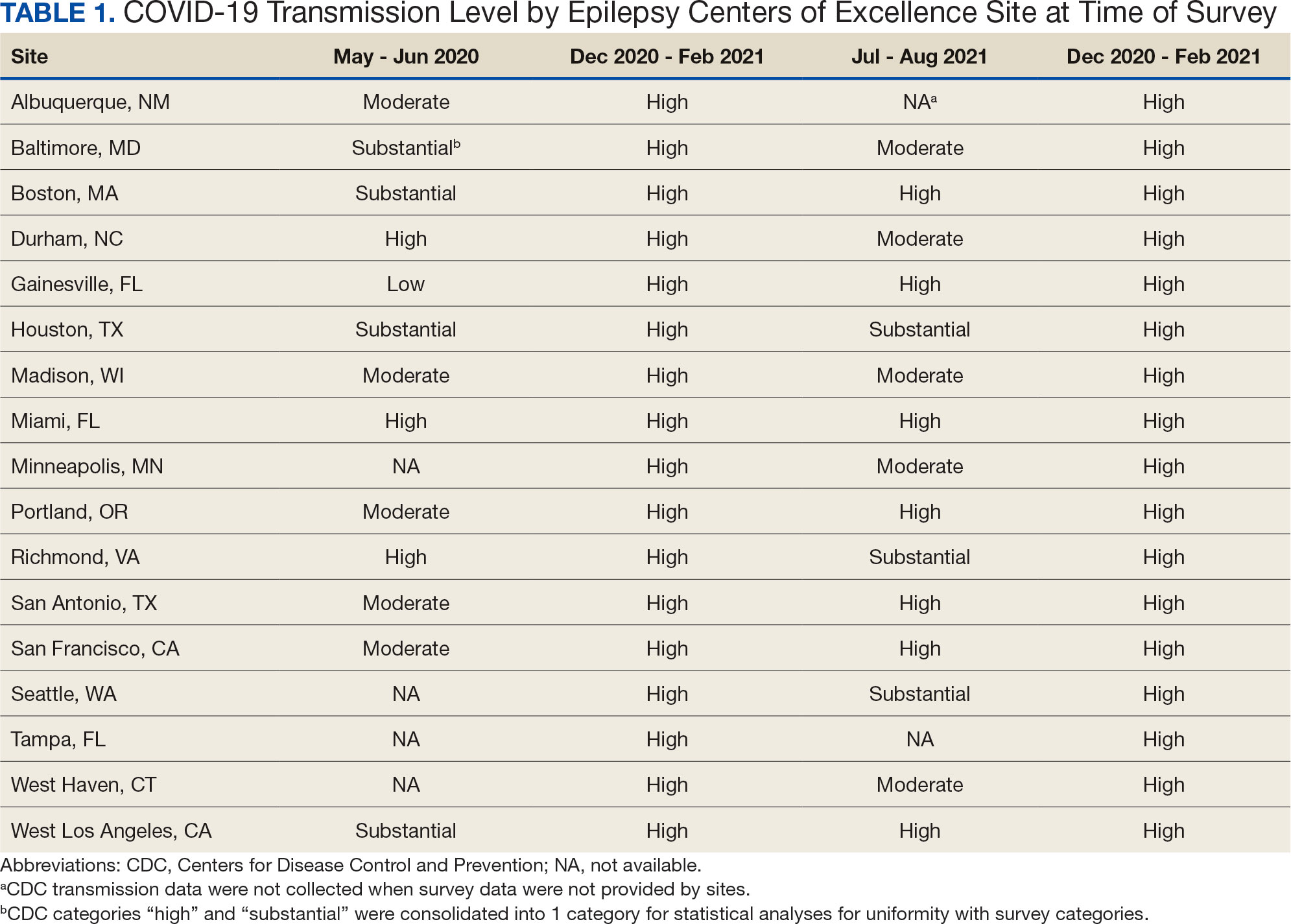
Data on the spread of COVID-19 were collected from the CDC archived dataset, US COVID-19 County Level of Community Transmission Historical Changes (Table 1).7 Administrative workload (patient counts) for EEG, EMU, and outpatient clinics were extracted from VHA administrative databases for the participating sites for the months prior to each survey: T1, April 2020; T2, November 2020; T3, June 2021; and T4, May 2022 (Table 2).
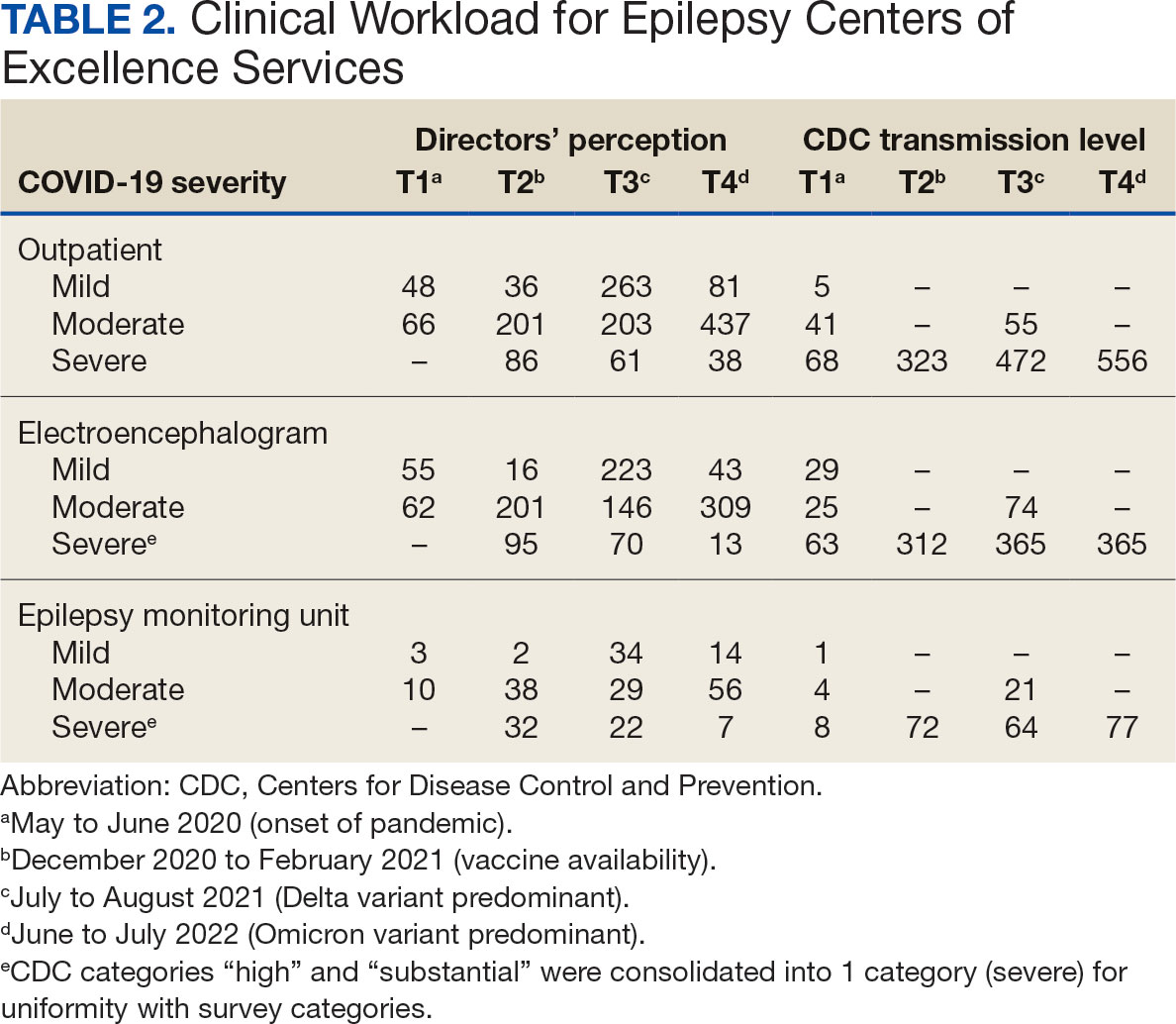
Survey Structure and Content
The survey was developed by the ECoE and was not validated prior to its use due to the time-sensitive nature of gathering information during the pandemic. The first survey (T1) was an emailed spreadsheet with open-ended questions to gauge availability of services (ie, outpatient clinic, EEG, EMU), assess whether safety precautions were being introduced, and understand whether national or local guidelines were thought to be helpful. Responses from this and subsequent surveys were standardized into yes/no and multiple choice formats. Subsequent surveys were administered online using a Research Electronic Data Capture tool.8,9
Availability of outpatient epilepsy services across the 4 time periods were categorized as unlimited (in-person with no restrictions), limited (in-person with restrictions), planned (not currently performed but scheduled for the near future), and unavailable (no in-person services offered) (eAppendices 1-6, available in article PDF).
Statistical Analyses
Analyses were performed to compare survey responses to workload and CDC data on COVID-19 community spread. The following associations were examined: (1) CDC COVID-19 spread vs respondents’ perception of spread; (2) respondents’ perception of spread vs availability of services; (3) CDC COVID-19 spread vs availability of services; (4) respondents’ perception of spread vs workload; and (5) CDC COVID-19 spread vs workload. Availability of services was dichotomized for analyses, with limited or fully available services classified as available. As services were mostly open at T3 regardless of the spread of the virus, and the CDC COVID-19 spread classification for all sites was severe or high at T2 and T4, corresponding associations were not tested at these time points. For associations 1 through 3, Fisher exact tests were used; for associations 4 and 5, Mann-Whitney U tests (where the COVID-19 spread fell into 2 categories) and Kruskal-Wallis tests (for 3 categories of COVID-19 spread) were performed. All tests were 2-tailed and performed at 0.05 error rate. Bonferroni corrections were applied to adjust P values for multiple hypotheses tests.
RESULTS
From the 17 sites invited, responses at each time point were obtained from 13 (T1),17 (T2), 15 (T3), and 16 (T4) centers. There was no significant association between self-reported COVID-19 spread and CDC classification of COVID spread. There were no associations between COVID-19 community spread (respondent reported or CDC severity level) and outpatient clinic availability (self-reported or workload captured). At T3, a positive association was found between the CDC spread level and workload (P = .008), but this was not significant after Bonferroni correction (P = .06).
EEG availability surpassed EMU availability at all time points, although EMU services made some recovery at T3 and T4. No associations were found between COVID-19 community spread (self-reported or CDC severity level) and outpatient EEG or EMU availability (self-reported or workload captured). At T3, there was a positive association between EEG workload and CDC COVID-19 severity level (P = .04), but this was not significant after Bonferroni correction (P = .30).
For outpatient EEG, staff and patient mask use were universally implemented by T2, while the use of full personal protective equipment (PPE) occurred at a subset of sites (T2, 6/17 [35%]; T3, 3/15 [20%]; T4: 4/16 [25%]). COVID-19 testing was rarely implemented prior to outpatient EEG (T1, 0 sites; T2, 1 site; T3, 1 site; T4, 0 sites). Within the EMU, safety precautions including COVID-19 testing, patient mask usage, staff mask usage, and aerosolization demonstrated a sustained majority usage across the 4 surveys.
National and Local Guidelines
The open-ended survey at T1 asked site directors, “Should there be national recommendations on how EEGs and related procedures should be done during the pandemic or should this be left to local conditions?” Responses were mixed, with 5 respondents desiring a national standard, 4 respondents favoring a local response, and 4 respondents believing a national standard should be in place but with modifications based on local outbreak levels and needs.
Surveys performed at T2 through T4 asked, “Which of the following do you feel was/will be helpful in adapting to COVID-19–related changes?” Overall, there was substantial agreement that guidelines were helpful. Most sites anticipated permanent changes in enhanced safety precautions and telehealth.
DISCUSSION
This longitudinal study across 4 time points describes how epilepsy services within the VHA and ECoE adapted to the COVID-19 pandemic. The first survey, conducted 2 months after COVID-19 was declared a pandemic, allowed a comparison with other concurrent US national surveys.1,2,10 The subsequent surveys describe longitudinal adaptations to balance patient and staff safety with service availability and is a unique feature of the current report. Results demonstrate flexibility and adaptability by the ECoEs surveyed, which surprisingly did not show significant associations between CDC COVID-19 spread data and administrative workload data.
Trends in Availability of Services
The most significant impact of COVID-19 restrictions was during T1. There were no significant relationships between service availability/workload and objective CDC COVID-19 spread levels or subjective self-reported COVID-19 spread. Respondents’ perceptions of local COVID-19 spread showed no association with CDC COVID-19 spread data. It appears that subjective perception of spread may be unreliable and factors other than actual or perceived COVID-19 spread were likely driving patterns for service availability.
In-person outpatient visits were most impacted at T1, similar to other civilian surveys, with only 1 site reporting in-person outpatient visits without limitations.1,2 These numbers significantly changed by T2, with all sites offering either limited or unlimited in-person visits. While the surveys did not evaluate factors leading to this rapid recovery, it may be related to the availability of COVID-19 vaccinations within the VHA during this time.11 The US Department of Veterans Affairs was the first federal agency to mandate employee vaccination.12 By the most recent time point (T4), all responding sites offered outpatient visits. Outpatient EEGs followed a similar trend, with T1 being the most restrictive and full, unrestricted outpatient EEGs available by T3.
Fiscal year (FY) trends from ECoE annual reports suggest that encounters slowly recovered over the course of the pandemic. In FY 2019 there were 13,143 outpatient encounters and 6394 EEGs, which dropped to 8097 outpatient encounters and 4432 EEGs in FY 2020 before rising to 8489 outpatient encounters and 5604 EEGs in FY 2021 and 9772 outpatient encounters and 5062 EEGs in FY 2022. Thus, while clinicians described availability of services, patients may have remained hesitant or were otherwise unable to fulfill in-person appointments. The increased availability of home EEG (145 encounter days in 2021 and 436 encounter days in 2022) may be filling this gap.
In contrast to outpatient clinics and EEG, EMU availability showed relatively slower reimplementation. In the last survey, about 30% of sites were still not offering EMU or had limited services. Early trends regarding reduced staffing and patient reluctance for elective admission cited in other surveys may have also affected EMU availability within the VHA.2,13 Consistent with trends in availability, ECoE annual report data suggest EMU patient participation was about one-half of prepandemic rates: 3069 encounters in FY 2019 dropped to 1614 encounters in 2020. By 2021, rates were about two-thirds of prepandemic rates with 2058 encounters in 2021 and 2101 encounters in 2022.
Early survey results (T1) from this study echo trends from other surveys. In the AES survey (April to June 2020), about a quarter of respondents (22%) reported doing fewer EEG studies than usual. The Italian national survey (April 2020) revealed reduced presurgical evaluations (81%), ambulatory EEG (78%), standard EEG (5%) and long-term EEG (32%).4 In the NAEC survey (end of 2020)—which roughly corresponded to T2—outpatient EEGs were still < 75% of pre-COVID levels in one-half of the centers.
National and Local Guidelines
Both national and local guidelines were perceived as useful by most respondents, with national guidelines being more beneficial. This aligns with the NAEC survey, where there was a perceived need for detailed recommendations for PPE and COVID-19 testing of patients, visitors, and staff. Based on national and local guidelines, ECoE implemented safety procedures, as reflected in responses. Staff masking procedures appeared to be the most widely adopted for all services, while the use of full PPE waned as the pandemic progressed. COVID-19 testing was rarely used for routine outpatient visits but common in EMU admissions. This is similar to a survey conducted by the American Academy of Neurology which found full PPE implementation intermittently in outpatient settings and more frequently in inpatient settings.14
Telehealth Attitudes
While most sites anticipated permanent implementation of safety precautions and telehealth, the latter was consistently reported as more likely to be sustained. The VHA had a large and well-developed system of telehealth services that considerably predated the pandemic.15,16 Through this established infrastructure, remote services were quickly increased across the VHA.17-19 This telehealth structure was supplemented by the ability of VHA clinicians to practice across state lines, following a 2018 federal rule.20 The AES survey noted the VHA ECoE's longstanding experience with telehealth as a model for telemedicine use in providing direct patient care, remote EEG analysis, and clinician-to-clinician consultation.1
Trends in the number of telehealth patients seen, observed through patterns in ECoE annual reports are consistent with positive views toward this method of service provision. Specifically, these annual reports capture trends in Video Telehealth Clinic (local station), Video Telehealth Clinic (different station), Home Video Telehealth, Telephone Clinic, and eConsults. Though video telehealth at in-person stations had a precipitous drop in 2020 that continued to wane in subsequent years (898 encounters in 2019; 455 encounters in 2020; 90 encounters in 2021; 88 encounters in 2022), use of home video telehealth rose over time (143 encounters in 2019; 1003 encounters in 2020; 3206 encounters in 2021; 3315 encounters in 2022). Use of telephone services rose drastically in 2020 but has since become a less frequently used service method (2636 in 2019; 5923 in 2020; 5319 in 2021; 3704 in 2022).
Limitations
While the survey encouraged a high response rate, this limited its scope and interpretability. While the availability of services was evaluated, the underlying reasons were not queried. Follow-up questions about barriers to reopening may have allowed for a better understanding of why some services, such as EMU, continued to operate suboptimally later in the pandemic. Similarly, asking about unique strategies or barriers for telehealth would have allowed for a better understanding of its current and future use. We hypothesize that staffing changes during the pandemic may have influenced the availability of services, but changes to staffing were not assessed via the survey and were not readily available via other sources (eg, ECoE annual reports) at the time of publication. An additional limitation is the lack of comparable surveys in the literature for time points T2 to T4, as most analogous surveys were performed early in 2020.
Conclusions
This longitudinal study performed at 4 time points during the COVID-19 pandemic is the first to offer a comprehensive picture of changes to epilepsy and EEG services over time, given that other similar surveys lacked follow-up. Results reveal a significant limitation of services at VHA ECoE shortly after the onset of the pandemic, with return to near-complete operational status 2 years later. While safety precautions and telehealth are predicted to continue, telehealth is perceived as a more permanent change in services.
Albert DVF, Das RR, Acharya JN, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on epilepsy care: a survey of the American Epilepsy Society membership. Epilepsy Curr. 2020;20(5):316-324. doi:10.1177/1535759720956994
Ahrens SM, Ostendorf AP, Lado FA, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on epilepsy center practice in the United States. Neurology. 2022;98(19):e1893-e1901. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000200285
Cross JH, Kwon CS, Asadi-Pooya AA, et al. Epilepsy care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Epilepsia. 2021;62(10):2322-2332. doi:10.1111/epi.17045
Assenza G, Lanzone J, Ricci L, et al. Electroencephalography at the time of Covid-19 pandemic in Italy. Neurol Sci. 2020;41(8):1999-2004. doi:10.1007/s10072-020-04546-8
US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Veteran population. Updated September 7, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/veteran_population.asp
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE). Annual report fiscal year 2019. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.epilepsy.va.gov/docs/FY19AnnualReport-VHAEpilepsyCentersofExcellence.pdf
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. United States COVID-19 county level of community transmission historical changes – ARCHIVED. Updated February 20, 2024. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://data.cdc.gov/Public-Health-Surveillance/United-States-COVID-19-County-Level-of-Community-T/nra9-vzzn
Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377-381. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, et al. The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform. 2019;95:103208. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208
World Health Organization. Rolling updates on coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Updated July 31, 2020. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen
US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA announces initial plans for COVID-19 vaccine distribution. News release. December 10, 2020. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.va.gov/opa/pressrel/pressrelease.cfm?id=5580
Steinhauer J. V.A. Issues Vaccine Mandate for Health Care Workers, a First for a Federal Agency. The New York Times. August 16, 2021. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/26/us/politics/veterans-affairs-coronavirus-covid-19.html
Zafar SF, Khozein RJ, LaRoche SM, Westover MB, Gilmore EJ. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on continuous EEG utilization. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(7):567-574. doi:10.1097/WNP.0000000000000802
Qureshi AI, Rheaume C, Huang W, et al. COVID-19 exposure during neurology practice. Neurologist. 2021;26(6):225-230. doi:10.1097/NRL.0000000000000346
Darkins A, Cruise C, Armstrong M, Peters J, Finn M. Enhancing access of combat-wounded veterans to specialist rehabilitation services: the VA Polytrauma Telehealth Network. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(1):182-187. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.027
Darkins A, Ryan P, Kobb R, et al. Care coordination/home telehealth: the systematic implementation of health informatics, home telehealth, and disease management to support the care of veteran patients with chronic conditions. Telemed J E Health. 2008;14(10):1118-1126. doi:10.1089/tmj.2008.0021
Gentry MT, Puspitasari AJ, McKean AJ, et al. Clinician satisfaction with rapid adoption and implementation of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemed J E Health. 2021;27(12):1385-1392. doi:10.1089/tmj.2020.0575
Connolly SL, Stolzmann KL, Heyworth L, et al. Patient and provider predictors of telemental health use prior to and during the COVID-19 pandemic within the Department of Veterans Affairs. Am Psychol. 2022;77(2):249-261. doi:10.1037/amp0000895
Shelton CJ, Kim A, Hassan AM, Bhat A, Barnello J, Castro CA. System-wide implementation of telehealth to support military veterans and their families in response to COVID-19: a paradigm shift. J Mil Veteran Fam Health. 2020;6(S2):50-57. doi:10.3138/jmvfh-CO19-0003
VA expands telehealth by allowing health care providers to treat patients across state lines. News release. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. May 11, 2018. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-expands-telehealth-by-allowing-health-care-providers-to-treat-patients-across-state-lines/
The COVID-19 pandemic affected diverse workplaces globally, leading to temporary and permanent changes across the health care landscape. Included among the impacted areas of care were epilepsy and electroencephalogram (EEG) clinicians and services. Surveys among epilepsy specialists and neurophysiologists conducted at the onset of the pandemic to evaluate working conditions include analyses from the American Epilepsy Society (AES), the National Association of Epilepsy Centers (NAEC), the International League Against Epilepsy, and an Italian national survey.1-4 These investigations revealed reductions in epilepsy monitoring unit (EMU) admissions (23% decline), epilepsy surgery (6% decline), inpatient EEG (22% of respondents reported decline), and patients having difficulty accessing epilepsy professionals (28% of respondents reported decline) or obtaining medications (20% of respondents reported decline).1-3
While such research provided evidence for changes to epilepsy care in 2020, there are limited data on subsequent adaptations during the pandemic. These studies did not incorporate data on the spread of COVID-19 or administrative workload numbers to analyze service delivery beyond self reports. This study aimed to address this gap in the literature by highlighting results from longitudinal national surveys conducted at the Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE), a specialty care service within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), which annually serves > 9 million veterans.5 The ECoE represents epileptologists and neurophysiologists across the United States at the 17 primary facilities that were established at the time of this survey (2 ECoEs have been added since survey completion) in 4 geographical regions and for which other regional facilities refer patients for diagnostic services or specialty care.6
National surveys were conducted among the ECoE directors regarding adaptations made from May 2020 to June 2022 to provide a comprehensive account of limitations they experienced and how adjustments have been made to improve patient care. Survey responses were compared to administrative workload numbers and COVID-19 spread data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to provide a comprehensive analysis of performance during the pandemic.
METHODS
Data were collected as part of a quality improvement initiative by the VHA ECoE; institutional review board approval was not required. An 18-item survey covering 5 broad domains was sent to ECoE directors 4 separate times to accumulate data from 4 time periods: May to June 2020 (T1); December 2020 to February 2021 (T2); July to August 2021 (T3); and June to July 2022 (T4). These periods correspond to the following phases of the pandemic: T1, onset of pandemic; T2, vaccine availability; T3, Delta variant predominant; T4, Omicron variant predominant.

Data on the spread of COVID-19 were collected from the CDC archived dataset, US COVID-19 County Level of Community Transmission Historical Changes (Table 1).7 Administrative workload (patient counts) for EEG, EMU, and outpatient clinics were extracted from VHA administrative databases for the participating sites for the months prior to each survey: T1, April 2020; T2, November 2020; T3, June 2021; and T4, May 2022 (Table 2).

Survey Structure and Content
The survey was developed by the ECoE and was not validated prior to its use due to the time-sensitive nature of gathering information during the pandemic. The first survey (T1) was an emailed spreadsheet with open-ended questions to gauge availability of services (ie, outpatient clinic, EEG, EMU), assess whether safety precautions were being introduced, and understand whether national or local guidelines were thought to be helpful. Responses from this and subsequent surveys were standardized into yes/no and multiple choice formats. Subsequent surveys were administered online using a Research Electronic Data Capture tool.8,9
Availability of outpatient epilepsy services across the 4 time periods were categorized as unlimited (in-person with no restrictions), limited (in-person with restrictions), planned (not currently performed but scheduled for the near future), and unavailable (no in-person services offered) (eAppendices 1-6, available in article PDF).
Statistical Analyses
Analyses were performed to compare survey responses to workload and CDC data on COVID-19 community spread. The following associations were examined: (1) CDC COVID-19 spread vs respondents’ perception of spread; (2) respondents’ perception of spread vs availability of services; (3) CDC COVID-19 spread vs availability of services; (4) respondents’ perception of spread vs workload; and (5) CDC COVID-19 spread vs workload. Availability of services was dichotomized for analyses, with limited or fully available services classified as available. As services were mostly open at T3 regardless of the spread of the virus, and the CDC COVID-19 spread classification for all sites was severe or high at T2 and T4, corresponding associations were not tested at these time points. For associations 1 through 3, Fisher exact tests were used; for associations 4 and 5, Mann-Whitney U tests (where the COVID-19 spread fell into 2 categories) and Kruskal-Wallis tests (for 3 categories of COVID-19 spread) were performed. All tests were 2-tailed and performed at 0.05 error rate. Bonferroni corrections were applied to adjust P values for multiple hypotheses tests.
RESULTS
From the 17 sites invited, responses at each time point were obtained from 13 (T1),17 (T2), 15 (T3), and 16 (T4) centers. There was no significant association between self-reported COVID-19 spread and CDC classification of COVID spread. There were no associations between COVID-19 community spread (respondent reported or CDC severity level) and outpatient clinic availability (self-reported or workload captured). At T3, a positive association was found between the CDC spread level and workload (P = .008), but this was not significant after Bonferroni correction (P = .06).
EEG availability surpassed EMU availability at all time points, although EMU services made some recovery at T3 and T4. No associations were found between COVID-19 community spread (self-reported or CDC severity level) and outpatient EEG or EMU availability (self-reported or workload captured). At T3, there was a positive association between EEG workload and CDC COVID-19 severity level (P = .04), but this was not significant after Bonferroni correction (P = .30).
For outpatient EEG, staff and patient mask use were universally implemented by T2, while the use of full personal protective equipment (PPE) occurred at a subset of sites (T2, 6/17 [35%]; T3, 3/15 [20%]; T4: 4/16 [25%]). COVID-19 testing was rarely implemented prior to outpatient EEG (T1, 0 sites; T2, 1 site; T3, 1 site; T4, 0 sites). Within the EMU, safety precautions including COVID-19 testing, patient mask usage, staff mask usage, and aerosolization demonstrated a sustained majority usage across the 4 surveys.
National and Local Guidelines
The open-ended survey at T1 asked site directors, “Should there be national recommendations on how EEGs and related procedures should be done during the pandemic or should this be left to local conditions?” Responses were mixed, with 5 respondents desiring a national standard, 4 respondents favoring a local response, and 4 respondents believing a national standard should be in place but with modifications based on local outbreak levels and needs.
Surveys performed at T2 through T4 asked, “Which of the following do you feel was/will be helpful in adapting to COVID-19–related changes?” Overall, there was substantial agreement that guidelines were helpful. Most sites anticipated permanent changes in enhanced safety precautions and telehealth.
DISCUSSION
This longitudinal study across 4 time points describes how epilepsy services within the VHA and ECoE adapted to the COVID-19 pandemic. The first survey, conducted 2 months after COVID-19 was declared a pandemic, allowed a comparison with other concurrent US national surveys.1,2,10 The subsequent surveys describe longitudinal adaptations to balance patient and staff safety with service availability and is a unique feature of the current report. Results demonstrate flexibility and adaptability by the ECoEs surveyed, which surprisingly did not show significant associations between CDC COVID-19 spread data and administrative workload data.
Trends in Availability of Services
The most significant impact of COVID-19 restrictions was during T1. There were no significant relationships between service availability/workload and objective CDC COVID-19 spread levels or subjective self-reported COVID-19 spread. Respondents’ perceptions of local COVID-19 spread showed no association with CDC COVID-19 spread data. It appears that subjective perception of spread may be unreliable and factors other than actual or perceived COVID-19 spread were likely driving patterns for service availability.
In-person outpatient visits were most impacted at T1, similar to other civilian surveys, with only 1 site reporting in-person outpatient visits without limitations.1,2 These numbers significantly changed by T2, with all sites offering either limited or unlimited in-person visits. While the surveys did not evaluate factors leading to this rapid recovery, it may be related to the availability of COVID-19 vaccinations within the VHA during this time.11 The US Department of Veterans Affairs was the first federal agency to mandate employee vaccination.12 By the most recent time point (T4), all responding sites offered outpatient visits. Outpatient EEGs followed a similar trend, with T1 being the most restrictive and full, unrestricted outpatient EEGs available by T3.
Fiscal year (FY) trends from ECoE annual reports suggest that encounters slowly recovered over the course of the pandemic. In FY 2019 there were 13,143 outpatient encounters and 6394 EEGs, which dropped to 8097 outpatient encounters and 4432 EEGs in FY 2020 before rising to 8489 outpatient encounters and 5604 EEGs in FY 2021 and 9772 outpatient encounters and 5062 EEGs in FY 2022. Thus, while clinicians described availability of services, patients may have remained hesitant or were otherwise unable to fulfill in-person appointments. The increased availability of home EEG (145 encounter days in 2021 and 436 encounter days in 2022) may be filling this gap.
In contrast to outpatient clinics and EEG, EMU availability showed relatively slower reimplementation. In the last survey, about 30% of sites were still not offering EMU or had limited services. Early trends regarding reduced staffing and patient reluctance for elective admission cited in other surveys may have also affected EMU availability within the VHA.2,13 Consistent with trends in availability, ECoE annual report data suggest EMU patient participation was about one-half of prepandemic rates: 3069 encounters in FY 2019 dropped to 1614 encounters in 2020. By 2021, rates were about two-thirds of prepandemic rates with 2058 encounters in 2021 and 2101 encounters in 2022.
Early survey results (T1) from this study echo trends from other surveys. In the AES survey (April to June 2020), about a quarter of respondents (22%) reported doing fewer EEG studies than usual. The Italian national survey (April 2020) revealed reduced presurgical evaluations (81%), ambulatory EEG (78%), standard EEG (5%) and long-term EEG (32%).4 In the NAEC survey (end of 2020)—which roughly corresponded to T2—outpatient EEGs were still < 75% of pre-COVID levels in one-half of the centers.
National and Local Guidelines
Both national and local guidelines were perceived as useful by most respondents, with national guidelines being more beneficial. This aligns with the NAEC survey, where there was a perceived need for detailed recommendations for PPE and COVID-19 testing of patients, visitors, and staff. Based on national and local guidelines, ECoE implemented safety procedures, as reflected in responses. Staff masking procedures appeared to be the most widely adopted for all services, while the use of full PPE waned as the pandemic progressed. COVID-19 testing was rarely used for routine outpatient visits but common in EMU admissions. This is similar to a survey conducted by the American Academy of Neurology which found full PPE implementation intermittently in outpatient settings and more frequently in inpatient settings.14
Telehealth Attitudes
While most sites anticipated permanent implementation of safety precautions and telehealth, the latter was consistently reported as more likely to be sustained. The VHA had a large and well-developed system of telehealth services that considerably predated the pandemic.15,16 Through this established infrastructure, remote services were quickly increased across the VHA.17-19 This telehealth structure was supplemented by the ability of VHA clinicians to practice across state lines, following a 2018 federal rule.20 The AES survey noted the VHA ECoE's longstanding experience with telehealth as a model for telemedicine use in providing direct patient care, remote EEG analysis, and clinician-to-clinician consultation.1
Trends in the number of telehealth patients seen, observed through patterns in ECoE annual reports are consistent with positive views toward this method of service provision. Specifically, these annual reports capture trends in Video Telehealth Clinic (local station), Video Telehealth Clinic (different station), Home Video Telehealth, Telephone Clinic, and eConsults. Though video telehealth at in-person stations had a precipitous drop in 2020 that continued to wane in subsequent years (898 encounters in 2019; 455 encounters in 2020; 90 encounters in 2021; 88 encounters in 2022), use of home video telehealth rose over time (143 encounters in 2019; 1003 encounters in 2020; 3206 encounters in 2021; 3315 encounters in 2022). Use of telephone services rose drastically in 2020 but has since become a less frequently used service method (2636 in 2019; 5923 in 2020; 5319 in 2021; 3704 in 2022).
Limitations
While the survey encouraged a high response rate, this limited its scope and interpretability. While the availability of services was evaluated, the underlying reasons were not queried. Follow-up questions about barriers to reopening may have allowed for a better understanding of why some services, such as EMU, continued to operate suboptimally later in the pandemic. Similarly, asking about unique strategies or barriers for telehealth would have allowed for a better understanding of its current and future use. We hypothesize that staffing changes during the pandemic may have influenced the availability of services, but changes to staffing were not assessed via the survey and were not readily available via other sources (eg, ECoE annual reports) at the time of publication. An additional limitation is the lack of comparable surveys in the literature for time points T2 to T4, as most analogous surveys were performed early in 2020.
Conclusions
This longitudinal study performed at 4 time points during the COVID-19 pandemic is the first to offer a comprehensive picture of changes to epilepsy and EEG services over time, given that other similar surveys lacked follow-up. Results reveal a significant limitation of services at VHA ECoE shortly after the onset of the pandemic, with return to near-complete operational status 2 years later. While safety precautions and telehealth are predicted to continue, telehealth is perceived as a more permanent change in services.
The COVID-19 pandemic affected diverse workplaces globally, leading to temporary and permanent changes across the health care landscape. Included among the impacted areas of care were epilepsy and electroencephalogram (EEG) clinicians and services. Surveys among epilepsy specialists and neurophysiologists conducted at the onset of the pandemic to evaluate working conditions include analyses from the American Epilepsy Society (AES), the National Association of Epilepsy Centers (NAEC), the International League Against Epilepsy, and an Italian national survey.1-4 These investigations revealed reductions in epilepsy monitoring unit (EMU) admissions (23% decline), epilepsy surgery (6% decline), inpatient EEG (22% of respondents reported decline), and patients having difficulty accessing epilepsy professionals (28% of respondents reported decline) or obtaining medications (20% of respondents reported decline).1-3
While such research provided evidence for changes to epilepsy care in 2020, there are limited data on subsequent adaptations during the pandemic. These studies did not incorporate data on the spread of COVID-19 or administrative workload numbers to analyze service delivery beyond self reports. This study aimed to address this gap in the literature by highlighting results from longitudinal national surveys conducted at the Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE), a specialty care service within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), which annually serves > 9 million veterans.5 The ECoE represents epileptologists and neurophysiologists across the United States at the 17 primary facilities that were established at the time of this survey (2 ECoEs have been added since survey completion) in 4 geographical regions and for which other regional facilities refer patients for diagnostic services or specialty care.6
National surveys were conducted among the ECoE directors regarding adaptations made from May 2020 to June 2022 to provide a comprehensive account of limitations they experienced and how adjustments have been made to improve patient care. Survey responses were compared to administrative workload numbers and COVID-19 spread data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to provide a comprehensive analysis of performance during the pandemic.
METHODS
Data were collected as part of a quality improvement initiative by the VHA ECoE; institutional review board approval was not required. An 18-item survey covering 5 broad domains was sent to ECoE directors 4 separate times to accumulate data from 4 time periods: May to June 2020 (T1); December 2020 to February 2021 (T2); July to August 2021 (T3); and June to July 2022 (T4). These periods correspond to the following phases of the pandemic: T1, onset of pandemic; T2, vaccine availability; T3, Delta variant predominant; T4, Omicron variant predominant.

Data on the spread of COVID-19 were collected from the CDC archived dataset, US COVID-19 County Level of Community Transmission Historical Changes (Table 1).7 Administrative workload (patient counts) for EEG, EMU, and outpatient clinics were extracted from VHA administrative databases for the participating sites for the months prior to each survey: T1, April 2020; T2, November 2020; T3, June 2021; and T4, May 2022 (Table 2).

Survey Structure and Content
The survey was developed by the ECoE and was not validated prior to its use due to the time-sensitive nature of gathering information during the pandemic. The first survey (T1) was an emailed spreadsheet with open-ended questions to gauge availability of services (ie, outpatient clinic, EEG, EMU), assess whether safety precautions were being introduced, and understand whether national or local guidelines were thought to be helpful. Responses from this and subsequent surveys were standardized into yes/no and multiple choice formats. Subsequent surveys were administered online using a Research Electronic Data Capture tool.8,9
Availability of outpatient epilepsy services across the 4 time periods were categorized as unlimited (in-person with no restrictions), limited (in-person with restrictions), planned (not currently performed but scheduled for the near future), and unavailable (no in-person services offered) (eAppendices 1-6, available in article PDF).
Statistical Analyses
Analyses were performed to compare survey responses to workload and CDC data on COVID-19 community spread. The following associations were examined: (1) CDC COVID-19 spread vs respondents’ perception of spread; (2) respondents’ perception of spread vs availability of services; (3) CDC COVID-19 spread vs availability of services; (4) respondents’ perception of spread vs workload; and (5) CDC COVID-19 spread vs workload. Availability of services was dichotomized for analyses, with limited or fully available services classified as available. As services were mostly open at T3 regardless of the spread of the virus, and the CDC COVID-19 spread classification for all sites was severe or high at T2 and T4, corresponding associations were not tested at these time points. For associations 1 through 3, Fisher exact tests were used; for associations 4 and 5, Mann-Whitney U tests (where the COVID-19 spread fell into 2 categories) and Kruskal-Wallis tests (for 3 categories of COVID-19 spread) were performed. All tests were 2-tailed and performed at 0.05 error rate. Bonferroni corrections were applied to adjust P values for multiple hypotheses tests.
RESULTS
From the 17 sites invited, responses at each time point were obtained from 13 (T1),17 (T2), 15 (T3), and 16 (T4) centers. There was no significant association between self-reported COVID-19 spread and CDC classification of COVID spread. There were no associations between COVID-19 community spread (respondent reported or CDC severity level) and outpatient clinic availability (self-reported or workload captured). At T3, a positive association was found between the CDC spread level and workload (P = .008), but this was not significant after Bonferroni correction (P = .06).
EEG availability surpassed EMU availability at all time points, although EMU services made some recovery at T3 and T4. No associations were found between COVID-19 community spread (self-reported or CDC severity level) and outpatient EEG or EMU availability (self-reported or workload captured). At T3, there was a positive association between EEG workload and CDC COVID-19 severity level (P = .04), but this was not significant after Bonferroni correction (P = .30).
For outpatient EEG, staff and patient mask use were universally implemented by T2, while the use of full personal protective equipment (PPE) occurred at a subset of sites (T2, 6/17 [35%]; T3, 3/15 [20%]; T4: 4/16 [25%]). COVID-19 testing was rarely implemented prior to outpatient EEG (T1, 0 sites; T2, 1 site; T3, 1 site; T4, 0 sites). Within the EMU, safety precautions including COVID-19 testing, patient mask usage, staff mask usage, and aerosolization demonstrated a sustained majority usage across the 4 surveys.
National and Local Guidelines
The open-ended survey at T1 asked site directors, “Should there be national recommendations on how EEGs and related procedures should be done during the pandemic or should this be left to local conditions?” Responses were mixed, with 5 respondents desiring a national standard, 4 respondents favoring a local response, and 4 respondents believing a national standard should be in place but with modifications based on local outbreak levels and needs.
Surveys performed at T2 through T4 asked, “Which of the following do you feel was/will be helpful in adapting to COVID-19–related changes?” Overall, there was substantial agreement that guidelines were helpful. Most sites anticipated permanent changes in enhanced safety precautions and telehealth.
DISCUSSION
This longitudinal study across 4 time points describes how epilepsy services within the VHA and ECoE adapted to the COVID-19 pandemic. The first survey, conducted 2 months after COVID-19 was declared a pandemic, allowed a comparison with other concurrent US national surveys.1,2,10 The subsequent surveys describe longitudinal adaptations to balance patient and staff safety with service availability and is a unique feature of the current report. Results demonstrate flexibility and adaptability by the ECoEs surveyed, which surprisingly did not show significant associations between CDC COVID-19 spread data and administrative workload data.
Trends in Availability of Services
The most significant impact of COVID-19 restrictions was during T1. There were no significant relationships between service availability/workload and objective CDC COVID-19 spread levels or subjective self-reported COVID-19 spread. Respondents’ perceptions of local COVID-19 spread showed no association with CDC COVID-19 spread data. It appears that subjective perception of spread may be unreliable and factors other than actual or perceived COVID-19 spread were likely driving patterns for service availability.
In-person outpatient visits were most impacted at T1, similar to other civilian surveys, with only 1 site reporting in-person outpatient visits without limitations.1,2 These numbers significantly changed by T2, with all sites offering either limited or unlimited in-person visits. While the surveys did not evaluate factors leading to this rapid recovery, it may be related to the availability of COVID-19 vaccinations within the VHA during this time.11 The US Department of Veterans Affairs was the first federal agency to mandate employee vaccination.12 By the most recent time point (T4), all responding sites offered outpatient visits. Outpatient EEGs followed a similar trend, with T1 being the most restrictive and full, unrestricted outpatient EEGs available by T3.
Fiscal year (FY) trends from ECoE annual reports suggest that encounters slowly recovered over the course of the pandemic. In FY 2019 there were 13,143 outpatient encounters and 6394 EEGs, which dropped to 8097 outpatient encounters and 4432 EEGs in FY 2020 before rising to 8489 outpatient encounters and 5604 EEGs in FY 2021 and 9772 outpatient encounters and 5062 EEGs in FY 2022. Thus, while clinicians described availability of services, patients may have remained hesitant or were otherwise unable to fulfill in-person appointments. The increased availability of home EEG (145 encounter days in 2021 and 436 encounter days in 2022) may be filling this gap.
In contrast to outpatient clinics and EEG, EMU availability showed relatively slower reimplementation. In the last survey, about 30% of sites were still not offering EMU or had limited services. Early trends regarding reduced staffing and patient reluctance for elective admission cited in other surveys may have also affected EMU availability within the VHA.2,13 Consistent with trends in availability, ECoE annual report data suggest EMU patient participation was about one-half of prepandemic rates: 3069 encounters in FY 2019 dropped to 1614 encounters in 2020. By 2021, rates were about two-thirds of prepandemic rates with 2058 encounters in 2021 and 2101 encounters in 2022.
Early survey results (T1) from this study echo trends from other surveys. In the AES survey (April to June 2020), about a quarter of respondents (22%) reported doing fewer EEG studies than usual. The Italian national survey (April 2020) revealed reduced presurgical evaluations (81%), ambulatory EEG (78%), standard EEG (5%) and long-term EEG (32%).4 In the NAEC survey (end of 2020)—which roughly corresponded to T2—outpatient EEGs were still < 75% of pre-COVID levels in one-half of the centers.
National and Local Guidelines
Both national and local guidelines were perceived as useful by most respondents, with national guidelines being more beneficial. This aligns with the NAEC survey, where there was a perceived need for detailed recommendations for PPE and COVID-19 testing of patients, visitors, and staff. Based on national and local guidelines, ECoE implemented safety procedures, as reflected in responses. Staff masking procedures appeared to be the most widely adopted for all services, while the use of full PPE waned as the pandemic progressed. COVID-19 testing was rarely used for routine outpatient visits but common in EMU admissions. This is similar to a survey conducted by the American Academy of Neurology which found full PPE implementation intermittently in outpatient settings and more frequently in inpatient settings.14
Telehealth Attitudes
While most sites anticipated permanent implementation of safety precautions and telehealth, the latter was consistently reported as more likely to be sustained. The VHA had a large and well-developed system of telehealth services that considerably predated the pandemic.15,16 Through this established infrastructure, remote services were quickly increased across the VHA.17-19 This telehealth structure was supplemented by the ability of VHA clinicians to practice across state lines, following a 2018 federal rule.20 The AES survey noted the VHA ECoE's longstanding experience with telehealth as a model for telemedicine use in providing direct patient care, remote EEG analysis, and clinician-to-clinician consultation.1
Trends in the number of telehealth patients seen, observed through patterns in ECoE annual reports are consistent with positive views toward this method of service provision. Specifically, these annual reports capture trends in Video Telehealth Clinic (local station), Video Telehealth Clinic (different station), Home Video Telehealth, Telephone Clinic, and eConsults. Though video telehealth at in-person stations had a precipitous drop in 2020 that continued to wane in subsequent years (898 encounters in 2019; 455 encounters in 2020; 90 encounters in 2021; 88 encounters in 2022), use of home video telehealth rose over time (143 encounters in 2019; 1003 encounters in 2020; 3206 encounters in 2021; 3315 encounters in 2022). Use of telephone services rose drastically in 2020 but has since become a less frequently used service method (2636 in 2019; 5923 in 2020; 5319 in 2021; 3704 in 2022).
Limitations
While the survey encouraged a high response rate, this limited its scope and interpretability. While the availability of services was evaluated, the underlying reasons were not queried. Follow-up questions about barriers to reopening may have allowed for a better understanding of why some services, such as EMU, continued to operate suboptimally later in the pandemic. Similarly, asking about unique strategies or barriers for telehealth would have allowed for a better understanding of its current and future use. We hypothesize that staffing changes during the pandemic may have influenced the availability of services, but changes to staffing were not assessed via the survey and were not readily available via other sources (eg, ECoE annual reports) at the time of publication. An additional limitation is the lack of comparable surveys in the literature for time points T2 to T4, as most analogous surveys were performed early in 2020.
Conclusions
This longitudinal study performed at 4 time points during the COVID-19 pandemic is the first to offer a comprehensive picture of changes to epilepsy and EEG services over time, given that other similar surveys lacked follow-up. Results reveal a significant limitation of services at VHA ECoE shortly after the onset of the pandemic, with return to near-complete operational status 2 years later. While safety precautions and telehealth are predicted to continue, telehealth is perceived as a more permanent change in services.
Albert DVF, Das RR, Acharya JN, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on epilepsy care: a survey of the American Epilepsy Society membership. Epilepsy Curr. 2020;20(5):316-324. doi:10.1177/1535759720956994
Ahrens SM, Ostendorf AP, Lado FA, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on epilepsy center practice in the United States. Neurology. 2022;98(19):e1893-e1901. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000200285
Cross JH, Kwon CS, Asadi-Pooya AA, et al. Epilepsy care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Epilepsia. 2021;62(10):2322-2332. doi:10.1111/epi.17045
Assenza G, Lanzone J, Ricci L, et al. Electroencephalography at the time of Covid-19 pandemic in Italy. Neurol Sci. 2020;41(8):1999-2004. doi:10.1007/s10072-020-04546-8
US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Veteran population. Updated September 7, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/veteran_population.asp
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE). Annual report fiscal year 2019. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.epilepsy.va.gov/docs/FY19AnnualReport-VHAEpilepsyCentersofExcellence.pdf
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. United States COVID-19 county level of community transmission historical changes – ARCHIVED. Updated February 20, 2024. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://data.cdc.gov/Public-Health-Surveillance/United-States-COVID-19-County-Level-of-Community-T/nra9-vzzn
Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377-381. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, et al. The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform. 2019;95:103208. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208
World Health Organization. Rolling updates on coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Updated July 31, 2020. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen
US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA announces initial plans for COVID-19 vaccine distribution. News release. December 10, 2020. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.va.gov/opa/pressrel/pressrelease.cfm?id=5580
Steinhauer J. V.A. Issues Vaccine Mandate for Health Care Workers, a First for a Federal Agency. The New York Times. August 16, 2021. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/26/us/politics/veterans-affairs-coronavirus-covid-19.html
Zafar SF, Khozein RJ, LaRoche SM, Westover MB, Gilmore EJ. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on continuous EEG utilization. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(7):567-574. doi:10.1097/WNP.0000000000000802
Qureshi AI, Rheaume C, Huang W, et al. COVID-19 exposure during neurology practice. Neurologist. 2021;26(6):225-230. doi:10.1097/NRL.0000000000000346
Darkins A, Cruise C, Armstrong M, Peters J, Finn M. Enhancing access of combat-wounded veterans to specialist rehabilitation services: the VA Polytrauma Telehealth Network. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(1):182-187. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.027
Darkins A, Ryan P, Kobb R, et al. Care coordination/home telehealth: the systematic implementation of health informatics, home telehealth, and disease management to support the care of veteran patients with chronic conditions. Telemed J E Health. 2008;14(10):1118-1126. doi:10.1089/tmj.2008.0021
Gentry MT, Puspitasari AJ, McKean AJ, et al. Clinician satisfaction with rapid adoption and implementation of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemed J E Health. 2021;27(12):1385-1392. doi:10.1089/tmj.2020.0575
Connolly SL, Stolzmann KL, Heyworth L, et al. Patient and provider predictors of telemental health use prior to and during the COVID-19 pandemic within the Department of Veterans Affairs. Am Psychol. 2022;77(2):249-261. doi:10.1037/amp0000895
Shelton CJ, Kim A, Hassan AM, Bhat A, Barnello J, Castro CA. System-wide implementation of telehealth to support military veterans and their families in response to COVID-19: a paradigm shift. J Mil Veteran Fam Health. 2020;6(S2):50-57. doi:10.3138/jmvfh-CO19-0003
VA expands telehealth by allowing health care providers to treat patients across state lines. News release. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. May 11, 2018. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-expands-telehealth-by-allowing-health-care-providers-to-treat-patients-across-state-lines/
Albert DVF, Das RR, Acharya JN, et al. The impact of COVID-19 on epilepsy care: a survey of the American Epilepsy Society membership. Epilepsy Curr. 2020;20(5):316-324. doi:10.1177/1535759720956994
Ahrens SM, Ostendorf AP, Lado FA, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on epilepsy center practice in the United States. Neurology. 2022;98(19):e1893-e1901. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000200285
Cross JH, Kwon CS, Asadi-Pooya AA, et al. Epilepsy care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Epilepsia. 2021;62(10):2322-2332. doi:10.1111/epi.17045
Assenza G, Lanzone J, Ricci L, et al. Electroencephalography at the time of Covid-19 pandemic in Italy. Neurol Sci. 2020;41(8):1999-2004. doi:10.1007/s10072-020-04546-8
US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Veteran population. Updated September 7, 2022. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/veteran_population.asp
US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Epilepsy Centers of Excellence (ECoE). Annual report fiscal year 2019. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.epilepsy.va.gov/docs/FY19AnnualReport-VHAEpilepsyCentersofExcellence.pdf
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. United States COVID-19 county level of community transmission historical changes – ARCHIVED. Updated February 20, 2024. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://data.cdc.gov/Public-Health-Surveillance/United-States-COVID-19-County-Level-of-Community-T/nra9-vzzn
Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377-381. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, et al. The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform. 2019;95:103208. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208
World Health Organization. Rolling updates on coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Updated July 31, 2020. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen
US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA announces initial plans for COVID-19 vaccine distribution. News release. December 10, 2020. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.va.gov/opa/pressrel/pressrelease.cfm?id=5580
Steinhauer J. V.A. Issues Vaccine Mandate for Health Care Workers, a First for a Federal Agency. The New York Times. August 16, 2021. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/07/26/us/politics/veterans-affairs-coronavirus-covid-19.html
Zafar SF, Khozein RJ, LaRoche SM, Westover MB, Gilmore EJ. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on continuous EEG utilization. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;39(7):567-574. doi:10.1097/WNP.0000000000000802
Qureshi AI, Rheaume C, Huang W, et al. COVID-19 exposure during neurology practice. Neurologist. 2021;26(6):225-230. doi:10.1097/NRL.0000000000000346
Darkins A, Cruise C, Armstrong M, Peters J, Finn M. Enhancing access of combat-wounded veterans to specialist rehabilitation services: the VA Polytrauma Telehealth Network. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(1):182-187. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.027
Darkins A, Ryan P, Kobb R, et al. Care coordination/home telehealth: the systematic implementation of health informatics, home telehealth, and disease management to support the care of veteran patients with chronic conditions. Telemed J E Health. 2008;14(10):1118-1126. doi:10.1089/tmj.2008.0021
Gentry MT, Puspitasari AJ, McKean AJ, et al. Clinician satisfaction with rapid adoption and implementation of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemed J E Health. 2021;27(12):1385-1392. doi:10.1089/tmj.2020.0575
Connolly SL, Stolzmann KL, Heyworth L, et al. Patient and provider predictors of telemental health use prior to and during the COVID-19 pandemic within the Department of Veterans Affairs. Am Psychol. 2022;77(2):249-261. doi:10.1037/amp0000895
Shelton CJ, Kim A, Hassan AM, Bhat A, Barnello J, Castro CA. System-wide implementation of telehealth to support military veterans and their families in response to COVID-19: a paradigm shift. J Mil Veteran Fam Health. 2020;6(S2):50-57. doi:10.3138/jmvfh-CO19-0003
VA expands telehealth by allowing health care providers to treat patients across state lines. News release. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. May 11, 2018. Accessed October 25, 2024. https://news.va.gov/press-room/va-expands-telehealth-by-allowing-health-care-providers-to-treat-patients-across-state-lines/
Managing Diabetes and Dementia in Long-Term Care
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — Conditions like diabetes and dementia are common in patients who are admitted to long-term care facilities, but aggressive management of these conditions in long-term care residents is not recommended, according to a presentation given at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
Hospitalizations for hypoglycemia are risky for patients with diabetes who are residents of long-term care facilities, particularly those aged 75 years or older, said Adam Gurau, MD, a family physician in Toronto. Gurau completed a fellowship in care of the elderly at the University of Toronto, in Ontario, Canada.
“A lot of studies have shown diabetes-related hospitalizations,” said Gurau. He cited a 2014 study that found that hypoglycemia hospitalization rates were twice as high in older patients (age, 75 years or older) as in younger patients (age, 65-74 years).
“It is important to keep in mind that our residents in long-term care are at increasing risk for hypoglycemia, and we really should try to reduce [this risk] and not use dangerous medications or potentially dangerous [means of] diabetes management,” said Gurau.
A Canadian study that examined the composite risk for emergency department visits, hospitalizations, or death within 30 days of reaching intensive glycemic control with high-risk agents (such as insulin or sulfonylureas) suggested little benefit and possible harm in using these agents in adults aged 75 years or older.
In addition, current guidelines on diabetes management encourage a different approach. “Looking at some of the more recent North American guidelines, many of them actually now recommend relaxing glycemic targets to reduce overtreatment and prevent hypoglycemia,” said Gurau.
Deprescribing Medications
Medication reviews present opportunities for taking a global view of a patient’s treatments and determining whether any drug can be removed from the list. “What we want to do is optimize medications,” said Gurau. “We’re not talking about adding medications. We’re talking about removing medications, which is, I think, what we should be doing.”
Some research suggests that patients are open to deprescribing. One survey examined older adults (mean age, 79.1 years) with three or more chronic conditions who had been prescribed at least five medications. The researchers found that most participants (77%) were willing to deprescribe one or more medicines if a doctor advised that it was possible. “General practitioners may be able to increase deprescribing by building trust with their patients and communicating evidence about the risks of medication use,” the researchers wrote.
About 62% of seniors living in a residential care home have a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease or another dementia, according to the Alzheimer Society of Canada. Evidence suggests that nonpharmacologic approaches, such as massage and touch therapy and music, can manage neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as aggression and agitation, that are associated with dementia in older adults, noted Gurau.
“We want to focus on nonpharmacologic approaches for many of these [long-term care] residents,” said Gurau. “We have to do as much as we can to exhaust all the nonpharmacologic approaches.”
Preventing Hospitalizations
Another challenge to tackle in long-term care is the unnecessary transfer of residents to hospital emergency departments, according to Gurau. “In many situations, it’s worth trying as hard as we can to treat them in the nursing home, as opposed to having them go to hospital.”
Researchers estimated that 25% of the transfers from long-term care facilities in Canada to hospital emergency departments in 2014 were potentially preventable.
Urinary tract infections accounted for 30% of hospital emergency department visits for potentially preventable conditions by older patients who are residents in long-term care, according to 2013-2014 data from the Canadian Institute for Health Information.
“There are lots of downsides to going to the hospital [from long-term care],” Gurau told this news organization. “There are risks for infections, risks for increasing delirium and agitation [in patients with dementia], and risks for other behavior that can really impact somebody’s life.”
Gurau reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — Conditions like diabetes and dementia are common in patients who are admitted to long-term care facilities, but aggressive management of these conditions in long-term care residents is not recommended, according to a presentation given at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
Hospitalizations for hypoglycemia are risky for patients with diabetes who are residents of long-term care facilities, particularly those aged 75 years or older, said Adam Gurau, MD, a family physician in Toronto. Gurau completed a fellowship in care of the elderly at the University of Toronto, in Ontario, Canada.
“A lot of studies have shown diabetes-related hospitalizations,” said Gurau. He cited a 2014 study that found that hypoglycemia hospitalization rates were twice as high in older patients (age, 75 years or older) as in younger patients (age, 65-74 years).
“It is important to keep in mind that our residents in long-term care are at increasing risk for hypoglycemia, and we really should try to reduce [this risk] and not use dangerous medications or potentially dangerous [means of] diabetes management,” said Gurau.
A Canadian study that examined the composite risk for emergency department visits, hospitalizations, or death within 30 days of reaching intensive glycemic control with high-risk agents (such as insulin or sulfonylureas) suggested little benefit and possible harm in using these agents in adults aged 75 years or older.
In addition, current guidelines on diabetes management encourage a different approach. “Looking at some of the more recent North American guidelines, many of them actually now recommend relaxing glycemic targets to reduce overtreatment and prevent hypoglycemia,” said Gurau.
Deprescribing Medications
Medication reviews present opportunities for taking a global view of a patient’s treatments and determining whether any drug can be removed from the list. “What we want to do is optimize medications,” said Gurau. “We’re not talking about adding medications. We’re talking about removing medications, which is, I think, what we should be doing.”
Some research suggests that patients are open to deprescribing. One survey examined older adults (mean age, 79.1 years) with three or more chronic conditions who had been prescribed at least five medications. The researchers found that most participants (77%) were willing to deprescribe one or more medicines if a doctor advised that it was possible. “General practitioners may be able to increase deprescribing by building trust with their patients and communicating evidence about the risks of medication use,” the researchers wrote.
About 62% of seniors living in a residential care home have a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease or another dementia, according to the Alzheimer Society of Canada. Evidence suggests that nonpharmacologic approaches, such as massage and touch therapy and music, can manage neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as aggression and agitation, that are associated with dementia in older adults, noted Gurau.
“We want to focus on nonpharmacologic approaches for many of these [long-term care] residents,” said Gurau. “We have to do as much as we can to exhaust all the nonpharmacologic approaches.”
Preventing Hospitalizations
Another challenge to tackle in long-term care is the unnecessary transfer of residents to hospital emergency departments, according to Gurau. “In many situations, it’s worth trying as hard as we can to treat them in the nursing home, as opposed to having them go to hospital.”
Researchers estimated that 25% of the transfers from long-term care facilities in Canada to hospital emergency departments in 2014 were potentially preventable.
Urinary tract infections accounted for 30% of hospital emergency department visits for potentially preventable conditions by older patients who are residents in long-term care, according to 2013-2014 data from the Canadian Institute for Health Information.
“There are lots of downsides to going to the hospital [from long-term care],” Gurau told this news organization. “There are risks for infections, risks for increasing delirium and agitation [in patients with dementia], and risks for other behavior that can really impact somebody’s life.”
Gurau reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — Conditions like diabetes and dementia are common in patients who are admitted to long-term care facilities, but aggressive management of these conditions in long-term care residents is not recommended, according to a presentation given at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
Hospitalizations for hypoglycemia are risky for patients with diabetes who are residents of long-term care facilities, particularly those aged 75 years or older, said Adam Gurau, MD, a family physician in Toronto. Gurau completed a fellowship in care of the elderly at the University of Toronto, in Ontario, Canada.
“A lot of studies have shown diabetes-related hospitalizations,” said Gurau. He cited a 2014 study that found that hypoglycemia hospitalization rates were twice as high in older patients (age, 75 years or older) as in younger patients (age, 65-74 years).
“It is important to keep in mind that our residents in long-term care are at increasing risk for hypoglycemia, and we really should try to reduce [this risk] and not use dangerous medications or potentially dangerous [means of] diabetes management,” said Gurau.
A Canadian study that examined the composite risk for emergency department visits, hospitalizations, or death within 30 days of reaching intensive glycemic control with high-risk agents (such as insulin or sulfonylureas) suggested little benefit and possible harm in using these agents in adults aged 75 years or older.
In addition, current guidelines on diabetes management encourage a different approach. “Looking at some of the more recent North American guidelines, many of them actually now recommend relaxing glycemic targets to reduce overtreatment and prevent hypoglycemia,” said Gurau.
Deprescribing Medications
Medication reviews present opportunities for taking a global view of a patient’s treatments and determining whether any drug can be removed from the list. “What we want to do is optimize medications,” said Gurau. “We’re not talking about adding medications. We’re talking about removing medications, which is, I think, what we should be doing.”
Some research suggests that patients are open to deprescribing. One survey examined older adults (mean age, 79.1 years) with three or more chronic conditions who had been prescribed at least five medications. The researchers found that most participants (77%) were willing to deprescribe one or more medicines if a doctor advised that it was possible. “General practitioners may be able to increase deprescribing by building trust with their patients and communicating evidence about the risks of medication use,” the researchers wrote.
About 62% of seniors living in a residential care home have a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease or another dementia, according to the Alzheimer Society of Canada. Evidence suggests that nonpharmacologic approaches, such as massage and touch therapy and music, can manage neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as aggression and agitation, that are associated with dementia in older adults, noted Gurau.
“We want to focus on nonpharmacologic approaches for many of these [long-term care] residents,” said Gurau. “We have to do as much as we can to exhaust all the nonpharmacologic approaches.”
Preventing Hospitalizations
Another challenge to tackle in long-term care is the unnecessary transfer of residents to hospital emergency departments, according to Gurau. “In many situations, it’s worth trying as hard as we can to treat them in the nursing home, as opposed to having them go to hospital.”
Researchers estimated that 25% of the transfers from long-term care facilities in Canada to hospital emergency departments in 2014 were potentially preventable.
Urinary tract infections accounted for 30% of hospital emergency department visits for potentially preventable conditions by older patients who are residents in long-term care, according to 2013-2014 data from the Canadian Institute for Health Information.
“There are lots of downsides to going to the hospital [from long-term care],” Gurau told this news organization. “There are risks for infections, risks for increasing delirium and agitation [in patients with dementia], and risks for other behavior that can really impact somebody’s life.”
Gurau reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM FMF 2024
First Phase 3 Drug Trial in IgG4-Related Disease Has Success
WASHINGTON — The B cell–depleting agent inebilizumab (Uplizna) dramatically reduced the risk of flares and increased year-long remission of IgG4-related disease (RD), new research has found.
In a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 135 adults with active IgG4-RD, treatment with inebilizumab resulted in a significant 87% reduction in flare risk and nearly fivefold greater likelihood of flare-free remission at 1 year. The results were published online November 14 in The New England Journal of Medicine and were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The drug’s manufacturer, Amgen, released top-line results of the trial, called MITIGATE, in June 2024.
Until now, the mainstay of management for the chronic multiorgan disease IgG4-RD has been glucocorticoids, which can cause numerous adverse effects. “It is hoped that inebilizumab can be used as an important steroid-sparing medication in this disease to reduce steroid toxicity,” lead author John H. Stone, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview, noting that it may not entirely eliminate the need for steroid treatment, but for many, it appears to work after the remission induction period as a monotherapy without steroids.
Asked to comment, Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, head of the Section of Clinical Immunology and manager of the Clinical Immunology Clinic at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, said: “There has been anecdotal or observational evidence for some effect with other immunosuppressive agents, including rituximab, but no robust clinical trial until this study. This clearly has demonstrated efficacy by reducing the risk of flares. And most importantly, putting people into remission means no active disease in any given organ. ... This gives us another tool in the toolbox to attack B cell–directed diseases, and I think it really makes a lot of sense.”
Calabrese cautioned, though, that “this is a disease that extends over many years. This is just a 1-year study. Label extensions will be important.”
And several questions remain, Calabrese noted: “How long do patients need to remain on drug? What will happen when the drug is stopped? Can they be retreated? These are the natural questions that arise in any sentinel study like this. But this is extremely encouraging. And I think it’s great for patients. I also think it’s a clarion call to increase awareness about this disease since there’s now strong evidence of effective treatment.”
Underrecognized, Often Misdiagnosed as Cancer
Indeed, IgG4-RD, a chronic, relapsing, autoimmune, fibro-inflammatory multiorgan disease, was only first described in Japan in 2003. Since then, it has been reported all over the world yet remains vastly underrecognized. It is often misdiagnosed as cancer because it produces lesions in multiple organs. It received an ICD-10 code only about a year ago. A previous study estimated a prevalence of about 5.3 persons per 100,000 but that is likely to be a three- to fourfold underestimate, said Stone, who is also executive chairman of the IgG4ward! Foundation.
“Nobody had heard of the disease until about 20 years ago. ... And there are many people in the world who have still not heard of it despite the fact that it is a multiorgan autoimmune disease and is probably as common, or more common, than many other diseases that rheumatologists spend a lot of time thinking about, such as scleroderma.”
While knowledge about the disease is increasing in rheumatology circles, it’s less well-recognized among many of the specialties where patients present, depending on the location of their lesions. These include gastroenterology, ophthalmology, pulmonary medicine, neurology, and nephrology. “All would be likely to see this disease,” Stone said.
The disease can be mistaken for tumors in many of those locations and even as metastatic cancer, he noted, adding that “any time a patient has a mass lesion in a typical organ, the pancreas, the major salivary glands, the lungs, or the kidneys, this should be on the differential diagnosis.”
The diagnosis of IgG4-RD is a clinical one, involving “quadrangulation between clinical features, serological findings, IgG4 levels in the blood, radiology studies, and then pathology biopsies when those are available,” Stone said.
Calabrese characterized the current situation as “we’re all blind men on the elephant. To the neurologist or the neurosurgeon, it’s a mass in the brain. It could present to the ophthalmologist as an [eye] tumor. It can be thyroid gland failure, pulmonary disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis, hepatobiliary disease, and beyond. So, whoever sees that patient, there’s often a long lag time in recognizing it.”
And interestingly, Stone noted that unlike other autoimmune diseases, IgG4-RD primarily affects middle-aged men rather than younger-to-middle-aged women. And when IgG4-RD is diagnosed, glucocorticoid treatment can be particularly toxic when the pancreas is involved, heightening the risk for hyperglycemia and potentially causing diabetes.
Dramatic Improvement in Flares, Remission Achievement
MITIGATE is a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in which 135 adults (mean age 58.2 years, 88 men) with active IgG4-RD were randomized 1:1 to receive 300-mg intravenous infusions of inebilizumab or placebo on days 1 and 15, and again at week 26. At baseline, 62 (45.9%) participants had newly diagnosed IgG4-RD and 73 (54.1%) had recurrent disease.
Both groups received identical glucocorticoid tapers. Overall, 127 (94.1%) completed the 52 weeks of treatment.
By 52 weeks, only seven patients in the inebilizumab group (10%) had experienced disease flares vs 40 (60%) in the placebo group, a significant difference with a hazard ratio of 0.13 (P < .001).
The percentage of participants achieving flare-free, treatment-free complete remission was 59 with inebilizumab (57%), compared with just 15 (22%) in the placebo group (odds ratio [OR], 4.68; P < .001). And for flare-free, glucocorticoid-free complete remission, those proportions were 40 (59%) vs 15 (22%), respectively (OR, 4.96; P < .001).
Excluding the 8-week glucocorticoid taper period, mean total glucocorticoid use was 1264.2 mg less in the inebilizumab than the placebo group, a significant reduction. Overall, 61 participants (90%) were able to entirely discontinue glucocorticoids during the trial, compared with just 25 (37%) in the placebo group.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 12 participants (18%) in the inebilizumab group and 8 (12%) in the placebo group; serious adverse events occurred in 12 (18%) and 6 (9%), respectively. However, no serious adverse event occurred in more than one participant, and there were no deaths. Adverse events led to withdrawal from the trial in six patients (9%) in the inebilizumab group and three patients (4%) in the placebo group.
Adverse events that occurred in more than 10% of participants in the inebilizumab group were COVID-19 in 16 participants (24%), lymphopenia in 11 (16%), and urinary tract infection in 8 (12%).
Importantly, Stone noted, B-cell depletion can reduce responses to vaccines, so patients should receive all recommended vaccinations, including COVID-19, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and others, prior to initiating therapy.
Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in 2020. In October 2024, the FDA granted Amgen breakthrough therapy designation for use in IgG4-RD. The company is also developing the drug for use in myasthenia gravis.
The study was funded by Amgen. Stone has reported being a consultant for Amgen, Zenas, Argenx, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Sanofi, and Horizon Pharma. Calabrese has reported being a consultant and/or speaker for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Jansen, Sanofi, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — The B cell–depleting agent inebilizumab (Uplizna) dramatically reduced the risk of flares and increased year-long remission of IgG4-related disease (RD), new research has found.
In a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 135 adults with active IgG4-RD, treatment with inebilizumab resulted in a significant 87% reduction in flare risk and nearly fivefold greater likelihood of flare-free remission at 1 year. The results were published online November 14 in The New England Journal of Medicine and were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The drug’s manufacturer, Amgen, released top-line results of the trial, called MITIGATE, in June 2024.
Until now, the mainstay of management for the chronic multiorgan disease IgG4-RD has been glucocorticoids, which can cause numerous adverse effects. “It is hoped that inebilizumab can be used as an important steroid-sparing medication in this disease to reduce steroid toxicity,” lead author John H. Stone, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview, noting that it may not entirely eliminate the need for steroid treatment, but for many, it appears to work after the remission induction period as a monotherapy without steroids.
Asked to comment, Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, head of the Section of Clinical Immunology and manager of the Clinical Immunology Clinic at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, said: “There has been anecdotal or observational evidence for some effect with other immunosuppressive agents, including rituximab, but no robust clinical trial until this study. This clearly has demonstrated efficacy by reducing the risk of flares. And most importantly, putting people into remission means no active disease in any given organ. ... This gives us another tool in the toolbox to attack B cell–directed diseases, and I think it really makes a lot of sense.”
Calabrese cautioned, though, that “this is a disease that extends over many years. This is just a 1-year study. Label extensions will be important.”
And several questions remain, Calabrese noted: “How long do patients need to remain on drug? What will happen when the drug is stopped? Can they be retreated? These are the natural questions that arise in any sentinel study like this. But this is extremely encouraging. And I think it’s great for patients. I also think it’s a clarion call to increase awareness about this disease since there’s now strong evidence of effective treatment.”
Underrecognized, Often Misdiagnosed as Cancer
Indeed, IgG4-RD, a chronic, relapsing, autoimmune, fibro-inflammatory multiorgan disease, was only first described in Japan in 2003. Since then, it has been reported all over the world yet remains vastly underrecognized. It is often misdiagnosed as cancer because it produces lesions in multiple organs. It received an ICD-10 code only about a year ago. A previous study estimated a prevalence of about 5.3 persons per 100,000 but that is likely to be a three- to fourfold underestimate, said Stone, who is also executive chairman of the IgG4ward! Foundation.
“Nobody had heard of the disease until about 20 years ago. ... And there are many people in the world who have still not heard of it despite the fact that it is a multiorgan autoimmune disease and is probably as common, or more common, than many other diseases that rheumatologists spend a lot of time thinking about, such as scleroderma.”
While knowledge about the disease is increasing in rheumatology circles, it’s less well-recognized among many of the specialties where patients present, depending on the location of their lesions. These include gastroenterology, ophthalmology, pulmonary medicine, neurology, and nephrology. “All would be likely to see this disease,” Stone said.
The disease can be mistaken for tumors in many of those locations and even as metastatic cancer, he noted, adding that “any time a patient has a mass lesion in a typical organ, the pancreas, the major salivary glands, the lungs, or the kidneys, this should be on the differential diagnosis.”
The diagnosis of IgG4-RD is a clinical one, involving “quadrangulation between clinical features, serological findings, IgG4 levels in the blood, radiology studies, and then pathology biopsies when those are available,” Stone said.
Calabrese characterized the current situation as “we’re all blind men on the elephant. To the neurologist or the neurosurgeon, it’s a mass in the brain. It could present to the ophthalmologist as an [eye] tumor. It can be thyroid gland failure, pulmonary disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis, hepatobiliary disease, and beyond. So, whoever sees that patient, there’s often a long lag time in recognizing it.”
And interestingly, Stone noted that unlike other autoimmune diseases, IgG4-RD primarily affects middle-aged men rather than younger-to-middle-aged women. And when IgG4-RD is diagnosed, glucocorticoid treatment can be particularly toxic when the pancreas is involved, heightening the risk for hyperglycemia and potentially causing diabetes.
Dramatic Improvement in Flares, Remission Achievement
MITIGATE is a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in which 135 adults (mean age 58.2 years, 88 men) with active IgG4-RD were randomized 1:1 to receive 300-mg intravenous infusions of inebilizumab or placebo on days 1 and 15, and again at week 26. At baseline, 62 (45.9%) participants had newly diagnosed IgG4-RD and 73 (54.1%) had recurrent disease.
Both groups received identical glucocorticoid tapers. Overall, 127 (94.1%) completed the 52 weeks of treatment.
By 52 weeks, only seven patients in the inebilizumab group (10%) had experienced disease flares vs 40 (60%) in the placebo group, a significant difference with a hazard ratio of 0.13 (P < .001).
The percentage of participants achieving flare-free, treatment-free complete remission was 59 with inebilizumab (57%), compared with just 15 (22%) in the placebo group (odds ratio [OR], 4.68; P < .001). And for flare-free, glucocorticoid-free complete remission, those proportions were 40 (59%) vs 15 (22%), respectively (OR, 4.96; P < .001).
Excluding the 8-week glucocorticoid taper period, mean total glucocorticoid use was 1264.2 mg less in the inebilizumab than the placebo group, a significant reduction. Overall, 61 participants (90%) were able to entirely discontinue glucocorticoids during the trial, compared with just 25 (37%) in the placebo group.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 12 participants (18%) in the inebilizumab group and 8 (12%) in the placebo group; serious adverse events occurred in 12 (18%) and 6 (9%), respectively. However, no serious adverse event occurred in more than one participant, and there were no deaths. Adverse events led to withdrawal from the trial in six patients (9%) in the inebilizumab group and three patients (4%) in the placebo group.
Adverse events that occurred in more than 10% of participants in the inebilizumab group were COVID-19 in 16 participants (24%), lymphopenia in 11 (16%), and urinary tract infection in 8 (12%).
Importantly, Stone noted, B-cell depletion can reduce responses to vaccines, so patients should receive all recommended vaccinations, including COVID-19, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and others, prior to initiating therapy.
Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in 2020. In October 2024, the FDA granted Amgen breakthrough therapy designation for use in IgG4-RD. The company is also developing the drug for use in myasthenia gravis.
The study was funded by Amgen. Stone has reported being a consultant for Amgen, Zenas, Argenx, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Sanofi, and Horizon Pharma. Calabrese has reported being a consultant and/or speaker for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Jansen, Sanofi, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — The B cell–depleting agent inebilizumab (Uplizna) dramatically reduced the risk of flares and increased year-long remission of IgG4-related disease (RD), new research has found.
In a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 135 adults with active IgG4-RD, treatment with inebilizumab resulted in a significant 87% reduction in flare risk and nearly fivefold greater likelihood of flare-free remission at 1 year. The results were published online November 14 in The New England Journal of Medicine and were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The drug’s manufacturer, Amgen, released top-line results of the trial, called MITIGATE, in June 2024.
Until now, the mainstay of management for the chronic multiorgan disease IgG4-RD has been glucocorticoids, which can cause numerous adverse effects. “It is hoped that inebilizumab can be used as an important steroid-sparing medication in this disease to reduce steroid toxicity,” lead author John H. Stone, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview, noting that it may not entirely eliminate the need for steroid treatment, but for many, it appears to work after the remission induction period as a monotherapy without steroids.
Asked to comment, Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, head of the Section of Clinical Immunology and manager of the Clinical Immunology Clinic at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, said: “There has been anecdotal or observational evidence for some effect with other immunosuppressive agents, including rituximab, but no robust clinical trial until this study. This clearly has demonstrated efficacy by reducing the risk of flares. And most importantly, putting people into remission means no active disease in any given organ. ... This gives us another tool in the toolbox to attack B cell–directed diseases, and I think it really makes a lot of sense.”
Calabrese cautioned, though, that “this is a disease that extends over many years. This is just a 1-year study. Label extensions will be important.”
And several questions remain, Calabrese noted: “How long do patients need to remain on drug? What will happen when the drug is stopped? Can they be retreated? These are the natural questions that arise in any sentinel study like this. But this is extremely encouraging. And I think it’s great for patients. I also think it’s a clarion call to increase awareness about this disease since there’s now strong evidence of effective treatment.”
Underrecognized, Often Misdiagnosed as Cancer
Indeed, IgG4-RD, a chronic, relapsing, autoimmune, fibro-inflammatory multiorgan disease, was only first described in Japan in 2003. Since then, it has been reported all over the world yet remains vastly underrecognized. It is often misdiagnosed as cancer because it produces lesions in multiple organs. It received an ICD-10 code only about a year ago. A previous study estimated a prevalence of about 5.3 persons per 100,000 but that is likely to be a three- to fourfold underestimate, said Stone, who is also executive chairman of the IgG4ward! Foundation.
“Nobody had heard of the disease until about 20 years ago. ... And there are many people in the world who have still not heard of it despite the fact that it is a multiorgan autoimmune disease and is probably as common, or more common, than many other diseases that rheumatologists spend a lot of time thinking about, such as scleroderma.”
While knowledge about the disease is increasing in rheumatology circles, it’s less well-recognized among many of the specialties where patients present, depending on the location of their lesions. These include gastroenterology, ophthalmology, pulmonary medicine, neurology, and nephrology. “All would be likely to see this disease,” Stone said.
The disease can be mistaken for tumors in many of those locations and even as metastatic cancer, he noted, adding that “any time a patient has a mass lesion in a typical organ, the pancreas, the major salivary glands, the lungs, or the kidneys, this should be on the differential diagnosis.”
The diagnosis of IgG4-RD is a clinical one, involving “quadrangulation between clinical features, serological findings, IgG4 levels in the blood, radiology studies, and then pathology biopsies when those are available,” Stone said.
Calabrese characterized the current situation as “we’re all blind men on the elephant. To the neurologist or the neurosurgeon, it’s a mass in the brain. It could present to the ophthalmologist as an [eye] tumor. It can be thyroid gland failure, pulmonary disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis, hepatobiliary disease, and beyond. So, whoever sees that patient, there’s often a long lag time in recognizing it.”
And interestingly, Stone noted that unlike other autoimmune diseases, IgG4-RD primarily affects middle-aged men rather than younger-to-middle-aged women. And when IgG4-RD is diagnosed, glucocorticoid treatment can be particularly toxic when the pancreas is involved, heightening the risk for hyperglycemia and potentially causing diabetes.
Dramatic Improvement in Flares, Remission Achievement
MITIGATE is a phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in which 135 adults (mean age 58.2 years, 88 men) with active IgG4-RD were randomized 1:1 to receive 300-mg intravenous infusions of inebilizumab or placebo on days 1 and 15, and again at week 26. At baseline, 62 (45.9%) participants had newly diagnosed IgG4-RD and 73 (54.1%) had recurrent disease.
Both groups received identical glucocorticoid tapers. Overall, 127 (94.1%) completed the 52 weeks of treatment.
By 52 weeks, only seven patients in the inebilizumab group (10%) had experienced disease flares vs 40 (60%) in the placebo group, a significant difference with a hazard ratio of 0.13 (P < .001).
The percentage of participants achieving flare-free, treatment-free complete remission was 59 with inebilizumab (57%), compared with just 15 (22%) in the placebo group (odds ratio [OR], 4.68; P < .001). And for flare-free, glucocorticoid-free complete remission, those proportions were 40 (59%) vs 15 (22%), respectively (OR, 4.96; P < .001).
Excluding the 8-week glucocorticoid taper period, mean total glucocorticoid use was 1264.2 mg less in the inebilizumab than the placebo group, a significant reduction. Overall, 61 participants (90%) were able to entirely discontinue glucocorticoids during the trial, compared with just 25 (37%) in the placebo group.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 12 participants (18%) in the inebilizumab group and 8 (12%) in the placebo group; serious adverse events occurred in 12 (18%) and 6 (9%), respectively. However, no serious adverse event occurred in more than one participant, and there were no deaths. Adverse events led to withdrawal from the trial in six patients (9%) in the inebilizumab group and three patients (4%) in the placebo group.
Adverse events that occurred in more than 10% of participants in the inebilizumab group were COVID-19 in 16 participants (24%), lymphopenia in 11 (16%), and urinary tract infection in 8 (12%).
Importantly, Stone noted, B-cell depletion can reduce responses to vaccines, so patients should receive all recommended vaccinations, including COVID-19, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and others, prior to initiating therapy.
Uplizna (inebilizumab-cdon) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in 2020. In October 2024, the FDA granted Amgen breakthrough therapy designation for use in IgG4-RD. The company is also developing the drug for use in myasthenia gravis.
The study was funded by Amgen. Stone has reported being a consultant for Amgen, Zenas, Argenx, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Sanofi, and Horizon Pharma. Calabrese has reported being a consultant and/or speaker for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Jansen, Sanofi, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
The Use of Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease in Primary Care
In our previous case-based review, I teased the opportunity to use biomarkers to increase the accuracy and expediency of the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). These tests are no longer confined to the research setting but are now available to specialists and primary care clinicians alike. Given that most cognitive disorders are first identified in primary care, however, I believe that their greatest impact will be in our clinical space.
The pathologic processes associated with AD can be detected approximately 2 decades before the advent of clinical symptoms, and the symptomatic period of cognitive impairment is estimated to occupy just the final third of the disease course of AD. Using imaging studies, primarily PET, as well as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and even blood biomarkers for beta amyloid and tau, the pathologic drivers of AD, clinicians can identify patients with AD pathology before any symptoms are present. Importantly for our present-day interventions, the application of biomarkers can also help to diagnose AD earlier.
Amyloid PET identifies one of the earliest markers of potential AD, but a barrier common to advanced diagnostic imaging has been cost. Medicare has now approved coverage for amyloid PET in cases of suspected cognitive impairment. In a large study of more than 16,000 older adults in the United States, PET scans were positive in 55.3% of cases with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The PET positivity rate among adults with other dementia was 70.1%. The application of PET resulted in a change in care in more than 60% of patients with MCI and dementia. One quarter of participants had their diagnosis changed from AD to another form of dementia, and 10% were changed from a diagnosis of other dementia to AD.
Liquid biomarkers can involve either CSF or blood samples. To date, CSF testing has yielded more consistent results and has defined protocols for assessment. Still, collection of CSF is more challenging than collection of blood, and patients and their families may object to lumbar puncture. CSF assessment therefore remains generally in the province of specialists and research centers.
Primary care clinicians have been waiting for a reliable blood-based biomarker for AD, and that wait may be about to end. A study published in July 2024 included 1213 adults being evaluated for cognitive symptoms in Sweden. They completed a test measuring the ratio of phosphorylated tau 217 vs nonphosphorylated tau 217, with or without a test for serum amyloid ratios as well. These tests were compared with clinicians’ clinical diagnoses as well as CSF results, which were considered the gold standard.
Using only clinical tools, primary care clinicians’ and specialists’ diagnostic accuracy for MCI and dementia were just 61% and 73%, respectively. These values were substantially weaker vs the performance of either the serum tau or amyloid ratios (both 90% accurate). The authors concluded that serum testing has the potential to improve clinical care of patients with cognitive impairment.
Where does that leave us today? Commercially available blood biomarkers are available now which use different tests and cutoff values. These may be helpful but will probably be difficult to compare and interpret for primary care clinicians. In addition, insurance is less likely to cover these tests. Amyloid PET scans are a very reasonable option to augment clinician judgment of suspected cognitive impairment, but not all geographic areas will have ready access to this imaging study.
Still, it is an exciting time to have more objective tools at our disposal to identify MCI and AD. These tools can only be optimized by clinicians who recognize symptoms and perform the baseline testing necessary to determine pretest probability of MCI or dementia.
Charles P. Vega, Health Sciences Clinical Professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In our previous case-based review, I teased the opportunity to use biomarkers to increase the accuracy and expediency of the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). These tests are no longer confined to the research setting but are now available to specialists and primary care clinicians alike. Given that most cognitive disorders are first identified in primary care, however, I believe that their greatest impact will be in our clinical space.
The pathologic processes associated with AD can be detected approximately 2 decades before the advent of clinical symptoms, and the symptomatic period of cognitive impairment is estimated to occupy just the final third of the disease course of AD. Using imaging studies, primarily PET, as well as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and even blood biomarkers for beta amyloid and tau, the pathologic drivers of AD, clinicians can identify patients with AD pathology before any symptoms are present. Importantly for our present-day interventions, the application of biomarkers can also help to diagnose AD earlier.
Amyloid PET identifies one of the earliest markers of potential AD, but a barrier common to advanced diagnostic imaging has been cost. Medicare has now approved coverage for amyloid PET in cases of suspected cognitive impairment. In a large study of more than 16,000 older adults in the United States, PET scans were positive in 55.3% of cases with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The PET positivity rate among adults with other dementia was 70.1%. The application of PET resulted in a change in care in more than 60% of patients with MCI and dementia. One quarter of participants had their diagnosis changed from AD to another form of dementia, and 10% were changed from a diagnosis of other dementia to AD.
Liquid biomarkers can involve either CSF or blood samples. To date, CSF testing has yielded more consistent results and has defined protocols for assessment. Still, collection of CSF is more challenging than collection of blood, and patients and their families may object to lumbar puncture. CSF assessment therefore remains generally in the province of specialists and research centers.
Primary care clinicians have been waiting for a reliable blood-based biomarker for AD, and that wait may be about to end. A study published in July 2024 included 1213 adults being evaluated for cognitive symptoms in Sweden. They completed a test measuring the ratio of phosphorylated tau 217 vs nonphosphorylated tau 217, with or without a test for serum amyloid ratios as well. These tests were compared with clinicians’ clinical diagnoses as well as CSF results, which were considered the gold standard.
Using only clinical tools, primary care clinicians’ and specialists’ diagnostic accuracy for MCI and dementia were just 61% and 73%, respectively. These values were substantially weaker vs the performance of either the serum tau or amyloid ratios (both 90% accurate). The authors concluded that serum testing has the potential to improve clinical care of patients with cognitive impairment.
Where does that leave us today? Commercially available blood biomarkers are available now which use different tests and cutoff values. These may be helpful but will probably be difficult to compare and interpret for primary care clinicians. In addition, insurance is less likely to cover these tests. Amyloid PET scans are a very reasonable option to augment clinician judgment of suspected cognitive impairment, but not all geographic areas will have ready access to this imaging study.
Still, it is an exciting time to have more objective tools at our disposal to identify MCI and AD. These tools can only be optimized by clinicians who recognize symptoms and perform the baseline testing necessary to determine pretest probability of MCI or dementia.
Charles P. Vega, Health Sciences Clinical Professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In our previous case-based review, I teased the opportunity to use biomarkers to increase the accuracy and expediency of the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). These tests are no longer confined to the research setting but are now available to specialists and primary care clinicians alike. Given that most cognitive disorders are first identified in primary care, however, I believe that their greatest impact will be in our clinical space.
The pathologic processes associated with AD can be detected approximately 2 decades before the advent of clinical symptoms, and the symptomatic period of cognitive impairment is estimated to occupy just the final third of the disease course of AD. Using imaging studies, primarily PET, as well as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and even blood biomarkers for beta amyloid and tau, the pathologic drivers of AD, clinicians can identify patients with AD pathology before any symptoms are present. Importantly for our present-day interventions, the application of biomarkers can also help to diagnose AD earlier.
Amyloid PET identifies one of the earliest markers of potential AD, but a barrier common to advanced diagnostic imaging has been cost. Medicare has now approved coverage for amyloid PET in cases of suspected cognitive impairment. In a large study of more than 16,000 older adults in the United States, PET scans were positive in 55.3% of cases with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The PET positivity rate among adults with other dementia was 70.1%. The application of PET resulted in a change in care in more than 60% of patients with MCI and dementia. One quarter of participants had their diagnosis changed from AD to another form of dementia, and 10% were changed from a diagnosis of other dementia to AD.
Liquid biomarkers can involve either CSF or blood samples. To date, CSF testing has yielded more consistent results and has defined protocols for assessment. Still, collection of CSF is more challenging than collection of blood, and patients and their families may object to lumbar puncture. CSF assessment therefore remains generally in the province of specialists and research centers.
Primary care clinicians have been waiting for a reliable blood-based biomarker for AD, and that wait may be about to end. A study published in July 2024 included 1213 adults being evaluated for cognitive symptoms in Sweden. They completed a test measuring the ratio of phosphorylated tau 217 vs nonphosphorylated tau 217, with or without a test for serum amyloid ratios as well. These tests were compared with clinicians’ clinical diagnoses as well as CSF results, which were considered the gold standard.
Using only clinical tools, primary care clinicians’ and specialists’ diagnostic accuracy for MCI and dementia were just 61% and 73%, respectively. These values were substantially weaker vs the performance of either the serum tau or amyloid ratios (both 90% accurate). The authors concluded that serum testing has the potential to improve clinical care of patients with cognitive impairment.
Where does that leave us today? Commercially available blood biomarkers are available now which use different tests and cutoff values. These may be helpful but will probably be difficult to compare and interpret for primary care clinicians. In addition, insurance is less likely to cover these tests. Amyloid PET scans are a very reasonable option to augment clinician judgment of suspected cognitive impairment, but not all geographic areas will have ready access to this imaging study.
Still, it is an exciting time to have more objective tools at our disposal to identify MCI and AD. These tools can only be optimized by clinicians who recognize symptoms and perform the baseline testing necessary to determine pretest probability of MCI or dementia.
Charles P. Vega, Health Sciences Clinical Professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A New and Early Predictor of Dementia?
, in new findings that may provide a potential opportunity to identify high-risk populations for targeted enrollment in clinical trials of dementia prevention and treatment.
Results of an international study assessing frailty trajectories showed frailty levels notably increased in the 4-9 years before dementia diagnosis. Even among study participants whose baseline frailty measurement was taken prior to that acceleration period, frailty was still positively associated with dementia risk, the investigators noted.
“We found that with every four to five additional health problems, there is on average a 40% higher risk of developing dementia, while the risk is lower for people who are more physically fit,” said study investigator David Ward, PhD, of the Centre for Health Services Research, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A Promising Biomarker
An accessible biomarker for both biologic age and dementia risk is essential for advancing dementia prevention and treatment strategies, the investigators noted, adding that growing evidence suggests frailty may be a promising candidate for this role.
To learn more about the association between frailty and dementia, Ward and his team analyzed data on 29,849 participants aged 60 years or above (mean age, 71.6 years; 62% women) who participated in four cohort studies: the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA; n = 6771), the Health and Retirement Study (HRS; n = 9045), the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP; n = 1451), and the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC; n = 12,582).
The primary outcome was all-cause dementia. Depending on the cohort, dementia diagnoses were determined through cognitive testing, self- or family report of physician diagnosis, or a diagnosis by the study physician. Participants were excluded if they had cognitive impairment at baseline.
Investigators retrospectively determined frailty index scores by gathering information on health and functional outcomes for participants from each cohort. Only participants with frailty data on at least 30 deficits were included.
Commonly included deficits included high blood pressure, cancer, and chronic pain, as well as functional problems such as hearing impairment, difficulty with mobility, and challenges managing finances.
Investigators conducted follow-up visits with participants until they developed dementia or until the study ended, with follow-up periods varying across cohorts.
After adjustment for potential confounders, frailty scores were modeled using backward time scales.
Among participants who developed incident dementia (n = 3154), covariate-adjusted expected frailty index scores were, on average, higher in women than in men by 18.5% in ELSA, 20.9% in HRS, and 16.2% in MAP. There were no differences in frailty scores between sexes in the NACC cohort.
When measured on a timeline, as compared with those who didn’t develop dementia, frailty scores were significantly and consistently higher in the dementia groups 8-20 before dementia onset (20 years in HRS; 13 in MAP; 12 in ELSA; 8 in NACC).
Increases in the rates of frailty index scores began accelerating 4-9 years before dementia onset for the various cohorts, investigators noted.
In all four cohorts, each 0.1 increase in frailty scores was positively associated with increased dementia risk.
Adjusted hazard ratios [aHRs] ranged from 1.18 in the HRS cohort to 1.73 in the NACC cohort, which showed the strongest association.
In participants whose baseline frailty measurement was conducted before the predementia acceleration period began, the association of frailty scores and dementia risk was positive. These aHRs ranged from 1.18 in the HRS cohort to 1.43 in the NACC cohort.
The ‘Four Pillars’ of Prevention
The good news, investigators said, is that the long trajectory of frailty symptoms preceding dementia onset provides plenty of opportunity for intervention.
To slow the development of frailty, Ward suggested adhering to the “four pillars of frailty prevention and management,” which include good nutrition with plenty of protein, exercise, optimizing medications for chronic conditions, and maintaining a strong social network.
Ward suggested neurologists track frailty in their patients and pointed to a recent article focused on helping neurologists use frailty measures to influence care planning.
Study limitations include the possibility of reverse causality and the fact that investigators could not adjust for genetic risk for dementia.
Unclear Pathway
Commenting on the findings, Lycia Neumann, PhD, senior director of Health Services Research at the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that many studies over the years have shown a link between frailty and dementia. However, she cautioned that a link does not imply causation.
The pathway from frailty to dementia is not 100% clear, and both are complex conditions, said Neumann, who was not part of the study.
“Adopting healthy lifestyle behaviors early and consistently can help decrease the risk of — or postpone the onset of — both frailty and cognitive decline,” she said. Neumann added that physical activity, a healthy diet, social engagement, and controlling diabetes and blood pressure can also reduce the risk for dementia as well as cardiovascular disease.
The study was funded in part by the Deep Dementia Phenotyping Network through the Frailty and Dementia Special Interest Group. Ward and Neumann reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, in new findings that may provide a potential opportunity to identify high-risk populations for targeted enrollment in clinical trials of dementia prevention and treatment.
Results of an international study assessing frailty trajectories showed frailty levels notably increased in the 4-9 years before dementia diagnosis. Even among study participants whose baseline frailty measurement was taken prior to that acceleration period, frailty was still positively associated with dementia risk, the investigators noted.
“We found that with every four to five additional health problems, there is on average a 40% higher risk of developing dementia, while the risk is lower for people who are more physically fit,” said study investigator David Ward, PhD, of the Centre for Health Services Research, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A Promising Biomarker
An accessible biomarker for both biologic age and dementia risk is essential for advancing dementia prevention and treatment strategies, the investigators noted, adding that growing evidence suggests frailty may be a promising candidate for this role.
To learn more about the association between frailty and dementia, Ward and his team analyzed data on 29,849 participants aged 60 years or above (mean age, 71.6 years; 62% women) who participated in four cohort studies: the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA; n = 6771), the Health and Retirement Study (HRS; n = 9045), the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP; n = 1451), and the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC; n = 12,582).
The primary outcome was all-cause dementia. Depending on the cohort, dementia diagnoses were determined through cognitive testing, self- or family report of physician diagnosis, or a diagnosis by the study physician. Participants were excluded if they had cognitive impairment at baseline.
Investigators retrospectively determined frailty index scores by gathering information on health and functional outcomes for participants from each cohort. Only participants with frailty data on at least 30 deficits were included.
Commonly included deficits included high blood pressure, cancer, and chronic pain, as well as functional problems such as hearing impairment, difficulty with mobility, and challenges managing finances.
Investigators conducted follow-up visits with participants until they developed dementia or until the study ended, with follow-up periods varying across cohorts.
After adjustment for potential confounders, frailty scores were modeled using backward time scales.
Among participants who developed incident dementia (n = 3154), covariate-adjusted expected frailty index scores were, on average, higher in women than in men by 18.5% in ELSA, 20.9% in HRS, and 16.2% in MAP. There were no differences in frailty scores between sexes in the NACC cohort.
When measured on a timeline, as compared with those who didn’t develop dementia, frailty scores were significantly and consistently higher in the dementia groups 8-20 before dementia onset (20 years in HRS; 13 in MAP; 12 in ELSA; 8 in NACC).
Increases in the rates of frailty index scores began accelerating 4-9 years before dementia onset for the various cohorts, investigators noted.
In all four cohorts, each 0.1 increase in frailty scores was positively associated with increased dementia risk.
Adjusted hazard ratios [aHRs] ranged from 1.18 in the HRS cohort to 1.73 in the NACC cohort, which showed the strongest association.
In participants whose baseline frailty measurement was conducted before the predementia acceleration period began, the association of frailty scores and dementia risk was positive. These aHRs ranged from 1.18 in the HRS cohort to 1.43 in the NACC cohort.
The ‘Four Pillars’ of Prevention
The good news, investigators said, is that the long trajectory of frailty symptoms preceding dementia onset provides plenty of opportunity for intervention.
To slow the development of frailty, Ward suggested adhering to the “four pillars of frailty prevention and management,” which include good nutrition with plenty of protein, exercise, optimizing medications for chronic conditions, and maintaining a strong social network.
Ward suggested neurologists track frailty in their patients and pointed to a recent article focused on helping neurologists use frailty measures to influence care planning.
Study limitations include the possibility of reverse causality and the fact that investigators could not adjust for genetic risk for dementia.
Unclear Pathway
Commenting on the findings, Lycia Neumann, PhD, senior director of Health Services Research at the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that many studies over the years have shown a link between frailty and dementia. However, she cautioned that a link does not imply causation.
The pathway from frailty to dementia is not 100% clear, and both are complex conditions, said Neumann, who was not part of the study.
“Adopting healthy lifestyle behaviors early and consistently can help decrease the risk of — or postpone the onset of — both frailty and cognitive decline,” she said. Neumann added that physical activity, a healthy diet, social engagement, and controlling diabetes and blood pressure can also reduce the risk for dementia as well as cardiovascular disease.
The study was funded in part by the Deep Dementia Phenotyping Network through the Frailty and Dementia Special Interest Group. Ward and Neumann reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, in new findings that may provide a potential opportunity to identify high-risk populations for targeted enrollment in clinical trials of dementia prevention and treatment.
Results of an international study assessing frailty trajectories showed frailty levels notably increased in the 4-9 years before dementia diagnosis. Even among study participants whose baseline frailty measurement was taken prior to that acceleration period, frailty was still positively associated with dementia risk, the investigators noted.
“We found that with every four to five additional health problems, there is on average a 40% higher risk of developing dementia, while the risk is lower for people who are more physically fit,” said study investigator David Ward, PhD, of the Centre for Health Services Research, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
A Promising Biomarker
An accessible biomarker for both biologic age and dementia risk is essential for advancing dementia prevention and treatment strategies, the investigators noted, adding that growing evidence suggests frailty may be a promising candidate for this role.
To learn more about the association between frailty and dementia, Ward and his team analyzed data on 29,849 participants aged 60 years or above (mean age, 71.6 years; 62% women) who participated in four cohort studies: the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA; n = 6771), the Health and Retirement Study (HRS; n = 9045), the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP; n = 1451), and the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC; n = 12,582).
The primary outcome was all-cause dementia. Depending on the cohort, dementia diagnoses were determined through cognitive testing, self- or family report of physician diagnosis, or a diagnosis by the study physician. Participants were excluded if they had cognitive impairment at baseline.
Investigators retrospectively determined frailty index scores by gathering information on health and functional outcomes for participants from each cohort. Only participants with frailty data on at least 30 deficits were included.
Commonly included deficits included high blood pressure, cancer, and chronic pain, as well as functional problems such as hearing impairment, difficulty with mobility, and challenges managing finances.
Investigators conducted follow-up visits with participants until they developed dementia or until the study ended, with follow-up periods varying across cohorts.
After adjustment for potential confounders, frailty scores were modeled using backward time scales.
Among participants who developed incident dementia (n = 3154), covariate-adjusted expected frailty index scores were, on average, higher in women than in men by 18.5% in ELSA, 20.9% in HRS, and 16.2% in MAP. There were no differences in frailty scores between sexes in the NACC cohort.
When measured on a timeline, as compared with those who didn’t develop dementia, frailty scores were significantly and consistently higher in the dementia groups 8-20 before dementia onset (20 years in HRS; 13 in MAP; 12 in ELSA; 8 in NACC).
Increases in the rates of frailty index scores began accelerating 4-9 years before dementia onset for the various cohorts, investigators noted.
In all four cohorts, each 0.1 increase in frailty scores was positively associated with increased dementia risk.
Adjusted hazard ratios [aHRs] ranged from 1.18 in the HRS cohort to 1.73 in the NACC cohort, which showed the strongest association.
In participants whose baseline frailty measurement was conducted before the predementia acceleration period began, the association of frailty scores and dementia risk was positive. These aHRs ranged from 1.18 in the HRS cohort to 1.43 in the NACC cohort.
The ‘Four Pillars’ of Prevention
The good news, investigators said, is that the long trajectory of frailty symptoms preceding dementia onset provides plenty of opportunity for intervention.
To slow the development of frailty, Ward suggested adhering to the “four pillars of frailty prevention and management,” which include good nutrition with plenty of protein, exercise, optimizing medications for chronic conditions, and maintaining a strong social network.
Ward suggested neurologists track frailty in their patients and pointed to a recent article focused on helping neurologists use frailty measures to influence care planning.
Study limitations include the possibility of reverse causality and the fact that investigators could not adjust for genetic risk for dementia.
Unclear Pathway
Commenting on the findings, Lycia Neumann, PhD, senior director of Health Services Research at the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that many studies over the years have shown a link between frailty and dementia. However, she cautioned that a link does not imply causation.
The pathway from frailty to dementia is not 100% clear, and both are complex conditions, said Neumann, who was not part of the study.
“Adopting healthy lifestyle behaviors early and consistently can help decrease the risk of — or postpone the onset of — both frailty and cognitive decline,” she said. Neumann added that physical activity, a healthy diet, social engagement, and controlling diabetes and blood pressure can also reduce the risk for dementia as well as cardiovascular disease.
The study was funded in part by the Deep Dementia Phenotyping Network through the Frailty and Dementia Special Interest Group. Ward and Neumann reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.

