User login
AAP updates hyperbilirubinemia guideline
Raising phototherapy thresholds and revising risk assessment are among the key changes in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ updated guidelines for managing hyperbilirubinemia in infants 35 weeks’ gestation and older.
“More than 80% of newborn infants will have some degree of jaundice,” Alex R. Kemper, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors wrote. Careful monitoring is needed manage high bilirubin concentrations and avoid acute bilirubin encephalopathy (ABE) and kernicterus, a disabling neurologic condition.
The current revision, published in Pediatrics, updates and replaces the 2004 AAP clinical practice guidelines for the management and prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns of at least 35 weeks’ gestation.
The guideline committee reviewed evidence published since the previous guidelines were issued in 2004, and addressed similar issues of prevention, risk assessment, monitoring, and treatment.
A notable change from 2004 was the inclusion of a 2009 recommendation update for “universal predischarge bilirubin screening with measures of total serum bilirubin (TSB) or transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) linked to specific recommendations for follow-up,” the authors wrote.
In terms of prevention, recommendations include a direct antiglobulin test (DAT) for infants whose mother’s antibody screen was positive or unknown. In addition, exclusive breastfeeding is known to be associated with hyperbilirubinemia, but clinicians should support breastfeeding while monitoring for signs of hyperbilirubinemia because of suboptimal feeding, the authors noted. However, the guidelines recommend against oral supplementation with water or dextrose water to prevent hyperbilirubinemia.
For assessment and monitoring, the guidelines advise the use of total serum bilirubin (TSB) as the definitive test for hyperbilirubinemia to guide phototherapy and escalation of care, including exchange transfusion. “The presence of hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors lowers the threshold for treatment with phototherapy and the level at which care should be escalated,” the authors wrote. They also emphasized the need to consider glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a genetic condition that decreases protection against oxidative stress and has been identified as a leading cause of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia worldwide.
The guidelines recommend assessing all infants for jaundice at least every 12 hours after delivery until discharge, with TSB or TcB measured as soon as possible for those with suspected jaundice. The complete guidelines include charts for TSB levels to guide escalation of care. “Blood for TSB can be obtained at the time it is collected for newborn screening tests to avoid an additional heel stick,” the authors noted.
The rate of increase in TSB or TcB, if more than one measure is available, may identify infants at higher risk of hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines, and a possible delay of hospital discharge may be needed for infants if appropriate follow-up is not feasible.
In terms of treatment, new evidence that bilirubin neurotoxicity does not occur until concentrations well above those given in the 2004 guidelines justified raising the treatment thresholds, although by a narrow range. “With the increased phototherapy thresholds, appropriately following the current guidelines including bilirubin screening during the birth hospitalization and timely postdischarge follow-up is important,” the authors wrote. The new thresholds, outlined in the complete guidelines, are based on gestational age, hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors, and the age of the infant in hours. However, infants may be treated at lower levels, based on individual circumstances, family preferences, and shared decision-making with clinicians. Home-based phototherapy may be used in some infants, but should not be used if there is a question about the device quality, delivery time, and ability of caregivers to use the device correctly.
“Discontinuing phototherapy is an option when the TSB has decreased by at least 2 mg/dL below the hour-specific threshold at the initiation of phototherapy,” and follow-up should be based on risk of rebound hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines.
“This clinical practice guideline provides indications and approaches for phototherapy and escalation of care and when treatment and monitoring can be safely discontinued,” However, clinicians should understand the rationale for the recommendations and combine them with their clinical judgment, including shared decision-making when appropriate, the authors concluded.
Updated evidence supports escalating care
The take-home message for pediatricians is that neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is a very common finding, and complications are rare, but the condition can result in devastating life-long results, Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Previous guidelines published in 2004 and updated in 2009 included evidence-based recommendations, but additional research was still needed to provide guidance for providers to prevent complications of hyperbilirubinemia,” said Dr. Haut, who was not involved in producing the guidelines.
“New data documenting additional risk factors, the importance of ongoing breastfeeding support, and addressing hyperbilirubinemia as an urgent problem” are additions to prevention methods in the latest published guidelines, she said.
“Acute encephalopathy and kernicterus can result from hyperbilirubinemia with severe and devastating neurologic effects, but are preventable by early identification and treatment,” said Dr. Haut. Therefore, “it is not surprising that the AAP utilized continuing and more recent evidence to support new recommendations. Both maternal and neonatal risk factors have long been considered in the development of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, but recent recommendations incorporate additional risk factor evaluation and urgency in time to appropriate care. Detailed thresholds for phototherapy and exchange transfusion will benefit the families of full-term infants without other risk factors and escalate care for those neonates with risk factors.”
However, potential barriers to following the guidelines persist, Dr. Haut noted.
“Frequent infant follow-up can be challenging for busy primary care offices with outpatient laboratory results often taking much longer to obtain than in a hospital setting,” she said.
Also, “taking a newborn to the emergency department or an inpatient laboratory can be frightening for families with the risk of illness exposure. Frequent monitoring of serum bilirubin levels is disturbing for parents and inconvenient immediately postpartum,” Dr. Haut explained. “Few practices utilize transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring which may be one method of added screening.”
In addition, “despite the importance of breastfeeding, ongoing support is not readily available for mothers after hospital discharge. A lactation specialist in the office setting can take the burden off providers and add opportunity for family education.”
As for additional research, “continued evaluation of the comparison of transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring and serum levels along with the use of transcutaneous monitoring in facilities outside the hospital setting may be warranted,” Dr. Haut said. “Data collection on incidence and accompanying risk factors of neonates who develop acute hyperbilirubinemia encephalopathy and kernicterus is a long-term study opportunity.”
The guidelines received no external funding. Lead author Dr. Kemper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Raising phototherapy thresholds and revising risk assessment are among the key changes in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ updated guidelines for managing hyperbilirubinemia in infants 35 weeks’ gestation and older.
“More than 80% of newborn infants will have some degree of jaundice,” Alex R. Kemper, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors wrote. Careful monitoring is needed manage high bilirubin concentrations and avoid acute bilirubin encephalopathy (ABE) and kernicterus, a disabling neurologic condition.
The current revision, published in Pediatrics, updates and replaces the 2004 AAP clinical practice guidelines for the management and prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns of at least 35 weeks’ gestation.
The guideline committee reviewed evidence published since the previous guidelines were issued in 2004, and addressed similar issues of prevention, risk assessment, monitoring, and treatment.
A notable change from 2004 was the inclusion of a 2009 recommendation update for “universal predischarge bilirubin screening with measures of total serum bilirubin (TSB) or transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) linked to specific recommendations for follow-up,” the authors wrote.
In terms of prevention, recommendations include a direct antiglobulin test (DAT) for infants whose mother’s antibody screen was positive or unknown. In addition, exclusive breastfeeding is known to be associated with hyperbilirubinemia, but clinicians should support breastfeeding while monitoring for signs of hyperbilirubinemia because of suboptimal feeding, the authors noted. However, the guidelines recommend against oral supplementation with water or dextrose water to prevent hyperbilirubinemia.
For assessment and monitoring, the guidelines advise the use of total serum bilirubin (TSB) as the definitive test for hyperbilirubinemia to guide phototherapy and escalation of care, including exchange transfusion. “The presence of hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors lowers the threshold for treatment with phototherapy and the level at which care should be escalated,” the authors wrote. They also emphasized the need to consider glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a genetic condition that decreases protection against oxidative stress and has been identified as a leading cause of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia worldwide.
The guidelines recommend assessing all infants for jaundice at least every 12 hours after delivery until discharge, with TSB or TcB measured as soon as possible for those with suspected jaundice. The complete guidelines include charts for TSB levels to guide escalation of care. “Blood for TSB can be obtained at the time it is collected for newborn screening tests to avoid an additional heel stick,” the authors noted.
The rate of increase in TSB or TcB, if more than one measure is available, may identify infants at higher risk of hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines, and a possible delay of hospital discharge may be needed for infants if appropriate follow-up is not feasible.
In terms of treatment, new evidence that bilirubin neurotoxicity does not occur until concentrations well above those given in the 2004 guidelines justified raising the treatment thresholds, although by a narrow range. “With the increased phototherapy thresholds, appropriately following the current guidelines including bilirubin screening during the birth hospitalization and timely postdischarge follow-up is important,” the authors wrote. The new thresholds, outlined in the complete guidelines, are based on gestational age, hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors, and the age of the infant in hours. However, infants may be treated at lower levels, based on individual circumstances, family preferences, and shared decision-making with clinicians. Home-based phototherapy may be used in some infants, but should not be used if there is a question about the device quality, delivery time, and ability of caregivers to use the device correctly.
“Discontinuing phototherapy is an option when the TSB has decreased by at least 2 mg/dL below the hour-specific threshold at the initiation of phototherapy,” and follow-up should be based on risk of rebound hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines.
“This clinical practice guideline provides indications and approaches for phototherapy and escalation of care and when treatment and monitoring can be safely discontinued,” However, clinicians should understand the rationale for the recommendations and combine them with their clinical judgment, including shared decision-making when appropriate, the authors concluded.
Updated evidence supports escalating care
The take-home message for pediatricians is that neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is a very common finding, and complications are rare, but the condition can result in devastating life-long results, Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Previous guidelines published in 2004 and updated in 2009 included evidence-based recommendations, but additional research was still needed to provide guidance for providers to prevent complications of hyperbilirubinemia,” said Dr. Haut, who was not involved in producing the guidelines.
“New data documenting additional risk factors, the importance of ongoing breastfeeding support, and addressing hyperbilirubinemia as an urgent problem” are additions to prevention methods in the latest published guidelines, she said.
“Acute encephalopathy and kernicterus can result from hyperbilirubinemia with severe and devastating neurologic effects, but are preventable by early identification and treatment,” said Dr. Haut. Therefore, “it is not surprising that the AAP utilized continuing and more recent evidence to support new recommendations. Both maternal and neonatal risk factors have long been considered in the development of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, but recent recommendations incorporate additional risk factor evaluation and urgency in time to appropriate care. Detailed thresholds for phototherapy and exchange transfusion will benefit the families of full-term infants without other risk factors and escalate care for those neonates with risk factors.”
However, potential barriers to following the guidelines persist, Dr. Haut noted.
“Frequent infant follow-up can be challenging for busy primary care offices with outpatient laboratory results often taking much longer to obtain than in a hospital setting,” she said.
Also, “taking a newborn to the emergency department or an inpatient laboratory can be frightening for families with the risk of illness exposure. Frequent monitoring of serum bilirubin levels is disturbing for parents and inconvenient immediately postpartum,” Dr. Haut explained. “Few practices utilize transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring which may be one method of added screening.”
In addition, “despite the importance of breastfeeding, ongoing support is not readily available for mothers after hospital discharge. A lactation specialist in the office setting can take the burden off providers and add opportunity for family education.”
As for additional research, “continued evaluation of the comparison of transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring and serum levels along with the use of transcutaneous monitoring in facilities outside the hospital setting may be warranted,” Dr. Haut said. “Data collection on incidence and accompanying risk factors of neonates who develop acute hyperbilirubinemia encephalopathy and kernicterus is a long-term study opportunity.”
The guidelines received no external funding. Lead author Dr. Kemper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Raising phototherapy thresholds and revising risk assessment are among the key changes in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ updated guidelines for managing hyperbilirubinemia in infants 35 weeks’ gestation and older.
“More than 80% of newborn infants will have some degree of jaundice,” Alex R. Kemper, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, and coauthors wrote. Careful monitoring is needed manage high bilirubin concentrations and avoid acute bilirubin encephalopathy (ABE) and kernicterus, a disabling neurologic condition.
The current revision, published in Pediatrics, updates and replaces the 2004 AAP clinical practice guidelines for the management and prevention of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns of at least 35 weeks’ gestation.
The guideline committee reviewed evidence published since the previous guidelines were issued in 2004, and addressed similar issues of prevention, risk assessment, monitoring, and treatment.
A notable change from 2004 was the inclusion of a 2009 recommendation update for “universal predischarge bilirubin screening with measures of total serum bilirubin (TSB) or transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) linked to specific recommendations for follow-up,” the authors wrote.
In terms of prevention, recommendations include a direct antiglobulin test (DAT) for infants whose mother’s antibody screen was positive or unknown. In addition, exclusive breastfeeding is known to be associated with hyperbilirubinemia, but clinicians should support breastfeeding while monitoring for signs of hyperbilirubinemia because of suboptimal feeding, the authors noted. However, the guidelines recommend against oral supplementation with water or dextrose water to prevent hyperbilirubinemia.
For assessment and monitoring, the guidelines advise the use of total serum bilirubin (TSB) as the definitive test for hyperbilirubinemia to guide phototherapy and escalation of care, including exchange transfusion. “The presence of hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors lowers the threshold for treatment with phototherapy and the level at which care should be escalated,” the authors wrote. They also emphasized the need to consider glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a genetic condition that decreases protection against oxidative stress and has been identified as a leading cause of hazardous hyperbilirubinemia worldwide.
The guidelines recommend assessing all infants for jaundice at least every 12 hours after delivery until discharge, with TSB or TcB measured as soon as possible for those with suspected jaundice. The complete guidelines include charts for TSB levels to guide escalation of care. “Blood for TSB can be obtained at the time it is collected for newborn screening tests to avoid an additional heel stick,” the authors noted.
The rate of increase in TSB or TcB, if more than one measure is available, may identify infants at higher risk of hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines, and a possible delay of hospital discharge may be needed for infants if appropriate follow-up is not feasible.
In terms of treatment, new evidence that bilirubin neurotoxicity does not occur until concentrations well above those given in the 2004 guidelines justified raising the treatment thresholds, although by a narrow range. “With the increased phototherapy thresholds, appropriately following the current guidelines including bilirubin screening during the birth hospitalization and timely postdischarge follow-up is important,” the authors wrote. The new thresholds, outlined in the complete guidelines, are based on gestational age, hyperbilirubinemia neurotoxicity risk factors, and the age of the infant in hours. However, infants may be treated at lower levels, based on individual circumstances, family preferences, and shared decision-making with clinicians. Home-based phototherapy may be used in some infants, but should not be used if there is a question about the device quality, delivery time, and ability of caregivers to use the device correctly.
“Discontinuing phototherapy is an option when the TSB has decreased by at least 2 mg/dL below the hour-specific threshold at the initiation of phototherapy,” and follow-up should be based on risk of rebound hyperbilirubinemia, according to the guidelines.
“This clinical practice guideline provides indications and approaches for phototherapy and escalation of care and when treatment and monitoring can be safely discontinued,” However, clinicians should understand the rationale for the recommendations and combine them with their clinical judgment, including shared decision-making when appropriate, the authors concluded.
Updated evidence supports escalating care
The take-home message for pediatricians is that neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is a very common finding, and complications are rare, but the condition can result in devastating life-long results, Cathy Haut, DNP, CPNP-AC, CPNP-PC, a pediatric nurse practitioner in Rehoboth Beach, Del., said in an interview.
“Previous guidelines published in 2004 and updated in 2009 included evidence-based recommendations, but additional research was still needed to provide guidance for providers to prevent complications of hyperbilirubinemia,” said Dr. Haut, who was not involved in producing the guidelines.
“New data documenting additional risk factors, the importance of ongoing breastfeeding support, and addressing hyperbilirubinemia as an urgent problem” are additions to prevention methods in the latest published guidelines, she said.
“Acute encephalopathy and kernicterus can result from hyperbilirubinemia with severe and devastating neurologic effects, but are preventable by early identification and treatment,” said Dr. Haut. Therefore, “it is not surprising that the AAP utilized continuing and more recent evidence to support new recommendations. Both maternal and neonatal risk factors have long been considered in the development of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, but recent recommendations incorporate additional risk factor evaluation and urgency in time to appropriate care. Detailed thresholds for phototherapy and exchange transfusion will benefit the families of full-term infants without other risk factors and escalate care for those neonates with risk factors.”
However, potential barriers to following the guidelines persist, Dr. Haut noted.
“Frequent infant follow-up can be challenging for busy primary care offices with outpatient laboratory results often taking much longer to obtain than in a hospital setting,” she said.
Also, “taking a newborn to the emergency department or an inpatient laboratory can be frightening for families with the risk of illness exposure. Frequent monitoring of serum bilirubin levels is disturbing for parents and inconvenient immediately postpartum,” Dr. Haut explained. “Few practices utilize transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring which may be one method of added screening.”
In addition, “despite the importance of breastfeeding, ongoing support is not readily available for mothers after hospital discharge. A lactation specialist in the office setting can take the burden off providers and add opportunity for family education.”
As for additional research, “continued evaluation of the comparison of transcutaneous bilirubin monitoring and serum levels along with the use of transcutaneous monitoring in facilities outside the hospital setting may be warranted,” Dr. Haut said. “Data collection on incidence and accompanying risk factors of neonates who develop acute hyperbilirubinemia encephalopathy and kernicterus is a long-term study opportunity.”
The guidelines received no external funding. Lead author Dr. Kemper had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Haut had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Death risk doubles for Black infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) who were born to Black mothers were significantly more likely to die or to have a longer hospital stay than infants of other ethnicities, based on data from more than 800 infants.
The overall incidence of BPD is rising, in part because of improved survival for extremely preterm infants, wrote Tamorah R. Lewis, MD, of the University of Missouri, Kansas City, and colleagues.
Previous studies suggest that racial disparities may affect outcomes for preterm infants with a range of neonatal morbidities during neonatal ICU (NICU) hospitalization, including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, and necrotizing enterocolitis. However, the association of racial disparities with outcomes for preterm infants with BPD remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers, on behalf of the Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Collaborative, reviewed data from 834 preterm infants enrolled in the BPD Collaborative registry from Jan. 1, 2015, to July 19, 2021, at eight centers in the United States.
The study infants were born at less than 32 weeks’ gestation and were diagnosed with severe BPD according to the 2001 National Institutes of Health Consensus Criteria. The study population included 276 Black infants and 558 white infants. The median gestational age was 24 weeks, and 41% of the infants were female.
The primary outcomes were infant death and length of hospital stay.
Although death was infrequent (4% overall), Black maternal race was significantly associated with an increased risk of death from BPD (adjusted odds ratio, 2.1). Black maternal race also was significantly associated with a longer hospital stay for the infants, with an adjusted between-group difference of 10 days.
Infants of Black mothers also were more likely than those with White mothers to receive invasive respiratory support at the time of delivery. Black infants were more likely than White infants to have lower gestational age, lower birth weight and length, and smaller head circumference.
However, the proportions of cesarean deliveries, gender distribution, and infants small for gestational age were similar between Black and White infant groups. Medication exposure at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) also was similar for Black and White infants, and 50% of patients overall were treated with nasal continuous positive airway pressure at 36 weeks’ PMA. Awareness of the increased risk of death and longer hospital stay for Black infants is critical, “given the highly variable outcomes for patients with BPD and the uncertainty regarding demographic factors that contribute to late respiratory morbidity in severe BPD,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including variations among study centers in the identification and recording of maternal race, lack of data on paternal race, and the focus specifically on Black maternal race and not other ethnicities. Given the documented health disparities for Black individuals in the United States, “we restricted our cohort to only those patients born to Black or White mothers to estimate the association of Black maternal race and adverse in-hospital outcomes in infants with severe BPD,” the researchers wrote
Other limitations include the lack of data surrounding infant death and inability to adjust for all potential modifiers of BPD pathogenesis and progression, such as BPD comorbidities.
Prospective studies are needed to identify the sociodemographic mechanisms that may contribute to health outcome disparities for Black infants with severe BPD, the researchers emphasized.
In the meantime, the results highlight the need for more attention to variations in care for infants with BPD of different races, and approaches to family-centered care should consider “the precise needs of high-risk, structurally disadvantaged families while informing the design of prospective trials that improve outcomes for high-risk subgroups of children with severe BPD,” they concluded.
Data raise questions about the origin of disparities
The current study findings contribute to the knowledge and awareness of disparities in the high-risk NICU population, Nicolas A. Bamat, MD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Further, their findings oppose the central tendency in the literature: that infants of Black mothers have less severe lung disease of prematurity during the birth hospitalization.”
The editorial authors noted that the study’s inclusion of racial characteristics as confounding variables to assess the effect of race on health “can imply questionable assumptions about where in a causal pathway racism begins to exert an effect,” whether after a diagnosis of BPD, during pregnancy in response to inequitable obstetric care, or “centuries ago, propagating forward through the shared experience of communities oppressed by the legacy of racism and its ongoing contemporary manifestations.”
The editorial authors added that, “in lung disease of prematurity, few variables are reliable antecedents to race as an exposure. Complex adjustment is necessary to reduce bias in targeted research questions.” However, the current study findings highlight the need to move toward more equitable neonatal care, and to prioritize interventions to reduce racial health disparities at the level of the NICU as well as at the hospital and government policy levels.
Consider range of contributing factors and confounders
The current study is important because “it is imperative to measure racial outcomes in health care in order to highlight and address disparities and biases,” Tim Joos, MD, said in an interview. However, “it can be difficult to determine how much race is a factor in itself versus a proxy for other important characteristics, such as socioeconomic status and level of education, that can confound the results.”
In the current study, the twofold-increased death rate in the premature infants of Black mothers is concerning and deserves further attention, Dr. Joos said. “The 10-day longer length of stay for infants of Black mothers seems quite shocking at first glance, but because of the long hospital stays for these extremely premature infants in general, it is about 7% longer than the infants born to White mothers.”
The take-home message is that this difference is still significant, and can reflect many factors including disease severity and complications, need for feeding assistance, teaching, and setting up home supports, said Dr. Joos.
As for additional research, “it would be useful for hospitals to break down why the differences exist, although I worry a provider or institution will feel they need to discharge Black families sooner to avoid being biased. Family preference and comfort level should be given high priority,” he emphasized.
The study received no outside funding, but lead author Dr. Lewis was supported by the National Institute on Child Health and Development and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Several coauthors were supported by other grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Barnat and one coauthor were supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) who were born to Black mothers were significantly more likely to die or to have a longer hospital stay than infants of other ethnicities, based on data from more than 800 infants.
The overall incidence of BPD is rising, in part because of improved survival for extremely preterm infants, wrote Tamorah R. Lewis, MD, of the University of Missouri, Kansas City, and colleagues.
Previous studies suggest that racial disparities may affect outcomes for preterm infants with a range of neonatal morbidities during neonatal ICU (NICU) hospitalization, including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, and necrotizing enterocolitis. However, the association of racial disparities with outcomes for preterm infants with BPD remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers, on behalf of the Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Collaborative, reviewed data from 834 preterm infants enrolled in the BPD Collaborative registry from Jan. 1, 2015, to July 19, 2021, at eight centers in the United States.
The study infants were born at less than 32 weeks’ gestation and were diagnosed with severe BPD according to the 2001 National Institutes of Health Consensus Criteria. The study population included 276 Black infants and 558 white infants. The median gestational age was 24 weeks, and 41% of the infants were female.
The primary outcomes were infant death and length of hospital stay.
Although death was infrequent (4% overall), Black maternal race was significantly associated with an increased risk of death from BPD (adjusted odds ratio, 2.1). Black maternal race also was significantly associated with a longer hospital stay for the infants, with an adjusted between-group difference of 10 days.
Infants of Black mothers also were more likely than those with White mothers to receive invasive respiratory support at the time of delivery. Black infants were more likely than White infants to have lower gestational age, lower birth weight and length, and smaller head circumference.
However, the proportions of cesarean deliveries, gender distribution, and infants small for gestational age were similar between Black and White infant groups. Medication exposure at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) also was similar for Black and White infants, and 50% of patients overall were treated with nasal continuous positive airway pressure at 36 weeks’ PMA. Awareness of the increased risk of death and longer hospital stay for Black infants is critical, “given the highly variable outcomes for patients with BPD and the uncertainty regarding demographic factors that contribute to late respiratory morbidity in severe BPD,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including variations among study centers in the identification and recording of maternal race, lack of data on paternal race, and the focus specifically on Black maternal race and not other ethnicities. Given the documented health disparities for Black individuals in the United States, “we restricted our cohort to only those patients born to Black or White mothers to estimate the association of Black maternal race and adverse in-hospital outcomes in infants with severe BPD,” the researchers wrote
Other limitations include the lack of data surrounding infant death and inability to adjust for all potential modifiers of BPD pathogenesis and progression, such as BPD comorbidities.
Prospective studies are needed to identify the sociodemographic mechanisms that may contribute to health outcome disparities for Black infants with severe BPD, the researchers emphasized.
In the meantime, the results highlight the need for more attention to variations in care for infants with BPD of different races, and approaches to family-centered care should consider “the precise needs of high-risk, structurally disadvantaged families while informing the design of prospective trials that improve outcomes for high-risk subgroups of children with severe BPD,” they concluded.
Data raise questions about the origin of disparities
The current study findings contribute to the knowledge and awareness of disparities in the high-risk NICU population, Nicolas A. Bamat, MD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Further, their findings oppose the central tendency in the literature: that infants of Black mothers have less severe lung disease of prematurity during the birth hospitalization.”
The editorial authors noted that the study’s inclusion of racial characteristics as confounding variables to assess the effect of race on health “can imply questionable assumptions about where in a causal pathway racism begins to exert an effect,” whether after a diagnosis of BPD, during pregnancy in response to inequitable obstetric care, or “centuries ago, propagating forward through the shared experience of communities oppressed by the legacy of racism and its ongoing contemporary manifestations.”
The editorial authors added that, “in lung disease of prematurity, few variables are reliable antecedents to race as an exposure. Complex adjustment is necessary to reduce bias in targeted research questions.” However, the current study findings highlight the need to move toward more equitable neonatal care, and to prioritize interventions to reduce racial health disparities at the level of the NICU as well as at the hospital and government policy levels.
Consider range of contributing factors and confounders
The current study is important because “it is imperative to measure racial outcomes in health care in order to highlight and address disparities and biases,” Tim Joos, MD, said in an interview. However, “it can be difficult to determine how much race is a factor in itself versus a proxy for other important characteristics, such as socioeconomic status and level of education, that can confound the results.”
In the current study, the twofold-increased death rate in the premature infants of Black mothers is concerning and deserves further attention, Dr. Joos said. “The 10-day longer length of stay for infants of Black mothers seems quite shocking at first glance, but because of the long hospital stays for these extremely premature infants in general, it is about 7% longer than the infants born to White mothers.”
The take-home message is that this difference is still significant, and can reflect many factors including disease severity and complications, need for feeding assistance, teaching, and setting up home supports, said Dr. Joos.
As for additional research, “it would be useful for hospitals to break down why the differences exist, although I worry a provider or institution will feel they need to discharge Black families sooner to avoid being biased. Family preference and comfort level should be given high priority,” he emphasized.
The study received no outside funding, but lead author Dr. Lewis was supported by the National Institute on Child Health and Development and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Several coauthors were supported by other grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Barnat and one coauthor were supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) who were born to Black mothers were significantly more likely to die or to have a longer hospital stay than infants of other ethnicities, based on data from more than 800 infants.
The overall incidence of BPD is rising, in part because of improved survival for extremely preterm infants, wrote Tamorah R. Lewis, MD, of the University of Missouri, Kansas City, and colleagues.
Previous studies suggest that racial disparities may affect outcomes for preterm infants with a range of neonatal morbidities during neonatal ICU (NICU) hospitalization, including respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, and necrotizing enterocolitis. However, the association of racial disparities with outcomes for preterm infants with BPD remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers, on behalf of the Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Collaborative, reviewed data from 834 preterm infants enrolled in the BPD Collaborative registry from Jan. 1, 2015, to July 19, 2021, at eight centers in the United States.
The study infants were born at less than 32 weeks’ gestation and were diagnosed with severe BPD according to the 2001 National Institutes of Health Consensus Criteria. The study population included 276 Black infants and 558 white infants. The median gestational age was 24 weeks, and 41% of the infants were female.
The primary outcomes were infant death and length of hospital stay.
Although death was infrequent (4% overall), Black maternal race was significantly associated with an increased risk of death from BPD (adjusted odds ratio, 2.1). Black maternal race also was significantly associated with a longer hospital stay for the infants, with an adjusted between-group difference of 10 days.
Infants of Black mothers also were more likely than those with White mothers to receive invasive respiratory support at the time of delivery. Black infants were more likely than White infants to have lower gestational age, lower birth weight and length, and smaller head circumference.
However, the proportions of cesarean deliveries, gender distribution, and infants small for gestational age were similar between Black and White infant groups. Medication exposure at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) also was similar for Black and White infants, and 50% of patients overall were treated with nasal continuous positive airway pressure at 36 weeks’ PMA. Awareness of the increased risk of death and longer hospital stay for Black infants is critical, “given the highly variable outcomes for patients with BPD and the uncertainty regarding demographic factors that contribute to late respiratory morbidity in severe BPD,” the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including variations among study centers in the identification and recording of maternal race, lack of data on paternal race, and the focus specifically on Black maternal race and not other ethnicities. Given the documented health disparities for Black individuals in the United States, “we restricted our cohort to only those patients born to Black or White mothers to estimate the association of Black maternal race and adverse in-hospital outcomes in infants with severe BPD,” the researchers wrote
Other limitations include the lack of data surrounding infant death and inability to adjust for all potential modifiers of BPD pathogenesis and progression, such as BPD comorbidities.
Prospective studies are needed to identify the sociodemographic mechanisms that may contribute to health outcome disparities for Black infants with severe BPD, the researchers emphasized.
In the meantime, the results highlight the need for more attention to variations in care for infants with BPD of different races, and approaches to family-centered care should consider “the precise needs of high-risk, structurally disadvantaged families while informing the design of prospective trials that improve outcomes for high-risk subgroups of children with severe BPD,” they concluded.
Data raise questions about the origin of disparities
The current study findings contribute to the knowledge and awareness of disparities in the high-risk NICU population, Nicolas A. Bamat, MD, and colleagues wrote in an accompanying editorial. “Further, their findings oppose the central tendency in the literature: that infants of Black mothers have less severe lung disease of prematurity during the birth hospitalization.”
The editorial authors noted that the study’s inclusion of racial characteristics as confounding variables to assess the effect of race on health “can imply questionable assumptions about where in a causal pathway racism begins to exert an effect,” whether after a diagnosis of BPD, during pregnancy in response to inequitable obstetric care, or “centuries ago, propagating forward through the shared experience of communities oppressed by the legacy of racism and its ongoing contemporary manifestations.”
The editorial authors added that, “in lung disease of prematurity, few variables are reliable antecedents to race as an exposure. Complex adjustment is necessary to reduce bias in targeted research questions.” However, the current study findings highlight the need to move toward more equitable neonatal care, and to prioritize interventions to reduce racial health disparities at the level of the NICU as well as at the hospital and government policy levels.
Consider range of contributing factors and confounders
The current study is important because “it is imperative to measure racial outcomes in health care in order to highlight and address disparities and biases,” Tim Joos, MD, said in an interview. However, “it can be difficult to determine how much race is a factor in itself versus a proxy for other important characteristics, such as socioeconomic status and level of education, that can confound the results.”
In the current study, the twofold-increased death rate in the premature infants of Black mothers is concerning and deserves further attention, Dr. Joos said. “The 10-day longer length of stay for infants of Black mothers seems quite shocking at first glance, but because of the long hospital stays for these extremely premature infants in general, it is about 7% longer than the infants born to White mothers.”
The take-home message is that this difference is still significant, and can reflect many factors including disease severity and complications, need for feeding assistance, teaching, and setting up home supports, said Dr. Joos.
As for additional research, “it would be useful for hospitals to break down why the differences exist, although I worry a provider or institution will feel they need to discharge Black families sooner to avoid being biased. Family preference and comfort level should be given high priority,” he emphasized.
The study received no outside funding, but lead author Dr. Lewis was supported by the National Institute on Child Health and Development and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Several coauthors were supported by other grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Barnat and one coauthor were supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Moms’ cooing swapped with morphine for newborns in withdrawal
Four years ago, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C., embarked on a dramatic change in how it cares for newborns exposed to opioids in the womb.
Until then, most of the 700 or so babies who underwent opioid withdrawal each year in the hospital system spent their first weeks in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), isolated from their parents and treated with regular doses of morphine to ease their symptoms.
Now, most babies stay in the hospital for just a few days under a new approach called Eat, Sleep, Console. These young patients stay in private rooms where they can bond with their parents and volunteer caregivers. The usual course of treatment is no longer extended therapy with opioid replacements. Instead, mothers are encouraged to stay overnight and are taught how to sooth their babies with swaddling, rocking, and cooing.
As a result, the average length of stay for newborns with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) has dropped from 12 days to 6. Use of morphine has fallen by 79%, from 2.25 to 0.45 mg/kg per stay, according to results of a quality improvement pilot project at one of Atrium’s community hospitals.
Similar outcomes from other hospitals around the country have led to widespread uptake of Eat, Sleep, Console since its advent in 2017. That year, according to federal data, seven newborns were diagnosed with NAS for every 1,000 births.
Advocates say the family-centric model helps parents feel less stigmatized and more confident in their ability to care for their babies, who can have symptoms such as irritability and difficulty feeding for months.
The approach “really empowers families to do what they do best, which is take care of each other,” Douglas Dodds, MD, a pediatrician who led the effort at Atrium, told this news organization.
Questioning the old protocols
Numerous state perinatal collaboratives, hospital associations, and health systems say the program is the new standard of care for infants with NAS and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS).
Twenty-six hospitals have adopted Eat, Sleep, Console as part of a clinical trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health and a program called Advancing Clinical Trials in Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome (ACT NOW). Researchers are comparing the approach to previous care protocols in regard to 12 outcomes, including time to medical readiness for discharge, frequency of opioid replacement therapy, and safety problems, such as seizures during treatment.
The transition has been swift. Less than a decade ago, most hospitals used the Finnegan Neonatal Abstinence Scoring System, which was developed in the 1970s to assess babies whose mothers had used heroin during pregnancy.
The Finnegan score entails monitoring babies every 3 hours for 21 symptoms, including high-pitched crying, sneezing, gastrointestinal problems, and yawning. If a baby scores an 8 or more three times in a row, most protocols using the traditional Finnegan approach recommend that providers move infants to an NICU, where they receive morphine or methadone. Once opioid replacement therapy is started, the protocols require a gradual weaning that lasts 3-4 weeks.
As the opioid epidemic grew and NICUs around the country began to fill with babies experiencing NAS or NOW, some clinicians began to question the Finnegan-driven approach.
“You have these miserable babies who are going through this really tough experience, and our first move is to separate them from their moms,” said Matthew Grossman, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital, New Haven, Conn., who created Eat, Sleep, Console.
Dr. Grossman, associate professor and vice chair for quality in the department of pediatrics at Yale University, said he noticed that when mothers stayed overnight with their babies, the infants tended to have fewer withdrawal symptoms. Indeed, previous studies had demonstrated the benefits of breastfeeding and allowing mothers and babies to share a room.
“If you think of mom as a medicine, then you can’t put the baby in a unit where the mom can’t be there,” Dr. Grossman told this news organization. “It would be like taking a kid with pneumonia and putting him in a unit that doesn’t have antibiotics.”
Despite its prominence, the Finnegan score has never been validated for guiding the treatment of NAS. In addition, Finnegan scores can be inconsistent, and the assessment requires disturbing an infant to check signs such as its startle reflex, which, as Dr. Grossman and his fellow researchers pointed out, flies in the face of American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendations to prioritize swaddling and minimize stimulation for infants with NAS.
By contrast, Eat, Sleep, Console offers a simplified assessment. Interventions are called for if a baby eats less than an ounce of food at a time/does not breastfeed, sleeps less than an hour at a stretch, or takes more than 10 minutes to be consoled. After nonpharmacologic interventions have been tried, doses of medication are used as needed. Babies who are doing well can be discharged in as few as 4 days.
Quashing bias against parents with substance abuse disorder
Even with the promise of shorter stays and better care, switching to nonpharmacologic care presents hurdles for hospitals. Among these is a lack of physical space for mothers to room with their babies in a quiet environment.
“In many community hospitals, the only place for infants to go is a neonatal intensive care unit, outside of the newborn nursery,” said Stephen Patrick, MD, MPH, associate professor and director of the Center for Child Health Policy at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who researches stigma associated with opioid use during pregnancy.
Administrators at SSM St. Mary’s Hospital in St. Louis initially balked at providing private rooms for mothers and their babies with NAS and NOWS, according to Kimberly Spence, MD, a neonatologist at SSM Health. She said the initial plan was to put the babies in a busy, brightly lit nursery.
But resistance waned as the hospital convinced health plans to pay for private rooms for the 5-7 days it typically takes a baby to go through withdrawal, said Dr. Spence, associate professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University.
“We were able to provide enough data that this is evidence-based medicine and babies do better with their moms, and that ethically, this is the right thing to do, to reduce transfers to an NICU,” she said.
In addition, news stories about the family-centric approach and shorter stays for infants, along with SSM’s launch of an outpatient clinic to treat pregnant women with opioid use disorder, helped the system to attract more patients and increase its market share, said Dr. Spence.
Another challenge was getting physicians and nurses to set aside any judgments of parents with substance abuse disorder, according to Dr. Grossman and others.
“A lot of faculty and staff on the medical team didn’t feel like we should trust moms with their babies’ medical care” at SSM, Dr. Spence said.
Some hospitals conduct anti-bias training to teach providers that substance abuse is a disease that deserves proper medical treatment and not the moral failing of a patient. Such education may involve explaining that babies’ outcomes are improved when women undergo treatment with methadone or buprenorphine during pregnancy, even though use of those medications does pose a risk of NAS.
Creating a system that supports parents with substance abuse disorders may help to change perceptions. At Atrium Health, some staff members now enjoy working with these families because they can make a profound impact, Dr. Dodds said. He said they’ve learned that families suffering from substance abuse disorder “are not that different than any other family.”
Dr. Dodds, Dr. Patrick, Dr. Spence, and Dr. Grossman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four years ago, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C., embarked on a dramatic change in how it cares for newborns exposed to opioids in the womb.
Until then, most of the 700 or so babies who underwent opioid withdrawal each year in the hospital system spent their first weeks in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), isolated from their parents and treated with regular doses of morphine to ease their symptoms.
Now, most babies stay in the hospital for just a few days under a new approach called Eat, Sleep, Console. These young patients stay in private rooms where they can bond with their parents and volunteer caregivers. The usual course of treatment is no longer extended therapy with opioid replacements. Instead, mothers are encouraged to stay overnight and are taught how to sooth their babies with swaddling, rocking, and cooing.
As a result, the average length of stay for newborns with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) has dropped from 12 days to 6. Use of morphine has fallen by 79%, from 2.25 to 0.45 mg/kg per stay, according to results of a quality improvement pilot project at one of Atrium’s community hospitals.
Similar outcomes from other hospitals around the country have led to widespread uptake of Eat, Sleep, Console since its advent in 2017. That year, according to federal data, seven newborns were diagnosed with NAS for every 1,000 births.
Advocates say the family-centric model helps parents feel less stigmatized and more confident in their ability to care for their babies, who can have symptoms such as irritability and difficulty feeding for months.
The approach “really empowers families to do what they do best, which is take care of each other,” Douglas Dodds, MD, a pediatrician who led the effort at Atrium, told this news organization.
Questioning the old protocols
Numerous state perinatal collaboratives, hospital associations, and health systems say the program is the new standard of care for infants with NAS and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS).
Twenty-six hospitals have adopted Eat, Sleep, Console as part of a clinical trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health and a program called Advancing Clinical Trials in Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome (ACT NOW). Researchers are comparing the approach to previous care protocols in regard to 12 outcomes, including time to medical readiness for discharge, frequency of opioid replacement therapy, and safety problems, such as seizures during treatment.
The transition has been swift. Less than a decade ago, most hospitals used the Finnegan Neonatal Abstinence Scoring System, which was developed in the 1970s to assess babies whose mothers had used heroin during pregnancy.
The Finnegan score entails monitoring babies every 3 hours for 21 symptoms, including high-pitched crying, sneezing, gastrointestinal problems, and yawning. If a baby scores an 8 or more three times in a row, most protocols using the traditional Finnegan approach recommend that providers move infants to an NICU, where they receive morphine or methadone. Once opioid replacement therapy is started, the protocols require a gradual weaning that lasts 3-4 weeks.
As the opioid epidemic grew and NICUs around the country began to fill with babies experiencing NAS or NOW, some clinicians began to question the Finnegan-driven approach.
“You have these miserable babies who are going through this really tough experience, and our first move is to separate them from their moms,” said Matthew Grossman, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital, New Haven, Conn., who created Eat, Sleep, Console.
Dr. Grossman, associate professor and vice chair for quality in the department of pediatrics at Yale University, said he noticed that when mothers stayed overnight with their babies, the infants tended to have fewer withdrawal symptoms. Indeed, previous studies had demonstrated the benefits of breastfeeding and allowing mothers and babies to share a room.
“If you think of mom as a medicine, then you can’t put the baby in a unit where the mom can’t be there,” Dr. Grossman told this news organization. “It would be like taking a kid with pneumonia and putting him in a unit that doesn’t have antibiotics.”
Despite its prominence, the Finnegan score has never been validated for guiding the treatment of NAS. In addition, Finnegan scores can be inconsistent, and the assessment requires disturbing an infant to check signs such as its startle reflex, which, as Dr. Grossman and his fellow researchers pointed out, flies in the face of American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendations to prioritize swaddling and minimize stimulation for infants with NAS.
By contrast, Eat, Sleep, Console offers a simplified assessment. Interventions are called for if a baby eats less than an ounce of food at a time/does not breastfeed, sleeps less than an hour at a stretch, or takes more than 10 minutes to be consoled. After nonpharmacologic interventions have been tried, doses of medication are used as needed. Babies who are doing well can be discharged in as few as 4 days.
Quashing bias against parents with substance abuse disorder
Even with the promise of shorter stays and better care, switching to nonpharmacologic care presents hurdles for hospitals. Among these is a lack of physical space for mothers to room with their babies in a quiet environment.
“In many community hospitals, the only place for infants to go is a neonatal intensive care unit, outside of the newborn nursery,” said Stephen Patrick, MD, MPH, associate professor and director of the Center for Child Health Policy at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who researches stigma associated with opioid use during pregnancy.
Administrators at SSM St. Mary’s Hospital in St. Louis initially balked at providing private rooms for mothers and their babies with NAS and NOWS, according to Kimberly Spence, MD, a neonatologist at SSM Health. She said the initial plan was to put the babies in a busy, brightly lit nursery.
But resistance waned as the hospital convinced health plans to pay for private rooms for the 5-7 days it typically takes a baby to go through withdrawal, said Dr. Spence, associate professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University.
“We were able to provide enough data that this is evidence-based medicine and babies do better with their moms, and that ethically, this is the right thing to do, to reduce transfers to an NICU,” she said.
In addition, news stories about the family-centric approach and shorter stays for infants, along with SSM’s launch of an outpatient clinic to treat pregnant women with opioid use disorder, helped the system to attract more patients and increase its market share, said Dr. Spence.
Another challenge was getting physicians and nurses to set aside any judgments of parents with substance abuse disorder, according to Dr. Grossman and others.
“A lot of faculty and staff on the medical team didn’t feel like we should trust moms with their babies’ medical care” at SSM, Dr. Spence said.
Some hospitals conduct anti-bias training to teach providers that substance abuse is a disease that deserves proper medical treatment and not the moral failing of a patient. Such education may involve explaining that babies’ outcomes are improved when women undergo treatment with methadone or buprenorphine during pregnancy, even though use of those medications does pose a risk of NAS.
Creating a system that supports parents with substance abuse disorders may help to change perceptions. At Atrium Health, some staff members now enjoy working with these families because they can make a profound impact, Dr. Dodds said. He said they’ve learned that families suffering from substance abuse disorder “are not that different than any other family.”
Dr. Dodds, Dr. Patrick, Dr. Spence, and Dr. Grossman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four years ago, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C., embarked on a dramatic change in how it cares for newborns exposed to opioids in the womb.
Until then, most of the 700 or so babies who underwent opioid withdrawal each year in the hospital system spent their first weeks in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), isolated from their parents and treated with regular doses of morphine to ease their symptoms.
Now, most babies stay in the hospital for just a few days under a new approach called Eat, Sleep, Console. These young patients stay in private rooms where they can bond with their parents and volunteer caregivers. The usual course of treatment is no longer extended therapy with opioid replacements. Instead, mothers are encouraged to stay overnight and are taught how to sooth their babies with swaddling, rocking, and cooing.
As a result, the average length of stay for newborns with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) has dropped from 12 days to 6. Use of morphine has fallen by 79%, from 2.25 to 0.45 mg/kg per stay, according to results of a quality improvement pilot project at one of Atrium’s community hospitals.
Similar outcomes from other hospitals around the country have led to widespread uptake of Eat, Sleep, Console since its advent in 2017. That year, according to federal data, seven newborns were diagnosed with NAS for every 1,000 births.
Advocates say the family-centric model helps parents feel less stigmatized and more confident in their ability to care for their babies, who can have symptoms such as irritability and difficulty feeding for months.
The approach “really empowers families to do what they do best, which is take care of each other,” Douglas Dodds, MD, a pediatrician who led the effort at Atrium, told this news organization.
Questioning the old protocols
Numerous state perinatal collaboratives, hospital associations, and health systems say the program is the new standard of care for infants with NAS and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS).
Twenty-six hospitals have adopted Eat, Sleep, Console as part of a clinical trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health and a program called Advancing Clinical Trials in Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome (ACT NOW). Researchers are comparing the approach to previous care protocols in regard to 12 outcomes, including time to medical readiness for discharge, frequency of opioid replacement therapy, and safety problems, such as seizures during treatment.
The transition has been swift. Less than a decade ago, most hospitals used the Finnegan Neonatal Abstinence Scoring System, which was developed in the 1970s to assess babies whose mothers had used heroin during pregnancy.
The Finnegan score entails monitoring babies every 3 hours for 21 symptoms, including high-pitched crying, sneezing, gastrointestinal problems, and yawning. If a baby scores an 8 or more three times in a row, most protocols using the traditional Finnegan approach recommend that providers move infants to an NICU, where they receive morphine or methadone. Once opioid replacement therapy is started, the protocols require a gradual weaning that lasts 3-4 weeks.
As the opioid epidemic grew and NICUs around the country began to fill with babies experiencing NAS or NOW, some clinicians began to question the Finnegan-driven approach.
“You have these miserable babies who are going through this really tough experience, and our first move is to separate them from their moms,” said Matthew Grossman, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital, New Haven, Conn., who created Eat, Sleep, Console.
Dr. Grossman, associate professor and vice chair for quality in the department of pediatrics at Yale University, said he noticed that when mothers stayed overnight with their babies, the infants tended to have fewer withdrawal symptoms. Indeed, previous studies had demonstrated the benefits of breastfeeding and allowing mothers and babies to share a room.
“If you think of mom as a medicine, then you can’t put the baby in a unit where the mom can’t be there,” Dr. Grossman told this news organization. “It would be like taking a kid with pneumonia and putting him in a unit that doesn’t have antibiotics.”
Despite its prominence, the Finnegan score has never been validated for guiding the treatment of NAS. In addition, Finnegan scores can be inconsistent, and the assessment requires disturbing an infant to check signs such as its startle reflex, which, as Dr. Grossman and his fellow researchers pointed out, flies in the face of American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendations to prioritize swaddling and minimize stimulation for infants with NAS.
By contrast, Eat, Sleep, Console offers a simplified assessment. Interventions are called for if a baby eats less than an ounce of food at a time/does not breastfeed, sleeps less than an hour at a stretch, or takes more than 10 minutes to be consoled. After nonpharmacologic interventions have been tried, doses of medication are used as needed. Babies who are doing well can be discharged in as few as 4 days.
Quashing bias against parents with substance abuse disorder
Even with the promise of shorter stays and better care, switching to nonpharmacologic care presents hurdles for hospitals. Among these is a lack of physical space for mothers to room with their babies in a quiet environment.
“In many community hospitals, the only place for infants to go is a neonatal intensive care unit, outside of the newborn nursery,” said Stephen Patrick, MD, MPH, associate professor and director of the Center for Child Health Policy at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who researches stigma associated with opioid use during pregnancy.
Administrators at SSM St. Mary’s Hospital in St. Louis initially balked at providing private rooms for mothers and their babies with NAS and NOWS, according to Kimberly Spence, MD, a neonatologist at SSM Health. She said the initial plan was to put the babies in a busy, brightly lit nursery.
But resistance waned as the hospital convinced health plans to pay for private rooms for the 5-7 days it typically takes a baby to go through withdrawal, said Dr. Spence, associate professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University.
“We were able to provide enough data that this is evidence-based medicine and babies do better with their moms, and that ethically, this is the right thing to do, to reduce transfers to an NICU,” she said.
In addition, news stories about the family-centric approach and shorter stays for infants, along with SSM’s launch of an outpatient clinic to treat pregnant women with opioid use disorder, helped the system to attract more patients and increase its market share, said Dr. Spence.
Another challenge was getting physicians and nurses to set aside any judgments of parents with substance abuse disorder, according to Dr. Grossman and others.
“A lot of faculty and staff on the medical team didn’t feel like we should trust moms with their babies’ medical care” at SSM, Dr. Spence said.
Some hospitals conduct anti-bias training to teach providers that substance abuse is a disease that deserves proper medical treatment and not the moral failing of a patient. Such education may involve explaining that babies’ outcomes are improved when women undergo treatment with methadone or buprenorphine during pregnancy, even though use of those medications does pose a risk of NAS.
Creating a system that supports parents with substance abuse disorders may help to change perceptions. At Atrium Health, some staff members now enjoy working with these families because they can make a profound impact, Dr. Dodds said. He said they’ve learned that families suffering from substance abuse disorder “are not that different than any other family.”
Dr. Dodds, Dr. Patrick, Dr. Spence, and Dr. Grossman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
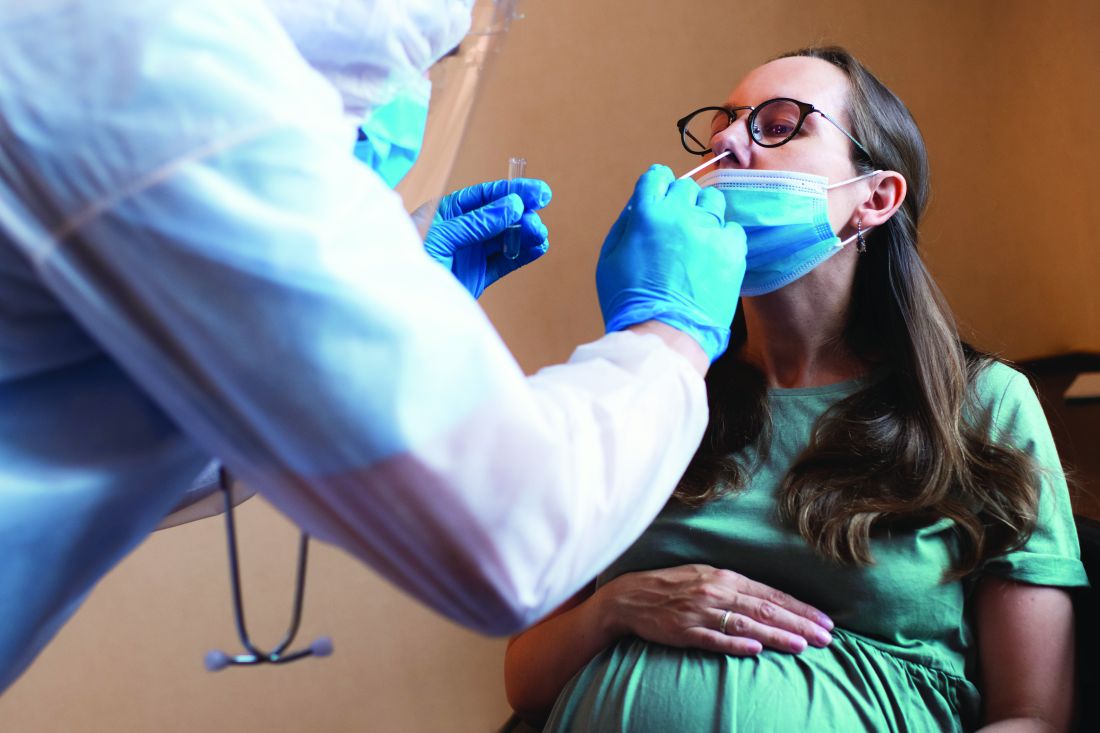
COVID-19 infection late in pregnancy linked to sevenfold risk of preterm birth
Pregnant women who get infected with SARS-CoV-2 in their third trimester are almost three times as likely to have a preterm birth, while infection after 34 weeks’ gestation raises this risk sevenfold, based on the largest matched population-based cohort study published to date.
These findings support previous studies, underscoring the need for pregnant women and their families to take preventive measures against infection, lead author Noga Fallach, MA, of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, Tel Aviv, and colleagues reported.
Past research has suggested that COVID-19 may cause low birth weights and preterm birth in pregnant women, but those studies didn’t report outcomes for each trimester, the investigators wrote in PLoS ONE, noting that “timing of viral infection during fetal development may affect birth and other health outcomes.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators looked back at data from 2,703 pregnant women in Israel who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 from Feb. 21, 2020, to July 2, 2021. Pregnancy outcomes in these women were compared with outcomes in an equal number of uninfected pregnant women. Vaccination status was not reported.
Comparing the two groups showed that catching COVID-19 in the third trimester was linked with nearly triple the risk of preterm birth (odds ratio, 2.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.63-4.67), and more than quadruple the risk if COVID-19 symptoms were present (OR, 4.28; 95% CI, 1.94-9.41). Women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after 34 weeks’ gestation were seven times more likely than uninfected women to deliver early (OR, 7.10; 95% CI, 2.44-20.61).
Pregnant women who caught COVID-19 in the first two trimesters were not significantly more likely to have a preterm birth. Infection was not associated with abnormally low birth rates, or pregnancy loss, in any trimester.
Tal Patalon, MD, coauthor and head of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, focused on these more optimistic findings in an interview.
“The results are encouraging, and reassuring that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy is not associated with any type of pregnancy loss,” Dr. Patalon said.
She also pointed out that the women in the study were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are no longer common.
“It should be remembered that the research group tested the COVID-19 pre-Delta variants, and does not refer to the dominant variant today, which is Omicron,” Dr. Patalon said.
Still, the investigators concluded that the “results underline the importance of preventive measures taken against SARS-CoV-2 infection among pregnant women and their families.”
Sonja A. Rasmussen, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, said that the issue with out-of-date variants in published research has been one of the “real challenges” in studying the ever-evolving COVID-19 pandemic; however, it’s not a good enough reason to dismiss this study.
“I think at this point, we need to assume that it applies to Omicron too,” Dr. Rasmussen said, noting that other respiratory viruses, like influenza, have also been shown to increase the risk of preterm birth when contracted in late pregnancy.
While the present findings highlight the risk of infection in the third trimester, Dr. Rasmussen advised women in all stages of pregnancy to protect themselves against COVID-19, based on the knowledge that illness in a mother can affect normal growth and development in a fetus, even if it doesn’t lead to preterm birth.
“A mom getting sick during pregnancy is not good for the baby,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “The baby’s really dependent on the mom. So you want that baby to have good nutrition throughout the pregnancy. It’s just as important earlier on as later. And you want that baby to get good oxygenation no matter what time [in the pregnancy]. I know that people want a little bit of a break [from preventive measures]. But I would emphasize that if you’re pregnant, we do all sorts of things during pregnancy to make sure that our babies are safe and healthy, and I would continue that for the whole pregnancy.”
Specifically, Dr. Rasmussen advised social distancing, use of an N95 mask, and vaccination. Getting vaccinated during pregnancy helps newborns fight off infection until 6 months of age, she added, when they become eligible for vaccination themselves. This added benefit was recently reported in a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine , for which Dr. Rasmussen cowrote an editorial .
“Vaccines have been approved for 6 months and older,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “But what do you do in those first 6 months of life? That’s a high-risk time for kids.”
Despite these risks, convincing pregnant women to get vaccinated remains a key challenge for health care providers, according to Dr. Rasmussen, even with an abundance of safety data. “Early on [in the pandemic], we said we didn’t know a lot about risks. We knew that other vaccines were safe during pregnancy, but we didn’t have a lot of information about a COVID-19 vaccine. But now we have a lot of data on safety during pregnancy, and these vaccines appear to be completely safe, based on the information we have. There have been many, many pregnant women vaccinated in the United States and in other countries.”
For reluctant expecting mothers, Dr. Rasmussen offered some words of advice: “I know that you worry about anything you do when you’re pregnant. But this is something that you can do to help your baby – now, to make a preterm birth less likely, and later, after the baby is born.
“The most important thing is for the pregnant person to hear this [vaccine recommendation] from their doctor,” she added. “If they’re going to listen to anybody, they’re going to listen to their physician. That’s what the data have shown for a long time.”
The investigators and Dr. Rasmussen disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Pregnant women who get infected with SARS-CoV-2 in their third trimester are almost three times as likely to have a preterm birth, while infection after 34 weeks’ gestation raises this risk sevenfold, based on the largest matched population-based cohort study published to date.
These findings support previous studies, underscoring the need for pregnant women and their families to take preventive measures against infection, lead author Noga Fallach, MA, of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, Tel Aviv, and colleagues reported.
Past research has suggested that COVID-19 may cause low birth weights and preterm birth in pregnant women, but those studies didn’t report outcomes for each trimester, the investigators wrote in PLoS ONE, noting that “timing of viral infection during fetal development may affect birth and other health outcomes.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators looked back at data from 2,703 pregnant women in Israel who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 from Feb. 21, 2020, to July 2, 2021. Pregnancy outcomes in these women were compared with outcomes in an equal number of uninfected pregnant women. Vaccination status was not reported.
Comparing the two groups showed that catching COVID-19 in the third trimester was linked with nearly triple the risk of preterm birth (odds ratio, 2.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.63-4.67), and more than quadruple the risk if COVID-19 symptoms were present (OR, 4.28; 95% CI, 1.94-9.41). Women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after 34 weeks’ gestation were seven times more likely than uninfected women to deliver early (OR, 7.10; 95% CI, 2.44-20.61).
Pregnant women who caught COVID-19 in the first two trimesters were not significantly more likely to have a preterm birth. Infection was not associated with abnormally low birth rates, or pregnancy loss, in any trimester.
Tal Patalon, MD, coauthor and head of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, focused on these more optimistic findings in an interview.
“The results are encouraging, and reassuring that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy is not associated with any type of pregnancy loss,” Dr. Patalon said.
She also pointed out that the women in the study were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are no longer common.
“It should be remembered that the research group tested the COVID-19 pre-Delta variants, and does not refer to the dominant variant today, which is Omicron,” Dr. Patalon said.
Still, the investigators concluded that the “results underline the importance of preventive measures taken against SARS-CoV-2 infection among pregnant women and their families.”
Sonja A. Rasmussen, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, said that the issue with out-of-date variants in published research has been one of the “real challenges” in studying the ever-evolving COVID-19 pandemic; however, it’s not a good enough reason to dismiss this study.
“I think at this point, we need to assume that it applies to Omicron too,” Dr. Rasmussen said, noting that other respiratory viruses, like influenza, have also been shown to increase the risk of preterm birth when contracted in late pregnancy.
While the present findings highlight the risk of infection in the third trimester, Dr. Rasmussen advised women in all stages of pregnancy to protect themselves against COVID-19, based on the knowledge that illness in a mother can affect normal growth and development in a fetus, even if it doesn’t lead to preterm birth.
“A mom getting sick during pregnancy is not good for the baby,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “The baby’s really dependent on the mom. So you want that baby to have good nutrition throughout the pregnancy. It’s just as important earlier on as later. And you want that baby to get good oxygenation no matter what time [in the pregnancy]. I know that people want a little bit of a break [from preventive measures]. But I would emphasize that if you’re pregnant, we do all sorts of things during pregnancy to make sure that our babies are safe and healthy, and I would continue that for the whole pregnancy.”
Specifically, Dr. Rasmussen advised social distancing, use of an N95 mask, and vaccination. Getting vaccinated during pregnancy helps newborns fight off infection until 6 months of age, she added, when they become eligible for vaccination themselves. This added benefit was recently reported in a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine , for which Dr. Rasmussen cowrote an editorial .
“Vaccines have been approved for 6 months and older,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “But what do you do in those first 6 months of life? That’s a high-risk time for kids.”
Despite these risks, convincing pregnant women to get vaccinated remains a key challenge for health care providers, according to Dr. Rasmussen, even with an abundance of safety data. “Early on [in the pandemic], we said we didn’t know a lot about risks. We knew that other vaccines were safe during pregnancy, but we didn’t have a lot of information about a COVID-19 vaccine. But now we have a lot of data on safety during pregnancy, and these vaccines appear to be completely safe, based on the information we have. There have been many, many pregnant women vaccinated in the United States and in other countries.”
For reluctant expecting mothers, Dr. Rasmussen offered some words of advice: “I know that you worry about anything you do when you’re pregnant. But this is something that you can do to help your baby – now, to make a preterm birth less likely, and later, after the baby is born.
“The most important thing is for the pregnant person to hear this [vaccine recommendation] from their doctor,” she added. “If they’re going to listen to anybody, they’re going to listen to their physician. That’s what the data have shown for a long time.”
The investigators and Dr. Rasmussen disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Pregnant women who get infected with SARS-CoV-2 in their third trimester are almost three times as likely to have a preterm birth, while infection after 34 weeks’ gestation raises this risk sevenfold, based on the largest matched population-based cohort study published to date.
These findings support previous studies, underscoring the need for pregnant women and their families to take preventive measures against infection, lead author Noga Fallach, MA, of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, Tel Aviv, and colleagues reported.
Past research has suggested that COVID-19 may cause low birth weights and preterm birth in pregnant women, but those studies didn’t report outcomes for each trimester, the investigators wrote in PLoS ONE, noting that “timing of viral infection during fetal development may affect birth and other health outcomes.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators looked back at data from 2,703 pregnant women in Israel who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 from Feb. 21, 2020, to July 2, 2021. Pregnancy outcomes in these women were compared with outcomes in an equal number of uninfected pregnant women. Vaccination status was not reported.
Comparing the two groups showed that catching COVID-19 in the third trimester was linked with nearly triple the risk of preterm birth (odds ratio, 2.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.63-4.67), and more than quadruple the risk if COVID-19 symptoms were present (OR, 4.28; 95% CI, 1.94-9.41). Women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after 34 weeks’ gestation were seven times more likely than uninfected women to deliver early (OR, 7.10; 95% CI, 2.44-20.61).
Pregnant women who caught COVID-19 in the first two trimesters were not significantly more likely to have a preterm birth. Infection was not associated with abnormally low birth rates, or pregnancy loss, in any trimester.
Tal Patalon, MD, coauthor and head of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, focused on these more optimistic findings in an interview.
“The results are encouraging, and reassuring that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy is not associated with any type of pregnancy loss,” Dr. Patalon said.
She also pointed out that the women in the study were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are no longer common.
“It should be remembered that the research group tested the COVID-19 pre-Delta variants, and does not refer to the dominant variant today, which is Omicron,” Dr. Patalon said.
Still, the investigators concluded that the “results underline the importance of preventive measures taken against SARS-CoV-2 infection among pregnant women and their families.”
Sonja A. Rasmussen, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, said that the issue with out-of-date variants in published research has been one of the “real challenges” in studying the ever-evolving COVID-19 pandemic; however, it’s not a good enough reason to dismiss this study.
“I think at this point, we need to assume that it applies to Omicron too,” Dr. Rasmussen said, noting that other respiratory viruses, like influenza, have also been shown to increase the risk of preterm birth when contracted in late pregnancy.
While the present findings highlight the risk of infection in the third trimester, Dr. Rasmussen advised women in all stages of pregnancy to protect themselves against COVID-19, based on the knowledge that illness in a mother can affect normal growth and development in a fetus, even if it doesn’t lead to preterm birth.
“A mom getting sick during pregnancy is not good for the baby,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “The baby’s really dependent on the mom. So you want that baby to have good nutrition throughout the pregnancy. It’s just as important earlier on as later. And you want that baby to get good oxygenation no matter what time [in the pregnancy]. I know that people want a little bit of a break [from preventive measures]. But I would emphasize that if you’re pregnant, we do all sorts of things during pregnancy to make sure that our babies are safe and healthy, and I would continue that for the whole pregnancy.”
Specifically, Dr. Rasmussen advised social distancing, use of an N95 mask, and vaccination. Getting vaccinated during pregnancy helps newborns fight off infection until 6 months of age, she added, when they become eligible for vaccination themselves. This added benefit was recently reported in a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine , for which Dr. Rasmussen cowrote an editorial .
“Vaccines have been approved for 6 months and older,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “But what do you do in those first 6 months of life? That’s a high-risk time for kids.”
Despite these risks, convincing pregnant women to get vaccinated remains a key challenge for health care providers, according to Dr. Rasmussen, even with an abundance of safety data. “Early on [in the pandemic], we said we didn’t know a lot about risks. We knew that other vaccines were safe during pregnancy, but we didn’t have a lot of information about a COVID-19 vaccine. But now we have a lot of data on safety during pregnancy, and these vaccines appear to be completely safe, based on the information we have. There have been many, many pregnant women vaccinated in the United States and in other countries.”
For reluctant expecting mothers, Dr. Rasmussen offered some words of advice: “I know that you worry about anything you do when you’re pregnant. But this is something that you can do to help your baby – now, to make a preterm birth less likely, and later, after the baby is born.
“The most important thing is for the pregnant person to hear this [vaccine recommendation] from their doctor,” she added. “If they’re going to listen to anybody, they’re going to listen to their physician. That’s what the data have shown for a long time.”
The investigators and Dr. Rasmussen disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM PLOS ONE
Recommendations on breastfeeding: A case of too much information
The American Academy of Pediatrics is built on good intentions. It wants the best for children in the world, and it hopes to support its members in their efforts to achieve this goal. But from time to time, the academy loses sight of reality and makes recommendations that are counterproductive to its stated goals.
The recent release of its new policy “Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk” is another unfortunate example of poorly aimed recommendations. A careful reading of the document reveals it to be a well-researched treatise on breastfeeding and the value of human milk, including a discussion of the numerous impediments to the universal adoption of breastfeeding in our society. However, when a document of this breadth and complexity is released to the public it is never surprising that the messages deserving the most attention are lost in the press coverage. Most of the headlines I saw mentioned pediatricians supporting breastfeeding for a year or 2.
Who was the target audience? If it was pediatricians, most of us don’t need a longer list of the health benefits of breastfeeding. We already believe it is the best nutritional source for human babies and realize that the institutional framework in this country continues to be unfriendly to women who intend to breastfeed.
If the audience is politicians and public health decision-makers, the new policy contains a wealth of supportive evidence. However, most pediatricians I know are too busy or lack the skills and enthusiasm to become political activists. For the rest of population, including parents, the recommendations represent a collection of TMI (too much information).
If the audience is women who are considering breastfeeding I suspect nearly 100% already know pediatricians think it is the preferred way to feed their babies. And, likewise, a longer list won’t convince them to try nursing. Additional evidence may simply make them feel more guilty when they aren’t successful.
Many pregnant women have already been told that breastfeeding can be a challenge and given their situation breast milk alone for the first 6 months may sound like an unreasonable goal. The new recommendation that breastfeeding for a year or 2 is good is not a message they want to hear.
On the other hand, if the target audience is women who will be comforted to hear an official statement that normalizes breastfeeding longer than a year, the new policy statement has hit the nail on the head.
Of course the new policy document is sprinkled with caveats that vaguely hint at the possibility that pediatricians are sensitive human beings who under certain circumstances may be able to compromise when it comes to the duration of breastfeeding and the introduction of formula. But this whiff of reality is certainly not the dominant odor in these new recommendations.
Don’t get me wrong: I think the academy was overdue for a policy revision on breastfeeding. However, it should have been one that was reality based. It should acknowledge that there are institutional and societal biases against breastfeeding, and it should remind pediatricians that they can effect change by discussing these realities honestly with parents, while making it clear that we are there for them and their children regardless of how they feed their baby. Pediatricians believe that breastfeeding is the best but not the only way to feed a baby. We have (or will provide) the skills to assist parents succeed in whatever method they choose and strive to minimize the impediments that are within our power to change.
If the academy had chosen to release a separate statement simply supporting mothers who chose to nurse longer than a year, then that would have been a good idea. However, when presented as part of the larger document, that message dominated in the media and only served to fuel the guilt that many new mothers must endure.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
The American Academy of Pediatrics is built on good intentions. It wants the best for children in the world, and it hopes to support its members in their efforts to achieve this goal. But from time to time, the academy loses sight of reality and makes recommendations that are counterproductive to its stated goals.
The recent release of its new policy “Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk” is another unfortunate example of poorly aimed recommendations. A careful reading of the document reveals it to be a well-researched treatise on breastfeeding and the value of human milk, including a discussion of the numerous impediments to the universal adoption of breastfeeding in our society. However, when a document of this breadth and complexity is released to the public it is never surprising that the messages deserving the most attention are lost in the press coverage. Most of the headlines I saw mentioned pediatricians supporting breastfeeding for a year or 2.
Who was the target audience? If it was pediatricians, most of us don’t need a longer list of the health benefits of breastfeeding. We already believe it is the best nutritional source for human babies and realize that the institutional framework in this country continues to be unfriendly to women who intend to breastfeed.
If the audience is politicians and public health decision-makers, the new policy contains a wealth of supportive evidence. However, most pediatricians I know are too busy or lack the skills and enthusiasm to become political activists. For the rest of population, including parents, the recommendations represent a collection of TMI (too much information).
If the audience is women who are considering breastfeeding I suspect nearly 100% already know pediatricians think it is the preferred way to feed their babies. And, likewise, a longer list won’t convince them to try nursing. Additional evidence may simply make them feel more guilty when they aren’t successful.
Many pregnant women have already been told that breastfeeding can be a challenge and given their situation breast milk alone for the first 6 months may sound like an unreasonable goal. The new recommendation that breastfeeding for a year or 2 is good is not a message they want to hear.
On the other hand, if the target audience is women who will be comforted to hear an official statement that normalizes breastfeeding longer than a year, the new policy statement has hit the nail on the head.
Of course the new policy document is sprinkled with caveats that vaguely hint at the possibility that pediatricians are sensitive human beings who under certain circumstances may be able to compromise when it comes to the duration of breastfeeding and the introduction of formula. But this whiff of reality is certainly not the dominant odor in these new recommendations.
Don’t get me wrong: I think the academy was overdue for a policy revision on breastfeeding. However, it should have been one that was reality based. It should acknowledge that there are institutional and societal biases against breastfeeding, and it should remind pediatricians that they can effect change by discussing these realities honestly with parents, while making it clear that we are there for them and their children regardless of how they feed their baby. Pediatricians believe that breastfeeding is the best but not the only way to feed a baby. We have (or will provide) the skills to assist parents succeed in whatever method they choose and strive to minimize the impediments that are within our power to change.
If the academy had chosen to release a separate statement simply supporting mothers who chose to nurse longer than a year, then that would have been a good idea. However, when presented as part of the larger document, that message dominated in the media and only served to fuel the guilt that many new mothers must endure.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
The American Academy of Pediatrics is built on good intentions. It wants the best for children in the world, and it hopes to support its members in their efforts to achieve this goal. But from time to time, the academy loses sight of reality and makes recommendations that are counterproductive to its stated goals.
The recent release of its new policy “Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk” is another unfortunate example of poorly aimed recommendations. A careful reading of the document reveals it to be a well-researched treatise on breastfeeding and the value of human milk, including a discussion of the numerous impediments to the universal adoption of breastfeeding in our society. However, when a document of this breadth and complexity is released to the public it is never surprising that the messages deserving the most attention are lost in the press coverage. Most of the headlines I saw mentioned pediatricians supporting breastfeeding for a year or 2.
Who was the target audience? If it was pediatricians, most of us don’t need a longer list of the health benefits of breastfeeding. We already believe it is the best nutritional source for human babies and realize that the institutional framework in this country continues to be unfriendly to women who intend to breastfeed.
If the audience is politicians and public health decision-makers, the new policy contains a wealth of supportive evidence. However, most pediatricians I know are too busy or lack the skills and enthusiasm to become political activists. For the rest of population, including parents, the recommendations represent a collection of TMI (too much information).
If the audience is women who are considering breastfeeding I suspect nearly 100% already know pediatricians think it is the preferred way to feed their babies. And, likewise, a longer list won’t convince them to try nursing. Additional evidence may simply make them feel more guilty when they aren’t successful.
Many pregnant women have already been told that breastfeeding can be a challenge and given their situation breast milk alone for the first 6 months may sound like an unreasonable goal. The new recommendation that breastfeeding for a year or 2 is good is not a message they want to hear.
On the other hand, if the target audience is women who will be comforted to hear an official statement that normalizes breastfeeding longer than a year, the new policy statement has hit the nail on the head.
Of course the new policy document is sprinkled with caveats that vaguely hint at the possibility that pediatricians are sensitive human beings who under certain circumstances may be able to compromise when it comes to the duration of breastfeeding and the introduction of formula. But this whiff of reality is certainly not the dominant odor in these new recommendations.
Don’t get me wrong: I think the academy was overdue for a policy revision on breastfeeding. However, it should have been one that was reality based. It should acknowledge that there are institutional and societal biases against breastfeeding, and it should remind pediatricians that they can effect change by discussing these realities honestly with parents, while making it clear that we are there for them and their children regardless of how they feed their baby. Pediatricians believe that breastfeeding is the best but not the only way to feed a baby. We have (or will provide) the skills to assist parents succeed in whatever method they choose and strive to minimize the impediments that are within our power to change.
If the academy had chosen to release a separate statement simply supporting mothers who chose to nurse longer than a year, then that would have been a good idea. However, when presented as part of the larger document, that message dominated in the media and only served to fuel the guilt that many new mothers must endure.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
FDA allows import of 2 million cans of baby formula from U.K.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is easing rules to allow infant formula imports from the United Kingdom, which would bring about 2 million cans to the U.S. in coming weeks.
Kendal Nutricare will be able to offer certain infant formula products under the Kendamil brand to ease the nationwide formula shortage.
“Importantly, we anticipate additional infant formula products may be safely and quickly imported in the U.S. in the near-term, based on ongoing discussions with manufacturers and suppliers worldwide,” Robert Califf, MD, the FDA commissioner, said in a statement.
Kendal Nutricare has more than 40,000 cans in stock for immediate dispatch, the FDA said, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is talking to the company about the best ways to get the products to the U.S. as quickly as possible.
Kendamil has set up a website for consumers to receive updates and find products once they arrive in the U.S.
After an evaluation, the FDA said it had no safety or nutrition concerns about the products. The evaluation reviewed the company’s microbiological testing, labeling, and information about facility production and inspection history.
On May 24, the FDA announced that Abbott Nutrition will release about 300,000 cans of its EleCare specialty amino acid-based formula to families that need urgent, life-sustaining supplies. The products had more tests for microbes before release.
Although some EleCare products were included in Abbott’s infant formula recall earlier this year, the cans that will be released were in different lots, have never been released, and have been maintained in storage, the FDA said.
“These EleCare product lots were not part of the recall but have been on hold due to concerns that they were produced under unsanitary conditions observed at Abbott Nutrition’s Sturgis, Michigan, facility,” the FDA wrote.
The FDA encourages parents and caregivers to talk with their health care providers to weigh the potential risk of bacterial infection with the critical need for the product, based on its special dietary formulation for infants with severe food allergies or gut disorders.
The FDA also said that Abbott confirmed the EleCare products will be the first formula produced at the Sturgis facility when it restarts production soon. Other specialty metabolic formulas will follow.
Abbott plans to restart production at the Sturgis facility on June 4, the company said in a statement, noting that the early batches of EleCare would be available to consumers around June 20.
The products being released now are EleCare (for infants under 1 year) and EleCare Jr. (for ages 1 and older). Those who want to request products should contact their health care providers or call Abbott directly at 800-881-0876.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is easing rules to allow infant formula imports from the United Kingdom, which would bring about 2 million cans to the U.S. in coming weeks.
Kendal Nutricare will be able to offer certain infant formula products under the Kendamil brand to ease the nationwide formula shortage.
“Importantly, we anticipate additional infant formula products may be safely and quickly imported in the U.S. in the near-term, based on ongoing discussions with manufacturers and suppliers worldwide,” Robert Califf, MD, the FDA commissioner, said in a statement.
Kendal Nutricare has more than 40,000 cans in stock for immediate dispatch, the FDA said, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is talking to the company about the best ways to get the products to the U.S. as quickly as possible.
Kendamil has set up a website for consumers to receive updates and find products once they arrive in the U.S.
After an evaluation, the FDA said it had no safety or nutrition concerns about the products. The evaluation reviewed the company’s microbiological testing, labeling, and information about facility production and inspection history.
On May 24, the FDA announced that Abbott Nutrition will release about 300,000 cans of its EleCare specialty amino acid-based formula to families that need urgent, life-sustaining supplies. The products had more tests for microbes before release.
Although some EleCare products were included in Abbott’s infant formula recall earlier this year, the cans that will be released were in different lots, have never been released, and have been maintained in storage, the FDA said.
“These EleCare product lots were not part of the recall but have been on hold due to concerns that they were produced under unsanitary conditions observed at Abbott Nutrition’s Sturgis, Michigan, facility,” the FDA wrote.
The FDA encourages parents and caregivers to talk with their health care providers to weigh the potential risk of bacterial infection with the critical need for the product, based on its special dietary formulation for infants with severe food allergies or gut disorders.
The FDA also said that Abbott confirmed the EleCare products will be the first formula produced at the Sturgis facility when it restarts production soon. Other specialty metabolic formulas will follow.
Abbott plans to restart production at the Sturgis facility on June 4, the company said in a statement, noting that the early batches of EleCare would be available to consumers around June 20.
The products being released now are EleCare (for infants under 1 year) and EleCare Jr. (for ages 1 and older). Those who want to request products should contact their health care providers or call Abbott directly at 800-881-0876.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is easing rules to allow infant formula imports from the United Kingdom, which would bring about 2 million cans to the U.S. in coming weeks.
Kendal Nutricare will be able to offer certain infant formula products under the Kendamil brand to ease the nationwide formula shortage.
“Importantly, we anticipate additional infant formula products may be safely and quickly imported in the U.S. in the near-term, based on ongoing discussions with manufacturers and suppliers worldwide,” Robert Califf, MD, the FDA commissioner, said in a statement.
Kendal Nutricare has more than 40,000 cans in stock for immediate dispatch, the FDA said, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is talking to the company about the best ways to get the products to the U.S. as quickly as possible.
Kendamil has set up a website for consumers to receive updates and find products once they arrive in the U.S.
After an evaluation, the FDA said it had no safety or nutrition concerns about the products. The evaluation reviewed the company’s microbiological testing, labeling, and information about facility production and inspection history.
On May 24, the FDA announced that Abbott Nutrition will release about 300,000 cans of its EleCare specialty amino acid-based formula to families that need urgent, life-sustaining supplies. The products had more tests for microbes before release.
Although some EleCare products were included in Abbott’s infant formula recall earlier this year, the cans that will be released were in different lots, have never been released, and have been maintained in storage, the FDA said.
“These EleCare product lots were not part of the recall but have been on hold due to concerns that they were produced under unsanitary conditions observed at Abbott Nutrition’s Sturgis, Michigan, facility,” the FDA wrote.
The FDA encourages parents and caregivers to talk with their health care providers to weigh the potential risk of bacterial infection with the critical need for the product, based on its special dietary formulation for infants with severe food allergies or gut disorders.
The FDA also said that Abbott confirmed the EleCare products will be the first formula produced at the Sturgis facility when it restarts production soon. Other specialty metabolic formulas will follow.
Abbott plans to restart production at the Sturgis facility on June 4, the company said in a statement, noting that the early batches of EleCare would be available to consumers around June 20.
The products being released now are EleCare (for infants under 1 year) and EleCare Jr. (for ages 1 and older). Those who want to request products should contact their health care providers or call Abbott directly at 800-881-0876.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The baby formula shortage continues
Meghan Block of Weymouth, Mass., starts her search at 5 a.m. every morning – combing local retailer websites for baby formula.
Her own children have been off it for years. But her cousin in New Hampshire has a 2-month-old son who needs hypoallergenic formula, and the nationwide shortage has left the new mom scrambling to find what her baby needs.
“I’d equate this to how we were all frantically looking for vaccine appointments when they first rolled out,” Ms. Block said. “Parents are all mobilizing for each other.”
She added, “What people aren’t talking about is the stress on new mothers this is causing. If you’re on the edge of the baby blues and postpartum depression, and you can’t find food for your babies – these parents could be in crisis.”
For weeks, a pandemic-induced supply chain shortage – along with a massive recall from top formula manufacturer Abbott Nutrition – has left shelves empty and parents panicked, fearing their dwindling formula supplies will disappear entirely.
Abbott announced that its previously shuttered Michigan factory would reopen, but it remains unclear how soon that will make a noticeable difference.
The Food and Drug Administration announced Monday, May 16, that it would ease restrictions for selling foreign-made baby formula in the U.S. to broaden supply.
President Joe Biden invoked the the Defense Production Act on May 18, which requires suppliers to send resources to formula plants before giving them to other customers. The president is also authorizing the Defense Department to use commercial aircraft to pick up infant formula overseas that meets federal standards and fly it to the U.S. – a measure dubbed “Operation Fly Formula.”
But in the meantime, hospital staff and pediatricians are fielding questions from parents that they can’t always answer.
“People want to know if the shortage is ending soon, and that’s hard to predict. Even with the factory back online, the end could still be 1-3 months away,” Joshua Wechsler, MD, pediatric gastroenterologist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, said in an interview.
Most formulas on the market have comparable alternatives, Dr. Wechsler said, but there are fewer options for parents of special-needs babies – those with allergies and specific dietary requirements.
This has required around-the-clock work from dietitians and pediatricians to find sufficient options for these babies and monitor their ability to tolerate new kinds of formula.
“We’re advising parents not to dilute formula, not to buy it from sources you’re unfamiliar with, and no homemade formulas,” Dr. Wechsler said.
He said in some instances he has seen weight loss among babies whose supplies were stretching thin, and in very rare cases, hospitalizations.
According to recent reports, two children were hospitalized in mid-May at Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital, Memphis, Tenn., as a result of the formula shortage.
Those most affected by the crisis, doctors say, are lower-income families. Half of the infant formula purchased in the United States is through Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) benefits, a federal assistance program, which provides formula for free but only limited types and brands.
But in most cases, hospitals and pediatricians have the means to provide caregivers with supplementary formula, said Amy Hair, MD, program director of neonatal nutrition at Texas Children’s Hospital.
“Here in the hospital, we’re OK, because we’re able to switch through different options for patients and we’re sending families home with a short supply to bridge them over,” Dr. Hair said. “We encourage patients to talk to their pediatricians, who usually have in-office supplies.”
She also advises parents to look in smaller pharmacies and stores rather than bigger retailers, along with ordering it straight from the formula manufacturers online.
“We’re reassuring families we think this is temporary,” Dr. Hair said. “Providers have been dealing with this for a while, so we have some strategies in place to help caregivers through the shortage.”
In the meantime, parents continue to lean on each other for help and resources. Ms. Block’s cousin in New Hampshire, Jamie Boudreau, said she has friends and family on the lookout across the country for hypoallergenic formula for her son.
She currently has about a 1-month supply, but she worries constantly that will be depleted before the shortage ends.
“It’s definitely been very stressful,” Ms. Boudreau said. “I, as an adult, can go days without eating, but my tiny 2-month-old little boy – he can’t go more than 3 hours. What am I going to do if in 4 weeks I don’t have any more?”
Meghan Block of Weymouth, Mass., starts her search at 5 a.m. every morning – combing local retailer websites for baby formula.
Her own children have been off it for years. But her cousin in New Hampshire has a 2-month-old son who needs hypoallergenic formula, and the nationwide shortage has left the new mom scrambling to find what her baby needs.
“I’d equate this to how we were all frantically looking for vaccine appointments when they first rolled out,” Ms. Block said. “Parents are all mobilizing for each other.”
She added, “What people aren’t talking about is the stress on new mothers this is causing. If you’re on the edge of the baby blues and postpartum depression, and you can’t find food for your babies – these parents could be in crisis.”
For weeks, a pandemic-induced supply chain shortage – along with a massive recall from top formula manufacturer Abbott Nutrition – has left shelves empty and parents panicked, fearing their dwindling formula supplies will disappear entirely.
Abbott announced that its previously shuttered Michigan factory would reopen, but it remains unclear how soon that will make a noticeable difference.
The Food and Drug Administration announced Monday, May 16, that it would ease restrictions for selling foreign-made baby formula in the U.S. to broaden supply.
President Joe Biden invoked the the Defense Production Act on May 18, which requires suppliers to send resources to formula plants before giving them to other customers. The president is also authorizing the Defense Department to use commercial aircraft to pick up infant formula overseas that meets federal standards and fly it to the U.S. – a measure dubbed “Operation Fly Formula.”
But in the meantime, hospital staff and pediatricians are fielding questions from parents that they can’t always answer.
“People want to know if the shortage is ending soon, and that’s hard to predict. Even with the factory back online, the end could still be 1-3 months away,” Joshua Wechsler, MD, pediatric gastroenterologist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, said in an interview.
Most formulas on the market have comparable alternatives, Dr. Wechsler said, but there are fewer options for parents of special-needs babies – those with allergies and specific dietary requirements.
This has required around-the-clock work from dietitians and pediatricians to find sufficient options for these babies and monitor their ability to tolerate new kinds of formula.
“We’re advising parents not to dilute formula, not to buy it from sources you’re unfamiliar with, and no homemade formulas,” Dr. Wechsler said.
He said in some instances he has seen weight loss among babies whose supplies were stretching thin, and in very rare cases, hospitalizations.
According to recent reports, two children were hospitalized in mid-May at Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital, Memphis, Tenn., as a result of the formula shortage.
Those most affected by the crisis, doctors say, are lower-income families. Half of the infant formula purchased in the United States is through Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) benefits, a federal assistance program, which provides formula for free but only limited types and brands.
But in most cases, hospitals and pediatricians have the means to provide caregivers with supplementary formula, said Amy Hair, MD, program director of neonatal nutrition at Texas Children’s Hospital.
“Here in the hospital, we’re OK, because we’re able to switch through different options for patients and we’re sending families home with a short supply to bridge them over,” Dr. Hair said. “We encourage patients to talk to their pediatricians, who usually have in-office supplies.”
She also advises parents to look in smaller pharmacies and stores rather than bigger retailers, along with ordering it straight from the formula manufacturers online.
“We’re reassuring families we think this is temporary,” Dr. Hair said. “Providers have been dealing with this for a while, so we have some strategies in place to help caregivers through the shortage.”
In the meantime, parents continue to lean on each other for help and resources. Ms. Block’s cousin in New Hampshire, Jamie Boudreau, said she has friends and family on the lookout across the country for hypoallergenic formula for her son.
She currently has about a 1-month supply, but she worries constantly that will be depleted before the shortage ends.
“It’s definitely been very stressful,” Ms. Boudreau said. “I, as an adult, can go days without eating, but my tiny 2-month-old little boy – he can’t go more than 3 hours. What am I going to do if in 4 weeks I don’t have any more?”
Meghan Block of Weymouth, Mass., starts her search at 5 a.m. every morning – combing local retailer websites for baby formula.
Her own children have been off it for years. But her cousin in New Hampshire has a 2-month-old son who needs hypoallergenic formula, and the nationwide shortage has left the new mom scrambling to find what her baby needs.
“I’d equate this to how we were all frantically looking for vaccine appointments when they first rolled out,” Ms. Block said. “Parents are all mobilizing for each other.”
She added, “What people aren’t talking about is the stress on new mothers this is causing. If you’re on the edge of the baby blues and postpartum depression, and you can’t find food for your babies – these parents could be in crisis.”
For weeks, a pandemic-induced supply chain shortage – along with a massive recall from top formula manufacturer Abbott Nutrition – has left shelves empty and parents panicked, fearing their dwindling formula supplies will disappear entirely.
Abbott announced that its previously shuttered Michigan factory would reopen, but it remains unclear how soon that will make a noticeable difference.
The Food and Drug Administration announced Monday, May 16, that it would ease restrictions for selling foreign-made baby formula in the U.S. to broaden supply.
President Joe Biden invoked the the Defense Production Act on May 18, which requires suppliers to send resources to formula plants before giving them to other customers. The president is also authorizing the Defense Department to use commercial aircraft to pick up infant formula overseas that meets federal standards and fly it to the U.S. – a measure dubbed “Operation Fly Formula.”
But in the meantime, hospital staff and pediatricians are fielding questions from parents that they can’t always answer.
“People want to know if the shortage is ending soon, and that’s hard to predict. Even with the factory back online, the end could still be 1-3 months away,” Joshua Wechsler, MD, pediatric gastroenterologist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, said in an interview.
Most formulas on the market have comparable alternatives, Dr. Wechsler said, but there are fewer options for parents of special-needs babies – those with allergies and specific dietary requirements.
This has required around-the-clock work from dietitians and pediatricians to find sufficient options for these babies and monitor their ability to tolerate new kinds of formula.
“We’re advising parents not to dilute formula, not to buy it from sources you’re unfamiliar with, and no homemade formulas,” Dr. Wechsler said.
He said in some instances he has seen weight loss among babies whose supplies were stretching thin, and in very rare cases, hospitalizations.
According to recent reports, two children were hospitalized in mid-May at Le Bonheur Children’s Hospital, Memphis, Tenn., as a result of the formula shortage.
Those most affected by the crisis, doctors say, are lower-income families. Half of the infant formula purchased in the United States is through Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) benefits, a federal assistance program, which provides formula for free but only limited types and brands.
But in most cases, hospitals and pediatricians have the means to provide caregivers with supplementary formula, said Amy Hair, MD, program director of neonatal nutrition at Texas Children’s Hospital.
“Here in the hospital, we’re OK, because we’re able to switch through different options for patients and we’re sending families home with a short supply to bridge them over,” Dr. Hair said. “We encourage patients to talk to their pediatricians, who usually have in-office supplies.”
She also advises parents to look in smaller pharmacies and stores rather than bigger retailers, along with ordering it straight from the formula manufacturers online.
“We’re reassuring families we think this is temporary,” Dr. Hair said. “Providers have been dealing with this for a while, so we have some strategies in place to help caregivers through the shortage.”
In the meantime, parents continue to lean on each other for help and resources. Ms. Block’s cousin in New Hampshire, Jamie Boudreau, said she has friends and family on the lookout across the country for hypoallergenic formula for her son.
She currently has about a 1-month supply, but she worries constantly that will be depleted before the shortage ends.
“It’s definitely been very stressful,” Ms. Boudreau said. “I, as an adult, can go days without eating, but my tiny 2-month-old little boy – he can’t go more than 3 hours. What am I going to do if in 4 weeks I don’t have any more?”
Low butyrylcholinesterase: A possible biomarker of SIDS risk?
Reduced levels of the cholinergic-system enzyme butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) may provide another piece of the puzzle for sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), preliminary data from Australian researchers suggested.
A small case-control study led by Carmel T. Harrington, PhD,* a sleep medicine expert and honorary research fellow at the Children’s Hospital at Westmead (Australia), found that measurements in 722 dried blood spots taken during neonatal screening 2 or 3 days after birth were lower in babies who subsequently died of SIDS, compared with those of matched surviving controls and other babies who died of non-SIDS causes.
In groups in which cases were reported as SIDS death (n = 26) there was strong evidence that lower BChE-specific activity was associated with death (odds ratio, 0.73 per U/mg; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.89, P = .0014). In groups with a non-SIDS death (n = 41), there was no evidence of a linear association between BChE activity and death (OR, 1.001 per U/mg; 95% CI, 0.89-1.13, P = .99). A cohort of 655 age- and sex-matched controls served as a reference group.
Writing online in eBioMedicine, the researchers concluded that a previously unidentified cholinergic deficit, identifiable by abnormal BChE-specific activity, is present at birth in SIDS babies and represents a measurable, specific vulnerability prior to their death. “The finding presents the possibility of identifying infants at future risk for SIDS and it provides a specific avenue for future research into interventions prior to death.”
They hypothesized that the association is evidence of an altered cholinergic homeostasis and claim theirs is the first study to identify a measurable biochemical marker in babies who succumbed to SIDS. The marker “could plausibly produce functional alterations to an infant’s autonomic and arousal responses to an exogenous stressor leaving them vulnerable to sudden death.”
Commenting in a press release, Dr. Harrington said that “babies have a very powerful mechanism to let us know when they are not happy. Usually, if a baby is confronted with a life-threatening situation, such as difficulty breathing during sleep because they are on their tummies, they will arouse and cry out. What this research shows is that some babies don’t have this same robust arousal response.” Despite the sparse data, she believes that BChE is likely involved.
Providing a U.S. perspective on the study but not involved in it, Fern R. Hauck, MD, MS, a professor of family medicine and public health at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, said that “the media coverage presenting this as the ‘cause of SIDS,’ for which we may find a cure within 5 years, is very disturbing and very misleading. The data are very preliminary and results are based on only 26 SIDS cases.” In addition, the blood samples were more than 2 years old.
This research needs to be repeated in other labs in larger and diverse SIDS populations, she added. “Furthermore, we are not provided any racial-ethnic information about the SIDS cases in this study. In the U.S., the infants who are at greatest risk of dying from SIDS are most commonly African American and Native American/Alaska Native, and thus, these studies would need to be repeated in U.S. populations.”
Dr. Hauck added that, while the differences in blood levels of this enzyme were statistically different, even if this is confirmed by larger studies, there was enough overlap in the blood levels between cases and controls that it could not be used as a blood test at this point with any reasonable predictive value.
As the authors pointed out, she said, the leading theory of SIDS causation is that multiple factors interact. “While everyone would be happy to find one single explanation, it is not so simple. This research does, however, bring into focus the issues of arousal in SIDS and work on biomarkers. The arousal issue is one researchers have been working on for a long time.”
The SIDS research community has long been interested in biomarkers, Dr. Hauck continued. “Dr. Hannah Kinney’s first autoradiography study reported decreased muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding in the arcuate nucleus in SIDS, which the butyrylcholinesterase work further elaborates. More recently, Dr. Kinney reported abnormal cholinergic binding in the mesopontine reticular formation that is related to arousal and REM.”
Moreover, Robin Haynes and colleagues reported in 2017 that differences in serotonin can similarly be found in newborns on a newborn blood test, she said. “Like the butyrylcholinesterase research, there is a lot of work to do before understanding how specifically it can identify risk. The problem with using it prematurely is that it will unnecessarily alarm parents that their baby will die, and, to make it worse, be inaccurate in our warning.”
She also expressed concern that with the focus on a biomarker, parents will forget that SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths have come down considerably in the United States thanks to greater emphasis on promoting safe infant sleep behaviors.
The research was supported by a crowdfunding campaign and by NSW Health Pathology. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Hauck disclosed no conflicts of interest.
* This story was corrected on 5/20/2022.
Reduced levels of the cholinergic-system enzyme butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) may provide another piece of the puzzle for sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), preliminary data from Australian researchers suggested.
A small case-control study led by Carmel T. Harrington, PhD,* a sleep medicine expert and honorary research fellow at the Children’s Hospital at Westmead (Australia), found that measurements in 722 dried blood spots taken during neonatal screening 2 or 3 days after birth were lower in babies who subsequently died of SIDS, compared with those of matched surviving controls and other babies who died of non-SIDS causes.
In groups in which cases were reported as SIDS death (n = 26) there was strong evidence that lower BChE-specific activity was associated with death (odds ratio, 0.73 per U/mg; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.89, P = .0014). In groups with a non-SIDS death (n = 41), there was no evidence of a linear association between BChE activity and death (OR, 1.001 per U/mg; 95% CI, 0.89-1.13, P = .99). A cohort of 655 age- and sex-matched controls served as a reference group.
Writing online in eBioMedicine, the researchers concluded that a previously unidentified cholinergic deficit, identifiable by abnormal BChE-specific activity, is present at birth in SIDS babies and represents a measurable, specific vulnerability prior to their death. “The finding presents the possibility of identifying infants at future risk for SIDS and it provides a specific avenue for future research into interventions prior to death.”
They hypothesized that the association is evidence of an altered cholinergic homeostasis and claim theirs is the first study to identify a measurable biochemical marker in babies who succumbed to SIDS. The marker “could plausibly produce functional alterations to an infant’s autonomic and arousal responses to an exogenous stressor leaving them vulnerable to sudden death.”
Commenting in a press release, Dr. Harrington said that “babies have a very powerful mechanism to let us know when they are not happy. Usually, if a baby is confronted with a life-threatening situation, such as difficulty breathing during sleep because they are on their tummies, they will arouse and cry out. What this research shows is that some babies don’t have this same robust arousal response.” Despite the sparse data, she believes that BChE is likely involved.
Providing a U.S. perspective on the study but not involved in it, Fern R. Hauck, MD, MS, a professor of family medicine and public health at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, said that “the media coverage presenting this as the ‘cause of SIDS,’ for which we may find a cure within 5 years, is very disturbing and very misleading. The data are very preliminary and results are based on only 26 SIDS cases.” In addition, the blood samples were more than 2 years old.
This research needs to be repeated in other labs in larger and diverse SIDS populations, she added. “Furthermore, we are not provided any racial-ethnic information about the SIDS cases in this study. In the U.S., the infants who are at greatest risk of dying from SIDS are most commonly African American and Native American/Alaska Native, and thus, these studies would need to be repeated in U.S. populations.”
Dr. Hauck added that, while the differences in blood levels of this enzyme were statistically different, even if this is confirmed by larger studies, there was enough overlap in the blood levels between cases and controls that it could not be used as a blood test at this point with any reasonable predictive value.
As the authors pointed out, she said, the leading theory of SIDS causation is that multiple factors interact. “While everyone would be happy to find one single explanation, it is not so simple. This research does, however, bring into focus the issues of arousal in SIDS and work on biomarkers. The arousal issue is one researchers have been working on for a long time.”
The SIDS research community has long been interested in biomarkers, Dr. Hauck continued. “Dr. Hannah Kinney’s first autoradiography study reported decreased muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding in the arcuate nucleus in SIDS, which the butyrylcholinesterase work further elaborates. More recently, Dr. Kinney reported abnormal cholinergic binding in the mesopontine reticular formation that is related to arousal and REM.”
Moreover, Robin Haynes and colleagues reported in 2017 that differences in serotonin can similarly be found in newborns on a newborn blood test, she said. “Like the butyrylcholinesterase research, there is a lot of work to do before understanding how specifically it can identify risk. The problem with using it prematurely is that it will unnecessarily alarm parents that their baby will die, and, to make it worse, be inaccurate in our warning.”
She also expressed concern that with the focus on a biomarker, parents will forget that SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths have come down considerably in the United States thanks to greater emphasis on promoting safe infant sleep behaviors.
The research was supported by a crowdfunding campaign and by NSW Health Pathology. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Hauck disclosed no conflicts of interest.
* This story was corrected on 5/20/2022.
Reduced levels of the cholinergic-system enzyme butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) may provide another piece of the puzzle for sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), preliminary data from Australian researchers suggested.
A small case-control study led by Carmel T. Harrington, PhD,* a sleep medicine expert and honorary research fellow at the Children’s Hospital at Westmead (Australia), found that measurements in 722 dried blood spots taken during neonatal screening 2 or 3 days after birth were lower in babies who subsequently died of SIDS, compared with those of matched surviving controls and other babies who died of non-SIDS causes.
In groups in which cases were reported as SIDS death (n = 26) there was strong evidence that lower BChE-specific activity was associated with death (odds ratio, 0.73 per U/mg; 95% confidence interval, 0.60-0.89, P = .0014). In groups with a non-SIDS death (n = 41), there was no evidence of a linear association between BChE activity and death (OR, 1.001 per U/mg; 95% CI, 0.89-1.13, P = .99). A cohort of 655 age- and sex-matched controls served as a reference group.
Writing online in eBioMedicine, the researchers concluded that a previously unidentified cholinergic deficit, identifiable by abnormal BChE-specific activity, is present at birth in SIDS babies and represents a measurable, specific vulnerability prior to their death. “The finding presents the possibility of identifying infants at future risk for SIDS and it provides a specific avenue for future research into interventions prior to death.”
They hypothesized that the association is evidence of an altered cholinergic homeostasis and claim theirs is the first study to identify a measurable biochemical marker in babies who succumbed to SIDS. The marker “could plausibly produce functional alterations to an infant’s autonomic and arousal responses to an exogenous stressor leaving them vulnerable to sudden death.”
Commenting in a press release, Dr. Harrington said that “babies have a very powerful mechanism to let us know when they are not happy. Usually, if a baby is confronted with a life-threatening situation, such as difficulty breathing during sleep because they are on their tummies, they will arouse and cry out. What this research shows is that some babies don’t have this same robust arousal response.” Despite the sparse data, she believes that BChE is likely involved.
Providing a U.S. perspective on the study but not involved in it, Fern R. Hauck, MD, MS, a professor of family medicine and public health at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, said that “the media coverage presenting this as the ‘cause of SIDS,’ for which we may find a cure within 5 years, is very disturbing and very misleading. The data are very preliminary and results are based on only 26 SIDS cases.” In addition, the blood samples were more than 2 years old.
This research needs to be repeated in other labs in larger and diverse SIDS populations, she added. “Furthermore, we are not provided any racial-ethnic information about the SIDS cases in this study. In the U.S., the infants who are at greatest risk of dying from SIDS are most commonly African American and Native American/Alaska Native, and thus, these studies would need to be repeated in U.S. populations.”
Dr. Hauck added that, while the differences in blood levels of this enzyme were statistically different, even if this is confirmed by larger studies, there was enough overlap in the blood levels between cases and controls that it could not be used as a blood test at this point with any reasonable predictive value.
As the authors pointed out, she said, the leading theory of SIDS causation is that multiple factors interact. “While everyone would be happy to find one single explanation, it is not so simple. This research does, however, bring into focus the issues of arousal in SIDS and work on biomarkers. The arousal issue is one researchers have been working on for a long time.”
The SIDS research community has long been interested in biomarkers, Dr. Hauck continued. “Dr. Hannah Kinney’s first autoradiography study reported decreased muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding in the arcuate nucleus in SIDS, which the butyrylcholinesterase work further elaborates. More recently, Dr. Kinney reported abnormal cholinergic binding in the mesopontine reticular formation that is related to arousal and REM.”
Moreover, Robin Haynes and colleagues reported in 2017 that differences in serotonin can similarly be found in newborns on a newborn blood test, she said. “Like the butyrylcholinesterase research, there is a lot of work to do before understanding how specifically it can identify risk. The problem with using it prematurely is that it will unnecessarily alarm parents that their baby will die, and, to make it worse, be inaccurate in our warning.”
She also expressed concern that with the focus on a biomarker, parents will forget that SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths have come down considerably in the United States thanks to greater emphasis on promoting safe infant sleep behaviors.
The research was supported by a crowdfunding campaign and by NSW Health Pathology. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Hauck disclosed no conflicts of interest.
* This story was corrected on 5/20/2022.
FROM EBIOMEDICINE
FDA working to improve U.S. baby formula supply
The Food and Drug Administration announced on May 10 that it is taking several steps to improve the supply of baby formula in the United States.
The nationwide formula shortage has grown worse in recent weeks due to supply chain issues and a recall of certain Abbott Nutrition products, including major labels such as Similac, Alimentum, and EleCare.
“We recognize that many consumers have been unable to access infant formula and critical medical foods they are accustomed to using and are frustrated by their inability to do so,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement.
“We are doing everything in our power to ensure there is adequate product available where and when they need it,” he said.
About three-quarters of babies are fed formula for the first 6 months of their lives as a substitute for human milk, Axios reported.
In mid-February, the FDA warned consumers not to use certain powdered infant formula products from Abbott’s facility in Sturgis, Mich. Since then, the FDA has been working with Abbott and other manufacturers to increase the supply in the U.S. market.
“In fact, other infant formula manufacturers are meeting or exceeding capacity levels to meet current demand,” the FDA said in the statement. “Notably, more infant formula was purchased in the month of April than in the month prior to the recall.”
The FDA released a list of steps the agency is taking to increase supply, such as meeting with major infant formula makers to increase output and prioritize product lines in high demand, particularly specialty formulas for infants with allergies or specific diet needs.
But other manufacturers have struggled to quickly increase production because their operations tend to focus on a steady level of supply, according to The New York Times.
“Some industries are very good at ramping up and ramping down,” Rudi Leuschner, PhD, an associate professor of supply chain management at Rutgers Business School, Newark, N.J., told the newspaper.
“You flip a switch and they can produce 10 times as much,” he said. “Baby formula is not that type of a product.”
The FDA is also keeping an eye on the infant formula shortage by using the agency’s 21 Forward food supply chain continuity system. The system was developed during the pandemic to provide a full understanding of how COVID-19 is impacting food supply chains, the FDA said.
The FDA is compiling data on trends for in-stock rates at national and regional levels to understand where infant formula is available and where it should go.
Products are also being brought in from other countries, the FDA said. The agency is trying to speed up the process to get more formula into the U.S. and move it more quickly around the country.
For babies on a special diet, the FDA has decided to release some Abbott products that have been on hold at the Sturgis facility to those who need an urgent supply of metabolic formulas, on a case-by-case basis.
“In these circumstances, the benefit of allowing caregivers, in consultation with their health care providers, to access these products may outweigh the potential risk of bacterial infection,” the FDA said in the statement.
The FDA continues to advise against making homemade infant formulas and recommends talking to the child’s health care provider for recommendations on changing feeding practices or switching to other formulas, if necessary.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
The Food and Drug Administration announced on May 10 that it is taking several steps to improve the supply of baby formula in the United States.
The nationwide formula shortage has grown worse in recent weeks due to supply chain issues and a recall of certain Abbott Nutrition products, including major labels such as Similac, Alimentum, and EleCare.
“We recognize that many consumers have been unable to access infant formula and critical medical foods they are accustomed to using and are frustrated by their inability to do so,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement.
“We are doing everything in our power to ensure there is adequate product available where and when they need it,” he said.
About three-quarters of babies are fed formula for the first 6 months of their lives as a substitute for human milk, Axios reported.
In mid-February, the FDA warned consumers not to use certain powdered infant formula products from Abbott’s facility in Sturgis, Mich. Since then, the FDA has been working with Abbott and other manufacturers to increase the supply in the U.S. market.
“In fact, other infant formula manufacturers are meeting or exceeding capacity levels to meet current demand,” the FDA said in the statement. “Notably, more infant formula was purchased in the month of April than in the month prior to the recall.”
The FDA released a list of steps the agency is taking to increase supply, such as meeting with major infant formula makers to increase output and prioritize product lines in high demand, particularly specialty formulas for infants with allergies or specific diet needs.
But other manufacturers have struggled to quickly increase production because their operations tend to focus on a steady level of supply, according to The New York Times.
“Some industries are very good at ramping up and ramping down,” Rudi Leuschner, PhD, an associate professor of supply chain management at Rutgers Business School, Newark, N.J., told the newspaper.
“You flip a switch and they can produce 10 times as much,” he said. “Baby formula is not that type of a product.”
The FDA is also keeping an eye on the infant formula shortage by using the agency’s 21 Forward food supply chain continuity system. The system was developed during the pandemic to provide a full understanding of how COVID-19 is impacting food supply chains, the FDA said.
The FDA is compiling data on trends for in-stock rates at national and regional levels to understand where infant formula is available and where it should go.
Products are also being brought in from other countries, the FDA said. The agency is trying to speed up the process to get more formula into the U.S. and move it more quickly around the country.
For babies on a special diet, the FDA has decided to release some Abbott products that have been on hold at the Sturgis facility to those who need an urgent supply of metabolic formulas, on a case-by-case basis.
“In these circumstances, the benefit of allowing caregivers, in consultation with their health care providers, to access these products may outweigh the potential risk of bacterial infection,” the FDA said in the statement.
The FDA continues to advise against making homemade infant formulas and recommends talking to the child’s health care provider for recommendations on changing feeding practices or switching to other formulas, if necessary.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
The Food and Drug Administration announced on May 10 that it is taking several steps to improve the supply of baby formula in the United States.
The nationwide formula shortage has grown worse in recent weeks due to supply chain issues and a recall of certain Abbott Nutrition products, including major labels such as Similac, Alimentum, and EleCare.
“We recognize that many consumers have been unable to access infant formula and critical medical foods they are accustomed to using and are frustrated by their inability to do so,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement.
“We are doing everything in our power to ensure there is adequate product available where and when they need it,” he said.
About three-quarters of babies are fed formula for the first 6 months of their lives as a substitute for human milk, Axios reported.
In mid-February, the FDA warned consumers not to use certain powdered infant formula products from Abbott’s facility in Sturgis, Mich. Since then, the FDA has been working with Abbott and other manufacturers to increase the supply in the U.S. market.
“In fact, other infant formula manufacturers are meeting or exceeding capacity levels to meet current demand,” the FDA said in the statement. “Notably, more infant formula was purchased in the month of April than in the month prior to the recall.”
The FDA released a list of steps the agency is taking to increase supply, such as meeting with major infant formula makers to increase output and prioritize product lines in high demand, particularly specialty formulas for infants with allergies or specific diet needs.
But other manufacturers have struggled to quickly increase production because their operations tend to focus on a steady level of supply, according to The New York Times.
“Some industries are very good at ramping up and ramping down,” Rudi Leuschner, PhD, an associate professor of supply chain management at Rutgers Business School, Newark, N.J., told the newspaper.
“You flip a switch and they can produce 10 times as much,” he said. “Baby formula is not that type of a product.”
The FDA is also keeping an eye on the infant formula shortage by using the agency’s 21 Forward food supply chain continuity system. The system was developed during the pandemic to provide a full understanding of how COVID-19 is impacting food supply chains, the FDA said.
The FDA is compiling data on trends for in-stock rates at national and regional levels to understand where infant formula is available and where it should go.
Products are also being brought in from other countries, the FDA said. The agency is trying to speed up the process to get more formula into the U.S. and move it more quickly around the country.
For babies on a special diet, the FDA has decided to release some Abbott products that have been on hold at the Sturgis facility to those who need an urgent supply of metabolic formulas, on a case-by-case basis.
“In these circumstances, the benefit of allowing caregivers, in consultation with their health care providers, to access these products may outweigh the potential risk of bacterial infection,” the FDA said in the statement.
The FDA continues to advise against making homemade infant formulas and recommends talking to the child’s health care provider for recommendations on changing feeding practices or switching to other formulas, if necessary.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
Tactile stimulation for inadequate neonatal respiration at birth
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].