User login
FDA finalizes guidance for power morcellators in gynecologic surgery
The agency noted that physicians should conduct a thorough preoperative screening and that the devices should only be used for hysterectomies and myomectomies. Clinicians should not use the devices in cases involving uterine malignancy or suspected uterine malignancy.
In addition, clinicians should not use morcellators to remove uterine tissue containing suspected fibroids in women older than 50 years or who are postmenopausal. Nor should the devices be used for women who are “candidates for removal of tissue (en bloc) through the vagina or via a minilaparotomy incision,” the agency said.
The safety communication, which was issued on Dec. 29, 2020, updates previous guidance from February 2020. The updated recommendations are consistent with final labeling guidance for laparoscopic power morcellators, also issued by the FDA on Dec. 29.
Risk of disease spread
Prior evidence suggests that use of uncontained power morcellators in women with malignant uterine tissue can spread disease.
Even among women who do not have malignant uterine tissue, containment is important. The agency noted an association between uncontained power morcellation and the spread of benign uterine tissue, such as parasitic myomas and disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis, which could require additional surgeries.
In 2016, the FDA approved the PneumoLiner, a containment system for isolating uterine tissue that is not suspected of containing cancer.
“While unsuspected cancer can occur at any age, the prevalence of unsuspected cancer in women undergoing hysterectomy for fibroids increases with age such that the benefit-risk profile of using [laparoscopic power morcellators] is worse in older women when compared to younger women,” according to the new labeling guidance. “Also, the surgical technique of en bloc tissue removal eliminates the need to perform morcellation, thereby reducing the risk of iatrogenic dissemination and upstaging of an occult sarcoma. A thorough preoperative screening should be conducted; however, it is important to note that no screening procedure that can reliably detect sarcoma preoperatively has been identified.”
“The FDA will continue to review the latest data and scientific literature on laparoscopic power morcellation, including gathering real-world evidence from patients, providers and others, and encouraging innovation to better detect uterine cancer and develop containment systems for gynecologic surgery,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in a news release. “The FDA seeks to ensure women and their health care providers are fully informed when considering laparoscopic power morcellators for gynecologic surgeries.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency noted that physicians should conduct a thorough preoperative screening and that the devices should only be used for hysterectomies and myomectomies. Clinicians should not use the devices in cases involving uterine malignancy or suspected uterine malignancy.
In addition, clinicians should not use morcellators to remove uterine tissue containing suspected fibroids in women older than 50 years or who are postmenopausal. Nor should the devices be used for women who are “candidates for removal of tissue (en bloc) through the vagina or via a minilaparotomy incision,” the agency said.
The safety communication, which was issued on Dec. 29, 2020, updates previous guidance from February 2020. The updated recommendations are consistent with final labeling guidance for laparoscopic power morcellators, also issued by the FDA on Dec. 29.
Risk of disease spread
Prior evidence suggests that use of uncontained power morcellators in women with malignant uterine tissue can spread disease.
Even among women who do not have malignant uterine tissue, containment is important. The agency noted an association between uncontained power morcellation and the spread of benign uterine tissue, such as parasitic myomas and disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis, which could require additional surgeries.
In 2016, the FDA approved the PneumoLiner, a containment system for isolating uterine tissue that is not suspected of containing cancer.
“While unsuspected cancer can occur at any age, the prevalence of unsuspected cancer in women undergoing hysterectomy for fibroids increases with age such that the benefit-risk profile of using [laparoscopic power morcellators] is worse in older women when compared to younger women,” according to the new labeling guidance. “Also, the surgical technique of en bloc tissue removal eliminates the need to perform morcellation, thereby reducing the risk of iatrogenic dissemination and upstaging of an occult sarcoma. A thorough preoperative screening should be conducted; however, it is important to note that no screening procedure that can reliably detect sarcoma preoperatively has been identified.”
“The FDA will continue to review the latest data and scientific literature on laparoscopic power morcellation, including gathering real-world evidence from patients, providers and others, and encouraging innovation to better detect uterine cancer and develop containment systems for gynecologic surgery,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in a news release. “The FDA seeks to ensure women and their health care providers are fully informed when considering laparoscopic power morcellators for gynecologic surgeries.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency noted that physicians should conduct a thorough preoperative screening and that the devices should only be used for hysterectomies and myomectomies. Clinicians should not use the devices in cases involving uterine malignancy or suspected uterine malignancy.
In addition, clinicians should not use morcellators to remove uterine tissue containing suspected fibroids in women older than 50 years or who are postmenopausal. Nor should the devices be used for women who are “candidates for removal of tissue (en bloc) through the vagina or via a minilaparotomy incision,” the agency said.
The safety communication, which was issued on Dec. 29, 2020, updates previous guidance from February 2020. The updated recommendations are consistent with final labeling guidance for laparoscopic power morcellators, also issued by the FDA on Dec. 29.
Risk of disease spread
Prior evidence suggests that use of uncontained power morcellators in women with malignant uterine tissue can spread disease.
Even among women who do not have malignant uterine tissue, containment is important. The agency noted an association between uncontained power morcellation and the spread of benign uterine tissue, such as parasitic myomas and disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis, which could require additional surgeries.
In 2016, the FDA approved the PneumoLiner, a containment system for isolating uterine tissue that is not suspected of containing cancer.
“While unsuspected cancer can occur at any age, the prevalence of unsuspected cancer in women undergoing hysterectomy for fibroids increases with age such that the benefit-risk profile of using [laparoscopic power morcellators] is worse in older women when compared to younger women,” according to the new labeling guidance. “Also, the surgical technique of en bloc tissue removal eliminates the need to perform morcellation, thereby reducing the risk of iatrogenic dissemination and upstaging of an occult sarcoma. A thorough preoperative screening should be conducted; however, it is important to note that no screening procedure that can reliably detect sarcoma preoperatively has been identified.”
“The FDA will continue to review the latest data and scientific literature on laparoscopic power morcellation, including gathering real-world evidence from patients, providers and others, and encouraging innovation to better detect uterine cancer and develop containment systems for gynecologic surgery,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in a news release. “The FDA seeks to ensure women and their health care providers are fully informed when considering laparoscopic power morcellators for gynecologic surgeries.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Risk of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer linked to number of oral sex partners
Having oral sex with more than 10 previous partners was associated with a 4.3 times’ greater likelihood of developing human papillomavirus (HPV)–related oropharyngeal cancer, according to new findings.
The study also found that having more partners in a shorter period (i.e., greater oral sex intensity) and starting oral sex at a younger age were associated with higher odds of having HPV-related cancer of the mouth and throat.
The new study, published online on Jan. 11 in Cancer, confirms previous findings and adds more nuance, say the researchers.
Previous studies have demonstrated that oral sex is a strong risk factor for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, which has increased in incidence in recent decades, particularly cancer of the base of the tongue and palatine and lingual tonsils.
“Our research adds more nuance in our understanding of how people acquire oral HPV infection and HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer,” said study author Gypsyamber D’Souza, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. “It suggests that risk of infection is not only from the number of oral sexual partners but that the timing and type of partner also influence risk.”
The results of the study do not change the clinical care or screening of patients, Dr. D’Souza noted, but the study does add context for patients and providers in understanding, “Why did I get HPV-oropharyngeal cancer?” she said.
“We know that people who develop HPV-oropharyngeal cancer have a wide range of sexual histories, but we do not suggest sexual history be used for screening, as many patients have low-risk sexual histories,” she said. “By chance, it only takes one partner who is infected to acquire the infection, while others who have had many partners by chance do not get exposed, or who are exposed but clear the infection.”
Reinforces the need for vaccination
Approached for comment, Joseph Califano, MD, physician-in-chief at the Moores Cancer Center and director of the Head and Neck Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, noted that similar data have been published before. The novelty here is in the timing and intensity of oral sex. “It’s not new data, but it certainly reinforces what we knew,” he said in an interview.
These new data are not going to change monitoring, he suggested. “It’s not going to change how we screen, because we don’t do population-based screening for oropharyngeal cancer,” Dr. Califano said.
“It does underline the fact that vaccination is really the key to preventing HPV-mediated cancers,” he said.
He pointed out that some data show lower rates of high-risk oral HPV shedding by children who have been appropriately vaccinated.
“This paper really highlights the fact we need to get people vaccinated early, before sexual debut,” he said. “In this case, sexual debut doesn’t necessarily mean intercourse but oral sex, and that’s a different concept of when sex starts.”
These new data “reinforce the fact that early exposure is what we need to focus on,” he said.
Details of the new findings
The current study by Dr. D’Souza and colleagues included 163 patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer who were enrolled in the Papillomavirus Role in Oral Cancer Viral Etiology (PROVE) study. These patients were compared with 345 matched control persons.
All participants completed a behavioral survey and provided a blood sample. For the patients with cancer, a tumor sample was obtained.
The majority of participants were male (85% and 82%), were aged 50-69 years, were currently married or living with a partner, and identified as heterosexual. Case patients were more likely to report a history of sexually transmitted infection than were control participants (P = .003).
Case patients were more likely to have ever performed oral sex compared to control persons (98.8% vs 90.4%; P < .001) and to have performed oral sex at the time of their sexual debut (33.3% of case patients vs 21.4% of control persons; P = .004; odds ratio [OR], 1.8).
Significantly more case patients than control persons reported starting oral sex before they were 18 years old (37.4% of cases vs. 22.6% of controls; P < .001; OR, 3.1), and they had a greater number of lifetime oral sex partners (44.8% of cases and 19.1% of controls reported having more than 10 partners; P < .001; OR, 4.3).
Intensity of oral sexual exposure, which the authors measured by number of partners per 10 years, was also significantly higher among cases than controls (30.8% vs 11.1%; P < .001; OR, 5.6).
After adjustment for confounders (such as the lifetime number of oral sex partners and tobacco use), ever performing oral sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 4.4), early age of first oral sex encounter (20 years: aOR, 1.8), and oral sex intensity (aOR, 2.8) all remained significantly associated with increased odds of HPV-oropharyngeal cancer.
The type of sexual partner, such as partners who were older (OR, 1.7) and having a partner who engaged in extramarital sex (OR, 1.6), were also associated with increased odds of developing HPV-oropharyngeal cancer. In addition, seropositivity for antibodies to HPV16 E6 (OR, 286) and any HPV16 E protein (E1, E2, E6, E7; OR, 163) were also associated with increased odds of developing the disease.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Califano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having oral sex with more than 10 previous partners was associated with a 4.3 times’ greater likelihood of developing human papillomavirus (HPV)–related oropharyngeal cancer, according to new findings.
The study also found that having more partners in a shorter period (i.e., greater oral sex intensity) and starting oral sex at a younger age were associated with higher odds of having HPV-related cancer of the mouth and throat.
The new study, published online on Jan. 11 in Cancer, confirms previous findings and adds more nuance, say the researchers.
Previous studies have demonstrated that oral sex is a strong risk factor for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, which has increased in incidence in recent decades, particularly cancer of the base of the tongue and palatine and lingual tonsils.
“Our research adds more nuance in our understanding of how people acquire oral HPV infection and HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer,” said study author Gypsyamber D’Souza, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. “It suggests that risk of infection is not only from the number of oral sexual partners but that the timing and type of partner also influence risk.”
The results of the study do not change the clinical care or screening of patients, Dr. D’Souza noted, but the study does add context for patients and providers in understanding, “Why did I get HPV-oropharyngeal cancer?” she said.
“We know that people who develop HPV-oropharyngeal cancer have a wide range of sexual histories, but we do not suggest sexual history be used for screening, as many patients have low-risk sexual histories,” she said. “By chance, it only takes one partner who is infected to acquire the infection, while others who have had many partners by chance do not get exposed, or who are exposed but clear the infection.”
Reinforces the need for vaccination
Approached for comment, Joseph Califano, MD, physician-in-chief at the Moores Cancer Center and director of the Head and Neck Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, noted that similar data have been published before. The novelty here is in the timing and intensity of oral sex. “It’s not new data, but it certainly reinforces what we knew,” he said in an interview.
These new data are not going to change monitoring, he suggested. “It’s not going to change how we screen, because we don’t do population-based screening for oropharyngeal cancer,” Dr. Califano said.
“It does underline the fact that vaccination is really the key to preventing HPV-mediated cancers,” he said.
He pointed out that some data show lower rates of high-risk oral HPV shedding by children who have been appropriately vaccinated.
“This paper really highlights the fact we need to get people vaccinated early, before sexual debut,” he said. “In this case, sexual debut doesn’t necessarily mean intercourse but oral sex, and that’s a different concept of when sex starts.”
These new data “reinforce the fact that early exposure is what we need to focus on,” he said.
Details of the new findings
The current study by Dr. D’Souza and colleagues included 163 patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer who were enrolled in the Papillomavirus Role in Oral Cancer Viral Etiology (PROVE) study. These patients were compared with 345 matched control persons.
All participants completed a behavioral survey and provided a blood sample. For the patients with cancer, a tumor sample was obtained.
The majority of participants were male (85% and 82%), were aged 50-69 years, were currently married or living with a partner, and identified as heterosexual. Case patients were more likely to report a history of sexually transmitted infection than were control participants (P = .003).
Case patients were more likely to have ever performed oral sex compared to control persons (98.8% vs 90.4%; P < .001) and to have performed oral sex at the time of their sexual debut (33.3% of case patients vs 21.4% of control persons; P = .004; odds ratio [OR], 1.8).
Significantly more case patients than control persons reported starting oral sex before they were 18 years old (37.4% of cases vs. 22.6% of controls; P < .001; OR, 3.1), and they had a greater number of lifetime oral sex partners (44.8% of cases and 19.1% of controls reported having more than 10 partners; P < .001; OR, 4.3).
Intensity of oral sexual exposure, which the authors measured by number of partners per 10 years, was also significantly higher among cases than controls (30.8% vs 11.1%; P < .001; OR, 5.6).
After adjustment for confounders (such as the lifetime number of oral sex partners and tobacco use), ever performing oral sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 4.4), early age of first oral sex encounter (20 years: aOR, 1.8), and oral sex intensity (aOR, 2.8) all remained significantly associated with increased odds of HPV-oropharyngeal cancer.
The type of sexual partner, such as partners who were older (OR, 1.7) and having a partner who engaged in extramarital sex (OR, 1.6), were also associated with increased odds of developing HPV-oropharyngeal cancer. In addition, seropositivity for antibodies to HPV16 E6 (OR, 286) and any HPV16 E protein (E1, E2, E6, E7; OR, 163) were also associated with increased odds of developing the disease.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Califano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having oral sex with more than 10 previous partners was associated with a 4.3 times’ greater likelihood of developing human papillomavirus (HPV)–related oropharyngeal cancer, according to new findings.
The study also found that having more partners in a shorter period (i.e., greater oral sex intensity) and starting oral sex at a younger age were associated with higher odds of having HPV-related cancer of the mouth and throat.
The new study, published online on Jan. 11 in Cancer, confirms previous findings and adds more nuance, say the researchers.
Previous studies have demonstrated that oral sex is a strong risk factor for HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, which has increased in incidence in recent decades, particularly cancer of the base of the tongue and palatine and lingual tonsils.
“Our research adds more nuance in our understanding of how people acquire oral HPV infection and HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer,” said study author Gypsyamber D’Souza, PhD, professor of epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. “It suggests that risk of infection is not only from the number of oral sexual partners but that the timing and type of partner also influence risk.”
The results of the study do not change the clinical care or screening of patients, Dr. D’Souza noted, but the study does add context for patients and providers in understanding, “Why did I get HPV-oropharyngeal cancer?” she said.
“We know that people who develop HPV-oropharyngeal cancer have a wide range of sexual histories, but we do not suggest sexual history be used for screening, as many patients have low-risk sexual histories,” she said. “By chance, it only takes one partner who is infected to acquire the infection, while others who have had many partners by chance do not get exposed, or who are exposed but clear the infection.”
Reinforces the need for vaccination
Approached for comment, Joseph Califano, MD, physician-in-chief at the Moores Cancer Center and director of the Head and Neck Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, noted that similar data have been published before. The novelty here is in the timing and intensity of oral sex. “It’s not new data, but it certainly reinforces what we knew,” he said in an interview.
These new data are not going to change monitoring, he suggested. “It’s not going to change how we screen, because we don’t do population-based screening for oropharyngeal cancer,” Dr. Califano said.
“It does underline the fact that vaccination is really the key to preventing HPV-mediated cancers,” he said.
He pointed out that some data show lower rates of high-risk oral HPV shedding by children who have been appropriately vaccinated.
“This paper really highlights the fact we need to get people vaccinated early, before sexual debut,” he said. “In this case, sexual debut doesn’t necessarily mean intercourse but oral sex, and that’s a different concept of when sex starts.”
These new data “reinforce the fact that early exposure is what we need to focus on,” he said.
Details of the new findings
The current study by Dr. D’Souza and colleagues included 163 patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer who were enrolled in the Papillomavirus Role in Oral Cancer Viral Etiology (PROVE) study. These patients were compared with 345 matched control persons.
All participants completed a behavioral survey and provided a blood sample. For the patients with cancer, a tumor sample was obtained.
The majority of participants were male (85% and 82%), were aged 50-69 years, were currently married or living with a partner, and identified as heterosexual. Case patients were more likely to report a history of sexually transmitted infection than were control participants (P = .003).
Case patients were more likely to have ever performed oral sex compared to control persons (98.8% vs 90.4%; P < .001) and to have performed oral sex at the time of their sexual debut (33.3% of case patients vs 21.4% of control persons; P = .004; odds ratio [OR], 1.8).
Significantly more case patients than control persons reported starting oral sex before they were 18 years old (37.4% of cases vs. 22.6% of controls; P < .001; OR, 3.1), and they had a greater number of lifetime oral sex partners (44.8% of cases and 19.1% of controls reported having more than 10 partners; P < .001; OR, 4.3).
Intensity of oral sexual exposure, which the authors measured by number of partners per 10 years, was also significantly higher among cases than controls (30.8% vs 11.1%; P < .001; OR, 5.6).
After adjustment for confounders (such as the lifetime number of oral sex partners and tobacco use), ever performing oral sex (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 4.4), early age of first oral sex encounter (20 years: aOR, 1.8), and oral sex intensity (aOR, 2.8) all remained significantly associated with increased odds of HPV-oropharyngeal cancer.
The type of sexual partner, such as partners who were older (OR, 1.7) and having a partner who engaged in extramarital sex (OR, 1.6), were also associated with increased odds of developing HPV-oropharyngeal cancer. In addition, seropositivity for antibodies to HPV16 E6 (OR, 286) and any HPV16 E protein (E1, E2, E6, E7; OR, 163) were also associated with increased odds of developing the disease.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research and the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Califano have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Home pregnancy tests—Is ectopic always on your mind?
CASE Unidentified ectopic pregnancy leads to rupture*
A 33-year-old woman (G1 P0010) with 2 positive home pregnancy tests presents to the emergency department (ED) reporting intermittent vaginal bleeding for 3 days. Her last menstrual period was 10 weeks ago, but she reports that her menses are always irregular. She has a history of asymptomatic chlamydia, as well as spontaneous abortion 2 years prior. At present, she denies abdominal pain or vaginal discharge.
Upon examination her vital signs are: temperature, 98.3 °F; pulse, 112 bpm, with a resting rate of 16 bpm; blood pressure (BP), 142/91 mm Hg; pulse O2, 99%; height, 4’ 3”; weight, 115 lb. Her labs are: hemoglobin, 12.1 g/dL; hematocrit, 38%; serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) 236 mIU/mL. Upon pelvic examination, no active bleeding is noted. She agrees to be followed up by her gynecologist and is given a prescription for serum hCG in 2 days. She is instructed to return to the ED should she have pain or increased vaginal bleeding.
Three days later, the patient follows up with her gynecologist reporting mild cramping. She notes having had an episode of heavy vaginal bleeding and a “weakly positive” home pregnancy test. Transvaginal ultrasonography notes endometrial thickness 0.59 mm and unremarkable adnexa. A urine pregnancy test performed in the office is positive; urinalysis is positive for nitrites. With the bleeding slowed, the gynecologist’s overall impression is that the patient has undergone complete spontaneous abortion. She prescribes Macrobid for the urinary tract infection. She does not obtain the ED-prescribed serum HCG levels, as she feels, since complete spontaneous abortion has occurred there is no need to obtain a follow-up serum HCG.
Five days later, the patient returns to the ED reporting abdominal pain after eating. Fever and productive cough of 2 days are noted. The patient states that she had a recent miscarriage. The overall impression of the patient’s condition is bronchitis, and it is noted on the patient’s record, “unlikely ectopic pregnancy and pregnancy test may be false positive,” hence a pregnancy test is not ordered. Examination reveals mild suprapubic tenderness with no rebound; no pelvic exam is performed. The patient is instructed to follow up with a health care clinic within a week, and to return to the ED with severe abdominal pain, higher fever, or any new concerning symptoms. A Zithromax Z-pak is prescribed.
Four days later, the patient is brought by ambulance to the ED of the local major medical center with severe abdominal pain involving the right lower quadrant. She states that she had a miscarriage 3 weeks prior and was recently treated for bronchitis. She has dizziness when standing. Her vital signs are: temperature, 97.8 °F; heart rate, 95 bpm; BP, 72/48 mm Hg; pulse O2, 100%. She reports her abdominal pain to be 6/10.
The patient is given a Lactated Ringer’s bolus of 1,000 mL for a hypotensive episode. Computed tomography is obtained and notes, “low attenuation in the left adnexa with a dilated fallopian tube.” A large heterogeneous collection of fluid in the pelvis is noted with active extravasation, consistent with an “acute bleed.”
The patient is brought to the operating room with a diagnosis of probable ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Intraoperatively she is noted to have a right ruptured ectopic and left tubo-ovarian abscess. The surgeon proceeds with right salpingectomy and left salpingo-oophorectomy. Three liters of hemoperitoneum is found.
She is followed postoperatively with serum hCG until levels are negative. Her postoperative course is uneventful. Her only future option for pregnancy is through assisted reproductive technology (ART) with in vitro fertilization (IVF). The patient sues the gynecologist and second ED physician for presumed inappropriate assessment for ectopic pregnancy.
*The “facts” of this case are a composite, drawn from several cases to illustrate medical and legal issues. The statement of facts should be considered hypothetical.
Continue to: WHAT’S THE VERDICT?...
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
A defense verdict is returned.
Medical considerations
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is 2% of all pregnancies, with a higher incidence (about 4%) among infertility patients.1 Up to 10% of ectopic pregnancies have no symptoms.2
Clinical presentations. Classic signs of ectopic pregnancy include:
- abdominal pain
- vaginal bleeding
- late menses (often noted).
A recent case of ectopic pregnancy presenting with chest pain was reported.3 Clinicians must never lose site of the fact that ectopic pregnancy is the most common cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester, with an incidence of 1% to 10% of all first-trimester deaths.4
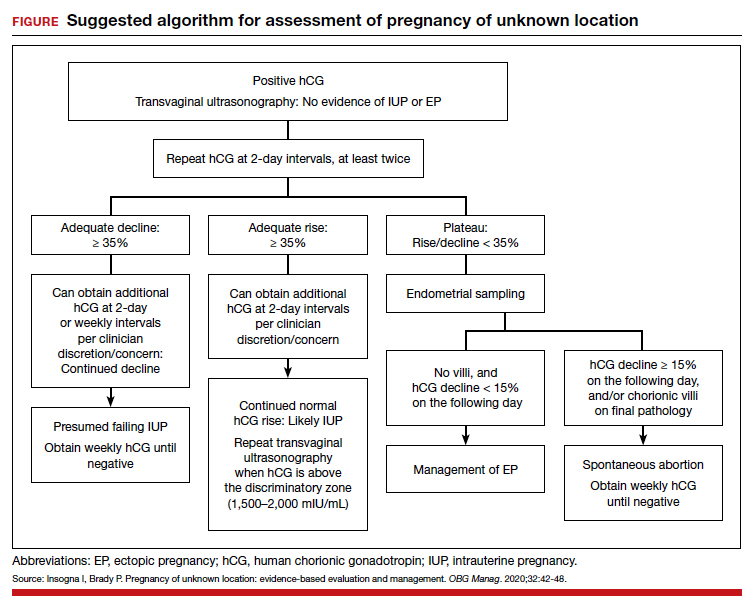
Risk factors include pelvic inflammatory disease, as demonstrated in the opening case. “The silent epidemic of chlamydia” comes to mind, and tobacco smoking can adversely affect tubal cilia, as can pelvic adhesions and/or prior tubal surgery. All of these factors can predispose a patient to ectopic pregnancy; in addition, intrauterine devices, endometriosis, tubal ligation (or ligation reversal), all can set the stage for an ectopic pregnancy.5 Appropriate serum hCG monitoring during early pregnancy can assist in sorting out pregnancies of unknown location (PUL; FIGURE). First trimester ultrasonography, at 5 weeks gestation, usually identifies early intrauterine gestation.
Imaging. With regard to pelvic sonography, the earliest sign of an intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) is a sac eccentrically located in the decidua.6 As the IUP progresses, it becomes equated with a “double decidual sign,” with double rings of tissue around the sac.6 If the pregnancy is located in an adnexal mass, it is frequently inhomogeneous or noncystic in appearance (ie, “the blob” sign); the positive predictive value (PPV) is 96%.2 The PPV of transvaginal ultrasound is 80%, as paratubal, paraovarian, ovarian cyst, and hydrosalpinx can affect the interpretation.7
Heterotopic pregnancy includes an intrauterine gestation and an ectopic pregnancy. This presentation includes the presence of a “pseudosac” in the endometrial cavity plus an extrauterine gestation. Heterotopic pregnancies have become somewhat more common as ART/IVF has unfolded, especially prior to the predominance of single embryo transfer.
Managing ectopic pregnancy
For cases of early pregnancy complicated by intermittent bleeding and/or pain, monitoring with serum hCG levels at 48-hour intervals to distinguish a viable IUP from an abnormal IUP or an ectopic is appropriate. The “discriminatory zone” collates serum hCG levels with findings on ultrasonography. Specific lower limits of serum hCG levels are not clear cut, with recommendations of 3,500 mIU/mL to provide sonographic evidence of an intrauterine gestation “to avoid misdiagnosis and possible interruption of intrauterine pregnancy,” as conveyed in the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 2018 practice bulletin.8 Serum progesterone levels also have been suggested to complement hCG levels; a progesterone level of <20 nmol/L is consistent with an abnormal pregnancy, whereas levels >25 nmol/L are suggestive of a viable pregnancy.2 Inhibin A levels also have been suggested to be helpful, but they are not an ideal monitoring tool.
While most ectopic pregnancies are located in the fallopian tube, other locations also can be abdominal or ovarian. In addition, cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy can occur and often is associated with delay in diagnosis and greater morbidity due to such delay.9 With regard to ovarian ectopic, Spiegelberg criteria are established for diagnosis (TABLE 1).10
Appropriate management of an ectopic pregnancy is dependent upon the gestational age, serum hCG levels, and imaging findings, as well as the patient’s symptoms and exam findings. Treatment is established in large part on a case-by-case basis and includes, for early pregnancy, expectant management and use of methotrexate (TABLE 2).11 Dilation and curettage may be used to identify the pregnancy’s location when the serum hCG level is below 2,000 mIU/mL and there is no evidence of an IUP on ultrasound. Surgical treatment can include minimally invasive salpingostomy or salpingectomy and, depending on circumstance, laparotomy may be indicated.
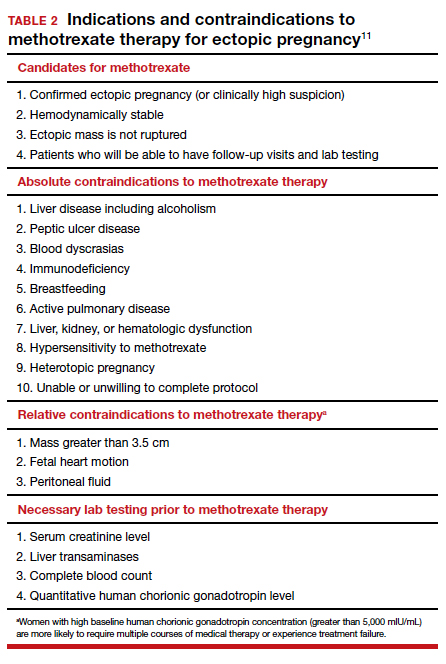
Fertility following ectopic pregnancy varies and is affected by location, treatment, predisposing factors, total number of ectopic pregnancies, and other factors. Ectopic pregnancy, although rare, also can occur with use of IVF. Humans are not unique with regard to ectopic pregnancies, as they also occur in sheep.12
Continue to: Legal perspective...
Legal perspective
Lawsuits related to ectopic pregnancy are not a new phenomenon. In fact, in 1897, a physician in Ohio who misdiagnosed an “extrauterine pregnancy” as appendicitis was the center of a malpractice lawsuit.13 Unrecognized or mishandled ectopic pregnancy can result in serious injuries—in the range of 1% to 10% (see above) of maternal deaths are related to ectopic pregnancy.14 Ectopic pregnancy cases, therefore, have been the subject of substantial litigation over the years. An informal, noncomprehensive review of malpractice lawsuits brought from 2000 to 2019, found more than 300 ectopic pregnancy cases. Given the large number of malpractice claims against ObGyns,15 ectopic pregnancy cases are only a small portion of all ObGyn malpractice cases.16
A common claim: negligent diagnosis or treatment
The most common basis for lawsuits in cases of ectopic pregnancy is the clinician’s negligent failure to properly diagnose the ectopic nature of the pregnancy. There are also a number of cases claiming negligent treatment of an identified ectopic pregnancy. Not every missed diagnosis, or unsuccessful treatment, leads to liability, of course. It is only when a diagnosis or treatment fails to meet the standard of care within the profession that there should be liability. That standard of care is generally defined by what a reasonably prudent physician would do under the circumstances. Expert witnesses, who are familiar with the standard of practice within the specialty, are usually necessary to establish what that practice is. Both the plaintiff and the defense obtain experts, the former to prove what the standard of care is and that the standard was not met in the case at hand. The defense experts are usually arguing that the standard of care was met.17 Inadequate diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy or other condition may arise from a failure to take a sufficient history, conduct an appropriately thorough physical examination, recognize any of the symptoms that would suggest it is present, use and conduct ultrasound correctly, or follow-up appropriately with additional testing.18
A malpractice claim of negligent treatment can involve any the following circumstances19:
- failure to establish an appropriate treatment plan
- prescribing inappropriate medications for the patient (eg, methotrexate, when it is contraindicated)
- delivering the wrong medication or the wrong amount of the right medication
- performing a procedure badly
- undertaking a new treatment without adequate instruction and preparation.
Given the nature and risks of ectopic pregnancy, ongoing, frequent contact with the patient is essential from the point at which the condition is suspected. The greater the risk of harm (probability or consequence), the more careful any professional ought to be. Because ectopic pregnancy is not an uncommon occurrence, and because it can have devastating effects, including death, a reasonably prudent practitioner would be especially aware of the clinical presentations discussed above.20 In the opening case, the treatment plan was not well documented.
Negligence must lead to patient harm. In addition to negligence (proving that the physician did not act in accordance with the standard of care), to prevail in a malpractice case, the plaintiff-patient must prove that the negligence caused the injury, or worsened it. If the failure to make a diagnosis would not have made any difference in a harm the patient suffered, there are no damages and no liability. Suppose, for example, that a physician negligently failed to diagnose ectopic pregnancy, but performed surgery expecting to find the misdiagnosed condition. In the course of the surgery, however, the surgeon discovered and appropriately treated the ectopic pregnancy. (A version of this happened in the old 19th century case mentioned above.) The negligence of the physician did not cause harm, so there are no damages and no liability.
Continue to: Informed consent is vital...
Informed consent is vital
A part of malpractice is informed consent (or the absence of it)—issues that can arise in any medical care.21 It is wise to pay particular attention in cases where the nature of the illness is unknown, and where there are significant uncertainties and the nature of testing and treatment may change substantially over a period of a few days or few weeks. As always, informed consent should include a discussion of what process or procedure is proposed, its risks and benefits, alternative approaches that might be available, and the risk of doing nothing. Frequently, the uncertainty of ectopic pregnancy complicates the informed consent process.22
Because communication with the patient is an essential function of informed consent, the consent process should productively be used in PUL and similar cases to inform the patient about the uncertainty, and the testing and (nonsurgical) treatment that will occur. This is an opportunity to reinforce the message that the patient must maintain ongoing communication with the physician’s office about changes in her condition, and appear for each appointment scheduled. If more invasive procedures—notably surgery—become required, a separate consent process should be completed, because the risks and considerations are now meaningfully different than when treatment began. As a general matter, any possible treatment that may result in infertility or reduced reproductive capacity should specifically be included in the consent process.
In the hypothetical case, the gynecologist failed to obtain a follow-up serum hCG level. In addition, the record did not reflect ectopic pregnancy in the differential diagnosis. As noted above, the patient had predisposing factors for an ectopic pregnancy. The physician should have acknowledged the history of sexually transmitted disease predisposing her to an ectopic pregnancy. Monitoring of serum hCG levels until they are negative is appropriate with ectopic, or presumed ectopic, pregnancy management. Appropriate monitoring did not occur in this case. Each of these errors (following up on serum hCG levels and the inadequacy of notations about the possibility of ectopic pregnancy) seem inconsistent with the usual standard of care. Furthermore, as a result of the outcome, the only future option for the patient to pursue pregnancy was IVF.
Other legal issues
There are a number of other legal issues that are associated with the topic of ectopic pregnancy. There is evidence, for example, that Catholic and non-Catholic hospitals treat ectopic pregnancies differently,23 which may reflect different views on taking a life or the use of methotrexate and its association with abortion.24 In addition, the possibility of an increase in future ectopic pregnancies is one of the “risks” of abortion that pro-life organizations have pushed to see included in abortion informed consent.25 This has led some commentators to conclude that some Catholic hospitals violate federal law in managing ectopic pregnancy. There is also evidence of “overwhelming rates of medical misinformation on pregnancy center websites, including a link between abortion and ectopic pregnancy.”26
The fact that cesarean deliveries are related to an increased risk for ectopic pregnancy (because of the risk of cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy) also has been cited as information that should play a role in the consent process for cesarean delivery.27 In terms of liability, failed tubal ligation leads to a 33% risk of ectopic pregnancy.28 The risk of ectopic pregnancy is also commonly included in surrogacy contracts.29
Why the outcome was for the defense
The opening hypothetical case illustrates some of the uncertainties of medical malpractice cases. As noted, there appeared a deviation from the usual standard of care, particularly the failure to follow up on the serum hCG level. The weakness in the medical record, failing to note the possibility of ectopic pregnancy, also was probably an error but, apparently, the court felt that this did not result in any harm to the patient.
The question arises of how there would be a defense verdict in light of the failure to track consecutive serum hCG levels. A speculative explanation is that there are many uncertainties in most lawsuits. Procedural problems may result in a case being limited, expert witnesses are essential to both the plaintiff and defense, with the quality of their review and testimony possibly uneven. Judges and juries may rely on one expert witness rather than another, juries vary, and the quality of advocacy differs. Any of these situations can contribute to the unpredictability of the outcome of a case. In the case above, the liability was somewhat uncertain, and the various other factors tipped in favor of a defense verdict. ●
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ectopic pregnancy—United States, 1990‒1992. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1995;44:46-48.
- Kirk E, Bottomley C, Bourne T. Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy and current concepts in the management of pregnancy of unknown location. Hum Reprod Update. 2012;20:250-261.
- Dichter E, Espinosa J, Baird J, Lucerna A. An unusual emergency department case: ruptured ectopic pregnancy presenting as chest pain. World J Emerg Med. 2017;8:71-73.
- Cecchino GN, Araujo E, Elito J. Methotrexate for ectopic pregnancy: when and how. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;290:417- 423.
- Barnhart KT, Sammel MD, Cracia CR, et al. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy in women with symptomatic firsttrimester pregnancies. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:36-43.
- Carusi D. Pregnancy of unknown location: evaluation and management. Semin Perinatol. 2019;43:95-100.
- Barnhart KT, Fay CA, Suescum M, et al. Clinical factors affecting the accuracy of ultrasonography in symptomatic first-trimester pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:299-306.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Practice Bulletin No. 193: tubal ectopic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e91-e103.
- Bouyer J, Coste J, Fernandez H, et al. Sites of ectopic pregnancy: a 10-year population-based study of 1800 cases. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:3224-3230.
- Spiegelberg O. Zur casuistic der ovarial schwangerschaft. Arch Gynecol. 1978;13:73.
- OB Hospitalist Group. Methotrexate use for ectopic pregnancies guidelines. https://www.obhg.com/wp-content /uploads/2020/01/Methotrexate-Use-for-EctopicPregnancies_2016-updates.pdf. Accessed December 10, 2020.
- Brozos C, Kargiannis I, Kiossis E, et al. Ectopic pregnancy through a caesarean scar in a ewe. N Z Vet J. 2013;61:373-375.
- Tucker v. Gillette, 12 Ohio Cir. Dec. 401 (Cir. Ct. 1901).
- Creanga AA, Syverson C, Seed K, et al. Pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, 2011–2013. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:366-373.
- Matthews LR, Alvi FA, Milad MP. Reproductive surgery malpractice patterns. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:e42-e43.
- Kim B. The impact of malpractice risk on the use of obstetrics procedures. J Legal Studies. 2006;36:S79-S120.
- Abinader R, Warsof S. Complications involving obstetrical ultrasound. In: Warsof S, Shwayder JM, eds. Legal Concepts and Best Practices in Obstetrics: The Nuts and Bolts Guide to Mitigating Risk. 2019;45-48.
- Creanga AA, Shapiro-Mendoza CK, Bish CL, et al. Trends in ectopic pregnancy mortality in the United States: 1980-2007. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:837-843.
- Shwayder JM. IUP diagnosed and treated as ectopic: How bad can it get? Contemporary OB/GYN. 2019;64:49-46.
- Kaplan AI. Should this ectopic pregnancy have been diagnosed earlier? Contemporary OB/GYN. 2017;62:53.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Ethics. Committee opinion 439: informed consent. Reaffirmed 2015. https://www.acog.org/clinical /clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2009/08 /informed-consent. Accessed December 9, 2020.
- Shwayder JM. Liability in ob/gyn ultrasound. Contemporary OB/GYN. 2017;62:32-49.
- Fisher LN. Institutional religious exemptions: a balancing approach. BYU Law Review. 2014;415-444.
- Makdisi J. Aquinas’s prohibition of killing reconsidered. J Catholic Legal Stud. 2019:57:67-128.
- Franzonello A. Remarks of Anna Franzonello. Alb Law J Sci Tech. 2012;23:519-530.
- Malcolm HE. Pregnancy centers and the limits of mandated disclosure. Columbia Law Rev. 2019;119:1133-1168.
- Kukura E. Contested care: the limitations of evidencebased maternity care reform. Berkeley J Gender Law Justice. 2016;31:241-298.
- Donley G. Contraceptive equity: curing the sex discrimination in the ACA’s mandate. Alabama Law Rev. 2019;71:499-560.
- Berk H. Savvy surrogates and rock star parents: compensation provisions, contracting practices, and the value of womb work. Law Social Inquiry. 2020;45:398-431.
CASE Unidentified ectopic pregnancy leads to rupture*
A 33-year-old woman (G1 P0010) with 2 positive home pregnancy tests presents to the emergency department (ED) reporting intermittent vaginal bleeding for 3 days. Her last menstrual period was 10 weeks ago, but she reports that her menses are always irregular. She has a history of asymptomatic chlamydia, as well as spontaneous abortion 2 years prior. At present, she denies abdominal pain or vaginal discharge.
Upon examination her vital signs are: temperature, 98.3 °F; pulse, 112 bpm, with a resting rate of 16 bpm; blood pressure (BP), 142/91 mm Hg; pulse O2, 99%; height, 4’ 3”; weight, 115 lb. Her labs are: hemoglobin, 12.1 g/dL; hematocrit, 38%; serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) 236 mIU/mL. Upon pelvic examination, no active bleeding is noted. She agrees to be followed up by her gynecologist and is given a prescription for serum hCG in 2 days. She is instructed to return to the ED should she have pain or increased vaginal bleeding.
Three days later, the patient follows up with her gynecologist reporting mild cramping. She notes having had an episode of heavy vaginal bleeding and a “weakly positive” home pregnancy test. Transvaginal ultrasonography notes endometrial thickness 0.59 mm and unremarkable adnexa. A urine pregnancy test performed in the office is positive; urinalysis is positive for nitrites. With the bleeding slowed, the gynecologist’s overall impression is that the patient has undergone complete spontaneous abortion. She prescribes Macrobid for the urinary tract infection. She does not obtain the ED-prescribed serum HCG levels, as she feels, since complete spontaneous abortion has occurred there is no need to obtain a follow-up serum HCG.
Five days later, the patient returns to the ED reporting abdominal pain after eating. Fever and productive cough of 2 days are noted. The patient states that she had a recent miscarriage. The overall impression of the patient’s condition is bronchitis, and it is noted on the patient’s record, “unlikely ectopic pregnancy and pregnancy test may be false positive,” hence a pregnancy test is not ordered. Examination reveals mild suprapubic tenderness with no rebound; no pelvic exam is performed. The patient is instructed to follow up with a health care clinic within a week, and to return to the ED with severe abdominal pain, higher fever, or any new concerning symptoms. A Zithromax Z-pak is prescribed.
Four days later, the patient is brought by ambulance to the ED of the local major medical center with severe abdominal pain involving the right lower quadrant. She states that she had a miscarriage 3 weeks prior and was recently treated for bronchitis. She has dizziness when standing. Her vital signs are: temperature, 97.8 °F; heart rate, 95 bpm; BP, 72/48 mm Hg; pulse O2, 100%. She reports her abdominal pain to be 6/10.
The patient is given a Lactated Ringer’s bolus of 1,000 mL for a hypotensive episode. Computed tomography is obtained and notes, “low attenuation in the left adnexa with a dilated fallopian tube.” A large heterogeneous collection of fluid in the pelvis is noted with active extravasation, consistent with an “acute bleed.”
The patient is brought to the operating room with a diagnosis of probable ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Intraoperatively she is noted to have a right ruptured ectopic and left tubo-ovarian abscess. The surgeon proceeds with right salpingectomy and left salpingo-oophorectomy. Three liters of hemoperitoneum is found.
She is followed postoperatively with serum hCG until levels are negative. Her postoperative course is uneventful. Her only future option for pregnancy is through assisted reproductive technology (ART) with in vitro fertilization (IVF). The patient sues the gynecologist and second ED physician for presumed inappropriate assessment for ectopic pregnancy.
*The “facts” of this case are a composite, drawn from several cases to illustrate medical and legal issues. The statement of facts should be considered hypothetical.
Continue to: WHAT’S THE VERDICT?...
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
A defense verdict is returned.
Medical considerations
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is 2% of all pregnancies, with a higher incidence (about 4%) among infertility patients.1 Up to 10% of ectopic pregnancies have no symptoms.2
Clinical presentations. Classic signs of ectopic pregnancy include:
- abdominal pain
- vaginal bleeding
- late menses (often noted).
A recent case of ectopic pregnancy presenting with chest pain was reported.3 Clinicians must never lose site of the fact that ectopic pregnancy is the most common cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester, with an incidence of 1% to 10% of all first-trimester deaths.4
Risk factors include pelvic inflammatory disease, as demonstrated in the opening case. “The silent epidemic of chlamydia” comes to mind, and tobacco smoking can adversely affect tubal cilia, as can pelvic adhesions and/or prior tubal surgery. All of these factors can predispose a patient to ectopic pregnancy; in addition, intrauterine devices, endometriosis, tubal ligation (or ligation reversal), all can set the stage for an ectopic pregnancy.5 Appropriate serum hCG monitoring during early pregnancy can assist in sorting out pregnancies of unknown location (PUL; FIGURE). First trimester ultrasonography, at 5 weeks gestation, usually identifies early intrauterine gestation.

Imaging. With regard to pelvic sonography, the earliest sign of an intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) is a sac eccentrically located in the decidua.6 As the IUP progresses, it becomes equated with a “double decidual sign,” with double rings of tissue around the sac.6 If the pregnancy is located in an adnexal mass, it is frequently inhomogeneous or noncystic in appearance (ie, “the blob” sign); the positive predictive value (PPV) is 96%.2 The PPV of transvaginal ultrasound is 80%, as paratubal, paraovarian, ovarian cyst, and hydrosalpinx can affect the interpretation.7
Heterotopic pregnancy includes an intrauterine gestation and an ectopic pregnancy. This presentation includes the presence of a “pseudosac” in the endometrial cavity plus an extrauterine gestation. Heterotopic pregnancies have become somewhat more common as ART/IVF has unfolded, especially prior to the predominance of single embryo transfer.
Managing ectopic pregnancy
For cases of early pregnancy complicated by intermittent bleeding and/or pain, monitoring with serum hCG levels at 48-hour intervals to distinguish a viable IUP from an abnormal IUP or an ectopic is appropriate. The “discriminatory zone” collates serum hCG levels with findings on ultrasonography. Specific lower limits of serum hCG levels are not clear cut, with recommendations of 3,500 mIU/mL to provide sonographic evidence of an intrauterine gestation “to avoid misdiagnosis and possible interruption of intrauterine pregnancy,” as conveyed in the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 2018 practice bulletin.8 Serum progesterone levels also have been suggested to complement hCG levels; a progesterone level of <20 nmol/L is consistent with an abnormal pregnancy, whereas levels >25 nmol/L are suggestive of a viable pregnancy.2 Inhibin A levels also have been suggested to be helpful, but they are not an ideal monitoring tool.
While most ectopic pregnancies are located in the fallopian tube, other locations also can be abdominal or ovarian. In addition, cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy can occur and often is associated with delay in diagnosis and greater morbidity due to such delay.9 With regard to ovarian ectopic, Spiegelberg criteria are established for diagnosis (TABLE 1).10
Appropriate management of an ectopic pregnancy is dependent upon the gestational age, serum hCG levels, and imaging findings, as well as the patient’s symptoms and exam findings. Treatment is established in large part on a case-by-case basis and includes, for early pregnancy, expectant management and use of methotrexate (TABLE 2).11 Dilation and curettage may be used to identify the pregnancy’s location when the serum hCG level is below 2,000 mIU/mL and there is no evidence of an IUP on ultrasound. Surgical treatment can include minimally invasive salpingostomy or salpingectomy and, depending on circumstance, laparotomy may be indicated.

Fertility following ectopic pregnancy varies and is affected by location, treatment, predisposing factors, total number of ectopic pregnancies, and other factors. Ectopic pregnancy, although rare, also can occur with use of IVF. Humans are not unique with regard to ectopic pregnancies, as they also occur in sheep.12
Continue to: Legal perspective...
Legal perspective
Lawsuits related to ectopic pregnancy are not a new phenomenon. In fact, in 1897, a physician in Ohio who misdiagnosed an “extrauterine pregnancy” as appendicitis was the center of a malpractice lawsuit.13 Unrecognized or mishandled ectopic pregnancy can result in serious injuries—in the range of 1% to 10% (see above) of maternal deaths are related to ectopic pregnancy.14 Ectopic pregnancy cases, therefore, have been the subject of substantial litigation over the years. An informal, noncomprehensive review of malpractice lawsuits brought from 2000 to 2019, found more than 300 ectopic pregnancy cases. Given the large number of malpractice claims against ObGyns,15 ectopic pregnancy cases are only a small portion of all ObGyn malpractice cases.16
A common claim: negligent diagnosis or treatment
The most common basis for lawsuits in cases of ectopic pregnancy is the clinician’s negligent failure to properly diagnose the ectopic nature of the pregnancy. There are also a number of cases claiming negligent treatment of an identified ectopic pregnancy. Not every missed diagnosis, or unsuccessful treatment, leads to liability, of course. It is only when a diagnosis or treatment fails to meet the standard of care within the profession that there should be liability. That standard of care is generally defined by what a reasonably prudent physician would do under the circumstances. Expert witnesses, who are familiar with the standard of practice within the specialty, are usually necessary to establish what that practice is. Both the plaintiff and the defense obtain experts, the former to prove what the standard of care is and that the standard was not met in the case at hand. The defense experts are usually arguing that the standard of care was met.17 Inadequate diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy or other condition may arise from a failure to take a sufficient history, conduct an appropriately thorough physical examination, recognize any of the symptoms that would suggest it is present, use and conduct ultrasound correctly, or follow-up appropriately with additional testing.18
A malpractice claim of negligent treatment can involve any the following circumstances19:
- failure to establish an appropriate treatment plan
- prescribing inappropriate medications for the patient (eg, methotrexate, when it is contraindicated)
- delivering the wrong medication or the wrong amount of the right medication
- performing a procedure badly
- undertaking a new treatment without adequate instruction and preparation.
Given the nature and risks of ectopic pregnancy, ongoing, frequent contact with the patient is essential from the point at which the condition is suspected. The greater the risk of harm (probability or consequence), the more careful any professional ought to be. Because ectopic pregnancy is not an uncommon occurrence, and because it can have devastating effects, including death, a reasonably prudent practitioner would be especially aware of the clinical presentations discussed above.20 In the opening case, the treatment plan was not well documented.
Negligence must lead to patient harm. In addition to negligence (proving that the physician did not act in accordance with the standard of care), to prevail in a malpractice case, the plaintiff-patient must prove that the negligence caused the injury, or worsened it. If the failure to make a diagnosis would not have made any difference in a harm the patient suffered, there are no damages and no liability. Suppose, for example, that a physician negligently failed to diagnose ectopic pregnancy, but performed surgery expecting to find the misdiagnosed condition. In the course of the surgery, however, the surgeon discovered and appropriately treated the ectopic pregnancy. (A version of this happened in the old 19th century case mentioned above.) The negligence of the physician did not cause harm, so there are no damages and no liability.
Continue to: Informed consent is vital...
Informed consent is vital
A part of malpractice is informed consent (or the absence of it)—issues that can arise in any medical care.21 It is wise to pay particular attention in cases where the nature of the illness is unknown, and where there are significant uncertainties and the nature of testing and treatment may change substantially over a period of a few days or few weeks. As always, informed consent should include a discussion of what process or procedure is proposed, its risks and benefits, alternative approaches that might be available, and the risk of doing nothing. Frequently, the uncertainty of ectopic pregnancy complicates the informed consent process.22
Because communication with the patient is an essential function of informed consent, the consent process should productively be used in PUL and similar cases to inform the patient about the uncertainty, and the testing and (nonsurgical) treatment that will occur. This is an opportunity to reinforce the message that the patient must maintain ongoing communication with the physician’s office about changes in her condition, and appear for each appointment scheduled. If more invasive procedures—notably surgery—become required, a separate consent process should be completed, because the risks and considerations are now meaningfully different than when treatment began. As a general matter, any possible treatment that may result in infertility or reduced reproductive capacity should specifically be included in the consent process.
In the hypothetical case, the gynecologist failed to obtain a follow-up serum hCG level. In addition, the record did not reflect ectopic pregnancy in the differential diagnosis. As noted above, the patient had predisposing factors for an ectopic pregnancy. The physician should have acknowledged the history of sexually transmitted disease predisposing her to an ectopic pregnancy. Monitoring of serum hCG levels until they are negative is appropriate with ectopic, or presumed ectopic, pregnancy management. Appropriate monitoring did not occur in this case. Each of these errors (following up on serum hCG levels and the inadequacy of notations about the possibility of ectopic pregnancy) seem inconsistent with the usual standard of care. Furthermore, as a result of the outcome, the only future option for the patient to pursue pregnancy was IVF.
Other legal issues
There are a number of other legal issues that are associated with the topic of ectopic pregnancy. There is evidence, for example, that Catholic and non-Catholic hospitals treat ectopic pregnancies differently,23 which may reflect different views on taking a life or the use of methotrexate and its association with abortion.24 In addition, the possibility of an increase in future ectopic pregnancies is one of the “risks” of abortion that pro-life organizations have pushed to see included in abortion informed consent.25 This has led some commentators to conclude that some Catholic hospitals violate federal law in managing ectopic pregnancy. There is also evidence of “overwhelming rates of medical misinformation on pregnancy center websites, including a link between abortion and ectopic pregnancy.”26
The fact that cesarean deliveries are related to an increased risk for ectopic pregnancy (because of the risk of cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy) also has been cited as information that should play a role in the consent process for cesarean delivery.27 In terms of liability, failed tubal ligation leads to a 33% risk of ectopic pregnancy.28 The risk of ectopic pregnancy is also commonly included in surrogacy contracts.29
Why the outcome was for the defense
The opening hypothetical case illustrates some of the uncertainties of medical malpractice cases. As noted, there appeared a deviation from the usual standard of care, particularly the failure to follow up on the serum hCG level. The weakness in the medical record, failing to note the possibility of ectopic pregnancy, also was probably an error but, apparently, the court felt that this did not result in any harm to the patient.
The question arises of how there would be a defense verdict in light of the failure to track consecutive serum hCG levels. A speculative explanation is that there are many uncertainties in most lawsuits. Procedural problems may result in a case being limited, expert witnesses are essential to both the plaintiff and defense, with the quality of their review and testimony possibly uneven. Judges and juries may rely on one expert witness rather than another, juries vary, and the quality of advocacy differs. Any of these situations can contribute to the unpredictability of the outcome of a case. In the case above, the liability was somewhat uncertain, and the various other factors tipped in favor of a defense verdict. ●
CASE Unidentified ectopic pregnancy leads to rupture*
A 33-year-old woman (G1 P0010) with 2 positive home pregnancy tests presents to the emergency department (ED) reporting intermittent vaginal bleeding for 3 days. Her last menstrual period was 10 weeks ago, but she reports that her menses are always irregular. She has a history of asymptomatic chlamydia, as well as spontaneous abortion 2 years prior. At present, she denies abdominal pain or vaginal discharge.
Upon examination her vital signs are: temperature, 98.3 °F; pulse, 112 bpm, with a resting rate of 16 bpm; blood pressure (BP), 142/91 mm Hg; pulse O2, 99%; height, 4’ 3”; weight, 115 lb. Her labs are: hemoglobin, 12.1 g/dL; hematocrit, 38%; serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) 236 mIU/mL. Upon pelvic examination, no active bleeding is noted. She agrees to be followed up by her gynecologist and is given a prescription for serum hCG in 2 days. She is instructed to return to the ED should she have pain or increased vaginal bleeding.
Three days later, the patient follows up with her gynecologist reporting mild cramping. She notes having had an episode of heavy vaginal bleeding and a “weakly positive” home pregnancy test. Transvaginal ultrasonography notes endometrial thickness 0.59 mm and unremarkable adnexa. A urine pregnancy test performed in the office is positive; urinalysis is positive for nitrites. With the bleeding slowed, the gynecologist’s overall impression is that the patient has undergone complete spontaneous abortion. She prescribes Macrobid for the urinary tract infection. She does not obtain the ED-prescribed serum HCG levels, as she feels, since complete spontaneous abortion has occurred there is no need to obtain a follow-up serum HCG.
Five days later, the patient returns to the ED reporting abdominal pain after eating. Fever and productive cough of 2 days are noted. The patient states that she had a recent miscarriage. The overall impression of the patient’s condition is bronchitis, and it is noted on the patient’s record, “unlikely ectopic pregnancy and pregnancy test may be false positive,” hence a pregnancy test is not ordered. Examination reveals mild suprapubic tenderness with no rebound; no pelvic exam is performed. The patient is instructed to follow up with a health care clinic within a week, and to return to the ED with severe abdominal pain, higher fever, or any new concerning symptoms. A Zithromax Z-pak is prescribed.
Four days later, the patient is brought by ambulance to the ED of the local major medical center with severe abdominal pain involving the right lower quadrant. She states that she had a miscarriage 3 weeks prior and was recently treated for bronchitis. She has dizziness when standing. Her vital signs are: temperature, 97.8 °F; heart rate, 95 bpm; BP, 72/48 mm Hg; pulse O2, 100%. She reports her abdominal pain to be 6/10.
The patient is given a Lactated Ringer’s bolus of 1,000 mL for a hypotensive episode. Computed tomography is obtained and notes, “low attenuation in the left adnexa with a dilated fallopian tube.” A large heterogeneous collection of fluid in the pelvis is noted with active extravasation, consistent with an “acute bleed.”
The patient is brought to the operating room with a diagnosis of probable ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Intraoperatively she is noted to have a right ruptured ectopic and left tubo-ovarian abscess. The surgeon proceeds with right salpingectomy and left salpingo-oophorectomy. Three liters of hemoperitoneum is found.
She is followed postoperatively with serum hCG until levels are negative. Her postoperative course is uneventful. Her only future option for pregnancy is through assisted reproductive technology (ART) with in vitro fertilization (IVF). The patient sues the gynecologist and second ED physician for presumed inappropriate assessment for ectopic pregnancy.
*The “facts” of this case are a composite, drawn from several cases to illustrate medical and legal issues. The statement of facts should be considered hypothetical.
Continue to: WHAT’S THE VERDICT?...
WHAT’S THE VERDICT?
A defense verdict is returned.
Medical considerations
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is 2% of all pregnancies, with a higher incidence (about 4%) among infertility patients.1 Up to 10% of ectopic pregnancies have no symptoms.2
Clinical presentations. Classic signs of ectopic pregnancy include:
- abdominal pain
- vaginal bleeding
- late menses (often noted).
A recent case of ectopic pregnancy presenting with chest pain was reported.3 Clinicians must never lose site of the fact that ectopic pregnancy is the most common cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester, with an incidence of 1% to 10% of all first-trimester deaths.4
Risk factors include pelvic inflammatory disease, as demonstrated in the opening case. “The silent epidemic of chlamydia” comes to mind, and tobacco smoking can adversely affect tubal cilia, as can pelvic adhesions and/or prior tubal surgery. All of these factors can predispose a patient to ectopic pregnancy; in addition, intrauterine devices, endometriosis, tubal ligation (or ligation reversal), all can set the stage for an ectopic pregnancy.5 Appropriate serum hCG monitoring during early pregnancy can assist in sorting out pregnancies of unknown location (PUL; FIGURE). First trimester ultrasonography, at 5 weeks gestation, usually identifies early intrauterine gestation.

Imaging. With regard to pelvic sonography, the earliest sign of an intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) is a sac eccentrically located in the decidua.6 As the IUP progresses, it becomes equated with a “double decidual sign,” with double rings of tissue around the sac.6 If the pregnancy is located in an adnexal mass, it is frequently inhomogeneous or noncystic in appearance (ie, “the blob” sign); the positive predictive value (PPV) is 96%.2 The PPV of transvaginal ultrasound is 80%, as paratubal, paraovarian, ovarian cyst, and hydrosalpinx can affect the interpretation.7
Heterotopic pregnancy includes an intrauterine gestation and an ectopic pregnancy. This presentation includes the presence of a “pseudosac” in the endometrial cavity plus an extrauterine gestation. Heterotopic pregnancies have become somewhat more common as ART/IVF has unfolded, especially prior to the predominance of single embryo transfer.
Managing ectopic pregnancy
For cases of early pregnancy complicated by intermittent bleeding and/or pain, monitoring with serum hCG levels at 48-hour intervals to distinguish a viable IUP from an abnormal IUP or an ectopic is appropriate. The “discriminatory zone” collates serum hCG levels with findings on ultrasonography. Specific lower limits of serum hCG levels are not clear cut, with recommendations of 3,500 mIU/mL to provide sonographic evidence of an intrauterine gestation “to avoid misdiagnosis and possible interruption of intrauterine pregnancy,” as conveyed in the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 2018 practice bulletin.8 Serum progesterone levels also have been suggested to complement hCG levels; a progesterone level of <20 nmol/L is consistent with an abnormal pregnancy, whereas levels >25 nmol/L are suggestive of a viable pregnancy.2 Inhibin A levels also have been suggested to be helpful, but they are not an ideal monitoring tool.
While most ectopic pregnancies are located in the fallopian tube, other locations also can be abdominal or ovarian. In addition, cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy can occur and often is associated with delay in diagnosis and greater morbidity due to such delay.9 With regard to ovarian ectopic, Spiegelberg criteria are established for diagnosis (TABLE 1).10
Appropriate management of an ectopic pregnancy is dependent upon the gestational age, serum hCG levels, and imaging findings, as well as the patient’s symptoms and exam findings. Treatment is established in large part on a case-by-case basis and includes, for early pregnancy, expectant management and use of methotrexate (TABLE 2).11 Dilation and curettage may be used to identify the pregnancy’s location when the serum hCG level is below 2,000 mIU/mL and there is no evidence of an IUP on ultrasound. Surgical treatment can include minimally invasive salpingostomy or salpingectomy and, depending on circumstance, laparotomy may be indicated.

Fertility following ectopic pregnancy varies and is affected by location, treatment, predisposing factors, total number of ectopic pregnancies, and other factors. Ectopic pregnancy, although rare, also can occur with use of IVF. Humans are not unique with regard to ectopic pregnancies, as they also occur in sheep.12
Continue to: Legal perspective...
Legal perspective
Lawsuits related to ectopic pregnancy are not a new phenomenon. In fact, in 1897, a physician in Ohio who misdiagnosed an “extrauterine pregnancy” as appendicitis was the center of a malpractice lawsuit.13 Unrecognized or mishandled ectopic pregnancy can result in serious injuries—in the range of 1% to 10% (see above) of maternal deaths are related to ectopic pregnancy.14 Ectopic pregnancy cases, therefore, have been the subject of substantial litigation over the years. An informal, noncomprehensive review of malpractice lawsuits brought from 2000 to 2019, found more than 300 ectopic pregnancy cases. Given the large number of malpractice claims against ObGyns,15 ectopic pregnancy cases are only a small portion of all ObGyn malpractice cases.16
A common claim: negligent diagnosis or treatment
The most common basis for lawsuits in cases of ectopic pregnancy is the clinician’s negligent failure to properly diagnose the ectopic nature of the pregnancy. There are also a number of cases claiming negligent treatment of an identified ectopic pregnancy. Not every missed diagnosis, or unsuccessful treatment, leads to liability, of course. It is only when a diagnosis or treatment fails to meet the standard of care within the profession that there should be liability. That standard of care is generally defined by what a reasonably prudent physician would do under the circumstances. Expert witnesses, who are familiar with the standard of practice within the specialty, are usually necessary to establish what that practice is. Both the plaintiff and the defense obtain experts, the former to prove what the standard of care is and that the standard was not met in the case at hand. The defense experts are usually arguing that the standard of care was met.17 Inadequate diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy or other condition may arise from a failure to take a sufficient history, conduct an appropriately thorough physical examination, recognize any of the symptoms that would suggest it is present, use and conduct ultrasound correctly, or follow-up appropriately with additional testing.18
A malpractice claim of negligent treatment can involve any the following circumstances19:
- failure to establish an appropriate treatment plan
- prescribing inappropriate medications for the patient (eg, methotrexate, when it is contraindicated)
- delivering the wrong medication or the wrong amount of the right medication
- performing a procedure badly
- undertaking a new treatment without adequate instruction and preparation.
Given the nature and risks of ectopic pregnancy, ongoing, frequent contact with the patient is essential from the point at which the condition is suspected. The greater the risk of harm (probability or consequence), the more careful any professional ought to be. Because ectopic pregnancy is not an uncommon occurrence, and because it can have devastating effects, including death, a reasonably prudent practitioner would be especially aware of the clinical presentations discussed above.20 In the opening case, the treatment plan was not well documented.
Negligence must lead to patient harm. In addition to negligence (proving that the physician did not act in accordance with the standard of care), to prevail in a malpractice case, the plaintiff-patient must prove that the negligence caused the injury, or worsened it. If the failure to make a diagnosis would not have made any difference in a harm the patient suffered, there are no damages and no liability. Suppose, for example, that a physician negligently failed to diagnose ectopic pregnancy, but performed surgery expecting to find the misdiagnosed condition. In the course of the surgery, however, the surgeon discovered and appropriately treated the ectopic pregnancy. (A version of this happened in the old 19th century case mentioned above.) The negligence of the physician did not cause harm, so there are no damages and no liability.
Continue to: Informed consent is vital...
Informed consent is vital
A part of malpractice is informed consent (or the absence of it)—issues that can arise in any medical care.21 It is wise to pay particular attention in cases where the nature of the illness is unknown, and where there are significant uncertainties and the nature of testing and treatment may change substantially over a period of a few days or few weeks. As always, informed consent should include a discussion of what process or procedure is proposed, its risks and benefits, alternative approaches that might be available, and the risk of doing nothing. Frequently, the uncertainty of ectopic pregnancy complicates the informed consent process.22
Because communication with the patient is an essential function of informed consent, the consent process should productively be used in PUL and similar cases to inform the patient about the uncertainty, and the testing and (nonsurgical) treatment that will occur. This is an opportunity to reinforce the message that the patient must maintain ongoing communication with the physician’s office about changes in her condition, and appear for each appointment scheduled. If more invasive procedures—notably surgery—become required, a separate consent process should be completed, because the risks and considerations are now meaningfully different than when treatment began. As a general matter, any possible treatment that may result in infertility or reduced reproductive capacity should specifically be included in the consent process.
In the hypothetical case, the gynecologist failed to obtain a follow-up serum hCG level. In addition, the record did not reflect ectopic pregnancy in the differential diagnosis. As noted above, the patient had predisposing factors for an ectopic pregnancy. The physician should have acknowledged the history of sexually transmitted disease predisposing her to an ectopic pregnancy. Monitoring of serum hCG levels until they are negative is appropriate with ectopic, or presumed ectopic, pregnancy management. Appropriate monitoring did not occur in this case. Each of these errors (following up on serum hCG levels and the inadequacy of notations about the possibility of ectopic pregnancy) seem inconsistent with the usual standard of care. Furthermore, as a result of the outcome, the only future option for the patient to pursue pregnancy was IVF.
Other legal issues
There are a number of other legal issues that are associated with the topic of ectopic pregnancy. There is evidence, for example, that Catholic and non-Catholic hospitals treat ectopic pregnancies differently,23 which may reflect different views on taking a life or the use of methotrexate and its association with abortion.24 In addition, the possibility of an increase in future ectopic pregnancies is one of the “risks” of abortion that pro-life organizations have pushed to see included in abortion informed consent.25 This has led some commentators to conclude that some Catholic hospitals violate federal law in managing ectopic pregnancy. There is also evidence of “overwhelming rates of medical misinformation on pregnancy center websites, including a link between abortion and ectopic pregnancy.”26
The fact that cesarean deliveries are related to an increased risk for ectopic pregnancy (because of the risk of cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy) also has been cited as information that should play a role in the consent process for cesarean delivery.27 In terms of liability, failed tubal ligation leads to a 33% risk of ectopic pregnancy.28 The risk of ectopic pregnancy is also commonly included in surrogacy contracts.29
Why the outcome was for the defense
The opening hypothetical case illustrates some of the uncertainties of medical malpractice cases. As noted, there appeared a deviation from the usual standard of care, particularly the failure to follow up on the serum hCG level. The weakness in the medical record, failing to note the possibility of ectopic pregnancy, also was probably an error but, apparently, the court felt that this did not result in any harm to the patient.
The question arises of how there would be a defense verdict in light of the failure to track consecutive serum hCG levels. A speculative explanation is that there are many uncertainties in most lawsuits. Procedural problems may result in a case being limited, expert witnesses are essential to both the plaintiff and defense, with the quality of their review and testimony possibly uneven. Judges and juries may rely on one expert witness rather than another, juries vary, and the quality of advocacy differs. Any of these situations can contribute to the unpredictability of the outcome of a case. In the case above, the liability was somewhat uncertain, and the various other factors tipped in favor of a defense verdict. ●
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ectopic pregnancy—United States, 1990‒1992. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1995;44:46-48.
- Kirk E, Bottomley C, Bourne T. Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy and current concepts in the management of pregnancy of unknown location. Hum Reprod Update. 2012;20:250-261.
- Dichter E, Espinosa J, Baird J, Lucerna A. An unusual emergency department case: ruptured ectopic pregnancy presenting as chest pain. World J Emerg Med. 2017;8:71-73.
- Cecchino GN, Araujo E, Elito J. Methotrexate for ectopic pregnancy: when and how. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;290:417- 423.
- Barnhart KT, Sammel MD, Cracia CR, et al. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy in women with symptomatic firsttrimester pregnancies. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:36-43.
- Carusi D. Pregnancy of unknown location: evaluation and management. Semin Perinatol. 2019;43:95-100.
- Barnhart KT, Fay CA, Suescum M, et al. Clinical factors affecting the accuracy of ultrasonography in symptomatic first-trimester pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:299-306.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Practice Bulletin No. 193: tubal ectopic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e91-e103.
- Bouyer J, Coste J, Fernandez H, et al. Sites of ectopic pregnancy: a 10-year population-based study of 1800 cases. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:3224-3230.
- Spiegelberg O. Zur casuistic der ovarial schwangerschaft. Arch Gynecol. 1978;13:73.
- OB Hospitalist Group. Methotrexate use for ectopic pregnancies guidelines. https://www.obhg.com/wp-content /uploads/2020/01/Methotrexate-Use-for-EctopicPregnancies_2016-updates.pdf. Accessed December 10, 2020.
- Brozos C, Kargiannis I, Kiossis E, et al. Ectopic pregnancy through a caesarean scar in a ewe. N Z Vet J. 2013;61:373-375.
- Tucker v. Gillette, 12 Ohio Cir. Dec. 401 (Cir. Ct. 1901).
- Creanga AA, Syverson C, Seed K, et al. Pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, 2011–2013. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:366-373.
- Matthews LR, Alvi FA, Milad MP. Reproductive surgery malpractice patterns. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:e42-e43.
- Kim B. The impact of malpractice risk on the use of obstetrics procedures. J Legal Studies. 2006;36:S79-S120.
- Abinader R, Warsof S. Complications involving obstetrical ultrasound. In: Warsof S, Shwayder JM, eds. Legal Concepts and Best Practices in Obstetrics: The Nuts and Bolts Guide to Mitigating Risk. 2019;45-48.
- Creanga AA, Shapiro-Mendoza CK, Bish CL, et al. Trends in ectopic pregnancy mortality in the United States: 1980-2007. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:837-843.
- Shwayder JM. IUP diagnosed and treated as ectopic: How bad can it get? Contemporary OB/GYN. 2019;64:49-46.
- Kaplan AI. Should this ectopic pregnancy have been diagnosed earlier? Contemporary OB/GYN. 2017;62:53.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Ethics. Committee opinion 439: informed consent. Reaffirmed 2015. https://www.acog.org/clinical /clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2009/08 /informed-consent. Accessed December 9, 2020.
- Shwayder JM. Liability in ob/gyn ultrasound. Contemporary OB/GYN. 2017;62:32-49.
- Fisher LN. Institutional religious exemptions: a balancing approach. BYU Law Review. 2014;415-444.
- Makdisi J. Aquinas’s prohibition of killing reconsidered. J Catholic Legal Stud. 2019:57:67-128.
- Franzonello A. Remarks of Anna Franzonello. Alb Law J Sci Tech. 2012;23:519-530.
- Malcolm HE. Pregnancy centers and the limits of mandated disclosure. Columbia Law Rev. 2019;119:1133-1168.
- Kukura E. Contested care: the limitations of evidencebased maternity care reform. Berkeley J Gender Law Justice. 2016;31:241-298.
- Donley G. Contraceptive equity: curing the sex discrimination in the ACA’s mandate. Alabama Law Rev. 2019;71:499-560.
- Berk H. Savvy surrogates and rock star parents: compensation provisions, contracting practices, and the value of womb work. Law Social Inquiry. 2020;45:398-431.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ectopic pregnancy—United States, 1990‒1992. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1995;44:46-48.
- Kirk E, Bottomley C, Bourne T. Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy and current concepts in the management of pregnancy of unknown location. Hum Reprod Update. 2012;20:250-261.
- Dichter E, Espinosa J, Baird J, Lucerna A. An unusual emergency department case: ruptured ectopic pregnancy presenting as chest pain. World J Emerg Med. 2017;8:71-73.
- Cecchino GN, Araujo E, Elito J. Methotrexate for ectopic pregnancy: when and how. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;290:417- 423.
- Barnhart KT, Sammel MD, Cracia CR, et al. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy in women with symptomatic firsttrimester pregnancies. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:36-43.
- Carusi D. Pregnancy of unknown location: evaluation and management. Semin Perinatol. 2019;43:95-100.
- Barnhart KT, Fay CA, Suescum M, et al. Clinical factors affecting the accuracy of ultrasonography in symptomatic first-trimester pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:299-306.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Practice Bulletin No. 193: tubal ectopic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e91-e103.
- Bouyer J, Coste J, Fernandez H, et al. Sites of ectopic pregnancy: a 10-year population-based study of 1800 cases. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:3224-3230.
- Spiegelberg O. Zur casuistic der ovarial schwangerschaft. Arch Gynecol. 1978;13:73.
- OB Hospitalist Group. Methotrexate use for ectopic pregnancies guidelines. https://www.obhg.com/wp-content /uploads/2020/01/Methotrexate-Use-for-EctopicPregnancies_2016-updates.pdf. Accessed December 10, 2020.
- Brozos C, Kargiannis I, Kiossis E, et al. Ectopic pregnancy through a caesarean scar in a ewe. N Z Vet J. 2013;61:373-375.
- Tucker v. Gillette, 12 Ohio Cir. Dec. 401 (Cir. Ct. 1901).
- Creanga AA, Syverson C, Seed K, et al. Pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, 2011–2013. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:366-373.
- Matthews LR, Alvi FA, Milad MP. Reproductive surgery malpractice patterns. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:e42-e43.
- Kim B. The impact of malpractice risk on the use of obstetrics procedures. J Legal Studies. 2006;36:S79-S120.
- Abinader R, Warsof S. Complications involving obstetrical ultrasound. In: Warsof S, Shwayder JM, eds. Legal Concepts and Best Practices in Obstetrics: The Nuts and Bolts Guide to Mitigating Risk. 2019;45-48.
- Creanga AA, Shapiro-Mendoza CK, Bish CL, et al. Trends in ectopic pregnancy mortality in the United States: 1980-2007. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:837-843.
- Shwayder JM. IUP diagnosed and treated as ectopic: How bad can it get? Contemporary OB/GYN. 2019;64:49-46.
- Kaplan AI. Should this ectopic pregnancy have been diagnosed earlier? Contemporary OB/GYN. 2017;62:53.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Ethics. Committee opinion 439: informed consent. Reaffirmed 2015. https://www.acog.org/clinical /clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2009/08 /informed-consent. Accessed December 9, 2020.
- Shwayder JM. Liability in ob/gyn ultrasound. Contemporary OB/GYN. 2017;62:32-49.
- Fisher LN. Institutional religious exemptions: a balancing approach. BYU Law Review. 2014;415-444.
- Makdisi J. Aquinas’s prohibition of killing reconsidered. J Catholic Legal Stud. 2019:57:67-128.
- Franzonello A. Remarks of Anna Franzonello. Alb Law J Sci Tech. 2012;23:519-530.
- Malcolm HE. Pregnancy centers and the limits of mandated disclosure. Columbia Law Rev. 2019;119:1133-1168.
- Kukura E. Contested care: the limitations of evidencebased maternity care reform. Berkeley J Gender Law Justice. 2016;31:241-298.
- Donley G. Contraceptive equity: curing the sex discrimination in the ACA’s mandate. Alabama Law Rev. 2019;71:499-560.
- Berk H. Savvy surrogates and rock star parents: compensation provisions, contracting practices, and the value of womb work. Law Social Inquiry. 2020;45:398-431.
Still happening: Pelvic exams on anesthetized patients. Why?
“When I was doing ob.gyn. as a med student, the attending would have me do a pelvic right after the patient was under and before we started surgery,” said one participant in an online forum. “We didn’t exactly get permission but it was for teaching purposes.”
Yet others don’t see what the commotion is about. “There are a hundred things that are done during a surgery that don’t require your specific consent (some of them much more ‘humiliating’ than a pelvic exam). ... There’s not really much left to be shy about during a gyn/rectal/prostate surgery, let me put it that way,” one doctor wrote.
However, many physicians are adamantly opposed to the practice, and laws intended to stop or limit it are being enacted throughout the nation.
Renewed concerns have prompted new state laws
A few states have required consent for pelvic exams for many years, beginning with California in 2003. But up until 2019, providing pelvic exams without informed consent was illegal in only six states.
Continuing reports of unauthorized pelvic exams indicate that the practice has not disappeared. University of Michigan professor Maya M. Hammoud, MD, past president of the Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and many others attribute renewed interest in the issue to a 2018 article in the journal Bioethics by Phoebe Friesen, a medical ethicist at McGill University, Montreal, that laid out the ethical arguments against the practice.
Starting in 2019, an outpouring of new state bills have been introduced, and nine more states have passed laws. In addition, 14 other states considered similar bills but did not pass them, in some cases because teaching institutions argued that they were already dealing with the issue. This happened in Connecticut and Massachusetts, after representatives of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., met with legislators.
Laws against the practice have been passed by 15 states, including California, Florida, Illinois, and New York. Some teaching institutions have recently been clamping down on the practice, while many teaching physicians insist that at this point, it has all but ended.
A practice that may still continue
For many years, ethicists, women’s rights groups, state legislators, and organized medicine have been trying to eliminate the practice of unauthorized pelvic exams by medical students. Several key medical groups have come out against it, including the American Medical Association, the Association of American Medical Colleges, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Fifteen years ago, studies found a substantial number of cases, but my sense is that most of that has stopped,” said Dr. Hammoud.
Yet despite these changes, there are some disturbing signs that the practice persists.
“I don’t have data, but anecdotally I see it still going on,” said Peter Ubel, MD, a professor at Duke University, Durham, N.C., who was involved in one of those early studies. “Every so often when I’m making a speech, a medical student tells me about performing a pelvic exam without getting permission.
“Perhaps in some cases the attending [physician] did get permission and didn’t tell the medical student, but that would also be a problem,” Dr. Ubel said. “The medical student should be informed that permission was given. This helps them be sensitive to the need to get consent.”
In a 2019 survey of medical students, 92% said they performed a pelvic exam on an anesthetized female patient, and of those, 61% did so without explicit patient consent.
The survey – involving 101 medical students at seven U.S. medical schools – also found that 11% of the medical students said they were extremely uncomfortable with the practice. But nearly one-third of the medical students said that opting out might jeopardize their grades and future careers.
“I tried to opt out once from doing a pelvic exam when I hadn’t met the patient beforehand,” one of them wrote. “The resident told me no.”
Some physicians defend the practice
Why do many medical students and doctors think that getting consent for pelvic exams is not necessary?
Some argue that patients implicitly give consent when they walk through the doors of a teaching hospital. “Sorry, but you inherently agree to that when you’re seen in an academic teaching hospital,” wrote one participant in a Student Doctor Network forum. “You agree to have residents and medical students participate in your care, not just an attending. If you just want an attending, then you are free to go to a nonteaching hospital. That’s the deal.”
Others argued that since the anesthetized patient couldn’t feel what was going on, it shouldn’t matter. “Things like pelvic exams, rectal exams, or even heroic trauma surgery occur for training purposes when there is no memory, no sensation and no harm to be done [and] society gains a better practitioner of the art of medicine,” a physician in Columbus, Ohio, wrote on Quora, an online forum.
Some doctors argue that they don’t ask for specific consent when they touch a variety of other body parts, and pelvic exams should be no different. Pelvic exams are needed before surgery of the pelvic area, but they have also been given to women undergoing surgery in a different part of the body.
In 2019 a woman told Deseret News in Utah that she had been recovering from stomach surgery when a resident physician mentioned something she had noticed “when we looked at your cervix.” When she asked why the physician had examined her cervix to prepare for stomach surgery, “no one could give her a good answer.”
A ‘positive goal’ doesn’t make it okay
What is missing in many defenses of the practice is any recognition that genitals are the most intimate part of the body, and that a patient’s desire for privacy ought to come first. In a survey of women undergoing gynecologic surgery, 72% expected to be asked for consent before medical students undertook pelvic examinations under anesthesia.
Overruling patients’ concerns about their own privacy is unethical, said Eli Y. Adashi, MD, professor of medical science and former dean of medicine and biological sciences at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Dr. Adashi said the principle of patient autonomy in medical ethics directs that patients must be involved in decision-making about their care – even when caretakers are pursuing a positive goal, such as helping to educate future doctors.
“Conducting pelvic exams on unconscious women without their specific consent is simply untenable and never has been tenable, and it ought to be discontinued if it hasn’t been already,” says Dr. Adashi, who wrote an opinion piece on the issue for JAMA.
Furthermore, it has been shown that ignoring the need to get consent for pelvic exams makes physicians less concerned about getting patient consent in general. A study led by Dr. Ubel found that medical students who had completed an ob.gyn. clerkship thought getting patients’ consent was significantly less important than those who had not completed that clerkship.
Why give pelvic exams to anesthetized women?
Despite the controversy, a number of medical educators continue to direct medical students to perform pelvic exams on anesthetized women. Why is that?
“Pelvic exams are not easy to do,” Dr. Hammoud said. “Learners need to keep working on them; they have to do a lot of them in order to do them well.”
To teach pelvic exams, most medical schools provide standardized patients – paid volunteers who submit to exams and critique the medical student’s work afterwards – but these encounters are limited because of their cost, says Guy Benrubi, MD, professor and emeritus chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville.
He said teaching programs therefore need to supplement exams on standardized patients with exams on unpaid volunteers who provide consent. Programs prefer anesthetized patients, Dr. Benrubi said, because they are easier for novices to work on. “With patients under anesthesia, the muscles are relaxed and it’s easier for learners to detect organs. All the same, you need to get consent.”
Teaching institutions stiffen consent requirements
Faced with growing opposition to pelvic exams without consent, teaching institutions as well as gynecologic educators have recently been tightening their policies.
Dr. Hammoud said she has always informed patients orally about the possibility of medical students performing pelvic exams on them, but now some institutions, including her own, want a more involved process. The university recently began consent in writing for pelvic exams.
In addition, the university also now requires that medical students meet patients before performing pelvic exams and that teaching physicians explain the students’ involvement.
Dr. Hammoud said some institutions now require a separate consent form for pelvic exams, but the University of Michigan simply directs that the possibility of the patient getting a pelvic exam be part of the consent form.
This requirement, called “explicit consent,” was endorsed by APGO. It differs from having a separate consent form for pelvic exams, which would highlight the possibility of a pelvic exam, as many women’s rights activists are calling for.
Why not have a separate form? Dr. Hammoud is concerned that it would unnecessarily alarm patients. “When you point out a certain issue, you’re in effect saying to the patient that this is not normal,” she said, noting that, when asked for consent to do the exams, most women agree to it.
New wave of state laws prompted by renewed concerns
Dr. Hammoud thinks the laws are unnecessary. “These laws are excessive for the vast majority of physicians who practice ethically. The profession should come up with its own standards rather than having a plethora of laws.”
Several of the more recent laws have a broader scope than the original laws. The original laws simply state that medical students or physicians must get informed consent, but they did not stipulate how informed consent should be obtained. (The laws also typically prohibit pelvic exams when surgery will be in a different area of the body.)
The new laws often follow this format, but some go well beyond it. Some also apply to rectal exams (Maine and Maryland), to men as well as women (Utah and Maryland) requires separate consent (Utah), and require consent for all pelvic exams (Florida).
The struggle over Florida’s law
The original Florida bill was drafted in 2019 by state Sen. Lauren Book, a Democrat who is a victims’ rights advocate working with women who have undergone sexual trauma. In written comments for this article, she says not getting consent for pelvic exams is still going on.
“This disturbing practice is commonplace at medical schools and teaching hospitals across the country – including several Florida universities, based on accounts from current and former medical students and faculty,” Sen. Book stated. “At best, these exams have been wrongful learning experiences for medical students or at worst, the equivalent of a sexual assault.”
Dr. Ubel took exception to linking the teaching activities to sexual assault. “I understand why many women would be horrified by this practice, but it’s not as bad as it seems,” he said. “There is nothing sexual or prurient about these exams, and they are motivated purely by a desire to teach people to be better doctors. That said, patients have the right to say, ‘I don’t want it done to me.’ ”
In early 2020, Dr. Benrubi was part of a coalition of medical groups that was trying to influence Sen. Book’s bill as it went through the legislature. Sen. Book’s original bill was relatively mild, “but then, late in the process, it was changed into a more sweeping bill with some unclear language,” he said.
The final version was passed and signed into law by Gov. Ron DeSantis, a conservative Republican, in June.
Dr. Benrubi said that a large number of state legislators, including Sen. Book, have been agreeable to fixing the bill. This was supposed to happen in a special session in the fall, but that never materialized, and so the fix will have to wait until the regular session in early 2021.
“The law should not apply to patients undergoing routine pelvic exams,” Dr. Benrubi said. “It should only apply to women patients under anesthesia.”
But while organized medicine wants to walk back the law, Dr. Book wants to expand it. “This upcoming session, I look forward to working with physicians to continue to hone this new law, and to work toward inclusion for males. Everyone has a right to consent.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“When I was doing ob.gyn. as a med student, the attending would have me do a pelvic right after the patient was under and before we started surgery,” said one participant in an online forum. “We didn’t exactly get permission but it was for teaching purposes.”
Yet others don’t see what the commotion is about. “There are a hundred things that are done during a surgery that don’t require your specific consent (some of them much more ‘humiliating’ than a pelvic exam). ... There’s not really much left to be shy about during a gyn/rectal/prostate surgery, let me put it that way,” one doctor wrote.
However, many physicians are adamantly opposed to the practice, and laws intended to stop or limit it are being enacted throughout the nation.
Renewed concerns have prompted new state laws
A few states have required consent for pelvic exams for many years, beginning with California in 2003. But up until 2019, providing pelvic exams without informed consent was illegal in only six states.
Continuing reports of unauthorized pelvic exams indicate that the practice has not disappeared. University of Michigan professor Maya M. Hammoud, MD, past president of the Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and many others attribute renewed interest in the issue to a 2018 article in the journal Bioethics by Phoebe Friesen, a medical ethicist at McGill University, Montreal, that laid out the ethical arguments against the practice.
Starting in 2019, an outpouring of new state bills have been introduced, and nine more states have passed laws. In addition, 14 other states considered similar bills but did not pass them, in some cases because teaching institutions argued that they were already dealing with the issue. This happened in Connecticut and Massachusetts, after representatives of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., met with legislators.
Laws against the practice have been passed by 15 states, including California, Florida, Illinois, and New York. Some teaching institutions have recently been clamping down on the practice, while many teaching physicians insist that at this point, it has all but ended.
A practice that may still continue
For many years, ethicists, women’s rights groups, state legislators, and organized medicine have been trying to eliminate the practice of unauthorized pelvic exams by medical students. Several key medical groups have come out against it, including the American Medical Association, the Association of American Medical Colleges, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Fifteen years ago, studies found a substantial number of cases, but my sense is that most of that has stopped,” said Dr. Hammoud.
Yet despite these changes, there are some disturbing signs that the practice persists.
“I don’t have data, but anecdotally I see it still going on,” said Peter Ubel, MD, a professor at Duke University, Durham, N.C., who was involved in one of those early studies. “Every so often when I’m making a speech, a medical student tells me about performing a pelvic exam without getting permission.
“Perhaps in some cases the attending [physician] did get permission and didn’t tell the medical student, but that would also be a problem,” Dr. Ubel said. “The medical student should be informed that permission was given. This helps them be sensitive to the need to get consent.”
In a 2019 survey of medical students, 92% said they performed a pelvic exam on an anesthetized female patient, and of those, 61% did so without explicit patient consent.
The survey – involving 101 medical students at seven U.S. medical schools – also found that 11% of the medical students said they were extremely uncomfortable with the practice. But nearly one-third of the medical students said that opting out might jeopardize their grades and future careers.
“I tried to opt out once from doing a pelvic exam when I hadn’t met the patient beforehand,” one of them wrote. “The resident told me no.”
Some physicians defend the practice
Why do many medical students and doctors think that getting consent for pelvic exams is not necessary?
Some argue that patients implicitly give consent when they walk through the doors of a teaching hospital. “Sorry, but you inherently agree to that when you’re seen in an academic teaching hospital,” wrote one participant in a Student Doctor Network forum. “You agree to have residents and medical students participate in your care, not just an attending. If you just want an attending, then you are free to go to a nonteaching hospital. That’s the deal.”
Others argued that since the anesthetized patient couldn’t feel what was going on, it shouldn’t matter. “Things like pelvic exams, rectal exams, or even heroic trauma surgery occur for training purposes when there is no memory, no sensation and no harm to be done [and] society gains a better practitioner of the art of medicine,” a physician in Columbus, Ohio, wrote on Quora, an online forum.
Some doctors argue that they don’t ask for specific consent when they touch a variety of other body parts, and pelvic exams should be no different. Pelvic exams are needed before surgery of the pelvic area, but they have also been given to women undergoing surgery in a different part of the body.
In 2019 a woman told Deseret News in Utah that she had been recovering from stomach surgery when a resident physician mentioned something she had noticed “when we looked at your cervix.” When she asked why the physician had examined her cervix to prepare for stomach surgery, “no one could give her a good answer.”
A ‘positive goal’ doesn’t make it okay
What is missing in many defenses of the practice is any recognition that genitals are the most intimate part of the body, and that a patient’s desire for privacy ought to come first. In a survey of women undergoing gynecologic surgery, 72% expected to be asked for consent before medical students undertook pelvic examinations under anesthesia.
Overruling patients’ concerns about their own privacy is unethical, said Eli Y. Adashi, MD, professor of medical science and former dean of medicine and biological sciences at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Dr. Adashi said the principle of patient autonomy in medical ethics directs that patients must be involved in decision-making about their care – even when caretakers are pursuing a positive goal, such as helping to educate future doctors.
“Conducting pelvic exams on unconscious women without their specific consent is simply untenable and never has been tenable, and it ought to be discontinued if it hasn’t been already,” says Dr. Adashi, who wrote an opinion piece on the issue for JAMA.
Furthermore, it has been shown that ignoring the need to get consent for pelvic exams makes physicians less concerned about getting patient consent in general. A study led by Dr. Ubel found that medical students who had completed an ob.gyn. clerkship thought getting patients’ consent was significantly less important than those who had not completed that clerkship.
Why give pelvic exams to anesthetized women?
Despite the controversy, a number of medical educators continue to direct medical students to perform pelvic exams on anesthetized women. Why is that?
“Pelvic exams are not easy to do,” Dr. Hammoud said. “Learners need to keep working on them; they have to do a lot of them in order to do them well.”
To teach pelvic exams, most medical schools provide standardized patients – paid volunteers who submit to exams and critique the medical student’s work afterwards – but these encounters are limited because of their cost, says Guy Benrubi, MD, professor and emeritus chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville.
He said teaching programs therefore need to supplement exams on standardized patients with exams on unpaid volunteers who provide consent. Programs prefer anesthetized patients, Dr. Benrubi said, because they are easier for novices to work on. “With patients under anesthesia, the muscles are relaxed and it’s easier for learners to detect organs. All the same, you need to get consent.”
Teaching institutions stiffen consent requirements
Faced with growing opposition to pelvic exams without consent, teaching institutions as well as gynecologic educators have recently been tightening their policies.
Dr. Hammoud said she has always informed patients orally about the possibility of medical students performing pelvic exams on them, but now some institutions, including her own, want a more involved process. The university recently began consent in writing for pelvic exams.
In addition, the university also now requires that medical students meet patients before performing pelvic exams and that teaching physicians explain the students’ involvement.
Dr. Hammoud said some institutions now require a separate consent form for pelvic exams, but the University of Michigan simply directs that the possibility of the patient getting a pelvic exam be part of the consent form.
This requirement, called “explicit consent,” was endorsed by APGO. It differs from having a separate consent form for pelvic exams, which would highlight the possibility of a pelvic exam, as many women’s rights activists are calling for.
Why not have a separate form? Dr. Hammoud is concerned that it would unnecessarily alarm patients. “When you point out a certain issue, you’re in effect saying to the patient that this is not normal,” she said, noting that, when asked for consent to do the exams, most women agree to it.
New wave of state laws prompted by renewed concerns
Dr. Hammoud thinks the laws are unnecessary. “These laws are excessive for the vast majority of physicians who practice ethically. The profession should come up with its own standards rather than having a plethora of laws.”
Several of the more recent laws have a broader scope than the original laws. The original laws simply state that medical students or physicians must get informed consent, but they did not stipulate how informed consent should be obtained. (The laws also typically prohibit pelvic exams when surgery will be in a different area of the body.)
The new laws often follow this format, but some go well beyond it. Some also apply to rectal exams (Maine and Maryland), to men as well as women (Utah and Maryland) requires separate consent (Utah), and require consent for all pelvic exams (Florida).
The struggle over Florida’s law
The original Florida bill was drafted in 2019 by state Sen. Lauren Book, a Democrat who is a victims’ rights advocate working with women who have undergone sexual trauma. In written comments for this article, she says not getting consent for pelvic exams is still going on.
“This disturbing practice is commonplace at medical schools and teaching hospitals across the country – including several Florida universities, based on accounts from current and former medical students and faculty,” Sen. Book stated. “At best, these exams have been wrongful learning experiences for medical students or at worst, the equivalent of a sexual assault.”
Dr. Ubel took exception to linking the teaching activities to sexual assault. “I understand why many women would be horrified by this practice, but it’s not as bad as it seems,” he said. “There is nothing sexual or prurient about these exams, and they are motivated purely by a desire to teach people to be better doctors. That said, patients have the right to say, ‘I don’t want it done to me.’ ”
In early 2020, Dr. Benrubi was part of a coalition of medical groups that was trying to influence Sen. Book’s bill as it went through the legislature. Sen. Book’s original bill was relatively mild, “but then, late in the process, it was changed into a more sweeping bill with some unclear language,” he said.
The final version was passed and signed into law by Gov. Ron DeSantis, a conservative Republican, in June.
Dr. Benrubi said that a large number of state legislators, including Sen. Book, have been agreeable to fixing the bill. This was supposed to happen in a special session in the fall, but that never materialized, and so the fix will have to wait until the regular session in early 2021.
“The law should not apply to patients undergoing routine pelvic exams,” Dr. Benrubi said. “It should only apply to women patients under anesthesia.”
But while organized medicine wants to walk back the law, Dr. Book wants to expand it. “This upcoming session, I look forward to working with physicians to continue to hone this new law, and to work toward inclusion for males. Everyone has a right to consent.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“When I was doing ob.gyn. as a med student, the attending would have me do a pelvic right after the patient was under and before we started surgery,” said one participant in an online forum. “We didn’t exactly get permission but it was for teaching purposes.”
Yet others don’t see what the commotion is about. “There are a hundred things that are done during a surgery that don’t require your specific consent (some of them much more ‘humiliating’ than a pelvic exam). ... There’s not really much left to be shy about during a gyn/rectal/prostate surgery, let me put it that way,” one doctor wrote.
However, many physicians are adamantly opposed to the practice, and laws intended to stop or limit it are being enacted throughout the nation.
Renewed concerns have prompted new state laws
A few states have required consent for pelvic exams for many years, beginning with California in 2003. But up until 2019, providing pelvic exams without informed consent was illegal in only six states.
Continuing reports of unauthorized pelvic exams indicate that the practice has not disappeared. University of Michigan professor Maya M. Hammoud, MD, past president of the Association of Professors of Gynecology and Obstetrics, and many others attribute renewed interest in the issue to a 2018 article in the journal Bioethics by Phoebe Friesen, a medical ethicist at McGill University, Montreal, that laid out the ethical arguments against the practice.
Starting in 2019, an outpouring of new state bills have been introduced, and nine more states have passed laws. In addition, 14 other states considered similar bills but did not pass them, in some cases because teaching institutions argued that they were already dealing with the issue. This happened in Connecticut and Massachusetts, after representatives of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., met with legislators.
Laws against the practice have been passed by 15 states, including California, Florida, Illinois, and New York. Some teaching institutions have recently been clamping down on the practice, while many teaching physicians insist that at this point, it has all but ended.
A practice that may still continue
For many years, ethicists, women’s rights groups, state legislators, and organized medicine have been trying to eliminate the practice of unauthorized pelvic exams by medical students. Several key medical groups have come out against it, including the American Medical Association, the Association of American Medical Colleges, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Fifteen years ago, studies found a substantial number of cases, but my sense is that most of that has stopped,” said Dr. Hammoud.
Yet despite these changes, there are some disturbing signs that the practice persists.
“I don’t have data, but anecdotally I see it still going on,” said Peter Ubel, MD, a professor at Duke University, Durham, N.C., who was involved in one of those early studies. “Every so often when I’m making a speech, a medical student tells me about performing a pelvic exam without getting permission.
“Perhaps in some cases the attending [physician] did get permission and didn’t tell the medical student, but that would also be a problem,” Dr. Ubel said. “The medical student should be informed that permission was given. This helps them be sensitive to the need to get consent.”
In a 2019 survey of medical students, 92% said they performed a pelvic exam on an anesthetized female patient, and of those, 61% did so without explicit patient consent.
The survey – involving 101 medical students at seven U.S. medical schools – also found that 11% of the medical students said they were extremely uncomfortable with the practice. But nearly one-third of the medical students said that opting out might jeopardize their grades and future careers.
“I tried to opt out once from doing a pelvic exam when I hadn’t met the patient beforehand,” one of them wrote. “The resident told me no.”
Some physicians defend the practice
Why do many medical students and doctors think that getting consent for pelvic exams is not necessary?
Some argue that patients implicitly give consent when they walk through the doors of a teaching hospital. “Sorry, but you inherently agree to that when you’re seen in an academic teaching hospital,” wrote one participant in a Student Doctor Network forum. “You agree to have residents and medical students participate in your care, not just an attending. If you just want an attending, then you are free to go to a nonteaching hospital. That’s the deal.”
Others argued that since the anesthetized patient couldn’t feel what was going on, it shouldn’t matter. “Things like pelvic exams, rectal exams, or even heroic trauma surgery occur for training purposes when there is no memory, no sensation and no harm to be done [and] society gains a better practitioner of the art of medicine,” a physician in Columbus, Ohio, wrote on Quora, an online forum.
Some doctors argue that they don’t ask for specific consent when they touch a variety of other body parts, and pelvic exams should be no different. Pelvic exams are needed before surgery of the pelvic area, but they have also been given to women undergoing surgery in a different part of the body.
In 2019 a woman told Deseret News in Utah that she had been recovering from stomach surgery when a resident physician mentioned something she had noticed “when we looked at your cervix.” When she asked why the physician had examined her cervix to prepare for stomach surgery, “no one could give her a good answer.”
A ‘positive goal’ doesn’t make it okay
What is missing in many defenses of the practice is any recognition that genitals are the most intimate part of the body, and that a patient’s desire for privacy ought to come first. In a survey of women undergoing gynecologic surgery, 72% expected to be asked for consent before medical students undertook pelvic examinations under anesthesia.
Overruling patients’ concerns about their own privacy is unethical, said Eli Y. Adashi, MD, professor of medical science and former dean of medicine and biological sciences at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Dr. Adashi said the principle of patient autonomy in medical ethics directs that patients must be involved in decision-making about their care – even when caretakers are pursuing a positive goal, such as helping to educate future doctors.
“Conducting pelvic exams on unconscious women without their specific consent is simply untenable and never has been tenable, and it ought to be discontinued if it hasn’t been already,” says Dr. Adashi, who wrote an opinion piece on the issue for JAMA.
Furthermore, it has been shown that ignoring the need to get consent for pelvic exams makes physicians less concerned about getting patient consent in general. A study led by Dr. Ubel found that medical students who had completed an ob.gyn. clerkship thought getting patients’ consent was significantly less important than those who had not completed that clerkship.
Why give pelvic exams to anesthetized women?
Despite the controversy, a number of medical educators continue to direct medical students to perform pelvic exams on anesthetized women. Why is that?
“Pelvic exams are not easy to do,” Dr. Hammoud said. “Learners need to keep working on them; they have to do a lot of them in order to do them well.”
To teach pelvic exams, most medical schools provide standardized patients – paid volunteers who submit to exams and critique the medical student’s work afterwards – but these encounters are limited because of their cost, says Guy Benrubi, MD, professor and emeritus chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville.
He said teaching programs therefore need to supplement exams on standardized patients with exams on unpaid volunteers who provide consent. Programs prefer anesthetized patients, Dr. Benrubi said, because they are easier for novices to work on. “With patients under anesthesia, the muscles are relaxed and it’s easier for learners to detect organs. All the same, you need to get consent.”
Teaching institutions stiffen consent requirements
Faced with growing opposition to pelvic exams without consent, teaching institutions as well as gynecologic educators have recently been tightening their policies.
Dr. Hammoud said she has always informed patients orally about the possibility of medical students performing pelvic exams on them, but now some institutions, including her own, want a more involved process. The university recently began consent in writing for pelvic exams.
In addition, the university also now requires that medical students meet patients before performing pelvic exams and that teaching physicians explain the students’ involvement.
Dr. Hammoud said some institutions now require a separate consent form for pelvic exams, but the University of Michigan simply directs that the possibility of the patient getting a pelvic exam be part of the consent form.
This requirement, called “explicit consent,” was endorsed by APGO. It differs from having a separate consent form for pelvic exams, which would highlight the possibility of a pelvic exam, as many women’s rights activists are calling for.
Why not have a separate form? Dr. Hammoud is concerned that it would unnecessarily alarm patients. “When you point out a certain issue, you’re in effect saying to the patient that this is not normal,” she said, noting that, when asked for consent to do the exams, most women agree to it.
New wave of state laws prompted by renewed concerns
Dr. Hammoud thinks the laws are unnecessary. “These laws are excessive for the vast majority of physicians who practice ethically. The profession should come up with its own standards rather than having a plethora of laws.”
Several of the more recent laws have a broader scope than the original laws. The original laws simply state that medical students or physicians must get informed consent, but they did not stipulate how informed consent should be obtained. (The laws also typically prohibit pelvic exams when surgery will be in a different area of the body.)
The new laws often follow this format, but some go well beyond it. Some also apply to rectal exams (Maine and Maryland), to men as well as women (Utah and Maryland) requires separate consent (Utah), and require consent for all pelvic exams (Florida).
The struggle over Florida’s law
The original Florida bill was drafted in 2019 by state Sen. Lauren Book, a Democrat who is a victims’ rights advocate working with women who have undergone sexual trauma. In written comments for this article, she says not getting consent for pelvic exams is still going on.
“This disturbing practice is commonplace at medical schools and teaching hospitals across the country – including several Florida universities, based on accounts from current and former medical students and faculty,” Sen. Book stated. “At best, these exams have been wrongful learning experiences for medical students or at worst, the equivalent of a sexual assault.”
Dr. Ubel took exception to linking the teaching activities to sexual assault. “I understand why many women would be horrified by this practice, but it’s not as bad as it seems,” he said. “There is nothing sexual or prurient about these exams, and they are motivated purely by a desire to teach people to be better doctors. That said, patients have the right to say, ‘I don’t want it done to me.’ ”
In early 2020, Dr. Benrubi was part of a coalition of medical groups that was trying to influence Sen. Book’s bill as it went through the legislature. Sen. Book’s original bill was relatively mild, “but then, late in the process, it was changed into a more sweeping bill with some unclear language,” he said.
The final version was passed and signed into law by Gov. Ron DeSantis, a conservative Republican, in June.
Dr. Benrubi said that a large number of state legislators, including Sen. Book, have been agreeable to fixing the bill. This was supposed to happen in a special session in the fall, but that never materialized, and so the fix will have to wait until the regular session in early 2021.
“The law should not apply to patients undergoing routine pelvic exams,” Dr. Benrubi said. “It should only apply to women patients under anesthesia.”
But while organized medicine wants to walk back the law, Dr. Book wants to expand it. “This upcoming session, I look forward to working with physicians to continue to hone this new law, and to work toward inclusion for males. Everyone has a right to consent.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is diagnostic hysteroscopy safe in patients with type 2 endometrial cancer?
Among women with type 2 endometrial cancer, diagnostic hysteroscopy may not be associated with increased odds of positive peritoneal cytology at the time of surgical staging or with decreased survival, according to a retrospective study of 127 patients.
a researcher said at the meeting sponsored by AAGL, held virtually this year.
Possible associations between cytology and procedures
Prior research has found that positive peritoneal cytology may correlate with greater likelihood of death among patients with endometrial cancer, and researchers have wondered whether pressure on the uterine cavity during hysteroscopy increases the presence of positive peritoneal cytology. “According to some systematic reviews ... it seems that it does,” said study author Luiz Brito, MD, PhD, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Campinas in Brazil.
Nevertheless, research suggests that “most of the time hysteroscopy does not have a powerful impact on the prognosis of these patients,” he said.
Studies have tended to focus on patients with type 1 endometrial cancer, however. Type 2 endometrial cancer, which is more aggressive, “is scarcely studied,” Dr. Brito said. One retrospective study that focused on type 2 endometrial cancer included 140 patients. Among patients who underwent hysteroscopy, 30% had positive cytology. In comparison, 12% of patients in the curettage group had positive cytology. But the difference in disease-specific survival between groups was not statistically significant, and about 33% of the patients in each group developed a recurrence.
To examine associations between diagnostic methods and outcomes in another group of patients with type 2 endometrial cancer, Dr. Brito and colleagues analyzed data from a hospital registry in Brazil.
The database included 1,183 patients with endometrial cancer between 2002 and 2017, including 235 patients with type 2 endometrial cancer. After excluding patients with synchronous tumor and those who did not undergo surgery or did not have peritoneal cytology performed, 127 patients remained for the analysis. The study included follow-up to December 2019.
The researchers compared the prevalence of positive peritoneal cytology among 43 patients who underwent hysteroscopy with that among 84 patients who underwent curettage. The groups had similar baseline characteristics.
Positive peritoneal cytology was more common in the curettage group than in the hysteroscopy group (10.7% vs. 4.6%), although the difference was not statistically significant. Lymphovascular invasion and advanced surgical staging were more common in the curettage group.
In a multivariate analysis, older age and advanced cancer staging were the only factors associated with decreased disease-free survival. Age, advanced cancer staging, and vascular invasion were associated with decreased disease-specific survival.
The researchers also had considered factors such as peritoneal cytology, diagnostic method, age of menarche, menopause time, parity, comorbidities, smoking status, body mass index, abnormal uterine bleeding, histological type, and adjuvant treatment.
A limitation of the study is that it relied on data from a public health system that often has long wait times for diagnosis and treatment, Dr. Brito noted.
Some doctors may forgo cytology
The available research raises questions about the role and relevance of peritoneal cytology in caring for patients with endometrial cancer, René Pareja, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Instituto Nacional de Cancerología, Bogotá, Colombia, said in a discussion following the presentation.
Peritoneal cytology has not been part of endometrial cancer staging since 2009, Dr. Pareja said. Still, guidelines recommend that surgeons collect cytology during surgical staging, with the idea that the results could inform adjuvant treatment decisions.
“Peritoneal cytology is recommended in the guidelines, but there are no recommendations on how to proceed if it is positive,” Dr. Pareja said. “While some gynecologic oncologists continue to take cytology during endometrial cancer staging, some have stopped doing so. And in Colombia, most of us are not performing pelvic cytology.”
Although some studies indicate that hysteroscopy may increase the rate of positive cytology, positive cytology may not be associated with worse oncological outcomes independent of other risk factors for recurrence, said Dr. Pareja.
So far, studies have been retrospective. Furthermore, the sensitivity and specificity of pelvic cytology tests are not 100%. “Should we continue performing pelvic cytology given the results of this and other studies?” Dr. Pareja asked.
Despite limited knowledge about this variable, physicians may want to be aware if a patient has positive cytology, Dr. Brito suggested. “At least it will give us some red flags so we can be attentive to these patients.”
If researchers were to design a prospective study that incorporates hysteroscopic variables, it could provide more complete answers about the relationship between hysteroscopy and peritoneal cytology and clarify the importance of positive cytology, Dr. Brito said.
Dr. Brito had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Pareja disclosed consulting for Johnson & Johnson.
SOURCE: Oliveira Brito LG et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2020.08.356.
Among women with type 2 endometrial cancer, diagnostic hysteroscopy may not be associated with increased odds of positive peritoneal cytology at the time of surgical staging or with decreased survival, according to a retrospective study of 127 patients.
a researcher said at the meeting sponsored by AAGL, held virtually this year.
Possible associations between cytology and procedures
Prior research has found that positive peritoneal cytology may correlate with greater likelihood of death among patients with endometrial cancer, and researchers have wondered whether pressure on the uterine cavity during hysteroscopy increases the presence of positive peritoneal cytology. “According to some systematic reviews ... it seems that it does,” said study author Luiz Brito, MD, PhD, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Campinas in Brazil.
Nevertheless, research suggests that “most of the time hysteroscopy does not have a powerful impact on the prognosis of these patients,” he said.
Studies have tended to focus on patients with type 1 endometrial cancer, however. Type 2 endometrial cancer, which is more aggressive, “is scarcely studied,” Dr. Brito said. One retrospective study that focused on type 2 endometrial cancer included 140 patients. Among patients who underwent hysteroscopy, 30% had positive cytology. In comparison, 12% of patients in the curettage group had positive cytology. But the difference in disease-specific survival between groups was not statistically significant, and about 33% of the patients in each group developed a recurrence.
To examine associations between diagnostic methods and outcomes in another group of patients with type 2 endometrial cancer, Dr. Brito and colleagues analyzed data from a hospital registry in Brazil.
The database included 1,183 patients with endometrial cancer between 2002 and 2017, including 235 patients with type 2 endometrial cancer. After excluding patients with synchronous tumor and those who did not undergo surgery or did not have peritoneal cytology performed, 127 patients remained for the analysis. The study included follow-up to December 2019.
The researchers compared the prevalence of positive peritoneal cytology among 43 patients who underwent hysteroscopy with that among 84 patients who underwent curettage. The groups had similar baseline characteristics.
Positive peritoneal cytology was more common in the curettage group than in the hysteroscopy group (10.7% vs. 4.6%), although the difference was not statistically significant. Lymphovascular invasion and advanced surgical staging were more common in the curettage group.
In a multivariate analysis, older age and advanced cancer staging were the only factors associated with decreased disease-free survival. Age, advanced cancer staging, and vascular invasion were associated with decreased disease-specific survival.
The researchers also had considered factors such as peritoneal cytology, diagnostic method, age of menarche, menopause time, parity, comorbidities, smoking status, body mass index, abnormal uterine bleeding, histological type, and adjuvant treatment.
A limitation of the study is that it relied on data from a public health system that often has long wait times for diagnosis and treatment, Dr. Brito noted.
Some doctors may forgo cytology
The available research raises questions about the role and relevance of peritoneal cytology in caring for patients with endometrial cancer, René Pareja, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Instituto Nacional de Cancerología, Bogotá, Colombia, said in a discussion following the presentation.
Peritoneal cytology has not been part of endometrial cancer staging since 2009, Dr. Pareja said. Still, guidelines recommend that surgeons collect cytology during surgical staging, with the idea that the results could inform adjuvant treatment decisions.
“Peritoneal cytology is recommended in the guidelines, but there are no recommendations on how to proceed if it is positive,” Dr. Pareja said. “While some gynecologic oncologists continue to take cytology during endometrial cancer staging, some have stopped doing so. And in Colombia, most of us are not performing pelvic cytology.”
Although some studies indicate that hysteroscopy may increase the rate of positive cytology, positive cytology may not be associated with worse oncological outcomes independent of other risk factors for recurrence, said Dr. Pareja.
So far, studies have been retrospective. Furthermore, the sensitivity and specificity of pelvic cytology tests are not 100%. “Should we continue performing pelvic cytology given the results of this and other studies?” Dr. Pareja asked.
Despite limited knowledge about this variable, physicians may want to be aware if a patient has positive cytology, Dr. Brito suggested. “At least it will give us some red flags so we can be attentive to these patients.”
If researchers were to design a prospective study that incorporates hysteroscopic variables, it could provide more complete answers about the relationship between hysteroscopy and peritoneal cytology and clarify the importance of positive cytology, Dr. Brito said.
Dr. Brito had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Pareja disclosed consulting for Johnson & Johnson.
SOURCE: Oliveira Brito LG et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2020.08.356.
Among women with type 2 endometrial cancer, diagnostic hysteroscopy may not be associated with increased odds of positive peritoneal cytology at the time of surgical staging or with decreased survival, according to a retrospective study of 127 patients.
a researcher said at the meeting sponsored by AAGL, held virtually this year.
Possible associations between cytology and procedures
Prior research has found that positive peritoneal cytology may correlate with greater likelihood of death among patients with endometrial cancer, and researchers have wondered whether pressure on the uterine cavity during hysteroscopy increases the presence of positive peritoneal cytology. “According to some systematic reviews ... it seems that it does,” said study author Luiz Brito, MD, PhD, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Campinas in Brazil.
Nevertheless, research suggests that “most of the time hysteroscopy does not have a powerful impact on the prognosis of these patients,” he said.
Studies have tended to focus on patients with type 1 endometrial cancer, however. Type 2 endometrial cancer, which is more aggressive, “is scarcely studied,” Dr. Brito said. One retrospective study that focused on type 2 endometrial cancer included 140 patients. Among patients who underwent hysteroscopy, 30% had positive cytology. In comparison, 12% of patients in the curettage group had positive cytology. But the difference in disease-specific survival between groups was not statistically significant, and about 33% of the patients in each group developed a recurrence.
To examine associations between diagnostic methods and outcomes in another group of patients with type 2 endometrial cancer, Dr. Brito and colleagues analyzed data from a hospital registry in Brazil.
The database included 1,183 patients with endometrial cancer between 2002 and 2017, including 235 patients with type 2 endometrial cancer. After excluding patients with synchronous tumor and those who did not undergo surgery or did not have peritoneal cytology performed, 127 patients remained for the analysis. The study included follow-up to December 2019.
The researchers compared the prevalence of positive peritoneal cytology among 43 patients who underwent hysteroscopy with that among 84 patients who underwent curettage. The groups had similar baseline characteristics.
Positive peritoneal cytology was more common in the curettage group than in the hysteroscopy group (10.7% vs. 4.6%), although the difference was not statistically significant. Lymphovascular invasion and advanced surgical staging were more common in the curettage group.
In a multivariate analysis, older age and advanced cancer staging were the only factors associated with decreased disease-free survival. Age, advanced cancer staging, and vascular invasion were associated with decreased disease-specific survival.
The researchers also had considered factors such as peritoneal cytology, diagnostic method, age of menarche, menopause time, parity, comorbidities, smoking status, body mass index, abnormal uterine bleeding, histological type, and adjuvant treatment.
A limitation of the study is that it relied on data from a public health system that often has long wait times for diagnosis and treatment, Dr. Brito noted.
Some doctors may forgo cytology
The available research raises questions about the role and relevance of peritoneal cytology in caring for patients with endometrial cancer, René Pareja, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Instituto Nacional de Cancerología, Bogotá, Colombia, said in a discussion following the presentation.
Peritoneal cytology has not been part of endometrial cancer staging since 2009, Dr. Pareja said. Still, guidelines recommend that surgeons collect cytology during surgical staging, with the idea that the results could inform adjuvant treatment decisions.
“Peritoneal cytology is recommended in the guidelines, but there are no recommendations on how to proceed if it is positive,” Dr. Pareja said. “While some gynecologic oncologists continue to take cytology during endometrial cancer staging, some have stopped doing so. And in Colombia, most of us are not performing pelvic cytology.”
Although some studies indicate that hysteroscopy may increase the rate of positive cytology, positive cytology may not be associated with worse oncological outcomes independent of other risk factors for recurrence, said Dr. Pareja.
So far, studies have been retrospective. Furthermore, the sensitivity and specificity of pelvic cytology tests are not 100%. “Should we continue performing pelvic cytology given the results of this and other studies?” Dr. Pareja asked.
Despite limited knowledge about this variable, physicians may want to be aware if a patient has positive cytology, Dr. Brito suggested. “At least it will give us some red flags so we can be attentive to these patients.”
If researchers were to design a prospective study that incorporates hysteroscopic variables, it could provide more complete answers about the relationship between hysteroscopy and peritoneal cytology and clarify the importance of positive cytology, Dr. Brito said.
Dr. Brito had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Pareja disclosed consulting for Johnson & Johnson.
SOURCE: Oliveira Brito LG et al. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2020 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2020.08.356.
FROM AAGL GLOBAL CONGRESS
Etonogestrel implants may be bent, fractured by trauma or during sports
In 2017, Global Pediatric Health published a case report series associated with the use of long-acting reversible contraceptives, specifically the etonogestrel implant.
In November 2020, the makers of the etonogestrel implant (Merck) recommended a change in practice with the release of a notice to health care providers certified in the training of this product. This mass marketing blast included an updated warning and cautions for prescribers as well as patient information on the potential risks of migration, fracture, and bent devices attributable to trauma or sports. “Broken or Bent Implant (Section 5.16). The addition of the following underlined language: “There have been reports of broken or bent implants, which may be related to external forces (e.g., manipulation of the implant or contact sports) while in the patient’s arm. There have also been reports of migration of a broken implant fragment within the arm.”
Clearly the etonogestrel subdermal hormonal implant is an effective form of contraception and particularly beneficial in nonadherent sexually active teens who struggle to remember oral contraceptives. But it is important to be aware of this alert. Little is known about the type of trauma or rate of external force required to cause migration, fracture, or bend implants. This update requires adequate counseling of potential risks and complications of the etonogestrel implant, including the risk of migration, fracture, or bent devices specifically in the event of contact sports and trauma.
Ms. Thew is medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Ms. Thew at [email protected].
In 2017, Global Pediatric Health published a case report series associated with the use of long-acting reversible contraceptives, specifically the etonogestrel implant.
In November 2020, the makers of the etonogestrel implant (Merck) recommended a change in practice with the release of a notice to health care providers certified in the training of this product. This mass marketing blast included an updated warning and cautions for prescribers as well as patient information on the potential risks of migration, fracture, and bent devices attributable to trauma or sports. “Broken or Bent Implant (Section 5.16). The addition of the following underlined language: “There have been reports of broken or bent implants, which may be related to external forces (e.g., manipulation of the implant or contact sports) while in the patient’s arm. There have also been reports of migration of a broken implant fragment within the arm.”
Clearly the etonogestrel subdermal hormonal implant is an effective form of contraception and particularly beneficial in nonadherent sexually active teens who struggle to remember oral contraceptives. But it is important to be aware of this alert. Little is known about the type of trauma or rate of external force required to cause migration, fracture, or bend implants. This update requires adequate counseling of potential risks and complications of the etonogestrel implant, including the risk of migration, fracture, or bent devices specifically in the event of contact sports and trauma.
Ms. Thew is medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Ms. Thew at [email protected].
In 2017, Global Pediatric Health published a case report series associated with the use of long-acting reversible contraceptives, specifically the etonogestrel implant.
In November 2020, the makers of the etonogestrel implant (Merck) recommended a change in practice with the release of a notice to health care providers certified in the training of this product. This mass marketing blast included an updated warning and cautions for prescribers as well as patient information on the potential risks of migration, fracture, and bent devices attributable to trauma or sports. “Broken or Bent Implant (Section 5.16). The addition of the following underlined language: “There have been reports of broken or bent implants, which may be related to external forces (e.g., manipulation of the implant or contact sports) while in the patient’s arm. There have also been reports of migration of a broken implant fragment within the arm.”
Clearly the etonogestrel subdermal hormonal implant is an effective form of contraception and particularly beneficial in nonadherent sexually active teens who struggle to remember oral contraceptives. But it is important to be aware of this alert. Little is known about the type of trauma or rate of external force required to cause migration, fracture, or bend implants. This update requires adequate counseling of potential risks and complications of the etonogestrel implant, including the risk of migration, fracture, or bent devices specifically in the event of contact sports and trauma.
Ms. Thew is medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Ms. Thew at [email protected].
Facing systemic racism in health care: Inequities in medical education
Finding inspiration among life’s challenges
Barbara Levy, MD: I am fortunate to have met Pierre serendipitously at a training that we were both attending and was impressed by Dr. Johnson’s life story, his passion and commitment, and his dedication—not only to his personal career but also to raising up other young men of color by trying to break down barriers that face them. His life story highlights those areas of systemic and structural problems that all of us together need to address if we are going to make any progress.
Pierre Johnson, MD: Thank you, Barbara. A little about myself: I am a board-certified ObGyn, and I specialize in minimally invasive surgery. I was born on the South side of Chicago, experiencing gang violence, drugs, and substandard, underserved schools. Long story short, I had a very rough upbringing. I had a single mom and several different issues at home. I am the oldest of 5 siblings, and life was tough.
But I knew that I wanted to do something different with my life. I saw that there was a need in my community as far as health care was concerned, in particular women’s health and childbirth. I knew early on that I wanted to be an ObGyn, and the reason had a lot to do with The Cosby Show. It was the only example of a positive, successful Black man that I saw. No one graduated from college in my family. There weren’t any models of young Black excellence around me. Saying that I wanted to be a doctor planted a seed. I was 9 when my mom became pregnant with my first sibling, and it was fascinating to me. The physiology of pregnancy, and eventually childbirth, was extremely fascinating to me; it set me off on my journey to be an ObGyn.
As I got older, things didn’t get any easier. I went to high school in one of the toughest areas on the South side of Chicago. Gang violence, and violence in and of itself, were all around me, but I was able to stay focused. I went on to Xavier University in Louisiana.
Dr. Levy: There are some important things that I learned from your book and from talking to you at our first meeting. Your mom’s ObGyn, when she was pregnant with your next youngest sibling, was also a Black ObGyn. He took some time to take you under wing?
Dr. Johnson: He did. My mom’s ObGyn was a Black man. Other than The Cosby Show, that’s the only time I saw something like that. When I spoke to him, he really took the time to answer my questions and show me that he was like me; he wasn’t just a far-off mythical person, or something that I could not obtain.
Continue to: Seeing is believing when it comes to success...
Seeing is believing when it comes to success
Dr. Levy: Do you think it was important to have a role model who wasn’t a sports star?
Dr. Johnson: If you can’t see it, you can’t achieve it. He took his time to really talk to me, and it’s the little things for kids that go a long way in their life experience. I still have a relationship with him to this day. How he handled me as a kid made me realize that this is something that I could do. That was extremely important for me.
Dr. Levy: One of the structural things I think we need to point out is that the ability to see yourself as someone successful is critical. When we see 1,000 images a day and they are all White, and they are all so different from where we are that it gets incorporated into our sense of being. I think that’s really difficult for those of us of with privilege to understand what that privilege is.
Dr. Johnson: Absolutely, and I’ll even go further. In residency, 2 White females were my classmates, and both of their parents were doctors. They had grandparents who were doctors. My mom was addicted to drugs; my father was not around. They had been talking medicine since they were 5. You have to make things equitable, but in medicine it’s really not equitable. In medicine, what we don’t realize is that there is an importance for all aspects of someone’s upbringing and environment, and it’s not just what they can regurgitate on a standardized test. If a patient can’t relate to you and tell you what is wrong with them, how can you adequately treat them?
Dr. Levy: Even if they are trying to tell me, but I can’t hear it because I don’t have the language and I don’t have the background. There are really good data to show, in fact, that Black male physicians do a better job at engaging Black men to manage their hypertension.1 When we look at the inequities in birth outcomes for women of color, indigenous women and Black women, there’s evidence that providers who come from a similar background do a better job.
Dr. Johnson: There was the study of Black infants that just came out about them dying at a 3-time higher rate in non-Black physicians’ hands.2 These things need to be recognized. They need to be discussed, and they need to be identified as issues and then, realistically, we need to start talking about solutions, not get offended by what actual statistics are saying.
Foundational inequities in education
Dr. Levy: To address some of the barriers that you faced: I know that you went to a high school that was not geared toward pushing students into professional careers. Your colleagues, however, had educations that prepared them for the standardized tests and other things that they would face academically.
Dr. Johnson: People think I am kidding when I say it, but when I went into college, I didn’t know what a periodic table was. I saw it, but I had no idea what these things meant. I didn’t have any sciences or any AP classes in high school. I did well, but grades are smoke and mirrors. The true test of medicine comes with testing. From the MCATs to the boards, every step of the way there is a standardized test.
Knowledge is something that you can obtain, but test taking is a cultivated skill that happens from a very early age. Trying to teach an adult or someone in their late teens a skill that they should have learned as a kid is difficult. For me, I did not have that, so I had to program myself. I had to learn how to fundamentally take tests as an adult, where most people understand how to do that going into college and professional school.
Dr. Levy: I was impressed with your resilience. I think all of us as human beings, if we fail a test, we take it personally and think it’s about our lack of knowledge. One of the insights that you came to was that failure on those things was not that you didn’t study hard enough. In fact, you probably studied 4 times harder than most other people. You had the knowledge. Being able to get that knowledge into a standardized structured test score was the huge challenge for you.
Dr. Johnson: That’s it. I can remember taking the MCAT, and if you looked at the step 1 book, I could regurgitate to you everything on that page. However, it’s not a test about do you know it or not. It’s an understanding of the English language and how to break things down to make things fit into particular scenarios.
Continue to: A college experience focused on growth and exposure...
A college experience focused on growth and exposure
Dr. Levy: I was impressed by the distinction between your experience at Xavier University where there was a lot of support and guidance and help in your premed program, and what happened to you when you hit medical school.
Dr. Johnson: Xavier University in Louisiana is the number 1 institution in the country for getting minorities into professional school. They understand that they have kids that are brilliant but underprepared, and just have not had the background to actually tackle some of these tough curriculums. I always had good grades in school. But by not being challenged, I didn’t know what I didn’t really know. So now that I was seeing biology, chemistry for the first time, and trying to tackle it; there’s a failure point. I didn’t know how to take tests, and I didn’t know how to study properly. The harder I tried, the worse things got for me.
Xavier has seen that story a multitude of times. If I went to a bigger or predominantly White university, a counselor would have told me, “Well, medicine’s maybe not for you. You can’t handle a premed curriculum.” Instead, I said, “Listen, I’m studying. I’m doing all of these things, and I’m not hacking it.” And they broke it down: “Let’s get you into study groups with kids that have had these type of AP classes before. We’ll have you watch how they study,” and everything started to click. That facilitation of how to adjust to this curriculum was a godsend. It’s the only reason I’m here. I am a prime example of being brilliant enough to be able to do it, but needing the infrastructure and a system set up.
Dr. Levy: There’s a great book by Carol Dweck called Mindset that talks about education of young kids and putting them into silos so early in life; the brilliant kids go into the AP courses and the rest are labeled as inadequate. It’s assumed in a fixed mindset based on their heredity and IQ, and not based on the fact that they have not been exposed to the right things.
Xavier was growing you into the man who could, in fact, do all of those things. I think that is one of the systemic and structural issues that we have—that fixed mindset that frames a kid who is not succeeding as therefore unable to succeed, as opposed to framing that child as not having the correct tools.
New tribulations of medical school
Dr. Johnson: Absolutely. I think what Xavier did for me is to at least let me understand what I needed to do, how to comprehend and retain information, which I never had been exposed to before. Those years were very important to establishing a foundation. When going to medical school, it was like, “There’s no more excuses. What could be the problem now?” Well, now let’s talk about taking tests—a whole different skill. Xavier focused on getting me to understand how to structure my thought process and knowledge base. In medical school I had to apply those skills (because if you can’t apply them, there’s no fit).
My second through fourth year of medical school, I was the only African-American kid in my class. I was spending 20-hour days sometimes just studying, trying to overcompensate by knowing as much as I possibly could and thinking that would propel me from the test-taking standpoint. Even though I didn’t have a lot of classmates in medical school that looked like me, I did have mentors that looked similarly, who really saw potential in me. Dr. Frederick Horvath, a nephrologist in Peoria said, “What are you doing? I want you to get out of these books, and let’s go out to lunch.”
He ended up buying me some instrumental books, really talked to me, listening to my background and understanding how driven I was as a person. He took me under his wing for the rest of medical school and said, “This is how you navigate through these spaces. Yes, you need to have a fund of knowledge to be able to take these tests, but you need to start understanding how to apply it to these questions.” I’m forever grateful to Dr. Horvath for doing that because it was a point in time where I was lost and struggling.
Continue to: Hitting a stride but facing racism head-on...
Hitting a stride but facing racism head-on
Dr. Levy: You talk about the systemic and pervasive racism that was on the wards when you hit them in fourth year. If you don’t mind sharing just a little bit of that, it would help people reading this to have a better understanding of the kinds of barriers that are out there.
Dr. Johnson: Even when I talk about it today, it bothers me.
I went to medical school in Peoria, Illinois, not far from the home of the Ku Klux Klan. At that time, once you got out of Chicago it was a very brutal place, with systemic racism throughout. I was a young Black kid going through a process that not many young Black kids from the South side of Chicago go through, and you had people who had never seen anyone like me. When I was going through my clinical rotations, I knew what I was up against. I was dressed “to the T” every day, arriving early, leaving late, trying to answer questions. I would look at the evaluations, and they would be disparaging. I would look at my counterparts, how their evaluations were, and how people would respond to them, and it would be completely different.
Surgery was the part of ObGyn that I really grew to love more than anything, even more than obstetrics. When general surgery came, I wanted to take it very seriously and learn as much as I possibly could. From the beginning, I knew there was a problem because the chief resident, an older White man, wouldn’t look me in the eye or talk to me. He would make disparaging remarks. The thing that stuck out in my mind the most was when I was in the operating room transporting patients, just like a medical student did, and he came up behind me and said, “You know, Pierre, this is where a small mind and a strong back come into play.” For me, it took me to a place where I had to corral my emotions and thoughts because I just wanted to lash out and just tell him how racist and horrible that was for him to say that to me. I explained this to the powers that be, the director of the department, and they basically blew it off to the side.
When it came down to the end of the evaluation period, I passed with flying colors. But they gave me an incomplete because of that chief resident and his remarks on my evaluations. He had 3 pages of report about me as a person and as a student. He said that he had difficulty in expressing his opinions about me because of possible cultural biases that he may have had. He put “cultural biases” in an evaluation, and they looked at that and said that was enough for me to have to remediate my time. I was required to do an extra month in Pontiac, Illinois, which is even more rural than Peoria, because of a racist person that did not give me a fair opportunity because I was Black.
Like everything else in life, it was a learning experience. It’s why I fight so hard today. It’s why I’m so passionate about equity, not only in medicine but also in all aspects of society. It shows why we have police brutality and Black men dying in the streets. It shows how this happens because there are cultural and implicit biases that play out in every part of life, and we are not honest about it. Until we are honest about it and until we say that this is happening and there is something that needs to be done to address it, it’s going to continue to happen. That is my fight.
Exposing the unspoken power struggle
Dr. Levy: I couldn’t agree more. Attributing things like that to the individual, where you talk about a White man in power and a power structure that didn’t literally physically beat you but did beat you into submission. You talk about how to succeed in medical school, and how you had to suck it up and submit to something that was incredibly unfair. You understood, you were old enough, mature enough, to understand that if you fought back, you were going to lose. The only opportunity you had was to submit to that inequity and push forward.
Dr. Johnson: When I did try to fight, the chair of the department told me that either I accept the consequences or I would not graduate from medical school and be forced to do another year. That struck a chord with me. I think that happens a lot in our society, and it needs to be exposed.
Past experiences reflected in today’s society
Dr. Levy: Can you talk about what you faced in your ObGyn residency in terms of the systemic pushback, people not taking your orders, people questioning you. I know that I have heard that a great deal, and I experienced that myself as a woman.
Dr. Johnson: We look at the things that are happening now, everything from George Floyd’s murder to Colin Kaepernick taking a knee. These things are 10 years past when I first started residency. The year before I started residency, there was a noose hanging on the capitol lawn of Springfield, Illinois’ capital city. There’s systemic racism and hatred there. When I first started on the wards of my first year of ObGyn, again, I was the very first Black resident of my program’s history. Nobody could relate to me.
I went from a year-long general surgery internship at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, DC, to ObGyn residency. In the first 2 months, there were complaints of, “He’s not answering his pages. He’s not being prompt.” I went to my program director and said, “Listen, I have never had one complaint like this. There’s a problem here. And there’s a problem when I’m on the floor: When trying to give orders to nurses, they’re not taking them. I had to tell a couple of nurses, ‘I’m Dr. Johnson. Don’t call me by my first name, especially not in front of patients.’”
My director was just not hearing me, because the entire scenario was something they had never been exposed to. Systemic racism is real, and unless you experience it, it’s very difficult to accept that it is happening. But biases happen when you are not cognizant. People are used to things a certain way. Things play out in the media that make your mind think a certain way, and you don’t even realize it. You may not even want to be that way.
Continue to: Unconscious bias is a barrier to ensuring equity...
Unconscious bias is a barrier to ensuring equity
Dr. Levy: One very important point you just made is that we as the system need to be able to recognize those unconscious things, the language that we use, the disparaging remarks, the things that put people down, as well as the things that keep people out of promotion.
There are some interesting data about both race and gender and the language that we use when we write recommendations for people, that we do things unconsciously. The big message to all of us at the end is to open our minds to where those things can occur. For myself, professionally, I keep a list of words that I use when I write recommendations. I measure myself to ensure that I am using the same language for men and women, for Black and White. I think we need to overcome the system and the structure to create real equity—not equality but equity.
It begins with being real about the issues
Dr. Johnson: It’s a bigger problem than the existence of bias and racism. I think these are systemic issues that have been cultivated over centuries that have never been addressed. The true issue is that we deny that these are problems and refuse to talk about it because it makes us uncomfortable. To truly make things more equitable, we have to push our levels of comfort to be able to talk about things in a healthy manner, be open and transparent, and to start to understand how we are thinking about certain things. When you can see it, you can start to implement changes and start to change mentalities and thought processes.
For me, people say, “You don’t look like a doctor.” I get that all the time—because I have tattoos and earrings. I wear my hair in a mohawk. The image of what success looks like has been manifested through our media and culture, and it has imprinted on our minds as to how things are supposed to be. If someone doesn’t fit those molds, we start to shun them out, or we start to exhibit biases against those things. What I am trying to do is change that thought process of what a successful or a professional person looks like. It doesn’t have a look. It is not a White or Black thing. It’s an intellect, a mindset, a way of living. You have to treat every person as an individual and take all the biases out of it and understand where they are coming from and what they have to offer to the profession.
Dr. Levy: I personally was so impressed by you when I met you. I was impressed by the tattoos and the earrings, and my initial response to them was exactly that biased, “Oh, who is this person?” I checked that at the door, listened to you, and was really impressed at your surgical skill, your knowledge, your background. I am really grateful that you have been willing to spend the time to share that with everyone.
Dr. Johnson: Thank you for this discussion.
To watch the full interview between Drs. Levy and Johnson, visit: https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/article/228507/facing-systemic-racism-health-care-inequities-medical-education. ●
- The Pulse of Perseverance:
Three Black Doctors on Their Journey to Success Pierre Johnson, MD; Maxime Madhere, MD; and Joseph Semien Jr, MD - Mindset:
The New Psychology of Success
Carol S. Dweck
- Benkert R, Peters R, Tate N, et al. Trust of nurse practitioners and physicians among African Americans with hypertension. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008;20:273-280.
- Greenwood BN, Hardeman RR, Huang L, et al. Physician– patient racial concordance and disparities in birthing mortality for newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020; 117:21194-21200.
Finding inspiration among life’s challenges
Barbara Levy, MD: I am fortunate to have met Pierre serendipitously at a training that we were both attending and was impressed by Dr. Johnson’s life story, his passion and commitment, and his dedication—not only to his personal career but also to raising up other young men of color by trying to break down barriers that face them. His life story highlights those areas of systemic and structural problems that all of us together need to address if we are going to make any progress.
Pierre Johnson, MD: Thank you, Barbara. A little about myself: I am a board-certified ObGyn, and I specialize in minimally invasive surgery. I was born on the South side of Chicago, experiencing gang violence, drugs, and substandard, underserved schools. Long story short, I had a very rough upbringing. I had a single mom and several different issues at home. I am the oldest of 5 siblings, and life was tough.
But I knew that I wanted to do something different with my life. I saw that there was a need in my community as far as health care was concerned, in particular women’s health and childbirth. I knew early on that I wanted to be an ObGyn, and the reason had a lot to do with The Cosby Show. It was the only example of a positive, successful Black man that I saw. No one graduated from college in my family. There weren’t any models of young Black excellence around me. Saying that I wanted to be a doctor planted a seed. I was 9 when my mom became pregnant with my first sibling, and it was fascinating to me. The physiology of pregnancy, and eventually childbirth, was extremely fascinating to me; it set me off on my journey to be an ObGyn.
As I got older, things didn’t get any easier. I went to high school in one of the toughest areas on the South side of Chicago. Gang violence, and violence in and of itself, were all around me, but I was able to stay focused. I went on to Xavier University in Louisiana.
Dr. Levy: There are some important things that I learned from your book and from talking to you at our first meeting. Your mom’s ObGyn, when she was pregnant with your next youngest sibling, was also a Black ObGyn. He took some time to take you under wing?
Dr. Johnson: He did. My mom’s ObGyn was a Black man. Other than The Cosby Show, that’s the only time I saw something like that. When I spoke to him, he really took the time to answer my questions and show me that he was like me; he wasn’t just a far-off mythical person, or something that I could not obtain.
Continue to: Seeing is believing when it comes to success...
Seeing is believing when it comes to success
Dr. Levy: Do you think it was important to have a role model who wasn’t a sports star?
Dr. Johnson: If you can’t see it, you can’t achieve it. He took his time to really talk to me, and it’s the little things for kids that go a long way in their life experience. I still have a relationship with him to this day. How he handled me as a kid made me realize that this is something that I could do. That was extremely important for me.
Dr. Levy: One of the structural things I think we need to point out is that the ability to see yourself as someone successful is critical. When we see 1,000 images a day and they are all White, and they are all so different from where we are that it gets incorporated into our sense of being. I think that’s really difficult for those of us of with privilege to understand what that privilege is.
Dr. Johnson: Absolutely, and I’ll even go further. In residency, 2 White females were my classmates, and both of their parents were doctors. They had grandparents who were doctors. My mom was addicted to drugs; my father was not around. They had been talking medicine since they were 5. You have to make things equitable, but in medicine it’s really not equitable. In medicine, what we don’t realize is that there is an importance for all aspects of someone’s upbringing and environment, and it’s not just what they can regurgitate on a standardized test. If a patient can’t relate to you and tell you what is wrong with them, how can you adequately treat them?
Dr. Levy: Even if they are trying to tell me, but I can’t hear it because I don’t have the language and I don’t have the background. There are really good data to show, in fact, that Black male physicians do a better job at engaging Black men to manage their hypertension.1 When we look at the inequities in birth outcomes for women of color, indigenous women and Black women, there’s evidence that providers who come from a similar background do a better job.
Dr. Johnson: There was the study of Black infants that just came out about them dying at a 3-time higher rate in non-Black physicians’ hands.2 These things need to be recognized. They need to be discussed, and they need to be identified as issues and then, realistically, we need to start talking about solutions, not get offended by what actual statistics are saying.
Foundational inequities in education
Dr. Levy: To address some of the barriers that you faced: I know that you went to a high school that was not geared toward pushing students into professional careers. Your colleagues, however, had educations that prepared them for the standardized tests and other things that they would face academically.
Dr. Johnson: People think I am kidding when I say it, but when I went into college, I didn’t know what a periodic table was. I saw it, but I had no idea what these things meant. I didn’t have any sciences or any AP classes in high school. I did well, but grades are smoke and mirrors. The true test of medicine comes with testing. From the MCATs to the boards, every step of the way there is a standardized test.
Knowledge is something that you can obtain, but test taking is a cultivated skill that happens from a very early age. Trying to teach an adult or someone in their late teens a skill that they should have learned as a kid is difficult. For me, I did not have that, so I had to program myself. I had to learn how to fundamentally take tests as an adult, where most people understand how to do that going into college and professional school.
Dr. Levy: I was impressed with your resilience. I think all of us as human beings, if we fail a test, we take it personally and think it’s about our lack of knowledge. One of the insights that you came to was that failure on those things was not that you didn’t study hard enough. In fact, you probably studied 4 times harder than most other people. You had the knowledge. Being able to get that knowledge into a standardized structured test score was the huge challenge for you.
Dr. Johnson: That’s it. I can remember taking the MCAT, and if you looked at the step 1 book, I could regurgitate to you everything on that page. However, it’s not a test about do you know it or not. It’s an understanding of the English language and how to break things down to make things fit into particular scenarios.
Continue to: A college experience focused on growth and exposure...
A college experience focused on growth and exposure
Dr. Levy: I was impressed by the distinction between your experience at Xavier University where there was a lot of support and guidance and help in your premed program, and what happened to you when you hit medical school.
Dr. Johnson: Xavier University in Louisiana is the number 1 institution in the country for getting minorities into professional school. They understand that they have kids that are brilliant but underprepared, and just have not had the background to actually tackle some of these tough curriculums. I always had good grades in school. But by not being challenged, I didn’t know what I didn’t really know. So now that I was seeing biology, chemistry for the first time, and trying to tackle it; there’s a failure point. I didn’t know how to take tests, and I didn’t know how to study properly. The harder I tried, the worse things got for me.
Xavier has seen that story a multitude of times. If I went to a bigger or predominantly White university, a counselor would have told me, “Well, medicine’s maybe not for you. You can’t handle a premed curriculum.” Instead, I said, “Listen, I’m studying. I’m doing all of these things, and I’m not hacking it.” And they broke it down: “Let’s get you into study groups with kids that have had these type of AP classes before. We’ll have you watch how they study,” and everything started to click. That facilitation of how to adjust to this curriculum was a godsend. It’s the only reason I’m here. I am a prime example of being brilliant enough to be able to do it, but needing the infrastructure and a system set up.
Dr. Levy: There’s a great book by Carol Dweck called Mindset that talks about education of young kids and putting them into silos so early in life; the brilliant kids go into the AP courses and the rest are labeled as inadequate. It’s assumed in a fixed mindset based on their heredity and IQ, and not based on the fact that they have not been exposed to the right things.
Xavier was growing you into the man who could, in fact, do all of those things. I think that is one of the systemic and structural issues that we have—that fixed mindset that frames a kid who is not succeeding as therefore unable to succeed, as opposed to framing that child as not having the correct tools.
New tribulations of medical school
Dr. Johnson: Absolutely. I think what Xavier did for me is to at least let me understand what I needed to do, how to comprehend and retain information, which I never had been exposed to before. Those years were very important to establishing a foundation. When going to medical school, it was like, “There’s no more excuses. What could be the problem now?” Well, now let’s talk about taking tests—a whole different skill. Xavier focused on getting me to understand how to structure my thought process and knowledge base. In medical school I had to apply those skills (because if you can’t apply them, there’s no fit).
My second through fourth year of medical school, I was the only African-American kid in my class. I was spending 20-hour days sometimes just studying, trying to overcompensate by knowing as much as I possibly could and thinking that would propel me from the test-taking standpoint. Even though I didn’t have a lot of classmates in medical school that looked like me, I did have mentors that looked similarly, who really saw potential in me. Dr. Frederick Horvath, a nephrologist in Peoria said, “What are you doing? I want you to get out of these books, and let’s go out to lunch.”
He ended up buying me some instrumental books, really talked to me, listening to my background and understanding how driven I was as a person. He took me under his wing for the rest of medical school and said, “This is how you navigate through these spaces. Yes, you need to have a fund of knowledge to be able to take these tests, but you need to start understanding how to apply it to these questions.” I’m forever grateful to Dr. Horvath for doing that because it was a point in time where I was lost and struggling.
Continue to: Hitting a stride but facing racism head-on...
Hitting a stride but facing racism head-on
Dr. Levy: You talk about the systemic and pervasive racism that was on the wards when you hit them in fourth year. If you don’t mind sharing just a little bit of that, it would help people reading this to have a better understanding of the kinds of barriers that are out there.
Dr. Johnson: Even when I talk about it today, it bothers me.
I went to medical school in Peoria, Illinois, not far from the home of the Ku Klux Klan. At that time, once you got out of Chicago it was a very brutal place, with systemic racism throughout. I was a young Black kid going through a process that not many young Black kids from the South side of Chicago go through, and you had people who had never seen anyone like me. When I was going through my clinical rotations, I knew what I was up against. I was dressed “to the T” every day, arriving early, leaving late, trying to answer questions. I would look at the evaluations, and they would be disparaging. I would look at my counterparts, how their evaluations were, and how people would respond to them, and it would be completely different.
Surgery was the part of ObGyn that I really grew to love more than anything, even more than obstetrics. When general surgery came, I wanted to take it very seriously and learn as much as I possibly could. From the beginning, I knew there was a problem because the chief resident, an older White man, wouldn’t look me in the eye or talk to me. He would make disparaging remarks. The thing that stuck out in my mind the most was when I was in the operating room transporting patients, just like a medical student did, and he came up behind me and said, “You know, Pierre, this is where a small mind and a strong back come into play.” For me, it took me to a place where I had to corral my emotions and thoughts because I just wanted to lash out and just tell him how racist and horrible that was for him to say that to me. I explained this to the powers that be, the director of the department, and they basically blew it off to the side.
When it came down to the end of the evaluation period, I passed with flying colors. But they gave me an incomplete because of that chief resident and his remarks on my evaluations. He had 3 pages of report about me as a person and as a student. He said that he had difficulty in expressing his opinions about me because of possible cultural biases that he may have had. He put “cultural biases” in an evaluation, and they looked at that and said that was enough for me to have to remediate my time. I was required to do an extra month in Pontiac, Illinois, which is even more rural than Peoria, because of a racist person that did not give me a fair opportunity because I was Black.
Like everything else in life, it was a learning experience. It’s why I fight so hard today. It’s why I’m so passionate about equity, not only in medicine but also in all aspects of society. It shows why we have police brutality and Black men dying in the streets. It shows how this happens because there are cultural and implicit biases that play out in every part of life, and we are not honest about it. Until we are honest about it and until we say that this is happening and there is something that needs to be done to address it, it’s going to continue to happen. That is my fight.
Exposing the unspoken power struggle
Dr. Levy: I couldn’t agree more. Attributing things like that to the individual, where you talk about a White man in power and a power structure that didn’t literally physically beat you but did beat you into submission. You talk about how to succeed in medical school, and how you had to suck it up and submit to something that was incredibly unfair. You understood, you were old enough, mature enough, to understand that if you fought back, you were going to lose. The only opportunity you had was to submit to that inequity and push forward.
Dr. Johnson: When I did try to fight, the chair of the department told me that either I accept the consequences or I would not graduate from medical school and be forced to do another year. That struck a chord with me. I think that happens a lot in our society, and it needs to be exposed.
Past experiences reflected in today’s society
Dr. Levy: Can you talk about what you faced in your ObGyn residency in terms of the systemic pushback, people not taking your orders, people questioning you. I know that I have heard that a great deal, and I experienced that myself as a woman.
Dr. Johnson: We look at the things that are happening now, everything from George Floyd’s murder to Colin Kaepernick taking a knee. These things are 10 years past when I first started residency. The year before I started residency, there was a noose hanging on the capitol lawn of Springfield, Illinois’ capital city. There’s systemic racism and hatred there. When I first started on the wards of my first year of ObGyn, again, I was the very first Black resident of my program’s history. Nobody could relate to me.
I went from a year-long general surgery internship at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, DC, to ObGyn residency. In the first 2 months, there were complaints of, “He’s not answering his pages. He’s not being prompt.” I went to my program director and said, “Listen, I have never had one complaint like this. There’s a problem here. And there’s a problem when I’m on the floor: When trying to give orders to nurses, they’re not taking them. I had to tell a couple of nurses, ‘I’m Dr. Johnson. Don’t call me by my first name, especially not in front of patients.’”
My director was just not hearing me, because the entire scenario was something they had never been exposed to. Systemic racism is real, and unless you experience it, it’s very difficult to accept that it is happening. But biases happen when you are not cognizant. People are used to things a certain way. Things play out in the media that make your mind think a certain way, and you don’t even realize it. You may not even want to be that way.
Continue to: Unconscious bias is a barrier to ensuring equity...
Unconscious bias is a barrier to ensuring equity
Dr. Levy: One very important point you just made is that we as the system need to be able to recognize those unconscious things, the language that we use, the disparaging remarks, the things that put people down, as well as the things that keep people out of promotion.
There are some interesting data about both race and gender and the language that we use when we write recommendations for people, that we do things unconsciously. The big message to all of us at the end is to open our minds to where those things can occur. For myself, professionally, I keep a list of words that I use when I write recommendations. I measure myself to ensure that I am using the same language for men and women, for Black and White. I think we need to overcome the system and the structure to create real equity—not equality but equity.
It begins with being real about the issues
Dr. Johnson: It’s a bigger problem than the existence of bias and racism. I think these are systemic issues that have been cultivated over centuries that have never been addressed. The true issue is that we deny that these are problems and refuse to talk about it because it makes us uncomfortable. To truly make things more equitable, we have to push our levels of comfort to be able to talk about things in a healthy manner, be open and transparent, and to start to understand how we are thinking about certain things. When you can see it, you can start to implement changes and start to change mentalities and thought processes.
For me, people say, “You don’t look like a doctor.” I get that all the time—because I have tattoos and earrings. I wear my hair in a mohawk. The image of what success looks like has been manifested through our media and culture, and it has imprinted on our minds as to how things are supposed to be. If someone doesn’t fit those molds, we start to shun them out, or we start to exhibit biases against those things. What I am trying to do is change that thought process of what a successful or a professional person looks like. It doesn’t have a look. It is not a White or Black thing. It’s an intellect, a mindset, a way of living. You have to treat every person as an individual and take all the biases out of it and understand where they are coming from and what they have to offer to the profession.
Dr. Levy: I personally was so impressed by you when I met you. I was impressed by the tattoos and the earrings, and my initial response to them was exactly that biased, “Oh, who is this person?” I checked that at the door, listened to you, and was really impressed at your surgical skill, your knowledge, your background. I am really grateful that you have been willing to spend the time to share that with everyone.
Dr. Johnson: Thank you for this discussion.
To watch the full interview between Drs. Levy and Johnson, visit: https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/article/228507/facing-systemic-racism-health-care-inequities-medical-education. ●
- The Pulse of Perseverance:
Three Black Doctors on Their Journey to Success Pierre Johnson, MD; Maxime Madhere, MD; and Joseph Semien Jr, MD - Mindset:
The New Psychology of Success
Carol S. Dweck
Finding inspiration among life’s challenges
Barbara Levy, MD: I am fortunate to have met Pierre serendipitously at a training that we were both attending and was impressed by Dr. Johnson’s life story, his passion and commitment, and his dedication—not only to his personal career but also to raising up other young men of color by trying to break down barriers that face them. His life story highlights those areas of systemic and structural problems that all of us together need to address if we are going to make any progress.
Pierre Johnson, MD: Thank you, Barbara. A little about myself: I am a board-certified ObGyn, and I specialize in minimally invasive surgery. I was born on the South side of Chicago, experiencing gang violence, drugs, and substandard, underserved schools. Long story short, I had a very rough upbringing. I had a single mom and several different issues at home. I am the oldest of 5 siblings, and life was tough.
But I knew that I wanted to do something different with my life. I saw that there was a need in my community as far as health care was concerned, in particular women’s health and childbirth. I knew early on that I wanted to be an ObGyn, and the reason had a lot to do with The Cosby Show. It was the only example of a positive, successful Black man that I saw. No one graduated from college in my family. There weren’t any models of young Black excellence around me. Saying that I wanted to be a doctor planted a seed. I was 9 when my mom became pregnant with my first sibling, and it was fascinating to me. The physiology of pregnancy, and eventually childbirth, was extremely fascinating to me; it set me off on my journey to be an ObGyn.
As I got older, things didn’t get any easier. I went to high school in one of the toughest areas on the South side of Chicago. Gang violence, and violence in and of itself, were all around me, but I was able to stay focused. I went on to Xavier University in Louisiana.
Dr. Levy: There are some important things that I learned from your book and from talking to you at our first meeting. Your mom’s ObGyn, when she was pregnant with your next youngest sibling, was also a Black ObGyn. He took some time to take you under wing?
Dr. Johnson: He did. My mom’s ObGyn was a Black man. Other than The Cosby Show, that’s the only time I saw something like that. When I spoke to him, he really took the time to answer my questions and show me that he was like me; he wasn’t just a far-off mythical person, or something that I could not obtain.
Continue to: Seeing is believing when it comes to success...
Seeing is believing when it comes to success
Dr. Levy: Do you think it was important to have a role model who wasn’t a sports star?
Dr. Johnson: If you can’t see it, you can’t achieve it. He took his time to really talk to me, and it’s the little things for kids that go a long way in their life experience. I still have a relationship with him to this day. How he handled me as a kid made me realize that this is something that I could do. That was extremely important for me.
Dr. Levy: One of the structural things I think we need to point out is that the ability to see yourself as someone successful is critical. When we see 1,000 images a day and they are all White, and they are all so different from where we are that it gets incorporated into our sense of being. I think that’s really difficult for those of us of with privilege to understand what that privilege is.
Dr. Johnson: Absolutely, and I’ll even go further. In residency, 2 White females were my classmates, and both of their parents were doctors. They had grandparents who were doctors. My mom was addicted to drugs; my father was not around. They had been talking medicine since they were 5. You have to make things equitable, but in medicine it’s really not equitable. In medicine, what we don’t realize is that there is an importance for all aspects of someone’s upbringing and environment, and it’s not just what they can regurgitate on a standardized test. If a patient can’t relate to you and tell you what is wrong with them, how can you adequately treat them?
Dr. Levy: Even if they are trying to tell me, but I can’t hear it because I don’t have the language and I don’t have the background. There are really good data to show, in fact, that Black male physicians do a better job at engaging Black men to manage their hypertension.1 When we look at the inequities in birth outcomes for women of color, indigenous women and Black women, there’s evidence that providers who come from a similar background do a better job.
Dr. Johnson: There was the study of Black infants that just came out about them dying at a 3-time higher rate in non-Black physicians’ hands.2 These things need to be recognized. They need to be discussed, and they need to be identified as issues and then, realistically, we need to start talking about solutions, not get offended by what actual statistics are saying.
Foundational inequities in education
Dr. Levy: To address some of the barriers that you faced: I know that you went to a high school that was not geared toward pushing students into professional careers. Your colleagues, however, had educations that prepared them for the standardized tests and other things that they would face academically.
Dr. Johnson: People think I am kidding when I say it, but when I went into college, I didn’t know what a periodic table was. I saw it, but I had no idea what these things meant. I didn’t have any sciences or any AP classes in high school. I did well, but grades are smoke and mirrors. The true test of medicine comes with testing. From the MCATs to the boards, every step of the way there is a standardized test.
Knowledge is something that you can obtain, but test taking is a cultivated skill that happens from a very early age. Trying to teach an adult or someone in their late teens a skill that they should have learned as a kid is difficult. For me, I did not have that, so I had to program myself. I had to learn how to fundamentally take tests as an adult, where most people understand how to do that going into college and professional school.
Dr. Levy: I was impressed with your resilience. I think all of us as human beings, if we fail a test, we take it personally and think it’s about our lack of knowledge. One of the insights that you came to was that failure on those things was not that you didn’t study hard enough. In fact, you probably studied 4 times harder than most other people. You had the knowledge. Being able to get that knowledge into a standardized structured test score was the huge challenge for you.
Dr. Johnson: That’s it. I can remember taking the MCAT, and if you looked at the step 1 book, I could regurgitate to you everything on that page. However, it’s not a test about do you know it or not. It’s an understanding of the English language and how to break things down to make things fit into particular scenarios.
Continue to: A college experience focused on growth and exposure...
A college experience focused on growth and exposure
Dr. Levy: I was impressed by the distinction between your experience at Xavier University where there was a lot of support and guidance and help in your premed program, and what happened to you when you hit medical school.
Dr. Johnson: Xavier University in Louisiana is the number 1 institution in the country for getting minorities into professional school. They understand that they have kids that are brilliant but underprepared, and just have not had the background to actually tackle some of these tough curriculums. I always had good grades in school. But by not being challenged, I didn’t know what I didn’t really know. So now that I was seeing biology, chemistry for the first time, and trying to tackle it; there’s a failure point. I didn’t know how to take tests, and I didn’t know how to study properly. The harder I tried, the worse things got for me.
Xavier has seen that story a multitude of times. If I went to a bigger or predominantly White university, a counselor would have told me, “Well, medicine’s maybe not for you. You can’t handle a premed curriculum.” Instead, I said, “Listen, I’m studying. I’m doing all of these things, and I’m not hacking it.” And they broke it down: “Let’s get you into study groups with kids that have had these type of AP classes before. We’ll have you watch how they study,” and everything started to click. That facilitation of how to adjust to this curriculum was a godsend. It’s the only reason I’m here. I am a prime example of being brilliant enough to be able to do it, but needing the infrastructure and a system set up.
Dr. Levy: There’s a great book by Carol Dweck called Mindset that talks about education of young kids and putting them into silos so early in life; the brilliant kids go into the AP courses and the rest are labeled as inadequate. It’s assumed in a fixed mindset based on their heredity and IQ, and not based on the fact that they have not been exposed to the right things.
Xavier was growing you into the man who could, in fact, do all of those things. I think that is one of the systemic and structural issues that we have—that fixed mindset that frames a kid who is not succeeding as therefore unable to succeed, as opposed to framing that child as not having the correct tools.
New tribulations of medical school
Dr. Johnson: Absolutely. I think what Xavier did for me is to at least let me understand what I needed to do, how to comprehend and retain information, which I never had been exposed to before. Those years were very important to establishing a foundation. When going to medical school, it was like, “There’s no more excuses. What could be the problem now?” Well, now let’s talk about taking tests—a whole different skill. Xavier focused on getting me to understand how to structure my thought process and knowledge base. In medical school I had to apply those skills (because if you can’t apply them, there’s no fit).
My second through fourth year of medical school, I was the only African-American kid in my class. I was spending 20-hour days sometimes just studying, trying to overcompensate by knowing as much as I possibly could and thinking that would propel me from the test-taking standpoint. Even though I didn’t have a lot of classmates in medical school that looked like me, I did have mentors that looked similarly, who really saw potential in me. Dr. Frederick Horvath, a nephrologist in Peoria said, “What are you doing? I want you to get out of these books, and let’s go out to lunch.”
He ended up buying me some instrumental books, really talked to me, listening to my background and understanding how driven I was as a person. He took me under his wing for the rest of medical school and said, “This is how you navigate through these spaces. Yes, you need to have a fund of knowledge to be able to take these tests, but you need to start understanding how to apply it to these questions.” I’m forever grateful to Dr. Horvath for doing that because it was a point in time where I was lost and struggling.
Continue to: Hitting a stride but facing racism head-on...
Hitting a stride but facing racism head-on
Dr. Levy: You talk about the systemic and pervasive racism that was on the wards when you hit them in fourth year. If you don’t mind sharing just a little bit of that, it would help people reading this to have a better understanding of the kinds of barriers that are out there.
Dr. Johnson: Even when I talk about it today, it bothers me.
I went to medical school in Peoria, Illinois, not far from the home of the Ku Klux Klan. At that time, once you got out of Chicago it was a very brutal place, with systemic racism throughout. I was a young Black kid going through a process that not many young Black kids from the South side of Chicago go through, and you had people who had never seen anyone like me. When I was going through my clinical rotations, I knew what I was up against. I was dressed “to the T” every day, arriving early, leaving late, trying to answer questions. I would look at the evaluations, and they would be disparaging. I would look at my counterparts, how their evaluations were, and how people would respond to them, and it would be completely different.
Surgery was the part of ObGyn that I really grew to love more than anything, even more than obstetrics. When general surgery came, I wanted to take it very seriously and learn as much as I possibly could. From the beginning, I knew there was a problem because the chief resident, an older White man, wouldn’t look me in the eye or talk to me. He would make disparaging remarks. The thing that stuck out in my mind the most was when I was in the operating room transporting patients, just like a medical student did, and he came up behind me and said, “You know, Pierre, this is where a small mind and a strong back come into play.” For me, it took me to a place where I had to corral my emotions and thoughts because I just wanted to lash out and just tell him how racist and horrible that was for him to say that to me. I explained this to the powers that be, the director of the department, and they basically blew it off to the side.
When it came down to the end of the evaluation period, I passed with flying colors. But they gave me an incomplete because of that chief resident and his remarks on my evaluations. He had 3 pages of report about me as a person and as a student. He said that he had difficulty in expressing his opinions about me because of possible cultural biases that he may have had. He put “cultural biases” in an evaluation, and they looked at that and said that was enough for me to have to remediate my time. I was required to do an extra month in Pontiac, Illinois, which is even more rural than Peoria, because of a racist person that did not give me a fair opportunity because I was Black.
Like everything else in life, it was a learning experience. It’s why I fight so hard today. It’s why I’m so passionate about equity, not only in medicine but also in all aspects of society. It shows why we have police brutality and Black men dying in the streets. It shows how this happens because there are cultural and implicit biases that play out in every part of life, and we are not honest about it. Until we are honest about it and until we say that this is happening and there is something that needs to be done to address it, it’s going to continue to happen. That is my fight.
Exposing the unspoken power struggle
Dr. Levy: I couldn’t agree more. Attributing things like that to the individual, where you talk about a White man in power and a power structure that didn’t literally physically beat you but did beat you into submission. You talk about how to succeed in medical school, and how you had to suck it up and submit to something that was incredibly unfair. You understood, you were old enough, mature enough, to understand that if you fought back, you were going to lose. The only opportunity you had was to submit to that inequity and push forward.
Dr. Johnson: When I did try to fight, the chair of the department told me that either I accept the consequences or I would not graduate from medical school and be forced to do another year. That struck a chord with me. I think that happens a lot in our society, and it needs to be exposed.
Past experiences reflected in today’s society
Dr. Levy: Can you talk about what you faced in your ObGyn residency in terms of the systemic pushback, people not taking your orders, people questioning you. I know that I have heard that a great deal, and I experienced that myself as a woman.
Dr. Johnson: We look at the things that are happening now, everything from George Floyd’s murder to Colin Kaepernick taking a knee. These things are 10 years past when I first started residency. The year before I started residency, there was a noose hanging on the capitol lawn of Springfield, Illinois’ capital city. There’s systemic racism and hatred there. When I first started on the wards of my first year of ObGyn, again, I was the very first Black resident of my program’s history. Nobody could relate to me.
I went from a year-long general surgery internship at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, DC, to ObGyn residency. In the first 2 months, there were complaints of, “He’s not answering his pages. He’s not being prompt.” I went to my program director and said, “Listen, I have never had one complaint like this. There’s a problem here. And there’s a problem when I’m on the floor: When trying to give orders to nurses, they’re not taking them. I had to tell a couple of nurses, ‘I’m Dr. Johnson. Don’t call me by my first name, especially not in front of patients.’”
My director was just not hearing me, because the entire scenario was something they had never been exposed to. Systemic racism is real, and unless you experience it, it’s very difficult to accept that it is happening. But biases happen when you are not cognizant. People are used to things a certain way. Things play out in the media that make your mind think a certain way, and you don’t even realize it. You may not even want to be that way.
Continue to: Unconscious bias is a barrier to ensuring equity...
Unconscious bias is a barrier to ensuring equity
Dr. Levy: One very important point you just made is that we as the system need to be able to recognize those unconscious things, the language that we use, the disparaging remarks, the things that put people down, as well as the things that keep people out of promotion.
There are some interesting data about both race and gender and the language that we use when we write recommendations for people, that we do things unconsciously. The big message to all of us at the end is to open our minds to where those things can occur. For myself, professionally, I keep a list of words that I use when I write recommendations. I measure myself to ensure that I am using the same language for men and women, for Black and White. I think we need to overcome the system and the structure to create real equity—not equality but equity.
It begins with being real about the issues
Dr. Johnson: It’s a bigger problem than the existence of bias and racism. I think these are systemic issues that have been cultivated over centuries that have never been addressed. The true issue is that we deny that these are problems and refuse to talk about it because it makes us uncomfortable. To truly make things more equitable, we have to push our levels of comfort to be able to talk about things in a healthy manner, be open and transparent, and to start to understand how we are thinking about certain things. When you can see it, you can start to implement changes and start to change mentalities and thought processes.
For me, people say, “You don’t look like a doctor.” I get that all the time—because I have tattoos and earrings. I wear my hair in a mohawk. The image of what success looks like has been manifested through our media and culture, and it has imprinted on our minds as to how things are supposed to be. If someone doesn’t fit those molds, we start to shun them out, or we start to exhibit biases against those things. What I am trying to do is change that thought process of what a successful or a professional person looks like. It doesn’t have a look. It is not a White or Black thing. It’s an intellect, a mindset, a way of living. You have to treat every person as an individual and take all the biases out of it and understand where they are coming from and what they have to offer to the profession.
Dr. Levy: I personally was so impressed by you when I met you. I was impressed by the tattoos and the earrings, and my initial response to them was exactly that biased, “Oh, who is this person?” I checked that at the door, listened to you, and was really impressed at your surgical skill, your knowledge, your background. I am really grateful that you have been willing to spend the time to share that with everyone.
Dr. Johnson: Thank you for this discussion.
To watch the full interview between Drs. Levy and Johnson, visit: https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/article/228507/facing-systemic-racism-health-care-inequities-medical-education. ●
- The Pulse of Perseverance:
Three Black Doctors on Their Journey to Success Pierre Johnson, MD; Maxime Madhere, MD; and Joseph Semien Jr, MD - Mindset:
The New Psychology of Success
Carol S. Dweck
- Benkert R, Peters R, Tate N, et al. Trust of nurse practitioners and physicians among African Americans with hypertension. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008;20:273-280.
- Greenwood BN, Hardeman RR, Huang L, et al. Physician– patient racial concordance and disparities in birthing mortality for newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020; 117:21194-21200.
- Benkert R, Peters R, Tate N, et al. Trust of nurse practitioners and physicians among African Americans with hypertension. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008;20:273-280.
- Greenwood BN, Hardeman RR, Huang L, et al. Physician– patient racial concordance and disparities in birthing mortality for newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020; 117:21194-21200.
The pill toolbox: How to choose a combined oral contraceptive
In the era of long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), the pill can seem obsolete. However, it is still the second most commonly used birth control method in the United States, chosen by 19% of female contraceptive users as of 2015–2017.1 It also has noncontraceptive benefits, so it is important that obstetrician-gynecologists are well-versed in its uses. In this article, I will focus on combined oral contraceptives (COCs; TABLE 1), reviewing the major risks, benefits, and adverse effects of COCs before focusing on recommendations for particular formulations of COCs for various patient populations.
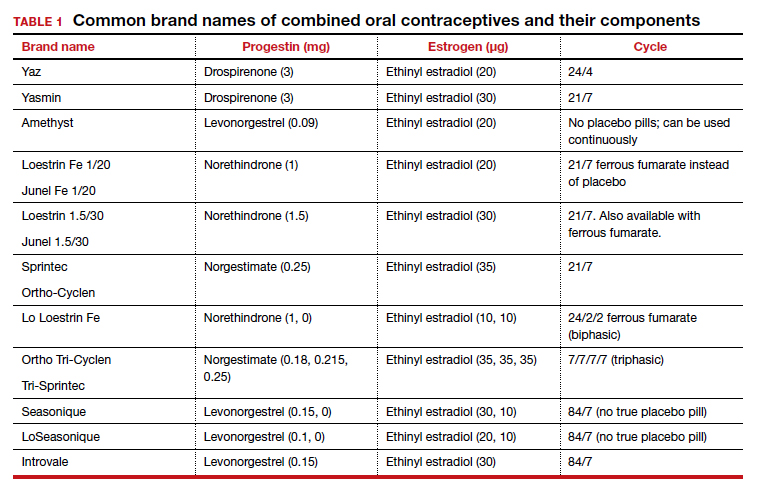
Benefits and risks
There are numerous noncontraceptive benefits of COCs, including menstrual cycle regulation; reduced risk of ovarian, endometrial, and colorectal cancer; and treatment of menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea, acne, menstrual migraine, premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder, pelvic pain due to endometriosis, and hirsutism.
Common patient concerns
In terms of adverse effects, there are more potential unwanted effects of concern to women than there are ones validated in the literature. Accepted adverse effects include nausea, breast tenderness, and decreased libido. However, one of the most common concerns voiced during contraceptive counseling is that COCs will cause weight gain. A 2014 Cochrane review identified 49 trials studying the weight gain question.2 Of those, only 4 had a placebo or nonintervention group. Of these 4, there was no significant difference in weight change between the COC-receiving group and the control group. When patients bring up their concerns, it may help to remind them that women tend to gain weight over time whether or not they are taking a COC.
Another common concern is that COCs cause mood changes. A 2016 review by Schaffir and colleagues sheds some light on this topic,3 albeit limited by the paucity of prospective studies. This review identified only 1 randomized controlled trial comparing depression incidence among women initiating a COC versus a placebo. There was no difference in the incidence of depression among the groups at 3 months. Among 4 large retrospective studies of women using COCs, the agents either had no or a beneficial effect on mood. Schaffir’s review reports that there may be greater mood adverse effects with COCs among women with underlying mood disorders.
Patients may worry that COC use will permanently impair their fertility or delay return to fertility after discontinuation. Research does indicate that return of fertility after stopping COCs often takes several months (compared with immediate fertility after discontinuing a barrier method). However, there still seem to be comparable conception rates within 12 months after discontinuing COCs as there are after discontinuing other common nonhormonal or hormonal contraceptive methods. Fertility is not impacted by the duration of COC use. In addition, return to fertility seems to be comparable after discontinuation of extended cycle or continuous COCs compared with traditional-cycle COCs.4
COC safety
Known major risks of COCs include venous thromboembolism (VTE). The risk of VTE is about double among COC users than among nonpregnant nonusers: 3–9 per 10,000 woman-years compared with 1–5.5 In a study by the US Food and Drug Administration, drospirenone-containing COCs had double the risk of VTE than other COCs. However, the position of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists on this increased risk of VTE with drospirenone-containing pills is that it is “possible” and “minimal.”5 It is important to remember that an alternative to COC use is pregnancy, in which the VTE risk is about double that among COC users, at 5–20 per 10,000 woman-years. This risk increases further in the postpartum period, to 40–65 per 10,000 woman-years.5
Another known major risk of COCs is arterial embolic disease, including cerebrovascular accidents and myocardial infarctions. Women at increased risk for these complications include those with hypertension, diabetes, and/or obesity and women who are aged 35 or older and smoke. Interestingly, women with migraines with aura are at increased risk for stroke but not for myocardial infarction. These women increase their risk of stroke 2- to 4-fold if they use COCs.
Continue to: Different pills for different problems...
Different pills for different problems
With so many pills on the market, it is important for clinicians to know how to choose a particular pill for a particular patient. The following discussion assumes that the patient in question desires a COC for contraception, then offers guidance on how to choose a pill with patient-specific noncontraceptive benefits (TABLE 2).
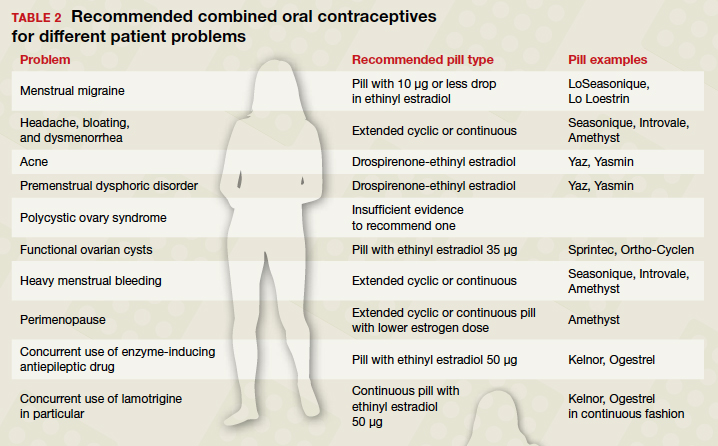
When HMB is a concern. Patients with heavy menstrual bleeding may experience fewer bleeding and/or spotting days with extended cyclic or continuous use of a COC rather than with traditional cyclic use.6 Examples of such COC options include:
- Introvale and Seasonique, both extended-cycle formulations
- Amethyst, which is formulated without placebo pills so that it can be used continuously
- any other COC prescribed with instructions for the patient to skip placebo pills.
An extrapolated benefit to extended-cycle or continuous COCs use for heavy menstrual bleeding is addressing anemia.
For premenstrual dysphoric disorder, the only randomized controlled trials showing improvement involve drospirenone-ethinyl estradiol pills (Yaz and Yasmin).7 There is also evidence that extended cyclic or continuous use of these formulations is more impactful for premenstrual dysphoric disorder than a traditional cycle.8
Keeping migraine avoidance and prevention in mind. Various studies have looked at the impact of different COC formulations on menstrual-related symptoms. There is evidence of greater improvement in headache, bloating, and dysmenorrhea with extended cyclic or continuous use compared with traditional cyclic use.6
In terms of headache, let us delve into menstrual migraine in particular. Menstrual migraines occur sometime between 2 days prior to 2 days after the first day of menses and are linked to a sharp drop in estrogen levels. COCs are contraindicated in women with menstrual migraines with aura because of the increased stroke risk. For women with menstrual migraines without aura, COCs can prevent migraines. Prevention depends on minimizing fluctuations in estrogen levels; any change in estrogen level greater than 10 µg of ethinyl estradiol may trigger an estrogen-related migraine. All currently available regimens of COCs that comprise 21 days of active pills and 7 days of placebo involve a drop of more than 10 µg. Options that involve a drop of 10 µg or less include any continuous formulation, the extended formulation LoSeasonique (levonorgestrel 0.1 mg and ethinyl estradiol 20 µg for 84 days, then ethinyl estradiol 10 µg for 7 days), and Lo Loestrin (ethinyl estradiol 10 µg and norethindrone 1 mg for 24 days, then ethinyl estradiol 10 µg for 2 days, then placebo for 2 days).9
What’s best for acne-prone patients? All COCs should improve acne by increasing levels of sex hormone binding globulin. However, some comparative studies have shown drospirenone-containing COCs to be the most effective for acne. This finding makes sense in light of studies demonstrating antiandrogenic effects of drospirenone.10
Managing PCOS symptoms. It seems logical, by extension, that drospirenone-containing COCs would be particularly beneficial for treating hirsutism associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Other low‒androgenic-potential progestins, such as a third-generation progestin (norgestimate or desogestrel), might similarly be hypothesized to be advantageous. However, there is currently insufficient evidence to recommend any one COC formulation over another for the indication of PCOS.11
Ovarian cysts: Can COCs be helpful? COCs are commonly prescribed by gynecologists for patients with functional ovarian cysts. It is important to note that COCs have not been found to hasten the resolution of existing cysts, so they should not be used for this purpose.12 Studies of early COCs, which had high doses of estrogen (on the order of 50 µg), showed lower rates of cysts among users. This effect seems to be attenuated with the lower-estrogen-dose pills that are currently available, but there still appears to be benefit. Therefore, for a patient prone to cysts who desires an oral contraceptive, a COC containing estrogen 35 µg is likely to be the most beneficial of COCs currently on the market.13,14
Lower-dosage COCs in perimenopause may be beneficial. COCs can ameliorate perimenopausal symptoms including abnormal uterine bleeding and vasomotor symptoms. Clinicians are often hesitant to prescribe COCs for perimenopausal women because of increased risk of VTE, stroke, myocardial infarction, and breast cancer with increasing age. However, age alone is not a contraindication to any contraceptive method. An extended cyclic or continuous regimen COC may be the best choice for a perimenopausal woman in order to avoid vasomotor symptoms that occur during hormone-free intervals. In addition, given the increasing risk of adverse effects like VTE with estrogen dose, a lower estrogen formulation is advisable.15
Patients with epilepsy who are taking antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are a special population when it comes to COCs. Certain AEDs induce hepatic enzymes involved in the metabolism and protein binding of COCs, which can result in contraceptive failure. Strong inducers are carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, perampanel, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and primidone. Weak inducers are clobazam, eslicarbazepine, felbamate, lamotrigine, rufinamide, and topiramate. Women taking any of the above AEDs are recommended to choose a different form of contraception than a COC. However, if they are limited to COCs for some reason, a preparation containing estrogen 50 µg is recommended. It is speculated that the efficacy and adverse effects of COCs with increased hormone doses, used in combination with enzyme-inducing AEDs, should be comparable to those with standard doses when not combined with AEDs; however, this speculation is unproven.16 There are few COCs on the market with estrogen doses of 50 µg, but a couple of examples are Kelnor and Ogestrel.
Additional factors have to be considered with concurrent COC use with the AED lamotrigine since COCs increase clearance of this agent. Therefore, patients taking lamotrigine who start COCs will need an increase in lamotrigine dose. To avoid fluctuations in lamotrigine serum levels, use of a continuous COC is recommended.17
Continue to: Pill types to minimize adverse effects or risks...
Pill types to minimize adverse effects or risks
For women who desire to use a COC for contraception but who are at risk for a particular complication or are bothered by a particular adverse effect, ObGyns can optimize the choice of pill (TABLE 3). For example, women who have adverse effects of nausea and/or breast tenderness may benefit from reducing the estrogen dose to 20 µg or lower.18

Considering VTE
As discussed previously, VTE is a risk with all COCs, but some pills confer greater risk than others. For one, VTE risk increases with estrogen dose. In addition, VTE risk depends on the type of progestin. Drospirenone and third-generation progestins (norgestimate, gestodene, and desogestrel) confer a higher risk of VTE than first- or second-generation progestins. For example, a pill with estradiol 30 µg and either a third-generation progestin or drospirenone has a 50% to 80% higher risk of VTE compared with a pill with estradiol 30 µg and levonorgestrel.
For patients at particularly high risk for VTE, COCs are contraindicated. For patients for whom COCs are considered medically appropriate but who are at higher risk (eg, obese women), it is wise to use a pill containing a first-generation (norethindrone) or second-generation progestin (levonorgestrel) combined with the lowest dose of estrogen that has tolerable adverse effects.19
What about hypertension concerns?
Let us turn our attention briefly to hypertension and its relation to COC use. While the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association redefined hypertension in 2017 using a threshold of 130/80 mm Hg, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) considers hypertension to be 140/90 mm Hg in terms of safety of using COCs. ACOG states, “women with blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg may use any hormonal contraceptive method.”20 In women with hypertension in the range of 140‒159 mm Hg systolic or 90‒99 mm Hg diastolic, COCs are category 3 according to the US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, meaning that the risks usually outweigh the benefits. For women with blood pressures of 160/110 mm Hg or greater, COCs are category 4 (contraindicated). If a woman with mild hypertension is started on a COC, a drospirenone-containing pill may be the best choice because of its diuretic effects. While other contemporary COCs have been associated with a mild increase in blood pressure, drospirenone-containing pills have not shown this association.21
Continue to: At issue: Break-through bleeding, mood, and weight gain...
At issue: Break-through bleeding, mood, and weight gain
For women bothered by intermenstrual bleeding, use of a COC with a third-generation progestin may be preferable to use of one with a first- or second-generation. It may be because of decreased abnormal bleeding that COCs with third-generation progestins have lower discontinuation rates.22 In addition, COCs containing estrogen 20 µg or less are associated with more intermenstrual bleeding than those with more than 20 µg estrogen.23 Keep in mind that it is common with any COC to have intermenstrual bleeding for the first several months.
For women with pre-existing mood disorders or who report mood changes with COCs, it appears that fluctuations in hormone levels are problematic. Consistently, there is evidence that monophasic pills are preferable to multiphasic and that extended cyclic or continuous use is preferable to traditional cyclic use for mitigating mood adverse effects. There is mixed evidence on whether a low dose of ethinyl estradiol is better for mood.3
Although it is discussed above that randomized controlled trials have not shown an association between COC use and weight gain, many women remain concerned. For these women, a drospirenone-containing COC may be the best choice. Drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid activity, so it may help prevent water retention.
A brief word about multiphasic COCs. While these pills were designed to mimic physiologic hormone fluctuations and minimize hormonal adverse effects, there is insufficient evidence to compare their effects to those of monophasic pills.24 Without such evidence, there is little reason to recommend a multiphasic pill to a patient over the more straightforward monophasic formulation.
Conclusion
There are more nuances to prescribing an optimal COC for a patient than may initially come to mind. It is useful to remember that any formulation of pill may be prescribed in an extended or continuous fashion, and there are benefits for such use for premenstrual dysphoric disorder, heavy menstrual bleeding, perimenopause, and menstrual symptoms. Although there are numerous brands of COCs available, a small cadre will suffice for almost all purposes. Such a “toolbox” of pills could include a pill formatted for continuous use (Seasonique), a low estrogen pill (Loestrin), a drospirenone-containing pill (Yaz), and a pill containing a third-generation progestin and a higher dose of estrogen (Sprintec). ●
- Daniels K, Abma JC. Current contraceptive status among women aged 15-49: United States, 2015-2017. NCHS Data Brief, no 327. Hyattsville, MD; 2018.
- Gallo MF, Lopez LM, Grimes DA, et al. Combination contraceptives: effects on weight. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD003987.
- Schaffir J, Worly BL, Gur TL. Combined hormonal contraception and its effects on mood: a critical review. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2016;21:347-355.
- Barnhart KT, Schreiber CA. Return to fertility following discontinuation of oral contraceptives. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:659-663.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion #540: Risk of Venous Thromboembolism Among Users of Drospirenone-Containing Oral Contraceptive Pills. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
- Edelman A, Micks E, Gallo MF, et al. Continuous or extended cycle vs. cyclic use of combined hormonal contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD004695.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin #110: Noncontraceptive Uses of Hormonal Contraceptives. Obstet Gynecol. 2010:206-218.
- Coffee AL, Kuehl TJ, Willis S, et al. Oral contraceptives and premenstrual symptoms: comparison of a 21/7 and extended regimen. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;195:1311-1319.
- Calhoun AH, Batur P. Combined hormonal contraceptives and migraine: an update on the evidence. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017;84:631-638.
- Arowojolu AO, Gallo MF, Lopez LM, et al. Combined oral contraceptive pills for treatment of acne. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012:CD004425.
- McCartney CR, Marshall JC. CLINICAL PRACTICE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:54-64.
- Grimes DA, Jones LB, Lopez LM, et al. Oral contraceptives for functional ovarian cysts. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD006134.
- Grimes DA, Godwin AJ, Rubin A, et al. Ovulation and follicular development associated with three low-dose oral contraceptives: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;83:29-34.
- Christensen JT, Boldsen JL, Westergaard JG. Functional ovarian cysts in premenopausal and gynecologically healthy women. Contraception. 2002;66:153-157.
- Hardman SM, Gebbie AE. Hormonal contraceptive regimens in the perimenopause. Maturitas. 2009;63:204-212.
- Zupanc ML. Antiepileptic drugs and hormonal contraceptives in adolescent women with epilepsy. Neurology. 2006;66 (6 suppl 3):S37-S45.
- Wegner I, Edelbroek PM, Bulk S, et al. Lamotrigine kinetics within the menstrual cycle, after menopause, and with oral contraceptives. Neurology. 2009;73:1388-1393.
- Stewart M, Black K. Choosing a combined oral contraceptive pill. Australian Prescriber. 2015;38:6-11.
- de Bastos M, Stegeman BH, Rosendaal FR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives: venous thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD010813.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin #206: use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- de Morais TL, Giribela C, Nisenbaum MG, et al. Effects of a contraceptive containing drospirenone and ethinylestradiol on blood pressure, metabolic profile and neurohumoral axis in hypertensive women at reproductive age. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014;182:113-117.
- Lawrie TA, Helmerhorst FM, Maitra NK, et al. Types of progestogens in combined oral contraception: effectiveness and side-effects. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011:CD004861.
- Gallo MF, Nanda K, Grimes DA, et al. 20 µg versus >20 µg estrogen combined oral contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013:CD003989.
- van Vliet HA, Grimes DA, Lopez LM, et al. Triphasic versus monophasic oral contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006:CD003553
In the era of long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), the pill can seem obsolete. However, it is still the second most commonly used birth control method in the United States, chosen by 19% of female contraceptive users as of 2015–2017.1 It also has noncontraceptive benefits, so it is important that obstetrician-gynecologists are well-versed in its uses. In this article, I will focus on combined oral contraceptives (COCs; TABLE 1), reviewing the major risks, benefits, and adverse effects of COCs before focusing on recommendations for particular formulations of COCs for various patient populations.

Benefits and risks
There are numerous noncontraceptive benefits of COCs, including menstrual cycle regulation; reduced risk of ovarian, endometrial, and colorectal cancer; and treatment of menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea, acne, menstrual migraine, premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder, pelvic pain due to endometriosis, and hirsutism.
Common patient concerns
In terms of adverse effects, there are more potential unwanted effects of concern to women than there are ones validated in the literature. Accepted adverse effects include nausea, breast tenderness, and decreased libido. However, one of the most common concerns voiced during contraceptive counseling is that COCs will cause weight gain. A 2014 Cochrane review identified 49 trials studying the weight gain question.2 Of those, only 4 had a placebo or nonintervention group. Of these 4, there was no significant difference in weight change between the COC-receiving group and the control group. When patients bring up their concerns, it may help to remind them that women tend to gain weight over time whether or not they are taking a COC.
Another common concern is that COCs cause mood changes. A 2016 review by Schaffir and colleagues sheds some light on this topic,3 albeit limited by the paucity of prospective studies. This review identified only 1 randomized controlled trial comparing depression incidence among women initiating a COC versus a placebo. There was no difference in the incidence of depression among the groups at 3 months. Among 4 large retrospective studies of women using COCs, the agents either had no or a beneficial effect on mood. Schaffir’s review reports that there may be greater mood adverse effects with COCs among women with underlying mood disorders.
Patients may worry that COC use will permanently impair their fertility or delay return to fertility after discontinuation. Research does indicate that return of fertility after stopping COCs often takes several months (compared with immediate fertility after discontinuing a barrier method). However, there still seem to be comparable conception rates within 12 months after discontinuing COCs as there are after discontinuing other common nonhormonal or hormonal contraceptive methods. Fertility is not impacted by the duration of COC use. In addition, return to fertility seems to be comparable after discontinuation of extended cycle or continuous COCs compared with traditional-cycle COCs.4
COC safety
Known major risks of COCs include venous thromboembolism (VTE). The risk of VTE is about double among COC users than among nonpregnant nonusers: 3–9 per 10,000 woman-years compared with 1–5.5 In a study by the US Food and Drug Administration, drospirenone-containing COCs had double the risk of VTE than other COCs. However, the position of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists on this increased risk of VTE with drospirenone-containing pills is that it is “possible” and “minimal.”5 It is important to remember that an alternative to COC use is pregnancy, in which the VTE risk is about double that among COC users, at 5–20 per 10,000 woman-years. This risk increases further in the postpartum period, to 40–65 per 10,000 woman-years.5
Another known major risk of COCs is arterial embolic disease, including cerebrovascular accidents and myocardial infarctions. Women at increased risk for these complications include those with hypertension, diabetes, and/or obesity and women who are aged 35 or older and smoke. Interestingly, women with migraines with aura are at increased risk for stroke but not for myocardial infarction. These women increase their risk of stroke 2- to 4-fold if they use COCs.
Continue to: Different pills for different problems...
Different pills for different problems
With so many pills on the market, it is important for clinicians to know how to choose a particular pill for a particular patient. The following discussion assumes that the patient in question desires a COC for contraception, then offers guidance on how to choose a pill with patient-specific noncontraceptive benefits (TABLE 2).

When HMB is a concern. Patients with heavy menstrual bleeding may experience fewer bleeding and/or spotting days with extended cyclic or continuous use of a COC rather than with traditional cyclic use.6 Examples of such COC options include:
- Introvale and Seasonique, both extended-cycle formulations
- Amethyst, which is formulated without placebo pills so that it can be used continuously
- any other COC prescribed with instructions for the patient to skip placebo pills.
An extrapolated benefit to extended-cycle or continuous COCs use for heavy menstrual bleeding is addressing anemia.
For premenstrual dysphoric disorder, the only randomized controlled trials showing improvement involve drospirenone-ethinyl estradiol pills (Yaz and Yasmin).7 There is also evidence that extended cyclic or continuous use of these formulations is more impactful for premenstrual dysphoric disorder than a traditional cycle.8
Keeping migraine avoidance and prevention in mind. Various studies have looked at the impact of different COC formulations on menstrual-related symptoms. There is evidence of greater improvement in headache, bloating, and dysmenorrhea with extended cyclic or continuous use compared with traditional cyclic use.6
In terms of headache, let us delve into menstrual migraine in particular. Menstrual migraines occur sometime between 2 days prior to 2 days after the first day of menses and are linked to a sharp drop in estrogen levels. COCs are contraindicated in women with menstrual migraines with aura because of the increased stroke risk. For women with menstrual migraines without aura, COCs can prevent migraines. Prevention depends on minimizing fluctuations in estrogen levels; any change in estrogen level greater than 10 µg of ethinyl estradiol may trigger an estrogen-related migraine. All currently available regimens of COCs that comprise 21 days of active pills and 7 days of placebo involve a drop of more than 10 µg. Options that involve a drop of 10 µg or less include any continuous formulation, the extended formulation LoSeasonique (levonorgestrel 0.1 mg and ethinyl estradiol 20 µg for 84 days, then ethinyl estradiol 10 µg for 7 days), and Lo Loestrin (ethinyl estradiol 10 µg and norethindrone 1 mg for 24 days, then ethinyl estradiol 10 µg for 2 days, then placebo for 2 days).9
What’s best for acne-prone patients? All COCs should improve acne by increasing levels of sex hormone binding globulin. However, some comparative studies have shown drospirenone-containing COCs to be the most effective for acne. This finding makes sense in light of studies demonstrating antiandrogenic effects of drospirenone.10
Managing PCOS symptoms. It seems logical, by extension, that drospirenone-containing COCs would be particularly beneficial for treating hirsutism associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Other low‒androgenic-potential progestins, such as a third-generation progestin (norgestimate or desogestrel), might similarly be hypothesized to be advantageous. However, there is currently insufficient evidence to recommend any one COC formulation over another for the indication of PCOS.11
Ovarian cysts: Can COCs be helpful? COCs are commonly prescribed by gynecologists for patients with functional ovarian cysts. It is important to note that COCs have not been found to hasten the resolution of existing cysts, so they should not be used for this purpose.12 Studies of early COCs, which had high doses of estrogen (on the order of 50 µg), showed lower rates of cysts among users. This effect seems to be attenuated with the lower-estrogen-dose pills that are currently available, but there still appears to be benefit. Therefore, for a patient prone to cysts who desires an oral contraceptive, a COC containing estrogen 35 µg is likely to be the most beneficial of COCs currently on the market.13,14
Lower-dosage COCs in perimenopause may be beneficial. COCs can ameliorate perimenopausal symptoms including abnormal uterine bleeding and vasomotor symptoms. Clinicians are often hesitant to prescribe COCs for perimenopausal women because of increased risk of VTE, stroke, myocardial infarction, and breast cancer with increasing age. However, age alone is not a contraindication to any contraceptive method. An extended cyclic or continuous regimen COC may be the best choice for a perimenopausal woman in order to avoid vasomotor symptoms that occur during hormone-free intervals. In addition, given the increasing risk of adverse effects like VTE with estrogen dose, a lower estrogen formulation is advisable.15
Patients with epilepsy who are taking antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are a special population when it comes to COCs. Certain AEDs induce hepatic enzymes involved in the metabolism and protein binding of COCs, which can result in contraceptive failure. Strong inducers are carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, perampanel, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and primidone. Weak inducers are clobazam, eslicarbazepine, felbamate, lamotrigine, rufinamide, and topiramate. Women taking any of the above AEDs are recommended to choose a different form of contraception than a COC. However, if they are limited to COCs for some reason, a preparation containing estrogen 50 µg is recommended. It is speculated that the efficacy and adverse effects of COCs with increased hormone doses, used in combination with enzyme-inducing AEDs, should be comparable to those with standard doses when not combined with AEDs; however, this speculation is unproven.16 There are few COCs on the market with estrogen doses of 50 µg, but a couple of examples are Kelnor and Ogestrel.
Additional factors have to be considered with concurrent COC use with the AED lamotrigine since COCs increase clearance of this agent. Therefore, patients taking lamotrigine who start COCs will need an increase in lamotrigine dose. To avoid fluctuations in lamotrigine serum levels, use of a continuous COC is recommended.17
Continue to: Pill types to minimize adverse effects or risks...
Pill types to minimize adverse effects or risks
For women who desire to use a COC for contraception but who are at risk for a particular complication or are bothered by a particular adverse effect, ObGyns can optimize the choice of pill (TABLE 3). For example, women who have adverse effects of nausea and/or breast tenderness may benefit from reducing the estrogen dose to 20 µg or lower.18

Considering VTE
As discussed previously, VTE is a risk with all COCs, but some pills confer greater risk than others. For one, VTE risk increases with estrogen dose. In addition, VTE risk depends on the type of progestin. Drospirenone and third-generation progestins (norgestimate, gestodene, and desogestrel) confer a higher risk of VTE than first- or second-generation progestins. For example, a pill with estradiol 30 µg and either a third-generation progestin or drospirenone has a 50% to 80% higher risk of VTE compared with a pill with estradiol 30 µg and levonorgestrel.
For patients at particularly high risk for VTE, COCs are contraindicated. For patients for whom COCs are considered medically appropriate but who are at higher risk (eg, obese women), it is wise to use a pill containing a first-generation (norethindrone) or second-generation progestin (levonorgestrel) combined with the lowest dose of estrogen that has tolerable adverse effects.19
What about hypertension concerns?
Let us turn our attention briefly to hypertension and its relation to COC use. While the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association redefined hypertension in 2017 using a threshold of 130/80 mm Hg, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) considers hypertension to be 140/90 mm Hg in terms of safety of using COCs. ACOG states, “women with blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg may use any hormonal contraceptive method.”20 In women with hypertension in the range of 140‒159 mm Hg systolic or 90‒99 mm Hg diastolic, COCs are category 3 according to the US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, meaning that the risks usually outweigh the benefits. For women with blood pressures of 160/110 mm Hg or greater, COCs are category 4 (contraindicated). If a woman with mild hypertension is started on a COC, a drospirenone-containing pill may be the best choice because of its diuretic effects. While other contemporary COCs have been associated with a mild increase in blood pressure, drospirenone-containing pills have not shown this association.21
Continue to: At issue: Break-through bleeding, mood, and weight gain...
At issue: Break-through bleeding, mood, and weight gain
For women bothered by intermenstrual bleeding, use of a COC with a third-generation progestin may be preferable to use of one with a first- or second-generation. It may be because of decreased abnormal bleeding that COCs with third-generation progestins have lower discontinuation rates.22 In addition, COCs containing estrogen 20 µg or less are associated with more intermenstrual bleeding than those with more than 20 µg estrogen.23 Keep in mind that it is common with any COC to have intermenstrual bleeding for the first several months.
For women with pre-existing mood disorders or who report mood changes with COCs, it appears that fluctuations in hormone levels are problematic. Consistently, there is evidence that monophasic pills are preferable to multiphasic and that extended cyclic or continuous use is preferable to traditional cyclic use for mitigating mood adverse effects. There is mixed evidence on whether a low dose of ethinyl estradiol is better for mood.3
Although it is discussed above that randomized controlled trials have not shown an association between COC use and weight gain, many women remain concerned. For these women, a drospirenone-containing COC may be the best choice. Drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid activity, so it may help prevent water retention.
A brief word about multiphasic COCs. While these pills were designed to mimic physiologic hormone fluctuations and minimize hormonal adverse effects, there is insufficient evidence to compare their effects to those of monophasic pills.24 Without such evidence, there is little reason to recommend a multiphasic pill to a patient over the more straightforward monophasic formulation.
Conclusion
There are more nuances to prescribing an optimal COC for a patient than may initially come to mind. It is useful to remember that any formulation of pill may be prescribed in an extended or continuous fashion, and there are benefits for such use for premenstrual dysphoric disorder, heavy menstrual bleeding, perimenopause, and menstrual symptoms. Although there are numerous brands of COCs available, a small cadre will suffice for almost all purposes. Such a “toolbox” of pills could include a pill formatted for continuous use (Seasonique), a low estrogen pill (Loestrin), a drospirenone-containing pill (Yaz), and a pill containing a third-generation progestin and a higher dose of estrogen (Sprintec). ●
In the era of long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), the pill can seem obsolete. However, it is still the second most commonly used birth control method in the United States, chosen by 19% of female contraceptive users as of 2015–2017.1 It also has noncontraceptive benefits, so it is important that obstetrician-gynecologists are well-versed in its uses. In this article, I will focus on combined oral contraceptives (COCs; TABLE 1), reviewing the major risks, benefits, and adverse effects of COCs before focusing on recommendations for particular formulations of COCs for various patient populations.

Benefits and risks
There are numerous noncontraceptive benefits of COCs, including menstrual cycle regulation; reduced risk of ovarian, endometrial, and colorectal cancer; and treatment of menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea, acne, menstrual migraine, premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder, pelvic pain due to endometriosis, and hirsutism.
Common patient concerns
In terms of adverse effects, there are more potential unwanted effects of concern to women than there are ones validated in the literature. Accepted adverse effects include nausea, breast tenderness, and decreased libido. However, one of the most common concerns voiced during contraceptive counseling is that COCs will cause weight gain. A 2014 Cochrane review identified 49 trials studying the weight gain question.2 Of those, only 4 had a placebo or nonintervention group. Of these 4, there was no significant difference in weight change between the COC-receiving group and the control group. When patients bring up their concerns, it may help to remind them that women tend to gain weight over time whether or not they are taking a COC.
Another common concern is that COCs cause mood changes. A 2016 review by Schaffir and colleagues sheds some light on this topic,3 albeit limited by the paucity of prospective studies. This review identified only 1 randomized controlled trial comparing depression incidence among women initiating a COC versus a placebo. There was no difference in the incidence of depression among the groups at 3 months. Among 4 large retrospective studies of women using COCs, the agents either had no or a beneficial effect on mood. Schaffir’s review reports that there may be greater mood adverse effects with COCs among women with underlying mood disorders.
Patients may worry that COC use will permanently impair their fertility or delay return to fertility after discontinuation. Research does indicate that return of fertility after stopping COCs often takes several months (compared with immediate fertility after discontinuing a barrier method). However, there still seem to be comparable conception rates within 12 months after discontinuing COCs as there are after discontinuing other common nonhormonal or hormonal contraceptive methods. Fertility is not impacted by the duration of COC use. In addition, return to fertility seems to be comparable after discontinuation of extended cycle or continuous COCs compared with traditional-cycle COCs.4
COC safety
Known major risks of COCs include venous thromboembolism (VTE). The risk of VTE is about double among COC users than among nonpregnant nonusers: 3–9 per 10,000 woman-years compared with 1–5.5 In a study by the US Food and Drug Administration, drospirenone-containing COCs had double the risk of VTE than other COCs. However, the position of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists on this increased risk of VTE with drospirenone-containing pills is that it is “possible” and “minimal.”5 It is important to remember that an alternative to COC use is pregnancy, in which the VTE risk is about double that among COC users, at 5–20 per 10,000 woman-years. This risk increases further in the postpartum period, to 40–65 per 10,000 woman-years.5
Another known major risk of COCs is arterial embolic disease, including cerebrovascular accidents and myocardial infarctions. Women at increased risk for these complications include those with hypertension, diabetes, and/or obesity and women who are aged 35 or older and smoke. Interestingly, women with migraines with aura are at increased risk for stroke but not for myocardial infarction. These women increase their risk of stroke 2- to 4-fold if they use COCs.
Continue to: Different pills for different problems...
Different pills for different problems
With so many pills on the market, it is important for clinicians to know how to choose a particular pill for a particular patient. The following discussion assumes that the patient in question desires a COC for contraception, then offers guidance on how to choose a pill with patient-specific noncontraceptive benefits (TABLE 2).

When HMB is a concern. Patients with heavy menstrual bleeding may experience fewer bleeding and/or spotting days with extended cyclic or continuous use of a COC rather than with traditional cyclic use.6 Examples of such COC options include:
- Introvale and Seasonique, both extended-cycle formulations
- Amethyst, which is formulated without placebo pills so that it can be used continuously
- any other COC prescribed with instructions for the patient to skip placebo pills.
An extrapolated benefit to extended-cycle or continuous COCs use for heavy menstrual bleeding is addressing anemia.
For premenstrual dysphoric disorder, the only randomized controlled trials showing improvement involve drospirenone-ethinyl estradiol pills (Yaz and Yasmin).7 There is also evidence that extended cyclic or continuous use of these formulations is more impactful for premenstrual dysphoric disorder than a traditional cycle.8
Keeping migraine avoidance and prevention in mind. Various studies have looked at the impact of different COC formulations on menstrual-related symptoms. There is evidence of greater improvement in headache, bloating, and dysmenorrhea with extended cyclic or continuous use compared with traditional cyclic use.6
In terms of headache, let us delve into menstrual migraine in particular. Menstrual migraines occur sometime between 2 days prior to 2 days after the first day of menses and are linked to a sharp drop in estrogen levels. COCs are contraindicated in women with menstrual migraines with aura because of the increased stroke risk. For women with menstrual migraines without aura, COCs can prevent migraines. Prevention depends on minimizing fluctuations in estrogen levels; any change in estrogen level greater than 10 µg of ethinyl estradiol may trigger an estrogen-related migraine. All currently available regimens of COCs that comprise 21 days of active pills and 7 days of placebo involve a drop of more than 10 µg. Options that involve a drop of 10 µg or less include any continuous formulation, the extended formulation LoSeasonique (levonorgestrel 0.1 mg and ethinyl estradiol 20 µg for 84 days, then ethinyl estradiol 10 µg for 7 days), and Lo Loestrin (ethinyl estradiol 10 µg and norethindrone 1 mg for 24 days, then ethinyl estradiol 10 µg for 2 days, then placebo for 2 days).9
What’s best for acne-prone patients? All COCs should improve acne by increasing levels of sex hormone binding globulin. However, some comparative studies have shown drospirenone-containing COCs to be the most effective for acne. This finding makes sense in light of studies demonstrating antiandrogenic effects of drospirenone.10
Managing PCOS symptoms. It seems logical, by extension, that drospirenone-containing COCs would be particularly beneficial for treating hirsutism associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Other low‒androgenic-potential progestins, such as a third-generation progestin (norgestimate or desogestrel), might similarly be hypothesized to be advantageous. However, there is currently insufficient evidence to recommend any one COC formulation over another for the indication of PCOS.11
Ovarian cysts: Can COCs be helpful? COCs are commonly prescribed by gynecologists for patients with functional ovarian cysts. It is important to note that COCs have not been found to hasten the resolution of existing cysts, so they should not be used for this purpose.12 Studies of early COCs, which had high doses of estrogen (on the order of 50 µg), showed lower rates of cysts among users. This effect seems to be attenuated with the lower-estrogen-dose pills that are currently available, but there still appears to be benefit. Therefore, for a patient prone to cysts who desires an oral contraceptive, a COC containing estrogen 35 µg is likely to be the most beneficial of COCs currently on the market.13,14
Lower-dosage COCs in perimenopause may be beneficial. COCs can ameliorate perimenopausal symptoms including abnormal uterine bleeding and vasomotor symptoms. Clinicians are often hesitant to prescribe COCs for perimenopausal women because of increased risk of VTE, stroke, myocardial infarction, and breast cancer with increasing age. However, age alone is not a contraindication to any contraceptive method. An extended cyclic or continuous regimen COC may be the best choice for a perimenopausal woman in order to avoid vasomotor symptoms that occur during hormone-free intervals. In addition, given the increasing risk of adverse effects like VTE with estrogen dose, a lower estrogen formulation is advisable.15
Patients with epilepsy who are taking antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are a special population when it comes to COCs. Certain AEDs induce hepatic enzymes involved in the metabolism and protein binding of COCs, which can result in contraceptive failure. Strong inducers are carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, perampanel, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and primidone. Weak inducers are clobazam, eslicarbazepine, felbamate, lamotrigine, rufinamide, and topiramate. Women taking any of the above AEDs are recommended to choose a different form of contraception than a COC. However, if they are limited to COCs for some reason, a preparation containing estrogen 50 µg is recommended. It is speculated that the efficacy and adverse effects of COCs with increased hormone doses, used in combination with enzyme-inducing AEDs, should be comparable to those with standard doses when not combined with AEDs; however, this speculation is unproven.16 There are few COCs on the market with estrogen doses of 50 µg, but a couple of examples are Kelnor and Ogestrel.
Additional factors have to be considered with concurrent COC use with the AED lamotrigine since COCs increase clearance of this agent. Therefore, patients taking lamotrigine who start COCs will need an increase in lamotrigine dose. To avoid fluctuations in lamotrigine serum levels, use of a continuous COC is recommended.17
Continue to: Pill types to minimize adverse effects or risks...
Pill types to minimize adverse effects or risks
For women who desire to use a COC for contraception but who are at risk for a particular complication or are bothered by a particular adverse effect, ObGyns can optimize the choice of pill (TABLE 3). For example, women who have adverse effects of nausea and/or breast tenderness may benefit from reducing the estrogen dose to 20 µg or lower.18

Considering VTE
As discussed previously, VTE is a risk with all COCs, but some pills confer greater risk than others. For one, VTE risk increases with estrogen dose. In addition, VTE risk depends on the type of progestin. Drospirenone and third-generation progestins (norgestimate, gestodene, and desogestrel) confer a higher risk of VTE than first- or second-generation progestins. For example, a pill with estradiol 30 µg and either a third-generation progestin or drospirenone has a 50% to 80% higher risk of VTE compared with a pill with estradiol 30 µg and levonorgestrel.
For patients at particularly high risk for VTE, COCs are contraindicated. For patients for whom COCs are considered medically appropriate but who are at higher risk (eg, obese women), it is wise to use a pill containing a first-generation (norethindrone) or second-generation progestin (levonorgestrel) combined with the lowest dose of estrogen that has tolerable adverse effects.19
What about hypertension concerns?
Let us turn our attention briefly to hypertension and its relation to COC use. While the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association redefined hypertension in 2017 using a threshold of 130/80 mm Hg, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) considers hypertension to be 140/90 mm Hg in terms of safety of using COCs. ACOG states, “women with blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg may use any hormonal contraceptive method.”20 In women with hypertension in the range of 140‒159 mm Hg systolic or 90‒99 mm Hg diastolic, COCs are category 3 according to the US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, meaning that the risks usually outweigh the benefits. For women with blood pressures of 160/110 mm Hg or greater, COCs are category 4 (contraindicated). If a woman with mild hypertension is started on a COC, a drospirenone-containing pill may be the best choice because of its diuretic effects. While other contemporary COCs have been associated with a mild increase in blood pressure, drospirenone-containing pills have not shown this association.21
Continue to: At issue: Break-through bleeding, mood, and weight gain...
At issue: Break-through bleeding, mood, and weight gain
For women bothered by intermenstrual bleeding, use of a COC with a third-generation progestin may be preferable to use of one with a first- or second-generation. It may be because of decreased abnormal bleeding that COCs with third-generation progestins have lower discontinuation rates.22 In addition, COCs containing estrogen 20 µg or less are associated with more intermenstrual bleeding than those with more than 20 µg estrogen.23 Keep in mind that it is common with any COC to have intermenstrual bleeding for the first several months.
For women with pre-existing mood disorders or who report mood changes with COCs, it appears that fluctuations in hormone levels are problematic. Consistently, there is evidence that monophasic pills are preferable to multiphasic and that extended cyclic or continuous use is preferable to traditional cyclic use for mitigating mood adverse effects. There is mixed evidence on whether a low dose of ethinyl estradiol is better for mood.3
Although it is discussed above that randomized controlled trials have not shown an association between COC use and weight gain, many women remain concerned. For these women, a drospirenone-containing COC may be the best choice. Drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid activity, so it may help prevent water retention.
A brief word about multiphasic COCs. While these pills were designed to mimic physiologic hormone fluctuations and minimize hormonal adverse effects, there is insufficient evidence to compare their effects to those of monophasic pills.24 Without such evidence, there is little reason to recommend a multiphasic pill to a patient over the more straightforward monophasic formulation.
Conclusion
There are more nuances to prescribing an optimal COC for a patient than may initially come to mind. It is useful to remember that any formulation of pill may be prescribed in an extended or continuous fashion, and there are benefits for such use for premenstrual dysphoric disorder, heavy menstrual bleeding, perimenopause, and menstrual symptoms. Although there are numerous brands of COCs available, a small cadre will suffice for almost all purposes. Such a “toolbox” of pills could include a pill formatted for continuous use (Seasonique), a low estrogen pill (Loestrin), a drospirenone-containing pill (Yaz), and a pill containing a third-generation progestin and a higher dose of estrogen (Sprintec). ●
- Daniels K, Abma JC. Current contraceptive status among women aged 15-49: United States, 2015-2017. NCHS Data Brief, no 327. Hyattsville, MD; 2018.
- Gallo MF, Lopez LM, Grimes DA, et al. Combination contraceptives: effects on weight. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD003987.
- Schaffir J, Worly BL, Gur TL. Combined hormonal contraception and its effects on mood: a critical review. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2016;21:347-355.
- Barnhart KT, Schreiber CA. Return to fertility following discontinuation of oral contraceptives. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:659-663.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion #540: Risk of Venous Thromboembolism Among Users of Drospirenone-Containing Oral Contraceptive Pills. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
- Edelman A, Micks E, Gallo MF, et al. Continuous or extended cycle vs. cyclic use of combined hormonal contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD004695.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin #110: Noncontraceptive Uses of Hormonal Contraceptives. Obstet Gynecol. 2010:206-218.
- Coffee AL, Kuehl TJ, Willis S, et al. Oral contraceptives and premenstrual symptoms: comparison of a 21/7 and extended regimen. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;195:1311-1319.
- Calhoun AH, Batur P. Combined hormonal contraceptives and migraine: an update on the evidence. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017;84:631-638.
- Arowojolu AO, Gallo MF, Lopez LM, et al. Combined oral contraceptive pills for treatment of acne. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012:CD004425.
- McCartney CR, Marshall JC. CLINICAL PRACTICE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:54-64.
- Grimes DA, Jones LB, Lopez LM, et al. Oral contraceptives for functional ovarian cysts. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD006134.
- Grimes DA, Godwin AJ, Rubin A, et al. Ovulation and follicular development associated with three low-dose oral contraceptives: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;83:29-34.
- Christensen JT, Boldsen JL, Westergaard JG. Functional ovarian cysts in premenopausal and gynecologically healthy women. Contraception. 2002;66:153-157.
- Hardman SM, Gebbie AE. Hormonal contraceptive regimens in the perimenopause. Maturitas. 2009;63:204-212.
- Zupanc ML. Antiepileptic drugs and hormonal contraceptives in adolescent women with epilepsy. Neurology. 2006;66 (6 suppl 3):S37-S45.
- Wegner I, Edelbroek PM, Bulk S, et al. Lamotrigine kinetics within the menstrual cycle, after menopause, and with oral contraceptives. Neurology. 2009;73:1388-1393.
- Stewart M, Black K. Choosing a combined oral contraceptive pill. Australian Prescriber. 2015;38:6-11.
- de Bastos M, Stegeman BH, Rosendaal FR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives: venous thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD010813.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin #206: use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- de Morais TL, Giribela C, Nisenbaum MG, et al. Effects of a contraceptive containing drospirenone and ethinylestradiol on blood pressure, metabolic profile and neurohumoral axis in hypertensive women at reproductive age. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014;182:113-117.
- Lawrie TA, Helmerhorst FM, Maitra NK, et al. Types of progestogens in combined oral contraception: effectiveness and side-effects. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011:CD004861.
- Gallo MF, Nanda K, Grimes DA, et al. 20 µg versus >20 µg estrogen combined oral contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013:CD003989.
- van Vliet HA, Grimes DA, Lopez LM, et al. Triphasic versus monophasic oral contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006:CD003553
- Daniels K, Abma JC. Current contraceptive status among women aged 15-49: United States, 2015-2017. NCHS Data Brief, no 327. Hyattsville, MD; 2018.
- Gallo MF, Lopez LM, Grimes DA, et al. Combination contraceptives: effects on weight. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD003987.
- Schaffir J, Worly BL, Gur TL. Combined hormonal contraception and its effects on mood: a critical review. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2016;21:347-355.
- Barnhart KT, Schreiber CA. Return to fertility following discontinuation of oral contraceptives. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:659-663.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion #540: Risk of Venous Thromboembolism Among Users of Drospirenone-Containing Oral Contraceptive Pills. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
- Edelman A, Micks E, Gallo MF, et al. Continuous or extended cycle vs. cyclic use of combined hormonal contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD004695.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin #110: Noncontraceptive Uses of Hormonal Contraceptives. Obstet Gynecol. 2010:206-218.
- Coffee AL, Kuehl TJ, Willis S, et al. Oral contraceptives and premenstrual symptoms: comparison of a 21/7 and extended regimen. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;195:1311-1319.
- Calhoun AH, Batur P. Combined hormonal contraceptives and migraine: an update on the evidence. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017;84:631-638.
- Arowojolu AO, Gallo MF, Lopez LM, et al. Combined oral contraceptive pills for treatment of acne. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012:CD004425.
- McCartney CR, Marshall JC. CLINICAL PRACTICE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:54-64.
- Grimes DA, Jones LB, Lopez LM, et al. Oral contraceptives for functional ovarian cysts. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD006134.
- Grimes DA, Godwin AJ, Rubin A, et al. Ovulation and follicular development associated with three low-dose oral contraceptives: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 1994;83:29-34.
- Christensen JT, Boldsen JL, Westergaard JG. Functional ovarian cysts in premenopausal and gynecologically healthy women. Contraception. 2002;66:153-157.
- Hardman SM, Gebbie AE. Hormonal contraceptive regimens in the perimenopause. Maturitas. 2009;63:204-212.
- Zupanc ML. Antiepileptic drugs and hormonal contraceptives in adolescent women with epilepsy. Neurology. 2006;66 (6 suppl 3):S37-S45.
- Wegner I, Edelbroek PM, Bulk S, et al. Lamotrigine kinetics within the menstrual cycle, after menopause, and with oral contraceptives. Neurology. 2009;73:1388-1393.
- Stewart M, Black K. Choosing a combined oral contraceptive pill. Australian Prescriber. 2015;38:6-11.
- de Bastos M, Stegeman BH, Rosendaal FR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives: venous thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014:CD010813.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin #206: use of hormonal contraception in women with coexisting medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e128-e150.
- de Morais TL, Giribela C, Nisenbaum MG, et al. Effects of a contraceptive containing drospirenone and ethinylestradiol on blood pressure, metabolic profile and neurohumoral axis in hypertensive women at reproductive age. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014;182:113-117.
- Lawrie TA, Helmerhorst FM, Maitra NK, et al. Types of progestogens in combined oral contraception: effectiveness and side-effects. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011:CD004861.
- Gallo MF, Nanda K, Grimes DA, et al. 20 µg versus >20 µg estrogen combined oral contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013:CD003989.
- van Vliet HA, Grimes DA, Lopez LM, et al. Triphasic versus monophasic oral contraceptives for contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006:CD003553
For obese postmenopausal women, what options may decrease endometrial cancer risk?
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy, with approximately 59,000 cases diagnosed annually,1 and a lifetime risk of approximately 3.1% in the United States.2 Type I endometrial cancer includes tumors with endometrioid histology that are grade 1 or 2. Type II endometrial cancer includes tumors that have grade 3 endometrioid or nonendometrioid histology, including serous, clear cell, mucinous, squamous transitional cell, mesonephric, and undifferentiated tumors.3 Type I endometrial cancer is hormone sensitive, generally stimulated by estrogen and suppressed by progestins.
Endometrial cancer is diagnosed at a mean age of 63 years,4 and only 15% of cases occur before age 50.5 Women with an elevated body mass index (BMI) have a markedly increased risk of both Types I and II endometrial cancer (TABLE).6 Hence, endometrial cancer is highly prevalent in obese postmenopausal women. For these women health interventions that may reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer include dieting, physical activity, bariatric surgery, and progestin therapy.

Educating patients is a priority
Many women do not know that postmenopausal bleeding is a sign of endometrial cancer. All postmenopausal women should be advised that if they develop vaginal bleeding they need to be evaluated by a clinician.7 Women who are knowledgeable about the link between postmenopausal vaginal bleeding and endometrial cancer can be encouraged to share this information with their postmenopausal friends in order to reach more people with this important information. All obese postmenopausal women should be advised that weight loss and increased physical activity can reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer.
How weight loss and physical activity affect risk
Intentional weight loss has been reported to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women. As part of the Women’s Health Initiative observational study, 36,794 postmenopausal women aged 50 to 79 years with a uterus had their body weight and height measured at entry into the study and after 3 years of follow-up.8 During the 11 years following study entry, there were 566 incident cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with women who had a stable weight, intentional weight loss of ≥5% was associated with a 40% reduction in the risk of endometrial cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.60; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.42–0.86). Compared with women who had a stable weight, women who had weight gain ≥10% had an increased risk of endometrial cancer (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.00–1.57).
High levels of physical activity may be associated with a decreased risk of endometrial cancer. In one study, compared with a sedentary lifestyle, higher levels of physical activity were reported to be associated with a decreased risk of endometrial cancer.9
Continue to: How bariatric surgery affects risk...
How bariatric surgery affects risk
Many cancers are associated with obesity, including endometrial, breast, colon, pancreas, gallbladder, and renal. Obesity is associated with increased conversion of androgens to estrogens in fat tissue, stimulating excessive endometrial proliferation and increasing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Bariatric surgery reliably causes sustained weight reduction. Multiple studies have reported that bariatric surgery reduces the risk of endometrial cancer.
Schauer and colleagues used data from the Kaiser Permanente health system to identify 22,198 obese people who had undergone bariatric surgery and 66,427 matched controls who were obese but did not have surgery.10 The study population was 81% female, with a mean age of 45 years and a mean BMI of 45 kg/m2. After an average 3.5 years of follow-up there were 2,542 incident cases of cancer, including 322 cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with conventional weight loss treatment, bariatric surgery reduced the risk of endometrial cancer by 50% (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.37–0.67; P<.001).10 In addition, bariatric surgery reduced the risk of colon and pancreatic cancer by 41% and 54%, respectively.10
In the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study, 1,420 women who underwent bariatric surgery and 1,447 matched controls who received conventional obesity treatment were followed for 18 years.11 At study entry, the mean age of the women was approximately 48 years, and the mean BMI was approximately 42 kg/m2. In follow-up there were 76 incident cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with women receiving conventional obesity treatment, women who had bariatric surgery had a non–statistically significant 49% decrease in the risk of developing endometrial cancer (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.24–1.10)
In a systematic review of 5 additional studies (not including publications 10 or 11) of the impact of bariatric surgery on the risk of developing endometrial cancer, the surgery was associated with a 68% risk reduction (odds ratio [OR], 0.32; 95% CI, 0.16–0.63) compared with matched obese women that did not have surgery.12
Although there are no randomized prospective studies showing that bariatric surgery reduces the risk of endometrial cancer, the weight of the observation evidence is strong. In addition, bariatric surgery was reported to reduce all-cause mortality in the SOS study.13 Hence, for obese postmenopausal women, if lifestyle changes do not result in sustained weight loss, bariatric surgery may be an optimal approach to improving health outcomes.
Continue to: Progestin treatment and endometrial cancer risk...
Progestin treatment and endometrial cancer risk
Estrogen stimulates endometrial cell proliferation. Hence, unopposed chronic exposure to estrogen is a major risk factor for developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Progestins block the proliferative effect of estrogen and cause cell differentiation, resulting in stromal decidualization. Progestins also reduce the concentration of estrogen and progesterone receptors and increase the activity of enzymes that convert estradiol to estrone, blocking estrogen-induced endometrial proliferation.14
In women with endometrial hyperplasia, progestins have been shown to be effective in resolving the hyperplasia in approximately 80% of cases. Both oral progestins and the 52-mg levonorgestrel-containing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) have been reported to be effective in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia. In a Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis, the 52-mg LNG-IUD was reported to be somewhat more effective in resolving endometrial hyperplasia than cyclic oral progestins (89% vs 72%, respectively).15
Other studies have also reported that the 52 mg LNG-IUD was more effective than oral progestin therapy for women with complex atypical endometrial hyperplasia.16 There are no large randomized clinical trials of progestin therapy on prevention for future development of endometrial cancer in obese postmenopausal women who have a normal endometrial histology. However, for an obese perimenopausal woman, insertion of a 52-mg LNG-IUD may help to minimize excessive uterine bleeding during the menopause transition and reduce the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia during the early postmenopause.
We can help our patients reduce their risk of endometrial cancer
Obese postmenopausal women are at increased risk for developing endometrial cancer. Gynecologists play an important role in the prevention and early detection of endometrial cancer. We can make a difference and improve the health of our obese peri- and postmenopausal women by recommending interventions that reduce the risk of endometrial cancer, thereby improving the health of our patients. ●
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Uterine cancer statistics. https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/uterine-cancer/statistics#:~:text=This%20year%2C%20an%20
estimated%2065%2C620,cancers%20occur%20in%20the%20endometrium. Accessed November 23, 2020. - Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD. April 15, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/. Accessed November 23, 2020.
- Noer MC, Antonsen SL, Ottesen B, et al. Type I versus Type II endometrial cancer: differential impact of comorbidity. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018;28:586-593.
- Sorosky JI. Endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:436-437.
- Gallup DG, Stock RJ. Adenocarcinoma of the endometrium in women 40 years of age or younger. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;64:417-420.
- Setiawan VW, Yang HP, Pike MC, et al. Type I and II endometrial cancers: have they different risk factors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2607-2618.
- Saccardi C, Vitagliano A, Marchetti M, et al. Endometrial cancer risk prediction according to indication of diagnostic hysteroscopy in postmenopausal women. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10:257.e1-e11.
- Luo J, Chlebowski RT, Hendryx M, et al. Intentional weight loss and endometrial cancer risk. J Clin Oncology. 2017;35:1189-1193.
- Friedenreich CM, Ryder-Burbidge C, McNeil J. Physical activity, obesity and sedentary behavior in cancer etiology: epidemiologic evidence and biological mechanisms. Mol Oncol. August 2, 2020. doi: 10.1001/1878-0261.12772.
- Schauer DP, Feigelson HS, Koebnick C, et al. Bariatric surgery and the risk of cancer in a large multisite cohort. Ann Surg. 2019;269:95-101.
- Anvenden A, Taube M, Peltonen M, et al. Long-term incidence of female-specific cancer after bariatric surgery or usual care in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;145:224-229.
- Winder AA, Kularatna M, MacCormick AD. Does bariatric surgery affect the incidence of endometrial cancer development? A systematic review. Obes Surg. 2018;28:1433-1440.
- Carlsson LM, Sjoholm K, Jacobson P, et al. Life expectancy after bariatric surgery in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1535-1543.
- Lessey BA, Young SL. In: Strauss JF, Barbieri RL (eds.) Yen and Jaffe’s Reproductive Endocrinology: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Clinical Management. 8th ed. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA; 2018:208-212.
- Mittermeier T, Farrant C, Wise MR. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for endometrial hyperplasia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;CD012658.
- Mandelbaum RS, Ciccone MA, Nusbaum DJ, et al. Progestin therapy for obese women with complex atypical hyperplasia: levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device vs systemic therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:103.e1-e13.
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy, with approximately 59,000 cases diagnosed annually,1 and a lifetime risk of approximately 3.1% in the United States.2 Type I endometrial cancer includes tumors with endometrioid histology that are grade 1 or 2. Type II endometrial cancer includes tumors that have grade 3 endometrioid or nonendometrioid histology, including serous, clear cell, mucinous, squamous transitional cell, mesonephric, and undifferentiated tumors.3 Type I endometrial cancer is hormone sensitive, generally stimulated by estrogen and suppressed by progestins.
Endometrial cancer is diagnosed at a mean age of 63 years,4 and only 15% of cases occur before age 50.5 Women with an elevated body mass index (BMI) have a markedly increased risk of both Types I and II endometrial cancer (TABLE).6 Hence, endometrial cancer is highly prevalent in obese postmenopausal women. For these women health interventions that may reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer include dieting, physical activity, bariatric surgery, and progestin therapy.

Educating patients is a priority
Many women do not know that postmenopausal bleeding is a sign of endometrial cancer. All postmenopausal women should be advised that if they develop vaginal bleeding they need to be evaluated by a clinician.7 Women who are knowledgeable about the link between postmenopausal vaginal bleeding and endometrial cancer can be encouraged to share this information with their postmenopausal friends in order to reach more people with this important information. All obese postmenopausal women should be advised that weight loss and increased physical activity can reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer.
How weight loss and physical activity affect risk
Intentional weight loss has been reported to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women. As part of the Women’s Health Initiative observational study, 36,794 postmenopausal women aged 50 to 79 years with a uterus had their body weight and height measured at entry into the study and after 3 years of follow-up.8 During the 11 years following study entry, there were 566 incident cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with women who had a stable weight, intentional weight loss of ≥5% was associated with a 40% reduction in the risk of endometrial cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.60; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.42–0.86). Compared with women who had a stable weight, women who had weight gain ≥10% had an increased risk of endometrial cancer (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.00–1.57).
High levels of physical activity may be associated with a decreased risk of endometrial cancer. In one study, compared with a sedentary lifestyle, higher levels of physical activity were reported to be associated with a decreased risk of endometrial cancer.9
Continue to: How bariatric surgery affects risk...
How bariatric surgery affects risk
Many cancers are associated with obesity, including endometrial, breast, colon, pancreas, gallbladder, and renal. Obesity is associated with increased conversion of androgens to estrogens in fat tissue, stimulating excessive endometrial proliferation and increasing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Bariatric surgery reliably causes sustained weight reduction. Multiple studies have reported that bariatric surgery reduces the risk of endometrial cancer.
Schauer and colleagues used data from the Kaiser Permanente health system to identify 22,198 obese people who had undergone bariatric surgery and 66,427 matched controls who were obese but did not have surgery.10 The study population was 81% female, with a mean age of 45 years and a mean BMI of 45 kg/m2. After an average 3.5 years of follow-up there were 2,542 incident cases of cancer, including 322 cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with conventional weight loss treatment, bariatric surgery reduced the risk of endometrial cancer by 50% (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.37–0.67; P<.001).10 In addition, bariatric surgery reduced the risk of colon and pancreatic cancer by 41% and 54%, respectively.10
In the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study, 1,420 women who underwent bariatric surgery and 1,447 matched controls who received conventional obesity treatment were followed for 18 years.11 At study entry, the mean age of the women was approximately 48 years, and the mean BMI was approximately 42 kg/m2. In follow-up there were 76 incident cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with women receiving conventional obesity treatment, women who had bariatric surgery had a non–statistically significant 49% decrease in the risk of developing endometrial cancer (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.24–1.10)
In a systematic review of 5 additional studies (not including publications 10 or 11) of the impact of bariatric surgery on the risk of developing endometrial cancer, the surgery was associated with a 68% risk reduction (odds ratio [OR], 0.32; 95% CI, 0.16–0.63) compared with matched obese women that did not have surgery.12
Although there are no randomized prospective studies showing that bariatric surgery reduces the risk of endometrial cancer, the weight of the observation evidence is strong. In addition, bariatric surgery was reported to reduce all-cause mortality in the SOS study.13 Hence, for obese postmenopausal women, if lifestyle changes do not result in sustained weight loss, bariatric surgery may be an optimal approach to improving health outcomes.
Continue to: Progestin treatment and endometrial cancer risk...
Progestin treatment and endometrial cancer risk
Estrogen stimulates endometrial cell proliferation. Hence, unopposed chronic exposure to estrogen is a major risk factor for developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Progestins block the proliferative effect of estrogen and cause cell differentiation, resulting in stromal decidualization. Progestins also reduce the concentration of estrogen and progesterone receptors and increase the activity of enzymes that convert estradiol to estrone, blocking estrogen-induced endometrial proliferation.14
In women with endometrial hyperplasia, progestins have been shown to be effective in resolving the hyperplasia in approximately 80% of cases. Both oral progestins and the 52-mg levonorgestrel-containing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) have been reported to be effective in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia. In a Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis, the 52-mg LNG-IUD was reported to be somewhat more effective in resolving endometrial hyperplasia than cyclic oral progestins (89% vs 72%, respectively).15
Other studies have also reported that the 52 mg LNG-IUD was more effective than oral progestin therapy for women with complex atypical endometrial hyperplasia.16 There are no large randomized clinical trials of progestin therapy on prevention for future development of endometrial cancer in obese postmenopausal women who have a normal endometrial histology. However, for an obese perimenopausal woman, insertion of a 52-mg LNG-IUD may help to minimize excessive uterine bleeding during the menopause transition and reduce the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia during the early postmenopause.
We can help our patients reduce their risk of endometrial cancer
Obese postmenopausal women are at increased risk for developing endometrial cancer. Gynecologists play an important role in the prevention and early detection of endometrial cancer. We can make a difference and improve the health of our obese peri- and postmenopausal women by recommending interventions that reduce the risk of endometrial cancer, thereby improving the health of our patients. ●
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy, with approximately 59,000 cases diagnosed annually,1 and a lifetime risk of approximately 3.1% in the United States.2 Type I endometrial cancer includes tumors with endometrioid histology that are grade 1 or 2. Type II endometrial cancer includes tumors that have grade 3 endometrioid or nonendometrioid histology, including serous, clear cell, mucinous, squamous transitional cell, mesonephric, and undifferentiated tumors.3 Type I endometrial cancer is hormone sensitive, generally stimulated by estrogen and suppressed by progestins.
Endometrial cancer is diagnosed at a mean age of 63 years,4 and only 15% of cases occur before age 50.5 Women with an elevated body mass index (BMI) have a markedly increased risk of both Types I and II endometrial cancer (TABLE).6 Hence, endometrial cancer is highly prevalent in obese postmenopausal women. For these women health interventions that may reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer include dieting, physical activity, bariatric surgery, and progestin therapy.

Educating patients is a priority
Many women do not know that postmenopausal bleeding is a sign of endometrial cancer. All postmenopausal women should be advised that if they develop vaginal bleeding they need to be evaluated by a clinician.7 Women who are knowledgeable about the link between postmenopausal vaginal bleeding and endometrial cancer can be encouraged to share this information with their postmenopausal friends in order to reach more people with this important information. All obese postmenopausal women should be advised that weight loss and increased physical activity can reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer.
How weight loss and physical activity affect risk
Intentional weight loss has been reported to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women. As part of the Women’s Health Initiative observational study, 36,794 postmenopausal women aged 50 to 79 years with a uterus had their body weight and height measured at entry into the study and after 3 years of follow-up.8 During the 11 years following study entry, there were 566 incident cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with women who had a stable weight, intentional weight loss of ≥5% was associated with a 40% reduction in the risk of endometrial cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.60; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.42–0.86). Compared with women who had a stable weight, women who had weight gain ≥10% had an increased risk of endometrial cancer (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.00–1.57).
High levels of physical activity may be associated with a decreased risk of endometrial cancer. In one study, compared with a sedentary lifestyle, higher levels of physical activity were reported to be associated with a decreased risk of endometrial cancer.9
Continue to: How bariatric surgery affects risk...
How bariatric surgery affects risk
Many cancers are associated with obesity, including endometrial, breast, colon, pancreas, gallbladder, and renal. Obesity is associated with increased conversion of androgens to estrogens in fat tissue, stimulating excessive endometrial proliferation and increasing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Bariatric surgery reliably causes sustained weight reduction. Multiple studies have reported that bariatric surgery reduces the risk of endometrial cancer.
Schauer and colleagues used data from the Kaiser Permanente health system to identify 22,198 obese people who had undergone bariatric surgery and 66,427 matched controls who were obese but did not have surgery.10 The study population was 81% female, with a mean age of 45 years and a mean BMI of 45 kg/m2. After an average 3.5 years of follow-up there were 2,542 incident cases of cancer, including 322 cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with conventional weight loss treatment, bariatric surgery reduced the risk of endometrial cancer by 50% (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.37–0.67; P<.001).10 In addition, bariatric surgery reduced the risk of colon and pancreatic cancer by 41% and 54%, respectively.10
In the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study, 1,420 women who underwent bariatric surgery and 1,447 matched controls who received conventional obesity treatment were followed for 18 years.11 At study entry, the mean age of the women was approximately 48 years, and the mean BMI was approximately 42 kg/m2. In follow-up there were 76 incident cases of endometrial cancer. Compared with women receiving conventional obesity treatment, women who had bariatric surgery had a non–statistically significant 49% decrease in the risk of developing endometrial cancer (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.24–1.10)
In a systematic review of 5 additional studies (not including publications 10 or 11) of the impact of bariatric surgery on the risk of developing endometrial cancer, the surgery was associated with a 68% risk reduction (odds ratio [OR], 0.32; 95% CI, 0.16–0.63) compared with matched obese women that did not have surgery.12
Although there are no randomized prospective studies showing that bariatric surgery reduces the risk of endometrial cancer, the weight of the observation evidence is strong. In addition, bariatric surgery was reported to reduce all-cause mortality in the SOS study.13 Hence, for obese postmenopausal women, if lifestyle changes do not result in sustained weight loss, bariatric surgery may be an optimal approach to improving health outcomes.
Continue to: Progestin treatment and endometrial cancer risk...
Progestin treatment and endometrial cancer risk
Estrogen stimulates endometrial cell proliferation. Hence, unopposed chronic exposure to estrogen is a major risk factor for developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Progestins block the proliferative effect of estrogen and cause cell differentiation, resulting in stromal decidualization. Progestins also reduce the concentration of estrogen and progesterone receptors and increase the activity of enzymes that convert estradiol to estrone, blocking estrogen-induced endometrial proliferation.14
In women with endometrial hyperplasia, progestins have been shown to be effective in resolving the hyperplasia in approximately 80% of cases. Both oral progestins and the 52-mg levonorgestrel-containing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) have been reported to be effective in the treatment of endometrial hyperplasia. In a Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis, the 52-mg LNG-IUD was reported to be somewhat more effective in resolving endometrial hyperplasia than cyclic oral progestins (89% vs 72%, respectively).15
Other studies have also reported that the 52 mg LNG-IUD was more effective than oral progestin therapy for women with complex atypical endometrial hyperplasia.16 There are no large randomized clinical trials of progestin therapy on prevention for future development of endometrial cancer in obese postmenopausal women who have a normal endometrial histology. However, for an obese perimenopausal woman, insertion of a 52-mg LNG-IUD may help to minimize excessive uterine bleeding during the menopause transition and reduce the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia during the early postmenopause.
We can help our patients reduce their risk of endometrial cancer
Obese postmenopausal women are at increased risk for developing endometrial cancer. Gynecologists play an important role in the prevention and early detection of endometrial cancer. We can make a difference and improve the health of our obese peri- and postmenopausal women by recommending interventions that reduce the risk of endometrial cancer, thereby improving the health of our patients. ●
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Uterine cancer statistics. https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/uterine-cancer/statistics#:~:text=This%20year%2C%20an%20
estimated%2065%2C620,cancers%20occur%20in%20the%20endometrium. Accessed November 23, 2020. - Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD. April 15, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/. Accessed November 23, 2020.
- Noer MC, Antonsen SL, Ottesen B, et al. Type I versus Type II endometrial cancer: differential impact of comorbidity. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018;28:586-593.
- Sorosky JI. Endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:436-437.
- Gallup DG, Stock RJ. Adenocarcinoma of the endometrium in women 40 years of age or younger. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;64:417-420.
- Setiawan VW, Yang HP, Pike MC, et al. Type I and II endometrial cancers: have they different risk factors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2607-2618.
- Saccardi C, Vitagliano A, Marchetti M, et al. Endometrial cancer risk prediction according to indication of diagnostic hysteroscopy in postmenopausal women. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10:257.e1-e11.
- Luo J, Chlebowski RT, Hendryx M, et al. Intentional weight loss and endometrial cancer risk. J Clin Oncology. 2017;35:1189-1193.
- Friedenreich CM, Ryder-Burbidge C, McNeil J. Physical activity, obesity and sedentary behavior in cancer etiology: epidemiologic evidence and biological mechanisms. Mol Oncol. August 2, 2020. doi: 10.1001/1878-0261.12772.
- Schauer DP, Feigelson HS, Koebnick C, et al. Bariatric surgery and the risk of cancer in a large multisite cohort. Ann Surg. 2019;269:95-101.
- Anvenden A, Taube M, Peltonen M, et al. Long-term incidence of female-specific cancer after bariatric surgery or usual care in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;145:224-229.
- Winder AA, Kularatna M, MacCormick AD. Does bariatric surgery affect the incidence of endometrial cancer development? A systematic review. Obes Surg. 2018;28:1433-1440.
- Carlsson LM, Sjoholm K, Jacobson P, et al. Life expectancy after bariatric surgery in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1535-1543.
- Lessey BA, Young SL. In: Strauss JF, Barbieri RL (eds.) Yen and Jaffe’s Reproductive Endocrinology: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Clinical Management. 8th ed. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA; 2018:208-212.
- Mittermeier T, Farrant C, Wise MR. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for endometrial hyperplasia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;CD012658.
- Mandelbaum RS, Ciccone MA, Nusbaum DJ, et al. Progestin therapy for obese women with complex atypical hyperplasia: levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device vs systemic therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:103.e1-e13.
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Uterine cancer statistics. https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/uterine-cancer/statistics#:~:text=This%20year%2C%20an%20
estimated%2065%2C620,cancers%20occur%20in%20the%20endometrium. Accessed November 23, 2020. - Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD. April 15, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/. Accessed November 23, 2020.
- Noer MC, Antonsen SL, Ottesen B, et al. Type I versus Type II endometrial cancer: differential impact of comorbidity. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018;28:586-593.
- Sorosky JI. Endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:436-437.
- Gallup DG, Stock RJ. Adenocarcinoma of the endometrium in women 40 years of age or younger. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;64:417-420.
- Setiawan VW, Yang HP, Pike MC, et al. Type I and II endometrial cancers: have they different risk factors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2607-2618.
- Saccardi C, Vitagliano A, Marchetti M, et al. Endometrial cancer risk prediction according to indication of diagnostic hysteroscopy in postmenopausal women. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10:257.e1-e11.
- Luo J, Chlebowski RT, Hendryx M, et al. Intentional weight loss and endometrial cancer risk. J Clin Oncology. 2017;35:1189-1193.
- Friedenreich CM, Ryder-Burbidge C, McNeil J. Physical activity, obesity and sedentary behavior in cancer etiology: epidemiologic evidence and biological mechanisms. Mol Oncol. August 2, 2020. doi: 10.1001/1878-0261.12772.
- Schauer DP, Feigelson HS, Koebnick C, et al. Bariatric surgery and the risk of cancer in a large multisite cohort. Ann Surg. 2019;269:95-101.
- Anvenden A, Taube M, Peltonen M, et al. Long-term incidence of female-specific cancer after bariatric surgery or usual care in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;145:224-229.
- Winder AA, Kularatna M, MacCormick AD. Does bariatric surgery affect the incidence of endometrial cancer development? A systematic review. Obes Surg. 2018;28:1433-1440.
- Carlsson LM, Sjoholm K, Jacobson P, et al. Life expectancy after bariatric surgery in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1535-1543.
- Lessey BA, Young SL. In: Strauss JF, Barbieri RL (eds.) Yen and Jaffe’s Reproductive Endocrinology: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Clinical Management. 8th ed. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA; 2018:208-212.
- Mittermeier T, Farrant C, Wise MR. Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system for endometrial hyperplasia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;CD012658.
- Mandelbaum RS, Ciccone MA, Nusbaum DJ, et al. Progestin therapy for obese women with complex atypical hyperplasia: levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device vs systemic therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223:103.e1-e13.
Prophylactic antibiotics for myomectomy?
In the 1990s, researchers found that patients undergoing any type of surgical procedure were more than twice as likely to die if they developed postsurgical infection.1 Work to reduce surgical site infection (SSI) has and does continue, with perioperative antibiotics representing a good part of that effort. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists currently recommends such antibiotic therapy for women undergoing laparotomy and laparoscopic hysterectomy.2 ACOG does not, however, recommend prophylactic antibiotics for myomectomy procedures.3 Rates of infection for hysterectomy have been reported to be 3.9% for abdominal and 1.4% for minimally invasive approaches.4
To determine the current use of antibiotics during myomectomy and associated rates of SSI at their institutions, Dipti Banerjee, MD, and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis of women undergoing laparoscopic or abdominal myomectomy between February 2013 and December 2017 at the University of California, Los Angeles and Hoag Memorial Hospital in Orange County, California. They presented their study results at AAGL’s 49th Global Congress on MIGS, held virtually November 6-14, 2020.3
Rate of SSI after myomectomy
A total of 620 women underwent laparoscopic myomectomy and 563 underwent open myomectomy during the study period. Antibiotics were used in 76.9% of cases. SSI developed within 6 weeks of surgery in 34 women (2.9%) overall. The women undergoing abdominal myomectomy without antibiotics were more likely to experience SSI than the women who received antibiotics (odds ratio [OR], 4.89; confidence interval [CI], 1.80–13.27; P = .0006). For laparoscopic myomectomy, antibiotic use did not affect the odds of developing SSI (OR, 1.08; CI, 0.35–3.35).
Antibiotics were more likely to be used in certain cases
Antibiotics were more likely to be administered for patients who:
- were obese (body mass index ≥30 kg/m2) (P = .009)
- underwent previous abdominal surgery (P = .001)
- underwent laparotomy (P <.0001)
- had endometrial cavity entry (P <.0001)
- had >1 fibroid (P = .0004) or an aggregate fibroid weight >500 g (P <.0001).
More data on antibiotics for myomectomy
In a retrospective study conducted at 2 academic hospitals in Boston, Massachusetts, 1,211 women underwent myomectomy from 2009 to 2016. (Exclusions were use of vaginal or hysteroscopic myomectomy, chromopertubation, or conversion to hysterectomy.) More than 92% of the women received perioperative antibiotics at the time of surgery. Although demographics were similar between women receiving and not receiving antibiotics, women who received antibiotics were more likely to have longer operative times (median 140 vs 85 min), a greater myoma burden (7 vs 2 myomas removed and weight 255 vs 53 g), and lose blood during the procedure (137 vs 50 mL). These women also were 4 times less likely to have surgical site infection (adjusted OR, 3.77; 95% CI, 1.30–10.97; P = .015).5,6
Banerjee and colleagues say that their California study demonstrates “that the majority of surgeons elect to use antibiotics prophylactically” during myomectomy, despite current ACOG guidelines, and that their findings of benefit for abdominal myomectomy but not for laparoscopic myomectomy should inform future guidance on antibiotics for myomectomy surgery.3
- Kirkland KB, Briggs JP, Trivette SL, et al. The impact of surgical-site infections in the 1990s: attributable mortality, excess length of hospitalization, and extra costs. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1999;20:725-730.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin No. 195: prevention of infection after gynecologic procedures. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e172-e189.
- Banerjee D, Dejbakhsh S, Patel HH, et al. Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in myomectomy surgery. Paper presented at 49th Annual Meeting of the AAGL; November 2020.
- Uppal S, Harris J, Al-Niaimi A. Prophylactic antibiotic choice and risk of surgical site infection after hysterectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:321-329.
- Kim AJ, Clark NV, Jansen LJ, et al. Perioperative antibiotic use and associated infectious outcomes at the time of myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:626-635.
- Rebar RW. Should perioperative antibiotics at myomectomy be universal? NEJM J Watch. March 11, 2019.
In the 1990s, researchers found that patients undergoing any type of surgical procedure were more than twice as likely to die if they developed postsurgical infection.1 Work to reduce surgical site infection (SSI) has and does continue, with perioperative antibiotics representing a good part of that effort. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists currently recommends such antibiotic therapy for women undergoing laparotomy and laparoscopic hysterectomy.2 ACOG does not, however, recommend prophylactic antibiotics for myomectomy procedures.3 Rates of infection for hysterectomy have been reported to be 3.9% for abdominal and 1.4% for minimally invasive approaches.4
To determine the current use of antibiotics during myomectomy and associated rates of SSI at their institutions, Dipti Banerjee, MD, and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis of women undergoing laparoscopic or abdominal myomectomy between February 2013 and December 2017 at the University of California, Los Angeles and Hoag Memorial Hospital in Orange County, California. They presented their study results at AAGL’s 49th Global Congress on MIGS, held virtually November 6-14, 2020.3
Rate of SSI after myomectomy
A total of 620 women underwent laparoscopic myomectomy and 563 underwent open myomectomy during the study period. Antibiotics were used in 76.9% of cases. SSI developed within 6 weeks of surgery in 34 women (2.9%) overall. The women undergoing abdominal myomectomy without antibiotics were more likely to experience SSI than the women who received antibiotics (odds ratio [OR], 4.89; confidence interval [CI], 1.80–13.27; P = .0006). For laparoscopic myomectomy, antibiotic use did not affect the odds of developing SSI (OR, 1.08; CI, 0.35–3.35).
Antibiotics were more likely to be used in certain cases
Antibiotics were more likely to be administered for patients who:
- were obese (body mass index ≥30 kg/m2) (P = .009)
- underwent previous abdominal surgery (P = .001)
- underwent laparotomy (P <.0001)
- had endometrial cavity entry (P <.0001)
- had >1 fibroid (P = .0004) or an aggregate fibroid weight >500 g (P <.0001).
More data on antibiotics for myomectomy
In a retrospective study conducted at 2 academic hospitals in Boston, Massachusetts, 1,211 women underwent myomectomy from 2009 to 2016. (Exclusions were use of vaginal or hysteroscopic myomectomy, chromopertubation, or conversion to hysterectomy.) More than 92% of the women received perioperative antibiotics at the time of surgery. Although demographics were similar between women receiving and not receiving antibiotics, women who received antibiotics were more likely to have longer operative times (median 140 vs 85 min), a greater myoma burden (7 vs 2 myomas removed and weight 255 vs 53 g), and lose blood during the procedure (137 vs 50 mL). These women also were 4 times less likely to have surgical site infection (adjusted OR, 3.77; 95% CI, 1.30–10.97; P = .015).5,6
Banerjee and colleagues say that their California study demonstrates “that the majority of surgeons elect to use antibiotics prophylactically” during myomectomy, despite current ACOG guidelines, and that their findings of benefit for abdominal myomectomy but not for laparoscopic myomectomy should inform future guidance on antibiotics for myomectomy surgery.3
In the 1990s, researchers found that patients undergoing any type of surgical procedure were more than twice as likely to die if they developed postsurgical infection.1 Work to reduce surgical site infection (SSI) has and does continue, with perioperative antibiotics representing a good part of that effort. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists currently recommends such antibiotic therapy for women undergoing laparotomy and laparoscopic hysterectomy.2 ACOG does not, however, recommend prophylactic antibiotics for myomectomy procedures.3 Rates of infection for hysterectomy have been reported to be 3.9% for abdominal and 1.4% for minimally invasive approaches.4
To determine the current use of antibiotics during myomectomy and associated rates of SSI at their institutions, Dipti Banerjee, MD, and colleagues conducted a retrospective analysis of women undergoing laparoscopic or abdominal myomectomy between February 2013 and December 2017 at the University of California, Los Angeles and Hoag Memorial Hospital in Orange County, California. They presented their study results at AAGL’s 49th Global Congress on MIGS, held virtually November 6-14, 2020.3
Rate of SSI after myomectomy
A total of 620 women underwent laparoscopic myomectomy and 563 underwent open myomectomy during the study period. Antibiotics were used in 76.9% of cases. SSI developed within 6 weeks of surgery in 34 women (2.9%) overall. The women undergoing abdominal myomectomy without antibiotics were more likely to experience SSI than the women who received antibiotics (odds ratio [OR], 4.89; confidence interval [CI], 1.80–13.27; P = .0006). For laparoscopic myomectomy, antibiotic use did not affect the odds of developing SSI (OR, 1.08; CI, 0.35–3.35).
Antibiotics were more likely to be used in certain cases
Antibiotics were more likely to be administered for patients who:
- were obese (body mass index ≥30 kg/m2) (P = .009)
- underwent previous abdominal surgery (P = .001)
- underwent laparotomy (P <.0001)
- had endometrial cavity entry (P <.0001)
- had >1 fibroid (P = .0004) or an aggregate fibroid weight >500 g (P <.0001).
More data on antibiotics for myomectomy
In a retrospective study conducted at 2 academic hospitals in Boston, Massachusetts, 1,211 women underwent myomectomy from 2009 to 2016. (Exclusions were use of vaginal or hysteroscopic myomectomy, chromopertubation, or conversion to hysterectomy.) More than 92% of the women received perioperative antibiotics at the time of surgery. Although demographics were similar between women receiving and not receiving antibiotics, women who received antibiotics were more likely to have longer operative times (median 140 vs 85 min), a greater myoma burden (7 vs 2 myomas removed and weight 255 vs 53 g), and lose blood during the procedure (137 vs 50 mL). These women also were 4 times less likely to have surgical site infection (adjusted OR, 3.77; 95% CI, 1.30–10.97; P = .015).5,6
Banerjee and colleagues say that their California study demonstrates “that the majority of surgeons elect to use antibiotics prophylactically” during myomectomy, despite current ACOG guidelines, and that their findings of benefit for abdominal myomectomy but not for laparoscopic myomectomy should inform future guidance on antibiotics for myomectomy surgery.3
- Kirkland KB, Briggs JP, Trivette SL, et al. The impact of surgical-site infections in the 1990s: attributable mortality, excess length of hospitalization, and extra costs. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1999;20:725-730.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin No. 195: prevention of infection after gynecologic procedures. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e172-e189.
- Banerjee D, Dejbakhsh S, Patel HH, et al. Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in myomectomy surgery. Paper presented at 49th Annual Meeting of the AAGL; November 2020.
- Uppal S, Harris J, Al-Niaimi A. Prophylactic antibiotic choice and risk of surgical site infection after hysterectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:321-329.
- Kim AJ, Clark NV, Jansen LJ, et al. Perioperative antibiotic use and associated infectious outcomes at the time of myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:626-635.
- Rebar RW. Should perioperative antibiotics at myomectomy be universal? NEJM J Watch. March 11, 2019.
- Kirkland KB, Briggs JP, Trivette SL, et al. The impact of surgical-site infections in the 1990s: attributable mortality, excess length of hospitalization, and extra costs. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1999;20:725-730.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice Bulletin No. 195: prevention of infection after gynecologic procedures. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e172-e189.
- Banerjee D, Dejbakhsh S, Patel HH, et al. Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in myomectomy surgery. Paper presented at 49th Annual Meeting of the AAGL; November 2020.
- Uppal S, Harris J, Al-Niaimi A. Prophylactic antibiotic choice and risk of surgical site infection after hysterectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:321-329.
- Kim AJ, Clark NV, Jansen LJ, et al. Perioperative antibiotic use and associated infectious outcomes at the time of myomectomy. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:626-635.
- Rebar RW. Should perioperative antibiotics at myomectomy be universal? NEJM J Watch. March 11, 2019.