User login
ClinicalEdge only
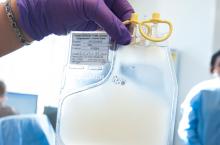
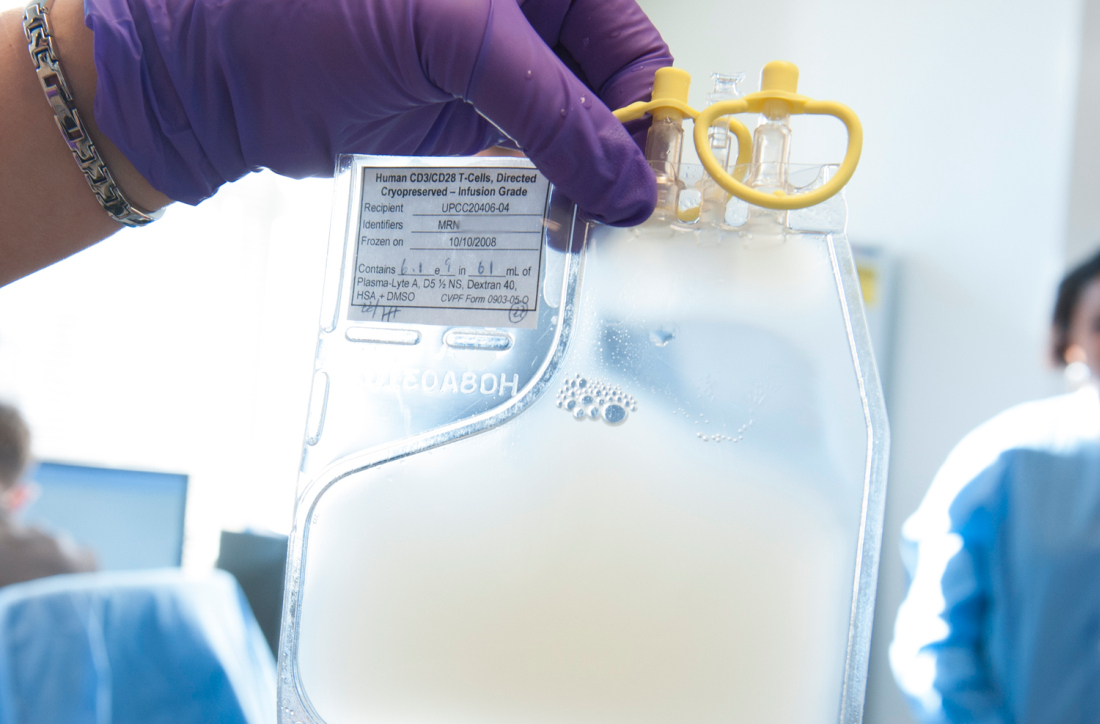
Survival data reported from largest CAR T trial in B-cell lymphoma
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Care coordination, equity can eliminate disparities for nonwhite patients with DLBCL
ORLANDO – Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who are members of an ethnic or racial minority do not have worse outcomes than whites when they receive appropriate treatment and institutional support, a study on disparities in cancer care shows.
Although previous studies have shown that minorities with DLBCL have worse outcomes than do whites, results of a study comparing outcomes from 155 patients of white heritage with those of 41 patients from black, Hispanic, or other minority backgrounds found no significant differences in either progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival in 2 years over follow-up, reported Nilanjan Ghosh, MD, PhD, from the Levine Cancer Institute, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C.
He attributes the results to his center’s robust nurse navigation program, equal access among all patients – regardless of ability to pay – to standard treatments, and to the availability of clinical trial participation and stem cell transplantation.
“I think a key message is that if you are able to offer the same treatment and clinical trials to people irrespective of their race or socioeconomic status and can provide support, you can get equal outcomes as long as the biology is the same in both groups,” he said at a briefing prior to presentation of data in an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Ghosh pointed to four separate studies that showed that minority populations with DLBCL have worse outcomes than did whites, and noted that both uninsured and Medicaid-insured patients have also been shown to have poorer results, suggesting a role of socioeconomic factors in determining who gets optimum care and who does not.
The investigators compared PFS and OS among white and nonwhite patients with DLBCL treated in their institution, which has a safety-net cancer center. They also looked at the frequencies of clinical trial participation and stem cell transplantation between the groups.
The study included all patients with de novo DLBCL who presented to their center during January 2016–January 2019. They used patient-reported descriptors of race/ethnicity to create one of two cohorts: either self-identified whites (155 patients) or nonwhites (41), a group that included black patients, Hispanic patients, Asian Americans, and Native Americans.
The authors collected data on demographics, disease characteristics (including revised International Prognostic Index and double-hit status), insurance data, treatment, trial enrollment, progression, and death.
They found that nonwhites were significantly younger at diagnosis (median 56 vs. 64 years; P = .007), with an even distribution between the sexes in each group.
Two-thirds of both white and nonwhite patients had government insurance (Medicare or Medicaid). Of the remaining patients, 33% of white had private insurance, compared with 27% of nonwhites. No whites were uninsured, but 3 of the 41 nonwhites (7%) had no insurance.
Of the 155 white patients, 121 (86%) received nurse navigation services, as did 33 of 41 (81%) of nonwhites. The services include lodging assistance for homeless patients, transportation services for patients without cars, and care coordination among primary care physicians, oncologists, and other specialists. The services are part of the center’s standard practice, with excess costs, if any, folded into the budget, Dr. Ghosh said.
Looking at disease characteristics and treatment, the investigators found that risk profiles were similar between the groups. A higher percentage of whites had double-hit lymphoma (11% vs. 7%), but this difference was not statistically significant.
The investigators also found that in their program race was not a barrier to optimum therapy, with 96% of whites and 98% of nonwhites receiving frontline therapy with an anthracycline and rituximab-based regimen, and 4% and 2%, respectively received a non–anthracycline based regimen.
In each group, 39% of patients had disease that either relapsed or was refractory to frontline therapy.
In all, 11% of whites and 12% of nonwhites enrolled in clinical trials, 11% and 19%, respectively, underwent stem cell transplantation.
For patients with relapsed/refractory disease, the 2-year PFS rates were 60% for whites, and 63% for nonwhites, and the 2-year OS rates were 74% and 81%, respectively.
Dr. Ghosh and colleagues concluded that “our safety net cancer center, with extensive nurse navigator support and access to standard treatments, stem cell transplants, and cutting-edge clinical trials may abrogate the inferior outcomes in minority populations that have been previously reported.”
The study was internally funded. Dr. Ghosh reported consulting fees, research funding, speakers bureau activity, and/or honoraria from multiple companies.
SOURCE: Hu B et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 425.
ORLANDO – Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who are members of an ethnic or racial minority do not have worse outcomes than whites when they receive appropriate treatment and institutional support, a study on disparities in cancer care shows.
Although previous studies have shown that minorities with DLBCL have worse outcomes than do whites, results of a study comparing outcomes from 155 patients of white heritage with those of 41 patients from black, Hispanic, or other minority backgrounds found no significant differences in either progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival in 2 years over follow-up, reported Nilanjan Ghosh, MD, PhD, from the Levine Cancer Institute, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C.
He attributes the results to his center’s robust nurse navigation program, equal access among all patients – regardless of ability to pay – to standard treatments, and to the availability of clinical trial participation and stem cell transplantation.
“I think a key message is that if you are able to offer the same treatment and clinical trials to people irrespective of their race or socioeconomic status and can provide support, you can get equal outcomes as long as the biology is the same in both groups,” he said at a briefing prior to presentation of data in an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Ghosh pointed to four separate studies that showed that minority populations with DLBCL have worse outcomes than did whites, and noted that both uninsured and Medicaid-insured patients have also been shown to have poorer results, suggesting a role of socioeconomic factors in determining who gets optimum care and who does not.
The investigators compared PFS and OS among white and nonwhite patients with DLBCL treated in their institution, which has a safety-net cancer center. They also looked at the frequencies of clinical trial participation and stem cell transplantation between the groups.
The study included all patients with de novo DLBCL who presented to their center during January 2016–January 2019. They used patient-reported descriptors of race/ethnicity to create one of two cohorts: either self-identified whites (155 patients) or nonwhites (41), a group that included black patients, Hispanic patients, Asian Americans, and Native Americans.
The authors collected data on demographics, disease characteristics (including revised International Prognostic Index and double-hit status), insurance data, treatment, trial enrollment, progression, and death.
They found that nonwhites were significantly younger at diagnosis (median 56 vs. 64 years; P = .007), with an even distribution between the sexes in each group.
Two-thirds of both white and nonwhite patients had government insurance (Medicare or Medicaid). Of the remaining patients, 33% of white had private insurance, compared with 27% of nonwhites. No whites were uninsured, but 3 of the 41 nonwhites (7%) had no insurance.
Of the 155 white patients, 121 (86%) received nurse navigation services, as did 33 of 41 (81%) of nonwhites. The services include lodging assistance for homeless patients, transportation services for patients without cars, and care coordination among primary care physicians, oncologists, and other specialists. The services are part of the center’s standard practice, with excess costs, if any, folded into the budget, Dr. Ghosh said.
Looking at disease characteristics and treatment, the investigators found that risk profiles were similar between the groups. A higher percentage of whites had double-hit lymphoma (11% vs. 7%), but this difference was not statistically significant.
The investigators also found that in their program race was not a barrier to optimum therapy, with 96% of whites and 98% of nonwhites receiving frontline therapy with an anthracycline and rituximab-based regimen, and 4% and 2%, respectively received a non–anthracycline based regimen.
In each group, 39% of patients had disease that either relapsed or was refractory to frontline therapy.
In all, 11% of whites and 12% of nonwhites enrolled in clinical trials, 11% and 19%, respectively, underwent stem cell transplantation.
For patients with relapsed/refractory disease, the 2-year PFS rates were 60% for whites, and 63% for nonwhites, and the 2-year OS rates were 74% and 81%, respectively.
Dr. Ghosh and colleagues concluded that “our safety net cancer center, with extensive nurse navigator support and access to standard treatments, stem cell transplants, and cutting-edge clinical trials may abrogate the inferior outcomes in minority populations that have been previously reported.”
The study was internally funded. Dr. Ghosh reported consulting fees, research funding, speakers bureau activity, and/or honoraria from multiple companies.
SOURCE: Hu B et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 425.
ORLANDO – Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who are members of an ethnic or racial minority do not have worse outcomes than whites when they receive appropriate treatment and institutional support, a study on disparities in cancer care shows.
Although previous studies have shown that minorities with DLBCL have worse outcomes than do whites, results of a study comparing outcomes from 155 patients of white heritage with those of 41 patients from black, Hispanic, or other minority backgrounds found no significant differences in either progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival in 2 years over follow-up, reported Nilanjan Ghosh, MD, PhD, from the Levine Cancer Institute, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C.
He attributes the results to his center’s robust nurse navigation program, equal access among all patients – regardless of ability to pay – to standard treatments, and to the availability of clinical trial participation and stem cell transplantation.
“I think a key message is that if you are able to offer the same treatment and clinical trials to people irrespective of their race or socioeconomic status and can provide support, you can get equal outcomes as long as the biology is the same in both groups,” he said at a briefing prior to presentation of data in an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Ghosh pointed to four separate studies that showed that minority populations with DLBCL have worse outcomes than did whites, and noted that both uninsured and Medicaid-insured patients have also been shown to have poorer results, suggesting a role of socioeconomic factors in determining who gets optimum care and who does not.
The investigators compared PFS and OS among white and nonwhite patients with DLBCL treated in their institution, which has a safety-net cancer center. They also looked at the frequencies of clinical trial participation and stem cell transplantation between the groups.
The study included all patients with de novo DLBCL who presented to their center during January 2016–January 2019. They used patient-reported descriptors of race/ethnicity to create one of two cohorts: either self-identified whites (155 patients) or nonwhites (41), a group that included black patients, Hispanic patients, Asian Americans, and Native Americans.
The authors collected data on demographics, disease characteristics (including revised International Prognostic Index and double-hit status), insurance data, treatment, trial enrollment, progression, and death.
They found that nonwhites were significantly younger at diagnosis (median 56 vs. 64 years; P = .007), with an even distribution between the sexes in each group.
Two-thirds of both white and nonwhite patients had government insurance (Medicare or Medicaid). Of the remaining patients, 33% of white had private insurance, compared with 27% of nonwhites. No whites were uninsured, but 3 of the 41 nonwhites (7%) had no insurance.
Of the 155 white patients, 121 (86%) received nurse navigation services, as did 33 of 41 (81%) of nonwhites. The services include lodging assistance for homeless patients, transportation services for patients without cars, and care coordination among primary care physicians, oncologists, and other specialists. The services are part of the center’s standard practice, with excess costs, if any, folded into the budget, Dr. Ghosh said.
Looking at disease characteristics and treatment, the investigators found that risk profiles were similar between the groups. A higher percentage of whites had double-hit lymphoma (11% vs. 7%), but this difference was not statistically significant.
The investigators also found that in their program race was not a barrier to optimum therapy, with 96% of whites and 98% of nonwhites receiving frontline therapy with an anthracycline and rituximab-based regimen, and 4% and 2%, respectively received a non–anthracycline based regimen.
In each group, 39% of patients had disease that either relapsed or was refractory to frontline therapy.
In all, 11% of whites and 12% of nonwhites enrolled in clinical trials, 11% and 19%, respectively, underwent stem cell transplantation.
For patients with relapsed/refractory disease, the 2-year PFS rates were 60% for whites, and 63% for nonwhites, and the 2-year OS rates were 74% and 81%, respectively.
Dr. Ghosh and colleagues concluded that “our safety net cancer center, with extensive nurse navigator support and access to standard treatments, stem cell transplants, and cutting-edge clinical trials may abrogate the inferior outcomes in minority populations that have been previously reported.”
The study was internally funded. Dr. Ghosh reported consulting fees, research funding, speakers bureau activity, and/or honoraria from multiple companies.
SOURCE: Hu B et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 425.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Adding polatuzumab extends survival in relapsed/refractory DLBCL
For patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding polatuzumab vedotin to bendamustine and rituximab can improve complete response rates and extend overall survival, according to findings from a phase 1b/2 trial.
Adding polatuzumab decreased mortality risk by 58%, reported lead author Laurie H. Sehn, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues.
“Patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL, including those who experienced treatment failure with [autologous stem cell transplant], have dismal outcomes with limited therapeutic options,” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. “To our knowledge, this is the first randomized trial demonstrating an [overall survival] benefit in patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL.”
In the first part of the study, 27 patients were treated with polatuzumab vedotin, bendamustine, and obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 27 months, this regimen returned a complete response rate of 29.6%, median progression-free survival of 6.3 months, and median overall survival of 10.8 months.
In the primary analysis, 80 patients were randomized to receive bendamustine and rituximab, with or without polatuzumab. Adding polatuzumab had a significant benefit, as 40.0% of these patients achieved a complete response, compared with 17.5% of patients who did not receive polatuzumab. After a median follow-up of 22.3 months, outcomes also were significantly improved with the addition of polatuzumab for both median progression-free survival (9.5 vs. 3.7 months) and overall survival (12.4 vs. 4.7 months).
Adding polatuzumab did come with some safety trade-offs. Rates of certain grade 3 or 4 adverse events were higher, including thrombocytopenia (41% vs. 23.1%), neutropenia (46.2% vs. 33.3%), and anemia (28.2% vs. 17.9%), while infection rates were comparable. Almost half of the patients treated with polatuzumab (43.6%) developed grade 1 or 2 peripheral neuropathy, but most cases resolved.
Combination therapy with polatuzumab, bendamustine, and rituximab “represents a novel, effective therapeutic regimen to address the unmet need of patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL,” the investigators wrote. Since just 25% of polatuzumab combination–treated patients had received prior autologous stem cell transplant, the investigators said they could not make definitive conclusions on this combination’s efficacy in the post-ASCT setting.
Additional trials involving polatuzumab in the relapsed/refractory setting are ongoing. For patients with treatment-naive DLBCL, a phase 3 trial (NCT03274492) is evaluating substitution of polatuzumab for vincristine in the R-CHOP regimen.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The investigators reported additional relationships with AbbVie, Kite Pharma, Lundbeck, and others.
SOURCE: Sehn LH et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00172.
For patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding polatuzumab vedotin to bendamustine and rituximab can improve complete response rates and extend overall survival, according to findings from a phase 1b/2 trial.
Adding polatuzumab decreased mortality risk by 58%, reported lead author Laurie H. Sehn, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues.
“Patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL, including those who experienced treatment failure with [autologous stem cell transplant], have dismal outcomes with limited therapeutic options,” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. “To our knowledge, this is the first randomized trial demonstrating an [overall survival] benefit in patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL.”
In the first part of the study, 27 patients were treated with polatuzumab vedotin, bendamustine, and obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 27 months, this regimen returned a complete response rate of 29.6%, median progression-free survival of 6.3 months, and median overall survival of 10.8 months.
In the primary analysis, 80 patients were randomized to receive bendamustine and rituximab, with or without polatuzumab. Adding polatuzumab had a significant benefit, as 40.0% of these patients achieved a complete response, compared with 17.5% of patients who did not receive polatuzumab. After a median follow-up of 22.3 months, outcomes also were significantly improved with the addition of polatuzumab for both median progression-free survival (9.5 vs. 3.7 months) and overall survival (12.4 vs. 4.7 months).
Adding polatuzumab did come with some safety trade-offs. Rates of certain grade 3 or 4 adverse events were higher, including thrombocytopenia (41% vs. 23.1%), neutropenia (46.2% vs. 33.3%), and anemia (28.2% vs. 17.9%), while infection rates were comparable. Almost half of the patients treated with polatuzumab (43.6%) developed grade 1 or 2 peripheral neuropathy, but most cases resolved.
Combination therapy with polatuzumab, bendamustine, and rituximab “represents a novel, effective therapeutic regimen to address the unmet need of patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL,” the investigators wrote. Since just 25% of polatuzumab combination–treated patients had received prior autologous stem cell transplant, the investigators said they could not make definitive conclusions on this combination’s efficacy in the post-ASCT setting.
Additional trials involving polatuzumab in the relapsed/refractory setting are ongoing. For patients with treatment-naive DLBCL, a phase 3 trial (NCT03274492) is evaluating substitution of polatuzumab for vincristine in the R-CHOP regimen.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The investigators reported additional relationships with AbbVie, Kite Pharma, Lundbeck, and others.
SOURCE: Sehn LH et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00172.
For patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding polatuzumab vedotin to bendamustine and rituximab can improve complete response rates and extend overall survival, according to findings from a phase 1b/2 trial.
Adding polatuzumab decreased mortality risk by 58%, reported lead author Laurie H. Sehn, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and colleagues.
“Patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL, including those who experienced treatment failure with [autologous stem cell transplant], have dismal outcomes with limited therapeutic options,” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology. “To our knowledge, this is the first randomized trial demonstrating an [overall survival] benefit in patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL.”
In the first part of the study, 27 patients were treated with polatuzumab vedotin, bendamustine, and obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 27 months, this regimen returned a complete response rate of 29.6%, median progression-free survival of 6.3 months, and median overall survival of 10.8 months.
In the primary analysis, 80 patients were randomized to receive bendamustine and rituximab, with or without polatuzumab. Adding polatuzumab had a significant benefit, as 40.0% of these patients achieved a complete response, compared with 17.5% of patients who did not receive polatuzumab. After a median follow-up of 22.3 months, outcomes also were significantly improved with the addition of polatuzumab for both median progression-free survival (9.5 vs. 3.7 months) and overall survival (12.4 vs. 4.7 months).
Adding polatuzumab did come with some safety trade-offs. Rates of certain grade 3 or 4 adverse events were higher, including thrombocytopenia (41% vs. 23.1%), neutropenia (46.2% vs. 33.3%), and anemia (28.2% vs. 17.9%), while infection rates were comparable. Almost half of the patients treated with polatuzumab (43.6%) developed grade 1 or 2 peripheral neuropathy, but most cases resolved.
Combination therapy with polatuzumab, bendamustine, and rituximab “represents a novel, effective therapeutic regimen to address the unmet need of patients with transplantation-ineligible [relapsed/refractory] DLBCL,” the investigators wrote. Since just 25% of polatuzumab combination–treated patients had received prior autologous stem cell transplant, the investigators said they could not make definitive conclusions on this combination’s efficacy in the post-ASCT setting.
Additional trials involving polatuzumab in the relapsed/refractory setting are ongoing. For patients with treatment-naive DLBCL, a phase 3 trial (NCT03274492) is evaluating substitution of polatuzumab for vincristine in the R-CHOP regimen.
The study was funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche and Genentech. The investigators reported additional relationships with AbbVie, Kite Pharma, Lundbeck, and others.
SOURCE: Sehn LH et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00172.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Armored CAR T cells elicit responses in NHL patients
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – An armored chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has demonstrated efficacy in vitro and in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
ICTCAR014, a dominant negative PD-1 armored CAR T-cell therapy, proved more cytotoxic than traditional CAR T-cell therapy in vitro and produced responses in 12 of 13 NHL patients who received it.
Xiaobin Victor Lu, PhD, of Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, Shanghai, China, presented results with ICTCAR014 at the meeting.
Dr. Lu explained that ICTCAR014 consists of CD19-targeted CAR T cells genetically engineered to overexpress a PD-1 dominant negative protein with an altered intracellular signaling domain. The dominant negative protein can act as a “decoy receptor” to bind and block the PD-L1/2 inhibitory signal, thereby enhancing the efficacy of CAR T cells.
Innovative Cellular Therapeutics is developing ICTCAR014 because there is “some room to improve” with commercially available CAR T-cell products, Dr. Lu said. Specifically, tisagenlecleucel produced a 52% response rate in the JULIET trial (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:45-56), and axicabtagene ciloleucel produced an 82% response rate in the ZUMA-1 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531-44).
There is also evidence to suggest that PD-1 blockade can modulate and “refuel” CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory NHL patients who fail or relapse after traditional anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy (Blood. 2017 Feb 23;129[8]:1039-41). This finding has prompted researchers to conduct trials of PD-1 inhibitors in combination with CAR T-cell therapies. But this combination approach may be expensive and cause more side effects than the armored CAR T-cell approach, Dr. Lu said.
In preclinical studies, Dr. Lu and colleagues found that ICTCAR014 was more effective than traditional anti-CD19 CAR T cells in killing Nalm6-PDL1 cells. In addition, the PD-1 dominant negative protein protected CAR T cells from exhaustion.
Dr. Lu also presented results in 13 NHL patients who have received ICTCAR014 in a phase 1 trial in China. Eleven patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and two had follicular lymphoma.
The objective response rate was 92.3% (12/13), which included five partial responses (38.5%) and seven complete responses (53.8%). Both follicular lymphoma patients and five DLBCL patients achieved a complete response. Five DLBCL patients achieved a partial response, and the remaining DLBCL patient did not respond.
Dr. Lu did not present safety data. However, he reported that there was no increased incidence of cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity in these patients, compared with patients receiving traditional CAR T-cell therapy.
Dr. Lu is employed by Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, which funded the research and is developing ICTCAR014.
SOURCE: Lu V et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O25.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – An armored chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has demonstrated efficacy in vitro and in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
ICTCAR014, a dominant negative PD-1 armored CAR T-cell therapy, proved more cytotoxic than traditional CAR T-cell therapy in vitro and produced responses in 12 of 13 NHL patients who received it.
Xiaobin Victor Lu, PhD, of Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, Shanghai, China, presented results with ICTCAR014 at the meeting.
Dr. Lu explained that ICTCAR014 consists of CD19-targeted CAR T cells genetically engineered to overexpress a PD-1 dominant negative protein with an altered intracellular signaling domain. The dominant negative protein can act as a “decoy receptor” to bind and block the PD-L1/2 inhibitory signal, thereby enhancing the efficacy of CAR T cells.
Innovative Cellular Therapeutics is developing ICTCAR014 because there is “some room to improve” with commercially available CAR T-cell products, Dr. Lu said. Specifically, tisagenlecleucel produced a 52% response rate in the JULIET trial (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:45-56), and axicabtagene ciloleucel produced an 82% response rate in the ZUMA-1 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531-44).
There is also evidence to suggest that PD-1 blockade can modulate and “refuel” CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory NHL patients who fail or relapse after traditional anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy (Blood. 2017 Feb 23;129[8]:1039-41). This finding has prompted researchers to conduct trials of PD-1 inhibitors in combination with CAR T-cell therapies. But this combination approach may be expensive and cause more side effects than the armored CAR T-cell approach, Dr. Lu said.
In preclinical studies, Dr. Lu and colleagues found that ICTCAR014 was more effective than traditional anti-CD19 CAR T cells in killing Nalm6-PDL1 cells. In addition, the PD-1 dominant negative protein protected CAR T cells from exhaustion.
Dr. Lu also presented results in 13 NHL patients who have received ICTCAR014 in a phase 1 trial in China. Eleven patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and two had follicular lymphoma.
The objective response rate was 92.3% (12/13), which included five partial responses (38.5%) and seven complete responses (53.8%). Both follicular lymphoma patients and five DLBCL patients achieved a complete response. Five DLBCL patients achieved a partial response, and the remaining DLBCL patient did not respond.
Dr. Lu did not present safety data. However, he reported that there was no increased incidence of cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity in these patients, compared with patients receiving traditional CAR T-cell therapy.
Dr. Lu is employed by Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, which funded the research and is developing ICTCAR014.
SOURCE: Lu V et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O25.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD – An armored chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has demonstrated efficacy in vitro and in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
ICTCAR014, a dominant negative PD-1 armored CAR T-cell therapy, proved more cytotoxic than traditional CAR T-cell therapy in vitro and produced responses in 12 of 13 NHL patients who received it.
Xiaobin Victor Lu, PhD, of Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, Shanghai, China, presented results with ICTCAR014 at the meeting.
Dr. Lu explained that ICTCAR014 consists of CD19-targeted CAR T cells genetically engineered to overexpress a PD-1 dominant negative protein with an altered intracellular signaling domain. The dominant negative protein can act as a “decoy receptor” to bind and block the PD-L1/2 inhibitory signal, thereby enhancing the efficacy of CAR T cells.
Innovative Cellular Therapeutics is developing ICTCAR014 because there is “some room to improve” with commercially available CAR T-cell products, Dr. Lu said. Specifically, tisagenlecleucel produced a 52% response rate in the JULIET trial (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:45-56), and axicabtagene ciloleucel produced an 82% response rate in the ZUMA-1 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531-44).
There is also evidence to suggest that PD-1 blockade can modulate and “refuel” CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory NHL patients who fail or relapse after traditional anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy (Blood. 2017 Feb 23;129[8]:1039-41). This finding has prompted researchers to conduct trials of PD-1 inhibitors in combination with CAR T-cell therapies. But this combination approach may be expensive and cause more side effects than the armored CAR T-cell approach, Dr. Lu said.
In preclinical studies, Dr. Lu and colleagues found that ICTCAR014 was more effective than traditional anti-CD19 CAR T cells in killing Nalm6-PDL1 cells. In addition, the PD-1 dominant negative protein protected CAR T cells from exhaustion.
Dr. Lu also presented results in 13 NHL patients who have received ICTCAR014 in a phase 1 trial in China. Eleven patients had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and two had follicular lymphoma.
The objective response rate was 92.3% (12/13), which included five partial responses (38.5%) and seven complete responses (53.8%). Both follicular lymphoma patients and five DLBCL patients achieved a complete response. Five DLBCL patients achieved a partial response, and the remaining DLBCL patient did not respond.
Dr. Lu did not present safety data. However, he reported that there was no increased incidence of cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity in these patients, compared with patients receiving traditional CAR T-cell therapy.
Dr. Lu is employed by Innovative Cellular Therapeutics, which funded the research and is developing ICTCAR014.
SOURCE: Lu V et al. SITC 2019, Abstract O25.
REPORTING FROM SITC 2019
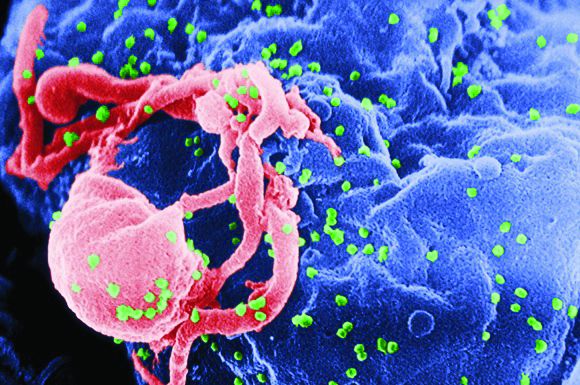
CAR T-cell therapy found safe, effective for HIV-associated lymphoma
HIV positivity does not preclude chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for patients with aggressive lymphoma, a report of two cases suggests. Both of the HIV-positive patients, one of whom had long-term psychiatric comorbidity, achieved durable remission on axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) without undue toxicity.
“To our knowledge, these are the first reported cases of CAR T-cell therapy administered to HIV-infected patients with lymphoma,” Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and his colleagues wrote in Cancer. “Patients with HIV and AIDS, as well as those with preexisting mental illness, should not be considered disqualified from CAR T-cell therapy and deserve ongoing studies to optimize efficacy and safety in this population.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two CAR T-cell products that target the B-cell antigen CD19 for the treatment of refractory lymphoma. But their efficacy and safety in HIV-positive patients are unknown because this group has been excluded from pivotal clinical trials.
Dr. Abramson and coauthors detail the two cases of successful anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with HIV-associated, refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
The first patient was an HIV-positive man with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of germinal center B-cell subtype who was intermittently adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His comorbidities included posttraumatic stress disorder and schizoaffective disorder.
Previous treatments for DLBCL included dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (EPOCH-R), and rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE). A recurrence precluded high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell support.
With close multidisciplinary management, including psychiatric consultation, the patient became a candidate for CAR T-cell therapy and received axicabtagene ciloleucel. He experienced grade 2 cytokine release syndrome and grade 3 neurologic toxicity, both of which resolved with treatment. Imaging showed complete remission at approximately 3 months that was sustained at 1 year. Additionally, he had an undetectable HIV viral load and was psychiatrically stable.
The second patient was a man with AIDS-associated, non–germinal center B-cell, Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL who was adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His lymphoma had recurred rapidly after initially responding to dose-adjusted EPOCH-R and then was refractory to combination rituximab and lenalidomide. He previously had hepatitis B virus, cytomegalovirus, and Mycobacterium avium complex infections.
Because of prolonged cytopenias and infectious complications after the previous lymphoma treatments, the patient was considered a poor candidate for high-dose chemotherapy. He underwent CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel and had a complete remission on day 28. Additionally, his HIV infection remained well controlled.
“Although much remains to be learned regarding CAR T-cell therapy in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies, with or without HIV infection, the cases presented herein demonstrate that patients with chemotherapy-refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma can successfully undergo autologous CAR T-cell manufacturing, and subsequently can safely tolerate CAR T-cell therapy and achieve a durable complete remission,” the researchers wrote. “These cases have further demonstrated the proactive, multidisciplinary care required to navigate a patient with high-risk lymphoma through CAR T-cell therapy with attention to significant medical and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Dr. Abramson reported that he has acted as a paid member of the scientific advisory board and as a paid consultant for Kite Pharma, which markets Yescarta, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. Cancer. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32411.
HIV positivity does not preclude chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for patients with aggressive lymphoma, a report of two cases suggests. Both of the HIV-positive patients, one of whom had long-term psychiatric comorbidity, achieved durable remission on axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) without undue toxicity.
“To our knowledge, these are the first reported cases of CAR T-cell therapy administered to HIV-infected patients with lymphoma,” Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and his colleagues wrote in Cancer. “Patients with HIV and AIDS, as well as those with preexisting mental illness, should not be considered disqualified from CAR T-cell therapy and deserve ongoing studies to optimize efficacy and safety in this population.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two CAR T-cell products that target the B-cell antigen CD19 for the treatment of refractory lymphoma. But their efficacy and safety in HIV-positive patients are unknown because this group has been excluded from pivotal clinical trials.
Dr. Abramson and coauthors detail the two cases of successful anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with HIV-associated, refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
The first patient was an HIV-positive man with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of germinal center B-cell subtype who was intermittently adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His comorbidities included posttraumatic stress disorder and schizoaffective disorder.
Previous treatments for DLBCL included dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (EPOCH-R), and rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE). A recurrence precluded high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell support.
With close multidisciplinary management, including psychiatric consultation, the patient became a candidate for CAR T-cell therapy and received axicabtagene ciloleucel. He experienced grade 2 cytokine release syndrome and grade 3 neurologic toxicity, both of which resolved with treatment. Imaging showed complete remission at approximately 3 months that was sustained at 1 year. Additionally, he had an undetectable HIV viral load and was psychiatrically stable.
The second patient was a man with AIDS-associated, non–germinal center B-cell, Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL who was adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His lymphoma had recurred rapidly after initially responding to dose-adjusted EPOCH-R and then was refractory to combination rituximab and lenalidomide. He previously had hepatitis B virus, cytomegalovirus, and Mycobacterium avium complex infections.
Because of prolonged cytopenias and infectious complications after the previous lymphoma treatments, the patient was considered a poor candidate for high-dose chemotherapy. He underwent CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel and had a complete remission on day 28. Additionally, his HIV infection remained well controlled.
“Although much remains to be learned regarding CAR T-cell therapy in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies, with or without HIV infection, the cases presented herein demonstrate that patients with chemotherapy-refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma can successfully undergo autologous CAR T-cell manufacturing, and subsequently can safely tolerate CAR T-cell therapy and achieve a durable complete remission,” the researchers wrote. “These cases have further demonstrated the proactive, multidisciplinary care required to navigate a patient with high-risk lymphoma through CAR T-cell therapy with attention to significant medical and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Dr. Abramson reported that he has acted as a paid member of the scientific advisory board and as a paid consultant for Kite Pharma, which markets Yescarta, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. Cancer. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32411.
HIV positivity does not preclude chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for patients with aggressive lymphoma, a report of two cases suggests. Both of the HIV-positive patients, one of whom had long-term psychiatric comorbidity, achieved durable remission on axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) without undue toxicity.
“To our knowledge, these are the first reported cases of CAR T-cell therapy administered to HIV-infected patients with lymphoma,” Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and his colleagues wrote in Cancer. “Patients with HIV and AIDS, as well as those with preexisting mental illness, should not be considered disqualified from CAR T-cell therapy and deserve ongoing studies to optimize efficacy and safety in this population.”
The Food and Drug Administration has approved two CAR T-cell products that target the B-cell antigen CD19 for the treatment of refractory lymphoma. But their efficacy and safety in HIV-positive patients are unknown because this group has been excluded from pivotal clinical trials.
Dr. Abramson and coauthors detail the two cases of successful anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with HIV-associated, refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
The first patient was an HIV-positive man with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of germinal center B-cell subtype who was intermittently adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His comorbidities included posttraumatic stress disorder and schizoaffective disorder.
Previous treatments for DLBCL included dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (EPOCH-R), and rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE). A recurrence precluded high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell support.
With close multidisciplinary management, including psychiatric consultation, the patient became a candidate for CAR T-cell therapy and received axicabtagene ciloleucel. He experienced grade 2 cytokine release syndrome and grade 3 neurologic toxicity, both of which resolved with treatment. Imaging showed complete remission at approximately 3 months that was sustained at 1 year. Additionally, he had an undetectable HIV viral load and was psychiatrically stable.
The second patient was a man with AIDS-associated, non–germinal center B-cell, Epstein-Barr virus–positive DLBCL who was adherent to antiretroviral therapy. His lymphoma had recurred rapidly after initially responding to dose-adjusted EPOCH-R and then was refractory to combination rituximab and lenalidomide. He previously had hepatitis B virus, cytomegalovirus, and Mycobacterium avium complex infections.
Because of prolonged cytopenias and infectious complications after the previous lymphoma treatments, the patient was considered a poor candidate for high-dose chemotherapy. He underwent CAR T-cell therapy with axicabtagene ciloleucel and had a complete remission on day 28. Additionally, his HIV infection remained well controlled.
“Although much remains to be learned regarding CAR T-cell therapy in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies, with or without HIV infection, the cases presented herein demonstrate that patients with chemotherapy-refractory, high-grade B-cell lymphoma can successfully undergo autologous CAR T-cell manufacturing, and subsequently can safely tolerate CAR T-cell therapy and achieve a durable complete remission,” the researchers wrote. “These cases have further demonstrated the proactive, multidisciplinary care required to navigate a patient with high-risk lymphoma through CAR T-cell therapy with attention to significant medical and psychiatric comorbidities.”
Dr. Abramson reported that he has acted as a paid member of the scientific advisory board and as a paid consultant for Kite Pharma, which markets Yescarta, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. Cancer. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32411.
FROM CANCER
Could home care replace inpatient HSCT?
Can receiving all posttransplant care at home benefit patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)? Researchers are conducting phase 2 trials to find out.
Nelson Chao, MD, and colleagues at Duke University in Durham, N.C., completed a phase 1 trial that suggested post-HSCT care at home was feasible and safe (Blood. 2017;130:745).
Now, the team is conducting phase 2 trials – NCT01725022 and NCT02218151 – comparing patients who receive all posttransplant care at home with patients treated in the hospital or in the outpatient setting with daily visits to the clinic.
The main goal is to determine if allogeneic HSCT recipients treated at home can maintain their normal microbiome and, as a result, have a lower risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). The researchers are also looking at other outcomes such as quality of life, treatment-related morbidities and mortality, and the cost of care for both allogeneic and autologous transplant recipients.
To be eligible for home care after HSCT, a patient must live within a 90-minute driving distance of Duke and have a caregiver available at home. The patient’s home must pass an inspection, showing it to be free of sources for potential infection, such as mold or pets that sleep in the patient’s bed.
When the time comes for treatment, the patient receives conditioning at the hospital but can return home the day before or the day of transplant. After discharge, the patient is visited by a nurse practitioner or physician assistant each morning for a physical examination and blood draw.
In the afternoon, the patient is visited by a clinic nurse who brings any necessary supplies or treatments, such as blood products or intravenous antibiotics. The patient also has daily video calls with an attending physician and can be admitted to the hospital for any events that cannot be managed in the home setting.
Patients can have visitors and spend time away from home, but precautions are necessary. Friends or family who are sick should not be allowed to visit, and patients should avoid crowds when they go out.

Initial findings
The Duke team has treated 41 HSCT recipients at home so far. Dr. Chao said it’s still too early to draw any conclusions about differences in outcomes between home care and inpatient/outpatient HSCT.
However, a preliminary analysis of costs suggests home care is cheaper than inpatient HSCT. The researchers found that, for the first several transplants, at day 60, the cost of home care was roughly half that of inpatient HSCT.
In addition, patients seem to be happy with posttransplant care at home.
“The patients love being at home, in their own environment, with their families,” Dr. Chao said. “Almost every single patient [in the phase 1 trial] said that he or she liked it much better. There was one patient in the phase 1 that felt a little isolated, and I can see why because we say, ‘You can stay home, but don’t have a whole lot of people in.’ ”
One patient’s experience
Beth Vanderkin said it was “a blessing” to receive care at home after undergoing HSCT at Duke.
Ms. Vanderkin was diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in 2014. After two chemotherapy regimens failed to shrink the tumor in her chest, she underwent radiotherapy and responded well. When a PET scan revealed the tumor had gone completely, she proceeded to transplant.
She received a haploidentical HSCT using cells donated by her eldest daughter, Hannah Eichhorst. Ms. Vanderkin received the transplant in the hospital, and for 2 weeks after that, she made daily visits to the transplant clinic.
After those 2 weeks, Ms. Vanderkin continued her treatment at home. Like other patients eligible for home care, Ms. Vanderkin lived close to Duke, had a caregiver available, and had passed a home inspection. The Duke team shipped the needed medical supplies to her house and arranged twice-daily visits from nurses and daily video calls with a doctor.
Ms. Vanderkin said receiving care at home was “a game changer.” She derived comfort from recovering in her own environment, could spend more time with her family, and didn’t have to miss special events. While receiving care at home, Ms. Vanderkin attended the homecoming event where her son, Josiah, was part of the court. Wearing a face mask and carrying a portable pump in her purse, Ms. Vanderkin joined other mothers in escorting their children onto the football field.
“I got to escort my son out onto the field, and he was crowned king that night,” Ms. Vanderkin said. “I didn’t do a lot of things [while receiving care at home], but there were things I didn’t have to miss because I was at home and not in the hospital.”
Ms. Vanderkin said home care was also beneficial for her husband, who was her caregiver. Thomas Vanderkin was able to work from home while caring for his wife, and the daily nurses’ visits allowed him to run errands without having to leave Ms. Vanderkin alone.
Since her experience with home care, Ms. Vanderkin has spent many more days in the hospital and clinic. She experienced a relapse after the transplant and went on to receive more chemotherapy as well as ipilimumab. She responded to that treatment and has now been cancer-free for 3 years.
The ipilimumab did cause side effects, including intestinal problems that resulted in the need for parenteral nutrition. This side effect was made more bearable, Ms. Vanderkin said, because she was able to receive the parenteral nutrition at home. She and her husband were comfortable with additional home care because of their positive experience with posttransplant care.
“I think we’re conditioned to think that, to receive the best care, we have to be sitting in a hospital room or a clinic, but I think there’s a lot of things we can probably do at home,” Ms. Vanderkin said. “And we might fare a lot better as patients if we’re in an environment that we feel comfortable in.”
Experience at other centers
The team at Duke is not the first to study HSCT care at home. In fact, researchers in Sweden have been studying posttransplant home care since 1998.
A pilot trial the group published in 2000 suggested that home care was safe and, in some ways, superior to inpatient HSCT (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000 Nov;26[10]:1057-60). Patients treated at home had a lower rate of bacteremia, fewer days of total parenteral nutrition, fewer erythrocyte transfusions, and fewer days on antibiotics and analgesics. Rates of fever, engraftment time, and acute GVHD were similar between the inpatient and home-care groups.
A study published by the same researchers in 2002 showed that patients who received home care had lower rates of grade 2-4 acute GVHD and transplant-related mortality compared to inpatients (Blood. 2002 Dec 15;100[13]:4317-24). Two-year overall survival was superior with home care as well.
On the other hand, a study the group published in 2013 showed no significant differences in 5-year survival, transplant-related mortality, relapse, or chronic GVHD between inpatients and those who received care at home (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.11.5189).
The phase 2 trials at Duke should provide more insight into patient outcomes, but results probably won’t be available for 2 more years, Dr. Chao said.
In the meantime, other U.S. researchers are studying home care as well. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center is conducting a pilot study to determine if HSCT care at home is feasible (NCT02671448).
Dr. Chao said home care should be possible for other centers, particularly those that already perform outpatient HSCT.
“Having the outpatient infrastructure to support these patients is a big step,” he said. “And I think we were able to do that mainly because we do most of our transplants in the outpatient setting already. So that jump to the home is a little less compared to a center that does no outpatient transplants.”
He added, “There’s a certain amount of inertia to overcome and a certain amount of apprehension from the caregivers initially because [patients aren’t] sitting in your unit all the time, but I don’t see this as a huge barrier.”
In fact, Dr. Chao said, if results with home care are favorable, it could potentially replace inpatient HSCT for certain patients.
Dr. Chao’s research is supported by Duke University, and he reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Can receiving all posttransplant care at home benefit patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)? Researchers are conducting phase 2 trials to find out.
Nelson Chao, MD, and colleagues at Duke University in Durham, N.C., completed a phase 1 trial that suggested post-HSCT care at home was feasible and safe (Blood. 2017;130:745).
Now, the team is conducting phase 2 trials – NCT01725022 and NCT02218151 – comparing patients who receive all posttransplant care at home with patients treated in the hospital or in the outpatient setting with daily visits to the clinic.
The main goal is to determine if allogeneic HSCT recipients treated at home can maintain their normal microbiome and, as a result, have a lower risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). The researchers are also looking at other outcomes such as quality of life, treatment-related morbidities and mortality, and the cost of care for both allogeneic and autologous transplant recipients.
To be eligible for home care after HSCT, a patient must live within a 90-minute driving distance of Duke and have a caregiver available at home. The patient’s home must pass an inspection, showing it to be free of sources for potential infection, such as mold or pets that sleep in the patient’s bed.
When the time comes for treatment, the patient receives conditioning at the hospital but can return home the day before or the day of transplant. After discharge, the patient is visited by a nurse practitioner or physician assistant each morning for a physical examination and blood draw.
In the afternoon, the patient is visited by a clinic nurse who brings any necessary supplies or treatments, such as blood products or intravenous antibiotics. The patient also has daily video calls with an attending physician and can be admitted to the hospital for any events that cannot be managed in the home setting.
Patients can have visitors and spend time away from home, but precautions are necessary. Friends or family who are sick should not be allowed to visit, and patients should avoid crowds when they go out.

Initial findings
The Duke team has treated 41 HSCT recipients at home so far. Dr. Chao said it’s still too early to draw any conclusions about differences in outcomes between home care and inpatient/outpatient HSCT.
However, a preliminary analysis of costs suggests home care is cheaper than inpatient HSCT. The researchers found that, for the first several transplants, at day 60, the cost of home care was roughly half that of inpatient HSCT.
In addition, patients seem to be happy with posttransplant care at home.
“The patients love being at home, in their own environment, with their families,” Dr. Chao said. “Almost every single patient [in the phase 1 trial] said that he or she liked it much better. There was one patient in the phase 1 that felt a little isolated, and I can see why because we say, ‘You can stay home, but don’t have a whole lot of people in.’ ”
One patient’s experience
Beth Vanderkin said it was “a blessing” to receive care at home after undergoing HSCT at Duke.
Ms. Vanderkin was diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in 2014. After two chemotherapy regimens failed to shrink the tumor in her chest, she underwent radiotherapy and responded well. When a PET scan revealed the tumor had gone completely, she proceeded to transplant.
She received a haploidentical HSCT using cells donated by her eldest daughter, Hannah Eichhorst. Ms. Vanderkin received the transplant in the hospital, and for 2 weeks after that, she made daily visits to the transplant clinic.
After those 2 weeks, Ms. Vanderkin continued her treatment at home. Like other patients eligible for home care, Ms. Vanderkin lived close to Duke, had a caregiver available, and had passed a home inspection. The Duke team shipped the needed medical supplies to her house and arranged twice-daily visits from nurses and daily video calls with a doctor.
Ms. Vanderkin said receiving care at home was “a game changer.” She derived comfort from recovering in her own environment, could spend more time with her family, and didn’t have to miss special events. While receiving care at home, Ms. Vanderkin attended the homecoming event where her son, Josiah, was part of the court. Wearing a face mask and carrying a portable pump in her purse, Ms. Vanderkin joined other mothers in escorting their children onto the football field.
“I got to escort my son out onto the field, and he was crowned king that night,” Ms. Vanderkin said. “I didn’t do a lot of things [while receiving care at home], but there were things I didn’t have to miss because I was at home and not in the hospital.”
Ms. Vanderkin said home care was also beneficial for her husband, who was her caregiver. Thomas Vanderkin was able to work from home while caring for his wife, and the daily nurses’ visits allowed him to run errands without having to leave Ms. Vanderkin alone.
Since her experience with home care, Ms. Vanderkin has spent many more days in the hospital and clinic. She experienced a relapse after the transplant and went on to receive more chemotherapy as well as ipilimumab. She responded to that treatment and has now been cancer-free for 3 years.
The ipilimumab did cause side effects, including intestinal problems that resulted in the need for parenteral nutrition. This side effect was made more bearable, Ms. Vanderkin said, because she was able to receive the parenteral nutrition at home. She and her husband were comfortable with additional home care because of their positive experience with posttransplant care.
“I think we’re conditioned to think that, to receive the best care, we have to be sitting in a hospital room or a clinic, but I think there’s a lot of things we can probably do at home,” Ms. Vanderkin said. “And we might fare a lot better as patients if we’re in an environment that we feel comfortable in.”
Experience at other centers
The team at Duke is not the first to study HSCT care at home. In fact, researchers in Sweden have been studying posttransplant home care since 1998.
A pilot trial the group published in 2000 suggested that home care was safe and, in some ways, superior to inpatient HSCT (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000 Nov;26[10]:1057-60). Patients treated at home had a lower rate of bacteremia, fewer days of total parenteral nutrition, fewer erythrocyte transfusions, and fewer days on antibiotics and analgesics. Rates of fever, engraftment time, and acute GVHD were similar between the inpatient and home-care groups.
A study published by the same researchers in 2002 showed that patients who received home care had lower rates of grade 2-4 acute GVHD and transplant-related mortality compared to inpatients (Blood. 2002 Dec 15;100[13]:4317-24). Two-year overall survival was superior with home care as well.
On the other hand, a study the group published in 2013 showed no significant differences in 5-year survival, transplant-related mortality, relapse, or chronic GVHD between inpatients and those who received care at home (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.11.5189).
The phase 2 trials at Duke should provide more insight into patient outcomes, but results probably won’t be available for 2 more years, Dr. Chao said.
In the meantime, other U.S. researchers are studying home care as well. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center is conducting a pilot study to determine if HSCT care at home is feasible (NCT02671448).
Dr. Chao said home care should be possible for other centers, particularly those that already perform outpatient HSCT.
“Having the outpatient infrastructure to support these patients is a big step,” he said. “And I think we were able to do that mainly because we do most of our transplants in the outpatient setting already. So that jump to the home is a little less compared to a center that does no outpatient transplants.”
He added, “There’s a certain amount of inertia to overcome and a certain amount of apprehension from the caregivers initially because [patients aren’t] sitting in your unit all the time, but I don’t see this as a huge barrier.”
In fact, Dr. Chao said, if results with home care are favorable, it could potentially replace inpatient HSCT for certain patients.
Dr. Chao’s research is supported by Duke University, and he reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Can receiving all posttransplant care at home benefit patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT)? Researchers are conducting phase 2 trials to find out.
Nelson Chao, MD, and colleagues at Duke University in Durham, N.C., completed a phase 1 trial that suggested post-HSCT care at home was feasible and safe (Blood. 2017;130:745).
Now, the team is conducting phase 2 trials – NCT01725022 and NCT02218151 – comparing patients who receive all posttransplant care at home with patients treated in the hospital or in the outpatient setting with daily visits to the clinic.
The main goal is to determine if allogeneic HSCT recipients treated at home can maintain their normal microbiome and, as a result, have a lower risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). The researchers are also looking at other outcomes such as quality of life, treatment-related morbidities and mortality, and the cost of care for both allogeneic and autologous transplant recipients.
To be eligible for home care after HSCT, a patient must live within a 90-minute driving distance of Duke and have a caregiver available at home. The patient’s home must pass an inspection, showing it to be free of sources for potential infection, such as mold or pets that sleep in the patient’s bed.
When the time comes for treatment, the patient receives conditioning at the hospital but can return home the day before or the day of transplant. After discharge, the patient is visited by a nurse practitioner or physician assistant each morning for a physical examination and blood draw.
In the afternoon, the patient is visited by a clinic nurse who brings any necessary supplies or treatments, such as blood products or intravenous antibiotics. The patient also has daily video calls with an attending physician and can be admitted to the hospital for any events that cannot be managed in the home setting.
Patients can have visitors and spend time away from home, but precautions are necessary. Friends or family who are sick should not be allowed to visit, and patients should avoid crowds when they go out.

Initial findings
The Duke team has treated 41 HSCT recipients at home so far. Dr. Chao said it’s still too early to draw any conclusions about differences in outcomes between home care and inpatient/outpatient HSCT.
However, a preliminary analysis of costs suggests home care is cheaper than inpatient HSCT. The researchers found that, for the first several transplants, at day 60, the cost of home care was roughly half that of inpatient HSCT.
In addition, patients seem to be happy with posttransplant care at home.
“The patients love being at home, in their own environment, with their families,” Dr. Chao said. “Almost every single patient [in the phase 1 trial] said that he or she liked it much better. There was one patient in the phase 1 that felt a little isolated, and I can see why because we say, ‘You can stay home, but don’t have a whole lot of people in.’ ”
One patient’s experience
Beth Vanderkin said it was “a blessing” to receive care at home after undergoing HSCT at Duke.
Ms. Vanderkin was diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in 2014. After two chemotherapy regimens failed to shrink the tumor in her chest, she underwent radiotherapy and responded well. When a PET scan revealed the tumor had gone completely, she proceeded to transplant.
She received a haploidentical HSCT using cells donated by her eldest daughter, Hannah Eichhorst. Ms. Vanderkin received the transplant in the hospital, and for 2 weeks after that, she made daily visits to the transplant clinic.
After those 2 weeks, Ms. Vanderkin continued her treatment at home. Like other patients eligible for home care, Ms. Vanderkin lived close to Duke, had a caregiver available, and had passed a home inspection. The Duke team shipped the needed medical supplies to her house and arranged twice-daily visits from nurses and daily video calls with a doctor.
Ms. Vanderkin said receiving care at home was “a game changer.” She derived comfort from recovering in her own environment, could spend more time with her family, and didn’t have to miss special events. While receiving care at home, Ms. Vanderkin attended the homecoming event where her son, Josiah, was part of the court. Wearing a face mask and carrying a portable pump in her purse, Ms. Vanderkin joined other mothers in escorting their children onto the football field.
“I got to escort my son out onto the field, and he was crowned king that night,” Ms. Vanderkin said. “I didn’t do a lot of things [while receiving care at home], but there were things I didn’t have to miss because I was at home and not in the hospital.”
Ms. Vanderkin said home care was also beneficial for her husband, who was her caregiver. Thomas Vanderkin was able to work from home while caring for his wife, and the daily nurses’ visits allowed him to run errands without having to leave Ms. Vanderkin alone.
Since her experience with home care, Ms. Vanderkin has spent many more days in the hospital and clinic. She experienced a relapse after the transplant and went on to receive more chemotherapy as well as ipilimumab. She responded to that treatment and has now been cancer-free for 3 years.
The ipilimumab did cause side effects, including intestinal problems that resulted in the need for parenteral nutrition. This side effect was made more bearable, Ms. Vanderkin said, because she was able to receive the parenteral nutrition at home. She and her husband were comfortable with additional home care because of their positive experience with posttransplant care.
“I think we’re conditioned to think that, to receive the best care, we have to be sitting in a hospital room or a clinic, but I think there’s a lot of things we can probably do at home,” Ms. Vanderkin said. “And we might fare a lot better as patients if we’re in an environment that we feel comfortable in.”
Experience at other centers
The team at Duke is not the first to study HSCT care at home. In fact, researchers in Sweden have been studying posttransplant home care since 1998.
A pilot trial the group published in 2000 suggested that home care was safe and, in some ways, superior to inpatient HSCT (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000 Nov;26[10]:1057-60). Patients treated at home had a lower rate of bacteremia, fewer days of total parenteral nutrition, fewer erythrocyte transfusions, and fewer days on antibiotics and analgesics. Rates of fever, engraftment time, and acute GVHD were similar between the inpatient and home-care groups.
A study published by the same researchers in 2002 showed that patients who received home care had lower rates of grade 2-4 acute GVHD and transplant-related mortality compared to inpatients (Blood. 2002 Dec 15;100[13]:4317-24). Two-year overall survival was superior with home care as well.
On the other hand, a study the group published in 2013 showed no significant differences in 5-year survival, transplant-related mortality, relapse, or chronic GVHD between inpatients and those who received care at home (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.11.5189).
The phase 2 trials at Duke should provide more insight into patient outcomes, but results probably won’t be available for 2 more years, Dr. Chao said.
In the meantime, other U.S. researchers are studying home care as well. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center is conducting a pilot study to determine if HSCT care at home is feasible (NCT02671448).
Dr. Chao said home care should be possible for other centers, particularly those that already perform outpatient HSCT.
“Having the outpatient infrastructure to support these patients is a big step,” he said. “And I think we were able to do that mainly because we do most of our transplants in the outpatient setting already. So that jump to the home is a little less compared to a center that does no outpatient transplants.”
He added, “There’s a certain amount of inertia to overcome and a certain amount of apprehension from the caregivers initially because [patients aren’t] sitting in your unit all the time, but I don’t see this as a huge barrier.”
In fact, Dr. Chao said, if results with home care are favorable, it could potentially replace inpatient HSCT for certain patients.
Dr. Chao’s research is supported by Duke University, and he reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Study confirms prognostic impact of MYC partner gene in DLBCL
MYC rearrangement (MYC-R) has negative prognostic significance in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in relation to the MYC partner gene, according to a retrospective study.
The negative prognostic effect of MYC-R was largely limited to patients with MYC–double hit/MYC–triple hit status and an immunoglobulin (IG) partner within 24 months following diagnosis.
“The primary objective of the study was to validate the prognostic relevance of [MYC–single hit] and [MYC–double hit/MYC–triple hit] status within the context of the MYC translocation partner (MYC-IG v. MYC-non-IG) in patients with DLBCL morphology,” wrote Andreas Rosenwald, MD, of the University of Würzburg (Germany) and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The researchers identified 5,117 patients who all received R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or R-CHOP–like immunochemotherapy, 2,383 of whom were evaluable for MYC-R and had complete clinical data. The cohort consisted of patients enrolled in various population-based registries and prospective clinical studies throughout North America and Europe.
The team used fluorescence in situ hybridization testing to identify MYC-R, in addition to BCL2 and/or BCL6 translocations if MYC-R was detected. Subsequently, these data were correlated with clinical endpoints.
After analysis, the researchers found that MYC-R was detected in 11% of patients. The presence of MYC-R was associated with significantly reduced survival, particularly within the initial 24 months following diagnosis.
Adverse prognostic implications were largely apparent in patients with accompanying rearrangement of BCL2 and/or BCL6 translocations (MYC–double-hit/MYC–triple hit status) and an immunoglobulin (IG) partner (hazard ratio, 2.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.6-3.6; P less than .001).
“These data suggest that little justification exists for altering initial therapeutic approaches in patients with DLBCL whose tumors carry an MYC translocation alone [MYC single hit],” they wrote. “However, for [MYC double hit/MYC triple hit] DLBCL, the major negative prognostic impact and 2-year effect support the practice of optimizing first-line treatment approaches to achieve maximum complete response rates because salvage treatment at relapse is not effective.”
Dr. Rosenwald and colleagues suggested that, in the future, diagnostic approaches should be implemented to detect patients in this high-risk group and that risk-modified treatment strategies should be further developed.
The study was supported by unrestricted grants to the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium from several pharmaceutical companies and Bloodwise. Dr. Rosenwald reported having no conflicts of interest, but several coauthors reported relationships with industry.
SOURCE: : Rosenwald A et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00743.
MYC rearrangement (MYC-R) has negative prognostic significance in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in relation to the MYC partner gene, according to a retrospective study.
The negative prognostic effect of MYC-R was largely limited to patients with MYC–double hit/MYC–triple hit status and an immunoglobulin (IG) partner within 24 months following diagnosis.
“The primary objective of the study was to validate the prognostic relevance of [MYC–single hit] and [MYC–double hit/MYC–triple hit] status within the context of the MYC translocation partner (MYC-IG v. MYC-non-IG) in patients with DLBCL morphology,” wrote Andreas Rosenwald, MD, of the University of Würzburg (Germany) and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The researchers identified 5,117 patients who all received R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or R-CHOP–like immunochemotherapy, 2,383 of whom were evaluable for MYC-R and had complete clinical data. The cohort consisted of patients enrolled in various population-based registries and prospective clinical studies throughout North America and Europe.
The team used fluorescence in situ hybridization testing to identify MYC-R, in addition to BCL2 and/or BCL6 translocations if MYC-R was detected. Subsequently, these data were correlated with clinical endpoints.
After analysis, the researchers found that MYC-R was detected in 11% of patients. The presence of MYC-R was associated with significantly reduced survival, particularly within the initial 24 months following diagnosis.
Adverse prognostic implications were largely apparent in patients with accompanying rearrangement of BCL2 and/or BCL6 translocations (MYC–double-hit/MYC–triple hit status) and an immunoglobulin (IG) partner (hazard ratio, 2.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.6-3.6; P less than .001).
“These data suggest that little justification exists for altering initial therapeutic approaches in patients with DLBCL whose tumors carry an MYC translocation alone [MYC single hit],” they wrote. “However, for [MYC double hit/MYC triple hit] DLBCL, the major negative prognostic impact and 2-year effect support the practice of optimizing first-line treatment approaches to achieve maximum complete response rates because salvage treatment at relapse is not effective.”
Dr. Rosenwald and colleagues suggested that, in the future, diagnostic approaches should be implemented to detect patients in this high-risk group and that risk-modified treatment strategies should be further developed.
The study was supported by unrestricted grants to the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium from several pharmaceutical companies and Bloodwise. Dr. Rosenwald reported having no conflicts of interest, but several coauthors reported relationships with industry.
SOURCE: : Rosenwald A et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00743.
MYC rearrangement (MYC-R) has negative prognostic significance in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in relation to the MYC partner gene, according to a retrospective study.
The negative prognostic effect of MYC-R was largely limited to patients with MYC–double hit/MYC–triple hit status and an immunoglobulin (IG) partner within 24 months following diagnosis.
“The primary objective of the study was to validate the prognostic relevance of [MYC–single hit] and [MYC–double hit/MYC–triple hit] status within the context of the MYC translocation partner (MYC-IG v. MYC-non-IG) in patients with DLBCL morphology,” wrote Andreas Rosenwald, MD, of the University of Würzburg (Germany) and colleagues in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The researchers identified 5,117 patients who all received R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or R-CHOP–like immunochemotherapy, 2,383 of whom were evaluable for MYC-R and had complete clinical data. The cohort consisted of patients enrolled in various population-based registries and prospective clinical studies throughout North America and Europe.
The team used fluorescence in situ hybridization testing to identify MYC-R, in addition to BCL2 and/or BCL6 translocations if MYC-R was detected. Subsequently, these data were correlated with clinical endpoints.
After analysis, the researchers found that MYC-R was detected in 11% of patients. The presence of MYC-R was associated with significantly reduced survival, particularly within the initial 24 months following diagnosis.
Adverse prognostic implications were largely apparent in patients with accompanying rearrangement of BCL2 and/or BCL6 translocations (MYC–double-hit/MYC–triple hit status) and an immunoglobulin (IG) partner (hazard ratio, 2.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.6-3.6; P less than .001).
“These data suggest that little justification exists for altering initial therapeutic approaches in patients with DLBCL whose tumors carry an MYC translocation alone [MYC single hit],” they wrote. “However, for [MYC double hit/MYC triple hit] DLBCL, the major negative prognostic impact and 2-year effect support the practice of optimizing first-line treatment approaches to achieve maximum complete response rates because salvage treatment at relapse is not effective.”
Dr. Rosenwald and colleagues suggested that, in the future, diagnostic approaches should be implemented to detect patients in this high-risk group and that risk-modified treatment strategies should be further developed.
The study was supported by unrestricted grants to the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium from several pharmaceutical companies and Bloodwise. Dr. Rosenwald reported having no conflicts of interest, but several coauthors reported relationships with industry.
SOURCE: : Rosenwald A et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00743.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Chemo-free combo gets high response rate in relapsed or refractory DLBCL
LUGANO, Switzerland – A chemotherapy-free combination of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and the novel anti-CD19 antibody tafasitamab (MOR208) continues to show encouraging clinical activity against relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma, with durable responses and promising progression-free and overall survival, investigators in the phase 2 L-MIND study reported.
After a median follow-up of 17.3 months, the overall response rate (ORR) – the primary endpoint in the single arm trial – was 60%, consisting of 42.5% complete responses (CR) and 17.5% partial responses (PR), reported Giles Salles, MD, PhD, of Claude Bernard University in Lyon, France.
“We see consistently high activity in transplant-ineligible subgroups, patients who have limited treatment options and who have really poor prognosis,” he said at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (15-ICML).
In a preclinical study, a combination of MOR208 and lenalidomide showed synergistic antileukemic and antilymphoma activity both in vivo and in vitro. In addition, both lenalidomide and MOR208 have shown significant activity against relapsed, refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
At the previous ICML meeting in 2017, Dr. Salles reported early interim results from the study, which showed that among 34 patients evaluable for response, the ORR was 56%, including complete responses in 32% of patients.
The L-MIND investigators enrolled transplant-ineligible patients 18 years and older with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0-2, and adequate organ function who had disease progression after 1-3 prior lines of therapy.
Patients with primary refractory DLBCL, double-hit or triple-hit DLBCL (i.e., mutations in Myc, BCL2, and/or BCL6), other non-Hodgkin lymphoma histological subtypes, or central nervous system lymphoma involvement were excluded.
Patients received tafasitamab 12 mg/kg intravenously on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 for cycles 1-3 and on days 1 and 15 of cycles 4-12. Lenalidomide 25 mg orally was delivered on days 1-21 of each cycle. Patients with stable disease or better at the end of 12 cycles could be maintained on tafasitamab at the same dose on days 1 and 15.
As noted, the combination was associated with an ORR among 80 patients of 60%, consisting of 34 CR (42.5%) complete responses and 14 (17.5%) PR. An additional 11 patients (13.75%) had stable disease, 13 (16.25%) had disease progression, and eight (10%) were not evaluable because of missing post-baseline tumor assessments.
The median duration of response in the entire cohort was 21.7 months. For patients with a CR, the median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff. For patients with a PR, the median duration of response was 4.4 months.
Hematologic treatment-emergent toxicities occurring in 10% or more of patients included (in descending order of frequency) neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and febrile neutropenia.
Nonhematologic treatment-emergent events occurring in at least 10% of patients included diarrhea, asthenia, peripheral edema, pyrexia, rash, decreased appetite, hypokalemia, fatigue, and similar events, the majority of which were grade 1 or 2 in severity.
“The durable responses and favorable overall survival I would say represent a remarkable outcome, and this combination of lenalidomide with tafasitamab results in a new chemo-free immunotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL,” Dr. Salles said.
The L-MIND study is funded by MorphoSys Ag. Dr. Salles reported receiving fees for advisory board/consulting activities and educational activities from MorphoSys and other companies.
SOURCE: Salles G et al. 15-ICML, Abstract 124.
LUGANO, Switzerland – A chemotherapy-free combination of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and the novel anti-CD19 antibody tafasitamab (MOR208) continues to show encouraging clinical activity against relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma, with durable responses and promising progression-free and overall survival, investigators in the phase 2 L-MIND study reported.
After a median follow-up of 17.3 months, the overall response rate (ORR) – the primary endpoint in the single arm trial – was 60%, consisting of 42.5% complete responses (CR) and 17.5% partial responses (PR), reported Giles Salles, MD, PhD, of Claude Bernard University in Lyon, France.
“We see consistently high activity in transplant-ineligible subgroups, patients who have limited treatment options and who have really poor prognosis,” he said at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (15-ICML).
In a preclinical study, a combination of MOR208 and lenalidomide showed synergistic antileukemic and antilymphoma activity both in vivo and in vitro. In addition, both lenalidomide and MOR208 have shown significant activity against relapsed, refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
At the previous ICML meeting in 2017, Dr. Salles reported early interim results from the study, which showed that among 34 patients evaluable for response, the ORR was 56%, including complete responses in 32% of patients.
The L-MIND investigators enrolled transplant-ineligible patients 18 years and older with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0-2, and adequate organ function who had disease progression after 1-3 prior lines of therapy.
Patients with primary refractory DLBCL, double-hit or triple-hit DLBCL (i.e., mutations in Myc, BCL2, and/or BCL6), other non-Hodgkin lymphoma histological subtypes, or central nervous system lymphoma involvement were excluded.
Patients received tafasitamab 12 mg/kg intravenously on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 for cycles 1-3 and on days 1 and 15 of cycles 4-12. Lenalidomide 25 mg orally was delivered on days 1-21 of each cycle. Patients with stable disease or better at the end of 12 cycles could be maintained on tafasitamab at the same dose on days 1 and 15.
As noted, the combination was associated with an ORR among 80 patients of 60%, consisting of 34 CR (42.5%) complete responses and 14 (17.5%) PR. An additional 11 patients (13.75%) had stable disease, 13 (16.25%) had disease progression, and eight (10%) were not evaluable because of missing post-baseline tumor assessments.
The median duration of response in the entire cohort was 21.7 months. For patients with a CR, the median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff. For patients with a PR, the median duration of response was 4.4 months.
Hematologic treatment-emergent toxicities occurring in 10% or more of patients included (in descending order of frequency) neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and febrile neutropenia.
Nonhematologic treatment-emergent events occurring in at least 10% of patients included diarrhea, asthenia, peripheral edema, pyrexia, rash, decreased appetite, hypokalemia, fatigue, and similar events, the majority of which were grade 1 or 2 in severity.
“The durable responses and favorable overall survival I would say represent a remarkable outcome, and this combination of lenalidomide with tafasitamab results in a new chemo-free immunotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL,” Dr. Salles said.
The L-MIND study is funded by MorphoSys Ag. Dr. Salles reported receiving fees for advisory board/consulting activities and educational activities from MorphoSys and other companies.
SOURCE: Salles G et al. 15-ICML, Abstract 124.
LUGANO, Switzerland – A chemotherapy-free combination of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and the novel anti-CD19 antibody tafasitamab (MOR208) continues to show encouraging clinical activity against relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma, with durable responses and promising progression-free and overall survival, investigators in the phase 2 L-MIND study reported.
After a median follow-up of 17.3 months, the overall response rate (ORR) – the primary endpoint in the single arm trial – was 60%, consisting of 42.5% complete responses (CR) and 17.5% partial responses (PR), reported Giles Salles, MD, PhD, of Claude Bernard University in Lyon, France.
“We see consistently high activity in transplant-ineligible subgroups, patients who have limited treatment options and who have really poor prognosis,” he said at the International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (15-ICML).
In a preclinical study, a combination of MOR208 and lenalidomide showed synergistic antileukemic and antilymphoma activity both in vivo and in vitro. In addition, both lenalidomide and MOR208 have shown significant activity against relapsed, refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas.
At the previous ICML meeting in 2017, Dr. Salles reported early interim results from the study, which showed that among 34 patients evaluable for response, the ORR was 56%, including complete responses in 32% of patients.
The L-MIND investigators enrolled transplant-ineligible patients 18 years and older with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0-2, and adequate organ function who had disease progression after 1-3 prior lines of therapy.
Patients with primary refractory DLBCL, double-hit or triple-hit DLBCL (i.e., mutations in Myc, BCL2, and/or BCL6), other non-Hodgkin lymphoma histological subtypes, or central nervous system lymphoma involvement were excluded.
Patients received tafasitamab 12 mg/kg intravenously on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 for cycles 1-3 and on days 1 and 15 of cycles 4-12. Lenalidomide 25 mg orally was delivered on days 1-21 of each cycle. Patients with stable disease or better at the end of 12 cycles could be maintained on tafasitamab at the same dose on days 1 and 15.
As noted, the combination was associated with an ORR among 80 patients of 60%, consisting of 34 CR (42.5%) complete responses and 14 (17.5%) PR. An additional 11 patients (13.75%) had stable disease, 13 (16.25%) had disease progression, and eight (10%) were not evaluable because of missing post-baseline tumor assessments.
The median duration of response in the entire cohort was 21.7 months. For patients with a CR, the median duration of response had not been reached at the time of data cutoff. For patients with a PR, the median duration of response was 4.4 months.
Hematologic treatment-emergent toxicities occurring in 10% or more of patients included (in descending order of frequency) neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and febrile neutropenia.
Nonhematologic treatment-emergent events occurring in at least 10% of patients included diarrhea, asthenia, peripheral edema, pyrexia, rash, decreased appetite, hypokalemia, fatigue, and similar events, the majority of which were grade 1 or 2 in severity.
“The durable responses and favorable overall survival I would say represent a remarkable outcome, and this combination of lenalidomide with tafasitamab results in a new chemo-free immunotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL,” Dr. Salles said.
The L-MIND study is funded by MorphoSys Ag. Dr. Salles reported receiving fees for advisory board/consulting activities and educational activities from MorphoSys and other companies.
SOURCE: Salles G et al. 15-ICML, Abstract 124.
REPORTING FROM 15-ICML
CAR T-cell therapy less effective in transformed follicular lymphoma
All complete responders with FL were still in remission at a median follow-up of 24 months, but the median duration of response was 10.2 months for patients with tFL.
Alexandre V. Hirayama, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, and colleagues reported these results in Blood.
The trial enrolled 21 adults with relapsed/refractory CD19+ B-cell malignancies, including 8 patients with FL and 13 with tFL. At baseline, the FL/tFL patients had a median age of 56 years (range, 51-62), and 67% were male. Most patients (n = 19) had stage III/IV disease, 17 had extranodal disease, 8 had bulky disease, and 6 had bone marrow involvement. The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-8), and 13 had received a transplant.
In this study, patients received a lymphodepleting regimen of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by 2 x 106 CD19 CAR T cells/kg. Five patients (one with FL and four with tFL) also received bridging chemotherapy between leukapheresis and lymphodepletion.
Grade 1-2 cytokine release syndrome occurred in 50% of FL patients and 39% of tFL patients (P = .35). Grade 1-2 neurotoxicity occurred in 50% and 23%, respectively (P = .67). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity.
Most FL patients (7 of 8; 88%) achieved a complete response (CR) to treatment, and all of these patients were still in CR at a median follow-up of 24 months (range, 5-37 months). One FL patient received a transplant while in CR.
Six of 13 tFL patients (46%) achieved a CR. At a median follow-up of 38 months (range, 3-39 months), the median duration of response was 10.2 months. The median progression-free survival was 11.2 months in patients who achieved a CR and 1.4 months in all tFL patients.
The researchers noted that peak CAR T-cell counts and the duration of CAR T-cell detection were similar between FL and tFL patients. However, tFL patients had higher serum interleukin-8 concentrations and higher lactate dehydrogenase levels before treatment.
Past research suggested that IL-8 mediates the recruitment of tumor-associated neutrophils, promotes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma progression, and can contribute to local immune suppression. Other studies have linked elevated lactate dehydrogenase to aggressive disease and a more immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
“Although these data raise the possibility that differences in the tumor microenvironment may, in part, contribute to differences in outcomes after CAR T-cell immunotherapy in FL and tFL patients, additional studies are required,” the researchers wrote.
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Life Science Discovery Fund, the Bezos family, the University of British Columbia Clinician Investigator Program, the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center’s Immunotherapy Integrated Research Center, and Juno Therapeutics/Celgene.
The researchers disclosed relationships with Celgene, Juno Therapeutics, Lyell Immunopharma, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Nohla, Kite Pharma, Gilead, Genentech, Novartis, Eureka Therapeutics, Nektar Therapeutics, Caribou Biosciences, Precision Biosciences, Aptevo, Humanigen, and Allogene.
SOURCE: Hirayama AV et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000905
All complete responders with FL were still in remission at a median follow-up of 24 months, but the median duration of response was 10.2 months for patients with tFL.
Alexandre V. Hirayama, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, and colleagues reported these results in Blood.
The trial enrolled 21 adults with relapsed/refractory CD19+ B-cell malignancies, including 8 patients with FL and 13 with tFL. At baseline, the FL/tFL patients had a median age of 56 years (range, 51-62), and 67% were male. Most patients (n = 19) had stage III/IV disease, 17 had extranodal disease, 8 had bulky disease, and 6 had bone marrow involvement. The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-8), and 13 had received a transplant.
In this study, patients received a lymphodepleting regimen of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by 2 x 106 CD19 CAR T cells/kg. Five patients (one with FL and four with tFL) also received bridging chemotherapy between leukapheresis and lymphodepletion.
Grade 1-2 cytokine release syndrome occurred in 50% of FL patients and 39% of tFL patients (P = .35). Grade 1-2 neurotoxicity occurred in 50% and 23%, respectively (P = .67). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity.
Most FL patients (7 of 8; 88%) achieved a complete response (CR) to treatment, and all of these patients were still in CR at a median follow-up of 24 months (range, 5-37 months). One FL patient received a transplant while in CR.
Six of 13 tFL patients (46%) achieved a CR. At a median follow-up of 38 months (range, 3-39 months), the median duration of response was 10.2 months. The median progression-free survival was 11.2 months in patients who achieved a CR and 1.4 months in all tFL patients.
The researchers noted that peak CAR T-cell counts and the duration of CAR T-cell detection were similar between FL and tFL patients. However, tFL patients had higher serum interleukin-8 concentrations and higher lactate dehydrogenase levels before treatment.
Past research suggested that IL-8 mediates the recruitment of tumor-associated neutrophils, promotes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma progression, and can contribute to local immune suppression. Other studies have linked elevated lactate dehydrogenase to aggressive disease and a more immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
“Although these data raise the possibility that differences in the tumor microenvironment may, in part, contribute to differences in outcomes after CAR T-cell immunotherapy in FL and tFL patients, additional studies are required,” the researchers wrote.
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Life Science Discovery Fund, the Bezos family, the University of British Columbia Clinician Investigator Program, the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center’s Immunotherapy Integrated Research Center, and Juno Therapeutics/Celgene.
The researchers disclosed relationships with Celgene, Juno Therapeutics, Lyell Immunopharma, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Nohla, Kite Pharma, Gilead, Genentech, Novartis, Eureka Therapeutics, Nektar Therapeutics, Caribou Biosciences, Precision Biosciences, Aptevo, Humanigen, and Allogene.
SOURCE: Hirayama AV et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000905
All complete responders with FL were still in remission at a median follow-up of 24 months, but the median duration of response was 10.2 months for patients with tFL.
Alexandre V. Hirayama, MD, of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, and colleagues reported these results in Blood.
The trial enrolled 21 adults with relapsed/refractory CD19+ B-cell malignancies, including 8 patients with FL and 13 with tFL. At baseline, the FL/tFL patients had a median age of 56 years (range, 51-62), and 67% were male. Most patients (n = 19) had stage III/IV disease, 17 had extranodal disease, 8 had bulky disease, and 6 had bone marrow involvement. The patients had received a median of 5 prior therapies (range, 2-8), and 13 had received a transplant.
In this study, patients received a lymphodepleting regimen of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine, followed by 2 x 106 CD19 CAR T cells/kg. Five patients (one with FL and four with tFL) also received bridging chemotherapy between leukapheresis and lymphodepletion.
Grade 1-2 cytokine release syndrome occurred in 50% of FL patients and 39% of tFL patients (P = .35). Grade 1-2 neurotoxicity occurred in 50% and 23%, respectively (P = .67). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher cytokine release syndrome or neurotoxicity.
Most FL patients (7 of 8; 88%) achieved a complete response (CR) to treatment, and all of these patients were still in CR at a median follow-up of 24 months (range, 5-37 months). One FL patient received a transplant while in CR.
Six of 13 tFL patients (46%) achieved a CR. At a median follow-up of 38 months (range, 3-39 months), the median duration of response was 10.2 months. The median progression-free survival was 11.2 months in patients who achieved a CR and 1.4 months in all tFL patients.
The researchers noted that peak CAR T-cell counts and the duration of CAR T-cell detection were similar between FL and tFL patients. However, tFL patients had higher serum interleukin-8 concentrations and higher lactate dehydrogenase levels before treatment.
Past research suggested that IL-8 mediates the recruitment of tumor-associated neutrophils, promotes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma progression, and can contribute to local immune suppression. Other studies have linked elevated lactate dehydrogenase to aggressive disease and a more immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
“Although these data raise the possibility that differences in the tumor microenvironment may, in part, contribute to differences in outcomes after CAR T-cell immunotherapy in FL and tFL patients, additional studies are required,” the researchers wrote.
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Life Science Discovery Fund, the Bezos family, the University of British Columbia Clinician Investigator Program, the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center’s Immunotherapy Integrated Research Center, and Juno Therapeutics/Celgene.
The researchers disclosed relationships with Celgene, Juno Therapeutics, Lyell Immunopharma, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Nohla, Kite Pharma, Gilead, Genentech, Novartis, Eureka Therapeutics, Nektar Therapeutics, Caribou Biosciences, Precision Biosciences, Aptevo, Humanigen, and Allogene.
SOURCE: Hirayama AV et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000905
FROM BLOOD
Flavopiridol elicits poor response in mantle cell lymphoma, DLBCL
Flavopiridol – also known as alvocidib – showed minimal clinical response in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and other B-cell lymphomas, according to results from a single-center, phase 1/2 trial.
“Promising preclinical data in cell lines derived from MCL and activated DLBCL led to a series of clinical trials of flavopiridol in various hematological malignancies,” wrote Milos D. Miljković, MD, and colleagues in the lymphoid malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md. The findings were published in a letter to the editor in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The study included 28 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL, DLBCL, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who received a hybrid dosing regimen of the novel CDK inhibitor. Flavopiridol was administered as a 30-minute bolus, followed by a 4-hour infusion.
The researchers used an intrapatient dose escalation between the first and successive cycles, in addition to a three-plus-three interpatient escalation, to lessen the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
The primary outcomes were the clinical response rate, maximum tolerated dose, dose-limiting toxicities, and toxicity profile of the hybrid dosing regimen.
Of 26 evaluable patients, one patient with DLBCL maintained a partial response for 84 days (overall response rate, 3.8%). One patient with MCL had a 50% decrease in the size of target lesions at 2 months, but this was not sustained at 4 months. In total, nine patients had stable disease for a disease control rate of 38.4%.
“[Flavopiridol] had minimal efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma, casting doubt on the utility of CDK inhibition in this disease,” the researchers wrote.
With respect to safety, there were eight dose-limiting toxicities reported in three patients. These included grade 3 TLS, elevated transaminase levels, hypoalbuminemia, hyperkalemia, non-neutropenic infection, and grade 4 metabolic acidosis and gastrointestinal perforation.
The most common treatment-related toxicities were hematologic, including neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and lymphopenia.
Dr. Miljković and colleagues noted that CDK inhibitor therapy may elicit better responses when used in combination with other agents.
“Ongoing trials of more specific CDK inhibitors in combination with other agents will help elucidate their role in lymphoma treatment,” they wrote.
The trial is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and the study authors are employees of the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Miljkovic MD et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jun 17. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1627540.
Flavopiridol – also known as alvocidib – showed minimal clinical response in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and other B-cell lymphomas, according to results from a single-center, phase 1/2 trial.
“Promising preclinical data in cell lines derived from MCL and activated DLBCL led to a series of clinical trials of flavopiridol in various hematological malignancies,” wrote Milos D. Miljković, MD, and colleagues in the lymphoid malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md. The findings were published in a letter to the editor in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The study included 28 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL, DLBCL, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who received a hybrid dosing regimen of the novel CDK inhibitor. Flavopiridol was administered as a 30-minute bolus, followed by a 4-hour infusion.
The researchers used an intrapatient dose escalation between the first and successive cycles, in addition to a three-plus-three interpatient escalation, to lessen the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
The primary outcomes were the clinical response rate, maximum tolerated dose, dose-limiting toxicities, and toxicity profile of the hybrid dosing regimen.
Of 26 evaluable patients, one patient with DLBCL maintained a partial response for 84 days (overall response rate, 3.8%). One patient with MCL had a 50% decrease in the size of target lesions at 2 months, but this was not sustained at 4 months. In total, nine patients had stable disease for a disease control rate of 38.4%.
“[Flavopiridol] had minimal efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma, casting doubt on the utility of CDK inhibition in this disease,” the researchers wrote.
With respect to safety, there were eight dose-limiting toxicities reported in three patients. These included grade 3 TLS, elevated transaminase levels, hypoalbuminemia, hyperkalemia, non-neutropenic infection, and grade 4 metabolic acidosis and gastrointestinal perforation.
The most common treatment-related toxicities were hematologic, including neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and lymphopenia.
Dr. Miljković and colleagues noted that CDK inhibitor therapy may elicit better responses when used in combination with other agents.
“Ongoing trials of more specific CDK inhibitors in combination with other agents will help elucidate their role in lymphoma treatment,” they wrote.
The trial is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and the study authors are employees of the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Miljkovic MD et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jun 17. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1627540.
Flavopiridol – also known as alvocidib – showed minimal clinical response in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and other B-cell lymphomas, according to results from a single-center, phase 1/2 trial.
“Promising preclinical data in cell lines derived from MCL and activated DLBCL led to a series of clinical trials of flavopiridol in various hematological malignancies,” wrote Milos D. Miljković, MD, and colleagues in the lymphoid malignancies branch of the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md. The findings were published in a letter to the editor in Leukemia & Lymphoma.
The study included 28 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL, DLBCL, transformed follicular lymphoma, and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who received a hybrid dosing regimen of the novel CDK inhibitor. Flavopiridol was administered as a 30-minute bolus, followed by a 4-hour infusion.
The researchers used an intrapatient dose escalation between the first and successive cycles, in addition to a three-plus-three interpatient escalation, to lessen the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS).
The primary outcomes were the clinical response rate, maximum tolerated dose, dose-limiting toxicities, and toxicity profile of the hybrid dosing regimen.
Of 26 evaluable patients, one patient with DLBCL maintained a partial response for 84 days (overall response rate, 3.8%). One patient with MCL had a 50% decrease in the size of target lesions at 2 months, but this was not sustained at 4 months. In total, nine patients had stable disease for a disease control rate of 38.4%.
“[Flavopiridol] had minimal efficacy in patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma, casting doubt on the utility of CDK inhibition in this disease,” the researchers wrote.
With respect to safety, there were eight dose-limiting toxicities reported in three patients. These included grade 3 TLS, elevated transaminase levels, hypoalbuminemia, hyperkalemia, non-neutropenic infection, and grade 4 metabolic acidosis and gastrointestinal perforation.
The most common treatment-related toxicities were hematologic, including neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and lymphopenia.
Dr. Miljković and colleagues noted that CDK inhibitor therapy may elicit better responses when used in combination with other agents.
“Ongoing trials of more specific CDK inhibitors in combination with other agents will help elucidate their role in lymphoma treatment,” they wrote.
The trial is sponsored by the National Cancer Institute and the study authors are employees of the National Cancer Institute.
SOURCE: Miljkovic MD et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jun 17. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2019.1627540.
FROM LEUKEMIA & LYMPHOMA