User login
ClinicalEdge only
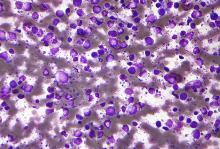
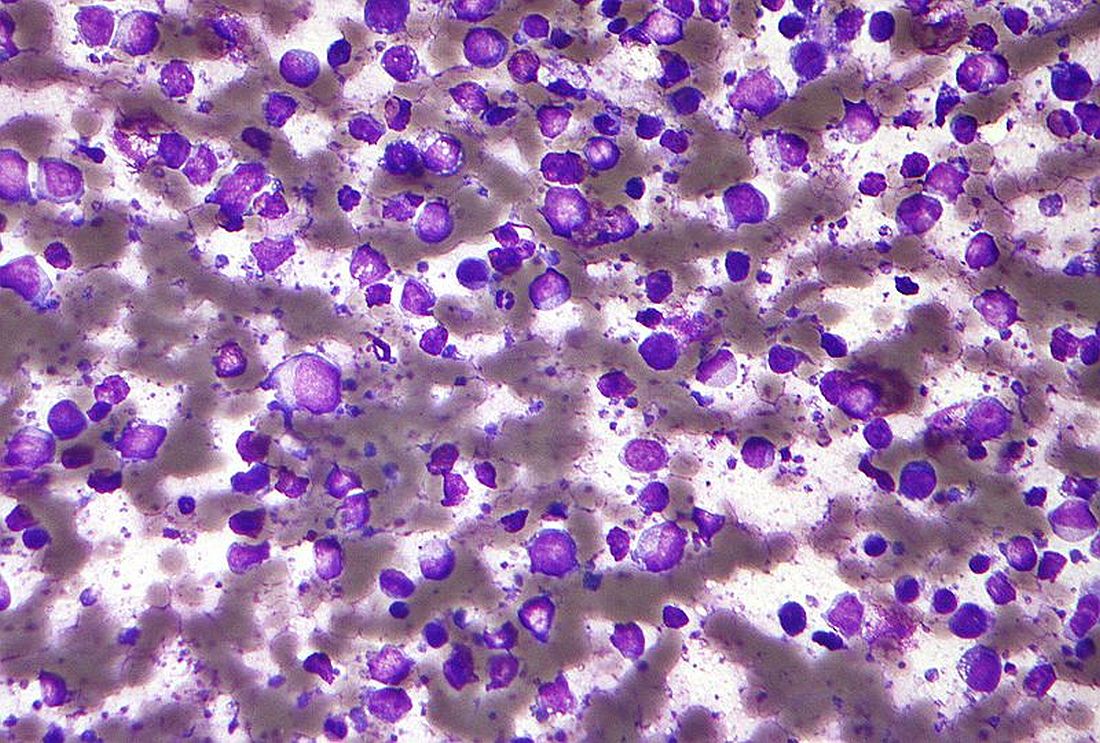
FDA approves new drug for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
A novel drug, tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi, MorphoSys US), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The product is a humanized Fc-modified cytolytic CD19 targeting monoclonal antibody. It mediates B-cell lysis through apoptosis and immune effector mechanism, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).
It is indicated for use in combination with lenalidomide for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL that is not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and in patients who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
Tafasitamab-cxix in combination with lenalidomide is the first treatment that approved by the FDA for second-line use for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, notes the manufacturer.
The approval “brings a new treatment option to patients in dire need across the United States,” said Gilles Salles, MD, chair of the clinical hematology department at the University of Lyon (France), and lead investigator of the L-MIND study.
The FDA granted an accelerated approval on the basis of overall response rate from an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial in 81 patients (known as L-MIND). Further trials are underway to confirm clinical benefit.
The L-MIND trial was conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who had received at least one, but no more than three, prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 targeting therapy (e.g., rituximab), who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy or who refused subsequent ASCT.
All patients received tafasitamab-cxix 12 mg/kg intravenously with lenalidomide (25 mg orally on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle) for a maximum of 12 cycles, followed by tafasitamab-cxix as monotherapy.
The best ORR (defined as complete and partial responders) in 71 patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL confirmed by central pathology was 55%, with complete responses in 37% and partial responses in 18% of patients. The median response duration was 21.7 months (range, 0-24).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were neutropenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, cough, fever, peripheral edema, respiratory tract infection, and decreased appetite.
Precautions and warnings include infusion-related reactions (6%), serious or severe myelosuppression (including neutropenia [50%], thrombocytopenia [18%], and anemia [7%]), infections (73%), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults worldwide, characterized by rapidly growing masses of malignant B-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow or other organs. It is an aggressive disease with about one in three patients not responding to initial therapy or relapsing thereafter, notes the manufacturer. In the United States each year approximately 10,000 patients who are not eligible for ASCT are diagnosed with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel drug, tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi, MorphoSys US), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The product is a humanized Fc-modified cytolytic CD19 targeting monoclonal antibody. It mediates B-cell lysis through apoptosis and immune effector mechanism, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).
It is indicated for use in combination with lenalidomide for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL that is not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and in patients who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
Tafasitamab-cxix in combination with lenalidomide is the first treatment that approved by the FDA for second-line use for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, notes the manufacturer.
The approval “brings a new treatment option to patients in dire need across the United States,” said Gilles Salles, MD, chair of the clinical hematology department at the University of Lyon (France), and lead investigator of the L-MIND study.
The FDA granted an accelerated approval on the basis of overall response rate from an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial in 81 patients (known as L-MIND). Further trials are underway to confirm clinical benefit.
The L-MIND trial was conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who had received at least one, but no more than three, prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 targeting therapy (e.g., rituximab), who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy or who refused subsequent ASCT.
All patients received tafasitamab-cxix 12 mg/kg intravenously with lenalidomide (25 mg orally on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle) for a maximum of 12 cycles, followed by tafasitamab-cxix as monotherapy.
The best ORR (defined as complete and partial responders) in 71 patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL confirmed by central pathology was 55%, with complete responses in 37% and partial responses in 18% of patients. The median response duration was 21.7 months (range, 0-24).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were neutropenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, cough, fever, peripheral edema, respiratory tract infection, and decreased appetite.
Precautions and warnings include infusion-related reactions (6%), serious or severe myelosuppression (including neutropenia [50%], thrombocytopenia [18%], and anemia [7%]), infections (73%), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults worldwide, characterized by rapidly growing masses of malignant B-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow or other organs. It is an aggressive disease with about one in three patients not responding to initial therapy or relapsing thereafter, notes the manufacturer. In the United States each year approximately 10,000 patients who are not eligible for ASCT are diagnosed with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel drug, tafasitamab-cxix (Monjuvi, MorphoSys US), has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
The product is a humanized Fc-modified cytolytic CD19 targeting monoclonal antibody. It mediates B-cell lysis through apoptosis and immune effector mechanism, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP).
It is indicated for use in combination with lenalidomide for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL that is not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and in patients who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
Tafasitamab-cxix in combination with lenalidomide is the first treatment that approved by the FDA for second-line use for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL, notes the manufacturer.
The approval “brings a new treatment option to patients in dire need across the United States,” said Gilles Salles, MD, chair of the clinical hematology department at the University of Lyon (France), and lead investigator of the L-MIND study.
The FDA granted an accelerated approval on the basis of overall response rate from an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial in 81 patients (known as L-MIND). Further trials are underway to confirm clinical benefit.
The L-MIND trial was conducted in patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who had received at least one, but no more than three, prior lines of therapy, including an anti-CD20 targeting therapy (e.g., rituximab), who were not eligible for high-dose chemotherapy or who refused subsequent ASCT.
All patients received tafasitamab-cxix 12 mg/kg intravenously with lenalidomide (25 mg orally on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle) for a maximum of 12 cycles, followed by tafasitamab-cxix as monotherapy.
The best ORR (defined as complete and partial responders) in 71 patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL confirmed by central pathology was 55%, with complete responses in 37% and partial responses in 18% of patients. The median response duration was 21.7 months (range, 0-24).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were neutropenia, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, cough, fever, peripheral edema, respiratory tract infection, and decreased appetite.
Precautions and warnings include infusion-related reactions (6%), serious or severe myelosuppression (including neutropenia [50%], thrombocytopenia [18%], and anemia [7%]), infections (73%), and embryo-fetal toxicity.
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults worldwide, characterized by rapidly growing masses of malignant B-cells in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow or other organs. It is an aggressive disease with about one in three patients not responding to initial therapy or relapsing thereafter, notes the manufacturer. In the United States each year approximately 10,000 patients who are not eligible for ASCT are diagnosed with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HSCT or systemic treatment should be offered to HIV+ patients with lymphoma
Systemic or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes, compared with nonsystemic treatment, according to the results of a large database study.
Researchers Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, and colleagues examined patients with lymphoma diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 from the National Cancer Database. Patients were categorized as HIV positive and HIV negative. First-line lymphoma treatment was categorized as no systemic therapy reported, systemic therapy, or HSCT. Multivariate analysis was used to predict treatment and survival, according to Dr. Jayakrishnan, a resident at the department of internal medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
A total of 11,160 HIV-positive vs. 349,607 HIV-negative patients were analyzed, including mostly men, with a comorbidity index of 0. The most common lymphoma among HIV-positive patients was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, according to the report in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Among HIV-positive patients, 792 had no systemic treatment, 10,328 underwent systemic treatment, and 40 received HSCT treatment. The results showed that treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes: 3-year overall survival was 43.6% for nonsystemic treatment versus 58.1% for systemic (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.61; P < .005) versus 62.2% for HSCT therapy (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.14-1.3; P = .08), the lack of significance in the latter could be caused in part by the small number of patients treated. Outcomes for both treatment regimens were lower, however, compared with non-HIV patients.
“The present study demonstrates improvement in survival outcomes for HIV-positive patients with lymphoma with treatments when feasible, but these outcomes are poor when compared to HIV-negative patients,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Clin Lymph Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.003.
Systemic or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes, compared with nonsystemic treatment, according to the results of a large database study.
Researchers Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, and colleagues examined patients with lymphoma diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 from the National Cancer Database. Patients were categorized as HIV positive and HIV negative. First-line lymphoma treatment was categorized as no systemic therapy reported, systemic therapy, or HSCT. Multivariate analysis was used to predict treatment and survival, according to Dr. Jayakrishnan, a resident at the department of internal medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
A total of 11,160 HIV-positive vs. 349,607 HIV-negative patients were analyzed, including mostly men, with a comorbidity index of 0. The most common lymphoma among HIV-positive patients was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, according to the report in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Among HIV-positive patients, 792 had no systemic treatment, 10,328 underwent systemic treatment, and 40 received HSCT treatment. The results showed that treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes: 3-year overall survival was 43.6% for nonsystemic treatment versus 58.1% for systemic (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.61; P < .005) versus 62.2% for HSCT therapy (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.14-1.3; P = .08), the lack of significance in the latter could be caused in part by the small number of patients treated. Outcomes for both treatment regimens were lower, however, compared with non-HIV patients.
“The present study demonstrates improvement in survival outcomes for HIV-positive patients with lymphoma with treatments when feasible, but these outcomes are poor when compared to HIV-negative patients,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Clin Lymph Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.003.
Systemic or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes, compared with nonsystemic treatment, according to the results of a large database study.
Researchers Thejus T. Jayakrishnan, MD, and colleagues examined patients with lymphoma diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 from the National Cancer Database. Patients were categorized as HIV positive and HIV negative. First-line lymphoma treatment was categorized as no systemic therapy reported, systemic therapy, or HSCT. Multivariate analysis was used to predict treatment and survival, according to Dr. Jayakrishnan, a resident at the department of internal medicine, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh.
A total of 11,160 HIV-positive vs. 349,607 HIV-negative patients were analyzed, including mostly men, with a comorbidity index of 0. The most common lymphoma among HIV-positive patients was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, according to the report in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
Among HIV-positive patients, 792 had no systemic treatment, 10,328 underwent systemic treatment, and 40 received HSCT treatment. The results showed that treatment of HIV-positive lymphoma patients resulted in improved outcomes: 3-year overall survival was 43.6% for nonsystemic treatment versus 58.1% for systemic (hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.61; P < .005) versus 62.2% for HSCT therapy (HR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.14-1.3; P = .08), the lack of significance in the latter could be caused in part by the small number of patients treated. Outcomes for both treatment regimens were lower, however, compared with non-HIV patients.
“The present study demonstrates improvement in survival outcomes for HIV-positive patients with lymphoma with treatments when feasible, but these outcomes are poor when compared to HIV-negative patients,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jayakrishnan TT et al. Clin Lymph Myeloma Leuk. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.003.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
FDA approves selinexor for relapsed/refractory DLBCL
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval of selinexor, a nuclear transport inhibitor, for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Selinexor (marketed as XPOVIO by Karyopharm Therapeutics) is intended for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma, after at least two lines of systemic therapy, according to the FDA’s announcement.
The FDA granted selinexor accelerated approval for this indication based on the response rate seen in the SADAL trial. Continued approval for this indication “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” according to the FDA.
The SADAL trial (NCT02227251) was a phase 2, single-arm, open-label study of patients with DLBCL who had previously received two to five systemic regimens. The patients received selinexor at 60 mg orally on days 1 and 3 of each week.
Results in 134 patients showed an overall response rate of 29% (95% confidence interval: 22-38), with complete responses in 13% of patients. Of 39 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 38% had a response duration of at least 6 months, and 15% had a response duration of at least 12 months, according to the FDA announcement.
The most common adverse reactions in this trial were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, appetite decrease, weight decrease, constipation, vomiting, and pyrexia. Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities occurred in 15% or more of the patients, and comprised thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia, and hyponatremia.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients, most often from infection. Gastrointestinal toxicity occurred in 80% of patients, and any-grade hyponatremia occurred in 61%. Central neurological adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients, including dizziness and mental status changes, according to the announcement.
Warnings and precautions for adverse events – including thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, gastrointestinal toxicity, hyponatremia, serious infection, neurological toxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity – are provided in the prescribing information.
Selinexor acts through the inhibition of exportin-1 and leads to an accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins, a reduction in oncoproteins, and apoptosis of cancer cells. The drug was previously approved in 2019 for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
The SADAL trial was sponsored by Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2020. Approval announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval of selinexor, a nuclear transport inhibitor, for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Selinexor (marketed as XPOVIO by Karyopharm Therapeutics) is intended for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma, after at least two lines of systemic therapy, according to the FDA’s announcement.
The FDA granted selinexor accelerated approval for this indication based on the response rate seen in the SADAL trial. Continued approval for this indication “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” according to the FDA.
The SADAL trial (NCT02227251) was a phase 2, single-arm, open-label study of patients with DLBCL who had previously received two to five systemic regimens. The patients received selinexor at 60 mg orally on days 1 and 3 of each week.
Results in 134 patients showed an overall response rate of 29% (95% confidence interval: 22-38), with complete responses in 13% of patients. Of 39 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 38% had a response duration of at least 6 months, and 15% had a response duration of at least 12 months, according to the FDA announcement.
The most common adverse reactions in this trial were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, appetite decrease, weight decrease, constipation, vomiting, and pyrexia. Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities occurred in 15% or more of the patients, and comprised thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia, and hyponatremia.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients, most often from infection. Gastrointestinal toxicity occurred in 80% of patients, and any-grade hyponatremia occurred in 61%. Central neurological adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients, including dizziness and mental status changes, according to the announcement.
Warnings and precautions for adverse events – including thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, gastrointestinal toxicity, hyponatremia, serious infection, neurological toxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity – are provided in the prescribing information.
Selinexor acts through the inhibition of exportin-1 and leads to an accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins, a reduction in oncoproteins, and apoptosis of cancer cells. The drug was previously approved in 2019 for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
The SADAL trial was sponsored by Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2020. Approval announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval of selinexor, a nuclear transport inhibitor, for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Selinexor (marketed as XPOVIO by Karyopharm Therapeutics) is intended for adult patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, not otherwise specified, including DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma, after at least two lines of systemic therapy, according to the FDA’s announcement.
The FDA granted selinexor accelerated approval for this indication based on the response rate seen in the SADAL trial. Continued approval for this indication “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” according to the FDA.
The SADAL trial (NCT02227251) was a phase 2, single-arm, open-label study of patients with DLBCL who had previously received two to five systemic regimens. The patients received selinexor at 60 mg orally on days 1 and 3 of each week.
Results in 134 patients showed an overall response rate of 29% (95% confidence interval: 22-38), with complete responses in 13% of patients. Of 39 patients who achieved a partial or complete response, 38% had a response duration of at least 6 months, and 15% had a response duration of at least 12 months, according to the FDA announcement.
The most common adverse reactions in this trial were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, appetite decrease, weight decrease, constipation, vomiting, and pyrexia. Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities occurred in 15% or more of the patients, and comprised thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia, and hyponatremia.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients, most often from infection. Gastrointestinal toxicity occurred in 80% of patients, and any-grade hyponatremia occurred in 61%. Central neurological adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients, including dizziness and mental status changes, according to the announcement.
Warnings and precautions for adverse events – including thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, gastrointestinal toxicity, hyponatremia, serious infection, neurological toxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity – are provided in the prescribing information.
Selinexor acts through the inhibition of exportin-1 and leads to an accumulation of tumor suppressor proteins, a reduction in oncoproteins, and apoptosis of cancer cells. The drug was previously approved in 2019 for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
The SADAL trial was sponsored by Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2020. Approval announcement.
FROM THE FDA
Adding avadomide shows promise for newly diagnosed DLBCL
For patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding avadomide to standard therapy may reduce the likelihood of treatment failure, based on phase 1 results.
The regimen was well tolerated and had a complete response rate of 79%, reported lead author Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Newly diagnosed DLBCL “remains a clinical challenge,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said, noting a treatment failure rate of 30%-50% for standard rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone every 21 days (R-CHOP-21), and worse outcomes among patients with high-risk disease.
In an effort to boost efficacy, the investigators turned to avadomide, a cereblon E3 ligase modulator, which previously demonstrated a complete response rate of 11% when used as monotherapy for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
The present phase 1 data included 35 adults with newly diagnosed DLBCL who had measurable lesions of at least 2.0 cm and International Prognostic Indices (IPI) between 3-5. Specifically, 51% of patients had an IPI of 3, while 49% had an IPI of 4-5.
All patients received standard R-CHOP with pegfilgrastim (to stimulate white blood cell growth), plus escalating doses of oral avadomide from 1-3 mg. Treatment was delivered, when tolerated, for up to six 21-day cycles. Depending on dose level, avadomide was given during either 2 or 3 out of 3 weeks. During treatment weeks, avadomide was given on 5 of 7 days.
The primary objectives were safety, tolerability, and complete response rate. Secondary objectives included biomarkers and additional efficacy measures, while exploratory analyses were also conducted to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Out of 34 patients evaluable for efficacy, the complete response rate was 79% and the objective response rate was 88%. After a median follow-up of 10 months, the 1-year progression-free survival rate was 80%.
“The combination showed promising efficacy,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said.
The regimen was also well tolerated and demonstrated an “acceptable safety profile consistent with either therapy alone,” Dr. Mehta-Shah added.
Most patients (91%) completed all six cycles of therapy. Median relative total dose intensities were 99% and 95% for avadomide and R-CHOP-21, respectively. Approximately two out of three patients (66%) required dose interruptions of avadomide, and 9% required dose reductions because of adverse events.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurred in six patients, including sepsis, febrile neutropenia caused by skin infections, febrile neutropenia with hypotension, febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, and neutropenia with bacterial hepatic infection. Based on these findings, the recommended phase 2 dose of avadomide was determined to be 3 mg given during 2 out of 3 weeks.
About 74% of patients had grade 3-4 treatment-emergent adverse events, the most common of which were neutropenia (54%), anemia (20%), leukopenia (20%), lymphopenia (14%), hypophosphatemia (14%), and febrile neutropenia (11%).
During the second cycle of therapy, one patient died because of concurrent pneumonia. After completion of therapy, two patients developed cardiac failure, and data gathered after each cycle showed that five patients had developed elevated levels of troponin or brain natriuretic peptide.
Flow cytometry showed that avadomide had proimmunomodulatory effects, including expansion of memory T-cell populations and enhanced proliferation of T cells and NK cells. The magnitude of this latter increase was greater than that observed in previous studies involving R-CHOP and durvalumab, Dr. Mehta-Shah noted.
“We look forward to following up on this data regarding the progression-free survival over a longer period of time,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said. “The results of this trial indicate that further evaluation of cereblon-modulating compounds combined with immunochemotherapy for patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is worthy of further exploration.”
Invited discussant Edward Yeh, MD, of the University of Missouri–Columbia, called cereblon modulators such as avadomide and thalidomide a “very exciting class of anticancer therapy.”
In a virtual presentation, Dr. Yeh noted that cereblon modulators have several advantages, including “good absorption, distribution, metabolism, [and] elimination,” plus relatively low susceptibility to mutation-directed drug resistance.
Despite some drawbacks, including difficulty to design and synthesize, Dr. Yeh suggested that this drug class may play a bigger role over time.
“We’re expecting more cancer therapy to come to fruition through the utilization of this posttranslational, protein-modification pathway,” he concluded.
The study was funded by Celgene. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, AstraZeneca, Roche, and others.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 3501.
For patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding avadomide to standard therapy may reduce the likelihood of treatment failure, based on phase 1 results.
The regimen was well tolerated and had a complete response rate of 79%, reported lead author Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Newly diagnosed DLBCL “remains a clinical challenge,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said, noting a treatment failure rate of 30%-50% for standard rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone every 21 days (R-CHOP-21), and worse outcomes among patients with high-risk disease.
In an effort to boost efficacy, the investigators turned to avadomide, a cereblon E3 ligase modulator, which previously demonstrated a complete response rate of 11% when used as monotherapy for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
The present phase 1 data included 35 adults with newly diagnosed DLBCL who had measurable lesions of at least 2.0 cm and International Prognostic Indices (IPI) between 3-5. Specifically, 51% of patients had an IPI of 3, while 49% had an IPI of 4-5.
All patients received standard R-CHOP with pegfilgrastim (to stimulate white blood cell growth), plus escalating doses of oral avadomide from 1-3 mg. Treatment was delivered, when tolerated, for up to six 21-day cycles. Depending on dose level, avadomide was given during either 2 or 3 out of 3 weeks. During treatment weeks, avadomide was given on 5 of 7 days.
The primary objectives were safety, tolerability, and complete response rate. Secondary objectives included biomarkers and additional efficacy measures, while exploratory analyses were also conducted to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Out of 34 patients evaluable for efficacy, the complete response rate was 79% and the objective response rate was 88%. After a median follow-up of 10 months, the 1-year progression-free survival rate was 80%.
“The combination showed promising efficacy,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said.
The regimen was also well tolerated and demonstrated an “acceptable safety profile consistent with either therapy alone,” Dr. Mehta-Shah added.
Most patients (91%) completed all six cycles of therapy. Median relative total dose intensities were 99% and 95% for avadomide and R-CHOP-21, respectively. Approximately two out of three patients (66%) required dose interruptions of avadomide, and 9% required dose reductions because of adverse events.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurred in six patients, including sepsis, febrile neutropenia caused by skin infections, febrile neutropenia with hypotension, febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, and neutropenia with bacterial hepatic infection. Based on these findings, the recommended phase 2 dose of avadomide was determined to be 3 mg given during 2 out of 3 weeks.
About 74% of patients had grade 3-4 treatment-emergent adverse events, the most common of which were neutropenia (54%), anemia (20%), leukopenia (20%), lymphopenia (14%), hypophosphatemia (14%), and febrile neutropenia (11%).
During the second cycle of therapy, one patient died because of concurrent pneumonia. After completion of therapy, two patients developed cardiac failure, and data gathered after each cycle showed that five patients had developed elevated levels of troponin or brain natriuretic peptide.
Flow cytometry showed that avadomide had proimmunomodulatory effects, including expansion of memory T-cell populations and enhanced proliferation of T cells and NK cells. The magnitude of this latter increase was greater than that observed in previous studies involving R-CHOP and durvalumab, Dr. Mehta-Shah noted.
“We look forward to following up on this data regarding the progression-free survival over a longer period of time,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said. “The results of this trial indicate that further evaluation of cereblon-modulating compounds combined with immunochemotherapy for patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is worthy of further exploration.”
Invited discussant Edward Yeh, MD, of the University of Missouri–Columbia, called cereblon modulators such as avadomide and thalidomide a “very exciting class of anticancer therapy.”
In a virtual presentation, Dr. Yeh noted that cereblon modulators have several advantages, including “good absorption, distribution, metabolism, [and] elimination,” plus relatively low susceptibility to mutation-directed drug resistance.
Despite some drawbacks, including difficulty to design and synthesize, Dr. Yeh suggested that this drug class may play a bigger role over time.
“We’re expecting more cancer therapy to come to fruition through the utilization of this posttranslational, protein-modification pathway,” he concluded.
The study was funded by Celgene. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, AstraZeneca, Roche, and others.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 3501.
For patients with newly diagnosed, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), adding avadomide to standard therapy may reduce the likelihood of treatment failure, based on phase 1 results.
The regimen was well tolerated and had a complete response rate of 79%, reported lead author Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University, St. Louis, who presented findings as part of the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program.
Newly diagnosed DLBCL “remains a clinical challenge,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said, noting a treatment failure rate of 30%-50% for standard rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone every 21 days (R-CHOP-21), and worse outcomes among patients with high-risk disease.
In an effort to boost efficacy, the investigators turned to avadomide, a cereblon E3 ligase modulator, which previously demonstrated a complete response rate of 11% when used as monotherapy for patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL.
The present phase 1 data included 35 adults with newly diagnosed DLBCL who had measurable lesions of at least 2.0 cm and International Prognostic Indices (IPI) between 3-5. Specifically, 51% of patients had an IPI of 3, while 49% had an IPI of 4-5.
All patients received standard R-CHOP with pegfilgrastim (to stimulate white blood cell growth), plus escalating doses of oral avadomide from 1-3 mg. Treatment was delivered, when tolerated, for up to six 21-day cycles. Depending on dose level, avadomide was given during either 2 or 3 out of 3 weeks. During treatment weeks, avadomide was given on 5 of 7 days.
The primary objectives were safety, tolerability, and complete response rate. Secondary objectives included biomarkers and additional efficacy measures, while exploratory analyses were also conducted to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Out of 34 patients evaluable for efficacy, the complete response rate was 79% and the objective response rate was 88%. After a median follow-up of 10 months, the 1-year progression-free survival rate was 80%.
“The combination showed promising efficacy,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said.
The regimen was also well tolerated and demonstrated an “acceptable safety profile consistent with either therapy alone,” Dr. Mehta-Shah added.
Most patients (91%) completed all six cycles of therapy. Median relative total dose intensities were 99% and 95% for avadomide and R-CHOP-21, respectively. Approximately two out of three patients (66%) required dose interruptions of avadomide, and 9% required dose reductions because of adverse events.
Dose-limiting toxicities occurred in six patients, including sepsis, febrile neutropenia caused by skin infections, febrile neutropenia with hypotension, febrile neutropenia, pneumonia, and neutropenia with bacterial hepatic infection. Based on these findings, the recommended phase 2 dose of avadomide was determined to be 3 mg given during 2 out of 3 weeks.
About 74% of patients had grade 3-4 treatment-emergent adverse events, the most common of which were neutropenia (54%), anemia (20%), leukopenia (20%), lymphopenia (14%), hypophosphatemia (14%), and febrile neutropenia (11%).
During the second cycle of therapy, one patient died because of concurrent pneumonia. After completion of therapy, two patients developed cardiac failure, and data gathered after each cycle showed that five patients had developed elevated levels of troponin or brain natriuretic peptide.
Flow cytometry showed that avadomide had proimmunomodulatory effects, including expansion of memory T-cell populations and enhanced proliferation of T cells and NK cells. The magnitude of this latter increase was greater than that observed in previous studies involving R-CHOP and durvalumab, Dr. Mehta-Shah noted.
“We look forward to following up on this data regarding the progression-free survival over a longer period of time,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said. “The results of this trial indicate that further evaluation of cereblon-modulating compounds combined with immunochemotherapy for patients with previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is worthy of further exploration.”
Invited discussant Edward Yeh, MD, of the University of Missouri–Columbia, called cereblon modulators such as avadomide and thalidomide a “very exciting class of anticancer therapy.”
In a virtual presentation, Dr. Yeh noted that cereblon modulators have several advantages, including “good absorption, distribution, metabolism, [and] elimination,” plus relatively low susceptibility to mutation-directed drug resistance.
Despite some drawbacks, including difficulty to design and synthesize, Dr. Yeh suggested that this drug class may play a bigger role over time.
“We’re expecting more cancer therapy to come to fruition through the utilization of this posttranslational, protein-modification pathway,” he concluded.
The study was funded by Celgene. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, AstraZeneca, Roche, and others.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 3501.
FROM ASCO 2020
Race and location appear to play a role in the incidence of CLL and DLBCL
Exposure to carcinogens has been implicated in the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), suggesting that an examination of the environment on a population-based level might provide some insights. On that basis, researchers performed a study that found that living in an urban vs. rural area was associated with an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) among diverse, urban populations.
The study, published online in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, found an increased incidence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in urban vs. rural Hispanics, and a similar increased incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in non-metropolitan urban non-Hispanic blacks.
A total of 482,096 adults aged 20 years and older with incident NHL were reported to 21 Surveillance, Epidemiology,and End Results (SEER) population-based registries for the period 2000 to 2016. Deanna Blansky of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, N.Y., and her colleagues compared patients by NHL subtype and urban-rural status, using rural-urban continuum codes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The researchers found 136,197 DLBCL, 70,882 follicular lymphoma (FL), and 120,319 CLL cases of patients aged ≥ 20 years. The DLBCL patients comprised 73.6% non-Hispanic white, 11.8% Hispanic, and 7.3% non-Hispanic black, with a similar distribution observed for FL and CLL. Patients were adjusted for age, sex, and family poverty.
The study showed that, overall, there was a higher DLBCL incidence rate in metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas overall (incidence rate ratio [IRR] = 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.11-1.30). Most pronounced was an increased DLBCL incidence among Hispanics in urban areas, compared with rural areas (rural IRR = 1.00; non-metropolitan urban IRR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.16-1.51; metropolitan urban = 1.55, 95% CI 1.36-1.76).
In contrast, metropolitan urban areas had a lower overall incidence of CLL than rural areas (8.4 vs. 9.7 per 100,000; IRR = .87; 95% CI .86-.89).
However, increased CLL incidence rates were found to be associated with non-metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas (IRR = 1.19; 95% CI 1.10-1.28), particularly among non-Hispanic Blacks (IRR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.27-1.72).
Unlike DLBCL and CLL, there were no differences observed in FL incidence rates by urban-rural status after adjusting for age, sex, and family poverty rates, the researchers reported.
“Overall, our findings suggest that factors related to urban status may be associated with DLBCL and CLL pathogenesis. Our results may help provide epidemiological clues to understanding the racial disparities seen among hematological malignancies, particularly regarding the risk of DLBCL in Hispanics and CLL in non-Hispanic Blacks,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. The researchers did not report conflict information.
SOURCE: Blansky D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 May 15; doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2020.05.010.
Exposure to carcinogens has been implicated in the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), suggesting that an examination of the environment on a population-based level might provide some insights. On that basis, researchers performed a study that found that living in an urban vs. rural area was associated with an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) among diverse, urban populations.
The study, published online in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, found an increased incidence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in urban vs. rural Hispanics, and a similar increased incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in non-metropolitan urban non-Hispanic blacks.
A total of 482,096 adults aged 20 years and older with incident NHL were reported to 21 Surveillance, Epidemiology,and End Results (SEER) population-based registries for the period 2000 to 2016. Deanna Blansky of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, N.Y., and her colleagues compared patients by NHL subtype and urban-rural status, using rural-urban continuum codes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The researchers found 136,197 DLBCL, 70,882 follicular lymphoma (FL), and 120,319 CLL cases of patients aged ≥ 20 years. The DLBCL patients comprised 73.6% non-Hispanic white, 11.8% Hispanic, and 7.3% non-Hispanic black, with a similar distribution observed for FL and CLL. Patients were adjusted for age, sex, and family poverty.
The study showed that, overall, there was a higher DLBCL incidence rate in metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas overall (incidence rate ratio [IRR] = 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.11-1.30). Most pronounced was an increased DLBCL incidence among Hispanics in urban areas, compared with rural areas (rural IRR = 1.00; non-metropolitan urban IRR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.16-1.51; metropolitan urban = 1.55, 95% CI 1.36-1.76).
In contrast, metropolitan urban areas had a lower overall incidence of CLL than rural areas (8.4 vs. 9.7 per 100,000; IRR = .87; 95% CI .86-.89).
However, increased CLL incidence rates were found to be associated with non-metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas (IRR = 1.19; 95% CI 1.10-1.28), particularly among non-Hispanic Blacks (IRR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.27-1.72).
Unlike DLBCL and CLL, there were no differences observed in FL incidence rates by urban-rural status after adjusting for age, sex, and family poverty rates, the researchers reported.
“Overall, our findings suggest that factors related to urban status may be associated with DLBCL and CLL pathogenesis. Our results may help provide epidemiological clues to understanding the racial disparities seen among hematological malignancies, particularly regarding the risk of DLBCL in Hispanics and CLL in non-Hispanic Blacks,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. The researchers did not report conflict information.
SOURCE: Blansky D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 May 15; doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2020.05.010.
Exposure to carcinogens has been implicated in the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), suggesting that an examination of the environment on a population-based level might provide some insights. On that basis, researchers performed a study that found that living in an urban vs. rural area was associated with an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) among diverse, urban populations.
The study, published online in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, found an increased incidence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in urban vs. rural Hispanics, and a similar increased incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in non-metropolitan urban non-Hispanic blacks.
A total of 482,096 adults aged 20 years and older with incident NHL were reported to 21 Surveillance, Epidemiology,and End Results (SEER) population-based registries for the period 2000 to 2016. Deanna Blansky of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, N.Y., and her colleagues compared patients by NHL subtype and urban-rural status, using rural-urban continuum codes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The researchers found 136,197 DLBCL, 70,882 follicular lymphoma (FL), and 120,319 CLL cases of patients aged ≥ 20 years. The DLBCL patients comprised 73.6% non-Hispanic white, 11.8% Hispanic, and 7.3% non-Hispanic black, with a similar distribution observed for FL and CLL. Patients were adjusted for age, sex, and family poverty.
The study showed that, overall, there was a higher DLBCL incidence rate in metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas overall (incidence rate ratio [IRR] = 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.11-1.30). Most pronounced was an increased DLBCL incidence among Hispanics in urban areas, compared with rural areas (rural IRR = 1.00; non-metropolitan urban IRR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.16-1.51; metropolitan urban = 1.55, 95% CI 1.36-1.76).
In contrast, metropolitan urban areas had a lower overall incidence of CLL than rural areas (8.4 vs. 9.7 per 100,000; IRR = .87; 95% CI .86-.89).
However, increased CLL incidence rates were found to be associated with non-metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas (IRR = 1.19; 95% CI 1.10-1.28), particularly among non-Hispanic Blacks (IRR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.27-1.72).
Unlike DLBCL and CLL, there were no differences observed in FL incidence rates by urban-rural status after adjusting for age, sex, and family poverty rates, the researchers reported.
“Overall, our findings suggest that factors related to urban status may be associated with DLBCL and CLL pathogenesis. Our results may help provide epidemiological clues to understanding the racial disparities seen among hematological malignancies, particularly regarding the risk of DLBCL in Hispanics and CLL in non-Hispanic Blacks,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. The researchers did not report conflict information.
SOURCE: Blansky D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 May 15; doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2020.05.010.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
DLBCL patients at academic centers had significantly better survival
Researchers used the U.S. National Cancer Database to identify patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL from 2004 to 2015. The researchers identified 27,690 patients for the study. The majority of the patients were white (89.3%) and men (53.7%), with an average age of 64 years. A total of 57.6% of the patients had been treated at nonacademic centers and 42.4% at academic centers, and no notable differences were seen in facility choice among the low- to high-risk International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk categories.
The researchers found that overall survival of the DLBCL patients at academic centers was 108.3 months versus 74.5 months at nonacademic centers (P < .001), according to the study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
In addition, the median survival for patients with high-risk disease treated at academic centers was more than twice that of high-risk patients treated at nonacademic centers (33.5 months vs. 14.4 months, respectively; P < .001). Although the median survival for the other risk categories was also improved, the difference was less pronounced in the groups with lower IPI scores, according to the researchers.
Long-term overall survival for all patients with DLBCL at academic centers was significantly improved at both 5 and 10 years (59% and 43% survival, respectively) compared with those patients treated at nonacademic centers (51% and 35% survival, respectively; P < .001).
Speculating on factors that might be involved in this discrepancy in survival, the researchers suggested that academic centers might provide increased access to clinical trials, improved physician expertise, as well as improved treatment facilities and supportive care.
“Our results should prompt further investigation in precisely determining the factors that might support this significant effect on decreased survival among those treated in the community and help ameliorate this discrepancy,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ermann DA et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(4): e17483.
Researchers used the U.S. National Cancer Database to identify patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL from 2004 to 2015. The researchers identified 27,690 patients for the study. The majority of the patients were white (89.3%) and men (53.7%), with an average age of 64 years. A total of 57.6% of the patients had been treated at nonacademic centers and 42.4% at academic centers, and no notable differences were seen in facility choice among the low- to high-risk International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk categories.
The researchers found that overall survival of the DLBCL patients at academic centers was 108.3 months versus 74.5 months at nonacademic centers (P < .001), according to the study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
In addition, the median survival for patients with high-risk disease treated at academic centers was more than twice that of high-risk patients treated at nonacademic centers (33.5 months vs. 14.4 months, respectively; P < .001). Although the median survival for the other risk categories was also improved, the difference was less pronounced in the groups with lower IPI scores, according to the researchers.
Long-term overall survival for all patients with DLBCL at academic centers was significantly improved at both 5 and 10 years (59% and 43% survival, respectively) compared with those patients treated at nonacademic centers (51% and 35% survival, respectively; P < .001).
Speculating on factors that might be involved in this discrepancy in survival, the researchers suggested that academic centers might provide increased access to clinical trials, improved physician expertise, as well as improved treatment facilities and supportive care.
“Our results should prompt further investigation in precisely determining the factors that might support this significant effect on decreased survival among those treated in the community and help ameliorate this discrepancy,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ermann DA et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(4): e17483.
Researchers used the U.S. National Cancer Database to identify patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL from 2004 to 2015. The researchers identified 27,690 patients for the study. The majority of the patients were white (89.3%) and men (53.7%), with an average age of 64 years. A total of 57.6% of the patients had been treated at nonacademic centers and 42.4% at academic centers, and no notable differences were seen in facility choice among the low- to high-risk International Prognostic Index (IPI) risk categories.
The researchers found that overall survival of the DLBCL patients at academic centers was 108.3 months versus 74.5 months at nonacademic centers (P < .001), according to the study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
In addition, the median survival for patients with high-risk disease treated at academic centers was more than twice that of high-risk patients treated at nonacademic centers (33.5 months vs. 14.4 months, respectively; P < .001). Although the median survival for the other risk categories was also improved, the difference was less pronounced in the groups with lower IPI scores, according to the researchers.
Long-term overall survival for all patients with DLBCL at academic centers was significantly improved at both 5 and 10 years (59% and 43% survival, respectively) compared with those patients treated at nonacademic centers (51% and 35% survival, respectively; P < .001).
Speculating on factors that might be involved in this discrepancy in survival, the researchers suggested that academic centers might provide increased access to clinical trials, improved physician expertise, as well as improved treatment facilities and supportive care.
“Our results should prompt further investigation in precisely determining the factors that might support this significant effect on decreased survival among those treated in the community and help ameliorate this discrepancy,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ermann DA et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20(4): e17483.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA AND LEUKEMIA
Safer CAR uses modified NK cells for advanced CLL, NHL
A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) construct using transduced natural killer cells instead of T cells was associated with a high complete remission rate without the cytokine release syndrome frequently seen with CAR T cell therapy, early clinical trial results show.
The construct, consisting of natural killer (NK) cells derived from umbilical cord blood that have been transduced to target CD19-expressing cells combined with interleukin 15 and equipped with an “off” switch, offers the prospect of an off-the-shelf CAR product, reported Enli Liu, MD, and colleagues at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
“We found that allogeneic CAR-NK cells can be delivered in adoptive transfer without the serious cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxic effects that have been associated with CAR T-cell therapy,” they wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The modified NK cells were delivered to 9 of 11 patients with only partial human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching, and in 2 patients with no matching, yet there were no cases of graft-versus host disease (GvHD), and no patients had symptoms of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity, or hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
CAR T cell production “is a cumbersome process that requires coordination and collection of the cells and there’s several weeks of manufacturing, during which time patients often can have their lymphoma worsen, and so at times it’s a little bit of a race against the clock to get those cells manufactured,” Brian Hill, MD, PhD, director of the lymphoid malignancies program at Taussig Cancer Institute at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
Dr. Hill, who was not involved in the study, said that the proof-of-principle study shows promising early results and offers the prospect of an effective and safe off-the-shelf therapeutic option for patients with lymphoid malignancies.
Advanced B-cell cancers
The investigators conducted a phase 1/2 trial in patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancies, including five patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), one patient with Richter’s transformation and one with accelerated CLL, three with transformed follicular lymphoma, two with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and one with follicular lymphoma (focally grade 3B).
The patients were all heavily pretreated, with 3 to as many as 11 prior lines of therapy.
The patients received cord blood-derived NK cells that had been transduced with a retroviral vector expressing genes that encode anti-CD19 CAR, interleukin-15, and inducible caspase 9 as a safety switch.
The cells were expanded in the lab and after the patients underwent lymphodepleting chemotherapy, they received the cells in a single infusion at one of three doses, either 1×105, 1×106, or 1×107 CAR-NK cells per kilogram of body weight.
As noted before, there were no cases of CRS, neurotoxicity, or GvHD and no increase over baseline in inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6, a key factor in the development and severity of CRS. The maximum tolerated dose was not reached.
Early efficacy
Of the 11 patients, 8 had a clinical response, and 7 had a complete remission, including 4 patients with lymphomas and 3 with CLL.
The patient with CLL with Richter’s transformation had a remission of the Richter’s component, but not of the CLL itself.
“This is particularly remarkable, because these patients are notoriously very difficult to treat, and the efficacy of autologous CAR T cell therapy in CLL and Richter’s patients has been hampered by lack of fitness of the patient’s own T cells when manufacturing the CAR T cell product, so this approach may obviate the need for autologous T cells in these patients,” Dr. Hill said.
The responses were rapid and occurred within 30 days of infusion at all dose levels. In addition, there was evidence of expansion and persistence of the modified NK cells at low levels for at least 1 year, despite the HLA mismatches between the NK cells and the recipients. The investigators speculated that the inclusion of interleukin-15 in the NL construct may at least partially account for the persistence of the cells and their antitumor activity.
Of the eight patients with a response, five had postremission therapy, including two patients with CLL who had minimal residual disease (MRD), one patient with follicular lymphoma and one with transformed follicular lymphoma who underwent hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation while in complete remission without evidence of MRD, and the patient with CLLL with Richter’s transformation with remission of the lymphoma component, who received a course of venetoclax.
The authors acknowledged that it may be difficult to assess the durability of response after CAR NK therapy in this study because of the allowed consolidation therapy for patients in remission.
They noted that although the patients in the current study each had a fresh CAR NK product manufactured for them, “we have shown that it is possible to produce more than 100 doses of CAR-NK cells from a single cord-blood unit. This capability, together with the apparently minimal HLA-matching requirements between the donor of CAR-NK cells and the patient, may pave the way for a truly off-the-shelf product that could increase treatment accessibility for many more patients.”
The National Institutes of Health supported the study. Dr. Liu disclosed a pending patent for methods of production of CAR-NK cells, and a patent held by MD Anderson for methods of treatment with NK cells. Dr. Hill is a member of the Hematology News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Liu E et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 6;382:545-53.
A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) construct using transduced natural killer cells instead of T cells was associated with a high complete remission rate without the cytokine release syndrome frequently seen with CAR T cell therapy, early clinical trial results show.
The construct, consisting of natural killer (NK) cells derived from umbilical cord blood that have been transduced to target CD19-expressing cells combined with interleukin 15 and equipped with an “off” switch, offers the prospect of an off-the-shelf CAR product, reported Enli Liu, MD, and colleagues at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
“We found that allogeneic CAR-NK cells can be delivered in adoptive transfer without the serious cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxic effects that have been associated with CAR T-cell therapy,” they wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The modified NK cells were delivered to 9 of 11 patients with only partial human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching, and in 2 patients with no matching, yet there were no cases of graft-versus host disease (GvHD), and no patients had symptoms of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity, or hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
CAR T cell production “is a cumbersome process that requires coordination and collection of the cells and there’s several weeks of manufacturing, during which time patients often can have their lymphoma worsen, and so at times it’s a little bit of a race against the clock to get those cells manufactured,” Brian Hill, MD, PhD, director of the lymphoid malignancies program at Taussig Cancer Institute at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
Dr. Hill, who was not involved in the study, said that the proof-of-principle study shows promising early results and offers the prospect of an effective and safe off-the-shelf therapeutic option for patients with lymphoid malignancies.
Advanced B-cell cancers
The investigators conducted a phase 1/2 trial in patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancies, including five patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), one patient with Richter’s transformation and one with accelerated CLL, three with transformed follicular lymphoma, two with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and one with follicular lymphoma (focally grade 3B).
The patients were all heavily pretreated, with 3 to as many as 11 prior lines of therapy.
The patients received cord blood-derived NK cells that had been transduced with a retroviral vector expressing genes that encode anti-CD19 CAR, interleukin-15, and inducible caspase 9 as a safety switch.
The cells were expanded in the lab and after the patients underwent lymphodepleting chemotherapy, they received the cells in a single infusion at one of three doses, either 1×105, 1×106, or 1×107 CAR-NK cells per kilogram of body weight.
As noted before, there were no cases of CRS, neurotoxicity, or GvHD and no increase over baseline in inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6, a key factor in the development and severity of CRS. The maximum tolerated dose was not reached.
Early efficacy
Of the 11 patients, 8 had a clinical response, and 7 had a complete remission, including 4 patients with lymphomas and 3 with CLL.
The patient with CLL with Richter’s transformation had a remission of the Richter’s component, but not of the CLL itself.
“This is particularly remarkable, because these patients are notoriously very difficult to treat, and the efficacy of autologous CAR T cell therapy in CLL and Richter’s patients has been hampered by lack of fitness of the patient’s own T cells when manufacturing the CAR T cell product, so this approach may obviate the need for autologous T cells in these patients,” Dr. Hill said.
The responses were rapid and occurred within 30 days of infusion at all dose levels. In addition, there was evidence of expansion and persistence of the modified NK cells at low levels for at least 1 year, despite the HLA mismatches between the NK cells and the recipients. The investigators speculated that the inclusion of interleukin-15 in the NL construct may at least partially account for the persistence of the cells and their antitumor activity.
Of the eight patients with a response, five had postremission therapy, including two patients with CLL who had minimal residual disease (MRD), one patient with follicular lymphoma and one with transformed follicular lymphoma who underwent hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation while in complete remission without evidence of MRD, and the patient with CLLL with Richter’s transformation with remission of the lymphoma component, who received a course of venetoclax.
The authors acknowledged that it may be difficult to assess the durability of response after CAR NK therapy in this study because of the allowed consolidation therapy for patients in remission.
They noted that although the patients in the current study each had a fresh CAR NK product manufactured for them, “we have shown that it is possible to produce more than 100 doses of CAR-NK cells from a single cord-blood unit. This capability, together with the apparently minimal HLA-matching requirements between the donor of CAR-NK cells and the patient, may pave the way for a truly off-the-shelf product that could increase treatment accessibility for many more patients.”
The National Institutes of Health supported the study. Dr. Liu disclosed a pending patent for methods of production of CAR-NK cells, and a patent held by MD Anderson for methods of treatment with NK cells. Dr. Hill is a member of the Hematology News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Liu E et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 6;382:545-53.
A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) construct using transduced natural killer cells instead of T cells was associated with a high complete remission rate without the cytokine release syndrome frequently seen with CAR T cell therapy, early clinical trial results show.
The construct, consisting of natural killer (NK) cells derived from umbilical cord blood that have been transduced to target CD19-expressing cells combined with interleukin 15 and equipped with an “off” switch, offers the prospect of an off-the-shelf CAR product, reported Enli Liu, MD, and colleagues at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
“We found that allogeneic CAR-NK cells can be delivered in adoptive transfer without the serious cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxic effects that have been associated with CAR T-cell therapy,” they wrote in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The modified NK cells were delivered to 9 of 11 patients with only partial human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching, and in 2 patients with no matching, yet there were no cases of graft-versus host disease (GvHD), and no patients had symptoms of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity, or hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
CAR T cell production “is a cumbersome process that requires coordination and collection of the cells and there’s several weeks of manufacturing, during which time patients often can have their lymphoma worsen, and so at times it’s a little bit of a race against the clock to get those cells manufactured,” Brian Hill, MD, PhD, director of the lymphoid malignancies program at Taussig Cancer Institute at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
Dr. Hill, who was not involved in the study, said that the proof-of-principle study shows promising early results and offers the prospect of an effective and safe off-the-shelf therapeutic option for patients with lymphoid malignancies.
Advanced B-cell cancers
The investigators conducted a phase 1/2 trial in patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancies, including five patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), one patient with Richter’s transformation and one with accelerated CLL, three with transformed follicular lymphoma, two with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and one with follicular lymphoma (focally grade 3B).
The patients were all heavily pretreated, with 3 to as many as 11 prior lines of therapy.
The patients received cord blood-derived NK cells that had been transduced with a retroviral vector expressing genes that encode anti-CD19 CAR, interleukin-15, and inducible caspase 9 as a safety switch.
The cells were expanded in the lab and after the patients underwent lymphodepleting chemotherapy, they received the cells in a single infusion at one of three doses, either 1×105, 1×106, or 1×107 CAR-NK cells per kilogram of body weight.
As noted before, there were no cases of CRS, neurotoxicity, or GvHD and no increase over baseline in inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6, a key factor in the development and severity of CRS. The maximum tolerated dose was not reached.
Early efficacy
Of the 11 patients, 8 had a clinical response, and 7 had a complete remission, including 4 patients with lymphomas and 3 with CLL.
The patient with CLL with Richter’s transformation had a remission of the Richter’s component, but not of the CLL itself.
“This is particularly remarkable, because these patients are notoriously very difficult to treat, and the efficacy of autologous CAR T cell therapy in CLL and Richter’s patients has been hampered by lack of fitness of the patient’s own T cells when manufacturing the CAR T cell product, so this approach may obviate the need for autologous T cells in these patients,” Dr. Hill said.
The responses were rapid and occurred within 30 days of infusion at all dose levels. In addition, there was evidence of expansion and persistence of the modified NK cells at low levels for at least 1 year, despite the HLA mismatches between the NK cells and the recipients. The investigators speculated that the inclusion of interleukin-15 in the NL construct may at least partially account for the persistence of the cells and their antitumor activity.
Of the eight patients with a response, five had postremission therapy, including two patients with CLL who had minimal residual disease (MRD), one patient with follicular lymphoma and one with transformed follicular lymphoma who underwent hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation while in complete remission without evidence of MRD, and the patient with CLLL with Richter’s transformation with remission of the lymphoma component, who received a course of venetoclax.
The authors acknowledged that it may be difficult to assess the durability of response after CAR NK therapy in this study because of the allowed consolidation therapy for patients in remission.
They noted that although the patients in the current study each had a fresh CAR NK product manufactured for them, “we have shown that it is possible to produce more than 100 doses of CAR-NK cells from a single cord-blood unit. This capability, together with the apparently minimal HLA-matching requirements between the donor of CAR-NK cells and the patient, may pave the way for a truly off-the-shelf product that could increase treatment accessibility for many more patients.”
The National Institutes of Health supported the study. Dr. Liu disclosed a pending patent for methods of production of CAR-NK cells, and a patent held by MD Anderson for methods of treatment with NK cells. Dr. Hill is a member of the Hematology News editorial advisory board.
SOURCE: Liu E et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 6;382:545-53.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
DLBCL tops cases of HBV-associated NHL in Europe
The majority of hepatitis B virus (HBV)–associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) cases in Western Europe were patients with advanced-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to results of a retrospective study.
The findings suggest additional research is needed to better understand the nature of HBV-related lymphomas in nonendemic regions.
“Our aim was to describe the characteristics and outcomes of patients with NHL and active hepatitis B in France and Italy, where the prevalence of HBV is low,” wrote Marine Lemaitre of the Centre Hospitalier de Versailles in Le Chesnay, France, and colleagues. The findings were published in the Journal of Infection.
The researchers retrospectively studied a cohort of 39 patients with B-cell NHL and active HBV infection. Clinical data was collected from medical records at three hematology centers in France and Italy. The team evaluated clinical characteristics, including histologic subtype of the lymphoma, type of treatment, patient demographics, and prognostic outcomes. In addition, they compared these data with a separate cohort of patients with B-cell NHL and active HCV infection. Among study patients, the median age at lymphoma diagnosis was 59 years (range, 29-88 years), and most were men. The most common subtype of lymphoma was DLBCL (62%), followed by other subtypes (38%), including marginal zone lymphomas, follicular lymphomas, and mantle cell lymphomas. With respect to treatment, 92% of patients with DLBCL were treated with R-CHOP or a similar regimen, while 90% of patients received antivirals, resulting in a complete remission for 75% of patients. At 12-month follow-up, 88% and 87% of patients with DLBCL and other B-cell lymphomas were alive, respectively.
“Patients had predominantly advanced-stage DLBCL, with frequent liver involvement, and frequent long-term hematological responses when they received a combination of immuno-chemotherapy and antiviral treatment,” the researchers explained. They also noted that extra-nodal involvement was frequently seen in both HBV- and HCV-associated NHL.
“Additional studies are needed to explore the lymphomagenesis of [these] association[s],” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lemaitre M et al. J Infect. 2019 Dec 14. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2019.12.005.
The majority of hepatitis B virus (HBV)–associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) cases in Western Europe were patients with advanced-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to results of a retrospective study.
The findings suggest additional research is needed to better understand the nature of HBV-related lymphomas in nonendemic regions.
“Our aim was to describe the characteristics and outcomes of patients with NHL and active hepatitis B in France and Italy, where the prevalence of HBV is low,” wrote Marine Lemaitre of the Centre Hospitalier de Versailles in Le Chesnay, France, and colleagues. The findings were published in the Journal of Infection.
The researchers retrospectively studied a cohort of 39 patients with B-cell NHL and active HBV infection. Clinical data was collected from medical records at three hematology centers in France and Italy. The team evaluated clinical characteristics, including histologic subtype of the lymphoma, type of treatment, patient demographics, and prognostic outcomes. In addition, they compared these data with a separate cohort of patients with B-cell NHL and active HCV infection. Among study patients, the median age at lymphoma diagnosis was 59 years (range, 29-88 years), and most were men. The most common subtype of lymphoma was DLBCL (62%), followed by other subtypes (38%), including marginal zone lymphomas, follicular lymphomas, and mantle cell lymphomas. With respect to treatment, 92% of patients with DLBCL were treated with R-CHOP or a similar regimen, while 90% of patients received antivirals, resulting in a complete remission for 75% of patients. At 12-month follow-up, 88% and 87% of patients with DLBCL and other B-cell lymphomas were alive, respectively.
“Patients had predominantly advanced-stage DLBCL, with frequent liver involvement, and frequent long-term hematological responses when they received a combination of immuno-chemotherapy and antiviral treatment,” the researchers explained. They also noted that extra-nodal involvement was frequently seen in both HBV- and HCV-associated NHL.
“Additional studies are needed to explore the lymphomagenesis of [these] association[s],” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lemaitre M et al. J Infect. 2019 Dec 14. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2019.12.005.
The majority of hepatitis B virus (HBV)–associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) cases in Western Europe were patients with advanced-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), according to results of a retrospective study.
The findings suggest additional research is needed to better understand the nature of HBV-related lymphomas in nonendemic regions.
“Our aim was to describe the characteristics and outcomes of patients with NHL and active hepatitis B in France and Italy, where the prevalence of HBV is low,” wrote Marine Lemaitre of the Centre Hospitalier de Versailles in Le Chesnay, France, and colleagues. The findings were published in the Journal of Infection.
The researchers retrospectively studied a cohort of 39 patients with B-cell NHL and active HBV infection. Clinical data was collected from medical records at three hematology centers in France and Italy. The team evaluated clinical characteristics, including histologic subtype of the lymphoma, type of treatment, patient demographics, and prognostic outcomes. In addition, they compared these data with a separate cohort of patients with B-cell NHL and active HCV infection. Among study patients, the median age at lymphoma diagnosis was 59 years (range, 29-88 years), and most were men. The most common subtype of lymphoma was DLBCL (62%), followed by other subtypes (38%), including marginal zone lymphomas, follicular lymphomas, and mantle cell lymphomas. With respect to treatment, 92% of patients with DLBCL were treated with R-CHOP or a similar regimen, while 90% of patients received antivirals, resulting in a complete remission for 75% of patients. At 12-month follow-up, 88% and 87% of patients with DLBCL and other B-cell lymphomas were alive, respectively.
“Patients had predominantly advanced-stage DLBCL, with frequent liver involvement, and frequent long-term hematological responses when they received a combination of immuno-chemotherapy and antiviral treatment,” the researchers explained. They also noted that extra-nodal involvement was frequently seen in both HBV- and HCV-associated NHL.
“Additional studies are needed to explore the lymphomagenesis of [these] association[s],” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lemaitre M et al. J Infect. 2019 Dec 14. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2019.12.005.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INFECTION
REGN1979 shows good activity in pretreated aggressive B-NHL
ORLANDO – A novel bispecific antibody directed against CD20 and CD3 was associated in a phase 1 trial with a high overall response rate among patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas in early clinical trials, including patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that had progressed following chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Among 22 patients previously treated for relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma of grade 1-3a, there were 21 responses (95%), including 17 complete responses (CR) and 4 partial responses (PR), with the remaining patient having stable disease at 12 weeks of follow-up, reported Rajat Bannerji, MD, PhD, from the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey in New Brunswick.
“We had activity that was fairly robust in this heavily pretreated population with follicular lymphoma, large-cell patients who had not received CAR T and large-cell patients who had received CAR T, mantle cell, and marginal zone [lymphoma],” he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
REGN1979 is an anti-CD20 and anti-CD3 bispecific IgG4 antibody. It is designed to cross-link and activate CD3-expressing T cells on contact with CD20-positive B cells to kill CD20-positive tumor cells independent of T-cell receptor recognition.
The antibody is administered via an escalating dose schedule consisting of initial, intermediate, and step-up doses.
In addition to the follicular lymphoma response rates noted before, patients with heavily pretreated DLBCL who received the antibody at a dose of 80 mg or higher had an overall response rate of 57.9% (11 patients) including 42.1% CR (8 patients), and 15.8% PR (3 patients). Two patients had stable disease at the 12-week assessment, three had disease progression, and three were not available for assessment.
Among seven patients with DLBCL treated at 80 mg or above who had not received CAR T therapy, five had a CR, one had stable disease, and one had disease progression. Of 12 patients with prior CAR T exposure, 3 had complete responses, 3 had partial responses, 1 had stable disease, 2 had progressive disease, and 3 were not available for assessment.
Among six patients with mantle cell lymphoma and six with marginal zone lymphoma treated across all disease levels, the ORR in each cohort was 67%, with two of six patients in each cohort having a complete response, and two having a partial response.
The safety analysis of all 110 patients enrolled showed that no patients experience a dose-limiting toxicity during the escalation phase, and no maximum tolerated doses were identified.
The most common treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were pyrexia in 88 patients, cytokine release syndrome in 65, chills in 56, fatigue in 40, and anemia in 39.
The most common grade 3-4 AEs were anemia in 24, and hypophosphatemia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia in 21 patients each.
Neurologic AEs were transient and did not require treatment discontinuation, and there were no grade 4 neurologic AEs or deaths from neurologic side effects.
Six patients discontinued the study drug because of treatment-related AEs that included cytomegalovirus infection, grade 3 hemolysis, fatigue, pneumonia, and toxoplasmosis.
A total of 15 patients died during the study, 10 of which were caused by progressive disease, with other deaths caused by gastric perforation, cardiac arrest, lung infection, pneumonia, and 1 from fungal pneumonia 7 months after treatment discontinuation. In addition, after the data cutoff, one patient with mantle cell lymphoma blastoid variant with bone-marrow involvement and bulky disease who was enrolled in an expansion cohort died from tumor lysis syndrome.
The dose-escalation portion of the trial has been completed and expansion cohorts are being enrolled. In addition, REGN1979 is being investigated in a phase 2 global multiarm trial.
The study is supported by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Bannerji reported research funding, travel support, and consulting fees from Regeneron and others.
SOURCE: Bannerji R et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 762.
ORLANDO – A novel bispecific antibody directed against CD20 and CD3 was associated in a phase 1 trial with a high overall response rate among patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas in early clinical trials, including patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that had progressed following chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Among 22 patients previously treated for relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma of grade 1-3a, there were 21 responses (95%), including 17 complete responses (CR) and 4 partial responses (PR), with the remaining patient having stable disease at 12 weeks of follow-up, reported Rajat Bannerji, MD, PhD, from the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey in New Brunswick.
“We had activity that was fairly robust in this heavily pretreated population with follicular lymphoma, large-cell patients who had not received CAR T and large-cell patients who had received CAR T, mantle cell, and marginal zone [lymphoma],” he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
REGN1979 is an anti-CD20 and anti-CD3 bispecific IgG4 antibody. It is designed to cross-link and activate CD3-expressing T cells on contact with CD20-positive B cells to kill CD20-positive tumor cells independent of T-cell receptor recognition.
The antibody is administered via an escalating dose schedule consisting of initial, intermediate, and step-up doses.
In addition to the follicular lymphoma response rates noted before, patients with heavily pretreated DLBCL who received the antibody at a dose of 80 mg or higher had an overall response rate of 57.9% (11 patients) including 42.1% CR (8 patients), and 15.8% PR (3 patients). Two patients had stable disease at the 12-week assessment, three had disease progression, and three were not available for assessment.
Among seven patients with DLBCL treated at 80 mg or above who had not received CAR T therapy, five had a CR, one had stable disease, and one had disease progression. Of 12 patients with prior CAR T exposure, 3 had complete responses, 3 had partial responses, 1 had stable disease, 2 had progressive disease, and 3 were not available for assessment.
Among six patients with mantle cell lymphoma and six with marginal zone lymphoma treated across all disease levels, the ORR in each cohort was 67%, with two of six patients in each cohort having a complete response, and two having a partial response.
The safety analysis of all 110 patients enrolled showed that no patients experience a dose-limiting toxicity during the escalation phase, and no maximum tolerated doses were identified.
The most common treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were pyrexia in 88 patients, cytokine release syndrome in 65, chills in 56, fatigue in 40, and anemia in 39.
The most common grade 3-4 AEs were anemia in 24, and hypophosphatemia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia in 21 patients each.
Neurologic AEs were transient and did not require treatment discontinuation, and there were no grade 4 neurologic AEs or deaths from neurologic side effects.
Six patients discontinued the study drug because of treatment-related AEs that included cytomegalovirus infection, grade 3 hemolysis, fatigue, pneumonia, and toxoplasmosis.
A total of 15 patients died during the study, 10 of which were caused by progressive disease, with other deaths caused by gastric perforation, cardiac arrest, lung infection, pneumonia, and 1 from fungal pneumonia 7 months after treatment discontinuation. In addition, after the data cutoff, one patient with mantle cell lymphoma blastoid variant with bone-marrow involvement and bulky disease who was enrolled in an expansion cohort died from tumor lysis syndrome.
The dose-escalation portion of the trial has been completed and expansion cohorts are being enrolled. In addition, REGN1979 is being investigated in a phase 2 global multiarm trial.
The study is supported by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Bannerji reported research funding, travel support, and consulting fees from Regeneron and others.
SOURCE: Bannerji R et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 762.
ORLANDO – A novel bispecific antibody directed against CD20 and CD3 was associated in a phase 1 trial with a high overall response rate among patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas in early clinical trials, including patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that had progressed following chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Among 22 patients previously treated for relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma of grade 1-3a, there were 21 responses (95%), including 17 complete responses (CR) and 4 partial responses (PR), with the remaining patient having stable disease at 12 weeks of follow-up, reported Rajat Bannerji, MD, PhD, from the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey in New Brunswick.
“We had activity that was fairly robust in this heavily pretreated population with follicular lymphoma, large-cell patients who had not received CAR T and large-cell patients who had received CAR T, mantle cell, and marginal zone [lymphoma],” he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
REGN1979 is an anti-CD20 and anti-CD3 bispecific IgG4 antibody. It is designed to cross-link and activate CD3-expressing T cells on contact with CD20-positive B cells to kill CD20-positive tumor cells independent of T-cell receptor recognition.
The antibody is administered via an escalating dose schedule consisting of initial, intermediate, and step-up doses.
In addition to the follicular lymphoma response rates noted before, patients with heavily pretreated DLBCL who received the antibody at a dose of 80 mg or higher had an overall response rate of 57.9% (11 patients) including 42.1% CR (8 patients), and 15.8% PR (3 patients). Two patients had stable disease at the 12-week assessment, three had disease progression, and three were not available for assessment.
Among seven patients with DLBCL treated at 80 mg or above who had not received CAR T therapy, five had a CR, one had stable disease, and one had disease progression. Of 12 patients with prior CAR T exposure, 3 had complete responses, 3 had partial responses, 1 had stable disease, 2 had progressive disease, and 3 were not available for assessment.
Among six patients with mantle cell lymphoma and six with marginal zone lymphoma treated across all disease levels, the ORR in each cohort was 67%, with two of six patients in each cohort having a complete response, and two having a partial response.
The safety analysis of all 110 patients enrolled showed that no patients experience a dose-limiting toxicity during the escalation phase, and no maximum tolerated doses were identified.
The most common treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were pyrexia in 88 patients, cytokine release syndrome in 65, chills in 56, fatigue in 40, and anemia in 39.
The most common grade 3-4 AEs were anemia in 24, and hypophosphatemia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia in 21 patients each.
Neurologic AEs were transient and did not require treatment discontinuation, and there were no grade 4 neurologic AEs or deaths from neurologic side effects.
Six patients discontinued the study drug because of treatment-related AEs that included cytomegalovirus infection, grade 3 hemolysis, fatigue, pneumonia, and toxoplasmosis.
A total of 15 patients died during the study, 10 of which were caused by progressive disease, with other deaths caused by gastric perforation, cardiac arrest, lung infection, pneumonia, and 1 from fungal pneumonia 7 months after treatment discontinuation. In addition, after the data cutoff, one patient with mantle cell lymphoma blastoid variant with bone-marrow involvement and bulky disease who was enrolled in an expansion cohort died from tumor lysis syndrome.
The dose-escalation portion of the trial has been completed and expansion cohorts are being enrolled. In addition, REGN1979 is being investigated in a phase 2 global multiarm trial.
The study is supported by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Bannerji reported research funding, travel support, and consulting fees from Regeneron and others.
SOURCE: Bannerji R et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 762.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
NCCN guidelines highlight ‘complicated’ treatment for pediatric lymphomas
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has released its first set of guidelines for managing pediatric aggressive mature B-cell lymphomas.
The guidelines highlight the complexities of treating pediatric Burkitt lymphoma (BL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), as recommendations include a range of multiagent regimens for different patient groups at various time points.
“The treatment of this disease is relatively complicated,” said Kimberly J. Davies, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and chair of the guidelines panel. “The chemotherapy regimens have a lot of drugs, a lot of nuances to how they’re supposed to be given. These guidelines delineate that treatment and help the provider … make sure they are delivering the treatment a patient needs.”
The guidelines recommend different regimens according to a patient’s risk group, but the same treatment approach should be used for patients with BL and those with DLBCL.
“The biggest difference between pediatric and adult patients is that pediatric patients are more uniformly treated, regardless of what type of aggressive B-cell lymphoma they have,” said Matthew Barth, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., and vice chair of the NCCN guidelines panel.
“Adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma are generally treated with different chemotherapy regimens, but, in pediatrics, we use the same treatment regimens for both diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma,” he added.
As an example, the new guidelines recommend that pediatric patients with low-risk BL/DLBCL receive the POG9219 regimen (N Engl J Med. 1997 Oct 30;337[18]:1259-66) or FAB/LMB96 regimen A (Br J Haematol. 2008 Jun;141[6]:840-7) as induction, or they should be enrolled in a clinical trial.
On the other hand, induction for high-risk pediatric BL/DLBCL patients should consist of rituximab and a chemotherapy regimen used in the COG ANHL1131 trial. The recommendation to incorporate rituximab in high-risk pediatric patients is based on results from that trial (J Clin Oncol. 2016 May 20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.34.15_suppl.10507).
“Until recent clinical trial data was available, we weren’t really sure how to incorporate rituximab into the treatment of pediatric patients with mature B-cell lymphomas,” Dr. Barth said. “We now have evidence that rituximab is clearly beneficial for patients who are in higher-risk groups.”
Dr. Barth and Dr. Davies both noted that pediatric BL and DLBCL have high cure rates. Long-term survival rates range from about 80% to more than 90%, according to the American Cancer Society. However, the patients who do relapse or progress can be difficult to treat.
“We have quite good cure rates at this point in time, which is a great success, but that means that a very small population of patients don’t respond to initial therapy, and … it’s hard to know what the best treatment for those patients is,” Dr. Davies said.
She noted that studies are underway to determine if immunotherapies, including chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, might improve outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory disease.
For now, the NCCN guidelines recommend clinical trial enrollment for relapsed/refractory patients. Alternatively, these patients can receive additional chemotherapy, and responders can proceed to transplant. Patients who don’t achieve at least a partial response may go on to a clinical trial or receive best supportive care.
Dr. Davies and Dr. Barth reported having no conflicts of interest.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has released its first set of guidelines for managing pediatric aggressive mature B-cell lymphomas.
The guidelines highlight the complexities of treating pediatric Burkitt lymphoma (BL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), as recommendations include a range of multiagent regimens for different patient groups at various time points.
“The treatment of this disease is relatively complicated,” said Kimberly J. Davies, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and chair of the guidelines panel. “The chemotherapy regimens have a lot of drugs, a lot of nuances to how they’re supposed to be given. These guidelines delineate that treatment and help the provider … make sure they are delivering the treatment a patient needs.”
The guidelines recommend different regimens according to a patient’s risk group, but the same treatment approach should be used for patients with BL and those with DLBCL.
“The biggest difference between pediatric and adult patients is that pediatric patients are more uniformly treated, regardless of what type of aggressive B-cell lymphoma they have,” said Matthew Barth, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., and vice chair of the NCCN guidelines panel.
“Adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma are generally treated with different chemotherapy regimens, but, in pediatrics, we use the same treatment regimens for both diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma,” he added.
As an example, the new guidelines recommend that pediatric patients with low-risk BL/DLBCL receive the POG9219 regimen (N Engl J Med. 1997 Oct 30;337[18]:1259-66) or FAB/LMB96 regimen A (Br J Haematol. 2008 Jun;141[6]:840-7) as induction, or they should be enrolled in a clinical trial.
On the other hand, induction for high-risk pediatric BL/DLBCL patients should consist of rituximab and a chemotherapy regimen used in the COG ANHL1131 trial. The recommendation to incorporate rituximab in high-risk pediatric patients is based on results from that trial (J Clin Oncol. 2016 May 20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.34.15_suppl.10507).
“Until recent clinical trial data was available, we weren’t really sure how to incorporate rituximab into the treatment of pediatric patients with mature B-cell lymphomas,” Dr. Barth said. “We now have evidence that rituximab is clearly beneficial for patients who are in higher-risk groups.”
Dr. Barth and Dr. Davies both noted that pediatric BL and DLBCL have high cure rates. Long-term survival rates range from about 80% to more than 90%, according to the American Cancer Society. However, the patients who do relapse or progress can be difficult to treat.
“We have quite good cure rates at this point in time, which is a great success, but that means that a very small population of patients don’t respond to initial therapy, and … it’s hard to know what the best treatment for those patients is,” Dr. Davies said.
She noted that studies are underway to determine if immunotherapies, including chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, might improve outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory disease.
For now, the NCCN guidelines recommend clinical trial enrollment for relapsed/refractory patients. Alternatively, these patients can receive additional chemotherapy, and responders can proceed to transplant. Patients who don’t achieve at least a partial response may go on to a clinical trial or receive best supportive care.
Dr. Davies and Dr. Barth reported having no conflicts of interest.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has released its first set of guidelines for managing pediatric aggressive mature B-cell lymphomas.
The guidelines highlight the complexities of treating pediatric Burkitt lymphoma (BL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), as recommendations include a range of multiagent regimens for different patient groups at various time points.
“The treatment of this disease is relatively complicated,” said Kimberly J. Davies, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and chair of the guidelines panel. “The chemotherapy regimens have a lot of drugs, a lot of nuances to how they’re supposed to be given. These guidelines delineate that treatment and help the provider … make sure they are delivering the treatment a patient needs.”
The guidelines recommend different regimens according to a patient’s risk group, but the same treatment approach should be used for patients with BL and those with DLBCL.
“The biggest difference between pediatric and adult patients is that pediatric patients are more uniformly treated, regardless of what type of aggressive B-cell lymphoma they have,” said Matthew Barth, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, N.Y., and vice chair of the NCCN guidelines panel.
“Adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma are generally treated with different chemotherapy regimens, but, in pediatrics, we use the same treatment regimens for both diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma,” he added.
As an example, the new guidelines recommend that pediatric patients with low-risk BL/DLBCL receive the POG9219 regimen (N Engl J Med. 1997 Oct 30;337[18]:1259-66) or FAB/LMB96 regimen A (Br J Haematol. 2008 Jun;141[6]:840-7) as induction, or they should be enrolled in a clinical trial.
On the other hand, induction for high-risk pediatric BL/DLBCL patients should consist of rituximab and a chemotherapy regimen used in the COG ANHL1131 trial. The recommendation to incorporate rituximab in high-risk pediatric patients is based on results from that trial (J Clin Oncol. 2016 May 20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.34.15_suppl.10507).
“Until recent clinical trial data was available, we weren’t really sure how to incorporate rituximab into the treatment of pediatric patients with mature B-cell lymphomas,” Dr. Barth said. “We now have evidence that rituximab is clearly beneficial for patients who are in higher-risk groups.”
Dr. Barth and Dr. Davies both noted that pediatric BL and DLBCL have high cure rates. Long-term survival rates range from about 80% to more than 90%, according to the American Cancer Society. However, the patients who do relapse or progress can be difficult to treat.
“We have quite good cure rates at this point in time, which is a great success, but that means that a very small population of patients don’t respond to initial therapy, and … it’s hard to know what the best treatment for those patients is,” Dr. Davies said.
She noted that studies are underway to determine if immunotherapies, including chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, might improve outcomes in patients with relapsed or refractory disease.
For now, the NCCN guidelines recommend clinical trial enrollment for relapsed/refractory patients. Alternatively, these patients can receive additional chemotherapy, and responders can proceed to transplant. Patients who don’t achieve at least a partial response may go on to a clinical trial or receive best supportive care.
Dr. Davies and Dr. Barth reported having no conflicts of interest.