User login
VIDEO: Pioglitazone benefited NASH patients with and without T2DM
Pioglitazone therapy given for 18 months benefited patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) similarly regardless of whether they had type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes, according to the results of a randomized prospective trial.
SOURCE: AMERICAN GASTROENTEROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
The primary outcome, at least a 2-point reduction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score compared with placebo, without worsening fibrosis, was met by 48% of NASH patients with T2DM and by 46% of those with prediabetes, reported Fernando Bril, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and his associates. The report was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
NASH resolved completely in 44% with T2DM and 26% of patients without it, respectively, perhaps indicating that pioglitazone acts slightly differently when patients with NASH have T2DM, according to the investigators. “Although the effects on fibrosis appear to be similar in both groups, pioglitazone may contribute to halting [its] rapid progression [in T2DM],” they wrote. “These differences will deserve further exploration in larger clinical trials.”
The trial (NCT00994682) enrolled 101 patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH, of whom 52 had T2DM and 49 had prediabetes based on clinical history, baseline fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and an oral glucose tolerance test, as per American Diabetes Association guidelines. After a 4-week run-in period, patients were randomly assigned to receive either pioglitazone (45 mg per day) or placebo for 18 months. All patients received lifestyle counseling and a hypocaloric (500-kcal reduced) diet.
Compared with placebo, pioglitazone improved most secondary outcomes similarly regardless of whether patients were T2DM or prediabetes. The two exceptions were fibrosis and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue. Patients with T2DM only experienced improved fibrosis in the setting of pioglitazone therapy (P = .035 vs. baseline). In prediabetic patients, fibrosis lessened moderately over time, regardless of whether they received pioglitazone or placebo. Insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue improved much more markedly with treatment in patients with T2DM (P less than .001 vs. baseline) than in those with prediabetes (P = .002 for T2DM vs. prediabetes).
Compared with placebo, pioglitazone improved hepatic and skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity similarly, regardless of diabetes status. Likewise, intrahepatic triglyceride content, as measured by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy, fell by 11% in pioglitazone recipients with T2DM and by 9% of those with prediabetes, a nonsignificant difference. Pioglitazone also led to a statistically similar decrease in plasma alanine aminotransferase level regardless of whether patients had T2DM (50 U/L) or were prediabetic (36 U/L).
This trial’s key takeaway is that pioglitazone improves liver histology in NASH whether or not patients are diabetic, said the researchers. “We believed that it was essential to compare its efficacy in patients with [and] without T2DM because of the vast number of patients with prediabetes and NASH and given the significant metabolic and cardioprotective effects of pioglitazone among patients without T2DM,” they wrote. The natural history of NASH is worse in the presence of T2DM, which might explain pioglitazone’s superior effects on fibrosis and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue in this population, they added.
The Burroughs Wellcome Fund, the American Diabetes Association, and the Veteran’s Affairs Merit Award supported the work. Senior author Kenneth Cusi, MD, disclosed nonfinancial support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, grants from Novartis and Janssen Research and Development, and consulting relationships with Eli Lilly, Tobira Therapeutics, and Pfizer. The other authors had no conflicts.
Source: Bril F, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Feb 24. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.12.001.
Pioglitazone therapy given for 18 months benefited patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) similarly regardless of whether they had type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes, according to the results of a randomized prospective trial.
SOURCE: AMERICAN GASTROENTEROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
The primary outcome, at least a 2-point reduction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score compared with placebo, without worsening fibrosis, was met by 48% of NASH patients with T2DM and by 46% of those with prediabetes, reported Fernando Bril, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and his associates. The report was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
NASH resolved completely in 44% with T2DM and 26% of patients without it, respectively, perhaps indicating that pioglitazone acts slightly differently when patients with NASH have T2DM, according to the investigators. “Although the effects on fibrosis appear to be similar in both groups, pioglitazone may contribute to halting [its] rapid progression [in T2DM],” they wrote. “These differences will deserve further exploration in larger clinical trials.”
The trial (NCT00994682) enrolled 101 patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH, of whom 52 had T2DM and 49 had prediabetes based on clinical history, baseline fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and an oral glucose tolerance test, as per American Diabetes Association guidelines. After a 4-week run-in period, patients were randomly assigned to receive either pioglitazone (45 mg per day) or placebo for 18 months. All patients received lifestyle counseling and a hypocaloric (500-kcal reduced) diet.
Compared with placebo, pioglitazone improved most secondary outcomes similarly regardless of whether patients were T2DM or prediabetes. The two exceptions were fibrosis and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue. Patients with T2DM only experienced improved fibrosis in the setting of pioglitazone therapy (P = .035 vs. baseline). In prediabetic patients, fibrosis lessened moderately over time, regardless of whether they received pioglitazone or placebo. Insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue improved much more markedly with treatment in patients with T2DM (P less than .001 vs. baseline) than in those with prediabetes (P = .002 for T2DM vs. prediabetes).
Compared with placebo, pioglitazone improved hepatic and skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity similarly, regardless of diabetes status. Likewise, intrahepatic triglyceride content, as measured by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy, fell by 11% in pioglitazone recipients with T2DM and by 9% of those with prediabetes, a nonsignificant difference. Pioglitazone also led to a statistically similar decrease in plasma alanine aminotransferase level regardless of whether patients had T2DM (50 U/L) or were prediabetic (36 U/L).
This trial’s key takeaway is that pioglitazone improves liver histology in NASH whether or not patients are diabetic, said the researchers. “We believed that it was essential to compare its efficacy in patients with [and] without T2DM because of the vast number of patients with prediabetes and NASH and given the significant metabolic and cardioprotective effects of pioglitazone among patients without T2DM,” they wrote. The natural history of NASH is worse in the presence of T2DM, which might explain pioglitazone’s superior effects on fibrosis and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue in this population, they added.
The Burroughs Wellcome Fund, the American Diabetes Association, and the Veteran’s Affairs Merit Award supported the work. Senior author Kenneth Cusi, MD, disclosed nonfinancial support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, grants from Novartis and Janssen Research and Development, and consulting relationships with Eli Lilly, Tobira Therapeutics, and Pfizer. The other authors had no conflicts.
Source: Bril F, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Feb 24. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.12.001.
Pioglitazone therapy given for 18 months benefited patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) similarly regardless of whether they had type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes, according to the results of a randomized prospective trial.
SOURCE: AMERICAN GASTROENTEROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
The primary outcome, at least a 2-point reduction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score compared with placebo, without worsening fibrosis, was met by 48% of NASH patients with T2DM and by 46% of those with prediabetes, reported Fernando Bril, MD, of the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism at the University of Florida, Gainesville, and his associates. The report was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
NASH resolved completely in 44% with T2DM and 26% of patients without it, respectively, perhaps indicating that pioglitazone acts slightly differently when patients with NASH have T2DM, according to the investigators. “Although the effects on fibrosis appear to be similar in both groups, pioglitazone may contribute to halting [its] rapid progression [in T2DM],” they wrote. “These differences will deserve further exploration in larger clinical trials.”
The trial (NCT00994682) enrolled 101 patients with biopsy-confirmed NASH, of whom 52 had T2DM and 49 had prediabetes based on clinical history, baseline fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c, and an oral glucose tolerance test, as per American Diabetes Association guidelines. After a 4-week run-in period, patients were randomly assigned to receive either pioglitazone (45 mg per day) or placebo for 18 months. All patients received lifestyle counseling and a hypocaloric (500-kcal reduced) diet.
Compared with placebo, pioglitazone improved most secondary outcomes similarly regardless of whether patients were T2DM or prediabetes. The two exceptions were fibrosis and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue. Patients with T2DM only experienced improved fibrosis in the setting of pioglitazone therapy (P = .035 vs. baseline). In prediabetic patients, fibrosis lessened moderately over time, regardless of whether they received pioglitazone or placebo. Insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue improved much more markedly with treatment in patients with T2DM (P less than .001 vs. baseline) than in those with prediabetes (P = .002 for T2DM vs. prediabetes).
Compared with placebo, pioglitazone improved hepatic and skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity similarly, regardless of diabetes status. Likewise, intrahepatic triglyceride content, as measured by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy, fell by 11% in pioglitazone recipients with T2DM and by 9% of those with prediabetes, a nonsignificant difference. Pioglitazone also led to a statistically similar decrease in plasma alanine aminotransferase level regardless of whether patients had T2DM (50 U/L) or were prediabetic (36 U/L).
This trial’s key takeaway is that pioglitazone improves liver histology in NASH whether or not patients are diabetic, said the researchers. “We believed that it was essential to compare its efficacy in patients with [and] without T2DM because of the vast number of patients with prediabetes and NASH and given the significant metabolic and cardioprotective effects of pioglitazone among patients without T2DM,” they wrote. The natural history of NASH is worse in the presence of T2DM, which might explain pioglitazone’s superior effects on fibrosis and insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue in this population, they added.
The Burroughs Wellcome Fund, the American Diabetes Association, and the Veteran’s Affairs Merit Award supported the work. Senior author Kenneth Cusi, MD, disclosed nonfinancial support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, grants from Novartis and Janssen Research and Development, and consulting relationships with Eli Lilly, Tobira Therapeutics, and Pfizer. The other authors had no conflicts.
Source: Bril F, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Feb 24. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.12.001.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Pioglitazone improved liver measures in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis whether or not they were diabetic.
Major finding: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score fell by at least 2 points, without worsening fibrosis, in 48% of T2DM patients and 46% of patients with prediabetes.
Data source: A prospective study of 101 patients with NASH, of whom 52 had type 2 diabetes and 49 had prediabetes.
Disclosures: The Burroughs Wellcome Fund, the American Diabetes Association, and the Veteran’s Affairs Merit Award supported the work. Senior author Kenneth Cusi, MD, disclosed nonfinancial support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, grants from Novartis and Janssen Research and Development, and consulting relationships with Eli Lilly and Company, Tobira Therapeutics, and Pfizer. The other authors had no conflicts.
Source: Bril F et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Feb 24. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.12.001.
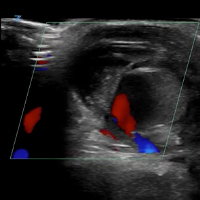
VIDEO: Ultrasound with Doppler
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
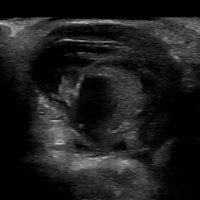
VIDEO: Initial Bedside Ultrasound of Pulsatile Hand Mass



Cenk Ayata, MD, & Messoud Ashina, MD



Bridget Mueller, MD, PhD
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Paul Rizzoli, MD
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Christopher Gottschalk, MD
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
VIDEO: Adipogenic genes upregulated in high-BMI sucralose users
CHICAGO – , there was significant upregulation of genes that promote intracellular glucose transport. Genes known to be adipogenic and those governing sweet taste receptors also were significantly upregulated with sucralose exposure.
“Effects of sucralose are particularly more detrimental in obese individuals who are prediabetic or diabetic, rather than nonobese consumers of low-calorie sweetener,” said Sabyasachi Sen, MD, during a press conference at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
These new findings, together with in vitro examination of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) exposed to sucralose, are helping solve the puzzle of how a sweetener that delivers no energy may contribute to metabolic derangement, said Dr. Sen, professor of endocrinology at George Washington University in Washington.
Dr. Sen and his collaborators first exposed the MSCs to concentrations of sucralose ranging from 0 mM to 0.2 mM – a physiologic level for high sucralose consumers – to the supraphysiologic concentration of 1 mM.
The adipogenic genes CEBPa and FABP4 were upregulated in the sucralose-exposed MSCs, which also showed more intracellular fat droplet accumulation. Reactive oxygen species increased in the MSCs in a dose-dependent fashion as well, said Dr. Sen in a video interview.
All of this upregulation, said Dr. Sen, was pushing the MSCs toward becoming fat cells. “At the same time, we saw that there are certain genes that were upregulating that were allowing more glucose to enter the cell.” The increase in reactive oxygen species paralleled what was seen in a similar model that used glucose rather than sucralose, he said.
The investigators then took subcutaneous fat biopsies from four normal-weight individuals (body mass index, 23.4-24.8 kg/m2), and from 14 obese individuals (BMI, 32-64 kg/m2). Each group had sucralose users and nonusers. Using mRNA gene expression profiles, they saw that glucose transporter genes, adipogenic genes, and antioxidant genes were upregulated among sucralose consumers with obesity, significantly more than for the normal-weight participants.
The pattern, said Dr. Sen, was strikingly similar to what had been seen with the MSC-sucralose exposure findings. “The upregulation that we saw in the petri dish could now be seen in the human fat samples,” he said.
“We think that the sucralose is … allowing more glucose to enter the cell,” said Dr. Sen. “We think that we actually have figured out a mechanism.” He and his colleagues next plan to tag glucose molecules to follow what actually happens as they enter cells in the presence of sucralose.
When Dr. Sen’s patients ask whether they should switch to low-calorie sweetened beverages, he answers with an emphatic “no.” “I say, ‘It’s not going to do you any good, because it still may allow glucose to enter the cells … you’re going to come back to the same status quo’ ” in the context of obesity and insulin resistance, he said.
Dr. Sen reported that he has no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Sen S et al. ENDO 2018, Abstract SUN-071.
CHICAGO – , there was significant upregulation of genes that promote intracellular glucose transport. Genes known to be adipogenic and those governing sweet taste receptors also were significantly upregulated with sucralose exposure.
“Effects of sucralose are particularly more detrimental in obese individuals who are prediabetic or diabetic, rather than nonobese consumers of low-calorie sweetener,” said Sabyasachi Sen, MD, during a press conference at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
These new findings, together with in vitro examination of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) exposed to sucralose, are helping solve the puzzle of how a sweetener that delivers no energy may contribute to metabolic derangement, said Dr. Sen, professor of endocrinology at George Washington University in Washington.
Dr. Sen and his collaborators first exposed the MSCs to concentrations of sucralose ranging from 0 mM to 0.2 mM – a physiologic level for high sucralose consumers – to the supraphysiologic concentration of 1 mM.
The adipogenic genes CEBPa and FABP4 were upregulated in the sucralose-exposed MSCs, which also showed more intracellular fat droplet accumulation. Reactive oxygen species increased in the MSCs in a dose-dependent fashion as well, said Dr. Sen in a video interview.
All of this upregulation, said Dr. Sen, was pushing the MSCs toward becoming fat cells. “At the same time, we saw that there are certain genes that were upregulating that were allowing more glucose to enter the cell.” The increase in reactive oxygen species paralleled what was seen in a similar model that used glucose rather than sucralose, he said.
The investigators then took subcutaneous fat biopsies from four normal-weight individuals (body mass index, 23.4-24.8 kg/m2), and from 14 obese individuals (BMI, 32-64 kg/m2). Each group had sucralose users and nonusers. Using mRNA gene expression profiles, they saw that glucose transporter genes, adipogenic genes, and antioxidant genes were upregulated among sucralose consumers with obesity, significantly more than for the normal-weight participants.
The pattern, said Dr. Sen, was strikingly similar to what had been seen with the MSC-sucralose exposure findings. “The upregulation that we saw in the petri dish could now be seen in the human fat samples,” he said.
“We think that the sucralose is … allowing more glucose to enter the cell,” said Dr. Sen. “We think that we actually have figured out a mechanism.” He and his colleagues next plan to tag glucose molecules to follow what actually happens as they enter cells in the presence of sucralose.
When Dr. Sen’s patients ask whether they should switch to low-calorie sweetened beverages, he answers with an emphatic “no.” “I say, ‘It’s not going to do you any good, because it still may allow glucose to enter the cells … you’re going to come back to the same status quo’ ” in the context of obesity and insulin resistance, he said.
Dr. Sen reported that he has no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Sen S et al. ENDO 2018, Abstract SUN-071.
CHICAGO – , there was significant upregulation of genes that promote intracellular glucose transport. Genes known to be adipogenic and those governing sweet taste receptors also were significantly upregulated with sucralose exposure.
“Effects of sucralose are particularly more detrimental in obese individuals who are prediabetic or diabetic, rather than nonobese consumers of low-calorie sweetener,” said Sabyasachi Sen, MD, during a press conference at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
These new findings, together with in vitro examination of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) exposed to sucralose, are helping solve the puzzle of how a sweetener that delivers no energy may contribute to metabolic derangement, said Dr. Sen, professor of endocrinology at George Washington University in Washington.
Dr. Sen and his collaborators first exposed the MSCs to concentrations of sucralose ranging from 0 mM to 0.2 mM – a physiologic level for high sucralose consumers – to the supraphysiologic concentration of 1 mM.
The adipogenic genes CEBPa and FABP4 were upregulated in the sucralose-exposed MSCs, which also showed more intracellular fat droplet accumulation. Reactive oxygen species increased in the MSCs in a dose-dependent fashion as well, said Dr. Sen in a video interview.
All of this upregulation, said Dr. Sen, was pushing the MSCs toward becoming fat cells. “At the same time, we saw that there are certain genes that were upregulating that were allowing more glucose to enter the cell.” The increase in reactive oxygen species paralleled what was seen in a similar model that used glucose rather than sucralose, he said.
The investigators then took subcutaneous fat biopsies from four normal-weight individuals (body mass index, 23.4-24.8 kg/m2), and from 14 obese individuals (BMI, 32-64 kg/m2). Each group had sucralose users and nonusers. Using mRNA gene expression profiles, they saw that glucose transporter genes, adipogenic genes, and antioxidant genes were upregulated among sucralose consumers with obesity, significantly more than for the normal-weight participants.
The pattern, said Dr. Sen, was strikingly similar to what had been seen with the MSC-sucralose exposure findings. “The upregulation that we saw in the petri dish could now be seen in the human fat samples,” he said.
“We think that the sucralose is … allowing more glucose to enter the cell,” said Dr. Sen. “We think that we actually have figured out a mechanism.” He and his colleagues next plan to tag glucose molecules to follow what actually happens as they enter cells in the presence of sucralose.
When Dr. Sen’s patients ask whether they should switch to low-calorie sweetened beverages, he answers with an emphatic “no.” “I say, ‘It’s not going to do you any good, because it still may allow glucose to enter the cells … you’re going to come back to the same status quo’ ” in the context of obesity and insulin resistance, he said.
Dr. Sen reported that he has no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Sen S et al. ENDO 2018, Abstract SUN-071.
REPORTING FROM ENDO 2018
VIDEO: How to prepare PTCL patients for transplant
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – according to Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“If you’re really trying to go to transplant, you want a complete remission or close to it. So that’s often been combination chemotherapy. But I think what we’re learning is, when some of the newer agents are combined, we’re seeing higher complete response rates. And we’re doing a better job at picking subtype specific approaches,” Dr. Horwitz said in a video interview at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Horwitz also explored the role for reduced-intensity regimens in older patients, the use of radiation conditioning, and which new agents look most promising in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Dr. Horwitz had previously disclosed financial relationships with Celgene, Forty Seven, Huya Bioscience International, Infinity, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Millennium, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Horwitz SM. TCLF 2018.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – according to Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“If you’re really trying to go to transplant, you want a complete remission or close to it. So that’s often been combination chemotherapy. But I think what we’re learning is, when some of the newer agents are combined, we’re seeing higher complete response rates. And we’re doing a better job at picking subtype specific approaches,” Dr. Horwitz said in a video interview at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Horwitz also explored the role for reduced-intensity regimens in older patients, the use of radiation conditioning, and which new agents look most promising in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Dr. Horwitz had previously disclosed financial relationships with Celgene, Forty Seven, Huya Bioscience International, Infinity, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Millennium, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Horwitz SM. TCLF 2018.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – according to Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“If you’re really trying to go to transplant, you want a complete remission or close to it. So that’s often been combination chemotherapy. But I think what we’re learning is, when some of the newer agents are combined, we’re seeing higher complete response rates. And we’re doing a better job at picking subtype specific approaches,” Dr. Horwitz said in a video interview at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Horwitz also explored the role for reduced-intensity regimens in older patients, the use of radiation conditioning, and which new agents look most promising in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Dr. Horwitz had previously disclosed financial relationships with Celgene, Forty Seven, Huya Bioscience International, Infinity, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Millennium, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda. The T-Cell Lymphoma Forum is held by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
SOURCE: Horwitz SM. TCLF 2018.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2018
VIDEO: Everolimus/letrozole promising for recurrent endometrial cancer
NEW ORLEANS – Combined treatment for 28 days with the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus plus the aromatase inhibitor letrozole in 37 women with recurrent endometrial cancer produced an overall objective response rate of 24% and an average progression-free survival rate of 6.3 months in a randomized phase 2 study with a total of 74 patients. The treatment was also relatively well tolerated, with more serious adverse vents of anemia and hyperglycemia.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
But the most attention-grabbing finding of this study was that, in the subset of 15 women who had received no prior chemotherapy, the objective response rate on this regimen was 53% and median progression-free survival was 21.6 months, Brian M. Slomovitz, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology.
This level of response in the chemotherapy-naive subgroup was “very high, and not what we expected,” Dr. Slomovitz, , professor of ob.gyn. and human genetics and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of Miami, said in a video interview. “This is something we need to further investigate to see if we can make this part of standard care.”
Although he conceded that the data from this study were too limited to warrant a regulatory indication, he suggested that it might be enough to gain the everolimus plus letrozole combination used in the study citation as a treatment option in clinical guidelines. The next step should be a phase 3 trial that compares the everolimus plus letrozole combination with the traditional chemotherapy regimen of carboplatin plus paclitaxel, Dr. Slomovitz added.
The Everolimus and Letrozole or Hormonal Therapy to Treat Endometrial Cancer phase 2 trial, initiated by the Gynecologic Oncology Group, ran at 26 U.S. centers, and randomized patients with stage III or IV recurrent, advanced, or persistent endometrial cancer who had either no or at most one prior course of chemotherapy. The study design also excluded patients who had previously been treated with an mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor or hormonal therapy for their endometrial cancer. The control arm placed 37 patients on a standard hormonal therapy regimen of tamoxifen plus medroxyprogesterone, with 36 of patients in this subgroup evaluable.
The overall results in the two treatment arms were roughly similar, except for the striking benefit seen with everolimus(Afinitor) plus letrozole(Femara) in the chemotherapy-naive patents; 15 patients in each arm had not received any chemotherapy before entering the study. In this subgroup, among the patients who received conventional hormonal therapy, the objective response rate was 43% and progression-free survival was 6.6 months.
The two arms also differed by their pattern of grade 3 or 4 adverse events. Among the patients on everolimus plus letrozole, the most common were anemia (24%) and hyperglycemia (14%), both expected consequences of the regimen. The hormonal therapy arm led to an 8% incidence of thromboembolic events, which did not occur in the everolimus plus letrozole arm.
Another attraction of the everolimus and letrozole regimen is that it is oral and avoids the need for drug infusions, Dr. Slomovitz noted.
The investigator-initiated study received funding from Novartis, the company that markets everolimus and letrozole. Dr. Slomovitz has been an advisor to Advaxis, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Genmab, Jannsen, and Tesaro, and he has received research funding from Novartis.
SOURCE: Slomovitz BM et al. SGO 2018, abstract 1.
The results from this study are exciting, with fairly compelling response rates. The rate of progression-free survival with everolimus and letrozole treatment is very impressive, compared with traditional chemotherapy using carboplatin and paclitaxel. The median progression-free survival rate of 21.6 months seen among the chemotherapy naive patients who received everolimus and letrozole showed a 7-month edge over the 14-month median progression-free survival previously reported with chemotherapy. This difference is very provocative and could be practice changing, but it of course needs further evaluation.
Paola A. Gehrig, MD , is professor of ob.gyn. and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill. She made these comments as designated discussant for the study. She had no disclosures.
The results from this study are exciting, with fairly compelling response rates. The rate of progression-free survival with everolimus and letrozole treatment is very impressive, compared with traditional chemotherapy using carboplatin and paclitaxel. The median progression-free survival rate of 21.6 months seen among the chemotherapy naive patients who received everolimus and letrozole showed a 7-month edge over the 14-month median progression-free survival previously reported with chemotherapy. This difference is very provocative and could be practice changing, but it of course needs further evaluation.
Paola A. Gehrig, MD , is professor of ob.gyn. and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill. She made these comments as designated discussant for the study. She had no disclosures.
The results from this study are exciting, with fairly compelling response rates. The rate of progression-free survival with everolimus and letrozole treatment is very impressive, compared with traditional chemotherapy using carboplatin and paclitaxel. The median progression-free survival rate of 21.6 months seen among the chemotherapy naive patients who received everolimus and letrozole showed a 7-month edge over the 14-month median progression-free survival previously reported with chemotherapy. This difference is very provocative and could be practice changing, but it of course needs further evaluation.
Paola A. Gehrig, MD , is professor of ob.gyn. and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill. She made these comments as designated discussant for the study. She had no disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – Combined treatment for 28 days with the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus plus the aromatase inhibitor letrozole in 37 women with recurrent endometrial cancer produced an overall objective response rate of 24% and an average progression-free survival rate of 6.3 months in a randomized phase 2 study with a total of 74 patients. The treatment was also relatively well tolerated, with more serious adverse vents of anemia and hyperglycemia.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
But the most attention-grabbing finding of this study was that, in the subset of 15 women who had received no prior chemotherapy, the objective response rate on this regimen was 53% and median progression-free survival was 21.6 months, Brian M. Slomovitz, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology.
This level of response in the chemotherapy-naive subgroup was “very high, and not what we expected,” Dr. Slomovitz, , professor of ob.gyn. and human genetics and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of Miami, said in a video interview. “This is something we need to further investigate to see if we can make this part of standard care.”
Although he conceded that the data from this study were too limited to warrant a regulatory indication, he suggested that it might be enough to gain the everolimus plus letrozole combination used in the study citation as a treatment option in clinical guidelines. The next step should be a phase 3 trial that compares the everolimus plus letrozole combination with the traditional chemotherapy regimen of carboplatin plus paclitaxel, Dr. Slomovitz added.
The Everolimus and Letrozole or Hormonal Therapy to Treat Endometrial Cancer phase 2 trial, initiated by the Gynecologic Oncology Group, ran at 26 U.S. centers, and randomized patients with stage III or IV recurrent, advanced, or persistent endometrial cancer who had either no or at most one prior course of chemotherapy. The study design also excluded patients who had previously been treated with an mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor or hormonal therapy for their endometrial cancer. The control arm placed 37 patients on a standard hormonal therapy regimen of tamoxifen plus medroxyprogesterone, with 36 of patients in this subgroup evaluable.
The overall results in the two treatment arms were roughly similar, except for the striking benefit seen with everolimus(Afinitor) plus letrozole(Femara) in the chemotherapy-naive patents; 15 patients in each arm had not received any chemotherapy before entering the study. In this subgroup, among the patients who received conventional hormonal therapy, the objective response rate was 43% and progression-free survival was 6.6 months.
The two arms also differed by their pattern of grade 3 or 4 adverse events. Among the patients on everolimus plus letrozole, the most common were anemia (24%) and hyperglycemia (14%), both expected consequences of the regimen. The hormonal therapy arm led to an 8% incidence of thromboembolic events, which did not occur in the everolimus plus letrozole arm.
Another attraction of the everolimus and letrozole regimen is that it is oral and avoids the need for drug infusions, Dr. Slomovitz noted.
The investigator-initiated study received funding from Novartis, the company that markets everolimus and letrozole. Dr. Slomovitz has been an advisor to Advaxis, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Genmab, Jannsen, and Tesaro, and he has received research funding from Novartis.
SOURCE: Slomovitz BM et al. SGO 2018, abstract 1.
NEW ORLEANS – Combined treatment for 28 days with the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus plus the aromatase inhibitor letrozole in 37 women with recurrent endometrial cancer produced an overall objective response rate of 24% and an average progression-free survival rate of 6.3 months in a randomized phase 2 study with a total of 74 patients. The treatment was also relatively well tolerated, with more serious adverse vents of anemia and hyperglycemia.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
But the most attention-grabbing finding of this study was that, in the subset of 15 women who had received no prior chemotherapy, the objective response rate on this regimen was 53% and median progression-free survival was 21.6 months, Brian M. Slomovitz, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology.
This level of response in the chemotherapy-naive subgroup was “very high, and not what we expected,” Dr. Slomovitz, , professor of ob.gyn. and human genetics and director of gynecologic oncology at the University of Miami, said in a video interview. “This is something we need to further investigate to see if we can make this part of standard care.”
Although he conceded that the data from this study were too limited to warrant a regulatory indication, he suggested that it might be enough to gain the everolimus plus letrozole combination used in the study citation as a treatment option in clinical guidelines. The next step should be a phase 3 trial that compares the everolimus plus letrozole combination with the traditional chemotherapy regimen of carboplatin plus paclitaxel, Dr. Slomovitz added.
The Everolimus and Letrozole or Hormonal Therapy to Treat Endometrial Cancer phase 2 trial, initiated by the Gynecologic Oncology Group, ran at 26 U.S. centers, and randomized patients with stage III or IV recurrent, advanced, or persistent endometrial cancer who had either no or at most one prior course of chemotherapy. The study design also excluded patients who had previously been treated with an mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor or hormonal therapy for their endometrial cancer. The control arm placed 37 patients on a standard hormonal therapy regimen of tamoxifen plus medroxyprogesterone, with 36 of patients in this subgroup evaluable.
The overall results in the two treatment arms were roughly similar, except for the striking benefit seen with everolimus(Afinitor) plus letrozole(Femara) in the chemotherapy-naive patents; 15 patients in each arm had not received any chemotherapy before entering the study. In this subgroup, among the patients who received conventional hormonal therapy, the objective response rate was 43% and progression-free survival was 6.6 months.
The two arms also differed by their pattern of grade 3 or 4 adverse events. Among the patients on everolimus plus letrozole, the most common were anemia (24%) and hyperglycemia (14%), both expected consequences of the regimen. The hormonal therapy arm led to an 8% incidence of thromboembolic events, which did not occur in the everolimus plus letrozole arm.
Another attraction of the everolimus and letrozole regimen is that it is oral and avoids the need for drug infusions, Dr. Slomovitz noted.
The investigator-initiated study received funding from Novartis, the company that markets everolimus and letrozole. Dr. Slomovitz has been an advisor to Advaxis, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Genmab, Jannsen, and Tesaro, and he has received research funding from Novartis.
SOURCE: Slomovitz BM et al. SGO 2018, abstract 1.
REPORTING FROM SGO 2018
Key clinical point: Treatment of recurrent endometrial cancer with everolimus and letrozole shows promise.
Major finding: Among 15 chemotherapy-naive patients, objective responses occurred in 53% and median progression-free survival was 21.6 months.
Study details: A multicenter, phase 2 randomized study in 74 patients.
Disclosures: The investigator-initiated study received funding from Novartis, the company that markets everolimus(Afinitor) and letrozole(Femara). Dr. Slomovitz has been an advisor to Advaxis, AstraZeneca, Clovis, Genmab, Jannsen, and Tesaro, and he has received research funding from Novartis.
Source: Slomovitz BM et al. SGO 2018, abstract 1.