User login
How providers are adjusting to clinical care post PHE
The first day of seeing patients without a mask was, for Sterling Ransone Jr., MD, “unsettling.”
“I can’t tell you how weird it was the first day that I walked down the hall from my office to where my exam rooms are, to not have a mask on after 3 years of the habit,” said Dr. Ransone, a family physician in Deltaville, Va., and board chair of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
The White House recently lifted the public health emergency order that overhauled the way health care providers operated and advised patients over the past 3 years.
For Dr. Ransone, this transition entails getting used to his bare face, reminding patients of the latest and varying symptoms of the virus, and parting ways with sick patients if they refuse to wear a mask.
As states, hospitals, and health care systems around the country relax their mask mandates for care providers, clinicians will have to fall back on their own policies that patients with potential symptoms mask up.
“Now that it’s up to our offices, we have to have a little bit more backbone,” Dr. Ransone said. “If they’re not willing to follow a health-related policy that will protect the vulnerable, we will not see them. And so for us, it’s been pretty straightforward.”
Despite the policy, Dr. Ransone has cared for patients who don’t disclose they are feeling sick until he enters the room.
“And I wasn’t masked,” Dr. Ransone said. So, “I will wear masks for the rest of the day just to try to protect the rest of my patients in case I was exposed.”
Masks are optional for both patients and staff at the University of Maryland Medical System, but Niharika Khanna, MD, MBBS, said she still wears one with her patients, and her office advises staff to do the same. If patients are experiencing respiratory symptoms, like a cough, they are asked to wear one.
“When the patient first walks up to you, you have no idea what they have,” Dr. Khanna said.
Dr. Khanna is especially mindful of immunocompromised patients who have cancer, and Dr. Ransone cares for several patients who have received kidney transplants and are on potent immunosuppressive drugs.
“I know they’re appreciating our efforts to protect them, and I think the other patients are realizing that it’s a wise thing to do,” Dr. Ransone said.
Some patients have anxiety about the end of masking in doctor offices, but others have been excited about interacting more with their care teams, according to William Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer for the American Cancer Society. Many clinicians will advise their most immunocompromised patients the same as they did prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There’s always been guidelines that oncologists have given to patients who are immunocompromised – we always told them to avoid crowded places, crowded scenes, be outside more than inside,” Dr. Dahut said. “Those general recommendations will continue.”
The AAFP supports masking to limit COVID’s spread, but the “most important thing people can do is to get vaccinated,” Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, president of the AAFP, said.
But the accessibility of vaccinations is also shifting.
Testing shifts
The government will continue to provide free COVID-19 vaccines because it still has supplies on hand. When this stock runs out, commercial insurance providers will be required to cover the immunizations, as they are considered preventive, but people without insurance will have to pay out of pocket.
The AAFP is pushing the Biden administration and Congress to keep the purchase price of those vaccines low enough that clinicians can keep them in stock, according to Dr. Iroku-Malize. Once the federal government transitions COVID-19 vaccines to the commercial market – as early as later in 2023 – it may pose some challenges for providers.
“If the price of the vaccines is too high, physician practices may struggle to make the upfront investment in COVID-19 vaccines,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “Patients often prefer to receive vaccine counseling and administration from their usual source of primary care, like their family physician.”
The federal government has also said it still has a supply of treatments for the public to access for free, but has not revealed how much it has on hand or given a timeline for the transition to the private market.
COVID-19 tests, meanwhile, are no longer covered because of the end of the public health emergency, and cost about $45 per kit on average, according to an analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Pediatrician Lisa Costello, MD, MPH, knows that price point will be a challenge for some families she cares for at West Virginia University Medicine Children’s Hospital in Morgantown. Many still ask her where they can access free tests.
“Testing if you’re a higher risk person is something we need to ensure that people continue to be educated about,” Dr. Costello said.
She’s hopeful that COVID-19 vaccines and treatments such as Paxlovid will stay free in the coming months so patients can continue to easily access them.
Future of telehealth
Relaxed regulations of prescribing controlled substances via telehealth and across state lines allowed clinicians to treat patients near and far during the pandemic. But many providers were worried about a proposal from the Drug Enforcement Administration to clamp down on the prescribing of controlled substances via telehealth, according to A. Mark Fendrick, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“We were all panicking about what was going to happen to what is for many clinicians a very valuable policy,” Dr. Fendrick said of the telehealth flexibilities introduced during COVID-19.
The DEA, after getting 38,000 comments on their proposed regulations, pulled back on that plan, delaying the cliff until November.
Dr. Fendrick said that telehealth has allowed clinicians to reach patients who have historically faced barriers to care, such as lacking transportation.
“The benefits of that outweigh the potential harms,” he said. “Every policy you make that tightens access because you want to decrease the untoward and unfortunate outcomes will also decrease access to clinical indications.”
The AAFP said it hopes for clear guidance from the DEA in the coming months on what the new telehealth landscape for prescribing will look like.
Medicaid changes
About half of the patients who see Dr. Khanna have insurance through Medicaid.
During the public health emergency, states were not allowed to remove anyone from Medicaid, regardless of whether they no longer qualified for the program or not. But a law passed by Congress last year requires states to once again check Medicaid eligibility. As many as 15 million people could lose their Medicaid coverage.
That could affect the treatments Dr. Khanna recommends for her patients who get kicked off because those who become uninsured or transition to private insurance will have to pay more out of pocket. Maryland will start removals in June.
“When you have an uninsured patient versus Medicaid, it’s a huge difference in what you can ask the patient to do – the medications you can provide, the testing you can provide,” Dr. Khanna said.
States were authorized to remove people from Medicaid as of April 1, with Arkansas, New Hampshire, and South Dakota starting right away. But many states are just now getting the review process going. About a dozen states, including Indiana, Ohio, Utah, and West Virginia, started removing people in May 2023.
Uninsurance rates hit record lows across the United States during the pandemic. Keeping Americans on health insurance is a top priority for the AAFP, Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “We know health care coverage disruptions prevent people from seeking and accessing the care they need.”
Many people who are removed from Medicaid will be eligible for health insurance through employers, or through the Affordable Care Act’s private marketplace. But premiums and deductibles are often higher in these plans, which studies have shown result in patients delaying medical visits and not filling prescriptions or receiving treatment.
Staying mindful
Hospitals that receive federal funds will still have to report COVID-19 test results to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services through 2024, although private labs will no longer be obligated to do so. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will also continue to monitor virus levels in communities through wastewater. But some states will no longer collect data.
Gone are the days when clinicians and others would watch for daily totals of case counts with the type of fervor typically reserved for live scoring updates during sports games, according to Dr. Costello.
“We just have to be mindful of the numbers that might be coming in,” Dr. Costello said.
Dr. Ransone, however, cautioned that clinicians not become complacent. In early May, Dr. Ransone saw two patients with conjunctivitis, what patients thought was simply pink eye – a symptom of the latest COVID-19 variant. Both patients told him it wasn’t possible they had COVID-19 because they didn’t have coughs.
“I don’t want to see physician offices fall into that trap that it’s over and be a potential nidus for infection for other patients,” Dr. Ransone said. “It’s incumbent upon us to remind people of the current symptoms so that folks will know when they need to wear a mask when they’re around their grandmother.”
The move away from universal masking in the office has benefits. Many of his older patients have difficulty hearing and had used lip reading to help understand him, he said. During the pandemic, masks got in the way of that form of communication. Now they can see his mouth again and better decipher what he says.
“Being able to have that face-to-face contact, without a mask intervening, has been really beneficial for a lot of my older patients,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first day of seeing patients without a mask was, for Sterling Ransone Jr., MD, “unsettling.”
“I can’t tell you how weird it was the first day that I walked down the hall from my office to where my exam rooms are, to not have a mask on after 3 years of the habit,” said Dr. Ransone, a family physician in Deltaville, Va., and board chair of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
The White House recently lifted the public health emergency order that overhauled the way health care providers operated and advised patients over the past 3 years.
For Dr. Ransone, this transition entails getting used to his bare face, reminding patients of the latest and varying symptoms of the virus, and parting ways with sick patients if they refuse to wear a mask.
As states, hospitals, and health care systems around the country relax their mask mandates for care providers, clinicians will have to fall back on their own policies that patients with potential symptoms mask up.
“Now that it’s up to our offices, we have to have a little bit more backbone,” Dr. Ransone said. “If they’re not willing to follow a health-related policy that will protect the vulnerable, we will not see them. And so for us, it’s been pretty straightforward.”
Despite the policy, Dr. Ransone has cared for patients who don’t disclose they are feeling sick until he enters the room.
“And I wasn’t masked,” Dr. Ransone said. So, “I will wear masks for the rest of the day just to try to protect the rest of my patients in case I was exposed.”
Masks are optional for both patients and staff at the University of Maryland Medical System, but Niharika Khanna, MD, MBBS, said she still wears one with her patients, and her office advises staff to do the same. If patients are experiencing respiratory symptoms, like a cough, they are asked to wear one.
“When the patient first walks up to you, you have no idea what they have,” Dr. Khanna said.
Dr. Khanna is especially mindful of immunocompromised patients who have cancer, and Dr. Ransone cares for several patients who have received kidney transplants and are on potent immunosuppressive drugs.
“I know they’re appreciating our efforts to protect them, and I think the other patients are realizing that it’s a wise thing to do,” Dr. Ransone said.
Some patients have anxiety about the end of masking in doctor offices, but others have been excited about interacting more with their care teams, according to William Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer for the American Cancer Society. Many clinicians will advise their most immunocompromised patients the same as they did prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There’s always been guidelines that oncologists have given to patients who are immunocompromised – we always told them to avoid crowded places, crowded scenes, be outside more than inside,” Dr. Dahut said. “Those general recommendations will continue.”
The AAFP supports masking to limit COVID’s spread, but the “most important thing people can do is to get vaccinated,” Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, president of the AAFP, said.
But the accessibility of vaccinations is also shifting.
Testing shifts
The government will continue to provide free COVID-19 vaccines because it still has supplies on hand. When this stock runs out, commercial insurance providers will be required to cover the immunizations, as they are considered preventive, but people without insurance will have to pay out of pocket.
The AAFP is pushing the Biden administration and Congress to keep the purchase price of those vaccines low enough that clinicians can keep them in stock, according to Dr. Iroku-Malize. Once the federal government transitions COVID-19 vaccines to the commercial market – as early as later in 2023 – it may pose some challenges for providers.
“If the price of the vaccines is too high, physician practices may struggle to make the upfront investment in COVID-19 vaccines,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “Patients often prefer to receive vaccine counseling and administration from their usual source of primary care, like their family physician.”
The federal government has also said it still has a supply of treatments for the public to access for free, but has not revealed how much it has on hand or given a timeline for the transition to the private market.
COVID-19 tests, meanwhile, are no longer covered because of the end of the public health emergency, and cost about $45 per kit on average, according to an analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Pediatrician Lisa Costello, MD, MPH, knows that price point will be a challenge for some families she cares for at West Virginia University Medicine Children’s Hospital in Morgantown. Many still ask her where they can access free tests.
“Testing if you’re a higher risk person is something we need to ensure that people continue to be educated about,” Dr. Costello said.
She’s hopeful that COVID-19 vaccines and treatments such as Paxlovid will stay free in the coming months so patients can continue to easily access them.
Future of telehealth
Relaxed regulations of prescribing controlled substances via telehealth and across state lines allowed clinicians to treat patients near and far during the pandemic. But many providers were worried about a proposal from the Drug Enforcement Administration to clamp down on the prescribing of controlled substances via telehealth, according to A. Mark Fendrick, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“We were all panicking about what was going to happen to what is for many clinicians a very valuable policy,” Dr. Fendrick said of the telehealth flexibilities introduced during COVID-19.
The DEA, after getting 38,000 comments on their proposed regulations, pulled back on that plan, delaying the cliff until November.
Dr. Fendrick said that telehealth has allowed clinicians to reach patients who have historically faced barriers to care, such as lacking transportation.
“The benefits of that outweigh the potential harms,” he said. “Every policy you make that tightens access because you want to decrease the untoward and unfortunate outcomes will also decrease access to clinical indications.”
The AAFP said it hopes for clear guidance from the DEA in the coming months on what the new telehealth landscape for prescribing will look like.
Medicaid changes
About half of the patients who see Dr. Khanna have insurance through Medicaid.
During the public health emergency, states were not allowed to remove anyone from Medicaid, regardless of whether they no longer qualified for the program or not. But a law passed by Congress last year requires states to once again check Medicaid eligibility. As many as 15 million people could lose their Medicaid coverage.
That could affect the treatments Dr. Khanna recommends for her patients who get kicked off because those who become uninsured or transition to private insurance will have to pay more out of pocket. Maryland will start removals in June.
“When you have an uninsured patient versus Medicaid, it’s a huge difference in what you can ask the patient to do – the medications you can provide, the testing you can provide,” Dr. Khanna said.
States were authorized to remove people from Medicaid as of April 1, with Arkansas, New Hampshire, and South Dakota starting right away. But many states are just now getting the review process going. About a dozen states, including Indiana, Ohio, Utah, and West Virginia, started removing people in May 2023.
Uninsurance rates hit record lows across the United States during the pandemic. Keeping Americans on health insurance is a top priority for the AAFP, Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “We know health care coverage disruptions prevent people from seeking and accessing the care they need.”
Many people who are removed from Medicaid will be eligible for health insurance through employers, or through the Affordable Care Act’s private marketplace. But premiums and deductibles are often higher in these plans, which studies have shown result in patients delaying medical visits and not filling prescriptions or receiving treatment.
Staying mindful
Hospitals that receive federal funds will still have to report COVID-19 test results to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services through 2024, although private labs will no longer be obligated to do so. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will also continue to monitor virus levels in communities through wastewater. But some states will no longer collect data.
Gone are the days when clinicians and others would watch for daily totals of case counts with the type of fervor typically reserved for live scoring updates during sports games, according to Dr. Costello.
“We just have to be mindful of the numbers that might be coming in,” Dr. Costello said.
Dr. Ransone, however, cautioned that clinicians not become complacent. In early May, Dr. Ransone saw two patients with conjunctivitis, what patients thought was simply pink eye – a symptom of the latest COVID-19 variant. Both patients told him it wasn’t possible they had COVID-19 because they didn’t have coughs.
“I don’t want to see physician offices fall into that trap that it’s over and be a potential nidus for infection for other patients,” Dr. Ransone said. “It’s incumbent upon us to remind people of the current symptoms so that folks will know when they need to wear a mask when they’re around their grandmother.”
The move away from universal masking in the office has benefits. Many of his older patients have difficulty hearing and had used lip reading to help understand him, he said. During the pandemic, masks got in the way of that form of communication. Now they can see his mouth again and better decipher what he says.
“Being able to have that face-to-face contact, without a mask intervening, has been really beneficial for a lot of my older patients,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first day of seeing patients without a mask was, for Sterling Ransone Jr., MD, “unsettling.”
“I can’t tell you how weird it was the first day that I walked down the hall from my office to where my exam rooms are, to not have a mask on after 3 years of the habit,” said Dr. Ransone, a family physician in Deltaville, Va., and board chair of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
The White House recently lifted the public health emergency order that overhauled the way health care providers operated and advised patients over the past 3 years.
For Dr. Ransone, this transition entails getting used to his bare face, reminding patients of the latest and varying symptoms of the virus, and parting ways with sick patients if they refuse to wear a mask.
As states, hospitals, and health care systems around the country relax their mask mandates for care providers, clinicians will have to fall back on their own policies that patients with potential symptoms mask up.
“Now that it’s up to our offices, we have to have a little bit more backbone,” Dr. Ransone said. “If they’re not willing to follow a health-related policy that will protect the vulnerable, we will not see them. And so for us, it’s been pretty straightforward.”
Despite the policy, Dr. Ransone has cared for patients who don’t disclose they are feeling sick until he enters the room.
“And I wasn’t masked,” Dr. Ransone said. So, “I will wear masks for the rest of the day just to try to protect the rest of my patients in case I was exposed.”
Masks are optional for both patients and staff at the University of Maryland Medical System, but Niharika Khanna, MD, MBBS, said she still wears one with her patients, and her office advises staff to do the same. If patients are experiencing respiratory symptoms, like a cough, they are asked to wear one.
“When the patient first walks up to you, you have no idea what they have,” Dr. Khanna said.
Dr. Khanna is especially mindful of immunocompromised patients who have cancer, and Dr. Ransone cares for several patients who have received kidney transplants and are on potent immunosuppressive drugs.
“I know they’re appreciating our efforts to protect them, and I think the other patients are realizing that it’s a wise thing to do,” Dr. Ransone said.
Some patients have anxiety about the end of masking in doctor offices, but others have been excited about interacting more with their care teams, according to William Dahut, MD, chief scientific officer for the American Cancer Society. Many clinicians will advise their most immunocompromised patients the same as they did prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There’s always been guidelines that oncologists have given to patients who are immunocompromised – we always told them to avoid crowded places, crowded scenes, be outside more than inside,” Dr. Dahut said. “Those general recommendations will continue.”
The AAFP supports masking to limit COVID’s spread, but the “most important thing people can do is to get vaccinated,” Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, president of the AAFP, said.
But the accessibility of vaccinations is also shifting.
Testing shifts
The government will continue to provide free COVID-19 vaccines because it still has supplies on hand. When this stock runs out, commercial insurance providers will be required to cover the immunizations, as they are considered preventive, but people without insurance will have to pay out of pocket.
The AAFP is pushing the Biden administration and Congress to keep the purchase price of those vaccines low enough that clinicians can keep them in stock, according to Dr. Iroku-Malize. Once the federal government transitions COVID-19 vaccines to the commercial market – as early as later in 2023 – it may pose some challenges for providers.
“If the price of the vaccines is too high, physician practices may struggle to make the upfront investment in COVID-19 vaccines,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “Patients often prefer to receive vaccine counseling and administration from their usual source of primary care, like their family physician.”
The federal government has also said it still has a supply of treatments for the public to access for free, but has not revealed how much it has on hand or given a timeline for the transition to the private market.
COVID-19 tests, meanwhile, are no longer covered because of the end of the public health emergency, and cost about $45 per kit on average, according to an analysis by the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Pediatrician Lisa Costello, MD, MPH, knows that price point will be a challenge for some families she cares for at West Virginia University Medicine Children’s Hospital in Morgantown. Many still ask her where they can access free tests.
“Testing if you’re a higher risk person is something we need to ensure that people continue to be educated about,” Dr. Costello said.
She’s hopeful that COVID-19 vaccines and treatments such as Paxlovid will stay free in the coming months so patients can continue to easily access them.
Future of telehealth
Relaxed regulations of prescribing controlled substances via telehealth and across state lines allowed clinicians to treat patients near and far during the pandemic. But many providers were worried about a proposal from the Drug Enforcement Administration to clamp down on the prescribing of controlled substances via telehealth, according to A. Mark Fendrick, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“We were all panicking about what was going to happen to what is for many clinicians a very valuable policy,” Dr. Fendrick said of the telehealth flexibilities introduced during COVID-19.
The DEA, after getting 38,000 comments on their proposed regulations, pulled back on that plan, delaying the cliff until November.
Dr. Fendrick said that telehealth has allowed clinicians to reach patients who have historically faced barriers to care, such as lacking transportation.
“The benefits of that outweigh the potential harms,” he said. “Every policy you make that tightens access because you want to decrease the untoward and unfortunate outcomes will also decrease access to clinical indications.”
The AAFP said it hopes for clear guidance from the DEA in the coming months on what the new telehealth landscape for prescribing will look like.
Medicaid changes
About half of the patients who see Dr. Khanna have insurance through Medicaid.
During the public health emergency, states were not allowed to remove anyone from Medicaid, regardless of whether they no longer qualified for the program or not. But a law passed by Congress last year requires states to once again check Medicaid eligibility. As many as 15 million people could lose their Medicaid coverage.
That could affect the treatments Dr. Khanna recommends for her patients who get kicked off because those who become uninsured or transition to private insurance will have to pay more out of pocket. Maryland will start removals in June.
“When you have an uninsured patient versus Medicaid, it’s a huge difference in what you can ask the patient to do – the medications you can provide, the testing you can provide,” Dr. Khanna said.
States were authorized to remove people from Medicaid as of April 1, with Arkansas, New Hampshire, and South Dakota starting right away. But many states are just now getting the review process going. About a dozen states, including Indiana, Ohio, Utah, and West Virginia, started removing people in May 2023.
Uninsurance rates hit record lows across the United States during the pandemic. Keeping Americans on health insurance is a top priority for the AAFP, Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “We know health care coverage disruptions prevent people from seeking and accessing the care they need.”
Many people who are removed from Medicaid will be eligible for health insurance through employers, or through the Affordable Care Act’s private marketplace. But premiums and deductibles are often higher in these plans, which studies have shown result in patients delaying medical visits and not filling prescriptions or receiving treatment.
Staying mindful
Hospitals that receive federal funds will still have to report COVID-19 test results to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services through 2024, although private labs will no longer be obligated to do so. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will also continue to monitor virus levels in communities through wastewater. But some states will no longer collect data.
Gone are the days when clinicians and others would watch for daily totals of case counts with the type of fervor typically reserved for live scoring updates during sports games, according to Dr. Costello.
“We just have to be mindful of the numbers that might be coming in,” Dr. Costello said.
Dr. Ransone, however, cautioned that clinicians not become complacent. In early May, Dr. Ransone saw two patients with conjunctivitis, what patients thought was simply pink eye – a symptom of the latest COVID-19 variant. Both patients told him it wasn’t possible they had COVID-19 because they didn’t have coughs.
“I don’t want to see physician offices fall into that trap that it’s over and be a potential nidus for infection for other patients,” Dr. Ransone said. “It’s incumbent upon us to remind people of the current symptoms so that folks will know when they need to wear a mask when they’re around their grandmother.”
The move away from universal masking in the office has benefits. Many of his older patients have difficulty hearing and had used lip reading to help understand him, he said. During the pandemic, masks got in the way of that form of communication. Now they can see his mouth again and better decipher what he says.
“Being able to have that face-to-face contact, without a mask intervening, has been really beneficial for a lot of my older patients,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The antimicrobial peptide that even Pharma can love
Fastest peptide north, south, east, aaaaand west of the Pecos
Bacterial infections are supposed to be simple. You get infected, you get an antibiotic to treat it. Easy. Some bacteria, though, don’t play by the rules. Those antibiotics may kill 99.9% of germs, but what about the 0.1% that gets left behind? With their fallen comrades out of the way, the accidentally drug resistant species are free to inherit the Earth.
Antibiotic resistance is thus a major concern for the medical community. Naturally, anything that prevents doctors from successfully curing sick people is a priority. Unless you’re a major pharmaceutical company that has been loath to develop new drugs that can beat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Blah blah, time and money, blah blah, long time between development and market application, blah blah, no profit. We all know the story with pharmaceutical companies.
Research from other sources has continued, however, and Brazilian scientists recently published research involving a peptide known as plantaricin 149. This peptide, derived from the bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum, has been known for nearly 30 years to have antibacterial properties. Pln149 in its natural state, though, is not particularly efficient at bacteria-killing. Fortunately, we have science and technology on our side.
The researchers synthesized 20 analogs of Pln149, of which Pln149-PEP20 had the best results. The elegantly named compound is less than half the size of the original peptide, less toxic, and far better at killing any and all drug-resistant bacteria the researchers threw at it. How much better? Pln149-PEP20 started killing bacteria less than an hour after being introduced in lab trials.
The research is just in its early days – just because something is less toxic doesn’t necessarily mean you want to go and help yourself to it – but we can only hope that those lovely pharmaceutical companies deign to look down upon us and actually develop a drug utilizing Pln149-PEP20 to, you know, actually help sick people, instead of trying to build monopolies or avoiding paying billions in taxes. Yeah, we couldn’t keep a straight face through that last sentence either.
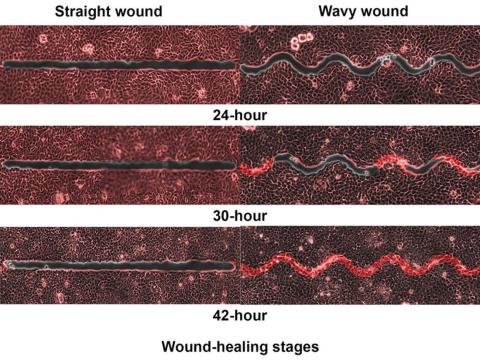
Speed healing: The wavy wound gets the swirl
Did you know that wavy wounds heal faster than straight wounds? Well, we didn’t, but apparently quite a few people did, because somebody has been trying to figure out why wavy wounds heal faster than straight ones. Do the surgeons know about this? How about you dermatologists? Wavy over straight? We’re the media. We’re supposed to report this kind of stuff. Maybe hit us with a tweet next time you do something important, or push a TikTok our way, okay?
You could be more like the investigators at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, who figured out the why and then released a statement about it.
They created synthetic wounds – some straight, some wavy – in micropatterned hydrogel substrates that mimicked human skin. Then they used an advanced optical technique known as particle image velocimetry to measure fluid flow and learn how cells moved to close the wound gaps.
The wavy wounds “induced more complex collective cell movements, such as a swirly, vortex-like motion,” according to the written statement from NTU Singapore. In the straight wounds, cell movements paralleled the wound front, “moving in straight lines like a marching band,” they pointed out, unlike some researchers who never call us unless they need money.
Complex epithelial cell movements are better, it turns out. Over an observation period of 64 hours the NTU team found that the healing efficiency of wavy gaps – measured by the area covered by the cells over time – is nearly five times faster than straight gaps.
The complex motion “enabled cells to quickly connect with similar cells on the opposite site of the wound edge, forming a bridge and closing the wavy wound gaps faster than straight gaps,” explained lead author Xu Hongmei, a doctoral student at NTU’s School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, who seems to have time to toss out a tumblr or two to keep the press informed.
As for the rest of you, would it kill you to pick up a phone once in a while? Maybe let a journalist know that you’re still alive? We have feelings too, you know, and we worry.
A little Jekyll, a little Hyde, and a little shop of horrors
More “Little Shop of Horrors” references are coming, so be prepared.
We begin with Triphyophyllum peltatum. This woody vine is of great interest to medical and pharmaceutical researchers because its constituents have shown promise against pancreatic cancer and leukemia cells, among others, along with the pathogens that cause malaria and other diseases. There is another side, however. T. peltatum also has a tendency to turn into a realistic Audrey II when deprived.
No, of course they’re not craving human flesh, but it does become … carnivorous in its appetite.
T. peltatum, native to the West African tropics and not found in a New York florist shop, has the unique ability to change its diet and development based on the environmental circumstances. For some unknown reason, the leaves would develop adhesive traps in the form of sticky drops that capture insect prey. The plant is notoriously hard to grow, however, so no one could study the transformation under lab conditions. Until now.
A group of German scientists “exposed the plant to different stress factors, including deficiencies of various nutrients, and studied how it responded to each,” said Dr. Traud Winkelmann of Leibniz University Hannover. “Only in one case were we able to observe the formation of traps: in the case of a lack of phosphorus.”
Well, there you have it: phosphorus. We need it for healthy bones and teeth, which this plant doesn’t have to worry about, unlike its Tony Award–nominated counterpart. The investigators hope that their findings could lead to “future molecular analyses that will help understand the origins of carnivory,” but we’re guessing that a certain singing alien species will be left out of that research.
Fastest peptide north, south, east, aaaaand west of the Pecos
Bacterial infections are supposed to be simple. You get infected, you get an antibiotic to treat it. Easy. Some bacteria, though, don’t play by the rules. Those antibiotics may kill 99.9% of germs, but what about the 0.1% that gets left behind? With their fallen comrades out of the way, the accidentally drug resistant species are free to inherit the Earth.
Antibiotic resistance is thus a major concern for the medical community. Naturally, anything that prevents doctors from successfully curing sick people is a priority. Unless you’re a major pharmaceutical company that has been loath to develop new drugs that can beat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Blah blah, time and money, blah blah, long time between development and market application, blah blah, no profit. We all know the story with pharmaceutical companies.
Research from other sources has continued, however, and Brazilian scientists recently published research involving a peptide known as plantaricin 149. This peptide, derived from the bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum, has been known for nearly 30 years to have antibacterial properties. Pln149 in its natural state, though, is not particularly efficient at bacteria-killing. Fortunately, we have science and technology on our side.
The researchers synthesized 20 analogs of Pln149, of which Pln149-PEP20 had the best results. The elegantly named compound is less than half the size of the original peptide, less toxic, and far better at killing any and all drug-resistant bacteria the researchers threw at it. How much better? Pln149-PEP20 started killing bacteria less than an hour after being introduced in lab trials.
The research is just in its early days – just because something is less toxic doesn’t necessarily mean you want to go and help yourself to it – but we can only hope that those lovely pharmaceutical companies deign to look down upon us and actually develop a drug utilizing Pln149-PEP20 to, you know, actually help sick people, instead of trying to build monopolies or avoiding paying billions in taxes. Yeah, we couldn’t keep a straight face through that last sentence either.
Speed healing: The wavy wound gets the swirl
Did you know that wavy wounds heal faster than straight wounds? Well, we didn’t, but apparently quite a few people did, because somebody has been trying to figure out why wavy wounds heal faster than straight ones. Do the surgeons know about this? How about you dermatologists? Wavy over straight? We’re the media. We’re supposed to report this kind of stuff. Maybe hit us with a tweet next time you do something important, or push a TikTok our way, okay?
You could be more like the investigators at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, who figured out the why and then released a statement about it.
They created synthetic wounds – some straight, some wavy – in micropatterned hydrogel substrates that mimicked human skin. Then they used an advanced optical technique known as particle image velocimetry to measure fluid flow and learn how cells moved to close the wound gaps.
The wavy wounds “induced more complex collective cell movements, such as a swirly, vortex-like motion,” according to the written statement from NTU Singapore. In the straight wounds, cell movements paralleled the wound front, “moving in straight lines like a marching band,” they pointed out, unlike some researchers who never call us unless they need money.
Complex epithelial cell movements are better, it turns out. Over an observation period of 64 hours the NTU team found that the healing efficiency of wavy gaps – measured by the area covered by the cells over time – is nearly five times faster than straight gaps.
The complex motion “enabled cells to quickly connect with similar cells on the opposite site of the wound edge, forming a bridge and closing the wavy wound gaps faster than straight gaps,” explained lead author Xu Hongmei, a doctoral student at NTU’s School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, who seems to have time to toss out a tumblr or two to keep the press informed.
As for the rest of you, would it kill you to pick up a phone once in a while? Maybe let a journalist know that you’re still alive? We have feelings too, you know, and we worry.
A little Jekyll, a little Hyde, and a little shop of horrors
More “Little Shop of Horrors” references are coming, so be prepared.
We begin with Triphyophyllum peltatum. This woody vine is of great interest to medical and pharmaceutical researchers because its constituents have shown promise against pancreatic cancer and leukemia cells, among others, along with the pathogens that cause malaria and other diseases. There is another side, however. T. peltatum also has a tendency to turn into a realistic Audrey II when deprived.
No, of course they’re not craving human flesh, but it does become … carnivorous in its appetite.
T. peltatum, native to the West African tropics and not found in a New York florist shop, has the unique ability to change its diet and development based on the environmental circumstances. For some unknown reason, the leaves would develop adhesive traps in the form of sticky drops that capture insect prey. The plant is notoriously hard to grow, however, so no one could study the transformation under lab conditions. Until now.
A group of German scientists “exposed the plant to different stress factors, including deficiencies of various nutrients, and studied how it responded to each,” said Dr. Traud Winkelmann of Leibniz University Hannover. “Only in one case were we able to observe the formation of traps: in the case of a lack of phosphorus.”
Well, there you have it: phosphorus. We need it for healthy bones and teeth, which this plant doesn’t have to worry about, unlike its Tony Award–nominated counterpart. The investigators hope that their findings could lead to “future molecular analyses that will help understand the origins of carnivory,” but we’re guessing that a certain singing alien species will be left out of that research.
Fastest peptide north, south, east, aaaaand west of the Pecos
Bacterial infections are supposed to be simple. You get infected, you get an antibiotic to treat it. Easy. Some bacteria, though, don’t play by the rules. Those antibiotics may kill 99.9% of germs, but what about the 0.1% that gets left behind? With their fallen comrades out of the way, the accidentally drug resistant species are free to inherit the Earth.
Antibiotic resistance is thus a major concern for the medical community. Naturally, anything that prevents doctors from successfully curing sick people is a priority. Unless you’re a major pharmaceutical company that has been loath to develop new drugs that can beat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Blah blah, time and money, blah blah, long time between development and market application, blah blah, no profit. We all know the story with pharmaceutical companies.
Research from other sources has continued, however, and Brazilian scientists recently published research involving a peptide known as plantaricin 149. This peptide, derived from the bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum, has been known for nearly 30 years to have antibacterial properties. Pln149 in its natural state, though, is not particularly efficient at bacteria-killing. Fortunately, we have science and technology on our side.
The researchers synthesized 20 analogs of Pln149, of which Pln149-PEP20 had the best results. The elegantly named compound is less than half the size of the original peptide, less toxic, and far better at killing any and all drug-resistant bacteria the researchers threw at it. How much better? Pln149-PEP20 started killing bacteria less than an hour after being introduced in lab trials.
The research is just in its early days – just because something is less toxic doesn’t necessarily mean you want to go and help yourself to it – but we can only hope that those lovely pharmaceutical companies deign to look down upon us and actually develop a drug utilizing Pln149-PEP20 to, you know, actually help sick people, instead of trying to build monopolies or avoiding paying billions in taxes. Yeah, we couldn’t keep a straight face through that last sentence either.
Speed healing: The wavy wound gets the swirl
Did you know that wavy wounds heal faster than straight wounds? Well, we didn’t, but apparently quite a few people did, because somebody has been trying to figure out why wavy wounds heal faster than straight ones. Do the surgeons know about this? How about you dermatologists? Wavy over straight? We’re the media. We’re supposed to report this kind of stuff. Maybe hit us with a tweet next time you do something important, or push a TikTok our way, okay?
You could be more like the investigators at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, who figured out the why and then released a statement about it.
They created synthetic wounds – some straight, some wavy – in micropatterned hydrogel substrates that mimicked human skin. Then they used an advanced optical technique known as particle image velocimetry to measure fluid flow and learn how cells moved to close the wound gaps.
The wavy wounds “induced more complex collective cell movements, such as a swirly, vortex-like motion,” according to the written statement from NTU Singapore. In the straight wounds, cell movements paralleled the wound front, “moving in straight lines like a marching band,” they pointed out, unlike some researchers who never call us unless they need money.
Complex epithelial cell movements are better, it turns out. Over an observation period of 64 hours the NTU team found that the healing efficiency of wavy gaps – measured by the area covered by the cells over time – is nearly five times faster than straight gaps.
The complex motion “enabled cells to quickly connect with similar cells on the opposite site of the wound edge, forming a bridge and closing the wavy wound gaps faster than straight gaps,” explained lead author Xu Hongmei, a doctoral student at NTU’s School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, who seems to have time to toss out a tumblr or two to keep the press informed.
As for the rest of you, would it kill you to pick up a phone once in a while? Maybe let a journalist know that you’re still alive? We have feelings too, you know, and we worry.
A little Jekyll, a little Hyde, and a little shop of horrors
More “Little Shop of Horrors” references are coming, so be prepared.
We begin with Triphyophyllum peltatum. This woody vine is of great interest to medical and pharmaceutical researchers because its constituents have shown promise against pancreatic cancer and leukemia cells, among others, along with the pathogens that cause malaria and other diseases. There is another side, however. T. peltatum also has a tendency to turn into a realistic Audrey II when deprived.
No, of course they’re not craving human flesh, but it does become … carnivorous in its appetite.
T. peltatum, native to the West African tropics and not found in a New York florist shop, has the unique ability to change its diet and development based on the environmental circumstances. For some unknown reason, the leaves would develop adhesive traps in the form of sticky drops that capture insect prey. The plant is notoriously hard to grow, however, so no one could study the transformation under lab conditions. Until now.
A group of German scientists “exposed the plant to different stress factors, including deficiencies of various nutrients, and studied how it responded to each,” said Dr. Traud Winkelmann of Leibniz University Hannover. “Only in one case were we able to observe the formation of traps: in the case of a lack of phosphorus.”
Well, there you have it: phosphorus. We need it for healthy bones and teeth, which this plant doesn’t have to worry about, unlike its Tony Award–nominated counterpart. The investigators hope that their findings could lead to “future molecular analyses that will help understand the origins of carnivory,” but we’re guessing that a certain singing alien species will be left out of that research.
DLBCL: Major new treatment breakthroughs
Significant breakthroughs have come in just the past few weeks and months, through the use of CAR T-cell and immunotherapies and with the approval in April by the Food and Drug Administration of polatuzumab for frontline DLBCL.
“Until the publishing of data from the POLARIX study (NCT03274492), which led to the approval of polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (pola + R-CHP), we had not had a breakthrough in frontline DLBCL therapies since the addition of rituximab 22 years ago,” said Dr. Charalambos Andreadis, MD, of the University of California at San Francisco’s Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Pola + R-CHP is an improvement over the standard-of-care treatment, R-CHOP (rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), giving treatment naive patients an increase in PFS without an increase in side effects,” Dr. Andreadis said.
R-CHP-polatuzumab was approved only for patients with an International Prognostic Indices score between 2 and 5, leaving patients with IPI scores of 0 or 1 with the frontline standard of care (SoC) treatment of R-CHOP, which has a cure rate of between 60% and 70%.
“The highest likelihood of relapse is in the first year following treatment. After 2 years in remission, patients’ chance of relapsing is the same as the general populations’ chance of getting DLBCL for the first time. This is why even a slight increase in the progression-free survival rate with the addition of pola is so significant,” Dr. Andreadis noted.
Historically, patients with relapsed or refractory (RR) DLBCL who did not respond to R-CHOP or who experienced disease relapse less than a year after primary intervention were treated with alternative chemotherapy regimens, often followed by autologous stem cell transplants (ASCT). Randomized control studies have shown that CAR T-cell therapies yield higher success rates than chemotherapy and ASCT, leading to the SoC in RR patients being CAR-T cell therapy directly following failed primary treatment.
“There are many new CAR T-cell platforms in development, as well as novel combination strategies that aim to target critical genetic pathways,” Kieron Dunleavy, MD, professor of medicine at the Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center at Georgetown University Hospital, said in an interview. “While access to CAR T-cell therapies is becoming easier and more feasible in many centers, fast access continues to be an issue for many patients, often depending on geography and socioeconomic factors.”
Asked about the latest breakthroughs in treating DLBCL, Dr. Dunleavy said, “A significant proportion of patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL do not have easy access to CAR T-cell therapies, so this needs to be addressed and improved. Sometimes the rapidity of clinical progression in DLBCL can make these therapies challenging to deliver, considering logistical issues like apheresis and insurance approvals, which are frequently complex. This highlights the need for alternative and ‘easier to deliver’ CAR-T cells and our continued prioritization of developing alternative effective agents for DLBCL.
“Currently, commercially approved CAR T-cells in DLBCL target the CD-19 marker on lymphoma cells but CAR T-cells targeting other and more than one antigen as well as alternative anti CD19 agents like loncastuximab and tafasitamab are similarly FDA approved and available for patients,” Dr. Dunleavy concluded.
Dr. Dunleavy is affiliated with the MedStar Georgetown Lymphoma group, where Rep. Raskin publicly announced that he had completed 4 months of chemotherapy treatment for DLBCL. On April 27, in an open letter to the U.S. public, he wrote that he rang the bell at MedStar to mark his preliminary diagnosis of being “in remission,” with a “90% prognosis of no relapse.”
Interviewed about the latest advances in treating DLBCL, Jason Westin, MD, associate professor of lymphoma and myeloma at the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, said that even with improvements in overall survival possible with CAR T-cell therapies, “usually, a clinical trial should be considered strongly, as it is often the best option for patients, both in a newly diagnosed or in a relapsed setting, as they allow access to tomorrow’s breakthrough therapies today.”
Dr. Westin cited the example of bispecific T-cell engagers (BITE) as a promising therapy that is available to patients in clinical trials. These agents bind to one side to the lymphoma cell, but they also have a binding arm for T-cells, so they activate a patient’s own immune cells to kill lymphoma cells, in some cases offering a cure when CAR T-cell therapy has failed.
The first BITE to be approved, mosunetuzumab, is authorized only for the treatment of follicular lymphoma. However, data from a recent clinical study indicated that the agent yields complete responses in 24% of heavily pretreated patients with RR DLBCL.
Another BITE, glofitamab, was approved in Canada in March 2023 for use in RR DLBCL. Based on its high efficacy, it soon may be approved elsewhere.
Dr. Andreadis noted, “We are finally at a point where for both treatment naive and RR DLBCL patients, there are several promising options on the horizon that don’t involve ASCT. Furthermore, these breakthroughs reinforce each other, as there are studies in which therapies like BITE are being brought to the front line and pola to RR cases.”
The growing field of new frontline and RR DLBCL therapies lend credence to the optimism of specialists who treat DLBCL – and to the sanguine note that Congressman Raskin struck in published comments about his treatment for DLBCL.
Dr. Andreadis reported ties with BMS, Novartis, Roche, Genmab, Merck, Gilead, AbbVie, and J&J. Dr. Dunleavy disclosed relationships with ONO Pharmaceuticals, Kymera, Merck, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Amgen, ADC Therapeutics, MorphoSys and Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Cellectar. Dr. Westin reported ties with Kite/Gilead, BMS, Novartis, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Morphosys/Incyte, ADC Therapeutics, Kymera, Nurix, and MonteRosa.
Significant breakthroughs have come in just the past few weeks and months, through the use of CAR T-cell and immunotherapies and with the approval in April by the Food and Drug Administration of polatuzumab for frontline DLBCL.
“Until the publishing of data from the POLARIX study (NCT03274492), which led to the approval of polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (pola + R-CHP), we had not had a breakthrough in frontline DLBCL therapies since the addition of rituximab 22 years ago,” said Dr. Charalambos Andreadis, MD, of the University of California at San Francisco’s Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Pola + R-CHP is an improvement over the standard-of-care treatment, R-CHOP (rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), giving treatment naive patients an increase in PFS without an increase in side effects,” Dr. Andreadis said.
R-CHP-polatuzumab was approved only for patients with an International Prognostic Indices score between 2 and 5, leaving patients with IPI scores of 0 or 1 with the frontline standard of care (SoC) treatment of R-CHOP, which has a cure rate of between 60% and 70%.
“The highest likelihood of relapse is in the first year following treatment. After 2 years in remission, patients’ chance of relapsing is the same as the general populations’ chance of getting DLBCL for the first time. This is why even a slight increase in the progression-free survival rate with the addition of pola is so significant,” Dr. Andreadis noted.
Historically, patients with relapsed or refractory (RR) DLBCL who did not respond to R-CHOP or who experienced disease relapse less than a year after primary intervention were treated with alternative chemotherapy regimens, often followed by autologous stem cell transplants (ASCT). Randomized control studies have shown that CAR T-cell therapies yield higher success rates than chemotherapy and ASCT, leading to the SoC in RR patients being CAR-T cell therapy directly following failed primary treatment.
“There are many new CAR T-cell platforms in development, as well as novel combination strategies that aim to target critical genetic pathways,” Kieron Dunleavy, MD, professor of medicine at the Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center at Georgetown University Hospital, said in an interview. “While access to CAR T-cell therapies is becoming easier and more feasible in many centers, fast access continues to be an issue for many patients, often depending on geography and socioeconomic factors.”
Asked about the latest breakthroughs in treating DLBCL, Dr. Dunleavy said, “A significant proportion of patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL do not have easy access to CAR T-cell therapies, so this needs to be addressed and improved. Sometimes the rapidity of clinical progression in DLBCL can make these therapies challenging to deliver, considering logistical issues like apheresis and insurance approvals, which are frequently complex. This highlights the need for alternative and ‘easier to deliver’ CAR-T cells and our continued prioritization of developing alternative effective agents for DLBCL.
“Currently, commercially approved CAR T-cells in DLBCL target the CD-19 marker on lymphoma cells but CAR T-cells targeting other and more than one antigen as well as alternative anti CD19 agents like loncastuximab and tafasitamab are similarly FDA approved and available for patients,” Dr. Dunleavy concluded.
Dr. Dunleavy is affiliated with the MedStar Georgetown Lymphoma group, where Rep. Raskin publicly announced that he had completed 4 months of chemotherapy treatment for DLBCL. On April 27, in an open letter to the U.S. public, he wrote that he rang the bell at MedStar to mark his preliminary diagnosis of being “in remission,” with a “90% prognosis of no relapse.”
Interviewed about the latest advances in treating DLBCL, Jason Westin, MD, associate professor of lymphoma and myeloma at the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, said that even with improvements in overall survival possible with CAR T-cell therapies, “usually, a clinical trial should be considered strongly, as it is often the best option for patients, both in a newly diagnosed or in a relapsed setting, as they allow access to tomorrow’s breakthrough therapies today.”
Dr. Westin cited the example of bispecific T-cell engagers (BITE) as a promising therapy that is available to patients in clinical trials. These agents bind to one side to the lymphoma cell, but they also have a binding arm for T-cells, so they activate a patient’s own immune cells to kill lymphoma cells, in some cases offering a cure when CAR T-cell therapy has failed.
The first BITE to be approved, mosunetuzumab, is authorized only for the treatment of follicular lymphoma. However, data from a recent clinical study indicated that the agent yields complete responses in 24% of heavily pretreated patients with RR DLBCL.
Another BITE, glofitamab, was approved in Canada in March 2023 for use in RR DLBCL. Based on its high efficacy, it soon may be approved elsewhere.
Dr. Andreadis noted, “We are finally at a point where for both treatment naive and RR DLBCL patients, there are several promising options on the horizon that don’t involve ASCT. Furthermore, these breakthroughs reinforce each other, as there are studies in which therapies like BITE are being brought to the front line and pola to RR cases.”
The growing field of new frontline and RR DLBCL therapies lend credence to the optimism of specialists who treat DLBCL – and to the sanguine note that Congressman Raskin struck in published comments about his treatment for DLBCL.
Dr. Andreadis reported ties with BMS, Novartis, Roche, Genmab, Merck, Gilead, AbbVie, and J&J. Dr. Dunleavy disclosed relationships with ONO Pharmaceuticals, Kymera, Merck, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Amgen, ADC Therapeutics, MorphoSys and Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Cellectar. Dr. Westin reported ties with Kite/Gilead, BMS, Novartis, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Morphosys/Incyte, ADC Therapeutics, Kymera, Nurix, and MonteRosa.
Significant breakthroughs have come in just the past few weeks and months, through the use of CAR T-cell and immunotherapies and with the approval in April by the Food and Drug Administration of polatuzumab for frontline DLBCL.
“Until the publishing of data from the POLARIX study (NCT03274492), which led to the approval of polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (pola + R-CHP), we had not had a breakthrough in frontline DLBCL therapies since the addition of rituximab 22 years ago,” said Dr. Charalambos Andreadis, MD, of the University of California at San Francisco’s Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Pola + R-CHP is an improvement over the standard-of-care treatment, R-CHOP (rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), giving treatment naive patients an increase in PFS without an increase in side effects,” Dr. Andreadis said.
R-CHP-polatuzumab was approved only for patients with an International Prognostic Indices score between 2 and 5, leaving patients with IPI scores of 0 or 1 with the frontline standard of care (SoC) treatment of R-CHOP, which has a cure rate of between 60% and 70%.
“The highest likelihood of relapse is in the first year following treatment. After 2 years in remission, patients’ chance of relapsing is the same as the general populations’ chance of getting DLBCL for the first time. This is why even a slight increase in the progression-free survival rate with the addition of pola is so significant,” Dr. Andreadis noted.
Historically, patients with relapsed or refractory (RR) DLBCL who did not respond to R-CHOP or who experienced disease relapse less than a year after primary intervention were treated with alternative chemotherapy regimens, often followed by autologous stem cell transplants (ASCT). Randomized control studies have shown that CAR T-cell therapies yield higher success rates than chemotherapy and ASCT, leading to the SoC in RR patients being CAR-T cell therapy directly following failed primary treatment.
“There are many new CAR T-cell platforms in development, as well as novel combination strategies that aim to target critical genetic pathways,” Kieron Dunleavy, MD, professor of medicine at the Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center at Georgetown University Hospital, said in an interview. “While access to CAR T-cell therapies is becoming easier and more feasible in many centers, fast access continues to be an issue for many patients, often depending on geography and socioeconomic factors.”
Asked about the latest breakthroughs in treating DLBCL, Dr. Dunleavy said, “A significant proportion of patients with relapsed or refractory DLBCL do not have easy access to CAR T-cell therapies, so this needs to be addressed and improved. Sometimes the rapidity of clinical progression in DLBCL can make these therapies challenging to deliver, considering logistical issues like apheresis and insurance approvals, which are frequently complex. This highlights the need for alternative and ‘easier to deliver’ CAR-T cells and our continued prioritization of developing alternative effective agents for DLBCL.
“Currently, commercially approved CAR T-cells in DLBCL target the CD-19 marker on lymphoma cells but CAR T-cells targeting other and more than one antigen as well as alternative anti CD19 agents like loncastuximab and tafasitamab are similarly FDA approved and available for patients,” Dr. Dunleavy concluded.
Dr. Dunleavy is affiliated with the MedStar Georgetown Lymphoma group, where Rep. Raskin publicly announced that he had completed 4 months of chemotherapy treatment for DLBCL. On April 27, in an open letter to the U.S. public, he wrote that he rang the bell at MedStar to mark his preliminary diagnosis of being “in remission,” with a “90% prognosis of no relapse.”
Interviewed about the latest advances in treating DLBCL, Jason Westin, MD, associate professor of lymphoma and myeloma at the MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, said that even with improvements in overall survival possible with CAR T-cell therapies, “usually, a clinical trial should be considered strongly, as it is often the best option for patients, both in a newly diagnosed or in a relapsed setting, as they allow access to tomorrow’s breakthrough therapies today.”
Dr. Westin cited the example of bispecific T-cell engagers (BITE) as a promising therapy that is available to patients in clinical trials. These agents bind to one side to the lymphoma cell, but they also have a binding arm for T-cells, so they activate a patient’s own immune cells to kill lymphoma cells, in some cases offering a cure when CAR T-cell therapy has failed.
The first BITE to be approved, mosunetuzumab, is authorized only for the treatment of follicular lymphoma. However, data from a recent clinical study indicated that the agent yields complete responses in 24% of heavily pretreated patients with RR DLBCL.
Another BITE, glofitamab, was approved in Canada in March 2023 for use in RR DLBCL. Based on its high efficacy, it soon may be approved elsewhere.
Dr. Andreadis noted, “We are finally at a point where for both treatment naive and RR DLBCL patients, there are several promising options on the horizon that don’t involve ASCT. Furthermore, these breakthroughs reinforce each other, as there are studies in which therapies like BITE are being brought to the front line and pola to RR cases.”
The growing field of new frontline and RR DLBCL therapies lend credence to the optimism of specialists who treat DLBCL – and to the sanguine note that Congressman Raskin struck in published comments about his treatment for DLBCL.
Dr. Andreadis reported ties with BMS, Novartis, Roche, Genmab, Merck, Gilead, AbbVie, and J&J. Dr. Dunleavy disclosed relationships with ONO Pharmaceuticals, Kymera, Merck, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Amgen, ADC Therapeutics, MorphoSys and Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Cellectar. Dr. Westin reported ties with Kite/Gilead, BMS, Novartis, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Morphosys/Incyte, ADC Therapeutics, Kymera, Nurix, and MonteRosa.
Here’s how we can rebuild trust in vaccines
When people ask Paul Offit, MD, what worries him the most about the COVID-19 pandemic, he names two concerns. “One is the lack of socialization and education that came from keeping kids out of school for so long,” Dr. Offit said in a recent interview. “And I think vaccines have suffered.”
Dr. Offit is director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. He has watched with alarm as the American public appears to be losing faith in the lifesaving vaccines the public health community has worked hard to promote. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that the proportion of kids entering kindergarten who have received state-required vaccines dipped to 94% in the 2020-2021 school year – a full point less than the year before the pandemic – then dropped by another percentage point, to 93%, the following year.
Although a couple of percentage points may sound trivial, were only 93% of kindergarteners to receive the vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR), approximately 250,000 vulnerable 5-year-olds could spark the next big outbreak, such as the recent measles outbreaks in Ohio and Minnesota.
Dr. Offit is one of many public health officials and clinicians who are working to reverse the concerning trends in pediatric vaccinations.
“I just don’t want to see an outbreak of something that we could have avoided because we were not protected enough,” Judith Shlay, MD, associate director of the Public Health Institute at Denver Health, said.
Official stumbles in part to blame
Disruptions in health care from the COVID-19 pandemic certainly played a role in the decline. Parents were afraid to expose their children to other sick kids, providers shifted to a telehealth model, and routine preventive care was difficult to access.
But Dr. Offit also blamed erosion of trust on mistakes made by government and public health institutions for the alarming trend. “I think that health care professionals have lost some level of trust in the Food and Drug Administration and CDC.”
He cited as an example poor messaging during a large outbreak in Massachusetts in summer 2021, when the CDC published a report that highlighted the high proportion of COVID-19 cases among vaccinated people. Health officials called those cases “breakthrough” infections, although most were mild or asymptomatic.
Dr. Offit said the CDC should have focused the message instead on the low rate (1%) of hospitalizations and the low number of deaths from the infections. Instead, they had to walk back their promise that vaccinated people didn’t need to wear masks. At other times, the Biden administration pressured public health officials by promising to make booster shots available to the American public when the FDA and CDC felt they lacked evidence to recommend the injections.
Rupali Limaye, PhD, an associate professor of international health at the Bloomberg School of Public Health at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, studies vaccine behavior and decision-making. She would go a step further in characterizing the roots of worsening vaccine hesitancy.
“In the last 20 years, we’ve seen there’s less and less trust in health care providers in general,” Dr. Limaye said. “More people are turning to their social networks or social contacts for that kind of information.” In the maelstrom of the COVID-19 pandemic, digital social networks facilitated the spread of misinformation about COVID-19 faster than scientists could unravel the mysteries of the disease.
“There’s always been this underlying hesitancy for some people about vaccines,” Dr. Shlay said. But she has noticed more resistance to the COVID-19 vaccine from parents nervous about the new mRNA technology. “There was a lot of politicization of the vaccine, even though the mRNA vaccine technology has been around for a long time,” she said.
Multipronged approaches
Dr. Shlay is committed to restoring childhood vaccination uptake to prepandemic levels now that clinics are open again. To do so, she is relying on a combination of quality improvement strategies and outreach to undervaccinated populations.
Denver Health, for instance, offers vaccinations at any inpatient or outpatient visit – not just well-child visits – with the help of alerts built into their electronic health records that notify clinicians if a patient is due for a vaccine.
COVID-19 revealed marked health inequities in underserved communities as Black, Hispanic, and people from other minority communities experienced higher rates of COVID-19 cases and deaths, compared with White people. The Public Health Institute, which is part of Denver Health, has responded with vaccine outreach teams that go to schools, shelters, churches, and community-based organizations to vaccinate children. They focus their efforts on areas where immunization rates are low. Health centers in schools throughout Colorado vaccinate students, and the Public Health Institute partners with Denver-area public schools to provide vaccines to students in schools that don’t have such centers. (They also provide dental care and behavioral health services.)
But it is unlikely that restoring clinic operations and making vaccines more accessible will fill the gap. After 3 years of fear and mistrust, parents are still nervous about routine shots. To help clinicians facilitate conversations about vaccination, Denver Health trains providers in communication techniques using motivational interviewing (MI), a collaborative goal-oriented approach that encourages changes in health behaviors.
Dr. Shlay, who stressed the value of persistence, advised, “Through motivational interviewing, discussing things, talking about it, you can actually address most of the concerns.”
Giving parents a boost in the right direction
That spirit drives the work of Boost Oregon, a parent-led nonprofit organization founded in 2015 that helps parents make science-based decisions for themselves and their families. Even before the pandemic, primary care providers needed better strategies for addressing parents who had concerns about vaccines and found themselves failing in the effort while trying to see 20 patients a day.
For families that have questions about vaccines, Boost Oregon holds community meetings in which parents meet with clinicians, share their concerns with other parents, and get answers to their questions in a nonjudgmental way. The 1- to 2-hour sessions enable deeper discussions of the issues than many clinicians can manage in a 20-minute patient visit.
Boost Oregon also trains providers in communication techniques using MI. Ryan Hassan, MD, a pediatrician in private practice who serves as the medical director for the organization, has made the approach an integral part of his day. A key realization for him about the use of MI is that if providers want to build trust with parents, they need to accept that their role is not simply to educate but also to listen.
“Even if it’s the wildest conspiracy theory I’ve ever heard, that is my opportunity to show them that I’m listening and to empathize,” Dr. Hassan said.
His next step, a central tenet of MI, is to make reflective statements that summarize the parent’s concerns, demonstrate empathy, and help him get to the heart of their concerns. He then tailors his message to their issues.
Dr. Hassan tells people who are learning the technique to acknowledge that patients have the autonomy to make their own decisions. Coercing them into a decision is unhelpful and potentially counterproductive. “You can’t change anyone else’s mind,” he said. “You have to help them change their own mind.”
Dr. Limaye reinforced that message. Overwhelmed by conflicting messages on the internet, people are just trying to find answers. She trains providers not to dismiss patients’ concerns, because dismissal erodes trust.
“When you’re dealing with misinformation and conspiracy, to me, one thing to keep in mind is that it’s the long game,” Dr. Limaye said, “You’re not going to be able to sway them in one conversation.”
Can the powers of social media be harnessed for pro-vaccine messaging? Dr. Limaye has studied social media strategies to promote vaccine acceptance and has identified several elements that can be useful for swaying opinions about vaccine.
One is the messenger – as people trust their physicians less, “it’s important to find influencers that people might trust to actually spread a message,” she said. Another factor is that as society has become more polarized, interaction with the leadership of groups that hold influence has become key. To promote vaccine acceptance, for example, leaders of moms’ groups on Facebook could be equipped with evidence-based information.
“It’s important for us to reach out and engage with those that are leaders in those groups, because they kind of hold the power,” Dr. Limaye said.
Framing the message is critical. Dr. Limaye has found that personal narratives can be persuasive and that to influence vaccine behavior, it is necessary to tailor the approach to the specific audience. Danish researchers, for example, in 2017 launched a campaign to increase uptake of HPV vaccinations among teenagers. The researchers provided facts about the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine, cited posts by clinicians about the importance of immunization against the virus, and relayed personal stories, such as one about a father who chose to vaccinate his daughter and another about a blogger’s encounter with a woman with cervical cancer. The researchers found that the highest engagement rates were achieved through personal content and that such content generated the highest proportion of positive comments.
According to Dr. Limaye, to change behavior, social media messaging must address the issues of risk perception and self-efficacy. For risk perception regarding vaccines, a successful message needs to address the parents’ questions about whether their child is at risk for catching a disease, such as measles or pertussis, and if they are, whether the child will wind up in the hospital.
Self-efficacy is the belief that one can accomplish a task. An effective message would provide information on where to find free or low-cost vaccines and would identify locations that are easy to reach and that have expanded hours for working parents, Dr. Limaye said.
What’s the best approach for boosting vaccination rates in the post-pandemic era? In the 1850s, Massachusetts enacted the first vaccine mandate in the United States to prevent smallpox, and by the 1900s, similar laws had been passed in almost half of states. But recent polls suggest that support for vaccine mandates is dwindling. In a poll by the Kaiser Family Foundation last fall, 71% of adults said that healthy children should be required to be vaccinated against measles before entering school, which was down from 82% in a similar poll in 2019.
So perhaps a better approach for promoting vaccine confidence in the 21st century would involve wider use of MI by clinicians and more focus by public health agencies taking advantage of the potential power of social media. As Dr. Offit put it, “I think trust is the key thing.”
Dr. Offit, Dr. Limaye, Dr. Shlay, and Dr. Hassan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When people ask Paul Offit, MD, what worries him the most about the COVID-19 pandemic, he names two concerns. “One is the lack of socialization and education that came from keeping kids out of school for so long,” Dr. Offit said in a recent interview. “And I think vaccines have suffered.”
Dr. Offit is director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. He has watched with alarm as the American public appears to be losing faith in the lifesaving vaccines the public health community has worked hard to promote. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that the proportion of kids entering kindergarten who have received state-required vaccines dipped to 94% in the 2020-2021 school year – a full point less than the year before the pandemic – then dropped by another percentage point, to 93%, the following year.
Although a couple of percentage points may sound trivial, were only 93% of kindergarteners to receive the vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR), approximately 250,000 vulnerable 5-year-olds could spark the next big outbreak, such as the recent measles outbreaks in Ohio and Minnesota.
Dr. Offit is one of many public health officials and clinicians who are working to reverse the concerning trends in pediatric vaccinations.
“I just don’t want to see an outbreak of something that we could have avoided because we were not protected enough,” Judith Shlay, MD, associate director of the Public Health Institute at Denver Health, said.
Official stumbles in part to blame
Disruptions in health care from the COVID-19 pandemic certainly played a role in the decline. Parents were afraid to expose their children to other sick kids, providers shifted to a telehealth model, and routine preventive care was difficult to access.
But Dr. Offit also blamed erosion of trust on mistakes made by government and public health institutions for the alarming trend. “I think that health care professionals have lost some level of trust in the Food and Drug Administration and CDC.”
He cited as an example poor messaging during a large outbreak in Massachusetts in summer 2021, when the CDC published a report that highlighted the high proportion of COVID-19 cases among vaccinated people. Health officials called those cases “breakthrough” infections, although most were mild or asymptomatic.
Dr. Offit said the CDC should have focused the message instead on the low rate (1%) of hospitalizations and the low number of deaths from the infections. Instead, they had to walk back their promise that vaccinated people didn’t need to wear masks. At other times, the Biden administration pressured public health officials by promising to make booster shots available to the American public when the FDA and CDC felt they lacked evidence to recommend the injections.
Rupali Limaye, PhD, an associate professor of international health at the Bloomberg School of Public Health at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, studies vaccine behavior and decision-making. She would go a step further in characterizing the roots of worsening vaccine hesitancy.
“In the last 20 years, we’ve seen there’s less and less trust in health care providers in general,” Dr. Limaye said. “More people are turning to their social networks or social contacts for that kind of information.” In the maelstrom of the COVID-19 pandemic, digital social networks facilitated the spread of misinformation about COVID-19 faster than scientists could unravel the mysteries of the disease.
“There’s always been this underlying hesitancy for some people about vaccines,” Dr. Shlay said. But she has noticed more resistance to the COVID-19 vaccine from parents nervous about the new mRNA technology. “There was a lot of politicization of the vaccine, even though the mRNA vaccine technology has been around for a long time,” she said.
Multipronged approaches
Dr. Shlay is committed to restoring childhood vaccination uptake to prepandemic levels now that clinics are open again. To do so, she is relying on a combination of quality improvement strategies and outreach to undervaccinated populations.
Denver Health, for instance, offers vaccinations at any inpatient or outpatient visit – not just well-child visits – with the help of alerts built into their electronic health records that notify clinicians if a patient is due for a vaccine.
COVID-19 revealed marked health inequities in underserved communities as Black, Hispanic, and people from other minority communities experienced higher rates of COVID-19 cases and deaths, compared with White people. The Public Health Institute, which is part of Denver Health, has responded with vaccine outreach teams that go to schools, shelters, churches, and community-based organizations to vaccinate children. They focus their efforts on areas where immunization rates are low. Health centers in schools throughout Colorado vaccinate students, and the Public Health Institute partners with Denver-area public schools to provide vaccines to students in schools that don’t have such centers. (They also provide dental care and behavioral health services.)
But it is unlikely that restoring clinic operations and making vaccines more accessible will fill the gap. After 3 years of fear and mistrust, parents are still nervous about routine shots. To help clinicians facilitate conversations about vaccination, Denver Health trains providers in communication techniques using motivational interviewing (MI), a collaborative goal-oriented approach that encourages changes in health behaviors.
Dr. Shlay, who stressed the value of persistence, advised, “Through motivational interviewing, discussing things, talking about it, you can actually address most of the concerns.”
Giving parents a boost in the right direction
That spirit drives the work of Boost Oregon, a parent-led nonprofit organization founded in 2015 that helps parents make science-based decisions for themselves and their families. Even before the pandemic, primary care providers needed better strategies for addressing parents who had concerns about vaccines and found themselves failing in the effort while trying to see 20 patients a day.
For families that have questions about vaccines, Boost Oregon holds community meetings in which parents meet with clinicians, share their concerns with other parents, and get answers to their questions in a nonjudgmental way. The 1- to 2-hour sessions enable deeper discussions of the issues than many clinicians can manage in a 20-minute patient visit.
Boost Oregon also trains providers in communication techniques using MI. Ryan Hassan, MD, a pediatrician in private practice who serves as the medical director for the organization, has made the approach an integral part of his day. A key realization for him about the use of MI is that if providers want to build trust with parents, they need to accept that their role is not simply to educate but also to listen.
“Even if it’s the wildest conspiracy theory I’ve ever heard, that is my opportunity to show them that I’m listening and to empathize,” Dr. Hassan said.
His next step, a central tenet of MI, is to make reflective statements that summarize the parent’s concerns, demonstrate empathy, and help him get to the heart of their concerns. He then tailors his message to their issues.
Dr. Hassan tells people who are learning the technique to acknowledge that patients have the autonomy to make their own decisions. Coercing them into a decision is unhelpful and potentially counterproductive. “You can’t change anyone else’s mind,” he said. “You have to help them change their own mind.”
Dr. Limaye reinforced that message. Overwhelmed by conflicting messages on the internet, people are just trying to find answers. She trains providers not to dismiss patients’ concerns, because dismissal erodes trust.
“When you’re dealing with misinformation and conspiracy, to me, one thing to keep in mind is that it’s the long game,” Dr. Limaye said, “You’re not going to be able to sway them in one conversation.”
Can the powers of social media be harnessed for pro-vaccine messaging? Dr. Limaye has studied social media strategies to promote vaccine acceptance and has identified several elements that can be useful for swaying opinions about vaccine.
One is the messenger – as people trust their physicians less, “it’s important to find influencers that people might trust to actually spread a message,” she said. Another factor is that as society has become more polarized, interaction with the leadership of groups that hold influence has become key. To promote vaccine acceptance, for example, leaders of moms’ groups on Facebook could be equipped with evidence-based information.
“It’s important for us to reach out and engage with those that are leaders in those groups, because they kind of hold the power,” Dr. Limaye said.
Framing the message is critical. Dr. Limaye has found that personal narratives can be persuasive and that to influence vaccine behavior, it is necessary to tailor the approach to the specific audience. Danish researchers, for example, in 2017 launched a campaign to increase uptake of HPV vaccinations among teenagers. The researchers provided facts about the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine, cited posts by clinicians about the importance of immunization against the virus, and relayed personal stories, such as one about a father who chose to vaccinate his daughter and another about a blogger’s encounter with a woman with cervical cancer. The researchers found that the highest engagement rates were achieved through personal content and that such content generated the highest proportion of positive comments.
According to Dr. Limaye, to change behavior, social media messaging must address the issues of risk perception and self-efficacy. For risk perception regarding vaccines, a successful message needs to address the parents’ questions about whether their child is at risk for catching a disease, such as measles or pertussis, and if they are, whether the child will wind up in the hospital.
Self-efficacy is the belief that one can accomplish a task. An effective message would provide information on where to find free or low-cost vaccines and would identify locations that are easy to reach and that have expanded hours for working parents, Dr. Limaye said.
What’s the best approach for boosting vaccination rates in the post-pandemic era? In the 1850s, Massachusetts enacted the first vaccine mandate in the United States to prevent smallpox, and by the 1900s, similar laws had been passed in almost half of states. But recent polls suggest that support for vaccine mandates is dwindling. In a poll by the Kaiser Family Foundation last fall, 71% of adults said that healthy children should be required to be vaccinated against measles before entering school, which was down from 82% in a similar poll in 2019.
So perhaps a better approach for promoting vaccine confidence in the 21st century would involve wider use of MI by clinicians and more focus by public health agencies taking advantage of the potential power of social media. As Dr. Offit put it, “I think trust is the key thing.”
Dr. Offit, Dr. Limaye, Dr. Shlay, and Dr. Hassan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When people ask Paul Offit, MD, what worries him the most about the COVID-19 pandemic, he names two concerns. “One is the lack of socialization and education that came from keeping kids out of school for so long,” Dr. Offit said in a recent interview. “And I think vaccines have suffered.”
Dr. Offit is director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. He has watched with alarm as the American public appears to be losing faith in the lifesaving vaccines the public health community has worked hard to promote. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that the proportion of kids entering kindergarten who have received state-required vaccines dipped to 94% in the 2020-2021 school year – a full point less than the year before the pandemic – then dropped by another percentage point, to 93%, the following year.
Although a couple of percentage points may sound trivial, were only 93% of kindergarteners to receive the vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR), approximately 250,000 vulnerable 5-year-olds could spark the next big outbreak, such as the recent measles outbreaks in Ohio and Minnesota.
Dr. Offit is one of many public health officials and clinicians who are working to reverse the concerning trends in pediatric vaccinations.
“I just don’t want to see an outbreak of something that we could have avoided because we were not protected enough,” Judith Shlay, MD, associate director of the Public Health Institute at Denver Health, said.
Official stumbles in part to blame
Disruptions in health care from the COVID-19 pandemic certainly played a role in the decline. Parents were afraid to expose their children to other sick kids, providers shifted to a telehealth model, and routine preventive care was difficult to access.
But Dr. Offit also blamed erosion of trust on mistakes made by government and public health institutions for the alarming trend. “I think that health care professionals have lost some level of trust in the Food and Drug Administration and CDC.”
He cited as an example poor messaging during a large outbreak in Massachusetts in summer 2021, when the CDC published a report that highlighted the high proportion of COVID-19 cases among vaccinated people. Health officials called those cases “breakthrough” infections, although most were mild or asymptomatic.
Dr. Offit said the CDC should have focused the message instead on the low rate (1%) of hospitalizations and the low number of deaths from the infections. Instead, they had to walk back their promise that vaccinated people didn’t need to wear masks. At other times, the Biden administration pressured public health officials by promising to make booster shots available to the American public when the FDA and CDC felt they lacked evidence to recommend the injections.
Rupali Limaye, PhD, an associate professor of international health at the Bloomberg School of Public Health at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, studies vaccine behavior and decision-making. She would go a step further in characterizing the roots of worsening vaccine hesitancy.
“In the last 20 years, we’ve seen there’s less and less trust in health care providers in general,” Dr. Limaye said. “More people are turning to their social networks or social contacts for that kind of information.” In the maelstrom of the COVID-19 pandemic, digital social networks facilitated the spread of misinformation about COVID-19 faster than scientists could unravel the mysteries of the disease.
“There’s always been this underlying hesitancy for some people about vaccines,” Dr. Shlay said. But she has noticed more resistance to the COVID-19 vaccine from parents nervous about the new mRNA technology. “There was a lot of politicization of the vaccine, even though the mRNA vaccine technology has been around for a long time,” she said.
Multipronged approaches
Dr. Shlay is committed to restoring childhood vaccination uptake to prepandemic levels now that clinics are open again. To do so, she is relying on a combination of quality improvement strategies and outreach to undervaccinated populations.
Denver Health, for instance, offers vaccinations at any inpatient or outpatient visit – not just well-child visits – with the help of alerts built into their electronic health records that notify clinicians if a patient is due for a vaccine.
COVID-19 revealed marked health inequities in underserved communities as Black, Hispanic, and people from other minority communities experienced higher rates of COVID-19 cases and deaths, compared with White people. The Public Health Institute, which is part of Denver Health, has responded with vaccine outreach teams that go to schools, shelters, churches, and community-based organizations to vaccinate children. They focus their efforts on areas where immunization rates are low. Health centers in schools throughout Colorado vaccinate students, and the Public Health Institute partners with Denver-area public schools to provide vaccines to students in schools that don’t have such centers. (They also provide dental care and behavioral health services.)
But it is unlikely that restoring clinic operations and making vaccines more accessible will fill the gap. After 3 years of fear and mistrust, parents are still nervous about routine shots. To help clinicians facilitate conversations about vaccination, Denver Health trains providers in communication techniques using motivational interviewing (MI), a collaborative goal-oriented approach that encourages changes in health behaviors.
Dr. Shlay, who stressed the value of persistence, advised, “Through motivational interviewing, discussing things, talking about it, you can actually address most of the concerns.”
Giving parents a boost in the right direction
That spirit drives the work of Boost Oregon, a parent-led nonprofit organization founded in 2015 that helps parents make science-based decisions for themselves and their families. Even before the pandemic, primary care providers needed better strategies for addressing parents who had concerns about vaccines and found themselves failing in the effort while trying to see 20 patients a day.
For families that have questions about vaccines, Boost Oregon holds community meetings in which parents meet with clinicians, share their concerns with other parents, and get answers to their questions in a nonjudgmental way. The 1- to 2-hour sessions enable deeper discussions of the issues than many clinicians can manage in a 20-minute patient visit.
Boost Oregon also trains providers in communication techniques using MI. Ryan Hassan, MD, a pediatrician in private practice who serves as the medical director for the organization, has made the approach an integral part of his day. A key realization for him about the use of MI is that if providers want to build trust with parents, they need to accept that their role is not simply to educate but also to listen.
“Even if it’s the wildest conspiracy theory I’ve ever heard, that is my opportunity to show them that I’m listening and to empathize,” Dr. Hassan said.
His next step, a central tenet of MI, is to make reflective statements that summarize the parent’s concerns, demonstrate empathy, and help him get to the heart of their concerns. He then tailors his message to their issues.
Dr. Hassan tells people who are learning the technique to acknowledge that patients have the autonomy to make their own decisions. Coercing them into a decision is unhelpful and potentially counterproductive. “You can’t change anyone else’s mind,” he said. “You have to help them change their own mind.”
Dr. Limaye reinforced that message. Overwhelmed by conflicting messages on the internet, people are just trying to find answers. She trains providers not to dismiss patients’ concerns, because dismissal erodes trust.
“When you’re dealing with misinformation and conspiracy, to me, one thing to keep in mind is that it’s the long game,” Dr. Limaye said, “You’re not going to be able to sway them in one conversation.”
Can the powers of social media be harnessed for pro-vaccine messaging? Dr. Limaye has studied social media strategies to promote vaccine acceptance and has identified several elements that can be useful for swaying opinions about vaccine.
One is the messenger – as people trust their physicians less, “it’s important to find influencers that people might trust to actually spread a message,” she said. Another factor is that as society has become more polarized, interaction with the leadership of groups that hold influence has become key. To promote vaccine acceptance, for example, leaders of moms’ groups on Facebook could be equipped with evidence-based information.
“It’s important for us to reach out and engage with those that are leaders in those groups, because they kind of hold the power,” Dr. Limaye said.
Framing the message is critical. Dr. Limaye has found that personal narratives can be persuasive and that to influence vaccine behavior, it is necessary to tailor the approach to the specific audience. Danish researchers, for example, in 2017 launched a campaign to increase uptake of HPV vaccinations among teenagers. The researchers provided facts about the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine, cited posts by clinicians about the importance of immunization against the virus, and relayed personal stories, such as one about a father who chose to vaccinate his daughter and another about a blogger’s encounter with a woman with cervical cancer. The researchers found that the highest engagement rates were achieved through personal content and that such content generated the highest proportion of positive comments.
According to Dr. Limaye, to change behavior, social media messaging must address the issues of risk perception and self-efficacy. For risk perception regarding vaccines, a successful message needs to address the parents’ questions about whether their child is at risk for catching a disease, such as measles or pertussis, and if they are, whether the child will wind up in the hospital.
Self-efficacy is the belief that one can accomplish a task. An effective message would provide information on where to find free or low-cost vaccines and would identify locations that are easy to reach and that have expanded hours for working parents, Dr. Limaye said.
What’s the best approach for boosting vaccination rates in the post-pandemic era? In the 1850s, Massachusetts enacted the first vaccine mandate in the United States to prevent smallpox, and by the 1900s, similar laws had been passed in almost half of states. But recent polls suggest that support for vaccine mandates is dwindling. In a poll by the Kaiser Family Foundation last fall, 71% of adults said that healthy children should be required to be vaccinated against measles before entering school, which was down from 82% in a similar poll in 2019.
So perhaps a better approach for promoting vaccine confidence in the 21st century would involve wider use of MI by clinicians and more focus by public health agencies taking advantage of the potential power of social media. As Dr. Offit put it, “I think trust is the key thing.”
Dr. Offit, Dr. Limaye, Dr. Shlay, and Dr. Hassan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Boys may carry the weight, or overweight, of adults’ infertility
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Axial spondyloarthritis versus axial psoriatic arthritis: Different entities?
Are there clinically significant differences between axial spondyloarthritis with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with axial symptoms? Does it matter?
It all depends on whom you ask, but right now the evidence seems to be tipping in favor of the “splitters” who cite evidence supporting their contention that axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA)/ankylosing spondylitis (AS) with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) with axial symptoms are distinct clinical entities that require more precise diagnosis and treatment.
“Lumpers,” in contrast, argue that they are different points on the same clinical spectrum.
The debate is not just of academic interest, but has real consequences for patients, say specialists on both sides of the aisle.
Overlapping features, different presentations
“Axial SpA and axPsA have overlapping features but also meaningful differences in genetics, clinical presentation, imaging, and immunophenotype. Efforts are underway to develop classification criteria for axPsA to aid research efforts as well as clinical diagnosis and management,” Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at Swedish Medical Center/Providence–St. Joseph Health in Seattle, and colleagues contend.
In an editorial published in the International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, Dr. Mease and colleagues noted that, although HLA-B*27 is a genetic risk factor for both axPsA and axSpA, some HLA-B alleles are significantly associated with axPsA, whereas other alleles are associated with axSpA.
In addition, while genes in the interleukin-23 and IL-17 pathway are associated with increased risk for axSpA, genes in the IL-13 pathway have been identified as risk markers for axPsA, they noted.
Two cohorts better than one?
Dafna Gladman, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Schroeder Arthritis Institute at Toronto Western Hospital, and colleagues have a unique perspective on the similarities and differences between the disease entities.
Her group’s research uses data on cohorts of patients treated in two separate clinics at Toronto Western Hospital: one for patients with PsA, and one for patients with axial spondyloarthritis, including those with ankylosing spondylitis, nonradiographic axSpA, and spondylitis associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
“Our work has shown that there are differences, and one of the reasons that it’s now important is that the anti–IL-23 medications, both the IL-12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab [Stelara] and the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab [Tremfya] work for psoriatic arthritis, whereas IL-23 did not work in ankylosing spondylitis, so that provided further impetus to look into the distinction between the two groups,” Dr. Gladman said in an interview.
Dr. Gladman and colleagues published a study in Rheumatology in which they compared clinical presentations and features of patients with AS with or without psoriasis with patients with axPsA.
They found that patients with AS with or without psoriasis tended to be younger, had a higher proportion of males to females, and were more likely to be positive for HLA-B*27. Patients with AS also had more back pain at presentation, worse axial disease activity scores, worse global assessments by physicians, and higher grades of sacroiliitis, and they were more likely to be taking biologic agents.
“What that showed, right off the top, that whether we’re looking at the total group or we’re looking specifically at those patients who have psoriasis or don’t have psoriasis, they are different from those with psoriatic arthritis with axial disease,” she said.
They concluded that “axPsA seems to be a distinct entity.”
Two clinics, same presentation
Because the aforementioned study included all patients with PsA with or without peripheral disease, the investigators decided to filter out some of the background noise and conduct a second study in which they compared patients who presented to the two clinics with the same presentation, either with spinal disease and psoriasis to the spondylitis clinic, or with psoriasis and isolated axial disease to the PsA clinic.
The results, published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showed that just 2.03% of patients with PsA had isolated axial disease, and an additional 29.38% had axial and peripheral disease.
In this study, “you can see that even in that group there are distinct differences. The patients that are labeled psoriatic spondylitis are different from those that are labeled ankylosing spondylitis with psoriasis,” Dr. Gladman said.
Isolated axial disease in patients with PsA was associated with HLA-B*27 positivity and lower Health Assessment Questionnaire scores. In addition, patients who were HLA-B*27 positive also had a nearly eightfold higher risk for developing peripheral disease over time.
Patients with isolated axial PsA were significantly more likely to be diagnosed at an older age (mean, 37.44 vs. 29.65 years), had higher Psoriasis Area Severity Index scores and a higher likelihood of having psoriatic nail lesions than patients with AS with isolated axial disease and psoriasis.
In contrast, patients with isolated axSpA with psoriasis were more likely to have inflammatory back pain, spinal pain, joint pain/swelling, and areas of localized tenderness, and they had greater severity of morning stiffness.
Dr. Gladman noted that, although AS and PsA are associated with the same gene that encodes for the IL-23 receptor, each condition is associated with a different single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Same disease, different flavors?
But as Mark Twain said, it is difference of opinion that makes horse races, and some specialists in rheumatology say that axSpA amd axPsA are just two sides of the same coin.
“There are always different schools of thought. I believe that they are not different diseases, but a spectrum of diseases,” said Shailendra Singh, MD, a rheumatologist at Unity Health Medical Center in Searcy, Ark., and past president of the Arkansas Rheumatology Association.
In an interview, Dr. Singh said that the spectrum ranges from diseases with primarily axial involvement, such as AS, to those with primarily peripheral involvement, such as reactive arthritis.
He pointed out that these conditions have overlapping symptoms, including enthesitis, dactylitis, and uveitis, and inflammatory arthritis.
Daniel Wendling, MD, PhD, from the Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Besançon (France), Université de Franche-Comté, and colleagues agreed.
“The criteria currently available for both SpA [ASAS (Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society) criteria] and PsA [CASPAR (Classification for Psoriatic Arthritis) criteria] are classification criteria, not diagnostic criteria. They are not very stringent and are not exclusive. Thus, the same patient can easily be classified simultaneously in both entities, making the distinction between axSpA with psoriasis and axPsA theoretical,” they wrote in an editorial published in Joint Bone Spine.
They cited as an example of the allegedly fuzzy criteria a prospective study conducted by the investigators in Bath, England, in which modified New York criteria for AS were met by 24% of patients with AS, and CASPAR criteria for PsA were met by an equal number of patients with AS.
Therapeutic implications
Dr. Wendling and colleagues acknowledge the differences cited in studies by Dr. Gladman, Dr. Mease, and others between patients with axPsA and those with axSpA, but argue that the differences are not that great and not so clear.
“It should also be emphasized that, although some differences between axPsA and axSpA reach statistical significance, they are mostly at the margin, with low odd ratios,” they wrote.
“It is also important to consider the variability in the definition of axPsA, sometimes simply ‘physician reported’ and elsewhere based on the modified New York radiographic criteria; the latter are only present late in the course of the disease, and this may induce bias,” they continued.
Dr. Singh agreed that, as noted by Dr. Gladman, some patients will respond to anti–IL-17, anti–IL-23, and anti–IL-12/23 agents, whereas others will have better responses with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, and still others, such as those with peripheral involvement in the hands and feet may fare better with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs such as methotrexate.
Answers to come?
Dr. Gladman noted that the information available to date about the efficacy of IL-23 inhibition in axPsA is based on a post hoc analysis of the PSUMMIT 1 and 2 controlled trials in PsA, and is not definitive.
The randomized, controlled STAR trial, currently recruiting patients, is designed to see whether guselkumab can reduce axial symptoms and inflammation in patients with active axPsA.
“What I say is, there is a rationale for [anti–IL-23] to work in psoriatic arthritis, and not work in ankylosing spondylitis,” she said.
In contrast, IL-17 inhibitors, anti-TNF agents, and Janus kinase inhibitors show efficacy against both axPsA and AS. Rituximab is ineffective against PsA, but has shown efficacy against AS, especially in patients with neurologic complications from anti-TNF agents.
“There may be other medications that would work more specifically in axial psoriatic arthritis that don’t work in ankylosing spondylitis, but at least recognizing that there may be some differences, and that therefore a correct diagnosis should be obtained, might be important,” she said.
Ideally, the picture will become clearer with results from the ongoing Axial Involvement in Psoriatic Arthritis cohort, a joint project of ASAS and the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. The multinational, cross-sectional study is designed “to systematically evaluate clinical and imaging manifestations indicative of axial involvement in patients with PsA and to develop classification criteria and a unified nomenclature for axial involvement in PsA that would allow defining a homogeneous subgroup of patients for research.”
Stay tuned.
Dr. Gladman’s research is supported by a grant from the Krembil Foundation. Dr. Singh disclosed research support from various companies. Funding sources and conflict of interest disclosures from other works cited are contained in their respective references.
Are there clinically significant differences between axial spondyloarthritis with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with axial symptoms? Does it matter?
It all depends on whom you ask, but right now the evidence seems to be tipping in favor of the “splitters” who cite evidence supporting their contention that axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA)/ankylosing spondylitis (AS) with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) with axial symptoms are distinct clinical entities that require more precise diagnosis and treatment.
“Lumpers,” in contrast, argue that they are different points on the same clinical spectrum.
The debate is not just of academic interest, but has real consequences for patients, say specialists on both sides of the aisle.
Overlapping features, different presentations
“Axial SpA and axPsA have overlapping features but also meaningful differences in genetics, clinical presentation, imaging, and immunophenotype. Efforts are underway to develop classification criteria for axPsA to aid research efforts as well as clinical diagnosis and management,” Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at Swedish Medical Center/Providence–St. Joseph Health in Seattle, and colleagues contend.
In an editorial published in the International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, Dr. Mease and colleagues noted that, although HLA-B*27 is a genetic risk factor for both axPsA and axSpA, some HLA-B alleles are significantly associated with axPsA, whereas other alleles are associated with axSpA.
In addition, while genes in the interleukin-23 and IL-17 pathway are associated with increased risk for axSpA, genes in the IL-13 pathway have been identified as risk markers for axPsA, they noted.
Two cohorts better than one?
Dafna Gladman, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Schroeder Arthritis Institute at Toronto Western Hospital, and colleagues have a unique perspective on the similarities and differences between the disease entities.
Her group’s research uses data on cohorts of patients treated in two separate clinics at Toronto Western Hospital: one for patients with PsA, and one for patients with axial spondyloarthritis, including those with ankylosing spondylitis, nonradiographic axSpA, and spondylitis associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
“Our work has shown that there are differences, and one of the reasons that it’s now important is that the anti–IL-23 medications, both the IL-12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab [Stelara] and the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab [Tremfya] work for psoriatic arthritis, whereas IL-23 did not work in ankylosing spondylitis, so that provided further impetus to look into the distinction between the two groups,” Dr. Gladman said in an interview.
Dr. Gladman and colleagues published a study in Rheumatology in which they compared clinical presentations and features of patients with AS with or without psoriasis with patients with axPsA.
They found that patients with AS with or without psoriasis tended to be younger, had a higher proportion of males to females, and were more likely to be positive for HLA-B*27. Patients with AS also had more back pain at presentation, worse axial disease activity scores, worse global assessments by physicians, and higher grades of sacroiliitis, and they were more likely to be taking biologic agents.
“What that showed, right off the top, that whether we’re looking at the total group or we’re looking specifically at those patients who have psoriasis or don’t have psoriasis, they are different from those with psoriatic arthritis with axial disease,” she said.
They concluded that “axPsA seems to be a distinct entity.”
Two clinics, same presentation
Because the aforementioned study included all patients with PsA with or without peripheral disease, the investigators decided to filter out some of the background noise and conduct a second study in which they compared patients who presented to the two clinics with the same presentation, either with spinal disease and psoriasis to the spondylitis clinic, or with psoriasis and isolated axial disease to the PsA clinic.
The results, published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showed that just 2.03% of patients with PsA had isolated axial disease, and an additional 29.38% had axial and peripheral disease.
In this study, “you can see that even in that group there are distinct differences. The patients that are labeled psoriatic spondylitis are different from those that are labeled ankylosing spondylitis with psoriasis,” Dr. Gladman said.
Isolated axial disease in patients with PsA was associated with HLA-B*27 positivity and lower Health Assessment Questionnaire scores. In addition, patients who were HLA-B*27 positive also had a nearly eightfold higher risk for developing peripheral disease over time.
Patients with isolated axial PsA were significantly more likely to be diagnosed at an older age (mean, 37.44 vs. 29.65 years), had higher Psoriasis Area Severity Index scores and a higher likelihood of having psoriatic nail lesions than patients with AS with isolated axial disease and psoriasis.
In contrast, patients with isolated axSpA with psoriasis were more likely to have inflammatory back pain, spinal pain, joint pain/swelling, and areas of localized tenderness, and they had greater severity of morning stiffness.
Dr. Gladman noted that, although AS and PsA are associated with the same gene that encodes for the IL-23 receptor, each condition is associated with a different single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Same disease, different flavors?
But as Mark Twain said, it is difference of opinion that makes horse races, and some specialists in rheumatology say that axSpA amd axPsA are just two sides of the same coin.
“There are always different schools of thought. I believe that they are not different diseases, but a spectrum of diseases,” said Shailendra Singh, MD, a rheumatologist at Unity Health Medical Center in Searcy, Ark., and past president of the Arkansas Rheumatology Association.
In an interview, Dr. Singh said that the spectrum ranges from diseases with primarily axial involvement, such as AS, to those with primarily peripheral involvement, such as reactive arthritis.
He pointed out that these conditions have overlapping symptoms, including enthesitis, dactylitis, and uveitis, and inflammatory arthritis.
Daniel Wendling, MD, PhD, from the Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Besançon (France), Université de Franche-Comté, and colleagues agreed.
“The criteria currently available for both SpA [ASAS (Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society) criteria] and PsA [CASPAR (Classification for Psoriatic Arthritis) criteria] are classification criteria, not diagnostic criteria. They are not very stringent and are not exclusive. Thus, the same patient can easily be classified simultaneously in both entities, making the distinction between axSpA with psoriasis and axPsA theoretical,” they wrote in an editorial published in Joint Bone Spine.
They cited as an example of the allegedly fuzzy criteria a prospective study conducted by the investigators in Bath, England, in which modified New York criteria for AS were met by 24% of patients with AS, and CASPAR criteria for PsA were met by an equal number of patients with AS.
Therapeutic implications
Dr. Wendling and colleagues acknowledge the differences cited in studies by Dr. Gladman, Dr. Mease, and others between patients with axPsA and those with axSpA, but argue that the differences are not that great and not so clear.
“It should also be emphasized that, although some differences between axPsA and axSpA reach statistical significance, they are mostly at the margin, with low odd ratios,” they wrote.
“It is also important to consider the variability in the definition of axPsA, sometimes simply ‘physician reported’ and elsewhere based on the modified New York radiographic criteria; the latter are only present late in the course of the disease, and this may induce bias,” they continued.
Dr. Singh agreed that, as noted by Dr. Gladman, some patients will respond to anti–IL-17, anti–IL-23, and anti–IL-12/23 agents, whereas others will have better responses with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, and still others, such as those with peripheral involvement in the hands and feet may fare better with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs such as methotrexate.
Answers to come?
Dr. Gladman noted that the information available to date about the efficacy of IL-23 inhibition in axPsA is based on a post hoc analysis of the PSUMMIT 1 and 2 controlled trials in PsA, and is not definitive.
The randomized, controlled STAR trial, currently recruiting patients, is designed to see whether guselkumab can reduce axial symptoms and inflammation in patients with active axPsA.
“What I say is, there is a rationale for [anti–IL-23] to work in psoriatic arthritis, and not work in ankylosing spondylitis,” she said.
In contrast, IL-17 inhibitors, anti-TNF agents, and Janus kinase inhibitors show efficacy against both axPsA and AS. Rituximab is ineffective against PsA, but has shown efficacy against AS, especially in patients with neurologic complications from anti-TNF agents.
“There may be other medications that would work more specifically in axial psoriatic arthritis that don’t work in ankylosing spondylitis, but at least recognizing that there may be some differences, and that therefore a correct diagnosis should be obtained, might be important,” she said.
Ideally, the picture will become clearer with results from the ongoing Axial Involvement in Psoriatic Arthritis cohort, a joint project of ASAS and the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. The multinational, cross-sectional study is designed “to systematically evaluate clinical and imaging manifestations indicative of axial involvement in patients with PsA and to develop classification criteria and a unified nomenclature for axial involvement in PsA that would allow defining a homogeneous subgroup of patients for research.”
Stay tuned.
Dr. Gladman’s research is supported by a grant from the Krembil Foundation. Dr. Singh disclosed research support from various companies. Funding sources and conflict of interest disclosures from other works cited are contained in their respective references.
Are there clinically significant differences between axial spondyloarthritis with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with axial symptoms? Does it matter?
It all depends on whom you ask, but right now the evidence seems to be tipping in favor of the “splitters” who cite evidence supporting their contention that axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA)/ankylosing spondylitis (AS) with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) with axial symptoms are distinct clinical entities that require more precise diagnosis and treatment.
“Lumpers,” in contrast, argue that they are different points on the same clinical spectrum.
The debate is not just of academic interest, but has real consequences for patients, say specialists on both sides of the aisle.
Overlapping features, different presentations
“Axial SpA and axPsA have overlapping features but also meaningful differences in genetics, clinical presentation, imaging, and immunophenotype. Efforts are underway to develop classification criteria for axPsA to aid research efforts as well as clinical diagnosis and management,” Philip J. Mease, MD, director of rheumatology research at Swedish Medical Center/Providence–St. Joseph Health in Seattle, and colleagues contend.
In an editorial published in the International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, Dr. Mease and colleagues noted that, although HLA-B*27 is a genetic risk factor for both axPsA and axSpA, some HLA-B alleles are significantly associated with axPsA, whereas other alleles are associated with axSpA.
In addition, while genes in the interleukin-23 and IL-17 pathway are associated with increased risk for axSpA, genes in the IL-13 pathway have been identified as risk markers for axPsA, they noted.
Two cohorts better than one?
Dafna Gladman, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Schroeder Arthritis Institute at Toronto Western Hospital, and colleagues have a unique perspective on the similarities and differences between the disease entities.
Her group’s research uses data on cohorts of patients treated in two separate clinics at Toronto Western Hospital: one for patients with PsA, and one for patients with axial spondyloarthritis, including those with ankylosing spondylitis, nonradiographic axSpA, and spondylitis associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
“Our work has shown that there are differences, and one of the reasons that it’s now important is that the anti–IL-23 medications, both the IL-12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab [Stelara] and the IL-23 inhibitor guselkumab [Tremfya] work for psoriatic arthritis, whereas IL-23 did not work in ankylosing spondylitis, so that provided further impetus to look into the distinction between the two groups,” Dr. Gladman said in an interview.
Dr. Gladman and colleagues published a study in Rheumatology in which they compared clinical presentations and features of patients with AS with or without psoriasis with patients with axPsA.
They found that patients with AS with or without psoriasis tended to be younger, had a higher proportion of males to females, and were more likely to be positive for HLA-B*27. Patients with AS also had more back pain at presentation, worse axial disease activity scores, worse global assessments by physicians, and higher grades of sacroiliitis, and they were more likely to be taking biologic agents.
“What that showed, right off the top, that whether we’re looking at the total group or we’re looking specifically at those patients who have psoriasis or don’t have psoriasis, they are different from those with psoriatic arthritis with axial disease,” she said.
They concluded that “axPsA seems to be a distinct entity.”
Two clinics, same presentation
Because the aforementioned study included all patients with PsA with or without peripheral disease, the investigators decided to filter out some of the background noise and conduct a second study in which they compared patients who presented to the two clinics with the same presentation, either with spinal disease and psoriasis to the spondylitis clinic, or with psoriasis and isolated axial disease to the PsA clinic.
The results, published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showed that just 2.03% of patients with PsA had isolated axial disease, and an additional 29.38% had axial and peripheral disease.
In this study, “you can see that even in that group there are distinct differences. The patients that are labeled psoriatic spondylitis are different from those that are labeled ankylosing spondylitis with psoriasis,” Dr. Gladman said.
Isolated axial disease in patients with PsA was associated with HLA-B*27 positivity and lower Health Assessment Questionnaire scores. In addition, patients who were HLA-B*27 positive also had a nearly eightfold higher risk for developing peripheral disease over time.
Patients with isolated axial PsA were significantly more likely to be diagnosed at an older age (mean, 37.44 vs. 29.65 years), had higher Psoriasis Area Severity Index scores and a higher likelihood of having psoriatic nail lesions than patients with AS with isolated axial disease and psoriasis.
In contrast, patients with isolated axSpA with psoriasis were more likely to have inflammatory back pain, spinal pain, joint pain/swelling, and areas of localized tenderness, and they had greater severity of morning stiffness.
Dr. Gladman noted that, although AS and PsA are associated with the same gene that encodes for the IL-23 receptor, each condition is associated with a different single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Same disease, different flavors?
But as Mark Twain said, it is difference of opinion that makes horse races, and some specialists in rheumatology say that axSpA amd axPsA are just two sides of the same coin.
“There are always different schools of thought. I believe that they are not different diseases, but a spectrum of diseases,” said Shailendra Singh, MD, a rheumatologist at Unity Health Medical Center in Searcy, Ark., and past president of the Arkansas Rheumatology Association.
In an interview, Dr. Singh said that the spectrum ranges from diseases with primarily axial involvement, such as AS, to those with primarily peripheral involvement, such as reactive arthritis.
He pointed out that these conditions have overlapping symptoms, including enthesitis, dactylitis, and uveitis, and inflammatory arthritis.
Daniel Wendling, MD, PhD, from the Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire de Besançon (France), Université de Franche-Comté, and colleagues agreed.
“The criteria currently available for both SpA [ASAS (Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society) criteria] and PsA [CASPAR (Classification for Psoriatic Arthritis) criteria] are classification criteria, not diagnostic criteria. They are not very stringent and are not exclusive. Thus, the same patient can easily be classified simultaneously in both entities, making the distinction between axSpA with psoriasis and axPsA theoretical,” they wrote in an editorial published in Joint Bone Spine.
They cited as an example of the allegedly fuzzy criteria a prospective study conducted by the investigators in Bath, England, in which modified New York criteria for AS were met by 24% of patients with AS, and CASPAR criteria for PsA were met by an equal number of patients with AS.
Therapeutic implications
Dr. Wendling and colleagues acknowledge the differences cited in studies by Dr. Gladman, Dr. Mease, and others between patients with axPsA and those with axSpA, but argue that the differences are not that great and not so clear.
“It should also be emphasized that, although some differences between axPsA and axSpA reach statistical significance, they are mostly at the margin, with low odd ratios,” they wrote.
“It is also important to consider the variability in the definition of axPsA, sometimes simply ‘physician reported’ and elsewhere based on the modified New York radiographic criteria; the latter are only present late in the course of the disease, and this may induce bias,” they continued.
Dr. Singh agreed that, as noted by Dr. Gladman, some patients will respond to anti–IL-17, anti–IL-23, and anti–IL-12/23 agents, whereas others will have better responses with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, and still others, such as those with peripheral involvement in the hands and feet may fare better with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs such as methotrexate.
Answers to come?
Dr. Gladman noted that the information available to date about the efficacy of IL-23 inhibition in axPsA is based on a post hoc analysis of the PSUMMIT 1 and 2 controlled trials in PsA, and is not definitive.
The randomized, controlled STAR trial, currently recruiting patients, is designed to see whether guselkumab can reduce axial symptoms and inflammation in patients with active axPsA.
“What I say is, there is a rationale for [anti–IL-23] to work in psoriatic arthritis, and not work in ankylosing spondylitis,” she said.
In contrast, IL-17 inhibitors, anti-TNF agents, and Janus kinase inhibitors show efficacy against both axPsA and AS. Rituximab is ineffective against PsA, but has shown efficacy against AS, especially in patients with neurologic complications from anti-TNF agents.
“There may be other medications that would work more specifically in axial psoriatic arthritis that don’t work in ankylosing spondylitis, but at least recognizing that there may be some differences, and that therefore a correct diagnosis should be obtained, might be important,” she said.
Ideally, the picture will become clearer with results from the ongoing Axial Involvement in Psoriatic Arthritis cohort, a joint project of ASAS and the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. The multinational, cross-sectional study is designed “to systematically evaluate clinical and imaging manifestations indicative of axial involvement in patients with PsA and to develop classification criteria and a unified nomenclature for axial involvement in PsA that would allow defining a homogeneous subgroup of patients for research.”
Stay tuned.
Dr. Gladman’s research is supported by a grant from the Krembil Foundation. Dr. Singh disclosed research support from various companies. Funding sources and conflict of interest disclosures from other works cited are contained in their respective references.
The breathtaking effects of climate change
To see the harmful effects of climate change firsthand, you need look no farther than the nearest pulmonary clinic.
The causes and effects are unmistakable: pollen storms leading to allergy sufferers flooding into allergists’ offices; rising air pollution levels increasing risk for obstructive airway diseases, cardiopulmonary complications, and non–small cell lung cancer; melting snowpacks and atmospheric rivers inundating neighborhoods and leaving moldy debris and incipient fungal infections in their wake.
“The reason why we think climate change is going to change the type of disease patterns and the severity of illness that we see in patients with respiratory diseases is that it changes a lot of the environment as well as the exposures,” said Bathmapriya Balakrishnan, BMedSci, BMBS, from the section of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine in the department of medicine at West Virginia University, Morgantown.
“What we’re going to see is not just new diseases but also exacerbation of chronic diseases, things like asthma [and] COPD. And there’s also concern that patients who are otherwise healthy, because they now have more exposures that are due to climate change, can then develop these diseases,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Balakrishnan is the lead author of a comprehensive, evidence-based review focused on the effects of climate change and air pollution across the spectrum of pulmonary disorders. The review is published online ahead of print in the journal Chest.
“ To inform health care providers of evidence-based methods and improve patient counselling, further research regarding measures that limit exposure is needed. Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality and minimize exposure is a key preventative measure for decreasing morbidity and mortality while improving quality of life,” Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues write.
Similarly, in a statement on the effects of climate change on respiratory health, the American Public Health Association succinctly summarized the problem: “Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in pollutants and allergens. Poor air quality leads to reduced lung function, increased risk of asthma complications, heart attacks, heart failure, and death. Air pollution and allergens are the main exposures affecting lung and heart health in this changing climate.”
Early spring
Stanley Fineman, MD, MBA, a past president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology and an allergist in private practice in Atlanta, has seen firsthand how global warming and an earlier start to spring allergy season is affecting his patients.
“The season, at least in our area metro Atlanta, started earlier and has been lasting longer. The pollen counts are very high,” he told this news organization.
“In February we started seeing pollen counts over 1,000 [grams per cubic meter], which is unheard of, and in March about half the days we counted levels that were over 1,000, which is also unheard of. In April it was over 1,000 almost half the days.”
Dr. Fineman and colleagues both in Atlanta and across the country have reported sharp increases in the proportion of new adult patients and in existing patients who have experienced exacerbation of previously mild disease.
“Probably what’s happened is that they may have had some allergic sensitivity that resulted in milder manifestations, but this year they’re getting major manifestations,” Dr. Fineman said.
In a 2014 article in the journal European Respiratory Review, Gennaro D’Amato, MD, from High Speciality Hospital Antonio Cardarelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues outlined the main effects of climate on pollen levels: “1) an increase in plant growth and faster plant growth; 2) an increase in the amount of pollen produced by each plant; 3) an increase in the amount of allergenic proteins contained in pollen; 4) an increase in the start time of plant growth and, therefore, the start of pollen production; 5) an earlier and longer pollen season; 6) change in the geospatial distribution of pollen, that is plant ranges and long-distance atmospheric transport moving polewards,” they write.
Bad air
In addition to pollen, the ambient air in many places is increasingly becoming saturated with bioallergenic proteins such as bacteria, viruses, animal dander, insects, molds, and plant species, Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues noted, adding that “atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide have also been found to increase pollen productivity. These changes result in greater over-the-counter medication use, emergency department visits, and outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses.”
The rash of violent storms that has washed over much of the United States in recent months is also likely to increase the incidence of so-called “thunderstorm asthma,” caused when large quantities of respirable particulate matter are released before or during a thunderstorm.
Air pollution from the burning of carbon-based fuels and from wildfires sparked by hotter and drier conditions increase airborne particulate matter that can seriously exacerbate asthma, COPD, and other obstructive airway conditions.
In addition, as previously reported by Medscape, exposure to particulate matter has been implicated as a possible cause of non–small cell lung cancer in persons who have never smoked.
Critical care challenges
Among the myriad other effects of climate change postulated in evidence enumerated by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues are chest infections and pleural diseases, such as aspergillosis infections that occur after catastrophic flooding; increased incidence of Mycobacterium avium complex infections and hypersensitivity pneumonitis; increased demands on critical care specialists from natural disasters; pollution-induced cardiac arrest; and heat prostration and heat stroke from increasingly prevalent heat waves.
The reviewers also examined evidence suggesting links between climate change and pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, sleep disorders, and occupational pulmonary disorders.
Power to the patients
“Pulmonologists should counsel patients on ways to minimize outdoor and indoor pollution, using tight-fitting respirators and home air-purifying systems without encroaching on patients’ beliefs and choices,” the authors advise.
“Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality daily, in inclement weather, and during disasters would help minimize exposure and thus improve overall health. The pulmonologist can play an important role in emphasizing the impact of climate change on pulmonary disorders during patient care encounters,” they write.
Ms. Balakrishan adds that another important mitigation measure that can be taken today is education.
“In medical school we don’t really learn about the impact of climate change – at least in my generation of physicians, climate change or global warming weren’t part of the medical curriculum – but now I think that there’s a lot of advocacy work being done by medical students who actually want more education on climate change and its effects on pulmonary diseases,” she said.
The study by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues was unfunded. Ms. Balakrishnan reports no relevant financial relationships. Co-author Mary-Beth Scholand, MD, has received personal fees from serving on advisory boards and speakers bureaus for Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Veracyte, and United Therapeutics. Co-author Sean Callahan, MD, has received personal fees for serving on advisory boards for Gilead and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Fineman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
To see the harmful effects of climate change firsthand, you need look no farther than the nearest pulmonary clinic.
The causes and effects are unmistakable: pollen storms leading to allergy sufferers flooding into allergists’ offices; rising air pollution levels increasing risk for obstructive airway diseases, cardiopulmonary complications, and non–small cell lung cancer; melting snowpacks and atmospheric rivers inundating neighborhoods and leaving moldy debris and incipient fungal infections in their wake.
“The reason why we think climate change is going to change the type of disease patterns and the severity of illness that we see in patients with respiratory diseases is that it changes a lot of the environment as well as the exposures,” said Bathmapriya Balakrishnan, BMedSci, BMBS, from the section of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine in the department of medicine at West Virginia University, Morgantown.
“What we’re going to see is not just new diseases but also exacerbation of chronic diseases, things like asthma [and] COPD. And there’s also concern that patients who are otherwise healthy, because they now have more exposures that are due to climate change, can then develop these diseases,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Balakrishnan is the lead author of a comprehensive, evidence-based review focused on the effects of climate change and air pollution across the spectrum of pulmonary disorders. The review is published online ahead of print in the journal Chest.
“ To inform health care providers of evidence-based methods and improve patient counselling, further research regarding measures that limit exposure is needed. Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality and minimize exposure is a key preventative measure for decreasing morbidity and mortality while improving quality of life,” Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues write.
Similarly, in a statement on the effects of climate change on respiratory health, the American Public Health Association succinctly summarized the problem: “Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in pollutants and allergens. Poor air quality leads to reduced lung function, increased risk of asthma complications, heart attacks, heart failure, and death. Air pollution and allergens are the main exposures affecting lung and heart health in this changing climate.”
Early spring
Stanley Fineman, MD, MBA, a past president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology and an allergist in private practice in Atlanta, has seen firsthand how global warming and an earlier start to spring allergy season is affecting his patients.
“The season, at least in our area metro Atlanta, started earlier and has been lasting longer. The pollen counts are very high,” he told this news organization.
“In February we started seeing pollen counts over 1,000 [grams per cubic meter], which is unheard of, and in March about half the days we counted levels that were over 1,000, which is also unheard of. In April it was over 1,000 almost half the days.”
Dr. Fineman and colleagues both in Atlanta and across the country have reported sharp increases in the proportion of new adult patients and in existing patients who have experienced exacerbation of previously mild disease.
“Probably what’s happened is that they may have had some allergic sensitivity that resulted in milder manifestations, but this year they’re getting major manifestations,” Dr. Fineman said.
In a 2014 article in the journal European Respiratory Review, Gennaro D’Amato, MD, from High Speciality Hospital Antonio Cardarelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues outlined the main effects of climate on pollen levels: “1) an increase in plant growth and faster plant growth; 2) an increase in the amount of pollen produced by each plant; 3) an increase in the amount of allergenic proteins contained in pollen; 4) an increase in the start time of plant growth and, therefore, the start of pollen production; 5) an earlier and longer pollen season; 6) change in the geospatial distribution of pollen, that is plant ranges and long-distance atmospheric transport moving polewards,” they write.
Bad air
In addition to pollen, the ambient air in many places is increasingly becoming saturated with bioallergenic proteins such as bacteria, viruses, animal dander, insects, molds, and plant species, Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues noted, adding that “atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide have also been found to increase pollen productivity. These changes result in greater over-the-counter medication use, emergency department visits, and outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses.”
The rash of violent storms that has washed over much of the United States in recent months is also likely to increase the incidence of so-called “thunderstorm asthma,” caused when large quantities of respirable particulate matter are released before or during a thunderstorm.
Air pollution from the burning of carbon-based fuels and from wildfires sparked by hotter and drier conditions increase airborne particulate matter that can seriously exacerbate asthma, COPD, and other obstructive airway conditions.
In addition, as previously reported by Medscape, exposure to particulate matter has been implicated as a possible cause of non–small cell lung cancer in persons who have never smoked.
Critical care challenges
Among the myriad other effects of climate change postulated in evidence enumerated by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues are chest infections and pleural diseases, such as aspergillosis infections that occur after catastrophic flooding; increased incidence of Mycobacterium avium complex infections and hypersensitivity pneumonitis; increased demands on critical care specialists from natural disasters; pollution-induced cardiac arrest; and heat prostration and heat stroke from increasingly prevalent heat waves.
The reviewers also examined evidence suggesting links between climate change and pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, sleep disorders, and occupational pulmonary disorders.
Power to the patients
“Pulmonologists should counsel patients on ways to minimize outdoor and indoor pollution, using tight-fitting respirators and home air-purifying systems without encroaching on patients’ beliefs and choices,” the authors advise.
“Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality daily, in inclement weather, and during disasters would help minimize exposure and thus improve overall health. The pulmonologist can play an important role in emphasizing the impact of climate change on pulmonary disorders during patient care encounters,” they write.
Ms. Balakrishan adds that another important mitigation measure that can be taken today is education.
“In medical school we don’t really learn about the impact of climate change – at least in my generation of physicians, climate change or global warming weren’t part of the medical curriculum – but now I think that there’s a lot of advocacy work being done by medical students who actually want more education on climate change and its effects on pulmonary diseases,” she said.
The study by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues was unfunded. Ms. Balakrishnan reports no relevant financial relationships. Co-author Mary-Beth Scholand, MD, has received personal fees from serving on advisory boards and speakers bureaus for Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Veracyte, and United Therapeutics. Co-author Sean Callahan, MD, has received personal fees for serving on advisory boards for Gilead and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Fineman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
To see the harmful effects of climate change firsthand, you need look no farther than the nearest pulmonary clinic.
The causes and effects are unmistakable: pollen storms leading to allergy sufferers flooding into allergists’ offices; rising air pollution levels increasing risk for obstructive airway diseases, cardiopulmonary complications, and non–small cell lung cancer; melting snowpacks and atmospheric rivers inundating neighborhoods and leaving moldy debris and incipient fungal infections in their wake.
“The reason why we think climate change is going to change the type of disease patterns and the severity of illness that we see in patients with respiratory diseases is that it changes a lot of the environment as well as the exposures,” said Bathmapriya Balakrishnan, BMedSci, BMBS, from the section of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine in the department of medicine at West Virginia University, Morgantown.
“What we’re going to see is not just new diseases but also exacerbation of chronic diseases, things like asthma [and] COPD. And there’s also concern that patients who are otherwise healthy, because they now have more exposures that are due to climate change, can then develop these diseases,” she said in an interview.
Ms. Balakrishnan is the lead author of a comprehensive, evidence-based review focused on the effects of climate change and air pollution across the spectrum of pulmonary disorders. The review is published online ahead of print in the journal Chest.
“ To inform health care providers of evidence-based methods and improve patient counselling, further research regarding measures that limit exposure is needed. Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality and minimize exposure is a key preventative measure for decreasing morbidity and mortality while improving quality of life,” Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues write.
Similarly, in a statement on the effects of climate change on respiratory health, the American Public Health Association succinctly summarized the problem: “Warmer temperatures lead to an increase in pollutants and allergens. Poor air quality leads to reduced lung function, increased risk of asthma complications, heart attacks, heart failure, and death. Air pollution and allergens are the main exposures affecting lung and heart health in this changing climate.”
Early spring
Stanley Fineman, MD, MBA, a past president of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology and an allergist in private practice in Atlanta, has seen firsthand how global warming and an earlier start to spring allergy season is affecting his patients.
“The season, at least in our area metro Atlanta, started earlier and has been lasting longer. The pollen counts are very high,” he told this news organization.
“In February we started seeing pollen counts over 1,000 [grams per cubic meter], which is unheard of, and in March about half the days we counted levels that were over 1,000, which is also unheard of. In April it was over 1,000 almost half the days.”
Dr. Fineman and colleagues both in Atlanta and across the country have reported sharp increases in the proportion of new adult patients and in existing patients who have experienced exacerbation of previously mild disease.
“Probably what’s happened is that they may have had some allergic sensitivity that resulted in milder manifestations, but this year they’re getting major manifestations,” Dr. Fineman said.
In a 2014 article in the journal European Respiratory Review, Gennaro D’Amato, MD, from High Speciality Hospital Antonio Cardarelli, Naples, Italy, and colleagues outlined the main effects of climate on pollen levels: “1) an increase in plant growth and faster plant growth; 2) an increase in the amount of pollen produced by each plant; 3) an increase in the amount of allergenic proteins contained in pollen; 4) an increase in the start time of plant growth and, therefore, the start of pollen production; 5) an earlier and longer pollen season; 6) change in the geospatial distribution of pollen, that is plant ranges and long-distance atmospheric transport moving polewards,” they write.
Bad air
In addition to pollen, the ambient air in many places is increasingly becoming saturated with bioallergenic proteins such as bacteria, viruses, animal dander, insects, molds, and plant species, Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues noted, adding that “atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide have also been found to increase pollen productivity. These changes result in greater over-the-counter medication use, emergency department visits, and outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses.”
The rash of violent storms that has washed over much of the United States in recent months is also likely to increase the incidence of so-called “thunderstorm asthma,” caused when large quantities of respirable particulate matter are released before or during a thunderstorm.
Air pollution from the burning of carbon-based fuels and from wildfires sparked by hotter and drier conditions increase airborne particulate matter that can seriously exacerbate asthma, COPD, and other obstructive airway conditions.
In addition, as previously reported by Medscape, exposure to particulate matter has been implicated as a possible cause of non–small cell lung cancer in persons who have never smoked.
Critical care challenges
Among the myriad other effects of climate change postulated in evidence enumerated by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues are chest infections and pleural diseases, such as aspergillosis infections that occur after catastrophic flooding; increased incidence of Mycobacterium avium complex infections and hypersensitivity pneumonitis; increased demands on critical care specialists from natural disasters; pollution-induced cardiac arrest; and heat prostration and heat stroke from increasingly prevalent heat waves.
The reviewers also examined evidence suggesting links between climate change and pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, sleep disorders, and occupational pulmonary disorders.
Power to the patients
“Pulmonologists should counsel patients on ways to minimize outdoor and indoor pollution, using tight-fitting respirators and home air-purifying systems without encroaching on patients’ beliefs and choices,” the authors advise.
“Empowering patients with resources to monitor air quality daily, in inclement weather, and during disasters would help minimize exposure and thus improve overall health. The pulmonologist can play an important role in emphasizing the impact of climate change on pulmonary disorders during patient care encounters,” they write.
Ms. Balakrishan adds that another important mitigation measure that can be taken today is education.
“In medical school we don’t really learn about the impact of climate change – at least in my generation of physicians, climate change or global warming weren’t part of the medical curriculum – but now I think that there’s a lot of advocacy work being done by medical students who actually want more education on climate change and its effects on pulmonary diseases,” she said.
The study by Ms. Balakrishnan and colleagues was unfunded. Ms. Balakrishnan reports no relevant financial relationships. Co-author Mary-Beth Scholand, MD, has received personal fees from serving on advisory boards and speakers bureaus for Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim, Veracyte, and United Therapeutics. Co-author Sean Callahan, MD, has received personal fees for serving on advisory boards for Gilead and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Fineman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Scarred med student inspired by dermatologist who treated her
It’s not uncommon for a medical student to change specialty plans. For Jamie Harris, a second-year student at the University of Florida School of Medicine, Gainesville, that decision came as the result of a vicious dog and an empathetic doctor.
, a New York dermatologist whose approach involves early and aggressive treatment. After treating her, Dr. Bhanusali offered to have Ms. Harris shadow him.
She returned to school to shadow other dermatologists and to research the specialty before taking Dr. Bhanusali up on his offer. Ms. Harris sat in on procedures and meetings with patients and studied Dr. Bhanusali’s approach to the specialty. “I just fell in love with dermatology,” Ms. Harris told this news organization. “I knew that what I wanted for my own career was exactly how he runs his practice and how he treats patients.”
Life-changing injury
In 2020, Ms. Harris was a sophomore in the University of Florida’s medical honors program, an accelerated track that allows students to earn both a bachelor of science degree and a doctor of medicine degree in 7 years. She had finished studying at a friend’s apartment and was watching television when the rescue dog the friend adopted lunged at Ms. Harris, biting her on the face. “I was just cowering in the corner of the couch,” she recalls. “I didn’t go into fight-or-flight mode; I just went into hide mode.”
After receiving stitches in the emergency department, she visited several dermatologists and plastic surgeons for further treatment. There was scarring from her forehead to her chin, which was particularly severe on her upper cheek just under her eye. But because there was no infection or medical problems, the doctors turned her away. “They said, ‘OK, you look great.’ I did not look great,” she said.
Ms. Harris’ doctors advised her to wait a year before starting treatment for the scarring, a traditional approach. She was frustrated. “At the time, I was interested in becoming a pediatrician and thought, ‘No kid is going to want me as their doctor.’ ” But she accepted the medical advice – until her mother remembered a news story she’d seen.
Bridger Walker, a 6-year-old Wyoming boy, made headlines when he saved his younger sister from a dog that was attacking, but he was bitten multiple times as a result. Dr. Bhanusali treated the boy’s scarring.
Ms. Harris and her mother contacted the doctor, and after meeting via Zoom, Dr. Bhanusali agreed to treat her right away. He used lasers to resurface the skin, which created a suitable foundation for the scar cream, and he administered steroid injections to soften the scar tissue.
‘I see you’
Dr. Bhansali said he was impressed with the young student he treated. “There’s curiosity, and then there’s genuine passion. She has the latter,” he said in an interview. “Having gone through this, she will understand the value of research and keeping up with the literature and that just because something is being done a certain way today doesn’t mean it has to be that way tomorrow.”
Ms. Harris agrees that the experience will make her a better dermatologist. “One of the best parts about dermatology is that you can see your results in real time and really see what’s working and what’s not working. The potential for innovation is just amazing.”
But Ms. Harris believes she also gained empathy with dermatology patients. “I know exactly what it’s like to look in the mirror and not even recognize yourself, just have your eyes go straight to one thing and feel like the whole world is staring at you,” she said. “I’ll be able to reassure people that no matter what their concern is, whether it’s eczema or acne, whether it’s one pimple, I see you, and I know exactly how that feels.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not uncommon for a medical student to change specialty plans. For Jamie Harris, a second-year student at the University of Florida School of Medicine, Gainesville, that decision came as the result of a vicious dog and an empathetic doctor.
, a New York dermatologist whose approach involves early and aggressive treatment. After treating her, Dr. Bhanusali offered to have Ms. Harris shadow him.
She returned to school to shadow other dermatologists and to research the specialty before taking Dr. Bhanusali up on his offer. Ms. Harris sat in on procedures and meetings with patients and studied Dr. Bhanusali’s approach to the specialty. “I just fell in love with dermatology,” Ms. Harris told this news organization. “I knew that what I wanted for my own career was exactly how he runs his practice and how he treats patients.”

Life-changing injury
In 2020, Ms. Harris was a sophomore in the University of Florida’s medical honors program, an accelerated track that allows students to earn both a bachelor of science degree and a doctor of medicine degree in 7 years. She had finished studying at a friend’s apartment and was watching television when the rescue dog the friend adopted lunged at Ms. Harris, biting her on the face. “I was just cowering in the corner of the couch,” she recalls. “I didn’t go into fight-or-flight mode; I just went into hide mode.”
After receiving stitches in the emergency department, she visited several dermatologists and plastic surgeons for further treatment. There was scarring from her forehead to her chin, which was particularly severe on her upper cheek just under her eye. But because there was no infection or medical problems, the doctors turned her away. “They said, ‘OK, you look great.’ I did not look great,” she said.
Ms. Harris’ doctors advised her to wait a year before starting treatment for the scarring, a traditional approach. She was frustrated. “At the time, I was interested in becoming a pediatrician and thought, ‘No kid is going to want me as their doctor.’ ” But she accepted the medical advice – until her mother remembered a news story she’d seen.
Bridger Walker, a 6-year-old Wyoming boy, made headlines when he saved his younger sister from a dog that was attacking, but he was bitten multiple times as a result. Dr. Bhanusali treated the boy’s scarring.
Ms. Harris and her mother contacted the doctor, and after meeting via Zoom, Dr. Bhanusali agreed to treat her right away. He used lasers to resurface the skin, which created a suitable foundation for the scar cream, and he administered steroid injections to soften the scar tissue.
‘I see you’
Dr. Bhansali said he was impressed with the young student he treated. “There’s curiosity, and then there’s genuine passion. She has the latter,” he said in an interview. “Having gone through this, she will understand the value of research and keeping up with the literature and that just because something is being done a certain way today doesn’t mean it has to be that way tomorrow.”
Ms. Harris agrees that the experience will make her a better dermatologist. “One of the best parts about dermatology is that you can see your results in real time and really see what’s working and what’s not working. The potential for innovation is just amazing.”
But Ms. Harris believes she also gained empathy with dermatology patients. “I know exactly what it’s like to look in the mirror and not even recognize yourself, just have your eyes go straight to one thing and feel like the whole world is staring at you,” she said. “I’ll be able to reassure people that no matter what their concern is, whether it’s eczema or acne, whether it’s one pimple, I see you, and I know exactly how that feels.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s not uncommon for a medical student to change specialty plans. For Jamie Harris, a second-year student at the University of Florida School of Medicine, Gainesville, that decision came as the result of a vicious dog and an empathetic doctor.
, a New York dermatologist whose approach involves early and aggressive treatment. After treating her, Dr. Bhanusali offered to have Ms. Harris shadow him.
She returned to school to shadow other dermatologists and to research the specialty before taking Dr. Bhanusali up on his offer. Ms. Harris sat in on procedures and meetings with patients and studied Dr. Bhanusali’s approach to the specialty. “I just fell in love with dermatology,” Ms. Harris told this news organization. “I knew that what I wanted for my own career was exactly how he runs his practice and how he treats patients.”

Life-changing injury
In 2020, Ms. Harris was a sophomore in the University of Florida’s medical honors program, an accelerated track that allows students to earn both a bachelor of science degree and a doctor of medicine degree in 7 years. She had finished studying at a friend’s apartment and was watching television when the rescue dog the friend adopted lunged at Ms. Harris, biting her on the face. “I was just cowering in the corner of the couch,” she recalls. “I didn’t go into fight-or-flight mode; I just went into hide mode.”
After receiving stitches in the emergency department, she visited several dermatologists and plastic surgeons for further treatment. There was scarring from her forehead to her chin, which was particularly severe on her upper cheek just under her eye. But because there was no infection or medical problems, the doctors turned her away. “They said, ‘OK, you look great.’ I did not look great,” she said.
Ms. Harris’ doctors advised her to wait a year before starting treatment for the scarring, a traditional approach. She was frustrated. “At the time, I was interested in becoming a pediatrician and thought, ‘No kid is going to want me as their doctor.’ ” But she accepted the medical advice – until her mother remembered a news story she’d seen.
Bridger Walker, a 6-year-old Wyoming boy, made headlines when he saved his younger sister from a dog that was attacking, but he was bitten multiple times as a result. Dr. Bhanusali treated the boy’s scarring.
Ms. Harris and her mother contacted the doctor, and after meeting via Zoom, Dr. Bhanusali agreed to treat her right away. He used lasers to resurface the skin, which created a suitable foundation for the scar cream, and he administered steroid injections to soften the scar tissue.
‘I see you’
Dr. Bhansali said he was impressed with the young student he treated. “There’s curiosity, and then there’s genuine passion. She has the latter,” he said in an interview. “Having gone through this, she will understand the value of research and keeping up with the literature and that just because something is being done a certain way today doesn’t mean it has to be that way tomorrow.”
Ms. Harris agrees that the experience will make her a better dermatologist. “One of the best parts about dermatology is that you can see your results in real time and really see what’s working and what’s not working. The potential for innovation is just amazing.”
But Ms. Harris believes she also gained empathy with dermatology patients. “I know exactly what it’s like to look in the mirror and not even recognize yourself, just have your eyes go straight to one thing and feel like the whole world is staring at you,” she said. “I’ll be able to reassure people that no matter what their concern is, whether it’s eczema or acne, whether it’s one pimple, I see you, and I know exactly how that feels.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical-level empathy? Yup, ChatGPT can fake that
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Researchers seek to understand post-COVID autoimmune disease risk
Since the COVID-19 pandemic started more than 3 years ago, the longer-lasting effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection have continued to reveal themselves. Approximately 28% of Americans report having ever experienced post-COVID conditions, such as brain fog, postexertional malaise, and joint pain, and 11% say they are still experiencing these long-term effects. Now, new research is showing that people who have had COVID are more likely to newly develop an autoimmune disease. Exactly why this is happening is less clear, experts say.
Two preprint studies and one study published in a peer-reviewed journal provide strong evidence that patients who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 are at elevated risk of developing an autoimmune disease. The studies retrospectively reviewed medical records from three countries and compared the incidence of new-onset autoimmune disease among patients who had polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 and those who had never been diagnosed with the virus.
A study analyzing the health records of 3.8 million U.S. patients – more than 888,460 with confirmed COVID-19 – found that the COVID-19 group was two to three times as likely to develop various autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and systemic sclerosis. A U.K. preprint study that included more than 458,000 people with confirmed COVID found that those who had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2 were 22% more likely to develop an autoimmune disease compared with the control group. In this cohort, the diseases most strongly associated with COVID-19 were type 1 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis. A preprint study from German researchers found that COVID-19 patients were almost 43% more likely to develop an autoimmune disease, compared with those who had never been infected. COVID-19 was most strongly linked to vasculitis.
These large studies are telling us, “Yes, this link is there, so we have to accept it,” Sonia Sharma, PhD, of the Center for Autoimmunity and Inflammation at the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology, told this news organization. But this is not the first time that autoimmune diseases have been linked to previous infections.
Researchers have known for decades that Epstein-Barr virus infection is linked to several autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. More recent research suggests the virus may activate certain genes associated with these immune disorders. Hepatitis C virus can induce cryoglobulinemia, and infection with cytomegalovirus has been implicated in several autoimmune diseases. Bacterial infections have also been linked to autoimmunity, such as group A streptococcus and rheumatic fever, as well as salmonella and reactive arthritis, to name only a few.
“In a way, this isn’t necessarily a new concept to physicians, particularly rheumatologists,” said Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “There’s a fine line between appropriately clearing an infection and the body overreacting and setting off a cascade where the immune system is chronically overactive that can manifest as an autoimmune disease,” he told this news organization.
A dysregulated response to infection
It takes the immune system a week or two to develop antigen-specific antibodies to a new pathogen. But for patients with serious infections – in this instance, COVID-19 – that’s time they don’t have. Therefore, the immune system has an alternative pathway, called extrafollicular activation, that creates fast-acting antibodies, explained Matthew Woodruff, PhD, an instructor of immunology and rheumatology at Emory University, Atlanta.
The trade-off is that these antibodies are not as specific and can target the body’s own tissues. This dysregulation of antibody selection is generally short lived and fades when more targeted antibodies are produced and take over, but in some cases, this process can lead to high levels of self-targeting antibodies that can harm the body’s organs and tissues. Research also suggests that for patients who experience long COVID, the same autoantibodies that drive the initial immune response are detectable in the body months after infection, though it is not known whether these lingering immune cells cause these longer-lasting symptoms.
“If you have a virus that causes hyperinflammation plus organ damage, that is a recipe for disaster,” Dr. Sharma said. “It’s a recipe for autoantibodies and autoreactive T cells that down the road can attack the body’s own tissues, especially in people whose immune system is trained in such a way to cause self-reactivity,” she added.
This hyperinflammation can result in rare but serious complications, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adults, which can occur 2-6 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection. But even in these patients with severe illness, organ-specific complications tend to resolve in 6 months with “no significant sequelae 1 year after diagnosis,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. And while long COVID can last for a year or longer, data suggest that symptoms do eventually resolve for most people. What is not clear is why acute autoimmunity triggered by COVID-19 can become a chronic condition in certain patients.
Predisposition to autoimmunity
P. J. Utz, MD, PhD, professor of immunology and rheumatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that people who develop autoimmune disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection may have already been predisposed toward autoimmunity. Especially for autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and lupus, autoantibodies can appear and circulate in the body for more than a decade in some people before they present with any clinical symptoms. “Their immune system is primed such that if they get infected with something – or they have some other environmental trigger that maybe we don’t know about yet – that is enough to then push them over the edge so that they get full-blown autoimmunity,” he said. What is not known is whether these patients’ conditions would have advanced to true clinical disease had they not been infected, he said.
He also noted that the presence of autoantibodies does not necessarily mean someone has autoimmune disease; healthy people can also have autoantibodies, and everyone develops them with age. “My advice would be, ‘Don’t lose sleep over this,’ “ he said.
Dr. Sparks agreed that while these retrospective studies did show an elevated risk of autoimmune disease after COVID-19, that risk appears to be relatively small. “As a practicing rheumatologist, we aren’t seeing a stampede of patients with new-onset rheumatic diseases,” he said. “It’s not like we’re overwhelmed with autoimmune patients, even though almost everyone’s had COVID. So, if there is a risk, it’s very modest.”
Dr. Sparks is supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Utz receives research funding from Pfizer. Dr. Sharma and Dr. Woodruff have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic started more than 3 years ago, the longer-lasting effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection have continued to reveal themselves. Approximately 28% of Americans report having ever experienced post-COVID conditions, such as brain fog, postexertional malaise, and joint pain, and 11% say they are still experiencing these long-term effects. Now, new research is showing that people who have had COVID are more likely to newly develop an autoimmune disease. Exactly why this is happening is less clear, experts say.
Two preprint studies and one study published in a peer-reviewed journal provide strong evidence that patients who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 are at elevated risk of developing an autoimmune disease. The studies retrospectively reviewed medical records from three countries and compared the incidence of new-onset autoimmune disease among patients who had polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 and those who had never been diagnosed with the virus.
A study analyzing the health records of 3.8 million U.S. patients – more than 888,460 with confirmed COVID-19 – found that the COVID-19 group was two to three times as likely to develop various autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and systemic sclerosis. A U.K. preprint study that included more than 458,000 people with confirmed COVID found that those who had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2 were 22% more likely to develop an autoimmune disease compared with the control group. In this cohort, the diseases most strongly associated with COVID-19 were type 1 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis. A preprint study from German researchers found that COVID-19 patients were almost 43% more likely to develop an autoimmune disease, compared with those who had never been infected. COVID-19 was most strongly linked to vasculitis.
These large studies are telling us, “Yes, this link is there, so we have to accept it,” Sonia Sharma, PhD, of the Center for Autoimmunity and Inflammation at the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology, told this news organization. But this is not the first time that autoimmune diseases have been linked to previous infections.
Researchers have known for decades that Epstein-Barr virus infection is linked to several autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. More recent research suggests the virus may activate certain genes associated with these immune disorders. Hepatitis C virus can induce cryoglobulinemia, and infection with cytomegalovirus has been implicated in several autoimmune diseases. Bacterial infections have also been linked to autoimmunity, such as group A streptococcus and rheumatic fever, as well as salmonella and reactive arthritis, to name only a few.
“In a way, this isn’t necessarily a new concept to physicians, particularly rheumatologists,” said Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “There’s a fine line between appropriately clearing an infection and the body overreacting and setting off a cascade where the immune system is chronically overactive that can manifest as an autoimmune disease,” he told this news organization.
A dysregulated response to infection
It takes the immune system a week or two to develop antigen-specific antibodies to a new pathogen. But for patients with serious infections – in this instance, COVID-19 – that’s time they don’t have. Therefore, the immune system has an alternative pathway, called extrafollicular activation, that creates fast-acting antibodies, explained Matthew Woodruff, PhD, an instructor of immunology and rheumatology at Emory University, Atlanta.
The trade-off is that these antibodies are not as specific and can target the body’s own tissues. This dysregulation of antibody selection is generally short lived and fades when more targeted antibodies are produced and take over, but in some cases, this process can lead to high levels of self-targeting antibodies that can harm the body’s organs and tissues. Research also suggests that for patients who experience long COVID, the same autoantibodies that drive the initial immune response are detectable in the body months after infection, though it is not known whether these lingering immune cells cause these longer-lasting symptoms.
“If you have a virus that causes hyperinflammation plus organ damage, that is a recipe for disaster,” Dr. Sharma said. “It’s a recipe for autoantibodies and autoreactive T cells that down the road can attack the body’s own tissues, especially in people whose immune system is trained in such a way to cause self-reactivity,” she added.
This hyperinflammation can result in rare but serious complications, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adults, which can occur 2-6 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection. But even in these patients with severe illness, organ-specific complications tend to resolve in 6 months with “no significant sequelae 1 year after diagnosis,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. And while long COVID can last for a year or longer, data suggest that symptoms do eventually resolve for most people. What is not clear is why acute autoimmunity triggered by COVID-19 can become a chronic condition in certain patients.
Predisposition to autoimmunity
P. J. Utz, MD, PhD, professor of immunology and rheumatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that people who develop autoimmune disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection may have already been predisposed toward autoimmunity. Especially for autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and lupus, autoantibodies can appear and circulate in the body for more than a decade in some people before they present with any clinical symptoms. “Their immune system is primed such that if they get infected with something – or they have some other environmental trigger that maybe we don’t know about yet – that is enough to then push them over the edge so that they get full-blown autoimmunity,” he said. What is not known is whether these patients’ conditions would have advanced to true clinical disease had they not been infected, he said.
He also noted that the presence of autoantibodies does not necessarily mean someone has autoimmune disease; healthy people can also have autoantibodies, and everyone develops them with age. “My advice would be, ‘Don’t lose sleep over this,’ “ he said.
Dr. Sparks agreed that while these retrospective studies did show an elevated risk of autoimmune disease after COVID-19, that risk appears to be relatively small. “As a practicing rheumatologist, we aren’t seeing a stampede of patients with new-onset rheumatic diseases,” he said. “It’s not like we’re overwhelmed with autoimmune patients, even though almost everyone’s had COVID. So, if there is a risk, it’s very modest.”
Dr. Sparks is supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Utz receives research funding from Pfizer. Dr. Sharma and Dr. Woodruff have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic started more than 3 years ago, the longer-lasting effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection have continued to reveal themselves. Approximately 28% of Americans report having ever experienced post-COVID conditions, such as brain fog, postexertional malaise, and joint pain, and 11% say they are still experiencing these long-term effects. Now, new research is showing that people who have had COVID are more likely to newly develop an autoimmune disease. Exactly why this is happening is less clear, experts say.
Two preprint studies and one study published in a peer-reviewed journal provide strong evidence that patients who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 are at elevated risk of developing an autoimmune disease. The studies retrospectively reviewed medical records from three countries and compared the incidence of new-onset autoimmune disease among patients who had polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 and those who had never been diagnosed with the virus.
A study analyzing the health records of 3.8 million U.S. patients – more than 888,460 with confirmed COVID-19 – found that the COVID-19 group was two to three times as likely to develop various autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and systemic sclerosis. A U.K. preprint study that included more than 458,000 people with confirmed COVID found that those who had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2 were 22% more likely to develop an autoimmune disease compared with the control group. In this cohort, the diseases most strongly associated with COVID-19 were type 1 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis. A preprint study from German researchers found that COVID-19 patients were almost 43% more likely to develop an autoimmune disease, compared with those who had never been infected. COVID-19 was most strongly linked to vasculitis.
These large studies are telling us, “Yes, this link is there, so we have to accept it,” Sonia Sharma, PhD, of the Center for Autoimmunity and Inflammation at the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology, told this news organization. But this is not the first time that autoimmune diseases have been linked to previous infections.
Researchers have known for decades that Epstein-Barr virus infection is linked to several autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. More recent research suggests the virus may activate certain genes associated with these immune disorders. Hepatitis C virus can induce cryoglobulinemia, and infection with cytomegalovirus has been implicated in several autoimmune diseases. Bacterial infections have also been linked to autoimmunity, such as group A streptococcus and rheumatic fever, as well as salmonella and reactive arthritis, to name only a few.
“In a way, this isn’t necessarily a new concept to physicians, particularly rheumatologists,” said Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “There’s a fine line between appropriately clearing an infection and the body overreacting and setting off a cascade where the immune system is chronically overactive that can manifest as an autoimmune disease,” he told this news organization.
A dysregulated response to infection
It takes the immune system a week or two to develop antigen-specific antibodies to a new pathogen. But for patients with serious infections – in this instance, COVID-19 – that’s time they don’t have. Therefore, the immune system has an alternative pathway, called extrafollicular activation, that creates fast-acting antibodies, explained Matthew Woodruff, PhD, an instructor of immunology and rheumatology at Emory University, Atlanta.
The trade-off is that these antibodies are not as specific and can target the body’s own tissues. This dysregulation of antibody selection is generally short lived and fades when more targeted antibodies are produced and take over, but in some cases, this process can lead to high levels of self-targeting antibodies that can harm the body’s organs and tissues. Research also suggests that for patients who experience long COVID, the same autoantibodies that drive the initial immune response are detectable in the body months after infection, though it is not known whether these lingering immune cells cause these longer-lasting symptoms.
“If you have a virus that causes hyperinflammation plus organ damage, that is a recipe for disaster,” Dr. Sharma said. “It’s a recipe for autoantibodies and autoreactive T cells that down the road can attack the body’s own tissues, especially in people whose immune system is trained in such a way to cause self-reactivity,” she added.
This hyperinflammation can result in rare but serious complications, such as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adults, which can occur 2-6 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection. But even in these patients with severe illness, organ-specific complications tend to resolve in 6 months with “no significant sequelae 1 year after diagnosis,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. And while long COVID can last for a year or longer, data suggest that symptoms do eventually resolve for most people. What is not clear is why acute autoimmunity triggered by COVID-19 can become a chronic condition in certain patients.
Predisposition to autoimmunity
P. J. Utz, MD, PhD, professor of immunology and rheumatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that people who develop autoimmune disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection may have already been predisposed toward autoimmunity. Especially for autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and lupus, autoantibodies can appear and circulate in the body for more than a decade in some people before they present with any clinical symptoms. “Their immune system is primed such that if they get infected with something – or they have some other environmental trigger that maybe we don’t know about yet – that is enough to then push them over the edge so that they get full-blown autoimmunity,” he said. What is not known is whether these patients’ conditions would have advanced to true clinical disease had they not been infected, he said.
He also noted that the presence of autoantibodies does not necessarily mean someone has autoimmune disease; healthy people can also have autoantibodies, and everyone develops them with age. “My advice would be, ‘Don’t lose sleep over this,’ “ he said.
Dr. Sparks agreed that while these retrospective studies did show an elevated risk of autoimmune disease after COVID-19, that risk appears to be relatively small. “As a practicing rheumatologist, we aren’t seeing a stampede of patients with new-onset rheumatic diseases,” he said. “It’s not like we’re overwhelmed with autoimmune patients, even though almost everyone’s had COVID. So, if there is a risk, it’s very modest.”
Dr. Sparks is supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Utz receives research funding from Pfizer. Dr. Sharma and Dr. Woodruff have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.