User login
POCUS for hospitalists: The SHM position statement
Background: POCUS is becoming more prevalent in the daily practice of hospitalists; however, there are currently no established standards or guidelines for the use of POCUS for hospitalists.
Study design: Position statement.
Setting: SHM Executive Committee and Multi-Institutional POCUS faculty meeting through the Society of Hospital Medicine 2018 Annual Conference reviewed and approved this statement.
Synopsis: In contrast to the comprehensive ultrasound exam, POCUS is used by hospitalists to answer focused questions, by the same clinician who is generating the clinical question, to evaluate multiple body systems, or to serially investigate changes clinical status or evaluate responses to therapy.
This position statement provides guidance on the use of POCUS by hospitalists and the administrators who oversee it by outlining POCUS in terms of common diagnostic and procedural applications; training; assessments by the categories of basic knowledge, image acquisition, interpretation, clinical integration, and certification and maintenance of skills; and program management.
Bottom line: This position statement by the SHM provides guidance for hospitalists and administrators on the use and oversight of POCUS.
Citation: Soni NJ et al. Point-of-care ultrasound for hospitalists: A position statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. J Hosp Med. 2019 Jan 2;14:E1-E6.
Dr. Wang is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System.
Background: POCUS is becoming more prevalent in the daily practice of hospitalists; however, there are currently no established standards or guidelines for the use of POCUS for hospitalists.
Study design: Position statement.
Setting: SHM Executive Committee and Multi-Institutional POCUS faculty meeting through the Society of Hospital Medicine 2018 Annual Conference reviewed and approved this statement.
Synopsis: In contrast to the comprehensive ultrasound exam, POCUS is used by hospitalists to answer focused questions, by the same clinician who is generating the clinical question, to evaluate multiple body systems, or to serially investigate changes clinical status or evaluate responses to therapy.
This position statement provides guidance on the use of POCUS by hospitalists and the administrators who oversee it by outlining POCUS in terms of common diagnostic and procedural applications; training; assessments by the categories of basic knowledge, image acquisition, interpretation, clinical integration, and certification and maintenance of skills; and program management.
Bottom line: This position statement by the SHM provides guidance for hospitalists and administrators on the use and oversight of POCUS.
Citation: Soni NJ et al. Point-of-care ultrasound for hospitalists: A position statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. J Hosp Med. 2019 Jan 2;14:E1-E6.
Dr. Wang is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System.
Background: POCUS is becoming more prevalent in the daily practice of hospitalists; however, there are currently no established standards or guidelines for the use of POCUS for hospitalists.
Study design: Position statement.
Setting: SHM Executive Committee and Multi-Institutional POCUS faculty meeting through the Society of Hospital Medicine 2018 Annual Conference reviewed and approved this statement.
Synopsis: In contrast to the comprehensive ultrasound exam, POCUS is used by hospitalists to answer focused questions, by the same clinician who is generating the clinical question, to evaluate multiple body systems, or to serially investigate changes clinical status or evaluate responses to therapy.
This position statement provides guidance on the use of POCUS by hospitalists and the administrators who oversee it by outlining POCUS in terms of common diagnostic and procedural applications; training; assessments by the categories of basic knowledge, image acquisition, interpretation, clinical integration, and certification and maintenance of skills; and program management.
Bottom line: This position statement by the SHM provides guidance for hospitalists and administrators on the use and oversight of POCUS.
Citation: Soni NJ et al. Point-of-care ultrasound for hospitalists: A position statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. J Hosp Med. 2019 Jan 2;14:E1-E6.
Dr. Wang is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System.
Effects of hospitalization on readmission rate
Background: There is increasing concern that the patient experience in the hospital may be associated with post-hospital adverse outcomes, including new or recurrent illnesses after discharge or unplanned return to the hospital or readmission.
Study design: Prospective cohort that included 207 patients.
Setting: Two academic hospitals in Toronto.
Synopsis: These patients had been admitted to the internal medicine ward for more than 48 hours and were interviewed at discharge using a standardized questionnaire to assess four domains of the trauma of hospitalization defined as the cumulative effects of patient-reported sleep disturbance, mobility, nutrition, and mood. Among these patients, 64.3% experienced disturbance in more than one domain, and patients who experienced disturbance in three to four domains had a 15.8% greater absolute risk of 30-day readmission or ED visit.
Because this is an observational study, causal inferences were not possible; however, hospitalists should keep in mind the possible association of the patient experience and the link to clinical outcomes.
Bottom line: Trauma of hospitalization is common and may be associated with an increased 30-day risk of readmission or ED visit.
Citation: Rawal J et al. Association of the trauma of hospitalization with 30-day readmission or emergency department visit. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(1):38-45.
Dr. Wang is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System.
Background: There is increasing concern that the patient experience in the hospital may be associated with post-hospital adverse outcomes, including new or recurrent illnesses after discharge or unplanned return to the hospital or readmission.
Study design: Prospective cohort that included 207 patients.
Setting: Two academic hospitals in Toronto.
Synopsis: These patients had been admitted to the internal medicine ward for more than 48 hours and were interviewed at discharge using a standardized questionnaire to assess four domains of the trauma of hospitalization defined as the cumulative effects of patient-reported sleep disturbance, mobility, nutrition, and mood. Among these patients, 64.3% experienced disturbance in more than one domain, and patients who experienced disturbance in three to four domains had a 15.8% greater absolute risk of 30-day readmission or ED visit.
Because this is an observational study, causal inferences were not possible; however, hospitalists should keep in mind the possible association of the patient experience and the link to clinical outcomes.
Bottom line: Trauma of hospitalization is common and may be associated with an increased 30-day risk of readmission or ED visit.
Citation: Rawal J et al. Association of the trauma of hospitalization with 30-day readmission or emergency department visit. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(1):38-45.
Dr. Wang is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System.
Background: There is increasing concern that the patient experience in the hospital may be associated with post-hospital adverse outcomes, including new or recurrent illnesses after discharge or unplanned return to the hospital or readmission.
Study design: Prospective cohort that included 207 patients.
Setting: Two academic hospitals in Toronto.
Synopsis: These patients had been admitted to the internal medicine ward for more than 48 hours and were interviewed at discharge using a standardized questionnaire to assess four domains of the trauma of hospitalization defined as the cumulative effects of patient-reported sleep disturbance, mobility, nutrition, and mood. Among these patients, 64.3% experienced disturbance in more than one domain, and patients who experienced disturbance in three to four domains had a 15.8% greater absolute risk of 30-day readmission or ED visit.
Because this is an observational study, causal inferences were not possible; however, hospitalists should keep in mind the possible association of the patient experience and the link to clinical outcomes.
Bottom line: Trauma of hospitalization is common and may be associated with an increased 30-day risk of readmission or ED visit.
Citation: Rawal J et al. Association of the trauma of hospitalization with 30-day readmission or emergency department visit. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(1):38-45.
Dr. Wang is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System.
Skip supplemental O2 in nonhypoxic ACS
PARIS – A massive randomized trial that included all New Zealanders with a suspected acute coronary syndrome during a 2-year period has provided definitive evidence that giving high-flow supplemental oxygen to those who are nonhypoxemic is of no clinical benefit, although it wasn’t harmful, either.

“Patients who have a normal blood oxygen saturation level are very unlikely to benefit from supplemental oxygen,” Ralph Stewart, MbChB, said in presenting the results of the NZOTACS (New Zealand Oxygen Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes) trial at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“It’s amazing that oxygen has been used in patients with suspected heart attack for over 50 years, and during that time there’s never been definite evidence that it improves outcomes. And more recently some have even suggested giving high-level oxygen might actually cause harm,” observed Dr. Stewart, a cardiologist at Auckland City Hospital and the University of Auckland (New Zealand).
The primary outcome in NZOTACS was 30-day all-cause mortality. In the overall study population, the rate was 3.0% in the group assigned to the routine high-flow oxygen protocol and closely similar at 3.1% in those randomized to the conservative oxygen strategy. And there was reassuringly no signal that the liberal oxygen protocol caused any harm.
To conduct this cluster randomized crossover trial, Dr. Stewart and his coinvestigators divided New Zealand into quadrants and, taking advantage of the coordinated health care systems operative in the nation of 4.8 million, they arranged for all ambulances, emergency departments, and hospitals in each geographic region to utilize each supplemental oxygen strategy for a total of 12 months.
In the liberal oxygen strategy, patients with suspected ACS on the basis of ischemic chest pain or ECG changes received high-flow oxygen by face mask at 6-8 L/min regardless of their blood oxygen saturation (SaO2) level. The oxygen was stopped only upon clinical resolution of myocardial ischemia. In contrast, in the low-oxygen protocol, supplemental oxygen was reserved for patients with an initial SaO2 below 90%, with a target SaO2 of 90%-94%.
Roughly 90% of the nearly 41,000 study participants had a normal SaO2 of 90% or more. Their 30-day mortality was 2.1% with the high-oxygen protocol and similar at 1.9% with the conservative oxygen protocol.
In contrast, there was a suggestion of benefit for the routine liberal oxygen strategy in the subgroup of patients with ST-elevation MI. Their 30-day mortality was 8.8% with high-flow oxygen and 10.6% with the conservative oxygen protocol. The resultant 19% relative risk reduction barely missed statistical significance. There was also a trend for possible benefit of routine high-flow oxygen in the roughly 12% of NZOTACS participants with an SaO2 below 95%, a lower bar than the 90% SaO2 that defines hypoxemia. Their death rate at 30 days was 10.1% if they got supplemental oxygen and 11.1% if they only received oxygen in the event their SaO2 was below 90%. But these exploratory findings must be viewed as hypothesis-generating, and a large confirmatory study would be required, Dr. Stewart noted.
Discussant Robin Hofmann, MD, PhD, commented that, based on the NZOTACS results, he believes a couple of changes to the current ESC guidelines on management of ACS are in order. The guidelines now state that oxygen is indicated in patients with suspected ACS and hypoxemia as defined by an SaO2 below 90%, giving that recommendation a Class I Level of Evidence C. That should now be upgraded to the strongest-possible Class I A recommendation, according to Dr. Hofmann, a cardiologist at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
The ESC guidelines also state that oxygen isn’t routinely recommended in patients with an SaO2 of 90% or more, rating that guidance Class III B. On the basis of NZOTACS coupled with earlier far smaller studies, that should be changed to a Class III A recommendation, meaning simply don’t do it. The hint provided by NZOTACS of a possible small benefit for oxygen in patients with an SaO2 below 95% isn’t strong enough evidence to carry the day, in Dr. Hofmann’s view.
Dr. Stewart and Dr. Hofmann reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The NZOTACS trial was funded by the National Heart Foundation of New Zealand.
SOURCE: Stewart R. ESC 2019, Hotline Session 2.
PARIS – A massive randomized trial that included all New Zealanders with a suspected acute coronary syndrome during a 2-year period has provided definitive evidence that giving high-flow supplemental oxygen to those who are nonhypoxemic is of no clinical benefit, although it wasn’t harmful, either.

“Patients who have a normal blood oxygen saturation level are very unlikely to benefit from supplemental oxygen,” Ralph Stewart, MbChB, said in presenting the results of the NZOTACS (New Zealand Oxygen Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes) trial at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“It’s amazing that oxygen has been used in patients with suspected heart attack for over 50 years, and during that time there’s never been definite evidence that it improves outcomes. And more recently some have even suggested giving high-level oxygen might actually cause harm,” observed Dr. Stewart, a cardiologist at Auckland City Hospital and the University of Auckland (New Zealand).
The primary outcome in NZOTACS was 30-day all-cause mortality. In the overall study population, the rate was 3.0% in the group assigned to the routine high-flow oxygen protocol and closely similar at 3.1% in those randomized to the conservative oxygen strategy. And there was reassuringly no signal that the liberal oxygen protocol caused any harm.
To conduct this cluster randomized crossover trial, Dr. Stewart and his coinvestigators divided New Zealand into quadrants and, taking advantage of the coordinated health care systems operative in the nation of 4.8 million, they arranged for all ambulances, emergency departments, and hospitals in each geographic region to utilize each supplemental oxygen strategy for a total of 12 months.
In the liberal oxygen strategy, patients with suspected ACS on the basis of ischemic chest pain or ECG changes received high-flow oxygen by face mask at 6-8 L/min regardless of their blood oxygen saturation (SaO2) level. The oxygen was stopped only upon clinical resolution of myocardial ischemia. In contrast, in the low-oxygen protocol, supplemental oxygen was reserved for patients with an initial SaO2 below 90%, with a target SaO2 of 90%-94%.
Roughly 90% of the nearly 41,000 study participants had a normal SaO2 of 90% or more. Their 30-day mortality was 2.1% with the high-oxygen protocol and similar at 1.9% with the conservative oxygen protocol.
In contrast, there was a suggestion of benefit for the routine liberal oxygen strategy in the subgroup of patients with ST-elevation MI. Their 30-day mortality was 8.8% with high-flow oxygen and 10.6% with the conservative oxygen protocol. The resultant 19% relative risk reduction barely missed statistical significance. There was also a trend for possible benefit of routine high-flow oxygen in the roughly 12% of NZOTACS participants with an SaO2 below 95%, a lower bar than the 90% SaO2 that defines hypoxemia. Their death rate at 30 days was 10.1% if they got supplemental oxygen and 11.1% if they only received oxygen in the event their SaO2 was below 90%. But these exploratory findings must be viewed as hypothesis-generating, and a large confirmatory study would be required, Dr. Stewart noted.
Discussant Robin Hofmann, MD, PhD, commented that, based on the NZOTACS results, he believes a couple of changes to the current ESC guidelines on management of ACS are in order. The guidelines now state that oxygen is indicated in patients with suspected ACS and hypoxemia as defined by an SaO2 below 90%, giving that recommendation a Class I Level of Evidence C. That should now be upgraded to the strongest-possible Class I A recommendation, according to Dr. Hofmann, a cardiologist at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
The ESC guidelines also state that oxygen isn’t routinely recommended in patients with an SaO2 of 90% or more, rating that guidance Class III B. On the basis of NZOTACS coupled with earlier far smaller studies, that should be changed to a Class III A recommendation, meaning simply don’t do it. The hint provided by NZOTACS of a possible small benefit for oxygen in patients with an SaO2 below 95% isn’t strong enough evidence to carry the day, in Dr. Hofmann’s view.
Dr. Stewart and Dr. Hofmann reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The NZOTACS trial was funded by the National Heart Foundation of New Zealand.
SOURCE: Stewart R. ESC 2019, Hotline Session 2.
PARIS – A massive randomized trial that included all New Zealanders with a suspected acute coronary syndrome during a 2-year period has provided definitive evidence that giving high-flow supplemental oxygen to those who are nonhypoxemic is of no clinical benefit, although it wasn’t harmful, either.

“Patients who have a normal blood oxygen saturation level are very unlikely to benefit from supplemental oxygen,” Ralph Stewart, MbChB, said in presenting the results of the NZOTACS (New Zealand Oxygen Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndromes) trial at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“It’s amazing that oxygen has been used in patients with suspected heart attack for over 50 years, and during that time there’s never been definite evidence that it improves outcomes. And more recently some have even suggested giving high-level oxygen might actually cause harm,” observed Dr. Stewart, a cardiologist at Auckland City Hospital and the University of Auckland (New Zealand).
The primary outcome in NZOTACS was 30-day all-cause mortality. In the overall study population, the rate was 3.0% in the group assigned to the routine high-flow oxygen protocol and closely similar at 3.1% in those randomized to the conservative oxygen strategy. And there was reassuringly no signal that the liberal oxygen protocol caused any harm.
To conduct this cluster randomized crossover trial, Dr. Stewart and his coinvestigators divided New Zealand into quadrants and, taking advantage of the coordinated health care systems operative in the nation of 4.8 million, they arranged for all ambulances, emergency departments, and hospitals in each geographic region to utilize each supplemental oxygen strategy for a total of 12 months.
In the liberal oxygen strategy, patients with suspected ACS on the basis of ischemic chest pain or ECG changes received high-flow oxygen by face mask at 6-8 L/min regardless of their blood oxygen saturation (SaO2) level. The oxygen was stopped only upon clinical resolution of myocardial ischemia. In contrast, in the low-oxygen protocol, supplemental oxygen was reserved for patients with an initial SaO2 below 90%, with a target SaO2 of 90%-94%.
Roughly 90% of the nearly 41,000 study participants had a normal SaO2 of 90% or more. Their 30-day mortality was 2.1% with the high-oxygen protocol and similar at 1.9% with the conservative oxygen protocol.
In contrast, there was a suggestion of benefit for the routine liberal oxygen strategy in the subgroup of patients with ST-elevation MI. Their 30-day mortality was 8.8% with high-flow oxygen and 10.6% with the conservative oxygen protocol. The resultant 19% relative risk reduction barely missed statistical significance. There was also a trend for possible benefit of routine high-flow oxygen in the roughly 12% of NZOTACS participants with an SaO2 below 95%, a lower bar than the 90% SaO2 that defines hypoxemia. Their death rate at 30 days was 10.1% if they got supplemental oxygen and 11.1% if they only received oxygen in the event their SaO2 was below 90%. But these exploratory findings must be viewed as hypothesis-generating, and a large confirmatory study would be required, Dr. Stewart noted.
Discussant Robin Hofmann, MD, PhD, commented that, based on the NZOTACS results, he believes a couple of changes to the current ESC guidelines on management of ACS are in order. The guidelines now state that oxygen is indicated in patients with suspected ACS and hypoxemia as defined by an SaO2 below 90%, giving that recommendation a Class I Level of Evidence C. That should now be upgraded to the strongest-possible Class I A recommendation, according to Dr. Hofmann, a cardiologist at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm.
The ESC guidelines also state that oxygen isn’t routinely recommended in patients with an SaO2 of 90% or more, rating that guidance Class III B. On the basis of NZOTACS coupled with earlier far smaller studies, that should be changed to a Class III A recommendation, meaning simply don’t do it. The hint provided by NZOTACS of a possible small benefit for oxygen in patients with an SaO2 below 95% isn’t strong enough evidence to carry the day, in Dr. Hofmann’s view.
Dr. Stewart and Dr. Hofmann reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The NZOTACS trial was funded by the National Heart Foundation of New Zealand.
SOURCE: Stewart R. ESC 2019, Hotline Session 2.
REPORTING FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2019
Using ultrasound guidance for adult abdominal paracentesis
Background: Abdominal paracentesis is a commonly performed procedure, and with appropriate training, hospitalists can deliver similar outcomes when compared to interventional radiologists.
Study design: Position statement.
Setting: The Society of Hospital Medicine Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) Task Force developed these guidelines after reviewing available literature and voted on the appropriateness and consensus of a recommendation.
Synopsis: A total of 794 articles were screened, and 91 articles were included and incorporated into the recommendations. The 12 recommendations fall into three categories (clinical outcomes, technique, and training), and all 12 recommendations achieved consensus as strong recommendations.
To improve clinical outcomes, the authors recommended ultrasound guidance in performing paracentesis to reduce the risk of serious complications, to avoid attempting paracentesis with insufficient fluid, and to improve overall procedure success.
The authors advocated for several technique recommendations, including using the ultrasound to assess volume and location of intraperitoneal fluid, to identify the needle insertion site and confirm in multiple planes, to use color flow Doppler to identify abdominal wall vessels, to mark the insertion site immediately prior to the procedure, and to consider real-time ultrasound guidance.
When health care professionals are learning ultrasound-guided paracentesis, the authors recommended use of dedicated training sessions with simulation if available and that competency should be demonstrated before independently attempting the procedure.
Bottom line: These recommendations from SHM POCUS Task Force provides consensus guidelines on the use of ultrasound guidance when performing or learning abdominal paracentesis.
Citation: Cho J et al. Recommendations on the use of ultrasound guidance for adult abdominal paracentesis: A position statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. 2019 Jan 2. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3095.
Dr. Schmit is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System, also in San Antonio.
Background: Abdominal paracentesis is a commonly performed procedure, and with appropriate training, hospitalists can deliver similar outcomes when compared to interventional radiologists.
Study design: Position statement.
Setting: The Society of Hospital Medicine Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) Task Force developed these guidelines after reviewing available literature and voted on the appropriateness and consensus of a recommendation.
Synopsis: A total of 794 articles were screened, and 91 articles were included and incorporated into the recommendations. The 12 recommendations fall into three categories (clinical outcomes, technique, and training), and all 12 recommendations achieved consensus as strong recommendations.
To improve clinical outcomes, the authors recommended ultrasound guidance in performing paracentesis to reduce the risk of serious complications, to avoid attempting paracentesis with insufficient fluid, and to improve overall procedure success.
The authors advocated for several technique recommendations, including using the ultrasound to assess volume and location of intraperitoneal fluid, to identify the needle insertion site and confirm in multiple planes, to use color flow Doppler to identify abdominal wall vessels, to mark the insertion site immediately prior to the procedure, and to consider real-time ultrasound guidance.
When health care professionals are learning ultrasound-guided paracentesis, the authors recommended use of dedicated training sessions with simulation if available and that competency should be demonstrated before independently attempting the procedure.
Bottom line: These recommendations from SHM POCUS Task Force provides consensus guidelines on the use of ultrasound guidance when performing or learning abdominal paracentesis.
Citation: Cho J et al. Recommendations on the use of ultrasound guidance for adult abdominal paracentesis: A position statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. 2019 Jan 2. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3095.
Dr. Schmit is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System, also in San Antonio.
Background: Abdominal paracentesis is a commonly performed procedure, and with appropriate training, hospitalists can deliver similar outcomes when compared to interventional radiologists.
Study design: Position statement.
Setting: The Society of Hospital Medicine Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) Task Force developed these guidelines after reviewing available literature and voted on the appropriateness and consensus of a recommendation.
Synopsis: A total of 794 articles were screened, and 91 articles were included and incorporated into the recommendations. The 12 recommendations fall into three categories (clinical outcomes, technique, and training), and all 12 recommendations achieved consensus as strong recommendations.
To improve clinical outcomes, the authors recommended ultrasound guidance in performing paracentesis to reduce the risk of serious complications, to avoid attempting paracentesis with insufficient fluid, and to improve overall procedure success.
The authors advocated for several technique recommendations, including using the ultrasound to assess volume and location of intraperitoneal fluid, to identify the needle insertion site and confirm in multiple planes, to use color flow Doppler to identify abdominal wall vessels, to mark the insertion site immediately prior to the procedure, and to consider real-time ultrasound guidance.
When health care professionals are learning ultrasound-guided paracentesis, the authors recommended use of dedicated training sessions with simulation if available and that competency should be demonstrated before independently attempting the procedure.
Bottom line: These recommendations from SHM POCUS Task Force provides consensus guidelines on the use of ultrasound guidance when performing or learning abdominal paracentesis.
Citation: Cho J et al. Recommendations on the use of ultrasound guidance for adult abdominal paracentesis: A position statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. 2019 Jan 2. doi: 10.12788/jhm.3095.
Dr. Schmit is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System, also in San Antonio.
A quarter of ICU admissions caused by substance abuse
according to results from a retrospective chart review.
The abuse of illicit drugs topped substance abuse–related ICU stays, accounting for 13% of total admissions, which represented 11% of total charges.
“We conducted a study to provide updated data on ICU utilization and costs related to licit and illicit abuse at a large county hospital,” wrote Donald Westerhausen, MD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis, and colleagues. The findings were reported in Chest .
The single-center study comprised 594 patients who were admitted for prescription, alcohol, or illicit drug use between May 2017 and October 2017. The team used laboratory data, in addition to medical history, to define substance abuse–related admissions.
A total of 611 admissions occurred during the 6-month study period. The researchers collected information on patient demographics, hospital charges, insurance coverage, and other clinical parameters.
After analysis, they found that patients admitted for substance abuse were generally younger than were those admitted for other reasons (44 years vs. 59 years; P less than .001). In addition, patients were more often male (64% vs. 48%), had greater mortality (14%), and experienced longer hospital stays (median, 6 days).
In total, 25.7% of ICU admissions were related to substance abuse, which comprised 23.1% of charges. In particular, 9.5% and 2.9% of admissions were related to alcohol use and prescription drugs, which represented 7.6% and 4.2% of total charges, respectively.
“Polysubstance abuse was the most frequent subcategory of illicit and prescription drug admissions,” the researchers wrote.
They acknowledged two limitations of the study: the short duration and single-center design. Future studies should account for seasonal differences in ICU admissions, they noted.
“Identifying and accurately describing the landscape of this current health crisis will help us take appropriate action in the future,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Westerhausen D et al. Chest. 2019 Sep 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.2180.
according to results from a retrospective chart review.
The abuse of illicit drugs topped substance abuse–related ICU stays, accounting for 13% of total admissions, which represented 11% of total charges.
“We conducted a study to provide updated data on ICU utilization and costs related to licit and illicit abuse at a large county hospital,” wrote Donald Westerhausen, MD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis, and colleagues. The findings were reported in Chest .
The single-center study comprised 594 patients who were admitted for prescription, alcohol, or illicit drug use between May 2017 and October 2017. The team used laboratory data, in addition to medical history, to define substance abuse–related admissions.
A total of 611 admissions occurred during the 6-month study period. The researchers collected information on patient demographics, hospital charges, insurance coverage, and other clinical parameters.
After analysis, they found that patients admitted for substance abuse were generally younger than were those admitted for other reasons (44 years vs. 59 years; P less than .001). In addition, patients were more often male (64% vs. 48%), had greater mortality (14%), and experienced longer hospital stays (median, 6 days).
In total, 25.7% of ICU admissions were related to substance abuse, which comprised 23.1% of charges. In particular, 9.5% and 2.9% of admissions were related to alcohol use and prescription drugs, which represented 7.6% and 4.2% of total charges, respectively.
“Polysubstance abuse was the most frequent subcategory of illicit and prescription drug admissions,” the researchers wrote.
They acknowledged two limitations of the study: the short duration and single-center design. Future studies should account for seasonal differences in ICU admissions, they noted.
“Identifying and accurately describing the landscape of this current health crisis will help us take appropriate action in the future,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Westerhausen D et al. Chest. 2019 Sep 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.2180.
according to results from a retrospective chart review.
The abuse of illicit drugs topped substance abuse–related ICU stays, accounting for 13% of total admissions, which represented 11% of total charges.
“We conducted a study to provide updated data on ICU utilization and costs related to licit and illicit abuse at a large county hospital,” wrote Donald Westerhausen, MD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis, and colleagues. The findings were reported in Chest .
The single-center study comprised 594 patients who were admitted for prescription, alcohol, or illicit drug use between May 2017 and October 2017. The team used laboratory data, in addition to medical history, to define substance abuse–related admissions.
A total of 611 admissions occurred during the 6-month study period. The researchers collected information on patient demographics, hospital charges, insurance coverage, and other clinical parameters.
After analysis, they found that patients admitted for substance abuse were generally younger than were those admitted for other reasons (44 years vs. 59 years; P less than .001). In addition, patients were more often male (64% vs. 48%), had greater mortality (14%), and experienced longer hospital stays (median, 6 days).
In total, 25.7% of ICU admissions were related to substance abuse, which comprised 23.1% of charges. In particular, 9.5% and 2.9% of admissions were related to alcohol use and prescription drugs, which represented 7.6% and 4.2% of total charges, respectively.
“Polysubstance abuse was the most frequent subcategory of illicit and prescription drug admissions,” the researchers wrote.
They acknowledged two limitations of the study: the short duration and single-center design. Future studies should account for seasonal differences in ICU admissions, they noted.
“Identifying and accurately describing the landscape of this current health crisis will help us take appropriate action in the future,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Westerhausen D et al. Chest. 2019 Sep 5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.2180.
FROM CHEST
Is it safe to discharge patients with anemia?
Background: Anemia is common in hospitalized patients and is associated with short- and long-term morbidity and mortality. Current evidence shows that reduced red blood cell (RBC) use and more restrictive transfusion practices do not increase short-term mortality; however, few data exist on the long-term outcomes of anemia.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Integrated health care system (Kaiser Permanente) with 21 hospitals located in Northern California.
Synopsis: From 2010 to 2014, there were 801,261 hospitalizations among 445,371 patients who survived to discharge. The prevalence of moderate anemia (hemoglobin between 7 and 10 g/dL) at hospital discharge increased from 20% to 25% (P less than .001) while RBC transfusions decreased by 28% (P less than .001). Resolution of moderate anemia within 6 months of hospital discharge decreased from 42% to 34% (P less than .001). RBC transfusion and rehospitalization rates at 6 months decreased as well. During the study period, adjusted 6-month mortality decreased from 16.1% to 15.6% (P = .04) in patients with moderate anemia.
Given the retrospective design of this study, data must be interpreted with caution in determining a causal relationship. The authors also acknowledge that there may be unmeasured confounding variables not accounted for in the study results.
Bottom line: Despite higher rates of moderate anemia at discharge, there was not an associated rise in subsequent RBC transfusions, readmissions, or mortality in the 6 months after hospital discharge.
Citation: Roubinian NH et al. Long-term outcomes among patients discharged from the hospital with moderate anemia: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.7326/M17-3253.
Dr. Schmit is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System, also in San Antonio.
Background: Anemia is common in hospitalized patients and is associated with short- and long-term morbidity and mortality. Current evidence shows that reduced red blood cell (RBC) use and more restrictive transfusion practices do not increase short-term mortality; however, few data exist on the long-term outcomes of anemia.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Integrated health care system (Kaiser Permanente) with 21 hospitals located in Northern California.
Synopsis: From 2010 to 2014, there were 801,261 hospitalizations among 445,371 patients who survived to discharge. The prevalence of moderate anemia (hemoglobin between 7 and 10 g/dL) at hospital discharge increased from 20% to 25% (P less than .001) while RBC transfusions decreased by 28% (P less than .001). Resolution of moderate anemia within 6 months of hospital discharge decreased from 42% to 34% (P less than .001). RBC transfusion and rehospitalization rates at 6 months decreased as well. During the study period, adjusted 6-month mortality decreased from 16.1% to 15.6% (P = .04) in patients with moderate anemia.
Given the retrospective design of this study, data must be interpreted with caution in determining a causal relationship. The authors also acknowledge that there may be unmeasured confounding variables not accounted for in the study results.
Bottom line: Despite higher rates of moderate anemia at discharge, there was not an associated rise in subsequent RBC transfusions, readmissions, or mortality in the 6 months after hospital discharge.
Citation: Roubinian NH et al. Long-term outcomes among patients discharged from the hospital with moderate anemia: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.7326/M17-3253.
Dr. Schmit is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System, also in San Antonio.
Background: Anemia is common in hospitalized patients and is associated with short- and long-term morbidity and mortality. Current evidence shows that reduced red blood cell (RBC) use and more restrictive transfusion practices do not increase short-term mortality; however, few data exist on the long-term outcomes of anemia.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Integrated health care system (Kaiser Permanente) with 21 hospitals located in Northern California.
Synopsis: From 2010 to 2014, there were 801,261 hospitalizations among 445,371 patients who survived to discharge. The prevalence of moderate anemia (hemoglobin between 7 and 10 g/dL) at hospital discharge increased from 20% to 25% (P less than .001) while RBC transfusions decreased by 28% (P less than .001). Resolution of moderate anemia within 6 months of hospital discharge decreased from 42% to 34% (P less than .001). RBC transfusion and rehospitalization rates at 6 months decreased as well. During the study period, adjusted 6-month mortality decreased from 16.1% to 15.6% (P = .04) in patients with moderate anemia.
Given the retrospective design of this study, data must be interpreted with caution in determining a causal relationship. The authors also acknowledge that there may be unmeasured confounding variables not accounted for in the study results.
Bottom line: Despite higher rates of moderate anemia at discharge, there was not an associated rise in subsequent RBC transfusions, readmissions, or mortality in the 6 months after hospital discharge.
Citation: Roubinian NH et al. Long-term outcomes among patients discharged from the hospital with moderate anemia: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.7326/M17-3253.
Dr. Schmit is an associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at UT Health San Antonio and a hospitalist at South Texas Veterans Health Care System, also in San Antonio.
Beta-blockers effective, safe for HFrEF with renal dysfunction
PARIS – Beta-blocking drugs were as effective for improving survival in patients with moderately severe renal dysfunction as they were in patients with normal renal function in a meta-analysis of more than 13,000 patients, a finding that seemed to solidify the role for this drug class for essentially all similar heart failure patients, regardless of their renal function.
This evidence could reshape usual care because “renal impairment is often considered a barrier in clinical practice” for starting a beta-blocker drug in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), Dipak Kotecha, MBChB, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“We have shown with sufficient sample size that beta-blockers are effective in reducing mortality in patient with HFrEF and in sinus rhythm, even in those with an eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate] of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2,” said Dr. Kotecha, a cardiologist at the University of Birmingham (England). “The results suggest that renal impairment should not obstruct the prescription and maintenance of beta-blockers in patients with HFrEF.”
“This important study was a novel attempt to look at [HFrEF] patients with renal insufficiency to see whether they received the same benefit from beta-blockers as other patients, and they did. So renal insufficiency is not a reason to withhold beta-blockers” from these patients, commented Mariell Jessup, MD, a heart failure physician and chief science and medical officer for the American Heart Association in Dallas. “The onus is on clinicians to find a reason not to give a beta-blocker to a patient with HFrEF because they are generally well tolerated and they can have enormous benefit, as we saw in this study,” she said in a video interview.
The analysis run by Dr. Kotecha and associates used data collected in 11 of the pivotal randomized, controlled trial run for beta-blockers during the 1990s and early 2000s, with each study comparing bucindolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol, metoprolol XL, or nebivolol against placebo. The studies collectively enrolled 18,637 patients, which the investigators whittled down in their analysis to 17,433 after excluding patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction below 50% or who were undocumented. The subgroup with HFrEF included 13,861 patient in sinus rhythm at entry, 2,879 with atrial fibrillation, and 693 with an unknown atrial status. The main analysis ran in the 13,861 patients with HFrEF and in sinus rhythm; 14% of this cohort had an eGFR of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and 27% had an eGFR of 45-59 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The median age of all patients in the main analysis was 65 years, 23% were women, and their median left ventricular ejection fraction was 27%.
During follow-up of about 3 years, the impact of beta-blocker treatment on survival, compared with placebo, was “substantial” for all strata of patients by renal function, except for those with eGFRs below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2. (Survival was similar regardless of beta-blocker treatment in the small number of patients with severe renal dysfunction.) The number needed to treat to prevent 1 death in patients with an eGFR of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was 21, the same as among patients with an eGFR of 90 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or more, Dr. Kotecha said.
Among the subgroup of patients with atrial fibrillation, beta-blockers appeared to exert no survival benefit, compared with placebo. The investigators did not assess the survival benefits exerted by any individual beta-blocker, compared with the others, and Dr. Kotecha stressed that “my belief is that this is a class effect” and is roughly similar across all the beta-blockers used in the studies.
The analysis also showed good safety and tolerability of the beta-blockers in patients with renal dysfunction. The incidence of adverse events leading to treatment termination was very similar in the beta-blocker and placebo arms, and more than three-quarters of patients in each of the two subgroups with renal dysfunction were maintained on more than 50% of their target beta-blocker dosage.
Dr. Kotecha has been an advisor to Bayer, a speaker on behalf of Atricure, and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Menarini. Dr. Jessup had no disclosures.
This analysis of individual patient data is very important and extends our knowledge. The results confirm that beta-blocker treatment reduces mortality in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and in sinus rhythm who also have moderately severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate as low as 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2. This is good news for patients with HFrEF and kidney disease. Clinicians often use comorbidities as a reason not to prescribe or up-titrate beta-blockers. These results show that beta-blockers can be used at guideline-directed dosages, even in patients with renal dysfunction. The findings highlight the importance of not looking for excuses to not treat patients with a beta-blocker. Do not worry about renal function.
Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, professor of cardiology at King’s College, London, made these comments as designated discussant for Dr. Kotecha’s report. She had no disclosures.
This analysis of individual patient data is very important and extends our knowledge. The results confirm that beta-blocker treatment reduces mortality in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and in sinus rhythm who also have moderately severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate as low as 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2. This is good news for patients with HFrEF and kidney disease. Clinicians often use comorbidities as a reason not to prescribe or up-titrate beta-blockers. These results show that beta-blockers can be used at guideline-directed dosages, even in patients with renal dysfunction. The findings highlight the importance of not looking for excuses to not treat patients with a beta-blocker. Do not worry about renal function.
Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, professor of cardiology at King’s College, London, made these comments as designated discussant for Dr. Kotecha’s report. She had no disclosures.
This analysis of individual patient data is very important and extends our knowledge. The results confirm that beta-blocker treatment reduces mortality in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and in sinus rhythm who also have moderately severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate as low as 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2. This is good news for patients with HFrEF and kidney disease. Clinicians often use comorbidities as a reason not to prescribe or up-titrate beta-blockers. These results show that beta-blockers can be used at guideline-directed dosages, even in patients with renal dysfunction. The findings highlight the importance of not looking for excuses to not treat patients with a beta-blocker. Do not worry about renal function.
Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, professor of cardiology at King’s College, London, made these comments as designated discussant for Dr. Kotecha’s report. She had no disclosures.
PARIS – Beta-blocking drugs were as effective for improving survival in patients with moderately severe renal dysfunction as they were in patients with normal renal function in a meta-analysis of more than 13,000 patients, a finding that seemed to solidify the role for this drug class for essentially all similar heart failure patients, regardless of their renal function.
This evidence could reshape usual care because “renal impairment is often considered a barrier in clinical practice” for starting a beta-blocker drug in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), Dipak Kotecha, MBChB, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“We have shown with sufficient sample size that beta-blockers are effective in reducing mortality in patient with HFrEF and in sinus rhythm, even in those with an eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate] of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2,” said Dr. Kotecha, a cardiologist at the University of Birmingham (England). “The results suggest that renal impairment should not obstruct the prescription and maintenance of beta-blockers in patients with HFrEF.”
“This important study was a novel attempt to look at [HFrEF] patients with renal insufficiency to see whether they received the same benefit from beta-blockers as other patients, and they did. So renal insufficiency is not a reason to withhold beta-blockers” from these patients, commented Mariell Jessup, MD, a heart failure physician and chief science and medical officer for the American Heart Association in Dallas. “The onus is on clinicians to find a reason not to give a beta-blocker to a patient with HFrEF because they are generally well tolerated and they can have enormous benefit, as we saw in this study,” she said in a video interview.
The analysis run by Dr. Kotecha and associates used data collected in 11 of the pivotal randomized, controlled trial run for beta-blockers during the 1990s and early 2000s, with each study comparing bucindolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol, metoprolol XL, or nebivolol against placebo. The studies collectively enrolled 18,637 patients, which the investigators whittled down in their analysis to 17,433 after excluding patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction below 50% or who were undocumented. The subgroup with HFrEF included 13,861 patient in sinus rhythm at entry, 2,879 with atrial fibrillation, and 693 with an unknown atrial status. The main analysis ran in the 13,861 patients with HFrEF and in sinus rhythm; 14% of this cohort had an eGFR of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and 27% had an eGFR of 45-59 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The median age of all patients in the main analysis was 65 years, 23% were women, and their median left ventricular ejection fraction was 27%.
During follow-up of about 3 years, the impact of beta-blocker treatment on survival, compared with placebo, was “substantial” for all strata of patients by renal function, except for those with eGFRs below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2. (Survival was similar regardless of beta-blocker treatment in the small number of patients with severe renal dysfunction.) The number needed to treat to prevent 1 death in patients with an eGFR of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was 21, the same as among patients with an eGFR of 90 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or more, Dr. Kotecha said.
Among the subgroup of patients with atrial fibrillation, beta-blockers appeared to exert no survival benefit, compared with placebo. The investigators did not assess the survival benefits exerted by any individual beta-blocker, compared with the others, and Dr. Kotecha stressed that “my belief is that this is a class effect” and is roughly similar across all the beta-blockers used in the studies.
The analysis also showed good safety and tolerability of the beta-blockers in patients with renal dysfunction. The incidence of adverse events leading to treatment termination was very similar in the beta-blocker and placebo arms, and more than three-quarters of patients in each of the two subgroups with renal dysfunction were maintained on more than 50% of their target beta-blocker dosage.
Dr. Kotecha has been an advisor to Bayer, a speaker on behalf of Atricure, and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Menarini. Dr. Jessup had no disclosures.
PARIS – Beta-blocking drugs were as effective for improving survival in patients with moderately severe renal dysfunction as they were in patients with normal renal function in a meta-analysis of more than 13,000 patients, a finding that seemed to solidify the role for this drug class for essentially all similar heart failure patients, regardless of their renal function.
This evidence could reshape usual care because “renal impairment is often considered a barrier in clinical practice” for starting a beta-blocker drug in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), Dipak Kotecha, MBChB, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“We have shown with sufficient sample size that beta-blockers are effective in reducing mortality in patient with HFrEF and in sinus rhythm, even in those with an eGFR [estimated glomerular filtration rate] of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2,” said Dr. Kotecha, a cardiologist at the University of Birmingham (England). “The results suggest that renal impairment should not obstruct the prescription and maintenance of beta-blockers in patients with HFrEF.”
“This important study was a novel attempt to look at [HFrEF] patients with renal insufficiency to see whether they received the same benefit from beta-blockers as other patients, and they did. So renal insufficiency is not a reason to withhold beta-blockers” from these patients, commented Mariell Jessup, MD, a heart failure physician and chief science and medical officer for the American Heart Association in Dallas. “The onus is on clinicians to find a reason not to give a beta-blocker to a patient with HFrEF because they are generally well tolerated and they can have enormous benefit, as we saw in this study,” she said in a video interview.
The analysis run by Dr. Kotecha and associates used data collected in 11 of the pivotal randomized, controlled trial run for beta-blockers during the 1990s and early 2000s, with each study comparing bucindolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol, metoprolol XL, or nebivolol against placebo. The studies collectively enrolled 18,637 patients, which the investigators whittled down in their analysis to 17,433 after excluding patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction below 50% or who were undocumented. The subgroup with HFrEF included 13,861 patient in sinus rhythm at entry, 2,879 with atrial fibrillation, and 693 with an unknown atrial status. The main analysis ran in the 13,861 patients with HFrEF and in sinus rhythm; 14% of this cohort had an eGFR of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and 27% had an eGFR of 45-59 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The median age of all patients in the main analysis was 65 years, 23% were women, and their median left ventricular ejection fraction was 27%.
During follow-up of about 3 years, the impact of beta-blocker treatment on survival, compared with placebo, was “substantial” for all strata of patients by renal function, except for those with eGFRs below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2. (Survival was similar regardless of beta-blocker treatment in the small number of patients with severe renal dysfunction.) The number needed to treat to prevent 1 death in patients with an eGFR of 30-44 mL/min per 1.73 m2 was 21, the same as among patients with an eGFR of 90 mL/min per 1.73 m2 or more, Dr. Kotecha said.
Among the subgroup of patients with atrial fibrillation, beta-blockers appeared to exert no survival benefit, compared with placebo. The investigators did not assess the survival benefits exerted by any individual beta-blocker, compared with the others, and Dr. Kotecha stressed that “my belief is that this is a class effect” and is roughly similar across all the beta-blockers used in the studies.
The analysis also showed good safety and tolerability of the beta-blockers in patients with renal dysfunction. The incidence of adverse events leading to treatment termination was very similar in the beta-blocker and placebo arms, and more than three-quarters of patients in each of the two subgroups with renal dysfunction were maintained on more than 50% of their target beta-blocker dosage.
Dr. Kotecha has been an advisor to Bayer, a speaker on behalf of Atricure, and has received research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Menarini. Dr. Jessup had no disclosures.
REPORTING FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2019
Machine learning–derived risk score predicts heart failure risk in diabetes patients
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Reversal agents for direct-acting oral anticoagulants
Summary of guidelines published in the Journal of Hospital Medicine
When on call for admissions, a hospitalist receives a request from a colleague to admit an octogenarian man with an acute uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis to start heparin, bridging to warfarin. The patient has no evidence of postphlebitic syndrome, pulmonary embolism, or right-sided heart strain. The hospitalist asks her colleague if he had considered treating the patient in the ambulatory setting using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC). After all, this would save the patient an unnecessary hospitalization, weekly international normalized ratio checks, and other important lifestyle changes. In response, the colleague voices concern that the “new drugs don’t have antidotes.”
DOACs have several benefits over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) and heparins. DOACs have quicker onset of action, can be taken by mouth, in general do not require dosage adjustment, and have fewer dietary and lifestyle modifications, compared with VKAs and heparins. In atrial fibrillation, DOACs have been shown to have lower all-cause and bleeding-related mortality than warfarin (see Table 1).1 Observational studies also suggest less risk of major bleeding with DOACs over warfarin but no difference in overall mortality when used to treat venous thromboembolism (see Table 2).2 Because of these combined advantages, DOACs are increasingly prescribed, accounting for approximately half of all oral anticoagulant prescriptions in 2014.3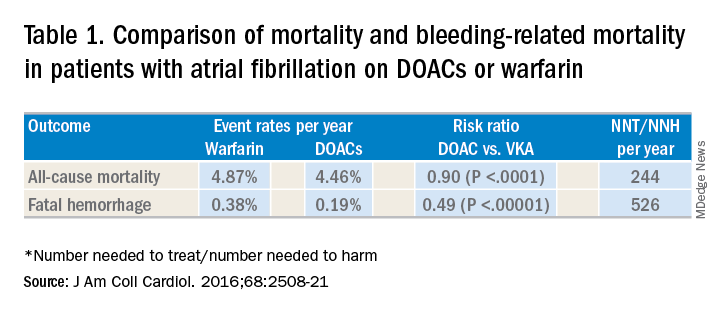
Although DOACs have been shown to be as good if not superior to VKAs and heparins in these circumstances, there are situations where a DOAC should not be used. There is limited data on the safety of DOACs in patients with mechanical heart valves, liver failure, and chronic kidney disease with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min.4 Therefore, warfarin is still the preferred agent in these settings. There is some data that apixaban may be safe in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than 10 mL/min, but long-term safety studies have not been performed in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis.5 Finally, in patients requiring concomitant inducers or inhibitors of the P-glycoprotein or cytochrome P450 enzymes like antiepileptics and protease inhibitors, VKAs and heparins are favored.4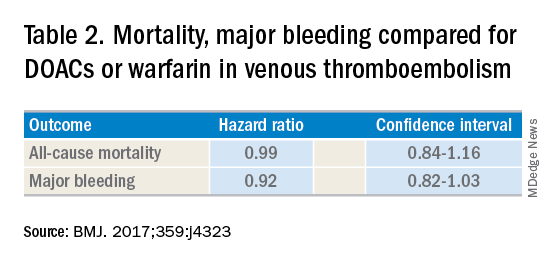
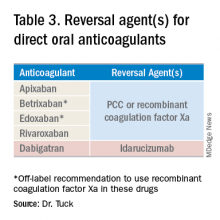
Notwithstanding their advantages, when DOACs first hit the market there were concerns that reversal agents were not available. In the August issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s Clinical Guideline Highlights for the Hospitalist, Emily Gottenborg, MD, and Gregory Misky, MD, summarized guideline recommendations for reversal of the newer agents.6 This includes use of idarucizumab for patients on dabigatran and use of prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) or recombinant coagulation factor Xa (andexanet alfa) for patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding.
Idarucizumab is a monoclonal antibody developed to reverse the effects of dabigatran, the only DOAC that directly inhibits thrombin. In 2017, researchers reported on a cohort of subjects receiving idarucizumab for uncontrolled bleeding or who were on dabigatran and about to undergo an urgent procedure.7 Of those with uncontrolled bleeding, two-thirds had confirmed bleeding cessation within 24 hours. Periprocedural hemostasis was achieved in 93.4% of patients undergoing urgent procedures. However, it should be noted that use of idarucizumab conferred an increase risk (6.3%) of thrombosis within 90 days. Based on these findings, guidelines recommend use of idarucizumab in patients experiencing life-threatening bleeding, balanced against the risk of thrombosis.8
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding in patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban.9 The approval came after a study by the ANNEXA-4 investigators showed that recombinant coagulation factor Xa quickly and effectively achieved hemostasis.10 Full study results were published in April 2019, demonstrating 82% of patients receiving the drug attained clinical hemostasis.11 However, as with idarucizumab, up to 10% of patients had a thrombotic event in the follow-up period. Use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to betrixaban and edoxaban is considered off label but is recommended by guidelines.8 Studies on investigational reversal agents for betrixaban and edoxaban are ongoing.
Both unactivated and activated PCC contain clotting factor X. Their use to control bleeding related to DOAC use is based on observational studies. In a systematic review of the nonrandomized studies, the efficacy of PCC to stem major bleeding was 69% and the risk for thromboembolism was 4%.12 There are no head-to-head studies comparing use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa and PCC. Therefore, guidelines are to use either recombinant factor Xa or PCC for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to DOAC use.7
As thrombosis risk heightens after use of any reversal agent, the recommendations are to resume anticoagulation within 90 days if the patient is at moderate or high risk for recurrent thromboembolism.8
After discussion with the hospitalist about the new agents available to reverse anticoagulation, the colleague decided to place the patient on a DOAC and keep the patient in his nursing home. Thankfully, the patient did not thereafter experience sustained bleeding necessitating use of these reversal agents. More importantly for the patient, he was able to stay in the comfort of his home.
Dr. Tuck is associate section chief for hospital medicine at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
References
1. Gómez-Outes A et al. Causes of death in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2508-21.
2. Jun M et al. Comparative safety of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in venous thromboembolism: multicentre, population-based, observational study. BMJ. 2017;359:j4323.
3. Barnes GD et al. National trends in ambulatory oral anticoagulant use. Am J Med. 2015;128:(1300-5).e2.
4. Reddy P et al. Practical approach to VTE management in hospitalized patients. Am J Ther. 2017;24(4):e442-67.
5. Kimachi M et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for preventing stroke and systemic embolic events among atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 6;11:CD011373.
6. Gottenborg E et al. Clinical guideline highlights for the hospitalist: The management of anticoagulation in the hospitalized adult. J Hosp Med. 2019; 14(8):499-500.
7. Pollack CV Jr et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal – full cohort analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):431-41.
8. Witt DM et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3257-91.
9. Malarky M et al. FDA accelerated approval letter. Retrieved July 15, 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/113285/download
10. Connolly SJ et al. Andexanet alfa for acute major bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(12):1131-41.
11. Connolly SJ et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(14):1326-35.
12. Piran S et al. Management of direct factor Xa inhibitor–related major bleeding with prothrombin complex concentrate: A meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):158-67.
Summary of guidelines published in the Journal of Hospital Medicine
Summary of guidelines published in the Journal of Hospital Medicine
When on call for admissions, a hospitalist receives a request from a colleague to admit an octogenarian man with an acute uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis to start heparin, bridging to warfarin. The patient has no evidence of postphlebitic syndrome, pulmonary embolism, or right-sided heart strain. The hospitalist asks her colleague if he had considered treating the patient in the ambulatory setting using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC). After all, this would save the patient an unnecessary hospitalization, weekly international normalized ratio checks, and other important lifestyle changes. In response, the colleague voices concern that the “new drugs don’t have antidotes.”
DOACs have several benefits over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) and heparins. DOACs have quicker onset of action, can be taken by mouth, in general do not require dosage adjustment, and have fewer dietary and lifestyle modifications, compared with VKAs and heparins. In atrial fibrillation, DOACs have been shown to have lower all-cause and bleeding-related mortality than warfarin (see Table 1).1 Observational studies also suggest less risk of major bleeding with DOACs over warfarin but no difference in overall mortality when used to treat venous thromboembolism (see Table 2).2 Because of these combined advantages, DOACs are increasingly prescribed, accounting for approximately half of all oral anticoagulant prescriptions in 2014.3
Although DOACs have been shown to be as good if not superior to VKAs and heparins in these circumstances, there are situations where a DOAC should not be used. There is limited data on the safety of DOACs in patients with mechanical heart valves, liver failure, and chronic kidney disease with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min.4 Therefore, warfarin is still the preferred agent in these settings. There is some data that apixaban may be safe in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than 10 mL/min, but long-term safety studies have not been performed in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis.5 Finally, in patients requiring concomitant inducers or inhibitors of the P-glycoprotein or cytochrome P450 enzymes like antiepileptics and protease inhibitors, VKAs and heparins are favored.4
Notwithstanding their advantages, when DOACs first hit the market there were concerns that reversal agents were not available. In the August issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s Clinical Guideline Highlights for the Hospitalist, Emily Gottenborg, MD, and Gregory Misky, MD, summarized guideline recommendations for reversal of the newer agents.6 This includes use of idarucizumab for patients on dabigatran and use of prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) or recombinant coagulation factor Xa (andexanet alfa) for patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding.
Idarucizumab is a monoclonal antibody developed to reverse the effects of dabigatran, the only DOAC that directly inhibits thrombin. In 2017, researchers reported on a cohort of subjects receiving idarucizumab for uncontrolled bleeding or who were on dabigatran and about to undergo an urgent procedure.7 Of those with uncontrolled bleeding, two-thirds had confirmed bleeding cessation within 24 hours. Periprocedural hemostasis was achieved in 93.4% of patients undergoing urgent procedures. However, it should be noted that use of idarucizumab conferred an increase risk (6.3%) of thrombosis within 90 days. Based on these findings, guidelines recommend use of idarucizumab in patients experiencing life-threatening bleeding, balanced against the risk of thrombosis.8
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding in patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban.9 The approval came after a study by the ANNEXA-4 investigators showed that recombinant coagulation factor Xa quickly and effectively achieved hemostasis.10 Full study results were published in April 2019, demonstrating 82% of patients receiving the drug attained clinical hemostasis.11 However, as with idarucizumab, up to 10% of patients had a thrombotic event in the follow-up period. Use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to betrixaban and edoxaban is considered off label but is recommended by guidelines.8 Studies on investigational reversal agents for betrixaban and edoxaban are ongoing.
Both unactivated and activated PCC contain clotting factor X. Their use to control bleeding related to DOAC use is based on observational studies. In a systematic review of the nonrandomized studies, the efficacy of PCC to stem major bleeding was 69% and the risk for thromboembolism was 4%.12 There are no head-to-head studies comparing use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa and PCC. Therefore, guidelines are to use either recombinant factor Xa or PCC for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to DOAC use.7
As thrombosis risk heightens after use of any reversal agent, the recommendations are to resume anticoagulation within 90 days if the patient is at moderate or high risk for recurrent thromboembolism.8
After discussion with the hospitalist about the new agents available to reverse anticoagulation, the colleague decided to place the patient on a DOAC and keep the patient in his nursing home. Thankfully, the patient did not thereafter experience sustained bleeding necessitating use of these reversal agents. More importantly for the patient, he was able to stay in the comfort of his home.
Dr. Tuck is associate section chief for hospital medicine at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
References
1. Gómez-Outes A et al. Causes of death in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2508-21.
2. Jun M et al. Comparative safety of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in venous thromboembolism: multicentre, population-based, observational study. BMJ. 2017;359:j4323.
3. Barnes GD et al. National trends in ambulatory oral anticoagulant use. Am J Med. 2015;128:(1300-5).e2.
4. Reddy P et al. Practical approach to VTE management in hospitalized patients. Am J Ther. 2017;24(4):e442-67.
5. Kimachi M et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for preventing stroke and systemic embolic events among atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 6;11:CD011373.
6. Gottenborg E et al. Clinical guideline highlights for the hospitalist: The management of anticoagulation in the hospitalized adult. J Hosp Med. 2019; 14(8):499-500.
7. Pollack CV Jr et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal – full cohort analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):431-41.
8. Witt DM et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3257-91.
9. Malarky M et al. FDA accelerated approval letter. Retrieved July 15, 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/113285/download
10. Connolly SJ et al. Andexanet alfa for acute major bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(12):1131-41.
11. Connolly SJ et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(14):1326-35.
12. Piran S et al. Management of direct factor Xa inhibitor–related major bleeding with prothrombin complex concentrate: A meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):158-67.
When on call for admissions, a hospitalist receives a request from a colleague to admit an octogenarian man with an acute uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis to start heparin, bridging to warfarin. The patient has no evidence of postphlebitic syndrome, pulmonary embolism, or right-sided heart strain. The hospitalist asks her colleague if he had considered treating the patient in the ambulatory setting using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC). After all, this would save the patient an unnecessary hospitalization, weekly international normalized ratio checks, and other important lifestyle changes. In response, the colleague voices concern that the “new drugs don’t have antidotes.”
DOACs have several benefits over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) and heparins. DOACs have quicker onset of action, can be taken by mouth, in general do not require dosage adjustment, and have fewer dietary and lifestyle modifications, compared with VKAs and heparins. In atrial fibrillation, DOACs have been shown to have lower all-cause and bleeding-related mortality than warfarin (see Table 1).1 Observational studies also suggest less risk of major bleeding with DOACs over warfarin but no difference in overall mortality when used to treat venous thromboembolism (see Table 2).2 Because of these combined advantages, DOACs are increasingly prescribed, accounting for approximately half of all oral anticoagulant prescriptions in 2014.3
Although DOACs have been shown to be as good if not superior to VKAs and heparins in these circumstances, there are situations where a DOAC should not be used. There is limited data on the safety of DOACs in patients with mechanical heart valves, liver failure, and chronic kidney disease with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min.4 Therefore, warfarin is still the preferred agent in these settings. There is some data that apixaban may be safe in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than 10 mL/min, but long-term safety studies have not been performed in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis.5 Finally, in patients requiring concomitant inducers or inhibitors of the P-glycoprotein or cytochrome P450 enzymes like antiepileptics and protease inhibitors, VKAs and heparins are favored.4
Notwithstanding their advantages, when DOACs first hit the market there were concerns that reversal agents were not available. In the August issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s Clinical Guideline Highlights for the Hospitalist, Emily Gottenborg, MD, and Gregory Misky, MD, summarized guideline recommendations for reversal of the newer agents.6 This includes use of idarucizumab for patients on dabigatran and use of prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) or recombinant coagulation factor Xa (andexanet alfa) for patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding.
Idarucizumab is a monoclonal antibody developed to reverse the effects of dabigatran, the only DOAC that directly inhibits thrombin. In 2017, researchers reported on a cohort of subjects receiving idarucizumab for uncontrolled bleeding or who were on dabigatran and about to undergo an urgent procedure.7 Of those with uncontrolled bleeding, two-thirds had confirmed bleeding cessation within 24 hours. Periprocedural hemostasis was achieved in 93.4% of patients undergoing urgent procedures. However, it should be noted that use of idarucizumab conferred an increase risk (6.3%) of thrombosis within 90 days. Based on these findings, guidelines recommend use of idarucizumab in patients experiencing life-threatening bleeding, balanced against the risk of thrombosis.8
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding in patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban.9 The approval came after a study by the ANNEXA-4 investigators showed that recombinant coagulation factor Xa quickly and effectively achieved hemostasis.10 Full study results were published in April 2019, demonstrating 82% of patients receiving the drug attained clinical hemostasis.11 However, as with idarucizumab, up to 10% of patients had a thrombotic event in the follow-up period. Use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to betrixaban and edoxaban is considered off label but is recommended by guidelines.8 Studies on investigational reversal agents for betrixaban and edoxaban are ongoing.
Both unactivated and activated PCC contain clotting factor X. Their use to control bleeding related to DOAC use is based on observational studies. In a systematic review of the nonrandomized studies, the efficacy of PCC to stem major bleeding was 69% and the risk for thromboembolism was 4%.12 There are no head-to-head studies comparing use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa and PCC. Therefore, guidelines are to use either recombinant factor Xa or PCC for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to DOAC use.7
As thrombosis risk heightens after use of any reversal agent, the recommendations are to resume anticoagulation within 90 days if the patient is at moderate or high risk for recurrent thromboembolism.8
After discussion with the hospitalist about the new agents available to reverse anticoagulation, the colleague decided to place the patient on a DOAC and keep the patient in his nursing home. Thankfully, the patient did not thereafter experience sustained bleeding necessitating use of these reversal agents. More importantly for the patient, he was able to stay in the comfort of his home.
Dr. Tuck is associate section chief for hospital medicine at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
References
1. Gómez-Outes A et al. Causes of death in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2508-21.
2. Jun M et al. Comparative safety of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in venous thromboembolism: multicentre, population-based, observational study. BMJ. 2017;359:j4323.
3. Barnes GD et al. National trends in ambulatory oral anticoagulant use. Am J Med. 2015;128:(1300-5).e2.
4. Reddy P et al. Practical approach to VTE management in hospitalized patients. Am J Ther. 2017;24(4):e442-67.
5. Kimachi M et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for preventing stroke and systemic embolic events among atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 6;11:CD011373.
6. Gottenborg E et al. Clinical guideline highlights for the hospitalist: The management of anticoagulation in the hospitalized adult. J Hosp Med. 2019; 14(8):499-500.
7. Pollack CV Jr et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal – full cohort analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):431-41.
8. Witt DM et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3257-91.
9. Malarky M et al. FDA accelerated approval letter. Retrieved July 15, 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/113285/download
10. Connolly SJ et al. Andexanet alfa for acute major bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(12):1131-41.
11. Connolly SJ et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(14):1326-35.
12. Piran S et al. Management of direct factor Xa inhibitor–related major bleeding with prothrombin complex concentrate: A meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):158-67.
Drug abuse–linked infective endocarditis spiking in U.S.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC increased from 48 cases/100,000 in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study identifying about a more than 950,000 cases of IC from the National Inpatient Sample registry.
Disclosures: None.
Source: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.