User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'medstat-accordion-set article-series')]
Porous pill printing and prognostic poop
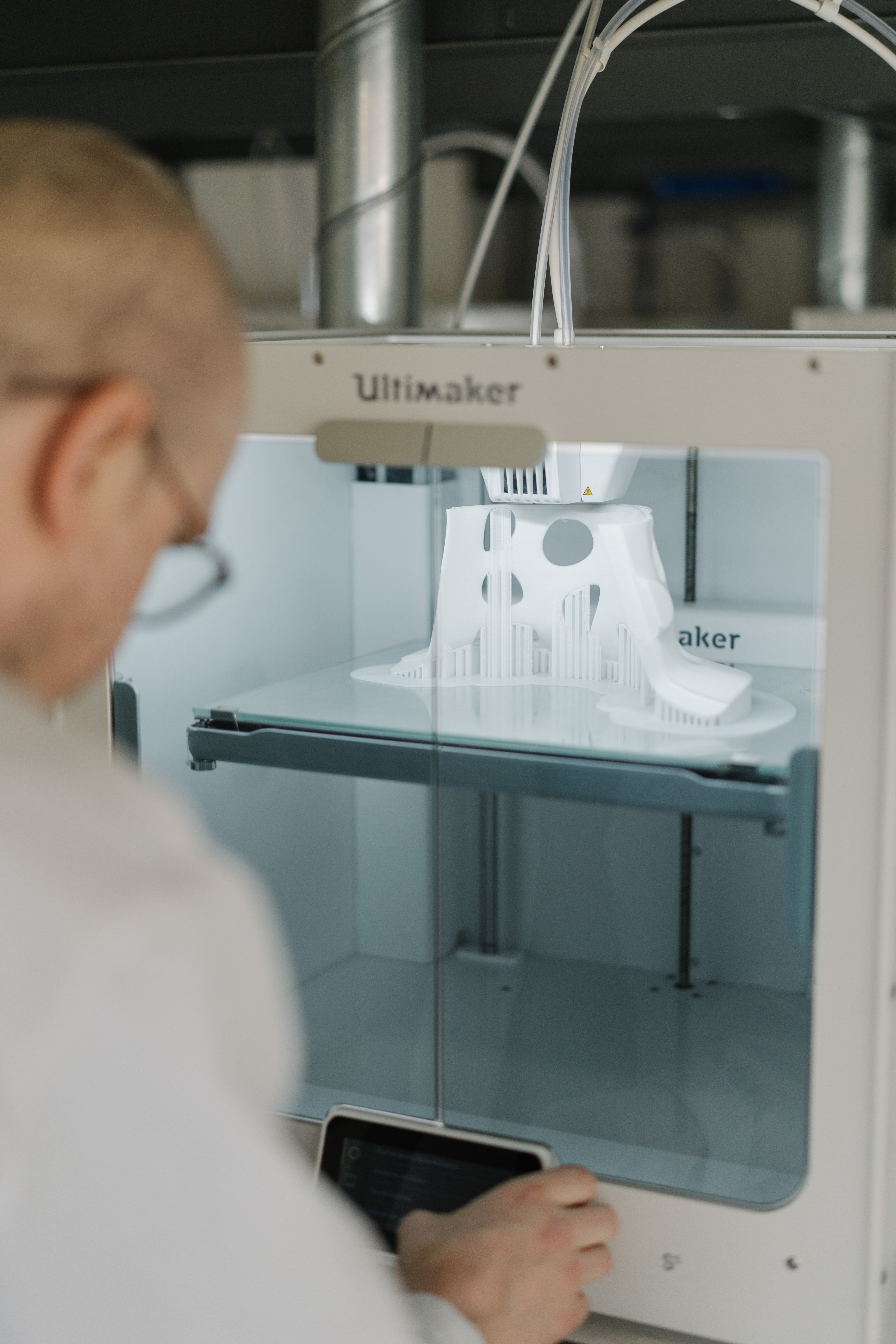
Printing meds per patient
What if there was a way to get exact doses of a medication, tailored specifically for each and every patient that needed it? Well, apparently it’s as easy as getting them out of a printer.
Researchers from the University of East Anglia in England may have found a new method to do just that.
Currently, medicine is “manufactured in ‘one-size-fits-all’ fashion,” said Dr. Sheng Qi, the research lead. But no patient is exactly the same, so why shouldn’t their medications be just as unique? Research on pharmaceutical 3D printing has been developing over the past 5 years, with the most common method requiring the drug to be put into “spaghetti-like filaments” before printing.
Dr. Qi and his team developed a process that bypasses the filaments, allowing them to 3D-print pills with varied porous structures that can regulate the rate of release of the drug into the body. This could be revolutionary for elderly patients and patients with complicated conditions – who often take many different drugs – to ensure more accurate doses that provide maximum benefits and minimal adverse effects.
Just as a custom-tailored suit perfectly fits the body for which it was made, the ability to tailor medication could have the same effect on a patient’s health. The only difference is what’s coming through the printer would be pills, not fabric.
It’s hip to be Pfizered
COVID-19 vaccination levels are rising, but we’ve heard a rumor that some people are still a bit reticent to participate. So how can physicians get more people to come in for a shot?
Make sure that they’re giving patients the right vaccine, for one thing. And by “right” vaccine, we mean, of course, the cool vaccine. Yes, the Internet has decided that the Pfizer vaccine is cooler than the others, according to the Atlantic.
There is, it seems, such a thing as “Pfizer superiority complex,” the article noted, while adding that, “on TikTok, hundreds of videos use a soundtrack of a woman explaining – slowly, voice full of disdain, like the rudest preschool teacher on Earth – ‘Only hot people get the Pfizer vaccine.’ ” A reporter from Slate was welcomed “to the ruling class” after sharing her upcoming Pfizer vaccination.
For the ultimate test of coolness, we surveyed the LOTME staff about the COVID-19 vaccines they had received. The results? Two Pfizers (coincidentally, the only two who knew what the hell TikTok is), one Moderna, one Johnson & Johnson, and one Godbold’s Vegetable Balsam (coincidentally, the same one who told us to get off his lawn).
And yes, we are checking on that last one.
Allergies stink!
A baby’s first bowel movement might mean more than just being the first of many diaper changes.
That particular bowel movement, called meconium, is a mixture of materials that have gone into a baby’s mouth late in the pregnancy, such as skin cells and amniotic fluid. Sounds lovely, right? The contents also include certain biochemicals and gut bacteria, and a lack of these can show an increased risk of allergies, eczema, and asthma.
Studies show that certain gut bacteria actually teach the immune system to accept compounds that are not harmful. Since allergies and other conditions are caused by a person’s immune system telling them harmless compounds are bad, it makes sense that lacking gut bacteria might show potential for developing such conditions.
Charisse Petersen, a researcher at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, told NewScientist that parents could help decrease the development of allergies by not giving their children antibiotics that aren’t necessary and by letting kids play outside more.
Tom Marrs of King’s College London even noted that having a dog in the house is linked to a lower risk of allergies, so it might be time to get that puppy that the kids have been begging you for all through the pandemic.
Indiana Jones and the outhouse of parasites
Some archaeological finds are more impressive than others. Sometimes you find evidence of some long-lost civilization, sometimes you find a 200-year-old outhouse. That was the case with an outhouse buried near Dartmouth College that belonged to Mill Olcott, a wealthy businessman and politician who was a graduate of the college, and his family.
Now, that’s not particularly medically interesting, but the contents of the outhouse were very well preserved. That treasure trove included some fecal samples, and that’s where the story gets good, since they were preserved enough to be analyzed for parasites. Now, researchers know that parasites were very common in urban areas back in those days, when medicinal knowledge and sanitation were still deep in the dark ages, but whether or not people who lived in rural areas, wealthy or not, had them as well was a mystery.
Of course, 200-year-old poop is 200-year-old poop, so, in a task we wouldn’t envy anyone, the samples were rehydrated and run through several sieves to isolate the ancient goodies within. When all was said and done, both tapeworm and whipworm eggs were found, a surprise considering parasitic preference for warmer environments – not something northern New England is known for. But don’t forget, parasites can be your friend, too.
We will probably never know just which member of the Olcott household the poop belonged to, but the researchers noted that it was almost certain the entire house was infected. They added that, without proper infrastructure, even wealth was unable to protect people from disease. Hmm, we can’t think of any relevance that has in today’s world. Nope, absolutely none, since our health infrastructure is literally without flaw.
Printing meds per patient
What if there was a way to get exact doses of a medication, tailored specifically for each and every patient that needed it? Well, apparently it’s as easy as getting them out of a printer.
Researchers from the University of East Anglia in England may have found a new method to do just that.
Currently, medicine is “manufactured in ‘one-size-fits-all’ fashion,” said Dr. Sheng Qi, the research lead. But no patient is exactly the same, so why shouldn’t their medications be just as unique? Research on pharmaceutical 3D printing has been developing over the past 5 years, with the most common method requiring the drug to be put into “spaghetti-like filaments” before printing.
Dr. Qi and his team developed a process that bypasses the filaments, allowing them to 3D-print pills with varied porous structures that can regulate the rate of release of the drug into the body. This could be revolutionary for elderly patients and patients with complicated conditions – who often take many different drugs – to ensure more accurate doses that provide maximum benefits and minimal adverse effects.
Just as a custom-tailored suit perfectly fits the body for which it was made, the ability to tailor medication could have the same effect on a patient’s health. The only difference is what’s coming through the printer would be pills, not fabric.
It’s hip to be Pfizered
COVID-19 vaccination levels are rising, but we’ve heard a rumor that some people are still a bit reticent to participate. So how can physicians get more people to come in for a shot?
Make sure that they’re giving patients the right vaccine, for one thing. And by “right” vaccine, we mean, of course, the cool vaccine. Yes, the Internet has decided that the Pfizer vaccine is cooler than the others, according to the Atlantic.
There is, it seems, such a thing as “Pfizer superiority complex,” the article noted, while adding that, “on TikTok, hundreds of videos use a soundtrack of a woman explaining – slowly, voice full of disdain, like the rudest preschool teacher on Earth – ‘Only hot people get the Pfizer vaccine.’ ” A reporter from Slate was welcomed “to the ruling class” after sharing her upcoming Pfizer vaccination.
For the ultimate test of coolness, we surveyed the LOTME staff about the COVID-19 vaccines they had received. The results? Two Pfizers (coincidentally, the only two who knew what the hell TikTok is), one Moderna, one Johnson & Johnson, and one Godbold’s Vegetable Balsam (coincidentally, the same one who told us to get off his lawn).
And yes, we are checking on that last one.
Allergies stink!
A baby’s first bowel movement might mean more than just being the first of many diaper changes.
That particular bowel movement, called meconium, is a mixture of materials that have gone into a baby’s mouth late in the pregnancy, such as skin cells and amniotic fluid. Sounds lovely, right? The contents also include certain biochemicals and gut bacteria, and a lack of these can show an increased risk of allergies, eczema, and asthma.
Studies show that certain gut bacteria actually teach the immune system to accept compounds that are not harmful. Since allergies and other conditions are caused by a person’s immune system telling them harmless compounds are bad, it makes sense that lacking gut bacteria might show potential for developing such conditions.
Charisse Petersen, a researcher at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, told NewScientist that parents could help decrease the development of allergies by not giving their children antibiotics that aren’t necessary and by letting kids play outside more.
Tom Marrs of King’s College London even noted that having a dog in the house is linked to a lower risk of allergies, so it might be time to get that puppy that the kids have been begging you for all through the pandemic.
Indiana Jones and the outhouse of parasites
Some archaeological finds are more impressive than others. Sometimes you find evidence of some long-lost civilization, sometimes you find a 200-year-old outhouse. That was the case with an outhouse buried near Dartmouth College that belonged to Mill Olcott, a wealthy businessman and politician who was a graduate of the college, and his family.
Now, that’s not particularly medically interesting, but the contents of the outhouse were very well preserved. That treasure trove included some fecal samples, and that’s where the story gets good, since they were preserved enough to be analyzed for parasites. Now, researchers know that parasites were very common in urban areas back in those days, when medicinal knowledge and sanitation were still deep in the dark ages, but whether or not people who lived in rural areas, wealthy or not, had them as well was a mystery.
Of course, 200-year-old poop is 200-year-old poop, so, in a task we wouldn’t envy anyone, the samples were rehydrated and run through several sieves to isolate the ancient goodies within. When all was said and done, both tapeworm and whipworm eggs were found, a surprise considering parasitic preference for warmer environments – not something northern New England is known for. But don’t forget, parasites can be your friend, too.
We will probably never know just which member of the Olcott household the poop belonged to, but the researchers noted that it was almost certain the entire house was infected. They added that, without proper infrastructure, even wealth was unable to protect people from disease. Hmm, we can’t think of any relevance that has in today’s world. Nope, absolutely none, since our health infrastructure is literally without flaw.
Printing meds per patient
What if there was a way to get exact doses of a medication, tailored specifically for each and every patient that needed it? Well, apparently it’s as easy as getting them out of a printer.
Researchers from the University of East Anglia in England may have found a new method to do just that.
Currently, medicine is “manufactured in ‘one-size-fits-all’ fashion,” said Dr. Sheng Qi, the research lead. But no patient is exactly the same, so why shouldn’t their medications be just as unique? Research on pharmaceutical 3D printing has been developing over the past 5 years, with the most common method requiring the drug to be put into “spaghetti-like filaments” before printing.
Dr. Qi and his team developed a process that bypasses the filaments, allowing them to 3D-print pills with varied porous structures that can regulate the rate of release of the drug into the body. This could be revolutionary for elderly patients and patients with complicated conditions – who often take many different drugs – to ensure more accurate doses that provide maximum benefits and minimal adverse effects.
Just as a custom-tailored suit perfectly fits the body for which it was made, the ability to tailor medication could have the same effect on a patient’s health. The only difference is what’s coming through the printer would be pills, not fabric.
It’s hip to be Pfizered
COVID-19 vaccination levels are rising, but we’ve heard a rumor that some people are still a bit reticent to participate. So how can physicians get more people to come in for a shot?
Make sure that they’re giving patients the right vaccine, for one thing. And by “right” vaccine, we mean, of course, the cool vaccine. Yes, the Internet has decided that the Pfizer vaccine is cooler than the others, according to the Atlantic.
There is, it seems, such a thing as “Pfizer superiority complex,” the article noted, while adding that, “on TikTok, hundreds of videos use a soundtrack of a woman explaining – slowly, voice full of disdain, like the rudest preschool teacher on Earth – ‘Only hot people get the Pfizer vaccine.’ ” A reporter from Slate was welcomed “to the ruling class” after sharing her upcoming Pfizer vaccination.
For the ultimate test of coolness, we surveyed the LOTME staff about the COVID-19 vaccines they had received. The results? Two Pfizers (coincidentally, the only two who knew what the hell TikTok is), one Moderna, one Johnson & Johnson, and one Godbold’s Vegetable Balsam (coincidentally, the same one who told us to get off his lawn).
And yes, we are checking on that last one.
Allergies stink!
A baby’s first bowel movement might mean more than just being the first of many diaper changes.
That particular bowel movement, called meconium, is a mixture of materials that have gone into a baby’s mouth late in the pregnancy, such as skin cells and amniotic fluid. Sounds lovely, right? The contents also include certain biochemicals and gut bacteria, and a lack of these can show an increased risk of allergies, eczema, and asthma.
Studies show that certain gut bacteria actually teach the immune system to accept compounds that are not harmful. Since allergies and other conditions are caused by a person’s immune system telling them harmless compounds are bad, it makes sense that lacking gut bacteria might show potential for developing such conditions.
Charisse Petersen, a researcher at the University of British Columbia in Vancouver, told NewScientist that parents could help decrease the development of allergies by not giving their children antibiotics that aren’t necessary and by letting kids play outside more.
Tom Marrs of King’s College London even noted that having a dog in the house is linked to a lower risk of allergies, so it might be time to get that puppy that the kids have been begging you for all through the pandemic.
Indiana Jones and the outhouse of parasites
Some archaeological finds are more impressive than others. Sometimes you find evidence of some long-lost civilization, sometimes you find a 200-year-old outhouse. That was the case with an outhouse buried near Dartmouth College that belonged to Mill Olcott, a wealthy businessman and politician who was a graduate of the college, and his family.
Now, that’s not particularly medically interesting, but the contents of the outhouse were very well preserved. That treasure trove included some fecal samples, and that’s where the story gets good, since they were preserved enough to be analyzed for parasites. Now, researchers know that parasites were very common in urban areas back in those days, when medicinal knowledge and sanitation were still deep in the dark ages, but whether or not people who lived in rural areas, wealthy or not, had them as well was a mystery.
Of course, 200-year-old poop is 200-year-old poop, so, in a task we wouldn’t envy anyone, the samples were rehydrated and run through several sieves to isolate the ancient goodies within. When all was said and done, both tapeworm and whipworm eggs were found, a surprise considering parasitic preference for warmer environments – not something northern New England is known for. But don’t forget, parasites can be your friend, too.
We will probably never know just which member of the Olcott household the poop belonged to, but the researchers noted that it was almost certain the entire house was infected. They added that, without proper infrastructure, even wealth was unable to protect people from disease. Hmm, we can’t think of any relevance that has in today’s world. Nope, absolutely none, since our health infrastructure is literally without flaw.
Restrict J&J COVID vaccine in women under 50?
Use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines should be considered as the preferable option in the United States rather than Johnson & Johnson’s (J&J) Janssen COVID-19 vaccine in women aged under 50 years, according to one group of experts.
The group made their recommendation in an editorial in JAMA published online April 30, 2021, accompanying a paper describing details of 12 case reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) with thrombocytopenia following the J&J COVID-19 vaccine, also known as the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.
The editorialists are Ruth A. Karron, MD, professor of international health at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore; Nigel S. Key, MD, professor of hematology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; and Joshua M. Sharfstein, MD, associate dean for public health practice at Johns Hopkins
They noted that, after an initial pause following reports of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) linked to the J&J vaccine, and on the recommendation of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the United States has permitted the use of the J&J vaccine in all adults with information on the risk of TTS added to educational materials.
The editorialists pointed out that no cases of TTS have been confirmed following administration of more than 180 million doses of the mRNA vaccines in the United States.
They said that, while the J&J vaccine will still be needed for individuals with allergies to components of the mRNA vaccines and for those who live in remote locations where the cold chain for transport and storage of mRNA vaccines cannot be maintained, “U.S. public health agencies and clinicians should consider recommending mRNA vaccines as safer options for those who may be at substantially higher risk for TTS after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, currently women younger than 50 years.”
In the main JAMA paper, a group led by Isaac See, MD, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 Response Team, reported full details of 12 cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia following the J&J COVID-19 vaccine reported to the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
The 12 U.S. case reports, 3 of which were fatal, show many similarities to cases described in Europe after the AstraZeneca vaccine.
The authors noted that, by April 12, approximately 7 million doses of the J&J vaccine had been given in the United States. The 12 cases of CVST and thrombocytopenia following receipt of the vaccine were reported to VAERS between March 2 and April 21. All 12 cases were in White women, 11 of whom were aged under 50 years.
As of April 25, a further two cases have been confirmed and reported to VAERS; one in a man younger than 40 years, the other in a woman aged between 40 and 59 years.
In the 12 cases reported in detail, symptoms started between 6 and 15 days post vaccination.
At least one risk factor for CVST was identified in seven patients (obesity in six, hypothyroidism in one, and use of combined oral contraceptives in one). None of the patients was pregnant or within 12 weeks post partum, had prior thrombosis, a personal or family history of thrombophilia, or documented prior exposure to heparin.
In addition to CVST, seven patients had intracerebral hemorrhage and eight had non-CVST thromboses.
One patient reported a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection approximately 4 months prior to vaccination. Of the other 11 patients, 4 had negative serologic tests and 7 were not tested.
All 12 patients were hospitalized and 10 were admitted to an ICU. At the time of the last follow-up, three patients had died (all of whom had intraparenchymal hemorrhage), three remained in the ICU, two were still hospitalized but not in an ICU, and four had been discharged home.
The authors pointed out that the U.S. cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia following the J&J vaccine have many similarities to those reported in Europe after the AstraZeneca vaccine, occurring primarily in women younger than 40 years and in patients without diagnosed thrombophilia. Both European and U.S. patients had a median platelet nadir count of 19 x 103/mcL and several also had non-CVST large-vessel thrombosis.
In the European cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia, 50% of patients died, compared with 25% of U.S. patients.
Like the European cases, the U.S. cases had positive heparin-PF4 HIT antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests in the absence of prior exposure to heparin, as would be seen in autoimmune HIT.
However, in the initial European CVST reports, 88% of patients tested with functional platelet HIT antibody tests had positive results, compared with only 11% of the U.S. cases. But the authors noted that lack of standardization in functional platelet HIT antibody assays may lead to differences in results by different laboratories.
“It may be important to notify testing laboratories that postvaccination TTS is being evaluated, so that testing methods can be adjusted if needed,” they said.
They concluded that these case reports suggest that the pathogenesis of TTS may be similar to autoimmune HIT, triggered by the formation of antibodies directed against PF4, a constituent of platelet alpha granules released during platelet activation. In contrast to classic HIT in which exogenous heparin triggers antibody formation, in autoimmune HIT, an endogenous polyanion triggers PF4 antibody formation.
They noted that the precise mechanism of TTS in relation to COVID-19 vaccination has not yet been established. The Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety has stated that a platform-specific mechanism related to adenovirus vector vaccines cannot be excluded. Both the J&J and AstraZeneca vaccines use an adenoviral vector, but they are different; J&J uses a human vector, while AstraZeneca uses a chimpanzee vector.
They also pointed out that CVST and thrombocytopenia following SARS-CoV-2 infection has been reported in at least two cases, but HIT testing was not done in these cases. There have not so far been any reports to VAERS of CVST with thrombocytopenia following mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
The authors said these findings have important clinical and public health implications, noting that the CDC has updated its interim clinical considerations for use of authorized COVID-19 vaccines to indicate that women aged 18-49 years should be aware of the increased risk of TTS after receipt of the J&J vaccine, and to use a nonheparin anticoagulant in suspected cases.
They noted that a subacute presentation of headache is present in 90% of patients with typical CVST. While headache is a common symptom after the J&J vaccination, most headaches begin and resolve within 2 days. Whereas in the U.S. cases of CVST after vaccination, headache symptoms began at least 6 days after vaccination and persisted for at least a week for most.
“Urgent consultation with a neurologist is prudent when a patient is suspected or confirmed to have CVST. In addition, since the median time from symptom onset to hospitalization was 7 days in the U.S. CVST case series, patient and clinician education might shorten the time to clinical evaluation and therefore treatment,” they stated.
The authors also note that VAERS is a passive surveillance system, so cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia may be underreported.
In their accompanying editorial, Dr. Karron and colleagues pointed out that, in addition to the 12 patients with CVST with thrombocytopenia described in this case series, at least three patients without CVST but meeting diagnostic criteria for TTS have been reported to VAERS (as of April 21), all in women aged 18-59 years (median age, 37 years).
The editorialists reported that the rate of CVST with thrombocytopenia after the J&J vaccine is approximately 5 per million women aged 18-50 years. This is compared with a background rate of approximately 0.05-0.13 per million per month.
They said that the availability of an interim standardized case definition of this adverse effect will facilitate prospective case ascertainment through review of large linked databases and active case finding.
This will also permit greater understanding of whether individuals who are otherwise at increased risk for hypercoagulation in general and for CVST in particular (for example, women taking hormonal contraceptive medications or who are pregnant) are also at increased risk for TTS.
Obtaining this information will support dynamic country-specific assessments of the risks of each vaccine, compared with the risk of COVID-19 disease for their populations and subpopulations, they added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines should be considered as the preferable option in the United States rather than Johnson & Johnson’s (J&J) Janssen COVID-19 vaccine in women aged under 50 years, according to one group of experts.
The group made their recommendation in an editorial in JAMA published online April 30, 2021, accompanying a paper describing details of 12 case reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) with thrombocytopenia following the J&J COVID-19 vaccine, also known as the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.
The editorialists are Ruth A. Karron, MD, professor of international health at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore; Nigel S. Key, MD, professor of hematology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; and Joshua M. Sharfstein, MD, associate dean for public health practice at Johns Hopkins
They noted that, after an initial pause following reports of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) linked to the J&J vaccine, and on the recommendation of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the United States has permitted the use of the J&J vaccine in all adults with information on the risk of TTS added to educational materials.
The editorialists pointed out that no cases of TTS have been confirmed following administration of more than 180 million doses of the mRNA vaccines in the United States.
They said that, while the J&J vaccine will still be needed for individuals with allergies to components of the mRNA vaccines and for those who live in remote locations where the cold chain for transport and storage of mRNA vaccines cannot be maintained, “U.S. public health agencies and clinicians should consider recommending mRNA vaccines as safer options for those who may be at substantially higher risk for TTS after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, currently women younger than 50 years.”
In the main JAMA paper, a group led by Isaac See, MD, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 Response Team, reported full details of 12 cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia following the J&J COVID-19 vaccine reported to the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
The 12 U.S. case reports, 3 of which were fatal, show many similarities to cases described in Europe after the AstraZeneca vaccine.
The authors noted that, by April 12, approximately 7 million doses of the J&J vaccine had been given in the United States. The 12 cases of CVST and thrombocytopenia following receipt of the vaccine were reported to VAERS between March 2 and April 21. All 12 cases were in White women, 11 of whom were aged under 50 years.
As of April 25, a further two cases have been confirmed and reported to VAERS; one in a man younger than 40 years, the other in a woman aged between 40 and 59 years.
In the 12 cases reported in detail, symptoms started between 6 and 15 days post vaccination.
At least one risk factor for CVST was identified in seven patients (obesity in six, hypothyroidism in one, and use of combined oral contraceptives in one). None of the patients was pregnant or within 12 weeks post partum, had prior thrombosis, a personal or family history of thrombophilia, or documented prior exposure to heparin.
In addition to CVST, seven patients had intracerebral hemorrhage and eight had non-CVST thromboses.
One patient reported a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection approximately 4 months prior to vaccination. Of the other 11 patients, 4 had negative serologic tests and 7 were not tested.
All 12 patients were hospitalized and 10 were admitted to an ICU. At the time of the last follow-up, three patients had died (all of whom had intraparenchymal hemorrhage), three remained in the ICU, two were still hospitalized but not in an ICU, and four had been discharged home.
The authors pointed out that the U.S. cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia following the J&J vaccine have many similarities to those reported in Europe after the AstraZeneca vaccine, occurring primarily in women younger than 40 years and in patients without diagnosed thrombophilia. Both European and U.S. patients had a median platelet nadir count of 19 x 103/mcL and several also had non-CVST large-vessel thrombosis.
In the European cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia, 50% of patients died, compared with 25% of U.S. patients.
Like the European cases, the U.S. cases had positive heparin-PF4 HIT antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests in the absence of prior exposure to heparin, as would be seen in autoimmune HIT.
However, in the initial European CVST reports, 88% of patients tested with functional platelet HIT antibody tests had positive results, compared with only 11% of the U.S. cases. But the authors noted that lack of standardization in functional platelet HIT antibody assays may lead to differences in results by different laboratories.
“It may be important to notify testing laboratories that postvaccination TTS is being evaluated, so that testing methods can be adjusted if needed,” they said.
They concluded that these case reports suggest that the pathogenesis of TTS may be similar to autoimmune HIT, triggered by the formation of antibodies directed against PF4, a constituent of platelet alpha granules released during platelet activation. In contrast to classic HIT in which exogenous heparin triggers antibody formation, in autoimmune HIT, an endogenous polyanion triggers PF4 antibody formation.
They noted that the precise mechanism of TTS in relation to COVID-19 vaccination has not yet been established. The Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety has stated that a platform-specific mechanism related to adenovirus vector vaccines cannot be excluded. Both the J&J and AstraZeneca vaccines use an adenoviral vector, but they are different; J&J uses a human vector, while AstraZeneca uses a chimpanzee vector.
They also pointed out that CVST and thrombocytopenia following SARS-CoV-2 infection has been reported in at least two cases, but HIT testing was not done in these cases. There have not so far been any reports to VAERS of CVST with thrombocytopenia following mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
The authors said these findings have important clinical and public health implications, noting that the CDC has updated its interim clinical considerations for use of authorized COVID-19 vaccines to indicate that women aged 18-49 years should be aware of the increased risk of TTS after receipt of the J&J vaccine, and to use a nonheparin anticoagulant in suspected cases.
They noted that a subacute presentation of headache is present in 90% of patients with typical CVST. While headache is a common symptom after the J&J vaccination, most headaches begin and resolve within 2 days. Whereas in the U.S. cases of CVST after vaccination, headache symptoms began at least 6 days after vaccination and persisted for at least a week for most.
“Urgent consultation with a neurologist is prudent when a patient is suspected or confirmed to have CVST. In addition, since the median time from symptom onset to hospitalization was 7 days in the U.S. CVST case series, patient and clinician education might shorten the time to clinical evaluation and therefore treatment,” they stated.
The authors also note that VAERS is a passive surveillance system, so cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia may be underreported.
In their accompanying editorial, Dr. Karron and colleagues pointed out that, in addition to the 12 patients with CVST with thrombocytopenia described in this case series, at least three patients without CVST but meeting diagnostic criteria for TTS have been reported to VAERS (as of April 21), all in women aged 18-59 years (median age, 37 years).
The editorialists reported that the rate of CVST with thrombocytopenia after the J&J vaccine is approximately 5 per million women aged 18-50 years. This is compared with a background rate of approximately 0.05-0.13 per million per month.
They said that the availability of an interim standardized case definition of this adverse effect will facilitate prospective case ascertainment through review of large linked databases and active case finding.
This will also permit greater understanding of whether individuals who are otherwise at increased risk for hypercoagulation in general and for CVST in particular (for example, women taking hormonal contraceptive medications or who are pregnant) are also at increased risk for TTS.
Obtaining this information will support dynamic country-specific assessments of the risks of each vaccine, compared with the risk of COVID-19 disease for their populations and subpopulations, they added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines should be considered as the preferable option in the United States rather than Johnson & Johnson’s (J&J) Janssen COVID-19 vaccine in women aged under 50 years, according to one group of experts.
The group made their recommendation in an editorial in JAMA published online April 30, 2021, accompanying a paper describing details of 12 case reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) with thrombocytopenia following the J&J COVID-19 vaccine, also known as the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.
The editorialists are Ruth A. Karron, MD, professor of international health at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore; Nigel S. Key, MD, professor of hematology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; and Joshua M. Sharfstein, MD, associate dean for public health practice at Johns Hopkins
They noted that, after an initial pause following reports of thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS) linked to the J&J vaccine, and on the recommendation of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the United States has permitted the use of the J&J vaccine in all adults with information on the risk of TTS added to educational materials.
The editorialists pointed out that no cases of TTS have been confirmed following administration of more than 180 million doses of the mRNA vaccines in the United States.
They said that, while the J&J vaccine will still be needed for individuals with allergies to components of the mRNA vaccines and for those who live in remote locations where the cold chain for transport and storage of mRNA vaccines cannot be maintained, “U.S. public health agencies and clinicians should consider recommending mRNA vaccines as safer options for those who may be at substantially higher risk for TTS after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, currently women younger than 50 years.”
In the main JAMA paper, a group led by Isaac See, MD, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 Response Team, reported full details of 12 cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia following the J&J COVID-19 vaccine reported to the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
The 12 U.S. case reports, 3 of which were fatal, show many similarities to cases described in Europe after the AstraZeneca vaccine.
The authors noted that, by April 12, approximately 7 million doses of the J&J vaccine had been given in the United States. The 12 cases of CVST and thrombocytopenia following receipt of the vaccine were reported to VAERS between March 2 and April 21. All 12 cases were in White women, 11 of whom were aged under 50 years.
As of April 25, a further two cases have been confirmed and reported to VAERS; one in a man younger than 40 years, the other in a woman aged between 40 and 59 years.
In the 12 cases reported in detail, symptoms started between 6 and 15 days post vaccination.
At least one risk factor for CVST was identified in seven patients (obesity in six, hypothyroidism in one, and use of combined oral contraceptives in one). None of the patients was pregnant or within 12 weeks post partum, had prior thrombosis, a personal or family history of thrombophilia, or documented prior exposure to heparin.
In addition to CVST, seven patients had intracerebral hemorrhage and eight had non-CVST thromboses.
One patient reported a history of SARS-CoV-2 infection approximately 4 months prior to vaccination. Of the other 11 patients, 4 had negative serologic tests and 7 were not tested.
All 12 patients were hospitalized and 10 were admitted to an ICU. At the time of the last follow-up, three patients had died (all of whom had intraparenchymal hemorrhage), three remained in the ICU, two were still hospitalized but not in an ICU, and four had been discharged home.
The authors pointed out that the U.S. cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia following the J&J vaccine have many similarities to those reported in Europe after the AstraZeneca vaccine, occurring primarily in women younger than 40 years and in patients without diagnosed thrombophilia. Both European and U.S. patients had a median platelet nadir count of 19 x 103/mcL and several also had non-CVST large-vessel thrombosis.
In the European cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia, 50% of patients died, compared with 25% of U.S. patients.
Like the European cases, the U.S. cases had positive heparin-PF4 HIT antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests in the absence of prior exposure to heparin, as would be seen in autoimmune HIT.
However, in the initial European CVST reports, 88% of patients tested with functional platelet HIT antibody tests had positive results, compared with only 11% of the U.S. cases. But the authors noted that lack of standardization in functional platelet HIT antibody assays may lead to differences in results by different laboratories.
“It may be important to notify testing laboratories that postvaccination TTS is being evaluated, so that testing methods can be adjusted if needed,” they said.
They concluded that these case reports suggest that the pathogenesis of TTS may be similar to autoimmune HIT, triggered by the formation of antibodies directed against PF4, a constituent of platelet alpha granules released during platelet activation. In contrast to classic HIT in which exogenous heparin triggers antibody formation, in autoimmune HIT, an endogenous polyanion triggers PF4 antibody formation.
They noted that the precise mechanism of TTS in relation to COVID-19 vaccination has not yet been established. The Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety has stated that a platform-specific mechanism related to adenovirus vector vaccines cannot be excluded. Both the J&J and AstraZeneca vaccines use an adenoviral vector, but they are different; J&J uses a human vector, while AstraZeneca uses a chimpanzee vector.
They also pointed out that CVST and thrombocytopenia following SARS-CoV-2 infection has been reported in at least two cases, but HIT testing was not done in these cases. There have not so far been any reports to VAERS of CVST with thrombocytopenia following mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
The authors said these findings have important clinical and public health implications, noting that the CDC has updated its interim clinical considerations for use of authorized COVID-19 vaccines to indicate that women aged 18-49 years should be aware of the increased risk of TTS after receipt of the J&J vaccine, and to use a nonheparin anticoagulant in suspected cases.
They noted that a subacute presentation of headache is present in 90% of patients with typical CVST. While headache is a common symptom after the J&J vaccination, most headaches begin and resolve within 2 days. Whereas in the U.S. cases of CVST after vaccination, headache symptoms began at least 6 days after vaccination and persisted for at least a week for most.
“Urgent consultation with a neurologist is prudent when a patient is suspected or confirmed to have CVST. In addition, since the median time from symptom onset to hospitalization was 7 days in the U.S. CVST case series, patient and clinician education might shorten the time to clinical evaluation and therefore treatment,” they stated.
The authors also note that VAERS is a passive surveillance system, so cases of CVST with thrombocytopenia may be underreported.
In their accompanying editorial, Dr. Karron and colleagues pointed out that, in addition to the 12 patients with CVST with thrombocytopenia described in this case series, at least three patients without CVST but meeting diagnostic criteria for TTS have been reported to VAERS (as of April 21), all in women aged 18-59 years (median age, 37 years).
The editorialists reported that the rate of CVST with thrombocytopenia after the J&J vaccine is approximately 5 per million women aged 18-50 years. This is compared with a background rate of approximately 0.05-0.13 per million per month.
They said that the availability of an interim standardized case definition of this adverse effect will facilitate prospective case ascertainment through review of large linked databases and active case finding.
This will also permit greater understanding of whether individuals who are otherwise at increased risk for hypercoagulation in general and for CVST in particular (for example, women taking hormonal contraceptive medications or who are pregnant) are also at increased risk for TTS.
Obtaining this information will support dynamic country-specific assessments of the risks of each vaccine, compared with the risk of COVID-19 disease for their populations and subpopulations, they added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
High variability found in studies assessing hemophilia-related pain
Chronic pain is a common condition among people with hemophilia and is associated with joint deterioration because of repeated joint bleeds. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the prevalence of chronic pain because of hemophilia and to analyze its interference in the lives of patients, according to Ana Cristina Paredes, a PhD student at the University of Minho, Braga, Portugal, and colleagues.
The manuscripts included in the study, which was published online in the Journal of Pain, were mostly observational, cross-sectional studies and one prospective investigation, published between 2009 and 2019.
The issue of pain is particularly important among people with hemophilia, as many adult patients suffer from distinct degrees of arthropathy and associated chronic pain, due to the lifelong occurrence of hemarthrosis, the authors noted. In an important distinction, according to the authors, people with hemophilia may therefore experience both acute pain during bleeds and chronic pain caused by joint deterioration. Acute pain ceases with the resolution of the bleeding episode, but the chronic pain is significantly more challenging, since it persists in time and may trigger changes in the nervous system, leading to peripheral or central sensitization.
Data in the assessed studies were collected from a variety of sources: hemophilia centers, online surveys, by mail, or through a national database, with return rates ranging from 29.2% to 98%. Overall, these studies comprised 4,772 adults, with individual sample sizes ranging from 21 to 2,253 patients, the authors added.
Conflicting results
Overall, there was a widely varying prevalence of hemophilia-related chronic pain reported across studies. Additionally, methodologies and sample characteristics varied widely. The meta-analyses revealed high heterogeneity between studies, and, therefore, pooled prevalence estimates values must be interpreted with caution, the authors stated.
All of the 11 selected studies included for meta-analysis and review reported on the prevalence of chronic pain caused by hemophilia. Chronic pain was assessed using direct questions developed by the authors in eight studies and using the European Haemophilia Therapy Standardization Board definition in three studies. The prevalence for global samples ranged widely from 17% to 84%.
Although there was high heterogeneity, the random-effects meta-analysis including all studies demonstrated a pooled prevalence of 46% of patients reporting chronic pain. Subgroup analyses of studies including all disease severities (mild, moderate, and severe; seven studies) revealed a pooled prevalence of 48%, but also with high heterogeneity. Looking at severe patients only (six studies), the chronic pain prevalence ranged from 33% to 86.4%, with a pooled prevalence of 53% and high heterogeneity, the authors added.
The wide disparity of the chronic pain prevalence seen across the studies is likely because of the fact that some investigations inquired about pain without distinguishing between acute (hemarthrosis-related) or chronic (arthropathy-related) pain, and without clarifying if the only focus is pain caused by hemophilia, or including all causes of pain complaints, according to the researchers.
“Concerning hemophilia-related chronic pain interference, it is striking that the existing literature does not distinguish between the impact of acute or chronic pain. Such a distinction is needed and should be made in future studies to ensure accurate accounts of hemophilia-related pain and to fully understand its interference according to the type of pain (acute vs. chronic). This information is relevant to promote targeted and effective treatment approaches,” the researchers concluded.
The research was supported by a Novo Nordisk HERO Research Grant 2015, the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, and the Foundation for Science and Technology in Portugal. The authors declared they had no conflicts of interest.
Chronic pain is a common condition among people with hemophilia and is associated with joint deterioration because of repeated joint bleeds. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the prevalence of chronic pain because of hemophilia and to analyze its interference in the lives of patients, according to Ana Cristina Paredes, a PhD student at the University of Minho, Braga, Portugal, and colleagues.
The manuscripts included in the study, which was published online in the Journal of Pain, were mostly observational, cross-sectional studies and one prospective investigation, published between 2009 and 2019.
The issue of pain is particularly important among people with hemophilia, as many adult patients suffer from distinct degrees of arthropathy and associated chronic pain, due to the lifelong occurrence of hemarthrosis, the authors noted. In an important distinction, according to the authors, people with hemophilia may therefore experience both acute pain during bleeds and chronic pain caused by joint deterioration. Acute pain ceases with the resolution of the bleeding episode, but the chronic pain is significantly more challenging, since it persists in time and may trigger changes in the nervous system, leading to peripheral or central sensitization.
Data in the assessed studies were collected from a variety of sources: hemophilia centers, online surveys, by mail, or through a national database, with return rates ranging from 29.2% to 98%. Overall, these studies comprised 4,772 adults, with individual sample sizes ranging from 21 to 2,253 patients, the authors added.
Conflicting results
Overall, there was a widely varying prevalence of hemophilia-related chronic pain reported across studies. Additionally, methodologies and sample characteristics varied widely. The meta-analyses revealed high heterogeneity between studies, and, therefore, pooled prevalence estimates values must be interpreted with caution, the authors stated.
All of the 11 selected studies included for meta-analysis and review reported on the prevalence of chronic pain caused by hemophilia. Chronic pain was assessed using direct questions developed by the authors in eight studies and using the European Haemophilia Therapy Standardization Board definition in three studies. The prevalence for global samples ranged widely from 17% to 84%.
Although there was high heterogeneity, the random-effects meta-analysis including all studies demonstrated a pooled prevalence of 46% of patients reporting chronic pain. Subgroup analyses of studies including all disease severities (mild, moderate, and severe; seven studies) revealed a pooled prevalence of 48%, but also with high heterogeneity. Looking at severe patients only (six studies), the chronic pain prevalence ranged from 33% to 86.4%, with a pooled prevalence of 53% and high heterogeneity, the authors added.
The wide disparity of the chronic pain prevalence seen across the studies is likely because of the fact that some investigations inquired about pain without distinguishing between acute (hemarthrosis-related) or chronic (arthropathy-related) pain, and without clarifying if the only focus is pain caused by hemophilia, or including all causes of pain complaints, according to the researchers.
“Concerning hemophilia-related chronic pain interference, it is striking that the existing literature does not distinguish between the impact of acute or chronic pain. Such a distinction is needed and should be made in future studies to ensure accurate accounts of hemophilia-related pain and to fully understand its interference according to the type of pain (acute vs. chronic). This information is relevant to promote targeted and effective treatment approaches,” the researchers concluded.
The research was supported by a Novo Nordisk HERO Research Grant 2015, the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, and the Foundation for Science and Technology in Portugal. The authors declared they had no conflicts of interest.
Chronic pain is a common condition among people with hemophilia and is associated with joint deterioration because of repeated joint bleeds. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the prevalence of chronic pain because of hemophilia and to analyze its interference in the lives of patients, according to Ana Cristina Paredes, a PhD student at the University of Minho, Braga, Portugal, and colleagues.
The manuscripts included in the study, which was published online in the Journal of Pain, were mostly observational, cross-sectional studies and one prospective investigation, published between 2009 and 2019.
The issue of pain is particularly important among people with hemophilia, as many adult patients suffer from distinct degrees of arthropathy and associated chronic pain, due to the lifelong occurrence of hemarthrosis, the authors noted. In an important distinction, according to the authors, people with hemophilia may therefore experience both acute pain during bleeds and chronic pain caused by joint deterioration. Acute pain ceases with the resolution of the bleeding episode, but the chronic pain is significantly more challenging, since it persists in time and may trigger changes in the nervous system, leading to peripheral or central sensitization.
Data in the assessed studies were collected from a variety of sources: hemophilia centers, online surveys, by mail, or through a national database, with return rates ranging from 29.2% to 98%. Overall, these studies comprised 4,772 adults, with individual sample sizes ranging from 21 to 2,253 patients, the authors added.
Conflicting results
Overall, there was a widely varying prevalence of hemophilia-related chronic pain reported across studies. Additionally, methodologies and sample characteristics varied widely. The meta-analyses revealed high heterogeneity between studies, and, therefore, pooled prevalence estimates values must be interpreted with caution, the authors stated.
All of the 11 selected studies included for meta-analysis and review reported on the prevalence of chronic pain caused by hemophilia. Chronic pain was assessed using direct questions developed by the authors in eight studies and using the European Haemophilia Therapy Standardization Board definition in three studies. The prevalence for global samples ranged widely from 17% to 84%.
Although there was high heterogeneity, the random-effects meta-analysis including all studies demonstrated a pooled prevalence of 46% of patients reporting chronic pain. Subgroup analyses of studies including all disease severities (mild, moderate, and severe; seven studies) revealed a pooled prevalence of 48%, but also with high heterogeneity. Looking at severe patients only (six studies), the chronic pain prevalence ranged from 33% to 86.4%, with a pooled prevalence of 53% and high heterogeneity, the authors added.
The wide disparity of the chronic pain prevalence seen across the studies is likely because of the fact that some investigations inquired about pain without distinguishing between acute (hemarthrosis-related) or chronic (arthropathy-related) pain, and without clarifying if the only focus is pain caused by hemophilia, or including all causes of pain complaints, according to the researchers.
“Concerning hemophilia-related chronic pain interference, it is striking that the existing literature does not distinguish between the impact of acute or chronic pain. Such a distinction is needed and should be made in future studies to ensure accurate accounts of hemophilia-related pain and to fully understand its interference according to the type of pain (acute vs. chronic). This information is relevant to promote targeted and effective treatment approaches,” the researchers concluded.
The research was supported by a Novo Nordisk HERO Research Grant 2015, the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, and the Foundation for Science and Technology in Portugal. The authors declared they had no conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PAIN
Weight cycling linked to cartilage degeneration in knee OA
Repetitive weight loss and gain in overweight or obese patients with knee osteoarthritis is associated with significantly greater cartilage and bone marrow edema degeneration than stable weight or steady weight loss, research suggests.
A presentation at the OARSI 2021 World Congress outlined the results of a study using Osteoarthritis Initiative data from 2,271 individuals with knee osteoarthritis and a body mass index (BMI) of 25 kg/m2 or above, which examined the effects of “weight cycling” on OA outcomes.
Gabby Joseph, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco, told the conference – which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International – that previous studies had shown weight loss improves OA symptoms and slow progression, and weight gain increases OA risk. However no studies had yet examined the effects of weight cycling.
The study compared 4 years of MRI data for those who showed less than 3% loss or gain in weight over that time – the control group – versus those who lost more than 5% over that time and those who gained more than 5%. Among these were 249 individuals in the top 10% of annual weight change over that period, who were designated as weight cyclers. They tended to be younger, female, and with slightly higher average BMI than noncyclers.
Weight cyclers had significantly greater progression of cartilage degeneration and bone marrow edema degeneration – as measured by whole-organ magnetic resonance score – than did noncyclers, regardless of their overall weight gain or loss by the end of the study period.
However, the study did not see any significant differences in meniscus progression between cyclers and noncyclers, and cartilage thickness decreased in all groups over the 4 years with no significant effects associated with weight gain, loss, or cycling. Dr. Joseph commented that future studies could use voxel-based relaxometry to more closely study localized cartilage abnormalities.
Researchers also examined the effect of weight cycling on changes to walking speed, and found weight cyclers had significantly lower walking speeds by the end of the 4 years, regardless of overall weight change.
“What we’ve seen is that fluctuations are not beneficial for your joints,” Dr. Joseph told the conference. “When we advise patients that they want to lose weight, we want to do this in a very steady fashion; we don’t want yo-yo dieting.” She gave the example of one patient who started the study with a BMI of 36, went up to 40 then went down to 32.
Commenting on the study, Lisa Carlesso, PhD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., said it addresses an important issue because weight cycling is common as people struggle to maintain weight loss.
While it is difficult to speculate on the physiological mechanisms that might explain the effect, Dr. Carlesso noted that there were significantly more women than men among the weight cyclers.
“We know, for example, that obese women with knee OA have significantly higher levels of the adipokine leptin, compared to men, and leptin is involved in cartilage degeneration,” Dr. Carlesso said. “Similarly, we don’t have any information about joint alignment or measures of joint load, two things that could factor into the structural changes found.”
She suggested both these possibilities could be explored in future studies of weight cycling and its effects.
“It has opened up new lines of inquiry to be examined to mechanistically explain the relationship between cycling and worse cartilage and bone marrow degeneration,” Dr. Carlesso said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Repetitive weight loss and gain in overweight or obese patients with knee osteoarthritis is associated with significantly greater cartilage and bone marrow edema degeneration than stable weight or steady weight loss, research suggests.
A presentation at the OARSI 2021 World Congress outlined the results of a study using Osteoarthritis Initiative data from 2,271 individuals with knee osteoarthritis and a body mass index (BMI) of 25 kg/m2 or above, which examined the effects of “weight cycling” on OA outcomes.
Gabby Joseph, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco, told the conference – which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International – that previous studies had shown weight loss improves OA symptoms and slow progression, and weight gain increases OA risk. However no studies had yet examined the effects of weight cycling.
The study compared 4 years of MRI data for those who showed less than 3% loss or gain in weight over that time – the control group – versus those who lost more than 5% over that time and those who gained more than 5%. Among these were 249 individuals in the top 10% of annual weight change over that period, who were designated as weight cyclers. They tended to be younger, female, and with slightly higher average BMI than noncyclers.
Weight cyclers had significantly greater progression of cartilage degeneration and bone marrow edema degeneration – as measured by whole-organ magnetic resonance score – than did noncyclers, regardless of their overall weight gain or loss by the end of the study period.
However, the study did not see any significant differences in meniscus progression between cyclers and noncyclers, and cartilage thickness decreased in all groups over the 4 years with no significant effects associated with weight gain, loss, or cycling. Dr. Joseph commented that future studies could use voxel-based relaxometry to more closely study localized cartilage abnormalities.
Researchers also examined the effect of weight cycling on changes to walking speed, and found weight cyclers had significantly lower walking speeds by the end of the 4 years, regardless of overall weight change.
“What we’ve seen is that fluctuations are not beneficial for your joints,” Dr. Joseph told the conference. “When we advise patients that they want to lose weight, we want to do this in a very steady fashion; we don’t want yo-yo dieting.” She gave the example of one patient who started the study with a BMI of 36, went up to 40 then went down to 32.
Commenting on the study, Lisa Carlesso, PhD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., said it addresses an important issue because weight cycling is common as people struggle to maintain weight loss.
While it is difficult to speculate on the physiological mechanisms that might explain the effect, Dr. Carlesso noted that there were significantly more women than men among the weight cyclers.
“We know, for example, that obese women with knee OA have significantly higher levels of the adipokine leptin, compared to men, and leptin is involved in cartilage degeneration,” Dr. Carlesso said. “Similarly, we don’t have any information about joint alignment or measures of joint load, two things that could factor into the structural changes found.”
She suggested both these possibilities could be explored in future studies of weight cycling and its effects.
“It has opened up new lines of inquiry to be examined to mechanistically explain the relationship between cycling and worse cartilage and bone marrow degeneration,” Dr. Carlesso said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
Repetitive weight loss and gain in overweight or obese patients with knee osteoarthritis is associated with significantly greater cartilage and bone marrow edema degeneration than stable weight or steady weight loss, research suggests.
A presentation at the OARSI 2021 World Congress outlined the results of a study using Osteoarthritis Initiative data from 2,271 individuals with knee osteoarthritis and a body mass index (BMI) of 25 kg/m2 or above, which examined the effects of “weight cycling” on OA outcomes.
Gabby Joseph, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco, told the conference – which was sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International – that previous studies had shown weight loss improves OA symptoms and slow progression, and weight gain increases OA risk. However no studies had yet examined the effects of weight cycling.
The study compared 4 years of MRI data for those who showed less than 3% loss or gain in weight over that time – the control group – versus those who lost more than 5% over that time and those who gained more than 5%. Among these were 249 individuals in the top 10% of annual weight change over that period, who were designated as weight cyclers. They tended to be younger, female, and with slightly higher average BMI than noncyclers.
Weight cyclers had significantly greater progression of cartilage degeneration and bone marrow edema degeneration – as measured by whole-organ magnetic resonance score – than did noncyclers, regardless of their overall weight gain or loss by the end of the study period.
However, the study did not see any significant differences in meniscus progression between cyclers and noncyclers, and cartilage thickness decreased in all groups over the 4 years with no significant effects associated with weight gain, loss, or cycling. Dr. Joseph commented that future studies could use voxel-based relaxometry to more closely study localized cartilage abnormalities.
Researchers also examined the effect of weight cycling on changes to walking speed, and found weight cyclers had significantly lower walking speeds by the end of the 4 years, regardless of overall weight change.
“What we’ve seen is that fluctuations are not beneficial for your joints,” Dr. Joseph told the conference. “When we advise patients that they want to lose weight, we want to do this in a very steady fashion; we don’t want yo-yo dieting.” She gave the example of one patient who started the study with a BMI of 36, went up to 40 then went down to 32.
Commenting on the study, Lisa Carlesso, PhD, of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., said it addresses an important issue because weight cycling is common as people struggle to maintain weight loss.
While it is difficult to speculate on the physiological mechanisms that might explain the effect, Dr. Carlesso noted that there were significantly more women than men among the weight cyclers.
“We know, for example, that obese women with knee OA have significantly higher levels of the adipokine leptin, compared to men, and leptin is involved in cartilage degeneration,” Dr. Carlesso said. “Similarly, we don’t have any information about joint alignment or measures of joint load, two things that could factor into the structural changes found.”
She suggested both these possibilities could be explored in future studies of weight cycling and its effects.
“It has opened up new lines of inquiry to be examined to mechanistically explain the relationship between cycling and worse cartilage and bone marrow degeneration,” Dr. Carlesso said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM OARSI 2021
FDA set to okay Pfizer vaccine in younger teens
The Food and Drug Administration could expand the use of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine to teens early next week, The New York Times and CNN reported, both citing unnamed officials familiar with the agency’s plans.
In late March, Pfizer submitted data to the FDA showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12 to 15. Their vaccine is already authorized for use teens and adults ages 16 and older.
The move would make about 17 million more Americans eligible for vaccination and would be a major step toward getting both adolescents and teens back into classrooms full time by next fall.
“Across the globe, we are longing for a normal life. This is especially true for our children. The initial results we have seen in the adolescent studies suggest that children are particularly well protected by vaccination, which is very encouraging given the trends we have seen in recent weeks regarding the spread of the B.1.1.7 U.K. variant,” Ugur Sahin, CEO and co-founder of Pfizer partner BioNTech, said in a March 31 press release.
Getting schools fully reopened for in-person learning has been a goal of both the Trump and Biden administrations, but it has been tricky to pull off, as some parents and teachers have been reluctant to return to classrooms with so much uncertainty about the risk and the role of children in spreading the virus.
A recent study of roughly 150,000 school-aged children in Israel found that while kids under age 10 were unlikely to catch or spread the virus as they reentered classrooms. Older children, though, were a different story. The study found that children ages 10-19 had risks of catching the virus that were as high as adults ages 20-60.
The risk for severe illness and death from COVID-19 rises with age.
Children and teens are at relatively low risk from severe outcomes after a COVID-19 infection compared to adults, but they can catch it and some will get really sick with it, especially if they have an underlying health condition, like obesity or asthma that makes them more vulnerable.
Beyond the initial infection, children can get a rare late complication called MIS-C, that while treatable, can be severe and requires hospitalization. Emerging reports also suggest there are some kids that become long haulers in much the same way adults do, dealing with lingering problems for months after they first get sick.
As new variants of the coronavirus circulate in the United States, some states have seen big increases in the number of children and teens with COVID. In Michigan, for example, which recently dealt with a spring surge of cases dominated by the B.1.1.7 variant, cases in children and teens quadrupled in April compared to February.
Beyond individual protection, vaccinating children and teens has been seen as important to achieving strong community protection, or herd immunity, against the new coronavirus.
If the FDA expands the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will likely meet to review data on the safety and efficacy of the vaccine. The committee may then vote on new recommendations for use of the vaccine in the United States.
Not everyone agrees with the idea that American adolescents, who are at relatively low risk of bad outcomes, could get access to COVID vaccines ahead of vulnerable essential workers and seniors in other parts of the world that are still fighting the pandemic with little access to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration could expand the use of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine to teens early next week, The New York Times and CNN reported, both citing unnamed officials familiar with the agency’s plans.
In late March, Pfizer submitted data to the FDA showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12 to 15. Their vaccine is already authorized for use teens and adults ages 16 and older.
The move would make about 17 million more Americans eligible for vaccination and would be a major step toward getting both adolescents and teens back into classrooms full time by next fall.
“Across the globe, we are longing for a normal life. This is especially true for our children. The initial results we have seen in the adolescent studies suggest that children are particularly well protected by vaccination, which is very encouraging given the trends we have seen in recent weeks regarding the spread of the B.1.1.7 U.K. variant,” Ugur Sahin, CEO and co-founder of Pfizer partner BioNTech, said in a March 31 press release.
Getting schools fully reopened for in-person learning has been a goal of both the Trump and Biden administrations, but it has been tricky to pull off, as some parents and teachers have been reluctant to return to classrooms with so much uncertainty about the risk and the role of children in spreading the virus.
A recent study of roughly 150,000 school-aged children in Israel found that while kids under age 10 were unlikely to catch or spread the virus as they reentered classrooms. Older children, though, were a different story. The study found that children ages 10-19 had risks of catching the virus that were as high as adults ages 20-60.
The risk for severe illness and death from COVID-19 rises with age.
Children and teens are at relatively low risk from severe outcomes after a COVID-19 infection compared to adults, but they can catch it and some will get really sick with it, especially if they have an underlying health condition, like obesity or asthma that makes them more vulnerable.
Beyond the initial infection, children can get a rare late complication called MIS-C, that while treatable, can be severe and requires hospitalization. Emerging reports also suggest there are some kids that become long haulers in much the same way adults do, dealing with lingering problems for months after they first get sick.
As new variants of the coronavirus circulate in the United States, some states have seen big increases in the number of children and teens with COVID. In Michigan, for example, which recently dealt with a spring surge of cases dominated by the B.1.1.7 variant, cases in children and teens quadrupled in April compared to February.
Beyond individual protection, vaccinating children and teens has been seen as important to achieving strong community protection, or herd immunity, against the new coronavirus.
If the FDA expands the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will likely meet to review data on the safety and efficacy of the vaccine. The committee may then vote on new recommendations for use of the vaccine in the United States.
Not everyone agrees with the idea that American adolescents, who are at relatively low risk of bad outcomes, could get access to COVID vaccines ahead of vulnerable essential workers and seniors in other parts of the world that are still fighting the pandemic with little access to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration could expand the use of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine to teens early next week, The New York Times and CNN reported, both citing unnamed officials familiar with the agency’s plans.
In late March, Pfizer submitted data to the FDA showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12 to 15. Their vaccine is already authorized for use teens and adults ages 16 and older.
The move would make about 17 million more Americans eligible for vaccination and would be a major step toward getting both adolescents and teens back into classrooms full time by next fall.
“Across the globe, we are longing for a normal life. This is especially true for our children. The initial results we have seen in the adolescent studies suggest that children are particularly well protected by vaccination, which is very encouraging given the trends we have seen in recent weeks regarding the spread of the B.1.1.7 U.K. variant,” Ugur Sahin, CEO and co-founder of Pfizer partner BioNTech, said in a March 31 press release.
Getting schools fully reopened for in-person learning has been a goal of both the Trump and Biden administrations, but it has been tricky to pull off, as some parents and teachers have been reluctant to return to classrooms with so much uncertainty about the risk and the role of children in spreading the virus.
A recent study of roughly 150,000 school-aged children in Israel found that while kids under age 10 were unlikely to catch or spread the virus as they reentered classrooms. Older children, though, were a different story. The study found that children ages 10-19 had risks of catching the virus that were as high as adults ages 20-60.
The risk for severe illness and death from COVID-19 rises with age.
Children and teens are at relatively low risk from severe outcomes after a COVID-19 infection compared to adults, but they can catch it and some will get really sick with it, especially if they have an underlying health condition, like obesity or asthma that makes them more vulnerable.
Beyond the initial infection, children can get a rare late complication called MIS-C, that while treatable, can be severe and requires hospitalization. Emerging reports also suggest there are some kids that become long haulers in much the same way adults do, dealing with lingering problems for months after they first get sick.
As new variants of the coronavirus circulate in the United States, some states have seen big increases in the number of children and teens with COVID. In Michigan, for example, which recently dealt with a spring surge of cases dominated by the B.1.1.7 variant, cases in children and teens quadrupled in April compared to February.
Beyond individual protection, vaccinating children and teens has been seen as important to achieving strong community protection, or herd immunity, against the new coronavirus.
If the FDA expands the authorization for the Pfizer vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will likely meet to review data on the safety and efficacy of the vaccine. The committee may then vote on new recommendations for use of the vaccine in the United States.
Not everyone agrees with the idea that American adolescents, who are at relatively low risk of bad outcomes, could get access to COVID vaccines ahead of vulnerable essential workers and seniors in other parts of the world that are still fighting the pandemic with little access to vaccines.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Baricitinib continuation rate high in real-world practice
Around three-quarters of patients remained on treatment with baricitinib (Olumiant) for rheumatoid arthritis after their first 6-month assessment in an independent analysis of British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR) data.
The rate of continuation was even higher, at almost 85%, in patients who had not previously been treated with a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (b/ts DMARD) before being given baricitinib. The 6-month continuation rate was also higher, at 80%, in patients who received baricitinib without additional DMARDs or steroid therapy.
Overall, the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) score was reduced from a baseline of 5.7 to 3.4, with similar reductions seen among the subgroups of patients who had received baricitinib as monotherapy, after prior b/tsDMARDs, or no prior b/tsDMARDs.
“We’ve looked at an RA study population using data from the BSR biologics registry, to try and have a look at how patients with baricitinib are being treated and how they’re doing in this real-world setting, within the U.K.,” explained consultant rheumatologist Christopher J. Edwards, MD, of University Hospital Southampton (England) at the British Society for Rheumatology annual conference.
“Overall, effectiveness and tolerability seem to be pretty good indeed,” he said. “Sample size, of course, was small and it will be nice to see a little bit more data collected over time that allow us to be more confident in any conclusions.”
‘Getting to grips’ with baricitinib
Baricitinib is a drug that clinicians in the United Kingdom are “just getting to grips with,” observed Jon Packham, BM, DM, a consultant rheumatologist at Haywood Hospital in Stoke-on-Trent (England) who was not involved in the analysis.
“We look forward to when we’ve got a few more patients through that 6-month hurdle and we were getting even more data coming through,” Dr. Packham said.
Baricitinib was given marketing authorization in Europe for the treatment of moderate to severe RA in 2017 and so is a relatively new addition into the BSRBR-RA, which has been running for the past 20 years. It includes data on patients with RA who are newly starting a bDMARD or tsDMARD, and patients are followed up every 6 months for the first 3 years of their treatment and then annually thereafter.
Dr. Edwards presented data on some of the baseline characteristics and status of patients at the first 6-month follow-up of the BSRBR-RA. He was clear that this analysis was done independently of the BSRBR-RA study team and performed under an agreement between Eli Lilly and the BSR to allow access to the data.
Between Jan. 1, 2018, and March 31, 2019, there were 409 patients who were just starting baricitinib treatment and who were entered into the BSRBR-RA. The mean age of patients was 61 years, and the majority (76%) was female. On average, patients starting baricitinib had been diagnosed with RA for 11 years, and 62% had previously been treated with a biologic.
As per the European label, most patients were being treated with baricitinib in combination with a conventional synthetic DMARD (61%), with 40% of patients receiving it in combination with methotrexate. Around 38% of patients received baricitinib as monotherapy, and just under 30% were receiving concomitant glucocorticoids.
The majority (84%) were prescribed a 4-mg daily dose of baricitinib, with the remainder on a daily dose of 2 mg.
There were 163 patients with data available at the first 6-month follow up, and of those, 103 had prior experience of being treated with a b/ts DMARD, 59 did not, and 65 had been given baricitinib as monotherapy.
Reasons for discontinuation
Overall, around a quarter of patients discontinued treatment with baricitinib, and “the reasons for this were lack of efficacy in approximately a quarter and adverse events in about two-thirds of the patients,” Dr. Edwards said.
Breaking down the types of adverse events was not part of this analysis, and that information is likely to come from the BSRBR-RA study team directly.
“We have some experience in our practice in Southampton,” Dr. Edwards observed. This experience was outlined in a separate abstract at the meeting and presented by Dr. May Nwe Lwin, a clinical research fellow within Dr. Edwards’ group.
Dr. Lwin presented data on 83 patients who had received baricitinib at University Hospital Southampton between October 2017 and July 2020, 55 (65.2%) of whom remain on treatment to date, with mean follow-up of 17 months. Of the 28 patients who stopped baricitinib, 21 stopped within 12 months.
“Patients who continued on baricitinib appeared more likely to be older and female,” Dr. Lwin said.
The mean age of patients who continued on treatment after 12 months was 61.5 years but was 49 years for those who stopped earlier. The percentage of women continuing treatment at 12 months versus those stopping earlier were a respective 82% and 67%. Both findings were significant (P < .001) but “could mean nothing, or could be very interesting data to explore more,” Dr. Lwin suggested.
“However, there was no significant difference in discontinuation rates for those using mono or combination therapy, and also no effect of disease duration or seropositivity,” Dr. Lwin said.
“Most people stopped baricitinib in the first 3 months of their treatment,” Dr. Lwin reported, noting that the most common reason was a lack of efficacy in 64% of patients, with 28.5% of patients discontinuing because of side effects.
“When you look at the adverse events, the reasons for discontinuation are quite variable,” Dr. Lwin said. These included infections (one urinary tract infection, two chest infections, and a urinary tract infection), and one case each of discitis, deranged liver function, lymphoma, and personality change.
Update on the long-term safety profile
Also at the BSR annual conference, an update on the long-term safety profile of baricitinib seen in clinical trials was presented, using data from the ‘All-BARI-RA’ dataset. This includes data from nine clinical trials and one long-term extension study.
“We recently published a long-term safety analysis of this molecule involving 3,700-plus patients with exposure up to 7 years,” said Kevin L. Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health Sciences University in Portland.
Dr. Winthrop provided an update on this, adding in another 13,148 patient-years of follow-up and giving data on the safety experience with baricitinib with up to 8.4 years of exposure for some patients.
“In short, not much has changed,” Dr. Winthrop said, noting that event rates have remained stable.
The overall major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) and overall deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism event rate were both 0.5 per 100 patient-years. Referring to the latter, Dr. Winthrop called them “rock solid stable” and “it’s been that way really all the way through the development program.”
Overall, event rates per 100 patient-years for serious infections, herpes zoster, and tuberculosis were a respective 2.7, 3.0, and 0.2. Serious infection rates over time have remained similar, but “clearly age is a risk factor for infection,” Dr. Winthrop said. “I would just say it’s similar to what we see with all biologics and small molecules in this setting.”
Malignancy and death rates were also higher in older patients, but after age adjustment, these had been stable across the different analysis points.
“Malignancy overall, excluding NMSC [nonmelanoma skin cancer], the event rate is 0.9 per 100 patient-years, very similar to what we’ve seen in the prior data cuts,” he said. “The same is true for lymphoma,” he added, with an overall event rate of 0.1 per 100 patient-years.
This updated analysis, Dr. Winthrop concluded, “suggests a safety profile really very similar to what was published recently.”Dr. Edwards has received research and educational grants and advisory panel and speaker fees from Eli Lilly and from multiple other pharmaceutical companies. The analysis of BSRBR-RA data he presented was sponsored by Eli Lilly and performed independently of the BSRBR-RA study team. Dr. Packham reported no conflicts of interest; he chaired the oral abstracts sessions in which Dr. Edwards presented his findings.
Dr. Lwin did not report having any disclosures.
Dr. Winthrop has acted as a consultant to Eli Lilly and several other pharmaceutical companies and had received research or grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. The work he presented was sponsored by Eli Lilly.
Around three-quarters of patients remained on treatment with baricitinib (Olumiant) for rheumatoid arthritis after their first 6-month assessment in an independent analysis of British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR) data.
The rate of continuation was even higher, at almost 85%, in patients who had not previously been treated with a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (b/ts DMARD) before being given baricitinib. The 6-month continuation rate was also higher, at 80%, in patients who received baricitinib without additional DMARDs or steroid therapy.
Overall, the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) score was reduced from a baseline of 5.7 to 3.4, with similar reductions seen among the subgroups of patients who had received baricitinib as monotherapy, after prior b/tsDMARDs, or no prior b/tsDMARDs.
“We’ve looked at an RA study population using data from the BSR biologics registry, to try and have a look at how patients with baricitinib are being treated and how they’re doing in this real-world setting, within the U.K.,” explained consultant rheumatologist Christopher J. Edwards, MD, of University Hospital Southampton (England) at the British Society for Rheumatology annual conference.
“Overall, effectiveness and tolerability seem to be pretty good indeed,” he said. “Sample size, of course, was small and it will be nice to see a little bit more data collected over time that allow us to be more confident in any conclusions.”
‘Getting to grips’ with baricitinib
Baricitinib is a drug that clinicians in the United Kingdom are “just getting to grips with,” observed Jon Packham, BM, DM, a consultant rheumatologist at Haywood Hospital in Stoke-on-Trent (England) who was not involved in the analysis.
“We look forward to when we’ve got a few more patients through that 6-month hurdle and we were getting even more data coming through,” Dr. Packham said.
Baricitinib was given marketing authorization in Europe for the treatment of moderate to severe RA in 2017 and so is a relatively new addition into the BSRBR-RA, which has been running for the past 20 years. It includes data on patients with RA who are newly starting a bDMARD or tsDMARD, and patients are followed up every 6 months for the first 3 years of their treatment and then annually thereafter.
Dr. Edwards presented data on some of the baseline characteristics and status of patients at the first 6-month follow-up of the BSRBR-RA. He was clear that this analysis was done independently of the BSRBR-RA study team and performed under an agreement between Eli Lilly and the BSR to allow access to the data.
Between Jan. 1, 2018, and March 31, 2019, there were 409 patients who were just starting baricitinib treatment and who were entered into the BSRBR-RA. The mean age of patients was 61 years, and the majority (76%) was female. On average, patients starting baricitinib had been diagnosed with RA for 11 years, and 62% had previously been treated with a biologic.
As per the European label, most patients were being treated with baricitinib in combination with a conventional synthetic DMARD (61%), with 40% of patients receiving it in combination with methotrexate. Around 38% of patients received baricitinib as monotherapy, and just under 30% were receiving concomitant glucocorticoids.
The majority (84%) were prescribed a 4-mg daily dose of baricitinib, with the remainder on a daily dose of 2 mg.
There were 163 patients with data available at the first 6-month follow up, and of those, 103 had prior experience of being treated with a b/ts DMARD, 59 did not, and 65 had been given baricitinib as monotherapy.
Reasons for discontinuation
Overall, around a quarter of patients discontinued treatment with baricitinib, and “the reasons for this were lack of efficacy in approximately a quarter and adverse events in about two-thirds of the patients,” Dr. Edwards said.
Breaking down the types of adverse events was not part of this analysis, and that information is likely to come from the BSRBR-RA study team directly.
“We have some experience in our practice in Southampton,” Dr. Edwards observed. This experience was outlined in a separate abstract at the meeting and presented by Dr. May Nwe Lwin, a clinical research fellow within Dr. Edwards’ group.
Dr. Lwin presented data on 83 patients who had received baricitinib at University Hospital Southampton between October 2017 and July 2020, 55 (65.2%) of whom remain on treatment to date, with mean follow-up of 17 months. Of the 28 patients who stopped baricitinib, 21 stopped within 12 months.
“Patients who continued on baricitinib appeared more likely to be older and female,” Dr. Lwin said.
The mean age of patients who continued on treatment after 12 months was 61.5 years but was 49 years for those who stopped earlier. The percentage of women continuing treatment at 12 months versus those stopping earlier were a respective 82% and 67%. Both findings were significant (P < .001) but “could mean nothing, or could be very interesting data to explore more,” Dr. Lwin suggested.
“However, there was no significant difference in discontinuation rates for those using mono or combination therapy, and also no effect of disease duration or seropositivity,” Dr. Lwin said.
“Most people stopped baricitinib in the first 3 months of their treatment,” Dr. Lwin reported, noting that the most common reason was a lack of efficacy in 64% of patients, with 28.5% of patients discontinuing because of side effects.
“When you look at the adverse events, the reasons for discontinuation are quite variable,” Dr. Lwin said. These included infections (one urinary tract infection, two chest infections, and a urinary tract infection), and one case each of discitis, deranged liver function, lymphoma, and personality change.
Update on the long-term safety profile
Also at the BSR annual conference, an update on the long-term safety profile of baricitinib seen in clinical trials was presented, using data from the ‘All-BARI-RA’ dataset. This includes data from nine clinical trials and one long-term extension study.
“We recently published a long-term safety analysis of this molecule involving 3,700-plus patients with exposure up to 7 years,” said Kevin L. Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health Sciences University in Portland.
Dr. Winthrop provided an update on this, adding in another 13,148 patient-years of follow-up and giving data on the safety experience with baricitinib with up to 8.4 years of exposure for some patients.
“In short, not much has changed,” Dr. Winthrop said, noting that event rates have remained stable.
The overall major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) and overall deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism event rate were both 0.5 per 100 patient-years. Referring to the latter, Dr. Winthrop called them “rock solid stable” and “it’s been that way really all the way through the development program.”
Overall, event rates per 100 patient-years for serious infections, herpes zoster, and tuberculosis were a respective 2.7, 3.0, and 0.2. Serious infection rates over time have remained similar, but “clearly age is a risk factor for infection,” Dr. Winthrop said. “I would just say it’s similar to what we see with all biologics and small molecules in this setting.”
Malignancy and death rates were also higher in older patients, but after age adjustment, these had been stable across the different analysis points.
“Malignancy overall, excluding NMSC [nonmelanoma skin cancer], the event rate is 0.9 per 100 patient-years, very similar to what we’ve seen in the prior data cuts,” he said. “The same is true for lymphoma,” he added, with an overall event rate of 0.1 per 100 patient-years.
This updated analysis, Dr. Winthrop concluded, “suggests a safety profile really very similar to what was published recently.”Dr. Edwards has received research and educational grants and advisory panel and speaker fees from Eli Lilly and from multiple other pharmaceutical companies. The analysis of BSRBR-RA data he presented was sponsored by Eli Lilly and performed independently of the BSRBR-RA study team. Dr. Packham reported no conflicts of interest; he chaired the oral abstracts sessions in which Dr. Edwards presented his findings.
Dr. Lwin did not report having any disclosures.
Dr. Winthrop has acted as a consultant to Eli Lilly and several other pharmaceutical companies and had received research or grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. The work he presented was sponsored by Eli Lilly.
Around three-quarters of patients remained on treatment with baricitinib (Olumiant) for rheumatoid arthritis after their first 6-month assessment in an independent analysis of British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR) data.
The rate of continuation was even higher, at almost 85%, in patients who had not previously been treated with a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (b/ts DMARD) before being given baricitinib. The 6-month continuation rate was also higher, at 80%, in patients who received baricitinib without additional DMARDs or steroid therapy.
Overall, the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints using erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) score was reduced from a baseline of 5.7 to 3.4, with similar reductions seen among the subgroups of patients who had received baricitinib as monotherapy, after prior b/tsDMARDs, or no prior b/tsDMARDs.
“We’ve looked at an RA study population using data from the BSR biologics registry, to try and have a look at how patients with baricitinib are being treated and how they’re doing in this real-world setting, within the U.K.,” explained consultant rheumatologist Christopher J. Edwards, MD, of University Hospital Southampton (England) at the British Society for Rheumatology annual conference.
“Overall, effectiveness and tolerability seem to be pretty good indeed,” he said. “Sample size, of course, was small and it will be nice to see a little bit more data collected over time that allow us to be more confident in any conclusions.”
‘Getting to grips’ with baricitinib
Baricitinib is a drug that clinicians in the United Kingdom are “just getting to grips with,” observed Jon Packham, BM, DM, a consultant rheumatologist at Haywood Hospital in Stoke-on-Trent (England) who was not involved in the analysis.
“We look forward to when we’ve got a few more patients through that 6-month hurdle and we were getting even more data coming through,” Dr. Packham said.
Baricitinib was given marketing authorization in Europe for the treatment of moderate to severe RA in 2017 and so is a relatively new addition into the BSRBR-RA, which has been running for the past 20 years. It includes data on patients with RA who are newly starting a bDMARD or tsDMARD, and patients are followed up every 6 months for the first 3 years of their treatment and then annually thereafter.
Dr. Edwards presented data on some of the baseline characteristics and status of patients at the first 6-month follow-up of the BSRBR-RA. He was clear that this analysis was done independently of the BSRBR-RA study team and performed under an agreement between Eli Lilly and the BSR to allow access to the data.
Between Jan. 1, 2018, and March 31, 2019, there were 409 patients who were just starting baricitinib treatment and who were entered into the BSRBR-RA. The mean age of patients was 61 years, and the majority (76%) was female. On average, patients starting baricitinib had been diagnosed with RA for 11 years, and 62% had previously been treated with a biologic.
As per the European label, most patients were being treated with baricitinib in combination with a conventional synthetic DMARD (61%), with 40% of patients receiving it in combination with methotrexate. Around 38% of patients received baricitinib as monotherapy, and just under 30% were receiving concomitant glucocorticoids.
The majority (84%) were prescribed a 4-mg daily dose of baricitinib, with the remainder on a daily dose of 2 mg.
There were 163 patients with data available at the first 6-month follow up, and of those, 103 had prior experience of being treated with a b/ts DMARD, 59 did not, and 65 had been given baricitinib as monotherapy.
Reasons for discontinuation
Overall, around a quarter of patients discontinued treatment with baricitinib, and “the reasons for this were lack of efficacy in approximately a quarter and adverse events in about two-thirds of the patients,” Dr. Edwards said.
Breaking down the types of adverse events was not part of this analysis, and that information is likely to come from the BSRBR-RA study team directly.
“We have some experience in our practice in Southampton,” Dr. Edwards observed. This experience was outlined in a separate abstract at the meeting and presented by Dr. May Nwe Lwin, a clinical research fellow within Dr. Edwards’ group.
Dr. Lwin presented data on 83 patients who had received baricitinib at University Hospital Southampton between October 2017 and July 2020, 55 (65.2%) of whom remain on treatment to date, with mean follow-up of 17 months. Of the 28 patients who stopped baricitinib, 21 stopped within 12 months.
“Patients who continued on baricitinib appeared more likely to be older and female,” Dr. Lwin said.
The mean age of patients who continued on treatment after 12 months was 61.5 years but was 49 years for those who stopped earlier. The percentage of women continuing treatment at 12 months versus those stopping earlier were a respective 82% and 67%. Both findings were significant (P < .001) but “could mean nothing, or could be very interesting data to explore more,” Dr. Lwin suggested.
“However, there was no significant difference in discontinuation rates for those using mono or combination therapy, and also no effect of disease duration or seropositivity,” Dr. Lwin said.
“Most people stopped baricitinib in the first 3 months of their treatment,” Dr. Lwin reported, noting that the most common reason was a lack of efficacy in 64% of patients, with 28.5% of patients discontinuing because of side effects.
“When you look at the adverse events, the reasons for discontinuation are quite variable,” Dr. Lwin said. These included infections (one urinary tract infection, two chest infections, and a urinary tract infection), and one case each of discitis, deranged liver function, lymphoma, and personality change.
Update on the long-term safety profile
Also at the BSR annual conference, an update on the long-term safety profile of baricitinib seen in clinical trials was presented, using data from the ‘All-BARI-RA’ dataset. This includes data from nine clinical trials and one long-term extension study.
“We recently published a long-term safety analysis of this molecule involving 3,700-plus patients with exposure up to 7 years,” said Kevin L. Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious diseases and epidemiology at Oregon Health Sciences University in Portland.
Dr. Winthrop provided an update on this, adding in another 13,148 patient-years of follow-up and giving data on the safety experience with baricitinib with up to 8.4 years of exposure for some patients.
“In short, not much has changed,” Dr. Winthrop said, noting that event rates have remained stable.
The overall major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) and overall deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism event rate were both 0.5 per 100 patient-years. Referring to the latter, Dr. Winthrop called them “rock solid stable” and “it’s been that way really all the way through the development program.”
Overall, event rates per 100 patient-years for serious infections, herpes zoster, and tuberculosis were a respective 2.7, 3.0, and 0.2. Serious infection rates over time have remained similar, but “clearly age is a risk factor for infection,” Dr. Winthrop said. “I would just say it’s similar to what we see with all biologics and small molecules in this setting.”
Malignancy and death rates were also higher in older patients, but after age adjustment, these had been stable across the different analysis points.
“Malignancy overall, excluding NMSC [nonmelanoma skin cancer], the event rate is 0.9 per 100 patient-years, very similar to what we’ve seen in the prior data cuts,” he said. “The same is true for lymphoma,” he added, with an overall event rate of 0.1 per 100 patient-years.
This updated analysis, Dr. Winthrop concluded, “suggests a safety profile really very similar to what was published recently.”Dr. Edwards has received research and educational grants and advisory panel and speaker fees from Eli Lilly and from multiple other pharmaceutical companies. The analysis of BSRBR-RA data he presented was sponsored by Eli Lilly and performed independently of the BSRBR-RA study team. Dr. Packham reported no conflicts of interest; he chaired the oral abstracts sessions in which Dr. Edwards presented his findings.
Dr. Lwin did not report having any disclosures.
Dr. Winthrop has acted as a consultant to Eli Lilly and several other pharmaceutical companies and had received research or grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. The work he presented was sponsored by Eli Lilly.
FROM BSR 2021
Clinical Edge Journal Scan: PsA May 2021
Although PsA affects men and women equally, the impact of the disease is often worse in women. In a large study from the Netherlands, in which 855 patients were carefully evaluated and follow up, Mulder MLM et al show that both subjective and objective measures of disease activity is more severe in women than men. The PsA Disease Activity Score, a validated composite measure of PsA disease activity, was also higher in women than men. The impact of disease on quality of life and function was significantly more in women and they were less often meeting treatment target. Further research into the impact of sex and gender in PsA is warranted and sex/gender-specific measures for managing PsA is required.
Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) are important new molecules increasingly being used in the management of inflammatory diseases. Tofacitinib is already available for the treatment of PsA. McInnes IB et al published results on the efficacy of upadacitinib, a more selective JAK1i already approved for treatment of RA, in treating PsA. In this phase 3 trial involving 1,704 patients with PsA who had an inadequate response to at least 1 nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, the proportion of patients achieving at least 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response was significantly higher with upadacitinib 15 mg (70.6%) and 30 mg (78.5%) than with placebo (36.2%; P less than .001). Upadacitinib 15mg was found to have comparable efficacy as adalimumab (ACR20 65.0%), a well-established anti-TNF agent. However, adverse events were more frequent with upadacitinib.
Adverse events when on treatment with JAKi have recently come into sharp focus. Reassuringly, results from the OPAL Balance study, a 36-month, long-term extension phase 3 study involving 686 adult patients with active PsA on treatment with tofacitinib confirmed the long-term safety and efficacy of tofacitinib in patients with PsA. Nash P et al reported 1 instance of mortality occurred in tofacitinib group during the risk period (incidence, 0.1 patients with events [95% confidence interval, 0.0-0.3] per 100 person-years). The incidences of adverse events for herpes zoster, serious infections, opportunistic infections, adjudicated malignancies, and major adverse cardiovascular events were consistent with previous reports. However, given the reports of higher adverse events with tofacitinib compared to anti-TNF drugs in high-risk rheumatoid arthritis patients, more data is required to fully understand the risk profile of JAKi in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, including PsA.
With several drugs currently available to treat PsA and the paucity of head-to-head trials between them, choosing the most efficacious drug for treating patients with PsA has become challenging. To address this issue a network meta-analysis of 26 phase 3, randomized controlled trials that evaluated 13 targeted therapies among adults with active PsA was conducted. In a study sponsored by Janssen, Mease PJ et al report that guselkumab 100 mg every 8 weeks and every 4 weeks were comparable to anti IL-17A and subcutaneous anti-TNF agents for achieving ACR20 response. Guselkumab showed better Psoriasis Area Severity Index 90 and 75 responses than most of the other agents. The results indicate that guselkumab is as effective as other established agents in treating PsA, but formal head-to-head clinical trials will provide better evidence of relative efficacy and safety.
Although PsA affects men and women equally, the impact of the disease is often worse in women. In a large study from the Netherlands, in which 855 patients were carefully evaluated and follow up, Mulder MLM et al show that both subjective and objective measures of disease activity is more severe in women than men. The PsA Disease Activity Score, a validated composite measure of PsA disease activity, was also higher in women than men. The impact of disease on quality of life and function was significantly more in women and they were less often meeting treatment target. Further research into the impact of sex and gender in PsA is warranted and sex/gender-specific measures for managing PsA is required.
Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) are important new molecules increasingly being used in the management of inflammatory diseases. Tofacitinib is already available for the treatment of PsA. McInnes IB et al published results on the efficacy of upadacitinib, a more selective JAK1i already approved for treatment of RA, in treating PsA. In this phase 3 trial involving 1,704 patients with PsA who had an inadequate response to at least 1 nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, the proportion of patients achieving at least 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response was significantly higher with upadacitinib 15 mg (70.6%) and 30 mg (78.5%) than with placebo (36.2%; P less than .001). Upadacitinib 15mg was found to have comparable efficacy as adalimumab (ACR20 65.0%), a well-established anti-TNF agent. However, adverse events were more frequent with upadacitinib.
Adverse events when on treatment with JAKi have recently come into sharp focus. Reassuringly, results from the OPAL Balance study, a 36-month, long-term extension phase 3 study involving 686 adult patients with active PsA on treatment with tofacitinib confirmed the long-term safety and efficacy of tofacitinib in patients with PsA. Nash P et al reported 1 instance of mortality occurred in tofacitinib group during the risk period (incidence, 0.1 patients with events [95% confidence interval, 0.0-0.3] per 100 person-years). The incidences of adverse events for herpes zoster, serious infections, opportunistic infections, adjudicated malignancies, and major adverse cardiovascular events were consistent with previous reports. However, given the reports of higher adverse events with tofacitinib compared to anti-TNF drugs in high-risk rheumatoid arthritis patients, more data is required to fully understand the risk profile of JAKi in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, including PsA.
With several drugs currently available to treat PsA and the paucity of head-to-head trials between them, choosing the most efficacious drug for treating patients with PsA has become challenging. To address this issue a network meta-analysis of 26 phase 3, randomized controlled trials that evaluated 13 targeted therapies among adults with active PsA was conducted. In a study sponsored by Janssen, Mease PJ et al report that guselkumab 100 mg every 8 weeks and every 4 weeks were comparable to anti IL-17A and subcutaneous anti-TNF agents for achieving ACR20 response. Guselkumab showed better Psoriasis Area Severity Index 90 and 75 responses than most of the other agents. The results indicate that guselkumab is as effective as other established agents in treating PsA, but formal head-to-head clinical trials will provide better evidence of relative efficacy and safety.
Although PsA affects men and women equally, the impact of the disease is often worse in women. In a large study from the Netherlands, in which 855 patients were carefully evaluated and follow up, Mulder MLM et al show that both subjective and objective measures of disease activity is more severe in women than men. The PsA Disease Activity Score, a validated composite measure of PsA disease activity, was also higher in women than men. The impact of disease on quality of life and function was significantly more in women and they were less often meeting treatment target. Further research into the impact of sex and gender in PsA is warranted and sex/gender-specific measures for managing PsA is required.
Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) are important new molecules increasingly being used in the management of inflammatory diseases. Tofacitinib is already available for the treatment of PsA. McInnes IB et al published results on the efficacy of upadacitinib, a more selective JAK1i already approved for treatment of RA, in treating PsA. In this phase 3 trial involving 1,704 patients with PsA who had an inadequate response to at least 1 nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, the proportion of patients achieving at least 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response was significantly higher with upadacitinib 15 mg (70.6%) and 30 mg (78.5%) than with placebo (36.2%; P less than .001). Upadacitinib 15mg was found to have comparable efficacy as adalimumab (ACR20 65.0%), a well-established anti-TNF agent. However, adverse events were more frequent with upadacitinib.
Adverse events when on treatment with JAKi have recently come into sharp focus. Reassuringly, results from the OPAL Balance study, a 36-month, long-term extension phase 3 study involving 686 adult patients with active PsA on treatment with tofacitinib confirmed the long-term safety and efficacy of tofacitinib in patients with PsA. Nash P et al reported 1 instance of mortality occurred in tofacitinib group during the risk period (incidence, 0.1 patients with events [95% confidence interval, 0.0-0.3] per 100 person-years). The incidences of adverse events for herpes zoster, serious infections, opportunistic infections, adjudicated malignancies, and major adverse cardiovascular events were consistent with previous reports. However, given the reports of higher adverse events with tofacitinib compared to anti-TNF drugs in high-risk rheumatoid arthritis patients, more data is required to fully understand the risk profile of JAKi in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, including PsA.
With several drugs currently available to treat PsA and the paucity of head-to-head trials between them, choosing the most efficacious drug for treating patients with PsA has become challenging. To address this issue a network meta-analysis of 26 phase 3, randomized controlled trials that evaluated 13 targeted therapies among adults with active PsA was conducted. In a study sponsored by Janssen, Mease PJ et al report that guselkumab 100 mg every 8 weeks and every 4 weeks were comparable to anti IL-17A and subcutaneous anti-TNF agents for achieving ACR20 response. Guselkumab showed better Psoriasis Area Severity Index 90 and 75 responses than most of the other agents. The results indicate that guselkumab is as effective as other established agents in treating PsA, but formal head-to-head clinical trials will provide better evidence of relative efficacy and safety.
IL-12/23i demonstrates better persistence and adherence than TNFi and tsDMARDs
Key clinical point: In this real-world analysis of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), interleukin-12/23 inhibitor (IL-12/23i) demonstrated longer persistence and higher adherence than tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs).
Major finding: At 1 year, persistence was significantly longer among patients who initiated IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (269 vs. 215 days) or tsDMARD (269 vs. 213 days; both P less than .001). Adherence was significantly higher among patients who initiated IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (0.64 vs. 0.56; P = .004) or tsDMARDs (0.64 vs. 0.58; P = .027).
Study details: In this retrospective observational analysis, 7,205 patients with PsA who newly initiated a targeted immune modulator were matched (1:1) in IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (n=238), IL-12/23i vs. tsDMARD (n=238), and IL-12/23i vs. IL-17i (n=189) patient pairs.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC. LA Walsh declared receiving grants and/or serving as a consultant for various pharmaceutical companies. Q Cai, I Lin, CD Pericone, and SD Chakravarty declared being current employees of Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC and stockholders in Johnson & Johnson.
Source: Walsh JA et al. Adv Ther. 2021 Mar 23. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01687-w.
Key clinical point: In this real-world analysis of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), interleukin-12/23 inhibitor (IL-12/23i) demonstrated longer persistence and higher adherence than tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs).
Major finding: At 1 year, persistence was significantly longer among patients who initiated IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (269 vs. 215 days) or tsDMARD (269 vs. 213 days; both P less than .001). Adherence was significantly higher among patients who initiated IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (0.64 vs. 0.56; P = .004) or tsDMARDs (0.64 vs. 0.58; P = .027).
Study details: In this retrospective observational analysis, 7,205 patients with PsA who newly initiated a targeted immune modulator were matched (1:1) in IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (n=238), IL-12/23i vs. tsDMARD (n=238), and IL-12/23i vs. IL-17i (n=189) patient pairs.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC. LA Walsh declared receiving grants and/or serving as a consultant for various pharmaceutical companies. Q Cai, I Lin, CD Pericone, and SD Chakravarty declared being current employees of Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC and stockholders in Johnson & Johnson.
Source: Walsh JA et al. Adv Ther. 2021 Mar 23. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01687-w.
Key clinical point: In this real-world analysis of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), interleukin-12/23 inhibitor (IL-12/23i) demonstrated longer persistence and higher adherence than tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs).
Major finding: At 1 year, persistence was significantly longer among patients who initiated IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (269 vs. 215 days) or tsDMARD (269 vs. 213 days; both P less than .001). Adherence was significantly higher among patients who initiated IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (0.64 vs. 0.56; P = .004) or tsDMARDs (0.64 vs. 0.58; P = .027).
Study details: In this retrospective observational analysis, 7,205 patients with PsA who newly initiated a targeted immune modulator were matched (1:1) in IL-12/23i vs. TNFi (n=238), IL-12/23i vs. tsDMARD (n=238), and IL-12/23i vs. IL-17i (n=189) patient pairs.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC. LA Walsh declared receiving grants and/or serving as a consultant for various pharmaceutical companies. Q Cai, I Lin, CD Pericone, and SD Chakravarty declared being current employees of Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC and stockholders in Johnson & Johnson.
Source: Walsh JA et al. Adv Ther. 2021 Mar 23. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01687-w.
PsA-associated fatigue correlates with QoL, functional impairment, and disease activity
Key clinical point: Fatigue is a prevalent phenomenon among patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and strongly correlated with quality of life (QoL), disease activity, and levels of serum interleukin-17 (IL-17).
Major finding: Level of PsA disease activity was significantly correlated with measures of fatigue, functional capacity, and QoL (P less than .001). Moreover, QoL (P = .001), disease activity (P = .019), and serum IL-17 (P = .029) were significant independent predictive factors for fatigue.
Study details: The findings come from an analysis of 80 adults with PsA from the outpatient clinics of Physical Medicine, Rheumatology, & Rehabilitation Department, Tanta University Hospitals randomly selected during the period from December 2019 to August 2020.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. All the authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gado SE et al. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Apr 2. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1905522.
Key clinical point: Fatigue is a prevalent phenomenon among patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and strongly correlated with quality of life (QoL), disease activity, and levels of serum interleukin-17 (IL-17).
Major finding: Level of PsA disease activity was significantly correlated with measures of fatigue, functional capacity, and QoL (P less than .001). Moreover, QoL (P = .001), disease activity (P = .019), and serum IL-17 (P = .029) were significant independent predictive factors for fatigue.
Study details: The findings come from an analysis of 80 adults with PsA from the outpatient clinics of Physical Medicine, Rheumatology, & Rehabilitation Department, Tanta University Hospitals randomly selected during the period from December 2019 to August 2020.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. All the authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gado SE et al. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Apr 2. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1905522.
Key clinical point: Fatigue is a prevalent phenomenon among patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and strongly correlated with quality of life (QoL), disease activity, and levels of serum interleukin-17 (IL-17).
Major finding: Level of PsA disease activity was significantly correlated with measures of fatigue, functional capacity, and QoL (P less than .001). Moreover, QoL (P = .001), disease activity (P = .019), and serum IL-17 (P = .029) were significant independent predictive factors for fatigue.
Study details: The findings come from an analysis of 80 adults with PsA from the outpatient clinics of Physical Medicine, Rheumatology, & Rehabilitation Department, Tanta University Hospitals randomly selected during the period from December 2019 to August 2020.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. All the authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Gado SE et al. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Apr 2. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1905522.
TNF-α inhibitors outperform IL-12/23 antagonists and PDE4 therapy
Key clinical point: Among biologic-naive individuals with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), interleukin-12/23 (IL-12/23) antagonists were less effective than tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors. PDE4 treatment was significantly less effective than TNF-α inhibitors among biologic-experienced individuals.
Major finding: Among biologic-naïve individuals, IL-12/23 was less effective than TNF-α (adjusted relative risk [aRR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.45-0.89), whereas PDE4 treatment was less effective than TNF-α inhibitor among biologic-experienced individuals (aRR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.96).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study of 2,730 commercially insured and Medicare Advantage beneficiaries with PsA.
Disclosures: The authors did not declare any specific funding for this research. GC Alexander declared being Chair of FDA’s peripheral and central nervous system advisory committee, serving as a paid advisor to IQVIA, and being a consultant and holding equity in Monument Analytics. JR Curtis declared receiving consultancies and funding from pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Zhang H et al. RMD Open. 2021 Apr 16. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001399.
Key clinical point: Among biologic-naive individuals with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), interleukin-12/23 (IL-12/23) antagonists were less effective than tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors. PDE4 treatment was significantly less effective than TNF-α inhibitors among biologic-experienced individuals.
Major finding: Among biologic-naïve individuals, IL-12/23 was less effective than TNF-α (adjusted relative risk [aRR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.45-0.89), whereas PDE4 treatment was less effective than TNF-α inhibitor among biologic-experienced individuals (aRR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.96).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study of 2,730 commercially insured and Medicare Advantage beneficiaries with PsA.
Disclosures: The authors did not declare any specific funding for this research. GC Alexander declared being Chair of FDA’s peripheral and central nervous system advisory committee, serving as a paid advisor to IQVIA, and being a consultant and holding equity in Monument Analytics. JR Curtis declared receiving consultancies and funding from pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Zhang H et al. RMD Open. 2021 Apr 16. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001399.
Key clinical point: Among biologic-naive individuals with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), interleukin-12/23 (IL-12/23) antagonists were less effective than tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors. PDE4 treatment was significantly less effective than TNF-α inhibitors among biologic-experienced individuals.
Major finding: Among biologic-naïve individuals, IL-12/23 was less effective than TNF-α (adjusted relative risk [aRR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.45-0.89), whereas PDE4 treatment was less effective than TNF-α inhibitor among biologic-experienced individuals (aRR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.96).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study of 2,730 commercially insured and Medicare Advantage beneficiaries with PsA.
Disclosures: The authors did not declare any specific funding for this research. GC Alexander declared being Chair of FDA’s peripheral and central nervous system advisory committee, serving as a paid advisor to IQVIA, and being a consultant and holding equity in Monument Analytics. JR Curtis declared receiving consultancies and funding from pharmaceutical companies.
Source: Zhang H et al. RMD Open. 2021 Apr 16. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001399.