User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
CMS loosens clinician scope-of-practice, telehealth rules for COVID-19 crisis
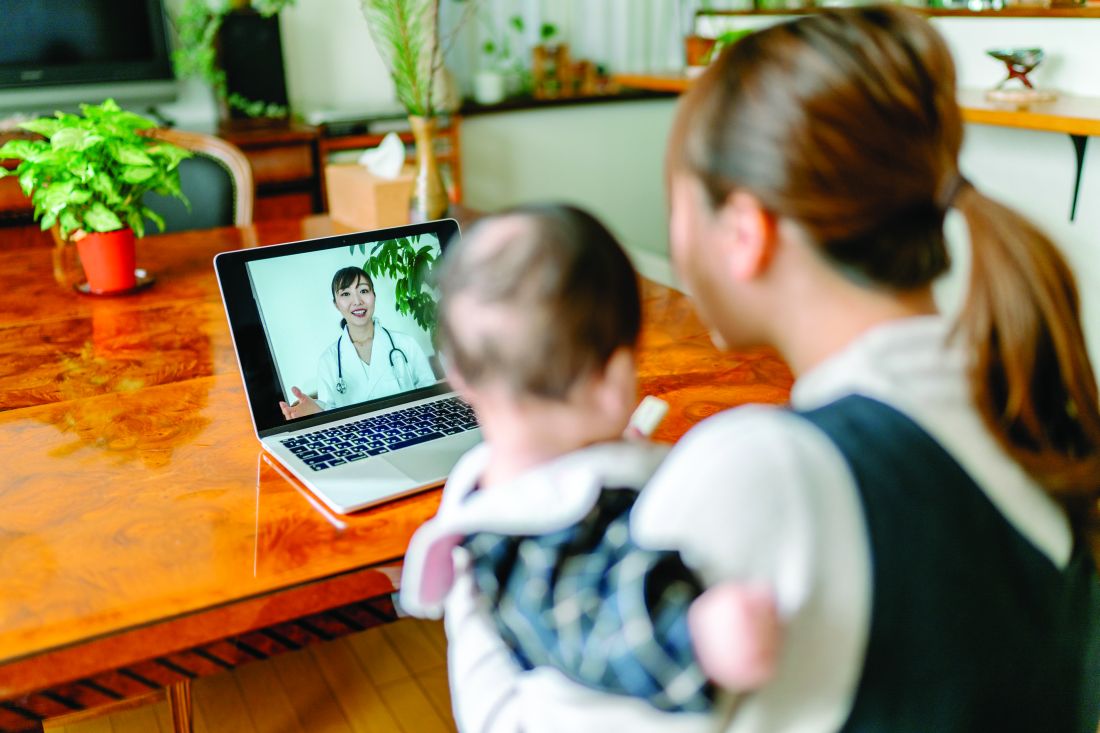
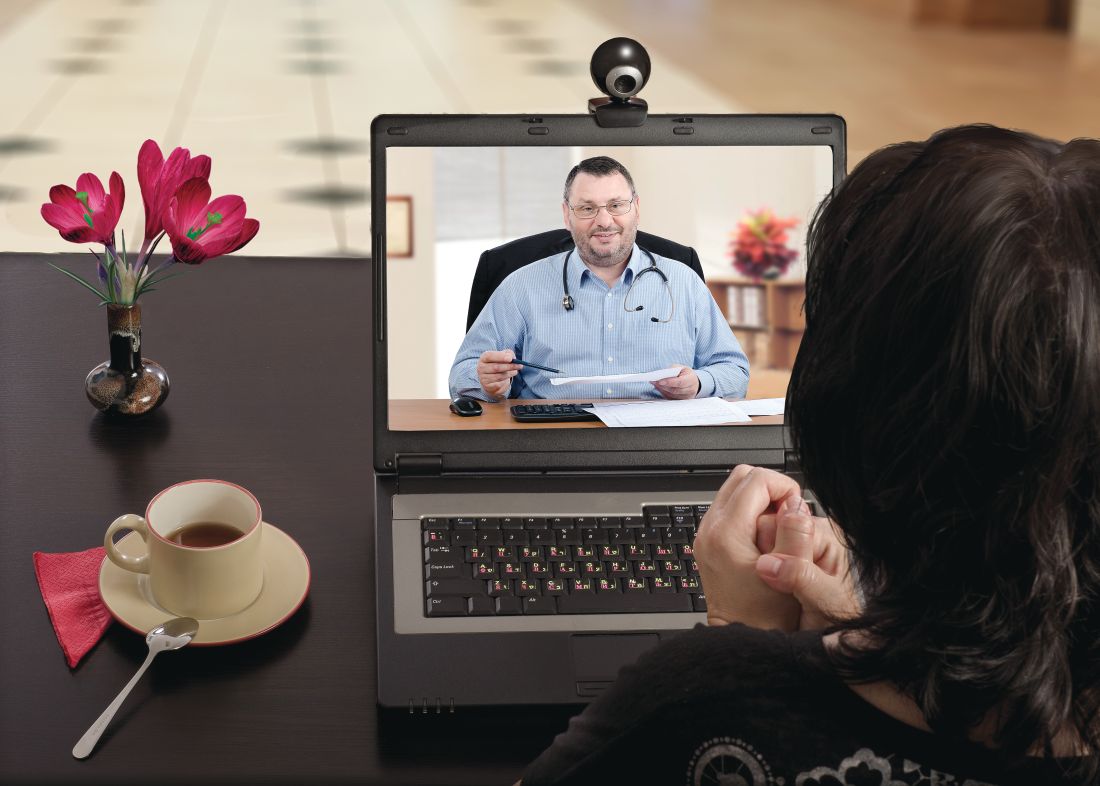
To boost the capacity of frontline clinicians and facilities to fight COVID-19, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) on Thursday announced it is temporarily suspending rules to allow physicians to provide telehealth services across state lines, and will permit midlevel practitioners to provide as much care as their state licenses allow.
Physicians can now care for patients at rural hospitals across state lines via phone, radio, or online communications without having to be physically present.
“Remotely located physicians, coordinating with nurse practitioners at rural hospitals, will provide staffs at such facilities additional flexibility to meet the needs of their patients,” a CMS news release said.
At skilled nursing facilities, nurse practitioners will now be able to perform some medical exams that doctors normally conduct on Medicare patients, whether they are COVID-19-related or not, CMS said.
Occupational therapists from home health agencies can now perform initial assessments on certain homebound patients, allowing home health services to start sooner and freeing home health nurses to do more direct patient care.
In addition, hospice nurses will be relieved of hospice aide in-service training tasks so they can spend more time with patients.
“It’s all hands on deck during this crisis,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma in the press release. “All frontline medical professionals need to be able to work at the highest level they were trained for. CMS is making sure there are no regulatory obstacles to increasing the medical workforce to handle the patient surge during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
The announcement did not directly address the question of whether CMS’ new telemedicine and scope-of-practice policies override state laws. The agency said, “CMS sets and enforces essential quality and safety standards that supplement state scope-of-practice and licensure laws for healthcare workers. CMS has continuously examined its regulations to identify areas where federal requirements may be more stringent than state laws and requirements.”
On March 20, Vice President Pence announced that physicians would be allowed to practice across state lines during the COVID-19 crisis, as reported by Medscape Medical News. Until now, however, CMS had not changed its regulations to allow doctors to conduct telehealth consultations in states other than the ones in which they are licensed.
Other Changes
As part of other rule changes to support the healthcare workforce, CMS said on March 30 that it will pay for more than 80 additional services when furnished via telehealth.
These include emergency department visits, initial skilled nursing facility and discharge visits, and home visits. In addition, the agency said it would cover phone visits with Medicare beneficiaries.
Moreover, while virtual “check-in” visits had previously been limited to established patients, CMS said that doctors would be able to provide these services to both new and established patients.
Among its other regulatory changes in recent weeks, CMS has also temporarily:
- Permitted physicians whose privileges will expire to continue practicing at a hospital, and allowed new physicians to begin working prior to full hospital medical staff/governing body review and approval
- Lifted regulatory requirements regarding hospital personnel qualified to perform specific respiratory care procedures, allowing these professionals to operate to the fullest extent of their licensure
- Waived federal minimum personnel qualifications for clinical nurse specialists, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants so they can work at rural hospitals as long as they meet state licensure requirements
- Allowed physicians and nonphysician practitioners to use telehealth to care for patients at long-term care facilities, rather than having to treat patients at those facilities in person
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To boost the capacity of frontline clinicians and facilities to fight COVID-19, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) on Thursday announced it is temporarily suspending rules to allow physicians to provide telehealth services across state lines, and will permit midlevel practitioners to provide as much care as their state licenses allow.
Physicians can now care for patients at rural hospitals across state lines via phone, radio, or online communications without having to be physically present.
“Remotely located physicians, coordinating with nurse practitioners at rural hospitals, will provide staffs at such facilities additional flexibility to meet the needs of their patients,” a CMS news release said.
At skilled nursing facilities, nurse practitioners will now be able to perform some medical exams that doctors normally conduct on Medicare patients, whether they are COVID-19-related or not, CMS said.
Occupational therapists from home health agencies can now perform initial assessments on certain homebound patients, allowing home health services to start sooner and freeing home health nurses to do more direct patient care.
In addition, hospice nurses will be relieved of hospice aide in-service training tasks so they can spend more time with patients.
“It’s all hands on deck during this crisis,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma in the press release. “All frontline medical professionals need to be able to work at the highest level they were trained for. CMS is making sure there are no regulatory obstacles to increasing the medical workforce to handle the patient surge during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
The announcement did not directly address the question of whether CMS’ new telemedicine and scope-of-practice policies override state laws. The agency said, “CMS sets and enforces essential quality and safety standards that supplement state scope-of-practice and licensure laws for healthcare workers. CMS has continuously examined its regulations to identify areas where federal requirements may be more stringent than state laws and requirements.”
On March 20, Vice President Pence announced that physicians would be allowed to practice across state lines during the COVID-19 crisis, as reported by Medscape Medical News. Until now, however, CMS had not changed its regulations to allow doctors to conduct telehealth consultations in states other than the ones in which they are licensed.
Other Changes
As part of other rule changes to support the healthcare workforce, CMS said on March 30 that it will pay for more than 80 additional services when furnished via telehealth.
These include emergency department visits, initial skilled nursing facility and discharge visits, and home visits. In addition, the agency said it would cover phone visits with Medicare beneficiaries.
Moreover, while virtual “check-in” visits had previously been limited to established patients, CMS said that doctors would be able to provide these services to both new and established patients.
Among its other regulatory changes in recent weeks, CMS has also temporarily:
- Permitted physicians whose privileges will expire to continue practicing at a hospital, and allowed new physicians to begin working prior to full hospital medical staff/governing body review and approval
- Lifted regulatory requirements regarding hospital personnel qualified to perform specific respiratory care procedures, allowing these professionals to operate to the fullest extent of their licensure
- Waived federal minimum personnel qualifications for clinical nurse specialists, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants so they can work at rural hospitals as long as they meet state licensure requirements
- Allowed physicians and nonphysician practitioners to use telehealth to care for patients at long-term care facilities, rather than having to treat patients at those facilities in person
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To boost the capacity of frontline clinicians and facilities to fight COVID-19, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) on Thursday announced it is temporarily suspending rules to allow physicians to provide telehealth services across state lines, and will permit midlevel practitioners to provide as much care as their state licenses allow.
Physicians can now care for patients at rural hospitals across state lines via phone, radio, or online communications without having to be physically present.
“Remotely located physicians, coordinating with nurse practitioners at rural hospitals, will provide staffs at such facilities additional flexibility to meet the needs of their patients,” a CMS news release said.
At skilled nursing facilities, nurse practitioners will now be able to perform some medical exams that doctors normally conduct on Medicare patients, whether they are COVID-19-related or not, CMS said.
Occupational therapists from home health agencies can now perform initial assessments on certain homebound patients, allowing home health services to start sooner and freeing home health nurses to do more direct patient care.
In addition, hospice nurses will be relieved of hospice aide in-service training tasks so they can spend more time with patients.
“It’s all hands on deck during this crisis,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma in the press release. “All frontline medical professionals need to be able to work at the highest level they were trained for. CMS is making sure there are no regulatory obstacles to increasing the medical workforce to handle the patient surge during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
The announcement did not directly address the question of whether CMS’ new telemedicine and scope-of-practice policies override state laws. The agency said, “CMS sets and enforces essential quality and safety standards that supplement state scope-of-practice and licensure laws for healthcare workers. CMS has continuously examined its regulations to identify areas where federal requirements may be more stringent than state laws and requirements.”
On March 20, Vice President Pence announced that physicians would be allowed to practice across state lines during the COVID-19 crisis, as reported by Medscape Medical News. Until now, however, CMS had not changed its regulations to allow doctors to conduct telehealth consultations in states other than the ones in which they are licensed.
Other Changes
As part of other rule changes to support the healthcare workforce, CMS said on March 30 that it will pay for more than 80 additional services when furnished via telehealth.
These include emergency department visits, initial skilled nursing facility and discharge visits, and home visits. In addition, the agency said it would cover phone visits with Medicare beneficiaries.
Moreover, while virtual “check-in” visits had previously been limited to established patients, CMS said that doctors would be able to provide these services to both new and established patients.
Among its other regulatory changes in recent weeks, CMS has also temporarily:
- Permitted physicians whose privileges will expire to continue practicing at a hospital, and allowed new physicians to begin working prior to full hospital medical staff/governing body review and approval
- Lifted regulatory requirements regarding hospital personnel qualified to perform specific respiratory care procedures, allowing these professionals to operate to the fullest extent of their licensure
- Waived federal minimum personnel qualifications for clinical nurse specialists, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants so they can work at rural hospitals as long as they meet state licensure requirements
- Allowed physicians and nonphysician practitioners to use telehealth to care for patients at long-term care facilities, rather than having to treat patients at those facilities in person
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What do early remdesivir data suggest?
New data on the investigational antiviral drug remdesivir (Gilead) suggest clinical improvement in 36 of 53 patients (68%) hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to a new study published online April 10 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
But experts are warning that these data come from compassionate use in a wide variety of patients, with no randomization and no control group.
“It is impossible to know the outcome for this relatively small group of patients had they not received remdesivir,” commented Stephen Griffin, PhD, associate professor at the University of Leeds School of Medicine, United Kingdom, who was not involved with the study.
“As the authors point out, a randomized clinical trial is necessary to determine the true effectiveness of this drug,” Griffin added in comments he provided to the Science Media Centre in London. Such trials are underway.
“The data from this paper are almost uninterpretable,” said Stephen Evans, MSc, FRCP, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who provided comments to the Science Media Centre.
Evans notes that the authors describe multiple caveats that limit interpretation of the results, including the small sample size, the relatively short follow-up, missing data, no follow-up on eight patients, and lack of a randomized control group.
Meanwhile, Josh Farkas, MD, who writes the PulmCrit blog, details his criticisms in a piece entitled, “Eleven reasons the NEJM paper on remdesivir reveals nothing.” Beyond the issues the authors list, he points out several more, including cherry picking of patients. “Remdesivir was aggressively sought-after by thousands of patients with COVID-19,” he writes. “Of these patients, 61 ended up receiving the drug. Why did these patients receive medication, out of scores of patients applying to receive it?”
Also, there are no follow-up data for 8 of the 61 patients who received an initial dose of the drug, leaving 53 for the published analysis, continues Farkas, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Vermont in Burlington.
“What happened to these patients? Did they die from anaphylaxis? Did they get well, sign out against medical advice, and go party? This is unknown — but I’m worried that these patients actually didn’t fare so well,” Farkas writes.
Farkas, like Evans and Griffin, concludes that the data are largely unusable. “Until [a randomized controlled trial] is performed, further compassionate use of remdesivir probably isn’t justified,” he writes.
Data from Compassionate Use Program
The data in the NEJM article come from a compassionate use program set up by Gilead. The company says it has provided emergency access to remdesivir for several hundred patients in the United States, Europe, and Japan.
The authors, led by Jonathan Grein, MD, from Cedars–Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, report on 61 patients who received remdesivir as part of this program.
The authors, several of whom are employees of Gilead, note that data on 8 patients could not be analyzed (including 7 patients with no posttreatment data and 1 with a dosing error).
Of the 53 patients whose data were included, 22 were in the United States, 22 in Europe or Canada, and 9 in Japan.
These were patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and had an oxygen saturation of 94% or less while they were breathing ambient air, or who were receiving oxygen support.
Patients received a 10-day course of remdesivir, consisting of 200 mg administered intravenously on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for the remaining 9 days of treatment.
At baseline, 30 patients (57%) were receiving mechanical ventilation and 4 (8%) were receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
During a median follow-up of 18 days, 36 patients (68%) had an improvement in oxygen-support class, including 17 (57%) of 30 patients receiving mechanical ventilation who were extubated.
A total of 25 patients (47%) were discharged, and 7 patients (13%) died; mortality was 18% (6 of 34) among patients receiving invasive ventilation and 5% (1 of 19) among those not receiving invasive ventilation.
While the authors acknowledge limitations of the data they collected, they nevertheless comment that “comparisons with contemporaneous cohorts from the literature, in whom general care is expected to be consistent with that of our cohort, suggest that remdesivir may have clinical benefit in patients with severe COVID-19.”
“Currently there is no proven treatment for COVID-19. We cannot draw definitive conclusions from these data, but the observations from this group of hospitalized patients who received remdesivir are hopeful,” said Grein in a Cedars–Sinai press release. “We look forward to the results of controlled clinical trials to potentially validate these findings.”
Experts are not convinced, however.
“The drug was being used in patients who were severely ill, but reporting on 61 out of several hundred makes it clear that generalizations about the efficacy and safety must be treated with great caution,” said Evans. “There is some evidence suggesting efficacy, but we simply do not know what would have happened to these patients had they not been given the drug.”
“I would say it’s impossible to discern whether there is a treatment effect or not,” said Duncan Richards, MA, DM, FRCP, clinical pharmacologist and professor of clinical therapeutics, University of Oxford, UK. “This is in part due to the mixed patient population, ranging from those needing low dose oxygen, who are more likely to survive anyway, to much more severe cases ... [who] show a much more mixed picture.”
“There are ongoing large international randomized controlled trials with remdesivir — we really need to see those data, “ he said in comments to Science Media Centre. “Safe and effective treatments for COVID-19 are critically needed and should be expedited wherever possible, but it’s important not to compromise on the quality of the research.”
Multiple coauthors are employees of Gilead, the company developing remdesivir. Griffin, Evans, and Farkas have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Richards consults for GlaxoSmithKline in the field of drug safety. GSK does not manufacture any of the products mentioned.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 10. Full text.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data on the investigational antiviral drug remdesivir (Gilead) suggest clinical improvement in 36 of 53 patients (68%) hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to a new study published online April 10 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
But experts are warning that these data come from compassionate use in a wide variety of patients, with no randomization and no control group.
“It is impossible to know the outcome for this relatively small group of patients had they not received remdesivir,” commented Stephen Griffin, PhD, associate professor at the University of Leeds School of Medicine, United Kingdom, who was not involved with the study.
“As the authors point out, a randomized clinical trial is necessary to determine the true effectiveness of this drug,” Griffin added in comments he provided to the Science Media Centre in London. Such trials are underway.
“The data from this paper are almost uninterpretable,” said Stephen Evans, MSc, FRCP, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who provided comments to the Science Media Centre.
Evans notes that the authors describe multiple caveats that limit interpretation of the results, including the small sample size, the relatively short follow-up, missing data, no follow-up on eight patients, and lack of a randomized control group.
Meanwhile, Josh Farkas, MD, who writes the PulmCrit blog, details his criticisms in a piece entitled, “Eleven reasons the NEJM paper on remdesivir reveals nothing.” Beyond the issues the authors list, he points out several more, including cherry picking of patients. “Remdesivir was aggressively sought-after by thousands of patients with COVID-19,” he writes. “Of these patients, 61 ended up receiving the drug. Why did these patients receive medication, out of scores of patients applying to receive it?”
Also, there are no follow-up data for 8 of the 61 patients who received an initial dose of the drug, leaving 53 for the published analysis, continues Farkas, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Vermont in Burlington.
“What happened to these patients? Did they die from anaphylaxis? Did they get well, sign out against medical advice, and go party? This is unknown — but I’m worried that these patients actually didn’t fare so well,” Farkas writes.
Farkas, like Evans and Griffin, concludes that the data are largely unusable. “Until [a randomized controlled trial] is performed, further compassionate use of remdesivir probably isn’t justified,” he writes.
Data from Compassionate Use Program
The data in the NEJM article come from a compassionate use program set up by Gilead. The company says it has provided emergency access to remdesivir for several hundred patients in the United States, Europe, and Japan.
The authors, led by Jonathan Grein, MD, from Cedars–Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, report on 61 patients who received remdesivir as part of this program.
The authors, several of whom are employees of Gilead, note that data on 8 patients could not be analyzed (including 7 patients with no posttreatment data and 1 with a dosing error).
Of the 53 patients whose data were included, 22 were in the United States, 22 in Europe or Canada, and 9 in Japan.
These were patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and had an oxygen saturation of 94% or less while they were breathing ambient air, or who were receiving oxygen support.
Patients received a 10-day course of remdesivir, consisting of 200 mg administered intravenously on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for the remaining 9 days of treatment.
At baseline, 30 patients (57%) were receiving mechanical ventilation and 4 (8%) were receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
During a median follow-up of 18 days, 36 patients (68%) had an improvement in oxygen-support class, including 17 (57%) of 30 patients receiving mechanical ventilation who were extubated.
A total of 25 patients (47%) were discharged, and 7 patients (13%) died; mortality was 18% (6 of 34) among patients receiving invasive ventilation and 5% (1 of 19) among those not receiving invasive ventilation.
While the authors acknowledge limitations of the data they collected, they nevertheless comment that “comparisons with contemporaneous cohorts from the literature, in whom general care is expected to be consistent with that of our cohort, suggest that remdesivir may have clinical benefit in patients with severe COVID-19.”
“Currently there is no proven treatment for COVID-19. We cannot draw definitive conclusions from these data, but the observations from this group of hospitalized patients who received remdesivir are hopeful,” said Grein in a Cedars–Sinai press release. “We look forward to the results of controlled clinical trials to potentially validate these findings.”
Experts are not convinced, however.
“The drug was being used in patients who were severely ill, but reporting on 61 out of several hundred makes it clear that generalizations about the efficacy and safety must be treated with great caution,” said Evans. “There is some evidence suggesting efficacy, but we simply do not know what would have happened to these patients had they not been given the drug.”
“I would say it’s impossible to discern whether there is a treatment effect or not,” said Duncan Richards, MA, DM, FRCP, clinical pharmacologist and professor of clinical therapeutics, University of Oxford, UK. “This is in part due to the mixed patient population, ranging from those needing low dose oxygen, who are more likely to survive anyway, to much more severe cases ... [who] show a much more mixed picture.”
“There are ongoing large international randomized controlled trials with remdesivir — we really need to see those data, “ he said in comments to Science Media Centre. “Safe and effective treatments for COVID-19 are critically needed and should be expedited wherever possible, but it’s important not to compromise on the quality of the research.”
Multiple coauthors are employees of Gilead, the company developing remdesivir. Griffin, Evans, and Farkas have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Richards consults for GlaxoSmithKline in the field of drug safety. GSK does not manufacture any of the products mentioned.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 10. Full text.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data on the investigational antiviral drug remdesivir (Gilead) suggest clinical improvement in 36 of 53 patients (68%) hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to a new study published online April 10 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
But experts are warning that these data come from compassionate use in a wide variety of patients, with no randomization and no control group.
“It is impossible to know the outcome for this relatively small group of patients had they not received remdesivir,” commented Stephen Griffin, PhD, associate professor at the University of Leeds School of Medicine, United Kingdom, who was not involved with the study.
“As the authors point out, a randomized clinical trial is necessary to determine the true effectiveness of this drug,” Griffin added in comments he provided to the Science Media Centre in London. Such trials are underway.
“The data from this paper are almost uninterpretable,” said Stephen Evans, MSc, FRCP, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who provided comments to the Science Media Centre.
Evans notes that the authors describe multiple caveats that limit interpretation of the results, including the small sample size, the relatively short follow-up, missing data, no follow-up on eight patients, and lack of a randomized control group.
Meanwhile, Josh Farkas, MD, who writes the PulmCrit blog, details his criticisms in a piece entitled, “Eleven reasons the NEJM paper on remdesivir reveals nothing.” Beyond the issues the authors list, he points out several more, including cherry picking of patients. “Remdesivir was aggressively sought-after by thousands of patients with COVID-19,” he writes. “Of these patients, 61 ended up receiving the drug. Why did these patients receive medication, out of scores of patients applying to receive it?”
Also, there are no follow-up data for 8 of the 61 patients who received an initial dose of the drug, leaving 53 for the published analysis, continues Farkas, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Vermont in Burlington.
“What happened to these patients? Did they die from anaphylaxis? Did they get well, sign out against medical advice, and go party? This is unknown — but I’m worried that these patients actually didn’t fare so well,” Farkas writes.
Farkas, like Evans and Griffin, concludes that the data are largely unusable. “Until [a randomized controlled trial] is performed, further compassionate use of remdesivir probably isn’t justified,” he writes.
Data from Compassionate Use Program
The data in the NEJM article come from a compassionate use program set up by Gilead. The company says it has provided emergency access to remdesivir for several hundred patients in the United States, Europe, and Japan.
The authors, led by Jonathan Grein, MD, from Cedars–Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, report on 61 patients who received remdesivir as part of this program.
The authors, several of whom are employees of Gilead, note that data on 8 patients could not be analyzed (including 7 patients with no posttreatment data and 1 with a dosing error).
Of the 53 patients whose data were included, 22 were in the United States, 22 in Europe or Canada, and 9 in Japan.
These were patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and had an oxygen saturation of 94% or less while they were breathing ambient air, or who were receiving oxygen support.
Patients received a 10-day course of remdesivir, consisting of 200 mg administered intravenously on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for the remaining 9 days of treatment.
At baseline, 30 patients (57%) were receiving mechanical ventilation and 4 (8%) were receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
During a median follow-up of 18 days, 36 patients (68%) had an improvement in oxygen-support class, including 17 (57%) of 30 patients receiving mechanical ventilation who were extubated.
A total of 25 patients (47%) were discharged, and 7 patients (13%) died; mortality was 18% (6 of 34) among patients receiving invasive ventilation and 5% (1 of 19) among those not receiving invasive ventilation.
While the authors acknowledge limitations of the data they collected, they nevertheless comment that “comparisons with contemporaneous cohorts from the literature, in whom general care is expected to be consistent with that of our cohort, suggest that remdesivir may have clinical benefit in patients with severe COVID-19.”
“Currently there is no proven treatment for COVID-19. We cannot draw definitive conclusions from these data, but the observations from this group of hospitalized patients who received remdesivir are hopeful,” said Grein in a Cedars–Sinai press release. “We look forward to the results of controlled clinical trials to potentially validate these findings.”
Experts are not convinced, however.
“The drug was being used in patients who were severely ill, but reporting on 61 out of several hundred makes it clear that generalizations about the efficacy and safety must be treated with great caution,” said Evans. “There is some evidence suggesting efficacy, but we simply do not know what would have happened to these patients had they not been given the drug.”
“I would say it’s impossible to discern whether there is a treatment effect or not,” said Duncan Richards, MA, DM, FRCP, clinical pharmacologist and professor of clinical therapeutics, University of Oxford, UK. “This is in part due to the mixed patient population, ranging from those needing low dose oxygen, who are more likely to survive anyway, to much more severe cases ... [who] show a much more mixed picture.”
“There are ongoing large international randomized controlled trials with remdesivir — we really need to see those data, “ he said in comments to Science Media Centre. “Safe and effective treatments for COVID-19 are critically needed and should be expedited wherever possible, but it’s important not to compromise on the quality of the research.”
Multiple coauthors are employees of Gilead, the company developing remdesivir. Griffin, Evans, and Farkas have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Richards consults for GlaxoSmithKline in the field of drug safety. GSK does not manufacture any of the products mentioned.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 10. Full text.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remdesivir tops list of promising COVID-19 treatments in review of nearly 300 trials
, according to authors of a recent review covering nearly 300 active clinical treatment trials underway for the disease.
Remdesivir, which has potent in vitro activity against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration and is currently being tested in randomized trials, according to the review authors, led by James M. Sanders, PhD, of the department of pharmacy at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
By contrast, oseltamivir has not demonstrated efficacy against the virus, corticosteroids are not recommended, and promising data from a small French hydroxychloroquine study are balanced by “several major limitations” including small sample size and exclusion of early dropouts from the analysis, among others, Dr. Sanders and coauthors said in their report.
“These limitations coupled with concerns of additive cardiotoxicity with combination therapy [i.e., hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin] do not support adoption of this regimen without additional studies,” the researchers wrote. Their report is in JAMA.
Dr. Sanders and colleagues identified 291 COVID-19–specific studies listed in ClinicalTrials.gov through April 2, including 29 placebo-controlled trials.
This might represent just a sliver of the treatments that could combat COVID-19, according to the researchers, who said more than 3,000 small-molecule drug candidates with potential activity against human coronaviruses have been identified.
“This large amount of potential agents will hopefully yield more candidate therapeutics in the race to find effective treatments or preventive strategies against COVID-19,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
Remdesivir for COVID-19
Remdesivir, an investigational nucleotide analog, is one promising agent because of its broad-spectrum and potent activity against SARS-CoV-2 and other novel coronaviruses, they said, adding that phase 1 trials demonstrated the drug was well tolerated without observed liver or kidney toxicity.
There have been “successful” case reports of remdesivir use in COVID-19, and at least five ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the drug’s safety and antiviral activity in this disease. Among those studies is a National Institutes of Health–sponsored adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that will provide data on the use of remdesivir versus supportive care.
“As the results from randomized controlled trials are anticipated, inclusion of this agent for treatment of COVID-19 may be considered,” Dr. Sanders and colleagues wrote in their report. To date, remdesivir remains investigational and needs to be obtained via compassionate use, through expanded access, or by participating in a clinical trial, they added.
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine
Among the published hydroxychloroquine studies is a “promising” 36-patient open-label nonrandomized French study, in which the antimalarial agent given every 8 hours improved virologic clearance by day 6 versus controls (70% vs. 12.5%, respectively), the review authors said. Moreover, viral clearance was 100% for 6 patients who received hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin, compared to 57% (8 of 14) for patients treated with hydroxychloroquine alone. However, that study had several important limitations, including the small sample size, variable viral loads at baseline between groups, and a lack of safety and clinical outcomes reporting, according to the investigators. Moreover, six patients in the hydroxychloroquine group were taken out of the analysis because of early treatment stoppage due to medical intolerance or critical illness, the authors noted.
One prospective study including 30 patients in China demonstrated no difference in virologic outcomes for patients randomized to hydroxychloroquine plus standard of care versus standard of care alone, they added. There is also a case series of more than 100 patients with COVID-19 that reportedly improved viral clearance and reduced disease progression, though they said results haven’t been published or presented beyond a news briefing in China.
Randomized, controlled trials of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 treatment are underway, and studies are planned or enrolling to look at chloroquine prophylaxis in health care personnel and hydroxychloroquine for postexposure prophylaxis, authors said.
In results from one of those randomized trials, just reported, a higher dose of chloroquine was associated with a cardiac adverse event and an increased mortality risk, leading to the closure of that study arm. In the parallel, double-blinded, phase IIb clinical trial, patients in Brazil with SARS-CoV-2 infection received low or high doses of chloroquine plus ceftriaxone and azithromycin. According to the preprint publication, a higher rate of heart rate–corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation and a “trend toward higher lethality” was observed in the high-dose group, leading investigators to “strongly recommend” the higher dose be abandoned.
“No apparent benefit of chloroquine was seen regarding lethality in our patients so far, but we will still enroll patients in the low chloroquine dose group to complete the originally planned sample size,” said investigators of the study, which at the time of the report had enrolled 81 out of an anticipated 440 patients.
Other COVID-19 pharmacologic therapies under study
Treatments of note in the review included the following:
- Tocilizumab. This monoclonal antibody IL-6 receptor antagonist, approved by the FDA for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and for cytokine release syndrome related to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has yielded success in small series of patients with severe cases of COVID-19, according to authors. In one 21-patient report, 91% had clinical improvement, usually after a single dose. In China, tocilizumab is included in COVID-19 treatment guidelines, and several randomized clinical trials are underway in China including patients with COVID-19 with severe pneumonia.
- Immunoglobulin therapy. Antibodies from recovered COVID-19 patients could help with free virus and infected cell immune clearance, the authors said, adding that further studies are warranted beyond a few small published case series that suggest promise. Furthermore, on March 24 the FDA released guidance for screening donors for COVID-19 convalescent plasma and on emergency investigational new drug applications based on this modality.
- Lopinavir/ritonavir. Despite demonstrated in vitro activity against other novel coronaviruses, there is no published in vitro data for lopinavir/ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2, and likely a “limited role” for this combination anticipated in treating COVID-19, according to the review authors. In an open-label randomized clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282), there were no differences in clinical improvement, viral clearance, or mortality for antiviral treatment versus standard care. Delayed treatment initiation may explain the ineffectiveness, though a subgroup analysis didn’t show a shorter time to clinical improvement for those who got the treatment earlier.
- Ribavirin. Likewise, this antiviral medication has efficacy and safety data suggesting “limited value” for treatment of COVID-19. Treatment of SARS yielded “inconclusive results” for ribavirin, which was also associated with substantial toxicity that included hemolytic anemia in 60% of SARS patients.
- Oseltamivir. While it may treat influenza, it has no documented activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro: “This agent has no role in the management of COVID-19 once influenza has been excluded,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
- Corticosteroids. They could decrease inflammatory responses in the lung, but they could also lead to delays in viral clearance and increases in secondary infection risk. Guidelines for COVID-19 say to avoid corticosteroids, and the authors of the review concur, saying that potential harms and lack of proven benefit mean they usually should not be used outside of a randomized clinical trial setting.
- Vaccines. Clearly, vaccines represent the “most effective long-term strategy” to prevent future COVID-19 outbreaks, though at least 12-18 months would be required until vaccines can be widely deployed, authors said.
Dr. Sanders reported no potential conflicts. Senior author James B. Cutrell, MD, also of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, reported nonfinancial support from Gilead and Regeneron outside of the study. No other authors reported disclosures.
, according to authors of a recent review covering nearly 300 active clinical treatment trials underway for the disease.
Remdesivir, which has potent in vitro activity against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration and is currently being tested in randomized trials, according to the review authors, led by James M. Sanders, PhD, of the department of pharmacy at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
By contrast, oseltamivir has not demonstrated efficacy against the virus, corticosteroids are not recommended, and promising data from a small French hydroxychloroquine study are balanced by “several major limitations” including small sample size and exclusion of early dropouts from the analysis, among others, Dr. Sanders and coauthors said in their report.
“These limitations coupled with concerns of additive cardiotoxicity with combination therapy [i.e., hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin] do not support adoption of this regimen without additional studies,” the researchers wrote. Their report is in JAMA.
Dr. Sanders and colleagues identified 291 COVID-19–specific studies listed in ClinicalTrials.gov through April 2, including 29 placebo-controlled trials.
This might represent just a sliver of the treatments that could combat COVID-19, according to the researchers, who said more than 3,000 small-molecule drug candidates with potential activity against human coronaviruses have been identified.
“This large amount of potential agents will hopefully yield more candidate therapeutics in the race to find effective treatments or preventive strategies against COVID-19,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
Remdesivir for COVID-19
Remdesivir, an investigational nucleotide analog, is one promising agent because of its broad-spectrum and potent activity against SARS-CoV-2 and other novel coronaviruses, they said, adding that phase 1 trials demonstrated the drug was well tolerated without observed liver or kidney toxicity.
There have been “successful” case reports of remdesivir use in COVID-19, and at least five ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the drug’s safety and antiviral activity in this disease. Among those studies is a National Institutes of Health–sponsored adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that will provide data on the use of remdesivir versus supportive care.
“As the results from randomized controlled trials are anticipated, inclusion of this agent for treatment of COVID-19 may be considered,” Dr. Sanders and colleagues wrote in their report. To date, remdesivir remains investigational and needs to be obtained via compassionate use, through expanded access, or by participating in a clinical trial, they added.
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine
Among the published hydroxychloroquine studies is a “promising” 36-patient open-label nonrandomized French study, in which the antimalarial agent given every 8 hours improved virologic clearance by day 6 versus controls (70% vs. 12.5%, respectively), the review authors said. Moreover, viral clearance was 100% for 6 patients who received hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin, compared to 57% (8 of 14) for patients treated with hydroxychloroquine alone. However, that study had several important limitations, including the small sample size, variable viral loads at baseline between groups, and a lack of safety and clinical outcomes reporting, according to the investigators. Moreover, six patients in the hydroxychloroquine group were taken out of the analysis because of early treatment stoppage due to medical intolerance or critical illness, the authors noted.
One prospective study including 30 patients in China demonstrated no difference in virologic outcomes for patients randomized to hydroxychloroquine plus standard of care versus standard of care alone, they added. There is also a case series of more than 100 patients with COVID-19 that reportedly improved viral clearance and reduced disease progression, though they said results haven’t been published or presented beyond a news briefing in China.
Randomized, controlled trials of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 treatment are underway, and studies are planned or enrolling to look at chloroquine prophylaxis in health care personnel and hydroxychloroquine for postexposure prophylaxis, authors said.
In results from one of those randomized trials, just reported, a higher dose of chloroquine was associated with a cardiac adverse event and an increased mortality risk, leading to the closure of that study arm. In the parallel, double-blinded, phase IIb clinical trial, patients in Brazil with SARS-CoV-2 infection received low or high doses of chloroquine plus ceftriaxone and azithromycin. According to the preprint publication, a higher rate of heart rate–corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation and a “trend toward higher lethality” was observed in the high-dose group, leading investigators to “strongly recommend” the higher dose be abandoned.
“No apparent benefit of chloroquine was seen regarding lethality in our patients so far, but we will still enroll patients in the low chloroquine dose group to complete the originally planned sample size,” said investigators of the study, which at the time of the report had enrolled 81 out of an anticipated 440 patients.
Other COVID-19 pharmacologic therapies under study
Treatments of note in the review included the following:
- Tocilizumab. This monoclonal antibody IL-6 receptor antagonist, approved by the FDA for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and for cytokine release syndrome related to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has yielded success in small series of patients with severe cases of COVID-19, according to authors. In one 21-patient report, 91% had clinical improvement, usually after a single dose. In China, tocilizumab is included in COVID-19 treatment guidelines, and several randomized clinical trials are underway in China including patients with COVID-19 with severe pneumonia.
- Immunoglobulin therapy. Antibodies from recovered COVID-19 patients could help with free virus and infected cell immune clearance, the authors said, adding that further studies are warranted beyond a few small published case series that suggest promise. Furthermore, on March 24 the FDA released guidance for screening donors for COVID-19 convalescent plasma and on emergency investigational new drug applications based on this modality.
- Lopinavir/ritonavir. Despite demonstrated in vitro activity against other novel coronaviruses, there is no published in vitro data for lopinavir/ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2, and likely a “limited role” for this combination anticipated in treating COVID-19, according to the review authors. In an open-label randomized clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282), there were no differences in clinical improvement, viral clearance, or mortality for antiviral treatment versus standard care. Delayed treatment initiation may explain the ineffectiveness, though a subgroup analysis didn’t show a shorter time to clinical improvement for those who got the treatment earlier.
- Ribavirin. Likewise, this antiviral medication has efficacy and safety data suggesting “limited value” for treatment of COVID-19. Treatment of SARS yielded “inconclusive results” for ribavirin, which was also associated with substantial toxicity that included hemolytic anemia in 60% of SARS patients.
- Oseltamivir. While it may treat influenza, it has no documented activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro: “This agent has no role in the management of COVID-19 once influenza has been excluded,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
- Corticosteroids. They could decrease inflammatory responses in the lung, but they could also lead to delays in viral clearance and increases in secondary infection risk. Guidelines for COVID-19 say to avoid corticosteroids, and the authors of the review concur, saying that potential harms and lack of proven benefit mean they usually should not be used outside of a randomized clinical trial setting.
- Vaccines. Clearly, vaccines represent the “most effective long-term strategy” to prevent future COVID-19 outbreaks, though at least 12-18 months would be required until vaccines can be widely deployed, authors said.
Dr. Sanders reported no potential conflicts. Senior author James B. Cutrell, MD, also of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, reported nonfinancial support from Gilead and Regeneron outside of the study. No other authors reported disclosures.
, according to authors of a recent review covering nearly 300 active clinical treatment trials underway for the disease.
Remdesivir, which has potent in vitro activity against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration and is currently being tested in randomized trials, according to the review authors, led by James M. Sanders, PhD, of the department of pharmacy at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
By contrast, oseltamivir has not demonstrated efficacy against the virus, corticosteroids are not recommended, and promising data from a small French hydroxychloroquine study are balanced by “several major limitations” including small sample size and exclusion of early dropouts from the analysis, among others, Dr. Sanders and coauthors said in their report.
“These limitations coupled with concerns of additive cardiotoxicity with combination therapy [i.e., hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin] do not support adoption of this regimen without additional studies,” the researchers wrote. Their report is in JAMA.
Dr. Sanders and colleagues identified 291 COVID-19–specific studies listed in ClinicalTrials.gov through April 2, including 29 placebo-controlled trials.
This might represent just a sliver of the treatments that could combat COVID-19, according to the researchers, who said more than 3,000 small-molecule drug candidates with potential activity against human coronaviruses have been identified.
“This large amount of potential agents will hopefully yield more candidate therapeutics in the race to find effective treatments or preventive strategies against COVID-19,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
Remdesivir for COVID-19
Remdesivir, an investigational nucleotide analog, is one promising agent because of its broad-spectrum and potent activity against SARS-CoV-2 and other novel coronaviruses, they said, adding that phase 1 trials demonstrated the drug was well tolerated without observed liver or kidney toxicity.
There have been “successful” case reports of remdesivir use in COVID-19, and at least five ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the drug’s safety and antiviral activity in this disease. Among those studies is a National Institutes of Health–sponsored adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that will provide data on the use of remdesivir versus supportive care.
“As the results from randomized controlled trials are anticipated, inclusion of this agent for treatment of COVID-19 may be considered,” Dr. Sanders and colleagues wrote in their report. To date, remdesivir remains investigational and needs to be obtained via compassionate use, through expanded access, or by participating in a clinical trial, they added.
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine
Among the published hydroxychloroquine studies is a “promising” 36-patient open-label nonrandomized French study, in which the antimalarial agent given every 8 hours improved virologic clearance by day 6 versus controls (70% vs. 12.5%, respectively), the review authors said. Moreover, viral clearance was 100% for 6 patients who received hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin, compared to 57% (8 of 14) for patients treated with hydroxychloroquine alone. However, that study had several important limitations, including the small sample size, variable viral loads at baseline between groups, and a lack of safety and clinical outcomes reporting, according to the investigators. Moreover, six patients in the hydroxychloroquine group were taken out of the analysis because of early treatment stoppage due to medical intolerance or critical illness, the authors noted.
One prospective study including 30 patients in China demonstrated no difference in virologic outcomes for patients randomized to hydroxychloroquine plus standard of care versus standard of care alone, they added. There is also a case series of more than 100 patients with COVID-19 that reportedly improved viral clearance and reduced disease progression, though they said results haven’t been published or presented beyond a news briefing in China.
Randomized, controlled trials of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 treatment are underway, and studies are planned or enrolling to look at chloroquine prophylaxis in health care personnel and hydroxychloroquine for postexposure prophylaxis, authors said.
In results from one of those randomized trials, just reported, a higher dose of chloroquine was associated with a cardiac adverse event and an increased mortality risk, leading to the closure of that study arm. In the parallel, double-blinded, phase IIb clinical trial, patients in Brazil with SARS-CoV-2 infection received low or high doses of chloroquine plus ceftriaxone and azithromycin. According to the preprint publication, a higher rate of heart rate–corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation and a “trend toward higher lethality” was observed in the high-dose group, leading investigators to “strongly recommend” the higher dose be abandoned.
“No apparent benefit of chloroquine was seen regarding lethality in our patients so far, but we will still enroll patients in the low chloroquine dose group to complete the originally planned sample size,” said investigators of the study, which at the time of the report had enrolled 81 out of an anticipated 440 patients.
Other COVID-19 pharmacologic therapies under study
Treatments of note in the review included the following:
- Tocilizumab. This monoclonal antibody IL-6 receptor antagonist, approved by the FDA for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and for cytokine release syndrome related to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has yielded success in small series of patients with severe cases of COVID-19, according to authors. In one 21-patient report, 91% had clinical improvement, usually after a single dose. In China, tocilizumab is included in COVID-19 treatment guidelines, and several randomized clinical trials are underway in China including patients with COVID-19 with severe pneumonia.
- Immunoglobulin therapy. Antibodies from recovered COVID-19 patients could help with free virus and infected cell immune clearance, the authors said, adding that further studies are warranted beyond a few small published case series that suggest promise. Furthermore, on March 24 the FDA released guidance for screening donors for COVID-19 convalescent plasma and on emergency investigational new drug applications based on this modality.
- Lopinavir/ritonavir. Despite demonstrated in vitro activity against other novel coronaviruses, there is no published in vitro data for lopinavir/ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2, and likely a “limited role” for this combination anticipated in treating COVID-19, according to the review authors. In an open-label randomized clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282), there were no differences in clinical improvement, viral clearance, or mortality for antiviral treatment versus standard care. Delayed treatment initiation may explain the ineffectiveness, though a subgroup analysis didn’t show a shorter time to clinical improvement for those who got the treatment earlier.
- Ribavirin. Likewise, this antiviral medication has efficacy and safety data suggesting “limited value” for treatment of COVID-19. Treatment of SARS yielded “inconclusive results” for ribavirin, which was also associated with substantial toxicity that included hemolytic anemia in 60% of SARS patients.
- Oseltamivir. While it may treat influenza, it has no documented activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro: “This agent has no role in the management of COVID-19 once influenza has been excluded,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
- Corticosteroids. They could decrease inflammatory responses in the lung, but they could also lead to delays in viral clearance and increases in secondary infection risk. Guidelines for COVID-19 say to avoid corticosteroids, and the authors of the review concur, saying that potential harms and lack of proven benefit mean they usually should not be used outside of a randomized clinical trial setting.
- Vaccines. Clearly, vaccines represent the “most effective long-term strategy” to prevent future COVID-19 outbreaks, though at least 12-18 months would be required until vaccines can be widely deployed, authors said.
Dr. Sanders reported no potential conflicts. Senior author James B. Cutrell, MD, also of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, reported nonfinancial support from Gilead and Regeneron outside of the study. No other authors reported disclosures.
FROM JAMA
Troponins touted as ‘ally’ in COVID-19 triage, but message is nuanced
, cardiologists in the United Kingdom advise in a recently published viewpoint.
The tests can be used to “inform the triage of patients to critical care, guide the use of supportive treatments, and facilitate targeted cardiac investigations in those most likely to benefit,” Nicholas Mills, MD, PhD, University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. He is senior author on the viewpoint published online April 6 in the journal Circulation.
Older adults and those with a history of underlying cardiovascular disease appear to be at greatest risk of dying from COVID-19. “From early reports it is clear that elevated cardiac troponin concentrations predict in-hospital mortality,” said Mills.
In a recent report on hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, for example, cardiac injury (hs-cTn above the 99th-percentile upper reference limit) was seen in 1 in 5 patients and was an independent predictor of dying in the hospital. Mortality was 10-fold higher in those with cardiac injury on presentation.
Elevated cardiac troponin in the setting of COVID-19, Mills said, “may reflect illness severity with myocardial injury arising due to myocardial oxygen supply–demand imbalance. Or it may be due to direct cardiac involvement through viral myocarditis or stress cardiomyopathy, or where the prothrombotic and proinflammatory state is precipitating acute coronary syndromes.”
In their viewpoint, the authors note that circulating cTn is a marker of myocardial injury, “including but not limited to myocardial infarction or myocarditis, and the clinical relevance of this distinction has never been so clear.”
Therefore, the consequence of not measuring cardiac troponin may be to “ignore the plethora of ischemic and nonischemic causes” of myocardial injury related to COVID-19. “Clinicians who have used troponin measurement as a binary test for myocardial infarction independent of clinical context and those who consider an elevated cardiac troponin concentration to be a mandate for invasive coronary angiography must recalibrate,” they write.
“Rather than encouraging avoidance of troponin testing, we must harness the unheralded engagement from the cardiovascular community due to COVID-19 to better understand the utility of this essential biomarker and to educate clinicians on its interpretation and implications for prognosis and clinical decision making.”
Based on “same logic” as recent ACC guidance
The viewpoint was to some extent a response to a recent informal guidance from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) that advised caution in use of troponin and natriuretic peptide tests in patients with COVID-19.
Even so, that ACC guidance and the new viewpoint in Circulation are based on the “same logic,” James Januzzi Jr, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. Both documents:
- Point out that troponins are frequently abnormal in patients with severe cases of COVID-19
- Caution that clinicians should not equate an abnormal hs-cTn with acute myocardial infarction
- Note that, in most cases, hs-cTn elevations are a result of noncoronary mechanisms
- Recognize the potential risk to caregivers and the continued unchecked spread of SARS-CoV-2 related to downstream testing that might not be needed
“The Circulation opinion piece states that clinicians often use troponin as a binary test for myocardial infarction and a mandate for downstream testing, suggesting clinicians will need to recalibrate that approach, something I agree with and which is the central message of the ACC position,” Januzzi said.
Probably the biggest difference between the two documents, he said, is in the Circulation authors’ apparent enthusiasm to use hs-cTn as a tool to judge disease severity in patients with COVID-19.
It’s been known for more than a decade that myocardial injury is “an important risk predictor” in critical illness, Januzzi explained. “So the link between cardiac injury and outcomes in critical illness is nothing new. The difference is the fact we are seeing so many patients with COVID-19 all at once, and the authors suggest that using troponin might help in triage decision making.”
“There may be [such] a role here, but the data have not been systematically collected, and whether troponin truly adds something beyond information already available at the bedside — for example, does it add anything not already obvious at the bedside? — has not yet been conclusively proven,” Januzzi cautioned.
“As well, there are no prospective data supporting troponin as a trigger for ICU triage or for deciding on specific treatments.”
Positive cTn status “common” in COVID-19 patients
In his experience, Barry Cohen, MD, Morristown Medical Center, New Jersey, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, that positive cTn status is “common in COVID-19 patients and appears to have prognostic value, not only in type 1 MI due to atherothrombotic disease (related to a proinflammatory and prothrombotic state), but more frequently type 2 MI (supply–demand mismatch), viral myocarditis, coronary microvascular ischemia, stress cardiomyopathy or tachyarrhythmias.”
Moreover, Cohen said, hs-cTn “has identified patients at increased risk for ventilation support (invasive and noninvasive), acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute kidney injury, and mortality.”
Echoing both the ACC document and the Circulation report, Cohen also said hs-cTn measurements “appear to help risk stratify COVID-19 patients, but clearly do not mean that a troponin-positive patient needs to go to the cath lab and be treated as having acute coronary syndrome. Only a minority of these patients require this intervention.”
Mills discloses receiving honoraria from Abbott Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics, Siemens Healthineers, and LumiraDx. Januzzi has previously disclosed receiving personal fees from the American College of Cardiology, Pfizer, Merck, AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Takeda; grants and personal fees from Novartis, Roche, Abbott, and Janssen; and grants from Singulex and Prevencio. Cohen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, cardiologists in the United Kingdom advise in a recently published viewpoint.
The tests can be used to “inform the triage of patients to critical care, guide the use of supportive treatments, and facilitate targeted cardiac investigations in those most likely to benefit,” Nicholas Mills, MD, PhD, University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. He is senior author on the viewpoint published online April 6 in the journal Circulation.
Older adults and those with a history of underlying cardiovascular disease appear to be at greatest risk of dying from COVID-19. “From early reports it is clear that elevated cardiac troponin concentrations predict in-hospital mortality,” said Mills.
In a recent report on hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, for example, cardiac injury (hs-cTn above the 99th-percentile upper reference limit) was seen in 1 in 5 patients and was an independent predictor of dying in the hospital. Mortality was 10-fold higher in those with cardiac injury on presentation.
Elevated cardiac troponin in the setting of COVID-19, Mills said, “may reflect illness severity with myocardial injury arising due to myocardial oxygen supply–demand imbalance. Or it may be due to direct cardiac involvement through viral myocarditis or stress cardiomyopathy, or where the prothrombotic and proinflammatory state is precipitating acute coronary syndromes.”
In their viewpoint, the authors note that circulating cTn is a marker of myocardial injury, “including but not limited to myocardial infarction or myocarditis, and the clinical relevance of this distinction has never been so clear.”
Therefore, the consequence of not measuring cardiac troponin may be to “ignore the plethora of ischemic and nonischemic causes” of myocardial injury related to COVID-19. “Clinicians who have used troponin measurement as a binary test for myocardial infarction independent of clinical context and those who consider an elevated cardiac troponin concentration to be a mandate for invasive coronary angiography must recalibrate,” they write.
“Rather than encouraging avoidance of troponin testing, we must harness the unheralded engagement from the cardiovascular community due to COVID-19 to better understand the utility of this essential biomarker and to educate clinicians on its interpretation and implications for prognosis and clinical decision making.”
Based on “same logic” as recent ACC guidance
The viewpoint was to some extent a response to a recent informal guidance from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) that advised caution in use of troponin and natriuretic peptide tests in patients with COVID-19.
Even so, that ACC guidance and the new viewpoint in Circulation are based on the “same logic,” James Januzzi Jr, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. Both documents:
- Point out that troponins are frequently abnormal in patients with severe cases of COVID-19
- Caution that clinicians should not equate an abnormal hs-cTn with acute myocardial infarction
- Note that, in most cases, hs-cTn elevations are a result of noncoronary mechanisms
- Recognize the potential risk to caregivers and the continued unchecked spread of SARS-CoV-2 related to downstream testing that might not be needed
“The Circulation opinion piece states that clinicians often use troponin as a binary test for myocardial infarction and a mandate for downstream testing, suggesting clinicians will need to recalibrate that approach, something I agree with and which is the central message of the ACC position,” Januzzi said.
Probably the biggest difference between the two documents, he said, is in the Circulation authors’ apparent enthusiasm to use hs-cTn as a tool to judge disease severity in patients with COVID-19.
It’s been known for more than a decade that myocardial injury is “an important risk predictor” in critical illness, Januzzi explained. “So the link between cardiac injury and outcomes in critical illness is nothing new. The difference is the fact we are seeing so many patients with COVID-19 all at once, and the authors suggest that using troponin might help in triage decision making.”
“There may be [such] a role here, but the data have not been systematically collected, and whether troponin truly adds something beyond information already available at the bedside — for example, does it add anything not already obvious at the bedside? — has not yet been conclusively proven,” Januzzi cautioned.
“As well, there are no prospective data supporting troponin as a trigger for ICU triage or for deciding on specific treatments.”
Positive cTn status “common” in COVID-19 patients
In his experience, Barry Cohen, MD, Morristown Medical Center, New Jersey, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, that positive cTn status is “common in COVID-19 patients and appears to have prognostic value, not only in type 1 MI due to atherothrombotic disease (related to a proinflammatory and prothrombotic state), but more frequently type 2 MI (supply–demand mismatch), viral myocarditis, coronary microvascular ischemia, stress cardiomyopathy or tachyarrhythmias.”
Moreover, Cohen said, hs-cTn “has identified patients at increased risk for ventilation support (invasive and noninvasive), acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute kidney injury, and mortality.”
Echoing both the ACC document and the Circulation report, Cohen also said hs-cTn measurements “appear to help risk stratify COVID-19 patients, but clearly do not mean that a troponin-positive patient needs to go to the cath lab and be treated as having acute coronary syndrome. Only a minority of these patients require this intervention.”
Mills discloses receiving honoraria from Abbott Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics, Siemens Healthineers, and LumiraDx. Januzzi has previously disclosed receiving personal fees from the American College of Cardiology, Pfizer, Merck, AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Takeda; grants and personal fees from Novartis, Roche, Abbott, and Janssen; and grants from Singulex and Prevencio. Cohen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, cardiologists in the United Kingdom advise in a recently published viewpoint.
The tests can be used to “inform the triage of patients to critical care, guide the use of supportive treatments, and facilitate targeted cardiac investigations in those most likely to benefit,” Nicholas Mills, MD, PhD, University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. He is senior author on the viewpoint published online April 6 in the journal Circulation.
Older adults and those with a history of underlying cardiovascular disease appear to be at greatest risk of dying from COVID-19. “From early reports it is clear that elevated cardiac troponin concentrations predict in-hospital mortality,” said Mills.
In a recent report on hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, for example, cardiac injury (hs-cTn above the 99th-percentile upper reference limit) was seen in 1 in 5 patients and was an independent predictor of dying in the hospital. Mortality was 10-fold higher in those with cardiac injury on presentation.
Elevated cardiac troponin in the setting of COVID-19, Mills said, “may reflect illness severity with myocardial injury arising due to myocardial oxygen supply–demand imbalance. Or it may be due to direct cardiac involvement through viral myocarditis or stress cardiomyopathy, or where the prothrombotic and proinflammatory state is precipitating acute coronary syndromes.”
In their viewpoint, the authors note that circulating cTn is a marker of myocardial injury, “including but not limited to myocardial infarction or myocarditis, and the clinical relevance of this distinction has never been so clear.”
Therefore, the consequence of not measuring cardiac troponin may be to “ignore the plethora of ischemic and nonischemic causes” of myocardial injury related to COVID-19. “Clinicians who have used troponin measurement as a binary test for myocardial infarction independent of clinical context and those who consider an elevated cardiac troponin concentration to be a mandate for invasive coronary angiography must recalibrate,” they write.
“Rather than encouraging avoidance of troponin testing, we must harness the unheralded engagement from the cardiovascular community due to COVID-19 to better understand the utility of this essential biomarker and to educate clinicians on its interpretation and implications for prognosis and clinical decision making.”
Based on “same logic” as recent ACC guidance
The viewpoint was to some extent a response to a recent informal guidance from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) that advised caution in use of troponin and natriuretic peptide tests in patients with COVID-19.
Even so, that ACC guidance and the new viewpoint in Circulation are based on the “same logic,” James Januzzi Jr, MD, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. Both documents:
- Point out that troponins are frequently abnormal in patients with severe cases of COVID-19
- Caution that clinicians should not equate an abnormal hs-cTn with acute myocardial infarction
- Note that, in most cases, hs-cTn elevations are a result of noncoronary mechanisms
- Recognize the potential risk to caregivers and the continued unchecked spread of SARS-CoV-2 related to downstream testing that might not be needed
“The Circulation opinion piece states that clinicians often use troponin as a binary test for myocardial infarction and a mandate for downstream testing, suggesting clinicians will need to recalibrate that approach, something I agree with and which is the central message of the ACC position,” Januzzi said.
Probably the biggest difference between the two documents, he said, is in the Circulation authors’ apparent enthusiasm to use hs-cTn as a tool to judge disease severity in patients with COVID-19.
It’s been known for more than a decade that myocardial injury is “an important risk predictor” in critical illness, Januzzi explained. “So the link between cardiac injury and outcomes in critical illness is nothing new. The difference is the fact we are seeing so many patients with COVID-19 all at once, and the authors suggest that using troponin might help in triage decision making.”
“There may be [such] a role here, but the data have not been systematically collected, and whether troponin truly adds something beyond information already available at the bedside — for example, does it add anything not already obvious at the bedside? — has not yet been conclusively proven,” Januzzi cautioned.
“As well, there are no prospective data supporting troponin as a trigger for ICU triage or for deciding on specific treatments.”
Positive cTn status “common” in COVID-19 patients
In his experience, Barry Cohen, MD, Morristown Medical Center, New Jersey, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, that positive cTn status is “common in COVID-19 patients and appears to have prognostic value, not only in type 1 MI due to atherothrombotic disease (related to a proinflammatory and prothrombotic state), but more frequently type 2 MI (supply–demand mismatch), viral myocarditis, coronary microvascular ischemia, stress cardiomyopathy or tachyarrhythmias.”
Moreover, Cohen said, hs-cTn “has identified patients at increased risk for ventilation support (invasive and noninvasive), acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute kidney injury, and mortality.”
Echoing both the ACC document and the Circulation report, Cohen also said hs-cTn measurements “appear to help risk stratify COVID-19 patients, but clearly do not mean that a troponin-positive patient needs to go to the cath lab and be treated as having acute coronary syndrome. Only a minority of these patients require this intervention.”
Mills discloses receiving honoraria from Abbott Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics, Siemens Healthineers, and LumiraDx. Januzzi has previously disclosed receiving personal fees from the American College of Cardiology, Pfizer, Merck, AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Takeda; grants and personal fees from Novartis, Roche, Abbott, and Janssen; and grants from Singulex and Prevencio. Cohen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 pandemic brings unexpected pediatric consequences
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
ASH tackles COVID-19 with hematology-related FAQ, promotes new registries
The American Society of Hematology has committed a portion of its website to providing continually updated information addressing specific hematologic disorders in relation to COVID-19.
“As the world grapples with the novel coronavirus, ASH believes that we can help each other be as knowledgeable and prepared as possible,” wrote the society’s president, Stephanie J. Lee, MD, MPH.
On its website, ASH provides relevant COVID-19 information in a series of FAQ divided into malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases and disorders. In the malignant category, the various lymphomas and leukemias are individually addressed, as well as other conditions such as myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative neoplasms, and multiple myeloma. In the nonmalignant category, ASH has provided FAQ on aplastic anemia, thalassemia, sickle cell disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thromboembolism/anticoagulation, coagulopathy, and immune as well as thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
In addition to the continually updated series of relevant FAQ, as part of its response to the pandemic ASH is promoting two unique COVID-19 registries for physicians: the ASH Research Collaborative’s (ASH RC) Data Hub COVID-19 Registry and the Surveillance Epidemiology of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Under Research Exclusion Sickle Cell Disease (SECURE-SCD) Registry.
“The ASH Research Collaborative’s (ASH RC) Data Hub launched the COVID-19 Registry and is currently capturing data on people who test positive for COVID-19 and have been or are currently being treated for hematologic malignancy,” according to the website. The intention is to provide “near real-time observational data summaries,” which will hopefully provide useful information to clinicians treating hematologic malignancies in patients in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The registry allows clinicians to enter their own cases in a specified format to allow data analysis on clinical practice and patient outcomes that will be aggregated to provide rapid insights for clinicians to help them care for their patients, according to ASH.
The second registry specifically deals with COVID-19 cases in patients with sickle cell disease. It also allows clinicians to add cases with a similar intention of aggregating data to provide near real-time insights into patient care. “We are asking providers caring for these patients to report all of their cases of COVID-19 to this registry,” according to the registry website. The registry is for reporting COVID-19 cases in sickle cell disease patients “after sufficient time has passed to observe the disease course through resolution of acute illness and/or death.”
ASH also provides more generalized information for hematology practitioners dealing with COVID-19 on the topics of conducting their practice and using telemedicine, among others.
Correction, April 15, 2020: This story originally said incorrectly that ASH developed the 2 new registries. The registries are merely being promoted on the ASH website.
The American Society of Hematology has committed a portion of its website to providing continually updated information addressing specific hematologic disorders in relation to COVID-19.
“As the world grapples with the novel coronavirus, ASH believes that we can help each other be as knowledgeable and prepared as possible,” wrote the society’s president, Stephanie J. Lee, MD, MPH.
On its website, ASH provides relevant COVID-19 information in a series of FAQ divided into malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases and disorders. In the malignant category, the various lymphomas and leukemias are individually addressed, as well as other conditions such as myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative neoplasms, and multiple myeloma. In the nonmalignant category, ASH has provided FAQ on aplastic anemia, thalassemia, sickle cell disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thromboembolism/anticoagulation, coagulopathy, and immune as well as thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
In addition to the continually updated series of relevant FAQ, as part of its response to the pandemic ASH is promoting two unique COVID-19 registries for physicians: the ASH Research Collaborative’s (ASH RC) Data Hub COVID-19 Registry and the Surveillance Epidemiology of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Under Research Exclusion Sickle Cell Disease (SECURE-SCD) Registry.
“The ASH Research Collaborative’s (ASH RC) Data Hub launched the COVID-19 Registry and is currently capturing data on people who test positive for COVID-19 and have been or are currently being treated for hematologic malignancy,” according to the website. The intention is to provide “near real-time observational data summaries,” which will hopefully provide useful information to clinicians treating hematologic malignancies in patients in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The registry allows clinicians to enter their own cases in a specified format to allow data analysis on clinical practice and patient outcomes that will be aggregated to provide rapid insights for clinicians to help them care for their patients, according to ASH.
The second registry specifically deals with COVID-19 cases in patients with sickle cell disease. It also allows clinicians to add cases with a similar intention of aggregating data to provide near real-time insights into patient care. “We are asking providers caring for these patients to report all of their cases of COVID-19 to this registry,” according to the registry website. The registry is for reporting COVID-19 cases in sickle cell disease patients “after sufficient time has passed to observe the disease course through resolution of acute illness and/or death.”
ASH also provides more generalized information for hematology practitioners dealing with COVID-19 on the topics of conducting their practice and using telemedicine, among others.
Correction, April 15, 2020: This story originally said incorrectly that ASH developed the 2 new registries. The registries are merely being promoted on the ASH website.
The American Society of Hematology has committed a portion of its website to providing continually updated information addressing specific hematologic disorders in relation to COVID-19.
“As the world grapples with the novel coronavirus, ASH believes that we can help each other be as knowledgeable and prepared as possible,” wrote the society’s president, Stephanie J. Lee, MD, MPH.
On its website, ASH provides relevant COVID-19 information in a series of FAQ divided into malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases and disorders. In the malignant category, the various lymphomas and leukemias are individually addressed, as well as other conditions such as myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative neoplasms, and multiple myeloma. In the nonmalignant category, ASH has provided FAQ on aplastic anemia, thalassemia, sickle cell disease, pulmonary embolism, venous thromboembolism/anticoagulation, coagulopathy, and immune as well as thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
In addition to the continually updated series of relevant FAQ, as part of its response to the pandemic ASH is promoting two unique COVID-19 registries for physicians: the ASH Research Collaborative’s (ASH RC) Data Hub COVID-19 Registry and the Surveillance Epidemiology of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Under Research Exclusion Sickle Cell Disease (SECURE-SCD) Registry.
“The ASH Research Collaborative’s (ASH RC) Data Hub launched the COVID-19 Registry and is currently capturing data on people who test positive for COVID-19 and have been or are currently being treated for hematologic malignancy,” according to the website. The intention is to provide “near real-time observational data summaries,” which will hopefully provide useful information to clinicians treating hematologic malignancies in patients in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The registry allows clinicians to enter their own cases in a specified format to allow data analysis on clinical practice and patient outcomes that will be aggregated to provide rapid insights for clinicians to help them care for their patients, according to ASH.
The second registry specifically deals with COVID-19 cases in patients with sickle cell disease. It also allows clinicians to add cases with a similar intention of aggregating data to provide near real-time insights into patient care. “We are asking providers caring for these patients to report all of their cases of COVID-19 to this registry,” according to the registry website. The registry is for reporting COVID-19 cases in sickle cell disease patients “after sufficient time has passed to observe the disease course through resolution of acute illness and/or death.”
ASH also provides more generalized information for hematology practitioners dealing with COVID-19 on the topics of conducting their practice and using telemedicine, among others.
Correction, April 15, 2020: This story originally said incorrectly that ASH developed the 2 new registries. The registries are merely being promoted on the ASH website.
Ragweed SLIT tablets improve asthma outcome scores in patients with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis
during ragweed pollen season, compared with placebo, according to recent research that was to be presented as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled its annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
David I. Bernstein, MD, professor emeritus in the division of immunology, allergy and rheumatology at the University of Cincinnati and principal investigator at the Bernstein Clinical Research Center, examined exploratory endpoints of an international, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating ragweed SLIT tablets (Ragwitek; Merck) in 1,022 children with AR/C. The children enrolled were aged 5-17 years with ragweed AR/C, with 42.7% of the group having a history of asthma and the rest without asthma. Participants were included if they had a predicted first expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of ≥ 80% and if they required high-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) to control their asthma or had severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. The children were randomized to receive a 12 Amb a 1-unit dose of the ragweed SLIT tablet or placebo each day for 28 weeks.
The primary outcome was the total combined score (TCS), which was the sum of the daily symptom score and medication scores during ragweed season, but researchers also examined three exploratory endpoints. All patients were evaluated for their average asthma daily symptom score at the peak of ragweed pollen season and during the entire season, which was measured on a 0-3 scale based on symptoms of cough, wheeze, and chest tightness or shortness of breath. Within a subgroup of 406 participants with asthma, Dr. Bernstein and colleagues examined use of average daily short-acting beta agonists (SABA), and the number of times per week a participant would use a SABA at night at the peak of ragweed season as well as across the whole season.
Researchers found the TCS improved by 38% during ragweed pollen season in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets (least-square [LS] mean TCS, 7.12), compared with placebo (LS mean TCS, 4.39; P < .001). Among the asthma exploratory outcomes, asthma daily symptom scores improved by 30.7% during the peak of the season (–46.9% vs. –9.6%; LS mean difference, –0.13) and by 23.1% during the whole season (–38.7% vs. –2.3%; LS mean difference, –0.09), compared with the placebo group. The mean number of daily puffs of rescue medication also decreased by 68.1% in the peak of ragweed season (–87.6% vs. –39.0%; LS mean difference, −0.14) and by 61.4% during the whole season (–80.9% vs. −32.9%; LS mean difference, –0.12) among participants taking ragweed SLIT tablets, compared with placebo. Participants in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets also had fewer nights awake using rescue medication, with a relative improvement of 75.1% during peak season (−99.3% vs. −35.2%; LS mean difference, −0.08) and 52.2% during the whole season (−80.4% vs. −3.7%; LS mean difference, −0.03), compared with the placebo group.
This magnitude of difference in the number of nocturnal awakenings in the treated group, compared with the placebo group, is similar to what researchers have seen in trials evaluating ICS or mometasone/formoterol, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview.
“Even though the magnitude in terms of difference in asthma symptoms and requirements for short-acting beta agonists was less than that of other studies of other drugs, it may reflect the fact these participants have less severe asthma,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But, there was an effect, and we did see some interesting differences between the placebo group and the treated group. This, I think, does generate at least a hypothesis that this could be an effective treatment for seasonal asthma, which would require future studies to determine that.”
Dr. Bernstein said that there were no adverse events from ragweed SLIT tablets unique to children with or without asthma, and although the data from this study cannot be compared directly to an adult population, there appeared to be a greater effect size for children than in trials evaluating adults. Compared with treatment options like subcutaneous immunotherapy, ragweed SLIT tablets may offer a relatively safer and more effective option for children and their parents, he said.
“The problem with kids is that they don’t particularly like the idea of getting injections. There’s a lot of needle-type injection phobia,” Dr. Bernstein said. “For a child who has maybe one or two major problem pollen seasons like during the ragweed and grass, they could do this.”
Ragwitek was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of adults with allergic rhinitis. Dr. Bernstein noted that Merck submitted this trial to the Food and Drug Administration as evidence of its effectiveness in children to secure a pediatric indication for the treatment.
This trial was funded by Merck, the developers of Ragwitek. The authors received medical writing and editing assistance from Scott Medical Communications, which was funded by ALK. Dr. Bernstein reports being on the advisory board for ALK America and GlaxoSmithKline; a consultant for Gerson-Lehman and Guidepoint Global; and received grant support from Aimmune, ALK, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Avillion, Biocryst, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cipla, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer, Leo, Lupin, Menlo, Merck, Mylan, Novartis, Novum, Pearl, Regeneron, Shire, and TEVA. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bernstein D et al. AAAAI 2020, Abstract 270.
during ragweed pollen season, compared with placebo, according to recent research that was to be presented as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled its annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
David I. Bernstein, MD, professor emeritus in the division of immunology, allergy and rheumatology at the University of Cincinnati and principal investigator at the Bernstein Clinical Research Center, examined exploratory endpoints of an international, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating ragweed SLIT tablets (Ragwitek; Merck) in 1,022 children with AR/C. The children enrolled were aged 5-17 years with ragweed AR/C, with 42.7% of the group having a history of asthma and the rest without asthma. Participants were included if they had a predicted first expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of ≥ 80% and if they required high-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) to control their asthma or had severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. The children were randomized to receive a 12 Amb a 1-unit dose of the ragweed SLIT tablet or placebo each day for 28 weeks.
The primary outcome was the total combined score (TCS), which was the sum of the daily symptom score and medication scores during ragweed season, but researchers also examined three exploratory endpoints. All patients were evaluated for their average asthma daily symptom score at the peak of ragweed pollen season and during the entire season, which was measured on a 0-3 scale based on symptoms of cough, wheeze, and chest tightness or shortness of breath. Within a subgroup of 406 participants with asthma, Dr. Bernstein and colleagues examined use of average daily short-acting beta agonists (SABA), and the number of times per week a participant would use a SABA at night at the peak of ragweed season as well as across the whole season.
Researchers found the TCS improved by 38% during ragweed pollen season in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets (least-square [LS] mean TCS, 7.12), compared with placebo (LS mean TCS, 4.39; P < .001). Among the asthma exploratory outcomes, asthma daily symptom scores improved by 30.7% during the peak of the season (–46.9% vs. –9.6%; LS mean difference, –0.13) and by 23.1% during the whole season (–38.7% vs. –2.3%; LS mean difference, –0.09), compared with the placebo group. The mean number of daily puffs of rescue medication also decreased by 68.1% in the peak of ragweed season (–87.6% vs. –39.0%; LS mean difference, −0.14) and by 61.4% during the whole season (–80.9% vs. −32.9%; LS mean difference, –0.12) among participants taking ragweed SLIT tablets, compared with placebo. Participants in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets also had fewer nights awake using rescue medication, with a relative improvement of 75.1% during peak season (−99.3% vs. −35.2%; LS mean difference, −0.08) and 52.2% during the whole season (−80.4% vs. −3.7%; LS mean difference, −0.03), compared with the placebo group.
This magnitude of difference in the number of nocturnal awakenings in the treated group, compared with the placebo group, is similar to what researchers have seen in trials evaluating ICS or mometasone/formoterol, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview.
“Even though the magnitude in terms of difference in asthma symptoms and requirements for short-acting beta agonists was less than that of other studies of other drugs, it may reflect the fact these participants have less severe asthma,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But, there was an effect, and we did see some interesting differences between the placebo group and the treated group. This, I think, does generate at least a hypothesis that this could be an effective treatment for seasonal asthma, which would require future studies to determine that.”
Dr. Bernstein said that there were no adverse events from ragweed SLIT tablets unique to children with or without asthma, and although the data from this study cannot be compared directly to an adult population, there appeared to be a greater effect size for children than in trials evaluating adults. Compared with treatment options like subcutaneous immunotherapy, ragweed SLIT tablets may offer a relatively safer and more effective option for children and their parents, he said.
“The problem with kids is that they don’t particularly like the idea of getting injections. There’s a lot of needle-type injection phobia,” Dr. Bernstein said. “For a child who has maybe one or two major problem pollen seasons like during the ragweed and grass, they could do this.”
Ragwitek was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of adults with allergic rhinitis. Dr. Bernstein noted that Merck submitted this trial to the Food and Drug Administration as evidence of its effectiveness in children to secure a pediatric indication for the treatment.
This trial was funded by Merck, the developers of Ragwitek. The authors received medical writing and editing assistance from Scott Medical Communications, which was funded by ALK. Dr. Bernstein reports being on the advisory board for ALK America and GlaxoSmithKline; a consultant for Gerson-Lehman and Guidepoint Global; and received grant support from Aimmune, ALK, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Avillion, Biocryst, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cipla, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer, Leo, Lupin, Menlo, Merck, Mylan, Novartis, Novum, Pearl, Regeneron, Shire, and TEVA. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bernstein D et al. AAAAI 2020, Abstract 270.
during ragweed pollen season, compared with placebo, according to recent research that was to be presented as an abstract for the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology annual meeting. The AAAAI canceled its annual meeting and provided abstracts and access to presenters for press coverage.
David I. Bernstein, MD, professor emeritus in the division of immunology, allergy and rheumatology at the University of Cincinnati and principal investigator at the Bernstein Clinical Research Center, examined exploratory endpoints of an international, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating ragweed SLIT tablets (Ragwitek; Merck) in 1,022 children with AR/C. The children enrolled were aged 5-17 years with ragweed AR/C, with 42.7% of the group having a history of asthma and the rest without asthma. Participants were included if they had a predicted first expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of ≥ 80% and if they required high-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) to control their asthma or had severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. The children were randomized to receive a 12 Amb a 1-unit dose of the ragweed SLIT tablet or placebo each day for 28 weeks.
The primary outcome was the total combined score (TCS), which was the sum of the daily symptom score and medication scores during ragweed season, but researchers also examined three exploratory endpoints. All patients were evaluated for their average asthma daily symptom score at the peak of ragweed pollen season and during the entire season, which was measured on a 0-3 scale based on symptoms of cough, wheeze, and chest tightness or shortness of breath. Within a subgroup of 406 participants with asthma, Dr. Bernstein and colleagues examined use of average daily short-acting beta agonists (SABA), and the number of times per week a participant would use a SABA at night at the peak of ragweed season as well as across the whole season.
Researchers found the TCS improved by 38% during ragweed pollen season in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets (least-square [LS] mean TCS, 7.12), compared with placebo (LS mean TCS, 4.39; P < .001). Among the asthma exploratory outcomes, asthma daily symptom scores improved by 30.7% during the peak of the season (–46.9% vs. –9.6%; LS mean difference, –0.13) and by 23.1% during the whole season (–38.7% vs. –2.3%; LS mean difference, –0.09), compared with the placebo group. The mean number of daily puffs of rescue medication also decreased by 68.1% in the peak of ragweed season (–87.6% vs. –39.0%; LS mean difference, −0.14) and by 61.4% during the whole season (–80.9% vs. −32.9%; LS mean difference, –0.12) among participants taking ragweed SLIT tablets, compared with placebo. Participants in the group receiving ragweed SLIT tablets also had fewer nights awake using rescue medication, with a relative improvement of 75.1% during peak season (−99.3% vs. −35.2%; LS mean difference, −0.08) and 52.2% during the whole season (−80.4% vs. −3.7%; LS mean difference, −0.03), compared with the placebo group.
This magnitude of difference in the number of nocturnal awakenings in the treated group, compared with the placebo group, is similar to what researchers have seen in trials evaluating ICS or mometasone/formoterol, Dr. Bernstein said in an interview.
“Even though the magnitude in terms of difference in asthma symptoms and requirements for short-acting beta agonists was less than that of other studies of other drugs, it may reflect the fact these participants have less severe asthma,” said Dr. Bernstein. “But, there was an effect, and we did see some interesting differences between the placebo group and the treated group. This, I think, does generate at least a hypothesis that this could be an effective treatment for seasonal asthma, which would require future studies to determine that.”
Dr. Bernstein said that there were no adverse events from ragweed SLIT tablets unique to children with or without asthma, and although the data from this study cannot be compared directly to an adult population, there appeared to be a greater effect size for children than in trials evaluating adults. Compared with treatment options like subcutaneous immunotherapy, ragweed SLIT tablets may offer a relatively safer and more effective option for children and their parents, he said.
“The problem with kids is that they don’t particularly like the idea of getting injections. There’s a lot of needle-type injection phobia,” Dr. Bernstein said. “For a child who has maybe one or two major problem pollen seasons like during the ragweed and grass, they could do this.”
Ragwitek was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for the treatment of adults with allergic rhinitis. Dr. Bernstein noted that Merck submitted this trial to the Food and Drug Administration as evidence of its effectiveness in children to secure a pediatric indication for the treatment.
This trial was funded by Merck, the developers of Ragwitek. The authors received medical writing and editing assistance from Scott Medical Communications, which was funded by ALK. Dr. Bernstein reports being on the advisory board for ALK America and GlaxoSmithKline; a consultant for Gerson-Lehman and Guidepoint Global; and received grant support from Aimmune, ALK, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Avillion, Biocryst, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cipla, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer, Leo, Lupin, Menlo, Merck, Mylan, Novartis, Novum, Pearl, Regeneron, Shire, and TEVA. The other authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bernstein D et al. AAAAI 2020, Abstract 270.
FROM AAAAI
Parents would avoid cognitive effects in children over better chance of cancer cure
Parents of children with cancer and their physicians are willing to opt for less effective treatment to avoid risk of neurocognitive disorders later in life, according to results from a new study.
While some 80% of children with cancer survive to adulthood, most will experience chronic health conditions related to treatment, and many pediatric oncologists will adjust treatment strategies to lessen the likelihood of later effects. For their research published in Pediatrics, Katie A. Greenzang, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and colleagues aimed to learn how both parents and physicians weighed the risks and benefits.
In a survey of 95 parents and 41 physicians at Dana-Farber, Dr. Greenzang and colleagues proposed hypothetical scenarios involving five common late effects of childhood cancer treatment: neurocognitive impairment, infertility, cardiac toxicity, second malignancies, and impaired development. The parents surveyed, all of whom had children diagnosed with cancer within the previous year, were asked to make decisions as though on behalf of their children, while physicians were asked to do so as on behalf of a newly diagnosed patient.
Avoiding severe cognitive impairment mattered more than an increased chance of a cure to both parents and physicians. Neurocognitive impairment was the risk that most affected treatment choices, with parents more likely to choose a treatment associated with no or mild neurocognitive impairment, compared with one that caused severe impairment (odds ratio, 2.83 for no impairment vs. severe impairment; P less than .001), which was also the case with physicians (OR, 4.01; P less than .001).
Parents would accept an 18% chance of another malignancy for a 10% greater chance of a cure, while physicians accepted a 15% risk. Parents were willing to tolerate a 31% risk of cardiac toxicity in exchange for the better chance of a cure, while physicians accepted a 22% higher risk.
The results, the researchers wrote in their analysis, offered a window into the level and type of later-life risks that parents can accept when making choices about cancer treatment and where those choices appear to differ from those made by physicians.
“Oncologists increasingly design clinical trials [for children with cancer] with dual goals of optimizing cure while minimizing late effects,” Dr. Greenzang and colleagues wrote. “In doing so, they make judgments about the relative value of short- and long-term outcomes in patients’ lives. Yet oncologists have largely done so in the absence of information about how parents prioritize avoidance of late effects relative to the chance of cure.”
In an editorial comment accompanying the study, Tara A. Brinkman, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., and James G. Gurney, PhD, of the University of Memphis noted that the findings “may have narrow clinical application” because many of the late-life effects presented in the survey will not present singly but will co-occur in survivors of childhood cancer. “Hypothetical scenarios that do not depict the full burden of late effects may not reflect a realistic understanding of the complexity of decisions to be made in a real-life diagnostic setting,” they said.
But the editorialists praised the study for revealing that many parents did not accurately perceive the true likelihood of late effects for their children. Parents in the survey tended to underestimate the risk for all the late effects besides infertility, which revealed a need for “better education about late effects early in the diagnostic and treatment process,” Dr. Brinkman and Dr. Gurney said, emphasizing that discussions should begin at diagnosis and continue beyond treatment “and long into the maintenance and surveillance period after the declaration of cure.”
Dr. Greenzang and colleagues’ study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and an Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality grant. The investigators declared no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Brinkman and Dr. Gurney reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Greenzang et al. Pediatrics. 2020;145(5):e20193552.
Parents of children with cancer and their physicians are willing to opt for less effective treatment to avoid risk of neurocognitive disorders later in life, according to results from a new study.
While some 80% of children with cancer survive to adulthood, most will experience chronic health conditions related to treatment, and many pediatric oncologists will adjust treatment strategies to lessen the likelihood of later effects. For their research published in Pediatrics, Katie A. Greenzang, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and colleagues aimed to learn how both parents and physicians weighed the risks and benefits.
In a survey of 95 parents and 41 physicians at Dana-Farber, Dr. Greenzang and colleagues proposed hypothetical scenarios involving five common late effects of childhood cancer treatment: neurocognitive impairment, infertility, cardiac toxicity, second malignancies, and impaired development. The parents surveyed, all of whom had children diagnosed with cancer within the previous year, were asked to make decisions as though on behalf of their children, while physicians were asked to do so as on behalf of a newly diagnosed patient.
Avoiding severe cognitive impairment mattered more than an increased chance of a cure to both parents and physicians. Neurocognitive impairment was the risk that most affected treatment choices, with parents more likely to choose a treatment associated with no or mild neurocognitive impairment, compared with one that caused severe impairment (odds ratio, 2.83 for no impairment vs. severe impairment; P less than .001), which was also the case with physicians (OR, 4.01; P less than .001).
Parents would accept an 18% chance of another malignancy for a 10% greater chance of a cure, while physicians accepted a 15% risk. Parents were willing to tolerate a 31% risk of cardiac toxicity in exchange for the better chance of a cure, while physicians accepted a 22% higher risk.
The results, the researchers wrote in their analysis, offered a window into the level and type of later-life risks that parents can accept when making choices about cancer treatment and where those choices appear to differ from those made by physicians.
“Oncologists increasingly design clinical trials [for children with cancer] with dual goals of optimizing cure while minimizing late effects,” Dr. Greenzang and colleagues wrote. “In doing so, they make judgments about the relative value of short- and long-term outcomes in patients’ lives. Yet oncologists have largely done so in the absence of information about how parents prioritize avoidance of late effects relative to the chance of cure.”
In an editorial comment accompanying the study, Tara A. Brinkman, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., and James G. Gurney, PhD, of the University of Memphis noted that the findings “may have narrow clinical application” because many of the late-life effects presented in the survey will not present singly but will co-occur in survivors of childhood cancer. “Hypothetical scenarios that do not depict the full burden of late effects may not reflect a realistic understanding of the complexity of decisions to be made in a real-life diagnostic setting,” they said.
But the editorialists praised the study for revealing that many parents did not accurately perceive the true likelihood of late effects for their children. Parents in the survey tended to underestimate the risk for all the late effects besides infertility, which revealed a need for “better education about late effects early in the diagnostic and treatment process,” Dr. Brinkman and Dr. Gurney said, emphasizing that discussions should begin at diagnosis and continue beyond treatment “and long into the maintenance and surveillance period after the declaration of cure.”
Dr. Greenzang and colleagues’ study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and an Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality grant. The investigators declared no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Brinkman and Dr. Gurney reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Greenzang et al. Pediatrics. 2020;145(5):e20193552.
Parents of children with cancer and their physicians are willing to opt for less effective treatment to avoid risk of neurocognitive disorders later in life, according to results from a new study.
While some 80% of children with cancer survive to adulthood, most will experience chronic health conditions related to treatment, and many pediatric oncologists will adjust treatment strategies to lessen the likelihood of later effects. For their research published in Pediatrics, Katie A. Greenzang, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and colleagues aimed to learn how both parents and physicians weighed the risks and benefits.
In a survey of 95 parents and 41 physicians at Dana-Farber, Dr. Greenzang and colleagues proposed hypothetical scenarios involving five common late effects of childhood cancer treatment: neurocognitive impairment, infertility, cardiac toxicity, second malignancies, and impaired development. The parents surveyed, all of whom had children diagnosed with cancer within the previous year, were asked to make decisions as though on behalf of their children, while physicians were asked to do so as on behalf of a newly diagnosed patient.
Avoiding severe cognitive impairment mattered more than an increased chance of a cure to both parents and physicians. Neurocognitive impairment was the risk that most affected treatment choices, with parents more likely to choose a treatment associated with no or mild neurocognitive impairment, compared with one that caused severe impairment (odds ratio, 2.83 for no impairment vs. severe impairment; P less than .001), which was also the case with physicians (OR, 4.01; P less than .001).
Parents would accept an 18% chance of another malignancy for a 10% greater chance of a cure, while physicians accepted a 15% risk. Parents were willing to tolerate a 31% risk of cardiac toxicity in exchange for the better chance of a cure, while physicians accepted a 22% higher risk.
The results, the researchers wrote in their analysis, offered a window into the level and type of later-life risks that parents can accept when making choices about cancer treatment and where those choices appear to differ from those made by physicians.
“Oncologists increasingly design clinical trials [for children with cancer] with dual goals of optimizing cure while minimizing late effects,” Dr. Greenzang and colleagues wrote. “In doing so, they make judgments about the relative value of short- and long-term outcomes in patients’ lives. Yet oncologists have largely done so in the absence of information about how parents prioritize avoidance of late effects relative to the chance of cure.”
In an editorial comment accompanying the study, Tara A. Brinkman, PhD, of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., and James G. Gurney, PhD, of the University of Memphis noted that the findings “may have narrow clinical application” because many of the late-life effects presented in the survey will not present singly but will co-occur in survivors of childhood cancer. “Hypothetical scenarios that do not depict the full burden of late effects may not reflect a realistic understanding of the complexity of decisions to be made in a real-life diagnostic setting,” they said.
But the editorialists praised the study for revealing that many parents did not accurately perceive the true likelihood of late effects for their children. Parents in the survey tended to underestimate the risk for all the late effects besides infertility, which revealed a need for “better education about late effects early in the diagnostic and treatment process,” Dr. Brinkman and Dr. Gurney said, emphasizing that discussions should begin at diagnosis and continue beyond treatment “and long into the maintenance and surveillance period after the declaration of cure.”
Dr. Greenzang and colleagues’ study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and an Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality grant. The investigators declared no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Brinkman and Dr. Gurney reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Greenzang et al. Pediatrics. 2020;145(5):e20193552.
FROM PEDIATRICS
COVID 19: Confessions of an outpatient psychiatrist during the pandemic
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
Expert discusses her approach to using systemic agents in children and adolescents with severe skin disease
In the clinical opinion of Kaiane A. Habeshian, MD, dermatologists shouldn’t think twice about using systemic agents in pediatric patients with severe dermatologic diseases.
“By the time patients come to us pediatric dermatologists, they have been treated by multiple other doctors, and are frustrated,” Dr. Habeshian said during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. “Childhood eczema affects not only patients, but the whole family. For instance, if the child is not sleeping due to itch, their parents are probably not sleeping, either. Parental well-being and workplace productivity are affected, and finances are affected.”
Only a limited number of medications are Food and Drug Administration approved in pediatric patients for common dermatologic indications. These include dupilumab for atopic dermatitis (AD), etanercept and ustekinumab for psoriasis, adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa, and omalizumab for chronic idiopathic urticaria. “The approvals are mainly for the adolescent age group, except for etanercept, which is approved at the age of 4 years and above,” said Dr. Habeshian of the department of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington.
. “These agents are approved for other indications in infants and have many years of data to describe their use in these other conditions, although comprehensive randomized, controlled studies in pediatric patients for dermatologic conditions are lacking,” she said. “What’s in clinical trials for pediatric skin disease? There are multiple ongoing clinical studies of biologic agents in pediatric dermatology, mainly for psoriasis and also for dupilumab in younger patients, as well as a JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitor for alopecia areata.”
Dr. Habeshian noted that while some clinicians may have a knee-jerk reaction to go straight to dupilumab, which was approved in March of 2019 for adolescents with moderate to severe AD, that agent is not currently approved for the most sizable pediatric population with this condition – those under 12 years of age. “FDA approval is important in part because it helps establish safety and optimal dosing, which is often different and weight based in children,” she said. “In addition, FDA approval significantly impacts access to these newer, more expensive medications.”
Speaking from her experience treating patients in the DC/Maryland/Virginia area, Medicaid has consistently denied dupilumab coverage in children under age 12, “even in severe eczema that is suboptimally controlled with both methotrexate and cyclosporine, despite multiple levels of appeal, including letters of medical necessity and peer-to-peer evaluation,” she said. “This can vary across the country among states. However, dupilumab has been completely unattainable in those under 12 in our practice.”
When dupilumab is approved, most insurers first require step therapy with off-label agents for at least 3 months, as well as documented failure of topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, crisaborole ointment, and phototherapy (if done). “It’s important to document an objective measure of severity at the very first visit with the SCORAD [scoring atopic dermatitis] or IGA [investigator global assessment],” she said. “Often, that is required if there is any hope for coverage. A familiarity with these requirements is often acquired through trial and error, and may change over time. This can lead to many delays in getting patients these treatments.” Additional information to consider documenting include the disease impact on quality of life, sleep, and school attendance, any hospitalizations for AD flares or secondary infections, and comorbid disease such as asthma.
Meanwhile, dupilumab is under priority review for children aged 6-11 years with moderate to severe AD, with a target action date of May 26, 2020. “It’s unclear how recent events [with the COVID-19 pandemic] will impact that, but there is something to look forward to, and give us hope for our patients,” she said.
Typically, Dr. Habeshian starts her pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD on methotrexate, which she characterized as “a time-tested, affordable, and very accessible option. It requires a little bit less monitoring upon initiation than cyclosporine, and it can be used for longer periods of time before weaning is required.”
In cases when disease is severe or intolerable, she often starts methotrexate and cyclosporine together. “I will usually start right at the 0.5 mg/kg per week rather than titrating up, because this maximizes the response and reduces the amount of blood work needed, unless they have an underlying risk factor for GI distress, or obese patients who are at increased risk for LFT [liver function test] elevation,” she noted. “Patients will note some improvement as early as 2 weeks on methotrexate, but I counsel them to expect 4-6 weeks for maximum improvement. We do not do a test dose of methotrexate at our institution. If there is a slight LFT elevation upon checking labs, ensure that the labs were done at least 4-6 days after the dose, because transient LFT dose elevations are common in 3-4 days.”
GI distress is by far the most common clinical side effect of methotrexate. “We do not do much intramuscular injection of methotrexate, so we rely a lot on folic acid, which reduces the risk of GI distress and elevated LFTs without reducing efficacy,” she said. “We recommend daily folic acid for simplicity, or folic acid 6 days per week.”
Dr. Habeshian said that many pediatric patients can swallow the 2.5 mg tablets of methotrexate “because they’re quite small, and most patients don’t have a problem taking the methotrexate when it’s crushed and mixed with food such as apple sauce or pudding. However, it is critical to discuss proper handling to avoid lung toxicity.” This includes placing the pills in a plastic bag prior to crushing, avoiding inhalation, and avoiding handling near pregnant women and pets, she noted. In addition, she said, “in adolescents, we need to consider the teratogenicity of methotrexate, as well as the possibility of alcohol consumption worsening liver complications. If I prescribe methotrexate in patients of childbearing age, I will counsel them extensively regarding the risk of fetal death and birth defects. If needed, I will start combined oral contraceptives. Ultimately, I’m willing to use these medicines safely, with significant counseling.”
When addressing the risk of methotrexate overdose, she reminds parents to store the medication in a safe place, out of the reach of children. “Patients are at the highest risk of overdose complications if they are given the medication multiple days in a row rather than a one-time, single high dose,” she said. “The literature suggests that one-time overdoses of methotrexate – deliberate or accidental – are unlikely to cause acute bone marrow suppression or hepatitis. This is probably because GI absorption of methotrexate reaches a saturation point, and the kidneys passively and actively excrete the medication at quite a rapid pace so that the methotrexate is often undetectable in the blood at 24 hours post ingestion. I do prescribe a limited supply to help prevent accidental overdoses. In part, this is because if the patient is receiving the medication daily, they’ll run out very quickly, and it will come the family’s attention and to your attention that it’s not being administered correctly.”
Another treatment option to consider for cases of moderate to severe AD is cyclosporine, “which works extremely quickly,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is very good to rapidly control severe disease while methotrexate or other modes of treatment kick in. It’s best used as a bridge, given the risks of renal damage with long-term use. I like to limit its use to 6 months.”
Cyclosporine comes in two formulations: a modified oral formulation and a nonmodified oral formulation. The modified formulation is absorbed much better than the unmodified formulation. “We start at 5 mg/kg divided b.i.d., which is higher than the recommended dosing for dermatologic conditions in adults,” she said. “This is because children may not absorb the medication as well and may have improved renal clearance. Higher doses may be needed to achieve the desirable effect. In contrast to methotrexate, cyclosporine is available in a capsule, so it cannot be crushed.”
The choice of medication for psoriasis is generally guided by insurance step therapy requirements and is limited in the pediatric population (new guidelines on the care of pediatric psoriasis patients can be found at J Am Acad Dermatol 2020; 82[1]:161-201). In Dr. Habeshian’s experience, methotrexate is the go-to for most patients. “It treats concomitant psoriatic arthritis and can be used as monotherapy or combined with biologics,” she said. “Cyclosporine is useful for erythrodermic, pustular, and severe plaque psoriasis as a bridge. Other options include etanercept weekly in patients age 4-17 years and ustekinumab weekly dosing in patients age 12-17 years.”
Acitretin can be a useful adjunct for younger patients who are unable to obtain biologic agents. “It is most useful in widespread guttate and pustular psoriasis, but can be used be used in plaque psoriasis as well,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is usually dosed as 0.1-1 mg/kg per day. Improvement in plaque disease is generally seen in 2-3 months of therapy, so it has a slow onset, whereas improvement in pustular psoriasis is seen within 3 weeks.” The most common side effects are dry skin and mucous membranes, while an important consideration is the potential for inducing premature bone toxicity. “It is thought that the risk is relatively low if the daily and total doses are kept low,” she said. “There is no consensus for monitoring bone health. Some clinicians will consider radiography periodically.”
Dr. Habeshian concluded her talk by noting that clinicians should give vaccinations/boosters before starting systemic therapy in young children. “The safety and efficacy of live immunization administered to children on biologics is not known,” she said. “Therefore, if live vaccination is needed, it’s generally recommended to postpone initiating biologic treatment.” The MMR and varicella vaccines are given at 12-15 months of life, with a booster at 4-6 years. The varicella vaccine should be given at least 6 weeks before starting immunosuppressive therapy, and the MMR vaccine at least 4 weeks before starting therapy.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Habeshian reported having no disclosures.
In the clinical opinion of Kaiane A. Habeshian, MD, dermatologists shouldn’t think twice about using systemic agents in pediatric patients with severe dermatologic diseases.
“By the time patients come to us pediatric dermatologists, they have been treated by multiple other doctors, and are frustrated,” Dr. Habeshian said during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. “Childhood eczema affects not only patients, but the whole family. For instance, if the child is not sleeping due to itch, their parents are probably not sleeping, either. Parental well-being and workplace productivity are affected, and finances are affected.”
Only a limited number of medications are Food and Drug Administration approved in pediatric patients for common dermatologic indications. These include dupilumab for atopic dermatitis (AD), etanercept and ustekinumab for psoriasis, adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa, and omalizumab for chronic idiopathic urticaria. “The approvals are mainly for the adolescent age group, except for etanercept, which is approved at the age of 4 years and above,” said Dr. Habeshian of the department of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington.
. “These agents are approved for other indications in infants and have many years of data to describe their use in these other conditions, although comprehensive randomized, controlled studies in pediatric patients for dermatologic conditions are lacking,” she said. “What’s in clinical trials for pediatric skin disease? There are multiple ongoing clinical studies of biologic agents in pediatric dermatology, mainly for psoriasis and also for dupilumab in younger patients, as well as a JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitor for alopecia areata.”
Dr. Habeshian noted that while some clinicians may have a knee-jerk reaction to go straight to dupilumab, which was approved in March of 2019 for adolescents with moderate to severe AD, that agent is not currently approved for the most sizable pediatric population with this condition – those under 12 years of age. “FDA approval is important in part because it helps establish safety and optimal dosing, which is often different and weight based in children,” she said. “In addition, FDA approval significantly impacts access to these newer, more expensive medications.”
Speaking from her experience treating patients in the DC/Maryland/Virginia area, Medicaid has consistently denied dupilumab coverage in children under age 12, “even in severe eczema that is suboptimally controlled with both methotrexate and cyclosporine, despite multiple levels of appeal, including letters of medical necessity and peer-to-peer evaluation,” she said. “This can vary across the country among states. However, dupilumab has been completely unattainable in those under 12 in our practice.”
When dupilumab is approved, most insurers first require step therapy with off-label agents for at least 3 months, as well as documented failure of topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, crisaborole ointment, and phototherapy (if done). “It’s important to document an objective measure of severity at the very first visit with the SCORAD [scoring atopic dermatitis] or IGA [investigator global assessment],” she said. “Often, that is required if there is any hope for coverage. A familiarity with these requirements is often acquired through trial and error, and may change over time. This can lead to many delays in getting patients these treatments.” Additional information to consider documenting include the disease impact on quality of life, sleep, and school attendance, any hospitalizations for AD flares or secondary infections, and comorbid disease such as asthma.
Meanwhile, dupilumab is under priority review for children aged 6-11 years with moderate to severe AD, with a target action date of May 26, 2020. “It’s unclear how recent events [with the COVID-19 pandemic] will impact that, but there is something to look forward to, and give us hope for our patients,” she said.
Typically, Dr. Habeshian starts her pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD on methotrexate, which she characterized as “a time-tested, affordable, and very accessible option. It requires a little bit less monitoring upon initiation than cyclosporine, and it can be used for longer periods of time before weaning is required.”
In cases when disease is severe or intolerable, she often starts methotrexate and cyclosporine together. “I will usually start right at the 0.5 mg/kg per week rather than titrating up, because this maximizes the response and reduces the amount of blood work needed, unless they have an underlying risk factor for GI distress, or obese patients who are at increased risk for LFT [liver function test] elevation,” she noted. “Patients will note some improvement as early as 2 weeks on methotrexate, but I counsel them to expect 4-6 weeks for maximum improvement. We do not do a test dose of methotrexate at our institution. If there is a slight LFT elevation upon checking labs, ensure that the labs were done at least 4-6 days after the dose, because transient LFT dose elevations are common in 3-4 days.”
GI distress is by far the most common clinical side effect of methotrexate. “We do not do much intramuscular injection of methotrexate, so we rely a lot on folic acid, which reduces the risk of GI distress and elevated LFTs without reducing efficacy,” she said. “We recommend daily folic acid for simplicity, or folic acid 6 days per week.”
Dr. Habeshian said that many pediatric patients can swallow the 2.5 mg tablets of methotrexate “because they’re quite small, and most patients don’t have a problem taking the methotrexate when it’s crushed and mixed with food such as apple sauce or pudding. However, it is critical to discuss proper handling to avoid lung toxicity.” This includes placing the pills in a plastic bag prior to crushing, avoiding inhalation, and avoiding handling near pregnant women and pets, she noted. In addition, she said, “in adolescents, we need to consider the teratogenicity of methotrexate, as well as the possibility of alcohol consumption worsening liver complications. If I prescribe methotrexate in patients of childbearing age, I will counsel them extensively regarding the risk of fetal death and birth defects. If needed, I will start combined oral contraceptives. Ultimately, I’m willing to use these medicines safely, with significant counseling.”
When addressing the risk of methotrexate overdose, she reminds parents to store the medication in a safe place, out of the reach of children. “Patients are at the highest risk of overdose complications if they are given the medication multiple days in a row rather than a one-time, single high dose,” she said. “The literature suggests that one-time overdoses of methotrexate – deliberate or accidental – are unlikely to cause acute bone marrow suppression or hepatitis. This is probably because GI absorption of methotrexate reaches a saturation point, and the kidneys passively and actively excrete the medication at quite a rapid pace so that the methotrexate is often undetectable in the blood at 24 hours post ingestion. I do prescribe a limited supply to help prevent accidental overdoses. In part, this is because if the patient is receiving the medication daily, they’ll run out very quickly, and it will come the family’s attention and to your attention that it’s not being administered correctly.”
Another treatment option to consider for cases of moderate to severe AD is cyclosporine, “which works extremely quickly,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is very good to rapidly control severe disease while methotrexate or other modes of treatment kick in. It’s best used as a bridge, given the risks of renal damage with long-term use. I like to limit its use to 6 months.”
Cyclosporine comes in two formulations: a modified oral formulation and a nonmodified oral formulation. The modified formulation is absorbed much better than the unmodified formulation. “We start at 5 mg/kg divided b.i.d., which is higher than the recommended dosing for dermatologic conditions in adults,” she said. “This is because children may not absorb the medication as well and may have improved renal clearance. Higher doses may be needed to achieve the desirable effect. In contrast to methotrexate, cyclosporine is available in a capsule, so it cannot be crushed.”
The choice of medication for psoriasis is generally guided by insurance step therapy requirements and is limited in the pediatric population (new guidelines on the care of pediatric psoriasis patients can be found at J Am Acad Dermatol 2020; 82[1]:161-201). In Dr. Habeshian’s experience, methotrexate is the go-to for most patients. “It treats concomitant psoriatic arthritis and can be used as monotherapy or combined with biologics,” she said. “Cyclosporine is useful for erythrodermic, pustular, and severe plaque psoriasis as a bridge. Other options include etanercept weekly in patients age 4-17 years and ustekinumab weekly dosing in patients age 12-17 years.”
Acitretin can be a useful adjunct for younger patients who are unable to obtain biologic agents. “It is most useful in widespread guttate and pustular psoriasis, but can be used be used in plaque psoriasis as well,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is usually dosed as 0.1-1 mg/kg per day. Improvement in plaque disease is generally seen in 2-3 months of therapy, so it has a slow onset, whereas improvement in pustular psoriasis is seen within 3 weeks.” The most common side effects are dry skin and mucous membranes, while an important consideration is the potential for inducing premature bone toxicity. “It is thought that the risk is relatively low if the daily and total doses are kept low,” she said. “There is no consensus for monitoring bone health. Some clinicians will consider radiography periodically.”
Dr. Habeshian concluded her talk by noting that clinicians should give vaccinations/boosters before starting systemic therapy in young children. “The safety and efficacy of live immunization administered to children on biologics is not known,” she said. “Therefore, if live vaccination is needed, it’s generally recommended to postpone initiating biologic treatment.” The MMR and varicella vaccines are given at 12-15 months of life, with a booster at 4-6 years. The varicella vaccine should be given at least 6 weeks before starting immunosuppressive therapy, and the MMR vaccine at least 4 weeks before starting therapy.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Habeshian reported having no disclosures.
In the clinical opinion of Kaiane A. Habeshian, MD, dermatologists shouldn’t think twice about using systemic agents in pediatric patients with severe dermatologic diseases.
“By the time patients come to us pediatric dermatologists, they have been treated by multiple other doctors, and are frustrated,” Dr. Habeshian said during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. “Childhood eczema affects not only patients, but the whole family. For instance, if the child is not sleeping due to itch, their parents are probably not sleeping, either. Parental well-being and workplace productivity are affected, and finances are affected.”
Only a limited number of medications are Food and Drug Administration approved in pediatric patients for common dermatologic indications. These include dupilumab for atopic dermatitis (AD), etanercept and ustekinumab for psoriasis, adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa, and omalizumab for chronic idiopathic urticaria. “The approvals are mainly for the adolescent age group, except for etanercept, which is approved at the age of 4 years and above,” said Dr. Habeshian of the department of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital, Washington.
. “These agents are approved for other indications in infants and have many years of data to describe their use in these other conditions, although comprehensive randomized, controlled studies in pediatric patients for dermatologic conditions are lacking,” she said. “What’s in clinical trials for pediatric skin disease? There are multiple ongoing clinical studies of biologic agents in pediatric dermatology, mainly for psoriasis and also for dupilumab in younger patients, as well as a JAK [Janus kinase] inhibitor for alopecia areata.”
Dr. Habeshian noted that while some clinicians may have a knee-jerk reaction to go straight to dupilumab, which was approved in March of 2019 for adolescents with moderate to severe AD, that agent is not currently approved for the most sizable pediatric population with this condition – those under 12 years of age. “FDA approval is important in part because it helps establish safety and optimal dosing, which is often different and weight based in children,” she said. “In addition, FDA approval significantly impacts access to these newer, more expensive medications.”
Speaking from her experience treating patients in the DC/Maryland/Virginia area, Medicaid has consistently denied dupilumab coverage in children under age 12, “even in severe eczema that is suboptimally controlled with both methotrexate and cyclosporine, despite multiple levels of appeal, including letters of medical necessity and peer-to-peer evaluation,” she said. “This can vary across the country among states. However, dupilumab has been completely unattainable in those under 12 in our practice.”
When dupilumab is approved, most insurers first require step therapy with off-label agents for at least 3 months, as well as documented failure of topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, crisaborole ointment, and phototherapy (if done). “It’s important to document an objective measure of severity at the very first visit with the SCORAD [scoring atopic dermatitis] or IGA [investigator global assessment],” she said. “Often, that is required if there is any hope for coverage. A familiarity with these requirements is often acquired through trial and error, and may change over time. This can lead to many delays in getting patients these treatments.” Additional information to consider documenting include the disease impact on quality of life, sleep, and school attendance, any hospitalizations for AD flares or secondary infections, and comorbid disease such as asthma.
Meanwhile, dupilumab is under priority review for children aged 6-11 years with moderate to severe AD, with a target action date of May 26, 2020. “It’s unclear how recent events [with the COVID-19 pandemic] will impact that, but there is something to look forward to, and give us hope for our patients,” she said.
Typically, Dr. Habeshian starts her pediatric patients with moderate to severe AD on methotrexate, which she characterized as “a time-tested, affordable, and very accessible option. It requires a little bit less monitoring upon initiation than cyclosporine, and it can be used for longer periods of time before weaning is required.”
In cases when disease is severe or intolerable, she often starts methotrexate and cyclosporine together. “I will usually start right at the 0.5 mg/kg per week rather than titrating up, because this maximizes the response and reduces the amount of blood work needed, unless they have an underlying risk factor for GI distress, or obese patients who are at increased risk for LFT [liver function test] elevation,” she noted. “Patients will note some improvement as early as 2 weeks on methotrexate, but I counsel them to expect 4-6 weeks for maximum improvement. We do not do a test dose of methotrexate at our institution. If there is a slight LFT elevation upon checking labs, ensure that the labs were done at least 4-6 days after the dose, because transient LFT dose elevations are common in 3-4 days.”
GI distress is by far the most common clinical side effect of methotrexate. “We do not do much intramuscular injection of methotrexate, so we rely a lot on folic acid, which reduces the risk of GI distress and elevated LFTs without reducing efficacy,” she said. “We recommend daily folic acid for simplicity, or folic acid 6 days per week.”
Dr. Habeshian said that many pediatric patients can swallow the 2.5 mg tablets of methotrexate “because they’re quite small, and most patients don’t have a problem taking the methotrexate when it’s crushed and mixed with food such as apple sauce or pudding. However, it is critical to discuss proper handling to avoid lung toxicity.” This includes placing the pills in a plastic bag prior to crushing, avoiding inhalation, and avoiding handling near pregnant women and pets, she noted. In addition, she said, “in adolescents, we need to consider the teratogenicity of methotrexate, as well as the possibility of alcohol consumption worsening liver complications. If I prescribe methotrexate in patients of childbearing age, I will counsel them extensively regarding the risk of fetal death and birth defects. If needed, I will start combined oral contraceptives. Ultimately, I’m willing to use these medicines safely, with significant counseling.”
When addressing the risk of methotrexate overdose, she reminds parents to store the medication in a safe place, out of the reach of children. “Patients are at the highest risk of overdose complications if they are given the medication multiple days in a row rather than a one-time, single high dose,” she said. “The literature suggests that one-time overdoses of methotrexate – deliberate or accidental – are unlikely to cause acute bone marrow suppression or hepatitis. This is probably because GI absorption of methotrexate reaches a saturation point, and the kidneys passively and actively excrete the medication at quite a rapid pace so that the methotrexate is often undetectable in the blood at 24 hours post ingestion. I do prescribe a limited supply to help prevent accidental overdoses. In part, this is because if the patient is receiving the medication daily, they’ll run out very quickly, and it will come the family’s attention and to your attention that it’s not being administered correctly.”
Another treatment option to consider for cases of moderate to severe AD is cyclosporine, “which works extremely quickly,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is very good to rapidly control severe disease while methotrexate or other modes of treatment kick in. It’s best used as a bridge, given the risks of renal damage with long-term use. I like to limit its use to 6 months.”
Cyclosporine comes in two formulations: a modified oral formulation and a nonmodified oral formulation. The modified formulation is absorbed much better than the unmodified formulation. “We start at 5 mg/kg divided b.i.d., which is higher than the recommended dosing for dermatologic conditions in adults,” she said. “This is because children may not absorb the medication as well and may have improved renal clearance. Higher doses may be needed to achieve the desirable effect. In contrast to methotrexate, cyclosporine is available in a capsule, so it cannot be crushed.”
The choice of medication for psoriasis is generally guided by insurance step therapy requirements and is limited in the pediatric population (new guidelines on the care of pediatric psoriasis patients can be found at J Am Acad Dermatol 2020; 82[1]:161-201). In Dr. Habeshian’s experience, methotrexate is the go-to for most patients. “It treats concomitant psoriatic arthritis and can be used as monotherapy or combined with biologics,” she said. “Cyclosporine is useful for erythrodermic, pustular, and severe plaque psoriasis as a bridge. Other options include etanercept weekly in patients age 4-17 years and ustekinumab weekly dosing in patients age 12-17 years.”
Acitretin can be a useful adjunct for younger patients who are unable to obtain biologic agents. “It is most useful in widespread guttate and pustular psoriasis, but can be used be used in plaque psoriasis as well,” Dr. Habeshian said. “It is usually dosed as 0.1-1 mg/kg per day. Improvement in plaque disease is generally seen in 2-3 months of therapy, so it has a slow onset, whereas improvement in pustular psoriasis is seen within 3 weeks.” The most common side effects are dry skin and mucous membranes, while an important consideration is the potential for inducing premature bone toxicity. “It is thought that the risk is relatively low if the daily and total doses are kept low,” she said. “There is no consensus for monitoring bone health. Some clinicians will consider radiography periodically.”
Dr. Habeshian concluded her talk by noting that clinicians should give vaccinations/boosters before starting systemic therapy in young children. “The safety and efficacy of live immunization administered to children on biologics is not known,” she said. “Therefore, if live vaccination is needed, it’s generally recommended to postpone initiating biologic treatment.” The MMR and varicella vaccines are given at 12-15 months of life, with a booster at 4-6 years. The varicella vaccine should be given at least 6 weeks before starting immunosuppressive therapy, and the MMR vaccine at least 4 weeks before starting therapy.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Habeshian reported having no disclosures.