User login
Poor trial representation tied to worse breast cancer survival
Women with early-stage breast cancer who are poorly represented in clinical trials have worse survival than their well-represented peers, according to a real-world analysis.
The study shows that more than half of women with early breast cancer are not well represented in clinical trials because of age, comorbidities, or race, yet they receive therapies based on the results of these trials.
“The most interesting finding is that patients with comorbidities resulting in lab abnormalities that would typically exclude them from receiving medication on a trial are still frequently receiving these medications and have an almost threefold higher mortality,” Gabrielle Rocque, MD, with the division of hematology and oncology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, told this news organization.
“We need to do a deeper dive to better understand what is driving this mortality difference and test specific medications in patients with these conditions to understand the optimal treatment for this population,” Dr. Rocque added.
The study was published Feb. 1 in JCO Oncology Practice.
Many patient groups are not well represented in clinical trials, including patients of color, older patients, and those with comorbidities, and it remains unclear how treatment outcomes may differ among these patients, compared with those who are well represented in trials.
To investigate, Dr. Rocque and colleagues looked at 11,770 women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer between 2005 and 2015 in the American Society of Clinical Oncology CancerLinQ database.
White women between 45 and 69 years of age with no comorbid conditions were considered well represented and made up 48% of the cohort.
Non-White women and/or those younger than 45 years or older than 70 were considered under represented and made up 45% of the cohort. The unrepresented group (7%) included women with comorbidities – such as liver disease, renal insufficiency, thrombocytopenia, anemia, or uncontrolled diabetes – or concurrent cancer.
The majority of the women received a high-intensity chemotherapy regimen, including 58% of unrepresented, 66% of underrepresented, and 63% of well-represented patients.
Compared with well-represented women, unrepresented women had a higher risk of death at 5 years (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.71; 95% confidence interval, 2.08-3.52).
Overall, the team found no significant increase in the risk of death at 5 years in underrepresented vs. well-represented women (aHR, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.98-1.45). However, that risk varied with age. Among underrepresented women, those aged 70 and older had more than a twofold higher risk of 5-year mortality (aHR, 2.21), while those younger than 45 had a lower risk of 5-year mortality (aHR, 0.63), compared with those aged 45-69 years.
For three cancer subtypes, unrepresented patients had a greater than twofold higher risk of 5-year mortality, compared with well-represented patients (aHR, 2.50 for HER2-positive disease; aHR, 2.54 for HR-positive/HER2-negative disease; and aHR, 2.75 for triple-negative disease).
Underrepresented patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative disease had a 38% increased risk of 5-year mortality, compared with their well-represented peers (aHR, 1.38). However, there were no significant differences in 5-year mortality for underrepresented vs. well-represented patients with HER2-positive or triple-negative subtypes.
Risky business?
This analysis shows that unrepresented populations receive common treatment regimens at a similar rate as well-represented patients, the researchers note.
“By excluding patients with differing clinical conditions from trials but including them in the population to which drugs can be disseminated, one runs the risk of inadvertently causing injury,” the authors caution.
“To inform the practice of evidence-based medicine in an equitable manner, our findings support a need to both expand clinical trial inclusion criteria and report on clinical trial outcomes by clinical and demographic characteristics,” Dr. Rocque and colleagues conclude.
Charles Shapiro, MD, professor of medicine, hematology, and medical oncology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, is not surprised by the findings of this study.
“We know that clinical trials are too restrictive and include only a selected population largely without comorbidities, but in the real world, people have comorbidities,” Dr. Shapiro, who was not involved in the research, told this news organization.
The study “starkly illustrates” the poorer survival of populations not represented in clinical trials.
“It could be that we need to change clinical trials, maybe ask fewer questions or maybe ask more important questions and loosen the eligibility up, because in the real world, there are people with comorbidities and people who are over 70,” Dr. Shapiro stated.
Are strides being made to change that? “Not really,” Dr. Shapiro said in an interview.
The study was supported by grants from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the American Cancer Society. Dr. Rocque has served as a consultant or advisor for Pfizer; has received research funding from Carevive Systems, Genentech, and Pfizer; and has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Carevive. Dr. Shapiro has financial relationships with UptoDate, 2nd MD, and Anthenum.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with early-stage breast cancer who are poorly represented in clinical trials have worse survival than their well-represented peers, according to a real-world analysis.
The study shows that more than half of women with early breast cancer are not well represented in clinical trials because of age, comorbidities, or race, yet they receive therapies based on the results of these trials.
“The most interesting finding is that patients with comorbidities resulting in lab abnormalities that would typically exclude them from receiving medication on a trial are still frequently receiving these medications and have an almost threefold higher mortality,” Gabrielle Rocque, MD, with the division of hematology and oncology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, told this news organization.
“We need to do a deeper dive to better understand what is driving this mortality difference and test specific medications in patients with these conditions to understand the optimal treatment for this population,” Dr. Rocque added.
The study was published Feb. 1 in JCO Oncology Practice.
Many patient groups are not well represented in clinical trials, including patients of color, older patients, and those with comorbidities, and it remains unclear how treatment outcomes may differ among these patients, compared with those who are well represented in trials.
To investigate, Dr. Rocque and colleagues looked at 11,770 women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer between 2005 and 2015 in the American Society of Clinical Oncology CancerLinQ database.
White women between 45 and 69 years of age with no comorbid conditions were considered well represented and made up 48% of the cohort.
Non-White women and/or those younger than 45 years or older than 70 were considered under represented and made up 45% of the cohort. The unrepresented group (7%) included women with comorbidities – such as liver disease, renal insufficiency, thrombocytopenia, anemia, or uncontrolled diabetes – or concurrent cancer.
The majority of the women received a high-intensity chemotherapy regimen, including 58% of unrepresented, 66% of underrepresented, and 63% of well-represented patients.
Compared with well-represented women, unrepresented women had a higher risk of death at 5 years (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.71; 95% confidence interval, 2.08-3.52).
Overall, the team found no significant increase in the risk of death at 5 years in underrepresented vs. well-represented women (aHR, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.98-1.45). However, that risk varied with age. Among underrepresented women, those aged 70 and older had more than a twofold higher risk of 5-year mortality (aHR, 2.21), while those younger than 45 had a lower risk of 5-year mortality (aHR, 0.63), compared with those aged 45-69 years.
For three cancer subtypes, unrepresented patients had a greater than twofold higher risk of 5-year mortality, compared with well-represented patients (aHR, 2.50 for HER2-positive disease; aHR, 2.54 for HR-positive/HER2-negative disease; and aHR, 2.75 for triple-negative disease).
Underrepresented patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative disease had a 38% increased risk of 5-year mortality, compared with their well-represented peers (aHR, 1.38). However, there were no significant differences in 5-year mortality for underrepresented vs. well-represented patients with HER2-positive or triple-negative subtypes.
Risky business?
This analysis shows that unrepresented populations receive common treatment regimens at a similar rate as well-represented patients, the researchers note.
“By excluding patients with differing clinical conditions from trials but including them in the population to which drugs can be disseminated, one runs the risk of inadvertently causing injury,” the authors caution.
“To inform the practice of evidence-based medicine in an equitable manner, our findings support a need to both expand clinical trial inclusion criteria and report on clinical trial outcomes by clinical and demographic characteristics,” Dr. Rocque and colleagues conclude.
Charles Shapiro, MD, professor of medicine, hematology, and medical oncology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, is not surprised by the findings of this study.
“We know that clinical trials are too restrictive and include only a selected population largely without comorbidities, but in the real world, people have comorbidities,” Dr. Shapiro, who was not involved in the research, told this news organization.
The study “starkly illustrates” the poorer survival of populations not represented in clinical trials.
“It could be that we need to change clinical trials, maybe ask fewer questions or maybe ask more important questions and loosen the eligibility up, because in the real world, there are people with comorbidities and people who are over 70,” Dr. Shapiro stated.
Are strides being made to change that? “Not really,” Dr. Shapiro said in an interview.
The study was supported by grants from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the American Cancer Society. Dr. Rocque has served as a consultant or advisor for Pfizer; has received research funding from Carevive Systems, Genentech, and Pfizer; and has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Carevive. Dr. Shapiro has financial relationships with UptoDate, 2nd MD, and Anthenum.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women with early-stage breast cancer who are poorly represented in clinical trials have worse survival than their well-represented peers, according to a real-world analysis.
The study shows that more than half of women with early breast cancer are not well represented in clinical trials because of age, comorbidities, or race, yet they receive therapies based on the results of these trials.
“The most interesting finding is that patients with comorbidities resulting in lab abnormalities that would typically exclude them from receiving medication on a trial are still frequently receiving these medications and have an almost threefold higher mortality,” Gabrielle Rocque, MD, with the division of hematology and oncology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, told this news organization.
“We need to do a deeper dive to better understand what is driving this mortality difference and test specific medications in patients with these conditions to understand the optimal treatment for this population,” Dr. Rocque added.
The study was published Feb. 1 in JCO Oncology Practice.
Many patient groups are not well represented in clinical trials, including patients of color, older patients, and those with comorbidities, and it remains unclear how treatment outcomes may differ among these patients, compared with those who are well represented in trials.
To investigate, Dr. Rocque and colleagues looked at 11,770 women diagnosed with stage I-III breast cancer between 2005 and 2015 in the American Society of Clinical Oncology CancerLinQ database.
White women between 45 and 69 years of age with no comorbid conditions were considered well represented and made up 48% of the cohort.
Non-White women and/or those younger than 45 years or older than 70 were considered under represented and made up 45% of the cohort. The unrepresented group (7%) included women with comorbidities – such as liver disease, renal insufficiency, thrombocytopenia, anemia, or uncontrolled diabetes – or concurrent cancer.
The majority of the women received a high-intensity chemotherapy regimen, including 58% of unrepresented, 66% of underrepresented, and 63% of well-represented patients.
Compared with well-represented women, unrepresented women had a higher risk of death at 5 years (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.71; 95% confidence interval, 2.08-3.52).
Overall, the team found no significant increase in the risk of death at 5 years in underrepresented vs. well-represented women (aHR, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.98-1.45). However, that risk varied with age. Among underrepresented women, those aged 70 and older had more than a twofold higher risk of 5-year mortality (aHR, 2.21), while those younger than 45 had a lower risk of 5-year mortality (aHR, 0.63), compared with those aged 45-69 years.
For three cancer subtypes, unrepresented patients had a greater than twofold higher risk of 5-year mortality, compared with well-represented patients (aHR, 2.50 for HER2-positive disease; aHR, 2.54 for HR-positive/HER2-negative disease; and aHR, 2.75 for triple-negative disease).
Underrepresented patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative disease had a 38% increased risk of 5-year mortality, compared with their well-represented peers (aHR, 1.38). However, there were no significant differences in 5-year mortality for underrepresented vs. well-represented patients with HER2-positive or triple-negative subtypes.
Risky business?
This analysis shows that unrepresented populations receive common treatment regimens at a similar rate as well-represented patients, the researchers note.
“By excluding patients with differing clinical conditions from trials but including them in the population to which drugs can be disseminated, one runs the risk of inadvertently causing injury,” the authors caution.
“To inform the practice of evidence-based medicine in an equitable manner, our findings support a need to both expand clinical trial inclusion criteria and report on clinical trial outcomes by clinical and demographic characteristics,” Dr. Rocque and colleagues conclude.
Charles Shapiro, MD, professor of medicine, hematology, and medical oncology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, is not surprised by the findings of this study.
“We know that clinical trials are too restrictive and include only a selected population largely without comorbidities, but in the real world, people have comorbidities,” Dr. Shapiro, who was not involved in the research, told this news organization.
The study “starkly illustrates” the poorer survival of populations not represented in clinical trials.
“It could be that we need to change clinical trials, maybe ask fewer questions or maybe ask more important questions and loosen the eligibility up, because in the real world, there are people with comorbidities and people who are over 70,” Dr. Shapiro stated.
Are strides being made to change that? “Not really,” Dr. Shapiro said in an interview.
The study was supported by grants from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the American Cancer Society. Dr. Rocque has served as a consultant or advisor for Pfizer; has received research funding from Carevive Systems, Genentech, and Pfizer; and has received travel, accommodations, and expenses from Carevive. Dr. Shapiro has financial relationships with UptoDate, 2nd MD, and Anthenum.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JCO ONCOLOGY PRACTICE
Nonphysician practitioner (NPP) billing for evaluation and management (E/M) and critical care services: A sea change now in effect!
In the 2022 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) further refined E/M billing by addressing split/shared visits between nonphysician practitioners (such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants) (see https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2021-11-19/pdf/2021-23972.pdf, pp. 65150-9).
A split/shared visit is “an E/M visit in the facility setting that is performed in part by both a physician and an NPP who are in the same group, in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.” CMS recognized team-based care increased utilization of NPPs in the inpatient setting, typically under physician supervision rather than completely independent NPP practice. NPP-physician team-based care is widely prevalent on critical care, hospitalist, and specialty consultation services.
These new changes from CMS went into effect January 1, 2022. CMS now mandates the practitioner providing the “substantive portion” of the service must bill for the service. For the past 20 years, the substantive portion was largely defined by medical decision making (MDM): the physician often spent less face-to-face and/or non-face-to-face time than the NPP, but the physician could bill for the service based on MDM including a nuanced synthesis of data, and final approvals or revisions to decisions on additional evaluation and treatment. Beginning January 1, 2023, CMS will no longer define MDM as the substantive portion of the visit “because MDM is not necessarily quantifiable and can depend on patient characteristics (for example, risk).” Thus, CMS will define the “substantive portion” of the visit as the practitioner who spent >50% of the total of both face-to-face and non-face-to-face time, on the calendar day. 2022 is a transitional year allowing “the practitioner who spends more than half of the total time, or performs the history, exam, or MDM to be considered to have performed the substantive portion and can bill for the split (or shared) E/M visit.” During 2022, the visit level can be chosen based on MDM or time. In 2023, the visit level can still be chosen based upon MDM, but the billing provider is determined by who performed the “substantive portion” of the visit, which will be exclusively based upon which provider spent the most amount of time.
During 2022, when billing based on time, the practitioner spending the most time (the NPP or the physician) dictates who will be the billing provider. Alternatively, billing based on the substantive portion of the visit allows billing by the provider (NPP or physician) who completely performs the key component (history, physical examination, or medical decision making) that determines the level of the visit. With the new documentation guidelines, MDM is the only key component that can determine the visit level in the office setting. In 2023, only time-based billing will be in effect for choosing the billing provider in the inpatient hospital setting. Most importantly, time-based billing is already the only method for determining the billing provider for billing critical care services, based on the provider (NPP or physician) with the greater individual total of time.
This change represents a major shift in reimbursement for physician-NPP teams. Many physician compensation plans are based on a work relative value unit (wRVU) system. This time-based billing may shift attribution to the NPP and, thereby, disadvantage the physicians working with NPPs as they will no longer receive wRVU credit for team-based care delivery. This shift demands we all reexamine our compensation models, and how organizations attribute work value across their providers (both NPPs and physicians), with special consideration for how to credit physicians for their essential supervision of team-based care delivered and now billed by NPPs. Ideally, options for revising compensation models without changing the care delivery model would preserve the essential partnership between physicians and NPPs.
*The CHEST Health Policy and Advocacy Work Group includes Nikki Augustyn, Geoffrey D. Bass, MD, Jamie Cummings, Ian Nathanson, MD, FCCP, Emily Petraglia, Gulshan Sharma, MD, FCCP, Kelly Shriner, and John E. Studdard, MD, FCCP.
In the 2022 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) further refined E/M billing by addressing split/shared visits between nonphysician practitioners (such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants) (see https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2021-11-19/pdf/2021-23972.pdf, pp. 65150-9).
A split/shared visit is “an E/M visit in the facility setting that is performed in part by both a physician and an NPP who are in the same group, in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.” CMS recognized team-based care increased utilization of NPPs in the inpatient setting, typically under physician supervision rather than completely independent NPP practice. NPP-physician team-based care is widely prevalent on critical care, hospitalist, and specialty consultation services.
These new changes from CMS went into effect January 1, 2022. CMS now mandates the practitioner providing the “substantive portion” of the service must bill for the service. For the past 20 years, the substantive portion was largely defined by medical decision making (MDM): the physician often spent less face-to-face and/or non-face-to-face time than the NPP, but the physician could bill for the service based on MDM including a nuanced synthesis of data, and final approvals or revisions to decisions on additional evaluation and treatment. Beginning January 1, 2023, CMS will no longer define MDM as the substantive portion of the visit “because MDM is not necessarily quantifiable and can depend on patient characteristics (for example, risk).” Thus, CMS will define the “substantive portion” of the visit as the practitioner who spent >50% of the total of both face-to-face and non-face-to-face time, on the calendar day. 2022 is a transitional year allowing “the practitioner who spends more than half of the total time, or performs the history, exam, or MDM to be considered to have performed the substantive portion and can bill for the split (or shared) E/M visit.” During 2022, the visit level can be chosen based on MDM or time. In 2023, the visit level can still be chosen based upon MDM, but the billing provider is determined by who performed the “substantive portion” of the visit, which will be exclusively based upon which provider spent the most amount of time.
During 2022, when billing based on time, the practitioner spending the most time (the NPP or the physician) dictates who will be the billing provider. Alternatively, billing based on the substantive portion of the visit allows billing by the provider (NPP or physician) who completely performs the key component (history, physical examination, or medical decision making) that determines the level of the visit. With the new documentation guidelines, MDM is the only key component that can determine the visit level in the office setting. In 2023, only time-based billing will be in effect for choosing the billing provider in the inpatient hospital setting. Most importantly, time-based billing is already the only method for determining the billing provider for billing critical care services, based on the provider (NPP or physician) with the greater individual total of time.
This change represents a major shift in reimbursement for physician-NPP teams. Many physician compensation plans are based on a work relative value unit (wRVU) system. This time-based billing may shift attribution to the NPP and, thereby, disadvantage the physicians working with NPPs as they will no longer receive wRVU credit for team-based care delivery. This shift demands we all reexamine our compensation models, and how organizations attribute work value across their providers (both NPPs and physicians), with special consideration for how to credit physicians for their essential supervision of team-based care delivered and now billed by NPPs. Ideally, options for revising compensation models without changing the care delivery model would preserve the essential partnership between physicians and NPPs.
*The CHEST Health Policy and Advocacy Work Group includes Nikki Augustyn, Geoffrey D. Bass, MD, Jamie Cummings, Ian Nathanson, MD, FCCP, Emily Petraglia, Gulshan Sharma, MD, FCCP, Kelly Shriner, and John E. Studdard, MD, FCCP.
In the 2022 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) further refined E/M billing by addressing split/shared visits between nonphysician practitioners (such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants) (see https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2021-11-19/pdf/2021-23972.pdf, pp. 65150-9).
A split/shared visit is “an E/M visit in the facility setting that is performed in part by both a physician and an NPP who are in the same group, in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.” CMS recognized team-based care increased utilization of NPPs in the inpatient setting, typically under physician supervision rather than completely independent NPP practice. NPP-physician team-based care is widely prevalent on critical care, hospitalist, and specialty consultation services.
These new changes from CMS went into effect January 1, 2022. CMS now mandates the practitioner providing the “substantive portion” of the service must bill for the service. For the past 20 years, the substantive portion was largely defined by medical decision making (MDM): the physician often spent less face-to-face and/or non-face-to-face time than the NPP, but the physician could bill for the service based on MDM including a nuanced synthesis of data, and final approvals or revisions to decisions on additional evaluation and treatment. Beginning January 1, 2023, CMS will no longer define MDM as the substantive portion of the visit “because MDM is not necessarily quantifiable and can depend on patient characteristics (for example, risk).” Thus, CMS will define the “substantive portion” of the visit as the practitioner who spent >50% of the total of both face-to-face and non-face-to-face time, on the calendar day. 2022 is a transitional year allowing “the practitioner who spends more than half of the total time, or performs the history, exam, or MDM to be considered to have performed the substantive portion and can bill for the split (or shared) E/M visit.” During 2022, the visit level can be chosen based on MDM or time. In 2023, the visit level can still be chosen based upon MDM, but the billing provider is determined by who performed the “substantive portion” of the visit, which will be exclusively based upon which provider spent the most amount of time.
During 2022, when billing based on time, the practitioner spending the most time (the NPP or the physician) dictates who will be the billing provider. Alternatively, billing based on the substantive portion of the visit allows billing by the provider (NPP or physician) who completely performs the key component (history, physical examination, or medical decision making) that determines the level of the visit. With the new documentation guidelines, MDM is the only key component that can determine the visit level in the office setting. In 2023, only time-based billing will be in effect for choosing the billing provider in the inpatient hospital setting. Most importantly, time-based billing is already the only method for determining the billing provider for billing critical care services, based on the provider (NPP or physician) with the greater individual total of time.
This change represents a major shift in reimbursement for physician-NPP teams. Many physician compensation plans are based on a work relative value unit (wRVU) system. This time-based billing may shift attribution to the NPP and, thereby, disadvantage the physicians working with NPPs as they will no longer receive wRVU credit for team-based care delivery. This shift demands we all reexamine our compensation models, and how organizations attribute work value across their providers (both NPPs and physicians), with special consideration for how to credit physicians for their essential supervision of team-based care delivered and now billed by NPPs. Ideally, options for revising compensation models without changing the care delivery model would preserve the essential partnership between physicians and NPPs.
*The CHEST Health Policy and Advocacy Work Group includes Nikki Augustyn, Geoffrey D. Bass, MD, Jamie Cummings, Ian Nathanson, MD, FCCP, Emily Petraglia, Gulshan Sharma, MD, FCCP, Kelly Shriner, and John E. Studdard, MD, FCCP.
Register for the 2022 AGA Tech Summit
Innovative technologies for obesity management, emerging noninvasive diagnostic tools, and the AI revolution in health care are just some of the topics featured at the 2022 AGA Tech Summit, April 14-15, in San Francisco. Registration is now open.
This year’s Summit features a keynote lecture from Rajni Natesan, MD, MBA, chief medical officer for Braid Health, on how the power of data connectivity is being used in the transformation of health care.
The 2022 Summit continues to feature ancillary programs for physician innovators and trainees interested in innovation.
See the next big idea in gastroenterology. The Shark Tank competition is where GI innovators pitch their concepts to a panel of judges. Have an idea you think has potential
Get an exclusive behind-the-scenes tour of the MedTech world through the AGA Innovation Fellows Program. The program connects GI fellows in their third and fourth year, as well as those in advanced endoscopy fellowship programs, with successful physician innovators and industry thought leaders with the goals of sharpening their entrepreneurial talents and introducing careers in GI innovation.
Join the GI innovation community at the AGA Tech Summit and be part of it yourself.
Innovative technologies for obesity management, emerging noninvasive diagnostic tools, and the AI revolution in health care are just some of the topics featured at the 2022 AGA Tech Summit, April 14-15, in San Francisco. Registration is now open.
This year’s Summit features a keynote lecture from Rajni Natesan, MD, MBA, chief medical officer for Braid Health, on how the power of data connectivity is being used in the transformation of health care.
The 2022 Summit continues to feature ancillary programs for physician innovators and trainees interested in innovation.
See the next big idea in gastroenterology. The Shark Tank competition is where GI innovators pitch their concepts to a panel of judges. Have an idea you think has potential
Get an exclusive behind-the-scenes tour of the MedTech world through the AGA Innovation Fellows Program. The program connects GI fellows in their third and fourth year, as well as those in advanced endoscopy fellowship programs, with successful physician innovators and industry thought leaders with the goals of sharpening their entrepreneurial talents and introducing careers in GI innovation.
Join the GI innovation community at the AGA Tech Summit and be part of it yourself.
Innovative technologies for obesity management, emerging noninvasive diagnostic tools, and the AI revolution in health care are just some of the topics featured at the 2022 AGA Tech Summit, April 14-15, in San Francisco. Registration is now open.
This year’s Summit features a keynote lecture from Rajni Natesan, MD, MBA, chief medical officer for Braid Health, on how the power of data connectivity is being used in the transformation of health care.
The 2022 Summit continues to feature ancillary programs for physician innovators and trainees interested in innovation.
See the next big idea in gastroenterology. The Shark Tank competition is where GI innovators pitch their concepts to a panel of judges. Have an idea you think has potential
Get an exclusive behind-the-scenes tour of the MedTech world through the AGA Innovation Fellows Program. The program connects GI fellows in their third and fourth year, as well as those in advanced endoscopy fellowship programs, with successful physician innovators and industry thought leaders with the goals of sharpening their entrepreneurial talents and introducing careers in GI innovation.
Join the GI innovation community at the AGA Tech Summit and be part of it yourself.
Exploring the relationship of COVID-19 vaccines and fertility
Introduction
Amidst an aggressive vaccination campaign for COVID-19, misinformation has spread over the Internet, affecting public perception and making some people hesitant to participate in ongoing immunization campaigns. Of chief concern are issues pertaining to fertility or viability of sperm – information circulating on social networks posits that the coronavirus vaccine may influence infertility in men, which, according to physicians, is not grounded in reality. From the perspective of evidence-based medicine, there is a dearth of information suggesting an untoward effect of the vaccine on male fertility. The risk of adverse reactions arising from approved vaccines is negligible, with mild, albeit controllable, side effects demonstrated by patients in clinical trials. Therefore, there is no plausible reason for the general public to avoid vaccinations.1
Infertility following vaccination
The source of confusion can be traced back to a study conducted by researchers at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine; the general public has conflated a side effect of the virus, namely, infertility and erectile dysfunction, with that of the vaccine.2 According to Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, director of the urology program at Miller, “We were the first to demonstrate that the COVID virus, itself, can affect male fertility and be a potential cause for erectile dysfunction. We are now the first to examine if there is any impact of the COVID vaccine on male fertility potential, which we did not find.”3
Coronavirus can indeed cause significant damage to the testicular tissue of infected men by means of mediating ACE2 expression on Leydig and Sertoli cells of the testis. It should be noted that COVID-19 may potentially attack any type of cell in the body that expresses the enzyme ACE2. However, it is particularly harmful to cells with high levels of expression of this enzyme, such as testicular cells. The spermatogenesis process can be affected, thereby posing a risk to male fertility.4
Expanding on the theme of fertility during the pandemic, a number of false claims5-7 about the vaccine and its overall effect on the placenta and fertility have also emerged as a contentious topic for debate on social media; doctors continue to explain why the theories are not reasonable or a cause for concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides recommendations on COVID-19 vaccinations for pregnant and/or lactating women and encourages a shared decision process involving risk/benefit assessment with the prescribing physician.5 Pregnant women, especially those with underlying comorbid conditions, are susceptible to developing severe symptom manifestations of COVID-19 with the disease also being associated with an increased likelihood of premature birth. As far as lactating women are concerned, the evidence thus far has indicated that the risk of side effects of the vaccine is very low, suggesting that these women could be vaccinated.5
The vaccine is the best option
While more studies are needed to ascertain the relationship between COVID-19 and male infertility, the vaccine is currently the best option for those who are concerned about their fertility from exposure to the coronavirus. Because of delayed wholesale acceptance of vaccines by the general population, clinicians should continue to emphasize the importance of preventive care with respect to disease exposure.6
In addition, those who are concerned with fertility can opt for ways to preserve their reproductive capacity, such as the removal of semen for freezing sperm, albeit with adherence to sperm-washing procedures to preclude cross-contamination from viruses.8,9 For the preservation of sperm, the noninvasive method is often performed, preferably collected in several samples. Then, the semen is cryopreserved.8 In some instances, the sperm can also be removed directly from the testicles with a simple needle or by means of a minor surgical procedure.
A wait and try approach is advocated by clinicians for individuals who have already experienced COVID-19 symptoms and are therefore concerned about the prospect of childbearing.10 If the couple is unable to conceive after a year of trying, it is recommended that they consult a reproductive specialist; the clinician can carry out a comprehensive evaluation and order a series of tests to identify the source of the problem, indicating whether there are alternative methods for helping the couple to start a family (addressing the underlying factors involved in infertility, or treating via assisted reproduction procedures, such as in vitro fertilization).11
Dr. Aman is faculty member at the biology department of City Colleges of Chicago, and a postdoctoral researcher at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation (IMCHF). She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Islam is a medical writer for the IMCHF, Montreal, is based in New York, and disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Choudhry is a research assistant at the IMCHF and he has no disclosures. Dr. Zia Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the IMCHF. He has no disclosures.
References
1. Berry SD et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021 May;69(5):1140-6.
2. Achua JK et al. World J Men’s Health. 2021 Jan;39(1):65-74.
3. Broderick JM. Urology Times. 2021 June.
4. Huang C et al. Andrology. 2021 Jan;9(1):80-7.
5. Sajjadi NB et al. J Osteopath Med. 2021 Apr 12;121(6):583-7.
6. Sallam M et al. Vaccines. 2021 Jan;9(1):42.
7. Islam MS et al. PloS One. 2021 May 12;16(5):e0251605.
8. Tesarik J. J Fertil Preserv. 2021;2:art246111.
9. Adiga SK et al. Reprod BioMed Online. 2020 Dec;41(6):991-7.
10. FAQs related to COVID-19. Q: If I get sick or test positive for COVID-19, when is it safe to become pregnant? American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
11. Cross C. Wellness and Prevention: Why can’t I get pregnant? John Hopkins Medicine.
Introduction
Amidst an aggressive vaccination campaign for COVID-19, misinformation has spread over the Internet, affecting public perception and making some people hesitant to participate in ongoing immunization campaigns. Of chief concern are issues pertaining to fertility or viability of sperm – information circulating on social networks posits that the coronavirus vaccine may influence infertility in men, which, according to physicians, is not grounded in reality. From the perspective of evidence-based medicine, there is a dearth of information suggesting an untoward effect of the vaccine on male fertility. The risk of adverse reactions arising from approved vaccines is negligible, with mild, albeit controllable, side effects demonstrated by patients in clinical trials. Therefore, there is no plausible reason for the general public to avoid vaccinations.1
Infertility following vaccination
The source of confusion can be traced back to a study conducted by researchers at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine; the general public has conflated a side effect of the virus, namely, infertility and erectile dysfunction, with that of the vaccine.2 According to Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, director of the urology program at Miller, “We were the first to demonstrate that the COVID virus, itself, can affect male fertility and be a potential cause for erectile dysfunction. We are now the first to examine if there is any impact of the COVID vaccine on male fertility potential, which we did not find.”3
Coronavirus can indeed cause significant damage to the testicular tissue of infected men by means of mediating ACE2 expression on Leydig and Sertoli cells of the testis. It should be noted that COVID-19 may potentially attack any type of cell in the body that expresses the enzyme ACE2. However, it is particularly harmful to cells with high levels of expression of this enzyme, such as testicular cells. The spermatogenesis process can be affected, thereby posing a risk to male fertility.4
Expanding on the theme of fertility during the pandemic, a number of false claims5-7 about the vaccine and its overall effect on the placenta and fertility have also emerged as a contentious topic for debate on social media; doctors continue to explain why the theories are not reasonable or a cause for concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides recommendations on COVID-19 vaccinations for pregnant and/or lactating women and encourages a shared decision process involving risk/benefit assessment with the prescribing physician.5 Pregnant women, especially those with underlying comorbid conditions, are susceptible to developing severe symptom manifestations of COVID-19 with the disease also being associated with an increased likelihood of premature birth. As far as lactating women are concerned, the evidence thus far has indicated that the risk of side effects of the vaccine is very low, suggesting that these women could be vaccinated.5
The vaccine is the best option
While more studies are needed to ascertain the relationship between COVID-19 and male infertility, the vaccine is currently the best option for those who are concerned about their fertility from exposure to the coronavirus. Because of delayed wholesale acceptance of vaccines by the general population, clinicians should continue to emphasize the importance of preventive care with respect to disease exposure.6
In addition, those who are concerned with fertility can opt for ways to preserve their reproductive capacity, such as the removal of semen for freezing sperm, albeit with adherence to sperm-washing procedures to preclude cross-contamination from viruses.8,9 For the preservation of sperm, the noninvasive method is often performed, preferably collected in several samples. Then, the semen is cryopreserved.8 In some instances, the sperm can also be removed directly from the testicles with a simple needle or by means of a minor surgical procedure.
A wait and try approach is advocated by clinicians for individuals who have already experienced COVID-19 symptoms and are therefore concerned about the prospect of childbearing.10 If the couple is unable to conceive after a year of trying, it is recommended that they consult a reproductive specialist; the clinician can carry out a comprehensive evaluation and order a series of tests to identify the source of the problem, indicating whether there are alternative methods for helping the couple to start a family (addressing the underlying factors involved in infertility, or treating via assisted reproduction procedures, such as in vitro fertilization).11
Dr. Aman is faculty member at the biology department of City Colleges of Chicago, and a postdoctoral researcher at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation (IMCHF). She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Islam is a medical writer for the IMCHF, Montreal, is based in New York, and disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Choudhry is a research assistant at the IMCHF and he has no disclosures. Dr. Zia Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the IMCHF. He has no disclosures.
References
1. Berry SD et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021 May;69(5):1140-6.
2. Achua JK et al. World J Men’s Health. 2021 Jan;39(1):65-74.
3. Broderick JM. Urology Times. 2021 June.
4. Huang C et al. Andrology. 2021 Jan;9(1):80-7.
5. Sajjadi NB et al. J Osteopath Med. 2021 Apr 12;121(6):583-7.
6. Sallam M et al. Vaccines. 2021 Jan;9(1):42.
7. Islam MS et al. PloS One. 2021 May 12;16(5):e0251605.
8. Tesarik J. J Fertil Preserv. 2021;2:art246111.
9. Adiga SK et al. Reprod BioMed Online. 2020 Dec;41(6):991-7.
10. FAQs related to COVID-19. Q: If I get sick or test positive for COVID-19, when is it safe to become pregnant? American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
11. Cross C. Wellness and Prevention: Why can’t I get pregnant? John Hopkins Medicine.
Introduction
Amidst an aggressive vaccination campaign for COVID-19, misinformation has spread over the Internet, affecting public perception and making some people hesitant to participate in ongoing immunization campaigns. Of chief concern are issues pertaining to fertility or viability of sperm – information circulating on social networks posits that the coronavirus vaccine may influence infertility in men, which, according to physicians, is not grounded in reality. From the perspective of evidence-based medicine, there is a dearth of information suggesting an untoward effect of the vaccine on male fertility. The risk of adverse reactions arising from approved vaccines is negligible, with mild, albeit controllable, side effects demonstrated by patients in clinical trials. Therefore, there is no plausible reason for the general public to avoid vaccinations.1
Infertility following vaccination
The source of confusion can be traced back to a study conducted by researchers at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine; the general public has conflated a side effect of the virus, namely, infertility and erectile dysfunction, with that of the vaccine.2 According to Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, director of the urology program at Miller, “We were the first to demonstrate that the COVID virus, itself, can affect male fertility and be a potential cause for erectile dysfunction. We are now the first to examine if there is any impact of the COVID vaccine on male fertility potential, which we did not find.”3
Coronavirus can indeed cause significant damage to the testicular tissue of infected men by means of mediating ACE2 expression on Leydig and Sertoli cells of the testis. It should be noted that COVID-19 may potentially attack any type of cell in the body that expresses the enzyme ACE2. However, it is particularly harmful to cells with high levels of expression of this enzyme, such as testicular cells. The spermatogenesis process can be affected, thereby posing a risk to male fertility.4
Expanding on the theme of fertility during the pandemic, a number of false claims5-7 about the vaccine and its overall effect on the placenta and fertility have also emerged as a contentious topic for debate on social media; doctors continue to explain why the theories are not reasonable or a cause for concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides recommendations on COVID-19 vaccinations for pregnant and/or lactating women and encourages a shared decision process involving risk/benefit assessment with the prescribing physician.5 Pregnant women, especially those with underlying comorbid conditions, are susceptible to developing severe symptom manifestations of COVID-19 with the disease also being associated with an increased likelihood of premature birth. As far as lactating women are concerned, the evidence thus far has indicated that the risk of side effects of the vaccine is very low, suggesting that these women could be vaccinated.5
The vaccine is the best option
While more studies are needed to ascertain the relationship between COVID-19 and male infertility, the vaccine is currently the best option for those who are concerned about their fertility from exposure to the coronavirus. Because of delayed wholesale acceptance of vaccines by the general population, clinicians should continue to emphasize the importance of preventive care with respect to disease exposure.6
In addition, those who are concerned with fertility can opt for ways to preserve their reproductive capacity, such as the removal of semen for freezing sperm, albeit with adherence to sperm-washing procedures to preclude cross-contamination from viruses.8,9 For the preservation of sperm, the noninvasive method is often performed, preferably collected in several samples. Then, the semen is cryopreserved.8 In some instances, the sperm can also be removed directly from the testicles with a simple needle or by means of a minor surgical procedure.
A wait and try approach is advocated by clinicians for individuals who have already experienced COVID-19 symptoms and are therefore concerned about the prospect of childbearing.10 If the couple is unable to conceive after a year of trying, it is recommended that they consult a reproductive specialist; the clinician can carry out a comprehensive evaluation and order a series of tests to identify the source of the problem, indicating whether there are alternative methods for helping the couple to start a family (addressing the underlying factors involved in infertility, or treating via assisted reproduction procedures, such as in vitro fertilization).11
Dr. Aman is faculty member at the biology department of City Colleges of Chicago, and a postdoctoral researcher at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation (IMCHF). She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Islam is a medical writer for the IMCHF, Montreal, is based in New York, and disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Choudhry is a research assistant at the IMCHF and he has no disclosures. Dr. Zia Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the IMCHF. He has no disclosures.
References
1. Berry SD et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021 May;69(5):1140-6.
2. Achua JK et al. World J Men’s Health. 2021 Jan;39(1):65-74.
3. Broderick JM. Urology Times. 2021 June.
4. Huang C et al. Andrology. 2021 Jan;9(1):80-7.
5. Sajjadi NB et al. J Osteopath Med. 2021 Apr 12;121(6):583-7.
6. Sallam M et al. Vaccines. 2021 Jan;9(1):42.
7. Islam MS et al. PloS One. 2021 May 12;16(5):e0251605.
8. Tesarik J. J Fertil Preserv. 2021;2:art246111.
9. Adiga SK et al. Reprod BioMed Online. 2020 Dec;41(6):991-7.
10. FAQs related to COVID-19. Q: If I get sick or test positive for COVID-19, when is it safe to become pregnant? American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
11. Cross C. Wellness and Prevention: Why can’t I get pregnant? John Hopkins Medicine.
Federal sex education programs linked to decrease in teen pregnancy
The birth rate for U.S. teenagers dropped 3% in counties where a federally funded sex education program was introduced, a recently published paper says.
Researchers concentrated on the effects of the Teen Pregnancy Prevention program (TPP), which was introduced during the Obama administration and administered on the county level. TPP programs provide more information on sex, contraception, and reproductive health than abstinence-only programs, the paper said.
“Sex education in the United States has been hotly debated among researchers, policy makers, and the public,” Nicholas Mark, a doctoral candidate in New York University’s department of sociology and the lead author of the paper, said in a news release. “Our analysis provides evidence that funding for more comprehensive sex education led to an overall reduction in the teen birth rate at the county level of more than 3%.”
Researchers examined teen birth rates in 55 counties from 1996 to 2009, before TTP, and from 2010 to 2016, after TTP. Next, they compared teen birth rates in the 55 counties with teen birth rates in 2,800 counties that didn’t have the funding in the years before and after TPP was introduced.
In the 55 counties, teen birth rates fell 1.5% in the first year of TTP funding and fell about 7% by the fifth year of funding, for an average drop of 3%, the news release said.
“We’ve known for some time that abstinence-only programs are ineffective at reducing teen birth rates,” said Lawrence Wu, a professor in NYU’s department of sociology and the paper’s senior author. “This work shows that more wide-reaching sex education programs – those not limited to abstinence – are successful in lowering rates of teen births.”
The paper was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
The paper said the findings probably understate the true effect of more comprehensive sex education at the individual level.
The authors said the findings are important because U.S. women are more likely to become mothers in their teens than women in other developed nations, with many teen pregnancies reported as unintended, the authors said.
As of 2020, teen birth rates and the number of births to teen mothers had dropped steadily since 1990. Teen birth rates fell by 70% over 3 decades.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The birth rate for U.S. teenagers dropped 3% in counties where a federally funded sex education program was introduced, a recently published paper says.
Researchers concentrated on the effects of the Teen Pregnancy Prevention program (TPP), which was introduced during the Obama administration and administered on the county level. TPP programs provide more information on sex, contraception, and reproductive health than abstinence-only programs, the paper said.
“Sex education in the United States has been hotly debated among researchers, policy makers, and the public,” Nicholas Mark, a doctoral candidate in New York University’s department of sociology and the lead author of the paper, said in a news release. “Our analysis provides evidence that funding for more comprehensive sex education led to an overall reduction in the teen birth rate at the county level of more than 3%.”
Researchers examined teen birth rates in 55 counties from 1996 to 2009, before TTP, and from 2010 to 2016, after TTP. Next, they compared teen birth rates in the 55 counties with teen birth rates in 2,800 counties that didn’t have the funding in the years before and after TPP was introduced.
In the 55 counties, teen birth rates fell 1.5% in the first year of TTP funding and fell about 7% by the fifth year of funding, for an average drop of 3%, the news release said.
“We’ve known for some time that abstinence-only programs are ineffective at reducing teen birth rates,” said Lawrence Wu, a professor in NYU’s department of sociology and the paper’s senior author. “This work shows that more wide-reaching sex education programs – those not limited to abstinence – are successful in lowering rates of teen births.”
The paper was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
The paper said the findings probably understate the true effect of more comprehensive sex education at the individual level.
The authors said the findings are important because U.S. women are more likely to become mothers in their teens than women in other developed nations, with many teen pregnancies reported as unintended, the authors said.
As of 2020, teen birth rates and the number of births to teen mothers had dropped steadily since 1990. Teen birth rates fell by 70% over 3 decades.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The birth rate for U.S. teenagers dropped 3% in counties where a federally funded sex education program was introduced, a recently published paper says.
Researchers concentrated on the effects of the Teen Pregnancy Prevention program (TPP), which was introduced during the Obama administration and administered on the county level. TPP programs provide more information on sex, contraception, and reproductive health than abstinence-only programs, the paper said.
“Sex education in the United States has been hotly debated among researchers, policy makers, and the public,” Nicholas Mark, a doctoral candidate in New York University’s department of sociology and the lead author of the paper, said in a news release. “Our analysis provides evidence that funding for more comprehensive sex education led to an overall reduction in the teen birth rate at the county level of more than 3%.”
Researchers examined teen birth rates in 55 counties from 1996 to 2009, before TTP, and from 2010 to 2016, after TTP. Next, they compared teen birth rates in the 55 counties with teen birth rates in 2,800 counties that didn’t have the funding in the years before and after TPP was introduced.
In the 55 counties, teen birth rates fell 1.5% in the first year of TTP funding and fell about 7% by the fifth year of funding, for an average drop of 3%, the news release said.
“We’ve known for some time that abstinence-only programs are ineffective at reducing teen birth rates,” said Lawrence Wu, a professor in NYU’s department of sociology and the paper’s senior author. “This work shows that more wide-reaching sex education programs – those not limited to abstinence – are successful in lowering rates of teen births.”
The paper was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
The paper said the findings probably understate the true effect of more comprehensive sex education at the individual level.
The authors said the findings are important because U.S. women are more likely to become mothers in their teens than women in other developed nations, with many teen pregnancies reported as unintended, the authors said.
As of 2020, teen birth rates and the number of births to teen mothers had dropped steadily since 1990. Teen birth rates fell by 70% over 3 decades.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Simple ways to create your legacy
Creating a legacy of giving is easier than you think. Take some time to start creating your legacy while supporting the AGA Research Foundation. Gifts to charitable organizations, such as the AGA Research Foundation, in your plans ensure your support for our mission continues for years to come.
Here are two ideas to help you get started.
- Name the AGA Research Foundation as a beneficiary. This arrangement is one of the most tax-smart ways to support the AGA Research Foundation after your lifetime. When you leave retirement plan assets to us, we bypass any taxes and receive the full amount.
- Include the AGA Research Foundation in your will or living trust. This gift can be made by including as little as one sentence in your will or living trust. Plus, your gift can be modified throughout your lifetime as circumstances change.
Want to learn more about including a gift to the AGA Research Foundation in your plans? Visit our website at https://gastro.planmylegacy.org.
Creating a legacy of giving is easier than you think. Take some time to start creating your legacy while supporting the AGA Research Foundation. Gifts to charitable organizations, such as the AGA Research Foundation, in your plans ensure your support for our mission continues for years to come.
Here are two ideas to help you get started.
- Name the AGA Research Foundation as a beneficiary. This arrangement is one of the most tax-smart ways to support the AGA Research Foundation after your lifetime. When you leave retirement plan assets to us, we bypass any taxes and receive the full amount.
- Include the AGA Research Foundation in your will or living trust. This gift can be made by including as little as one sentence in your will or living trust. Plus, your gift can be modified throughout your lifetime as circumstances change.
Want to learn more about including a gift to the AGA Research Foundation in your plans? Visit our website at https://gastro.planmylegacy.org.
Creating a legacy of giving is easier than you think. Take some time to start creating your legacy while supporting the AGA Research Foundation. Gifts to charitable organizations, such as the AGA Research Foundation, in your plans ensure your support for our mission continues for years to come.
Here are two ideas to help you get started.
- Name the AGA Research Foundation as a beneficiary. This arrangement is one of the most tax-smart ways to support the AGA Research Foundation after your lifetime. When you leave retirement plan assets to us, we bypass any taxes and receive the full amount.
- Include the AGA Research Foundation in your will or living trust. This gift can be made by including as little as one sentence in your will or living trust. Plus, your gift can be modified throughout your lifetime as circumstances change.
Want to learn more about including a gift to the AGA Research Foundation in your plans? Visit our website at https://gastro.planmylegacy.org.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Prostate Cancer March 2022
Kishan et al conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the relative effects of the addition of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) to radiation therapy (RT) on metastasis-free survival (MFS) in patients with localized prostate cancer in the following three settings: 1) RT alone versus RT plus adjuvant ADT, 2) extension of ADT duration in the neoadjuvant setting before RT, and 3) extension of adjuvant ADT duration. MFS was increased in the adjuvant ADT setting, and prolongation of ADT duration was associated with a higher MFS than shorter duration. However, extension of neoadjuvant ADT was not associated with a higher MFS compared to a shorter duration. The meta-analysis further supports a longer versus shorter ADT duration, but it does not support a longer neoadjuvant ADT duration.
To determine the effects of salvage RT on outcomes in the setting of biochemical relapse, Tilki et al conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of a multi-institutional database of patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy (RP). MFS at 15 years post-RP was 84.3% in the RT group and 76.9% in the non-RT group, while overall survival (OS), also at 15 years post-RP, was 85.3% in the RT group versus 74.4% in the non-RT group (both analyses were statistically significant). While supportive of salvage RT, there was no data on prostate-specific antigen (PSA) doubling times, nor was it possible to control for imaging modality. It is possible that newer prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-based positron emission tomography imaging may affect MFS in studies such as these.
Prostatectomy (with or without lymph node dissection), external beam RT (EBRT) with ADT, or EBRT with brachytherapy (BT) with or without ADT are options in unfavorable intermediate-risk prostate cancer. The optimal use of BT in localized prostate cancer is somewhat uncertain, especially across the risk spectrum. Andruska et al conducted an analysis of the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to evaluate whether EBRT plus BT with or without ADT results in an improvement in overall survival (OS) compared with BT with or without ADT. OS was higher for the EBRT plus BT groups; however, when the ADT + EBRT + BT group was compared with EBRT + BT without ADT group, the improvement in OS was not statistically significant. Overall, the analysis favored EBRT + BT over BT alone, further supporting current guidelines.
Kishan et al conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the relative effects of the addition of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) to radiation therapy (RT) on metastasis-free survival (MFS) in patients with localized prostate cancer in the following three settings: 1) RT alone versus RT plus adjuvant ADT, 2) extension of ADT duration in the neoadjuvant setting before RT, and 3) extension of adjuvant ADT duration. MFS was increased in the adjuvant ADT setting, and prolongation of ADT duration was associated with a higher MFS than shorter duration. However, extension of neoadjuvant ADT was not associated with a higher MFS compared to a shorter duration. The meta-analysis further supports a longer versus shorter ADT duration, but it does not support a longer neoadjuvant ADT duration.
To determine the effects of salvage RT on outcomes in the setting of biochemical relapse, Tilki et al conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of a multi-institutional database of patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy (RP). MFS at 15 years post-RP was 84.3% in the RT group and 76.9% in the non-RT group, while overall survival (OS), also at 15 years post-RP, was 85.3% in the RT group versus 74.4% in the non-RT group (both analyses were statistically significant). While supportive of salvage RT, there was no data on prostate-specific antigen (PSA) doubling times, nor was it possible to control for imaging modality. It is possible that newer prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-based positron emission tomography imaging may affect MFS in studies such as these.
Prostatectomy (with or without lymph node dissection), external beam RT (EBRT) with ADT, or EBRT with brachytherapy (BT) with or without ADT are options in unfavorable intermediate-risk prostate cancer. The optimal use of BT in localized prostate cancer is somewhat uncertain, especially across the risk spectrum. Andruska et al conducted an analysis of the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to evaluate whether EBRT plus BT with or without ADT results in an improvement in overall survival (OS) compared with BT with or without ADT. OS was higher for the EBRT plus BT groups; however, when the ADT + EBRT + BT group was compared with EBRT + BT without ADT group, the improvement in OS was not statistically significant. Overall, the analysis favored EBRT + BT over BT alone, further supporting current guidelines.
Kishan et al conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the relative effects of the addition of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) to radiation therapy (RT) on metastasis-free survival (MFS) in patients with localized prostate cancer in the following three settings: 1) RT alone versus RT plus adjuvant ADT, 2) extension of ADT duration in the neoadjuvant setting before RT, and 3) extension of adjuvant ADT duration. MFS was increased in the adjuvant ADT setting, and prolongation of ADT duration was associated with a higher MFS than shorter duration. However, extension of neoadjuvant ADT was not associated with a higher MFS compared to a shorter duration. The meta-analysis further supports a longer versus shorter ADT duration, but it does not support a longer neoadjuvant ADT duration.
To determine the effects of salvage RT on outcomes in the setting of biochemical relapse, Tilki et al conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of a multi-institutional database of patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy (RP). MFS at 15 years post-RP was 84.3% in the RT group and 76.9% in the non-RT group, while overall survival (OS), also at 15 years post-RP, was 85.3% in the RT group versus 74.4% in the non-RT group (both analyses were statistically significant). While supportive of salvage RT, there was no data on prostate-specific antigen (PSA) doubling times, nor was it possible to control for imaging modality. It is possible that newer prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-based positron emission tomography imaging may affect MFS in studies such as these.
Prostatectomy (with or without lymph node dissection), external beam RT (EBRT) with ADT, or EBRT with brachytherapy (BT) with or without ADT are options in unfavorable intermediate-risk prostate cancer. The optimal use of BT in localized prostate cancer is somewhat uncertain, especially across the risk spectrum. Andruska et al conducted an analysis of the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to evaluate whether EBRT plus BT with or without ADT results in an improvement in overall survival (OS) compared with BT with or without ADT. OS was higher for the EBRT plus BT groups; however, when the ADT + EBRT + BT group was compared with EBRT + BT without ADT group, the improvement in OS was not statistically significant. Overall, the analysis favored EBRT + BT over BT alone, further supporting current guidelines.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Multiple Sclerosis March 2022
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: Prenatal Testing March 2022
Many neurocognitive disorders only present a phenotype after birth. Sukenik-Halevy et al sought to examine the ability to detect prenatal phenotypes in patients with a postnatally diagnosed neurocognitive syndrome and confirmed genetic diagnosis on ES. The team was not able to identify any specific prenatal phenotype associated with their cases of postnatally diagnosed neurocognitive syndromes. The interesting finding of this study is that, of the 122 patients studied, 35.3% (43) had no abnormal sonographic findings that could have been detected prenatally to suggest the need for ES testing. ES is typically used in a prenatal setting for fetuses with anomalies that have a normal KT and CMA. The results of this study raise the question of offering ES to all patients considering diagnostic genetic testing regardless of the indication, as it may be the only way to diagnose some cases of neurocognitive disorders prenatally.
Cell-free fetal DNA (cff DNA) testing for trisomy 21, 18, and 13 has classically be used for high-risk pregnant patients seeking aneuploidy screening. Dar et al sought to examine this type of testing in a low-risk population. They studied, prospectively, the performance of cff DNA testing for trisomy 21, 18, and 13 in both low and high-risk pregnant women with confirmation of results on diagnostic genetic testing. Negative predictive values (NPV) for both the low and high-risk groups were greater than 99.9%. Positive predictive value (PPV) was lower for the low-risk group in comparison to the high-risk group, with it important to note that PPV drops from 96.4% in the high-risk group to 81.8% in the low-risk group for trisomy 21. This means that low-risk patients with a positive result on cff DNA testing are at a higher risk for a false positive than patients at high-risk for an aneuploid fetus. This study shows the mounting evidence that cff DNA can be used in a low-risk population given the high NPV. Providers do still need to note the lower PPV with low-risk population patients and always offer diagnostic genetic testing with any abnormal cff DNA test result.
Many neurocognitive disorders only present a phenotype after birth. Sukenik-Halevy et al sought to examine the ability to detect prenatal phenotypes in patients with a postnatally diagnosed neurocognitive syndrome and confirmed genetic diagnosis on ES. The team was not able to identify any specific prenatal phenotype associated with their cases of postnatally diagnosed neurocognitive syndromes. The interesting finding of this study is that, of the 122 patients studied, 35.3% (43) had no abnormal sonographic findings that could have been detected prenatally to suggest the need for ES testing. ES is typically used in a prenatal setting for fetuses with anomalies that have a normal KT and CMA. The results of this study raise the question of offering ES to all patients considering diagnostic genetic testing regardless of the indication, as it may be the only way to diagnose some cases of neurocognitive disorders prenatally.
Cell-free fetal DNA (cff DNA) testing for trisomy 21, 18, and 13 has classically be used for high-risk pregnant patients seeking aneuploidy screening. Dar et al sought to examine this type of testing in a low-risk population. They studied, prospectively, the performance of cff DNA testing for trisomy 21, 18, and 13 in both low and high-risk pregnant women with confirmation of results on diagnostic genetic testing. Negative predictive values (NPV) for both the low and high-risk groups were greater than 99.9%. Positive predictive value (PPV) was lower for the low-risk group in comparison to the high-risk group, with it important to note that PPV drops from 96.4% in the high-risk group to 81.8% in the low-risk group for trisomy 21. This means that low-risk patients with a positive result on cff DNA testing are at a higher risk for a false positive than patients at high-risk for an aneuploid fetus. This study shows the mounting evidence that cff DNA can be used in a low-risk population given the high NPV. Providers do still need to note the lower PPV with low-risk population patients and always offer diagnostic genetic testing with any abnormal cff DNA test result.
Many neurocognitive disorders only present a phenotype after birth. Sukenik-Halevy et al sought to examine the ability to detect prenatal phenotypes in patients with a postnatally diagnosed neurocognitive syndrome and confirmed genetic diagnosis on ES. The team was not able to identify any specific prenatal phenotype associated with their cases of postnatally diagnosed neurocognitive syndromes. The interesting finding of this study is that, of the 122 patients studied, 35.3% (43) had no abnormal sonographic findings that could have been detected prenatally to suggest the need for ES testing. ES is typically used in a prenatal setting for fetuses with anomalies that have a normal KT and CMA. The results of this study raise the question of offering ES to all patients considering diagnostic genetic testing regardless of the indication, as it may be the only way to diagnose some cases of neurocognitive disorders prenatally.
Cell-free fetal DNA (cff DNA) testing for trisomy 21, 18, and 13 has classically be used for high-risk pregnant patients seeking aneuploidy screening. Dar et al sought to examine this type of testing in a low-risk population. They studied, prospectively, the performance of cff DNA testing for trisomy 21, 18, and 13 in both low and high-risk pregnant women with confirmation of results on diagnostic genetic testing. Negative predictive values (NPV) for both the low and high-risk groups were greater than 99.9%. Positive predictive value (PPV) was lower for the low-risk group in comparison to the high-risk group, with it important to note that PPV drops from 96.4% in the high-risk group to 81.8% in the low-risk group for trisomy 21. This means that low-risk patients with a positive result on cff DNA testing are at a higher risk for a false positive than patients at high-risk for an aneuploid fetus. This study shows the mounting evidence that cff DNA can be used in a low-risk population given the high NPV. Providers do still need to note the lower PPV with low-risk population patients and always offer diagnostic genetic testing with any abnormal cff DNA test result.
Treatment of Elephantiasic Pretibial Myxedema With Rituximab Therapy
To the Editor:
Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is bilateral, nonpitting, scaly thickening and induration of the skin that most commonly occurs on the anterior aspects of the legs and feet. Pretibial myxedema occurs in approximately 0.5% to 4.3% of patients with hyperthyroidism.1 Thyroid dermopathy often is thought of as the classic nonpitting PTM with skin induration and color change. However, rarer forms of PTM, including plaque, nodular, and elephantiasic, also are important to note.2
Elephantiasic PTM is extremely rare, occurring in less than 1% of patients with PTM.2 Elephantiasic PTM is characterized by the persistent swelling of 1 or both legs; thickening of the skin overlying the dorsum of the feet, ankles, and toes; and verrucous irregular plaques that often are fleshy and flattened. The clinical differential diagnosis of elephantiasic PTM includes elephantiasis nostra verrucosa, a late-stage complication of chronic lymphedema that can be related to a variety of infectious or noninfectious obstructive processes. Few effective therapeutic modalities exist in the treatment of elephantiasic PTM. We present a case of elephantiasic PTM.
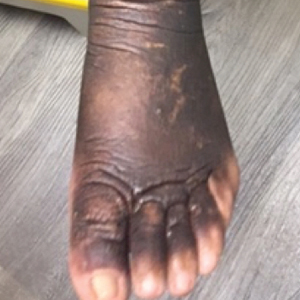
A 59-year-old man presented to dermatology with leonine facies with pronounced glabellar creases and indentations of the earlobes. He had diffuse woody induration, hyperpigmentation, and nonpitting edema of the lower extremities as well as several flesh-colored exophytic nodules scattered throughout the anterior shins and dorsal feet (Figure 1). On the left posterior calf, there was a large, 3-cm, exophytic, firm, flesh-colored nodule. Examination of the hands revealed mild hyperpigmentation of the distal digits, clubbing of the distal phalanges, and cheiroarthropathy.
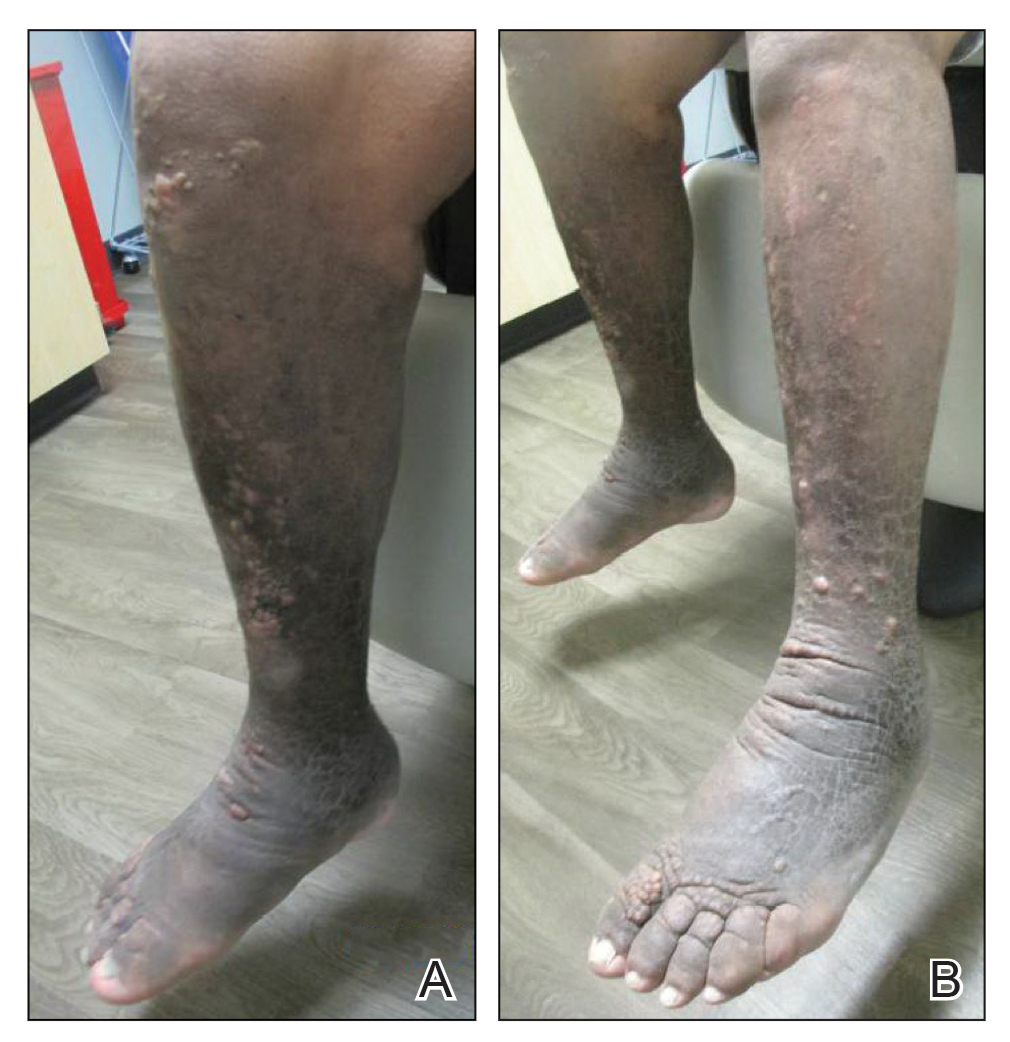
The patient was diagnosed with Graves disease after experiencing the classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including heat intolerance, tremor, palpitations, and anxiety. He received thyroid ablation and subsequently was supplemented with levothyroxine 75 mg daily. Twelve years later, he was diagnosed with Graves ophthalmopathy with ocular proptosis requiring multiple courses of retro-orbital irradiation and surgical procedures for decompression. Approximately 1 year later, he noted increased swelling, firmness, and darkening of the pretibial surfaces. Initially, he was referred to vascular surgery and underwent bilateral saphenous vein ablation. He also was referred to a lymphedema specialist, and workup revealed an unremarkable lymphatic system. Minimal improvement was noted following the saphenous vein ablation, and he subsequently was referred to dermatology for further workup.
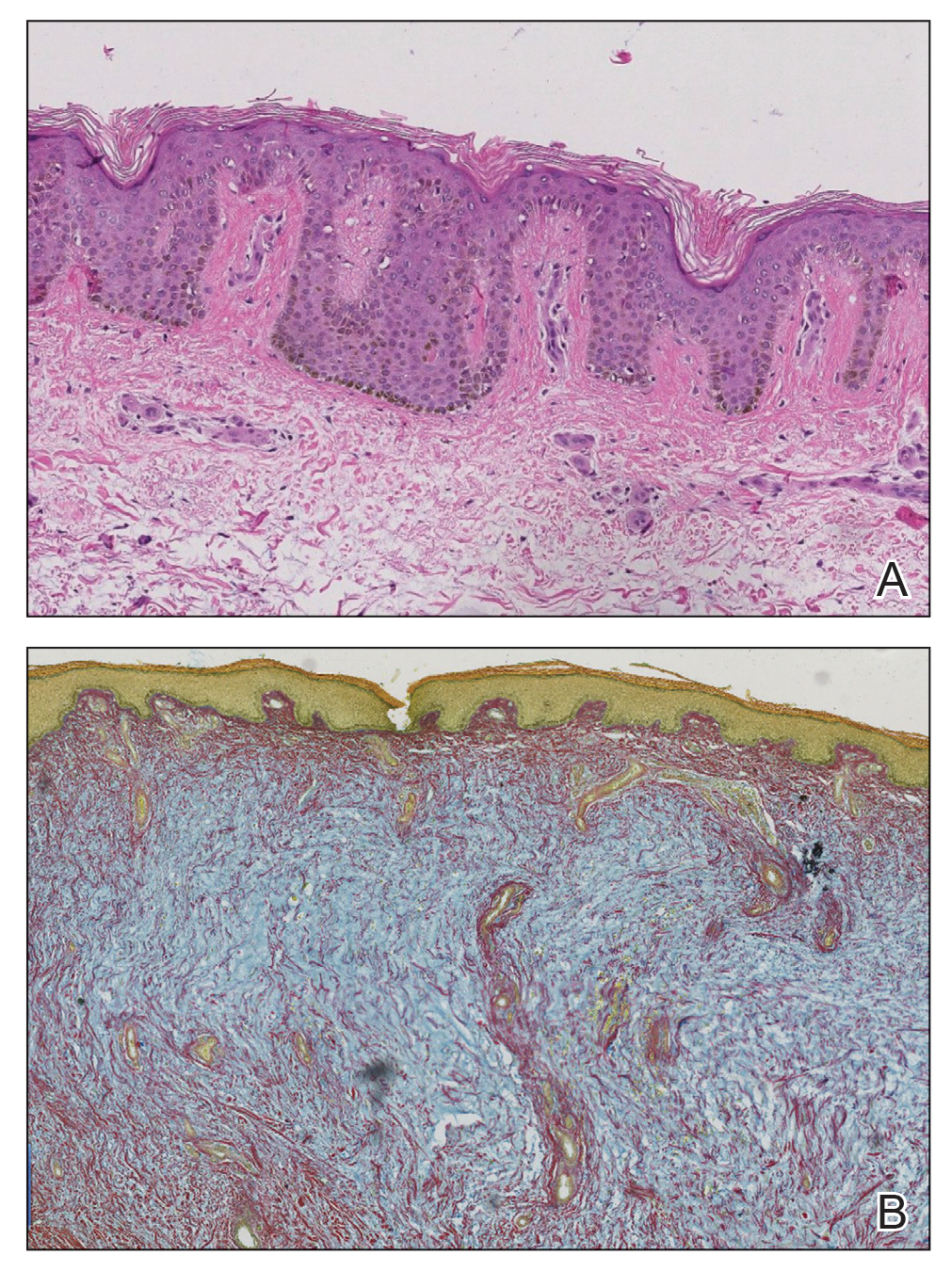
At the current presentation, laboratory analysis revealed a low thyrotropin level (0.03 mIU/L [reference range, 0.4–4.2 mIU/L]), and free thyroxine was within reference range. Radiography of the chest was unremarkable; however, radiography of the hand demonstrated arthrosis of the left fifth proximal interphalangeal joint. Nuclear medicine lymphoscintigraphy and lower extremity ultrasonography were unremarkable. Punch biopsies were performed of the left lateral leg and posterior calf. Hematoxylin and eosin staining demonstrated marked mucin deposition extending to the deep dermis along with deep fibroplasia and was read as consistent with PTM. Colloidal iron highlighted prominent mucin within the dermis (Figure 2).
The patient’s medical history, physical examination, laboratory analysis, imaging, and biopsies were considered, and a diagnosis of elephantiasic PTM was made. Minimal improvement was noted with initial therapeutic interventions including compression therapy and application of super high–potency topical corticosteroids. After further evaluation in our multidisciplinary rheumatology-dermatology clinic, the decision was made to initiate rituximab infusions.
Two months after 1 course of rituximab consisting of two 1000-mg infusions separated by 2 weeks, the patient showed substantial clinical improvement. There was striking improvement of the pretibial surfaces with resolution of the exophytic nodules and improvement of the induration (Figure 3). In addition, there was decreased induration of the glabella and earlobes and decreased fullness of the digital pulp on the hands. The patient also reported subjective improvements in mobility.
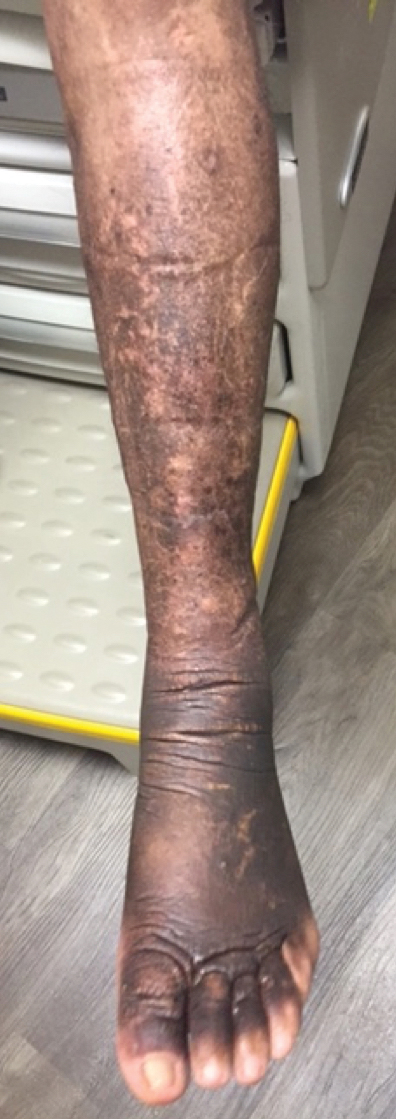
Our patient demonstrated all 3 aspects of the Diamond triad: PTM, exophthalmos, and acropachy. Patients present with all 3 features in less than 1% of reported cases of Graves disease.3 Although all 3 features are seen together infrequently, thyroid dermopathy and acropachy often are markers of severe Graves ophthalmopathy. In a study of 114 patients with Graves ophthalmopathy, patients who also had dermopathy and acropachy were more likely to have optic neuropathy or require orbital decompression.4
After overcoming the diagnostic dilemma that the elephantiasic presentation of PTM can present, therapeutic management remains a challenge. Heyes et al5 documented the successful treatment of highly recalcitrant elephantiasic PTM with rituximab and plasmapheresis therapy. In this case, a 44-year-old woman with an 11-year history of Graves disease and elephantiasic PTM received 29 rituximab infusions and 241 plasmapheresis treatments over the course of 3.5 years. Her elephantiasic PTM clinically resolved, and she was able to resume daily activities and wear normal shoes after being nonambulatory for years.5
Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody against CD20, a protein found primarily on the surface of B-cell lymphocytes. Although rituximab initially was approved by the US Food and Drug administration for the treatment of malignant lymphoma, it has had an increasing role in the treatment of autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Rituximab is postulated to target B lymphocytes and halt their progression to plasma cells. By limiting the population of long-lasting, antibody-producing plasma cells and decreasing the autoantibodies that cause many of the symptoms in Graves disease, rituximab may be an effective therapy to consider in the treatment of elephantiasic PTM.6
Although the exact mechanism is poorly understood, PTM likely is a sequela of hyperthyroidism because of the expression of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor proteins found on normal dermal fibroblasts. Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor autoantibodies are thought to stimulate these fibroblasts to produce glycosaminoglycans. Histopathologically, accumulation of glycosaminoglycans deposited in the reticular dermis with high concentrations of hyaluronic acid is observed in PTM.7
Treatment of elephantiasic PTM remains a therapeutic challenge. Given the rarity of the disease process and limited information on effective therapeutic modalities, rituximab should be viewed as a viable treatment option in the management of recalcitrant elephantiasic PTM.
- Schwartz KM, Fatourechi V, Ahmed DDF, et al. Dermopathy of Graves’ disease (pretibial myxedema): long-term outcome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:438-446.
- Kakati S, Doley B, Pal S, et al. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: a rare thyroid dermopathy in Graves’ disease. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005;53:571-572.
- Anderson CK, Miller OF 3rd. Triad of exophthalmos, pretibial myxedema, and acropachy in a patient with Graves’ disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:970-972.
- Fatourechi V, Bartley GB, Eghbali-Fatourechi GZ, et al. Graves’ dermopathy and acropachy are markers of severe Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Thyroid. 2003;13:1141-1144.
- Heyes C, Nolan R, Leahy M, et al. Treatment‐resistant elephantiasic thyroid dermopathy responding to rituximab and plasmapheresis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:E1-E4.
- Salvi M, Vannucchi G, Campi I, et al. Treatment of Graves’ disease and associated ophthalmopathy with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab: an open study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;156:33-40.
- Heufelder AE, Dutton CM, Sarkar G, et al. Detection of TSH receptor RNA in cultured fibroblasts from patients with Graves’ ophthalmopathy and pretibial dermopathy. Thyroid. 1993;3:297-300.
To the Editor:
Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is bilateral, nonpitting, scaly thickening and induration of the skin that most commonly occurs on the anterior aspects of the legs and feet. Pretibial myxedema occurs in approximately 0.5% to 4.3% of patients with hyperthyroidism.1 Thyroid dermopathy often is thought of as the classic nonpitting PTM with skin induration and color change. However, rarer forms of PTM, including plaque, nodular, and elephantiasic, also are important to note.2
Elephantiasic PTM is extremely rare, occurring in less than 1% of patients with PTM.2 Elephantiasic PTM is characterized by the persistent swelling of 1 or both legs; thickening of the skin overlying the dorsum of the feet, ankles, and toes; and verrucous irregular plaques that often are fleshy and flattened. The clinical differential diagnosis of elephantiasic PTM includes elephantiasis nostra verrucosa, a late-stage complication of chronic lymphedema that can be related to a variety of infectious or noninfectious obstructive processes. Few effective therapeutic modalities exist in the treatment of elephantiasic PTM. We present a case of elephantiasic PTM.
A 59-year-old man presented to dermatology with leonine facies with pronounced glabellar creases and indentations of the earlobes. He had diffuse woody induration, hyperpigmentation, and nonpitting edema of the lower extremities as well as several flesh-colored exophytic nodules scattered throughout the anterior shins and dorsal feet (Figure 1). On the left posterior calf, there was a large, 3-cm, exophytic, firm, flesh-colored nodule. Examination of the hands revealed mild hyperpigmentation of the distal digits, clubbing of the distal phalanges, and cheiroarthropathy.

The patient was diagnosed with Graves disease after experiencing the classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including heat intolerance, tremor, palpitations, and anxiety. He received thyroid ablation and subsequently was supplemented with levothyroxine 75 mg daily. Twelve years later, he was diagnosed with Graves ophthalmopathy with ocular proptosis requiring multiple courses of retro-orbital irradiation and surgical procedures for decompression. Approximately 1 year later, he noted increased swelling, firmness, and darkening of the pretibial surfaces. Initially, he was referred to vascular surgery and underwent bilateral saphenous vein ablation. He also was referred to a lymphedema specialist, and workup revealed an unremarkable lymphatic system. Minimal improvement was noted following the saphenous vein ablation, and he subsequently was referred to dermatology for further workup.
At the current presentation, laboratory analysis revealed a low thyrotropin level (0.03 mIU/L [reference range, 0.4–4.2 mIU/L]), and free thyroxine was within reference range. Radiography of the chest was unremarkable; however, radiography of the hand demonstrated arthrosis of the left fifth proximal interphalangeal joint. Nuclear medicine lymphoscintigraphy and lower extremity ultrasonography were unremarkable. Punch biopsies were performed of the left lateral leg and posterior calf. Hematoxylin and eosin staining demonstrated marked mucin deposition extending to the deep dermis along with deep fibroplasia and was read as consistent with PTM. Colloidal iron highlighted prominent mucin within the dermis (Figure 2).

The patient’s medical history, physical examination, laboratory analysis, imaging, and biopsies were considered, and a diagnosis of elephantiasic PTM was made. Minimal improvement was noted with initial therapeutic interventions including compression therapy and application of super high–potency topical corticosteroids. After further evaluation in our multidisciplinary rheumatology-dermatology clinic, the decision was made to initiate rituximab infusions.
Two months after 1 course of rituximab consisting of two 1000-mg infusions separated by 2 weeks, the patient showed substantial clinical improvement. There was striking improvement of the pretibial surfaces with resolution of the exophytic nodules and improvement of the induration (Figure 3). In addition, there was decreased induration of the glabella and earlobes and decreased fullness of the digital pulp on the hands. The patient also reported subjective improvements in mobility.

Our patient demonstrated all 3 aspects of the Diamond triad: PTM, exophthalmos, and acropachy. Patients present with all 3 features in less than 1% of reported cases of Graves disease.3 Although all 3 features are seen together infrequently, thyroid dermopathy and acropachy often are markers of severe Graves ophthalmopathy. In a study of 114 patients with Graves ophthalmopathy, patients who also had dermopathy and acropachy were more likely to have optic neuropathy or require orbital decompression.4
After overcoming the diagnostic dilemma that the elephantiasic presentation of PTM can present, therapeutic management remains a challenge. Heyes et al5 documented the successful treatment of highly recalcitrant elephantiasic PTM with rituximab and plasmapheresis therapy. In this case, a 44-year-old woman with an 11-year history of Graves disease and elephantiasic PTM received 29 rituximab infusions and 241 plasmapheresis treatments over the course of 3.5 years. Her elephantiasic PTM clinically resolved, and she was able to resume daily activities and wear normal shoes after being nonambulatory for years.5
Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody against CD20, a protein found primarily on the surface of B-cell lymphocytes. Although rituximab initially was approved by the US Food and Drug administration for the treatment of malignant lymphoma, it has had an increasing role in the treatment of autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Rituximab is postulated to target B lymphocytes and halt their progression to plasma cells. By limiting the population of long-lasting, antibody-producing plasma cells and decreasing the autoantibodies that cause many of the symptoms in Graves disease, rituximab may be an effective therapy to consider in the treatment of elephantiasic PTM.6
Although the exact mechanism is poorly understood, PTM likely is a sequela of hyperthyroidism because of the expression of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor proteins found on normal dermal fibroblasts. Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor autoantibodies are thought to stimulate these fibroblasts to produce glycosaminoglycans. Histopathologically, accumulation of glycosaminoglycans deposited in the reticular dermis with high concentrations of hyaluronic acid is observed in PTM.7
Treatment of elephantiasic PTM remains a therapeutic challenge. Given the rarity of the disease process and limited information on effective therapeutic modalities, rituximab should be viewed as a viable treatment option in the management of recalcitrant elephantiasic PTM.
To the Editor:
Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is bilateral, nonpitting, scaly thickening and induration of the skin that most commonly occurs on the anterior aspects of the legs and feet. Pretibial myxedema occurs in approximately 0.5% to 4.3% of patients with hyperthyroidism.1 Thyroid dermopathy often is thought of as the classic nonpitting PTM with skin induration and color change. However, rarer forms of PTM, including plaque, nodular, and elephantiasic, also are important to note.2
Elephantiasic PTM is extremely rare, occurring in less than 1% of patients with PTM.2 Elephantiasic PTM is characterized by the persistent swelling of 1 or both legs; thickening of the skin overlying the dorsum of the feet, ankles, and toes; and verrucous irregular plaques that often are fleshy and flattened. The clinical differential diagnosis of elephantiasic PTM includes elephantiasis nostra verrucosa, a late-stage complication of chronic lymphedema that can be related to a variety of infectious or noninfectious obstructive processes. Few effective therapeutic modalities exist in the treatment of elephantiasic PTM. We present a case of elephantiasic PTM.
A 59-year-old man presented to dermatology with leonine facies with pronounced glabellar creases and indentations of the earlobes. He had diffuse woody induration, hyperpigmentation, and nonpitting edema of the lower extremities as well as several flesh-colored exophytic nodules scattered throughout the anterior shins and dorsal feet (Figure 1). On the left posterior calf, there was a large, 3-cm, exophytic, firm, flesh-colored nodule. Examination of the hands revealed mild hyperpigmentation of the distal digits, clubbing of the distal phalanges, and cheiroarthropathy.

The patient was diagnosed with Graves disease after experiencing the classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including heat intolerance, tremor, palpitations, and anxiety. He received thyroid ablation and subsequently was supplemented with levothyroxine 75 mg daily. Twelve years later, he was diagnosed with Graves ophthalmopathy with ocular proptosis requiring multiple courses of retro-orbital irradiation and surgical procedures for decompression. Approximately 1 year later, he noted increased swelling, firmness, and darkening of the pretibial surfaces. Initially, he was referred to vascular surgery and underwent bilateral saphenous vein ablation. He also was referred to a lymphedema specialist, and workup revealed an unremarkable lymphatic system. Minimal improvement was noted following the saphenous vein ablation, and he subsequently was referred to dermatology for further workup.
At the current presentation, laboratory analysis revealed a low thyrotropin level (0.03 mIU/L [reference range, 0.4–4.2 mIU/L]), and free thyroxine was within reference range. Radiography of the chest was unremarkable; however, radiography of the hand demonstrated arthrosis of the left fifth proximal interphalangeal joint. Nuclear medicine lymphoscintigraphy and lower extremity ultrasonography were unremarkable. Punch biopsies were performed of the left lateral leg and posterior calf. Hematoxylin and eosin staining demonstrated marked mucin deposition extending to the deep dermis along with deep fibroplasia and was read as consistent with PTM. Colloidal iron highlighted prominent mucin within the dermis (Figure 2).

The patient’s medical history, physical examination, laboratory analysis, imaging, and biopsies were considered, and a diagnosis of elephantiasic PTM was made. Minimal improvement was noted with initial therapeutic interventions including compression therapy and application of super high–potency topical corticosteroids. After further evaluation in our multidisciplinary rheumatology-dermatology clinic, the decision was made to initiate rituximab infusions.
Two months after 1 course of rituximab consisting of two 1000-mg infusions separated by 2 weeks, the patient showed substantial clinical improvement. There was striking improvement of the pretibial surfaces with resolution of the exophytic nodules and improvement of the induration (Figure 3). In addition, there was decreased induration of the glabella and earlobes and decreased fullness of the digital pulp on the hands. The patient also reported subjective improvements in mobility.

Our patient demonstrated all 3 aspects of the Diamond triad: PTM, exophthalmos, and acropachy. Patients present with all 3 features in less than 1% of reported cases of Graves disease.3 Although all 3 features are seen together infrequently, thyroid dermopathy and acropachy often are markers of severe Graves ophthalmopathy. In a study of 114 patients with Graves ophthalmopathy, patients who also had dermopathy and acropachy were more likely to have optic neuropathy or require orbital decompression.4
After overcoming the diagnostic dilemma that the elephantiasic presentation of PTM can present, therapeutic management remains a challenge. Heyes et al5 documented the successful treatment of highly recalcitrant elephantiasic PTM with rituximab and plasmapheresis therapy. In this case, a 44-year-old woman with an 11-year history of Graves disease and elephantiasic PTM received 29 rituximab infusions and 241 plasmapheresis treatments over the course of 3.5 years. Her elephantiasic PTM clinically resolved, and she was able to resume daily activities and wear normal shoes after being nonambulatory for years.5
Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody against CD20, a protein found primarily on the surface of B-cell lymphocytes. Although rituximab initially was approved by the US Food and Drug administration for the treatment of malignant lymphoma, it has had an increasing role in the treatment of autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Rituximab is postulated to target B lymphocytes and halt their progression to plasma cells. By limiting the population of long-lasting, antibody-producing plasma cells and decreasing the autoantibodies that cause many of the symptoms in Graves disease, rituximab may be an effective therapy to consider in the treatment of elephantiasic PTM.6
Although the exact mechanism is poorly understood, PTM likely is a sequela of hyperthyroidism because of the expression of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor proteins found on normal dermal fibroblasts. Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor autoantibodies are thought to stimulate these fibroblasts to produce glycosaminoglycans. Histopathologically, accumulation of glycosaminoglycans deposited in the reticular dermis with high concentrations of hyaluronic acid is observed in PTM.7
Treatment of elephantiasic PTM remains a therapeutic challenge. Given the rarity of the disease process and limited information on effective therapeutic modalities, rituximab should be viewed as a viable treatment option in the management of recalcitrant elephantiasic PTM.
- Schwartz KM, Fatourechi V, Ahmed DDF, et al. Dermopathy of Graves’ disease (pretibial myxedema): long-term outcome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:438-446.
- Kakati S, Doley B, Pal S, et al. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: a rare thyroid dermopathy in Graves’ disease. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005;53:571-572.
- Anderson CK, Miller OF 3rd. Triad of exophthalmos, pretibial myxedema, and acropachy in a patient with Graves’ disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:970-972.
- Fatourechi V, Bartley GB, Eghbali-Fatourechi GZ, et al. Graves’ dermopathy and acropachy are markers of severe Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Thyroid. 2003;13:1141-1144.
- Heyes C, Nolan R, Leahy M, et al. Treatment‐resistant elephantiasic thyroid dermopathy responding to rituximab and plasmapheresis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:E1-E4.
- Salvi M, Vannucchi G, Campi I, et al. Treatment of Graves’ disease and associated ophthalmopathy with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab: an open study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;156:33-40.
- Heufelder AE, Dutton CM, Sarkar G, et al. Detection of TSH receptor RNA in cultured fibroblasts from patients with Graves’ ophthalmopathy and pretibial dermopathy. Thyroid. 1993;3:297-300.
- Schwartz KM, Fatourechi V, Ahmed DDF, et al. Dermopathy of Graves’ disease (pretibial myxedema): long-term outcome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:438-446.
- Kakati S, Doley B, Pal S, et al. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: a rare thyroid dermopathy in Graves’ disease. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005;53:571-572.
- Anderson CK, Miller OF 3rd. Triad of exophthalmos, pretibial myxedema, and acropachy in a patient with Graves’ disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:970-972.
- Fatourechi V, Bartley GB, Eghbali-Fatourechi GZ, et al. Graves’ dermopathy and acropachy are markers of severe Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Thyroid. 2003;13:1141-1144.
- Heyes C, Nolan R, Leahy M, et al. Treatment‐resistant elephantiasic thyroid dermopathy responding to rituximab and plasmapheresis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:E1-E4.
- Salvi M, Vannucchi G, Campi I, et al. Treatment of Graves’ disease and associated ophthalmopathy with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab: an open study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;156:33-40.
- Heufelder AE, Dutton CM, Sarkar G, et al. Detection of TSH receptor RNA in cultured fibroblasts from patients with Graves’ ophthalmopathy and pretibial dermopathy. Thyroid. 1993;3:297-300.
Practice Points
- Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is bilateral, nonpitting, scaly thickening and induration of the skin that most commonly occurs on the anterior aspects of the legs and feet.
- Although many therapeutic modalities have been described for the management of the elephantiasis variant of PTM, few treatments have shown notable efficacy.
- Rituximab may be an effective therapy to consider in the treatment of elephantiasic PTM.