User login
New hyperglycemia emergency guidance updates DKA definition
HAMBURG, GERMANY – along with many other updates to the last statement on the topic, published 14 years ago.
Based on extensive literature reviews and observations of current trends, the new document – due to be published soon – will cover diagnosis and management of the two most serious acute hyperglycemic emergencies seen in adults, DKA and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
New to the 2023 version will be a strong emphasis on the excess morbidity and mortality risks associated with the increasingly common “hybrid” presentation of the two conditions together, now seen in about a third of cases.
The new report will also more strongly urge clinicians to investigate why the person experienced the emergency.
While new-onset diabetes and infection are recognized precipitating causes for DKA, insulin omission related to finances, mental health, and social determinants should be identified, and patients directed to appropriate resources, said experts previewing the upcoming new report at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“The challenge is, although we were making progress for a long time in terms of those hyperglycemic crises, we’ve really plateaued and there are still people being admitted in large numbers, and when you look more globally even more so,” said American Diabetes Association Chief Science and Medical Officer Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD.
The new consensus report will be jointly endorsed by the ADA, the EASD, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, the Diabetes Technology Society, and the Joint British Diabetes Societies for Inpatient Care. The previous consensus statement on the subject was published in 2009 by the ADA alone.
New DKA and HHS definitions reflect emerging trends
The statement will revise the definition of DKA, partly spurred by the increasing occurrence and recognition of euglycemic ketoacidosis arising from the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. For all patients with hyperglycemic crisis, the hyperglycemia cutoff is now lowered to 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) from the previous 250 mg/dL.
However, the glucose cutoff has been removed entirely for people with a history of diabetes.
“Both of these changes are recognizing the wide range of glucose levels at the presence of DKA. Approximately 10% of DKA occurs with euglycemia or near-normoglycemia,” noted coauthor Shivani Misra, MD, PhD, senior clinical lecturer and honorary consultant in Metabolic Medicine at Imperial College, London.
For assessing ketosis in DKA, the new statement strongly recommends use of beta-hydroxybutyrate – either via point-of-care test or serum level measured in a laboratory – with a low cutoff of ≥ 3.0 mmol/L. Alternatively, a urine ketone strip value of 2+ or greater can be used.
However, beta-hydroxybutyrate testing is more widely available now than it was in 2009 and is strongly preferred over urine ketone measurement because it’s the predominant ketone during acidosis. Moreover, urine acetoacetate – measured by the strips – paradoxically increases during resolution of DKA, and drug interferences can occur with urine ketone measurement, Dr. Misra noted.
Metabolic acidosis is now defined as a pH < 7.3 and/or a bicarbonate concentration < 18 mmol/L, up from 15 in some prior guidelines including the United Kingdom’s. Also, anion gap has been removed from the main definition but, the document will say, can still be used in settings where ketone testing is unavailable.
As previously, the new statement will classify DKA by mild, moderate, and severe but now for the first time there are recommendations of care for each of those levels, as well as for HHS.
For HHS, the glucose cutoff of ≥ 600 mg/dL will stay the same. But now, the effective serum osmolality has been lowered from > 320 to > 300 mOsml/L to account for the effect of dehydration, along with an alternative criteria of total serum osmolality > 320 mOsm/L. The same two changes as with DKA for both ketones and acidosis have also been included for HHS.
Asked to comment, session audience member and independent diabetes industry consultant Charles Alexander, MD, told this news organization, “I liked the proposal to eliminate the anion gap in decision-making and to focus on measurement of blood ketones, principally beta-hydroxybutyrate, in the diagnosis of DKA and monitoring the effect of treatment.
“If someone is on an SGLT2 inhibitor, there is no need to look at blood glucose levels, which may be normal or near normal in the setting of DKA.”
But Dr. Alexander thinks that they should have eliminated glucose levels entirely as part of the DKA/HHS definition even for people without diabetes.
“The problem is that medical education for many years has taught us that DKA is a condition of high blood glucose, but it may not be. It is good that they said blood glucose levels were not important if the patient had a history of diabetes. However, a glucose of 200mg/dL may not be low enough if someone is on an SGLT2 inhibitor. There needs to be a much lower threshold for measuring blood ketones in anyone with nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, regardless of the blood glucose level.”
Acute management: IV fluids, insulin, and potassium
Like the 2009 statement, the new one will include detailed management flowcharts for DKA and HHS, but this time in color. This new statement includes individual algorithms for management with intravenous fluids, insulin, and potassium. Bicarbonate has been removed and relegated to a note at the bottom saying that it should only be considered if pH is < 7.0.
Under fluid treatment, the new statement offers more information about using crystalloids to treat dehydration and a recommendation to add dextrose to IV fluid therapy as a substrate when the glucose drops below 250 mg/dL, in order to prevent hypoglycemia. For euglycemic DKA, the recommendation is to include dextrose and normal saline simultaneously.
And for the first time, subcutaneous rather than IV insulin is considered acceptable for mild, but not moderate or severe, DKA.
Two options are suggested for IV insulin in HHS: The fluid can be given first and low-dose fixed-rate insulin infusion added, or fluids and insulin can be given at the same time.
Criteria for resolution of DKA are a venous pH of ≥ 7.3 or bicarbonate > 18 mmol/L, ketones < 0.6 mmol/L, and glucose ideally < 200 mg/dL (11.0 mmol/L). For HHS, resolution is suggested when the measured or calculated serum osmolality falls to < 300 mosm/kg, blood glucose is < 250mg/dL (13.9 mmol/L), urine output > 0.5 mL/kg/hour, and cognitive status is improved.
The statement also will provide detailed recommended options for transitioning from IV to subcutaneous insulin, but defers to clinical judgment for deciding when the patient can be discharged. The initiation or continuation of SGLT2 inhibitors is not recommended at any time during hospitalization for hyperglycemic crises.
Mitigating complications, preventing recurrence
In addition to listing potential complications of treating hyperglycemic crises, just as the 2009 statement did, the new one will offer mitigation strategies for some of the more common ones. For preventing hypoglycemia, frequent blood glucose monitoring is advised along with adding dextrose to the IV fluids when glucose drops below 250 mg/dL.
For prevention of hypokalemia, which occurs in about half of patients treated for DKA and HHS, the statement recommends potassium monitoring every 4 hours and replacement added to fluids.
Acute kidney injury, also occurring in about half of people treated for DKA and/or HHS, usually resolves with hydration. Daily renal function monitoring is advised.
Preventing recurrence: Many factors beyond clinical
Prevention of recurrence with readmission for DKA and/or HHS, occurring in up to 22% of U.S. patients within 30 days, entails close follow-up within 2-4 weeks after discharge (including via telemedicine), and assessment of possible causes, including mental health disorders and social determinants of health.
Appropriate education should be provided, including “structured education” involving problem-solving, sick day rules, injection techniques, a review of insulin doses, consideration of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), and home ketone testing.
Patients should be provided with an adequate supply of insulin and durable diabetes equipment, along with contact information for health care professionals who can assist them. Social service professionals can be helpful for patients who lack reliable access.
Dr. Gabbay told this news organization, “The eye-opening thing is we tend to typically think of DKA as how people tend to get diagnosed with diabetes and, yes, that’s true, but that’s only a minority of people. Those might be preventable by early screening, but all these other people and the number of recurrent episodes, that’s an area where it’s really a failure of the system where we can do better in ensuring that doesn’t happen.”
Education is only part of it, he stressed. “It’s not just an intelligence thing. It’s social factors, and there can be complex psychological issues and mental health issues. We need to screen for those things when we see someone coming back the second, third, fifth, or sixth time. We’ve all seen that. Just educating them to take their insulin is not the answer. …You’ve got to ask the questions and engage them to go a little deeper.”
Dr. Gabbay is an employee of the ADA. Dr. Alexander has reported being a nonpaid advisor for diaTribe and a consultant for Kinexum. Dr. Misra has received speaker fees from Sanofi and ABCD and an investigator-initiated research grant from Dexcom, and is a trustee for the Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation in the United Kingdom.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, GERMANY – along with many other updates to the last statement on the topic, published 14 years ago.
Based on extensive literature reviews and observations of current trends, the new document – due to be published soon – will cover diagnosis and management of the two most serious acute hyperglycemic emergencies seen in adults, DKA and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
New to the 2023 version will be a strong emphasis on the excess morbidity and mortality risks associated with the increasingly common “hybrid” presentation of the two conditions together, now seen in about a third of cases.
The new report will also more strongly urge clinicians to investigate why the person experienced the emergency.
While new-onset diabetes and infection are recognized precipitating causes for DKA, insulin omission related to finances, mental health, and social determinants should be identified, and patients directed to appropriate resources, said experts previewing the upcoming new report at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“The challenge is, although we were making progress for a long time in terms of those hyperglycemic crises, we’ve really plateaued and there are still people being admitted in large numbers, and when you look more globally even more so,” said American Diabetes Association Chief Science and Medical Officer Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD.
The new consensus report will be jointly endorsed by the ADA, the EASD, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, the Diabetes Technology Society, and the Joint British Diabetes Societies for Inpatient Care. The previous consensus statement on the subject was published in 2009 by the ADA alone.
New DKA and HHS definitions reflect emerging trends
The statement will revise the definition of DKA, partly spurred by the increasing occurrence and recognition of euglycemic ketoacidosis arising from the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. For all patients with hyperglycemic crisis, the hyperglycemia cutoff is now lowered to 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) from the previous 250 mg/dL.
However, the glucose cutoff has been removed entirely for people with a history of diabetes.
“Both of these changes are recognizing the wide range of glucose levels at the presence of DKA. Approximately 10% of DKA occurs with euglycemia or near-normoglycemia,” noted coauthor Shivani Misra, MD, PhD, senior clinical lecturer and honorary consultant in Metabolic Medicine at Imperial College, London.
For assessing ketosis in DKA, the new statement strongly recommends use of beta-hydroxybutyrate – either via point-of-care test or serum level measured in a laboratory – with a low cutoff of ≥ 3.0 mmol/L. Alternatively, a urine ketone strip value of 2+ or greater can be used.
However, beta-hydroxybutyrate testing is more widely available now than it was in 2009 and is strongly preferred over urine ketone measurement because it’s the predominant ketone during acidosis. Moreover, urine acetoacetate – measured by the strips – paradoxically increases during resolution of DKA, and drug interferences can occur with urine ketone measurement, Dr. Misra noted.
Metabolic acidosis is now defined as a pH < 7.3 and/or a bicarbonate concentration < 18 mmol/L, up from 15 in some prior guidelines including the United Kingdom’s. Also, anion gap has been removed from the main definition but, the document will say, can still be used in settings where ketone testing is unavailable.
As previously, the new statement will classify DKA by mild, moderate, and severe but now for the first time there are recommendations of care for each of those levels, as well as for HHS.
For HHS, the glucose cutoff of ≥ 600 mg/dL will stay the same. But now, the effective serum osmolality has been lowered from > 320 to > 300 mOsml/L to account for the effect of dehydration, along with an alternative criteria of total serum osmolality > 320 mOsm/L. The same two changes as with DKA for both ketones and acidosis have also been included for HHS.
Asked to comment, session audience member and independent diabetes industry consultant Charles Alexander, MD, told this news organization, “I liked the proposal to eliminate the anion gap in decision-making and to focus on measurement of blood ketones, principally beta-hydroxybutyrate, in the diagnosis of DKA and monitoring the effect of treatment.
“If someone is on an SGLT2 inhibitor, there is no need to look at blood glucose levels, which may be normal or near normal in the setting of DKA.”
But Dr. Alexander thinks that they should have eliminated glucose levels entirely as part of the DKA/HHS definition even for people without diabetes.
“The problem is that medical education for many years has taught us that DKA is a condition of high blood glucose, but it may not be. It is good that they said blood glucose levels were not important if the patient had a history of diabetes. However, a glucose of 200mg/dL may not be low enough if someone is on an SGLT2 inhibitor. There needs to be a much lower threshold for measuring blood ketones in anyone with nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, regardless of the blood glucose level.”
Acute management: IV fluids, insulin, and potassium
Like the 2009 statement, the new one will include detailed management flowcharts for DKA and HHS, but this time in color. This new statement includes individual algorithms for management with intravenous fluids, insulin, and potassium. Bicarbonate has been removed and relegated to a note at the bottom saying that it should only be considered if pH is < 7.0.
Under fluid treatment, the new statement offers more information about using crystalloids to treat dehydration and a recommendation to add dextrose to IV fluid therapy as a substrate when the glucose drops below 250 mg/dL, in order to prevent hypoglycemia. For euglycemic DKA, the recommendation is to include dextrose and normal saline simultaneously.
And for the first time, subcutaneous rather than IV insulin is considered acceptable for mild, but not moderate or severe, DKA.
Two options are suggested for IV insulin in HHS: The fluid can be given first and low-dose fixed-rate insulin infusion added, or fluids and insulin can be given at the same time.
Criteria for resolution of DKA are a venous pH of ≥ 7.3 or bicarbonate > 18 mmol/L, ketones < 0.6 mmol/L, and glucose ideally < 200 mg/dL (11.0 mmol/L). For HHS, resolution is suggested when the measured or calculated serum osmolality falls to < 300 mosm/kg, blood glucose is < 250mg/dL (13.9 mmol/L), urine output > 0.5 mL/kg/hour, and cognitive status is improved.
The statement also will provide detailed recommended options for transitioning from IV to subcutaneous insulin, but defers to clinical judgment for deciding when the patient can be discharged. The initiation or continuation of SGLT2 inhibitors is not recommended at any time during hospitalization for hyperglycemic crises.
Mitigating complications, preventing recurrence
In addition to listing potential complications of treating hyperglycemic crises, just as the 2009 statement did, the new one will offer mitigation strategies for some of the more common ones. For preventing hypoglycemia, frequent blood glucose monitoring is advised along with adding dextrose to the IV fluids when glucose drops below 250 mg/dL.
For prevention of hypokalemia, which occurs in about half of patients treated for DKA and HHS, the statement recommends potassium monitoring every 4 hours and replacement added to fluids.
Acute kidney injury, also occurring in about half of people treated for DKA and/or HHS, usually resolves with hydration. Daily renal function monitoring is advised.
Preventing recurrence: Many factors beyond clinical
Prevention of recurrence with readmission for DKA and/or HHS, occurring in up to 22% of U.S. patients within 30 days, entails close follow-up within 2-4 weeks after discharge (including via telemedicine), and assessment of possible causes, including mental health disorders and social determinants of health.
Appropriate education should be provided, including “structured education” involving problem-solving, sick day rules, injection techniques, a review of insulin doses, consideration of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), and home ketone testing.
Patients should be provided with an adequate supply of insulin and durable diabetes equipment, along with contact information for health care professionals who can assist them. Social service professionals can be helpful for patients who lack reliable access.
Dr. Gabbay told this news organization, “The eye-opening thing is we tend to typically think of DKA as how people tend to get diagnosed with diabetes and, yes, that’s true, but that’s only a minority of people. Those might be preventable by early screening, but all these other people and the number of recurrent episodes, that’s an area where it’s really a failure of the system where we can do better in ensuring that doesn’t happen.”
Education is only part of it, he stressed. “It’s not just an intelligence thing. It’s social factors, and there can be complex psychological issues and mental health issues. We need to screen for those things when we see someone coming back the second, third, fifth, or sixth time. We’ve all seen that. Just educating them to take their insulin is not the answer. …You’ve got to ask the questions and engage them to go a little deeper.”
Dr. Gabbay is an employee of the ADA. Dr. Alexander has reported being a nonpaid advisor for diaTribe and a consultant for Kinexum. Dr. Misra has received speaker fees from Sanofi and ABCD and an investigator-initiated research grant from Dexcom, and is a trustee for the Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation in the United Kingdom.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, GERMANY – along with many other updates to the last statement on the topic, published 14 years ago.
Based on extensive literature reviews and observations of current trends, the new document – due to be published soon – will cover diagnosis and management of the two most serious acute hyperglycemic emergencies seen in adults, DKA and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
New to the 2023 version will be a strong emphasis on the excess morbidity and mortality risks associated with the increasingly common “hybrid” presentation of the two conditions together, now seen in about a third of cases.
The new report will also more strongly urge clinicians to investigate why the person experienced the emergency.
While new-onset diabetes and infection are recognized precipitating causes for DKA, insulin omission related to finances, mental health, and social determinants should be identified, and patients directed to appropriate resources, said experts previewing the upcoming new report at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“The challenge is, although we were making progress for a long time in terms of those hyperglycemic crises, we’ve really plateaued and there are still people being admitted in large numbers, and when you look more globally even more so,” said American Diabetes Association Chief Science and Medical Officer Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD.
The new consensus report will be jointly endorsed by the ADA, the EASD, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, the Diabetes Technology Society, and the Joint British Diabetes Societies for Inpatient Care. The previous consensus statement on the subject was published in 2009 by the ADA alone.
New DKA and HHS definitions reflect emerging trends
The statement will revise the definition of DKA, partly spurred by the increasing occurrence and recognition of euglycemic ketoacidosis arising from the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. For all patients with hyperglycemic crisis, the hyperglycemia cutoff is now lowered to 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) from the previous 250 mg/dL.
However, the glucose cutoff has been removed entirely for people with a history of diabetes.
“Both of these changes are recognizing the wide range of glucose levels at the presence of DKA. Approximately 10% of DKA occurs with euglycemia or near-normoglycemia,” noted coauthor Shivani Misra, MD, PhD, senior clinical lecturer and honorary consultant in Metabolic Medicine at Imperial College, London.
For assessing ketosis in DKA, the new statement strongly recommends use of beta-hydroxybutyrate – either via point-of-care test or serum level measured in a laboratory – with a low cutoff of ≥ 3.0 mmol/L. Alternatively, a urine ketone strip value of 2+ or greater can be used.
However, beta-hydroxybutyrate testing is more widely available now than it was in 2009 and is strongly preferred over urine ketone measurement because it’s the predominant ketone during acidosis. Moreover, urine acetoacetate – measured by the strips – paradoxically increases during resolution of DKA, and drug interferences can occur with urine ketone measurement, Dr. Misra noted.
Metabolic acidosis is now defined as a pH < 7.3 and/or a bicarbonate concentration < 18 mmol/L, up from 15 in some prior guidelines including the United Kingdom’s. Also, anion gap has been removed from the main definition but, the document will say, can still be used in settings where ketone testing is unavailable.
As previously, the new statement will classify DKA by mild, moderate, and severe but now for the first time there are recommendations of care for each of those levels, as well as for HHS.
For HHS, the glucose cutoff of ≥ 600 mg/dL will stay the same. But now, the effective serum osmolality has been lowered from > 320 to > 300 mOsml/L to account for the effect of dehydration, along with an alternative criteria of total serum osmolality > 320 mOsm/L. The same two changes as with DKA for both ketones and acidosis have also been included for HHS.
Asked to comment, session audience member and independent diabetes industry consultant Charles Alexander, MD, told this news organization, “I liked the proposal to eliminate the anion gap in decision-making and to focus on measurement of blood ketones, principally beta-hydroxybutyrate, in the diagnosis of DKA and monitoring the effect of treatment.
“If someone is on an SGLT2 inhibitor, there is no need to look at blood glucose levels, which may be normal or near normal in the setting of DKA.”
But Dr. Alexander thinks that they should have eliminated glucose levels entirely as part of the DKA/HHS definition even for people without diabetes.
“The problem is that medical education for many years has taught us that DKA is a condition of high blood glucose, but it may not be. It is good that they said blood glucose levels were not important if the patient had a history of diabetes. However, a glucose of 200mg/dL may not be low enough if someone is on an SGLT2 inhibitor. There needs to be a much lower threshold for measuring blood ketones in anyone with nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, regardless of the blood glucose level.”
Acute management: IV fluids, insulin, and potassium
Like the 2009 statement, the new one will include detailed management flowcharts for DKA and HHS, but this time in color. This new statement includes individual algorithms for management with intravenous fluids, insulin, and potassium. Bicarbonate has been removed and relegated to a note at the bottom saying that it should only be considered if pH is < 7.0.
Under fluid treatment, the new statement offers more information about using crystalloids to treat dehydration and a recommendation to add dextrose to IV fluid therapy as a substrate when the glucose drops below 250 mg/dL, in order to prevent hypoglycemia. For euglycemic DKA, the recommendation is to include dextrose and normal saline simultaneously.
And for the first time, subcutaneous rather than IV insulin is considered acceptable for mild, but not moderate or severe, DKA.
Two options are suggested for IV insulin in HHS: The fluid can be given first and low-dose fixed-rate insulin infusion added, or fluids and insulin can be given at the same time.
Criteria for resolution of DKA are a venous pH of ≥ 7.3 or bicarbonate > 18 mmol/L, ketones < 0.6 mmol/L, and glucose ideally < 200 mg/dL (11.0 mmol/L). For HHS, resolution is suggested when the measured or calculated serum osmolality falls to < 300 mosm/kg, blood glucose is < 250mg/dL (13.9 mmol/L), urine output > 0.5 mL/kg/hour, and cognitive status is improved.
The statement also will provide detailed recommended options for transitioning from IV to subcutaneous insulin, but defers to clinical judgment for deciding when the patient can be discharged. The initiation or continuation of SGLT2 inhibitors is not recommended at any time during hospitalization for hyperglycemic crises.
Mitigating complications, preventing recurrence
In addition to listing potential complications of treating hyperglycemic crises, just as the 2009 statement did, the new one will offer mitigation strategies for some of the more common ones. For preventing hypoglycemia, frequent blood glucose monitoring is advised along with adding dextrose to the IV fluids when glucose drops below 250 mg/dL.
For prevention of hypokalemia, which occurs in about half of patients treated for DKA and HHS, the statement recommends potassium monitoring every 4 hours and replacement added to fluids.
Acute kidney injury, also occurring in about half of people treated for DKA and/or HHS, usually resolves with hydration. Daily renal function monitoring is advised.
Preventing recurrence: Many factors beyond clinical
Prevention of recurrence with readmission for DKA and/or HHS, occurring in up to 22% of U.S. patients within 30 days, entails close follow-up within 2-4 weeks after discharge (including via telemedicine), and assessment of possible causes, including mental health disorders and social determinants of health.
Appropriate education should be provided, including “structured education” involving problem-solving, sick day rules, injection techniques, a review of insulin doses, consideration of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), and home ketone testing.
Patients should be provided with an adequate supply of insulin and durable diabetes equipment, along with contact information for health care professionals who can assist them. Social service professionals can be helpful for patients who lack reliable access.
Dr. Gabbay told this news organization, “The eye-opening thing is we tend to typically think of DKA as how people tend to get diagnosed with diabetes and, yes, that’s true, but that’s only a minority of people. Those might be preventable by early screening, but all these other people and the number of recurrent episodes, that’s an area where it’s really a failure of the system where we can do better in ensuring that doesn’t happen.”
Education is only part of it, he stressed. “It’s not just an intelligence thing. It’s social factors, and there can be complex psychological issues and mental health issues. We need to screen for those things when we see someone coming back the second, third, fifth, or sixth time. We’ve all seen that. Just educating them to take their insulin is not the answer. …You’ve got to ask the questions and engage them to go a little deeper.”
Dr. Gabbay is an employee of the ADA. Dr. Alexander has reported being a nonpaid advisor for diaTribe and a consultant for Kinexum. Dr. Misra has received speaker fees from Sanofi and ABCD and an investigator-initiated research grant from Dexcom, and is a trustee for the Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation in the United Kingdom.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2023
Nonhealing Ulcer in a Patient With Crohn Disease
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
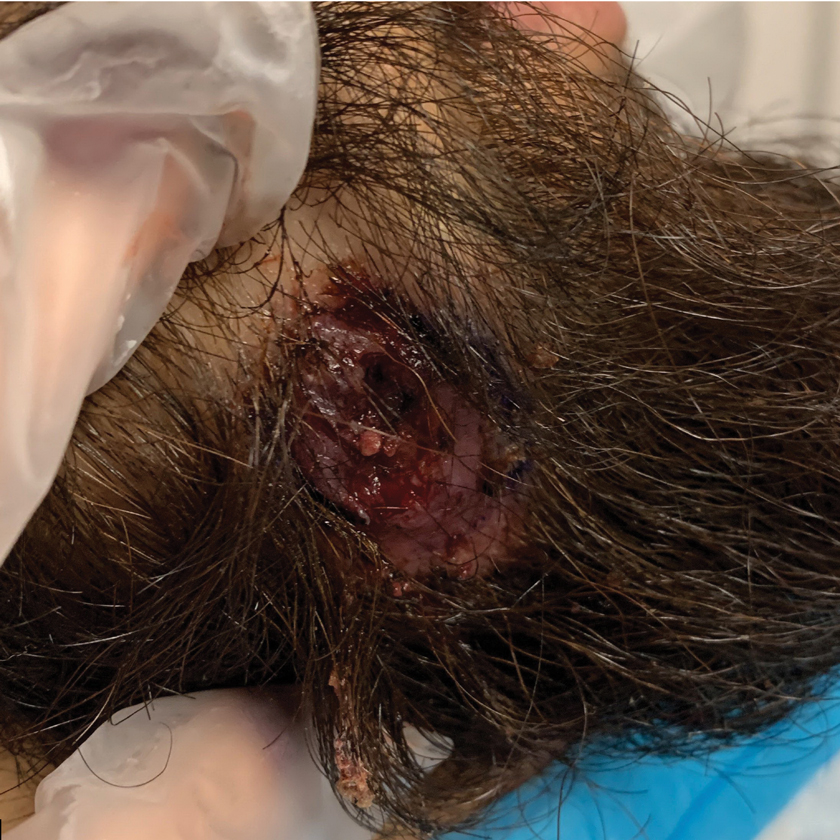
Upon further testing, cultures were positive for Mycobacterium abscessus. Our patient was referred to infectious disease for co-management, and his treatment plan consisted of intravenous amikacin 885 mg 3 times weekly, intravenous imipenem 1 g twice daily, azithromycin 500 mg/d, and omadacycline 150 mg/d for at least 3 months. Magnetic resonance imaging findings were consistent with a combination of cellulitis and osteomyelitis, and our patient was referred to plastic surgery for debridement. He subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Mycobacterium abscessus is classified as both a nontuberculous and rapidly growing mycobacterium. Mycobacterium abscessus recently has emerged as a pathogen of increasing public health concern, especially due to its high rate of antibiotic resistance.1-5 It is highly prevalent in the environment, and infection has been reported from a wide variety of environmental sources.6-8 Immunocompromised individuals, such as our patient, undergoing anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy are at increased risk for infection from all Mycobacterium species.9-11 Recognizing these infections quickly is a priority for patient care, as M abscessus can lead to disseminated infection and high mortality rates.1
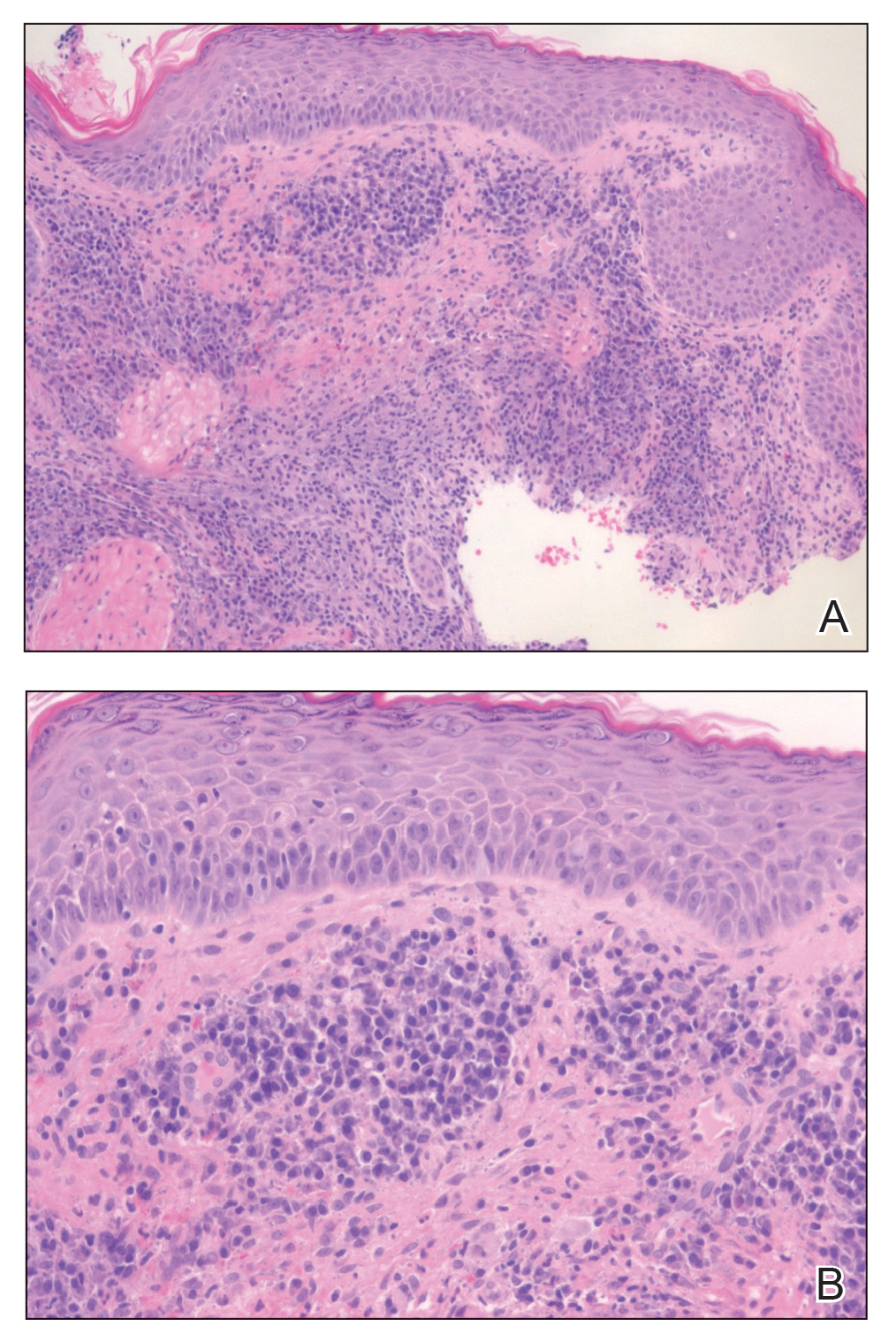
Histopathology of M abscessus consists of granulomatous inflammation with mixed granulomas12; however, these findings are not always appreciable, and staining does not always reveal visible organisms. In our patient, histopathology revealed patchy plasmalymphocytic infiltrates of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, which are signs of generalized inflammation (Figure). Therefore, cultures positive for M abscessus are the gold standard for diagnosis and established the diagnosis in this case.
The differential diagnoses for our patient’s ulceration included squamous cell carcinoma, pyoderma gangrenosum, aseptic abscess ulcer, and pyodermatitispyostomatitis vegetans. Immunosuppressive therapy is a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma13,14; however, ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma typically presents with prominent everted edges with a necrotic tumor base.15 Biopsy reveals cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, large nuclei, and variable keratin pearls.16 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory skin condition associated with Crohn disease and often is a diagnosis of exclusion characterized by neutrophilic infiltrates on biopsy.17-19 Aseptic abscess ulcers are characterized by neutrophil-filled lesions that respond to corticosteroids but not antibiotics.20 Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans is a rare skin manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease associated with a pustular eruption of the skin and/or mouth. Histopathology reveals pustules within or below the epidermis with many eosinophils or neutrophils. Granulomas do not occur as in M abscessus.21
Treatment of M abscessus infection requires the coadministration of several antibiotics across multiple classes to ensure complete disease resolution. High rates of antibiotic resistance are characterized by at least partial resistance to almost every antibiotic; clarithromycin has near-complete efficacy, but resistant strains have started to emerge. Amikacin and cefoxitin are other antibiotics that have reported a resistance rate of less than 50%, but they are only effective 90% and 70% of the time, respectively.1,22 The antibiotic omadacycline, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat acute bacterial skin and soft-tissue infections, also may have utility in treating M abscessus infections.23,24 Finally, phage therapy may offer a potential mode of treatment for this bacterium and was used to treat pulmonary infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis.25 Despite these newer innovations, the current standard of care involves clarithromycin or azithromycin in combination with a parenteral antibiotic such as cefoxitin, amikacin, or imipenem for at least 4 months.1
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Jeong SH, Kim SY, Huh HJ, et al. Mycobacteriological characteristics and treatment outcomes in extrapulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus complex infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;60:49-56.
- Strnad L, Winthrop KL. Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;39:362-376.
- Cardenas DD, Yasmin T, Ahmed S. A rare insidious case of skin and soft tissue infection due to Mycobacterium abscessus: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25725.
- Gonzalez-Santiago TM, Drage LA. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: skin and soft tissue infections. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:563-577.
- Dickison P, Howard V, O’Kane G, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection following penetrations through wetsuits. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;60:57-59.
- Choi H, Kim YI, Na CH, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection associated with shaving activity in a 75-year-old man. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2018;22:204.
- Costa-Silva M, Cesar A, Gomes NP, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection in a spa worker. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27:159-161.
- Besada E. Rapid growing mycobacteria and TNF-α blockers: case report of a fatal lung infection with Mycobacterium abscessus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:705-707.
- Mufti AH, Toye BW, Mckendry RR, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection after use of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor therapy: case report and review of infectious complications associated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor use. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;53:233-238.
- Lee SK, Kim SY, Kim EY, et al. Mycobacterial infections in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in South Korea. Lung. 2013;191:565-571.
- Rodríguez G, Ortegón M, Camargo D, et al. Iatrogenic Mycobacterium abscessus infection: histopathology of 71 patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:214-218.
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:161-168.
- Walker HS, Hardwicke J. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Surgery (Oxford). 2022;40:39-45.
- Browse NL. The skin. In: Browse NL, ed. An Introduction to the Symptoms and Signs of Surgical Disease. 3rd ed. London Arnold Publications; 2001:66-69.
- Weedon D. Squamous cell carcinoma. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010;691-700.
- Powell F, Schroeter A, Su W, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review of 86 patients. QJM Int J Med. 1985;55:173-186.
- Brunsting LA, Goeckerman WH, O’Leary PA. Pyoderma (ecthyma) gangrenosum: clinical and experimental observations in five cases occurring in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:743-768.
- Maverakis E, Ma C, Shinkai K, et al. Diagnostic criteria of ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum: a Delphi consensus of international experts. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:461-466.
- André MFJ, Piette JC, Kémény JL, et al. Aseptic abscesses: a study of 30 patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:145. doi:10.1097/md.0b013e18064f9f3
- Femiano F, Lanza A, Buonaiuto C, et al. Pyostomatitis vegetans: a review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:E114-E117.
- Kasperbauer SH, De Groote MA. The treatment of rapidly growing mycobacterial infections. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:67-78.
- Duah M, Beshay M. Omadacycline in first-line combination therapy for pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infection: a case series. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:953-956.
- Minhas R, Sharma S, Kundu S. Utilizing the promise of omadacycline in a resistant, non-tubercular mycobacterial pulmonary infection. Cureus. 2019;11:E5112.
- Dedrick RM, Guerrero-Bustamante CA, Garlena RA, et al. Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Med. 2019;25:730-733.
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
Upon further testing, cultures were positive for Mycobacterium abscessus. Our patient was referred to infectious disease for co-management, and his treatment plan consisted of intravenous amikacin 885 mg 3 times weekly, intravenous imipenem 1 g twice daily, azithromycin 500 mg/d, and omadacycline 150 mg/d for at least 3 months. Magnetic resonance imaging findings were consistent with a combination of cellulitis and osteomyelitis, and our patient was referred to plastic surgery for debridement. He subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Mycobacterium abscessus is classified as both a nontuberculous and rapidly growing mycobacterium. Mycobacterium abscessus recently has emerged as a pathogen of increasing public health concern, especially due to its high rate of antibiotic resistance.1-5 It is highly prevalent in the environment, and infection has been reported from a wide variety of environmental sources.6-8 Immunocompromised individuals, such as our patient, undergoing anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy are at increased risk for infection from all Mycobacterium species.9-11 Recognizing these infections quickly is a priority for patient care, as M abscessus can lead to disseminated infection and high mortality rates.1
Histopathology of M abscessus consists of granulomatous inflammation with mixed granulomas12; however, these findings are not always appreciable, and staining does not always reveal visible organisms. In our patient, histopathology revealed patchy plasmalymphocytic infiltrates of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, which are signs of generalized inflammation (Figure). Therefore, cultures positive for M abscessus are the gold standard for diagnosis and established the diagnosis in this case.

The differential diagnoses for our patient’s ulceration included squamous cell carcinoma, pyoderma gangrenosum, aseptic abscess ulcer, and pyodermatitispyostomatitis vegetans. Immunosuppressive therapy is a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma13,14; however, ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma typically presents with prominent everted edges with a necrotic tumor base.15 Biopsy reveals cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, large nuclei, and variable keratin pearls.16 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory skin condition associated with Crohn disease and often is a diagnosis of exclusion characterized by neutrophilic infiltrates on biopsy.17-19 Aseptic abscess ulcers are characterized by neutrophil-filled lesions that respond to corticosteroids but not antibiotics.20 Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans is a rare skin manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease associated with a pustular eruption of the skin and/or mouth. Histopathology reveals pustules within or below the epidermis with many eosinophils or neutrophils. Granulomas do not occur as in M abscessus.21
Treatment of M abscessus infection requires the coadministration of several antibiotics across multiple classes to ensure complete disease resolution. High rates of antibiotic resistance are characterized by at least partial resistance to almost every antibiotic; clarithromycin has near-complete efficacy, but resistant strains have started to emerge. Amikacin and cefoxitin are other antibiotics that have reported a resistance rate of less than 50%, but they are only effective 90% and 70% of the time, respectively.1,22 The antibiotic omadacycline, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat acute bacterial skin and soft-tissue infections, also may have utility in treating M abscessus infections.23,24 Finally, phage therapy may offer a potential mode of treatment for this bacterium and was used to treat pulmonary infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis.25 Despite these newer innovations, the current standard of care involves clarithromycin or azithromycin in combination with a parenteral antibiotic such as cefoxitin, amikacin, or imipenem for at least 4 months.1
The Diagnosis: Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
Upon further testing, cultures were positive for Mycobacterium abscessus. Our patient was referred to infectious disease for co-management, and his treatment plan consisted of intravenous amikacin 885 mg 3 times weekly, intravenous imipenem 1 g twice daily, azithromycin 500 mg/d, and omadacycline 150 mg/d for at least 3 months. Magnetic resonance imaging findings were consistent with a combination of cellulitis and osteomyelitis, and our patient was referred to plastic surgery for debridement. He subsequently was lost to follow-up.
Mycobacterium abscessus is classified as both a nontuberculous and rapidly growing mycobacterium. Mycobacterium abscessus recently has emerged as a pathogen of increasing public health concern, especially due to its high rate of antibiotic resistance.1-5 It is highly prevalent in the environment, and infection has been reported from a wide variety of environmental sources.6-8 Immunocompromised individuals, such as our patient, undergoing anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy are at increased risk for infection from all Mycobacterium species.9-11 Recognizing these infections quickly is a priority for patient care, as M abscessus can lead to disseminated infection and high mortality rates.1
Histopathology of M abscessus consists of granulomatous inflammation with mixed granulomas12; however, these findings are not always appreciable, and staining does not always reveal visible organisms. In our patient, histopathology revealed patchy plasmalymphocytic infiltrates of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, which are signs of generalized inflammation (Figure). Therefore, cultures positive for M abscessus are the gold standard for diagnosis and established the diagnosis in this case.

The differential diagnoses for our patient’s ulceration included squamous cell carcinoma, pyoderma gangrenosum, aseptic abscess ulcer, and pyodermatitispyostomatitis vegetans. Immunosuppressive therapy is a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma13,14; however, ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma typically presents with prominent everted edges with a necrotic tumor base.15 Biopsy reveals cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, large nuclei, and variable keratin pearls.16 Pyoderma gangrenosum is an inflammatory skin condition associated with Crohn disease and often is a diagnosis of exclusion characterized by neutrophilic infiltrates on biopsy.17-19 Aseptic abscess ulcers are characterized by neutrophil-filled lesions that respond to corticosteroids but not antibiotics.20 Pyodermatitis-pyostomatitis vegetans is a rare skin manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease associated with a pustular eruption of the skin and/or mouth. Histopathology reveals pustules within or below the epidermis with many eosinophils or neutrophils. Granulomas do not occur as in M abscessus.21
Treatment of M abscessus infection requires the coadministration of several antibiotics across multiple classes to ensure complete disease resolution. High rates of antibiotic resistance are characterized by at least partial resistance to almost every antibiotic; clarithromycin has near-complete efficacy, but resistant strains have started to emerge. Amikacin and cefoxitin are other antibiotics that have reported a resistance rate of less than 50%, but they are only effective 90% and 70% of the time, respectively.1,22 The antibiotic omadacycline, which is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat acute bacterial skin and soft-tissue infections, also may have utility in treating M abscessus infections.23,24 Finally, phage therapy may offer a potential mode of treatment for this bacterium and was used to treat pulmonary infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis.25 Despite these newer innovations, the current standard of care involves clarithromycin or azithromycin in combination with a parenteral antibiotic such as cefoxitin, amikacin, or imipenem for at least 4 months.1
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Jeong SH, Kim SY, Huh HJ, et al. Mycobacteriological characteristics and treatment outcomes in extrapulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus complex infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;60:49-56.
- Strnad L, Winthrop KL. Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;39:362-376.
- Cardenas DD, Yasmin T, Ahmed S. A rare insidious case of skin and soft tissue infection due to Mycobacterium abscessus: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25725.
- Gonzalez-Santiago TM, Drage LA. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: skin and soft tissue infections. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:563-577.
- Dickison P, Howard V, O’Kane G, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection following penetrations through wetsuits. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;60:57-59.
- Choi H, Kim YI, Na CH, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection associated with shaving activity in a 75-year-old man. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2018;22:204.
- Costa-Silva M, Cesar A, Gomes NP, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection in a spa worker. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27:159-161.
- Besada E. Rapid growing mycobacteria and TNF-α blockers: case report of a fatal lung infection with Mycobacterium abscessus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:705-707.
- Mufti AH, Toye BW, Mckendry RR, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection after use of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor therapy: case report and review of infectious complications associated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor use. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;53:233-238.
- Lee SK, Kim SY, Kim EY, et al. Mycobacterial infections in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in South Korea. Lung. 2013;191:565-571.
- Rodríguez G, Ortegón M, Camargo D, et al. Iatrogenic Mycobacterium abscessus infection: histopathology of 71 patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:214-218.
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:161-168.
- Walker HS, Hardwicke J. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Surgery (Oxford). 2022;40:39-45.
- Browse NL. The skin. In: Browse NL, ed. An Introduction to the Symptoms and Signs of Surgical Disease. 3rd ed. London Arnold Publications; 2001:66-69.
- Weedon D. Squamous cell carcinoma. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010;691-700.
- Powell F, Schroeter A, Su W, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review of 86 patients. QJM Int J Med. 1985;55:173-186.
- Brunsting LA, Goeckerman WH, O’Leary PA. Pyoderma (ecthyma) gangrenosum: clinical and experimental observations in five cases occurring in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:743-768.
- Maverakis E, Ma C, Shinkai K, et al. Diagnostic criteria of ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum: a Delphi consensus of international experts. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:461-466.
- André MFJ, Piette JC, Kémény JL, et al. Aseptic abscesses: a study of 30 patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:145. doi:10.1097/md.0b013e18064f9f3
- Femiano F, Lanza A, Buonaiuto C, et al. Pyostomatitis vegetans: a review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:E114-E117.
- Kasperbauer SH, De Groote MA. The treatment of rapidly growing mycobacterial infections. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:67-78.
- Duah M, Beshay M. Omadacycline in first-line combination therapy for pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infection: a case series. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:953-956.
- Minhas R, Sharma S, Kundu S. Utilizing the promise of omadacycline in a resistant, non-tubercular mycobacterial pulmonary infection. Cureus. 2019;11:E5112.
- Dedrick RM, Guerrero-Bustamante CA, Garlena RA, et al. Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Med. 2019;25:730-733.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Jeong SH, Kim SY, Huh HJ, et al. Mycobacteriological characteristics and treatment outcomes in extrapulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus complex infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;60:49-56.
- Strnad L, Winthrop KL. Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus complex. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;39:362-376.
- Cardenas DD, Yasmin T, Ahmed S. A rare insidious case of skin and soft tissue infection due to Mycobacterium abscessus: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25725.
- Gonzalez-Santiago TM, Drage LA. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: skin and soft tissue infections. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:563-577.
- Dickison P, Howard V, O’Kane G, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection following penetrations through wetsuits. Australas J Dermatol. 2019;60:57-59.
- Choi H, Kim YI, Na CH, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus skin infection associated with shaving activity in a 75-year-old man. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2018;22:204.
- Costa-Silva M, Cesar A, Gomes NP, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection in a spa worker. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2018;27:159-161.
- Besada E. Rapid growing mycobacteria and TNF-α blockers: case report of a fatal lung infection with Mycobacterium abscessus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:705-707.
- Mufti AH, Toye BW, Mckendry RR, et al. Mycobacterium abscessus infection after use of tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor therapy: case report and review of infectious complications associated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor use. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;53:233-238.
- Lee SK, Kim SY, Kim EY, et al. Mycobacterial infections in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in South Korea. Lung. 2013;191:565-571.
- Rodríguez G, Ortegón M, Camargo D, et al. Iatrogenic Mycobacterium abscessus infection: histopathology of 71 patients. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:214-218.
- Firnhaber JM. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am Fam Physician. 2012;86:161-168.
- Walker HS, Hardwicke J. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Surgery (Oxford). 2022;40:39-45.
- Browse NL. The skin. In: Browse NL, ed. An Introduction to the Symptoms and Signs of Surgical Disease. 3rd ed. London Arnold Publications; 2001:66-69.
- Weedon D. Squamous cell carcinoma. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010;691-700.
- Powell F, Schroeter A, Su W, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a review of 86 patients. QJM Int J Med. 1985;55:173-186.
- Brunsting LA, Goeckerman WH, O’Leary PA. Pyoderma (ecthyma) gangrenosum: clinical and experimental observations in five cases occurring in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1982;118:743-768.
- Maverakis E, Ma C, Shinkai K, et al. Diagnostic criteria of ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum: a Delphi consensus of international experts. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:461-466.
- André MFJ, Piette JC, Kémény JL, et al. Aseptic abscesses: a study of 30 patients with or without inflammatory bowel disease and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86:145. doi:10.1097/md.0b013e18064f9f3
- Femiano F, Lanza A, Buonaiuto C, et al. Pyostomatitis vegetans: a review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009;14:E114-E117.
- Kasperbauer SH, De Groote MA. The treatment of rapidly growing mycobacterial infections. Clin Chest Med. 2015;36:67-78.
- Duah M, Beshay M. Omadacycline in first-line combination therapy for pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus infection: a case series. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:953-956.
- Minhas R, Sharma S, Kundu S. Utilizing the promise of omadacycline in a resistant, non-tubercular mycobacterial pulmonary infection. Cureus. 2019;11:E5112.
- Dedrick RM, Guerrero-Bustamante CA, Garlena RA, et al. Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drug-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat Med. 2019;25:730-733.
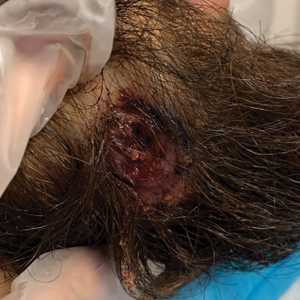
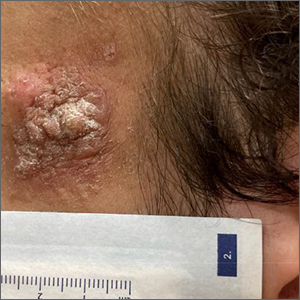
A 24-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic with a painful lesion on the right buccal cheek of 4 months’ duration that had not changed in size or appearance. He had a history of Crohn disease that was being treated with 6-mercaptopurine and infliximab. He underwent jaw surgery 7 years prior for correction of an underbite, followed by subsequent surgery to remove the hardware 1 year after the initial procedure. He experienced recurring skin abscesses following the initial jaw surgery roughly once a year that were treated with bedside incision and drainage procedures in the emergency department followed by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole with complete resolution; however, treatment with mupirocin ointment 2%, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and azithromycin did not provide symptomatic relief or resolution for the current lesion. Physical examination revealed a 4-cm ulceration with actively draining serosanguineous discharge. Two punch biopsies were performed; 48-hour bacterial and fungal cultures, as well as Giemsa, acid-fast bacilli, and periodic acid–Schiff staining were negative.
Take a closer look at sleep’s role in GERD
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
The ongoing longitudinal Nurses’ Health Study has served as an incredible database for evaluating disease states prospectively over decades, thanks to the robust input of its participants. Most recently, this allowed for an important analysis of the association between gastroesophageal reflux (GER) symptoms and sleep quality, the results of which were published in JAMA Network Open.
Approximately 49,000 women with a median age of 59 years (range, 48-69 years) provided data for this analysis. Starting in 2005, they were asked about their experience of GER symptoms. In 2017, they were also asked to respond to a questionnaire, a modified Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). This is a tool we’ve used a lot in prospective studies looking at gastrointestinal diseases and sleep-related abnormalities. It’s unique in that it looks not only at sleep but also at next-day function and daytime sleepiness, which is important here for its implications related to reflux disease and sleep fragmentation.
For those with GER symptoms occurring once a week and more than once a week, the approximate relative risk increased by 30% and 53%, respectively. Clearly, the association of GER symptoms and relative sleep quality was really important.
It should be noted that the PSQI is a disease-independent, validated instrument. It’s not specific to GER disease or any diseases. It’s cross validated across 17 different languages. I think what’s most important about its use in the assessment here is the incorporation of next-day function and asking participants about daytime sleepiness, which we’ll discuss in more detail shortly.
The many causes of interrupted sleep
We’ve all experienced sleep fragmentation, whether in the form of having been on call during our medical training or common experiences like hearing a child cry in the night, a noisy truck pass by, or a dog barking. You may or may not remember that these happened the next day, but they’ve nonetheless interrupted your sleep efficiency.
When you transition laterally across the stages of sleep, that’s what establishes the circadian rhythm and ensures sleep hygiene. Typically, we require approximately 7 hours of restful sleep to do that. But if you fragment or interrupt this process, you more or less move your way erratically through the night, disrupting sleep hygiene and efficiency.
If you have a cognitive awakening during those disruptions, you may recall those events the next day. Or, you may not remember it at all, and such amnestic events are normal for some people with sleep disruptions.
You may also have a sensory arousal, whether it’s due to GER symptoms, auditory stimuli, bumping your toe, or whatever disruptive event. Any of these can cause you to lose that laterality of smooth transition through sleep.
Approximately 20% of the U.S. population have reported GER symptoms at least once a week. Incident data indicate that number may be increasing by as much as 5% a year. Much of that increase is tied to obesity. But nonetheless, it’s a problem on the rise.
It’s important to know this as we start to look at sleep. If GER is acting as a trigger to sleep disruption, you need to ask your patients with this condition about next-day function.
In particular, the next-day function questions to ask are, “How do you feel when you get up? Are you awake and refreshed? Do you have early fatigue? Do you drag yourself out of bed, have daytime somnolence, loss of concentration, or irritability?”
Those are key parameters we can use for looking back to the night before and gauging sleep efficiency. If you’re not asking those questions, you may miss out on identifying a patient having sleep fragmentation.
Sleep’s role in inflammatory disease processes
I now perform an interval assessment of this type not just in my patients with GER disease but across all my patients. I do so because sleep is physiologically important in so many ways.
In patients who have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and a variety of other liver diseases, we’re finding an increased association with sleep fragmentation outside of sleep apnea.
The same is true with irritable bowel and other functional diseases.
When you have sleep fragmentation in inflammatory bowel disease, you turn on a variety of inflammatory proteins (e.g., C-reactive protein) and cytokines, such as interleukins and tumor necrosis factor alpha. These processes may actually tip somebody over to a pro-inflammatory state.
When it comes to what might be considered a relatively simpler condition like GER disease, Ronnie Fass and colleagues showed a number of years ago via Bernstein testing performed in patients with both fragmented and normal sleep that the sensory thresholds all get lowered in the former group. This is irrespective of whether you have a functional symptom or you’re awakened by bumping your toe, a headache, or having heartburn; your sensory thresholds are lower. As a result, the same stimulus provides a higher sense of awareness. By ramping up that awareness, you increase the interference with the next-day function.
We’ve shown that sleep fragmentation affects a variety of things, including immune function. This may be why many people get sick when they travel in between time zones.
There are also implications relating to things like obesity. When you have sleep dysfunction, you have effects on leptin and ghrelin, contrary to what you would normally want to have. This, in turn, causes adverse effects on stimulation or suppression of satiety or appetite. These are things that I counsel my patients about when I talk about reflux as well as those trying to lose weight.
Sleep disruption affects cortisol stimulation and has a significant correlation with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even mortality statistics.
Advice for counseling patients
This latest analysis from the Nurses’ Health Study reminds us that a lot of people have reflux and a lot of people have sleep fragmentation. We need to do better in asking our patients if they have symptoms specific not only to reflux but also to potentially sleep-related complications.
The more we do that, the more we individualize patient treatment rather than treating them as a disease state. This, in turn, will allow us to practice personalized medicine. The more we can engage our patients with reflux disease by asking the right questions about next-day function, the better we can do in improving their outcomes.
It’s time for us all to open our eyes to the value of closing them. Let’s talk to our patients with reflux disease in a little bit of a different light, providing a new perspective on strategies we can use to mitigate and deal with those symptoms, thereby preventing the consequences of sleep fragmentation.
Hopefully, this overview gives you some guidance the next time you have a conversation with your patients. It will apply across many, many disease states, and in almost everything we do in gastroenterology.
David A. Johnson, MD, is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Va., and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. He reported advising with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
The ongoing longitudinal Nurses’ Health Study has served as an incredible database for evaluating disease states prospectively over decades, thanks to the robust input of its participants. Most recently, this allowed for an important analysis of the association between gastroesophageal reflux (GER) symptoms and sleep quality, the results of which were published in JAMA Network Open.
Approximately 49,000 women with a median age of 59 years (range, 48-69 years) provided data for this analysis. Starting in 2005, they were asked about their experience of GER symptoms. In 2017, they were also asked to respond to a questionnaire, a modified Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). This is a tool we’ve used a lot in prospective studies looking at gastrointestinal diseases and sleep-related abnormalities. It’s unique in that it looks not only at sleep but also at next-day function and daytime sleepiness, which is important here for its implications related to reflux disease and sleep fragmentation.
For those with GER symptoms occurring once a week and more than once a week, the approximate relative risk increased by 30% and 53%, respectively. Clearly, the association of GER symptoms and relative sleep quality was really important.
It should be noted that the PSQI is a disease-independent, validated instrument. It’s not specific to GER disease or any diseases. It’s cross validated across 17 different languages. I think what’s most important about its use in the assessment here is the incorporation of next-day function and asking participants about daytime sleepiness, which we’ll discuss in more detail shortly.
The many causes of interrupted sleep
We’ve all experienced sleep fragmentation, whether in the form of having been on call during our medical training or common experiences like hearing a child cry in the night, a noisy truck pass by, or a dog barking. You may or may not remember that these happened the next day, but they’ve nonetheless interrupted your sleep efficiency.
When you transition laterally across the stages of sleep, that’s what establishes the circadian rhythm and ensures sleep hygiene. Typically, we require approximately 7 hours of restful sleep to do that. But if you fragment or interrupt this process, you more or less move your way erratically through the night, disrupting sleep hygiene and efficiency.
If you have a cognitive awakening during those disruptions, you may recall those events the next day. Or, you may not remember it at all, and such amnestic events are normal for some people with sleep disruptions.
You may also have a sensory arousal, whether it’s due to GER symptoms, auditory stimuli, bumping your toe, or whatever disruptive event. Any of these can cause you to lose that laterality of smooth transition through sleep.
Approximately 20% of the U.S. population have reported GER symptoms at least once a week. Incident data indicate that number may be increasing by as much as 5% a year. Much of that increase is tied to obesity. But nonetheless, it’s a problem on the rise.
It’s important to know this as we start to look at sleep. If GER is acting as a trigger to sleep disruption, you need to ask your patients with this condition about next-day function.
In particular, the next-day function questions to ask are, “How do you feel when you get up? Are you awake and refreshed? Do you have early fatigue? Do you drag yourself out of bed, have daytime somnolence, loss of concentration, or irritability?”
Those are key parameters we can use for looking back to the night before and gauging sleep efficiency. If you’re not asking those questions, you may miss out on identifying a patient having sleep fragmentation.
Sleep’s role in inflammatory disease processes
I now perform an interval assessment of this type not just in my patients with GER disease but across all my patients. I do so because sleep is physiologically important in so many ways.
In patients who have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and a variety of other liver diseases, we’re finding an increased association with sleep fragmentation outside of sleep apnea.
The same is true with irritable bowel and other functional diseases.
When you have sleep fragmentation in inflammatory bowel disease, you turn on a variety of inflammatory proteins (e.g., C-reactive protein) and cytokines, such as interleukins and tumor necrosis factor alpha. These processes may actually tip somebody over to a pro-inflammatory state.
When it comes to what might be considered a relatively simpler condition like GER disease, Ronnie Fass and colleagues showed a number of years ago via Bernstein testing performed in patients with both fragmented and normal sleep that the sensory thresholds all get lowered in the former group. This is irrespective of whether you have a functional symptom or you’re awakened by bumping your toe, a headache, or having heartburn; your sensory thresholds are lower. As a result, the same stimulus provides a higher sense of awareness. By ramping up that awareness, you increase the interference with the next-day function.
We’ve shown that sleep fragmentation affects a variety of things, including immune function. This may be why many people get sick when they travel in between time zones.
There are also implications relating to things like obesity. When you have sleep dysfunction, you have effects on leptin and ghrelin, contrary to what you would normally want to have. This, in turn, causes adverse effects on stimulation or suppression of satiety or appetite. These are things that I counsel my patients about when I talk about reflux as well as those trying to lose weight.
Sleep disruption affects cortisol stimulation and has a significant correlation with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even mortality statistics.
Advice for counseling patients
This latest analysis from the Nurses’ Health Study reminds us that a lot of people have reflux and a lot of people have sleep fragmentation. We need to do better in asking our patients if they have symptoms specific not only to reflux but also to potentially sleep-related complications.
The more we do that, the more we individualize patient treatment rather than treating them as a disease state. This, in turn, will allow us to practice personalized medicine. The more we can engage our patients with reflux disease by asking the right questions about next-day function, the better we can do in improving their outcomes.
It’s time for us all to open our eyes to the value of closing them. Let’s talk to our patients with reflux disease in a little bit of a different light, providing a new perspective on strategies we can use to mitigate and deal with those symptoms, thereby preventing the consequences of sleep fragmentation.
Hopefully, this overview gives you some guidance the next time you have a conversation with your patients. It will apply across many, many disease states, and in almost everything we do in gastroenterology.
David A. Johnson, MD, is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Va., and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. He reported advising with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
The ongoing longitudinal Nurses’ Health Study has served as an incredible database for evaluating disease states prospectively over decades, thanks to the robust input of its participants. Most recently, this allowed for an important analysis of the association between gastroesophageal reflux (GER) symptoms and sleep quality, the results of which were published in JAMA Network Open.
Approximately 49,000 women with a median age of 59 years (range, 48-69 years) provided data for this analysis. Starting in 2005, they were asked about their experience of GER symptoms. In 2017, they were also asked to respond to a questionnaire, a modified Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). This is a tool we’ve used a lot in prospective studies looking at gastrointestinal diseases and sleep-related abnormalities. It’s unique in that it looks not only at sleep but also at next-day function and daytime sleepiness, which is important here for its implications related to reflux disease and sleep fragmentation.
For those with GER symptoms occurring once a week and more than once a week, the approximate relative risk increased by 30% and 53%, respectively. Clearly, the association of GER symptoms and relative sleep quality was really important.
It should be noted that the PSQI is a disease-independent, validated instrument. It’s not specific to GER disease or any diseases. It’s cross validated across 17 different languages. I think what’s most important about its use in the assessment here is the incorporation of next-day function and asking participants about daytime sleepiness, which we’ll discuss in more detail shortly.
The many causes of interrupted sleep
We’ve all experienced sleep fragmentation, whether in the form of having been on call during our medical training or common experiences like hearing a child cry in the night, a noisy truck pass by, or a dog barking. You may or may not remember that these happened the next day, but they’ve nonetheless interrupted your sleep efficiency.
When you transition laterally across the stages of sleep, that’s what establishes the circadian rhythm and ensures sleep hygiene. Typically, we require approximately 7 hours of restful sleep to do that. But if you fragment or interrupt this process, you more or less move your way erratically through the night, disrupting sleep hygiene and efficiency.
If you have a cognitive awakening during those disruptions, you may recall those events the next day. Or, you may not remember it at all, and such amnestic events are normal for some people with sleep disruptions.
You may also have a sensory arousal, whether it’s due to GER symptoms, auditory stimuli, bumping your toe, or whatever disruptive event. Any of these can cause you to lose that laterality of smooth transition through sleep.
Approximately 20% of the U.S. population have reported GER symptoms at least once a week. Incident data indicate that number may be increasing by as much as 5% a year. Much of that increase is tied to obesity. But nonetheless, it’s a problem on the rise.
It’s important to know this as we start to look at sleep. If GER is acting as a trigger to sleep disruption, you need to ask your patients with this condition about next-day function.
In particular, the next-day function questions to ask are, “How do you feel when you get up? Are you awake and refreshed? Do you have early fatigue? Do you drag yourself out of bed, have daytime somnolence, loss of concentration, or irritability?”
Those are key parameters we can use for looking back to the night before and gauging sleep efficiency. If you’re not asking those questions, you may miss out on identifying a patient having sleep fragmentation.
Sleep’s role in inflammatory disease processes
I now perform an interval assessment of this type not just in my patients with GER disease but across all my patients. I do so because sleep is physiologically important in so many ways.
In patients who have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and a variety of other liver diseases, we’re finding an increased association with sleep fragmentation outside of sleep apnea.
The same is true with irritable bowel and other functional diseases.
When you have sleep fragmentation in inflammatory bowel disease, you turn on a variety of inflammatory proteins (e.g., C-reactive protein) and cytokines, such as interleukins and tumor necrosis factor alpha. These processes may actually tip somebody over to a pro-inflammatory state.
When it comes to what might be considered a relatively simpler condition like GER disease, Ronnie Fass and colleagues showed a number of years ago via Bernstein testing performed in patients with both fragmented and normal sleep that the sensory thresholds all get lowered in the former group. This is irrespective of whether you have a functional symptom or you’re awakened by bumping your toe, a headache, or having heartburn; your sensory thresholds are lower. As a result, the same stimulus provides a higher sense of awareness. By ramping up that awareness, you increase the interference with the next-day function.
We’ve shown that sleep fragmentation affects a variety of things, including immune function. This may be why many people get sick when they travel in between time zones.
There are also implications relating to things like obesity. When you have sleep dysfunction, you have effects on leptin and ghrelin, contrary to what you would normally want to have. This, in turn, causes adverse effects on stimulation or suppression of satiety or appetite. These are things that I counsel my patients about when I talk about reflux as well as those trying to lose weight.
Sleep disruption affects cortisol stimulation and has a significant correlation with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and even mortality statistics.
Advice for counseling patients
This latest analysis from the Nurses’ Health Study reminds us that a lot of people have reflux and a lot of people have sleep fragmentation. We need to do better in asking our patients if they have symptoms specific not only to reflux but also to potentially sleep-related complications.
The more we do that, the more we individualize patient treatment rather than treating them as a disease state. This, in turn, will allow us to practice personalized medicine. The more we can engage our patients with reflux disease by asking the right questions about next-day function, the better we can do in improving their outcomes.
It’s time for us all to open our eyes to the value of closing them. Let’s talk to our patients with reflux disease in a little bit of a different light, providing a new perspective on strategies we can use to mitigate and deal with those symptoms, thereby preventing the consequences of sleep fragmentation.
Hopefully, this overview gives you some guidance the next time you have a conversation with your patients. It will apply across many, many disease states, and in almost everything we do in gastroenterology.
David A. Johnson, MD, is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Va., and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. He reported advising with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Another day in the ED: Walking the line between empathy and desensitization
Patient after patient, emergency medicine physicians experience highs and lows, sometimes minutes apart. “It might be another Tuesday for us, but for the patient in that dramatic life moment on that day, it’s everything,” said Charissa Pacella, MD, chief of emergency medicine at UPMC Presbyterian in Pittsburgh.
Emergency department (ED) physicians frequently encounter fatal situations, feel frustration when they can’t save a person, and constantly see patients in distress. How do physicians weather the emotional storm of life in the ED with both their mental health and empathy intact?
Reserve time for emotions
Dr. Pacella, who has been practicing emergency medicine for 22 years, also serves in a leadership role for Physicians for Physicians, a confidential peer support program at UPMC for doctors struggling with the impact of adverse events and the stress they face. She said it’s essential to know how to compartmentalize and focus on the task at hand, but later revisit emotions from a personal perspective.
“We all separate our cognitive and leadership roles from our emotional response in the moment,” she said. “Everybody is just focused on doing the next right thing. And often it’s not until sometime later when you sit down or go home or maybe even going in for your next shift that it really hits you in a more emotional way.”
If you try to avoid or skip over this part of the process by shoving the emotions down and ignoring them, Dr. Pacella said, you leave out a crucial part of the care process. And over the course of a career, you’ll risk losing empathy and the human connection that most doctors went into medicine for, she told this news organization.
Connect with your colleagues
Physicians supporting each other is crucial, said Dr Pacella. And luckily, she added, connection tends to be a strength of the specialty.
“As emergency medicine physicians, we share a lot in common, and part of it is what brought us to choose this specialty in the first place. You picked it because there’s something appealing to you about the unknown. It’s a unique role, a unique environment, and a unique relationship you have with patients and being able to connect with colleagues,” she said.
Lisa Williford, MD, emergency medicine specialist at Texas Health Harris Methodist Hospital in Fort Worth, said her 14-year career has taught her that no matter how focused a medical professional can stay in the moment, emotions are happening at some level.
“During a level 1 trauma, there are a lot of people in the room – trauma surgeons, residents, nurses, x-ray techs, respiratory therapy, anesthesia – and every one of us is having emotions. It’s not realistic to think anyone is avoiding it.”
But beyond simply recognizing a shared experience, it’s important to talk to each other. It’s not just about how you’re feeling, but also what you do to help manage that emotional load.
“I’d say that more of us, especially since COVID, are learning that actually getting a therapist is a good thing, having a life coach is a good thing,” said Dr. Williford. Accepting mental health care and learning how to manage it is also a good thing.
Accept unpredictability
You may think you know how a difficult situation will affect you, but that assumption can put you in a vulnerable position. Dr. Pacella said she’s learned that for most physicians, a stress response to a critical incident often has less to do with the type of event and more about who is involved or your past experiences.
“I have reacted in a very emotional way at moments that I would never have expected or predicted,” said Dr. Pacella. “And it’s not always because of some awful event. It’s usually because of some emotional connection or trigger embedded in that encounter.”
For example, she said, you may have had a past case as an emergency physician where the outcome was not favorable, or the patient involved may remind you of yourself or someone you love.
“It might not necessarily be a horrible thing happening to a young, healthy person that triggers someone; it might be a minor problem involving a patient you, for whatever reason, identify with,” she said. “Or you may have had a similar patient where things didn’t go well for them. It’s just highly variable, even for an individual.”
Just as you can’t know what medical issues you’ll face in a day, you can’t predict how you’ll react. Approach each scenario with the knowledge that you may veer off emotional course – and prepare accordingly.
Bring mental wellness to the forefront of training
Dr. Williford, who also serves as regional director for ScribeNest, a doctor-operated company that trains medical scribes who are on the path to becoming medical professionals, said she feels strongly about bringing this conversation to the younger generation.
“For me, nobody at the med school level or residency level taught or talked about how to compartmentalize and cope with the traumatic experiences that we saw,” she said. “Only in the last decade have we started teaching our residents and medical students about burnout and resilience.
“I say things like, ‘Hey, we just witnessed an 18-year-old in cardiac arrest. We did CPR for an hour and didn’t get him back. And then you witnessed me tell his mom, who wailed. And then we turned around and treated an ankle sprain. Let’s sit down and talk about how jarring that all is and how nobody else experiences these things.’
“We have this expectation that our physicians know how to move on and connect with each new patient with care and empathy, but we have to tell our future doctors the actual steps we take to be able to do that.”
Seasoned physicians can lead the way for the next generation and turn the tide toward the normalization of talking about these struggles. By making it part of training, it becomes part of a physician’s skill set.
“With a happy, healthy career, we can pay it forward to the next generation and teach them how to be better than we were,” said Dr. Williford.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patient after patient, emergency medicine physicians experience highs and lows, sometimes minutes apart. “It might be another Tuesday for us, but for the patient in that dramatic life moment on that day, it’s everything,” said Charissa Pacella, MD, chief of emergency medicine at UPMC Presbyterian in Pittsburgh.
Emergency department (ED) physicians frequently encounter fatal situations, feel frustration when they can’t save a person, and constantly see patients in distress. How do physicians weather the emotional storm of life in the ED with both their mental health and empathy intact?
Reserve time for emotions
Dr. Pacella, who has been practicing emergency medicine for 22 years, also serves in a leadership role for Physicians for Physicians, a confidential peer support program at UPMC for doctors struggling with the impact of adverse events and the stress they face. She said it’s essential to know how to compartmentalize and focus on the task at hand, but later revisit emotions from a personal perspective.
“We all separate our cognitive and leadership roles from our emotional response in the moment,” she said. “Everybody is just focused on doing the next right thing. And often it’s not until sometime later when you sit down or go home or maybe even going in for your next shift that it really hits you in a more emotional way.”
If you try to avoid or skip over this part of the process by shoving the emotions down and ignoring them, Dr. Pacella said, you leave out a crucial part of the care process. And over the course of a career, you’ll risk losing empathy and the human connection that most doctors went into medicine for, she told this news organization.
Connect with your colleagues
Physicians supporting each other is crucial, said Dr Pacella. And luckily, she added, connection tends to be a strength of the specialty.
“As emergency medicine physicians, we share a lot in common, and part of it is what brought us to choose this specialty in the first place. You picked it because there’s something appealing to you about the unknown. It’s a unique role, a unique environment, and a unique relationship you have with patients and being able to connect with colleagues,” she said.
Lisa Williford, MD, emergency medicine specialist at Texas Health Harris Methodist Hospital in Fort Worth, said her 14-year career has taught her that no matter how focused a medical professional can stay in the moment, emotions are happening at some level.
“During a level 1 trauma, there are a lot of people in the room – trauma surgeons, residents, nurses, x-ray techs, respiratory therapy, anesthesia – and every one of us is having emotions. It’s not realistic to think anyone is avoiding it.”
But beyond simply recognizing a shared experience, it’s important to talk to each other. It’s not just about how you’re feeling, but also what you do to help manage that emotional load.
“I’d say that more of us, especially since COVID, are learning that actually getting a therapist is a good thing, having a life coach is a good thing,” said Dr. Williford. Accepting mental health care and learning how to manage it is also a good thing.
Accept unpredictability
You may think you know how a difficult situation will affect you, but that assumption can put you in a vulnerable position. Dr. Pacella said she’s learned that for most physicians, a stress response to a critical incident often has less to do with the type of event and more about who is involved or your past experiences.
“I have reacted in a very emotional way at moments that I would never have expected or predicted,” said Dr. Pacella. “And it’s not always because of some awful event. It’s usually because of some emotional connection or trigger embedded in that encounter.”
For example, she said, you may have had a past case as an emergency physician where the outcome was not favorable, or the patient involved may remind you of yourself or someone you love.
“It might not necessarily be a horrible thing happening to a young, healthy person that triggers someone; it might be a minor problem involving a patient you, for whatever reason, identify with,” she said. “Or you may have had a similar patient where things didn’t go well for them. It’s just highly variable, even for an individual.”
Just as you can’t know what medical issues you’ll face in a day, you can’t predict how you’ll react. Approach each scenario with the knowledge that you may veer off emotional course – and prepare accordingly.
Bring mental wellness to the forefront of training
Dr. Williford, who also serves as regional director for ScribeNest, a doctor-operated company that trains medical scribes who are on the path to becoming medical professionals, said she feels strongly about bringing this conversation to the younger generation.
“For me, nobody at the med school level or residency level taught or talked about how to compartmentalize and cope with the traumatic experiences that we saw,” she said. “Only in the last decade have we started teaching our residents and medical students about burnout and resilience.
“I say things like, ‘Hey, we just witnessed an 18-year-old in cardiac arrest. We did CPR for an hour and didn’t get him back. And then you witnessed me tell his mom, who wailed. And then we turned around and treated an ankle sprain. Let’s sit down and talk about how jarring that all is and how nobody else experiences these things.’
“We have this expectation that our physicians know how to move on and connect with each new patient with care and empathy, but we have to tell our future doctors the actual steps we take to be able to do that.”
Seasoned physicians can lead the way for the next generation and turn the tide toward the normalization of talking about these struggles. By making it part of training, it becomes part of a physician’s skill set.
“With a happy, healthy career, we can pay it forward to the next generation and teach them how to be better than we were,” said Dr. Williford.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patient after patient, emergency medicine physicians experience highs and lows, sometimes minutes apart. “It might be another Tuesday for us, but for the patient in that dramatic life moment on that day, it’s everything,” said Charissa Pacella, MD, chief of emergency medicine at UPMC Presbyterian in Pittsburgh.
Emergency department (ED) physicians frequently encounter fatal situations, feel frustration when they can’t save a person, and constantly see patients in distress. How do physicians weather the emotional storm of life in the ED with both their mental health and empathy intact?
Reserve time for emotions
Dr. Pacella, who has been practicing emergency medicine for 22 years, also serves in a leadership role for Physicians for Physicians, a confidential peer support program at UPMC for doctors struggling with the impact of adverse events and the stress they face. She said it’s essential to know how to compartmentalize and focus on the task at hand, but later revisit emotions from a personal perspective.
“We all separate our cognitive and leadership roles from our emotional response in the moment,” she said. “Everybody is just focused on doing the next right thing. And often it’s not until sometime later when you sit down or go home or maybe even going in for your next shift that it really hits you in a more emotional way.”
If you try to avoid or skip over this part of the process by shoving the emotions down and ignoring them, Dr. Pacella said, you leave out a crucial part of the care process. And over the course of a career, you’ll risk losing empathy and the human connection that most doctors went into medicine for, she told this news organization.
Connect with your colleagues
Physicians supporting each other is crucial, said Dr Pacella. And luckily, she added, connection tends to be a strength of the specialty.
“As emergency medicine physicians, we share a lot in common, and part of it is what brought us to choose this specialty in the first place. You picked it because there’s something appealing to you about the unknown. It’s a unique role, a unique environment, and a unique relationship you have with patients and being able to connect with colleagues,” she said.
Lisa Williford, MD, emergency medicine specialist at Texas Health Harris Methodist Hospital in Fort Worth, said her 14-year career has taught her that no matter how focused a medical professional can stay in the moment, emotions are happening at some level.
“During a level 1 trauma, there are a lot of people in the room – trauma surgeons, residents, nurses, x-ray techs, respiratory therapy, anesthesia – and every one of us is having emotions. It’s not realistic to think anyone is avoiding it.”
But beyond simply recognizing a shared experience, it’s important to talk to each other. It’s not just about how you’re feeling, but also what you do to help manage that emotional load.
“I’d say that more of us, especially since COVID, are learning that actually getting a therapist is a good thing, having a life coach is a good thing,” said Dr. Williford. Accepting mental health care and learning how to manage it is also a good thing.
Accept unpredictability
You may think you know how a difficult situation will affect you, but that assumption can put you in a vulnerable position. Dr. Pacella said she’s learned that for most physicians, a stress response to a critical incident often has less to do with the type of event and more about who is involved or your past experiences.
“I have reacted in a very emotional way at moments that I would never have expected or predicted,” said Dr. Pacella. “And it’s not always because of some awful event. It’s usually because of some emotional connection or trigger embedded in that encounter.”
For example, she said, you may have had a past case as an emergency physician where the outcome was not favorable, or the patient involved may remind you of yourself or someone you love.
“It might not necessarily be a horrible thing happening to a young, healthy person that triggers someone; it might be a minor problem involving a patient you, for whatever reason, identify with,” she said. “Or you may have had a similar patient where things didn’t go well for them. It’s just highly variable, even for an individual.”
Just as you can’t know what medical issues you’ll face in a day, you can’t predict how you’ll react. Approach each scenario with the knowledge that you may veer off emotional course – and prepare accordingly.
Bring mental wellness to the forefront of training
Dr. Williford, who also serves as regional director for ScribeNest, a doctor-operated company that trains medical scribes who are on the path to becoming medical professionals, said she feels strongly about bringing this conversation to the younger generation.
“For me, nobody at the med school level or residency level taught or talked about how to compartmentalize and cope with the traumatic experiences that we saw,” she said. “Only in the last decade have we started teaching our residents and medical students about burnout and resilience.
“I say things like, ‘Hey, we just witnessed an 18-year-old in cardiac arrest. We did CPR for an hour and didn’t get him back. And then you witnessed me tell his mom, who wailed. And then we turned around and treated an ankle sprain. Let’s sit down and talk about how jarring that all is and how nobody else experiences these things.’
“We have this expectation that our physicians know how to move on and connect with each new patient with care and empathy, but we have to tell our future doctors the actual steps we take to be able to do that.”
Seasoned physicians can lead the way for the next generation and turn the tide toward the normalization of talking about these struggles. By making it part of training, it becomes part of a physician’s skill set.
“With a happy, healthy career, we can pay it forward to the next generation and teach them how to be better than we were,” said Dr. Williford.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Young women rate top sources for STI self-testing
, based on surveys from 92 individuals.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening methods involve the use of self-collected samples outside of a clinical setting, and may help reach women who avoid screening or lack access to clinical care, wrote Stacey B. Griner, PhD, of the University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, and colleagues.
However, data on the methods used to promote DTC to the young female population are limited, and the goal of the current study was to identify preferred sources and communication channels for DTC STI information in this population, they said.
In a study published in Sexually Transmitted Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from 92 women aged 18-24 years at a single university who participated in an online survey. Of these, 24 also participated in in-depth interviews. The mean age of the participants was 20.0 years, and all reported being sexually active in the past year. Approximately two-thirds (68.5%) were White, 24% were Hispanic, 13% were Black or African American; 63.0% overall were heterosexual.
Participants received a description of DTC methods and were asked whether they were interested in receiving more information, and if so, what were their preferred sources for receiving the information. Potential sources included health care providers, friends, family members, partners, the Internet, college resources, classes, and other, and participants were asked to rank these choices in order of preference.
More than half of the participants identified health care providers as their preferred source of information (56.5%), followed by trusted websites (25%), and university-based resources or friends (6.5% for both).
Overall, participants who underwent STI screening in the past 12 months ranked college resources higher than those who had not undergone screening.
Race played a significant role in ranking partners and family members as resources. Compared with Black participants, White participants and those who were biracial/multiracial/another race ranked partners as a significantly more preferred source, but the differences between White and biracial/multiracial/another race were not significant. White participants and Black participants were similar in ranking family as a preferred information source, but White participants, compared with biracial/multiracial/other participants, ranked family as a significantly more preferred source.
Differences in rankings were similar across sexual orientations.
In-depth interviews were conducted on the college campus prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. The mean age of the interview participants was 19.5 years, and most were non-Hispanic White. Sexual orientation was varied, with 50% identifying as heterosexual and 50% identifying as a sexual minority.
In the interviews, health care providers were seen as influential for considering DTC methods, with gynecologists, other specialists, and more experienced physicians deemed the most trustworthy. Interviewees noted social media sites as a way to provide information and raise awareness of DTC methods, such as through the advertisements feature on Instagram. They also identified university orientation as a way to reach students and provide information about DTC options in the context of other health-related orientation topics such as sexual consent and alcohol use.
Many interviewees also mentioned friends as a resource for discussing sex, sexuality, and STI screening, and said they would be accepting of information, knowledge, and emotional support when learning about DTC from friends.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the cross-sectional design, use of data from a single campus setting, and the overrepresentation of White women, and more studies are needed to identify differences by region and campus type that might guide interventions, the researchers noted. The study also was limited by “the lack of specificity of what participants considered to be credible Internet information sources,” they said.
However, the results suggest that using health care providers, trusted websites, and established college resources as dissemination channels may help increase the awareness and use of DTC methods for STI screening in young women, they concluded.
The study was supported in part by the Doug Kirby Adolescent Sexual Health Research Grant from the Rural Center for AIDS/STD Prevention at Indiana University and by the University of South Florida College of Public Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on surveys from 92 individuals.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening methods involve the use of self-collected samples outside of a clinical setting, and may help reach women who avoid screening or lack access to clinical care, wrote Stacey B. Griner, PhD, of the University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, and colleagues.
However, data on the methods used to promote DTC to the young female population are limited, and the goal of the current study was to identify preferred sources and communication channels for DTC STI information in this population, they said.
In a study published in Sexually Transmitted Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from 92 women aged 18-24 years at a single university who participated in an online survey. Of these, 24 also participated in in-depth interviews. The mean age of the participants was 20.0 years, and all reported being sexually active in the past year. Approximately two-thirds (68.5%) were White, 24% were Hispanic, 13% were Black or African American; 63.0% overall were heterosexual.
Participants received a description of DTC methods and were asked whether they were interested in receiving more information, and if so, what were their preferred sources for receiving the information. Potential sources included health care providers, friends, family members, partners, the Internet, college resources, classes, and other, and participants were asked to rank these choices in order of preference.
More than half of the participants identified health care providers as their preferred source of information (56.5%), followed by trusted websites (25%), and university-based resources or friends (6.5% for both).
Overall, participants who underwent STI screening in the past 12 months ranked college resources higher than those who had not undergone screening.
Race played a significant role in ranking partners and family members as resources. Compared with Black participants, White participants and those who were biracial/multiracial/another race ranked partners as a significantly more preferred source, but the differences between White and biracial/multiracial/another race were not significant. White participants and Black participants were similar in ranking family as a preferred information source, but White participants, compared with biracial/multiracial/other participants, ranked family as a significantly more preferred source.
Differences in rankings were similar across sexual orientations.
In-depth interviews were conducted on the college campus prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. The mean age of the interview participants was 19.5 years, and most were non-Hispanic White. Sexual orientation was varied, with 50% identifying as heterosexual and 50% identifying as a sexual minority.
In the interviews, health care providers were seen as influential for considering DTC methods, with gynecologists, other specialists, and more experienced physicians deemed the most trustworthy. Interviewees noted social media sites as a way to provide information and raise awareness of DTC methods, such as through the advertisements feature on Instagram. They also identified university orientation as a way to reach students and provide information about DTC options in the context of other health-related orientation topics such as sexual consent and alcohol use.
Many interviewees also mentioned friends as a resource for discussing sex, sexuality, and STI screening, and said they would be accepting of information, knowledge, and emotional support when learning about DTC from friends.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the cross-sectional design, use of data from a single campus setting, and the overrepresentation of White women, and more studies are needed to identify differences by region and campus type that might guide interventions, the researchers noted. The study also was limited by “the lack of specificity of what participants considered to be credible Internet information sources,” they said.
However, the results suggest that using health care providers, trusted websites, and established college resources as dissemination channels may help increase the awareness and use of DTC methods for STI screening in young women, they concluded.
The study was supported in part by the Doug Kirby Adolescent Sexual Health Research Grant from the Rural Center for AIDS/STD Prevention at Indiana University and by the University of South Florida College of Public Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on surveys from 92 individuals.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening methods involve the use of self-collected samples outside of a clinical setting, and may help reach women who avoid screening or lack access to clinical care, wrote Stacey B. Griner, PhD, of the University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, and colleagues.
However, data on the methods used to promote DTC to the young female population are limited, and the goal of the current study was to identify preferred sources and communication channels for DTC STI information in this population, they said.
In a study published in Sexually Transmitted Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from 92 women aged 18-24 years at a single university who participated in an online survey. Of these, 24 also participated in in-depth interviews. The mean age of the participants was 20.0 years, and all reported being sexually active in the past year. Approximately two-thirds (68.5%) were White, 24% were Hispanic, 13% were Black or African American; 63.0% overall were heterosexual.
Participants received a description of DTC methods and were asked whether they were interested in receiving more information, and if so, what were their preferred sources for receiving the information. Potential sources included health care providers, friends, family members, partners, the Internet, college resources, classes, and other, and participants were asked to rank these choices in order of preference.
More than half of the participants identified health care providers as their preferred source of information (56.5%), followed by trusted websites (25%), and university-based resources or friends (6.5% for both).
Overall, participants who underwent STI screening in the past 12 months ranked college resources higher than those who had not undergone screening.
Race played a significant role in ranking partners and family members as resources. Compared with Black participants, White participants and those who were biracial/multiracial/another race ranked partners as a significantly more preferred source, but the differences between White and biracial/multiracial/another race were not significant. White participants and Black participants were similar in ranking family as a preferred information source, but White participants, compared with biracial/multiracial/other participants, ranked family as a significantly more preferred source.
Differences in rankings were similar across sexual orientations.
In-depth interviews were conducted on the college campus prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. The mean age of the interview participants was 19.5 years, and most were non-Hispanic White. Sexual orientation was varied, with 50% identifying as heterosexual and 50% identifying as a sexual minority.
In the interviews, health care providers were seen as influential for considering DTC methods, with gynecologists, other specialists, and more experienced physicians deemed the most trustworthy. Interviewees noted social media sites as a way to provide information and raise awareness of DTC methods, such as through the advertisements feature on Instagram. They also identified university orientation as a way to reach students and provide information about DTC options in the context of other health-related orientation topics such as sexual consent and alcohol use.
Many interviewees also mentioned friends as a resource for discussing sex, sexuality, and STI screening, and said they would be accepting of information, knowledge, and emotional support when learning about DTC from friends.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the cross-sectional design, use of data from a single campus setting, and the overrepresentation of White women, and more studies are needed to identify differences by region and campus type that might guide interventions, the researchers noted. The study also was limited by “the lack of specificity of what participants considered to be credible Internet information sources,” they said.
However, the results suggest that using health care providers, trusted websites, and established college resources as dissemination channels may help increase the awareness and use of DTC methods for STI screening in young women, they concluded.
The study was supported in part by the Doug Kirby Adolescent Sexual Health Research Grant from the Rural Center for AIDS/STD Prevention at Indiana University and by the University of South Florida College of Public Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
Management of Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Paxlovid tied to benefits in high-risk patients with COVID
In a cohort study from British Columbia that included nearly 7,000 patients with COVID-19, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a 2.5% reduction in risk for death or emergency hospitalization in clinically extremely vulnerable (CEV) patients who were severely immunocompromised. No significant benefit was observed in patients who were not immunocompromised.
“This finding could help substantially limit unnecessary use of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in older, otherwise healthy individuals,” lead author Colin R. Dormuth, ScD, associate professor of anesthesiology, pharmacology, and therapeutics at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, told this news organization. “Another finding that was surprising and might help place the role of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in context is that even in severely immunocompromised individuals who did not take [the drug], the risk of death or hospitalization with COVID-19 was less than 4% in our study population.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Who benefits?
The investigators analyzed medical records for 6,866 patients in British Columbia (median age, 70 years; 57% women) who presented between Feb. 1, 2022, and Feb. 3, 2023. Eligible patients belonged to one of four higher-risk groups who received priority for COVID-19 vaccination.
Two groups included CEV patients who were severely (CEV1) or moderately (CEV2) immunocompromised. The CEV3 group was not immunocompromised but had medical conditions associated with a high risk for complications from COVID-19. A fourth expanded eligibility (EXEL) group included higher-risk patients who were not in one of the other groups, such as unvaccinated patients older than age 70 years.
The investigators matched treated patients to untreated patients in the same vulnerability group according to age, sex, and month of infection. The primary outcome was death from any cause or emergency hospitalization with COVID-19 within 28 days.
Treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with statistically significant relative reductions in the primary outcome, compared with no treatment, for patients in the CEV1 (risk difference, −2.5%) and CEV2 (RD, −1.7%) groups. In the CEV3 group, the RD of −1.3% was not statistically significant. In the EXEL group, treatment was associated with a higher risk for the primary outcome (RD, 1.0%), but the result was not statistically significant.
The results were “robust across sex and older vs. younger age,” the authors note. “No reduction in the primary outcome was observed in lower-risk individuals, including those aged 70 years or older without serious comorbidities.”
The combination of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was approved for use in Canada based on interim efficacy and safety data from the Evaluation of Inhibition for COVID-19 in High-Risk Patients (EPIC-HR) trial, said Dr. Dormuth.
British Columbia’s eligibility criteria for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir coverage differ substantially from the criteria for participants in the EPIC-HR trial, he noted. Those patients were unvaccinated, had no natural immunity from a previous COVID-19 infection, and were infected with COVID-19 variants that were different from those now circulating. The current study was prompted by the need to look at a broader population of individuals in British Columbia with varying risks of complications from COVID-19 infection.
Before the study, a common view was that patients aged 70 and older would benefit from the drug, said Dr. Dormuth. “Our study, which accounted for medical conditions related to an individual’s vulnerability to complications, showed that older age on its own was not a reason to use nirmatrelvir and ritonavir once relevant medical conditions were taken into consideration.”
The researchers are working on a study to identify with greater specificity which comorbid conditions are most associated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir effectiveness, he added. “It could be that a relatively small number of conditions can be used to identify most individuals who would benefit from the drug.”
‘Signal toward benefit’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Abhijit Duggal, MD, vice chair of critical care at the Cleveland Clinic, who was not involved in this study, said, “I’m always very wary when we look at observational data and we start saying the effectiveness is not really as high as was seen in other studies. We are seeing an effect with all these studies that seems to be in the right direction.
“Having said that,” he added, “is the effect going to be potentially more in patients at higher risk? Absolutely. I think these postmarket studies are really showing that after vaccination, if someone does get infected, this is a secondary option available to us that can prevent progression of the disease, which would likely be more severe in immunocompromised patients.”
Dr. Duggal was a coinvestigator on a recent study of more than 68,000 patients that showed that nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir was associated with reductions in mortality and hospitalization in nonhospitalized patients infected with the Omicron variant, regardless of age, race and ethnicity, virus strain, vaccination status, previous infection status, or coexisting conditions.
“In all groups, there was a signal toward benefit,” said Dr. Duggal. “These studies tell us that these drugs do remain valid options. But their use needs to be discussed on a case-by-case basis with patients we feel are deteriorating or at a higher risk because of underlying disease processes.”
The study was supported by funding from the British Columbia Ministry of Health. Dr. Dormuth and Dr. Duggal report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cohort study from British Columbia that included nearly 7,000 patients with COVID-19, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a 2.5% reduction in risk for death or emergency hospitalization in clinically extremely vulnerable (CEV) patients who were severely immunocompromised. No significant benefit was observed in patients who were not immunocompromised.
“This finding could help substantially limit unnecessary use of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in older, otherwise healthy individuals,” lead author Colin R. Dormuth, ScD, associate professor of anesthesiology, pharmacology, and therapeutics at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, told this news organization. “Another finding that was surprising and might help place the role of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in context is that even in severely immunocompromised individuals who did not take [the drug], the risk of death or hospitalization with COVID-19 was less than 4% in our study population.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Who benefits?
The investigators analyzed medical records for 6,866 patients in British Columbia (median age, 70 years; 57% women) who presented between Feb. 1, 2022, and Feb. 3, 2023. Eligible patients belonged to one of four higher-risk groups who received priority for COVID-19 vaccination.
Two groups included CEV patients who were severely (CEV1) or moderately (CEV2) immunocompromised. The CEV3 group was not immunocompromised but had medical conditions associated with a high risk for complications from COVID-19. A fourth expanded eligibility (EXEL) group included higher-risk patients who were not in one of the other groups, such as unvaccinated patients older than age 70 years.
The investigators matched treated patients to untreated patients in the same vulnerability group according to age, sex, and month of infection. The primary outcome was death from any cause or emergency hospitalization with COVID-19 within 28 days.
Treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with statistically significant relative reductions in the primary outcome, compared with no treatment, for patients in the CEV1 (risk difference, −2.5%) and CEV2 (RD, −1.7%) groups. In the CEV3 group, the RD of −1.3% was not statistically significant. In the EXEL group, treatment was associated with a higher risk for the primary outcome (RD, 1.0%), but the result was not statistically significant.
The results were “robust across sex and older vs. younger age,” the authors note. “No reduction in the primary outcome was observed in lower-risk individuals, including those aged 70 years or older without serious comorbidities.”
The combination of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was approved for use in Canada based on interim efficacy and safety data from the Evaluation of Inhibition for COVID-19 in High-Risk Patients (EPIC-HR) trial, said Dr. Dormuth.
British Columbia’s eligibility criteria for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir coverage differ substantially from the criteria for participants in the EPIC-HR trial, he noted. Those patients were unvaccinated, had no natural immunity from a previous COVID-19 infection, and were infected with COVID-19 variants that were different from those now circulating. The current study was prompted by the need to look at a broader population of individuals in British Columbia with varying risks of complications from COVID-19 infection.
Before the study, a common view was that patients aged 70 and older would benefit from the drug, said Dr. Dormuth. “Our study, which accounted for medical conditions related to an individual’s vulnerability to complications, showed that older age on its own was not a reason to use nirmatrelvir and ritonavir once relevant medical conditions were taken into consideration.”
The researchers are working on a study to identify with greater specificity which comorbid conditions are most associated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir effectiveness, he added. “It could be that a relatively small number of conditions can be used to identify most individuals who would benefit from the drug.”
‘Signal toward benefit’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Abhijit Duggal, MD, vice chair of critical care at the Cleveland Clinic, who was not involved in this study, said, “I’m always very wary when we look at observational data and we start saying the effectiveness is not really as high as was seen in other studies. We are seeing an effect with all these studies that seems to be in the right direction.
“Having said that,” he added, “is the effect going to be potentially more in patients at higher risk? Absolutely. I think these postmarket studies are really showing that after vaccination, if someone does get infected, this is a secondary option available to us that can prevent progression of the disease, which would likely be more severe in immunocompromised patients.”
Dr. Duggal was a coinvestigator on a recent study of more than 68,000 patients that showed that nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir was associated with reductions in mortality and hospitalization in nonhospitalized patients infected with the Omicron variant, regardless of age, race and ethnicity, virus strain, vaccination status, previous infection status, or coexisting conditions.
“In all groups, there was a signal toward benefit,” said Dr. Duggal. “These studies tell us that these drugs do remain valid options. But their use needs to be discussed on a case-by-case basis with patients we feel are deteriorating or at a higher risk because of underlying disease processes.”
The study was supported by funding from the British Columbia Ministry of Health. Dr. Dormuth and Dr. Duggal report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cohort study from British Columbia that included nearly 7,000 patients with COVID-19, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a 2.5% reduction in risk for death or emergency hospitalization in clinically extremely vulnerable (CEV) patients who were severely immunocompromised. No significant benefit was observed in patients who were not immunocompromised.
“This finding could help substantially limit unnecessary use of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in older, otherwise healthy individuals,” lead author Colin R. Dormuth, ScD, associate professor of anesthesiology, pharmacology, and therapeutics at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, told this news organization. “Another finding that was surprising and might help place the role of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir in context is that even in severely immunocompromised individuals who did not take [the drug], the risk of death or hospitalization with COVID-19 was less than 4% in our study population.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Who benefits?
The investigators analyzed medical records for 6,866 patients in British Columbia (median age, 70 years; 57% women) who presented between Feb. 1, 2022, and Feb. 3, 2023. Eligible patients belonged to one of four higher-risk groups who received priority for COVID-19 vaccination.
Two groups included CEV patients who were severely (CEV1) or moderately (CEV2) immunocompromised. The CEV3 group was not immunocompromised but had medical conditions associated with a high risk for complications from COVID-19. A fourth expanded eligibility (EXEL) group included higher-risk patients who were not in one of the other groups, such as unvaccinated patients older than age 70 years.
The investigators matched treated patients to untreated patients in the same vulnerability group according to age, sex, and month of infection. The primary outcome was death from any cause or emergency hospitalization with COVID-19 within 28 days.
Treatment with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with statistically significant relative reductions in the primary outcome, compared with no treatment, for patients in the CEV1 (risk difference, −2.5%) and CEV2 (RD, −1.7%) groups. In the CEV3 group, the RD of −1.3% was not statistically significant. In the EXEL group, treatment was associated with a higher risk for the primary outcome (RD, 1.0%), but the result was not statistically significant.
The results were “robust across sex and older vs. younger age,” the authors note. “No reduction in the primary outcome was observed in lower-risk individuals, including those aged 70 years or older without serious comorbidities.”
The combination of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was approved for use in Canada based on interim efficacy and safety data from the Evaluation of Inhibition for COVID-19 in High-Risk Patients (EPIC-HR) trial, said Dr. Dormuth.
British Columbia’s eligibility criteria for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir coverage differ substantially from the criteria for participants in the EPIC-HR trial, he noted. Those patients were unvaccinated, had no natural immunity from a previous COVID-19 infection, and were infected with COVID-19 variants that were different from those now circulating. The current study was prompted by the need to look at a broader population of individuals in British Columbia with varying risks of complications from COVID-19 infection.
Before the study, a common view was that patients aged 70 and older would benefit from the drug, said Dr. Dormuth. “Our study, which accounted for medical conditions related to an individual’s vulnerability to complications, showed that older age on its own was not a reason to use nirmatrelvir and ritonavir once relevant medical conditions were taken into consideration.”
The researchers are working on a study to identify with greater specificity which comorbid conditions are most associated with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir effectiveness, he added. “It could be that a relatively small number of conditions can be used to identify most individuals who would benefit from the drug.”
‘Signal toward benefit’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, Abhijit Duggal, MD, vice chair of critical care at the Cleveland Clinic, who was not involved in this study, said, “I’m always very wary when we look at observational data and we start saying the effectiveness is not really as high as was seen in other studies. We are seeing an effect with all these studies that seems to be in the right direction.
“Having said that,” he added, “is the effect going to be potentially more in patients at higher risk? Absolutely. I think these postmarket studies are really showing that after vaccination, if someone does get infected, this is a secondary option available to us that can prevent progression of the disease, which would likely be more severe in immunocompromised patients.”
Dr. Duggal was a coinvestigator on a recent study of more than 68,000 patients that showed that nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir was associated with reductions in mortality and hospitalization in nonhospitalized patients infected with the Omicron variant, regardless of age, race and ethnicity, virus strain, vaccination status, previous infection status, or coexisting conditions.
“In all groups, there was a signal toward benefit,” said Dr. Duggal. “These studies tell us that these drugs do remain valid options. But their use needs to be discussed on a case-by-case basis with patients we feel are deteriorating or at a higher risk because of underlying disease processes.”
The study was supported by funding from the British Columbia Ministry of Health. Dr. Dormuth and Dr. Duggal report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Spreading out daily meals and snacks may boost heart failure survival
CLEVELAND – , an observational study suggests.
The new findings, based primarily on 15 years of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), may argue against time-restricted diet interventions like intermittent fasting for patients with HF, researchers say.
The study’s nearly 1,000 participants on medical therapy for HF reported a mean daily eating window of 11 hours and daily average of four “eating occasions,” defined as meals or snacks of at least 50 kcal.
A daily eating window of 11 or more hours, compared with less than 11 hours, corresponded to a greater than 40% drop in risk for CV mortality (P = .013) over 5-6 years, reported Hayley E. Billingsley, RD, CEP, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Va,, at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The analysis adjusted for caloric intake, daily number of eating occasions, body mass index (BMI), history of CV disease and cancer, diabetes, and a slew of other potential confounders.
Prior evidence, mostly from healthy people, has suggested that extended fasting during the day is associated with less physical activity, Ms. Billingsley said in an interview. So it may be that people with HF who spread out their calorie intake are more active throughout the day.
A longer time window for eating, therefore, may have indirect metabolic benefits and help preserve their lean body mass, possibly reducing CV risk in a patient group at risk for muscle wasting.
The findings add to earlier evidence from Ms. Billingsley’s center that suggests that expanded daily time windows for eating, especially later final food rather than earlier first food, may help boost CV fitness for patients with obesity and HF with preserved ejection fraction.
Intermittent fasting and other practices involving the timing of food intake have been studied for weight loss and metabolic health in mostly healthy people and patients with diabetes, she noted. “But it’s really underexplored in people with established cardiovascular disease.”
On the basis of admittedly “very preliminary” findings, it may be that some patients should not shorten their daily time windows for eating or engage in intermittent fasting, Ms. Billingsley said. It’s probably worth considering, before the approach is recommended, “what their risk is for malnutrition or sarcopenia.”
The current study included 991 persons who entered the NHANES database from 2003 to 2018. The patients self-identified as having HF, reported taking medications commonly prescribed in HF, and provided at least two “reliable” dietary recalls.
The average age of the patients was 68 years, and they had had HF for a mean of 9.5 years; 47% were women, three-fourths were White persons, two thirds had dyslipidemia, and a quarter had a history of cancer.
On average, their first eating occasion of the day was at about 8:30 a.m., and the last occasion was at about 7:30 p.m., for a time window of about 11 hours; daily calorie consumption averaged about 1,830 kcal.
About 52% died over the mean follow-up of 69 months; about 44% of deaths were from CV causes.
In a model adjusted for demographics, BMI, smoking status, times of eating occasions, CV disease, diabetes, and cancer history, the all-cause mortality hazard ratio for time windows ≥ 11 hours vs. < 11 hours was 0.236 (95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.715; P = .011).
The reduction was no longer significant on further adjustment for duration of HF, a score reflecting difficulty walking, nightly hours of sleep (which averaged 7.2 hours), daily number of eating occasions, and caloric intake, Ms. Billingsley reported.
But in the fully adjusted analysis, the HR for CV mortality for the longer vs. shorter time window was 0.368 (95% CI, 0.169-0.803; P = .013).
The issue deserves further exploration in a randomized trial, Ms. Billingsley proposed, perhaps one in which patients with HF wear accelerometers to track daily activity levels. “We’d love to do a pilot study of extending their eating window that really digs into what the mechanism of any benefit might be if we assign them to a longer time window and whether it’s related to physical activity.”
Ms. Billingsley reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CLEVELAND – , an observational study suggests.
The new findings, based primarily on 15 years of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), may argue against time-restricted diet interventions like intermittent fasting for patients with HF, researchers say.
The study’s nearly 1,000 participants on medical therapy for HF reported a mean daily eating window of 11 hours and daily average of four “eating occasions,” defined as meals or snacks of at least 50 kcal.
A daily eating window of 11 or more hours, compared with less than 11 hours, corresponded to a greater than 40% drop in risk for CV mortality (P = .013) over 5-6 years, reported Hayley E. Billingsley, RD, CEP, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Va,, at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The analysis adjusted for caloric intake, daily number of eating occasions, body mass index (BMI), history of CV disease and cancer, diabetes, and a slew of other potential confounders.
Prior evidence, mostly from healthy people, has suggested that extended fasting during the day is associated with less physical activity, Ms. Billingsley said in an interview. So it may be that people with HF who spread out their calorie intake are more active throughout the day.
A longer time window for eating, therefore, may have indirect metabolic benefits and help preserve their lean body mass, possibly reducing CV risk in a patient group at risk for muscle wasting.
The findings add to earlier evidence from Ms. Billingsley’s center that suggests that expanded daily time windows for eating, especially later final food rather than earlier first food, may help boost CV fitness for patients with obesity and HF with preserved ejection fraction.
Intermittent fasting and other practices involving the timing of food intake have been studied for weight loss and metabolic health in mostly healthy people and patients with diabetes, she noted. “But it’s really underexplored in people with established cardiovascular disease.”
On the basis of admittedly “very preliminary” findings, it may be that some patients should not shorten their daily time windows for eating or engage in intermittent fasting, Ms. Billingsley said. It’s probably worth considering, before the approach is recommended, “what their risk is for malnutrition or sarcopenia.”
The current study included 991 persons who entered the NHANES database from 2003 to 2018. The patients self-identified as having HF, reported taking medications commonly prescribed in HF, and provided at least two “reliable” dietary recalls.
The average age of the patients was 68 years, and they had had HF for a mean of 9.5 years; 47% were women, three-fourths were White persons, two thirds had dyslipidemia, and a quarter had a history of cancer.
On average, their first eating occasion of the day was at about 8:30 a.m., and the last occasion was at about 7:30 p.m., for a time window of about 11 hours; daily calorie consumption averaged about 1,830 kcal.
About 52% died over the mean follow-up of 69 months; about 44% of deaths were from CV causes.
In a model adjusted for demographics, BMI, smoking status, times of eating occasions, CV disease, diabetes, and cancer history, the all-cause mortality hazard ratio for time windows ≥ 11 hours vs. < 11 hours was 0.236 (95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.715; P = .011).
The reduction was no longer significant on further adjustment for duration of HF, a score reflecting difficulty walking, nightly hours of sleep (which averaged 7.2 hours), daily number of eating occasions, and caloric intake, Ms. Billingsley reported.
But in the fully adjusted analysis, the HR for CV mortality for the longer vs. shorter time window was 0.368 (95% CI, 0.169-0.803; P = .013).
The issue deserves further exploration in a randomized trial, Ms. Billingsley proposed, perhaps one in which patients with HF wear accelerometers to track daily activity levels. “We’d love to do a pilot study of extending their eating window that really digs into what the mechanism of any benefit might be if we assign them to a longer time window and whether it’s related to physical activity.”
Ms. Billingsley reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CLEVELAND – , an observational study suggests.
The new findings, based primarily on 15 years of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), may argue against time-restricted diet interventions like intermittent fasting for patients with HF, researchers say.
The study’s nearly 1,000 participants on medical therapy for HF reported a mean daily eating window of 11 hours and daily average of four “eating occasions,” defined as meals or snacks of at least 50 kcal.
A daily eating window of 11 or more hours, compared with less than 11 hours, corresponded to a greater than 40% drop in risk for CV mortality (P = .013) over 5-6 years, reported Hayley E. Billingsley, RD, CEP, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Va,, at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The analysis adjusted for caloric intake, daily number of eating occasions, body mass index (BMI), history of CV disease and cancer, diabetes, and a slew of other potential confounders.
Prior evidence, mostly from healthy people, has suggested that extended fasting during the day is associated with less physical activity, Ms. Billingsley said in an interview. So it may be that people with HF who spread out their calorie intake are more active throughout the day.
A longer time window for eating, therefore, may have indirect metabolic benefits and help preserve their lean body mass, possibly reducing CV risk in a patient group at risk for muscle wasting.
The findings add to earlier evidence from Ms. Billingsley’s center that suggests that expanded daily time windows for eating, especially later final food rather than earlier first food, may help boost CV fitness for patients with obesity and HF with preserved ejection fraction.
Intermittent fasting and other practices involving the timing of food intake have been studied for weight loss and metabolic health in mostly healthy people and patients with diabetes, she noted. “But it’s really underexplored in people with established cardiovascular disease.”
On the basis of admittedly “very preliminary” findings, it may be that some patients should not shorten their daily time windows for eating or engage in intermittent fasting, Ms. Billingsley said. It’s probably worth considering, before the approach is recommended, “what their risk is for malnutrition or sarcopenia.”
The current study included 991 persons who entered the NHANES database from 2003 to 2018. The patients self-identified as having HF, reported taking medications commonly prescribed in HF, and provided at least two “reliable” dietary recalls.
The average age of the patients was 68 years, and they had had HF for a mean of 9.5 years; 47% were women, three-fourths were White persons, two thirds had dyslipidemia, and a quarter had a history of cancer.
On average, their first eating occasion of the day was at about 8:30 a.m., and the last occasion was at about 7:30 p.m., for a time window of about 11 hours; daily calorie consumption averaged about 1,830 kcal.
About 52% died over the mean follow-up of 69 months; about 44% of deaths were from CV causes.
In a model adjusted for demographics, BMI, smoking status, times of eating occasions, CV disease, diabetes, and cancer history, the all-cause mortality hazard ratio for time windows ≥ 11 hours vs. < 11 hours was 0.236 (95% confidence interval, 0.07-0.715; P = .011).
The reduction was no longer significant on further adjustment for duration of HF, a score reflecting difficulty walking, nightly hours of sleep (which averaged 7.2 hours), daily number of eating occasions, and caloric intake, Ms. Billingsley reported.
But in the fully adjusted analysis, the HR for CV mortality for the longer vs. shorter time window was 0.368 (95% CI, 0.169-0.803; P = .013).
The issue deserves further exploration in a randomized trial, Ms. Billingsley proposed, perhaps one in which patients with HF wear accelerometers to track daily activity levels. “We’d love to do a pilot study of extending their eating window that really digs into what the mechanism of any benefit might be if we assign them to a longer time window and whether it’s related to physical activity.”
Ms. Billingsley reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AT HFSA 2023
Intravenous formulation of secukinumab gets FDA approval
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Enlarging lesion on temple
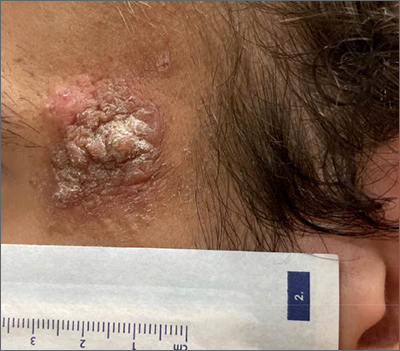
A shave biopsy revealed acanthosis, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and cytoplasmic viral-like inclusions without atypia, consistent with a diagnosis of a common wart. The biopsy ruled out other possible diagnoses, which included keratoacanthoma, seborrheic keratosis, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Cutaneous warts can manifest as common warts (verruca vulgaris), plantar warts (verruca plantaris), or plane warts (verruca plana). These benign skin lesions are caused by human papillomavirus and can manifest in areas of skin trauma; this is known as the Koebner phenomenon. Most warts can be diagnosed through clinical history and examination. Dermoscopy, if performed, may reveal thrombosed capillaries as dotted structures, but there is an increased risk of cross-contamination.1 That said, some dermatoscopes have disposable covers or can be cleaned with antiviral, antibacterial wipes. If the diagnosis is unclear or the exam is clinically suspicious, a biopsy may be required.
Cases with progressive enlargement and extensive involvement of the skin (as was seen here) are generally associated with certain predisposing conditions, such as atopic dermatitis and immunosuppression.2 Our patient screened negative for HIV infection, and further evaluation did not reveal any concerns for immunosuppression.
Treatment for a common wart depends on patient characteristics, preferences, cost, and possible adverse effects. Standard treatment options are topical salicylic acid and cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen. Depending on the location and type of the wart, multiple treatments may be required, and recurrences are common. Intralesional injection with bleomycin, 5‐fluorouracil, or cidofovir is often used for recurrent and refractory warts.
Patients unable to tolerate cryotherapy or local injections may benefit from thermotherapy by heating the wart with a pulsed dye laser.3 Observation is also a reasonable course of action for new warts, as they may spontaneously resolve within a year.
In this case, the patient opted for over-the-counter salicylic acid 17% to be applied nightly until resolution. Cryosurgery would be a next step for him if the lesion does not resolve after 3 months of treatment.
Image courtesy of Faryal Tahir, MD. Text courtesy of Faryal Tahir, MD, Assistant Professor, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Mun JH, Park SM, Ko HC, et al. Prevention of possible cross-infection among patients by dermoscopy: a brief review of the literature and our suggestion. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:33-34. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0304a07
2. Leiding JW, Holland SM. Warts and all: human papillomavirus in primary immunodeficiencies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1030-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.049
3. Zhu P, Qi RQ, Yang Y, et al. Clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous warts (2022). J Evid Based Med. 2022;15:284-301. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12494

A shave biopsy revealed acanthosis, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and cytoplasmic viral-like inclusions without atypia, consistent with a diagnosis of a common wart. The biopsy ruled out other possible diagnoses, which included keratoacanthoma, seborrheic keratosis, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Cutaneous warts can manifest as common warts (verruca vulgaris), plantar warts (verruca plantaris), or plane warts (verruca plana). These benign skin lesions are caused by human papillomavirus and can manifest in areas of skin trauma; this is known as the Koebner phenomenon. Most warts can be diagnosed through clinical history and examination. Dermoscopy, if performed, may reveal thrombosed capillaries as dotted structures, but there is an increased risk of cross-contamination.1 That said, some dermatoscopes have disposable covers or can be cleaned with antiviral, antibacterial wipes. If the diagnosis is unclear or the exam is clinically suspicious, a biopsy may be required.
Cases with progressive enlargement and extensive involvement of the skin (as was seen here) are generally associated with certain predisposing conditions, such as atopic dermatitis and immunosuppression.2 Our patient screened negative for HIV infection, and further evaluation did not reveal any concerns for immunosuppression.
Treatment for a common wart depends on patient characteristics, preferences, cost, and possible adverse effects. Standard treatment options are topical salicylic acid and cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen. Depending on the location and type of the wart, multiple treatments may be required, and recurrences are common. Intralesional injection with bleomycin, 5‐fluorouracil, or cidofovir is often used for recurrent and refractory warts.
Patients unable to tolerate cryotherapy or local injections may benefit from thermotherapy by heating the wart with a pulsed dye laser.3 Observation is also a reasonable course of action for new warts, as they may spontaneously resolve within a year.
In this case, the patient opted for over-the-counter salicylic acid 17% to be applied nightly until resolution. Cryosurgery would be a next step for him if the lesion does not resolve after 3 months of treatment.
Image courtesy of Faryal Tahir, MD. Text courtesy of Faryal Tahir, MD, Assistant Professor, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

A shave biopsy revealed acanthosis, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, parakeratosis, and cytoplasmic viral-like inclusions without atypia, consistent with a diagnosis of a common wart. The biopsy ruled out other possible diagnoses, which included keratoacanthoma, seborrheic keratosis, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Cutaneous warts can manifest as common warts (verruca vulgaris), plantar warts (verruca plantaris), or plane warts (verruca plana). These benign skin lesions are caused by human papillomavirus and can manifest in areas of skin trauma; this is known as the Koebner phenomenon. Most warts can be diagnosed through clinical history and examination. Dermoscopy, if performed, may reveal thrombosed capillaries as dotted structures, but there is an increased risk of cross-contamination.1 That said, some dermatoscopes have disposable covers or can be cleaned with antiviral, antibacterial wipes. If the diagnosis is unclear or the exam is clinically suspicious, a biopsy may be required.
Cases with progressive enlargement and extensive involvement of the skin (as was seen here) are generally associated with certain predisposing conditions, such as atopic dermatitis and immunosuppression.2 Our patient screened negative for HIV infection, and further evaluation did not reveal any concerns for immunosuppression.
Treatment for a common wart depends on patient characteristics, preferences, cost, and possible adverse effects. Standard treatment options are topical salicylic acid and cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen. Depending on the location and type of the wart, multiple treatments may be required, and recurrences are common. Intralesional injection with bleomycin, 5‐fluorouracil, or cidofovir is often used for recurrent and refractory warts.
Patients unable to tolerate cryotherapy or local injections may benefit from thermotherapy by heating the wart with a pulsed dye laser.3 Observation is also a reasonable course of action for new warts, as they may spontaneously resolve within a year.
In this case, the patient opted for over-the-counter salicylic acid 17% to be applied nightly until resolution. Cryosurgery would be a next step for him if the lesion does not resolve after 3 months of treatment.
Image courtesy of Faryal Tahir, MD. Text courtesy of Faryal Tahir, MD, Assistant Professor, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Mun JH, Park SM, Ko HC, et al. Prevention of possible cross-infection among patients by dermoscopy: a brief review of the literature and our suggestion. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:33-34. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0304a07
2. Leiding JW, Holland SM. Warts and all: human papillomavirus in primary immunodeficiencies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1030-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.049
3. Zhu P, Qi RQ, Yang Y, et al. Clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous warts (2022). J Evid Based Med. 2022;15:284-301. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12494
1. Mun JH, Park SM, Ko HC, et al. Prevention of possible cross-infection among patients by dermoscopy: a brief review of the literature and our suggestion. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:33-34. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0304a07
2. Leiding JW, Holland SM. Warts and all: human papillomavirus in primary immunodeficiencies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1030-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.049
3. Zhu P, Qi RQ, Yang Y, et al. Clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous warts (2022). J Evid Based Med. 2022;15:284-301. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12494