User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


Psoriasis elevates cancer risk
Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for several types of cancer, notably lymphoma and keratinocyte cancer, based on data from a systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 2 million patients.
Previous studies have identified an increased overall cancer risk in psoriasis patients, compared with the general population or controls without psoriasis, and both lymphomas and keratinocyte cancers occur more often in psoriasis patients, compared with controls, but additional larger studies have been conducted since the last meta-analysis was published in 2013, wrote Sofie Vaengebjerg, MD, of the University of Copenhagen and colleagues.
To better identify the risk of cancer in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients and to explore the impact of biologics, the researchers reviewed data from 112 studies totaling 2,053,932 patients in a study published in JAMA Dermatology.
Overall, the risk of any cancer was slightly higher in psoriasis patients (risk ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.33), compared with controls, with a prevalence of 4.78% and an incidence rate of 11.75 per 1,000 person-years. The most common cancer among psoriasis patients was keratinocyte cancer, with a risk ratio of 2.28 (95% CI, 1.73-3.01), a prevalence of 2.55%, and an incidence rate of 4.35 per 1,000 person-years.
Other cancers with significantly elevated risk among psoriasis patients were lymphomas (RR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.37-1.78), lung cancer (RR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.13-1.40), and bladder cancer (RR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.19).
No increased risk of cancer was noted among psoriasis patients who were treated with biologics. “However, patients receiving biologic agents are selected and the results might be reliant on selection bias, and studies investigating long-term safety of these drugs are still limited,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, psoriatic arthritis was not associated with any overall increase in cancer risk, with the exception of three studies showing an increased risk for breast cancer, the researchers noted. The overall cancer prevalence for psoriatic arthritis patients was 5.74%, with an incidence rate of 6.44 per 1,000 person-years.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inconsistencies in study design and characteristics and the small amount of data on biologic agents and psoriatic arthritis, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large number of patients, real-world study settings, inclusion of biologics, and analysis of cancer in psoriatic arthritis patients.
“Clinicians treating patients with psoriasis should be aware of this increased risk, especially for lymphomas, as immunogenic treatment might be associated with exacerbations,” and should be aware that more research is needed to assess cancer risk associated with biologics, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Vaengebjerg had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, LEO Pharma, UCB, Almirall, and Sanofi.
SOURCE: Vaengebjerg S et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Feb 19. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0024.
Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for several types of cancer, notably lymphoma and keratinocyte cancer, based on data from a systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 2 million patients.
Previous studies have identified an increased overall cancer risk in psoriasis patients, compared with the general population or controls without psoriasis, and both lymphomas and keratinocyte cancers occur more often in psoriasis patients, compared with controls, but additional larger studies have been conducted since the last meta-analysis was published in 2013, wrote Sofie Vaengebjerg, MD, of the University of Copenhagen and colleagues.
To better identify the risk of cancer in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients and to explore the impact of biologics, the researchers reviewed data from 112 studies totaling 2,053,932 patients in a study published in JAMA Dermatology.
Overall, the risk of any cancer was slightly higher in psoriasis patients (risk ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.33), compared with controls, with a prevalence of 4.78% and an incidence rate of 11.75 per 1,000 person-years. The most common cancer among psoriasis patients was keratinocyte cancer, with a risk ratio of 2.28 (95% CI, 1.73-3.01), a prevalence of 2.55%, and an incidence rate of 4.35 per 1,000 person-years.
Other cancers with significantly elevated risk among psoriasis patients were lymphomas (RR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.37-1.78), lung cancer (RR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.13-1.40), and bladder cancer (RR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.19).
No increased risk of cancer was noted among psoriasis patients who were treated with biologics. “However, patients receiving biologic agents are selected and the results might be reliant on selection bias, and studies investigating long-term safety of these drugs are still limited,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, psoriatic arthritis was not associated with any overall increase in cancer risk, with the exception of three studies showing an increased risk for breast cancer, the researchers noted. The overall cancer prevalence for psoriatic arthritis patients was 5.74%, with an incidence rate of 6.44 per 1,000 person-years.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inconsistencies in study design and characteristics and the small amount of data on biologic agents and psoriatic arthritis, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large number of patients, real-world study settings, inclusion of biologics, and analysis of cancer in psoriatic arthritis patients.
“Clinicians treating patients with psoriasis should be aware of this increased risk, especially for lymphomas, as immunogenic treatment might be associated with exacerbations,” and should be aware that more research is needed to assess cancer risk associated with biologics, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Vaengebjerg had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, LEO Pharma, UCB, Almirall, and Sanofi.
SOURCE: Vaengebjerg S et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Feb 19. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0024.
Psoriasis patients are at increased risk for several types of cancer, notably lymphoma and keratinocyte cancer, based on data from a systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 2 million patients.
Previous studies have identified an increased overall cancer risk in psoriasis patients, compared with the general population or controls without psoriasis, and both lymphomas and keratinocyte cancers occur more often in psoriasis patients, compared with controls, but additional larger studies have been conducted since the last meta-analysis was published in 2013, wrote Sofie Vaengebjerg, MD, of the University of Copenhagen and colleagues.
To better identify the risk of cancer in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients and to explore the impact of biologics, the researchers reviewed data from 112 studies totaling 2,053,932 patients in a study published in JAMA Dermatology.
Overall, the risk of any cancer was slightly higher in psoriasis patients (risk ratio, 1.21; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.33), compared with controls, with a prevalence of 4.78% and an incidence rate of 11.75 per 1,000 person-years. The most common cancer among psoriasis patients was keratinocyte cancer, with a risk ratio of 2.28 (95% CI, 1.73-3.01), a prevalence of 2.55%, and an incidence rate of 4.35 per 1,000 person-years.
Other cancers with significantly elevated risk among psoriasis patients were lymphomas (RR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.37-1.78), lung cancer (RR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.13-1.40), and bladder cancer (RR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.19).
No increased risk of cancer was noted among psoriasis patients who were treated with biologics. “However, patients receiving biologic agents are selected and the results might be reliant on selection bias, and studies investigating long-term safety of these drugs are still limited,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, psoriatic arthritis was not associated with any overall increase in cancer risk, with the exception of three studies showing an increased risk for breast cancer, the researchers noted. The overall cancer prevalence for psoriatic arthritis patients was 5.74%, with an incidence rate of 6.44 per 1,000 person-years.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inconsistencies in study design and characteristics and the small amount of data on biologic agents and psoriatic arthritis, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large number of patients, real-world study settings, inclusion of biologics, and analysis of cancer in psoriatic arthritis patients.
“Clinicians treating patients with psoriasis should be aware of this increased risk, especially for lymphomas, as immunogenic treatment might be associated with exacerbations,” and should be aware that more research is needed to assess cancer risk associated with biologics, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Vaengebjerg had no financial conflicts to disclose. Several coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Eli Lilly, LEO Pharma, UCB, Almirall, and Sanofi.
SOURCE: Vaengebjerg S et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Feb 19. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0024.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Number of sexual partners linked to cancer risk
A higher lifetime number of sexual partners was associated with a greater risk of being diagnosed with cancer in older adults, according to a recent study.
Additionally, among women, having had more lifetime partners was linked to higher odds of reporting a limiting long-standing condition.
Igor Grabovac, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna, and colleagues reported these results in BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health.
The exploratory analysis included 2,537 men and 3,185 women, aged 50 years and older, who were a part of the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. The mean age of study subjects was 64 years in men and 65 years in women, and most were either married or cohabitating.
Researchers collected data on sexual history using a self-administered questionnaire, which privately recorded the lifetime number of sexual partners among study participants. Data on other health outcomes, such as limiting long-standing illness and cancer diagnoses, were also self-reported.
Among male participants, 28.5% reported a history of 0-1 lifetime sexual partners, 29.0% had 2-4 partners, 20.2% had 5-9 partners, and 22.2% had 10 or more partners. The respective measures in women were 40.8%, 35.5%, 15.8%, and 7.8%.
Among all participants, a greater number of sexual partners was associated with being single, younger age, and being in the least or greatest brackets of household income.
The researchers found that, compared with having 0-1 sexual partners, a lifetime history of 10 or more sexual partners was associated with a greater risk of reported cancer in both men (odds ratio, 1.69; P = .047) and women (OR, 1.91; P = .038).
In addition, women with a lifetime history of 10 or more sexual partners had greater odds of reporting a limiting long-standing condition (OR, 1.64; P = .007).
“We observed no statistically significant association between number of lifetime sexual partners and self-rated health, CHD [coronary heart disease], or stroke in either sex, or with limiting long-standing illness in men,” the researchers explained.
They acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the self-reported nature of the data. As a result, further studies are required to establish causality.
“Sexual history may be a relevant clinical indicator for cancer risk in older patients,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Grabovac I et al. BMJ Sex Reprod Health. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1136/bmjsrh-2019-200352.
A higher lifetime number of sexual partners was associated with a greater risk of being diagnosed with cancer in older adults, according to a recent study.
Additionally, among women, having had more lifetime partners was linked to higher odds of reporting a limiting long-standing condition.
Igor Grabovac, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna, and colleagues reported these results in BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health.
The exploratory analysis included 2,537 men and 3,185 women, aged 50 years and older, who were a part of the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. The mean age of study subjects was 64 years in men and 65 years in women, and most were either married or cohabitating.
Researchers collected data on sexual history using a self-administered questionnaire, which privately recorded the lifetime number of sexual partners among study participants. Data on other health outcomes, such as limiting long-standing illness and cancer diagnoses, were also self-reported.
Among male participants, 28.5% reported a history of 0-1 lifetime sexual partners, 29.0% had 2-4 partners, 20.2% had 5-9 partners, and 22.2% had 10 or more partners. The respective measures in women were 40.8%, 35.5%, 15.8%, and 7.8%.
Among all participants, a greater number of sexual partners was associated with being single, younger age, and being in the least or greatest brackets of household income.
The researchers found that, compared with having 0-1 sexual partners, a lifetime history of 10 or more sexual partners was associated with a greater risk of reported cancer in both men (odds ratio, 1.69; P = .047) and women (OR, 1.91; P = .038).
In addition, women with a lifetime history of 10 or more sexual partners had greater odds of reporting a limiting long-standing condition (OR, 1.64; P = .007).
“We observed no statistically significant association between number of lifetime sexual partners and self-rated health, CHD [coronary heart disease], or stroke in either sex, or with limiting long-standing illness in men,” the researchers explained.
They acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the self-reported nature of the data. As a result, further studies are required to establish causality.
“Sexual history may be a relevant clinical indicator for cancer risk in older patients,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Grabovac I et al. BMJ Sex Reprod Health. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1136/bmjsrh-2019-200352.
A higher lifetime number of sexual partners was associated with a greater risk of being diagnosed with cancer in older adults, according to a recent study.
Additionally, among women, having had more lifetime partners was linked to higher odds of reporting a limiting long-standing condition.
Igor Grabovac, MD, of the Medical University of Vienna, and colleagues reported these results in BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health.
The exploratory analysis included 2,537 men and 3,185 women, aged 50 years and older, who were a part of the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. The mean age of study subjects was 64 years in men and 65 years in women, and most were either married or cohabitating.
Researchers collected data on sexual history using a self-administered questionnaire, which privately recorded the lifetime number of sexual partners among study participants. Data on other health outcomes, such as limiting long-standing illness and cancer diagnoses, were also self-reported.
Among male participants, 28.5% reported a history of 0-1 lifetime sexual partners, 29.0% had 2-4 partners, 20.2% had 5-9 partners, and 22.2% had 10 or more partners. The respective measures in women were 40.8%, 35.5%, 15.8%, and 7.8%.
Among all participants, a greater number of sexual partners was associated with being single, younger age, and being in the least or greatest brackets of household income.
The researchers found that, compared with having 0-1 sexual partners, a lifetime history of 10 or more sexual partners was associated with a greater risk of reported cancer in both men (odds ratio, 1.69; P = .047) and women (OR, 1.91; P = .038).
In addition, women with a lifetime history of 10 or more sexual partners had greater odds of reporting a limiting long-standing condition (OR, 1.64; P = .007).
“We observed no statistically significant association between number of lifetime sexual partners and self-rated health, CHD [coronary heart disease], or stroke in either sex, or with limiting long-standing illness in men,” the researchers explained.
They acknowledged that a key limitation of the study was the self-reported nature of the data. As a result, further studies are required to establish causality.
“Sexual history may be a relevant clinical indicator for cancer risk in older patients,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Grabovac I et al. BMJ Sex Reprod Health. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1136/bmjsrh-2019-200352.
FROM BMJ SEXUAL AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
Oncologists are average in terms of happiness, survey suggests
When it comes to physician happiness both in and outside the workplace, oncologists are about average, according to Medscape’s 2020 Lifestyle, Happiness, and Burnout Report.
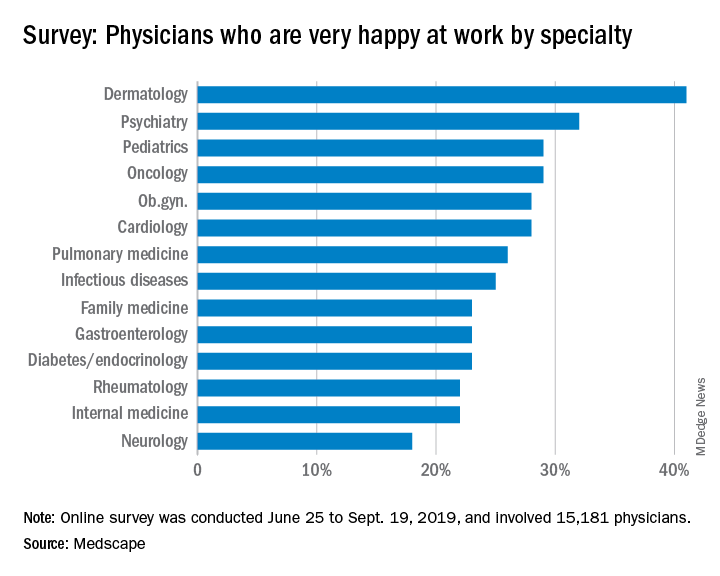
Oncologists landed in the middle of the pack among all physicians surveyed for happiness. Rheumatologists were most likely to report being very or extremely happy outside of work (60%) and neurologists were least likely to do so (44%), but about half of oncologists (51%) reported being very/extremely happy outside of work. For happiness at work, dermatologists topped the list (41%), neurologists came in last (18%), and oncologists remained in the middle (29%).
Oncologists were average when it came to burnout as well, matching the rate of overall physicians. Specifically, 32% of oncologists were burned out, 4% were depressed, and 9% were both burned out and depressed.
The most commonly reported factors contributing to burnout among oncologists were an overabundance of bureaucratic tasks (74%), spending too many hours at work (42%), and a lack of respect from colleagues in the workplace (36%).
Exercise was the most commonly reported way oncologists dealt with burnout (51%), followed by talking with family and friends (49%), and isolating themselves from others (38%). In addition, 57% of oncologists took 3-4 weeks’ vacation, compared with 44% of physicians overall; 29% of oncologists took less than 3 weeks’ vacation.
About 18% of oncologists said they had contemplated suicide, and 1% said they’d attempted it; 72% said they’d never had thoughts of suicide. Just under one-quarter of oncologists said they were currently seeking professional help or were planning to seek help for symptoms of depression and/or burnout.
“The survey results are concerning on several levels,” Maurie Markman, MD, of Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
“First, the data suggest a considerable number of oncologists are simply burned out from the day-to-day bureaucracy (paperwork, etc.) of medical practice, which has absolutely nothing to do with the actual care delivered. This likely impacts the willingness to continue in this role. Second, one must be concerned for the future recruitment of physicians to become clinical oncologists. And finally, one must wonder about the impact of these concerning figures on the quality of care being provided to cancer patients.”
This survey was conducted from June 25 to Sept. 19, 2019, and involved 15,181 physicians. Oncologists made up 1% of the survey pool.
When it comes to physician happiness both in and outside the workplace, oncologists are about average, according to Medscape’s 2020 Lifestyle, Happiness, and Burnout Report.

Oncologists landed in the middle of the pack among all physicians surveyed for happiness. Rheumatologists were most likely to report being very or extremely happy outside of work (60%) and neurologists were least likely to do so (44%), but about half of oncologists (51%) reported being very/extremely happy outside of work. For happiness at work, dermatologists topped the list (41%), neurologists came in last (18%), and oncologists remained in the middle (29%).
Oncologists were average when it came to burnout as well, matching the rate of overall physicians. Specifically, 32% of oncologists were burned out, 4% were depressed, and 9% were both burned out and depressed.
The most commonly reported factors contributing to burnout among oncologists were an overabundance of bureaucratic tasks (74%), spending too many hours at work (42%), and a lack of respect from colleagues in the workplace (36%).
Exercise was the most commonly reported way oncologists dealt with burnout (51%), followed by talking with family and friends (49%), and isolating themselves from others (38%). In addition, 57% of oncologists took 3-4 weeks’ vacation, compared with 44% of physicians overall; 29% of oncologists took less than 3 weeks’ vacation.
About 18% of oncologists said they had contemplated suicide, and 1% said they’d attempted it; 72% said they’d never had thoughts of suicide. Just under one-quarter of oncologists said they were currently seeking professional help or were planning to seek help for symptoms of depression and/or burnout.
“The survey results are concerning on several levels,” Maurie Markman, MD, of Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
“First, the data suggest a considerable number of oncologists are simply burned out from the day-to-day bureaucracy (paperwork, etc.) of medical practice, which has absolutely nothing to do with the actual care delivered. This likely impacts the willingness to continue in this role. Second, one must be concerned for the future recruitment of physicians to become clinical oncologists. And finally, one must wonder about the impact of these concerning figures on the quality of care being provided to cancer patients.”
This survey was conducted from June 25 to Sept. 19, 2019, and involved 15,181 physicians. Oncologists made up 1% of the survey pool.
When it comes to physician happiness both in and outside the workplace, oncologists are about average, according to Medscape’s 2020 Lifestyle, Happiness, and Burnout Report.

Oncologists landed in the middle of the pack among all physicians surveyed for happiness. Rheumatologists were most likely to report being very or extremely happy outside of work (60%) and neurologists were least likely to do so (44%), but about half of oncologists (51%) reported being very/extremely happy outside of work. For happiness at work, dermatologists topped the list (41%), neurologists came in last (18%), and oncologists remained in the middle (29%).
Oncologists were average when it came to burnout as well, matching the rate of overall physicians. Specifically, 32% of oncologists were burned out, 4% were depressed, and 9% were both burned out and depressed.
The most commonly reported factors contributing to burnout among oncologists were an overabundance of bureaucratic tasks (74%), spending too many hours at work (42%), and a lack of respect from colleagues in the workplace (36%).
Exercise was the most commonly reported way oncologists dealt with burnout (51%), followed by talking with family and friends (49%), and isolating themselves from others (38%). In addition, 57% of oncologists took 3-4 weeks’ vacation, compared with 44% of physicians overall; 29% of oncologists took less than 3 weeks’ vacation.
About 18% of oncologists said they had contemplated suicide, and 1% said they’d attempted it; 72% said they’d never had thoughts of suicide. Just under one-quarter of oncologists said they were currently seeking professional help or were planning to seek help for symptoms of depression and/or burnout.
“The survey results are concerning on several levels,” Maurie Markman, MD, of Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
“First, the data suggest a considerable number of oncologists are simply burned out from the day-to-day bureaucracy (paperwork, etc.) of medical practice, which has absolutely nothing to do with the actual care delivered. This likely impacts the willingness to continue in this role. Second, one must be concerned for the future recruitment of physicians to become clinical oncologists. And finally, one must wonder about the impact of these concerning figures on the quality of care being provided to cancer patients.”
This survey was conducted from June 25 to Sept. 19, 2019, and involved 15,181 physicians. Oncologists made up 1% of the survey pool.
Shorter time to metastases associated with worse RCC outcomes
in an international review of over 7,000 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
“Patients with synchronous disease, compared with patients with metachronous disease, have more adverse prognostic features, significantly shorter TTF [time to treatment failure], and poorer survival. This may help in patient counseling and may be taken into consideration in clinical trial designs in the future, in order to avoid an imbalance between treatment arms,” wrote investigators led by Frede Donskov, MD, a clinical professor at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, in European Urology Oncology.
In the largest study to date to address the impact of timing of metastases on outcomes from tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment, something that’s been unclear until now, Dr. Donskov and associates turned to the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) to compare outcomes of 3,906 patients with synchronous metastases, meaning metastases within 3 months of initial RCC diagnosis, with 3,480 with metachronous disease, meaning metastases after that point.
They found that more patients with synchronous versus metachronous disease had higher T stage (T1-2, 19% vs. 34%), N1 disease (21% vs. 6%), presence of sarcomatoid differentiation (15.8% vs. 7.9%), Karnofsky performance status less than 80 (25.9% vs. 15.1%), anemia (62.5% vs. 42.3%), elevated neutrophils (18.9% vs. 10.9%), elevated platelets (21.6% vs. 11.4%), bone metastases (40.4% vs. 29.8%); and IMDC poor risk (40.6% vs.11.3%).
Synchronous versus metachronous disease by intervals of more than 3-12 months, more than 1-2 years, more than 2-7 years, and more than 7 years correlated with poor TTF (5.6 months vs. 7.3, 8.0, 10.8, and 13.3 months; P less than .0001) and poor overall survival (median, 16.7 months vs. 23.8, 30.2, 34.8, and 41.7 months; P less than .0001).
On multivariable regressions adjusting for baseline variables, metachronous disease was protective versus synchronous RCC on overall survival and TTF, with a greater protective effect the longer it took for the disease to metastasize.
“Synchronous disease may represent a distinct pathologic and molecular phenotype ... a high proportion of patients with synchronous disease have tumors with punctuated evolution, harboring aggressive disease features, consolidating in worse risk factors, requiring systemic therapy earlier, and having almost half the expected survival after the initiation of targeted therapy, compared with the latest metastatic timing, as shown in our study,” the investigators wrote.
The findings “reflect the underlying aggressive tumor biology. Whether [time to metastasis] impacts outcome to checkpoint immunotherapy is yet to be elucidated,” they added.
Patients were a median of 59 years at diagnosis, and 72.9% were men. None of the synchronous patients had a surgical nephrectomy, compared with 95.4% of metachronous patients; 67.2% of patients in both groups were treated with the TKI sunitinib (Sutent).
The work was funded by the IMDC. The lead investigator reported institutional grants from Ipsen and Pfizer, maker of sunitinib.
SOURCE: Donskov F et al. Eur Urol Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.01.001.
in an international review of over 7,000 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
“Patients with synchronous disease, compared with patients with metachronous disease, have more adverse prognostic features, significantly shorter TTF [time to treatment failure], and poorer survival. This may help in patient counseling and may be taken into consideration in clinical trial designs in the future, in order to avoid an imbalance between treatment arms,” wrote investigators led by Frede Donskov, MD, a clinical professor at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, in European Urology Oncology.
In the largest study to date to address the impact of timing of metastases on outcomes from tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment, something that’s been unclear until now, Dr. Donskov and associates turned to the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) to compare outcomes of 3,906 patients with synchronous metastases, meaning metastases within 3 months of initial RCC diagnosis, with 3,480 with metachronous disease, meaning metastases after that point.
They found that more patients with synchronous versus metachronous disease had higher T stage (T1-2, 19% vs. 34%), N1 disease (21% vs. 6%), presence of sarcomatoid differentiation (15.8% vs. 7.9%), Karnofsky performance status less than 80 (25.9% vs. 15.1%), anemia (62.5% vs. 42.3%), elevated neutrophils (18.9% vs. 10.9%), elevated platelets (21.6% vs. 11.4%), bone metastases (40.4% vs. 29.8%); and IMDC poor risk (40.6% vs.11.3%).
Synchronous versus metachronous disease by intervals of more than 3-12 months, more than 1-2 years, more than 2-7 years, and more than 7 years correlated with poor TTF (5.6 months vs. 7.3, 8.0, 10.8, and 13.3 months; P less than .0001) and poor overall survival (median, 16.7 months vs. 23.8, 30.2, 34.8, and 41.7 months; P less than .0001).
On multivariable regressions adjusting for baseline variables, metachronous disease was protective versus synchronous RCC on overall survival and TTF, with a greater protective effect the longer it took for the disease to metastasize.
“Synchronous disease may represent a distinct pathologic and molecular phenotype ... a high proportion of patients with synchronous disease have tumors with punctuated evolution, harboring aggressive disease features, consolidating in worse risk factors, requiring systemic therapy earlier, and having almost half the expected survival after the initiation of targeted therapy, compared with the latest metastatic timing, as shown in our study,” the investigators wrote.
The findings “reflect the underlying aggressive tumor biology. Whether [time to metastasis] impacts outcome to checkpoint immunotherapy is yet to be elucidated,” they added.
Patients were a median of 59 years at diagnosis, and 72.9% were men. None of the synchronous patients had a surgical nephrectomy, compared with 95.4% of metachronous patients; 67.2% of patients in both groups were treated with the TKI sunitinib (Sutent).
The work was funded by the IMDC. The lead investigator reported institutional grants from Ipsen and Pfizer, maker of sunitinib.
SOURCE: Donskov F et al. Eur Urol Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.01.001.
in an international review of over 7,000 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
“Patients with synchronous disease, compared with patients with metachronous disease, have more adverse prognostic features, significantly shorter TTF [time to treatment failure], and poorer survival. This may help in patient counseling and may be taken into consideration in clinical trial designs in the future, in order to avoid an imbalance between treatment arms,” wrote investigators led by Frede Donskov, MD, a clinical professor at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, in European Urology Oncology.
In the largest study to date to address the impact of timing of metastases on outcomes from tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment, something that’s been unclear until now, Dr. Donskov and associates turned to the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) to compare outcomes of 3,906 patients with synchronous metastases, meaning metastases within 3 months of initial RCC diagnosis, with 3,480 with metachronous disease, meaning metastases after that point.
They found that more patients with synchronous versus metachronous disease had higher T stage (T1-2, 19% vs. 34%), N1 disease (21% vs. 6%), presence of sarcomatoid differentiation (15.8% vs. 7.9%), Karnofsky performance status less than 80 (25.9% vs. 15.1%), anemia (62.5% vs. 42.3%), elevated neutrophils (18.9% vs. 10.9%), elevated platelets (21.6% vs. 11.4%), bone metastases (40.4% vs. 29.8%); and IMDC poor risk (40.6% vs.11.3%).
Synchronous versus metachronous disease by intervals of more than 3-12 months, more than 1-2 years, more than 2-7 years, and more than 7 years correlated with poor TTF (5.6 months vs. 7.3, 8.0, 10.8, and 13.3 months; P less than .0001) and poor overall survival (median, 16.7 months vs. 23.8, 30.2, 34.8, and 41.7 months; P less than .0001).
On multivariable regressions adjusting for baseline variables, metachronous disease was protective versus synchronous RCC on overall survival and TTF, with a greater protective effect the longer it took for the disease to metastasize.
“Synchronous disease may represent a distinct pathologic and molecular phenotype ... a high proportion of patients with synchronous disease have tumors with punctuated evolution, harboring aggressive disease features, consolidating in worse risk factors, requiring systemic therapy earlier, and having almost half the expected survival after the initiation of targeted therapy, compared with the latest metastatic timing, as shown in our study,” the investigators wrote.
The findings “reflect the underlying aggressive tumor biology. Whether [time to metastasis] impacts outcome to checkpoint immunotherapy is yet to be elucidated,” they added.
Patients were a median of 59 years at diagnosis, and 72.9% were men. None of the synchronous patients had a surgical nephrectomy, compared with 95.4% of metachronous patients; 67.2% of patients in both groups were treated with the TKI sunitinib (Sutent).
The work was funded by the IMDC. The lead investigator reported institutional grants from Ipsen and Pfizer, maker of sunitinib.
SOURCE: Donskov F et al. Eur Urol Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.01.001.
FROM EUROPEAN UROLOGY ONCOLOGY
Glaring gap in CV event reporting in pivotal cancer trials
Clinical trials supporting Food and Drug Adminstration approval of contemporary cancer therapies frequently failed to capture major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and, when they did, reported rates 2.6-fold lower than noncancer trials, new research shows.
Overall, 51.3% of trials did not report MACE, with that number reaching 57.6% in trials enrolling patients with baseline cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Nearly 40% of trials did not report any CVD events in follow-up, the authors reported online Feb. 10, 2020, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020;75:620-8).
“Even in drug classes where there were established or emerging associations with cardiotoxic events, often there were no reported heart events or cardiovascular events across years of follow-up in trials that examined hundreds or even thousands of patients. That was actually pretty surprising,” senior author Daniel Addison, MD, codirector of the cardio-oncology program at the Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
The study was prompted by a series of events that crescendoed when his team was called to the ICU to determine whether a novel targeted agent played a role in the heart decline of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. “I had a resident ask me a very important question: ‘How do we really know for sure that the trial actually reflects the true risk of heart events?’ to which I told him, ‘it’s difficult to know,’ ” he said.
“I think many of us rely heavily on what we see in the trials, particularly when they make it to the top journals, and quite frankly, we generally take it at face value,” Dr. Addison observed.
Lower Rate of Reported Events
The investigators reviewed CV events reported in 97,365 patients (median age, 61 years; 46% female) enrolled in 189 phase 2 and 3 trials supporting FDA approval of 123 anticancer drugs from 1998 to 2018. Biologic, targeted, or immune-based therapies accounted for 72.5% of drug approvals.
Over 148,138 person-years of follow-up (median trial duration, 30 months), there were 1,148 incidents of MACE (375 heart failure, 253 MIs, 180 strokes, 65 atrial fibrillation, 29 coronary revascularizations, and 246 CVD deaths). MACE rates were higher in the intervention group than in the control group (792 vs. 356; P less than .01). Among the 64 trials that excluded patients with baseline CVD, there were 269 incidents of MACE.
To put this finding in context, the researchers examined the reported incidence of MACE among some 6,000 similarly aged participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). The overall weighted-average incidence rate was 1,408 per 100,000 person-years among MESA participants, compared with 542 events per 100,000 person-years among oncology trial participants (716 per 100,000 in the intervention arm). This represents a reported-to-expected ratio of 0.38 – a 2.6-fold lower rate of reported events (P less than .001) – and a risk difference of 866.
Further, MACE reporting was lower by a factor of 1.7 among all cancer trial participants irrespective of baseline CVD status (reported-to-expected ratio, 0.56; risk difference, 613; P less than .001).
There was no significant difference in MACE reporting between independent or industry-sponsored trials, the authors report.
No malicious intent
“There are likely some that might lean toward not wanting to attribute blame to a new drug when the drug is in a study, but I really think that the leading factor is lack of awareness,” Dr. Addison said. “I’ve talked with several cancer collaborators around the country who run large clinical trials, and I think often, when an event may be brought to someone’s attention, there is a tendency to just write it off as kind of a generic expected event due to age, or just something that’s not really pertinent to the study. So they don’t really focus on it as much.”
“Closer collaboration between cardiologists and cancer physicians is needed to better determine true cardiac risks among patients treated with these drugs.”
Breast cancer oncologist Marc E. Lippman, MD, of Georgetown University Medical Center and Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Washington, D.C., isn’t convinced a lack of awareness is the culprit.
“I don’t agree with that at all,” he said in an interview. “I think there are very, very clear rules and guidelines these days for adverse-event reporting. I think that’s not a very likely explanation – that it’s not on the radar.”
Part of the problem may be that some of the toxicities, particularly cardiovascular, may not emerge for years, he said. Participant screening for the trials also likely removed patients with high cardiovascular risk. “It’s very understandable to me – I’m not saying it’s good particularly – but I think it’s very understandable that, if you’re trying to develop a drug, the last thing you’d want to have is a lot of toxicity that you might have avoided by just being restrictive in who you let into the study,” Dr. Lippman said.
The underreported CVD events may also reflect the rapidly changing profile of cardiovascular toxicities associated with novel anticancer therapies.
“Providers, both cancer and noncancer, generally put cardiotoxicity in the box of anthracyclines and radiation, but particularly over the last decade, we’ve begun to understand it’s well beyond any one class of drugs,” Dr. Addison said.
“I agree completely,” Dr. Lippman said. For example, “the checkpoint inhibitors are so unbelievably different in terms of their toxicities that many people simply didn’t even know what they were getting into at first.”
One size does not fit all
Javid Moslehi, MD, director of the cardio-oncology program at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said echocardiography – recommended to detect changes in left ventricular function in patients exposed to anthracyclines or targeted agents like trastuzumab (Herceptin) – isn’t enough to address today’s cancer therapy–related CVD events.
“Initial drugs like anthracyclines or Herceptin in cardio-oncology were associated with systolic cardiac dysfunction, whereas the majority of issues we see in the cardio-oncology clinics today are vascular, metabolic, arrhythmogenic, and inflammatory,” he said in an interview. “Echocardiography misses the big and increasingly complex picture.”
His group, for example, has been studying myocarditis associated with immunotherapies, but none of the clinical trials require screening or surveillance for myocarditis with a cardiac biomarker like troponin.
The group also recently identified 303 deaths in patients exposed to ibrutinib, a drug that revolutionized the treatment of several B-cell malignancies but is associated with higher rates of atrial fibrillation, which is also associated with increased bleeding risk. “So there’s a little bit of a double whammy there, given that we often treat atrial fibrillation with anticoagulation and where we can cause complications in patients,” Dr. Moslehi noted.
Although there needs to be closer collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists on individual trials, cardiologists also have to realize that oncology care has become very personalized, he suggested.
“What’s probably relevant for the breast cancer patient may not be relevant for the prostate cancer patient and their respective treatments,” Dr. Moslehi said. “So if we were to say, ‘every person should get an echo,’ that may be less relevant to the prostate cancer patient where treatments can cause vascular and metabolic perturbations or to the patient treated with immunotherapy who may have myocarditis, where many of the echos can be normal. There’s no one-size-fits-all for these things.”
Wearable technologies like smartwatches could play a role in improving the reporting of CVD events with novel therapies but a lot more research needs to be done to validate these tools, Dr. Addison said. “But as we continue on into the 21st century, this is going to expand and may potentially help us,” he added.
In the interim, better standardization is needed of the cardiovascular events reported in oncology trials, particularly the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), said Dr. Moslehi, who also serves as chair of the American Heart Association’s subcommittee on cardio-oncology.
“Cardiovascular definitions are not exactly uniform and are not consistent with what we in cardiology consider to be important or relevant,” he said. “So I think there needs to be better standardization of these definitions, specifically within the CTCAE, which is what the oncologists use to identify adverse events.”
In a linked editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:629-31), Dr. Lippman and cardiologist Nanette Bishopric, MD, of the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute in Washington, D.C., suggested it may also be time to organize a consortium that can carry out “rigorous multicenter clinical investigations to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of emerging cancer treatments,” similar to the Thrombosis in Myocardial Infarction Study Group.
“The success of this consortium in pioneering and targeting multiple generations of drugs for the treatment of MI, involving tens of thousands of patients and thousands of collaborations across multiple national borders, is a model for how to move forward in providing the new hope of cancer cure without the trade-off of years lost to heart disease,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants, including a K12-CA133250 grant to Dr. Addison. Dr. Bishopric reported being on the scientific board of C&C Biopharma. Dr. Lippman reports being on the board of directors of and holding stock in Seattle Genetics. Dr. Moslehi reported having served on advisory boards for Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Deciphera, Audentes Pharmaceuticals, Nektar, Takeda, Ipsen, Myokardia, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Intrexon, and Regeneron.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical trials supporting Food and Drug Adminstration approval of contemporary cancer therapies frequently failed to capture major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and, when they did, reported rates 2.6-fold lower than noncancer trials, new research shows.
Overall, 51.3% of trials did not report MACE, with that number reaching 57.6% in trials enrolling patients with baseline cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Nearly 40% of trials did not report any CVD events in follow-up, the authors reported online Feb. 10, 2020, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020;75:620-8).
“Even in drug classes where there were established or emerging associations with cardiotoxic events, often there were no reported heart events or cardiovascular events across years of follow-up in trials that examined hundreds or even thousands of patients. That was actually pretty surprising,” senior author Daniel Addison, MD, codirector of the cardio-oncology program at the Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
The study was prompted by a series of events that crescendoed when his team was called to the ICU to determine whether a novel targeted agent played a role in the heart decline of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. “I had a resident ask me a very important question: ‘How do we really know for sure that the trial actually reflects the true risk of heart events?’ to which I told him, ‘it’s difficult to know,’ ” he said.
“I think many of us rely heavily on what we see in the trials, particularly when they make it to the top journals, and quite frankly, we generally take it at face value,” Dr. Addison observed.
Lower Rate of Reported Events
The investigators reviewed CV events reported in 97,365 patients (median age, 61 years; 46% female) enrolled in 189 phase 2 and 3 trials supporting FDA approval of 123 anticancer drugs from 1998 to 2018. Biologic, targeted, or immune-based therapies accounted for 72.5% of drug approvals.
Over 148,138 person-years of follow-up (median trial duration, 30 months), there were 1,148 incidents of MACE (375 heart failure, 253 MIs, 180 strokes, 65 atrial fibrillation, 29 coronary revascularizations, and 246 CVD deaths). MACE rates were higher in the intervention group than in the control group (792 vs. 356; P less than .01). Among the 64 trials that excluded patients with baseline CVD, there were 269 incidents of MACE.
To put this finding in context, the researchers examined the reported incidence of MACE among some 6,000 similarly aged participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). The overall weighted-average incidence rate was 1,408 per 100,000 person-years among MESA participants, compared with 542 events per 100,000 person-years among oncology trial participants (716 per 100,000 in the intervention arm). This represents a reported-to-expected ratio of 0.38 – a 2.6-fold lower rate of reported events (P less than .001) – and a risk difference of 866.
Further, MACE reporting was lower by a factor of 1.7 among all cancer trial participants irrespective of baseline CVD status (reported-to-expected ratio, 0.56; risk difference, 613; P less than .001).
There was no significant difference in MACE reporting between independent or industry-sponsored trials, the authors report.
No malicious intent
“There are likely some that might lean toward not wanting to attribute blame to a new drug when the drug is in a study, but I really think that the leading factor is lack of awareness,” Dr. Addison said. “I’ve talked with several cancer collaborators around the country who run large clinical trials, and I think often, when an event may be brought to someone’s attention, there is a tendency to just write it off as kind of a generic expected event due to age, or just something that’s not really pertinent to the study. So they don’t really focus on it as much.”
“Closer collaboration between cardiologists and cancer physicians is needed to better determine true cardiac risks among patients treated with these drugs.”
Breast cancer oncologist Marc E. Lippman, MD, of Georgetown University Medical Center and Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Washington, D.C., isn’t convinced a lack of awareness is the culprit.
“I don’t agree with that at all,” he said in an interview. “I think there are very, very clear rules and guidelines these days for adverse-event reporting. I think that’s not a very likely explanation – that it’s not on the radar.”
Part of the problem may be that some of the toxicities, particularly cardiovascular, may not emerge for years, he said. Participant screening for the trials also likely removed patients with high cardiovascular risk. “It’s very understandable to me – I’m not saying it’s good particularly – but I think it’s very understandable that, if you’re trying to develop a drug, the last thing you’d want to have is a lot of toxicity that you might have avoided by just being restrictive in who you let into the study,” Dr. Lippman said.
The underreported CVD events may also reflect the rapidly changing profile of cardiovascular toxicities associated with novel anticancer therapies.
“Providers, both cancer and noncancer, generally put cardiotoxicity in the box of anthracyclines and radiation, but particularly over the last decade, we’ve begun to understand it’s well beyond any one class of drugs,” Dr. Addison said.
“I agree completely,” Dr. Lippman said. For example, “the checkpoint inhibitors are so unbelievably different in terms of their toxicities that many people simply didn’t even know what they were getting into at first.”
One size does not fit all
Javid Moslehi, MD, director of the cardio-oncology program at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said echocardiography – recommended to detect changes in left ventricular function in patients exposed to anthracyclines or targeted agents like trastuzumab (Herceptin) – isn’t enough to address today’s cancer therapy–related CVD events.
“Initial drugs like anthracyclines or Herceptin in cardio-oncology were associated with systolic cardiac dysfunction, whereas the majority of issues we see in the cardio-oncology clinics today are vascular, metabolic, arrhythmogenic, and inflammatory,” he said in an interview. “Echocardiography misses the big and increasingly complex picture.”
His group, for example, has been studying myocarditis associated with immunotherapies, but none of the clinical trials require screening or surveillance for myocarditis with a cardiac biomarker like troponin.
The group also recently identified 303 deaths in patients exposed to ibrutinib, a drug that revolutionized the treatment of several B-cell malignancies but is associated with higher rates of atrial fibrillation, which is also associated with increased bleeding risk. “So there’s a little bit of a double whammy there, given that we often treat atrial fibrillation with anticoagulation and where we can cause complications in patients,” Dr. Moslehi noted.
Although there needs to be closer collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists on individual trials, cardiologists also have to realize that oncology care has become very personalized, he suggested.
“What’s probably relevant for the breast cancer patient may not be relevant for the prostate cancer patient and their respective treatments,” Dr. Moslehi said. “So if we were to say, ‘every person should get an echo,’ that may be less relevant to the prostate cancer patient where treatments can cause vascular and metabolic perturbations or to the patient treated with immunotherapy who may have myocarditis, where many of the echos can be normal. There’s no one-size-fits-all for these things.”
Wearable technologies like smartwatches could play a role in improving the reporting of CVD events with novel therapies but a lot more research needs to be done to validate these tools, Dr. Addison said. “But as we continue on into the 21st century, this is going to expand and may potentially help us,” he added.
In the interim, better standardization is needed of the cardiovascular events reported in oncology trials, particularly the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), said Dr. Moslehi, who also serves as chair of the American Heart Association’s subcommittee on cardio-oncology.
“Cardiovascular definitions are not exactly uniform and are not consistent with what we in cardiology consider to be important or relevant,” he said. “So I think there needs to be better standardization of these definitions, specifically within the CTCAE, which is what the oncologists use to identify adverse events.”
In a linked editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:629-31), Dr. Lippman and cardiologist Nanette Bishopric, MD, of the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute in Washington, D.C., suggested it may also be time to organize a consortium that can carry out “rigorous multicenter clinical investigations to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of emerging cancer treatments,” similar to the Thrombosis in Myocardial Infarction Study Group.
“The success of this consortium in pioneering and targeting multiple generations of drugs for the treatment of MI, involving tens of thousands of patients and thousands of collaborations across multiple national borders, is a model for how to move forward in providing the new hope of cancer cure without the trade-off of years lost to heart disease,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants, including a K12-CA133250 grant to Dr. Addison. Dr. Bishopric reported being on the scientific board of C&C Biopharma. Dr. Lippman reports being on the board of directors of and holding stock in Seattle Genetics. Dr. Moslehi reported having served on advisory boards for Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Deciphera, Audentes Pharmaceuticals, Nektar, Takeda, Ipsen, Myokardia, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Intrexon, and Regeneron.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical trials supporting Food and Drug Adminstration approval of contemporary cancer therapies frequently failed to capture major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and, when they did, reported rates 2.6-fold lower than noncancer trials, new research shows.
Overall, 51.3% of trials did not report MACE, with that number reaching 57.6% in trials enrolling patients with baseline cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Nearly 40% of trials did not report any CVD events in follow-up, the authors reported online Feb. 10, 2020, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020;75:620-8).
“Even in drug classes where there were established or emerging associations with cardiotoxic events, often there were no reported heart events or cardiovascular events across years of follow-up in trials that examined hundreds or even thousands of patients. That was actually pretty surprising,” senior author Daniel Addison, MD, codirector of the cardio-oncology program at the Ohio State University Medical Center, Columbus, said in an interview.
The study was prompted by a series of events that crescendoed when his team was called to the ICU to determine whether a novel targeted agent played a role in the heart decline of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. “I had a resident ask me a very important question: ‘How do we really know for sure that the trial actually reflects the true risk of heart events?’ to which I told him, ‘it’s difficult to know,’ ” he said.
“I think many of us rely heavily on what we see in the trials, particularly when they make it to the top journals, and quite frankly, we generally take it at face value,” Dr. Addison observed.
Lower Rate of Reported Events
The investigators reviewed CV events reported in 97,365 patients (median age, 61 years; 46% female) enrolled in 189 phase 2 and 3 trials supporting FDA approval of 123 anticancer drugs from 1998 to 2018. Biologic, targeted, or immune-based therapies accounted for 72.5% of drug approvals.
Over 148,138 person-years of follow-up (median trial duration, 30 months), there were 1,148 incidents of MACE (375 heart failure, 253 MIs, 180 strokes, 65 atrial fibrillation, 29 coronary revascularizations, and 246 CVD deaths). MACE rates were higher in the intervention group than in the control group (792 vs. 356; P less than .01). Among the 64 trials that excluded patients with baseline CVD, there were 269 incidents of MACE.
To put this finding in context, the researchers examined the reported incidence of MACE among some 6,000 similarly aged participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). The overall weighted-average incidence rate was 1,408 per 100,000 person-years among MESA participants, compared with 542 events per 100,000 person-years among oncology trial participants (716 per 100,000 in the intervention arm). This represents a reported-to-expected ratio of 0.38 – a 2.6-fold lower rate of reported events (P less than .001) – and a risk difference of 866.
Further, MACE reporting was lower by a factor of 1.7 among all cancer trial participants irrespective of baseline CVD status (reported-to-expected ratio, 0.56; risk difference, 613; P less than .001).
There was no significant difference in MACE reporting between independent or industry-sponsored trials, the authors report.
No malicious intent
“There are likely some that might lean toward not wanting to attribute blame to a new drug when the drug is in a study, but I really think that the leading factor is lack of awareness,” Dr. Addison said. “I’ve talked with several cancer collaborators around the country who run large clinical trials, and I think often, when an event may be brought to someone’s attention, there is a tendency to just write it off as kind of a generic expected event due to age, or just something that’s not really pertinent to the study. So they don’t really focus on it as much.”
“Closer collaboration between cardiologists and cancer physicians is needed to better determine true cardiac risks among patients treated with these drugs.”
Breast cancer oncologist Marc E. Lippman, MD, of Georgetown University Medical Center and Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, Washington, D.C., isn’t convinced a lack of awareness is the culprit.
“I don’t agree with that at all,” he said in an interview. “I think there are very, very clear rules and guidelines these days for adverse-event reporting. I think that’s not a very likely explanation – that it’s not on the radar.”
Part of the problem may be that some of the toxicities, particularly cardiovascular, may not emerge for years, he said. Participant screening for the trials also likely removed patients with high cardiovascular risk. “It’s very understandable to me – I’m not saying it’s good particularly – but I think it’s very understandable that, if you’re trying to develop a drug, the last thing you’d want to have is a lot of toxicity that you might have avoided by just being restrictive in who you let into the study,” Dr. Lippman said.
The underreported CVD events may also reflect the rapidly changing profile of cardiovascular toxicities associated with novel anticancer therapies.
“Providers, both cancer and noncancer, generally put cardiotoxicity in the box of anthracyclines and radiation, but particularly over the last decade, we’ve begun to understand it’s well beyond any one class of drugs,” Dr. Addison said.
“I agree completely,” Dr. Lippman said. For example, “the checkpoint inhibitors are so unbelievably different in terms of their toxicities that many people simply didn’t even know what they were getting into at first.”
One size does not fit all
Javid Moslehi, MD, director of the cardio-oncology program at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said echocardiography – recommended to detect changes in left ventricular function in patients exposed to anthracyclines or targeted agents like trastuzumab (Herceptin) – isn’t enough to address today’s cancer therapy–related CVD events.
“Initial drugs like anthracyclines or Herceptin in cardio-oncology were associated with systolic cardiac dysfunction, whereas the majority of issues we see in the cardio-oncology clinics today are vascular, metabolic, arrhythmogenic, and inflammatory,” he said in an interview. “Echocardiography misses the big and increasingly complex picture.”
His group, for example, has been studying myocarditis associated with immunotherapies, but none of the clinical trials require screening or surveillance for myocarditis with a cardiac biomarker like troponin.
The group also recently identified 303 deaths in patients exposed to ibrutinib, a drug that revolutionized the treatment of several B-cell malignancies but is associated with higher rates of atrial fibrillation, which is also associated with increased bleeding risk. “So there’s a little bit of a double whammy there, given that we often treat atrial fibrillation with anticoagulation and where we can cause complications in patients,” Dr. Moslehi noted.
Although there needs to be closer collaboration between cardiologists and oncologists on individual trials, cardiologists also have to realize that oncology care has become very personalized, he suggested.
“What’s probably relevant for the breast cancer patient may not be relevant for the prostate cancer patient and their respective treatments,” Dr. Moslehi said. “So if we were to say, ‘every person should get an echo,’ that may be less relevant to the prostate cancer patient where treatments can cause vascular and metabolic perturbations or to the patient treated with immunotherapy who may have myocarditis, where many of the echos can be normal. There’s no one-size-fits-all for these things.”
Wearable technologies like smartwatches could play a role in improving the reporting of CVD events with novel therapies but a lot more research needs to be done to validate these tools, Dr. Addison said. “But as we continue on into the 21st century, this is going to expand and may potentially help us,” he added.
In the interim, better standardization is needed of the cardiovascular events reported in oncology trials, particularly the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), said Dr. Moslehi, who also serves as chair of the American Heart Association’s subcommittee on cardio-oncology.
“Cardiovascular definitions are not exactly uniform and are not consistent with what we in cardiology consider to be important or relevant,” he said. “So I think there needs to be better standardization of these definitions, specifically within the CTCAE, which is what the oncologists use to identify adverse events.”
In a linked editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:629-31), Dr. Lippman and cardiologist Nanette Bishopric, MD, of the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute in Washington, D.C., suggested it may also be time to organize a consortium that can carry out “rigorous multicenter clinical investigations to evaluate the cardiotoxicity of emerging cancer treatments,” similar to the Thrombosis in Myocardial Infarction Study Group.
“The success of this consortium in pioneering and targeting multiple generations of drugs for the treatment of MI, involving tens of thousands of patients and thousands of collaborations across multiple national borders, is a model for how to move forward in providing the new hope of cancer cure without the trade-off of years lost to heart disease,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants, including a K12-CA133250 grant to Dr. Addison. Dr. Bishopric reported being on the scientific board of C&C Biopharma. Dr. Lippman reports being on the board of directors of and holding stock in Seattle Genetics. Dr. Moslehi reported having served on advisory boards for Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Deciphera, Audentes Pharmaceuticals, Nektar, Takeda, Ipsen, Myokardia, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Intrexon, and Regeneron.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older NHL survivors show worse cognitive decline
Older long-term survivors of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) may have worse cognitive outcomes compared with the noncancer aging population, according to a cross-sectional study.
The findings suggest additional research is needed to better understand cognitive decline in older survivors of NHL.
“The aim of the present study was to examine the difference in cognitive status between a group of long-term older survivors of NHL compared with a group of noncancer controls of the same age,” wrote Domenico La Carpia, MD, of Fondazione ANT Italia Onlus, Florence, Italy, and colleagues.
The researchers conducted a multicenter cross-sectional cohort study involving 63 long-term survivors of NHL and 61 age-matched controls. Their report was published in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
Eligible survivors and controls were aged 65 years and older. Among both groups, the mean age of study participants was 74 years, and most survivors were women (58.7%).
While cognitive decline was assessed via standardized neuropsychological testing, the team also evaluated polypharmacy, functional status, and level of multimorbidity in the cohort.
Other clinical data, including the time from complete remission, type of treatment received, and histopathological type of tumor, were collected from patient charts and included in the analysis.
After analysis, the researchers found that NHL survivors had a higher mean number of chronic conditions (3.4 vs. 2.3; P = .003), were receiving more medications (3.4 vs. 2.3; P = .03), and had worse functional status compared with controls.
In addition, survivors had impaired executive functioning compared with control subjects (Trail Making Test B-A, 47.9 vs. 32.1; P = .04), but scores on the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) did not differ between the groups.
“A small, statistically significant difference was also observed in verbal memory scores between the two groups,” they reported.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation was the cross-sectional nature of the study; hence, causality cannot be inferred from the data.
“Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older cancer survivors is advisable to identify those individuals who are at highest risk of developing disability and to implement tailored early interventions,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: La Carpia D et al. J Geriatr Oncol. 2020 Jan 31. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2020.01.007.
Older long-term survivors of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) may have worse cognitive outcomes compared with the noncancer aging population, according to a cross-sectional study.
The findings suggest additional research is needed to better understand cognitive decline in older survivors of NHL.
“The aim of the present study was to examine the difference in cognitive status between a group of long-term older survivors of NHL compared with a group of noncancer controls of the same age,” wrote Domenico La Carpia, MD, of Fondazione ANT Italia Onlus, Florence, Italy, and colleagues.
The researchers conducted a multicenter cross-sectional cohort study involving 63 long-term survivors of NHL and 61 age-matched controls. Their report was published in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
Eligible survivors and controls were aged 65 years and older. Among both groups, the mean age of study participants was 74 years, and most survivors were women (58.7%).
While cognitive decline was assessed via standardized neuropsychological testing, the team also evaluated polypharmacy, functional status, and level of multimorbidity in the cohort.
Other clinical data, including the time from complete remission, type of treatment received, and histopathological type of tumor, were collected from patient charts and included in the analysis.
After analysis, the researchers found that NHL survivors had a higher mean number of chronic conditions (3.4 vs. 2.3; P = .003), were receiving more medications (3.4 vs. 2.3; P = .03), and had worse functional status compared with controls.
In addition, survivors had impaired executive functioning compared with control subjects (Trail Making Test B-A, 47.9 vs. 32.1; P = .04), but scores on the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) did not differ between the groups.
“A small, statistically significant difference was also observed in verbal memory scores between the two groups,” they reported.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation was the cross-sectional nature of the study; hence, causality cannot be inferred from the data.
“Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older cancer survivors is advisable to identify those individuals who are at highest risk of developing disability and to implement tailored early interventions,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: La Carpia D et al. J Geriatr Oncol. 2020 Jan 31. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2020.01.007.
Older long-term survivors of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) may have worse cognitive outcomes compared with the noncancer aging population, according to a cross-sectional study.
The findings suggest additional research is needed to better understand cognitive decline in older survivors of NHL.
“The aim of the present study was to examine the difference in cognitive status between a group of long-term older survivors of NHL compared with a group of noncancer controls of the same age,” wrote Domenico La Carpia, MD, of Fondazione ANT Italia Onlus, Florence, Italy, and colleagues.
The researchers conducted a multicenter cross-sectional cohort study involving 63 long-term survivors of NHL and 61 age-matched controls. Their report was published in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology.
Eligible survivors and controls were aged 65 years and older. Among both groups, the mean age of study participants was 74 years, and most survivors were women (58.7%).
While cognitive decline was assessed via standardized neuropsychological testing, the team also evaluated polypharmacy, functional status, and level of multimorbidity in the cohort.
Other clinical data, including the time from complete remission, type of treatment received, and histopathological type of tumor, were collected from patient charts and included in the analysis.
After analysis, the researchers found that NHL survivors had a higher mean number of chronic conditions (3.4 vs. 2.3; P = .003), were receiving more medications (3.4 vs. 2.3; P = .03), and had worse functional status compared with controls.
In addition, survivors had impaired executive functioning compared with control subjects (Trail Making Test B-A, 47.9 vs. 32.1; P = .04), but scores on the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) did not differ between the groups.
“A small, statistically significant difference was also observed in verbal memory scores between the two groups,” they reported.
The researchers acknowledged that a key limitation was the cross-sectional nature of the study; hence, causality cannot be inferred from the data.
“Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older cancer survivors is advisable to identify those individuals who are at highest risk of developing disability and to implement tailored early interventions,” they concluded.
No funding sources were reported. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: La Carpia D et al. J Geriatr Oncol. 2020 Jan 31. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2020.01.007.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC ONCOLOGY
Breast cancer treatments veer from guidelines
Women with breast cancer may be receiving treatments that are discordant with guideline recommendations for genetic subtypes of disease, based on a retrospective analysis of more than 20,000 patients.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were particularly out of alignment with guidelines, reported lead author Allison W. Kurian, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
“Integrating genetic testing into breast cancer care has been complex and challenging,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. “There is wide variability in which clinicians order testing and disclose results, in the clinical significance of results, and in how clinicians interpret results to patients.”
According to the investigators, while germline testing is on the rise, little is known about how these test results are translating to clinical care.
To learn more, the investigators evaluated data from 20,568 women with stage 0-III breast cancer who entered the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries of Georgia and California between 2014 and 2016.
Three treatment types were evaluated: surgery (bilateral vs. unilateral mastectomy), radiotherapy after lumpectomy, and chemotherapy. Treatment selection was compared with test results for breast cancer–associated genes, such as BRCA1/2, TP53, PTEN, and others. Associations were then compared with guideline recommendations.
Data analysis suggested that many clinicians were correctly using genetic test results to guide surgical decisions. For example, almost two-thirds (61.7%) of women with a BRCA mutation underwent bilateral mastectomy, compared with one-quarter (24.3%) who were BRCA negative (odds ratio, 5.52). For other pathogenic variants, the rate of bilateral mastectomy was still elevated, albeit to a lesser degree (OR, 2.41).
Generally, these practices align with recommendations, the investigators wrote, noting that research supports bilateral mastectomy with BRCA1/2, TP53, and PTEN variants, while data are lacking for other genetic subtypes.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were more discordant with guidelines. For example, women with a BRCA mutation were 78% less likely to receive radiotherapy after lumpectomy (OR, 0.22) and 76% more likely to receive chemotherapy for early-stage, hormone-positive disease (OR, 1.76). According to investigators, these findings suggest possible trends in undertreatment and overtreatment, respectively.
“We believe more research is needed to confirm our results and to evaluate long-term outcomes of pathogenic variant carriers to understand treatment decision making and consequences,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the California Department of Public Health. The investigators reported relationships with Myriad Genetics, Genomic Health, Roche, and other companies.
SOURCE: Kurian AW et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6400.
Women with breast cancer may be receiving treatments that are discordant with guideline recommendations for genetic subtypes of disease, based on a retrospective analysis of more than 20,000 patients.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were particularly out of alignment with guidelines, reported lead author Allison W. Kurian, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
“Integrating genetic testing into breast cancer care has been complex and challenging,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. “There is wide variability in which clinicians order testing and disclose results, in the clinical significance of results, and in how clinicians interpret results to patients.”
According to the investigators, while germline testing is on the rise, little is known about how these test results are translating to clinical care.
To learn more, the investigators evaluated data from 20,568 women with stage 0-III breast cancer who entered the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries of Georgia and California between 2014 and 2016.
Three treatment types were evaluated: surgery (bilateral vs. unilateral mastectomy), radiotherapy after lumpectomy, and chemotherapy. Treatment selection was compared with test results for breast cancer–associated genes, such as BRCA1/2, TP53, PTEN, and others. Associations were then compared with guideline recommendations.
Data analysis suggested that many clinicians were correctly using genetic test results to guide surgical decisions. For example, almost two-thirds (61.7%) of women with a BRCA mutation underwent bilateral mastectomy, compared with one-quarter (24.3%) who were BRCA negative (odds ratio, 5.52). For other pathogenic variants, the rate of bilateral mastectomy was still elevated, albeit to a lesser degree (OR, 2.41).
Generally, these practices align with recommendations, the investigators wrote, noting that research supports bilateral mastectomy with BRCA1/2, TP53, and PTEN variants, while data are lacking for other genetic subtypes.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were more discordant with guidelines. For example, women with a BRCA mutation were 78% less likely to receive radiotherapy after lumpectomy (OR, 0.22) and 76% more likely to receive chemotherapy for early-stage, hormone-positive disease (OR, 1.76). According to investigators, these findings suggest possible trends in undertreatment and overtreatment, respectively.
“We believe more research is needed to confirm our results and to evaluate long-term outcomes of pathogenic variant carriers to understand treatment decision making and consequences,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the California Department of Public Health. The investigators reported relationships with Myriad Genetics, Genomic Health, Roche, and other companies.
SOURCE: Kurian AW et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6400.
Women with breast cancer may be receiving treatments that are discordant with guideline recommendations for genetic subtypes of disease, based on a retrospective analysis of more than 20,000 patients.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were particularly out of alignment with guidelines, reported lead author Allison W. Kurian, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
“Integrating genetic testing into breast cancer care has been complex and challenging,” the investigators wrote in JAMA Oncology. “There is wide variability in which clinicians order testing and disclose results, in the clinical significance of results, and in how clinicians interpret results to patients.”
According to the investigators, while germline testing is on the rise, little is known about how these test results are translating to clinical care.
To learn more, the investigators evaluated data from 20,568 women with stage 0-III breast cancer who entered the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registries of Georgia and California between 2014 and 2016.
Three treatment types were evaluated: surgery (bilateral vs. unilateral mastectomy), radiotherapy after lumpectomy, and chemotherapy. Treatment selection was compared with test results for breast cancer–associated genes, such as BRCA1/2, TP53, PTEN, and others. Associations were then compared with guideline recommendations.
Data analysis suggested that many clinicians were correctly using genetic test results to guide surgical decisions. For example, almost two-thirds (61.7%) of women with a BRCA mutation underwent bilateral mastectomy, compared with one-quarter (24.3%) who were BRCA negative (odds ratio, 5.52). For other pathogenic variants, the rate of bilateral mastectomy was still elevated, albeit to a lesser degree (OR, 2.41).
Generally, these practices align with recommendations, the investigators wrote, noting that research supports bilateral mastectomy with BRCA1/2, TP53, and PTEN variants, while data are lacking for other genetic subtypes.
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy practices were more discordant with guidelines. For example, women with a BRCA mutation were 78% less likely to receive radiotherapy after lumpectomy (OR, 0.22) and 76% more likely to receive chemotherapy for early-stage, hormone-positive disease (OR, 1.76). According to investigators, these findings suggest possible trends in undertreatment and overtreatment, respectively.
“We believe more research is needed to confirm our results and to evaluate long-term outcomes of pathogenic variant carriers to understand treatment decision making and consequences,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the California Department of Public Health. The investigators reported relationships with Myriad Genetics, Genomic Health, Roche, and other companies.
SOURCE: Kurian AW et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Feb 6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6400.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Survival for older AML patients better with HSCT from unrelated donors
For adults aged 50 and older in first or second remission after induction therapy for acute myeloid leukemia, hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSCT) from young matched unrelated donors was associated with better overall survival and lower risk for relapse than transplants from haploidentical donors, a retrospective study suggests,
Among 823 patients from the aged 50 to 75 with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in a transplant registry, hazard ratios for both mortality and relapse were significantly higher for patients who received transplants from haploidentical siblings or offspring, compared with patients who received transplants from HLA-matched unrelated donors aged 40 or younger, reported Miguel-Angel Perales, MD, who is affiliated with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and colleagues.
“Our findings lend support to our hypothesis that a young [matched unrelated donor] should be the donor of choice when available. Furthermore, the data presented here suggest comparable times to transplantation in both treatment groups, confirming timely access to unrelated donors is no longer a barrier,” they wrote in Haematologica.Allogeneic transplants from matched unrelated donors have been performed for more than 30 years for treatment of patients with advanced myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. More recently, T-cell-replete bone marrow or peripheral blood transplants from haploidentical relatives, with post-transplant cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil to lower risk for graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) have become commonplace worldwide, and are established treatment options for patients with myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. There are conflicting studies suggesting that outcomes with haploidentical transplants are equivalent or superior to those seen with matched unrelated donors, the authors noted, but pointed to a 2018 study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplant and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR). Those study results found that, among transplant recipients aged 55 through 76, graft failure, nonrelapse mortality, and overall mortality were higher when the donors were haploidentical offspring rather than HLA-matched siblings.
To see whether patients aged 50 and older with AML might benefit more with transplants from hapolidentical relatives or matched unrelated donors, the investigators used CIBMTR data to review outcomes for 823 adults with AML who received a transplant in first or second remission at one of 90 U.S. centers from 2008 through 2015.
Of this cohort, 192 patients received grafts from haploidentical donors (25% from siblings and 75% from offspring), and 631 received grafts from matched unrelated donors ranging from 18 to 40 years of age.
Although the two groups were generally similar in demographic and disease characteristics, patients in the matched unrelated donor group had significantly higher frequency of poor-risk cytogenetics (P = .03) and were significantly more likely to have received a myeloablative condition regimen than a reduced-intensity regimen (P less than .001).
In the haploidentical group, 76% of patients were in first complete remission, and the remaining 24% were in second complete remission. In the HLA-matched group the respective proportions were 83% and 17%.
The median follow-up was 42 months in the haploidentical group and 47 months in the HLA-matched group. Five-year overall survival rates were 32% and 42%, respectively.
In multivariable models controlling for donor and recipient age, sex, performance score, hematopoietic cell transplant comorbidity score, cytomegalovirus serostatus, disease status, cytogenetic risk, transplant conditioning regimen intensity and transplant period, the hazard ratio (HR) for the primary endpoint of overall mortality was 1.27 for haploidentical vs. HLA-matched grafts (P = .04). The HR for relapse risk with haploidentical transplants was 1.32 (P =.04). No significant differences in risk of nonrelapse mortality were found between the two study arms.
Bone marrow grafts from matched unrelated donors were associated with significantly higher risk for chronic GvHD than haploidentical grafts (HR, 3.12; P less than .001), but there was no difference in chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) incidence between peripheral blood grafts from matched unrelated donors and haploidentical grafts.
“These data support the view that matched unrelated donor transplant with donors younger than 40 years is to be preferred,” the investigators wrote.
But in an interview, coauthor
“Even though there appears to be that clinical benefit for this older AML patient population, that benefit is not huge, and when you’re also accounting for the process of finding a donor and just getting someone into transplant, a lot of us weren’t sure if this was really going to be practice changing as the field does move into haploidentical transplants being more common,” he said.
He noted that the better outcomes among patients who received transplants from matched unrelated donors may be at least in part explained by the higher proportion of patients with unrelated donors who received myeloablative conditioning regimens. In this study, 65% of patients with haploidentical donors underwent reduced-intensity conditioning with total body irradiation, cyclophosphamide, and fludarabine.“If we do a comparison of equal conditioning regimens, are we really going to see the same outcomes in this setting? This might actually argue that, if you’re going to do a haploidentical transplant, you might start thinking about those newer, more ablative conditioning regimens,” he said.Dr. Tomlinson added that the data are reassuring, because of the modest size of the benefit, and because “many, many of our studies are showing that haploidentical transplants do almost as well as the matched ones. The big question mark will be what are the long-term outcomes? What happens after 3 years from those transplants? And that is going to take a lot more high quality, mature data.”In an editorial accompanying the study, Richard E. Champlin, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, noted that the more frequent use of reduced-intensity conditioning used for most patients in the haploidentical group has been associated in other studies with higher relapse rates, compared with other, more intense reduced-intensity regimens.
While he agreed that the study by Dr. Perales and colleagues “should give pause for thought, however, for those considering jumping to haploidentical transplants as a preferred approach in general,” he also noted that the study’s conclusion might not apply to cases where time-to-transplant is critical, or when other conditioning and GvHD prophylaxis regimens are used.
“The ideal study would compare optimized versions of both haploidentical and unrelated donor transplants, and use “intention-to-treat” analysis, including all patients for whom a transplant is intended from the time of initial HLA typing,” he wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Office of Naval Research. Dr. Tomlinson reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Champlin did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Perales M-A et al. Haematologica. 2020 Jan 31;105(2):407-13.
For adults aged 50 and older in first or second remission after induction therapy for acute myeloid leukemia, hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSCT) from young matched unrelated donors was associated with better overall survival and lower risk for relapse than transplants from haploidentical donors, a retrospective study suggests,
Among 823 patients from the aged 50 to 75 with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in a transplant registry, hazard ratios for both mortality and relapse were significantly higher for patients who received transplants from haploidentical siblings or offspring, compared with patients who received transplants from HLA-matched unrelated donors aged 40 or younger, reported Miguel-Angel Perales, MD, who is affiliated with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and colleagues.
“Our findings lend support to our hypothesis that a young [matched unrelated donor] should be the donor of choice when available. Furthermore, the data presented here suggest comparable times to transplantation in both treatment groups, confirming timely access to unrelated donors is no longer a barrier,” they wrote in Haematologica.Allogeneic transplants from matched unrelated donors have been performed for more than 30 years for treatment of patients with advanced myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. More recently, T-cell-replete bone marrow or peripheral blood transplants from haploidentical relatives, with post-transplant cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil to lower risk for graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) have become commonplace worldwide, and are established treatment options for patients with myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. There are conflicting studies suggesting that outcomes with haploidentical transplants are equivalent or superior to those seen with matched unrelated donors, the authors noted, but pointed to a 2018 study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplant and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR). Those study results found that, among transplant recipients aged 55 through 76, graft failure, nonrelapse mortality, and overall mortality were higher when the donors were haploidentical offspring rather than HLA-matched siblings.
To see whether patients aged 50 and older with AML might benefit more with transplants from hapolidentical relatives or matched unrelated donors, the investigators used CIBMTR data to review outcomes for 823 adults with AML who received a transplant in first or second remission at one of 90 U.S. centers from 2008 through 2015.
Of this cohort, 192 patients received grafts from haploidentical donors (25% from siblings and 75% from offspring), and 631 received grafts from matched unrelated donors ranging from 18 to 40 years of age.
Although the two groups were generally similar in demographic and disease characteristics, patients in the matched unrelated donor group had significantly higher frequency of poor-risk cytogenetics (P = .03) and were significantly more likely to have received a myeloablative condition regimen than a reduced-intensity regimen (P less than .001).
In the haploidentical group, 76% of patients were in first complete remission, and the remaining 24% were in second complete remission. In the HLA-matched group the respective proportions were 83% and 17%.
The median follow-up was 42 months in the haploidentical group and 47 months in the HLA-matched group. Five-year overall survival rates were 32% and 42%, respectively.
In multivariable models controlling for donor and recipient age, sex, performance score, hematopoietic cell transplant comorbidity score, cytomegalovirus serostatus, disease status, cytogenetic risk, transplant conditioning regimen intensity and transplant period, the hazard ratio (HR) for the primary endpoint of overall mortality was 1.27 for haploidentical vs. HLA-matched grafts (P = .04). The HR for relapse risk with haploidentical transplants was 1.32 (P =.04). No significant differences in risk of nonrelapse mortality were found between the two study arms.
Bone marrow grafts from matched unrelated donors were associated with significantly higher risk for chronic GvHD than haploidentical grafts (HR, 3.12; P less than .001), but there was no difference in chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) incidence between peripheral blood grafts from matched unrelated donors and haploidentical grafts.
“These data support the view that matched unrelated donor transplant with donors younger than 40 years is to be preferred,” the investigators wrote.
But in an interview, coauthor
“Even though there appears to be that clinical benefit for this older AML patient population, that benefit is not huge, and when you’re also accounting for the process of finding a donor and just getting someone into transplant, a lot of us weren’t sure if this was really going to be practice changing as the field does move into haploidentical transplants being more common,” he said.
He noted that the better outcomes among patients who received transplants from matched unrelated donors may be at least in part explained by the higher proportion of patients with unrelated donors who received myeloablative conditioning regimens. In this study, 65% of patients with haploidentical donors underwent reduced-intensity conditioning with total body irradiation, cyclophosphamide, and fludarabine.“If we do a comparison of equal conditioning regimens, are we really going to see the same outcomes in this setting? This might actually argue that, if you’re going to do a haploidentical transplant, you might start thinking about those newer, more ablative conditioning regimens,” he said.Dr. Tomlinson added that the data are reassuring, because of the modest size of the benefit, and because “many, many of our studies are showing that haploidentical transplants do almost as well as the matched ones. The big question mark will be what are the long-term outcomes? What happens after 3 years from those transplants? And that is going to take a lot more high quality, mature data.”In an editorial accompanying the study, Richard E. Champlin, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, noted that the more frequent use of reduced-intensity conditioning used for most patients in the haploidentical group has been associated in other studies with higher relapse rates, compared with other, more intense reduced-intensity regimens.
While he agreed that the study by Dr. Perales and colleagues “should give pause for thought, however, for those considering jumping to haploidentical transplants as a preferred approach in general,” he also noted that the study’s conclusion might not apply to cases where time-to-transplant is critical, or when other conditioning and GvHD prophylaxis regimens are used.
“The ideal study would compare optimized versions of both haploidentical and unrelated donor transplants, and use “intention-to-treat” analysis, including all patients for whom a transplant is intended from the time of initial HLA typing,” he wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Office of Naval Research. Dr. Tomlinson reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Champlin did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Perales M-A et al. Haematologica. 2020 Jan 31;105(2):407-13.
For adults aged 50 and older in first or second remission after induction therapy for acute myeloid leukemia, hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSCT) from young matched unrelated donors was associated with better overall survival and lower risk for relapse than transplants from haploidentical donors, a retrospective study suggests,
Among 823 patients from the aged 50 to 75 with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in a transplant registry, hazard ratios for both mortality and relapse were significantly higher for patients who received transplants from haploidentical siblings or offspring, compared with patients who received transplants from HLA-matched unrelated donors aged 40 or younger, reported Miguel-Angel Perales, MD, who is affiliated with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and colleagues.
“Our findings lend support to our hypothesis that a young [matched unrelated donor] should be the donor of choice when available. Furthermore, the data presented here suggest comparable times to transplantation in both treatment groups, confirming timely access to unrelated donors is no longer a barrier,” they wrote in Haematologica.Allogeneic transplants from matched unrelated donors have been performed for more than 30 years for treatment of patients with advanced myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. More recently, T-cell-replete bone marrow or peripheral blood transplants from haploidentical relatives, with post-transplant cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil to lower risk for graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) have become commonplace worldwide, and are established treatment options for patients with myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. There are conflicting studies suggesting that outcomes with haploidentical transplants are equivalent or superior to those seen with matched unrelated donors, the authors noted, but pointed to a 2018 study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplant and the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR). Those study results found that, among transplant recipients aged 55 through 76, graft failure, nonrelapse mortality, and overall mortality were higher when the donors were haploidentical offspring rather than HLA-matched siblings.
To see whether patients aged 50 and older with AML might benefit more with transplants from hapolidentical relatives or matched unrelated donors, the investigators used CIBMTR data to review outcomes for 823 adults with AML who received a transplant in first or second remission at one of 90 U.S. centers from 2008 through 2015.
Of this cohort, 192 patients received grafts from haploidentical donors (25% from siblings and 75% from offspring), and 631 received grafts from matched unrelated donors ranging from 18 to 40 years of age.
Although the two groups were generally similar in demographic and disease characteristics, patients in the matched unrelated donor group had significantly higher frequency of poor-risk cytogenetics (P = .03) and were significantly more likely to have received a myeloablative condition regimen than a reduced-intensity regimen (P less than .001).
In the haploidentical group, 76% of patients were in first complete remission, and the remaining 24% were in second complete remission. In the HLA-matched group the respective proportions were 83% and 17%.
The median follow-up was 42 months in the haploidentical group and 47 months in the HLA-matched group. Five-year overall survival rates were 32% and 42%, respectively.
In multivariable models controlling for donor and recipient age, sex, performance score, hematopoietic cell transplant comorbidity score, cytomegalovirus serostatus, disease status, cytogenetic risk, transplant conditioning regimen intensity and transplant period, the hazard ratio (HR) for the primary endpoint of overall mortality was 1.27 for haploidentical vs. HLA-matched grafts (P = .04). The HR for relapse risk with haploidentical transplants was 1.32 (P =.04). No significant differences in risk of nonrelapse mortality were found between the two study arms.
Bone marrow grafts from matched unrelated donors were associated with significantly higher risk for chronic GvHD than haploidentical grafts (HR, 3.12; P less than .001), but there was no difference in chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) incidence between peripheral blood grafts from matched unrelated donors and haploidentical grafts.
“These data support the view that matched unrelated donor transplant with donors younger than 40 years is to be preferred,” the investigators wrote.
But in an interview, coauthor
“Even though there appears to be that clinical benefit for this older AML patient population, that benefit is not huge, and when you’re also accounting for the process of finding a donor and just getting someone into transplant, a lot of us weren’t sure if this was really going to be practice changing as the field does move into haploidentical transplants being more common,” he said.
He noted that the better outcomes among patients who received transplants from matched unrelated donors may be at least in part explained by the higher proportion of patients with unrelated donors who received myeloablative conditioning regimens. In this study, 65% of patients with haploidentical donors underwent reduced-intensity conditioning with total body irradiation, cyclophosphamide, and fludarabine.“If we do a comparison of equal conditioning regimens, are we really going to see the same outcomes in this setting? This might actually argue that, if you’re going to do a haploidentical transplant, you might start thinking about those newer, more ablative conditioning regimens,” he said.Dr. Tomlinson added that the data are reassuring, because of the modest size of the benefit, and because “many, many of our studies are showing that haploidentical transplants do almost as well as the matched ones. The big question mark will be what are the long-term outcomes? What happens after 3 years from those transplants? And that is going to take a lot more high quality, mature data.”In an editorial accompanying the study, Richard E. Champlin, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, noted that the more frequent use of reduced-intensity conditioning used for most patients in the haploidentical group has been associated in other studies with higher relapse rates, compared with other, more intense reduced-intensity regimens.
While he agreed that the study by Dr. Perales and colleagues “should give pause for thought, however, for those considering jumping to haploidentical transplants as a preferred approach in general,” he also noted that the study’s conclusion might not apply to cases where time-to-transplant is critical, or when other conditioning and GvHD prophylaxis regimens are used.
“The ideal study would compare optimized versions of both haploidentical and unrelated donor transplants, and use “intention-to-treat” analysis, including all patients for whom a transplant is intended from the time of initial HLA typing,” he wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Office of Naval Research. Dr. Tomlinson reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Champlin did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Perales M-A et al. Haematologica. 2020 Jan 31;105(2):407-13.
FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
Data emerging to support personalized nutrition in oncology
SAN DIEGO – When Dawn Lemanne, MD, MPH, meets with cancer patients and their families, the question invariably comes up: “What should I eat?”
“The answer always is, ‘It depends,’” Dr. Lemanne, an oncologist who founded Oregon Integrative Oncology in Ashland, said at Natural Supplements: An Evidence-Based Update, presented by Scripps Center for Integrative Medicine. “The answers are not the same for each of these patients.”
According to Dr. Lemanne, targeted nutrition is evolving as a key component of cancer care. One of the goals of this approach is to decrease mTOR signaling. Normally, mTOR signaling promotes cell proliferation and metabolism; aberrant mTOR signaling can contribute to cancer initiation and progression.
“When mTOR speaks it says, ‘grow,’” said Dr. Lemanne, who is also an assistant professor of clinical medicine at the Andrew Weil Center for Integrative Medicine at the University of Arizona in Tucson. This message is meant to be heard by normal tissues, to stimulate normal tissue proliferation, such as in growing children or when a wound needs to be healed.
“However, cancer cells can hear and respond to mTOR’s message,” she said. “Normal cells may listen to mTOR’s ‘grow’ message or not, depending on the task they perform. Once we reach adulthood, we all likely have some precancerous or cancerous cells around, but they’re usually dormant. That’s why once you’re an adult, however, you don’t want too much mTOR signaling, because that might stimulate growth of things you definitely don’t want to grow.”
Having excessive levels of the growth hormone insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) also appears to play a role in cancer risk. Researchers studying members of a South American clan with Laron dwarfism – an inherited IGF-1 deficiency – found that besides being very short, affected members of this family rarely develop cancer (Cells. 2019;8[6]:596). “They also don’t get diabetes,” Dr. Lemanne said. “What we see in those with Laron dwarfism is that mTOR signaling is missing.”
She went on to note that studying type 2 diabetes gives physicians “a clue as to what dietary measures we might offer our patients in terms of decreasing their risk of dying from cancer or getting cancer.” The most common types of cancer are indeed more common in patients with type 2 diabetes. In addition, once someone with type 2 diabetes is diagnosed with cancer, their prognosis is poorer, compared with a cancer patient without diabetes.
“Metformin is often prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes because it helps keep blood sugar low,” she said. “What’s fascinating is that diabetics on metformin develop cancer less frequently than diabetics not taking this drug. And also interesting, those diabetics who do develop cancer seem to do better if they’re on metformin before and after diagnosis.”
On the other hand, exogenous insulin therapy given to people with type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of cancer. Consistent with this is the two-decades-old finding that an elevated fasting insulin level also is associated with a poor breast cancer prognosis (J Clin Oncol. 2002 Jan 1;20[1]:42-51). “It’s really important to understand that, in a person destined to become a type 2 diabetic, the level of fasting insulin rises long before fasting glucose becomes abnormally high,” Dr. Lemanne explained. “A normal fasting glucose doesn’t let you off the hook in terms of checking your patient for insulin resistance.
“We will miss diagnosing many patients with dangerous insulin resistance and prediabetes if we don’t check the fasting glucose and the fasting insulin levels together. If the fasting insulin level is high, it’s important to limit carbohydrate intake enough to bring it down permanently, even when the fasting glucose is normal, or the patient is likely at increased risk for developing cancer.”
Two large, prospective randomized trials have examined breast cancer and diet: the Women’s Intervention Study (WINS) and the Women’s Health Eating and Living Study (WHEL). Patients in both trials had early stage breast cancer and were put on low-fat diets. In the end, there was a weak to negligible connection between breast cancer survival and dietary fat restriction. “That kind of shook up the oncology world,” Dr. Lemanne said, “because before these two studies, everyone ‘knew’ that dietary fat was related to breast cancer risk. These studies showed that wasn’t the case at all.”
According to Dr. Lemanne, unexpectedly, moderate carbohydrate restriction has been associated with lower risk of breast cancer recurrence in patients with postmenopausal hormone-receptor expressing breast cancer. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego, conducted a subanalysis of 265 postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer from the WHEL cohort (Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 23[7]:1273-9). The recurrence risk was halved in those who cut their carbohydrate intake after diagnosis. The amount of decrease was modest, only 27 grams per day – the equivalent of one banana. “That is on par with a lot of our drugs, and maybe a little bit better,” she said. The effect was strongest if the breast tumor expressed IGF-1 receptor. Dr. Lemanne pointed out that decreasing dietary carbohydrate load was not the only treatment. These patients also had appropriate conventional cancer treatments, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. “If we cut just some of the daily carb load in these patients, they might have a better cancer prognosis,” she said.
Overweight or obese patients with colon cancer also may benefit from moderate carbohydrate restriction. The CALGB 89803 study assessed 1,011 subjects with stage III colon cancer. It found that the subjects in the highest quintile of daily glycemic load and total carbohydrate intake had an increased risk of cancer recurrence and mortality (hazard ratio, 2.26; J Nat Cancer Inst. 2012;104[22]:1702-11). “This is pretty strong evidence that glycemic load and total carbohydrate intake play a role in colon cancer recurrence, but there’s a caveat here,” she said. “The effect was seen only in patients who were overweight or obese.” There was no association between carbohydrate intake and colon cancer recurrence in the absence of overweight or obesity.
Based on existing evidence, she said,
“That’s pretty modest; that’s 400 calories of carbohydrates per day,” Dr. Lemanne said. “I tell patients that they can have fruit, starchy vegetables, and even very small amounts of healthy whole grains, although I’m not a fan of grains due to the heavy carbohydrate load. All those things are OK. We’re not talking about jelly beans and white sugar.
“I also have them measure their fasting glucose each day, because different people have different blood glucose responses to the same food.” The goals she aims for with many of her patients are a fasting morning glucose between 79 and 83 mg/dL consistently, an HbA1c of 5.4 or less, and a BMI of 24.9 kg/m2 or less. “This set of goals, however, has to be individualized,” she said.
The ketogenic diet is another form of carb restriction, “but it’s much more drastic,” Dr. Lemanne said. “Most people require a carbohydrate load below 30 grams a day to enter a state of ketosis. But ketosis lowers the blood sugar and dampens the mTOR signaling.”
Evidence is emerging to support the use of a ketogenic diet as an adjunct to radiation therapy and as part of a complete course of treatment for glioblastoma multiforme and cancer cachexia. As an adjunct to radiation, a ketogenic diet decreases insulin and IGF-1 signaling. “This causes normal cells to enter dormancy, decreasing oxidative damage in normal cells,” Dr. Lemanne said. “There is also suppression of tumor angiogenesis, and thus poor DNA repair of radiation damage in tumor cells (Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33[1]:217-29). Being in ketosis widens the therapeutic window. There are many animal studies which show that the ketogenic diet is helpful in cancer, mainly when combined with other anticancer treatments, such as radiation. Unfortunately, the evidence in humans is very anecdotal.”
One study found that if you feed mice with cancer ketogenic chow versus standard chow, they have a modestly improved survival (a mean of 43 days vs. 33 days; PLoS ONE. 2012;7[5]:e36197). However, when radiation was added to the keto diet, there was a dramatic improvement in survival (P less than 0.001). In fact, 75% survived to 250 days. “That’s pretty spectacular,” Dr. Lemanne said.
A ketogenic diet is standard therapy for several nonmalignant conditions, including glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome, pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency syndrome, and refractory infantile epilepsy. The three major ketone bodies involved in human nutrition are acetoacetate, beta hydroxybutyrate, and acetone. Dr. Lemanne said beta hydroxybutyrate decreases inflammation and inhibits hexadecynoic acids (which induces apoptosis in cancer cells). Beta hydroxybutyrate also increases sirtuins, innate immunity, and seizure threshold; modulates circadian rhythm; and decreases insulin levels, she said.
In one case report from the scientific literature, a 38-year-old male with glioblastoma multiforme was placed on a hypocaloric ketogenic diet (Front Nutr. 2018 Mar 29;5:20). The patient had surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and hyperbaric oxygen, and was given high doses of green tea extract in an attempt to antagonize glutamine metabolism. Two years after the beginning of his treatment, he was alive and had maintained a good level of tumor regression.
“We’ll see how he does,” said Dr. Lemanne, who was not involved in the report. “In my experience, I have a patient right now with a diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme. She’s getting a keto diet in combo with intensive chemo, radiation, and surgery. She’s also had some hyperbaric oxygen and IV ozone therapy and is taking repurposed drugs. She has exceeded her expected survival, but she continues to have disease and symptoms. We are by no means out of the woods with this patient. But the keto diet has been quite feasible for her, because she has a lot of family and outside support.”
A ketogenic diet also may benefit patients with cancer cachexia, which is a loss of lean tissue. “Cancer cachexia is not completely understood,” Dr. Lemanne said. “What we know is that it is caused by inflammation created by the tumor itself, and this, in turn results in severe insulin resistance. Therefore, giving more calories as carbohydrate makes the cancer cachexia situation worse. Animal models of cancer cachexia have shown that the ketogenic diet normalizes metabolism and prevents lean tissue loss. Human studies are underway; we’ll see how they turn out.”
She closed her presentation by noting that in copious amounts of animal studies, fasting has been linked to improvements in chemotherapy efficacy and decreased side effects. In one study carried out at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, volunteers fasted up to 140 hours before chemotherapy and an additional 156 hours afterward (Aging. 2009;1[12]:988-1007). The researchers found that the fasting was well-tolerated.
“The patients had some mild light-headedness, but there were no adverse effects on tumor volume or serum tumor markers,” Dr. Lemanne said. A more recent study of patients on cisplatin found that acaloric fasting led to decreased DNA damage in white blood cells, decreased IFG-1, and better white blood cell counts (BMC Cancer. 2016 Jun 10;16:360). “The benefits are immediate, and the optimal fasting time appears to be 48 hours,” Dr. Lemanne said.
One of her patients is a 64-year-old man on adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy for cholangiocarcinoma. He fasts 24 hours before and 24 hours after each infusion, and has experienced no emesis or nausea. “His immune suppression and anemia are much milder than we expected, and he has not required any treatment for chemotherapy-related side effects,” Dr. Lemanne said. “That’s a big monetary value.”
Fasting 13 hours overnight has been associated with fewer breast cancer-related problems in patients already diagnosed with the disease. Chronic caloric restriction, just cutting calories by 25%-40% daily, has been shown to delay all diseases of aging, including cancer, and is associated with increased longevity in many species. “Chronic caloric restriction is difficult, however, because it results in chronic hunger and weight loss,” she said. “Occasional fasting is superior to chronic caloric restriction because it maintains normal weight, preserves lean muscle mass, enhances tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and diminishes the side effects of chemotherapy.”
Dr. Lemanne reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – When Dawn Lemanne, MD, MPH, meets with cancer patients and their families, the question invariably comes up: “What should I eat?”
“The answer always is, ‘It depends,’” Dr. Lemanne, an oncologist who founded Oregon Integrative Oncology in Ashland, said at Natural Supplements: An Evidence-Based Update, presented by Scripps Center for Integrative Medicine. “The answers are not the same for each of these patients.”
According to Dr. Lemanne, targeted nutrition is evolving as a key component of cancer care. One of the goals of this approach is to decrease mTOR signaling. Normally, mTOR signaling promotes cell proliferation and metabolism; aberrant mTOR signaling can contribute to cancer initiation and progression.
“When mTOR speaks it says, ‘grow,’” said Dr. Lemanne, who is also an assistant professor of clinical medicine at the Andrew Weil Center for Integrative Medicine at the University of Arizona in Tucson. This message is meant to be heard by normal tissues, to stimulate normal tissue proliferation, such as in growing children or when a wound needs to be healed.
“However, cancer cells can hear and respond to mTOR’s message,” she said. “Normal cells may listen to mTOR’s ‘grow’ message or not, depending on the task they perform. Once we reach adulthood, we all likely have some precancerous or cancerous cells around, but they’re usually dormant. That’s why once you’re an adult, however, you don’t want too much mTOR signaling, because that might stimulate growth of things you definitely don’t want to grow.”
Having excessive levels of the growth hormone insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) also appears to play a role in cancer risk. Researchers studying members of a South American clan with Laron dwarfism – an inherited IGF-1 deficiency – found that besides being very short, affected members of this family rarely develop cancer (Cells. 2019;8[6]:596). “They also don’t get diabetes,” Dr. Lemanne said. “What we see in those with Laron dwarfism is that mTOR signaling is missing.”
She went on to note that studying type 2 diabetes gives physicians “a clue as to what dietary measures we might offer our patients in terms of decreasing their risk of dying from cancer or getting cancer.” The most common types of cancer are indeed more common in patients with type 2 diabetes. In addition, once someone with type 2 diabetes is diagnosed with cancer, their prognosis is poorer, compared with a cancer patient without diabetes.
“Metformin is often prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes because it helps keep blood sugar low,” she said. “What’s fascinating is that diabetics on metformin develop cancer less frequently than diabetics not taking this drug. And also interesting, those diabetics who do develop cancer seem to do better if they’re on metformin before and after diagnosis.”
On the other hand, exogenous insulin therapy given to people with type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of cancer. Consistent with this is the two-decades-old finding that an elevated fasting insulin level also is associated with a poor breast cancer prognosis (J Clin Oncol. 2002 Jan 1;20[1]:42-51). “It’s really important to understand that, in a person destined to become a type 2 diabetic, the level of fasting insulin rises long before fasting glucose becomes abnormally high,” Dr. Lemanne explained. “A normal fasting glucose doesn’t let you off the hook in terms of checking your patient for insulin resistance.
“We will miss diagnosing many patients with dangerous insulin resistance and prediabetes if we don’t check the fasting glucose and the fasting insulin levels together. If the fasting insulin level is high, it’s important to limit carbohydrate intake enough to bring it down permanently, even when the fasting glucose is normal, or the patient is likely at increased risk for developing cancer.”
Two large, prospective randomized trials have examined breast cancer and diet: the Women’s Intervention Study (WINS) and the Women’s Health Eating and Living Study (WHEL). Patients in both trials had early stage breast cancer and were put on low-fat diets. In the end, there was a weak to negligible connection between breast cancer survival and dietary fat restriction. “That kind of shook up the oncology world,” Dr. Lemanne said, “because before these two studies, everyone ‘knew’ that dietary fat was related to breast cancer risk. These studies showed that wasn’t the case at all.”
According to Dr. Lemanne, unexpectedly, moderate carbohydrate restriction has been associated with lower risk of breast cancer recurrence in patients with postmenopausal hormone-receptor expressing breast cancer. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego, conducted a subanalysis of 265 postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer from the WHEL cohort (Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 23[7]:1273-9). The recurrence risk was halved in those who cut their carbohydrate intake after diagnosis. The amount of decrease was modest, only 27 grams per day – the equivalent of one banana. “That is on par with a lot of our drugs, and maybe a little bit better,” she said. The effect was strongest if the breast tumor expressed IGF-1 receptor. Dr. Lemanne pointed out that decreasing dietary carbohydrate load was not the only treatment. These patients also had appropriate conventional cancer treatments, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. “If we cut just some of the daily carb load in these patients, they might have a better cancer prognosis,” she said.
Overweight or obese patients with colon cancer also may benefit from moderate carbohydrate restriction. The CALGB 89803 study assessed 1,011 subjects with stage III colon cancer. It found that the subjects in the highest quintile of daily glycemic load and total carbohydrate intake had an increased risk of cancer recurrence and mortality (hazard ratio, 2.26; J Nat Cancer Inst. 2012;104[22]:1702-11). “This is pretty strong evidence that glycemic load and total carbohydrate intake play a role in colon cancer recurrence, but there’s a caveat here,” she said. “The effect was seen only in patients who were overweight or obese.” There was no association between carbohydrate intake and colon cancer recurrence in the absence of overweight or obesity.
Based on existing evidence, she said,
“That’s pretty modest; that’s 400 calories of carbohydrates per day,” Dr. Lemanne said. “I tell patients that they can have fruit, starchy vegetables, and even very small amounts of healthy whole grains, although I’m not a fan of grains due to the heavy carbohydrate load. All those things are OK. We’re not talking about jelly beans and white sugar.
“I also have them measure their fasting glucose each day, because different people have different blood glucose responses to the same food.” The goals she aims for with many of her patients are a fasting morning glucose between 79 and 83 mg/dL consistently, an HbA1c of 5.4 or less, and a BMI of 24.9 kg/m2 or less. “This set of goals, however, has to be individualized,” she said.
The ketogenic diet is another form of carb restriction, “but it’s much more drastic,” Dr. Lemanne said. “Most people require a carbohydrate load below 30 grams a day to enter a state of ketosis. But ketosis lowers the blood sugar and dampens the mTOR signaling.”
Evidence is emerging to support the use of a ketogenic diet as an adjunct to radiation therapy and as part of a complete course of treatment for glioblastoma multiforme and cancer cachexia. As an adjunct to radiation, a ketogenic diet decreases insulin and IGF-1 signaling. “This causes normal cells to enter dormancy, decreasing oxidative damage in normal cells,” Dr. Lemanne said. “There is also suppression of tumor angiogenesis, and thus poor DNA repair of radiation damage in tumor cells (Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33[1]:217-29). Being in ketosis widens the therapeutic window. There are many animal studies which show that the ketogenic diet is helpful in cancer, mainly when combined with other anticancer treatments, such as radiation. Unfortunately, the evidence in humans is very anecdotal.”
One study found that if you feed mice with cancer ketogenic chow versus standard chow, they have a modestly improved survival (a mean of 43 days vs. 33 days; PLoS ONE. 2012;7[5]:e36197). However, when radiation was added to the keto diet, there was a dramatic improvement in survival (P less than 0.001). In fact, 75% survived to 250 days. “That’s pretty spectacular,” Dr. Lemanne said.
A ketogenic diet is standard therapy for several nonmalignant conditions, including glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome, pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency syndrome, and refractory infantile epilepsy. The three major ketone bodies involved in human nutrition are acetoacetate, beta hydroxybutyrate, and acetone. Dr. Lemanne said beta hydroxybutyrate decreases inflammation and inhibits hexadecynoic acids (which induces apoptosis in cancer cells). Beta hydroxybutyrate also increases sirtuins, innate immunity, and seizure threshold; modulates circadian rhythm; and decreases insulin levels, she said.
In one case report from the scientific literature, a 38-year-old male with glioblastoma multiforme was placed on a hypocaloric ketogenic diet (Front Nutr. 2018 Mar 29;5:20). The patient had surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and hyperbaric oxygen, and was given high doses of green tea extract in an attempt to antagonize glutamine metabolism. Two years after the beginning of his treatment, he was alive and had maintained a good level of tumor regression.
“We’ll see how he does,” said Dr. Lemanne, who was not involved in the report. “In my experience, I have a patient right now with a diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme. She’s getting a keto diet in combo with intensive chemo, radiation, and surgery. She’s also had some hyperbaric oxygen and IV ozone therapy and is taking repurposed drugs. She has exceeded her expected survival, but she continues to have disease and symptoms. We are by no means out of the woods with this patient. But the keto diet has been quite feasible for her, because she has a lot of family and outside support.”
A ketogenic diet also may benefit patients with cancer cachexia, which is a loss of lean tissue. “Cancer cachexia is not completely understood,” Dr. Lemanne said. “What we know is that it is caused by inflammation created by the tumor itself, and this, in turn results in severe insulin resistance. Therefore, giving more calories as carbohydrate makes the cancer cachexia situation worse. Animal models of cancer cachexia have shown that the ketogenic diet normalizes metabolism and prevents lean tissue loss. Human studies are underway; we’ll see how they turn out.”
She closed her presentation by noting that in copious amounts of animal studies, fasting has been linked to improvements in chemotherapy efficacy and decreased side effects. In one study carried out at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, volunteers fasted up to 140 hours before chemotherapy and an additional 156 hours afterward (Aging. 2009;1[12]:988-1007). The researchers found that the fasting was well-tolerated.
“The patients had some mild light-headedness, but there were no adverse effects on tumor volume or serum tumor markers,” Dr. Lemanne said. A more recent study of patients on cisplatin found that acaloric fasting led to decreased DNA damage in white blood cells, decreased IFG-1, and better white blood cell counts (BMC Cancer. 2016 Jun 10;16:360). “The benefits are immediate, and the optimal fasting time appears to be 48 hours,” Dr. Lemanne said.
One of her patients is a 64-year-old man on adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy for cholangiocarcinoma. He fasts 24 hours before and 24 hours after each infusion, and has experienced no emesis or nausea. “His immune suppression and anemia are much milder than we expected, and he has not required any treatment for chemotherapy-related side effects,” Dr. Lemanne said. “That’s a big monetary value.”
Fasting 13 hours overnight has been associated with fewer breast cancer-related problems in patients already diagnosed with the disease. Chronic caloric restriction, just cutting calories by 25%-40% daily, has been shown to delay all diseases of aging, including cancer, and is associated with increased longevity in many species. “Chronic caloric restriction is difficult, however, because it results in chronic hunger and weight loss,” she said. “Occasional fasting is superior to chronic caloric restriction because it maintains normal weight, preserves lean muscle mass, enhances tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and diminishes the side effects of chemotherapy.”
Dr. Lemanne reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – When Dawn Lemanne, MD, MPH, meets with cancer patients and their families, the question invariably comes up: “What should I eat?”
“The answer always is, ‘It depends,’” Dr. Lemanne, an oncologist who founded Oregon Integrative Oncology in Ashland, said at Natural Supplements: An Evidence-Based Update, presented by Scripps Center for Integrative Medicine. “The answers are not the same for each of these patients.”
According to Dr. Lemanne, targeted nutrition is evolving as a key component of cancer care. One of the goals of this approach is to decrease mTOR signaling. Normally, mTOR signaling promotes cell proliferation and metabolism; aberrant mTOR signaling can contribute to cancer initiation and progression.
“When mTOR speaks it says, ‘grow,’” said Dr. Lemanne, who is also an assistant professor of clinical medicine at the Andrew Weil Center for Integrative Medicine at the University of Arizona in Tucson. This message is meant to be heard by normal tissues, to stimulate normal tissue proliferation, such as in growing children or when a wound needs to be healed.
“However, cancer cells can hear and respond to mTOR’s message,” she said. “Normal cells may listen to mTOR’s ‘grow’ message or not, depending on the task they perform. Once we reach adulthood, we all likely have some precancerous or cancerous cells around, but they’re usually dormant. That’s why once you’re an adult, however, you don’t want too much mTOR signaling, because that might stimulate growth of things you definitely don’t want to grow.”
Having excessive levels of the growth hormone insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) also appears to play a role in cancer risk. Researchers studying members of a South American clan with Laron dwarfism – an inherited IGF-1 deficiency – found that besides being very short, affected members of this family rarely develop cancer (Cells. 2019;8[6]:596). “They also don’t get diabetes,” Dr. Lemanne said. “What we see in those with Laron dwarfism is that mTOR signaling is missing.”
She went on to note that studying type 2 diabetes gives physicians “a clue as to what dietary measures we might offer our patients in terms of decreasing their risk of dying from cancer or getting cancer.” The most common types of cancer are indeed more common in patients with type 2 diabetes. In addition, once someone with type 2 diabetes is diagnosed with cancer, their prognosis is poorer, compared with a cancer patient without diabetes.
“Metformin is often prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes because it helps keep blood sugar low,” she said. “What’s fascinating is that diabetics on metformin develop cancer less frequently than diabetics not taking this drug. And also interesting, those diabetics who do develop cancer seem to do better if they’re on metformin before and after diagnosis.”
On the other hand, exogenous insulin therapy given to people with type 2 diabetes doubles the risk of cancer. Consistent with this is the two-decades-old finding that an elevated fasting insulin level also is associated with a poor breast cancer prognosis (J Clin Oncol. 2002 Jan 1;20[1]:42-51). “It’s really important to understand that, in a person destined to become a type 2 diabetic, the level of fasting insulin rises long before fasting glucose becomes abnormally high,” Dr. Lemanne explained. “A normal fasting glucose doesn’t let you off the hook in terms of checking your patient for insulin resistance.
“We will miss diagnosing many patients with dangerous insulin resistance and prediabetes if we don’t check the fasting glucose and the fasting insulin levels together. If the fasting insulin level is high, it’s important to limit carbohydrate intake enough to bring it down permanently, even when the fasting glucose is normal, or the patient is likely at increased risk for developing cancer.”
Two large, prospective randomized trials have examined breast cancer and diet: the Women’s Intervention Study (WINS) and the Women’s Health Eating and Living Study (WHEL). Patients in both trials had early stage breast cancer and were put on low-fat diets. In the end, there was a weak to negligible connection between breast cancer survival and dietary fat restriction. “That kind of shook up the oncology world,” Dr. Lemanne said, “because before these two studies, everyone ‘knew’ that dietary fat was related to breast cancer risk. These studies showed that wasn’t the case at all.”
According to Dr. Lemanne, unexpectedly, moderate carbohydrate restriction has been associated with lower risk of breast cancer recurrence in patients with postmenopausal hormone-receptor expressing breast cancer. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego, conducted a subanalysis of 265 postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer from the WHEL cohort (Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 23[7]:1273-9). The recurrence risk was halved in those who cut their carbohydrate intake after diagnosis. The amount of decrease was modest, only 27 grams per day – the equivalent of one banana. “That is on par with a lot of our drugs, and maybe a little bit better,” she said. The effect was strongest if the breast tumor expressed IGF-1 receptor. Dr. Lemanne pointed out that decreasing dietary carbohydrate load was not the only treatment. These patients also had appropriate conventional cancer treatments, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. “If we cut just some of the daily carb load in these patients, they might have a better cancer prognosis,” she said.
Overweight or obese patients with colon cancer also may benefit from moderate carbohydrate restriction. The CALGB 89803 study assessed 1,011 subjects with stage III colon cancer. It found that the subjects in the highest quintile of daily glycemic load and total carbohydrate intake had an increased risk of cancer recurrence and mortality (hazard ratio, 2.26; J Nat Cancer Inst. 2012;104[22]:1702-11). “This is pretty strong evidence that glycemic load and total carbohydrate intake play a role in colon cancer recurrence, but there’s a caveat here,” she said. “The effect was seen only in patients who were overweight or obese.” There was no association between carbohydrate intake and colon cancer recurrence in the absence of overweight or obesity.
Based on existing evidence, she said,
“That’s pretty modest; that’s 400 calories of carbohydrates per day,” Dr. Lemanne said. “I tell patients that they can have fruit, starchy vegetables, and even very small amounts of healthy whole grains, although I’m not a fan of grains due to the heavy carbohydrate load. All those things are OK. We’re not talking about jelly beans and white sugar.
“I also have them measure their fasting glucose each day, because different people have different blood glucose responses to the same food.” The goals she aims for with many of her patients are a fasting morning glucose between 79 and 83 mg/dL consistently, an HbA1c of 5.4 or less, and a BMI of 24.9 kg/m2 or less. “This set of goals, however, has to be individualized,” she said.
The ketogenic diet is another form of carb restriction, “but it’s much more drastic,” Dr. Lemanne said. “Most people require a carbohydrate load below 30 grams a day to enter a state of ketosis. But ketosis lowers the blood sugar and dampens the mTOR signaling.”
Evidence is emerging to support the use of a ketogenic diet as an adjunct to radiation therapy and as part of a complete course of treatment for glioblastoma multiforme and cancer cachexia. As an adjunct to radiation, a ketogenic diet decreases insulin and IGF-1 signaling. “This causes normal cells to enter dormancy, decreasing oxidative damage in normal cells,” Dr. Lemanne said. “There is also suppression of tumor angiogenesis, and thus poor DNA repair of radiation damage in tumor cells (Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33[1]:217-29). Being in ketosis widens the therapeutic window. There are many animal studies which show that the ketogenic diet is helpful in cancer, mainly when combined with other anticancer treatments, such as radiation. Unfortunately, the evidence in humans is very anecdotal.”
One study found that if you feed mice with cancer ketogenic chow versus standard chow, they have a modestly improved survival (a mean of 43 days vs. 33 days; PLoS ONE. 2012;7[5]:e36197). However, when radiation was added to the keto diet, there was a dramatic improvement in survival (P less than 0.001). In fact, 75% survived to 250 days. “That’s pretty spectacular,” Dr. Lemanne said.
A ketogenic diet is standard therapy for several nonmalignant conditions, including glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome, pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency syndrome, and refractory infantile epilepsy. The three major ketone bodies involved in human nutrition are acetoacetate, beta hydroxybutyrate, and acetone. Dr. Lemanne said beta hydroxybutyrate decreases inflammation and inhibits hexadecynoic acids (which induces apoptosis in cancer cells). Beta hydroxybutyrate also increases sirtuins, innate immunity, and seizure threshold; modulates circadian rhythm; and decreases insulin levels, she said.
In one case report from the scientific literature, a 38-year-old male with glioblastoma multiforme was placed on a hypocaloric ketogenic diet (Front Nutr. 2018 Mar 29;5:20). The patient had surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and hyperbaric oxygen, and was given high doses of green tea extract in an attempt to antagonize glutamine metabolism. Two years after the beginning of his treatment, he was alive and had maintained a good level of tumor regression.
“We’ll see how he does,” said Dr. Lemanne, who was not involved in the report. “In my experience, I have a patient right now with a diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme. She’s getting a keto diet in combo with intensive chemo, radiation, and surgery. She’s also had some hyperbaric oxygen and IV ozone therapy and is taking repurposed drugs. She has exceeded her expected survival, but she continues to have disease and symptoms. We are by no means out of the woods with this patient. But the keto diet has been quite feasible for her, because she has a lot of family and outside support.”
A ketogenic diet also may benefit patients with cancer cachexia, which is a loss of lean tissue. “Cancer cachexia is not completely understood,” Dr. Lemanne said. “What we know is that it is caused by inflammation created by the tumor itself, and this, in turn results in severe insulin resistance. Therefore, giving more calories as carbohydrate makes the cancer cachexia situation worse. Animal models of cancer cachexia have shown that the ketogenic diet normalizes metabolism and prevents lean tissue loss. Human studies are underway; we’ll see how they turn out.”
She closed her presentation by noting that in copious amounts of animal studies, fasting has been linked to improvements in chemotherapy efficacy and decreased side effects. In one study carried out at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, volunteers fasted up to 140 hours before chemotherapy and an additional 156 hours afterward (Aging. 2009;1[12]:988-1007). The researchers found that the fasting was well-tolerated.
“The patients had some mild light-headedness, but there were no adverse effects on tumor volume or serum tumor markers,” Dr. Lemanne said. A more recent study of patients on cisplatin found that acaloric fasting led to decreased DNA damage in white blood cells, decreased IFG-1, and better white blood cell counts (BMC Cancer. 2016 Jun 10;16:360). “The benefits are immediate, and the optimal fasting time appears to be 48 hours,” Dr. Lemanne said.
One of her patients is a 64-year-old man on adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy for cholangiocarcinoma. He fasts 24 hours before and 24 hours after each infusion, and has experienced no emesis or nausea. “His immune suppression and anemia are much milder than we expected, and he has not required any treatment for chemotherapy-related side effects,” Dr. Lemanne said. “That’s a big monetary value.”
Fasting 13 hours overnight has been associated with fewer breast cancer-related problems in patients already diagnosed with the disease. Chronic caloric restriction, just cutting calories by 25%-40% daily, has been shown to delay all diseases of aging, including cancer, and is associated with increased longevity in many species. “Chronic caloric restriction is difficult, however, because it results in chronic hunger and weight loss,” she said. “Occasional fasting is superior to chronic caloric restriction because it maintains normal weight, preserves lean muscle mass, enhances tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and diminishes the side effects of chemotherapy.”
Dr. Lemanne reported having no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM A NATURAL SUPPLEMENTS UPDATE
Equal Access Makes A Difference in Surviving Prostate Cancer
In the general US population, African American men are more than twice as likely as non-Hispanic white men to die of prostate cancer. Researchers from the University of California at San Diego, though, speculated that disparities in access to care and not racial differences might be driving the differing outcomes. They turned to the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) with its “equal-access medical system” to find out.
Using data from a longitudinal database of > 20 million veterans, the researchers followed 18,201 black and 41,834 white patients with prostate cancer who were diagnosed between 2000 and 2015 and received care through the VA. The results of the study were published in Cancer.
African American men at diagnosis were younger (median age, 63 vs 66 years), more likely to smoke, and had more general health problems than did white men. Black patients also had higher prostate-specific antigen levels (median, 6.7 ng/mL vs 6.2 ng/mL) but were less likely to have Gleason score 8 to 10 disease, a clinical T classification ≥ 3, or distant metastatic disease.
There was no difference between the groups in time from diagnosis to treatment. The 10-year prostate cancer-specific mortality rate was actually slightly lower for African American men: 4.4%, compared with 5.1% for white men.
Thus, the researchers concluded that because African American men who receive VA healthcare do not appear to present with more advanced disease, or experience worse outcomes than do white men—in contrast to national trends. Therefore, they determined that access to care may be an important determinant of racial equity.
“Prior outcomes for African Americans with prostate cancer don’t have to be a foregone conclusion,” the senior author, Brent Rose, MD, told The New York Times. “They are at least partly due to policy decisions we make about access to care.”
In the general US population, African American men are more than twice as likely as non-Hispanic white men to die of prostate cancer. Researchers from the University of California at San Diego, though, speculated that disparities in access to care and not racial differences might be driving the differing outcomes. They turned to the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) with its “equal-access medical system” to find out.
Using data from a longitudinal database of > 20 million veterans, the researchers followed 18,201 black and 41,834 white patients with prostate cancer who were diagnosed between 2000 and 2015 and received care through the VA. The results of the study were published in Cancer.
African American men at diagnosis were younger (median age, 63 vs 66 years), more likely to smoke, and had more general health problems than did white men. Black patients also had higher prostate-specific antigen levels (median, 6.7 ng/mL vs 6.2 ng/mL) but were less likely to have Gleason score 8 to 10 disease, a clinical T classification ≥ 3, or distant metastatic disease.
There was no difference between the groups in time from diagnosis to treatment. The 10-year prostate cancer-specific mortality rate was actually slightly lower for African American men: 4.4%, compared with 5.1% for white men.
Thus, the researchers concluded that because African American men who receive VA healthcare do not appear to present with more advanced disease, or experience worse outcomes than do white men—in contrast to national trends. Therefore, they determined that access to care may be an important determinant of racial equity.
“Prior outcomes for African Americans with prostate cancer don’t have to be a foregone conclusion,” the senior author, Brent Rose, MD, told The New York Times. “They are at least partly due to policy decisions we make about access to care.”
In the general US population, African American men are more than twice as likely as non-Hispanic white men to die of prostate cancer. Researchers from the University of California at San Diego, though, speculated that disparities in access to care and not racial differences might be driving the differing outcomes. They turned to the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) with its “equal-access medical system” to find out.
Using data from a longitudinal database of > 20 million veterans, the researchers followed 18,201 black and 41,834 white patients with prostate cancer who were diagnosed between 2000 and 2015 and received care through the VA. The results of the study were published in Cancer.
African American men at diagnosis were younger (median age, 63 vs 66 years), more likely to smoke, and had more general health problems than did white men. Black patients also had higher prostate-specific antigen levels (median, 6.7 ng/mL vs 6.2 ng/mL) but were less likely to have Gleason score 8 to 10 disease, a clinical T classification ≥ 3, or distant metastatic disease.
There was no difference between the groups in time from diagnosis to treatment. The 10-year prostate cancer-specific mortality rate was actually slightly lower for African American men: 4.4%, compared with 5.1% for white men.
Thus, the researchers concluded that because African American men who receive VA healthcare do not appear to present with more advanced disease, or experience worse outcomes than do white men—in contrast to national trends. Therefore, they determined that access to care may be an important determinant of racial equity.
“Prior outcomes for African Americans with prostate cancer don’t have to be a foregone conclusion,” the senior author, Brent Rose, MD, told The New York Times. “They are at least partly due to policy decisions we make about access to care.”



