User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Cell therapy promising as long-term limb-saving treatment in diabetes
Bone marrow derived autologous cell therapy (ACT) has been shown to significantly reduce the rate of major amputation at 5 years in people with diabetes who developed critical limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI).
In a study of 130 patients, 64% of 42 patients who were treated conservatively needed a major amputation at 5 years versus just 30% of 45 patients who had been treated with ACT (P = .011).
This compared favorably to the results seen with repeated percutaneous angioplasty (re-PTA), where just 20.9% of 43 patients underwent limb salvage (P = .002 vs. conservative therapy).
Furthermore, amputation-free survival was significantly longer in both active groups, Michal Dubský, MD, PhD, FRSPH, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Dubský, of the Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine and Charles University in Prague, also reported that fewer patients who had undergone re-PTA or ACT than conservative treatment had died by 5 years (25.8% and 35.6%, respectively, vs. 61.9%), but that the difference was significant only for the revascularization procedure (P = .012).
Based on these findings, “we believe that autologous cell therapy seems to be an appropriate alternative to repeated PTA even for patients with no-option chronic limb-threatening ischemia,” he said.
“This is a very important area,” said Andrew J.M. Boulton, MBBS, MD, FRCP, who chaired the oral abstract presentation session during which the findings were presented.
“It is very difficult to get an evidence base from randomized studies in this area, because of the nature of the patients: They’re very sick and we all deal with them in our clinics very regularly,” added Dr. Boulton, professor of medicine within the division of diabetes, endocrinology and gastroenterology at the University of Manchester (England).
Dr. Boulton called the findings a “very important addition to what we know.”
New option for no-option CLTI
CLTI is associated with persistent pain at rest, ulcers, and gangrene, and can be the end result of longstanding peripheral arterial disease. Within the first year of presentation, there’s a 30% chance of having a major amputation and a 25% chance of dying.
Importantly, said Dr. Dubský, “there is a big difference in this diagnosis” between patients with diabetes and those without. For instance, CLTI is more diffuse in patients with diabetes than in those without, different arteries are affected and the sclerosis seen can be more rigid and “full of calcium.”
While surgery to improve blood flow is the standard of care, not everyone is suitable. Bypass surgery or endovascular procedures can be performed in only 40%-50% of patients, and even then a therapeutic effect may be seen in only a quarter of patients.
“We need some new therapeutic modalities for this diagnosis, and one of them could be autologous cell therapy,” said Dr. Dubský.
Study details
Dr. Dubský and coinvestigators consecutively recruited 130 patients with diabetic foot and CLTI who had been seen at their clinic over a 5-year period. Of these, 87 had not been eligible for standard revascularization and underwent ACT or were treated conservatively.
Of the patients who were not eligible for standard revascularization (‘no-option CLTI), 45 had undergone ACT and 42 had been treated conservatively. Dr. Dubský acknowledged that “his study was not prospective and randomized.”
All patients in the study had at least one unsuccessful revascularization procedure and diabetic foot ulcers, and low tissue oxygenation. The latter was defined as transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TcPO2) of below 30 mm Hg.
There were little differences in demographic characteristics between the treatment groups, the average age ranged from 62 to 67 years, there were more men (70%-80%) than women; most patients (90%) had type 2 diabetes for at least 20 years. There were similar rates of ischemic heart disease, hypertension, dialysis, and immunosuppressive therapy.
There were no differences in baseline values of TcPO2 between the groups, and similar improvements were seen in both the ACT and re-PTA groups versus conservative group.
ACT in practice
With such promising results, what about the practicalities of harvesting a patient’s bone marrow to make the ACT?
“Bone marrow harvesting usually takes about 20 minutes,” Dr. Dubský said. It then takes another 45 minutes to separate the cells and make the cell suspension, and then maybe another 10 minutes or so to administer this to the patient, which is done by injecting into the calf muscles and small muscles of the foot, aided by computed tomography. The whole process may take up to 2 hours, he said.
“Patients are under local or general anesthesia, so there is no pain during the procedure,” Dr. Dubský reassured. “Afterwards we sometimes see small hematoma[s], with low-intensity pain that responds well to usual analgesic therapy.”
Computed tomography was used to help guide the injections, which was advantageous, Dr. Boulton pointed out, because it was “less invasive than angioplasty in these very sick people with very distal lesions, many of whom already have renal problems.”
“It is surprising though, that everybody had re-PTA and not one had vascular surgery,” he suggested. Dr. Boulton added, however: “These are very important observations; they help us a lot in an area where there’s unlikely to be a full RCT.”
The next step in this research is to see if combining ACT and re-PTA could lead to even better results.
The study was funded by the Czech Republic Ministry of Health. Dr. Dubský had nothing to disclose. Dr. Boulton made no statement about his conflicts of interest.
Bone marrow derived autologous cell therapy (ACT) has been shown to significantly reduce the rate of major amputation at 5 years in people with diabetes who developed critical limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI).
In a study of 130 patients, 64% of 42 patients who were treated conservatively needed a major amputation at 5 years versus just 30% of 45 patients who had been treated with ACT (P = .011).
This compared favorably to the results seen with repeated percutaneous angioplasty (re-PTA), where just 20.9% of 43 patients underwent limb salvage (P = .002 vs. conservative therapy).
Furthermore, amputation-free survival was significantly longer in both active groups, Michal Dubský, MD, PhD, FRSPH, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Dubský, of the Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine and Charles University in Prague, also reported that fewer patients who had undergone re-PTA or ACT than conservative treatment had died by 5 years (25.8% and 35.6%, respectively, vs. 61.9%), but that the difference was significant only for the revascularization procedure (P = .012).
Based on these findings, “we believe that autologous cell therapy seems to be an appropriate alternative to repeated PTA even for patients with no-option chronic limb-threatening ischemia,” he said.
“This is a very important area,” said Andrew J.M. Boulton, MBBS, MD, FRCP, who chaired the oral abstract presentation session during which the findings were presented.
“It is very difficult to get an evidence base from randomized studies in this area, because of the nature of the patients: They’re very sick and we all deal with them in our clinics very regularly,” added Dr. Boulton, professor of medicine within the division of diabetes, endocrinology and gastroenterology at the University of Manchester (England).
Dr. Boulton called the findings a “very important addition to what we know.”
New option for no-option CLTI
CLTI is associated with persistent pain at rest, ulcers, and gangrene, and can be the end result of longstanding peripheral arterial disease. Within the first year of presentation, there’s a 30% chance of having a major amputation and a 25% chance of dying.
Importantly, said Dr. Dubský, “there is a big difference in this diagnosis” between patients with diabetes and those without. For instance, CLTI is more diffuse in patients with diabetes than in those without, different arteries are affected and the sclerosis seen can be more rigid and “full of calcium.”
While surgery to improve blood flow is the standard of care, not everyone is suitable. Bypass surgery or endovascular procedures can be performed in only 40%-50% of patients, and even then a therapeutic effect may be seen in only a quarter of patients.
“We need some new therapeutic modalities for this diagnosis, and one of them could be autologous cell therapy,” said Dr. Dubský.
Study details
Dr. Dubský and coinvestigators consecutively recruited 130 patients with diabetic foot and CLTI who had been seen at their clinic over a 5-year period. Of these, 87 had not been eligible for standard revascularization and underwent ACT or were treated conservatively.
Of the patients who were not eligible for standard revascularization (‘no-option CLTI), 45 had undergone ACT and 42 had been treated conservatively. Dr. Dubský acknowledged that “his study was not prospective and randomized.”
All patients in the study had at least one unsuccessful revascularization procedure and diabetic foot ulcers, and low tissue oxygenation. The latter was defined as transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TcPO2) of below 30 mm Hg.
There were little differences in demographic characteristics between the treatment groups, the average age ranged from 62 to 67 years, there were more men (70%-80%) than women; most patients (90%) had type 2 diabetes for at least 20 years. There were similar rates of ischemic heart disease, hypertension, dialysis, and immunosuppressive therapy.
There were no differences in baseline values of TcPO2 between the groups, and similar improvements were seen in both the ACT and re-PTA groups versus conservative group.
ACT in practice
With such promising results, what about the practicalities of harvesting a patient’s bone marrow to make the ACT?
“Bone marrow harvesting usually takes about 20 minutes,” Dr. Dubský said. It then takes another 45 minutes to separate the cells and make the cell suspension, and then maybe another 10 minutes or so to administer this to the patient, which is done by injecting into the calf muscles and small muscles of the foot, aided by computed tomography. The whole process may take up to 2 hours, he said.
“Patients are under local or general anesthesia, so there is no pain during the procedure,” Dr. Dubský reassured. “Afterwards we sometimes see small hematoma[s], with low-intensity pain that responds well to usual analgesic therapy.”
Computed tomography was used to help guide the injections, which was advantageous, Dr. Boulton pointed out, because it was “less invasive than angioplasty in these very sick people with very distal lesions, many of whom already have renal problems.”
“It is surprising though, that everybody had re-PTA and not one had vascular surgery,” he suggested. Dr. Boulton added, however: “These are very important observations; they help us a lot in an area where there’s unlikely to be a full RCT.”
The next step in this research is to see if combining ACT and re-PTA could lead to even better results.
The study was funded by the Czech Republic Ministry of Health. Dr. Dubský had nothing to disclose. Dr. Boulton made no statement about his conflicts of interest.
Bone marrow derived autologous cell therapy (ACT) has been shown to significantly reduce the rate of major amputation at 5 years in people with diabetes who developed critical limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI).
In a study of 130 patients, 64% of 42 patients who were treated conservatively needed a major amputation at 5 years versus just 30% of 45 patients who had been treated with ACT (P = .011).
This compared favorably to the results seen with repeated percutaneous angioplasty (re-PTA), where just 20.9% of 43 patients underwent limb salvage (P = .002 vs. conservative therapy).
Furthermore, amputation-free survival was significantly longer in both active groups, Michal Dubský, MD, PhD, FRSPH, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Dubský, of the Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine and Charles University in Prague, also reported that fewer patients who had undergone re-PTA or ACT than conservative treatment had died by 5 years (25.8% and 35.6%, respectively, vs. 61.9%), but that the difference was significant only for the revascularization procedure (P = .012).
Based on these findings, “we believe that autologous cell therapy seems to be an appropriate alternative to repeated PTA even for patients with no-option chronic limb-threatening ischemia,” he said.
“This is a very important area,” said Andrew J.M. Boulton, MBBS, MD, FRCP, who chaired the oral abstract presentation session during which the findings were presented.
“It is very difficult to get an evidence base from randomized studies in this area, because of the nature of the patients: They’re very sick and we all deal with them in our clinics very regularly,” added Dr. Boulton, professor of medicine within the division of diabetes, endocrinology and gastroenterology at the University of Manchester (England).
Dr. Boulton called the findings a “very important addition to what we know.”
New option for no-option CLTI
CLTI is associated with persistent pain at rest, ulcers, and gangrene, and can be the end result of longstanding peripheral arterial disease. Within the first year of presentation, there’s a 30% chance of having a major amputation and a 25% chance of dying.
Importantly, said Dr. Dubský, “there is a big difference in this diagnosis” between patients with diabetes and those without. For instance, CLTI is more diffuse in patients with diabetes than in those without, different arteries are affected and the sclerosis seen can be more rigid and “full of calcium.”
While surgery to improve blood flow is the standard of care, not everyone is suitable. Bypass surgery or endovascular procedures can be performed in only 40%-50% of patients, and even then a therapeutic effect may be seen in only a quarter of patients.
“We need some new therapeutic modalities for this diagnosis, and one of them could be autologous cell therapy,” said Dr. Dubský.
Study details
Dr. Dubský and coinvestigators consecutively recruited 130 patients with diabetic foot and CLTI who had been seen at their clinic over a 5-year period. Of these, 87 had not been eligible for standard revascularization and underwent ACT or were treated conservatively.
Of the patients who were not eligible for standard revascularization (‘no-option CLTI), 45 had undergone ACT and 42 had been treated conservatively. Dr. Dubský acknowledged that “his study was not prospective and randomized.”
All patients in the study had at least one unsuccessful revascularization procedure and diabetic foot ulcers, and low tissue oxygenation. The latter was defined as transcutaneous oxygen pressure (TcPO2) of below 30 mm Hg.
There were little differences in demographic characteristics between the treatment groups, the average age ranged from 62 to 67 years, there were more men (70%-80%) than women; most patients (90%) had type 2 diabetes for at least 20 years. There were similar rates of ischemic heart disease, hypertension, dialysis, and immunosuppressive therapy.
There were no differences in baseline values of TcPO2 between the groups, and similar improvements were seen in both the ACT and re-PTA groups versus conservative group.
ACT in practice
With such promising results, what about the practicalities of harvesting a patient’s bone marrow to make the ACT?
“Bone marrow harvesting usually takes about 20 minutes,” Dr. Dubský said. It then takes another 45 minutes to separate the cells and make the cell suspension, and then maybe another 10 minutes or so to administer this to the patient, which is done by injecting into the calf muscles and small muscles of the foot, aided by computed tomography. The whole process may take up to 2 hours, he said.
“Patients are under local or general anesthesia, so there is no pain during the procedure,” Dr. Dubský reassured. “Afterwards we sometimes see small hematoma[s], with low-intensity pain that responds well to usual analgesic therapy.”
Computed tomography was used to help guide the injections, which was advantageous, Dr. Boulton pointed out, because it was “less invasive than angioplasty in these very sick people with very distal lesions, many of whom already have renal problems.”
“It is surprising though, that everybody had re-PTA and not one had vascular surgery,” he suggested. Dr. Boulton added, however: “These are very important observations; they help us a lot in an area where there’s unlikely to be a full RCT.”
The next step in this research is to see if combining ACT and re-PTA could lead to even better results.
The study was funded by the Czech Republic Ministry of Health. Dr. Dubský had nothing to disclose. Dr. Boulton made no statement about his conflicts of interest.
FROM EASD 2021
Drug cocktail significantly reduced severe COVID, death in outpatients
A monoclonal antibody combination of casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19–related hospitalizations and death from any cause in the phase 3 portion of an adaptive trial of outpatients.
Researchers, led by David Weinreich, MD, MBA, executive vice president of the drug cocktail’s manufacturer Regeneron, found in the randomized trial that the combination also resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more quickly, compared with placebo.
Findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
COVID-related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 18 of 1,355 patients (1.3%) in the group getting 2,400 mg infusions of the study drug, compared with 62 (4.6%) of 1,341 in the matching placebo group, indicating a relative risk reduction of 71.3%; P < .001.
Sunil Joshi, MD, president of the Duval County Medical Society Foundation and an immunologist in Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview that these findings confirm benefits of REGEN-COV and are very good news for a patient group that includes those age 65 and older with high blood pressure, diabetes, or obesity; and for people not vaccinated, who are all at high risk of hospitalization or death if they get COVID-19.
“Vaccines are critically important,” he said, “but if you were to be infected and know that there’s a way to keep yourself out of the hospital, this is very good news.”
Researchers seek lowest doses
This trial found that the effect was similar when researchers cut the doses in half. These outcomes occurred in 7 of 736 (1%) of patients given 1,200 mg of REGEN-COV and in 24 (3.2%) of 748 in the matching placebo group (relative risk reduction, 70.4%; P = .002).
Symptoms were resolved on average 4 days earlier with each REGEN-COV dose than with placebo (10 days vs. 14 days; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Dr. Weinreich said in an interview that trials will continue to find the lowest effective doses that can stand up to all evolving variants.
“This is one of those settings where you don’t want to underdose. You’ve got one shot at this,” he said. “We’d love to do lower doses. It would be more convenient and we could treat more patients, but if it generates more clinical failures or doesn’t work with certain variants, then you’ve done a huge disservice to the world.”
Also new in this study is that researchers tested not only seronegative patients, but patients at high risk regardless of blood antibody status, he said.
“It’s the first suggestion of data that if you’re breaking through a vaccine and you’re at high risk, the use of the cocktail is something to strongly consider because treatment early is better than treatment later,” Dr. Weinreich said.
In addition to efficacy, the phase 3 trial demonstrated the cocktail had a good safety profile. Serious adverse events occurred more often in the placebo group (4%) than in the 1,200-mg group (1.1%) and the 2,400-mg group (1.3%). Infusion reactions (grade 2 or higher) occurred in less than 0.3% of patients in all groups.
William Fales, MD, state medical director for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, said the results confirm the promise of REGEN-COV for reducing hospitalizations and death in a peer-reviewed publication.
COVID-19 a moving target
However, Dr. Fales noted that COVID-19 is a moving target with emerging variants. The criteria for populations at high risk have also broadened since the start of the study, he said.
“A great example is pregnancy is now included as high risk, and that would have likely been a specific contraindication of patients in this clinical trial,” he said.
Dr. Fales said Michigan has been using both REGEN-COV and the Eli Lilly combination of bamlanivimab and etesevimab, which also has an emergency use authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration, with positive results.
REGEN-COV has an EUA to treat people who are at high risk of serious consequences from COVID-19, including those who are already infected (nonhospitalized) or those in certain postexposure prophylaxis settings.
“We’re seeing very low hospitalization rates and few deaths in a state that is predominately Delta,” Dr. Fales said. “So, this makes us feel that we’re doing the right thing and supports the current efforts around the country to make monoclonal antibody therapy available to high-risk patients.”
Dr. Joshi noted that trial results have been emerging from other monoclonal antibody cocktails with different COVID-19 patient groups.
However, he said in an interview, “how much more effective they would be than this is something we’d have to look at, as 71% effectiveness in keeping people out of the hospital is pretty good for any treatment.”
“These are great numbers, but vaccination itself keeps you from getting the disease in the first place and not just for a short time period. This treatment is just that – a treatment. It gets you through that episode but it doesn’t mean you won’t get sick again. You don’t develop an immune response as you do with the vaccine,” he said.
Dr. Weinreich agreed: “This is not a substitute for a vaccine except for the small group who get the vaccine and their bodies can’t respond to it because they’re significantly immunocompromised.”
The results from this paper “are one piece of a large, multistudy, phase 3 program that basically spans from prophylaxis all the way to hospitalization and pretty much the gamut – all of them – have worked. All of these studies have shown dramatic improvement in whatever the definitive regulatory endpoint is,” Dr. Weinreich said.
He said discussions are ongoing for full regulatory approval in the United States and for expanding the EUA for other populations, including pre-exposure prophylaxis, “which the [United Kingdom’s] authority has already granted us but the FDA has not.”
The study is funded by Regeneron and the Department of Health & Human Services. Dr. Weinreich is a vice president of Regeneron. Dr. Joshi reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fales holds stock in Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A monoclonal antibody combination of casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19–related hospitalizations and death from any cause in the phase 3 portion of an adaptive trial of outpatients.
Researchers, led by David Weinreich, MD, MBA, executive vice president of the drug cocktail’s manufacturer Regeneron, found in the randomized trial that the combination also resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more quickly, compared with placebo.
Findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
COVID-related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 18 of 1,355 patients (1.3%) in the group getting 2,400 mg infusions of the study drug, compared with 62 (4.6%) of 1,341 in the matching placebo group, indicating a relative risk reduction of 71.3%; P < .001.
Sunil Joshi, MD, president of the Duval County Medical Society Foundation and an immunologist in Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview that these findings confirm benefits of REGEN-COV and are very good news for a patient group that includes those age 65 and older with high blood pressure, diabetes, or obesity; and for people not vaccinated, who are all at high risk of hospitalization or death if they get COVID-19.
“Vaccines are critically important,” he said, “but if you were to be infected and know that there’s a way to keep yourself out of the hospital, this is very good news.”
Researchers seek lowest doses
This trial found that the effect was similar when researchers cut the doses in half. These outcomes occurred in 7 of 736 (1%) of patients given 1,200 mg of REGEN-COV and in 24 (3.2%) of 748 in the matching placebo group (relative risk reduction, 70.4%; P = .002).
Symptoms were resolved on average 4 days earlier with each REGEN-COV dose than with placebo (10 days vs. 14 days; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Dr. Weinreich said in an interview that trials will continue to find the lowest effective doses that can stand up to all evolving variants.
“This is one of those settings where you don’t want to underdose. You’ve got one shot at this,” he said. “We’d love to do lower doses. It would be more convenient and we could treat more patients, but if it generates more clinical failures or doesn’t work with certain variants, then you’ve done a huge disservice to the world.”
Also new in this study is that researchers tested not only seronegative patients, but patients at high risk regardless of blood antibody status, he said.
“It’s the first suggestion of data that if you’re breaking through a vaccine and you’re at high risk, the use of the cocktail is something to strongly consider because treatment early is better than treatment later,” Dr. Weinreich said.
In addition to efficacy, the phase 3 trial demonstrated the cocktail had a good safety profile. Serious adverse events occurred more often in the placebo group (4%) than in the 1,200-mg group (1.1%) and the 2,400-mg group (1.3%). Infusion reactions (grade 2 or higher) occurred in less than 0.3% of patients in all groups.
William Fales, MD, state medical director for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, said the results confirm the promise of REGEN-COV for reducing hospitalizations and death in a peer-reviewed publication.
COVID-19 a moving target
However, Dr. Fales noted that COVID-19 is a moving target with emerging variants. The criteria for populations at high risk have also broadened since the start of the study, he said.
“A great example is pregnancy is now included as high risk, and that would have likely been a specific contraindication of patients in this clinical trial,” he said.
Dr. Fales said Michigan has been using both REGEN-COV and the Eli Lilly combination of bamlanivimab and etesevimab, which also has an emergency use authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration, with positive results.
REGEN-COV has an EUA to treat people who are at high risk of serious consequences from COVID-19, including those who are already infected (nonhospitalized) or those in certain postexposure prophylaxis settings.
“We’re seeing very low hospitalization rates and few deaths in a state that is predominately Delta,” Dr. Fales said. “So, this makes us feel that we’re doing the right thing and supports the current efforts around the country to make monoclonal antibody therapy available to high-risk patients.”
Dr. Joshi noted that trial results have been emerging from other monoclonal antibody cocktails with different COVID-19 patient groups.
However, he said in an interview, “how much more effective they would be than this is something we’d have to look at, as 71% effectiveness in keeping people out of the hospital is pretty good for any treatment.”
“These are great numbers, but vaccination itself keeps you from getting the disease in the first place and not just for a short time period. This treatment is just that – a treatment. It gets you through that episode but it doesn’t mean you won’t get sick again. You don’t develop an immune response as you do with the vaccine,” he said.
Dr. Weinreich agreed: “This is not a substitute for a vaccine except for the small group who get the vaccine and their bodies can’t respond to it because they’re significantly immunocompromised.”
The results from this paper “are one piece of a large, multistudy, phase 3 program that basically spans from prophylaxis all the way to hospitalization and pretty much the gamut – all of them – have worked. All of these studies have shown dramatic improvement in whatever the definitive regulatory endpoint is,” Dr. Weinreich said.
He said discussions are ongoing for full regulatory approval in the United States and for expanding the EUA for other populations, including pre-exposure prophylaxis, “which the [United Kingdom’s] authority has already granted us but the FDA has not.”
The study is funded by Regeneron and the Department of Health & Human Services. Dr. Weinreich is a vice president of Regeneron. Dr. Joshi reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fales holds stock in Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A monoclonal antibody combination of casirivimab and imdevimab (REGEN-COV) significantly reduced the risk of COVID-19–related hospitalizations and death from any cause in the phase 3 portion of an adaptive trial of outpatients.
Researchers, led by David Weinreich, MD, MBA, executive vice president of the drug cocktail’s manufacturer Regeneron, found in the randomized trial that the combination also resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more quickly, compared with placebo.
Findings were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
COVID-related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 18 of 1,355 patients (1.3%) in the group getting 2,400 mg infusions of the study drug, compared with 62 (4.6%) of 1,341 in the matching placebo group, indicating a relative risk reduction of 71.3%; P < .001.
Sunil Joshi, MD, president of the Duval County Medical Society Foundation and an immunologist in Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview that these findings confirm benefits of REGEN-COV and are very good news for a patient group that includes those age 65 and older with high blood pressure, diabetes, or obesity; and for people not vaccinated, who are all at high risk of hospitalization or death if they get COVID-19.
“Vaccines are critically important,” he said, “but if you were to be infected and know that there’s a way to keep yourself out of the hospital, this is very good news.”
Researchers seek lowest doses
This trial found that the effect was similar when researchers cut the doses in half. These outcomes occurred in 7 of 736 (1%) of patients given 1,200 mg of REGEN-COV and in 24 (3.2%) of 748 in the matching placebo group (relative risk reduction, 70.4%; P = .002).
Symptoms were resolved on average 4 days earlier with each REGEN-COV dose than with placebo (10 days vs. 14 days; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Dr. Weinreich said in an interview that trials will continue to find the lowest effective doses that can stand up to all evolving variants.
“This is one of those settings where you don’t want to underdose. You’ve got one shot at this,” he said. “We’d love to do lower doses. It would be more convenient and we could treat more patients, but if it generates more clinical failures or doesn’t work with certain variants, then you’ve done a huge disservice to the world.”
Also new in this study is that researchers tested not only seronegative patients, but patients at high risk regardless of blood antibody status, he said.
“It’s the first suggestion of data that if you’re breaking through a vaccine and you’re at high risk, the use of the cocktail is something to strongly consider because treatment early is better than treatment later,” Dr. Weinreich said.
In addition to efficacy, the phase 3 trial demonstrated the cocktail had a good safety profile. Serious adverse events occurred more often in the placebo group (4%) than in the 1,200-mg group (1.1%) and the 2,400-mg group (1.3%). Infusion reactions (grade 2 or higher) occurred in less than 0.3% of patients in all groups.
William Fales, MD, state medical director for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, said the results confirm the promise of REGEN-COV for reducing hospitalizations and death in a peer-reviewed publication.
COVID-19 a moving target
However, Dr. Fales noted that COVID-19 is a moving target with emerging variants. The criteria for populations at high risk have also broadened since the start of the study, he said.
“A great example is pregnancy is now included as high risk, and that would have likely been a specific contraindication of patients in this clinical trial,” he said.
Dr. Fales said Michigan has been using both REGEN-COV and the Eli Lilly combination of bamlanivimab and etesevimab, which also has an emergency use authorization (EUA) from the Food and Drug Administration, with positive results.
REGEN-COV has an EUA to treat people who are at high risk of serious consequences from COVID-19, including those who are already infected (nonhospitalized) or those in certain postexposure prophylaxis settings.
“We’re seeing very low hospitalization rates and few deaths in a state that is predominately Delta,” Dr. Fales said. “So, this makes us feel that we’re doing the right thing and supports the current efforts around the country to make monoclonal antibody therapy available to high-risk patients.”
Dr. Joshi noted that trial results have been emerging from other monoclonal antibody cocktails with different COVID-19 patient groups.
However, he said in an interview, “how much more effective they would be than this is something we’d have to look at, as 71% effectiveness in keeping people out of the hospital is pretty good for any treatment.”
“These are great numbers, but vaccination itself keeps you from getting the disease in the first place and not just for a short time period. This treatment is just that – a treatment. It gets you through that episode but it doesn’t mean you won’t get sick again. You don’t develop an immune response as you do with the vaccine,” he said.
Dr. Weinreich agreed: “This is not a substitute for a vaccine except for the small group who get the vaccine and their bodies can’t respond to it because they’re significantly immunocompromised.”
The results from this paper “are one piece of a large, multistudy, phase 3 program that basically spans from prophylaxis all the way to hospitalization and pretty much the gamut – all of them – have worked. All of these studies have shown dramatic improvement in whatever the definitive regulatory endpoint is,” Dr. Weinreich said.
He said discussions are ongoing for full regulatory approval in the United States and for expanding the EUA for other populations, including pre-exposure prophylaxis, “which the [United Kingdom’s] authority has already granted us but the FDA has not.”
The study is funded by Regeneron and the Department of Health & Human Services. Dr. Weinreich is a vice president of Regeneron. Dr. Joshi reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fales holds stock in Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
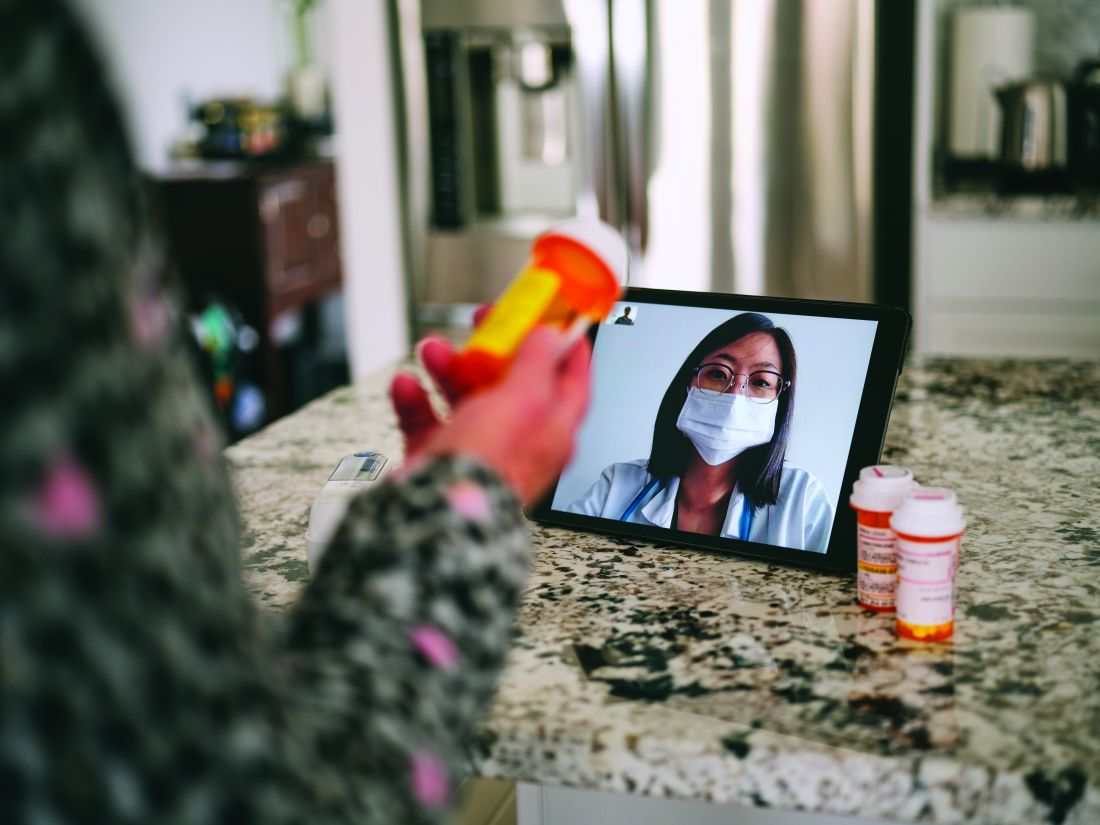
New data illustrate pandemic pivot to telehealth by patients, physicians
Telehealth use, although much higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, accounted for less than 20% of weekly outpatient visits 6 months into the pandemic, according to a new report from the American Medical Association. Ten percent of weekly visits were conducted via videoconferencing, and 8.1% of visits were conducted using the telephone.
Those figures may overstate the true level of telehealth use in fall 2020. A study by the Commonwealth Fund, Harvard University, Boston, and Phreesia found that in December of that year, only 8% of outpatient visits involved the use of telemedicine – and that was up from 6% in October. In contrast to the AMA results, which came from its 2020 benchmark survey of physicians, the Commonwealth Fund study used data from practice management systems and an online patient registration platform, as well as electronic health record data.
A more recent survey of hospital executives found that as of September 2021, hospital telehealth visits had leveled off at 10% to 20% of appointments. Similarly, a McKinsey survey in July showed that telehealth encounters made up 13% to 17% of evaluation and management visits across all specialties.
Big jump during pandemic
The AMA report offers a wealth of data on how physicians use telehealth and the differences between specialties in this area.
The report found that 70.3% of physicians worked in practices that used videoconferencing to provide patient visits in September 2020, compared to 14.3% of physicians in September 2018. Sixty-seven percent of physicians worked in practices that used telephone visits (the comparable figure for 2018 was unavailable).
Overall, 79% of physicians worked in a practice that used telehealth, compared to 25% in 2018.
Not every doctor in practices that utilized telehealth conducted virtual visits. In contrast to the 70.3% of doctors who were in practices that had video visits, only 59.1% of the respondents had personally conducted a videoconferencing visit in the previous week. The average numbers of weekly video and telephone visits per physician were 9.9 and 7.6, respectively, including those who did none.
There were big differences in virtual visit use among specialties as well. Eighty-five percent of psychiatrists were in practices that provided online appointments, according to the AMA survey, and three-quarters of primary care physicians said their practices offered telehealth appointments. Pediatricians were much less likely than family practice/general practice physicians (FPs/GPs) or general internists to do so.
The practices of many medical specialists were also highly likely to provide telehealth. Over 75% of practices in cardiology, endocrinology/diabetes, gastroenterology, nephrology, and neurology offered telehealth visits. About 88% of hematologists/oncologists offered video visits. Far fewer surgeons reported that their practice used virtual visits; the exceptions were urologists and dermatologists, 87% of whose practices used telehealth.
How telehealth was used
Across all specialties, 58% of physicians said clinicians in their practices used it to diagnose or treat patients; 59.2%, to manage patients with chronic disease; 50.4%, to provide acute care; and 34.3%, to provide preventive care.
Seventy-two percent of FP/GP and pediatric practices used telehealth to diagnose or treat patients. Just 64.9% of internists said their practices did so, and only 61.9% of them said their practices provided acute care via telehealth, versus 70% of FPs/GPs and pediatricians.
Among medical specialties, endocrinologists/diabetes physicians were those most likely to report the practice-level use of telehealth to diagnose or treat patients (71.9%), manage patients with chronic disease (92.1%), and provide preventive care (52.6%).
Significantly, 33% of medical specialists said their practices used remote patient monitoring. This finding was driven by high rates of use among cardiology practices (63.3%) and endocrinology practices (41.6%). Overall, the practice-level use of remote patient monitoring rose from 10.4% of practices in 2018 to 19.9% in 2020.
Virtual consults with peers
Some practices used telehealth to enable physicians to consult with colleagues. Twelve percent of respondents said their practices used telehealth to seek a second opinion from a health care professional in 2020, compared to 6.9% in 2018. Formal consultations via telehealth were also increasingly common: 17.2% of doctors said their practices did this in 2020, compared to 11.3% in 2018.
Also of note, 22.4% of physicians said their practices used telehealth for after-hours care or night calls in 2020, versus 9.9% in 2018.
The AMA report credited telehealth and expanded coverage and payment rules for enabling physician practices to keep their revenue streams positive and their practices open. However, the Commonwealth Fund study found “a substantial cumulative reduction in visits across all specialties over the course of the pandemic in 2020.” These ranged from a drop of 27% in pediatric visits to a decline of 8% in rheumatology visits during the period from March to December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth use, although much higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, accounted for less than 20% of weekly outpatient visits 6 months into the pandemic, according to a new report from the American Medical Association. Ten percent of weekly visits were conducted via videoconferencing, and 8.1% of visits were conducted using the telephone.
Those figures may overstate the true level of telehealth use in fall 2020. A study by the Commonwealth Fund, Harvard University, Boston, and Phreesia found that in December of that year, only 8% of outpatient visits involved the use of telemedicine – and that was up from 6% in October. In contrast to the AMA results, which came from its 2020 benchmark survey of physicians, the Commonwealth Fund study used data from practice management systems and an online patient registration platform, as well as electronic health record data.
A more recent survey of hospital executives found that as of September 2021, hospital telehealth visits had leveled off at 10% to 20% of appointments. Similarly, a McKinsey survey in July showed that telehealth encounters made up 13% to 17% of evaluation and management visits across all specialties.
Big jump during pandemic
The AMA report offers a wealth of data on how physicians use telehealth and the differences between specialties in this area.
The report found that 70.3% of physicians worked in practices that used videoconferencing to provide patient visits in September 2020, compared to 14.3% of physicians in September 2018. Sixty-seven percent of physicians worked in practices that used telephone visits (the comparable figure for 2018 was unavailable).
Overall, 79% of physicians worked in a practice that used telehealth, compared to 25% in 2018.
Not every doctor in practices that utilized telehealth conducted virtual visits. In contrast to the 70.3% of doctors who were in practices that had video visits, only 59.1% of the respondents had personally conducted a videoconferencing visit in the previous week. The average numbers of weekly video and telephone visits per physician were 9.9 and 7.6, respectively, including those who did none.
There were big differences in virtual visit use among specialties as well. Eighty-five percent of psychiatrists were in practices that provided online appointments, according to the AMA survey, and three-quarters of primary care physicians said their practices offered telehealth appointments. Pediatricians were much less likely than family practice/general practice physicians (FPs/GPs) or general internists to do so.
The practices of many medical specialists were also highly likely to provide telehealth. Over 75% of practices in cardiology, endocrinology/diabetes, gastroenterology, nephrology, and neurology offered telehealth visits. About 88% of hematologists/oncologists offered video visits. Far fewer surgeons reported that their practice used virtual visits; the exceptions were urologists and dermatologists, 87% of whose practices used telehealth.
How telehealth was used
Across all specialties, 58% of physicians said clinicians in their practices used it to diagnose or treat patients; 59.2%, to manage patients with chronic disease; 50.4%, to provide acute care; and 34.3%, to provide preventive care.
Seventy-two percent of FP/GP and pediatric practices used telehealth to diagnose or treat patients. Just 64.9% of internists said their practices did so, and only 61.9% of them said their practices provided acute care via telehealth, versus 70% of FPs/GPs and pediatricians.
Among medical specialties, endocrinologists/diabetes physicians were those most likely to report the practice-level use of telehealth to diagnose or treat patients (71.9%), manage patients with chronic disease (92.1%), and provide preventive care (52.6%).
Significantly, 33% of medical specialists said their practices used remote patient monitoring. This finding was driven by high rates of use among cardiology practices (63.3%) and endocrinology practices (41.6%). Overall, the practice-level use of remote patient monitoring rose from 10.4% of practices in 2018 to 19.9% in 2020.
Virtual consults with peers
Some practices used telehealth to enable physicians to consult with colleagues. Twelve percent of respondents said their practices used telehealth to seek a second opinion from a health care professional in 2020, compared to 6.9% in 2018. Formal consultations via telehealth were also increasingly common: 17.2% of doctors said their practices did this in 2020, compared to 11.3% in 2018.
Also of note, 22.4% of physicians said their practices used telehealth for after-hours care or night calls in 2020, versus 9.9% in 2018.
The AMA report credited telehealth and expanded coverage and payment rules for enabling physician practices to keep their revenue streams positive and their practices open. However, the Commonwealth Fund study found “a substantial cumulative reduction in visits across all specialties over the course of the pandemic in 2020.” These ranged from a drop of 27% in pediatric visits to a decline of 8% in rheumatology visits during the period from March to December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth use, although much higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, accounted for less than 20% of weekly outpatient visits 6 months into the pandemic, according to a new report from the American Medical Association. Ten percent of weekly visits were conducted via videoconferencing, and 8.1% of visits were conducted using the telephone.
Those figures may overstate the true level of telehealth use in fall 2020. A study by the Commonwealth Fund, Harvard University, Boston, and Phreesia found that in December of that year, only 8% of outpatient visits involved the use of telemedicine – and that was up from 6% in October. In contrast to the AMA results, which came from its 2020 benchmark survey of physicians, the Commonwealth Fund study used data from practice management systems and an online patient registration platform, as well as electronic health record data.
A more recent survey of hospital executives found that as of September 2021, hospital telehealth visits had leveled off at 10% to 20% of appointments. Similarly, a McKinsey survey in July showed that telehealth encounters made up 13% to 17% of evaluation and management visits across all specialties.
Big jump during pandemic
The AMA report offers a wealth of data on how physicians use telehealth and the differences between specialties in this area.
The report found that 70.3% of physicians worked in practices that used videoconferencing to provide patient visits in September 2020, compared to 14.3% of physicians in September 2018. Sixty-seven percent of physicians worked in practices that used telephone visits (the comparable figure for 2018 was unavailable).
Overall, 79% of physicians worked in a practice that used telehealth, compared to 25% in 2018.
Not every doctor in practices that utilized telehealth conducted virtual visits. In contrast to the 70.3% of doctors who were in practices that had video visits, only 59.1% of the respondents had personally conducted a videoconferencing visit in the previous week. The average numbers of weekly video and telephone visits per physician were 9.9 and 7.6, respectively, including those who did none.
There were big differences in virtual visit use among specialties as well. Eighty-five percent of psychiatrists were in practices that provided online appointments, according to the AMA survey, and three-quarters of primary care physicians said their practices offered telehealth appointments. Pediatricians were much less likely than family practice/general practice physicians (FPs/GPs) or general internists to do so.
The practices of many medical specialists were also highly likely to provide telehealth. Over 75% of practices in cardiology, endocrinology/diabetes, gastroenterology, nephrology, and neurology offered telehealth visits. About 88% of hematologists/oncologists offered video visits. Far fewer surgeons reported that their practice used virtual visits; the exceptions were urologists and dermatologists, 87% of whose practices used telehealth.
How telehealth was used
Across all specialties, 58% of physicians said clinicians in their practices used it to diagnose or treat patients; 59.2%, to manage patients with chronic disease; 50.4%, to provide acute care; and 34.3%, to provide preventive care.
Seventy-two percent of FP/GP and pediatric practices used telehealth to diagnose or treat patients. Just 64.9% of internists said their practices did so, and only 61.9% of them said their practices provided acute care via telehealth, versus 70% of FPs/GPs and pediatricians.
Among medical specialties, endocrinologists/diabetes physicians were those most likely to report the practice-level use of telehealth to diagnose or treat patients (71.9%), manage patients with chronic disease (92.1%), and provide preventive care (52.6%).
Significantly, 33% of medical specialists said their practices used remote patient monitoring. This finding was driven by high rates of use among cardiology practices (63.3%) and endocrinology practices (41.6%). Overall, the practice-level use of remote patient monitoring rose from 10.4% of practices in 2018 to 19.9% in 2020.
Virtual consults with peers
Some practices used telehealth to enable physicians to consult with colleagues. Twelve percent of respondents said their practices used telehealth to seek a second opinion from a health care professional in 2020, compared to 6.9% in 2018. Formal consultations via telehealth were also increasingly common: 17.2% of doctors said their practices did this in 2020, compared to 11.3% in 2018.
Also of note, 22.4% of physicians said their practices used telehealth for after-hours care or night calls in 2020, versus 9.9% in 2018.
The AMA report credited telehealth and expanded coverage and payment rules for enabling physician practices to keep their revenue streams positive and their practices open. However, the Commonwealth Fund study found “a substantial cumulative reduction in visits across all specialties over the course of the pandemic in 2020.” These ranged from a drop of 27% in pediatric visits to a decline of 8% in rheumatology visits during the period from March to December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
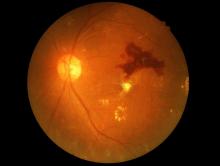
Retinopathy risk higher in young-onset T2D, more so in men
Men diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (T2D) by the age of 40 years appear significantly more likely to develop retinopathy than men who are diagnosed at an older age, Norwegian researchers report.
In a cross-sectional study of about 10,000 people, men with young-onset T2D were 72% more likely than men aged 50 years or older to have retinopathy.
While an increased retinopathy risk was also seen in women with young-onset T2D versus older women at first, this difference was not significant after adjusting for various confounding factors.
The effect of young-onset diabetes on retinopathy seems to be gender specific, Katrina Tibballs, MD, of the department of general practice at the University of Oslo, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“In the unadjusted analysis, the odds ratio for retinopathy was substantially higher in both [young-onset] men [odds ratio, 3.0] and women [OR, 2.46], compared with those 50 or older at diabetes diagnosis,” Dr. Tibballs said.
That relationship was not substantially altered after adjustment for variables such as level of education, country background, gender, and body mass index, with adjusted ORs of 2.56 and 2.55 for men and women, respectively.
However, further adjustment to include current age, duration of diabetes, and blood lipids and glycated hemoglobin levels, led to the difference no longer holding for women (OR, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 0.95-1.89) as it did for men (OR 1.72; 95% CI, 1.29-2.29).
First data in Norwegian population
Cross-sectional data on more than 10,000 people with T2D were used for the analysis. These came from the ROSA4 study, a general practice study conducted across Norway in 2014.
Just over 10% of the study population used in the analysis was under the age of 40 years at diagnosis of T2D; 21% were aged between 40 and 49 years, and 69% were at least 50 years old.
The mean age of those with young-onset T2D, defined as a diagnosis before the age of 40 years, was 33 years. These individuals had a longer disease duration than those in the other age groups (11.4 vs. 10.0 vs. 7.8 years).
“Looking at clinical characteristics, we say that individuals [with young-onset T2D] have a higher level of hemoglobin A1c than those with diabetes onset later in life,” Dr. Tibballs said.
“This is despite a substantially higher proportion [being] treated with insulin and fewer on lifestyle interventions alone.”
Gender differences were seen in A1c levels, with men with young-onset T2D having consistently higher levels than women, with levels increasing with diabetes duration.
Rise in retinopathy faster in men than in women
Dr. Tibballs reported that, not only did the prevalence of retinopathy rise faster in those of a younger age, but it also rose more quickly in men with young-onset T2D than it in their female counterparts.
“Comparing that [young-onset diabetes] and later-onset diabetes in men and women separately, we see a clearly higher prevalence of retinopathy with increasing diabetes duration for [young-onset] men,” she said.
In women, on the other hand, there was “no clear indication of a higher retinopathy prevalence in [young-onset diabetes], except in those with the longest diabetes duration.”
So, what do the results mean for practice? First, they confirm prior work showing that there is a strong association between retinopathy and age at diagnosis of T2D. Second, they suggest that this is despite intensive glucose-lowering treatment.
She speculated that men with young-onset T2D may have had a delayed diagnosis when compared with women and individuals with later onset diabetes, Dr. Tibballs said.
“This may in turn lead to delayed onset of glucose-lowering treatment, allowing for more time with high glycemic exposure and increased risk of acquiring complications, such as retinopathy at the time of diagnosis, or in the first years after,” said Dr. Tibballs.
These are cross-sectional data, “so we can’t say anything about whether this treatment is sufficient, but it is obviously not reducing HbA1c levels as much as we would like” added Dr. Tibballs, who is a primary care physician and PhD student.
The study was supported by The Norwegian Research Fund for General Practice. Dr. Tibballs had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Men diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (T2D) by the age of 40 years appear significantly more likely to develop retinopathy than men who are diagnosed at an older age, Norwegian researchers report.
In a cross-sectional study of about 10,000 people, men with young-onset T2D were 72% more likely than men aged 50 years or older to have retinopathy.
While an increased retinopathy risk was also seen in women with young-onset T2D versus older women at first, this difference was not significant after adjusting for various confounding factors.
The effect of young-onset diabetes on retinopathy seems to be gender specific, Katrina Tibballs, MD, of the department of general practice at the University of Oslo, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“In the unadjusted analysis, the odds ratio for retinopathy was substantially higher in both [young-onset] men [odds ratio, 3.0] and women [OR, 2.46], compared with those 50 or older at diabetes diagnosis,” Dr. Tibballs said.
That relationship was not substantially altered after adjustment for variables such as level of education, country background, gender, and body mass index, with adjusted ORs of 2.56 and 2.55 for men and women, respectively.
However, further adjustment to include current age, duration of diabetes, and blood lipids and glycated hemoglobin levels, led to the difference no longer holding for women (OR, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 0.95-1.89) as it did for men (OR 1.72; 95% CI, 1.29-2.29).
First data in Norwegian population
Cross-sectional data on more than 10,000 people with T2D were used for the analysis. These came from the ROSA4 study, a general practice study conducted across Norway in 2014.
Just over 10% of the study population used in the analysis was under the age of 40 years at diagnosis of T2D; 21% were aged between 40 and 49 years, and 69% were at least 50 years old.
The mean age of those with young-onset T2D, defined as a diagnosis before the age of 40 years, was 33 years. These individuals had a longer disease duration than those in the other age groups (11.4 vs. 10.0 vs. 7.8 years).
“Looking at clinical characteristics, we say that individuals [with young-onset T2D] have a higher level of hemoglobin A1c than those with diabetes onset later in life,” Dr. Tibballs said.
“This is despite a substantially higher proportion [being] treated with insulin and fewer on lifestyle interventions alone.”
Gender differences were seen in A1c levels, with men with young-onset T2D having consistently higher levels than women, with levels increasing with diabetes duration.
Rise in retinopathy faster in men than in women
Dr. Tibballs reported that, not only did the prevalence of retinopathy rise faster in those of a younger age, but it also rose more quickly in men with young-onset T2D than it in their female counterparts.
“Comparing that [young-onset diabetes] and later-onset diabetes in men and women separately, we see a clearly higher prevalence of retinopathy with increasing diabetes duration for [young-onset] men,” she said.
In women, on the other hand, there was “no clear indication of a higher retinopathy prevalence in [young-onset diabetes], except in those with the longest diabetes duration.”
So, what do the results mean for practice? First, they confirm prior work showing that there is a strong association between retinopathy and age at diagnosis of T2D. Second, they suggest that this is despite intensive glucose-lowering treatment.
She speculated that men with young-onset T2D may have had a delayed diagnosis when compared with women and individuals with later onset diabetes, Dr. Tibballs said.
“This may in turn lead to delayed onset of glucose-lowering treatment, allowing for more time with high glycemic exposure and increased risk of acquiring complications, such as retinopathy at the time of diagnosis, or in the first years after,” said Dr. Tibballs.
These are cross-sectional data, “so we can’t say anything about whether this treatment is sufficient, but it is obviously not reducing HbA1c levels as much as we would like” added Dr. Tibballs, who is a primary care physician and PhD student.
The study was supported by The Norwegian Research Fund for General Practice. Dr. Tibballs had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Men diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (T2D) by the age of 40 years appear significantly more likely to develop retinopathy than men who are diagnosed at an older age, Norwegian researchers report.
In a cross-sectional study of about 10,000 people, men with young-onset T2D were 72% more likely than men aged 50 years or older to have retinopathy.
While an increased retinopathy risk was also seen in women with young-onset T2D versus older women at first, this difference was not significant after adjusting for various confounding factors.
The effect of young-onset diabetes on retinopathy seems to be gender specific, Katrina Tibballs, MD, of the department of general practice at the University of Oslo, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“In the unadjusted analysis, the odds ratio for retinopathy was substantially higher in both [young-onset] men [odds ratio, 3.0] and women [OR, 2.46], compared with those 50 or older at diabetes diagnosis,” Dr. Tibballs said.
That relationship was not substantially altered after adjustment for variables such as level of education, country background, gender, and body mass index, with adjusted ORs of 2.56 and 2.55 for men and women, respectively.
However, further adjustment to include current age, duration of diabetes, and blood lipids and glycated hemoglobin levels, led to the difference no longer holding for women (OR, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 0.95-1.89) as it did for men (OR 1.72; 95% CI, 1.29-2.29).
First data in Norwegian population
Cross-sectional data on more than 10,000 people with T2D were used for the analysis. These came from the ROSA4 study, a general practice study conducted across Norway in 2014.
Just over 10% of the study population used in the analysis was under the age of 40 years at diagnosis of T2D; 21% were aged between 40 and 49 years, and 69% were at least 50 years old.
The mean age of those with young-onset T2D, defined as a diagnosis before the age of 40 years, was 33 years. These individuals had a longer disease duration than those in the other age groups (11.4 vs. 10.0 vs. 7.8 years).
“Looking at clinical characteristics, we say that individuals [with young-onset T2D] have a higher level of hemoglobin A1c than those with diabetes onset later in life,” Dr. Tibballs said.
“This is despite a substantially higher proportion [being] treated with insulin and fewer on lifestyle interventions alone.”
Gender differences were seen in A1c levels, with men with young-onset T2D having consistently higher levels than women, with levels increasing with diabetes duration.
Rise in retinopathy faster in men than in women
Dr. Tibballs reported that, not only did the prevalence of retinopathy rise faster in those of a younger age, but it also rose more quickly in men with young-onset T2D than it in their female counterparts.
“Comparing that [young-onset diabetes] and later-onset diabetes in men and women separately, we see a clearly higher prevalence of retinopathy with increasing diabetes duration for [young-onset] men,” she said.
In women, on the other hand, there was “no clear indication of a higher retinopathy prevalence in [young-onset diabetes], except in those with the longest diabetes duration.”
So, what do the results mean for practice? First, they confirm prior work showing that there is a strong association between retinopathy and age at diagnosis of T2D. Second, they suggest that this is despite intensive glucose-lowering treatment.
She speculated that men with young-onset T2D may have had a delayed diagnosis when compared with women and individuals with later onset diabetes, Dr. Tibballs said.
“This may in turn lead to delayed onset of glucose-lowering treatment, allowing for more time with high glycemic exposure and increased risk of acquiring complications, such as retinopathy at the time of diagnosis, or in the first years after,” said Dr. Tibballs.
These are cross-sectional data, “so we can’t say anything about whether this treatment is sufficient, but it is obviously not reducing HbA1c levels as much as we would like” added Dr. Tibballs, who is a primary care physician and PhD student.
The study was supported by The Norwegian Research Fund for General Practice. Dr. Tibballs had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM EASD 2021
Predicted pandemic retirement of many physicians hasn’t happened
The number of physicians who have chosen early retirement or have left medicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic may be considerably lower than previously thought, results of a new study suggest.
The research letter in the Journal of the American Medical Association, based on Medicare claims data, stated that “practice interruption rates were similar before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, except for a spike in April 2020.”
By contrast, in a Physicians Foundation Survey conducted in August 2020, 8% of physicians said they had closed their practices as a result of COVID, and 4% of the respondents said they planned to leave their practices within the next 12 months.
Similarly, a Jackson Physician Search survey in the fourth quarter of 2020 found that 54% of physicians surveyed had changed their employment plans. Of those doctors, 21% said they might hang up their white coat for early retirement. That works out to about 11% of the respondents.
The JAMA study’s authors analyzed the Medicare claims data from Jan. 1, 2019, to Dec. 30, 2020, to see how many physicians with Medicare patients had stopped filing claims for a period during those 2 years.
If a doctor had ceased submitting claims and then resumed filing them within 6 months after the last billing month, the lapse in filing was defined as “interruption with return.” If a physician stopped filing claims to Medicare and did not resume within 6 months, the gap in filing was called “interruption without return.”
In April 2020, 6.9% of physicians billing Medicare had a practice interruption, compared to 1.4% in 2019. But only 1.1% of physicians stopped practice in April 2020 and did not return, compared with 0.33% in 2019.
Physicians aged 55 or older had higher rates of interruption both with and without return than younger doctors did. The change in interruption rates for older doctors was 7.2% vs. 3.9% for younger physicians. The change in older physicians’ interruption-without-return rate was 1.3% vs. 0.34% for younger colleagues.
“Female physicians, specialists, physicians in smaller practices, those not in a health professional shortage area, and those practicing in a metropolitan area experienced greater increases in practice interruption rates in April 2020 vs. April 2019,” the study states. “But those groups typically had higher rates of return, so the overall changes in practice interruptions without return were similar across characteristics other than age.”
Significance for retirement rate
Discussing these results, the authors stressed that practice interruptions without return can’t necessarily be attributed to retirement, and that practice interruptions with return don’t necessarily signify that doctors had been furloughed from their practices.
Also, they said, “this measure of practice interruption likely misses meaningful interruptions that lasted for less than a month or did not involve complete cessation in treating Medicare patients.”
Nevertheless, “the study does capture a signal of some doctors probably retiring,” Jonathan Weiner, DPH, professor of health policy and management at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said in an interview.
But he added, “Some of those people who interrupted their practices and didn’t return may still come back. And there are probably a lot of other doctors who are leaving or changing practices that they didn’t capture.” For example, it’s possible that some doctors who went to work for other health care organizations stopped billing under their own names.
In Dr. Weiner’s view, the true percentage of physicians who have retired since the start of the pandemic is probably somewhere between the portion of doctors who interrupted their practice without return, according to the JAMA study, and the percentage of physicians who said they had closed their practices in the Physicians Foundation survey.
No mass exodus seen
Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president of recruiting for Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm, said in an interview that the real number may be closer to the interruption-without-return figure in the JAMA study.
While many physician practices were disrupted in spring of 2020, he said, “it really didn’t result in a mass exodus [from health care]. We’re not talking to a lot of candidates who retired or walked away from their practices. We are talking to candidates who slowed down last year and then realized that they wanted to get back into medicine. And now they’re actively looking.”
One change in job candidates’ attitude, Mr. Belkin said, is that, because of COVID-19–related burnout, their quality of life is more important to them.
“They want to know, ‘What’s the culture of the employer like? What did they do last year during COVID? How did they handle it? Have they put together any protocols for the next pandemic?’ “
Demand for doctors has returned
In the summer of 2020, there was a major drop in physician recruitment by hospitals and health systems, partly because of fewer patient visits and procedures. But demand for doctors has bounced back over the past year, Mr. Belkin noted. One reason is the pent-up need for care among patients who avoided health care providers in 2020.
Another reason is that some employed doctors – particularly older physicians – have slowed down. Many doctors prefer to work remotely 1 or 2 days a week, providing telehealth visits to patients. That has led to a loss of productivity in many health care organizations and, consequently, a need to hire additional physicians.
Nevertheless, not many doctors are heading for the exit earlier than physicians did before COVID-19.
“They may work reduced hours,” Mr. Belkin said. “But the sense from a physician’s perspective is that this is all they know. For them to walk away from their life in medicine, from who they are, is problematic. So they’re continuing to practice, but at a reduced capacity.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of physicians who have chosen early retirement or have left medicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic may be considerably lower than previously thought, results of a new study suggest.
The research letter in the Journal of the American Medical Association, based on Medicare claims data, stated that “practice interruption rates were similar before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, except for a spike in April 2020.”
By contrast, in a Physicians Foundation Survey conducted in August 2020, 8% of physicians said they had closed their practices as a result of COVID, and 4% of the respondents said they planned to leave their practices within the next 12 months.
Similarly, a Jackson Physician Search survey in the fourth quarter of 2020 found that 54% of physicians surveyed had changed their employment plans. Of those doctors, 21% said they might hang up their white coat for early retirement. That works out to about 11% of the respondents.
The JAMA study’s authors analyzed the Medicare claims data from Jan. 1, 2019, to Dec. 30, 2020, to see how many physicians with Medicare patients had stopped filing claims for a period during those 2 years.
If a doctor had ceased submitting claims and then resumed filing them within 6 months after the last billing month, the lapse in filing was defined as “interruption with return.” If a physician stopped filing claims to Medicare and did not resume within 6 months, the gap in filing was called “interruption without return.”
In April 2020, 6.9% of physicians billing Medicare had a practice interruption, compared to 1.4% in 2019. But only 1.1% of physicians stopped practice in April 2020 and did not return, compared with 0.33% in 2019.
Physicians aged 55 or older had higher rates of interruption both with and without return than younger doctors did. The change in interruption rates for older doctors was 7.2% vs. 3.9% for younger physicians. The change in older physicians’ interruption-without-return rate was 1.3% vs. 0.34% for younger colleagues.
“Female physicians, specialists, physicians in smaller practices, those not in a health professional shortage area, and those practicing in a metropolitan area experienced greater increases in practice interruption rates in April 2020 vs. April 2019,” the study states. “But those groups typically had higher rates of return, so the overall changes in practice interruptions without return were similar across characteristics other than age.”
Significance for retirement rate
Discussing these results, the authors stressed that practice interruptions without return can’t necessarily be attributed to retirement, and that practice interruptions with return don’t necessarily signify that doctors had been furloughed from their practices.
Also, they said, “this measure of practice interruption likely misses meaningful interruptions that lasted for less than a month or did not involve complete cessation in treating Medicare patients.”
Nevertheless, “the study does capture a signal of some doctors probably retiring,” Jonathan Weiner, DPH, professor of health policy and management at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said in an interview.
But he added, “Some of those people who interrupted their practices and didn’t return may still come back. And there are probably a lot of other doctors who are leaving or changing practices that they didn’t capture.” For example, it’s possible that some doctors who went to work for other health care organizations stopped billing under their own names.
In Dr. Weiner’s view, the true percentage of physicians who have retired since the start of the pandemic is probably somewhere between the portion of doctors who interrupted their practice without return, according to the JAMA study, and the percentage of physicians who said they had closed their practices in the Physicians Foundation survey.
No mass exodus seen
Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president of recruiting for Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm, said in an interview that the real number may be closer to the interruption-without-return figure in the JAMA study.
While many physician practices were disrupted in spring of 2020, he said, “it really didn’t result in a mass exodus [from health care]. We’re not talking to a lot of candidates who retired or walked away from their practices. We are talking to candidates who slowed down last year and then realized that they wanted to get back into medicine. And now they’re actively looking.”
One change in job candidates’ attitude, Mr. Belkin said, is that, because of COVID-19–related burnout, their quality of life is more important to them.
“They want to know, ‘What’s the culture of the employer like? What did they do last year during COVID? How did they handle it? Have they put together any protocols for the next pandemic?’ “
Demand for doctors has returned
In the summer of 2020, there was a major drop in physician recruitment by hospitals and health systems, partly because of fewer patient visits and procedures. But demand for doctors has bounced back over the past year, Mr. Belkin noted. One reason is the pent-up need for care among patients who avoided health care providers in 2020.
Another reason is that some employed doctors – particularly older physicians – have slowed down. Many doctors prefer to work remotely 1 or 2 days a week, providing telehealth visits to patients. That has led to a loss of productivity in many health care organizations and, consequently, a need to hire additional physicians.
Nevertheless, not many doctors are heading for the exit earlier than physicians did before COVID-19.
“They may work reduced hours,” Mr. Belkin said. “But the sense from a physician’s perspective is that this is all they know. For them to walk away from their life in medicine, from who they are, is problematic. So they’re continuing to practice, but at a reduced capacity.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of physicians who have chosen early retirement or have left medicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic may be considerably lower than previously thought, results of a new study suggest.
The research letter in the Journal of the American Medical Association, based on Medicare claims data, stated that “practice interruption rates were similar before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, except for a spike in April 2020.”
By contrast, in a Physicians Foundation Survey conducted in August 2020, 8% of physicians said they had closed their practices as a result of COVID, and 4% of the respondents said they planned to leave their practices within the next 12 months.
Similarly, a Jackson Physician Search survey in the fourth quarter of 2020 found that 54% of physicians surveyed had changed their employment plans. Of those doctors, 21% said they might hang up their white coat for early retirement. That works out to about 11% of the respondents.
The JAMA study’s authors analyzed the Medicare claims data from Jan. 1, 2019, to Dec. 30, 2020, to see how many physicians with Medicare patients had stopped filing claims for a period during those 2 years.
If a doctor had ceased submitting claims and then resumed filing them within 6 months after the last billing month, the lapse in filing was defined as “interruption with return.” If a physician stopped filing claims to Medicare and did not resume within 6 months, the gap in filing was called “interruption without return.”
In April 2020, 6.9% of physicians billing Medicare had a practice interruption, compared to 1.4% in 2019. But only 1.1% of physicians stopped practice in April 2020 and did not return, compared with 0.33% in 2019.
Physicians aged 55 or older had higher rates of interruption both with and without return than younger doctors did. The change in interruption rates for older doctors was 7.2% vs. 3.9% for younger physicians. The change in older physicians’ interruption-without-return rate was 1.3% vs. 0.34% for younger colleagues.
“Female physicians, specialists, physicians in smaller practices, those not in a health professional shortage area, and those practicing in a metropolitan area experienced greater increases in practice interruption rates in April 2020 vs. April 2019,” the study states. “But those groups typically had higher rates of return, so the overall changes in practice interruptions without return were similar across characteristics other than age.”
Significance for retirement rate
Discussing these results, the authors stressed that practice interruptions without return can’t necessarily be attributed to retirement, and that practice interruptions with return don’t necessarily signify that doctors had been furloughed from their practices.
Also, they said, “this measure of practice interruption likely misses meaningful interruptions that lasted for less than a month or did not involve complete cessation in treating Medicare patients.”
Nevertheless, “the study does capture a signal of some doctors probably retiring,” Jonathan Weiner, DPH, professor of health policy and management at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said in an interview.
But he added, “Some of those people who interrupted their practices and didn’t return may still come back. And there are probably a lot of other doctors who are leaving or changing practices that they didn’t capture.” For example, it’s possible that some doctors who went to work for other health care organizations stopped billing under their own names.
In Dr. Weiner’s view, the true percentage of physicians who have retired since the start of the pandemic is probably somewhere between the portion of doctors who interrupted their practice without return, according to the JAMA study, and the percentage of physicians who said they had closed their practices in the Physicians Foundation survey.
No mass exodus seen
Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president of recruiting for Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm, said in an interview that the real number may be closer to the interruption-without-return figure in the JAMA study.
While many physician practices were disrupted in spring of 2020, he said, “it really didn’t result in a mass exodus [from health care]. We’re not talking to a lot of candidates who retired or walked away from their practices. We are talking to candidates who slowed down last year and then realized that they wanted to get back into medicine. And now they’re actively looking.”
One change in job candidates’ attitude, Mr. Belkin said, is that, because of COVID-19–related burnout, their quality of life is more important to them.
“They want to know, ‘What’s the culture of the employer like? What did they do last year during COVID? How did they handle it? Have they put together any protocols for the next pandemic?’ “
Demand for doctors has returned
In the summer of 2020, there was a major drop in physician recruitment by hospitals and health systems, partly because of fewer patient visits and procedures. But demand for doctors has bounced back over the past year, Mr. Belkin noted. One reason is the pent-up need for care among patients who avoided health care providers in 2020.
Another reason is that some employed doctors – particularly older physicians – have slowed down. Many doctors prefer to work remotely 1 or 2 days a week, providing telehealth visits to patients. That has led to a loss of productivity in many health care organizations and, consequently, a need to hire additional physicians.
Nevertheless, not many doctors are heading for the exit earlier than physicians did before COVID-19.
“They may work reduced hours,” Mr. Belkin said. “But the sense from a physician’s perspective is that this is all they know. For them to walk away from their life in medicine, from who they are, is problematic. So they’re continuing to practice, but at a reduced capacity.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study finds paying people to participate in clinical trials is not unethical
Paying people to participate in clinical trials remains controversial. But to date, most reservations are based on hypothetical scenarios or expert opinion with few real-world data to support them.
Research released this week could change that.
Investigators offered nearly 1,300 participants in two clinical trials either no payment or incentives up to $500 to partake in a smoking cessation study or an analysis of a behavioral intervention to increase ambulation in hospitalized patients.
More cash was associated with greater agreement to participate in the smoking cessation study but not the ambulation trial.
But the bigger news may be that offering payment did not appear to get people to accept more risks or skew participation to lower-income individuals, as some ethicists have warned.
“With the publication of our study, investigators finally have data that they can cite to put to rest any lingering concerns about offering moderate incentives in low-risk trials,” lead author Scott D. Halpern, MD, PhD, the John M. Eisenberg Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Medical Ethics & Health Policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
This initial real-world data centers on low-risk interventions and more research is needed to analyze the ethics and effectiveness of paying people to join clinical trials with more inherent risk, the researchers note.
The study was published online Sept. 20 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
A good first step?
“Payments to research participants are notoriously controversial. Many people oppose payments altogether or insist on minimal payments out of concern that people might be unduly influenced to participate,” Ana S. Iltis, PhD, told this news organization when asked for comment. “Others worry that incentives will disproportionately motivate the less well-off to participate.”
“This is an important study that begins to assess whether these concerns are justified in a real-world context,” added Dr. Iltis, director of the Center for Bioethics, Health and Society and professor of philosophy at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Sang Ngo, Anthony S. Kim, MD, and Winston Chiong, MD, PhD, write: “This work is welcome, as it presents experimental data to a bioethical debate that so far has been largely driven by conjecture and competing suppositions.”
The commentary authors, however, question the conclusiveness of the findings. “Interpreting the authors’ findings is complex and illustrates some of the challenges inherent to applying empirical data to ethical problems,” they write.
Recruitment realities
When asked his advice for researchers considering financial incentives, Dr. Halpern said: “All researchers would happily include incentives in their trial budgets if not for concerns that the sponsor or institutional review board might not approve of them.”
“By far the biggest threat to a trial’s success is the inability to enroll enough participants,” he added.
Dr. Iltis agreed, framing the need to boost enrollment in ethical terms. “There is another important ethical issue that often gets ignored, and that is the issue of studies that fail to enroll enough participants and are never completed or are underpowered,” she said.
“These studies end up exposing people to research risks and burdens without a compensating social benefit.”
“If incentives help to increase enrollment and do not necessarily result in undue influence or unfair participant selection, then there might be ethical reasons to offer incentives,” Dr. Iltis added.
Building on previous work assessing financial incentives in hypothetical clinical trials, Dr. Halpern and colleagues studied 654 participants with major depressive disorder in a smoking cessation trial. They also studied another 642 participants in a study that compared a gamification strategy to usual care for encouraging hospitalized patients to get out of bed and walk.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues randomly assigned people in the smoking cessation study to receive no financial compensation, $200, or $500. In the ambulation trial, participants were randomly allocated to receive no compensation, $100, or $300.
Key findings
A total of 22% of those offered no incentive enrolled in the smoking cessation study. In contrast, 36% offered $200 agreed, as did 47% of those offered $500, which the investigators say supports offering cash incentives to boost enrollment. The differences were significant (P < .001).
In contrast, the amount offered did not significantly incentivize more people to participate in the ambulation trial (P = .62). Rates were 45% with no compensation, 48% with $100 payment, and 43% with $300 payment.
In an analysis that adjusted for demographic differences, financial well-being, and Research Attitudes Questionnaire (RAQ-7) scores, each increase in cash incentive increased the odds of enrollment in the smoking cessation trial by 70% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.70; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-2.17).
The same effect was not seen in the ambulation trial, where each higher cash incentive did not make a significant difference (aOR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.22).
“The ambulation trial was a lower-risk trial in which patients’ willingness to participate was higher in general. So there were likely fewer people whose participation decisions could be influenced by offers of money,” Dr. Halpern said.
Inducement vs. coercion
The incentives in the study “did not function as unjust inducements, as they were not preferentially motivating across groups with different income levels or financial well-being in either trial,” the researchers note.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues also checked for any perceptions of coercion. More than 70% of participants in each smoking cessation trial group perceived no coercion, as did more than 93% of participants in each ambulation trial group, according to scores on a modified Perceived Coercion Scale of the MacArthur Admission Experience Survey.
Furthermore, perception of risks did not significantly alter the association between cash incentives and enrollment in either trial.
After collecting the findings, Dr. Halpern and colleagues informed participants about their participation in RETAIN and explained the rationale for using different cash incentives. They also let all participants know they would ultimately receive the maximum incentive – either $500 or $300, depending on the trial.
Research implications
A study limitation was reliance on participant risk perception, as was an inability to measure perceived coercion among people who chose not to participant in the trials. Another potential limitation is that “neither of these parent trials posed particularly high risks. Future tests of incentives of different sizes, and in the context of higher-risk parent trials, including trials that test treatments of serious illnesses, are warranted,” the researchers note.
“While there are many more questions to ask and contexts in which to study the effects of incentives, this study calls on opponents of incentivizing research participants with money to be more humble,” Dr. Iltis said. “Incentives might not have the effects they assume they have and which they have long held make such incentives unethical.”
“I encourage researchers who are offering incentives to consider working with people doing ethics research to assess the effects of incentives in their studies,” Dr. Halpern said. “Real-world, as opposed to hypothetical studies that can improve our understanding of the impact of incentives can improve the ethical conduct of research over time.”
Responding to criticism
The authors of the invited commentary questioned the definitions Dr. Halpern and colleagues used for undue or unjust inducement. “Among bioethicists, there is no consensus about what counts as undue inducement or an unjust distribution of research burdens. In this article, the authors have operationalized these constructs based on their own interpretations of undue and unjust inducement, which may not capture all the concerns that scholars have raised about inducement.”
Asked to respond to this and other criticisms raised in the commentary, Dr. Halpern said: “Did our study answer all possible questions about incentives? Absolutely not. But when it comes to incentives for research participation, an ounce of data is worth a pound of conjecture.”
There was agreement, however, that the findings could now put the onus on opponents of financial incentives for trial participants.
“I agree with the commentary’s authors that our study essentially shifts the burden of proof, such that, as they say, ‘those who would limit [incentives’] application may owe us an applicable criterion,’ ” Dr. Halpern said.
The authors of the invited commentary also criticized use of the study’s noninferiority design to rule out undue or unjust inducement. They note this design “may be unfamiliar to many bioethicists and can place substantial evaluative demands on readers.”
“As for the authors’ claim that noninferiority designs are difficult to interpret and unfamiliar to most clinicians and ethicists, I certainly agree,” Dr. Halpern said. “But that is hardly a reason to not employ the most rigorous methods possible to answer important questions.”
The study was supported by funding from the National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paying people to participate in clinical trials remains controversial. But to date, most reservations are based on hypothetical scenarios or expert opinion with few real-world data to support them.
Research released this week could change that.
Investigators offered nearly 1,300 participants in two clinical trials either no payment or incentives up to $500 to partake in a smoking cessation study or an analysis of a behavioral intervention to increase ambulation in hospitalized patients.
More cash was associated with greater agreement to participate in the smoking cessation study but not the ambulation trial.
But the bigger news may be that offering payment did not appear to get people to accept more risks or skew participation to lower-income individuals, as some ethicists have warned.
“With the publication of our study, investigators finally have data that they can cite to put to rest any lingering concerns about offering moderate incentives in low-risk trials,” lead author Scott D. Halpern, MD, PhD, the John M. Eisenberg Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Medical Ethics & Health Policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
This initial real-world data centers on low-risk interventions and more research is needed to analyze the ethics and effectiveness of paying people to join clinical trials with more inherent risk, the researchers note.
The study was published online Sept. 20 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
A good first step?
“Payments to research participants are notoriously controversial. Many people oppose payments altogether or insist on minimal payments out of concern that people might be unduly influenced to participate,” Ana S. Iltis, PhD, told this news organization when asked for comment. “Others worry that incentives will disproportionately motivate the less well-off to participate.”
“This is an important study that begins to assess whether these concerns are justified in a real-world context,” added Dr. Iltis, director of the Center for Bioethics, Health and Society and professor of philosophy at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Sang Ngo, Anthony S. Kim, MD, and Winston Chiong, MD, PhD, write: “This work is welcome, as it presents experimental data to a bioethical debate that so far has been largely driven by conjecture and competing suppositions.”
The commentary authors, however, question the conclusiveness of the findings. “Interpreting the authors’ findings is complex and illustrates some of the challenges inherent to applying empirical data to ethical problems,” they write.
Recruitment realities
When asked his advice for researchers considering financial incentives, Dr. Halpern said: “All researchers would happily include incentives in their trial budgets if not for concerns that the sponsor or institutional review board might not approve of them.”
“By far the biggest threat to a trial’s success is the inability to enroll enough participants,” he added.
Dr. Iltis agreed, framing the need to boost enrollment in ethical terms. “There is another important ethical issue that often gets ignored, and that is the issue of studies that fail to enroll enough participants and are never completed or are underpowered,” she said.
“These studies end up exposing people to research risks and burdens without a compensating social benefit.”
“If incentives help to increase enrollment and do not necessarily result in undue influence or unfair participant selection, then there might be ethical reasons to offer incentives,” Dr. Iltis added.
Building on previous work assessing financial incentives in hypothetical clinical trials, Dr. Halpern and colleagues studied 654 participants with major depressive disorder in a smoking cessation trial. They also studied another 642 participants in a study that compared a gamification strategy to usual care for encouraging hospitalized patients to get out of bed and walk.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues randomly assigned people in the smoking cessation study to receive no financial compensation, $200, or $500. In the ambulation trial, participants were randomly allocated to receive no compensation, $100, or $300.
Key findings
A total of 22% of those offered no incentive enrolled in the smoking cessation study. In contrast, 36% offered $200 agreed, as did 47% of those offered $500, which the investigators say supports offering cash incentives to boost enrollment. The differences were significant (P < .001).
In contrast, the amount offered did not significantly incentivize more people to participate in the ambulation trial (P = .62). Rates were 45% with no compensation, 48% with $100 payment, and 43% with $300 payment.
In an analysis that adjusted for demographic differences, financial well-being, and Research Attitudes Questionnaire (RAQ-7) scores, each increase in cash incentive increased the odds of enrollment in the smoking cessation trial by 70% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.70; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-2.17).
The same effect was not seen in the ambulation trial, where each higher cash incentive did not make a significant difference (aOR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.22).
“The ambulation trial was a lower-risk trial in which patients’ willingness to participate was higher in general. So there were likely fewer people whose participation decisions could be influenced by offers of money,” Dr. Halpern said.
Inducement vs. coercion
The incentives in the study “did not function as unjust inducements, as they were not preferentially motivating across groups with different income levels or financial well-being in either trial,” the researchers note.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues also checked for any perceptions of coercion. More than 70% of participants in each smoking cessation trial group perceived no coercion, as did more than 93% of participants in each ambulation trial group, according to scores on a modified Perceived Coercion Scale of the MacArthur Admission Experience Survey.
Furthermore, perception of risks did not significantly alter the association between cash incentives and enrollment in either trial.
After collecting the findings, Dr. Halpern and colleagues informed participants about their participation in RETAIN and explained the rationale for using different cash incentives. They also let all participants know they would ultimately receive the maximum incentive – either $500 or $300, depending on the trial.
Research implications
A study limitation was reliance on participant risk perception, as was an inability to measure perceived coercion among people who chose not to participant in the trials. Another potential limitation is that “neither of these parent trials posed particularly high risks. Future tests of incentives of different sizes, and in the context of higher-risk parent trials, including trials that test treatments of serious illnesses, are warranted,” the researchers note.
“While there are many more questions to ask and contexts in which to study the effects of incentives, this study calls on opponents of incentivizing research participants with money to be more humble,” Dr. Iltis said. “Incentives might not have the effects they assume they have and which they have long held make such incentives unethical.”
“I encourage researchers who are offering incentives to consider working with people doing ethics research to assess the effects of incentives in their studies,” Dr. Halpern said. “Real-world, as opposed to hypothetical studies that can improve our understanding of the impact of incentives can improve the ethical conduct of research over time.”
Responding to criticism
The authors of the invited commentary questioned the definitions Dr. Halpern and colleagues used for undue or unjust inducement. “Among bioethicists, there is no consensus about what counts as undue inducement or an unjust distribution of research burdens. In this article, the authors have operationalized these constructs based on their own interpretations of undue and unjust inducement, which may not capture all the concerns that scholars have raised about inducement.”
Asked to respond to this and other criticisms raised in the commentary, Dr. Halpern said: “Did our study answer all possible questions about incentives? Absolutely not. But when it comes to incentives for research participation, an ounce of data is worth a pound of conjecture.”
There was agreement, however, that the findings could now put the onus on opponents of financial incentives for trial participants.
“I agree with the commentary’s authors that our study essentially shifts the burden of proof, such that, as they say, ‘those who would limit [incentives’] application may owe us an applicable criterion,’ ” Dr. Halpern said.
The authors of the invited commentary also criticized use of the study’s noninferiority design to rule out undue or unjust inducement. They note this design “may be unfamiliar to many bioethicists and can place substantial evaluative demands on readers.”
“As for the authors’ claim that noninferiority designs are difficult to interpret and unfamiliar to most clinicians and ethicists, I certainly agree,” Dr. Halpern said. “But that is hardly a reason to not employ the most rigorous methods possible to answer important questions.”
The study was supported by funding from the National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paying people to participate in clinical trials remains controversial. But to date, most reservations are based on hypothetical scenarios or expert opinion with few real-world data to support them.
Research released this week could change that.
Investigators offered nearly 1,300 participants in two clinical trials either no payment or incentives up to $500 to partake in a smoking cessation study or an analysis of a behavioral intervention to increase ambulation in hospitalized patients.
More cash was associated with greater agreement to participate in the smoking cessation study but not the ambulation trial.
But the bigger news may be that offering payment did not appear to get people to accept more risks or skew participation to lower-income individuals, as some ethicists have warned.
“With the publication of our study, investigators finally have data that they can cite to put to rest any lingering concerns about offering moderate incentives in low-risk trials,” lead author Scott D. Halpern, MD, PhD, the John M. Eisenberg Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Medical Ethics & Health Policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
This initial real-world data centers on low-risk interventions and more research is needed to analyze the ethics and effectiveness of paying people to join clinical trials with more inherent risk, the researchers note.
The study was published online Sept. 20 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
A good first step?
“Payments to research participants are notoriously controversial. Many people oppose payments altogether or insist on minimal payments out of concern that people might be unduly influenced to participate,” Ana S. Iltis, PhD, told this news organization when asked for comment. “Others worry that incentives will disproportionately motivate the less well-off to participate.”
“This is an important study that begins to assess whether these concerns are justified in a real-world context,” added Dr. Iltis, director of the Center for Bioethics, Health and Society and professor of philosophy at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Sang Ngo, Anthony S. Kim, MD, and Winston Chiong, MD, PhD, write: “This work is welcome, as it presents experimental data to a bioethical debate that so far has been largely driven by conjecture and competing suppositions.”
The commentary authors, however, question the conclusiveness of the findings. “Interpreting the authors’ findings is complex and illustrates some of the challenges inherent to applying empirical data to ethical problems,” they write.
Recruitment realities
When asked his advice for researchers considering financial incentives, Dr. Halpern said: “All researchers would happily include incentives in their trial budgets if not for concerns that the sponsor or institutional review board might not approve of them.”
“By far the biggest threat to a trial’s success is the inability to enroll enough participants,” he added.
Dr. Iltis agreed, framing the need to boost enrollment in ethical terms. “There is another important ethical issue that often gets ignored, and that is the issue of studies that fail to enroll enough participants and are never completed or are underpowered,” she said.
“These studies end up exposing people to research risks and burdens without a compensating social benefit.”
“If incentives help to increase enrollment and do not necessarily result in undue influence or unfair participant selection, then there might be ethical reasons to offer incentives,” Dr. Iltis added.
Building on previous work assessing financial incentives in hypothetical clinical trials, Dr. Halpern and colleagues studied 654 participants with major depressive disorder in a smoking cessation trial. They also studied another 642 participants in a study that compared a gamification strategy to usual care for encouraging hospitalized patients to get out of bed and walk.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues randomly assigned people in the smoking cessation study to receive no financial compensation, $200, or $500. In the ambulation trial, participants were randomly allocated to receive no compensation, $100, or $300.
Key findings
A total of 22% of those offered no incentive enrolled in the smoking cessation study. In contrast, 36% offered $200 agreed, as did 47% of those offered $500, which the investigators say supports offering cash incentives to boost enrollment. The differences were significant (P < .001).
In contrast, the amount offered did not significantly incentivize more people to participate in the ambulation trial (P = .62). Rates were 45% with no compensation, 48% with $100 payment, and 43% with $300 payment.
In an analysis that adjusted for demographic differences, financial well-being, and Research Attitudes Questionnaire (RAQ-7) scores, each increase in cash incentive increased the odds of enrollment in the smoking cessation trial by 70% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.70; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-2.17).
The same effect was not seen in the ambulation trial, where each higher cash incentive did not make a significant difference (aOR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.22).
“The ambulation trial was a lower-risk trial in which patients’ willingness to participate was higher in general. So there were likely fewer people whose participation decisions could be influenced by offers of money,” Dr. Halpern said.
Inducement vs. coercion
The incentives in the study “did not function as unjust inducements, as they were not preferentially motivating across groups with different income levels or financial well-being in either trial,” the researchers note.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues also checked for any perceptions of coercion. More than 70% of participants in each smoking cessation trial group perceived no coercion, as did more than 93% of participants in each ambulation trial group, according to scores on a modified Perceived Coercion Scale of the MacArthur Admission Experience Survey.
Furthermore, perception of risks did not significantly alter the association between cash incentives and enrollment in either trial.
After collecting the findings, Dr. Halpern and colleagues informed participants about their participation in RETAIN and explained the rationale for using different cash incentives. They also let all participants know they would ultimately receive the maximum incentive – either $500 or $300, depending on the trial.
Research implications
A study limitation was reliance on participant risk perception, as was an inability to measure perceived coercion among people who chose not to participant in the trials. Another potential limitation is that “neither of these parent trials posed particularly high risks. Future tests of incentives of different sizes, and in the context of higher-risk parent trials, including trials that test treatments of serious illnesses, are warranted,” the researchers note.
“While there are many more questions to ask and contexts in which to study the effects of incentives, this study calls on opponents of incentivizing research participants with money to be more humble,” Dr. Iltis said. “Incentives might not have the effects they assume they have and which they have long held make such incentives unethical.”
“I encourage researchers who are offering incentives to consider working with people doing ethics research to assess the effects of incentives in their studies,” Dr. Halpern said. “Real-world, as opposed to hypothetical studies that can improve our understanding of the impact of incentives can improve the ethical conduct of research over time.”
Responding to criticism
The authors of the invited commentary questioned the definitions Dr. Halpern and colleagues used for undue or unjust inducement. “Among bioethicists, there is no consensus about what counts as undue inducement or an unjust distribution of research burdens. In this article, the authors have operationalized these constructs based on their own interpretations of undue and unjust inducement, which may not capture all the concerns that scholars have raised about inducement.”
Asked to respond to this and other criticisms raised in the commentary, Dr. Halpern said: “Did our study answer all possible questions about incentives? Absolutely not. But when it comes to incentives for research participation, an ounce of data is worth a pound of conjecture.”
There was agreement, however, that the findings could now put the onus on opponents of financial incentives for trial participants.
“I agree with the commentary’s authors that our study essentially shifts the burden of proof, such that, as they say, ‘those who would limit [incentives’] application may owe us an applicable criterion,’ ” Dr. Halpern said.
The authors of the invited commentary also criticized use of the study’s noninferiority design to rule out undue or unjust inducement. They note this design “may be unfamiliar to many bioethicists and can place substantial evaluative demands on readers.”
“As for the authors’ claim that noninferiority designs are difficult to interpret and unfamiliar to most clinicians and ethicists, I certainly agree,” Dr. Halpern said. “But that is hardly a reason to not employ the most rigorous methods possible to answer important questions.”
The study was supported by funding from the National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could the osteoporosis drug alendronate ward off diabetes?
A nationwide, retrospective, case-control study of older adults in Denmark suggests that the bisphosphonate alendronate that is widely used to treat osteoporosis may protect against new-onset type 2 diabetes. But these preliminary findings need to be confirmed in a randomized controlled trial, experts said.
The registry study showed that from 2008 to 2018, among individuals in Denmark age 50 and older (with a mean age of 67), those who were taking alendronate were 36% less likely to have new-onset type 2 diabetes than age- and sex-matched individuals who were not taking the drug, after controlling for multiple risk factors.
The results also suggest that longer alendronate use and higher compliance might be more protective.
Rikke Viggers, MD, a PhD student in the department of clinical medicine, Aalborg (Denmark) University, presented the findings during an oral session at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“Excitingly, our research suggests that alendronate, an inexpensive medicine widely used to treat osteoporosis, may also protect against type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Viggers summarized in a press release issued by the EASD.
“Type 2 diabetes is a serious lifelong condition that can lead to other serious health issues such as stroke, heart disease, blindness, and limb amputation,” she noted, “and anything that prevents or even delays it will also reduce a person’s risk of all these other conditions.”
“We believe that doctors should consider this when prescribing osteoporosis drugs to those with prediabetes or at high risk of type 2 diabetes,” she added.
Preliminary results, need for RCT
However, these are preliminary results, Dr. Viggers cautioned during the oral presentation and in an email. “This is a registry-based study,” she stressed, “and we cannot conclude causality.”
“We do not know if this effect [of decreased risk of developing diabetes among people taking alendronate] is ‘real’ and what the mechanisms are.”
“It could be a direct effect on peripheral tissues, for example, muscle and adipose tissue,” Dr. Viggers speculated, “or an indirect effect through bone metabolites that may impact glucose metabolism.”
The group is now conducting a randomized controlled trial in patients with diabetes and osteopenia or osteoporosis to examine the relationship between alendronate and insulin sensitivity, bone indices, and glycemic control.
They also aim to investigate whether alendronate is the optimal antiosteoporotic therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes. Preliminary results suggest that other bisphosphonates have similar effects.
“Alendronate decreases bone turnover and may not be beneficial in healthy bones,” Dr. Viggers noted. “However, as far as I know, potential other side effects have not been tested in healthy bones,” so further research is needed.
Invited to comment, Charles P. Vega, MD, who presented a case and a crowd-sourced opinion about deprescribing bisphosphonates, noted that type 2 diabetes is most often diagnosed between age 40 and 60, although a few cases are diagnosed after age 65, and the study by Dr. Viggers and colleagues suggests that alendronate might help lower the risk of diabetes onset in these older adults.
“This is an interesting retrospective analysis,” said Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, family medicine, University of California, Irvine, but like the study authors, he cautioned that “it should be verified with other data.”
“A meta-analysis from clinical trials of bisphosphonates which followed blood glucose levels would be helpful,” he said.
Current registry study findings
Glucose homeostasis has been linked to bone metabolism, Dr. Viggers said, and bisphosphonates were associated with increased insulin sensitivity and decreased risk of diabetes risk in two registry studies from Denmark and Taiwan.
The researchers aimed to investigate if the risk of developing type 2 diabetes was altered by previous use of alendronate.
Using data from the national Danish Patient Registry, they identified 163,588 individuals age 50 and older newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in 2008-2018.
They matched each patient with three individuals of the same gender and age range who did not have diabetes, for a total of 490,764 controls.
Roughly two-thirds of participants were in their 50s or 60s, a quarter were in their 70s, and 10% were 80 or older. About half of participants were women (45%).
Compared to the patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes, the control participants were healthier: they were less likely to have obesity (6% vs. 17%) and had a lower mean Charlson Comorbidity Index (0.38 vs. 0.88).
Using data from the national Danish Health Service Prescription Registry, the researchers identified individuals who filled prescriptions for alendronate in 2008-2018.
After controlling for heavy smoking, alcohol abuse, obesity, pancreatitis, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, glucocorticoid use, marital status, household income, and Charlson Comorbidity Index, people taking alendronate were less likely to have new-onset diabetes than those not taking this drug (odds ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.62-0.66).
The odds of developing type 2 diabetes were even lower among those who took alendronate for 8 years or more versus never-users (OR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.40-0.56), after controlling for the same variables.
Session Chair Zhila Semnani-Azad, a PhD student in nutritional science, University of Toronto, wanted to know if the researchers accounted for physical activity and vitamin D use. Dr. Viggers replied that the registries did not have this information.
The study was funded by a Steno Collaborative Project grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Denmark. Dr. Viggers has disclosed receiving a grant from the foundation. Dr. Vega has disclosed serving as a consultant for Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A nationwide, retrospective, case-control study of older adults in Denmark suggests that the bisphosphonate alendronate that is widely used to treat osteoporosis may protect against new-onset type 2 diabetes. But these preliminary findings need to be confirmed in a randomized controlled trial, experts said.
The registry study showed that from 2008 to 2018, among individuals in Denmark age 50 and older (with a mean age of 67), those who were taking alendronate were 36% less likely to have new-onset type 2 diabetes than age- and sex-matched individuals who were not taking the drug, after controlling for multiple risk factors.
The results also suggest that longer alendronate use and higher compliance might be more protective.
Rikke Viggers, MD, a PhD student in the department of clinical medicine, Aalborg (Denmark) University, presented the findings during an oral session at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“Excitingly, our research suggests that alendronate, an inexpensive medicine widely used to treat osteoporosis, may also protect against type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Viggers summarized in a press release issued by the EASD.
“Type 2 diabetes is a serious lifelong condition that can lead to other serious health issues such as stroke, heart disease, blindness, and limb amputation,” she noted, “and anything that prevents or even delays it will also reduce a person’s risk of all these other conditions.”
“We believe that doctors should consider this when prescribing osteoporosis drugs to those with prediabetes or at high risk of type 2 diabetes,” she added.
Preliminary results, need for RCT
However, these are preliminary results, Dr. Viggers cautioned during the oral presentation and in an email. “This is a registry-based study,” she stressed, “and we cannot conclude causality.”
“We do not know if this effect [of decreased risk of developing diabetes among people taking alendronate] is ‘real’ and what the mechanisms are.”
“It could be a direct effect on peripheral tissues, for example, muscle and adipose tissue,” Dr. Viggers speculated, “or an indirect effect through bone metabolites that may impact glucose metabolism.”
The group is now conducting a randomized controlled trial in patients with diabetes and osteopenia or osteoporosis to examine the relationship between alendronate and insulin sensitivity, bone indices, and glycemic control.
They also aim to investigate whether alendronate is the optimal antiosteoporotic therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes. Preliminary results suggest that other bisphosphonates have similar effects.
“Alendronate decreases bone turnover and may not be beneficial in healthy bones,” Dr. Viggers noted. “However, as far as I know, potential other side effects have not been tested in healthy bones,” so further research is needed.
Invited to comment, Charles P. Vega, MD, who presented a case and a crowd-sourced opinion about deprescribing bisphosphonates, noted that type 2 diabetes is most often diagnosed between age 40 and 60, although a few cases are diagnosed after age 65, and the study by Dr. Viggers and colleagues suggests that alendronate might help lower the risk of diabetes onset in these older adults.
“This is an interesting retrospective analysis,” said Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, family medicine, University of California, Irvine, but like the study authors, he cautioned that “it should be verified with other data.”
“A meta-analysis from clinical trials of bisphosphonates which followed blood glucose levels would be helpful,” he said.
Current registry study findings
Glucose homeostasis has been linked to bone metabolism, Dr. Viggers said, and bisphosphonates were associated with increased insulin sensitivity and decreased risk of diabetes risk in two registry studies from Denmark and Taiwan.
The researchers aimed to investigate if the risk of developing type 2 diabetes was altered by previous use of alendronate.
Using data from the national Danish Patient Registry, they identified 163,588 individuals age 50 and older newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in 2008-2018.
They matched each patient with three individuals of the same gender and age range who did not have diabetes, for a total of 490,764 controls.
Roughly two-thirds of participants were in their 50s or 60s, a quarter were in their 70s, and 10% were 80 or older. About half of participants were women (45%).
Compared to the patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes, the control participants were healthier: they were less likely to have obesity (6% vs. 17%) and had a lower mean Charlson Comorbidity Index (0.38 vs. 0.88).
Using data from the national Danish Health Service Prescription Registry, the researchers identified individuals who filled prescriptions for alendronate in 2008-2018.
After controlling for heavy smoking, alcohol abuse, obesity, pancreatitis, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, glucocorticoid use, marital status, household income, and Charlson Comorbidity Index, people taking alendronate were less likely to have new-onset diabetes than those not taking this drug (odds ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.62-0.66).
The odds of developing type 2 diabetes were even lower among those who took alendronate for 8 years or more versus never-users (OR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.40-0.56), after controlling for the same variables.
Session Chair Zhila Semnani-Azad, a PhD student in nutritional science, University of Toronto, wanted to know if the researchers accounted for physical activity and vitamin D use. Dr. Viggers replied that the registries did not have this information.
The study was funded by a Steno Collaborative Project grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Denmark. Dr. Viggers has disclosed receiving a grant from the foundation. Dr. Vega has disclosed serving as a consultant for Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A nationwide, retrospective, case-control study of older adults in Denmark suggests that the bisphosphonate alendronate that is widely used to treat osteoporosis may protect against new-onset type 2 diabetes. But these preliminary findings need to be confirmed in a randomized controlled trial, experts said.
The registry study showed that from 2008 to 2018, among individuals in Denmark age 50 and older (with a mean age of 67), those who were taking alendronate were 36% less likely to have new-onset type 2 diabetes than age- and sex-matched individuals who were not taking the drug, after controlling for multiple risk factors.
The results also suggest that longer alendronate use and higher compliance might be more protective.
Rikke Viggers, MD, a PhD student in the department of clinical medicine, Aalborg (Denmark) University, presented the findings during an oral session at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
“Excitingly, our research suggests that alendronate, an inexpensive medicine widely used to treat osteoporosis, may also protect against type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Viggers summarized in a press release issued by the EASD.
“Type 2 diabetes is a serious lifelong condition that can lead to other serious health issues such as stroke, heart disease, blindness, and limb amputation,” she noted, “and anything that prevents or even delays it will also reduce a person’s risk of all these other conditions.”
“We believe that doctors should consider this when prescribing osteoporosis drugs to those with prediabetes or at high risk of type 2 diabetes,” she added.
Preliminary results, need for RCT
However, these are preliminary results, Dr. Viggers cautioned during the oral presentation and in an email. “This is a registry-based study,” she stressed, “and we cannot conclude causality.”
“We do not know if this effect [of decreased risk of developing diabetes among people taking alendronate] is ‘real’ and what the mechanisms are.”
“It could be a direct effect on peripheral tissues, for example, muscle and adipose tissue,” Dr. Viggers speculated, “or an indirect effect through bone metabolites that may impact glucose metabolism.”
The group is now conducting a randomized controlled trial in patients with diabetes and osteopenia or osteoporosis to examine the relationship between alendronate and insulin sensitivity, bone indices, and glycemic control.
They also aim to investigate whether alendronate is the optimal antiosteoporotic therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes. Preliminary results suggest that other bisphosphonates have similar effects.
“Alendronate decreases bone turnover and may not be beneficial in healthy bones,” Dr. Viggers noted. “However, as far as I know, potential other side effects have not been tested in healthy bones,” so further research is needed.
Invited to comment, Charles P. Vega, MD, who presented a case and a crowd-sourced opinion about deprescribing bisphosphonates, noted that type 2 diabetes is most often diagnosed between age 40 and 60, although a few cases are diagnosed after age 65, and the study by Dr. Viggers and colleagues suggests that alendronate might help lower the risk of diabetes onset in these older adults.
“This is an interesting retrospective analysis,” said Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, family medicine, University of California, Irvine, but like the study authors, he cautioned that “it should be verified with other data.”
“A meta-analysis from clinical trials of bisphosphonates which followed blood glucose levels would be helpful,” he said.
Current registry study findings
Glucose homeostasis has been linked to bone metabolism, Dr. Viggers said, and bisphosphonates were associated with increased insulin sensitivity and decreased risk of diabetes risk in two registry studies from Denmark and Taiwan.
The researchers aimed to investigate if the risk of developing type 2 diabetes was altered by previous use of alendronate.
Using data from the national Danish Patient Registry, they identified 163,588 individuals age 50 and older newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in 2008-2018.
They matched each patient with three individuals of the same gender and age range who did not have diabetes, for a total of 490,764 controls.
Roughly two-thirds of participants were in their 50s or 60s, a quarter were in their 70s, and 10% were 80 or older. About half of participants were women (45%).
Compared to the patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes, the control participants were healthier: they were less likely to have obesity (6% vs. 17%) and had a lower mean Charlson Comorbidity Index (0.38 vs. 0.88).
Using data from the national Danish Health Service Prescription Registry, the researchers identified individuals who filled prescriptions for alendronate in 2008-2018.
After controlling for heavy smoking, alcohol abuse, obesity, pancreatitis, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, glucocorticoid use, marital status, household income, and Charlson Comorbidity Index, people taking alendronate were less likely to have new-onset diabetes than those not taking this drug (odds ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.62-0.66).
The odds of developing type 2 diabetes were even lower among those who took alendronate for 8 years or more versus never-users (OR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.40-0.56), after controlling for the same variables.
Session Chair Zhila Semnani-Azad, a PhD student in nutritional science, University of Toronto, wanted to know if the researchers accounted for physical activity and vitamin D use. Dr. Viggers replied that the registries did not have this information.
The study was funded by a Steno Collaborative Project grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Denmark. Dr. Viggers has disclosed receiving a grant from the foundation. Dr. Vega has disclosed serving as a consultant for Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2021
Dr. Judy C. Washington shows URM physicians how to lead
For URM physicians, she also imparts a shared experience of being a minority in the field and helps prepare them for the challenges of facing racism or feeling marginalized or not equitably supported in academic life – and for making change.
While family medicine’s demographics have become more diverse over time, and more so than other specialties, they are not yet representative of the U.S. population. Within academia, male physicians who are Black or African American, or Hispanic or Latino, comprised about 4% and 5% of family medicine faculty, respectively, at the end of 2019, according to data from the Association of American Medical Colleges. For women, these numbers were about 9% and 4%, respectively. (Only those with an MD degree exclusively were included in the report.)
“When you have the privilege to serve in leadership, you have the responsibility to reach back and identify and help others who would not otherwise have the opportunity to be recognized,” Dr. Washington said.
Her mentorship work stems in large part from her long-time involvement and leadership roles in the Society of Teachers of Family Medicine (STFM) – roles she considers a pillar of her professional life. She currently serves as president of the STFM Foundation and is associate chief medical officer of the Atlantic Medical Group, a large multisite physician-led organization. She is also coordinator of women’s health for the Overlook Family Medicine Residency Program, which is affiliated with Atlantic Medical Group.
In Dr. Washington’s role as associate chief medical officer of Atlantic Medical Group in Summit, N.J., she focuses on physician engagement, satisfaction, and diversity. She also assists in areas such as population health. For the Overlook Family Medicine Residency Program also in Summit, she precepts residents in the obstetrics clinic and in the family medicine outpatient clinic.
Diana N. Carvajal, MD, MPH, one of Dr. Washington’s mentees, called her an “inspirational leader” for young academic faculty and said she is a familiar speaker at STFM meetings on topics of workforce diversity, equity, and leadership. She is “passionate” about mentorship, Dr. Carvajal said, and has understood “that URMs and women of color were not always getting [the mentorship they need to be successful].”
Guiding future leaders
Ivonne McLean, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and an attending at a community health center in the Bronx, called Dr. Washington for advice a couple of years ago when she was considering her next career move.
“She took a genuine interest in me. She never said, this is what you should do. But the questions she asked and the examples she gave from her own life were incredibly helpful to me [in deciding to pursue a research fellowship] ... it was a pivotal conversation,” said Dr. McLean, associate director of a reproductive health fellowship and a research fellow in a New York State–funded program.
“From a lived experience angle, she also told me, here are some of the challenges you’ll have as a woman of color, and here are some of the ways you can approach that,” she said.
Dr. Carvajal, also a URM family physician, credits Dr. Washington’s mentorship with the development of a day-long workshop – held before the annual Society of Teachers of Family Medicine (STFM) meeting – on the low and declining rates of Black males in medicine. “We’d planned it as a presentation, and [she heard of it and] helped us expand it,” she said, calling Dr. Washington “warm, welcoming, and encouraging.
“That work and collaboration with her and the others she brought [into the process] have resulted in publications and more presentations and strategy building for diversifying the workforce,” said Dr. Carvajal, assistant professor, director of reproductive health education in family medicine, and codirector of the research section, all in the department of family and community medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore.
STFM involvement
Dr. Washington, who says that all or almost all of her mentees are now leaders in their academic institutions and communities, has been instrumental in developing STFM’s mentoring programming and in facilitating the organization’s multifaceted URM Initiative.
She has been active in STFM since the start of her academic career, and in 2009, while serving as assistant program director for the residency program in which she’d trained, she joined two other African American women, Monique Y. Davis-Smith, MD, and Joedrecka Brown-Speights, MD, in cochairing the society’s Group on Minority and Multicultural Health.
It was in this space, that Dr. Washington said she “heard people’s stories of being in major academic institutions and not feeling supported, not being given roadmaps to success, not getting assistance with publishing, or just kind of feeling like an outsider ... of not being pulled in.” Hispanic and African American females, in particular, “were feeling marginalized,” she said.
In 2018, having co-led development of the STFM Quality Mentoring Program for URM faculty, Dr. Washington was asked to join the STFM Foundation and subsequently led the STFM Foundation’s fundraising campaign for a new URM Initiative. She exceeded her goal, increasing support for URM participation in meetings and activities, and then participated in an STFM steering committee to create broader and longer-lasting support for URM faculty, community teachers, and medical students and residents going into academic family medicine.
Increasing the percentage of URM family medicine faculty in leadership positions – and raising awareness of structural barriers to achievement – is one of the current pillars of the URM Initiative.
Navigating the ‘minority tax’
As part of her mentoring, Dr. Washington helps URM physicians navigate the minority tax – a term referring to the uncompensated citizenship tasks that are more often assigned to Black and other URM physicians than to White physicians, and that take time away from scholarship, further perpetuating inequities.
“Some of our young faculty members find themselves thrust into being the diversity and inclusion leaders in their institutions at a level at which they feel little power and little buy-in from [leadership],” she noted.
A commentary written by Dr. Washington and several colleagues on the minority tax as it impacts women – and the need to build a “tax shelter” to make academic medicine a more just environment for URM women – was published earlier this year in the Journal of Women’s Health.
She also answers e-mails and fields phone calls from young URM faculty who are mulling career moves and facing other familiar challenges.
Physicians who are URM, and African American physicians in particular, tend to “get pulled into the [often underserved] communities, into the patient care and community service areas,” Dr. Washington explained. “But unless you convert these projects into scholarship and publications, and unless you serve on a national committee outside of your institution, you’re not going to be promoted.”
Dr. Washington helps junior faculty envision themselves 5-plus years down the road, find what she calls scholarly “passion projects,” and prepare themselves for their next steps.
She helps her mentees navigate other parts of the continuum of unconscious bias and racism as well, from microaggressions from colleagues to overt discrimination from patients.
“I spend countless minutes fielding texts and phone calls from those who need support,” she wrote in a blog post. “They are a constant reminder that I must continue to speak up when I get the opportunity to do so.”
A journey through family medicine, and through bias and racism
Dr. Washington’s early days in medicine included graduating from Meharry Medical College in 1983 and the Mountainside Family Practice Residency Program in 1990. Following 6 years of working in a private practice in rural Maryland, she moved to academia, spending 6 years at East Tennessee State University and 4 years at the UMDNJ–New Jersey Medical School in Newark as an assistant professor of family medicine.
As had happened in rural Maryland, bias and racism have too often lurked during her career as a physician.
“I grew up in Alabama so I was pretty much ready to deal with racism in the South,” Dr. Washington said. “What I was not ready for was coming to the Northeast and seeing that you’re marginalized because you’re not invited into the room. Or if you do go into spaces when you’re the only one, you often don’t feel as welcomed as you thought you might be.”
Her ideas and contributions were too often dismissed, she wrote in a 2020 blog entry posted on her LinkedIn page. And during contract negotiations, “I was not aware of all the information that my White colleagues had. They had the advantage of inside information.”
Dr. Washington says that “it took a village” to make her who she is today: teachers in her segregated schools in Alabama, one of her college professors, her best friend in medical school – and STFM, “where the list [of her own mentors] is long.”
For URM physicians, she also imparts a shared experience of being a minority in the field and helps prepare them for the challenges of facing racism or feeling marginalized or not equitably supported in academic life – and for making change.
While family medicine’s demographics have become more diverse over time, and more so than other specialties, they are not yet representative of the U.S. population. Within academia, male physicians who are Black or African American, or Hispanic or Latino, comprised about 4% and 5% of family medicine faculty, respectively, at the end of 2019, according to data from the Association of American Medical Colleges. For women, these numbers were about 9% and 4%, respectively. (Only those with an MD degree exclusively were included in the report.)
“When you have the privilege to serve in leadership, you have the responsibility to reach back and identify and help others who would not otherwise have the opportunity to be recognized,” Dr. Washington said.
Her mentorship work stems in large part from her long-time involvement and leadership roles in the Society of Teachers of Family Medicine (STFM) – roles she considers a pillar of her professional life. She currently serves as president of the STFM Foundation and is associate chief medical officer of the Atlantic Medical Group, a large multisite physician-led organization. She is also coordinator of women’s health for the Overlook Family Medicine Residency Program, which is affiliated with Atlantic Medical Group.
In Dr. Washington’s role as associate chief medical officer of Atlantic Medical Group in Summit, N.J., she focuses on physician engagement, satisfaction, and diversity. She also assists in areas such as population health. For the Overlook Family Medicine Residency Program also in Summit, she precepts residents in the obstetrics clinic and in the family medicine outpatient clinic.
Diana N. Carvajal, MD, MPH, one of Dr. Washington’s mentees, called her an “inspirational leader” for young academic faculty and said she is a familiar speaker at STFM meetings on topics of workforce diversity, equity, and leadership. She is “passionate” about mentorship, Dr. Carvajal said, and has understood “that URMs and women of color were not always getting [the mentorship they need to be successful].”
Guiding future leaders
Ivonne McLean, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and an attending at a community health center in the Bronx, called Dr. Washington for advice a couple of years ago when she was considering her next career move.
“She took a genuine interest in me. She never said, this is what you should do. But the questions she asked and the examples she gave from her own life were incredibly helpful to me [in deciding to pursue a research fellowship] ... it was a pivotal conversation,” said Dr. McLean, associate director of a reproductive health fellowship and a research fellow in a New York State–funded program.
“From a lived experience angle, she also told me, here are some of the challenges you’ll have as a woman of color, and here are some of the ways you can approach that,” she said.
Dr. Carvajal, also a URM family physician, credits Dr. Washington’s mentorship with the development of a day-long workshop – held before the annual Society of Teachers of Family Medicine (STFM) meeting – on the low and declining rates of Black males in medicine. “We’d planned it as a presentation, and [she heard of it and] helped us expand it,” she said, calling Dr. Washington “warm, welcoming, and encouraging.
“That work and collaboration with her and the others she brought [into the process] have resulted in publications and more presentations and strategy building for diversifying the workforce,” said Dr. Carvajal, assistant professor, director of reproductive health education in family medicine, and codirector of the research section, all in the department of family and community medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore.
STFM involvement
Dr. Washington, who says that all or almost all of her mentees are now leaders in their academic institutions and communities, has been instrumental in developing STFM’s mentoring programming and in facilitating the organization’s multifaceted URM Initiative.
She has been active in STFM since the start of her academic career, and in 2009, while serving as assistant program director for the residency program in which she’d trained, she joined two other African American women, Monique Y. Davis-Smith, MD, and Joedrecka Brown-Speights, MD, in cochairing the society’s Group on Minority and Multicultural Health.
It was in this space, that Dr. Washington said she “heard people’s stories of being in major academic institutions and not feeling supported, not being given roadmaps to success, not getting assistance with publishing, or just kind of feeling like an outsider ... of not being pulled in.” Hispanic and African American females, in particular, “were feeling marginalized,” she said.
In 2018, having co-led development of the STFM Quality Mentoring Program for URM faculty, Dr. Washington was asked to join the STFM Foundation and subsequently led the STFM Foundation’s fundraising campaign for a new URM Initiative. She exceeded her goal, increasing support for URM participation in meetings and activities, and then participated in an STFM steering committee to create broader and longer-lasting support for URM faculty, community teachers, and medical students and residents going into academic family medicine.
Increasing the percentage of URM family medicine faculty in leadership positions – and raising awareness of structural barriers to achievement – is one of the current pillars of the URM Initiative.
Navigating the ‘minority tax’
As part of her mentoring, Dr. Washington helps URM physicians navigate the minority tax – a term referring to the uncompensated citizenship tasks that are more often assigned to Black and other URM physicians than to White physicians, and that take time away from scholarship, further perpetuating inequities.
“Some of our young faculty members find themselves thrust into being the diversity and inclusion leaders in their institutions at a level at which they feel little power and little buy-in from [leadership],” she noted.
A commentary written by Dr. Washington and several colleagues on the minority tax as it impacts women – and the need to build a “tax shelter” to make academic medicine a more just environment for URM women – was published earlier this year in the Journal of Women’s Health.
She also answers e-mails and fields phone calls from young URM faculty who are mulling career moves and facing other familiar challenges.
Physicians who are URM, and African American physicians in particular, tend to “get pulled into the [often underserved] communities, into the patient care and community service areas,” Dr. Washington explained. “But unless you convert these projects into scholarship and publications, and unless you serve on a national committee outside of your institution, you’re not going to be promoted.”
Dr. Washington helps junior faculty envision themselves 5-plus years down the road, find what she calls scholarly “passion projects,” and prepare themselves for their next steps.
She helps her mentees navigate other parts of the continuum of unconscious bias and racism as well, from microaggressions from colleagues to overt discrimination from patients.
“I spend countless minutes fielding texts and phone calls from those who need support,” she wrote in a blog post. “They are a constant reminder that I must continue to speak up when I get the opportunity to do so.”
A journey through family medicine, and through bias and racism
Dr. Washington’s early days in medicine included graduating from Meharry Medical College in 1983 and the Mountainside Family Practice Residency Program in 1990. Following 6 years of working in a private practice in rural Maryland, she moved to academia, spending 6 years at East Tennessee State University and 4 years at the UMDNJ–New Jersey Medical School in Newark as an assistant professor of family medicine.
As had happened in rural Maryland, bias and racism have too often lurked during her career as a physician.
“I grew up in Alabama so I was pretty much ready to deal with racism in the South,” Dr. Washington said. “What I was not ready for was coming to the Northeast and seeing that you’re marginalized because you’re not invited into the room. Or if you do go into spaces when you’re the only one, you often don’t feel as welcomed as you thought you might be.”
Her ideas and contributions were too often dismissed, she wrote in a 2020 blog entry posted on her LinkedIn page. And during contract negotiations, “I was not aware of all the information that my White colleagues had. They had the advantage of inside information.”
Dr. Washington says that “it took a village” to make her who she is today: teachers in her segregated schools in Alabama, one of her college professors, her best friend in medical school – and STFM, “where the list [of her own mentors] is long.”
For URM physicians, she also imparts a shared experience of being a minority in the field and helps prepare them for the challenges of facing racism or feeling marginalized or not equitably supported in academic life – and for making change.
While family medicine’s demographics have become more diverse over time, and more so than other specialties, they are not yet representative of the U.S. population. Within academia, male physicians who are Black or African American, or Hispanic or Latino, comprised about 4% and 5% of family medicine faculty, respectively, at the end of 2019, according to data from the Association of American Medical Colleges. For women, these numbers were about 9% and 4%, respectively. (Only those with an MD degree exclusively were included in the report.)
“When you have the privilege to serve in leadership, you have the responsibility to reach back and identify and help others who would not otherwise have the opportunity to be recognized,” Dr. Washington said.
Her mentorship work stems in large part from her long-time involvement and leadership roles in the Society of Teachers of Family Medicine (STFM) – roles she considers a pillar of her professional life. She currently serves as president of the STFM Foundation and is associate chief medical officer of the Atlantic Medical Group, a large multisite physician-led organization. She is also coordinator of women’s health for the Overlook Family Medicine Residency Program, which is affiliated with Atlantic Medical Group.
In Dr. Washington’s role as associate chief medical officer of Atlantic Medical Group in Summit, N.J., she focuses on physician engagement, satisfaction, and diversity. She also assists in areas such as population health. For the Overlook Family Medicine Residency Program also in Summit, she precepts residents in the obstetrics clinic and in the family medicine outpatient clinic.
Diana N. Carvajal, MD, MPH, one of Dr. Washington’s mentees, called her an “inspirational leader” for young academic faculty and said she is a familiar speaker at STFM meetings on topics of workforce diversity, equity, and leadership. She is “passionate” about mentorship, Dr. Carvajal said, and has understood “that URMs and women of color were not always getting [the mentorship they need to be successful].”
Guiding future leaders
Ivonne McLean, MD, assistant professor of family and community medicine at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and an attending at a community health center in the Bronx, called Dr. Washington for advice a couple of years ago when she was considering her next career move.
“She took a genuine interest in me. She never said, this is what you should do. But the questions she asked and the examples she gave from her own life were incredibly helpful to me [in deciding to pursue a research fellowship] ... it was a pivotal conversation,” said Dr. McLean, associate director of a reproductive health fellowship and a research fellow in a New York State–funded program.
“From a lived experience angle, she also told me, here are some of the challenges you’ll have as a woman of color, and here are some of the ways you can approach that,” she said.
Dr. Carvajal, also a URM family physician, credits Dr. Washington’s mentorship with the development of a day-long workshop – held before the annual Society of Teachers of Family Medicine (STFM) meeting – on the low and declining rates of Black males in medicine. “We’d planned it as a presentation, and [she heard of it and] helped us expand it,” she said, calling Dr. Washington “warm, welcoming, and encouraging.
“That work and collaboration with her and the others she brought [into the process] have resulted in publications and more presentations and strategy building for diversifying the workforce,” said Dr. Carvajal, assistant professor, director of reproductive health education in family medicine, and codirector of the research section, all in the department of family and community medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore.
STFM involvement
Dr. Washington, who says that all or almost all of her mentees are now leaders in their academic institutions and communities, has been instrumental in developing STFM’s mentoring programming and in facilitating the organization’s multifaceted URM Initiative.
She has been active in STFM since the start of her academic career, and in 2009, while serving as assistant program director for the residency program in which she’d trained, she joined two other African American women, Monique Y. Davis-Smith, MD, and Joedrecka Brown-Speights, MD, in cochairing the society’s Group on Minority and Multicultural Health.
It was in this space, that Dr. Washington said she “heard people’s stories of being in major academic institutions and not feeling supported, not being given roadmaps to success, not getting assistance with publishing, or just kind of feeling like an outsider ... of not being pulled in.” Hispanic and African American females, in particular, “were feeling marginalized,” she said.
In 2018, having co-led development of the STFM Quality Mentoring Program for URM faculty, Dr. Washington was asked to join the STFM Foundation and subsequently led the STFM Foundation’s fundraising campaign for a new URM Initiative. She exceeded her goal, increasing support for URM participation in meetings and activities, and then participated in an STFM steering committee to create broader and longer-lasting support for URM faculty, community teachers, and medical students and residents going into academic family medicine.
Increasing the percentage of URM family medicine faculty in leadership positions – and raising awareness of structural barriers to achievement – is one of the current pillars of the URM Initiative.
Navigating the ‘minority tax’
As part of her mentoring, Dr. Washington helps URM physicians navigate the minority tax – a term referring to the uncompensated citizenship tasks that are more often assigned to Black and other URM physicians than to White physicians, and that take time away from scholarship, further perpetuating inequities.
“Some of our young faculty members find themselves thrust into being the diversity and inclusion leaders in their institutions at a level at which they feel little power and little buy-in from [leadership],” she noted.
A commentary written by Dr. Washington and several colleagues on the minority tax as it impacts women – and the need to build a “tax shelter” to make academic medicine a more just environment for URM women – was published earlier this year in the Journal of Women’s Health.
She also answers e-mails and fields phone calls from young URM faculty who are mulling career moves and facing other familiar challenges.
Physicians who are URM, and African American physicians in particular, tend to “get pulled into the [often underserved] communities, into the patient care and community service areas,” Dr. Washington explained. “But unless you convert these projects into scholarship and publications, and unless you serve on a national committee outside of your institution, you’re not going to be promoted.”
Dr. Washington helps junior faculty envision themselves 5-plus years down the road, find what she calls scholarly “passion projects,” and prepare themselves for their next steps.
She helps her mentees navigate other parts of the continuum of unconscious bias and racism as well, from microaggressions from colleagues to overt discrimination from patients.
“I spend countless minutes fielding texts and phone calls from those who need support,” she wrote in a blog post. “They are a constant reminder that I must continue to speak up when I get the opportunity to do so.”
A journey through family medicine, and through bias and racism
Dr. Washington’s early days in medicine included graduating from Meharry Medical College in 1983 and the Mountainside Family Practice Residency Program in 1990. Following 6 years of working in a private practice in rural Maryland, she moved to academia, spending 6 years at East Tennessee State University and 4 years at the UMDNJ–New Jersey Medical School in Newark as an assistant professor of family medicine.
As had happened in rural Maryland, bias and racism have too often lurked during her career as a physician.
“I grew up in Alabama so I was pretty much ready to deal with racism in the South,” Dr. Washington said. “What I was not ready for was coming to the Northeast and seeing that you’re marginalized because you’re not invited into the room. Or if you do go into spaces when you’re the only one, you often don’t feel as welcomed as you thought you might be.”
Her ideas and contributions were too often dismissed, she wrote in a 2020 blog entry posted on her LinkedIn page. And during contract negotiations, “I was not aware of all the information that my White colleagues had. They had the advantage of inside information.”
Dr. Washington says that “it took a village” to make her who she is today: teachers in her segregated schools in Alabama, one of her college professors, her best friend in medical school – and STFM, “where the list [of her own mentors] is long.”
Booster shot back-and-forth creates uncertainty, confusion
Many people are confused — patients and healthcare providers alike — in the wake of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announcements about who is authorized to get a third or ‘booster’ shot of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
, healthcare providers report. At the same time, the uncertainty from changing federal messages about boosters is causing some chaos, especially in the form of vaccine misinformation.
The confusion started, in part, with the August 13 announcement that immunocompromised Americans were eligible for a booster shot. Next came the initial Biden administration intention to provide most U.S. adults with a third shot starting September 20 — an announcement later rolled back — followed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) limiting boosters to select groups last week.
“It was only 3% of the population that was going to be getting a third dose, then it was back to everyone being able to get the booster, and then it’s back to a select crew,” Louito Edje, MD, a family physician in private practice in Cincinnati, said in an interview with this news organization.
This kind of mixed messaging is generating more questions than answers.
“Even though that is following the science, translating the science into policy, it’s really fraught with confusion for patients, especially,” added Dr. Edje, professor educator in the departments of medical education and family and community medicine at UC Health and a fellow of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
When asked if he’s seeing more uncertainty about boosters, community pharmacist Brian Caswell, RPh, said: “I’m going to have to say yes because I’ve been confused myself at times.”
“Yes, there is a lot of confusion,” added Mr. Caswell, owner or co-owner of four pharmacies in Kansas and Missouri and president of the National Community Pharmacists Association.
Boosting misinformation?
“Unfortunately, confusion leads to an acceleration of misinformation,” Mr. Caswell said.
Dr. Edje shared an example. “The folks who have been hesitant to even get the first vaccine appear now a little less likely to want to go ahead and get vaccinated.”
These patients point to breakthrough COVID-19 cases of the Delta variant, which “reinforces that they don’t need to get vaccinated in the first place,” Dr. Edje said.
“That’s unfortunate because it’s a complete fallacy.”
Clearer communication from the federal government could help alleviate confusion, Mr. Caswell said. “I would like to see an official CDC chart that states who is eligible as of a certain date. Something that is accessible through their webpage or a social media source that can be updated. That would help all of us.”
“For myself, I’ve got patients from Kansas, Oklahoma, and Missouri that might be operating under different guidelines. That makes it even more confusing,” he said.
More clarity is needed for individuals seeking boosters as well. “It would help to be very clear with the general public, who are becoming very knowledgeable within this vaccine realm,” Mr. Caswell said.
‘Gaming the system’
Although most people seeking a booster shot at one of Caswell’s pharmacies are following official recommendations, there are some who remain ineligible but nonetheless come in for an additional vaccine.
“Even before this announcement last Friday, in the latter part of August when the CDC talked about a booster for immunocompromised, we had interest from people who did not meet the criteria,” Mr. Caswell said.
To the ineligible, he and his staff explain the approval process, why certain decisions are made, and point out that the number of eligible Americans is likely to expand in the future.
“The vast majority of them are understanding,” Mr. Caswell said. “But we’ve had some people who really didn’t want to accept the information, and I don’t know what they’ve done.”
“Some people are gaming the system to get their booster or second shot of J&J,” he said.
For example, Mr. Caswell had a patient who crossed over state lines from Missouri seeking a vaccine booster at Wolkar Drug, a pharmacy in Baxter Springs, Kan. “We found out later he had a J&J shot at a facility or provider in Missouri. He came over to Kansas, signed up for it and got a booster with Moderna.”
“We called and asked him if he was aware of it. He said, ‘yes.’ When we questioned him more about it, he hung up.”
Dr. Edje is likewise seeing interest from some ineligible patients, she said.
Crossing a liability line?
Mr. Caswell has asked for advice from lawyers and the State Board of Pharmacy on potential liability if a pharmacist gives a booster to a patient not eligible under the official FDA and CDC guidance.
“We ask patients direct questions about whether they’ve had the COVID vaccine, COVID, and a whole litany of questions they must answer. And we’re assuming they are going to be honest and forthright,” he said. “The pharmacist needs to make sure they make every effort to get that information from the patient.”
Normally, healthcare providers like Mr. Caswell report each COVID-19 vaccination to the state registry after administration. “We have not gone through a police action and checked the registry first,” he said.
But, if people continue to try ‘gaming the system,’ he said, he might have to start checking the state registry before giving someone a booster.
The American Academy of Family Physicians offers advice from the CDC about legal protections for providers.
“As outlined by CDC, any off-label use of the Comirnaty/Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine is not authorized at this time and may not be covered under the PREP Act or the PREP Act declaration. This means that clinicians providing the vaccine outside of the authorized/approved use may not have immunity from claims,” the AAFP website states.
“Per CDC, individuals who receive a third dose may not be eligible for compensation after a possible adverse event. Such use would be in violation of the CDC COVID-19 vaccination program provider agreement and therefore may not be reimbursable and may impact the ability of a provider to remain in the CDC program, in addition to other potential sanctions. Administration fees for off-label doses may not be reimbursed by payers.”
Despite confusion, demand is up
Even amid all the uncertainty, there appears to be a jump in enthusiasm for the booster shots.
“The requests have gone up quite a bit. We’ve seen a number of requests from people in person and over the phone looking to get a booster,” Mr. Caswell said. “Since the discussion at the federal level...there has been a lot of interest in the third shot booster, itself, as well as about a booster for J&J.”
“There is quite a bit of excitement out there,” he said.
Dr. Edje agreed: “I take care of a fair number of folks...including the elderly and healthcare professionals. They are already asking for the booster.”
Interestingly, Dr. Edje would like to get a booster herself but is not eligible for the Pfizer third shot. She is a participant in a Moderna vaccine trial and can only receive additional immunization as part of the study.
‘Walk, don’t run’
To quell any potential early rush to get a third shot, U.S. health officials are reminding booster-ineligible people that they still have some protection against COVID-19.
“If you’re a person who ultimately might get a booster that will make you optimally protected, you don’t necessarily need to get it tomorrow,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases told CNN.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, also weighed in. She told ABC that boosters for people who received a Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccine will be addressed with urgency.
“I want to reiterate that this is a very slow wane. There is no urgency here to go and get your booster immediately. You know, walk don’t run to your booster appointment,” she said.
“We will come and look at the data for Moderna and J&J in very short order.”
Dr. Edje and Mr. Caswell have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many people are confused — patients and healthcare providers alike — in the wake of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announcements about who is authorized to get a third or ‘booster’ shot of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
, healthcare providers report. At the same time, the uncertainty from changing federal messages about boosters is causing some chaos, especially in the form of vaccine misinformation.
The confusion started, in part, with the August 13 announcement that immunocompromised Americans were eligible for a booster shot. Next came the initial Biden administration intention to provide most U.S. adults with a third shot starting September 20 — an announcement later rolled back — followed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) limiting boosters to select groups last week.
“It was only 3% of the population that was going to be getting a third dose, then it was back to everyone being able to get the booster, and then it’s back to a select crew,” Louito Edje, MD, a family physician in private practice in Cincinnati, said in an interview with this news organization.
This kind of mixed messaging is generating more questions than answers.
“Even though that is following the science, translating the science into policy, it’s really fraught with confusion for patients, especially,” added Dr. Edje, professor educator in the departments of medical education and family and community medicine at UC Health and a fellow of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
When asked if he’s seeing more uncertainty about boosters, community pharmacist Brian Caswell, RPh, said: “I’m going to have to say yes because I’ve been confused myself at times.”
“Yes, there is a lot of confusion,” added Mr. Caswell, owner or co-owner of four pharmacies in Kansas and Missouri and president of the National Community Pharmacists Association.
Boosting misinformation?
“Unfortunately, confusion leads to an acceleration of misinformation,” Mr. Caswell said.
Dr. Edje shared an example. “The folks who have been hesitant to even get the first vaccine appear now a little less likely to want to go ahead and get vaccinated.”
These patients point to breakthrough COVID-19 cases of the Delta variant, which “reinforces that they don’t need to get vaccinated in the first place,” Dr. Edje said.
“That’s unfortunate because it’s a complete fallacy.”
Clearer communication from the federal government could help alleviate confusion, Mr. Caswell said. “I would like to see an official CDC chart that states who is eligible as of a certain date. Something that is accessible through their webpage or a social media source that can be updated. That would help all of us.”
“For myself, I’ve got patients from Kansas, Oklahoma, and Missouri that might be operating under different guidelines. That makes it even more confusing,” he said.
More clarity is needed for individuals seeking boosters as well. “It would help to be very clear with the general public, who are becoming very knowledgeable within this vaccine realm,” Mr. Caswell said.
‘Gaming the system’
Although most people seeking a booster shot at one of Caswell’s pharmacies are following official recommendations, there are some who remain ineligible but nonetheless come in for an additional vaccine.
“Even before this announcement last Friday, in the latter part of August when the CDC talked about a booster for immunocompromised, we had interest from people who did not meet the criteria,” Mr. Caswell said.
To the ineligible, he and his staff explain the approval process, why certain decisions are made, and point out that the number of eligible Americans is likely to expand in the future.
“The vast majority of them are understanding,” Mr. Caswell said. “But we’ve had some people who really didn’t want to accept the information, and I don’t know what they’ve done.”
“Some people are gaming the system to get their booster or second shot of J&J,” he said.
For example, Mr. Caswell had a patient who crossed over state lines from Missouri seeking a vaccine booster at Wolkar Drug, a pharmacy in Baxter Springs, Kan. “We found out later he had a J&J shot at a facility or provider in Missouri. He came over to Kansas, signed up for it and got a booster with Moderna.”
“We called and asked him if he was aware of it. He said, ‘yes.’ When we questioned him more about it, he hung up.”
Dr. Edje is likewise seeing interest from some ineligible patients, she said.
Crossing a liability line?
Mr. Caswell has asked for advice from lawyers and the State Board of Pharmacy on potential liability if a pharmacist gives a booster to a patient not eligible under the official FDA and CDC guidance.
“We ask patients direct questions about whether they’ve had the COVID vaccine, COVID, and a whole litany of questions they must answer. And we’re assuming they are going to be honest and forthright,” he said. “The pharmacist needs to make sure they make every effort to get that information from the patient.”
Normally, healthcare providers like Mr. Caswell report each COVID-19 vaccination to the state registry after administration. “We have not gone through a police action and checked the registry first,” he said.
But, if people continue to try ‘gaming the system,’ he said, he might have to start checking the state registry before giving someone a booster.
The American Academy of Family Physicians offers advice from the CDC about legal protections for providers.
“As outlined by CDC, any off-label use of the Comirnaty/Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine is not authorized at this time and may not be covered under the PREP Act or the PREP Act declaration. This means that clinicians providing the vaccine outside of the authorized/approved use may not have immunity from claims,” the AAFP website states.
“Per CDC, individuals who receive a third dose may not be eligible for compensation after a possible adverse event. Such use would be in violation of the CDC COVID-19 vaccination program provider agreement and therefore may not be reimbursable and may impact the ability of a provider to remain in the CDC program, in addition to other potential sanctions. Administration fees for off-label doses may not be reimbursed by payers.”
Despite confusion, demand is up
Even amid all the uncertainty, there appears to be a jump in enthusiasm for the booster shots.
“The requests have gone up quite a bit. We’ve seen a number of requests from people in person and over the phone looking to get a booster,” Mr. Caswell said. “Since the discussion at the federal level...there has been a lot of interest in the third shot booster, itself, as well as about a booster for J&J.”
“There is quite a bit of excitement out there,” he said.
Dr. Edje agreed: “I take care of a fair number of folks...including the elderly and healthcare professionals. They are already asking for the booster.”
Interestingly, Dr. Edje would like to get a booster herself but is not eligible for the Pfizer third shot. She is a participant in a Moderna vaccine trial and can only receive additional immunization as part of the study.
‘Walk, don’t run’
To quell any potential early rush to get a third shot, U.S. health officials are reminding booster-ineligible people that they still have some protection against COVID-19.
“If you’re a person who ultimately might get a booster that will make you optimally protected, you don’t necessarily need to get it tomorrow,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases told CNN.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, also weighed in. She told ABC that boosters for people who received a Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccine will be addressed with urgency.
“I want to reiterate that this is a very slow wane. There is no urgency here to go and get your booster immediately. You know, walk don’t run to your booster appointment,” she said.
“We will come and look at the data for Moderna and J&J in very short order.”
Dr. Edje and Mr. Caswell have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many people are confused — patients and healthcare providers alike — in the wake of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announcements about who is authorized to get a third or ‘booster’ shot of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
, healthcare providers report. At the same time, the uncertainty from changing federal messages about boosters is causing some chaos, especially in the form of vaccine misinformation.
The confusion started, in part, with the August 13 announcement that immunocompromised Americans were eligible for a booster shot. Next came the initial Biden administration intention to provide most U.S. adults with a third shot starting September 20 — an announcement later rolled back — followed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) limiting boosters to select groups last week.
“It was only 3% of the population that was going to be getting a third dose, then it was back to everyone being able to get the booster, and then it’s back to a select crew,” Louito Edje, MD, a family physician in private practice in Cincinnati, said in an interview with this news organization.
This kind of mixed messaging is generating more questions than answers.
“Even though that is following the science, translating the science into policy, it’s really fraught with confusion for patients, especially,” added Dr. Edje, professor educator in the departments of medical education and family and community medicine at UC Health and a fellow of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
When asked if he’s seeing more uncertainty about boosters, community pharmacist Brian Caswell, RPh, said: “I’m going to have to say yes because I’ve been confused myself at times.”
“Yes, there is a lot of confusion,” added Mr. Caswell, owner or co-owner of four pharmacies in Kansas and Missouri and president of the National Community Pharmacists Association.
Boosting misinformation?
“Unfortunately, confusion leads to an acceleration of misinformation,” Mr. Caswell said.
Dr. Edje shared an example. “The folks who have been hesitant to even get the first vaccine appear now a little less likely to want to go ahead and get vaccinated.”
These patients point to breakthrough COVID-19 cases of the Delta variant, which “reinforces that they don’t need to get vaccinated in the first place,” Dr. Edje said.
“That’s unfortunate because it’s a complete fallacy.”
Clearer communication from the federal government could help alleviate confusion, Mr. Caswell said. “I would like to see an official CDC chart that states who is eligible as of a certain date. Something that is accessible through their webpage or a social media source that can be updated. That would help all of us.”
“For myself, I’ve got patients from Kansas, Oklahoma, and Missouri that might be operating under different guidelines. That makes it even more confusing,” he said.
More clarity is needed for individuals seeking boosters as well. “It would help to be very clear with the general public, who are becoming very knowledgeable within this vaccine realm,” Mr. Caswell said.
‘Gaming the system’
Although most people seeking a booster shot at one of Caswell’s pharmacies are following official recommendations, there are some who remain ineligible but nonetheless come in for an additional vaccine.
“Even before this announcement last Friday, in the latter part of August when the CDC talked about a booster for immunocompromised, we had interest from people who did not meet the criteria,” Mr. Caswell said.
To the ineligible, he and his staff explain the approval process, why certain decisions are made, and point out that the number of eligible Americans is likely to expand in the future.
“The vast majority of them are understanding,” Mr. Caswell said. “But we’ve had some people who really didn’t want to accept the information, and I don’t know what they’ve done.”
“Some people are gaming the system to get their booster or second shot of J&J,” he said.
For example, Mr. Caswell had a patient who crossed over state lines from Missouri seeking a vaccine booster at Wolkar Drug, a pharmacy in Baxter Springs, Kan. “We found out later he had a J&J shot at a facility or provider in Missouri. He came over to Kansas, signed up for it and got a booster with Moderna.”
“We called and asked him if he was aware of it. He said, ‘yes.’ When we questioned him more about it, he hung up.”
Dr. Edje is likewise seeing interest from some ineligible patients, she said.
Crossing a liability line?
Mr. Caswell has asked for advice from lawyers and the State Board of Pharmacy on potential liability if a pharmacist gives a booster to a patient not eligible under the official FDA and CDC guidance.
“We ask patients direct questions about whether they’ve had the COVID vaccine, COVID, and a whole litany of questions they must answer. And we’re assuming they are going to be honest and forthright,” he said. “The pharmacist needs to make sure they make every effort to get that information from the patient.”
Normally, healthcare providers like Mr. Caswell report each COVID-19 vaccination to the state registry after administration. “We have not gone through a police action and checked the registry first,” he said.
But, if people continue to try ‘gaming the system,’ he said, he might have to start checking the state registry before giving someone a booster.
The American Academy of Family Physicians offers advice from the CDC about legal protections for providers.
“As outlined by CDC, any off-label use of the Comirnaty/Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine is not authorized at this time and may not be covered under the PREP Act or the PREP Act declaration. This means that clinicians providing the vaccine outside of the authorized/approved use may not have immunity from claims,” the AAFP website states.
“Per CDC, individuals who receive a third dose may not be eligible for compensation after a possible adverse event. Such use would be in violation of the CDC COVID-19 vaccination program provider agreement and therefore may not be reimbursable and may impact the ability of a provider to remain in the CDC program, in addition to other potential sanctions. Administration fees for off-label doses may not be reimbursed by payers.”
Despite confusion, demand is up
Even amid all the uncertainty, there appears to be a jump in enthusiasm for the booster shots.
“The requests have gone up quite a bit. We’ve seen a number of requests from people in person and over the phone looking to get a booster,” Mr. Caswell said. “Since the discussion at the federal level...there has been a lot of interest in the third shot booster, itself, as well as about a booster for J&J.”
“There is quite a bit of excitement out there,” he said.
Dr. Edje agreed: “I take care of a fair number of folks...including the elderly and healthcare professionals. They are already asking for the booster.”
Interestingly, Dr. Edje would like to get a booster herself but is not eligible for the Pfizer third shot. She is a participant in a Moderna vaccine trial and can only receive additional immunization as part of the study.
‘Walk, don’t run’
To quell any potential early rush to get a third shot, U.S. health officials are reminding booster-ineligible people that they still have some protection against COVID-19.
“If you’re a person who ultimately might get a booster that will make you optimally protected, you don’t necessarily need to get it tomorrow,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases told CNN.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, also weighed in. She told ABC that boosters for people who received a Moderna or Johnson & Johnson vaccine will be addressed with urgency.
“I want to reiterate that this is a very slow wane. There is no urgency here to go and get your booster immediately. You know, walk don’t run to your booster appointment,” she said.
“We will come and look at the data for Moderna and J&J in very short order.”
Dr. Edje and Mr. Caswell have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cook your amphibians before you eat them
Novel food for thought
When you were growing up, your parents probably told you to brush your teeth before you went to bed, warned you not to run with the scissors or play with matches, and punished you whenever you used the neighbor children to play Schrödinger’s cat.
They did those things for your own good, of course, and now the nation’s mother – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – is doing the same by warning us about novel outbreak–associated foods. As in, “Put down that novel outbreak–associated food! You don’t know where it’s been!”
Seriously, you don’t know where it’s been. CDC investigators identified 28 novel foods that were linked to 36 foodborne-disease outbreaks that occurred during 2007-2016, including moringa leaf (herb/spice), tempeh (grain), frog, sprouted nut butter, and skate.
The novel foods implicated in these outbreaks were more likely to be imported, compared with 14,216 outbreaks that occurred from 1973 to 2016, and about half didn’t require refrigeration. Two-thirds did not need to be cooked after purchase. Another thing your parents wouldn’t like: Some can’t be washed, like sheep milk, sugar cane, or the aforementioned nut butter.
We wanted to get a food expert to comment on these novel foods, but our editor said that the assistant manager of our local Burger King wasn’t expert enough, so we’ve commandeered someone else’s expert. Cynthia Sears, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, told Today.com all about the dangers of frogs: “Essentially all amphibians are contaminated, often with salmonella. Eating any amphibian that is not thoroughly cooked is a risk.”
Be sure to cook your amphibians before you eat them. Advice that your parents would be proud to share.
Dieters should stay away from diet drinks
When a drink is labeled “diet” many assume that the calorie-free beverage is the best choice. However, one of the largest studies to date on artificial sweeteners is out to set the record straight.
Artificial sweeteners, or nonnutritive sweeteners (NNS), are used in most if not all diet products to give the illusion of sweetness without the caloric guilt. Some studies say they help with weight loss for that very reason, but others say they can contribute to weight gain. So which is it?
Researchers at the University of Southern California sought to add some clarity to the research already out there.
They looked at an even-gendered split of 74 participants who drank 300 mL of drinks sweetened with NNS, table sugar, or water. The researchers then used functional MRI to see how parts of the brain responsible for appetite and cravings responded to images of high-calorie foods. They also looked at glucose, insulin, and other metabolic hormone levels, as well as how much food the participants ate at their free buffet. (In the participants’ defense, who can say no to a free buffet?)
The researchers made some interesting observations:
- Women who drank the NNS drink ate more than did the table-sugar group, but all men ate the same.
- Images of those calorie-packed goodies increased cravings and appetite for obese men and women in the NNS group, compared with the table-sugar group.
- For all participants who drank the NNS drink, there was a decrease in the hormone that tells the body it’s full.
“By studying different groups we were able to show that females and people with obesity may be more sensitive to artificial sweeteners. For these groups, drinking artificially sweetened drinks may trick the brain into feeling hungry, which may in turn result in more calories being consumed,” Kathleen Page, MD, the study’s corresponding author, said in a separate statement.
Today’s lesson? Don’t believe every label you read.
Instagram vegetables and the triumph of peer pressure
You and your family are sitting down for dinner. You’ve taken the time to prepare a healthy, nutritious meal. Vegetables, rice, seafood – all the right things. But the children around you refuse to partake. What can you do? Why, show them a highly liked photo of broccoli on Instagram!
In reality, kids will probably never like to eat their vegetables, but according to a study published in Appetite, viewing highly liked images on social media can compel adults to eat theirs.
The investigators recruited a group of 169 adults aged 18-28 (average age, 21) and showed them a series of mock Instagram posts of all sorts of food, everything from Brussels sprouts to chocolate cake, as well as nonfood images to act as a baseline. The images had a varying amount of likes. After viewing the images, study participants were offered a snack buffet consisting of grapes and cookies.
The results were a triumph of peer pressure. Those who viewed highly liked images of nutritious foods ate a significantly larger proportion of grapes, compared with those who saw highly liked images of unhealthy food or nonfood.
The authors cautioned that more research is needed, but they said that they’re onto something in the eternal struggle of getting people to eat better. If Mikey liked it, maybe you should, too. Just as long as you don’t try to encourage the eating of peas. That is a dark road none should take, and no one should ever be subjected to that cursed food.
It’s nice to share … hypertension?
You may have heard that, over time, you begin to resemble your spouse. You may have also heard that, as time goes by, your pet might start to resemble you, but that is a story for another time.
A lot of the time, it’s human nature that people partner with someone who is similar to them in physical and environmental status. If you like to go jogging at 5 a.m., you might want a spouse who does the same. A study done using data from couples in Japan and the Netherlands found that couples who had the same lifestyle had similar levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides. They also had similar illnesses such as hypertension and diabetes.
It’s important to note that many of the couples were not very genetically similar but had similar lifestyles. Encourage your partner to have a healthier lifestyle, so you can live on for many years to come!
Novel food for thought
When you were growing up, your parents probably told you to brush your teeth before you went to bed, warned you not to run with the scissors or play with matches, and punished you whenever you used the neighbor children to play Schrödinger’s cat.
They did those things for your own good, of course, and now the nation’s mother – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – is doing the same by warning us about novel outbreak–associated foods. As in, “Put down that novel outbreak–associated food! You don’t know where it’s been!”
Seriously, you don’t know where it’s been. CDC investigators identified 28 novel foods that were linked to 36 foodborne-disease outbreaks that occurred during 2007-2016, including moringa leaf (herb/spice), tempeh (grain), frog, sprouted nut butter, and skate.
The novel foods implicated in these outbreaks were more likely to be imported, compared with 14,216 outbreaks that occurred from 1973 to 2016, and about half didn’t require refrigeration. Two-thirds did not need to be cooked after purchase. Another thing your parents wouldn’t like: Some can’t be washed, like sheep milk, sugar cane, or the aforementioned nut butter.
We wanted to get a food expert to comment on these novel foods, but our editor said that the assistant manager of our local Burger King wasn’t expert enough, so we’ve commandeered someone else’s expert. Cynthia Sears, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, told Today.com all about the dangers of frogs: “Essentially all amphibians are contaminated, often with salmonella. Eating any amphibian that is not thoroughly cooked is a risk.”
Be sure to cook your amphibians before you eat them. Advice that your parents would be proud to share.
Dieters should stay away from diet drinks
When a drink is labeled “diet” many assume that the calorie-free beverage is the best choice. However, one of the largest studies to date on artificial sweeteners is out to set the record straight.
Artificial sweeteners, or nonnutritive sweeteners (NNS), are used in most if not all diet products to give the illusion of sweetness without the caloric guilt. Some studies say they help with weight loss for that very reason, but others say they can contribute to weight gain. So which is it?
Researchers at the University of Southern California sought to add some clarity to the research already out there.
They looked at an even-gendered split of 74 participants who drank 300 mL of drinks sweetened with NNS, table sugar, or water. The researchers then used functional MRI to see how parts of the brain responsible for appetite and cravings responded to images of high-calorie foods. They also looked at glucose, insulin, and other metabolic hormone levels, as well as how much food the participants ate at their free buffet. (In the participants’ defense, who can say no to a free buffet?)
The researchers made some interesting observations:
- Women who drank the NNS drink ate more than did the table-sugar group, but all men ate the same.
- Images of those calorie-packed goodies increased cravings and appetite for obese men and women in the NNS group, compared with the table-sugar group.
- For all participants who drank the NNS drink, there was a decrease in the hormone that tells the body it’s full.
“By studying different groups we were able to show that females and people with obesity may be more sensitive to artificial sweeteners. For these groups, drinking artificially sweetened drinks may trick the brain into feeling hungry, which may in turn result in more calories being consumed,” Kathleen Page, MD, the study’s corresponding author, said in a separate statement.
Today’s lesson? Don’t believe every label you read.
Instagram vegetables and the triumph of peer pressure
You and your family are sitting down for dinner. You’ve taken the time to prepare a healthy, nutritious meal. Vegetables, rice, seafood – all the right things. But the children around you refuse to partake. What can you do? Why, show them a highly liked photo of broccoli on Instagram!
In reality, kids will probably never like to eat their vegetables, but according to a study published in Appetite, viewing highly liked images on social media can compel adults to eat theirs.
The investigators recruited a group of 169 adults aged 18-28 (average age, 21) and showed them a series of mock Instagram posts of all sorts of food, everything from Brussels sprouts to chocolate cake, as well as nonfood images to act as a baseline. The images had a varying amount of likes. After viewing the images, study participants were offered a snack buffet consisting of grapes and cookies.
The results were a triumph of peer pressure. Those who viewed highly liked images of nutritious foods ate a significantly larger proportion of grapes, compared with those who saw highly liked images of unhealthy food or nonfood.
The authors cautioned that more research is needed, but they said that they’re onto something in the eternal struggle of getting people to eat better. If Mikey liked it, maybe you should, too. Just as long as you don’t try to encourage the eating of peas. That is a dark road none should take, and no one should ever be subjected to that cursed food.
It’s nice to share … hypertension?
You may have heard that, over time, you begin to resemble your spouse. You may have also heard that, as time goes by, your pet might start to resemble you, but that is a story for another time.
A lot of the time, it’s human nature that people partner with someone who is similar to them in physical and environmental status. If you like to go jogging at 5 a.m., you might want a spouse who does the same. A study done using data from couples in Japan and the Netherlands found that couples who had the same lifestyle had similar levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides. They also had similar illnesses such as hypertension and diabetes.
It’s important to note that many of the couples were not very genetically similar but had similar lifestyles. Encourage your partner to have a healthier lifestyle, so you can live on for many years to come!
Novel food for thought
When you were growing up, your parents probably told you to brush your teeth before you went to bed, warned you not to run with the scissors or play with matches, and punished you whenever you used the neighbor children to play Schrödinger’s cat.
They did those things for your own good, of course, and now the nation’s mother – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – is doing the same by warning us about novel outbreak–associated foods. As in, “Put down that novel outbreak–associated food! You don’t know where it’s been!”
Seriously, you don’t know where it’s been. CDC investigators identified 28 novel foods that were linked to 36 foodborne-disease outbreaks that occurred during 2007-2016, including moringa leaf (herb/spice), tempeh (grain), frog, sprouted nut butter, and skate.
The novel foods implicated in these outbreaks were more likely to be imported, compared with 14,216 outbreaks that occurred from 1973 to 2016, and about half didn’t require refrigeration. Two-thirds did not need to be cooked after purchase. Another thing your parents wouldn’t like: Some can’t be washed, like sheep milk, sugar cane, or the aforementioned nut butter.
We wanted to get a food expert to comment on these novel foods, but our editor said that the assistant manager of our local Burger King wasn’t expert enough, so we’ve commandeered someone else’s expert. Cynthia Sears, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, told Today.com all about the dangers of frogs: “Essentially all amphibians are contaminated, often with salmonella. Eating any amphibian that is not thoroughly cooked is a risk.”
Be sure to cook your amphibians before you eat them. Advice that your parents would be proud to share.
Dieters should stay away from diet drinks
When a drink is labeled “diet” many assume that the calorie-free beverage is the best choice. However, one of the largest studies to date on artificial sweeteners is out to set the record straight.
Artificial sweeteners, or nonnutritive sweeteners (NNS), are used in most if not all diet products to give the illusion of sweetness without the caloric guilt. Some studies say they help with weight loss for that very reason, but others say they can contribute to weight gain. So which is it?
Researchers at the University of Southern California sought to add some clarity to the research already out there.
They looked at an even-gendered split of 74 participants who drank 300 mL of drinks sweetened with NNS, table sugar, or water. The researchers then used functional MRI to see how parts of the brain responsible for appetite and cravings responded to images of high-calorie foods. They also looked at glucose, insulin, and other metabolic hormone levels, as well as how much food the participants ate at their free buffet. (In the participants’ defense, who can say no to a free buffet?)
The researchers made some interesting observations:
- Women who drank the NNS drink ate more than did the table-sugar group, but all men ate the same.
- Images of those calorie-packed goodies increased cravings and appetite for obese men and women in the NNS group, compared with the table-sugar group.
- For all participants who drank the NNS drink, there was a decrease in the hormone that tells the body it’s full.
“By studying different groups we were able to show that females and people with obesity may be more sensitive to artificial sweeteners. For these groups, drinking artificially sweetened drinks may trick the brain into feeling hungry, which may in turn result in more calories being consumed,” Kathleen Page, MD, the study’s corresponding author, said in a separate statement.
Today’s lesson? Don’t believe every label you read.
Instagram vegetables and the triumph of peer pressure
You and your family are sitting down for dinner. You’ve taken the time to prepare a healthy, nutritious meal. Vegetables, rice, seafood – all the right things. But the children around you refuse to partake. What can you do? Why, show them a highly liked photo of broccoli on Instagram!
In reality, kids will probably never like to eat their vegetables, but according to a study published in Appetite, viewing highly liked images on social media can compel adults to eat theirs.
The investigators recruited a group of 169 adults aged 18-28 (average age, 21) and showed them a series of mock Instagram posts of all sorts of food, everything from Brussels sprouts to chocolate cake, as well as nonfood images to act as a baseline. The images had a varying amount of likes. After viewing the images, study participants were offered a snack buffet consisting of grapes and cookies.
The results were a triumph of peer pressure. Those who viewed highly liked images of nutritious foods ate a significantly larger proportion of grapes, compared with those who saw highly liked images of unhealthy food or nonfood.
The authors cautioned that more research is needed, but they said that they’re onto something in the eternal struggle of getting people to eat better. If Mikey liked it, maybe you should, too. Just as long as you don’t try to encourage the eating of peas. That is a dark road none should take, and no one should ever be subjected to that cursed food.
It’s nice to share … hypertension?
You may have heard that, over time, you begin to resemble your spouse. You may have also heard that, as time goes by, your pet might start to resemble you, but that is a story for another time.
A lot of the time, it’s human nature that people partner with someone who is similar to them in physical and environmental status. If you like to go jogging at 5 a.m., you might want a spouse who does the same. A study done using data from couples in Japan and the Netherlands found that couples who had the same lifestyle had similar levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides. They also had similar illnesses such as hypertension and diabetes.
It’s important to note that many of the couples were not very genetically similar but had similar lifestyles. Encourage your partner to have a healthier lifestyle, so you can live on for many years to come!