User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
FDA Advisory panels consider easing isotretinoin requirements
for patients, pharmacies, and prescribers.
Isotretinoin, previously called Accutane, is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
In a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee, experts addressed ways to improve the modified iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (iPLEDGE REMS) for isotretinoin that caused chaos after its rollout at the end of 2021.
In January 2022, problems were multiplying with the program for clinicians, pharmacists, and patients, causing extensive delays and prescription denials. In response, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve problems.
March 28 was the first day of a 2-day meeting addressing what can be done to reduce burden with the iPLEDGE REMS while maintaining safety and preventing fetal exposure to the drug.
Key areas of concern
The meeting focused on several key areas.
The 19-day lockout period
The lockout is a current restriction for patients who can become pregnant and do not pick up their first prescription of isotretinoin within the specified 7-day prescription window. Currently, those who miss the window must wait 19 days from the date of the first pregnancy test to take an additional pregnancy test to be eligible to receive the drug.
Lindsey Crist, PharmD, a risk management analyst for the FDA, who presented the FDA review committee’s analysis, acknowledged that the lockout period causes delays in treatment and adds frustration and costs.
She said it’s important to remember that the lockout applies only to the first prescription. “It’s intended as an additional layer of screening to detect pregnancy,” she said.
“At least 12 pregnancies have been identified during the 19-day lockout from March 2017–September of 2022,” she noted.
The FDA is looking to the advisory committee to provide recommendations on whether the lockout period should be changed.
Home testing
During the pandemic, iPLEDGE rules have been relaxed from having a pregnancy test done only at a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified laboratory and home pregnancy tests have been allowed. The question now is whether home tests should continue to be allowed.
Ms. Crist said that the FDA’s review committee recommends ending the allowance of home tests, citing insufficient data on use and the discovery of instances of falsification of pregnancy tests.
“One study at an academic medical center reviewed the medical records of 89 patients who used home pregnancy tests while taking isotretinoin during the public health emergency. It found that 15.7% submitted falsified pregnancy test results,” she said.
Ms. Crist added, however, that the review committee recommends allowing the tests to be done in a provider’s office as an alternative.
Documenting counseling patients who cannot get pregnant
Currently, this documentation must be done monthly, primarily to counsel patients against drug sharing or giving blood. Proposed changes include extending the intervals for attestation or eliminating it to reduce burden on clinicians.
IPMG representative Gregory Wedin, PharmD, pharmacovigilance and risk management director for Upsher-Smith Laboratories, said, “while we cannot support eliminating or extending the confirmation interval to a year, the [iPLEDGE] sponsors are agreeable [to] a 120-day confirmation interval.”
He said that while extending to 120 days would reduce burden on prescribers, it comes with risk in reducing oversight by a certified iPLEDGE prescriber and potentially increasing the risk for drug sharing.
“A patient may be more likely to share their drug with another person the further along with therapy they get as their condition improves,” Mr. Wedin said.
On March 29, the panel will hear more recommendations for and against modifications to iPLEDGE REMS and will vote on select modifications at the end of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
for patients, pharmacies, and prescribers.
Isotretinoin, previously called Accutane, is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
In a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee, experts addressed ways to improve the modified iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (iPLEDGE REMS) for isotretinoin that caused chaos after its rollout at the end of 2021.
In January 2022, problems were multiplying with the program for clinicians, pharmacists, and patients, causing extensive delays and prescription denials. In response, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve problems.
March 28 was the first day of a 2-day meeting addressing what can be done to reduce burden with the iPLEDGE REMS while maintaining safety and preventing fetal exposure to the drug.
Key areas of concern
The meeting focused on several key areas.
The 19-day lockout period
The lockout is a current restriction for patients who can become pregnant and do not pick up their first prescription of isotretinoin within the specified 7-day prescription window. Currently, those who miss the window must wait 19 days from the date of the first pregnancy test to take an additional pregnancy test to be eligible to receive the drug.
Lindsey Crist, PharmD, a risk management analyst for the FDA, who presented the FDA review committee’s analysis, acknowledged that the lockout period causes delays in treatment and adds frustration and costs.
She said it’s important to remember that the lockout applies only to the first prescription. “It’s intended as an additional layer of screening to detect pregnancy,” she said.
“At least 12 pregnancies have been identified during the 19-day lockout from March 2017–September of 2022,” she noted.
The FDA is looking to the advisory committee to provide recommendations on whether the lockout period should be changed.
Home testing
During the pandemic, iPLEDGE rules have been relaxed from having a pregnancy test done only at a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified laboratory and home pregnancy tests have been allowed. The question now is whether home tests should continue to be allowed.
Ms. Crist said that the FDA’s review committee recommends ending the allowance of home tests, citing insufficient data on use and the discovery of instances of falsification of pregnancy tests.
“One study at an academic medical center reviewed the medical records of 89 patients who used home pregnancy tests while taking isotretinoin during the public health emergency. It found that 15.7% submitted falsified pregnancy test results,” she said.
Ms. Crist added, however, that the review committee recommends allowing the tests to be done in a provider’s office as an alternative.
Documenting counseling patients who cannot get pregnant
Currently, this documentation must be done monthly, primarily to counsel patients against drug sharing or giving blood. Proposed changes include extending the intervals for attestation or eliminating it to reduce burden on clinicians.
IPMG representative Gregory Wedin, PharmD, pharmacovigilance and risk management director for Upsher-Smith Laboratories, said, “while we cannot support eliminating or extending the confirmation interval to a year, the [iPLEDGE] sponsors are agreeable [to] a 120-day confirmation interval.”
He said that while extending to 120 days would reduce burden on prescribers, it comes with risk in reducing oversight by a certified iPLEDGE prescriber and potentially increasing the risk for drug sharing.
“A patient may be more likely to share their drug with another person the further along with therapy they get as their condition improves,” Mr. Wedin said.
On March 29, the panel will hear more recommendations for and against modifications to iPLEDGE REMS and will vote on select modifications at the end of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
for patients, pharmacies, and prescribers.
Isotretinoin, previously called Accutane, is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
In a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee, experts addressed ways to improve the modified iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (iPLEDGE REMS) for isotretinoin that caused chaos after its rollout at the end of 2021.
In January 2022, problems were multiplying with the program for clinicians, pharmacists, and patients, causing extensive delays and prescription denials. In response, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve problems.
March 28 was the first day of a 2-day meeting addressing what can be done to reduce burden with the iPLEDGE REMS while maintaining safety and preventing fetal exposure to the drug.
Key areas of concern
The meeting focused on several key areas.
The 19-day lockout period
The lockout is a current restriction for patients who can become pregnant and do not pick up their first prescription of isotretinoin within the specified 7-day prescription window. Currently, those who miss the window must wait 19 days from the date of the first pregnancy test to take an additional pregnancy test to be eligible to receive the drug.
Lindsey Crist, PharmD, a risk management analyst for the FDA, who presented the FDA review committee’s analysis, acknowledged that the lockout period causes delays in treatment and adds frustration and costs.
She said it’s important to remember that the lockout applies only to the first prescription. “It’s intended as an additional layer of screening to detect pregnancy,” she said.
“At least 12 pregnancies have been identified during the 19-day lockout from March 2017–September of 2022,” she noted.
The FDA is looking to the advisory committee to provide recommendations on whether the lockout period should be changed.
Home testing
During the pandemic, iPLEDGE rules have been relaxed from having a pregnancy test done only at a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified laboratory and home pregnancy tests have been allowed. The question now is whether home tests should continue to be allowed.
Ms. Crist said that the FDA’s review committee recommends ending the allowance of home tests, citing insufficient data on use and the discovery of instances of falsification of pregnancy tests.
“One study at an academic medical center reviewed the medical records of 89 patients who used home pregnancy tests while taking isotretinoin during the public health emergency. It found that 15.7% submitted falsified pregnancy test results,” she said.
Ms. Crist added, however, that the review committee recommends allowing the tests to be done in a provider’s office as an alternative.
Documenting counseling patients who cannot get pregnant
Currently, this documentation must be done monthly, primarily to counsel patients against drug sharing or giving blood. Proposed changes include extending the intervals for attestation or eliminating it to reduce burden on clinicians.
IPMG representative Gregory Wedin, PharmD, pharmacovigilance and risk management director for Upsher-Smith Laboratories, said, “while we cannot support eliminating or extending the confirmation interval to a year, the [iPLEDGE] sponsors are agreeable [to] a 120-day confirmation interval.”
He said that while extending to 120 days would reduce burden on prescribers, it comes with risk in reducing oversight by a certified iPLEDGE prescriber and potentially increasing the risk for drug sharing.
“A patient may be more likely to share their drug with another person the further along with therapy they get as their condition improves,” Mr. Wedin said.
On March 29, the panel will hear more recommendations for and against modifications to iPLEDGE REMS and will vote on select modifications at the end of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
JAK inhibitor ivarmacitinib shows efficacy for atopic dermatitis in a pivotal trial
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – The presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Two doses were studied in the placebo-controlled trial and both demonstrated “a favorable benefit-to-risk profile in patients with moderate to severe AD,” reported Yan Zhao, MD, a clinician and researcher in the department of dermatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing.
In the study, called QUARTZ3, 336 patients aged 12 and older at 51 sites in China and Canada were randomized to 4 mg once-daily ivarmacitinib, 8 mg once-daily QD ivarmacitinib, or placebo. The mean age of the population was 32 years and approximately one-third were female.
The mean duration of AD for participants was 10 years. The mean baseline Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was near 30. On the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) tool, approximately 40% had a score of 4, which is the highest score on the scale and indicates severe disease. The remaining patients had an IGA score of 3.
The co-primary endpoints were change in IGA and EASI scores at 16 weeks, and both improved rapidly, showing statistical significance relative to placebo by 4 weeks with no plateauing effect at the end of the 16-week trial. By week 16, the proportion of patients with an EASI score of 75, signifying a 75% improvement, was 66%, 54%, and 22% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups (P < .001 versus placebo for both doses of active therapy), respectively.
The pattern of the IGA response was similar. By week 16, the proportion of patients achieving an IGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) was 42%, 36%, and 9% for the 8-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, 4-mg dose of ivarmacitinib, and placebo groups, respectively. The advantage of either dose over placebo was highly significant (P < .001) at 8, 12, and 16 weeks.
For the WI-NRS (Worst Itch – Numeric Rating Scale), the advantage of the 8-mg dose relative to placebo was significant (P < .001) at the 1-week evaluation. By 2 weeks, the 4-mg dose had gained the same degree of statistical significance relative to placebo. After week 4, when the maximum proportion of patients with a WI-NRS score ≤ 4 was reached (50%, 35%, and 10% in the 8-mg, 4-mg, and placebo groups), and the relative advantage of active treatment persisted until the end of the 16-week study.
Two scales were used to evaluate change in quality of life. On the DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure), improvements were again rapid and sustained. By week 4, improvement with the 8-mg dose was about fourfold greater (P < .001) than improvement with placebo for DLQI and about sixfold greater (P < .001) for POEM. For the 4-mg dose, the relative differences were approximately threefold and fourfold greater, and both were significant (P <.001).
There was no further gain in these quality-of-life scales from week 4 to week 16, but the advantages relative to placebo were generally sustained, Dr. Zhao reported.
Ivarmacitinib was safe and well-tolerated, according to Dr. Zhao. The proportion of patients with a treatment-emergent adverse event that led to drug discontinuation was numerically higher (5.4%) in the placebo group than in the 8-mg (3.6%) or 4-mg group (2.7%). Rates of infection in the three groups were similar, and there were no major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) or thromboembolism observed in any group.
Ivarmacitinib, which has about a 10-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK2 and a more than 70-fold greater selectivity for JAK1 than JAK3, is being tested for rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and alopecia areata in addition to AD, Dr. Zhao said. She also reported that an application for new drug approval has been submitted in China. Efforts to pursue regulatory approval elsewhere are anticipated.
Currently, there are three JAK inhibitors licensed for the treatment of AD in the United States. Upadacitinib (Rinvoq) and abrocitinib (Cibinqo) are also once-daily oral JAK1-selective inhibitors. Regulatory approval for AD by the Food and Drug Administration was granted to both in early 2022 and both now have an indication for moderate to severe disease in patients ages 12 years and older.
In September 2021, the first U.S. approval of a drug in this class for AD was granted for a topical formulation of ruxolitinib (Opzelura), which has selectivity for both JAK1 and JAK2. The indication is for mild to moderate AD in patients aged 12 years and older.
In the phase 3 clinical trial that led to approval of abrocitinib for AD, the comparator groups included placebo and active treatment with 300 mg dupilumab administered subcutaneously every other week. The higher of two doses of abrocitinib (100 mg) was numerically superior to dupilumab in terms of EASI 75 response at week 12 and was statistically superior for relief of itch at week 2.
Relative to the first-generation JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (Xeljanz), both of the approved oral JAK inhibitors for AD, abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have greater JAK1-selectivity. However, selectivity for all JAK inhibitors is relative rather than absolute, according to a recent review article on oral JAK inhibitors for AD. Efficacy and safety are likely determined by relative inhibition of each of the four JAK enzymes (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2). Although JAK1 appears to be an important target for AD treatment, the clinical significance of the degree of selectivity among oral JAK inhibitors is not yet clear.
In an interview, the senior author of that review article, Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, emphasized this point. She said there is no evidence and no basis on which to speculate that any one drug in this class is better than another for AD. Dr. Guttman-Yassky is a professor and system chair of dermatology and immunology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The efficacy [of ivarmacitinib] seems, in general, to be in line with other JAK inhibitors,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky, who attended the late-breaker session during which these data were presented. Although she acknowledged that rapid control of pruritus is important clinically, she said the speed of itch relief as reported in the phase 3 ivarmacitinib trial does not distinguish it from other oral drugs in the class.
Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, agreed.
“The rapid effects on itch of ivarmacitinib are consistent with those observed by the already approved JAK1-selective inhibitors abrocitinib and upadacitinib,” he said in an interview.
This suggests that head-to-head trials will be needed to draw any conclusions about the relative efficacy and safety of existing and emerging oral JAK inhibitors for AD.
Dr. Zhao has reported a financial relationship with Reistone Biopharma, which is developing ivarmacitinib and provided funding for the trial. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Kwatra has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Aslan, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
COVID-19 potentially induced adult-onset IgA vasculitis
Plasma exchange successfully improved symptoms of immunoglobulin A vasculitis in an adult female patient who developed the condition after infection with COVID-19, according to a case report published in Cureus.
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) vasculitis can affect all ages, but is relatively rare in adults, and the etiology remains unclear, wrote Hassan Alwafi, MD, of Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia, and colleagues.
COVID-19 has been associated with pulmonary and extrapulmonary complications, but , the authors wrote.
The authors described a case of a 41-year-old otherwise healthy Saudi Arabian woman who presented with an ascending rash on both lower extremities, along with arthralgia. Blood tests showed high blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and inflammatory markers, and a negative immune panel. The patient had been infected with COVID-19 approximately 2 weeks before the onset of symptoms, but she was treated with supportive care and required no antiviral therapy of dexamethasone.
In addition, the patient’s urinalysis showed proteinuria and hematuria. After a kidney biopsy revealed additional abnormalities, the patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy.
A few days after the initiation of therapy, the patient experienced nosebleeds and coughing up blood. After a chest x-ray showed bilateral pleural effusion, the patient was transferred to the ICU. The patient was started on intravenous piperacillin-tazobactam, and received two doses of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange after consultation with a nephrologist. Ultimately, the initial rash and other clinical symptoms improved, and the patient was discharged with a tapering schedule of oral prednisolone.
In this case, COVID-19 may have played a role in the development of IgA vasculitis, the authors said.
The authors also listed 21 cases of IgA vasculitis following COVID-19 infection, including 14 children and 7 adults. Of these, three cases had combined kidney and lung involvement, the two pediatric cases died from respiratory failure, while the adult case was successfully treated with steroid monotherapy.
“As COVID-19 is a novel disease and its pathogenic mechanism of causing IgA vasculitis is not well understood, every patient who is infected with or recently recovered from COVID-19 and presents with a skin rash or arthralgia should have baseline blood and urine tests done and should be treated promptly to avoid the emergence of irreversible consequences,” the authors wrote in their discussion.
Although case reports cannot prove a cause-and-effect link, the data from the cases in the current review suggest that COVID-19 infection may be an indirect trigger for IgA vasculitis, including cases associated with pulmonary renal syndrome, they said. However, more research is needed, especially on the efficacy of treatments in adults, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Plasma exchange successfully improved symptoms of immunoglobulin A vasculitis in an adult female patient who developed the condition after infection with COVID-19, according to a case report published in Cureus.
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) vasculitis can affect all ages, but is relatively rare in adults, and the etiology remains unclear, wrote Hassan Alwafi, MD, of Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia, and colleagues.
COVID-19 has been associated with pulmonary and extrapulmonary complications, but , the authors wrote.
The authors described a case of a 41-year-old otherwise healthy Saudi Arabian woman who presented with an ascending rash on both lower extremities, along with arthralgia. Blood tests showed high blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and inflammatory markers, and a negative immune panel. The patient had been infected with COVID-19 approximately 2 weeks before the onset of symptoms, but she was treated with supportive care and required no antiviral therapy of dexamethasone.
In addition, the patient’s urinalysis showed proteinuria and hematuria. After a kidney biopsy revealed additional abnormalities, the patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy.
A few days after the initiation of therapy, the patient experienced nosebleeds and coughing up blood. After a chest x-ray showed bilateral pleural effusion, the patient was transferred to the ICU. The patient was started on intravenous piperacillin-tazobactam, and received two doses of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange after consultation with a nephrologist. Ultimately, the initial rash and other clinical symptoms improved, and the patient was discharged with a tapering schedule of oral prednisolone.
In this case, COVID-19 may have played a role in the development of IgA vasculitis, the authors said.
The authors also listed 21 cases of IgA vasculitis following COVID-19 infection, including 14 children and 7 adults. Of these, three cases had combined kidney and lung involvement, the two pediatric cases died from respiratory failure, while the adult case was successfully treated with steroid monotherapy.
“As COVID-19 is a novel disease and its pathogenic mechanism of causing IgA vasculitis is not well understood, every patient who is infected with or recently recovered from COVID-19 and presents with a skin rash or arthralgia should have baseline blood and urine tests done and should be treated promptly to avoid the emergence of irreversible consequences,” the authors wrote in their discussion.
Although case reports cannot prove a cause-and-effect link, the data from the cases in the current review suggest that COVID-19 infection may be an indirect trigger for IgA vasculitis, including cases associated with pulmonary renal syndrome, they said. However, more research is needed, especially on the efficacy of treatments in adults, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Plasma exchange successfully improved symptoms of immunoglobulin A vasculitis in an adult female patient who developed the condition after infection with COVID-19, according to a case report published in Cureus.
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) vasculitis can affect all ages, but is relatively rare in adults, and the etiology remains unclear, wrote Hassan Alwafi, MD, of Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, Saudi Arabia, and colleagues.
COVID-19 has been associated with pulmonary and extrapulmonary complications, but , the authors wrote.
The authors described a case of a 41-year-old otherwise healthy Saudi Arabian woman who presented with an ascending rash on both lower extremities, along with arthralgia. Blood tests showed high blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and inflammatory markers, and a negative immune panel. The patient had been infected with COVID-19 approximately 2 weeks before the onset of symptoms, but she was treated with supportive care and required no antiviral therapy of dexamethasone.
In addition, the patient’s urinalysis showed proteinuria and hematuria. After a kidney biopsy revealed additional abnormalities, the patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy.
A few days after the initiation of therapy, the patient experienced nosebleeds and coughing up blood. After a chest x-ray showed bilateral pleural effusion, the patient was transferred to the ICU. The patient was started on intravenous piperacillin-tazobactam, and received two doses of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange after consultation with a nephrologist. Ultimately, the initial rash and other clinical symptoms improved, and the patient was discharged with a tapering schedule of oral prednisolone.
In this case, COVID-19 may have played a role in the development of IgA vasculitis, the authors said.
The authors also listed 21 cases of IgA vasculitis following COVID-19 infection, including 14 children and 7 adults. Of these, three cases had combined kidney and lung involvement, the two pediatric cases died from respiratory failure, while the adult case was successfully treated with steroid monotherapy.
“As COVID-19 is a novel disease and its pathogenic mechanism of causing IgA vasculitis is not well understood, every patient who is infected with or recently recovered from COVID-19 and presents with a skin rash or arthralgia should have baseline blood and urine tests done and should be treated promptly to avoid the emergence of irreversible consequences,” the authors wrote in their discussion.
Although case reports cannot prove a cause-and-effect link, the data from the cases in the current review suggest that COVID-19 infection may be an indirect trigger for IgA vasculitis, including cases associated with pulmonary renal syndrome, they said. However, more research is needed, especially on the efficacy of treatments in adults, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CUREUS
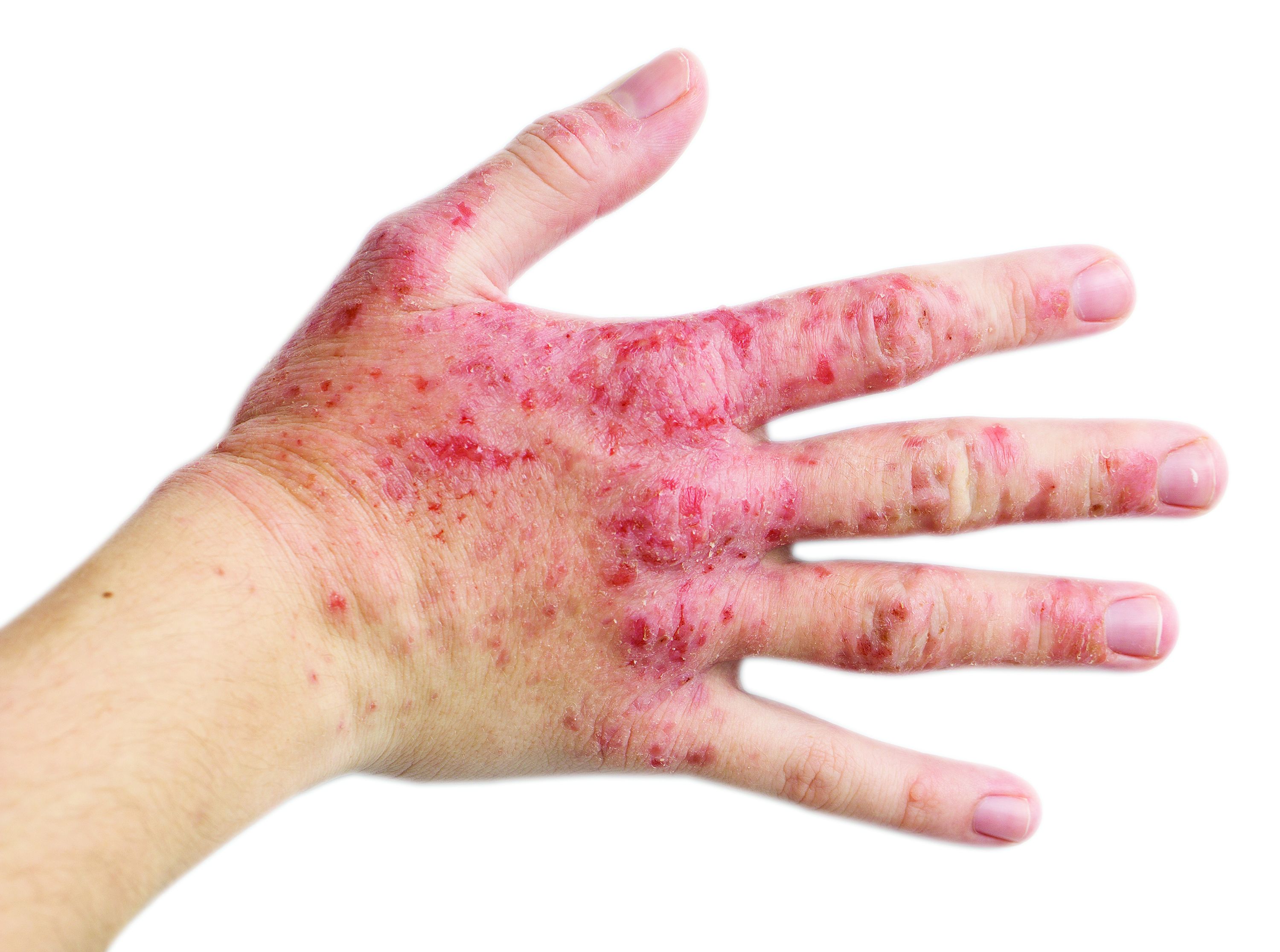
Topical delgocitinib shows promise for chronic hand eczema, pivotal trial shows
NEW ORLEANS – , compared with those who received vehicle cream, results from a pivotal phase 3 trial showed.
“Chronic hand eczema is the most frequent chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the hands,” Robert Bissonnette, MD, a dermatologist who is founder and CEO of Innovaderm Research, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during a late-breaking research session. “It’s associated with pain, pruritus, and has a huge impact on quality of life,” and results with current topical treatments are often unsatisfactory, he noted.
Delgocitinib is an investigational topical pan-JAK inhibitor that inhibits activation of the JAK-STAT pathway and targets key mediators of chronic hand eczema. In a phase 2b dose-ranging trial, twice-daily treatment with delgocitinib cream demonstrated significantly greater efficacy, compared with the cream vehicle, and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe chronic hand eczema.
For the phase 3 study, known as DELTA 1, researchers randomized 487 adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema to receive twice-daily applications of delgocitinib cream 20 mg/g or cream vehicle for 16 weeks. After week 16, patients had the option to enter a long-term extension trial, which is currently ongoing. DELTA 1 was limited to adults with a diagnosis of chronic hand eczema defined as hand eczema that had persisted for more than 3 months or had returned more than twice within the past 12 months; an Investigator’s Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema (IGA-CHE) score of 3 (moderate) or 4 (severe); a weekly average Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch score of 4 or more points, and a medical history of inadequate response to topical corticosteroids within the past 12 months or for whom treatment with topical corticosteroids was not medically advisable.
The IGA-CHE scale used in the trial was new, “where, in order to be almost clear, the only sign that could be present on the skin was barely perceptible erythema,” Dr. Bissonnette said. He noted that he has used many IGA scales over the more than 25 years he has been involved with clinical trials, and “this was the first that used a scale with a bar so high.” Key secondary endpoints include a 75% and 90% improvement in Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI) from baseline at week 16 and a 4-point or greater improvement in the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) from baseline at week 16.
The median age of patients was 44 years, 88% were White, 4% were Asian, 1% were Black, and the remainder were from other racial groups. One-third of patients (33%) had severe hand eczema based on their IGA-CHE score, the median HECSI was 65 (in line with severe disease), and the median DLQI was 12. As for previous chronic hand eczema treatments, 19% had undergone phototherapy, 14% had tried oral retinoids, and 12% had tried oral corticosteroids.
In the study, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients achieved the primary endpoint of IGA-CHE 0/1, compared with the cream vehicle group at week 4 (15.4% vs. 4.9%; P < .001); week 8 (22.8% vs. 10.5%; P = .001), and week 16 (19.7% vs. 9.9%; P = .006). “As early as week 2, there is a separation between cream and vehicle,” Dr. Bissonnette said. When reviewing the results and the patients in the trial, he said that, in his personal opinion, “I don’t think this is uniquely representative of the efficacy of the drug,” because of the IGA scale that was used, which set such a high bar for efficacy.
As for secondary endpoints, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients than those in the vehicle group achieved a HESCI-75 (49.2% vs. 23.5%), a HECSI-90 (29.5% vs. 12.3%), and a 4-point or greater improvement on the DLQI (74.4% vs 50%; P < .001 for all endpoints).
Delgocitinib had a similar safety profile as the vehicle over 16 weeks, with no difference between the delgocitinib and vehicle arms in the proportion of patients who had adverse events (45.2% vs. 50.6%, respectively) and serious adverse events (1.8% vs. 1.9%). The most common adverse events (defined as 5% or greater in any treatment group) during the study were COVID-19 infections and nasopharyngitis; rates were comparable in the two arms.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist who directs the Center for Eczema and Itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that chronic hand eczema can be functionally limiting for many patients. “Given its focal symptoms but multifaceted immunopathogenesis, topical JAK inhibition represents a rational strategy for targeted treatment,” Dr. Chovatiya told this news organization. He was not an investigator in the trial.
“In the phase 3 DELTA 1 study, topical delgocitinib cream was superior to vehicle control with nearly one out of five patients achieving clear or almost clear skin, with no difference in total adverse events between groups. While both comparative and long-term data would be helpful to better assess how delgocitinib cream stacks up against common topical anti-inflammatories and how it may be used for a chronic condition that typically requires ongoing treatment, these findings move us closer to a potential first-in-class approved therapy for chronic hand eczema.”
Dr. Bissonnette disclosed that he served as a consultant and investigator for the developer of delgocitinib, LEO Pharma, on this study. He has also received grants and research funding from many other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
NEW ORLEANS – , compared with those who received vehicle cream, results from a pivotal phase 3 trial showed.
“Chronic hand eczema is the most frequent chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the hands,” Robert Bissonnette, MD, a dermatologist who is founder and CEO of Innovaderm Research, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during a late-breaking research session. “It’s associated with pain, pruritus, and has a huge impact on quality of life,” and results with current topical treatments are often unsatisfactory, he noted.
Delgocitinib is an investigational topical pan-JAK inhibitor that inhibits activation of the JAK-STAT pathway and targets key mediators of chronic hand eczema. In a phase 2b dose-ranging trial, twice-daily treatment with delgocitinib cream demonstrated significantly greater efficacy, compared with the cream vehicle, and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe chronic hand eczema.
For the phase 3 study, known as DELTA 1, researchers randomized 487 adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema to receive twice-daily applications of delgocitinib cream 20 mg/g or cream vehicle for 16 weeks. After week 16, patients had the option to enter a long-term extension trial, which is currently ongoing. DELTA 1 was limited to adults with a diagnosis of chronic hand eczema defined as hand eczema that had persisted for more than 3 months or had returned more than twice within the past 12 months; an Investigator’s Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema (IGA-CHE) score of 3 (moderate) or 4 (severe); a weekly average Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch score of 4 or more points, and a medical history of inadequate response to topical corticosteroids within the past 12 months or for whom treatment with topical corticosteroids was not medically advisable.
The IGA-CHE scale used in the trial was new, “where, in order to be almost clear, the only sign that could be present on the skin was barely perceptible erythema,” Dr. Bissonnette said. He noted that he has used many IGA scales over the more than 25 years he has been involved with clinical trials, and “this was the first that used a scale with a bar so high.” Key secondary endpoints include a 75% and 90% improvement in Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI) from baseline at week 16 and a 4-point or greater improvement in the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) from baseline at week 16.
The median age of patients was 44 years, 88% were White, 4% were Asian, 1% were Black, and the remainder were from other racial groups. One-third of patients (33%) had severe hand eczema based on their IGA-CHE score, the median HECSI was 65 (in line with severe disease), and the median DLQI was 12. As for previous chronic hand eczema treatments, 19% had undergone phototherapy, 14% had tried oral retinoids, and 12% had tried oral corticosteroids.
In the study, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients achieved the primary endpoint of IGA-CHE 0/1, compared with the cream vehicle group at week 4 (15.4% vs. 4.9%; P < .001); week 8 (22.8% vs. 10.5%; P = .001), and week 16 (19.7% vs. 9.9%; P = .006). “As early as week 2, there is a separation between cream and vehicle,” Dr. Bissonnette said. When reviewing the results and the patients in the trial, he said that, in his personal opinion, “I don’t think this is uniquely representative of the efficacy of the drug,” because of the IGA scale that was used, which set such a high bar for efficacy.
As for secondary endpoints, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients than those in the vehicle group achieved a HESCI-75 (49.2% vs. 23.5%), a HECSI-90 (29.5% vs. 12.3%), and a 4-point or greater improvement on the DLQI (74.4% vs 50%; P < .001 for all endpoints).
Delgocitinib had a similar safety profile as the vehicle over 16 weeks, with no difference between the delgocitinib and vehicle arms in the proportion of patients who had adverse events (45.2% vs. 50.6%, respectively) and serious adverse events (1.8% vs. 1.9%). The most common adverse events (defined as 5% or greater in any treatment group) during the study were COVID-19 infections and nasopharyngitis; rates were comparable in the two arms.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist who directs the Center for Eczema and Itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that chronic hand eczema can be functionally limiting for many patients. “Given its focal symptoms but multifaceted immunopathogenesis, topical JAK inhibition represents a rational strategy for targeted treatment,” Dr. Chovatiya told this news organization. He was not an investigator in the trial.
“In the phase 3 DELTA 1 study, topical delgocitinib cream was superior to vehicle control with nearly one out of five patients achieving clear or almost clear skin, with no difference in total adverse events between groups. While both comparative and long-term data would be helpful to better assess how delgocitinib cream stacks up against common topical anti-inflammatories and how it may be used for a chronic condition that typically requires ongoing treatment, these findings move us closer to a potential first-in-class approved therapy for chronic hand eczema.”
Dr. Bissonnette disclosed that he served as a consultant and investigator for the developer of delgocitinib, LEO Pharma, on this study. He has also received grants and research funding from many other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
NEW ORLEANS – , compared with those who received vehicle cream, results from a pivotal phase 3 trial showed.
“Chronic hand eczema is the most frequent chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the hands,” Robert Bissonnette, MD, a dermatologist who is founder and CEO of Innovaderm Research, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during a late-breaking research session. “It’s associated with pain, pruritus, and has a huge impact on quality of life,” and results with current topical treatments are often unsatisfactory, he noted.
Delgocitinib is an investigational topical pan-JAK inhibitor that inhibits activation of the JAK-STAT pathway and targets key mediators of chronic hand eczema. In a phase 2b dose-ranging trial, twice-daily treatment with delgocitinib cream demonstrated significantly greater efficacy, compared with the cream vehicle, and was well tolerated in adults with mild to severe chronic hand eczema.
For the phase 3 study, known as DELTA 1, researchers randomized 487 adults with moderate to severe chronic hand eczema to receive twice-daily applications of delgocitinib cream 20 mg/g or cream vehicle for 16 weeks. After week 16, patients had the option to enter a long-term extension trial, which is currently ongoing. DELTA 1 was limited to adults with a diagnosis of chronic hand eczema defined as hand eczema that had persisted for more than 3 months or had returned more than twice within the past 12 months; an Investigator’s Global Assessment for chronic hand eczema (IGA-CHE) score of 3 (moderate) or 4 (severe); a weekly average Hand Eczema Symptom Diary (HESD) itch score of 4 or more points, and a medical history of inadequate response to topical corticosteroids within the past 12 months or for whom treatment with topical corticosteroids was not medically advisable.
The IGA-CHE scale used in the trial was new, “where, in order to be almost clear, the only sign that could be present on the skin was barely perceptible erythema,” Dr. Bissonnette said. He noted that he has used many IGA scales over the more than 25 years he has been involved with clinical trials, and “this was the first that used a scale with a bar so high.” Key secondary endpoints include a 75% and 90% improvement in Hand Eczema Severity Index (HECSI) from baseline at week 16 and a 4-point or greater improvement in the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) from baseline at week 16.
The median age of patients was 44 years, 88% were White, 4% were Asian, 1% were Black, and the remainder were from other racial groups. One-third of patients (33%) had severe hand eczema based on their IGA-CHE score, the median HECSI was 65 (in line with severe disease), and the median DLQI was 12. As for previous chronic hand eczema treatments, 19% had undergone phototherapy, 14% had tried oral retinoids, and 12% had tried oral corticosteroids.
In the study, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients achieved the primary endpoint of IGA-CHE 0/1, compared with the cream vehicle group at week 4 (15.4% vs. 4.9%; P < .001); week 8 (22.8% vs. 10.5%; P = .001), and week 16 (19.7% vs. 9.9%; P = .006). “As early as week 2, there is a separation between cream and vehicle,” Dr. Bissonnette said. When reviewing the results and the patients in the trial, he said that, in his personal opinion, “I don’t think this is uniquely representative of the efficacy of the drug,” because of the IGA scale that was used, which set such a high bar for efficacy.
As for secondary endpoints, a greater proportion of delgocitinib-treated patients than those in the vehicle group achieved a HESCI-75 (49.2% vs. 23.5%), a HECSI-90 (29.5% vs. 12.3%), and a 4-point or greater improvement on the DLQI (74.4% vs 50%; P < .001 for all endpoints).
Delgocitinib had a similar safety profile as the vehicle over 16 weeks, with no difference between the delgocitinib and vehicle arms in the proportion of patients who had adverse events (45.2% vs. 50.6%, respectively) and serious adverse events (1.8% vs. 1.9%). The most common adverse events (defined as 5% or greater in any treatment group) during the study were COVID-19 infections and nasopharyngitis; rates were comparable in the two arms.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, a dermatologist who directs the Center for Eczema and Itch at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was asked to comment on the study, said that chronic hand eczema can be functionally limiting for many patients. “Given its focal symptoms but multifaceted immunopathogenesis, topical JAK inhibition represents a rational strategy for targeted treatment,” Dr. Chovatiya told this news organization. He was not an investigator in the trial.
“In the phase 3 DELTA 1 study, topical delgocitinib cream was superior to vehicle control with nearly one out of five patients achieving clear or almost clear skin, with no difference in total adverse events between groups. While both comparative and long-term data would be helpful to better assess how delgocitinib cream stacks up against common topical anti-inflammatories and how it may be used for a chronic condition that typically requires ongoing treatment, these findings move us closer to a potential first-in-class approved therapy for chronic hand eczema.”
Dr. Bissonnette disclosed that he served as a consultant and investigator for the developer of delgocitinib, LEO Pharma, on this study. He has also received grants and research funding from many other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed that he is a consultant to, a speaker for, and/or a member of the advisory board for several pharmaceutical companies, including LEO Pharma.
AT AAD 2023
Luxe vacations, private jets: Medical device maker, surgeon to pay $46 million penalty in kickback scheme
according to experts familiar with the federal Anti-Kickback Statute.
Historically, enforcement actions have primarily focused on the person or organization offering the perks – and not necessarily the physicians accepting it, Steven W. Ortquist, founder and principal of Arete Compliance Solutions, LLC, in Phoenix, told this news organization.
But that’s changing.
“In recent years, we are seeing a trend toward holding physicians and others on the receiving end of the inducement accountable as well,” said Mr. Ortquist, who is a past board member and president of the Health Care Compliance Association. He noted that authorities usually pursue the inducing company first before moving on to individual clinicians or practices.
The Department of Justice followed a similar pattern in a recently announced kickback settlement that ensnared an intraocular lens distributor, an ophthalmology equipment supplier, two CEOs, and a surgeon. Precision Lens must pay more than $43 million for offering high-end vacations and other expensive perks to surgeons who used its cataract products.
The verdict marks the end of a 6-week civil jury trial, where evidence emerged that Paul Ehlen, owner of Precision Lens and its parent company, Cameron-Ehlen Group, maintained a secret “slush fund” for paying kickbacks to ophthalmic surgeons. The inducement scheme netted the Minnesota-based company millions in sales and led to the submission of 64,575 false Medicare claims from 2006 to 2015, a violation of the Anti-Kickback Statute and the False Claims Act.
According to court documents, physicians received luxury travel and entertainment packages, including skiing, fishing, and golfing excursions at exclusive destinations, often traveling via private jet to attend Broadway musicals and major sporting events. Mr. Ehlen and company representatives also sold frequent flyer miles to physicians at a steep discount, allowing them to take personal and business trips below fair market value.
Federal authorities initially announced an investigation into the business practices of Precision Lens in 2017 after receiving a whistleblower complaint from Kipp Fesenmaier, a former executive at Sightpath Medical, an ophthalmology supplier and “corporate partner” of Precision Lens. Mr. Fesenmaier alleged that both companies were involved in an inducement scheme.
Sightpath Medical and its CEO, James Tiffany, agreed to a $12 million settlement to resolve the kickback allegations.
The Department of Justice subsequently investigated Jitendra Swarup, MD, an ophthalmologist and cataract surgeon who allegedly received “unlawful remuneration from Sightpath, Precision, and Ehlen” and filed false insurance claims. In addition to accepting expensive hunting and fishing trips from the medical device companies, Dr. Swarup was paid more than $100,000 per year for consulting services he did not fully render.
Dr. Swarup agreed to a nearly $3 million settlement and participation in a 3-year corporate integrity agreement with the Office of Inspector General. In exchange for compliance with such contracts, the OIG permits physicians to continue participating in Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal health care programs.
In a statement from attorneys, Precision Lens and Mr. Ehlen pledged to appeal the verdict and “defend ... our wholly appropriate actions” while remaining focused on their commitment to health care clinicians and manufacturers.
‘Endless’ opportunities for inducement
Unfortunately, opportunities for inducement are “endless,” experts say. Extravagant trips, dinners, and gifts can trigger a violation, but so can nearly anything of value.
Just last year, Biotronik reached a $12.95 million settlement amid allegations that company representatives wined and dined physicians to induce their use of its pacemakers and defibrillators. To date, no physicians have been charged.
But after a record-breaking number of whistleblower judgments last fiscal year totaling more than $2 billion, physicians should take note, Radha Bhatnagar, Esq, director of compliance at The CM Group, told the news organization.
“When manufacturers offer physicians kickbacks with the added element of fraudulent Medicare or Medicaid reimbursements, that is typically when manufacturers and individuals face civil and criminal liability,” said Ms. Bhatnagar, something the Department of Justice alluded to when announcing a settlement involving 15 Texas physicians last year.
In another case, Kingsley R. Chin, an orthopedic surgeon and designer of a spinal implant, was indicted in 2021 for paying millions of dollars in sham consulting fees to physicians who used his products. At least six surgeons who accepted money from Dr. Chin were later named in a civil case and ordered to pay $3.3 million in penalties.
Jason Montone, DO, an orthopedic surgeon who accepted the illicit payments, agreed to a plea deal with a reduced prison sentence, 1 year of supervised release, and a fine of $379,000.
Although Dr. Chin’s sentencing hasn’t been announced, violating kickback laws can result in a sentence of up to 10 years.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to experts familiar with the federal Anti-Kickback Statute.
Historically, enforcement actions have primarily focused on the person or organization offering the perks – and not necessarily the physicians accepting it, Steven W. Ortquist, founder and principal of Arete Compliance Solutions, LLC, in Phoenix, told this news organization.
But that’s changing.
“In recent years, we are seeing a trend toward holding physicians and others on the receiving end of the inducement accountable as well,” said Mr. Ortquist, who is a past board member and president of the Health Care Compliance Association. He noted that authorities usually pursue the inducing company first before moving on to individual clinicians or practices.
The Department of Justice followed a similar pattern in a recently announced kickback settlement that ensnared an intraocular lens distributor, an ophthalmology equipment supplier, two CEOs, and a surgeon. Precision Lens must pay more than $43 million for offering high-end vacations and other expensive perks to surgeons who used its cataract products.
The verdict marks the end of a 6-week civil jury trial, where evidence emerged that Paul Ehlen, owner of Precision Lens and its parent company, Cameron-Ehlen Group, maintained a secret “slush fund” for paying kickbacks to ophthalmic surgeons. The inducement scheme netted the Minnesota-based company millions in sales and led to the submission of 64,575 false Medicare claims from 2006 to 2015, a violation of the Anti-Kickback Statute and the False Claims Act.
According to court documents, physicians received luxury travel and entertainment packages, including skiing, fishing, and golfing excursions at exclusive destinations, often traveling via private jet to attend Broadway musicals and major sporting events. Mr. Ehlen and company representatives also sold frequent flyer miles to physicians at a steep discount, allowing them to take personal and business trips below fair market value.
Federal authorities initially announced an investigation into the business practices of Precision Lens in 2017 after receiving a whistleblower complaint from Kipp Fesenmaier, a former executive at Sightpath Medical, an ophthalmology supplier and “corporate partner” of Precision Lens. Mr. Fesenmaier alleged that both companies were involved in an inducement scheme.
Sightpath Medical and its CEO, James Tiffany, agreed to a $12 million settlement to resolve the kickback allegations.
The Department of Justice subsequently investigated Jitendra Swarup, MD, an ophthalmologist and cataract surgeon who allegedly received “unlawful remuneration from Sightpath, Precision, and Ehlen” and filed false insurance claims. In addition to accepting expensive hunting and fishing trips from the medical device companies, Dr. Swarup was paid more than $100,000 per year for consulting services he did not fully render.
Dr. Swarup agreed to a nearly $3 million settlement and participation in a 3-year corporate integrity agreement with the Office of Inspector General. In exchange for compliance with such contracts, the OIG permits physicians to continue participating in Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal health care programs.
In a statement from attorneys, Precision Lens and Mr. Ehlen pledged to appeal the verdict and “defend ... our wholly appropriate actions” while remaining focused on their commitment to health care clinicians and manufacturers.
‘Endless’ opportunities for inducement
Unfortunately, opportunities for inducement are “endless,” experts say. Extravagant trips, dinners, and gifts can trigger a violation, but so can nearly anything of value.
Just last year, Biotronik reached a $12.95 million settlement amid allegations that company representatives wined and dined physicians to induce their use of its pacemakers and defibrillators. To date, no physicians have been charged.
But after a record-breaking number of whistleblower judgments last fiscal year totaling more than $2 billion, physicians should take note, Radha Bhatnagar, Esq, director of compliance at The CM Group, told the news organization.
“When manufacturers offer physicians kickbacks with the added element of fraudulent Medicare or Medicaid reimbursements, that is typically when manufacturers and individuals face civil and criminal liability,” said Ms. Bhatnagar, something the Department of Justice alluded to when announcing a settlement involving 15 Texas physicians last year.
In another case, Kingsley R. Chin, an orthopedic surgeon and designer of a spinal implant, was indicted in 2021 for paying millions of dollars in sham consulting fees to physicians who used his products. At least six surgeons who accepted money from Dr. Chin were later named in a civil case and ordered to pay $3.3 million in penalties.
Jason Montone, DO, an orthopedic surgeon who accepted the illicit payments, agreed to a plea deal with a reduced prison sentence, 1 year of supervised release, and a fine of $379,000.
Although Dr. Chin’s sentencing hasn’t been announced, violating kickback laws can result in a sentence of up to 10 years.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to experts familiar with the federal Anti-Kickback Statute.
Historically, enforcement actions have primarily focused on the person or organization offering the perks – and not necessarily the physicians accepting it, Steven W. Ortquist, founder and principal of Arete Compliance Solutions, LLC, in Phoenix, told this news organization.
But that’s changing.
“In recent years, we are seeing a trend toward holding physicians and others on the receiving end of the inducement accountable as well,” said Mr. Ortquist, who is a past board member and president of the Health Care Compliance Association. He noted that authorities usually pursue the inducing company first before moving on to individual clinicians or practices.
The Department of Justice followed a similar pattern in a recently announced kickback settlement that ensnared an intraocular lens distributor, an ophthalmology equipment supplier, two CEOs, and a surgeon. Precision Lens must pay more than $43 million for offering high-end vacations and other expensive perks to surgeons who used its cataract products.
The verdict marks the end of a 6-week civil jury trial, where evidence emerged that Paul Ehlen, owner of Precision Lens and its parent company, Cameron-Ehlen Group, maintained a secret “slush fund” for paying kickbacks to ophthalmic surgeons. The inducement scheme netted the Minnesota-based company millions in sales and led to the submission of 64,575 false Medicare claims from 2006 to 2015, a violation of the Anti-Kickback Statute and the False Claims Act.
According to court documents, physicians received luxury travel and entertainment packages, including skiing, fishing, and golfing excursions at exclusive destinations, often traveling via private jet to attend Broadway musicals and major sporting events. Mr. Ehlen and company representatives also sold frequent flyer miles to physicians at a steep discount, allowing them to take personal and business trips below fair market value.
Federal authorities initially announced an investigation into the business practices of Precision Lens in 2017 after receiving a whistleblower complaint from Kipp Fesenmaier, a former executive at Sightpath Medical, an ophthalmology supplier and “corporate partner” of Precision Lens. Mr. Fesenmaier alleged that both companies were involved in an inducement scheme.
Sightpath Medical and its CEO, James Tiffany, agreed to a $12 million settlement to resolve the kickback allegations.
The Department of Justice subsequently investigated Jitendra Swarup, MD, an ophthalmologist and cataract surgeon who allegedly received “unlawful remuneration from Sightpath, Precision, and Ehlen” and filed false insurance claims. In addition to accepting expensive hunting and fishing trips from the medical device companies, Dr. Swarup was paid more than $100,000 per year for consulting services he did not fully render.
Dr. Swarup agreed to a nearly $3 million settlement and participation in a 3-year corporate integrity agreement with the Office of Inspector General. In exchange for compliance with such contracts, the OIG permits physicians to continue participating in Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal health care programs.
In a statement from attorneys, Precision Lens and Mr. Ehlen pledged to appeal the verdict and “defend ... our wholly appropriate actions” while remaining focused on their commitment to health care clinicians and manufacturers.
‘Endless’ opportunities for inducement
Unfortunately, opportunities for inducement are “endless,” experts say. Extravagant trips, dinners, and gifts can trigger a violation, but so can nearly anything of value.
Just last year, Biotronik reached a $12.95 million settlement amid allegations that company representatives wined and dined physicians to induce their use of its pacemakers and defibrillators. To date, no physicians have been charged.
But after a record-breaking number of whistleblower judgments last fiscal year totaling more than $2 billion, physicians should take note, Radha Bhatnagar, Esq, director of compliance at The CM Group, told the news organization.
“When manufacturers offer physicians kickbacks with the added element of fraudulent Medicare or Medicaid reimbursements, that is typically when manufacturers and individuals face civil and criminal liability,” said Ms. Bhatnagar, something the Department of Justice alluded to when announcing a settlement involving 15 Texas physicians last year.
In another case, Kingsley R. Chin, an orthopedic surgeon and designer of a spinal implant, was indicted in 2021 for paying millions of dollars in sham consulting fees to physicians who used his products. At least six surgeons who accepted money from Dr. Chin were later named in a civil case and ordered to pay $3.3 million in penalties.
Jason Montone, DO, an orthopedic surgeon who accepted the illicit payments, agreed to a plea deal with a reduced prison sentence, 1 year of supervised release, and a fine of $379,000.
Although Dr. Chin’s sentencing hasn’t been announced, violating kickback laws can result in a sentence of up to 10 years.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Air pollution may be causing eczema
The finding points scientists toward how to better treat the skin ailment. There are now more than three times as many eczema cases as there were in the 1970s, and it now affects as many as 20% of children and 10% of adults.
“I think these authors are spot-on in recognizing that the incidence of allergic conditions is increasing concurrently with how different pollutants are increasing in our environment,” said Denver-based pediatric allergist and immunologist Jessica Hui, MD, according to NBC News. “We’re finally understanding more about why people are getting eczema.”
Some people get eczema because of genetics, but the new research built on the previous understanding of how chemicals called diisocyanates can trigger the eczema symptoms of severe itching, skin redness, and oozing or painful rashes. An experiment on mice showed that exposure to a specific part of diisocyanates, called isocyanates, disrupted oil production that the skin needs to stay healthy.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health “found that when bacteria that live on healthy skin are exposed to isocyanate, they must adapt to survive,” the agency summarized in a news release. “When they adapt, these bacteria shift their metabolism away from making the lipids, or oils, that skin needs to stay healthy. This finding suggests that eczema may be treatable by replacing the modified skin bacteria with healthy bacteria.”
The study was published in the journal Science Advances.
The chemicals also trigger a message to the brain that causes skin inflammation and itching, lead researcher Ian Myles, MD, told NBC News. Dr. Myles is also chief of the Epithelial Research Unit in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Laboratory of Clinical Immunology and Microbiology.
“So much of this is out of our control. I mean, you can’t shut the highways down,” he said of the environmental sources.
Previous research that explored attempting to restore healthy skin bacteria called Roseomonas mucosa to treat eczema symptoms had mixed results. The NIH says it has made the bacteria available “for commercial, nontherapeutic development ... as a potentially beneficial probiotic.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The finding points scientists toward how to better treat the skin ailment. There are now more than three times as many eczema cases as there were in the 1970s, and it now affects as many as 20% of children and 10% of adults.
“I think these authors are spot-on in recognizing that the incidence of allergic conditions is increasing concurrently with how different pollutants are increasing in our environment,” said Denver-based pediatric allergist and immunologist Jessica Hui, MD, according to NBC News. “We’re finally understanding more about why people are getting eczema.”
Some people get eczema because of genetics, but the new research built on the previous understanding of how chemicals called diisocyanates can trigger the eczema symptoms of severe itching, skin redness, and oozing or painful rashes. An experiment on mice showed that exposure to a specific part of diisocyanates, called isocyanates, disrupted oil production that the skin needs to stay healthy.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health “found that when bacteria that live on healthy skin are exposed to isocyanate, they must adapt to survive,” the agency summarized in a news release. “When they adapt, these bacteria shift their metabolism away from making the lipids, or oils, that skin needs to stay healthy. This finding suggests that eczema may be treatable by replacing the modified skin bacteria with healthy bacteria.”
The study was published in the journal Science Advances.
The chemicals also trigger a message to the brain that causes skin inflammation and itching, lead researcher Ian Myles, MD, told NBC News. Dr. Myles is also chief of the Epithelial Research Unit in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Laboratory of Clinical Immunology and Microbiology.
“So much of this is out of our control. I mean, you can’t shut the highways down,” he said of the environmental sources.
Previous research that explored attempting to restore healthy skin bacteria called Roseomonas mucosa to treat eczema symptoms had mixed results. The NIH says it has made the bacteria available “for commercial, nontherapeutic development ... as a potentially beneficial probiotic.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The finding points scientists toward how to better treat the skin ailment. There are now more than three times as many eczema cases as there were in the 1970s, and it now affects as many as 20% of children and 10% of adults.
“I think these authors are spot-on in recognizing that the incidence of allergic conditions is increasing concurrently with how different pollutants are increasing in our environment,” said Denver-based pediatric allergist and immunologist Jessica Hui, MD, according to NBC News. “We’re finally understanding more about why people are getting eczema.”
Some people get eczema because of genetics, but the new research built on the previous understanding of how chemicals called diisocyanates can trigger the eczema symptoms of severe itching, skin redness, and oozing or painful rashes. An experiment on mice showed that exposure to a specific part of diisocyanates, called isocyanates, disrupted oil production that the skin needs to stay healthy.
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health “found that when bacteria that live on healthy skin are exposed to isocyanate, they must adapt to survive,” the agency summarized in a news release. “When they adapt, these bacteria shift their metabolism away from making the lipids, or oils, that skin needs to stay healthy. This finding suggests that eczema may be treatable by replacing the modified skin bacteria with healthy bacteria.”
The study was published in the journal Science Advances.
The chemicals also trigger a message to the brain that causes skin inflammation and itching, lead researcher Ian Myles, MD, told NBC News. Dr. Myles is also chief of the Epithelial Research Unit in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Laboratory of Clinical Immunology and Microbiology.
“So much of this is out of our control. I mean, you can’t shut the highways down,” he said of the environmental sources.
Previous research that explored attempting to restore healthy skin bacteria called Roseomonas mucosa to treat eczema symptoms had mixed results. The NIH says it has made the bacteria available “for commercial, nontherapeutic development ... as a potentially beneficial probiotic.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
FDA approves new formulation of Hyrimoz adalimumab biosimilar
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a citrate-free, 100 mg/mL formulation of the biosimilar adalimumab-adaz (Hyrimoz), according to a statement from manufacturer Sandoz.
Hyrimoz, a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker that is biosimilar to its reference product Humira, was approved by the FDA in 2018 at a concentration of 50 mg/mL for rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis. The high-concentration formula is indicated for these same conditions.
Sandoz said that it intends to launch the citrate-free formulation in the United States on July 1. It will be one of up to nine other adalimumab biosimilars that are expected to launch in July. On January 31, Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) became the first adalimumab biosimilar to launch in the United States.
The current label for Hyrimoz contains a black box warning emphasizing certain risks, notably the increased risk for serious infections, such as tuberculosis or sepsis, and an increased risk of malignancy, particularly lymphomas.
Adverse effects associated with Hyrimoz with an incidence greater than 10% include upper respiratory infections and sinusitis, injection-site reactions, headache, and rash.
The approval for the high-concentration formulation was based on data from a phase 1 pharmacokinetics bridging study that compared Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL and citrate-free Hyrimoz 100 mg/mL.
“This study met all of the primary objectives, demonstrating comparable pharmacokinetics and showing similar safety and immunogenicity of the Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL and Hyrimoz [100 mg/mL],” according to Sandoz, a division of Novartis.
The approval for Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL in 2018 was based on preclinical and clinical research comparing Hyrimoz and Humira. In a phase 3 trial published in the British Journal of Dermatology, which included adults with clinically stable but active moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis, Hyrimoz and Humira showed a similar percentage of patients met the primary endpoint of a 75% reduction or more in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 75) score at 16 weeks, compared with baseline (66.8% and 65%, respectively).
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a citrate-free, 100 mg/mL formulation of the biosimilar adalimumab-adaz (Hyrimoz), according to a statement from manufacturer Sandoz.
Hyrimoz, a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker that is biosimilar to its reference product Humira, was approved by the FDA in 2018 at a concentration of 50 mg/mL for rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis. The high-concentration formula is indicated for these same conditions.
Sandoz said that it intends to launch the citrate-free formulation in the United States on July 1. It will be one of up to nine other adalimumab biosimilars that are expected to launch in July. On January 31, Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) became the first adalimumab biosimilar to launch in the United States.
The current label for Hyrimoz contains a black box warning emphasizing certain risks, notably the increased risk for serious infections, such as tuberculosis or sepsis, and an increased risk of malignancy, particularly lymphomas.
Adverse effects associated with Hyrimoz with an incidence greater than 10% include upper respiratory infections and sinusitis, injection-site reactions, headache, and rash.
The approval for the high-concentration formulation was based on data from a phase 1 pharmacokinetics bridging study that compared Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL and citrate-free Hyrimoz 100 mg/mL.
“This study met all of the primary objectives, demonstrating comparable pharmacokinetics and showing similar safety and immunogenicity of the Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL and Hyrimoz [100 mg/mL],” according to Sandoz, a division of Novartis.
The approval for Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL in 2018 was based on preclinical and clinical research comparing Hyrimoz and Humira. In a phase 3 trial published in the British Journal of Dermatology, which included adults with clinically stable but active moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis, Hyrimoz and Humira showed a similar percentage of patients met the primary endpoint of a 75% reduction or more in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 75) score at 16 weeks, compared with baseline (66.8% and 65%, respectively).
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a citrate-free, 100 mg/mL formulation of the biosimilar adalimumab-adaz (Hyrimoz), according to a statement from manufacturer Sandoz.
Hyrimoz, a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker that is biosimilar to its reference product Humira, was approved by the FDA in 2018 at a concentration of 50 mg/mL for rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis. The high-concentration formula is indicated for these same conditions.
Sandoz said that it intends to launch the citrate-free formulation in the United States on July 1. It will be one of up to nine other adalimumab biosimilars that are expected to launch in July. On January 31, Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) became the first adalimumab biosimilar to launch in the United States.
The current label for Hyrimoz contains a black box warning emphasizing certain risks, notably the increased risk for serious infections, such as tuberculosis or sepsis, and an increased risk of malignancy, particularly lymphomas.
Adverse effects associated with Hyrimoz with an incidence greater than 10% include upper respiratory infections and sinusitis, injection-site reactions, headache, and rash.
The approval for the high-concentration formulation was based on data from a phase 1 pharmacokinetics bridging study that compared Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL and citrate-free Hyrimoz 100 mg/mL.
“This study met all of the primary objectives, demonstrating comparable pharmacokinetics and showing similar safety and immunogenicity of the Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL and Hyrimoz [100 mg/mL],” according to Sandoz, a division of Novartis.
The approval for Hyrimoz 50 mg/mL in 2018 was based on preclinical and clinical research comparing Hyrimoz and Humira. In a phase 3 trial published in the British Journal of Dermatology, which included adults with clinically stable but active moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis, Hyrimoz and Humira showed a similar percentage of patients met the primary endpoint of a 75% reduction or more in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 75) score at 16 weeks, compared with baseline (66.8% and 65%, respectively).
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Anifrolumab shows promise in refractory discoid lupus erythematosus
a small retrospective study reports.
DLE, the most common form of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, can permanently scar and disfigure patients, and traditional treatments such as antimalarials, steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, thalidomide, retinoids, and lenalidomide don’t consistently improve refractory DLE, the authors noted.
“All patients demonstrated significant improvement in symptomatology and disease activity within 2 months of initiating anifrolumab,” lead study author Katharina Shaw, MD, of the department of dermatology of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published in JAMA Dermatology. “These early results highlight the potential for anifrolumab to be a viable therapeutic option for patients with DLE, particularly those with severe or recalcitrant disease.”
The Food and Drug Administration approved anifrolumab (Saphnelo), a human monoclonal antibody targeting type 1 interferon receptor subunit 1, in 2021 for adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus, but it has not been approved for the treatment of DLE.
Dr. Shaw and colleagues queried the medical records from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, to find all cases of DLE based on biopsy, expert opinion, or both from January 2000 to October 2022.
The researchers identified eight female patients who had received anifrolumab for at least 8 weeks. The women were aged between 19 and 75 years (median, 42.5 years), and all had DLE recalcitrant to standard therapies and had been treated with hydroxychloroquine and between 1 and 10 other drugs, most commonly methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF).
The authors looked for improvements in patient-reported symptoms and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index scores, including CLASI A (activity) score 0-70, and CLASI-D (damage) score 0-56.
All patients showed significantly improved symptoms and disease activity within 2 months of their first infusion of the treatment. The mean decrease and mean percentage decrease in CLASI-A scores were 17.1 and 65.1%, respectively. The mean decrease and mean percentage decrease in CLASI-D scores were 0.5 and 2.9%, respectively.
The rapid clinical improvements with anifrolumab, compared with improvements with traditional medications, were striking, the authors wrote. “Given the risk for permanent scarring, dyspigmentation, and alopecia with poorly controlled DLE, the importance of rapidly mitigating disease activity cannot be overemphasized.”
They acknowledged that the results are limited by the study’s small sample size and retrospective design, and they recommend larger related prospective studies.
Asked to comment on the results, Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric rheumatology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said that finding new DLE therapeutics is important because of the huge impact of uncontrolled DLE on patients’ quality of life, body image, and social roles.
Dr. Ardalan noted that he sees DLE in his pediatric patients, “either as an isolated finding or in the context of systemic lupus erythematosus. Anifrolumab is not approved by the FDA to treat DLE or children.
“Randomized controlled trials, including the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 studies of anifrolumab in systemic lupus, have indicated that lupus skin manifestations can improve in patients who receive anifrolumab,” said Dr. Ardalan, who was not involved in the study. “And we know that type I interferons are major drivers of cutaneous disease activity in patients with lupus, so targeting that mechanism with anifrolumab makes biological sense.”
The authors’ use of the validated CLASI classification system to quantify disease activity and damage over time, and their determination of the length of time for the drug to take effect are strengths of the study, he added.
Funding information was not provided. Two authors reported financial relationships with Pfizer, which does not manufacture anifrolumab. Dr. Ardalan reported no conflicts of interest with the study.
a small retrospective study reports.
DLE, the most common form of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, can permanently scar and disfigure patients, and traditional treatments such as antimalarials, steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, thalidomide, retinoids, and lenalidomide don’t consistently improve refractory DLE, the authors noted.
“All patients demonstrated significant improvement in symptomatology and disease activity within 2 months of initiating anifrolumab,” lead study author Katharina Shaw, MD, of the department of dermatology of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published in JAMA Dermatology. “These early results highlight the potential for anifrolumab to be a viable therapeutic option for patients with DLE, particularly those with severe or recalcitrant disease.”
The Food and Drug Administration approved anifrolumab (Saphnelo), a human monoclonal antibody targeting type 1 interferon receptor subunit 1, in 2021 for adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus, but it has not been approved for the treatment of DLE.
Dr. Shaw and colleagues queried the medical records from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, to find all cases of DLE based on biopsy, expert opinion, or both from January 2000 to October 2022.
The researchers identified eight female patients who had received anifrolumab for at least 8 weeks. The women were aged between 19 and 75 years (median, 42.5 years), and all had DLE recalcitrant to standard therapies and had been treated with hydroxychloroquine and between 1 and 10 other drugs, most commonly methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF).
The authors looked for improvements in patient-reported symptoms and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index scores, including CLASI A (activity) score 0-70, and CLASI-D (damage) score 0-56.
All patients showed significantly improved symptoms and disease activity within 2 months of their first infusion of the treatment. The mean decrease and mean percentage decrease in CLASI-A scores were 17.1 and 65.1%, respectively. The mean decrease and mean percentage decrease in CLASI-D scores were 0.5 and 2.9%, respectively.
The rapid clinical improvements with anifrolumab, compared with improvements with traditional medications, were striking, the authors wrote. “Given the risk for permanent scarring, dyspigmentation, and alopecia with poorly controlled DLE, the importance of rapidly mitigating disease activity cannot be overemphasized.”
They acknowledged that the results are limited by the study’s small sample size and retrospective design, and they recommend larger related prospective studies.
Asked to comment on the results, Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric rheumatology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said that finding new DLE therapeutics is important because of the huge impact of uncontrolled DLE on patients’ quality of life, body image, and social roles.
Dr. Ardalan noted that he sees DLE in his pediatric patients, “either as an isolated finding or in the context of systemic lupus erythematosus. Anifrolumab is not approved by the FDA to treat DLE or children.
“Randomized controlled trials, including the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 studies of anifrolumab in systemic lupus, have indicated that lupus skin manifestations can improve in patients who receive anifrolumab,” said Dr. Ardalan, who was not involved in the study. “And we know that type I interferons are major drivers of cutaneous disease activity in patients with lupus, so targeting that mechanism with anifrolumab makes biological sense.”
The authors’ use of the validated CLASI classification system to quantify disease activity and damage over time, and their determination of the length of time for the drug to take effect are strengths of the study, he added.
Funding information was not provided. Two authors reported financial relationships with Pfizer, which does not manufacture anifrolumab. Dr. Ardalan reported no conflicts of interest with the study.
a small retrospective study reports.
DLE, the most common form of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus, can permanently scar and disfigure patients, and traditional treatments such as antimalarials, steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, thalidomide, retinoids, and lenalidomide don’t consistently improve refractory DLE, the authors noted.
“All patients demonstrated significant improvement in symptomatology and disease activity within 2 months of initiating anifrolumab,” lead study author Katharina Shaw, MD, of the department of dermatology of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published in JAMA Dermatology. “These early results highlight the potential for anifrolumab to be a viable therapeutic option for patients with DLE, particularly those with severe or recalcitrant disease.”
The Food and Drug Administration approved anifrolumab (Saphnelo), a human monoclonal antibody targeting type 1 interferon receptor subunit 1, in 2021 for adults with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus, but it has not been approved for the treatment of DLE.
Dr. Shaw and colleagues queried the medical records from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, to find all cases of DLE based on biopsy, expert opinion, or both from January 2000 to October 2022.
The researchers identified eight female patients who had received anifrolumab for at least 8 weeks. The women were aged between 19 and 75 years (median, 42.5 years), and all had DLE recalcitrant to standard therapies and had been treated with hydroxychloroquine and between 1 and 10 other drugs, most commonly methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF).
The authors looked for improvements in patient-reported symptoms and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index scores, including CLASI A (activity) score 0-70, and CLASI-D (damage) score 0-56.
All patients showed significantly improved symptoms and disease activity within 2 months of their first infusion of the treatment. The mean decrease and mean percentage decrease in CLASI-A scores were 17.1 and 65.1%, respectively. The mean decrease and mean percentage decrease in CLASI-D scores were 0.5 and 2.9%, respectively.
The rapid clinical improvements with anifrolumab, compared with improvements with traditional medications, were striking, the authors wrote. “Given the risk for permanent scarring, dyspigmentation, and alopecia with poorly controlled DLE, the importance of rapidly mitigating disease activity cannot be overemphasized.”
They acknowledged that the results are limited by the study’s small sample size and retrospective design, and they recommend larger related prospective studies.
Asked to comment on the results, Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric rheumatology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said that finding new DLE therapeutics is important because of the huge impact of uncontrolled DLE on patients’ quality of life, body image, and social roles.
Dr. Ardalan noted that he sees DLE in his pediatric patients, “either as an isolated finding or in the context of systemic lupus erythematosus. Anifrolumab is not approved by the FDA to treat DLE or children.
“Randomized controlled trials, including the TULIP-1 and TULIP-2 studies of anifrolumab in systemic lupus, have indicated that lupus skin manifestations can improve in patients who receive anifrolumab,” said Dr. Ardalan, who was not involved in the study. “And we know that type I interferons are major drivers of cutaneous disease activity in patients with lupus, so targeting that mechanism with anifrolumab makes biological sense.”
The authors’ use of the validated CLASI classification system to quantify disease activity and damage over time, and their determination of the length of time for the drug to take effect are strengths of the study, he added.
Funding information was not provided. Two authors reported financial relationships with Pfizer, which does not manufacture anifrolumab. Dr. Ardalan reported no conflicts of interest with the study.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
New data forecast more oral PDE4 inhibitors for psoriasis
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – according to results of a phase 2 clinical trial presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The phase 2b data, which are prompting a phase 3 trial, suggest that the drug, called orismilast, “is a potential new addition to the psoriasis armamentarium,” reported Lars E. French, MD, professor and chair, department of dermatology, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany).
At the same session, findings from another study supported off-label use of oral roflumilast (Daliresp and generic), a PDE4 inhibitor approved for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only PDE4 inhibitors with an indication for psoriasis are roflumilast, approved as a cream (Zoryve), and apremilast (Otezla), approved as an oral therapy.
Phase 2 study of orismilast
In the orismilast trial, Dr. French attributed the efficacy observed to the potency of orismilast on the B and D subtypes of PDE4 associated with inflammation. One clue is that these specific subtypes are overly expressed in the skin of patients with either psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
“When compared to apremilast, orismilast is at least two to fivefold more potent on all PDE4 isoforms and up to 39 times more potent on some of the PDE4 B and D isoforms,” said Dr. French, referring to preclinical findings in human whole blood and blood cells and in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
The efficacy of orismilast in an immediate-release oral formulation was previously demonstrated in a recently published phase 2a trial, but the newest study tested a modified-release formulation of orismilast to test its potential to improve tolerability.
In the study, 202 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis (Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] score ≥ 12) were randomly assigned to one of three doses of orismilast or to placebo. Each of the three doses – 20 mg, 30 mg, or 40 mg – were administered twice daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI score at 16 weeks. Secondary endpoints included PASI 75 responses (signifying 75% clearance) and safety.
Relative to placebo, which was associated with a PASI improvement of 17%, all three of the tested orismilast doses were superior in a dose-dependent manner. The rates of response were 53%, 61%, and 64% for the 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg twice-daily doses, respectively.
The PASI improvements were rapid, Dr. French said. At 4 weeks, PASI scores climbed from baseline by nearly 40% for those on all orismilast doses, which was more than double the improvement in the placebo group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis with missing data counted as nonresponders, the proportion of patients reaching PASI-75 scores at 16 weeks were 39%, 49%, 45%, and 17%, in the 20-mg, 30-mg, 40-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportion of patients experiencing complete or near-complete skin clearance defined by a PASI 90 were 24%, 22%, 28%, and 8%, respectively.
The side-effect profile was consistent with other PDE4 inhibitors. The most common adverse events included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea and nausea, as well as headache and dizziness. But the majority of these events were of low grade, and they were largely confined to the first 4 weeks of treatment, which is a pattern reported with other PDE4 inhibitors in psoriasis and other chronic inflammatory diseases, such as COPD, according to Dr. French.
“There were no discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event in the arms receiving either the 20-mg or the 30-mg doses,” Dr. French reported. There were only two serious adverse events, and neither were considered by trial investigators to be related to orismilast.
Based on the limited therapeutic gain but greater risk for adverse events on the 40-mg twice-daily dose, “the question is now whether to move forward with the 20-mg or the 30-mg dose,” said Dr. French, who said planning of a phase 3 trial is underway.
Phase 2 study of roflumilast
However, this was not the only set of data on an oral PDE4 inhibitor presented as a late-breaker at the AAD meeting. For clinicians looking for a more immediate and less expensive alternative to apremilast, another study indicated that off-label use of oral roflumilast is an option.
In an investigator-initiated, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in Denmark, the rate of response to oral roflumilast at 24 weeks, including the clear or almost clear response, was on the same general order of magnitude as that seen in the orismilast study, reported Alexander Egeberg, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Copenhagen.
“At 24 weeks, 21.7% had achieved a PASI 90, and 8.7% achieved a PASI 100,” Dr. Egeberg said.
Oral roflumilast has been available for the treatment of COPD for more than 10 years and is now available in a generic formulation. This study was conducted independent of any pharmaceutical company involvement, and the high rate of response and low risk of adverse events suggests that patients can benefit from a PDE4 inhibitor in a very low-cost form.
“Generic oral roflumilast is cheaper than a Starbucks coffee,” Dr. Egeberg said.
In this trial, 46 patients were randomly assigned to placebo or to the COPD-approved roflumilast dose of 500 mcg once daily. The primary endpoint was change in PASI scores from baseline to week 12, which Dr. Egeberg pointed out is a shorter time frame than the 16 weeks more typical of psoriasis treatment studies.
At week 12, the median improvement in PASI was 34.8% in the roflumilast group versus 0% in the placebo group. Patients were then followed for an additional 12 weeks, but those randomized to placebo were switched to the active treatment. By week 24, the switch patients had largely caught up to those initiated on roflumilast for median PASI improvement (39.1% vs. 43.5%).
Similar to orismilast, roflumilast “was generally well tolerated,” Dr. Egeberg said. The adverse events were consistent with those associated with PDE4 inhibitors in previous trials, whether in psoriasis or COPD. There was only one serious adverse event, and it was not considered treatment related. Discontinuations for adverse events “were very low.”
In a population with a relatively high rate of smoking, Dr. Egeberg further reported, lung function was improved, a remark initially interpreted as a joke by some attending the presentation. However, Dr. Egeberg confirmed that lung function was monitored, and objective improvements were recorded.
By Danish law, the investigators were required to inform the manufacturers of roflumilast. Despite the results of this study, he is not aware of any plans to seek an indication for roflumilast in psoriasis, but he noted that the drug is readily available at a low price.
For those willing to offer this therapy off label, “you can start using it tomorrow if you’d like,” he said.
Dr. French reports financial relationships with Almirall, Amgen, Biotest, Galderma, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Pincell, Regeneron, UCB, and UNION Therapeutics, which provided funding for this trial. Dr. Egeberg reports financial relationships with Eli Lilly, Galderma, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
CT results in myositis inform cancer screening strategies
Targeting cancer screenings based on idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIM) subtype, autoantibodies, and age may help to maximize cancer detection while limiting false positives.
In a retrospective, single-center study conducted at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, researchers found that when screening patients with IIM for cancer via CT imaging, the diagnostic yield (number of cancers detected/tests performed) was highest in patients with dermatomyositis and the autoantibody anti–TIF1-gamma. Screening patients below age 40 years was associated with lower diagnostic yields and higher false positives, regardless of subtype.
Because of the well-known association between IIM and contemporaneous cancer, newly diagnosed patients with IIM often undergo screening. Yet, there is little research on the most efficient assessment approaches, Christopher Mecoli, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at John Hopkins University School of Medicine and lead author of the study, told this news organization. “There has been a lot written about how these patients should be evaluated for cancer. Unfortunately, the majority of literature is based on eminence,” he said. This study is “one of the first pieces of real data to inform that conversation,” he added.
The research was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
In the study, Dr. Mecoli and colleagues looked at 1,086 patients enrolled in the center’s Myositis Research Registry from 2003 through 2020. The analysis included patients with a diagnosis of dermatomyositis, polymyositis, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), and antisynthetase syndrome (ASyS). The researchers also looked at myositis-specific autoantibodies, including anti–TIF1-gamma, –Jo1, and –HMGCR. Patients were excluded from the analysis if they had a cancer diagnosis prior to their IIM onset.
Among patients included in the analysis, the average age of IIM onset was 49 years, and median follow-up duration was 5.3 years. Most patients were female (71%), 68% were white, 21% were Black, 3.6% were Asian, and 7.4% had a listed race of other or unknown. About 66% of all patients received a chest CT scan within 3 years of IIM onset, and 51% received an abdomen/pelvis CT in that same time frame. False positives were defined as the percentage of scans that led to a noncancerous biopsy.
During the study period, 62 patients had a cancer diagnosis within the first 3 years of IIM onset, with the most common cancers being breast (19%), melanoma (13%), and cervical/uterine (10%). Of 1,011 chest scans performed, 9 led to a cancer diagnosis (0.9%), compared with 12 of the 657 abdomen/pelvis (a/p) CT scans (1.8%). Patients with the dermatomyositis-specific autoantibody anti–TIF1-gamma had the highest diagnostic yield (2.9% in chest CT and 2.4% in a/p CT). Regardless of autoantibodies, dermatomyositis patients above 40 years of age had a diagnostic yield of 1.4% in chest CT and 2.7% in a/p CT. For patients under the age of 40 with polymyositis, IMNM, and ASyS, the diagnostic yield for all CT scans was 0.0%. The diagnostic yield in patients under 40 with dermatomyositis was also low (0.0% in chest CT, 0.8% in a/p CT).
The false-positive rate for all chest CT scans was 2.8%, with patients with IMNM and ASyS having the highest frequency of false positivity (both 4.4%). “Based on our data, CT chest imaging in ASyS and IMNM patients are associated with the most harm from a cancer screening perspective,” the authors write. In a/p CT, patients with dermatomyositis under 40 and patients with ASyS had the highest false-positive rates (4.9% and 3.8%, respectively).
“Age was a really big deal in terms of predicting diagnostic yield and false-positivity rate,” Dr. Mecoli said, particularly in patients with dermatomyositis. “This subgroup has historically been thought to have the biggest dissociation with cancer,” he said, but in patients under 40, “it doesn’t look like CT scans were that helpful. They were not picking up a lot of cancers, and they were leading to a lot of false-positive results.”
Still, Rohit Aggarwal, MD, of the division of rheumatology and clinical immunology at the University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, noted that the diagnostic yields of 1%-2% and even 2%-4% in higher-risk populations were high. By comparison, lung cancer screening trials had a diagnostic yield of about 1%, and trials examining CT screening for colorectal cancers had diagnostic yields of 0.5%, the authors write.
“The key message for me is that we should definitely perform CT scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis within 3 years of diagnosis – typically at presentation – if the patient has any risk factor for increased risk of cancer, which include dermatomyositis and age above 40,” Dr. Aggarwal toldthis news organization. He was not involved with the research. There are also other clinical factors to consider that were not included in the study, he added, such as severe dysphagia, patients with refractory treatment, and male sex.
Both Dr. Aggarwal and Dr. Mecoli agreed that there are limitations to this single-center, retrospective study that make it difficult to generalize the results. Similar studies should be conducted at other institutions to see if these associations hold true, Dr. Mecoli said. A prospective study could also help control for factors such as selection bias, Dr. Aggarwal added. “I don’t think these are definitive data, but I think these data were needed at retrospective levels” to plan future research, he said.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Jerome L. Greene Foundation, the Donald B. and Dorothy L. Stabler Foundation, the Huayi and Siuling Zhang Discovery Fund, and Dr. Peter Buck. Dr. Mecoli and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Targeting cancer screenings based on idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIM) subtype, autoantibodies, and age may help to maximize cancer detection while limiting false positives.
In a retrospective, single-center study conducted at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, researchers found that when screening patients with IIM for cancer via CT imaging, the diagnostic yield (number of cancers detected/tests performed) was highest in patients with dermatomyositis and the autoantibody anti–TIF1-gamma. Screening patients below age 40 years was associated with lower diagnostic yields and higher false positives, regardless of subtype.
Because of the well-known association between IIM and contemporaneous cancer, newly diagnosed patients with IIM often undergo screening. Yet, there is little research on the most efficient assessment approaches, Christopher Mecoli, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at John Hopkins University School of Medicine and lead author of the study, told this news organization. “There has been a lot written about how these patients should be evaluated for cancer. Unfortunately, the majority of literature is based on eminence,” he said. This study is “one of the first pieces of real data to inform that conversation,” he added.
The research was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
In the study, Dr. Mecoli and colleagues looked at 1,086 patients enrolled in the center’s Myositis Research Registry from 2003 through 2020. The analysis included patients with a diagnosis of dermatomyositis, polymyositis, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), and antisynthetase syndrome (ASyS). The researchers also looked at myositis-specific autoantibodies, including anti–TIF1-gamma, –Jo1, and –HMGCR. Patients were excluded from the analysis if they had a cancer diagnosis prior to their IIM onset.
Among patients included in the analysis, the average age of IIM onset was 49 years, and median follow-up duration was 5.3 years. Most patients were female (71%), 68% were white, 21% were Black, 3.6% were Asian, and 7.4% had a listed race of other or unknown. About 66% of all patients received a chest CT scan within 3 years of IIM onset, and 51% received an abdomen/pelvis CT in that same time frame. False positives were defined as the percentage of scans that led to a noncancerous biopsy.
During the study period, 62 patients had a cancer diagnosis within the first 3 years of IIM onset, with the most common cancers being breast (19%), melanoma (13%), and cervical/uterine (10%). Of 1,011 chest scans performed, 9 led to a cancer diagnosis (0.9%), compared with 12 of the 657 abdomen/pelvis (a/p) CT scans (1.8%). Patients with the dermatomyositis-specific autoantibody anti–TIF1-gamma had the highest diagnostic yield (2.9% in chest CT and 2.4% in a/p CT). Regardless of autoantibodies, dermatomyositis patients above 40 years of age had a diagnostic yield of 1.4% in chest CT and 2.7% in a/p CT. For patients under the age of 40 with polymyositis, IMNM, and ASyS, the diagnostic yield for all CT scans was 0.0%. The diagnostic yield in patients under 40 with dermatomyositis was also low (0.0% in chest CT, 0.8% in a/p CT).
The false-positive rate for all chest CT scans was 2.8%, with patients with IMNM and ASyS having the highest frequency of false positivity (both 4.4%). “Based on our data, CT chest imaging in ASyS and IMNM patients are associated with the most harm from a cancer screening perspective,” the authors write. In a/p CT, patients with dermatomyositis under 40 and patients with ASyS had the highest false-positive rates (4.9% and 3.8%, respectively).
“Age was a really big deal in terms of predicting diagnostic yield and false-positivity rate,” Dr. Mecoli said, particularly in patients with dermatomyositis. “This subgroup has historically been thought to have the biggest dissociation with cancer,” he said, but in patients under 40, “it doesn’t look like CT scans were that helpful. They were not picking up a lot of cancers, and they were leading to a lot of false-positive results.”
Still, Rohit Aggarwal, MD, of the division of rheumatology and clinical immunology at the University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, noted that the diagnostic yields of 1%-2% and even 2%-4% in higher-risk populations were high. By comparison, lung cancer screening trials had a diagnostic yield of about 1%, and trials examining CT screening for colorectal cancers had diagnostic yields of 0.5%, the authors write.
“The key message for me is that we should definitely perform CT scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis within 3 years of diagnosis – typically at presentation – if the patient has any risk factor for increased risk of cancer, which include dermatomyositis and age above 40,” Dr. Aggarwal toldthis news organization. He was not involved with the research. There are also other clinical factors to consider that were not included in the study, he added, such as severe dysphagia, patients with refractory treatment, and male sex.
Both Dr. Aggarwal and Dr. Mecoli agreed that there are limitations to this single-center, retrospective study that make it difficult to generalize the results. Similar studies should be conducted at other institutions to see if these associations hold true, Dr. Mecoli said. A prospective study could also help control for factors such as selection bias, Dr. Aggarwal added. “I don’t think these are definitive data, but I think these data were needed at retrospective levels” to plan future research, he said.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Jerome L. Greene Foundation, the Donald B. and Dorothy L. Stabler Foundation, the Huayi and Siuling Zhang Discovery Fund, and Dr. Peter Buck. Dr. Mecoli and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Targeting cancer screenings based on idiopathic inflammatory myositis (IIM) subtype, autoantibodies, and age may help to maximize cancer detection while limiting false positives.
In a retrospective, single-center study conducted at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, researchers found that when screening patients with IIM for cancer via CT imaging, the diagnostic yield (number of cancers detected/tests performed) was highest in patients with dermatomyositis and the autoantibody anti–TIF1-gamma. Screening patients below age 40 years was associated with lower diagnostic yields and higher false positives, regardless of subtype.
Because of the well-known association between IIM and contemporaneous cancer, newly diagnosed patients with IIM often undergo screening. Yet, there is little research on the most efficient assessment approaches, Christopher Mecoli, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at John Hopkins University School of Medicine and lead author of the study, told this news organization. “There has been a lot written about how these patients should be evaluated for cancer. Unfortunately, the majority of literature is based on eminence,” he said. This study is “one of the first pieces of real data to inform that conversation,” he added.
The research was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
In the study, Dr. Mecoli and colleagues looked at 1,086 patients enrolled in the center’s Myositis Research Registry from 2003 through 2020. The analysis included patients with a diagnosis of dermatomyositis, polymyositis, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), and antisynthetase syndrome (ASyS). The researchers also looked at myositis-specific autoantibodies, including anti–TIF1-gamma, –Jo1, and –HMGCR. Patients were excluded from the analysis if they had a cancer diagnosis prior to their IIM onset.
Among patients included in the analysis, the average age of IIM onset was 49 years, and median follow-up duration was 5.3 years. Most patients were female (71%), 68% were white, 21% were Black, 3.6% were Asian, and 7.4% had a listed race of other or unknown. About 66% of all patients received a chest CT scan within 3 years of IIM onset, and 51% received an abdomen/pelvis CT in that same time frame. False positives were defined as the percentage of scans that led to a noncancerous biopsy.
During the study period, 62 patients had a cancer diagnosis within the first 3 years of IIM onset, with the most common cancers being breast (19%), melanoma (13%), and cervical/uterine (10%). Of 1,011 chest scans performed, 9 led to a cancer diagnosis (0.9%), compared with 12 of the 657 abdomen/pelvis (a/p) CT scans (1.8%). Patients with the dermatomyositis-specific autoantibody anti–TIF1-gamma had the highest diagnostic yield (2.9% in chest CT and 2.4% in a/p CT). Regardless of autoantibodies, dermatomyositis patients above 40 years of age had a diagnostic yield of 1.4% in chest CT and 2.7% in a/p CT. For patients under the age of 40 with polymyositis, IMNM, and ASyS, the diagnostic yield for all CT scans was 0.0%. The diagnostic yield in patients under 40 with dermatomyositis was also low (0.0% in chest CT, 0.8% in a/p CT).
The false-positive rate for all chest CT scans was 2.8%, with patients with IMNM and ASyS having the highest frequency of false positivity (both 4.4%). “Based on our data, CT chest imaging in ASyS and IMNM patients are associated with the most harm from a cancer screening perspective,” the authors write. In a/p CT, patients with dermatomyositis under 40 and patients with ASyS had the highest false-positive rates (4.9% and 3.8%, respectively).
“Age was a really big deal in terms of predicting diagnostic yield and false-positivity rate,” Dr. Mecoli said, particularly in patients with dermatomyositis. “This subgroup has historically been thought to have the biggest dissociation with cancer,” he said, but in patients under 40, “it doesn’t look like CT scans were that helpful. They were not picking up a lot of cancers, and they were leading to a lot of false-positive results.”
Still, Rohit Aggarwal, MD, of the division of rheumatology and clinical immunology at the University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, noted that the diagnostic yields of 1%-2% and even 2%-4% in higher-risk populations were high. By comparison, lung cancer screening trials had a diagnostic yield of about 1%, and trials examining CT screening for colorectal cancers had diagnostic yields of 0.5%, the authors write.
“The key message for me is that we should definitely perform CT scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis within 3 years of diagnosis – typically at presentation – if the patient has any risk factor for increased risk of cancer, which include dermatomyositis and age above 40,” Dr. Aggarwal toldthis news organization. He was not involved with the research. There are also other clinical factors to consider that were not included in the study, he added, such as severe dysphagia, patients with refractory treatment, and male sex.
Both Dr. Aggarwal and Dr. Mecoli agreed that there are limitations to this single-center, retrospective study that make it difficult to generalize the results. Similar studies should be conducted at other institutions to see if these associations hold true, Dr. Mecoli said. A prospective study could also help control for factors such as selection bias, Dr. Aggarwal added. “I don’t think these are definitive data, but I think these data were needed at retrospective levels” to plan future research, he said.
The study was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Jerome L. Greene Foundation, the Donald B. and Dorothy L. Stabler Foundation, the Huayi and Siuling Zhang Discovery Fund, and Dr. Peter Buck. Dr. Mecoli and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH