User login
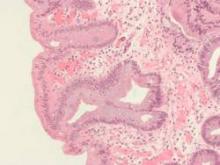
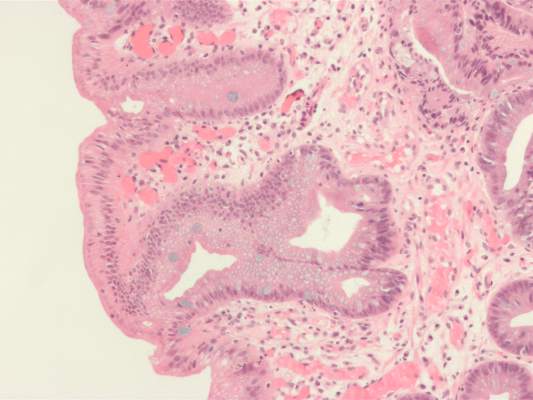
High serum insulin and leptin levels were significantly associated with Barrett’s esophagus, according to authors of a meta-analysis of nine observational studies published in the December issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Compared with population controls, patients with Barrett’s esophagus were twice as likely to have high serum leptin levels, and were 1.74 times as likely to have hyperinsulinemia, said Dr. Apoorva Chandar of Case Western Reserve University (Cleveland) and his associates.
Central obesity was known to increase the risk of esophageal inflammation, metaplasia, and adenocarcinoma (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013 [doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.05.009]), but this meta-analysis helped pinpoint the hormones that might mediate the relationship, the investigators said. However, the link between obesity and Barrett’s esophagus “is likely complex,” meriting additional longitudinal analyses, they added.
Metabolically active fat produces leptin and other adipokines. Elevated serum leptin has anti-apoptotic and angiogenic effects and also is a marker for insulin resistance, the researchers noted. “Several observational studies have examined the association of serum adipokines and insulin with Barrett’s esophagus, but evidence regarding this association remains inconclusive,” they said. Therefore, they reviewed observational studies published through April 2015 that examined relationships between Barrett’s esophagus, adipokines, and insulin. The studies included 10 separate cohorts of 1,432 patients with Barrett’s esophagus and 3,550 controls, enabling the researchers to estimate summary adjusted odds ratios (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 [doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.06.041]).
Compared with population controls, patients with Barrett’s esophagus were twice as likely to have high serum leptin levels (adjusted OR, 2.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31-3.78) and 1.74 times as likely to have elevated serum insulin levels (95% CI, 1.14 to 2.65). Total serum adiponectin was not linked to risk of Barrett’s esophagus, but increased serum levels of high molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin were (aOR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.16-2.63), and one study reported an inverse correlation between levels of low molecular weight leptin and Barrett’s esophagus risk. Low molecular weight adiponectin has anti-inflammatory effects, while HMW adiponectin is proinflammatory, the researchers noted.
“It is simplistic to assume that the effects of obesity on the development of Barrett’s esophagus are mediated by one single adipokine,” the researchers said. “Leptin and adiponectin seem to crosstalk, and both of these adipokines also affect insulin-signaling pathways.” Obesity is a chronic inflammatory state characterized by increases in other circulating cytokines, such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha, they noted. Their findings do not solely implicate leptin among the adipokines, but show that it “might be an important contributor, and support further studies on the effects of leptin on the leptin receptor in the proliferation of Barrett’s epithelium.” They also noted that although women have higher leptin levels than men, men are at much greater risk of Barrett’s esophagus, which their review could not explain. Studies to date are “not adequate” to assess gender-specific relationships between insulin, adipokines, and Barrett’s esophagus, they said.
Other evidence has linked insulin to Barrett’s esophagus, according to the researchers. Insulin and related signaling pathways are upregulated in tissue specimens of Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s esophagus is more likely to progress to esophageal adenocarcinoma in the setting of insulin resistance, they noted. “Given that recent studies have shown an association between Barrett’s esophagus and measures of central obesity and diabetes mellitus type 2, it is conceivable that hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance, which are known consequences of central obesity, are associated with Barrett’s esophagus pathogenesis,” they said.
However, their study did not link hyperinsulinemia to Barrett’s esophagus among subjects with GERD, possibly because of confounding or overmatching, they noted. More rigorous studies would be needed to fairly evaluate any relationship between insulin resistance and risk of Barrett’s esophagus, they concluded.
The National Cancer Institute funded the study. The investigators had no conflicts of interest.
Epidemiologic studies have shown that abdominal, especially visceral as opposed to cutaneous, obesity isassociated with increased risk of Barrett’s esophagus. The precise mechanisms are unclear; however, there is increasing evidence that this association is likely mediated through both the mechanical effect of increased abdominal pressure promoting gastroesophageal reflux and the nonmechanical metabolic and inflammatory effects of abdominal obesity. Adipose tissue produces and releases a variety of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors, including the adipokines leptin and adiponectin, as well as cytokines and chemokines. Leptin (higher levels in visceral fat) has proinflammatory effects that promote a low-grade inflammatory state, while adiponectin (less visceral fat) protects against the complications of obesity by exerting anti-inflammatory effects.

|
| Dr. Aaron Thrift |
Results from single-center studies examining associations of circulating adipokines, insulin, and inflammatory cytokines with Barrett’s esophagus have been conflicting, potentially due to methodologic shortcomings. In this article, Dr. Chandar and his colleagues conducted a meta-analysis and report that higher serum levels of leptin and insulin are associated with increased risk of Barrett’s esophagus, while there was no association between serum adiponectin and Barrett’s esophagus. This study highlights the complexity of these associations. For example, only leptin among the adipokines was associated with Barrett’s esophagus. Thus, additional longitudinal studies are required to further tease out these associations, and formal mediation analysis would help quantify how much of the obesity effect is through these hormones. From a clinical perspective, the importance of the findings of this paper is that these may be attractive targets for preventing Barrett’s esophagus.
Dr. Thrift is in the section of gastroenterology and hepatology, department of medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
Epidemiologic studies have shown that abdominal, especially visceral as opposed to cutaneous, obesity isassociated with increased risk of Barrett’s esophagus. The precise mechanisms are unclear; however, there is increasing evidence that this association is likely mediated through both the mechanical effect of increased abdominal pressure promoting gastroesophageal reflux and the nonmechanical metabolic and inflammatory effects of abdominal obesity. Adipose tissue produces and releases a variety of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors, including the adipokines leptin and adiponectin, as well as cytokines and chemokines. Leptin (higher levels in visceral fat) has proinflammatory effects that promote a low-grade inflammatory state, while adiponectin (less visceral fat) protects against the complications of obesity by exerting anti-inflammatory effects.

|
| Dr. Aaron Thrift |
Results from single-center studies examining associations of circulating adipokines, insulin, and inflammatory cytokines with Barrett’s esophagus have been conflicting, potentially due to methodologic shortcomings. In this article, Dr. Chandar and his colleagues conducted a meta-analysis and report that higher serum levels of leptin and insulin are associated with increased risk of Barrett’s esophagus, while there was no association between serum adiponectin and Barrett’s esophagus. This study highlights the complexity of these associations. For example, only leptin among the adipokines was associated with Barrett’s esophagus. Thus, additional longitudinal studies are required to further tease out these associations, and formal mediation analysis would help quantify how much of the obesity effect is through these hormones. From a clinical perspective, the importance of the findings of this paper is that these may be attractive targets for preventing Barrett’s esophagus.
Dr. Thrift is in the section of gastroenterology and hepatology, department of medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
Epidemiologic studies have shown that abdominal, especially visceral as opposed to cutaneous, obesity isassociated with increased risk of Barrett’s esophagus. The precise mechanisms are unclear; however, there is increasing evidence that this association is likely mediated through both the mechanical effect of increased abdominal pressure promoting gastroesophageal reflux and the nonmechanical metabolic and inflammatory effects of abdominal obesity. Adipose tissue produces and releases a variety of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors, including the adipokines leptin and adiponectin, as well as cytokines and chemokines. Leptin (higher levels in visceral fat) has proinflammatory effects that promote a low-grade inflammatory state, while adiponectin (less visceral fat) protects against the complications of obesity by exerting anti-inflammatory effects.

|
| Dr. Aaron Thrift |
Results from single-center studies examining associations of circulating adipokines, insulin, and inflammatory cytokines with Barrett’s esophagus have been conflicting, potentially due to methodologic shortcomings. In this article, Dr. Chandar and his colleagues conducted a meta-analysis and report that higher serum levels of leptin and insulin are associated with increased risk of Barrett’s esophagus, while there was no association between serum adiponectin and Barrett’s esophagus. This study highlights the complexity of these associations. For example, only leptin among the adipokines was associated with Barrett’s esophagus. Thus, additional longitudinal studies are required to further tease out these associations, and formal mediation analysis would help quantify how much of the obesity effect is through these hormones. From a clinical perspective, the importance of the findings of this paper is that these may be attractive targets for preventing Barrett’s esophagus.
Dr. Thrift is in the section of gastroenterology and hepatology, department of medicine, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston. He has no conflicts of interest.
High serum insulin and leptin levels were significantly associated with Barrett’s esophagus, according to authors of a meta-analysis of nine observational studies published in the December issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Compared with population controls, patients with Barrett’s esophagus were twice as likely to have high serum leptin levels, and were 1.74 times as likely to have hyperinsulinemia, said Dr. Apoorva Chandar of Case Western Reserve University (Cleveland) and his associates.
Central obesity was known to increase the risk of esophageal inflammation, metaplasia, and adenocarcinoma (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013 [doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.05.009]), but this meta-analysis helped pinpoint the hormones that might mediate the relationship, the investigators said. However, the link between obesity and Barrett’s esophagus “is likely complex,” meriting additional longitudinal analyses, they added.
Metabolically active fat produces leptin and other adipokines. Elevated serum leptin has anti-apoptotic and angiogenic effects and also is a marker for insulin resistance, the researchers noted. “Several observational studies have examined the association of serum adipokines and insulin with Barrett’s esophagus, but evidence regarding this association remains inconclusive,” they said. Therefore, they reviewed observational studies published through April 2015 that examined relationships between Barrett’s esophagus, adipokines, and insulin. The studies included 10 separate cohorts of 1,432 patients with Barrett’s esophagus and 3,550 controls, enabling the researchers to estimate summary adjusted odds ratios (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 [doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.06.041]).
Compared with population controls, patients with Barrett’s esophagus were twice as likely to have high serum leptin levels (adjusted OR, 2.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31-3.78) and 1.74 times as likely to have elevated serum insulin levels (95% CI, 1.14 to 2.65). Total serum adiponectin was not linked to risk of Barrett’s esophagus, but increased serum levels of high molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin were (aOR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.16-2.63), and one study reported an inverse correlation between levels of low molecular weight leptin and Barrett’s esophagus risk. Low molecular weight adiponectin has anti-inflammatory effects, while HMW adiponectin is proinflammatory, the researchers noted.
“It is simplistic to assume that the effects of obesity on the development of Barrett’s esophagus are mediated by one single adipokine,” the researchers said. “Leptin and adiponectin seem to crosstalk, and both of these adipokines also affect insulin-signaling pathways.” Obesity is a chronic inflammatory state characterized by increases in other circulating cytokines, such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha, they noted. Their findings do not solely implicate leptin among the adipokines, but show that it “might be an important contributor, and support further studies on the effects of leptin on the leptin receptor in the proliferation of Barrett’s epithelium.” They also noted that although women have higher leptin levels than men, men are at much greater risk of Barrett’s esophagus, which their review could not explain. Studies to date are “not adequate” to assess gender-specific relationships between insulin, adipokines, and Barrett’s esophagus, they said.
Other evidence has linked insulin to Barrett’s esophagus, according to the researchers. Insulin and related signaling pathways are upregulated in tissue specimens of Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s esophagus is more likely to progress to esophageal adenocarcinoma in the setting of insulin resistance, they noted. “Given that recent studies have shown an association between Barrett’s esophagus and measures of central obesity and diabetes mellitus type 2, it is conceivable that hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance, which are known consequences of central obesity, are associated with Barrett’s esophagus pathogenesis,” they said.
However, their study did not link hyperinsulinemia to Barrett’s esophagus among subjects with GERD, possibly because of confounding or overmatching, they noted. More rigorous studies would be needed to fairly evaluate any relationship between insulin resistance and risk of Barrett’s esophagus, they concluded.
The National Cancer Institute funded the study. The investigators had no conflicts of interest.
High serum insulin and leptin levels were significantly associated with Barrett’s esophagus, according to authors of a meta-analysis of nine observational studies published in the December issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Compared with population controls, patients with Barrett’s esophagus were twice as likely to have high serum leptin levels, and were 1.74 times as likely to have hyperinsulinemia, said Dr. Apoorva Chandar of Case Western Reserve University (Cleveland) and his associates.
Central obesity was known to increase the risk of esophageal inflammation, metaplasia, and adenocarcinoma (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013 [doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.05.009]), but this meta-analysis helped pinpoint the hormones that might mediate the relationship, the investigators said. However, the link between obesity and Barrett’s esophagus “is likely complex,” meriting additional longitudinal analyses, they added.
Metabolically active fat produces leptin and other adipokines. Elevated serum leptin has anti-apoptotic and angiogenic effects and also is a marker for insulin resistance, the researchers noted. “Several observational studies have examined the association of serum adipokines and insulin with Barrett’s esophagus, but evidence regarding this association remains inconclusive,” they said. Therefore, they reviewed observational studies published through April 2015 that examined relationships between Barrett’s esophagus, adipokines, and insulin. The studies included 10 separate cohorts of 1,432 patients with Barrett’s esophagus and 3,550 controls, enabling the researchers to estimate summary adjusted odds ratios (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 [doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.06.041]).
Compared with population controls, patients with Barrett’s esophagus were twice as likely to have high serum leptin levels (adjusted OR, 2.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31-3.78) and 1.74 times as likely to have elevated serum insulin levels (95% CI, 1.14 to 2.65). Total serum adiponectin was not linked to risk of Barrett’s esophagus, but increased serum levels of high molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin were (aOR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.16-2.63), and one study reported an inverse correlation between levels of low molecular weight leptin and Barrett’s esophagus risk. Low molecular weight adiponectin has anti-inflammatory effects, while HMW adiponectin is proinflammatory, the researchers noted.
“It is simplistic to assume that the effects of obesity on the development of Barrett’s esophagus are mediated by one single adipokine,” the researchers said. “Leptin and adiponectin seem to crosstalk, and both of these adipokines also affect insulin-signaling pathways.” Obesity is a chronic inflammatory state characterized by increases in other circulating cytokines, such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha, they noted. Their findings do not solely implicate leptin among the adipokines, but show that it “might be an important contributor, and support further studies on the effects of leptin on the leptin receptor in the proliferation of Barrett’s epithelium.” They also noted that although women have higher leptin levels than men, men are at much greater risk of Barrett’s esophagus, which their review could not explain. Studies to date are “not adequate” to assess gender-specific relationships between insulin, adipokines, and Barrett’s esophagus, they said.
Other evidence has linked insulin to Barrett’s esophagus, according to the researchers. Insulin and related signaling pathways are upregulated in tissue specimens of Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s esophagus is more likely to progress to esophageal adenocarcinoma in the setting of insulin resistance, they noted. “Given that recent studies have shown an association between Barrett’s esophagus and measures of central obesity and diabetes mellitus type 2, it is conceivable that hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance, which are known consequences of central obesity, are associated with Barrett’s esophagus pathogenesis,” they said.
However, their study did not link hyperinsulinemia to Barrett’s esophagus among subjects with GERD, possibly because of confounding or overmatching, they noted. More rigorous studies would be needed to fairly evaluate any relationship between insulin resistance and risk of Barrett’s esophagus, they concluded.
The National Cancer Institute funded the study. The investigators had no conflicts of interest.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Key clinical point: High serum levels of leptin and insulin were associated with Barrett’s esophagus in a meta-analysis.
Major finding: Compared with population controls, patients with Barrett’s esophagus were twice as likely to have high serum leptin levels, and were 1.74 times as likely to have hyperinsulinemia.
Data source: Meta-analysis of nine observational studies that included 1,432 Barrett’s esophagus patients and 3,550 controls.
Disclosures: The National Cancer Institute funded the study. The investigators had no conflicts of interest.