User login
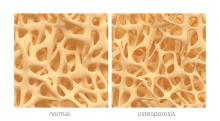
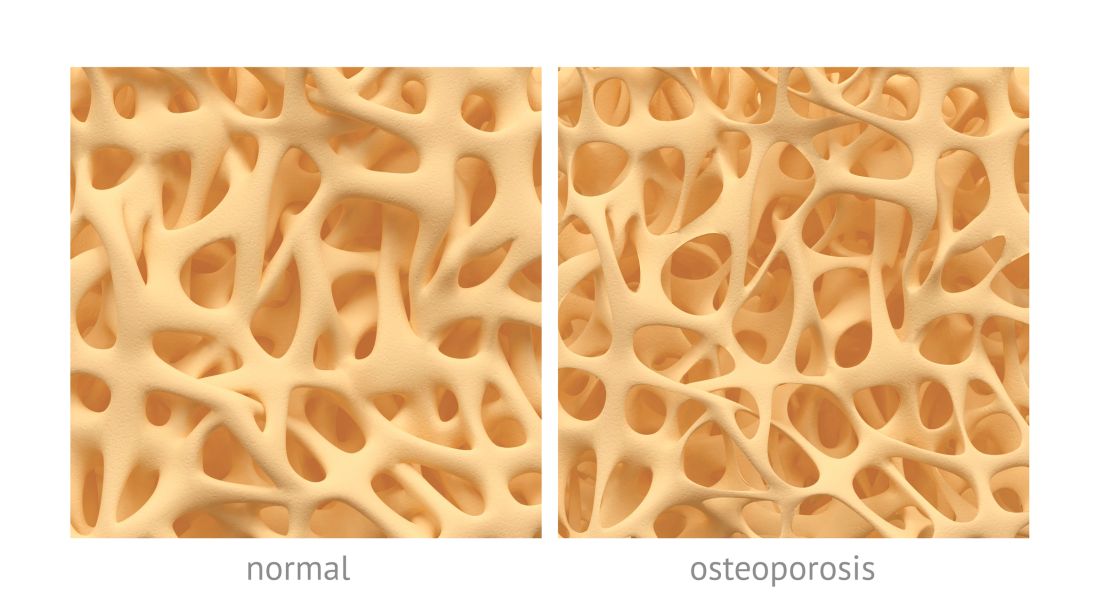
Average measures of bone mineral density were similar for individuals with high-trauma and low-trauma fractures, and both were significantly distinct from those with no fracture history, based on data from a cohort study of adults aged 40 years and older.
In the past, low-trauma fractures have typically been associated with osteoporosis, wrote William D. Leslie, MD, of the University of Manitoba, Canada, and his colleagues. However, features distinguishing between low- and high-trauma fractures are often arbitrary and “empirical data have questioned whether distinguishing low-trauma from high-trauma fractures is clinically useful for purposes of risk assessment and treatment,” they wrote.
In a study published in Osteoporosis International, the researchers reviewed data from 64,626 individuals with no prior fracture, 858 with high-trauma fractures, and 14,758 with low-trauma fractures. Overall, the average BMD Z-scores for individuals with no previous fracture were slightly positive, while those with either a high-trauma or low-trauma fracture were negative. The scores for individuals with high-trauma fractures or major osteoporotic fractures were similar to those with low-trauma fractures, and significantly lower (P less than .001) than among individuals with no prior fractures.
The study population included adults aged 40 years and older with baseline DXA scans between Jan. 1, 1996, and Mar. 31, 2016. Those with high-trauma fractures were younger than those with low-trauma fractures (65 years vs. 67 years), and fewer individuals with high-trauma fractures were women (77% vs. 87%).
Both high-trauma and low-trauma fractures were similarly and significantly associated with increased risk for incident major osteoporotic fractures (adjusted hazard ratios 1.31 and 1.55, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors including incomplete data on external injury codes, the retrospective study design, and the lack of analysis of the time since prior fractures, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, long-term follow-up, and large numbers of incident fractures, they wrote.
The results support data from previous studies and support “the inclusion of high-trauma clinical fractures in clinical assessment for underlying osteoporosis and in the evaluation for intervention to reduce future fracture risk,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Steven R. Cummings, MD, of California Pacific Medical Center Research Institute, San Francisco, and Richard Eastell, MD, of the University of Sheffield, England, wrote that the practice of rating fractures according to degree of trauma should be eliminated.
“The study adds evidence to the case that it is time to abandon the mistaken beliefs that fractures rated as high trauma are not associated with decreased BMD, indicate no higher risk of subsequent fracture, or are less likely to be prevented by treatments for osteoporosis,” they wrote.
Describing some fractures as due to trauma reinforces the mistaken belief that the fractures are simply due to the trauma, not decreased bone strength, they noted.
“Indeed, we recommend that people stop attempting to rate or record degree of trauma because such ratings are at best inaccurate and would promote the continued neglect of those patients who are misclassified as having fractures that do not warrant evaluation and treatment,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Leslie, the study’s first author, reported having no financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Cummings disclosed consultancy and grant funding from Amgen and Radius. Dr. Eastell disclosed consultancy funding from IDS, Roche Diagnostics, GSK Nutrition, FNIH, Mereo, Lilly, Sandoz, Nittobo, Abbvie, Samsung, and Haoma Medica and grant funding from Nittobo, IDS, Roche, Amgen, and Alexion.
SOURCE: Leslie WD et al. Osteroporos Int. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05274-2.
Average measures of bone mineral density were similar for individuals with high-trauma and low-trauma fractures, and both were significantly distinct from those with no fracture history, based on data from a cohort study of adults aged 40 years and older.
In the past, low-trauma fractures have typically been associated with osteoporosis, wrote William D. Leslie, MD, of the University of Manitoba, Canada, and his colleagues. However, features distinguishing between low- and high-trauma fractures are often arbitrary and “empirical data have questioned whether distinguishing low-trauma from high-trauma fractures is clinically useful for purposes of risk assessment and treatment,” they wrote.
In a study published in Osteoporosis International, the researchers reviewed data from 64,626 individuals with no prior fracture, 858 with high-trauma fractures, and 14,758 with low-trauma fractures. Overall, the average BMD Z-scores for individuals with no previous fracture were slightly positive, while those with either a high-trauma or low-trauma fracture were negative. The scores for individuals with high-trauma fractures or major osteoporotic fractures were similar to those with low-trauma fractures, and significantly lower (P less than .001) than among individuals with no prior fractures.
The study population included adults aged 40 years and older with baseline DXA scans between Jan. 1, 1996, and Mar. 31, 2016. Those with high-trauma fractures were younger than those with low-trauma fractures (65 years vs. 67 years), and fewer individuals with high-trauma fractures were women (77% vs. 87%).
Both high-trauma and low-trauma fractures were similarly and significantly associated with increased risk for incident major osteoporotic fractures (adjusted hazard ratios 1.31 and 1.55, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors including incomplete data on external injury codes, the retrospective study design, and the lack of analysis of the time since prior fractures, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, long-term follow-up, and large numbers of incident fractures, they wrote.
The results support data from previous studies and support “the inclusion of high-trauma clinical fractures in clinical assessment for underlying osteoporosis and in the evaluation for intervention to reduce future fracture risk,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Steven R. Cummings, MD, of California Pacific Medical Center Research Institute, San Francisco, and Richard Eastell, MD, of the University of Sheffield, England, wrote that the practice of rating fractures according to degree of trauma should be eliminated.
“The study adds evidence to the case that it is time to abandon the mistaken beliefs that fractures rated as high trauma are not associated with decreased BMD, indicate no higher risk of subsequent fracture, or are less likely to be prevented by treatments for osteoporosis,” they wrote.
Describing some fractures as due to trauma reinforces the mistaken belief that the fractures are simply due to the trauma, not decreased bone strength, they noted.
“Indeed, we recommend that people stop attempting to rate or record degree of trauma because such ratings are at best inaccurate and would promote the continued neglect of those patients who are misclassified as having fractures that do not warrant evaluation and treatment,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Leslie, the study’s first author, reported having no financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Cummings disclosed consultancy and grant funding from Amgen and Radius. Dr. Eastell disclosed consultancy funding from IDS, Roche Diagnostics, GSK Nutrition, FNIH, Mereo, Lilly, Sandoz, Nittobo, Abbvie, Samsung, and Haoma Medica and grant funding from Nittobo, IDS, Roche, Amgen, and Alexion.
SOURCE: Leslie WD et al. Osteroporos Int. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05274-2.
Average measures of bone mineral density were similar for individuals with high-trauma and low-trauma fractures, and both were significantly distinct from those with no fracture history, based on data from a cohort study of adults aged 40 years and older.
In the past, low-trauma fractures have typically been associated with osteoporosis, wrote William D. Leslie, MD, of the University of Manitoba, Canada, and his colleagues. However, features distinguishing between low- and high-trauma fractures are often arbitrary and “empirical data have questioned whether distinguishing low-trauma from high-trauma fractures is clinically useful for purposes of risk assessment and treatment,” they wrote.
In a study published in Osteoporosis International, the researchers reviewed data from 64,626 individuals with no prior fracture, 858 with high-trauma fractures, and 14,758 with low-trauma fractures. Overall, the average BMD Z-scores for individuals with no previous fracture were slightly positive, while those with either a high-trauma or low-trauma fracture were negative. The scores for individuals with high-trauma fractures or major osteoporotic fractures were similar to those with low-trauma fractures, and significantly lower (P less than .001) than among individuals with no prior fractures.
The study population included adults aged 40 years and older with baseline DXA scans between Jan. 1, 1996, and Mar. 31, 2016. Those with high-trauma fractures were younger than those with low-trauma fractures (65 years vs. 67 years), and fewer individuals with high-trauma fractures were women (77% vs. 87%).
Both high-trauma and low-trauma fractures were similarly and significantly associated with increased risk for incident major osteoporotic fractures (adjusted hazard ratios 1.31 and 1.55, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors including incomplete data on external injury codes, the retrospective study design, and the lack of analysis of the time since prior fractures, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size, long-term follow-up, and large numbers of incident fractures, they wrote.
The results support data from previous studies and support “the inclusion of high-trauma clinical fractures in clinical assessment for underlying osteoporosis and in the evaluation for intervention to reduce future fracture risk,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Steven R. Cummings, MD, of California Pacific Medical Center Research Institute, San Francisco, and Richard Eastell, MD, of the University of Sheffield, England, wrote that the practice of rating fractures according to degree of trauma should be eliminated.
“The study adds evidence to the case that it is time to abandon the mistaken beliefs that fractures rated as high trauma are not associated with decreased BMD, indicate no higher risk of subsequent fracture, or are less likely to be prevented by treatments for osteoporosis,” they wrote.
Describing some fractures as due to trauma reinforces the mistaken belief that the fractures are simply due to the trauma, not decreased bone strength, they noted.
“Indeed, we recommend that people stop attempting to rate or record degree of trauma because such ratings are at best inaccurate and would promote the continued neglect of those patients who are misclassified as having fractures that do not warrant evaluation and treatment,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Leslie, the study’s first author, reported having no financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Cummings disclosed consultancy and grant funding from Amgen and Radius. Dr. Eastell disclosed consultancy funding from IDS, Roche Diagnostics, GSK Nutrition, FNIH, Mereo, Lilly, Sandoz, Nittobo, Abbvie, Samsung, and Haoma Medica and grant funding from Nittobo, IDS, Roche, Amgen, and Alexion.
SOURCE: Leslie WD et al. Osteroporos Int. 2020 Mar 16. doi: 10.1007/s00198-019-05274-2.
FROM OSTEOPOROSIS INTERNATIONAL