User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Strong support for causal role of cannabis in schizophrenia
The long-observed association between cannabis use and schizophrenia is likely partially causal in nature, new research shows.
Investigators found a clear increase in the proportion of schizophrenia cases linked to cannabis use disorder over the past 25 years.
“In my view, the association is most likely causative, at least to a large extent,” first author Carsten Hjorthøj, PhD, from the Copenhagen Research Center for Mental Health, Copenhagen University Hospital, told this news organization.
“It is, of course, nearly impossible to use epidemiological studies to actually prove causation, but all the numbers behave exactly in the way that would be expected under the theory of causation,” said Dr. Hjorthøj.
The study was published online July 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Far from harmless
The findings are based on Danish national health registry data. The study sample included all people in Denmark born before Dec. 31, 2000 who were aged 16 years or older at some point from Jan. 1, 1972 to Dec. 31, 2016. The data analysis was conducted from August 2020 to April 2021.
Despite some fluctuation, there was a general increase in the population-attributable risk fraction (PARF) for cannabis use disorder with regard to schizophrenia over time, the researchers report. The PARF increased from about 2% in 1995 to about 4% in 2000 and has hovered from 6% to 8% since 2010.
“Although not in itself proof of causality, our study provides evidence of the theory of cannabis being a component cause of schizophrenia,” the investigators write.
The findings are “particularly important with the increasing legalization of cannabis for both medicinal and recreational uses seeming to lead to an increase in the perception of cannabis as relatively harmless and possibly in the uptake of cannabis use, especially among youth,” they add.
“Although psychosis is not the only outcome of interest in terms of cannabis use, our study clearly indicates that cannabis should not be considered harmless,” they conclude.
Cases linked to cannabis underestimated?
In an accompanying editorial, Tyler VanderWeele, PhD, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, notes that estimates in this study could be conservative as a result of underdiagnosis of cannabis use disorder and because it only examined cannabis use disorder.
“Cannabis use disorder is not responsible for most schizophrenia cases, but it is responsible for a nonnegligible and increasing proportion. This should be considered in discussions regarding legalization and regulation of the use of cannabis,” Dr. VanderWeele writes.
Experts with the Science Media Center, a U.K. nonprofit organization, also weighed in on the results.
Terrie Moffitt, PhD, with King’s College London, said the study “adds important evidence that patients with diagnosed cannabis use disorder are more at risk for psychosis now than they used to be.”
“ However, most cannabis users, even those who are dependent on it, never come in to clinics for treatment. Also, it is known that people who seek treatment tend to have multiple mental health problems, not solely cannabis problems,” Dr. Moffitt commented.
Emir Englund, PhD, also from King’s College London, said the study “strengthens an already well-established association between the two. However, it is unable to shed additional light on whether cannabis causes schizophrenia or not, due to the observational nature of the study.”
“In my opinion, the current scientific view of cannabis use as a ‘component cause’ which interacts with other risk factors to cause schizophrenia but is neither necessary nor sufficient to do so on its own still stands,” Dr. Englund said.
The study was supported by a grant from Lundbeckfonden. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. VanderWeele has received grants from the National Cancer Institute and the John Templeton Foundation. Dr. Moffitt and Dr. Englund have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The long-observed association between cannabis use and schizophrenia is likely partially causal in nature, new research shows.
Investigators found a clear increase in the proportion of schizophrenia cases linked to cannabis use disorder over the past 25 years.
“In my view, the association is most likely causative, at least to a large extent,” first author Carsten Hjorthøj, PhD, from the Copenhagen Research Center for Mental Health, Copenhagen University Hospital, told this news organization.
“It is, of course, nearly impossible to use epidemiological studies to actually prove causation, but all the numbers behave exactly in the way that would be expected under the theory of causation,” said Dr. Hjorthøj.
The study was published online July 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Far from harmless
The findings are based on Danish national health registry data. The study sample included all people in Denmark born before Dec. 31, 2000 who were aged 16 years or older at some point from Jan. 1, 1972 to Dec. 31, 2016. The data analysis was conducted from August 2020 to April 2021.
Despite some fluctuation, there was a general increase in the population-attributable risk fraction (PARF) for cannabis use disorder with regard to schizophrenia over time, the researchers report. The PARF increased from about 2% in 1995 to about 4% in 2000 and has hovered from 6% to 8% since 2010.
“Although not in itself proof of causality, our study provides evidence of the theory of cannabis being a component cause of schizophrenia,” the investigators write.
The findings are “particularly important with the increasing legalization of cannabis for both medicinal and recreational uses seeming to lead to an increase in the perception of cannabis as relatively harmless and possibly in the uptake of cannabis use, especially among youth,” they add.
“Although psychosis is not the only outcome of interest in terms of cannabis use, our study clearly indicates that cannabis should not be considered harmless,” they conclude.
Cases linked to cannabis underestimated?
In an accompanying editorial, Tyler VanderWeele, PhD, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, notes that estimates in this study could be conservative as a result of underdiagnosis of cannabis use disorder and because it only examined cannabis use disorder.
“Cannabis use disorder is not responsible for most schizophrenia cases, but it is responsible for a nonnegligible and increasing proportion. This should be considered in discussions regarding legalization and regulation of the use of cannabis,” Dr. VanderWeele writes.
Experts with the Science Media Center, a U.K. nonprofit organization, also weighed in on the results.
Terrie Moffitt, PhD, with King’s College London, said the study “adds important evidence that patients with diagnosed cannabis use disorder are more at risk for psychosis now than they used to be.”
“ However, most cannabis users, even those who are dependent on it, never come in to clinics for treatment. Also, it is known that people who seek treatment tend to have multiple mental health problems, not solely cannabis problems,” Dr. Moffitt commented.
Emir Englund, PhD, also from King’s College London, said the study “strengthens an already well-established association between the two. However, it is unable to shed additional light on whether cannabis causes schizophrenia or not, due to the observational nature of the study.”
“In my opinion, the current scientific view of cannabis use as a ‘component cause’ which interacts with other risk factors to cause schizophrenia but is neither necessary nor sufficient to do so on its own still stands,” Dr. Englund said.
The study was supported by a grant from Lundbeckfonden. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. VanderWeele has received grants from the National Cancer Institute and the John Templeton Foundation. Dr. Moffitt and Dr. Englund have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The long-observed association between cannabis use and schizophrenia is likely partially causal in nature, new research shows.
Investigators found a clear increase in the proportion of schizophrenia cases linked to cannabis use disorder over the past 25 years.
“In my view, the association is most likely causative, at least to a large extent,” first author Carsten Hjorthøj, PhD, from the Copenhagen Research Center for Mental Health, Copenhagen University Hospital, told this news organization.
“It is, of course, nearly impossible to use epidemiological studies to actually prove causation, but all the numbers behave exactly in the way that would be expected under the theory of causation,” said Dr. Hjorthøj.
The study was published online July 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Far from harmless
The findings are based on Danish national health registry data. The study sample included all people in Denmark born before Dec. 31, 2000 who were aged 16 years or older at some point from Jan. 1, 1972 to Dec. 31, 2016. The data analysis was conducted from August 2020 to April 2021.
Despite some fluctuation, there was a general increase in the population-attributable risk fraction (PARF) for cannabis use disorder with regard to schizophrenia over time, the researchers report. The PARF increased from about 2% in 1995 to about 4% in 2000 and has hovered from 6% to 8% since 2010.
“Although not in itself proof of causality, our study provides evidence of the theory of cannabis being a component cause of schizophrenia,” the investigators write.
The findings are “particularly important with the increasing legalization of cannabis for both medicinal and recreational uses seeming to lead to an increase in the perception of cannabis as relatively harmless and possibly in the uptake of cannabis use, especially among youth,” they add.
“Although psychosis is not the only outcome of interest in terms of cannabis use, our study clearly indicates that cannabis should not be considered harmless,” they conclude.
Cases linked to cannabis underestimated?
In an accompanying editorial, Tyler VanderWeele, PhD, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, notes that estimates in this study could be conservative as a result of underdiagnosis of cannabis use disorder and because it only examined cannabis use disorder.
“Cannabis use disorder is not responsible for most schizophrenia cases, but it is responsible for a nonnegligible and increasing proportion. This should be considered in discussions regarding legalization and regulation of the use of cannabis,” Dr. VanderWeele writes.
Experts with the Science Media Center, a U.K. nonprofit organization, also weighed in on the results.
Terrie Moffitt, PhD, with King’s College London, said the study “adds important evidence that patients with diagnosed cannabis use disorder are more at risk for psychosis now than they used to be.”
“ However, most cannabis users, even those who are dependent on it, never come in to clinics for treatment. Also, it is known that people who seek treatment tend to have multiple mental health problems, not solely cannabis problems,” Dr. Moffitt commented.
Emir Englund, PhD, also from King’s College London, said the study “strengthens an already well-established association between the two. However, it is unable to shed additional light on whether cannabis causes schizophrenia or not, due to the observational nature of the study.”
“In my opinion, the current scientific view of cannabis use as a ‘component cause’ which interacts with other risk factors to cause schizophrenia but is neither necessary nor sufficient to do so on its own still stands,” Dr. Englund said.
The study was supported by a grant from Lundbeckfonden. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. VanderWeele has received grants from the National Cancer Institute and the John Templeton Foundation. Dr. Moffitt and Dr. Englund have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood deprivation affects later executive function
Exposure to deprivation in early life was significantly associated with impaired executive functioning in children and adolescents, based on data from a systematic review and meta-analysis of 91 studies.
Previous research has shown connections between early-life adversity (ELA) and changes in psychological, cognitive, and neurobiological development, including increased risk of anxiety, depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, suicidality, and substance use disorder; however, research focusing on the associations between different types of ELA and specific processes is limited, wrote Dylan Johnson, MSc, of the University of Toronto and colleagues.
“We directly addressed this gap in the literature by examining the association between the type of ELA and executive functioning in children and youth,” they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 91 articles including 82 unique cohorts and 31,188 unique individuals aged 1-18 years.
The articles were selected from Embase, ERIC, MEDLINE, and PsycInfo databases and published up to Dec. 31, 2020. The primary outcomes were measures of the three domains of executive functioning: cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, and working memory. To correct for small sample sizes in some studies, the researchers standardized their measures of association into Hedges g effect sizes.
Overall, the pooled estimates of the association of any childhood adversity with the three domains of executive functioning showed significant heterogeneity, with Hedges g effects of –0.49 for cognitive flexibility, –0.39 for inhibitory control, and –0.47 for working memory.
The researchers also examined a subsample of ELA–executive functioning associations in categories of early-life exposure to threat, compared with early-life deprivation, including 56 of the original 91 articles. In this analysis, significantly lower inhibitory control was associated with deprivation compared to threat (Hedges g –0.43 vs. –0.27). Similarly, significantly lower working memory was associated with deprivation, compared with threat (Hedges g –0.54 vs. Hedges g –0.28). For both inhibitory control and working memory, the association of adversity was not moderated by the age or sex of the study participants, study design, outcome quality, or selection quality, the researchers noted.
No significant difference in affect of exposure threat vs. deprivation was noted for the association with cognitive flexibility. The reason for this discrepancy remains unclear, the researchers said. “Some evidence suggests that individuals who grow up in unpredictable environments may have reduced inhibitory control but enhanced cognitive flexibility,” they noted.
However, the overall results suggest that exposure to deprivation may be associated with neurodevelopmental changes that support the development of executive functioning, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the substantial heterogeneity in the pooled estimates and the need to consider variation in study design, the researchers noted. In addition, the cross-sectional design of many studies prevented conclusions about causality between ELA and executive functioning, they said.
“Future research should explore the differences between threat and deprivation when emotionally salient executive functioning measures are used,” the researchers emphasized. “Threat experiences are often associated with alterations in emotional processing, and different findings may be observed when investigating emotionally salient executive functioning outcomes,” they concluded.
Prevention and intervention plans needed
“Although numerous studies have examined associations between ELA and executive functioning, the associations of threat and deprivation with specific executive functioning domains (e.g., cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, and working memory) have not been explored comprehensively,” wrote Beth S. Slomine, PhD, and Nikeea Copeland-Linder, PhD, of the Kennedy Krieger Institute, Johns Hopkins University School, Baltimore, in an accompanying editorial.
The study is “critical and timely” because of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on children’s exposure to deprivation, the authors said. “Many children have experienced the death of family members or friends, food and housing insecurity owing to the economic recession, school closures, loss of critical support services, and increased isolation because of social distancing measures,” and these effects are even greater for children already living in poverty and those with developmental disabilities, they noted.
More resources are needed to develop and implement ELA prevention policies, as well as early intervention plans, the editorialists said.
“Early intervention programs have a great potential to reduce the risk of ELA and promote executive functioning development,” they said. “These programs, such as family support and preschool services, are viable solutions for children and their families,” they added. Although the pandemic prevented the use of many support services for children at risk, the adoption of telehealth technology means that “it is now more feasible for cognitive rehabilitation experts to implement the telehealth technology to train parents and school staff on how to assist with the delivery of interventions in real-world settings and how to promote executive functioning in daily life,” they noted.
Overall, the study findings highlight the urgency of identifying ELA and implementing strategies to reduce and prevent ELA, and to provide early intervention to mitigate the impact of ELA on executive function in children, the editorialists emphasized.
Data bring understanding, but barriers remain
“At this point, there are data demonstrating the significant impact that adverse childhood experiences have on health outcomes – from worsened mental health to an increased risk for cancer and diabetes,” said Kelly A. Curran, MD, of the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, in an interview.
“Physicians – myself included – tend to lump all these experiences together when thinking about future health outcomes,” Dr. Curran said. “However, there are evolving data that neurocognitive outcomes may be different based on the type of early-life adversity experienced. This meta-analysis examines the risk of different neurocognitive impact of threat versus deprivation types of adversity, which is important to pediatricians because it helps us to better understand the risks that our patients may experience,” she explained.
“The results of this meta-analysis were especially intriguing because I hadn’t previously considered the impact that different types of adversity had on neurocognitive development,” said Dr. Curran. “This study caused me to think about these experiences differently, and as I reflect on the patients I have cared for over the years, I can see the difference in their outcomes,” she said.
Many barriers persist in addressing the effects of early-life deprivation on executive function, Dr. Curran said.
“First are barriers around identification of these children and adolescents, who may not have regular contact with the medical system. Additionally, it’s important to provide resources for parents and caregivers – this includes creating a strong support network and providing education about the impact of these experiences,” she noted. “There are also barriers to identifying and connecting with what resources will help children at risk of poor neurodevelopmental outcomes,” she added.
“Now that we know that children who have experienced early-life deprivation are at increased risk of worsened neurodevelopmental outcomes, it will be important to understand what interventions can help improve their outcomes,” Dr. Curran said.
The study was supported by a Connaught New Researcher Award from the University of Toronto. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Slomine disclosed book royalties from Cambridge University Press unrelated to this study. Dr. Curran had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Exposure to deprivation in early life was significantly associated with impaired executive functioning in children and adolescents, based on data from a systematic review and meta-analysis of 91 studies.
Previous research has shown connections between early-life adversity (ELA) and changes in psychological, cognitive, and neurobiological development, including increased risk of anxiety, depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, suicidality, and substance use disorder; however, research focusing on the associations between different types of ELA and specific processes is limited, wrote Dylan Johnson, MSc, of the University of Toronto and colleagues.
“We directly addressed this gap in the literature by examining the association between the type of ELA and executive functioning in children and youth,” they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 91 articles including 82 unique cohorts and 31,188 unique individuals aged 1-18 years.
The articles were selected from Embase, ERIC, MEDLINE, and PsycInfo databases and published up to Dec. 31, 2020. The primary outcomes were measures of the three domains of executive functioning: cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, and working memory. To correct for small sample sizes in some studies, the researchers standardized their measures of association into Hedges g effect sizes.
Overall, the pooled estimates of the association of any childhood adversity with the three domains of executive functioning showed significant heterogeneity, with Hedges g effects of –0.49 for cognitive flexibility, –0.39 for inhibitory control, and –0.47 for working memory.
The researchers also examined a subsample of ELA–executive functioning associations in categories of early-life exposure to threat, compared with early-life deprivation, including 56 of the original 91 articles. In this analysis, significantly lower inhibitory control was associated with deprivation compared to threat (Hedges g –0.43 vs. –0.27). Similarly, significantly lower working memory was associated with deprivation, compared with threat (Hedges g –0.54 vs. Hedges g –0.28). For both inhibitory control and working memory, the association of adversity was not moderated by the age or sex of the study participants, study design, outcome quality, or selection quality, the researchers noted.
No significant difference in affect of exposure threat vs. deprivation was noted for the association with cognitive flexibility. The reason for this discrepancy remains unclear, the researchers said. “Some evidence suggests that individuals who grow up in unpredictable environments may have reduced inhibitory control but enhanced cognitive flexibility,” they noted.
However, the overall results suggest that exposure to deprivation may be associated with neurodevelopmental changes that support the development of executive functioning, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the substantial heterogeneity in the pooled estimates and the need to consider variation in study design, the researchers noted. In addition, the cross-sectional design of many studies prevented conclusions about causality between ELA and executive functioning, they said.
“Future research should explore the differences between threat and deprivation when emotionally salient executive functioning measures are used,” the researchers emphasized. “Threat experiences are often associated with alterations in emotional processing, and different findings may be observed when investigating emotionally salient executive functioning outcomes,” they concluded.
Prevention and intervention plans needed
“Although numerous studies have examined associations between ELA and executive functioning, the associations of threat and deprivation with specific executive functioning domains (e.g., cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, and working memory) have not been explored comprehensively,” wrote Beth S. Slomine, PhD, and Nikeea Copeland-Linder, PhD, of the Kennedy Krieger Institute, Johns Hopkins University School, Baltimore, in an accompanying editorial.
The study is “critical and timely” because of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on children’s exposure to deprivation, the authors said. “Many children have experienced the death of family members or friends, food and housing insecurity owing to the economic recession, school closures, loss of critical support services, and increased isolation because of social distancing measures,” and these effects are even greater for children already living in poverty and those with developmental disabilities, they noted.
More resources are needed to develop and implement ELA prevention policies, as well as early intervention plans, the editorialists said.
“Early intervention programs have a great potential to reduce the risk of ELA and promote executive functioning development,” they said. “These programs, such as family support and preschool services, are viable solutions for children and their families,” they added. Although the pandemic prevented the use of many support services for children at risk, the adoption of telehealth technology means that “it is now more feasible for cognitive rehabilitation experts to implement the telehealth technology to train parents and school staff on how to assist with the delivery of interventions in real-world settings and how to promote executive functioning in daily life,” they noted.
Overall, the study findings highlight the urgency of identifying ELA and implementing strategies to reduce and prevent ELA, and to provide early intervention to mitigate the impact of ELA on executive function in children, the editorialists emphasized.
Data bring understanding, but barriers remain
“At this point, there are data demonstrating the significant impact that adverse childhood experiences have on health outcomes – from worsened mental health to an increased risk for cancer and diabetes,” said Kelly A. Curran, MD, of the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, in an interview.
“Physicians – myself included – tend to lump all these experiences together when thinking about future health outcomes,” Dr. Curran said. “However, there are evolving data that neurocognitive outcomes may be different based on the type of early-life adversity experienced. This meta-analysis examines the risk of different neurocognitive impact of threat versus deprivation types of adversity, which is important to pediatricians because it helps us to better understand the risks that our patients may experience,” she explained.
“The results of this meta-analysis were especially intriguing because I hadn’t previously considered the impact that different types of adversity had on neurocognitive development,” said Dr. Curran. “This study caused me to think about these experiences differently, and as I reflect on the patients I have cared for over the years, I can see the difference in their outcomes,” she said.
Many barriers persist in addressing the effects of early-life deprivation on executive function, Dr. Curran said.
“First are barriers around identification of these children and adolescents, who may not have regular contact with the medical system. Additionally, it’s important to provide resources for parents and caregivers – this includes creating a strong support network and providing education about the impact of these experiences,” she noted. “There are also barriers to identifying and connecting with what resources will help children at risk of poor neurodevelopmental outcomes,” she added.
“Now that we know that children who have experienced early-life deprivation are at increased risk of worsened neurodevelopmental outcomes, it will be important to understand what interventions can help improve their outcomes,” Dr. Curran said.
The study was supported by a Connaught New Researcher Award from the University of Toronto. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Slomine disclosed book royalties from Cambridge University Press unrelated to this study. Dr. Curran had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Exposure to deprivation in early life was significantly associated with impaired executive functioning in children and adolescents, based on data from a systematic review and meta-analysis of 91 studies.
Previous research has shown connections between early-life adversity (ELA) and changes in psychological, cognitive, and neurobiological development, including increased risk of anxiety, depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, suicidality, and substance use disorder; however, research focusing on the associations between different types of ELA and specific processes is limited, wrote Dylan Johnson, MSc, of the University of Toronto and colleagues.
“We directly addressed this gap in the literature by examining the association between the type of ELA and executive functioning in children and youth,” they said.
In a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 91 articles including 82 unique cohorts and 31,188 unique individuals aged 1-18 years.
The articles were selected from Embase, ERIC, MEDLINE, and PsycInfo databases and published up to Dec. 31, 2020. The primary outcomes were measures of the three domains of executive functioning: cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, and working memory. To correct for small sample sizes in some studies, the researchers standardized their measures of association into Hedges g effect sizes.
Overall, the pooled estimates of the association of any childhood adversity with the three domains of executive functioning showed significant heterogeneity, with Hedges g effects of –0.49 for cognitive flexibility, –0.39 for inhibitory control, and –0.47 for working memory.
The researchers also examined a subsample of ELA–executive functioning associations in categories of early-life exposure to threat, compared with early-life deprivation, including 56 of the original 91 articles. In this analysis, significantly lower inhibitory control was associated with deprivation compared to threat (Hedges g –0.43 vs. –0.27). Similarly, significantly lower working memory was associated with deprivation, compared with threat (Hedges g –0.54 vs. Hedges g –0.28). For both inhibitory control and working memory, the association of adversity was not moderated by the age or sex of the study participants, study design, outcome quality, or selection quality, the researchers noted.
No significant difference in affect of exposure threat vs. deprivation was noted for the association with cognitive flexibility. The reason for this discrepancy remains unclear, the researchers said. “Some evidence suggests that individuals who grow up in unpredictable environments may have reduced inhibitory control but enhanced cognitive flexibility,” they noted.
However, the overall results suggest that exposure to deprivation may be associated with neurodevelopmental changes that support the development of executive functioning, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the substantial heterogeneity in the pooled estimates and the need to consider variation in study design, the researchers noted. In addition, the cross-sectional design of many studies prevented conclusions about causality between ELA and executive functioning, they said.
“Future research should explore the differences between threat and deprivation when emotionally salient executive functioning measures are used,” the researchers emphasized. “Threat experiences are often associated with alterations in emotional processing, and different findings may be observed when investigating emotionally salient executive functioning outcomes,” they concluded.
Prevention and intervention plans needed
“Although numerous studies have examined associations between ELA and executive functioning, the associations of threat and deprivation with specific executive functioning domains (e.g., cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control, and working memory) have not been explored comprehensively,” wrote Beth S. Slomine, PhD, and Nikeea Copeland-Linder, PhD, of the Kennedy Krieger Institute, Johns Hopkins University School, Baltimore, in an accompanying editorial.
The study is “critical and timely” because of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on children’s exposure to deprivation, the authors said. “Many children have experienced the death of family members or friends, food and housing insecurity owing to the economic recession, school closures, loss of critical support services, and increased isolation because of social distancing measures,” and these effects are even greater for children already living in poverty and those with developmental disabilities, they noted.
More resources are needed to develop and implement ELA prevention policies, as well as early intervention plans, the editorialists said.
“Early intervention programs have a great potential to reduce the risk of ELA and promote executive functioning development,” they said. “These programs, such as family support and preschool services, are viable solutions for children and their families,” they added. Although the pandemic prevented the use of many support services for children at risk, the adoption of telehealth technology means that “it is now more feasible for cognitive rehabilitation experts to implement the telehealth technology to train parents and school staff on how to assist with the delivery of interventions in real-world settings and how to promote executive functioning in daily life,” they noted.
Overall, the study findings highlight the urgency of identifying ELA and implementing strategies to reduce and prevent ELA, and to provide early intervention to mitigate the impact of ELA on executive function in children, the editorialists emphasized.
Data bring understanding, but barriers remain
“At this point, there are data demonstrating the significant impact that adverse childhood experiences have on health outcomes – from worsened mental health to an increased risk for cancer and diabetes,” said Kelly A. Curran, MD, of the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, in an interview.
“Physicians – myself included – tend to lump all these experiences together when thinking about future health outcomes,” Dr. Curran said. “However, there are evolving data that neurocognitive outcomes may be different based on the type of early-life adversity experienced. This meta-analysis examines the risk of different neurocognitive impact of threat versus deprivation types of adversity, which is important to pediatricians because it helps us to better understand the risks that our patients may experience,” she explained.
“The results of this meta-analysis were especially intriguing because I hadn’t previously considered the impact that different types of adversity had on neurocognitive development,” said Dr. Curran. “This study caused me to think about these experiences differently, and as I reflect on the patients I have cared for over the years, I can see the difference in their outcomes,” she said.
Many barriers persist in addressing the effects of early-life deprivation on executive function, Dr. Curran said.
“First are barriers around identification of these children and adolescents, who may not have regular contact with the medical system. Additionally, it’s important to provide resources for parents and caregivers – this includes creating a strong support network and providing education about the impact of these experiences,” she noted. “There are also barriers to identifying and connecting with what resources will help children at risk of poor neurodevelopmental outcomes,” she added.
“Now that we know that children who have experienced early-life deprivation are at increased risk of worsened neurodevelopmental outcomes, it will be important to understand what interventions can help improve their outcomes,” Dr. Curran said.
The study was supported by a Connaught New Researcher Award from the University of Toronto. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Dr. Slomine disclosed book royalties from Cambridge University Press unrelated to this study. Dr. Curran had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Church-based services may help close gaps in mental health care
Black individuals who received mental health services through a church-based program reported high levels of satisfaction, data from a small, qualitative study show.
“This model of providing mental health services adjacent to or supported by a trusted institution, with providers who may have a more nuanced and intimate knowledge of the experiences of and perceptions held by community members, may facilitate important therapy-mediating factors, such as trust,” wrote Angela Coombs, MD, of Columbia University, New York, and colleagues.
Black Americans continue to face barriers to mental health services, and fewer than one-third of Black Americans with a mental health condition receive formal mental health care, Dr. Coombs and colleagues reported. Barriers to treatment include stigma and distrust of medical institutions, and strategies are needed to address these barriers to improve access. Consequently, “one approach includes the development of mental health programming and supports with trusted institutions, such as churches,” they said. Data are limited, however, on the perspectives of individuals who have used church-based services.
In the study, published in Psychiatric Services, Dr. Coombs and colleagues recruited 15 adults aged 27-69 years who were receiving or had received mental health services at the HOPE (Healing On Purpose and Evolving) Center, a freestanding mental health clinic affiliated with the First Corinthian Baptist Church in Harlem, New York. At the time of the study in 2019, those attending the center (referred to as “innovators” rather than patients or clients to reduce stigma) received 10 free sessions of evidence-based psychotherapy.
Treatment included cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), religiously integrated CBT, and interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) to individuals, couples, and families. Group psychotherapy also was an option. Clinicians at the HOPE Center included licensed social workers with doctoral and master’s-level degrees, as well as supervised social work student interns.
Study participants took part in a 30-minute interview, in person or by phone, with a female psychiatrist who was not employed by the HOPE Center or involved in treating the patients. There were 15 participants: 13 women and 2 men, with mean ages of 48 and 51 years, respectively; 14 identified as Black, non-Hispanic. Most (13 individuals) identified as heterosexual, 11 had never married, and 14 had some college or technical school education.
Notably, 11 participants reported attending church once a week, and 13 said they considered religion or spirituality highly important. Participants “reported that services that could integrate their spiritual beliefs with their current mental health challenges enhanced the therapeutic experience,” the researchers said.
Positive messaging about mental health care from the church and senior pastor also encouraged the participants to take advantage of the HOPE Center services.
As one participant said, “I’ve always believed that I can handle my own issues ... but listening to the pastor always talking about the [HOPE] Center and not to be ashamed if you have weaknesses, that’s when I said, ‘You know what, let me just start seeking mental health services because I really need [them].’ ”
, including recognizing cycles of unproductive behavior, processing traumatic experiences and learning self-love, and embracing meditation at home.
“A common theme among participants was that the HOPE Center provided them with tools to destress, process trauma, and manage anxiety,” the researchers wrote. In particular, several participants cited group sessions on teaching and practicing mindfulness as their favorite services. They described the HOPE Center as a positive, peaceful, and welcoming environment where they felt safe.
Cost issues were important as well. Participants noted that the HOPE Center’s ability to provide services that were free made it easier for them to attend. “Although participants said that it was helpful that the HOPE Center provided referrals to external providers and agencies for additional services, some said they wished that the HOPE Center would provide long-term therapy,” the researchers noted.
Overall, “most participants said that establishing more mental health resources within faith-based spaces could accelerate normalization of seeking and receiving mental health care within religious Black communities,” they said.
The study findings were limited by the absence of clinical data – and data on participants’ frequency and location of church attendance, the researchers noted. In addition, the positive results could be tied to selection bias, Dr. Coombs and colleagues said. Another possible limitation is the overrepresentation of cisgender women among the participants. Still, “the perspectives shared by participants suggest that this model of care may address several important barriers to care faced by some Black American populations,” the researchers wrote.
Bridging gap between spirituality and mental health
In an interview, Atasha Jordan, MD, said Black Americans with mental illnesses have long lacked equal access to mental health services. “However, in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, published studies have shown that rates of mental illness increased concurrently with a rise in spirituality and faith. That said, we currently live in a time where mental health and spirituality are more likely to intersect,” noted Dr. Jordan, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She said it is not surprising that the study participants felt more comfortable receiving mental health services at a clinic that was church affiliated.
“We have known for years that people of faith are more likely to seek comfort for psychological distress from clergy, rather than mental health professionals. Providing a more familiar entry point to mental health services through a church-affiliated mental health clinic helps to bridge the existing gap between spirituality and mental health,” Dr. Jordan said. “For many Black Americans, spirituality is a central component of culturally-informed mental health care.
“Mental health providers may find improved service utilization and outcomes for their patients by collaborating with faith-based organizations or investing time to learn spiritually-based psychotherapies.”
Recently published data, notably a study published May 1, 2021, in Psychiatric Services, continue to support the existing knowledge “that many patients with psychiatric illnesses want increased attention paid to spirituality during their mental health care,” Dr. Jordan noted. “Moreover, they showed that nonreligious clinicians may be more apt than religious clinicians to provide objective, spiritually-oriented mental health care. In this vein, further research aimed at understanding the most effective methods to address spiritual health in times of mental distress can help all mental health providers better meet their patients’ psychiatric and psychological needs.”
Overcoming stigma, mistrust
During the pandemic, clinicians have seen an increase in mental health distress in the form of anxiety, depression, and trauma symptoms, Lorenzo Norris, MD, of George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview.
“Historically, African Americans have faced numerous barriers to mental health care, including stigma and mistrust of medical institutions,” Dr. Norris said. “At this time, perhaps more than in recent decades, novel ways of eliminating and navigating these barriers must be explored in an evidence-based fashion that will inform future interventions.”
Dr. Norris also found that the study findings make sense.
“Historically, the Black church has been a central institution in the community,” he said. “In my personal experience, the church served in a variety of roles, including but not limited to advocacy, employment, social services, peer support, and notably a trusted source of advice pertaining to health. In addition, Black churches may be in an ideal position to serve as culturally sensitive facilitators to build trust,” he said.
The study’s message for clinicians, according to Dr. Norris, is to “carefully consider partnering with faith-based organizations and community leaders if you want to supplement your efforts at decreasing mental health care disparities in the African American community.”
He pointed out, however, that in addition to the small number of participants, the study did not examine clinical outcomes. “So we must be careful how much we take from the initial conclusions,” Dr. Norris said.
Additional research is needed on a much larger scale to add support to the study findings, he said. “This study focused on one church and its particular program,” Dr. Norris noted. “There is likely a great deal of heterogeneity with Black churches and definitely among church members they serve,” he said. “Although it may be tempting to go with an ‘of course it will work’ approach, it is best to have additional qualitative and quantitative research of a much larger scale, with clinical controls that examine the ability of Black churches to address barriers African Americans face in receiving and utilizing mental health services,” he concluded.
Dr. Jordan disclosed receiving a 2021-2022 American Psychiatric Association/Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Minority Fellowship Program grant to study mental health literacy in the Black church. Dr. Norris disclosed serving as CEO of the Cleveland Clergy Alliance, a nonprofit organization providing outreach assistance as a mechanism to help seniors and the disabled population through community programming. The study authors reported no disclosures.
Black individuals who received mental health services through a church-based program reported high levels of satisfaction, data from a small, qualitative study show.
“This model of providing mental health services adjacent to or supported by a trusted institution, with providers who may have a more nuanced and intimate knowledge of the experiences of and perceptions held by community members, may facilitate important therapy-mediating factors, such as trust,” wrote Angela Coombs, MD, of Columbia University, New York, and colleagues.
Black Americans continue to face barriers to mental health services, and fewer than one-third of Black Americans with a mental health condition receive formal mental health care, Dr. Coombs and colleagues reported. Barriers to treatment include stigma and distrust of medical institutions, and strategies are needed to address these barriers to improve access. Consequently, “one approach includes the development of mental health programming and supports with trusted institutions, such as churches,” they said. Data are limited, however, on the perspectives of individuals who have used church-based services.
In the study, published in Psychiatric Services, Dr. Coombs and colleagues recruited 15 adults aged 27-69 years who were receiving or had received mental health services at the HOPE (Healing On Purpose and Evolving) Center, a freestanding mental health clinic affiliated with the First Corinthian Baptist Church in Harlem, New York. At the time of the study in 2019, those attending the center (referred to as “innovators” rather than patients or clients to reduce stigma) received 10 free sessions of evidence-based psychotherapy.
Treatment included cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), religiously integrated CBT, and interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) to individuals, couples, and families. Group psychotherapy also was an option. Clinicians at the HOPE Center included licensed social workers with doctoral and master’s-level degrees, as well as supervised social work student interns.
Study participants took part in a 30-minute interview, in person or by phone, with a female psychiatrist who was not employed by the HOPE Center or involved in treating the patients. There were 15 participants: 13 women and 2 men, with mean ages of 48 and 51 years, respectively; 14 identified as Black, non-Hispanic. Most (13 individuals) identified as heterosexual, 11 had never married, and 14 had some college or technical school education.
Notably, 11 participants reported attending church once a week, and 13 said they considered religion or spirituality highly important. Participants “reported that services that could integrate their spiritual beliefs with their current mental health challenges enhanced the therapeutic experience,” the researchers said.
Positive messaging about mental health care from the church and senior pastor also encouraged the participants to take advantage of the HOPE Center services.
As one participant said, “I’ve always believed that I can handle my own issues ... but listening to the pastor always talking about the [HOPE] Center and not to be ashamed if you have weaknesses, that’s when I said, ‘You know what, let me just start seeking mental health services because I really need [them].’ ”
, including recognizing cycles of unproductive behavior, processing traumatic experiences and learning self-love, and embracing meditation at home.
“A common theme among participants was that the HOPE Center provided them with tools to destress, process trauma, and manage anxiety,” the researchers wrote. In particular, several participants cited group sessions on teaching and practicing mindfulness as their favorite services. They described the HOPE Center as a positive, peaceful, and welcoming environment where they felt safe.
Cost issues were important as well. Participants noted that the HOPE Center’s ability to provide services that were free made it easier for them to attend. “Although participants said that it was helpful that the HOPE Center provided referrals to external providers and agencies for additional services, some said they wished that the HOPE Center would provide long-term therapy,” the researchers noted.
Overall, “most participants said that establishing more mental health resources within faith-based spaces could accelerate normalization of seeking and receiving mental health care within religious Black communities,” they said.
The study findings were limited by the absence of clinical data – and data on participants’ frequency and location of church attendance, the researchers noted. In addition, the positive results could be tied to selection bias, Dr. Coombs and colleagues said. Another possible limitation is the overrepresentation of cisgender women among the participants. Still, “the perspectives shared by participants suggest that this model of care may address several important barriers to care faced by some Black American populations,” the researchers wrote.
Bridging gap between spirituality and mental health
In an interview, Atasha Jordan, MD, said Black Americans with mental illnesses have long lacked equal access to mental health services. “However, in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, published studies have shown that rates of mental illness increased concurrently with a rise in spirituality and faith. That said, we currently live in a time where mental health and spirituality are more likely to intersect,” noted Dr. Jordan, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She said it is not surprising that the study participants felt more comfortable receiving mental health services at a clinic that was church affiliated.
“We have known for years that people of faith are more likely to seek comfort for psychological distress from clergy, rather than mental health professionals. Providing a more familiar entry point to mental health services through a church-affiliated mental health clinic helps to bridge the existing gap between spirituality and mental health,” Dr. Jordan said. “For many Black Americans, spirituality is a central component of culturally-informed mental health care.
“Mental health providers may find improved service utilization and outcomes for their patients by collaborating with faith-based organizations or investing time to learn spiritually-based psychotherapies.”
Recently published data, notably a study published May 1, 2021, in Psychiatric Services, continue to support the existing knowledge “that many patients with psychiatric illnesses want increased attention paid to spirituality during their mental health care,” Dr. Jordan noted. “Moreover, they showed that nonreligious clinicians may be more apt than religious clinicians to provide objective, spiritually-oriented mental health care. In this vein, further research aimed at understanding the most effective methods to address spiritual health in times of mental distress can help all mental health providers better meet their patients’ psychiatric and psychological needs.”
Overcoming stigma, mistrust
During the pandemic, clinicians have seen an increase in mental health distress in the form of anxiety, depression, and trauma symptoms, Lorenzo Norris, MD, of George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview.
“Historically, African Americans have faced numerous barriers to mental health care, including stigma and mistrust of medical institutions,” Dr. Norris said. “At this time, perhaps more than in recent decades, novel ways of eliminating and navigating these barriers must be explored in an evidence-based fashion that will inform future interventions.”
Dr. Norris also found that the study findings make sense.
“Historically, the Black church has been a central institution in the community,” he said. “In my personal experience, the church served in a variety of roles, including but not limited to advocacy, employment, social services, peer support, and notably a trusted source of advice pertaining to health. In addition, Black churches may be in an ideal position to serve as culturally sensitive facilitators to build trust,” he said.
The study’s message for clinicians, according to Dr. Norris, is to “carefully consider partnering with faith-based organizations and community leaders if you want to supplement your efforts at decreasing mental health care disparities in the African American community.”
He pointed out, however, that in addition to the small number of participants, the study did not examine clinical outcomes. “So we must be careful how much we take from the initial conclusions,” Dr. Norris said.
Additional research is needed on a much larger scale to add support to the study findings, he said. “This study focused on one church and its particular program,” Dr. Norris noted. “There is likely a great deal of heterogeneity with Black churches and definitely among church members they serve,” he said. “Although it may be tempting to go with an ‘of course it will work’ approach, it is best to have additional qualitative and quantitative research of a much larger scale, with clinical controls that examine the ability of Black churches to address barriers African Americans face in receiving and utilizing mental health services,” he concluded.
Dr. Jordan disclosed receiving a 2021-2022 American Psychiatric Association/Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Minority Fellowship Program grant to study mental health literacy in the Black church. Dr. Norris disclosed serving as CEO of the Cleveland Clergy Alliance, a nonprofit organization providing outreach assistance as a mechanism to help seniors and the disabled population through community programming. The study authors reported no disclosures.
Black individuals who received mental health services through a church-based program reported high levels of satisfaction, data from a small, qualitative study show.
“This model of providing mental health services adjacent to or supported by a trusted institution, with providers who may have a more nuanced and intimate knowledge of the experiences of and perceptions held by community members, may facilitate important therapy-mediating factors, such as trust,” wrote Angela Coombs, MD, of Columbia University, New York, and colleagues.
Black Americans continue to face barriers to mental health services, and fewer than one-third of Black Americans with a mental health condition receive formal mental health care, Dr. Coombs and colleagues reported. Barriers to treatment include stigma and distrust of medical institutions, and strategies are needed to address these barriers to improve access. Consequently, “one approach includes the development of mental health programming and supports with trusted institutions, such as churches,” they said. Data are limited, however, on the perspectives of individuals who have used church-based services.
In the study, published in Psychiatric Services, Dr. Coombs and colleagues recruited 15 adults aged 27-69 years who were receiving or had received mental health services at the HOPE (Healing On Purpose and Evolving) Center, a freestanding mental health clinic affiliated with the First Corinthian Baptist Church in Harlem, New York. At the time of the study in 2019, those attending the center (referred to as “innovators” rather than patients or clients to reduce stigma) received 10 free sessions of evidence-based psychotherapy.
Treatment included cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), religiously integrated CBT, and interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) to individuals, couples, and families. Group psychotherapy also was an option. Clinicians at the HOPE Center included licensed social workers with doctoral and master’s-level degrees, as well as supervised social work student interns.
Study participants took part in a 30-minute interview, in person or by phone, with a female psychiatrist who was not employed by the HOPE Center or involved in treating the patients. There were 15 participants: 13 women and 2 men, with mean ages of 48 and 51 years, respectively; 14 identified as Black, non-Hispanic. Most (13 individuals) identified as heterosexual, 11 had never married, and 14 had some college or technical school education.
Notably, 11 participants reported attending church once a week, and 13 said they considered religion or spirituality highly important. Participants “reported that services that could integrate their spiritual beliefs with their current mental health challenges enhanced the therapeutic experience,” the researchers said.
Positive messaging about mental health care from the church and senior pastor also encouraged the participants to take advantage of the HOPE Center services.
As one participant said, “I’ve always believed that I can handle my own issues ... but listening to the pastor always talking about the [HOPE] Center and not to be ashamed if you have weaknesses, that’s when I said, ‘You know what, let me just start seeking mental health services because I really need [them].’ ”
, including recognizing cycles of unproductive behavior, processing traumatic experiences and learning self-love, and embracing meditation at home.
“A common theme among participants was that the HOPE Center provided them with tools to destress, process trauma, and manage anxiety,” the researchers wrote. In particular, several participants cited group sessions on teaching and practicing mindfulness as their favorite services. They described the HOPE Center as a positive, peaceful, and welcoming environment where they felt safe.
Cost issues were important as well. Participants noted that the HOPE Center’s ability to provide services that were free made it easier for them to attend. “Although participants said that it was helpful that the HOPE Center provided referrals to external providers and agencies for additional services, some said they wished that the HOPE Center would provide long-term therapy,” the researchers noted.
Overall, “most participants said that establishing more mental health resources within faith-based spaces could accelerate normalization of seeking and receiving mental health care within religious Black communities,” they said.
The study findings were limited by the absence of clinical data – and data on participants’ frequency and location of church attendance, the researchers noted. In addition, the positive results could be tied to selection bias, Dr. Coombs and colleagues said. Another possible limitation is the overrepresentation of cisgender women among the participants. Still, “the perspectives shared by participants suggest that this model of care may address several important barriers to care faced by some Black American populations,” the researchers wrote.
Bridging gap between spirituality and mental health
In an interview, Atasha Jordan, MD, said Black Americans with mental illnesses have long lacked equal access to mental health services. “However, in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, published studies have shown that rates of mental illness increased concurrently with a rise in spirituality and faith. That said, we currently live in a time where mental health and spirituality are more likely to intersect,” noted Dr. Jordan, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She said it is not surprising that the study participants felt more comfortable receiving mental health services at a clinic that was church affiliated.
“We have known for years that people of faith are more likely to seek comfort for psychological distress from clergy, rather than mental health professionals. Providing a more familiar entry point to mental health services through a church-affiliated mental health clinic helps to bridge the existing gap between spirituality and mental health,” Dr. Jordan said. “For many Black Americans, spirituality is a central component of culturally-informed mental health care.
“Mental health providers may find improved service utilization and outcomes for their patients by collaborating with faith-based organizations or investing time to learn spiritually-based psychotherapies.”
Recently published data, notably a study published May 1, 2021, in Psychiatric Services, continue to support the existing knowledge “that many patients with psychiatric illnesses want increased attention paid to spirituality during their mental health care,” Dr. Jordan noted. “Moreover, they showed that nonreligious clinicians may be more apt than religious clinicians to provide objective, spiritually-oriented mental health care. In this vein, further research aimed at understanding the most effective methods to address spiritual health in times of mental distress can help all mental health providers better meet their patients’ psychiatric and psychological needs.”
Overcoming stigma, mistrust
During the pandemic, clinicians have seen an increase in mental health distress in the form of anxiety, depression, and trauma symptoms, Lorenzo Norris, MD, of George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview.
“Historically, African Americans have faced numerous barriers to mental health care, including stigma and mistrust of medical institutions,” Dr. Norris said. “At this time, perhaps more than in recent decades, novel ways of eliminating and navigating these barriers must be explored in an evidence-based fashion that will inform future interventions.”
Dr. Norris also found that the study findings make sense.
“Historically, the Black church has been a central institution in the community,” he said. “In my personal experience, the church served in a variety of roles, including but not limited to advocacy, employment, social services, peer support, and notably a trusted source of advice pertaining to health. In addition, Black churches may be in an ideal position to serve as culturally sensitive facilitators to build trust,” he said.
The study’s message for clinicians, according to Dr. Norris, is to “carefully consider partnering with faith-based organizations and community leaders if you want to supplement your efforts at decreasing mental health care disparities in the African American community.”
He pointed out, however, that in addition to the small number of participants, the study did not examine clinical outcomes. “So we must be careful how much we take from the initial conclusions,” Dr. Norris said.
Additional research is needed on a much larger scale to add support to the study findings, he said. “This study focused on one church and its particular program,” Dr. Norris noted. “There is likely a great deal of heterogeneity with Black churches and definitely among church members they serve,” he said. “Although it may be tempting to go with an ‘of course it will work’ approach, it is best to have additional qualitative and quantitative research of a much larger scale, with clinical controls that examine the ability of Black churches to address barriers African Americans face in receiving and utilizing mental health services,” he concluded.
Dr. Jordan disclosed receiving a 2021-2022 American Psychiatric Association/Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Minority Fellowship Program grant to study mental health literacy in the Black church. Dr. Norris disclosed serving as CEO of the Cleveland Clergy Alliance, a nonprofit organization providing outreach assistance as a mechanism to help seniors and the disabled population through community programming. The study authors reported no disclosures.
FROM PSYCHIATRIC SERVICES
Exploring your fishpond: Steps toward managing anxiety in the age of COVID
COVID-19’s ever-changing trajectory has led to a notable rise in anxiety-related disorders in the United States. The average share of U.S. adults reporting symptoms of anxiety and or depressive disorder rose from 11% in 2019 to more than 41% in January 2021, according to a report from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
With the arrival of vaccines, Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center, has noticed a shift in patients’ fears and concerns. In an interview, she explained how anxiety in patients has evolved along with the pandemic. She also offered strategies for gaining control, engaging with community, and managing anxiety.
Question: When you see patients at this point in the pandemic, what do you ask them?
Answer: I ask them how the pandemic has affected them. Responses have changed over time. In the beginning, I saw a lot of fear, dread of the unknown, a lot of frustration about being in lockdown. As the vaccines have come in and taken hold, there is both a sense of relief, but still a lot of anxiety. Part of that is we’re getting different messages and very much changing messages over time. Then there’s the people who are unvaccinated, and we’re also seeing the Delta variant taking hold in the rest of the world. There’s a lot of anxiety, fear, and some depression, although that’s gotten better with the vaccine.
Q: How do we distinguish between reasonable or rational anxiety and excessive or irrational anxiety?
A: There’s not a bright line between them. What’s rational for one person is not rational for another. What we’ve seen is a spectrum. A rational anxiety is: “I’m not ready to go to a party.” Irrational represents all these crazy theories that are made up, such as putting a microchip into your arm with the vaccine so that the government can track you.
Q: How do you talk to these people thinking irrational thoughts?
A: You must listen to them and not just shut them down. Work with them. Many people with irrational thoughts, or believe in conspiracy theories, may not want to go near a psychiatrist. But there’s also the patients in the psychiatric ward who believe COVID doesn’t exist and there’s government plots. Like any other delusional material, we work with this by talking to these patients and using medication as appropriate.
Q: Do you support prescribing medication for those patients who continue to experience anxiety that is irrational?
A: Patients based in inpatient psychiatry are usually delusional. The medication we usually prescribe for these patients is antipsychotics. If it’s an outpatient who’s anxious about COVID, but has rational anxiety, we usually use antidepressants or antianxiety agents such as Zoloft, Paxil, or Lexapro.
Q: What other strategies can psychiatrists share with patients?
A: What I’ve seen throughout COVID is often an overwhelming sense of dread and inability to control the situation. I tell patients to do things they can control. You can go out and get exercise. Especially during the winter, I recommend that people take a walk and get some sunshine.
It also helps with anxiety to reach out and help someone else. Is there a neighbor you’re concerned about? By and large, this is something many communities have done well. The challenge is we’ve been avoiding each other physically for a long time. So, some of the standard ways of helping each other out, like volunteering at a food bank, have been a little problematic. But there are ways to have minimal people on staff to reduce exposure.
One thing I recommend with any type of anxiety is to learn how to control your breathing. Take breaths through the nose several times a day and teach yourself how to slow down. Another thing that helps many people is contact with animals – especially horses, dogs, and cats. You may not be able to adopt an animal, but you could work at a rescue shelter or other facilities. People can benefit from the nonverbal cues of an animal. A friend of mine got a shelter cat. It sleeps with her and licks her when she feels anxious.
Meditation and yoga are also useful. This is not for everyone, but it’s a way to turn down the level of “buzz” or anxiety. Don’t overdo it on caffeine or other things that increase anxiety. I would stay away from illicit drugs, as they increase anxiety.
Q: What do you say to patients to give them a sense of hope?
A: A lot of people aren’t ready to return to normal; they want to keep the social isolation, the masks, the working from home. We need to show patients what they have control over to minimize their own risk. For example, if they want to wear a mask, then they should wear one. Patients also really like the option of telehealth appointments.
Another way to cope is to identify what’s better about the way things are now and concentrate on those improvements. Here in Maryland, the traffic is so much better in the morning than it once was. There are things I don’t miss, like going to the airport and waiting 5 hours for a flight.
Q: What advice can you give psychiatrists who are experiencing anxiety?
A: We must manage our own anxiety so we can help our patients. Strategies I’ve mentioned are also helpful to psychiatrists or other health care professionals (such as) taking a walk, getting exercise, controlling what you can control. For me, it’s getting dressed, going to work, seeing patients. Having a daily structure, a routine, is important. Many people struggled with this at first. They were working from home and didn’t get much done; they did too much videogaming. It helps to set regular appointments if you’re working from home.
Pre-COVID, many of us got a lot out of our professional meetings. We saw friends there. Now they’re either canceled or we’re doing them virtually, which isn’t the same thing. I think our profession could do a better job of reaching out to each other. We’re used to seeing each other once or twice a year at conventions. I’ve since found it hard to reach out to my colleagues via email. And everyone is tired of Zoom.
If they’re local, ask them to do a safe outdoor activity, a happy hour, a walk. If they’re not, maybe engage with them through a postcard or a phone call.
My colleagues and I go for walks at lunch. There’s a fishpond nearby and we talk to the fish and get a little silly. We sometimes take fish nets with us. People ask what the fish nets are for and we’ll say, “we’re chasing COVID away.”
Dr. Ritchie reported no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19’s ever-changing trajectory has led to a notable rise in anxiety-related disorders in the United States. The average share of U.S. adults reporting symptoms of anxiety and or depressive disorder rose from 11% in 2019 to more than 41% in January 2021, according to a report from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
With the arrival of vaccines, Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center, has noticed a shift in patients’ fears and concerns. In an interview, she explained how anxiety in patients has evolved along with the pandemic. She also offered strategies for gaining control, engaging with community, and managing anxiety.
Question: When you see patients at this point in the pandemic, what do you ask them?
Answer: I ask them how the pandemic has affected them. Responses have changed over time. In the beginning, I saw a lot of fear, dread of the unknown, a lot of frustration about being in lockdown. As the vaccines have come in and taken hold, there is both a sense of relief, but still a lot of anxiety. Part of that is we’re getting different messages and very much changing messages over time. Then there’s the people who are unvaccinated, and we’re also seeing the Delta variant taking hold in the rest of the world. There’s a lot of anxiety, fear, and some depression, although that’s gotten better with the vaccine.
Q: How do we distinguish between reasonable or rational anxiety and excessive or irrational anxiety?
A: There’s not a bright line between them. What’s rational for one person is not rational for another. What we’ve seen is a spectrum. A rational anxiety is: “I’m not ready to go to a party.” Irrational represents all these crazy theories that are made up, such as putting a microchip into your arm with the vaccine so that the government can track you.
Q: How do you talk to these people thinking irrational thoughts?
A: You must listen to them and not just shut them down. Work with them. Many people with irrational thoughts, or believe in conspiracy theories, may not want to go near a psychiatrist. But there’s also the patients in the psychiatric ward who believe COVID doesn’t exist and there’s government plots. Like any other delusional material, we work with this by talking to these patients and using medication as appropriate.
Q: Do you support prescribing medication for those patients who continue to experience anxiety that is irrational?
A: Patients based in inpatient psychiatry are usually delusional. The medication we usually prescribe for these patients is antipsychotics. If it’s an outpatient who’s anxious about COVID, but has rational anxiety, we usually use antidepressants or antianxiety agents such as Zoloft, Paxil, or Lexapro.
Q: What other strategies can psychiatrists share with patients?
A: What I’ve seen throughout COVID is often an overwhelming sense of dread and inability to control the situation. I tell patients to do things they can control. You can go out and get exercise. Especially during the winter, I recommend that people take a walk and get some sunshine.
It also helps with anxiety to reach out and help someone else. Is there a neighbor you’re concerned about? By and large, this is something many communities have done well. The challenge is we’ve been avoiding each other physically for a long time. So, some of the standard ways of helping each other out, like volunteering at a food bank, have been a little problematic. But there are ways to have minimal people on staff to reduce exposure.
One thing I recommend with any type of anxiety is to learn how to control your breathing. Take breaths through the nose several times a day and teach yourself how to slow down. Another thing that helps many people is contact with animals – especially horses, dogs, and cats. You may not be able to adopt an animal, but you could work at a rescue shelter or other facilities. People can benefit from the nonverbal cues of an animal. A friend of mine got a shelter cat. It sleeps with her and licks her when she feels anxious.
Meditation and yoga are also useful. This is not for everyone, but it’s a way to turn down the level of “buzz” or anxiety. Don’t overdo it on caffeine or other things that increase anxiety. I would stay away from illicit drugs, as they increase anxiety.
Q: What do you say to patients to give them a sense of hope?
A: A lot of people aren’t ready to return to normal; they want to keep the social isolation, the masks, the working from home. We need to show patients what they have control over to minimize their own risk. For example, if they want to wear a mask, then they should wear one. Patients also really like the option of telehealth appointments.
Another way to cope is to identify what’s better about the way things are now and concentrate on those improvements. Here in Maryland, the traffic is so much better in the morning than it once was. There are things I don’t miss, like going to the airport and waiting 5 hours for a flight.
Q: What advice can you give psychiatrists who are experiencing anxiety?
A: We must manage our own anxiety so we can help our patients. Strategies I’ve mentioned are also helpful to psychiatrists or other health care professionals (such as) taking a walk, getting exercise, controlling what you can control. For me, it’s getting dressed, going to work, seeing patients. Having a daily structure, a routine, is important. Many people struggled with this at first. They were working from home and didn’t get much done; they did too much videogaming. It helps to set regular appointments if you’re working from home.
Pre-COVID, many of us got a lot out of our professional meetings. We saw friends there. Now they’re either canceled or we’re doing them virtually, which isn’t the same thing. I think our profession could do a better job of reaching out to each other. We’re used to seeing each other once or twice a year at conventions. I’ve since found it hard to reach out to my colleagues via email. And everyone is tired of Zoom.
If they’re local, ask them to do a safe outdoor activity, a happy hour, a walk. If they’re not, maybe engage with them through a postcard or a phone call.
My colleagues and I go for walks at lunch. There’s a fishpond nearby and we talk to the fish and get a little silly. We sometimes take fish nets with us. People ask what the fish nets are for and we’ll say, “we’re chasing COVID away.”
Dr. Ritchie reported no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19’s ever-changing trajectory has led to a notable rise in anxiety-related disorders in the United States. The average share of U.S. adults reporting symptoms of anxiety and or depressive disorder rose from 11% in 2019 to more than 41% in January 2021, according to a report from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
With the arrival of vaccines, Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, chair of psychiatry at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center, has noticed a shift in patients’ fears and concerns. In an interview, she explained how anxiety in patients has evolved along with the pandemic. She also offered strategies for gaining control, engaging with community, and managing anxiety.
Question: When you see patients at this point in the pandemic, what do you ask them?
Answer: I ask them how the pandemic has affected them. Responses have changed over time. In the beginning, I saw a lot of fear, dread of the unknown, a lot of frustration about being in lockdown. As the vaccines have come in and taken hold, there is both a sense of relief, but still a lot of anxiety. Part of that is we’re getting different messages and very much changing messages over time. Then there’s the people who are unvaccinated, and we’re also seeing the Delta variant taking hold in the rest of the world. There’s a lot of anxiety, fear, and some depression, although that’s gotten better with the vaccine.
Q: How do we distinguish between reasonable or rational anxiety and excessive or irrational anxiety?
A: There’s not a bright line between them. What’s rational for one person is not rational for another. What we’ve seen is a spectrum. A rational anxiety is: “I’m not ready to go to a party.” Irrational represents all these crazy theories that are made up, such as putting a microchip into your arm with the vaccine so that the government can track you.
Q: How do you talk to these people thinking irrational thoughts?
A: You must listen to them and not just shut them down. Work with them. Many people with irrational thoughts, or believe in conspiracy theories, may not want to go near a psychiatrist. But there’s also the patients in the psychiatric ward who believe COVID doesn’t exist and there’s government plots. Like any other delusional material, we work with this by talking to these patients and using medication as appropriate.
Q: Do you support prescribing medication for those patients who continue to experience anxiety that is irrational?
A: Patients based in inpatient psychiatry are usually delusional. The medication we usually prescribe for these patients is antipsychotics. If it’s an outpatient who’s anxious about COVID, but has rational anxiety, we usually use antidepressants or antianxiety agents such as Zoloft, Paxil, or Lexapro.
Q: What other strategies can psychiatrists share with patients?
A: What I’ve seen throughout COVID is often an overwhelming sense of dread and inability to control the situation. I tell patients to do things they can control. You can go out and get exercise. Especially during the winter, I recommend that people take a walk and get some sunshine.
It also helps with anxiety to reach out and help someone else. Is there a neighbor you’re concerned about? By and large, this is something many communities have done well. The challenge is we’ve been avoiding each other physically for a long time. So, some of the standard ways of helping each other out, like volunteering at a food bank, have been a little problematic. But there are ways to have minimal people on staff to reduce exposure.
One thing I recommend with any type of anxiety is to learn how to control your breathing. Take breaths through the nose several times a day and teach yourself how to slow down. Another thing that helps many people is contact with animals – especially horses, dogs, and cats. You may not be able to adopt an animal, but you could work at a rescue shelter or other facilities. People can benefit from the nonverbal cues of an animal. A friend of mine got a shelter cat. It sleeps with her and licks her when she feels anxious.
Meditation and yoga are also useful. This is not for everyone, but it’s a way to turn down the level of “buzz” or anxiety. Don’t overdo it on caffeine or other things that increase anxiety. I would stay away from illicit drugs, as they increase anxiety.
Q: What do you say to patients to give them a sense of hope?
A: A lot of people aren’t ready to return to normal; they want to keep the social isolation, the masks, the working from home. We need to show patients what they have control over to minimize their own risk. For example, if they want to wear a mask, then they should wear one. Patients also really like the option of telehealth appointments.
Another way to cope is to identify what’s better about the way things are now and concentrate on those improvements. Here in Maryland, the traffic is so much better in the morning than it once was. There are things I don’t miss, like going to the airport and waiting 5 hours for a flight.
Q: What advice can you give psychiatrists who are experiencing anxiety?
A: We must manage our own anxiety so we can help our patients. Strategies I’ve mentioned are also helpful to psychiatrists or other health care professionals (such as) taking a walk, getting exercise, controlling what you can control. For me, it’s getting dressed, going to work, seeing patients. Having a daily structure, a routine, is important. Many people struggled with this at first. They were working from home and didn’t get much done; they did too much videogaming. It helps to set regular appointments if you’re working from home.
Pre-COVID, many of us got a lot out of our professional meetings. We saw friends there. Now they’re either canceled or we’re doing them virtually, which isn’t the same thing. I think our profession could do a better job of reaching out to each other. We’re used to seeing each other once or twice a year at conventions. I’ve since found it hard to reach out to my colleagues via email. And everyone is tired of Zoom.
If they’re local, ask them to do a safe outdoor activity, a happy hour, a walk. If they’re not, maybe engage with them through a postcard or a phone call.
My colleagues and I go for walks at lunch. There’s a fishpond nearby and we talk to the fish and get a little silly. We sometimes take fish nets with us. People ask what the fish nets are for and we’ll say, “we’re chasing COVID away.”
Dr. Ritchie reported no conflicts of interest.
Rising meth-related heart failure admissions a ‘crisis,’ costly for society
Rates of heart failure (HF) caused by methamphetamine abuse are climbing quickly in the western United States, at great financial and societal cost, suggests an analysis that documents the trends in California over a recent decade.
In the new study, methamphetamine-associated HF (meth-HF) admissions in the state rose by 585% between 2008 and 2018, and charges related those hospitalizations jumped 840%. Cases of HF unrelated to meth fell by 6% during the same period.
The recent explosion in meth-HF hospitalizations has also been costly for society in general, because most cases are younger adults in their most productive, prime earning years, Susan X. Zhao, MD, Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, Calif., said in an interview.
“Over the past 11 years, especially since 2018, it has really started to take off, with a pretty dramatic rise. And it happened without much attention, because when we think about drugs, we think about acute overdose and not so much about the chronic, smoldering, long-term effects,” said Dr. Zhao, who is lead author on the study published July 13, 2021, in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
“It’s really affecting a section of the population that is not supposed to be having heart failure problems. I think it is going to continue for the next decade until we put a stop to the parent problem, which is methamphetamine,” Dr. Zhao said. “We’re at the beginning, even though the rise has been pretty dramatic. The worst is yet to come.”
Under the radar
Methamphetamine-associated HF has been a growing problem for many years but has largely been “flying under the radar” because HF hospitalization data focus on Medicare-age patients, not the overwhelmingly younger meth-HF population, the report notes.
“We have to get this message out. Many of my patients with meth heart failure had no idea this would happen to them. They didn’t know,” Dr. Zhao said. “Once I tell them that this is what methamphetamines will do to you after years and years of use, they say they wish someone had told them.”
Dr. Zhao and colleagues looked at HF admission data collected by California’s Health and Human Services Agency to assess meth-HF trends and disease burden. They identified 1,033,076 HF hospitalizations during the decade, of which 42,565 (4.12%) were for meth-HF.
Patients hospitalized with meth-HF had a mean age of 49.6 years, compared with 72.2 for the other patients admitted with HF (P < .001). Virtually all of the patients hospitalized for meth-HF were younger than 65 years: 94.5%, compared with 30% for the other HF patients (P < .001).
Hospitalized patients with meth-HF were mostly men, their prevalence of 80% contrasting with 52.4% for patients with non–meth-related HF (P < .001).
Rates of hospitalization for meth-HF steadily increased during the study period. The age-adjusted rate of meth-HF hospitalization per 100,000 rose from 4.1 in 2008 to 28.1 in 2018. The rate of hospitalization for HF unrelated to meth actually declined, going from 342.3 in 2008 to 321.6 in 2018.
Charges for hospitalizations related to meth-HF shot up more than eight times, from $41.5 million in 2008 to $390.2 million in 2018. In contrast, charges for other HF hospitalizations rose by only 82%, from $3.5 billion to $6.3 billion.
Multiple layers of prevention
Dr. Zhao proposed ways that clinicians can communicate with their patients who are using or considering to use meth. “There are multiple layers of prevention. For people who are thinking of using meth, they need to get the message that something really bad can happen to them years down the road. They’re not going to die from it overnight, but it will damage the heart slowly,” she said.
The next layer of prevention can potentially help meth users who have not yet developed heart problems, Dr. Zhao said. “This would be the time to say, ‘you’re so lucky, your heart is still good. It’s time to stop because people like you, a few years from now are going to die prematurely from a very horrible, very suffering kind of death’.”
Importantly, in meth users who have already developed HF, even then it may not be too late to reverse the cardiomyopathy and symptoms. For up to a third of people with established meth-HF, “if they stop using meth, if they take good cardiac medications, and if the heart failure is in an early enough course, their heart can entirely revert to normal,” Dr. Zhao said, citing an earlier work from her and her colleagues.
Currently, methamphetamine abuse has taken especially strong root in rural areas in California and the Midwest. But Dr. Zhao predicts it will soon become prevalent throughout the United States.
Spotlight on an ‘epidemic’
The rapid growth of the methamphetamine “epidemic” has been well-documented in the United States and around the world, observed an accompanying editorial from Pavan Reddy, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Morningside, New York, and Uri Elkayam, MD, University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
They contend that more attention has been given to opioid overdose deaths; meth abuse does not seem to command the same attention, likely because meth is not as strongly associated with acute overdose.
But meth, wrote Dr. Reddy and Dr. Elkayam, “is a different drug with its own M.O., equally dangerous and costly to society but more insidious in nature, its effects potentially causing decades of mental and physical debilitation before ending in premature death.”
The current study “has turned a spotlight on a public health crisis that has grown unfettered for over 2 decades,” and is a call for the “medical community to recognize and manage cases of meth-HF with a comprehensive approach that addresses both mental and physical illness,” they concluded. “Only then can we hope to properly help these patients and with that, reduce the socioeconomic burden of meth-HF.”
A quietly building crisis
The sharp rise in meth-HF hospitalizations is an expected reflection of the methamphetamine crisis, which has been quietly building over the last few years, addiction psychiatrist Corneliu N. Stanciu, MD, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., said in an interview.
“This new version of methamphetamines looks like ice and is more potent and toxic than former versions traditionally made in home-built labs,” he said. Lately the vast majority of methamphetamines in the United States have come from Mexico, are less expensive with higher purity, “and can be manufactured in greater quantities.”
Some patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) also inject methamphetamines, which can make OUD treatment clinics good places to screen for meth abuse and educate about its cardiovascular implications, Dr. Stanciu said.
“Just as addiction treatment centers present an opportunity to implement cardiac screening and referrals,” he said, “cardiology visits and hospitalizations such as those for meth-HF also present a golden opportunity for involvement of substance use disorder interventions and referrals to get patients into treatment and prevent further damage through ongoing use.”
Dr. Zhao, Dr. Reddy, Dr. Eklayam, and Dr. Stanciu report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rates of heart failure (HF) caused by methamphetamine abuse are climbing quickly in the western United States, at great financial and societal cost, suggests an analysis that documents the trends in California over a recent decade.
In the new study, methamphetamine-associated HF (meth-HF) admissions in the state rose by 585% between 2008 and 2018, and charges related those hospitalizations jumped 840%. Cases of HF unrelated to meth fell by 6% during the same period.
The recent explosion in meth-HF hospitalizations has also been costly for society in general, because most cases are younger adults in their most productive, prime earning years, Susan X. Zhao, MD, Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, Calif., said in an interview.
“Over the past 11 years, especially since 2018, it has really started to take off, with a pretty dramatic rise. And it happened without much attention, because when we think about drugs, we think about acute overdose and not so much about the chronic, smoldering, long-term effects,” said Dr. Zhao, who is lead author on the study published July 13, 2021, in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
“It’s really affecting a section of the population that is not supposed to be having heart failure problems. I think it is going to continue for the next decade until we put a stop to the parent problem, which is methamphetamine,” Dr. Zhao said. “We’re at the beginning, even though the rise has been pretty dramatic. The worst is yet to come.”
Under the radar
Methamphetamine-associated HF has been a growing problem for many years but has largely been “flying under the radar” because HF hospitalization data focus on Medicare-age patients, not the overwhelmingly younger meth-HF population, the report notes.
“We have to get this message out. Many of my patients with meth heart failure had no idea this would happen to them. They didn’t know,” Dr. Zhao said. “Once I tell them that this is what methamphetamines will do to you after years and years of use, they say they wish someone had told them.”
Dr. Zhao and colleagues looked at HF admission data collected by California’s Health and Human Services Agency to assess meth-HF trends and disease burden. They identified 1,033,076 HF hospitalizations during the decade, of which 42,565 (4.12%) were for meth-HF.
Patients hospitalized with meth-HF had a mean age of 49.6 years, compared with 72.2 for the other patients admitted with HF (P < .001). Virtually all of the patients hospitalized for meth-HF were younger than 65 years: 94.5%, compared with 30% for the other HF patients (P < .001).
Hospitalized patients with meth-HF were mostly men, their prevalence of 80% contrasting with 52.4% for patients with non–meth-related HF (P < .001).
Rates of hospitalization for meth-HF steadily increased during the study period. The age-adjusted rate of meth-HF hospitalization per 100,000 rose from 4.1 in 2008 to 28.1 in 2018. The rate of hospitalization for HF unrelated to meth actually declined, going from 342.3 in 2008 to 321.6 in 2018.
Charges for hospitalizations related to meth-HF shot up more than eight times, from $41.5 million in 2008 to $390.2 million in 2018. In contrast, charges for other HF hospitalizations rose by only 82%, from $3.5 billion to $6.3 billion.
Multiple layers of prevention
Dr. Zhao proposed ways that clinicians can communicate with their patients who are using or considering to use meth. “There are multiple layers of prevention. For people who are thinking of using meth, they need to get the message that something really bad can happen to them years down the road. They’re not going to die from it overnight, but it will damage the heart slowly,” she said.
The next layer of prevention can potentially help meth users who have not yet developed heart problems, Dr. Zhao said. “This would be the time to say, ‘you’re so lucky, your heart is still good. It’s time to stop because people like you, a few years from now are going to die prematurely from a very horrible, very suffering kind of death’.”
Importantly, in meth users who have already developed HF, even then it may not be too late to reverse the cardiomyopathy and symptoms. For up to a third of people with established meth-HF, “if they stop using meth, if they take good cardiac medications, and if the heart failure is in an early enough course, their heart can entirely revert to normal,” Dr. Zhao said, citing an earlier work from her and her colleagues.
Currently, methamphetamine abuse has taken especially strong root in rural areas in California and the Midwest. But Dr. Zhao predicts it will soon become prevalent throughout the United States.
Spotlight on an ‘epidemic’
The rapid growth of the methamphetamine “epidemic” has been well-documented in the United States and around the world, observed an accompanying editorial from Pavan Reddy, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Morningside, New York, and Uri Elkayam, MD, University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
They contend that more attention has been given to opioid overdose deaths; meth abuse does not seem to command the same attention, likely because meth is not as strongly associated with acute overdose.
But meth, wrote Dr. Reddy and Dr. Elkayam, “is a different drug with its own M.O., equally dangerous and costly to society but more insidious in nature, its effects potentially causing decades of mental and physical debilitation before ending in premature death.”
The current study “has turned a spotlight on a public health crisis that has grown unfettered for over 2 decades,” and is a call for the “medical community to recognize and manage cases of meth-HF with a comprehensive approach that addresses both mental and physical illness,” they concluded. “Only then can we hope to properly help these patients and with that, reduce the socioeconomic burden of meth-HF.”
A quietly building crisis
The sharp rise in meth-HF hospitalizations is an expected reflection of the methamphetamine crisis, which has been quietly building over the last few years, addiction psychiatrist Corneliu N. Stanciu, MD, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., said in an interview.
“This new version of methamphetamines looks like ice and is more potent and toxic than former versions traditionally made in home-built labs,” he said. Lately the vast majority of methamphetamines in the United States have come from Mexico, are less expensive with higher purity, “and can be manufactured in greater quantities.”
Some patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) also inject methamphetamines, which can make OUD treatment clinics good places to screen for meth abuse and educate about its cardiovascular implications, Dr. Stanciu said.
“Just as addiction treatment centers present an opportunity to implement cardiac screening and referrals,” he said, “cardiology visits and hospitalizations such as those for meth-HF also present a golden opportunity for involvement of substance use disorder interventions and referrals to get patients into treatment and prevent further damage through ongoing use.”
Dr. Zhao, Dr. Reddy, Dr. Eklayam, and Dr. Stanciu report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rates of heart failure (HF) caused by methamphetamine abuse are climbing quickly in the western United States, at great financial and societal cost, suggests an analysis that documents the trends in California over a recent decade.
In the new study, methamphetamine-associated HF (meth-HF) admissions in the state rose by 585% between 2008 and 2018, and charges related those hospitalizations jumped 840%. Cases of HF unrelated to meth fell by 6% during the same period.
The recent explosion in meth-HF hospitalizations has also been costly for society in general, because most cases are younger adults in their most productive, prime earning years, Susan X. Zhao, MD, Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, Calif., said in an interview.
“Over the past 11 years, especially since 2018, it has really started to take off, with a pretty dramatic rise. And it happened without much attention, because when we think about drugs, we think about acute overdose and not so much about the chronic, smoldering, long-term effects,” said Dr. Zhao, who is lead author on the study published July 13, 2021, in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
“It’s really affecting a section of the population that is not supposed to be having heart failure problems. I think it is going to continue for the next decade until we put a stop to the parent problem, which is methamphetamine,” Dr. Zhao said. “We’re at the beginning, even though the rise has been pretty dramatic. The worst is yet to come.”
Under the radar
Methamphetamine-associated HF has been a growing problem for many years but has largely been “flying under the radar” because HF hospitalization data focus on Medicare-age patients, not the overwhelmingly younger meth-HF population, the report notes.
“We have to get this message out. Many of my patients with meth heart failure had no idea this would happen to them. They didn’t know,” Dr. Zhao said. “Once I tell them that this is what methamphetamines will do to you after years and years of use, they say they wish someone had told them.”
Dr. Zhao and colleagues looked at HF admission data collected by California’s Health and Human Services Agency to assess meth-HF trends and disease burden. They identified 1,033,076 HF hospitalizations during the decade, of which 42,565 (4.12%) were for meth-HF.
Patients hospitalized with meth-HF had a mean age of 49.6 years, compared with 72.2 for the other patients admitted with HF (P < .001). Virtually all of the patients hospitalized for meth-HF were younger than 65 years: 94.5%, compared with 30% for the other HF patients (P < .001).
Hospitalized patients with meth-HF were mostly men, their prevalence of 80% contrasting with 52.4% for patients with non–meth-related HF (P < .001).
Rates of hospitalization for meth-HF steadily increased during the study period. The age-adjusted rate of meth-HF hospitalization per 100,000 rose from 4.1 in 2008 to 28.1 in 2018. The rate of hospitalization for HF unrelated to meth actually declined, going from 342.3 in 2008 to 321.6 in 2018.
Charges for hospitalizations related to meth-HF shot up more than eight times, from $41.5 million in 2008 to $390.2 million in 2018. In contrast, charges for other HF hospitalizations rose by only 82%, from $3.5 billion to $6.3 billion.
Multiple layers of prevention
Dr. Zhao proposed ways that clinicians can communicate with their patients who are using or considering to use meth. “There are multiple layers of prevention. For people who are thinking of using meth, they need to get the message that something really bad can happen to them years down the road. They’re not going to die from it overnight, but it will damage the heart slowly,” she said.
The next layer of prevention can potentially help meth users who have not yet developed heart problems, Dr. Zhao said. “This would be the time to say, ‘you’re so lucky, your heart is still good. It’s time to stop because people like you, a few years from now are going to die prematurely from a very horrible, very suffering kind of death’.”
Importantly, in meth users who have already developed HF, even then it may not be too late to reverse the cardiomyopathy and symptoms. For up to a third of people with established meth-HF, “if they stop using meth, if they take good cardiac medications, and if the heart failure is in an early enough course, their heart can entirely revert to normal,” Dr. Zhao said, citing an earlier work from her and her colleagues.
Currently, methamphetamine abuse has taken especially strong root in rural areas in California and the Midwest. But Dr. Zhao predicts it will soon become prevalent throughout the United States.
Spotlight on an ‘epidemic’
The rapid growth of the methamphetamine “epidemic” has been well-documented in the United States and around the world, observed an accompanying editorial from Pavan Reddy, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Morningside, New York, and Uri Elkayam, MD, University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
They contend that more attention has been given to opioid overdose deaths; meth abuse does not seem to command the same attention, likely because meth is not as strongly associated with acute overdose.
But meth, wrote Dr. Reddy and Dr. Elkayam, “is a different drug with its own M.O., equally dangerous and costly to society but more insidious in nature, its effects potentially causing decades of mental and physical debilitation before ending in premature death.”
The current study “has turned a spotlight on a public health crisis that has grown unfettered for over 2 decades,” and is a call for the “medical community to recognize and manage cases of meth-HF with a comprehensive approach that addresses both mental and physical illness,” they concluded. “Only then can we hope to properly help these patients and with that, reduce the socioeconomic burden of meth-HF.”
A quietly building crisis
The sharp rise in meth-HF hospitalizations is an expected reflection of the methamphetamine crisis, which has been quietly building over the last few years, addiction psychiatrist Corneliu N. Stanciu, MD, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., said in an interview.
“This new version of methamphetamines looks like ice and is more potent and toxic than former versions traditionally made in home-built labs,” he said. Lately the vast majority of methamphetamines in the United States have come from Mexico, are less expensive with higher purity, “and can be manufactured in greater quantities.”
Some patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) also inject methamphetamines, which can make OUD treatment clinics good places to screen for meth abuse and educate about its cardiovascular implications, Dr. Stanciu said.
“Just as addiction treatment centers present an opportunity to implement cardiac screening and referrals,” he said, “cardiology visits and hospitalizations such as those for meth-HF also present a golden opportunity for involvement of substance use disorder interventions and referrals to get patients into treatment and prevent further damage through ongoing use.”
Dr. Zhao, Dr. Reddy, Dr. Eklayam, and Dr. Stanciu report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Common parasite now tied to impaired cognitive function
Investigators reviewed and conducted a meta-analysis of 13 studies that encompassed more than 13,000 healthy adults and found a modest but significant association between T. gondii seropositivity and impaired performance on cognitive tests of processing speed, working memory, short-term verbal memory, and executive function. The average age of the persons in the studies was close to 50 years.
“Our findings show that T. gondii could have a negative but small effect on cognition,” study investigator Arjen Sutterland, MD, of the Amsterdam Neuroscience Research Institute and the Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, University of Amsterdam, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 14, 2021, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Mental illness link
T. gondii is “an intracellular parasite that produces quiescent infection in approximately 30% of humans worldwide,” the authors wrote. The parasite that causes the infection not only settles in muscle and liver tissue but also can cross the blood-brain barrier and settle quiescently in brain tissue. It can be spread through contact with cat feces or by consuming contaminated meat.
Previous research has shown that neurocognitive changes associated with toxoplasmosis can occur in humans, and meta-analyses suggest an association with neuropsychiatric disorders. Some research has also tied T. gondii infection to increased motor vehicle crashes and suicide attempts.
Dr. Sutterland said he had been inspired by the work of E. Fuller Torrey and Bob Yolken, who proposed the connection between T. gondii and schizophrenia.
Some years ago, Dr. Sutterland and his group analyzed the mental health consequences of T. gondii infection and found “several interesting associations,” but they were unable to “rule out reverse causation – i.e., people with mental health disorders more often get these infections – as well as determine the impact on the population of this common infection.”
For the current study, the investigators analyzed studies that examined specifically cognitive functioning in otherwise healthy individuals in relation to T. gondii infection, “because reverse causation would be less likely in this population and a grasp of global impact would become more clear.”
The researchers conducted a literature search of studies conducted through June 7, 2019, that analyzed cognitive function among healthy participants for whom data on T. gondii seropositivity were available.
A total of 13 studies (n = 13,289 participants; mean age, 46.7 years; 49.6% male) were used in the review and meta-analysis. Some of the studies enrolled a healthy population sample; other studies compared participants with and those without psychiatric disorders. From these, the researchers extracted only the data concerning healthy participants.
The studies analyzed four cognitive domains: processing speed, working memory, short-term verbal memory, and executive functioning.
All cognitive domains affected
Of all the participants, 22.6% had antibodies against T. gondii.
Participants who were seropositive for T. gondii had less favorable functioning in all cognitive domains, with “small but significant” differences. 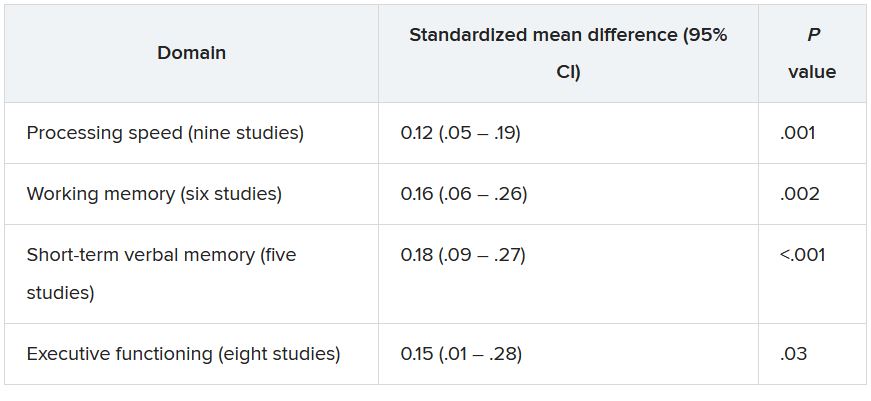
The researchers conducted a meta-regression analysis of mean age in the analysis of executive functioning and found greater effect sizes as age increased (Q = 6.17; R2 = 81%; P = .01).
The studies were of “high quality,” and there was “little suggestion of publication bias was detected,” the authors noted.
“Although the extent of the associations was modest, the ubiquitous prevalence of the quiescent infection worldwide ... suggests that the consequences for cognitive function of the population as a whole may be substantial, although it is difficult to quantify the global impact,” they wrote.
They note that because the studies were cross-sectional in nature, causality cannot be established.
Nevertheless, Dr. Sutterland suggested several possible mechanisms through which T. gondii might affect neurocognition.
“We know the parasite forms cysts in the brain and can influence dopaminergic neurotransmission, which, in turn, affects neurocognition. Alternatively, it is also possible that the immune response to the infection in the brain causes cognitive impairment. This remains an important question to explore further,” he said.
He noted that clinicians can reassure patients who test positive for T. gondii that although the infection can have a negative impact on cognition, the effect is “small.”
Prevention programs warranted
Commenting on the study in an interview, Shawn D. Gale, PhD, associate professor, department of psychology and neuroscience center, Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, called it a “great meta-analysis.” He noted that his group is researching the subject and has obtained similar findings. A big plus is that the researchers assessed several cognitive domains, not just one.
Although the data showed “mild effects,” the findings could be important on a population level. Because 30% of the world’s population are seropositive for T. gondii, a potentially large number of people are at risk for cognitive impairment, noted Dr. Gale, who was not involved with the study.
“If you look at the United States, perhaps 10%-15% of people might test positive [for T. gondii], but in Germany and France, the number comes closer to 50%, and in other places in the world – especially countries that have a harder time economically – the rates are even higher. So if it can affect cognition, even a small effect is a big deal,” Dr. Gale said.
“I think prevention will be the most important thing, and perhaps down the road, I hope that a vaccine will be considered,” Dr. Gale added.
“These findings indicate that primary prevention of the infection could have substantial global impact on mental health” and that public health programs to prevent T. gondii “are warranted.”
These programs might consist of hygienic measures, especially after human contact with contaminated sources, as well as research into vaccine development.
No source of funding for the study was listed. The authors and Dr. Gale reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators reviewed and conducted a meta-analysis of 13 studies that encompassed more than 13,000 healthy adults and found a modest but significant association between T. gondii seropositivity and impaired performance on cognitive tests of processing speed, working memory, short-term verbal memory, and executive function. The average age of the persons in the studies was close to 50 years.
“Our findings show that T. gondii could have a negative but small effect on cognition,” study investigator Arjen Sutterland, MD, of the Amsterdam Neuroscience Research Institute and the Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, University of Amsterdam, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 14, 2021, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Mental illness link
T. gondii is “an intracellular parasite that produces quiescent infection in approximately 30% of humans worldwide,” the authors wrote. The parasite that causes the infection not only settles in muscle and liver tissue but also can cross the blood-brain barrier and settle quiescently in brain tissue. It can be spread through contact with cat feces or by consuming contaminated meat.
Previous research has shown that neurocognitive changes associated with toxoplasmosis can occur in humans, and meta-analyses suggest an association with neuropsychiatric disorders. Some research has also tied T. gondii infection to increased motor vehicle crashes and suicide attempts.
Dr. Sutterland said he had been inspired by the work of E. Fuller Torrey and Bob Yolken, who proposed the connection between T. gondii and schizophrenia.
Some years ago, Dr. Sutterland and his group analyzed the mental health consequences of T. gondii infection and found “several interesting associations,” but they were unable to “rule out reverse causation – i.e., people with mental health disorders more often get these infections – as well as determine the impact on the population of this common infection.”
For the current study, the investigators analyzed studies that examined specifically cognitive functioning in otherwise healthy individuals in relation to T. gondii infection, “because reverse causation would be less likely in this population and a grasp of global impact would become more clear.”
The researchers conducted a literature search of studies conducted through June 7, 2019, that analyzed cognitive function among healthy participants for whom data on T. gondii seropositivity were available.
A total of 13 studies (n = 13,289 participants; mean age, 46.7 years; 49.6% male) were used in the review and meta-analysis. Some of the studies enrolled a healthy population sample; other studies compared participants with and those without psychiatric disorders. From these, the researchers extracted only the data concerning healthy participants.
The studies analyzed four cognitive domains: processing speed, working memory, short-term verbal memory, and executive functioning.
All cognitive domains affected
Of all the participants, 22.6% had antibodies against T. gondii.
Participants who were seropositive for T. gondii had less favorable functioning in all cognitive domains, with “small but significant” differences. 
The researchers conducted a meta-regression analysis of mean age in the analysis of executive functioning and found greater effect sizes as age increased (Q = 6.17; R2 = 81%; P = .01).
The studies were of “high quality,” and there was “little suggestion of publication bias was detected,” the authors noted.
“Although the extent of the associations was modest, the ubiquitous prevalence of the quiescent infection worldwide ... suggests that the consequences for cognitive function of the population as a whole may be substantial, although it is difficult to quantify the global impact,” they wrote.
They note that because the studies were cross-sectional in nature, causality cannot be established.
Nevertheless, Dr. Sutterland suggested several possible mechanisms through which T. gondii might affect neurocognition.
“We know the parasite forms cysts in the brain and can influence dopaminergic neurotransmission, which, in turn, affects neurocognition. Alternatively, it is also possible that the immune response to the infection in the brain causes cognitive impairment. This remains an important question to explore further,” he said.
He noted that clinicians can reassure patients who test positive for T. gondii that although the infection can have a negative impact on cognition, the effect is “small.”
Prevention programs warranted
Commenting on the study in an interview, Shawn D. Gale, PhD, associate professor, department of psychology and neuroscience center, Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, called it a “great meta-analysis.” He noted that his group is researching the subject and has obtained similar findings. A big plus is that the researchers assessed several cognitive domains, not just one.
Although the data showed “mild effects,” the findings could be important on a population level. Because 30% of the world’s population are seropositive for T. gondii, a potentially large number of people are at risk for cognitive impairment, noted Dr. Gale, who was not involved with the study.
“If you look at the United States, perhaps 10%-15% of people might test positive [for T. gondii], but in Germany and France, the number comes closer to 50%, and in other places in the world – especially countries that have a harder time economically – the rates are even higher. So if it can affect cognition, even a small effect is a big deal,” Dr. Gale said.
“I think prevention will be the most important thing, and perhaps down the road, I hope that a vaccine will be considered,” Dr. Gale added.
“These findings indicate that primary prevention of the infection could have substantial global impact on mental health” and that public health programs to prevent T. gondii “are warranted.”
These programs might consist of hygienic measures, especially after human contact with contaminated sources, as well as research into vaccine development.
No source of funding for the study was listed. The authors and Dr. Gale reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators reviewed and conducted a meta-analysis of 13 studies that encompassed more than 13,000 healthy adults and found a modest but significant association between T. gondii seropositivity and impaired performance on cognitive tests of processing speed, working memory, short-term verbal memory, and executive function. The average age of the persons in the studies was close to 50 years.
“Our findings show that T. gondii could have a negative but small effect on cognition,” study investigator Arjen Sutterland, MD, of the Amsterdam Neuroscience Research Institute and the Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, University of Amsterdam, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 14, 2021, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Mental illness link
T. gondii is “an intracellular parasite that produces quiescent infection in approximately 30% of humans worldwide,” the authors wrote. The parasite that causes the infection not only settles in muscle and liver tissue but also can cross the blood-brain barrier and settle quiescently in brain tissue. It can be spread through contact with cat feces or by consuming contaminated meat.
Previous research has shown that neurocognitive changes associated with toxoplasmosis can occur in humans, and meta-analyses suggest an association with neuropsychiatric disorders. Some research has also tied T. gondii infection to increased motor vehicle crashes and suicide attempts.
Dr. Sutterland said he had been inspired by the work of E. Fuller Torrey and Bob Yolken, who proposed the connection between T. gondii and schizophrenia.
Some years ago, Dr. Sutterland and his group analyzed the mental health consequences of T. gondii infection and found “several interesting associations,” but they were unable to “rule out reverse causation – i.e., people with mental health disorders more often get these infections – as well as determine the impact on the population of this common infection.”
For the current study, the investigators analyzed studies that examined specifically cognitive functioning in otherwise healthy individuals in relation to T. gondii infection, “because reverse causation would be less likely in this population and a grasp of global impact would become more clear.”
The researchers conducted a literature search of studies conducted through June 7, 2019, that analyzed cognitive function among healthy participants for whom data on T. gondii seropositivity were available.
A total of 13 studies (n = 13,289 participants; mean age, 46.7 years; 49.6% male) were used in the review and meta-analysis. Some of the studies enrolled a healthy population sample; other studies compared participants with and those without psychiatric disorders. From these, the researchers extracted only the data concerning healthy participants.
The studies analyzed four cognitive domains: processing speed, working memory, short-term verbal memory, and executive functioning.
All cognitive domains affected
Of all the participants, 22.6% had antibodies against T. gondii.
Participants who were seropositive for T. gondii had less favorable functioning in all cognitive domains, with “small but significant” differences. 
The researchers conducted a meta-regression analysis of mean age in the analysis of executive functioning and found greater effect sizes as age increased (Q = 6.17; R2 = 81%; P = .01).
The studies were of “high quality,” and there was “little suggestion of publication bias was detected,” the authors noted.
“Although the extent of the associations was modest, the ubiquitous prevalence of the quiescent infection worldwide ... suggests that the consequences for cognitive function of the population as a whole may be substantial, although it is difficult to quantify the global impact,” they wrote.
They note that because the studies were cross-sectional in nature, causality cannot be established.
Nevertheless, Dr. Sutterland suggested several possible mechanisms through which T. gondii might affect neurocognition.
“We know the parasite forms cysts in the brain and can influence dopaminergic neurotransmission, which, in turn, affects neurocognition. Alternatively, it is also possible that the immune response to the infection in the brain causes cognitive impairment. This remains an important question to explore further,” he said.
He noted that clinicians can reassure patients who test positive for T. gondii that although the infection can have a negative impact on cognition, the effect is “small.”
Prevention programs warranted
Commenting on the study in an interview, Shawn D. Gale, PhD, associate professor, department of psychology and neuroscience center, Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, called it a “great meta-analysis.” He noted that his group is researching the subject and has obtained similar findings. A big plus is that the researchers assessed several cognitive domains, not just one.
Although the data showed “mild effects,” the findings could be important on a population level. Because 30% of the world’s population are seropositive for T. gondii, a potentially large number of people are at risk for cognitive impairment, noted Dr. Gale, who was not involved with the study.
“If you look at the United States, perhaps 10%-15% of people might test positive [for T. gondii], but in Germany and France, the number comes closer to 50%, and in other places in the world – especially countries that have a harder time economically – the rates are even higher. So if it can affect cognition, even a small effect is a big deal,” Dr. Gale said.
“I think prevention will be the most important thing, and perhaps down the road, I hope that a vaccine will be considered,” Dr. Gale added.
“These findings indicate that primary prevention of the infection could have substantial global impact on mental health” and that public health programs to prevent T. gondii “are warranted.”
These programs might consist of hygienic measures, especially after human contact with contaminated sources, as well as research into vaccine development.
No source of funding for the study was listed. The authors and Dr. Gale reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Trauma, psychiatric comorbidities tied to functional motor disorders
Most adults with functional motor disorders (FMDs) report a history of psychological or physical trauma 6 months before the onset of symptoms, a retrospective study of 482 individuals suggests. Those challenges prevent more than half of those patients – most of whom are women – from working, the researchers found.
“This finding points to the huge socioeconomical burden of FMD and emphasizes the need for better diagnostic procedure and active management,” wrote Béatrice Garcin, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and associates.
FMDs are a common presentation of functional neurologic disorders, but clinical characteristics of FMDs are not well understood because large series of consecutive patients are limited, Dr. Garcin and associates said.
In the study, published in the Journal of Psychosomatic Research, the investigators reviewed data from consecutive patients with FMD who were seen at a single hospital in France between 2008 and 2016. Half of the patients had functional motor weakness (241) and half had functional movement disorders (241). All of the patients had been referred for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) as treatment for FMD.
The median age of the patients was 40 years, the median age at the onset of symptoms was 35.5 years, and 74% were women. The most common clinical presentations were tremor and dystonia (83.4%), and no demographic differences were observed between patients with functional motor weakness and functional movement disorders. Symptoms were bilateral in about half of the patients (51.7%), with left- and right-sided symptoms in 28.2% and 20.1%, respectively.
More than 80% of the patients reported a history of trauma within 6 months of the onset of their symptoms, mainly psychological trauma (50.6%). Another 20.1% reported a physical trauma, and 8.7% reported trauma from surgical procedures.
In addition, about two-thirds (66.4%) had psychiatric comorbidities; 52.7% of these were mood disorders: 49.3% depression and 3.3% bipolar disorder. “However, these results about psychiatric comorbidities should be taken with caution,” the researchers emphasized. “ and psychiatric diagnosis may lack precision because of the absence of systematic psychiatric interviews and psychiatric questionnaires in the present study.”
No significant differences appeared between the motor weakness and movement disorders groups in terms of occupation, level of education, medical somatic history, symptom onset, psychiatric comorbidities, or self-reported history of trauma. Patients in the motor weakness group were significantly younger at the time of TMS treatment and had a shorter disease duration prior to that treatment. No differences were noted between the groups with regard to clinical FMD phenotypes.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential selection bias because of enrollment at a neurology referral center, lack of a control group, and underrepresentation of children and older adults, the researchers noted. Also, symptom severity was not assessed and could not be compared among phenotypes or demographic groups.
However, the results contribute to the characterization of FMD patients. “Future studies are needed to clarify the characteristics of FMD patients and the consequences of their symptoms on disability and work status,” they said.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Garcin had no disclosures.
Most adults with functional motor disorders (FMDs) report a history of psychological or physical trauma 6 months before the onset of symptoms, a retrospective study of 482 individuals suggests. Those challenges prevent more than half of those patients – most of whom are women – from working, the researchers found.
“This finding points to the huge socioeconomical burden of FMD and emphasizes the need for better diagnostic procedure and active management,” wrote Béatrice Garcin, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and associates.
FMDs are a common presentation of functional neurologic disorders, but clinical characteristics of FMDs are not well understood because large series of consecutive patients are limited, Dr. Garcin and associates said.
In the study, published in the Journal of Psychosomatic Research, the investigators reviewed data from consecutive patients with FMD who were seen at a single hospital in France between 2008 and 2016. Half of the patients had functional motor weakness (241) and half had functional movement disorders (241). All of the patients had been referred for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) as treatment for FMD.
The median age of the patients was 40 years, the median age at the onset of symptoms was 35.5 years, and 74% were women. The most common clinical presentations were tremor and dystonia (83.4%), and no demographic differences were observed between patients with functional motor weakness and functional movement disorders. Symptoms were bilateral in about half of the patients (51.7%), with left- and right-sided symptoms in 28.2% and 20.1%, respectively.
More than 80% of the patients reported a history of trauma within 6 months of the onset of their symptoms, mainly psychological trauma (50.6%). Another 20.1% reported a physical trauma, and 8.7% reported trauma from surgical procedures.
In addition, about two-thirds (66.4%) had psychiatric comorbidities; 52.7% of these were mood disorders: 49.3% depression and 3.3% bipolar disorder. “However, these results about psychiatric comorbidities should be taken with caution,” the researchers emphasized. “ and psychiatric diagnosis may lack precision because of the absence of systematic psychiatric interviews and psychiatric questionnaires in the present study.”
No significant differences appeared between the motor weakness and movement disorders groups in terms of occupation, level of education, medical somatic history, symptom onset, psychiatric comorbidities, or self-reported history of trauma. Patients in the motor weakness group were significantly younger at the time of TMS treatment and had a shorter disease duration prior to that treatment. No differences were noted between the groups with regard to clinical FMD phenotypes.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential selection bias because of enrollment at a neurology referral center, lack of a control group, and underrepresentation of children and older adults, the researchers noted. Also, symptom severity was not assessed and could not be compared among phenotypes or demographic groups.
However, the results contribute to the characterization of FMD patients. “Future studies are needed to clarify the characteristics of FMD patients and the consequences of their symptoms on disability and work status,” they said.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Garcin had no disclosures.
Most adults with functional motor disorders (FMDs) report a history of psychological or physical trauma 6 months before the onset of symptoms, a retrospective study of 482 individuals suggests. Those challenges prevent more than half of those patients – most of whom are women – from working, the researchers found.
“This finding points to the huge socioeconomical burden of FMD and emphasizes the need for better diagnostic procedure and active management,” wrote Béatrice Garcin, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and associates.
FMDs are a common presentation of functional neurologic disorders, but clinical characteristics of FMDs are not well understood because large series of consecutive patients are limited, Dr. Garcin and associates said.
In the study, published in the Journal of Psychosomatic Research, the investigators reviewed data from consecutive patients with FMD who were seen at a single hospital in France between 2008 and 2016. Half of the patients had functional motor weakness (241) and half had functional movement disorders (241). All of the patients had been referred for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) as treatment for FMD.
The median age of the patients was 40 years, the median age at the onset of symptoms was 35.5 years, and 74% were women. The most common clinical presentations were tremor and dystonia (83.4%), and no demographic differences were observed between patients with functional motor weakness and functional movement disorders. Symptoms were bilateral in about half of the patients (51.7%), with left- and right-sided symptoms in 28.2% and 20.1%, respectively.
More than 80% of the patients reported a history of trauma within 6 months of the onset of their symptoms, mainly psychological trauma (50.6%). Another 20.1% reported a physical trauma, and 8.7% reported trauma from surgical procedures.
In addition, about two-thirds (66.4%) had psychiatric comorbidities; 52.7% of these were mood disorders: 49.3% depression and 3.3% bipolar disorder. “However, these results about psychiatric comorbidities should be taken with caution,” the researchers emphasized. “ and psychiatric diagnosis may lack precision because of the absence of systematic psychiatric interviews and psychiatric questionnaires in the present study.”
No significant differences appeared between the motor weakness and movement disorders groups in terms of occupation, level of education, medical somatic history, symptom onset, psychiatric comorbidities, or self-reported history of trauma. Patients in the motor weakness group were significantly younger at the time of TMS treatment and had a shorter disease duration prior to that treatment. No differences were noted between the groups with regard to clinical FMD phenotypes.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential selection bias because of enrollment at a neurology referral center, lack of a control group, and underrepresentation of children and older adults, the researchers noted. Also, symptom severity was not assessed and could not be compared among phenotypes or demographic groups.
However, the results contribute to the characterization of FMD patients. “Future studies are needed to clarify the characteristics of FMD patients and the consequences of their symptoms on disability and work status,” they said.
The study received no outside funding. Lead author Dr. Garcin had no disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PSYCHOSOMATIC RESEARCH
Twofold increased risk for death from COVID-19 in psych patients
compared with those without a psychiatric diagnosis, according to the results of the largest study of its kind to date.
These findings, the investigators noted, highlight the need to prioritize vaccination in patients with preexisting mental health disorders.
“We have proven beyond a shadow of a doubt that there are increased risks” among psychiatric patients who get COVID-19, study investigator Livia De Picker, MD, PhD, psychiatrist and postdoctoral researcher, University Psychiatric Hospital Campus Duffel and University of Antwerp (Belgium), told this news organization.
“Doctors need to look at these patients the same way they would other high-risk people, for example those with diabetes or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,” all of whom should be protected against COVID-19, Dr. De Picker added.
The study was published online July 15, 2021, in Lancet Psychiatry.
Risk by mental illness type
The systematic review included 33 studies from 22 countries that reported risk estimates for mortality, hospitalization, and ICU admission in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. The meta-analysis included 23 of these studies with a total of 1.47 million participants. Of these, 43,938 had a psychiatric disorder.
The primary outcome was mortality after COVID-19. Secondary outcomes included hospitalization and ICU admission after COVID-19. Researchers adjusted for age, sex, and other covariates.
Results showed the presence of any comorbid mental illness was associated with an increased risk for death after SARS-CoV-2 infection (odds ratio, 2.00; 95% confidence interval, 1.58-2.54; P < .0001).
When researchers stratified mortality risk by psychiatric disorder type, the most robust associations were for psychotic and mood disorders. Substance use disorders, intellectual disabilities, and developmental disorders were associated with higher mortality only in crude estimates. There was no increased death risk associated with anxiety disorders.
“That there are differences between the various types of disorders was an interesting finding,” said Dr. De Picker, adding that previous research “just lumped together all diagnostic categories.”
Potential mechanisms
The study did not explore why psychiatric illness raise the risk for death in the setting of COVID-19, so potential mechanisms are purely speculative. However, the investigators believe it may reflect biological processes such as immune-inflammatory alterations.
Psychotic disorders and mood disorders in particular, are associated with immune changes, including immunogenetic abnormalities, raised cytokine concentrations, autoantibodies, acute-phase proteins, and aberrant counts of leukocyte cell types, said Dr. De Picker.
She likened this to elderly people being at increased risk following COVID-19 because their immune system is compromised and less able to fight infection.
There are likely other factors at play, said Dr. De Picker. These could include social isolation and lifestyle factors like poor diet, physical inactivity, high alcohol and tobacco use, and sleep disturbances.
In addition, psychiatric patients have a higher prevalence of comorbidities including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory disease, which could also play a role.
The increased mortality might also reflect reduced access to care. “Some of these patients may be living in difficult socioeconomic conditions,” said Dr. De Picker.
She noted that, while the in-hospital mortality was not increased, the risk was significantly increased in samples that were outside of the hospital. This reinforces the need for providing close monitoring and early referral to hospital for psychiatric patients with COVID-19.
Mortality varied significantly among countries, with the lowest risk in Europe and the United States. This difference might be attributable to differences in health care systems and access to care, said Dr. De Picker.
Overall, the risk for hospitalization was about double for COVID patients with a mental illness, but when stratified by disorder, there was only a significantly increased risk for substance use and mood disorders. “But mood disorders were not even significant any more after adjusting for age, sex, and comorbid conditions, and we don’t see an increased risk for psychotic disorders whereas they had the highest mortality risks,” said Dr. De Picker.
Psych meds a risk factor?
The studies were primarily based on electronic medical records, so investigators were unable to carry out “a fine grain analysis” into clinical factors affecting outcomes, she noted.
Antipsychotics were consistently associated with an increased risk for mortality (adjusted OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.81-3.25), as were anxiolytics (aOR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.15-1.88).
“There are some theoretical reasons why we believe there could be a risk associated with these drugs,” said Dr. De Picker. For example, antipsychotics can increase the risk for cardiac arrhythmias and thromboembolic events, and cause interactions with drugs used to treat COVID-19.
As for anxiolytics, especially benzodiazepines, these drugs are associated with respiratory risk and with all-cause mortality. “So you could imagine that someone who is infected with a respiratory virus and [is] then using these drugs on top of that would have a worse outcome,” said Dr. De Picker.
In contrast to antipsychotics and anxiolytics, antidepressants did not increase mortality risk.
Dr. De Picker noted a new study by French researchers showing a protective effect of certain serotonergic antidepressants on COVID outcomes, including mortality.
There was no robust evidence of an increased risk for ICU admission for patients with mental disorders. However, the authors noted some studies included small samples of patients with psychiatric disorders, “contributing to a low certainty of evidence for ICU admission.”
Dr. De Picker criticized COVID vaccine policies that don’t prioritize patients with psychiatric disorders. In many countries, groups that were initially green-lighted for the vaccine included health care workers, the elderly, and those with underlying conditions such as diabetes, obesity and even mild hypertension – but not mental illness, which is also an underlying risk.
‘Outstanding’ research
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and chair of the American Psychiatric Association Council on Research, called it “outstanding” and the largest of its kind.
“There have been a number of studies that have come to similar conclusions, that people with psychiatric illness are at greater risk for poorer outcomes, but because any given study had a relatively limited sample, perhaps from one health system or one country, there were some inconsistencies,” said Dr. Alpert.
“This is the strongest report so far that has made the point that people with psychiatric illness are a vulnerable population for a negative outcome from COVID, including the most worrisome – mortality.”
The study helps drive home a “very important public health lesson” that applies to COVID-19 but goes “beyond,” said Dr. Alpert.
“As a society, we need to keep in mind that people with serious mental disorders are a vulnerable population for poorer outcomes in most general medical conditions,” he stressed, “whether it’s cancer or heart disease or diabetes, and special efforts need to be made to reach out to those populations.”
Dr. Alpert agreed that, at the start of the pandemic, psychiatric patients in the United States were not prioritized for vaccination, and although psychiatric patients may initially have found it difficult to navigate the health care system to learn where and how to get a COVID shot, today that barrier has mostly been removed.
“Our patients are at least as willing as any other subgroup to get the vaccine, and that includes people with psychotic disorders,” he said.
The study was supported by the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Immuno-NeuroPsychiatry network and Fondazione Centro San Raffaele (Milan). Dr. De Picker reported receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Janssen outside the submitted work. She is a member of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Immuno-NeuroPsychiatry Thematic Working Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
compared with those without a psychiatric diagnosis, according to the results of the largest study of its kind to date.
These findings, the investigators noted, highlight the need to prioritize vaccination in patients with preexisting mental health disorders.
“We have proven beyond a shadow of a doubt that there are increased risks” among psychiatric patients who get COVID-19, study investigator Livia De Picker, MD, PhD, psychiatrist and postdoctoral researcher, University Psychiatric Hospital Campus Duffel and University of Antwerp (Belgium), told this news organization.
“Doctors need to look at these patients the same way they would other high-risk people, for example those with diabetes or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,” all of whom should be protected against COVID-19, Dr. De Picker added.
The study was published online July 15, 2021, in Lancet Psychiatry.
Risk by mental illness type
The systematic review included 33 studies from 22 countries that reported risk estimates for mortality, hospitalization, and ICU admission in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. The meta-analysis included 23 of these studies with a total of 1.47 million participants. Of these, 43,938 had a psychiatric disorder.
The primary outcome was mortality after COVID-19. Secondary outcomes included hospitalization and ICU admission after COVID-19. Researchers adjusted for age, sex, and other covariates.
Results showed the presence of any comorbid mental illness was associated with an increased risk for death after SARS-CoV-2 infection (odds ratio, 2.00; 95% confidence interval, 1.58-2.54; P < .0001).
When researchers stratified mortality risk by psychiatric disorder type, the most robust associations were for psychotic and mood disorders. Substance use disorders, intellectual disabilities, and developmental disorders were associated with higher mortality only in crude estimates. There was no increased death risk associated with anxiety disorders.
“That there are differences between the various types of disorders was an interesting finding,” said Dr. De Picker, adding that previous research “just lumped together all diagnostic categories.”
Potential mechanisms
The study did not explore why psychiatric illness raise the risk for death in the setting of COVID-19, so potential mechanisms are purely speculative. However, the investigators believe it may reflect biological processes such as immune-inflammatory alterations.
Psychotic disorders and mood disorders in particular, are associated with immune changes, including immunogenetic abnormalities, raised cytokine concentrations, autoantibodies, acute-phase proteins, and aberrant counts of leukocyte cell types, said Dr. De Picker.
She likened this to elderly people being at increased risk following COVID-19 because their immune system is compromised and less able to fight infection.
There are likely other factors at play, said Dr. De Picker. These could include social isolation and lifestyle factors like poor diet, physical inactivity, high alcohol and tobacco use, and sleep disturbances.
In addition, psychiatric patients have a higher prevalence of comorbidities including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory disease, which could also play a role.
The increased mortality might also reflect reduced access to care. “Some of these patients may be living in difficult socioeconomic conditions,” said Dr. De Picker.
She noted that, while the in-hospital mortality was not increased, the risk was significantly increased in samples that were outside of the hospital. This reinforces the need for providing close monitoring and early referral to hospital for psychiatric patients with COVID-19.
Mortality varied significantly among countries, with the lowest risk in Europe and the United States. This difference might be attributable to differences in health care systems and access to care, said Dr. De Picker.
Overall, the risk for hospitalization was about double for COVID patients with a mental illness, but when stratified by disorder, there was only a significantly increased risk for substance use and mood disorders. “But mood disorders were not even significant any more after adjusting for age, sex, and comorbid conditions, and we don’t see an increased risk for psychotic disorders whereas they had the highest mortality risks,” said Dr. De Picker.
Psych meds a risk factor?
The studies were primarily based on electronic medical records, so investigators were unable to carry out “a fine grain analysis” into clinical factors affecting outcomes, she noted.
Antipsychotics were consistently associated with an increased risk for mortality (adjusted OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.81-3.25), as were anxiolytics (aOR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.15-1.88).
“There are some theoretical reasons why we believe there could be a risk associated with these drugs,” said Dr. De Picker. For example, antipsychotics can increase the risk for cardiac arrhythmias and thromboembolic events, and cause interactions with drugs used to treat COVID-19.
As for anxiolytics, especially benzodiazepines, these drugs are associated with respiratory risk and with all-cause mortality. “So you could imagine that someone who is infected with a respiratory virus and [is] then using these drugs on top of that would have a worse outcome,” said Dr. De Picker.
In contrast to antipsychotics and anxiolytics, antidepressants did not increase mortality risk.
Dr. De Picker noted a new study by French researchers showing a protective effect of certain serotonergic antidepressants on COVID outcomes, including mortality.
There was no robust evidence of an increased risk for ICU admission for patients with mental disorders. However, the authors noted some studies included small samples of patients with psychiatric disorders, “contributing to a low certainty of evidence for ICU admission.”
Dr. De Picker criticized COVID vaccine policies that don’t prioritize patients with psychiatric disorders. In many countries, groups that were initially green-lighted for the vaccine included health care workers, the elderly, and those with underlying conditions such as diabetes, obesity and even mild hypertension – but not mental illness, which is also an underlying risk.
‘Outstanding’ research
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and chair of the American Psychiatric Association Council on Research, called it “outstanding” and the largest of its kind.
“There have been a number of studies that have come to similar conclusions, that people with psychiatric illness are at greater risk for poorer outcomes, but because any given study had a relatively limited sample, perhaps from one health system or one country, there were some inconsistencies,” said Dr. Alpert.
“This is the strongest report so far that has made the point that people with psychiatric illness are a vulnerable population for a negative outcome from COVID, including the most worrisome – mortality.”
The study helps drive home a “very important public health lesson” that applies to COVID-19 but goes “beyond,” said Dr. Alpert.
“As a society, we need to keep in mind that people with serious mental disorders are a vulnerable population for poorer outcomes in most general medical conditions,” he stressed, “whether it’s cancer or heart disease or diabetes, and special efforts need to be made to reach out to those populations.”
Dr. Alpert agreed that, at the start of the pandemic, psychiatric patients in the United States were not prioritized for vaccination, and although psychiatric patients may initially have found it difficult to navigate the health care system to learn where and how to get a COVID shot, today that barrier has mostly been removed.
“Our patients are at least as willing as any other subgroup to get the vaccine, and that includes people with psychotic disorders,” he said.
The study was supported by the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Immuno-NeuroPsychiatry network and Fondazione Centro San Raffaele (Milan). Dr. De Picker reported receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Janssen outside the submitted work. She is a member of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Immuno-NeuroPsychiatry Thematic Working Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
compared with those without a psychiatric diagnosis, according to the results of the largest study of its kind to date.
These findings, the investigators noted, highlight the need to prioritize vaccination in patients with preexisting mental health disorders.
“We have proven beyond a shadow of a doubt that there are increased risks” among psychiatric patients who get COVID-19, study investigator Livia De Picker, MD, PhD, psychiatrist and postdoctoral researcher, University Psychiatric Hospital Campus Duffel and University of Antwerp (Belgium), told this news organization.
“Doctors need to look at these patients the same way they would other high-risk people, for example those with diabetes or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,” all of whom should be protected against COVID-19, Dr. De Picker added.
The study was published online July 15, 2021, in Lancet Psychiatry.
Risk by mental illness type
The systematic review included 33 studies from 22 countries that reported risk estimates for mortality, hospitalization, and ICU admission in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. The meta-analysis included 23 of these studies with a total of 1.47 million participants. Of these, 43,938 had a psychiatric disorder.
The primary outcome was mortality after COVID-19. Secondary outcomes included hospitalization and ICU admission after COVID-19. Researchers adjusted for age, sex, and other covariates.
Results showed the presence of any comorbid mental illness was associated with an increased risk for death after SARS-CoV-2 infection (odds ratio, 2.00; 95% confidence interval, 1.58-2.54; P < .0001).
When researchers stratified mortality risk by psychiatric disorder type, the most robust associations were for psychotic and mood disorders. Substance use disorders, intellectual disabilities, and developmental disorders were associated with higher mortality only in crude estimates. There was no increased death risk associated with anxiety disorders.
“That there are differences between the various types of disorders was an interesting finding,” said Dr. De Picker, adding that previous research “just lumped together all diagnostic categories.”
Potential mechanisms
The study did not explore why psychiatric illness raise the risk for death in the setting of COVID-19, so potential mechanisms are purely speculative. However, the investigators believe it may reflect biological processes such as immune-inflammatory alterations.
Psychotic disorders and mood disorders in particular, are associated with immune changes, including immunogenetic abnormalities, raised cytokine concentrations, autoantibodies, acute-phase proteins, and aberrant counts of leukocyte cell types, said Dr. De Picker.
She likened this to elderly people being at increased risk following COVID-19 because their immune system is compromised and less able to fight infection.
There are likely other factors at play, said Dr. De Picker. These could include social isolation and lifestyle factors like poor diet, physical inactivity, high alcohol and tobacco use, and sleep disturbances.
In addition, psychiatric patients have a higher prevalence of comorbidities including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory disease, which could also play a role.
The increased mortality might also reflect reduced access to care. “Some of these patients may be living in difficult socioeconomic conditions,” said Dr. De Picker.
She noted that, while the in-hospital mortality was not increased, the risk was significantly increased in samples that were outside of the hospital. This reinforces the need for providing close monitoring and early referral to hospital for psychiatric patients with COVID-19.
Mortality varied significantly among countries, with the lowest risk in Europe and the United States. This difference might be attributable to differences in health care systems and access to care, said Dr. De Picker.
Overall, the risk for hospitalization was about double for COVID patients with a mental illness, but when stratified by disorder, there was only a significantly increased risk for substance use and mood disorders. “But mood disorders were not even significant any more after adjusting for age, sex, and comorbid conditions, and we don’t see an increased risk for psychotic disorders whereas they had the highest mortality risks,” said Dr. De Picker.
Psych meds a risk factor?
The studies were primarily based on electronic medical records, so investigators were unable to carry out “a fine grain analysis” into clinical factors affecting outcomes, she noted.
Antipsychotics were consistently associated with an increased risk for mortality (adjusted OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.81-3.25), as were anxiolytics (aOR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.15-1.88).
“There are some theoretical reasons why we believe there could be a risk associated with these drugs,” said Dr. De Picker. For example, antipsychotics can increase the risk for cardiac arrhythmias and thromboembolic events, and cause interactions with drugs used to treat COVID-19.
As for anxiolytics, especially benzodiazepines, these drugs are associated with respiratory risk and with all-cause mortality. “So you could imagine that someone who is infected with a respiratory virus and [is] then using these drugs on top of that would have a worse outcome,” said Dr. De Picker.
In contrast to antipsychotics and anxiolytics, antidepressants did not increase mortality risk.
Dr. De Picker noted a new study by French researchers showing a protective effect of certain serotonergic antidepressants on COVID outcomes, including mortality.
There was no robust evidence of an increased risk for ICU admission for patients with mental disorders. However, the authors noted some studies included small samples of patients with psychiatric disorders, “contributing to a low certainty of evidence for ICU admission.”
Dr. De Picker criticized COVID vaccine policies that don’t prioritize patients with psychiatric disorders. In many countries, groups that were initially green-lighted for the vaccine included health care workers, the elderly, and those with underlying conditions such as diabetes, obesity and even mild hypertension – but not mental illness, which is also an underlying risk.
‘Outstanding’ research
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and chair of the American Psychiatric Association Council on Research, called it “outstanding” and the largest of its kind.
“There have been a number of studies that have come to similar conclusions, that people with psychiatric illness are at greater risk for poorer outcomes, but because any given study had a relatively limited sample, perhaps from one health system or one country, there were some inconsistencies,” said Dr. Alpert.
“This is the strongest report so far that has made the point that people with psychiatric illness are a vulnerable population for a negative outcome from COVID, including the most worrisome – mortality.”
The study helps drive home a “very important public health lesson” that applies to COVID-19 but goes “beyond,” said Dr. Alpert.
“As a society, we need to keep in mind that people with serious mental disorders are a vulnerable population for poorer outcomes in most general medical conditions,” he stressed, “whether it’s cancer or heart disease or diabetes, and special efforts need to be made to reach out to those populations.”
Dr. Alpert agreed that, at the start of the pandemic, psychiatric patients in the United States were not prioritized for vaccination, and although psychiatric patients may initially have found it difficult to navigate the health care system to learn where and how to get a COVID shot, today that barrier has mostly been removed.
“Our patients are at least as willing as any other subgroup to get the vaccine, and that includes people with psychotic disorders,” he said.
The study was supported by the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Immuno-NeuroPsychiatry network and Fondazione Centro San Raffaele (Milan). Dr. De Picker reported receiving grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Janssen outside the submitted work. She is a member of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Immuno-NeuroPsychiatry Thematic Working Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lucid abductions and Candy Crush addiction
I dream of alien abductions
There he goes! It’s lunchtime and your colleague Tom is going on and on again about that time he was abducted by aliens. It sounds ridiculous, but he does make some convincing arguments. Tom thinks it was real, but could it have all just been in his head?
Lucid dreaming may help explain alleged alien abductions. During a lucid dream, people know that they’re dreaming, and can also have some control over how the dreams play out. During some dream states, a person can feel intense sensations, such as terror and paralysis, so it’s no wonder these dreams feel so real.
In a recent study, scientists encouraged 152 participants who had self-identified as lucid dreamers to dream about aliens. Many (75%) of the participants were able to dream about alien encounters, and 15% “achieved relatively realistic experiences,” the investigators reported.
So cut Tom some slack. He’s not crazy, he might just have lucid dreaming privileges. Tell him he should dream about something more fun, like a vacation in the Bahamas.
Follow your heart: Drink more coffee
It seems like the world is divided into coffee drinkers and non–coffee drinkers. Then there’s decaf and regular drinkers. Whichever camp you fall into, know this: The widespread belief that caffeine consumption has an effect on your heart is all beans.
In what is the largest investigation of its kind, researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, looked into whether drinking caffeinated coffee was linked to a risk for heart arrhythmia. They also researched whether patients with genetic variants that affect their metabolism could change that association. Almost 400,000 people with a mean age of 56 years participated in the study. More than half of the participants were women.
The investigators analyzed the participants’ self-reported coffee consumption using a technique called Mendelian randomization to leverage genetic data with the participants’ relationship with caffeine, making it an even field and not relying on the participant consumption self-reporting for outcomes as in previous studies.
What they found, after the 4-year follow up, was nothing short of myth busting.
“We found no evidence that caffeine consumption leads to a greater risk of arrhythmias,” said senior and corresponding author Gregory Marcus, MD. “Our population-based study provides reassurance that common prohibitions against caffeine to reduce arrhythmia risk are likely unwarranted.”
There was no evidence of a heightened risk of arrhythmias in participants who were genetically predisposed to metabolize caffeine differently from those who were not. And, there was a 3% reduction of arrhythmias in patients who consumed higher amounts of coffee.
We are not lobbying for Big Caffeine, but this study adds to the reported health benefits linked to coffee, which already include reduced risk for cancer, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease, with an added bonus of anti-inflammatory benefits. So, the next time you’re hesitant to pour that second cup of Joe, just go for it. Your heart can take it.
Bored? Feeling down? Don’t play Candy Crush
Now hang on, aren’t those the perfect times to play video games? If there’s nothing else to do, why not open Candy Crush and mindlessly power through the levels?
Because, according to a study by a group of Canadian researchers, it’s actually the worst thing you can do. Well, maybe not literally, but it’s not helpful. Researchers recruited 60 Candy Crush players who were at various levels in the game. They had the participants play early levels that were far too easy or levels balanced with their gameplay abilities.
Players in the easy-level group got bored and quit far earlier than did those in the advanced-level group. The group playing to their abilities were able to access a “flow” state and focus all their attention on the game. While this is all well and good for their gaming performance, according to the researchers, it confirms the theory that playing to escape boredom or negative emotions is more likely to lead to addiction. As with all addictions, the temporary high can give way to a self-repeating loop, causing patients to ignore real life and deepen depression.
The researchers hope their findings will encourage game developers to “consider implementing responsible video gaming tools directly within their games.” Comedy gold. Perhaps Canadians’ idea of capitalism is a little different from that of those south of the border.
Hiccups and vaccine refusal
Tonight, LOTME News dives into the fetid cesspool that is international politics and comes out with … hiccups?
But first, a word from our sponsor, Fearless Boxing Club of South Etobicoke, Ontario.
Are you looking to flout public health restrictions? Do you want to spend time in an enclosed space with other people who haven’t gotten the COVID-19 vaccine? Do you “feel safer waiting until more research is done on the side effects being discovered right now”? (We are not making this up.)
Then join the Fearless Boxing Club, because we “will not be accepting any vaccinated members.” Our founders, Mohammed Abedeen and Krystal Glazier-Roscoe, are working hard to exclude “those who received the experimental COVID vaccine.” (Still not making it up.)
And now, back to the news.
Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro was hospitalized recently for a severe case of hiccups that may have been related to a stab wound he received in 2018. [Nope, didn’t make that up, either.]
Mr. Bolsonaro had been hiccuping for 10 days, and was experiencing abdominal pain and difficulty speaking, when he entered the hospital on July 14. Since being stabbed while on the campaign trail, he has undergone several operations, which may have led to the partial intestinal obstruction that caused his latest symptoms.
His medical team advised Mr. Bolsonaro to go on a diet to aid his recovery, but when he was released on July 18 he said, “I hope in 10 days I’ll be eating barbecued ribs.” (Maybe this is all just a lucid dream. Probably shouldn’t have had ribs right before bed.)
I dream of alien abductions
There he goes! It’s lunchtime and your colleague Tom is going on and on again about that time he was abducted by aliens. It sounds ridiculous, but he does make some convincing arguments. Tom thinks it was real, but could it have all just been in his head?
Lucid dreaming may help explain alleged alien abductions. During a lucid dream, people know that they’re dreaming, and can also have some control over how the dreams play out. During some dream states, a person can feel intense sensations, such as terror and paralysis, so it’s no wonder these dreams feel so real.
In a recent study, scientists encouraged 152 participants who had self-identified as lucid dreamers to dream about aliens. Many (75%) of the participants were able to dream about alien encounters, and 15% “achieved relatively realistic experiences,” the investigators reported.
So cut Tom some slack. He’s not crazy, he might just have lucid dreaming privileges. Tell him he should dream about something more fun, like a vacation in the Bahamas.
Follow your heart: Drink more coffee
It seems like the world is divided into coffee drinkers and non–coffee drinkers. Then there’s decaf and regular drinkers. Whichever camp you fall into, know this: The widespread belief that caffeine consumption has an effect on your heart is all beans.
In what is the largest investigation of its kind, researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, looked into whether drinking caffeinated coffee was linked to a risk for heart arrhythmia. They also researched whether patients with genetic variants that affect their metabolism could change that association. Almost 400,000 people with a mean age of 56 years participated in the study. More than half of the participants were women.
The investigators analyzed the participants’ self-reported coffee consumption using a technique called Mendelian randomization to leverage genetic data with the participants’ relationship with caffeine, making it an even field and not relying on the participant consumption self-reporting for outcomes as in previous studies.
What they found, after the 4-year follow up, was nothing short of myth busting.
“We found no evidence that caffeine consumption leads to a greater risk of arrhythmias,” said senior and corresponding author Gregory Marcus, MD. “Our population-based study provides reassurance that common prohibitions against caffeine to reduce arrhythmia risk are likely unwarranted.”
There was no evidence of a heightened risk of arrhythmias in participants who were genetically predisposed to metabolize caffeine differently from those who were not. And, there was a 3% reduction of arrhythmias in patients who consumed higher amounts of coffee.
We are not lobbying for Big Caffeine, but this study adds to the reported health benefits linked to coffee, which already include reduced risk for cancer, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease, with an added bonus of anti-inflammatory benefits. So, the next time you’re hesitant to pour that second cup of Joe, just go for it. Your heart can take it.
Bored? Feeling down? Don’t play Candy Crush
Now hang on, aren’t those the perfect times to play video games? If there’s nothing else to do, why not open Candy Crush and mindlessly power through the levels?
Because, according to a study by a group of Canadian researchers, it’s actually the worst thing you can do. Well, maybe not literally, but it’s not helpful. Researchers recruited 60 Candy Crush players who were at various levels in the game. They had the participants play early levels that were far too easy or levels balanced with their gameplay abilities.
Players in the easy-level group got bored and quit far earlier than did those in the advanced-level group. The group playing to their abilities were able to access a “flow” state and focus all their attention on the game. While this is all well and good for their gaming performance, according to the researchers, it confirms the theory that playing to escape boredom or negative emotions is more likely to lead to addiction. As with all addictions, the temporary high can give way to a self-repeating loop, causing patients to ignore real life and deepen depression.
The researchers hope their findings will encourage game developers to “consider implementing responsible video gaming tools directly within their games.” Comedy gold. Perhaps Canadians’ idea of capitalism is a little different from that of those south of the border.
Hiccups and vaccine refusal
Tonight, LOTME News dives into the fetid cesspool that is international politics and comes out with … hiccups?
But first, a word from our sponsor, Fearless Boxing Club of South Etobicoke, Ontario.
Are you looking to flout public health restrictions? Do you want to spend time in an enclosed space with other people who haven’t gotten the COVID-19 vaccine? Do you “feel safer waiting until more research is done on the side effects being discovered right now”? (We are not making this up.)
Then join the Fearless Boxing Club, because we “will not be accepting any vaccinated members.” Our founders, Mohammed Abedeen and Krystal Glazier-Roscoe, are working hard to exclude “those who received the experimental COVID vaccine.” (Still not making it up.)
And now, back to the news.
Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro was hospitalized recently for a severe case of hiccups that may have been related to a stab wound he received in 2018. [Nope, didn’t make that up, either.]
Mr. Bolsonaro had been hiccuping for 10 days, and was experiencing abdominal pain and difficulty speaking, when he entered the hospital on July 14. Since being stabbed while on the campaign trail, he has undergone several operations, which may have led to the partial intestinal obstruction that caused his latest symptoms.
His medical team advised Mr. Bolsonaro to go on a diet to aid his recovery, but when he was released on July 18 he said, “I hope in 10 days I’ll be eating barbecued ribs.” (Maybe this is all just a lucid dream. Probably shouldn’t have had ribs right before bed.)
I dream of alien abductions
There he goes! It’s lunchtime and your colleague Tom is going on and on again about that time he was abducted by aliens. It sounds ridiculous, but he does make some convincing arguments. Tom thinks it was real, but could it have all just been in his head?
Lucid dreaming may help explain alleged alien abductions. During a lucid dream, people know that they’re dreaming, and can also have some control over how the dreams play out. During some dream states, a person can feel intense sensations, such as terror and paralysis, so it’s no wonder these dreams feel so real.
In a recent study, scientists encouraged 152 participants who had self-identified as lucid dreamers to dream about aliens. Many (75%) of the participants were able to dream about alien encounters, and 15% “achieved relatively realistic experiences,” the investigators reported.
So cut Tom some slack. He’s not crazy, he might just have lucid dreaming privileges. Tell him he should dream about something more fun, like a vacation in the Bahamas.
Follow your heart: Drink more coffee
It seems like the world is divided into coffee drinkers and non–coffee drinkers. Then there’s decaf and regular drinkers. Whichever camp you fall into, know this: The widespread belief that caffeine consumption has an effect on your heart is all beans.
In what is the largest investigation of its kind, researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, looked into whether drinking caffeinated coffee was linked to a risk for heart arrhythmia. They also researched whether patients with genetic variants that affect their metabolism could change that association. Almost 400,000 people with a mean age of 56 years participated in the study. More than half of the participants were women.
The investigators analyzed the participants’ self-reported coffee consumption using a technique called Mendelian randomization to leverage genetic data with the participants’ relationship with caffeine, making it an even field and not relying on the participant consumption self-reporting for outcomes as in previous studies.
What they found, after the 4-year follow up, was nothing short of myth busting.
“We found no evidence that caffeine consumption leads to a greater risk of arrhythmias,” said senior and corresponding author Gregory Marcus, MD. “Our population-based study provides reassurance that common prohibitions against caffeine to reduce arrhythmia risk are likely unwarranted.”
There was no evidence of a heightened risk of arrhythmias in participants who were genetically predisposed to metabolize caffeine differently from those who were not. And, there was a 3% reduction of arrhythmias in patients who consumed higher amounts of coffee.
We are not lobbying for Big Caffeine, but this study adds to the reported health benefits linked to coffee, which already include reduced risk for cancer, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease, with an added bonus of anti-inflammatory benefits. So, the next time you’re hesitant to pour that second cup of Joe, just go for it. Your heart can take it.
Bored? Feeling down? Don’t play Candy Crush
Now hang on, aren’t those the perfect times to play video games? If there’s nothing else to do, why not open Candy Crush and mindlessly power through the levels?
Because, according to a study by a group of Canadian researchers, it’s actually the worst thing you can do. Well, maybe not literally, but it’s not helpful. Researchers recruited 60 Candy Crush players who were at various levels in the game. They had the participants play early levels that were far too easy or levels balanced with their gameplay abilities.
Players in the easy-level group got bored and quit far earlier than did those in the advanced-level group. The group playing to their abilities were able to access a “flow” state and focus all their attention on the game. While this is all well and good for their gaming performance, according to the researchers, it confirms the theory that playing to escape boredom or negative emotions is more likely to lead to addiction. As with all addictions, the temporary high can give way to a self-repeating loop, causing patients to ignore real life and deepen depression.
The researchers hope their findings will encourage game developers to “consider implementing responsible video gaming tools directly within their games.” Comedy gold. Perhaps Canadians’ idea of capitalism is a little different from that of those south of the border.
Hiccups and vaccine refusal
Tonight, LOTME News dives into the fetid cesspool that is international politics and comes out with … hiccups?
But first, a word from our sponsor, Fearless Boxing Club of South Etobicoke, Ontario.
Are you looking to flout public health restrictions? Do you want to spend time in an enclosed space with other people who haven’t gotten the COVID-19 vaccine? Do you “feel safer waiting until more research is done on the side effects being discovered right now”? (We are not making this up.)
Then join the Fearless Boxing Club, because we “will not be accepting any vaccinated members.” Our founders, Mohammed Abedeen and Krystal Glazier-Roscoe, are working hard to exclude “those who received the experimental COVID vaccine.” (Still not making it up.)
And now, back to the news.
Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro was hospitalized recently for a severe case of hiccups that may have been related to a stab wound he received in 2018. [Nope, didn’t make that up, either.]
Mr. Bolsonaro had been hiccuping for 10 days, and was experiencing abdominal pain and difficulty speaking, when he entered the hospital on July 14. Since being stabbed while on the campaign trail, he has undergone several operations, which may have led to the partial intestinal obstruction that caused his latest symptoms.
His medical team advised Mr. Bolsonaro to go on a diet to aid his recovery, but when he was released on July 18 he said, “I hope in 10 days I’ll be eating barbecued ribs.” (Maybe this is all just a lucid dream. Probably shouldn’t have had ribs right before bed.)
Is TikTok a tool in mental health care?
There was a time when I was on the cutting edge of psychiatry and technology. I was the first physician I knew to communicate with my patients by text messages, which left my colleagues aghast. And then, in 2006, I started a blog with two other psychiatrists; they chose to use pseudonyms, but I used my real (and uncommon) first name, well aware that this might leave me a bit exposed.
“You know your patients will read it,” one colleague said when I told him. Was that bad? I had no intention of writing anything I would be embarrassed to have others read. And yes, it’s obviously hard to know how people will react to what you say in another context, but I am a writer, and squelching this part of me would have left me feeling that I’m not living a genuine life. And so I write, always aware that others may be watching over my shoulder.
Social media has also been a part of my life. It is therefore with great interest that I took note of a new trend: Several of my psychiatrist colleagues were taking to TikTok to share their personal experiences in ways that probably would have been unthinkable just a few years past.
Psychiatry finds an unexpected new platform
TikTok is an app platform for sharing short-form videos, not the written word. It’s dominated by song and dance videos, sometimes lip-synced, and often recorded by the user holding a phone. The videos are brief, lasting mere seconds to a minute.
TikTok was launched in China in 2016 and became available worldwide in 2018. Since that time, it’s primarily become a venue for younger people, with 41% of users in the 16- to 24-year-old age range. They are skilled at navigating TikTok’s truly overwhelming amount of content, something I have yet to comfortably master as an observer, much less as someone who creates content.
David Puder, MD (@dr.davidpuder) is a psychiatrist in Florida who has not shied away from TikTok. He started making videos on the platform in 2020 as a way to promote his Psychiatry & Psychotherapy Podcast. His videos are casual and informative, and his TikTok description reads: “I am trying to teach things to help you connect better with others.”
“TikTok became another way of promoting mental health ideas,” said Dr. Puder. “There is a lot of bad information out there and my overarching purpose is to try to get people excited about mental health.”
Dr. Puder has nearly 112,000 TikTok followers. There’s a mix of creativity and acting that goes into the production of his videos, which he tends to record from his office or car. They vary in content. Some include music, while others are seconds-long mini-lectures on psychiatric topics. Some are purely educational but can include a joke about how many narcissists it takes to screw in a light bulb. They’re also where I learned that he is more likely to cry at sad movies than is his wife.
“I wish more doctors considered being out there,” Dr. Puder said, “but there is an internal resistance we have to exposing ourselves.”
TikTok and podcasting have been positive experiences for him. “I get emails from followers with notes of gratitude, and l have gotten feedback that people have become mental health professionals because of my social media.”
TikTok’s psychiatrist sensation
Melissa Shepard, MD (@doctorshepard_md) is also a psychiatrist who posts content on TikTok. With over a million followers, Dr. Shepard is TikTok’s psychiatrist sensation. She started posting mental health information on Instagram, and then in December 2019 began to cross-post on TikTok. She estimates that she has put up hundreds of videos but does not have an exact number. The Today Show used one of her TikTok videos for a segment on teen mental health.
“It has been cool to contribute to the conversation in this kind of way,” Dr. Shepard said.
The media attention has been a mixed bag for Dr. Shepard. As anyone who talks about psychiatry on social media knows, there are people who are vocal about their antipsychiatry opinions, and Dr. Shepard has not been spared. Sometimes the feedback has been hostile or even threatening.
“There have been ups and downs,” she said. “I have thought about stopping, but then I get these amazing messages from people who tell me that my videos made them realize they needed help. So while it has been a bumpy ride, I feel like I’m doing something good.”
Dr. Shepard’s videos are more personal in that she has used TikTok as a forum to discuss her own mental health struggles. “It’s scary, but it has also been liberating. I want people to know that they can succeed and that we need to get rid of the stigma because it gets in the way. When I was suffering from panic attacks and depression, I thought I was the only medical student with these issues and it meant I couldn’t become a doctor.”
Dr. Shepard estimates that half of her patients found her on TikTok. “I always ask myself, would I be okay with my patients seeing this? My patients are younger and they like that I’m on social media. It makes them feel like they know me before they start treatment.”
As we were talking, Dr. Shepard made note of the fact that having a public persona does not fit in with the “blank slate” rules of a psychodynamic psychotherapy.
She had me wondering how those rules might have been constructed if the internet and social media had existed when psychoanalysis was just developing. Perhaps we’d all be clicking “follow” on Sigmund Freud’s TikTok account.Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. She has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There was a time when I was on the cutting edge of psychiatry and technology. I was the first physician I knew to communicate with my patients by text messages, which left my colleagues aghast. And then, in 2006, I started a blog with two other psychiatrists; they chose to use pseudonyms, but I used my real (and uncommon) first name, well aware that this might leave me a bit exposed.
“You know your patients will read it,” one colleague said when I told him. Was that bad? I had no intention of writing anything I would be embarrassed to have others read. And yes, it’s obviously hard to know how people will react to what you say in another context, but I am a writer, and squelching this part of me would have left me feeling that I’m not living a genuine life. And so I write, always aware that others may be watching over my shoulder.
Social media has also been a part of my life. It is therefore with great interest that I took note of a new trend: Several of my psychiatrist colleagues were taking to TikTok to share their personal experiences in ways that probably would have been unthinkable just a few years past.
Psychiatry finds an unexpected new platform
TikTok is an app platform for sharing short-form videos, not the written word. It’s dominated by song and dance videos, sometimes lip-synced, and often recorded by the user holding a phone. The videos are brief, lasting mere seconds to a minute.
TikTok was launched in China in 2016 and became available worldwide in 2018. Since that time, it’s primarily become a venue for younger people, with 41% of users in the 16- to 24-year-old age range. They are skilled at navigating TikTok’s truly overwhelming amount of content, something I have yet to comfortably master as an observer, much less as someone who creates content.
David Puder, MD (@dr.davidpuder) is a psychiatrist in Florida who has not shied away from TikTok. He started making videos on the platform in 2020 as a way to promote his Psychiatry & Psychotherapy Podcast. His videos are casual and informative, and his TikTok description reads: “I am trying to teach things to help you connect better with others.”
“TikTok became another way of promoting mental health ideas,” said Dr. Puder. “There is a lot of bad information out there and my overarching purpose is to try to get people excited about mental health.”
Dr. Puder has nearly 112,000 TikTok followers. There’s a mix of creativity and acting that goes into the production of his videos, which he tends to record from his office or car. They vary in content. Some include music, while others are seconds-long mini-lectures on psychiatric topics. Some are purely educational but can include a joke about how many narcissists it takes to screw in a light bulb. They’re also where I learned that he is more likely to cry at sad movies than is his wife.
“I wish more doctors considered being out there,” Dr. Puder said, “but there is an internal resistance we have to exposing ourselves.”
TikTok and podcasting have been positive experiences for him. “I get emails from followers with notes of gratitude, and l have gotten feedback that people have become mental health professionals because of my social media.”
TikTok’s psychiatrist sensation
Melissa Shepard, MD (@doctorshepard_md) is also a psychiatrist who posts content on TikTok. With over a million followers, Dr. Shepard is TikTok’s psychiatrist sensation. She started posting mental health information on Instagram, and then in December 2019 began to cross-post on TikTok. She estimates that she has put up hundreds of videos but does not have an exact number. The Today Show used one of her TikTok videos for a segment on teen mental health.
“It has been cool to contribute to the conversation in this kind of way,” Dr. Shepard said.
The media attention has been a mixed bag for Dr. Shepard. As anyone who talks about psychiatry on social media knows, there are people who are vocal about their antipsychiatry opinions, and Dr. Shepard has not been spared. Sometimes the feedback has been hostile or even threatening.
“There have been ups and downs,” she said. “I have thought about stopping, but then I get these amazing messages from people who tell me that my videos made them realize they needed help. So while it has been a bumpy ride, I feel like I’m doing something good.”
Dr. Shepard’s videos are more personal in that she has used TikTok as a forum to discuss her own mental health struggles. “It’s scary, but it has also been liberating. I want people to know that they can succeed and that we need to get rid of the stigma because it gets in the way. When I was suffering from panic attacks and depression, I thought I was the only medical student with these issues and it meant I couldn’t become a doctor.”
Dr. Shepard estimates that half of her patients found her on TikTok. “I always ask myself, would I be okay with my patients seeing this? My patients are younger and they like that I’m on social media. It makes them feel like they know me before they start treatment.”
As we were talking, Dr. Shepard made note of the fact that having a public persona does not fit in with the “blank slate” rules of a psychodynamic psychotherapy.
She had me wondering how those rules might have been constructed if the internet and social media had existed when psychoanalysis was just developing. Perhaps we’d all be clicking “follow” on Sigmund Freud’s TikTok account.Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. She has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There was a time when I was on the cutting edge of psychiatry and technology. I was the first physician I knew to communicate with my patients by text messages, which left my colleagues aghast. And then, in 2006, I started a blog with two other psychiatrists; they chose to use pseudonyms, but I used my real (and uncommon) first name, well aware that this might leave me a bit exposed.
“You know your patients will read it,” one colleague said when I told him. Was that bad? I had no intention of writing anything I would be embarrassed to have others read. And yes, it’s obviously hard to know how people will react to what you say in another context, but I am a writer, and squelching this part of me would have left me feeling that I’m not living a genuine life. And so I write, always aware that others may be watching over my shoulder.
Social media has also been a part of my life. It is therefore with great interest that I took note of a new trend: Several of my psychiatrist colleagues were taking to TikTok to share their personal experiences in ways that probably would have been unthinkable just a few years past.
Psychiatry finds an unexpected new platform
TikTok is an app platform for sharing short-form videos, not the written word. It’s dominated by song and dance videos, sometimes lip-synced, and often recorded by the user holding a phone. The videos are brief, lasting mere seconds to a minute.
TikTok was launched in China in 2016 and became available worldwide in 2018. Since that time, it’s primarily become a venue for younger people, with 41% of users in the 16- to 24-year-old age range. They are skilled at navigating TikTok’s truly overwhelming amount of content, something I have yet to comfortably master as an observer, much less as someone who creates content.
David Puder, MD (@dr.davidpuder) is a psychiatrist in Florida who has not shied away from TikTok. He started making videos on the platform in 2020 as a way to promote his Psychiatry & Psychotherapy Podcast. His videos are casual and informative, and his TikTok description reads: “I am trying to teach things to help you connect better with others.”
“TikTok became another way of promoting mental health ideas,” said Dr. Puder. “There is a lot of bad information out there and my overarching purpose is to try to get people excited about mental health.”
Dr. Puder has nearly 112,000 TikTok followers. There’s a mix of creativity and acting that goes into the production of his videos, which he tends to record from his office or car. They vary in content. Some include music, while others are seconds-long mini-lectures on psychiatric topics. Some are purely educational but can include a joke about how many narcissists it takes to screw in a light bulb. They’re also where I learned that he is more likely to cry at sad movies than is his wife.
“I wish more doctors considered being out there,” Dr. Puder said, “but there is an internal resistance we have to exposing ourselves.”
TikTok and podcasting have been positive experiences for him. “I get emails from followers with notes of gratitude, and l have gotten feedback that people have become mental health professionals because of my social media.”
TikTok’s psychiatrist sensation
Melissa Shepard, MD (@doctorshepard_md) is also a psychiatrist who posts content on TikTok. With over a million followers, Dr. Shepard is TikTok’s psychiatrist sensation. She started posting mental health information on Instagram, and then in December 2019 began to cross-post on TikTok. She estimates that she has put up hundreds of videos but does not have an exact number. The Today Show used one of her TikTok videos for a segment on teen mental health.
“It has been cool to contribute to the conversation in this kind of way,” Dr. Shepard said.
The media attention has been a mixed bag for Dr. Shepard. As anyone who talks about psychiatry on social media knows, there are people who are vocal about their antipsychiatry opinions, and Dr. Shepard has not been spared. Sometimes the feedback has been hostile or even threatening.
“There have been ups and downs,” she said. “I have thought about stopping, but then I get these amazing messages from people who tell me that my videos made them realize they needed help. So while it has been a bumpy ride, I feel like I’m doing something good.”
Dr. Shepard’s videos are more personal in that she has used TikTok as a forum to discuss her own mental health struggles. “It’s scary, but it has also been liberating. I want people to know that they can succeed and that we need to get rid of the stigma because it gets in the way. When I was suffering from panic attacks and depression, I thought I was the only medical student with these issues and it meant I couldn’t become a doctor.”
Dr. Shepard estimates that half of her patients found her on TikTok. “I always ask myself, would I be okay with my patients seeing this? My patients are younger and they like that I’m on social media. It makes them feel like they know me before they start treatment.”
As we were talking, Dr. Shepard made note of the fact that having a public persona does not fit in with the “blank slate” rules of a psychodynamic psychotherapy.
She had me wondering how those rules might have been constructed if the internet and social media had existed when psychoanalysis was just developing. Perhaps we’d all be clicking “follow” on Sigmund Freud’s TikTok account.Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. She has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.











