User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


New return-to-play recommendations for athletes with COVID-19
The latest recommendations from sports cardiologists on getting athletes with COVID-19 back on the playing field safely emphasize a more judicious approach to screening for cardiac injury.
The new recommendations, made by the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Cardiology Section, are for adult athletes in competitive sports and also for two important groups: younger athletes taking part in competitive high school sports and older athletes aged 35 and older, the Masters athletes, who continue to be active throughout their lives. The document was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Because of the evolving nature of knowledge about COVID-19, updates on recommendations for safe return to play for athletes of all ages will continue to be made, senior author Aaron L. Baggish, MD, director of the cardiovascular performance program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said.
“The recommendations we released in May were entirely based on our experience taking care of hospitalized patients with COVID-19; we had no athletes in this population. We used a lot of conservative guesswork around how this would apply to otherwise healthy athletes,” Dr. Baggish said in an interview.
“But as sports started to open up, and we started to see large numbers of first professional and then college athletes come back into training, we realized that we needed to stop and ask whether the recommendations we put forward back in May were still appropriate,” Dr. Baggish said.
“Once we started to actually get into the trenches with these athletes, literally hundreds of them, and applying the testing strategies that we had initially recommended in everybody, we realized that we probably had some room for improvement, and that’s why we reconvened, to make these revisions,” he said.
Essentially, the recommendations now urge less cardiac testing. “Cardiac injury is not as common as we may have originally thought,” said Dr. Baggish.
“In the early days of COVID, people who were hospitalized had evidence of heart injury, and so we wondered if that prevalence would also be applicable to otherwise young, healthy people who got COVID. If that had been the case, we would have been in big trouble with respect to getting people back into sports. So this is why we started with a conservative screening approach and a lot of testing in order to not miss a huge burden of disease,” he said.
“But what we’ve learned over the past few months is that young people who get either asymptomatic or mild infection appear to have very, very low risk of having associated heart injury, so the need for testing in that population, when people who have infections recover fully, is almost certainly not going to be high yield,” Dr. Baggish said.
First iteration of the recommendations
Published in May in the early weeks of the pandemic, the first recommendations for safe return to play said that all athletes should stop training for at least 2 weeks after their symptoms resolve, then undergo “careful, clinical cardiovascular evaluation in combination with cardiac biomarkers and imaging.”
Additional testing with cardiac MRI, exercise testing, or ambulatory rhythm monitoring was to be done “based on the clinical course and initial testing.”
But experts caution that monitoring on such a scale in everyone is unnecessary and could even be counterproductive.
“Sending young athletes for extensive testing is not warranted and could send them to unnecessary testing, cardiac imaging, and so on,” Dr. Baggish said.
Only those athletes who continue to have symptoms or whose symptoms return when they get back to their athletic activities should go on for more screening.
“There, in essence, is the single main change from May, and that is a move away from screening with testing everyone, [and instead] confining that to the people who had moderate or greater severity disease,” he said.
Both iterations of the recommendations end with the same message.
“We are at the beginning of our knowledge about the cardiotoxic effects of COVID-19 but we are gathering evidence every day,” said Dr. Baggish. “Just as they did earlier, we acknowledge that our approaches are subject to change when we learn more about how COVID affects the heart, and specifically the hearts of athletes. This will be an ongoing process.”
Something to lean on
The recommendations are welcome, said James E. Udelson, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“It was a bit of the wild west out there, because each university, each college, all with good intentions, had been all struggling to figure out what to do, and how much to do. Probably the most important message from this new paper is the fact that now there is something out there that all coaches, athletes, families, schools, trainers can get some guidance from,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
Refining the cardiac screening criteria was a necessary step, Dr. Udelson said.
“How much cardiac imaging do you do? That is a matter of controversy,” said Dr. Udelson, who coauthored the commentary with Tufts cardiologist Ethan Rowin, MD, and Michael A. Curtis, MEd, a certified strength and conditioning specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “The problem is that if you use a very sensitive imaging test on a lot of people, sometimes you find things that you really didn’t need to know about. They’re really not important. And now, the athlete is told he or she cannot play for 3 months because they might have myocarditis.
“Should we be too sensitive, meaning do we want to pick up anything no matter whether it’s important or not?” he added. “There will be a lot of false positives, and we are going to disqualify a lot of people. Or do you tune it a different way?”
Dr. Udelson said he would like to see commercial sports donate money to support research into the potential cardiotoxicity of COVID-19.
“If the organizations that benefit from these athletes, like the National Collegiate Athletic Association and professional sports leagues, can fund some of this research, that would be a huge help,” Dr. Udelson said.
“These are the top sports cardiologists in the country, and they have to start somewhere, and these are all based on what we know right now, as well as their own extensive experience. We all know that we are just at the beginning of our knowledge of this. But we have to have something to guide this huge community out there that is really thirsty for help.”
Dr. Baggish reports receiving research funding for the study of athletes in competitive sports from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Football League Players Association; and the American Heart Association and receiving compensation for his role as team cardiologist from the US Olympic Committee/US Olympic Training Centers, US Soccer, US Rowing, the New England Patriots, the Boston Bruins, the New England Revolution, and Harvard University. Dr. Udelson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest recommendations from sports cardiologists on getting athletes with COVID-19 back on the playing field safely emphasize a more judicious approach to screening for cardiac injury.
The new recommendations, made by the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Cardiology Section, are for adult athletes in competitive sports and also for two important groups: younger athletes taking part in competitive high school sports and older athletes aged 35 and older, the Masters athletes, who continue to be active throughout their lives. The document was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Because of the evolving nature of knowledge about COVID-19, updates on recommendations for safe return to play for athletes of all ages will continue to be made, senior author Aaron L. Baggish, MD, director of the cardiovascular performance program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said.
“The recommendations we released in May were entirely based on our experience taking care of hospitalized patients with COVID-19; we had no athletes in this population. We used a lot of conservative guesswork around how this would apply to otherwise healthy athletes,” Dr. Baggish said in an interview.
“But as sports started to open up, and we started to see large numbers of first professional and then college athletes come back into training, we realized that we needed to stop and ask whether the recommendations we put forward back in May were still appropriate,” Dr. Baggish said.
“Once we started to actually get into the trenches with these athletes, literally hundreds of them, and applying the testing strategies that we had initially recommended in everybody, we realized that we probably had some room for improvement, and that’s why we reconvened, to make these revisions,” he said.
Essentially, the recommendations now urge less cardiac testing. “Cardiac injury is not as common as we may have originally thought,” said Dr. Baggish.
“In the early days of COVID, people who were hospitalized had evidence of heart injury, and so we wondered if that prevalence would also be applicable to otherwise young, healthy people who got COVID. If that had been the case, we would have been in big trouble with respect to getting people back into sports. So this is why we started with a conservative screening approach and a lot of testing in order to not miss a huge burden of disease,” he said.
“But what we’ve learned over the past few months is that young people who get either asymptomatic or mild infection appear to have very, very low risk of having associated heart injury, so the need for testing in that population, when people who have infections recover fully, is almost certainly not going to be high yield,” Dr. Baggish said.
First iteration of the recommendations
Published in May in the early weeks of the pandemic, the first recommendations for safe return to play said that all athletes should stop training for at least 2 weeks after their symptoms resolve, then undergo “careful, clinical cardiovascular evaluation in combination with cardiac biomarkers and imaging.”
Additional testing with cardiac MRI, exercise testing, or ambulatory rhythm monitoring was to be done “based on the clinical course and initial testing.”
But experts caution that monitoring on such a scale in everyone is unnecessary and could even be counterproductive.
“Sending young athletes for extensive testing is not warranted and could send them to unnecessary testing, cardiac imaging, and so on,” Dr. Baggish said.
Only those athletes who continue to have symptoms or whose symptoms return when they get back to their athletic activities should go on for more screening.
“There, in essence, is the single main change from May, and that is a move away from screening with testing everyone, [and instead] confining that to the people who had moderate or greater severity disease,” he said.
Both iterations of the recommendations end with the same message.
“We are at the beginning of our knowledge about the cardiotoxic effects of COVID-19 but we are gathering evidence every day,” said Dr. Baggish. “Just as they did earlier, we acknowledge that our approaches are subject to change when we learn more about how COVID affects the heart, and specifically the hearts of athletes. This will be an ongoing process.”
Something to lean on
The recommendations are welcome, said James E. Udelson, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“It was a bit of the wild west out there, because each university, each college, all with good intentions, had been all struggling to figure out what to do, and how much to do. Probably the most important message from this new paper is the fact that now there is something out there that all coaches, athletes, families, schools, trainers can get some guidance from,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
Refining the cardiac screening criteria was a necessary step, Dr. Udelson said.
“How much cardiac imaging do you do? That is a matter of controversy,” said Dr. Udelson, who coauthored the commentary with Tufts cardiologist Ethan Rowin, MD, and Michael A. Curtis, MEd, a certified strength and conditioning specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “The problem is that if you use a very sensitive imaging test on a lot of people, sometimes you find things that you really didn’t need to know about. They’re really not important. And now, the athlete is told he or she cannot play for 3 months because they might have myocarditis.
“Should we be too sensitive, meaning do we want to pick up anything no matter whether it’s important or not?” he added. “There will be a lot of false positives, and we are going to disqualify a lot of people. Or do you tune it a different way?”
Dr. Udelson said he would like to see commercial sports donate money to support research into the potential cardiotoxicity of COVID-19.
“If the organizations that benefit from these athletes, like the National Collegiate Athletic Association and professional sports leagues, can fund some of this research, that would be a huge help,” Dr. Udelson said.
“These are the top sports cardiologists in the country, and they have to start somewhere, and these are all based on what we know right now, as well as their own extensive experience. We all know that we are just at the beginning of our knowledge of this. But we have to have something to guide this huge community out there that is really thirsty for help.”
Dr. Baggish reports receiving research funding for the study of athletes in competitive sports from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Football League Players Association; and the American Heart Association and receiving compensation for his role as team cardiologist from the US Olympic Committee/US Olympic Training Centers, US Soccer, US Rowing, the New England Patriots, the Boston Bruins, the New England Revolution, and Harvard University. Dr. Udelson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest recommendations from sports cardiologists on getting athletes with COVID-19 back on the playing field safely emphasize a more judicious approach to screening for cardiac injury.
The new recommendations, made by the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Cardiology Section, are for adult athletes in competitive sports and also for two important groups: younger athletes taking part in competitive high school sports and older athletes aged 35 and older, the Masters athletes, who continue to be active throughout their lives. The document was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Because of the evolving nature of knowledge about COVID-19, updates on recommendations for safe return to play for athletes of all ages will continue to be made, senior author Aaron L. Baggish, MD, director of the cardiovascular performance program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said.
“The recommendations we released in May were entirely based on our experience taking care of hospitalized patients with COVID-19; we had no athletes in this population. We used a lot of conservative guesswork around how this would apply to otherwise healthy athletes,” Dr. Baggish said in an interview.
“But as sports started to open up, and we started to see large numbers of first professional and then college athletes come back into training, we realized that we needed to stop and ask whether the recommendations we put forward back in May were still appropriate,” Dr. Baggish said.
“Once we started to actually get into the trenches with these athletes, literally hundreds of them, and applying the testing strategies that we had initially recommended in everybody, we realized that we probably had some room for improvement, and that’s why we reconvened, to make these revisions,” he said.
Essentially, the recommendations now urge less cardiac testing. “Cardiac injury is not as common as we may have originally thought,” said Dr. Baggish.
“In the early days of COVID, people who were hospitalized had evidence of heart injury, and so we wondered if that prevalence would also be applicable to otherwise young, healthy people who got COVID. If that had been the case, we would have been in big trouble with respect to getting people back into sports. So this is why we started with a conservative screening approach and a lot of testing in order to not miss a huge burden of disease,” he said.
“But what we’ve learned over the past few months is that young people who get either asymptomatic or mild infection appear to have very, very low risk of having associated heart injury, so the need for testing in that population, when people who have infections recover fully, is almost certainly not going to be high yield,” Dr. Baggish said.
First iteration of the recommendations
Published in May in the early weeks of the pandemic, the first recommendations for safe return to play said that all athletes should stop training for at least 2 weeks after their symptoms resolve, then undergo “careful, clinical cardiovascular evaluation in combination with cardiac biomarkers and imaging.”
Additional testing with cardiac MRI, exercise testing, or ambulatory rhythm monitoring was to be done “based on the clinical course and initial testing.”
But experts caution that monitoring on such a scale in everyone is unnecessary and could even be counterproductive.
“Sending young athletes for extensive testing is not warranted and could send them to unnecessary testing, cardiac imaging, and so on,” Dr. Baggish said.
Only those athletes who continue to have symptoms or whose symptoms return when they get back to their athletic activities should go on for more screening.
“There, in essence, is the single main change from May, and that is a move away from screening with testing everyone, [and instead] confining that to the people who had moderate or greater severity disease,” he said.
Both iterations of the recommendations end with the same message.
“We are at the beginning of our knowledge about the cardiotoxic effects of COVID-19 but we are gathering evidence every day,” said Dr. Baggish. “Just as they did earlier, we acknowledge that our approaches are subject to change when we learn more about how COVID affects the heart, and specifically the hearts of athletes. This will be an ongoing process.”
Something to lean on
The recommendations are welcome, said James E. Udelson, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“It was a bit of the wild west out there, because each university, each college, all with good intentions, had been all struggling to figure out what to do, and how much to do. Probably the most important message from this new paper is the fact that now there is something out there that all coaches, athletes, families, schools, trainers can get some guidance from,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
Refining the cardiac screening criteria was a necessary step, Dr. Udelson said.
“How much cardiac imaging do you do? That is a matter of controversy,” said Dr. Udelson, who coauthored the commentary with Tufts cardiologist Ethan Rowin, MD, and Michael A. Curtis, MEd, a certified strength and conditioning specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “The problem is that if you use a very sensitive imaging test on a lot of people, sometimes you find things that you really didn’t need to know about. They’re really not important. And now, the athlete is told he or she cannot play for 3 months because they might have myocarditis.
“Should we be too sensitive, meaning do we want to pick up anything no matter whether it’s important or not?” he added. “There will be a lot of false positives, and we are going to disqualify a lot of people. Or do you tune it a different way?”
Dr. Udelson said he would like to see commercial sports donate money to support research into the potential cardiotoxicity of COVID-19.
“If the organizations that benefit from these athletes, like the National Collegiate Athletic Association and professional sports leagues, can fund some of this research, that would be a huge help,” Dr. Udelson said.
“These are the top sports cardiologists in the country, and they have to start somewhere, and these are all based on what we know right now, as well as their own extensive experience. We all know that we are just at the beginning of our knowledge of this. But we have to have something to guide this huge community out there that is really thirsty for help.”
Dr. Baggish reports receiving research funding for the study of athletes in competitive sports from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Football League Players Association; and the American Heart Association and receiving compensation for his role as team cardiologist from the US Olympic Committee/US Olympic Training Centers, US Soccer, US Rowing, the New England Patriots, the Boston Bruins, the New England Revolution, and Harvard University. Dr. Udelson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Burnout risk may be exacerbated by COVID crisis
New kinds of job stress multiply in unusual times
Clarissa Barnes, MD, a hospitalist at Avera McKennan Hospital in Sioux Falls, S.D., and until recently medical director of Avera’s LIGHT Program, a wellness-oriented service for doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, watched the COVID-19 crisis unfold up close in her community and her hospital. Sioux Falls traced its surge of COVID patients to an outbreak at a local meatpacking plant.
“In the beginning, we didn’t know much about the virus and its communicability, although we have since gotten a better handle on that,” she said. “We had questions: Should we give patients more fluids – or less? Steroids or not? In my experience as a hospitalist I never had patients die every day on my shift, but that was happening with COVID.” The crisis imposed serious stresses on frontline providers, and hospitalists were concerned about personal safety and exposure risk – not just for themselves but for their families.
“The first time I worked on the COVID unit, I moved into the guest room in our home, apart from my husband and our young children,” Dr. Barnes said. “Ultimately I caught the virus, although I have since recovered.” Her experience has highlighted how existing issues of job stress and burnout in hospital medicine have been exacerbated by COVID-19. Even physicians who consider themselves healthy may have little emotional reserve to draw upon in a crisis of this magnitude.
“We are social distancing at work, wearing masks, not eating together with our colleagues – with less camaraderie and social support than we used to have,” she said. “I feel exhausted and there’s no question that my colleagues and I have sacrificed a lot to deal with the pandemic.” Add to that the second front of the COVID-19 crisis, Dr. Barnes said, which is “fighting the medical information wars, trying to correct misinformation put out there by people. Physicians who have been on the front lines of the pandemic know how demoralizing it can be to have people negate your first-hand experience.”
The situation has gotten better in Sioux Falls, Dr. Barnes said, although cases have started rising in the state again. The stress, while not gone, is reduced. For some doctors, “COVID reminded us of why we do what we do. Some of the usual bureaucratic requirements were set aside and we could focus on what our patients needed and how to take care of them.”
Taking job stress seriously
Tiffani Panek, MA, SFHM, CLHM, administrator of the division of hospital medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore, said job stress is a major issue for hospitalist groups.
“We take it seriously here, and use a survey tool to measure morale in our group annually,” she said. “So far, knock on wood, Baltimore has not been one of the big hot spots, but we’ve definitely had waves of COVID patients.”
The Bayview hospitalist group has a diversified set of leaders, including a wellness director. “They’re always checking up on our people, keeping an eye on those who are most vulnerable. One of the stressors we hadn’t thought about before was for our people who live alone. With the isolation and lockdown, they haven’t been able to socialize, so we’ve made direct outreach, asking people how they were doing,” Ms. Panek said. “People know we’ve got their back – professionally and personally. They know, if there’s something we can do to help, we will do it.”
Bayview Medical Center has COVID-specific units and non-COVID units, and has tried to rotate hospitalist assignments because more than a couple days in a row spent wearing full personal protective equipment (PPE) is exhausting, Ms. Panek said. The group also allocated a respite room just outside the biocontainment unit, with a computer and opportunities for providers to just sit and take a breather – with appropriate social distancing. “It’s not fancy, but you just have to wear a mask, not full PPE.”
The Hopkins hospitalist group’s wellness director, Catherine Washburn, MD, also a working hospitalist, said providers are exhausted, and trying to transition to the new normal is a moving target.
“It’s hard for anyone to say what our lives will look like in 6 months,” she said. “People in our group have lost family members to COVID, or postponed major life events, like weddings. We acknowledge losses together as a group, and celebrate things worth celebrating, like babies or birthdays.”
Greatest COVID caseload
Joshua Case, MD, hospitalist medical director for 16 acute care hospitals of Northwell Health serving metropolitan New York City and Long Island, said his group’s hospitalists and other staff worked incredibly hard during the surge of COVID-19 patients in New York. “Northwell likely cared for more COVID patients than any other health care system in the U.S., if not the world.
“It’s vastly different now. We went from a peak of thousands of cases per day down to about 70-90 new cases a day across our system. We’re lucky our system recognized that COVID could be an issue early on, with all of the multifaceted stressors on patient care,” Dr. Case said. “We’ve done whatever we could to give people time off, especially as the census started to come down. We freed up as many supportive mental health services as we could, working with the health system’s employee assistance program.”
Northwell gave out numbers for the psychiatry department, with clinicians available 24/7 for a confidential call, along with outside volunteers and a network of trauma psychologists. “Our system also provided emergency child care for staff, including hospitalists, wherever we could, drawing upon community resources,” Dr. Case added.
“We recognize that we’re all in the same foxhole. That’s been a helpful attitude – recognizing that it’s okay to be upset in a crisis and to have trouble dealing with what’s going on,” he said. “We need to acknowledge that some of us are suffering and try to encourage people to face it head on. For a lot of physicians, especially those who were redeployed here from other departments, it was important just to have us ask if they were doing okay.”
Brian Schroeder, MHA, FACHE, FHM, assistant vice president for hospital and emergency medicine for Atrium Health, based in Charlotte, N.C., said one of the biggest sources of stress on his staff has been the constant pace of change – whether local hospital protocols, state policies, or guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “The updating is difficult to keep up with. A lot of our physicians get worried and anxious that they’re not following the latest guidelines or correctly doing what they should be doing to care for COVID patients. One thing we’ve done to alleviate some of that fear and anxiety is through weekly huddles with our hospital teams, focusing on changes relevant to their work. We also have weekly ‘all-hands’ meetings for our 250 providers across 13 acute and four postacute facilities.”
Before COVID, it was difficult to get everyone together as one big group from hospitals up to 5 hours apart, but with the Microsoft Teams platform, they can all meet together.
“At the height of the pandemic, we’d convene weekly and share national statistics, organizational statistics, testing updates, changes to protocols,” Mr. Schroeder said. As the pace of change has slowed, these meetings were cut back to monthly. “Our physicians feel we are passing on information as soon as we get it. They know we’ll always tell them what we know.”
Sarah Richards, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, who heads the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Well-Being Task Force, formed to address staff stress in the COVID environment, said there are things that health care systems can do to help mitigate job stress and burnout. But broader issues may need to be addressed at a national level. “SHM is trying to understand work-related stress – and to identify resources that could support doctors, so they can spend more of their time doing what they enjoy most, which is taking care of patients,” she said.
“We also recognize that people have had very different experiences, depending on geography, and at the individual level stressors are experienced very differently,” Dr. Richard noted. “One of the most common stressors we’ve heard from doctors is the challenge of caring for patients who are lonely and isolated in their hospital rooms, suffering and dying in new ways. In low-incidence areas, doctors are expressing guilt because they aren’t under as much stress as their colleagues. In high-incidence areas, doctors are already experiencing posttraumatic stress disorder.”
SHM’s Well-Being Task Force is working on a tool to help normalize these stressors and encourage open conversations about mental health issues. A guide called “HM COVID Check-in Guide for Self & Peers” is designed to help hospitalists break the culture of silence around well-being and burnout during COVID-19 and how people are handling and processing the pandemic experience. It is expected to be completed later this year, Dr. Richards said. Other SHM projects and resources for staff support are also in the works.
The impact on women doctors
In a recent Journal of Hospital Medicine article entitled “Collateral Damage: How COVID-19 is Adversely Impacting Women Physicians,” hospitalist Yemisi Jones, MD, medical director of continuing medical education at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues argue that preexisting gender inequities in compensation, academic rank and leadership positions for physicians have made the COVID-19 crisis even more burdensome on female hospitalists.1
“Increased childcare and schooling obligations, coupled with disproportionate household responsibilities and an inability to work from home, will likely result in female hospitalists struggling to meet family needs while pandemic-related work responsibilities are ramping up,” they write. COVID may intensify workplace inequalities, with a lack of recognition of the undue strain that group policies place on women.
“Often women suffer in silence,” said coauthor Jennifer O’Toole, MD, MEd, director of education in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and program director of the internal medicine–pediatrics residency. “We are not always the best self-advocates, although many of us are working on that.”
When women in hospital medicine take leadership roles, these often tend to involve mutual support activities, taking care of colleagues, and promoting collaborative work environments, Dr. Jones added. The stereotypical example is the committee that organizes celebrations when group members get married or have babies.
These activities can take a lot of time, she said. “We need to pay attention to that kind of role in our groups, because it’s important to the cohesiveness of the group. But it often goes unrecognized and doesn’t translate into the currency of promotion and leadership in medicine. When women go for promotions in the future, how will what happened during the COVID crisis impact their opportunities?”
What is the answer to overcoming these systemic inequities? Start with making sure women are part of the leadership team, with responsibilities for group policies, schedules, and other important decisions. “Look at your group’s leadership – particularly the higher positions. If it’s not diverse, ask why. ‘What is it about the structure of our group?’ Make a more concerted effort in your recruitment and retention,” Dr. Jones said.
The JHM article also recommends closely monitoring the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 on female hospitalists, inquiring specifically about the needs of women in the organization, and ensuring that diversity, inclusion, and equity efforts are not suspended during the pandemic. Gender-based disparities in pay also need a closer look, and not just one time but reviewed periodically and adjusted accordingly.
Mentoring for early career women is important, but more so is sponsorship – someone in a high-level leadership role in the group sponsoring women who are rising up the career ladder, Dr. O’Toole said. “Professional women tend to be overmentored and undersponsored.”
What are the answers?
Ultimately, listening is key to try to help people get through the pandemic, Dr. Washburn said. “People become burned out when they feel leadership doesn’t understand their needs or doesn’t hear their concerns. Our group leaders all do clinical work, so they are seen as one of us. They try very hard; they have listening ears. But listening is just the first step. Next step is to work creatively to get the identified needs met.”
A few years ago, Johns Hopkins developed training in enhanced communication in health care for all hospital providers, including nurses and doctors, encouraging them to get trained in how to actively listen and address their patients’ emotional and social experiences as well as disease, Dr. Washburn explained. Learning how to listen better to patients can enhance skills at listening to colleagues, and vice versa. “We recognize the importance of better communication – for reducing sentinel events in the hospital and also for preventing staff burnout.”
Dr. Barnes also does physician coaching, and says a lot of that work is helping people achieve clarity on their core values. “Healing patients is a core identify for physicians; we want to take care of people. But other things can get in the way of that, and hospitalist groups can work at minimizing those barriers. We also need to learn, as hospitalists, that we work in a group. You need to be creative in how you do your team building, especially now, when you can no longer get together for dinner. Whatever it is, how do we bring our team back together? The biggest source of support for many hospitalists, beyond their family, is the group.”
Dr. Case said there is a longer-term need to study the root causes of burnout in hospitalists and to identify the issues that cause job stress. “What is modifiable? How can we tackle it? I see that as big part of my job every day. Being a physician is hard enough as it is. Let’s work to resolve those issues that add needlessly to the stress.”
“I think the pandemic brought a magnifying glass to how important a concern staff stress is,” Ms. Panek said. Resilience is important.
“We were working in our group on creating a culture that values trust and transparency, and then the COVID crisis hit,” she said. “But you can still keep working on those things. We would not have been as good or as positive as we were in managing this crisis without that preexisting culture to draw upon. We always said it was important. Now we know that’s true.”
Reference
1. Jones Y et al. Collateral Damage: How COVID-19 Is Adversely Impacting Women Physicians. J Hosp Med. 2020 August;15(8):507-9.
New kinds of job stress multiply in unusual times
New kinds of job stress multiply in unusual times
Clarissa Barnes, MD, a hospitalist at Avera McKennan Hospital in Sioux Falls, S.D., and until recently medical director of Avera’s LIGHT Program, a wellness-oriented service for doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, watched the COVID-19 crisis unfold up close in her community and her hospital. Sioux Falls traced its surge of COVID patients to an outbreak at a local meatpacking plant.
“In the beginning, we didn’t know much about the virus and its communicability, although we have since gotten a better handle on that,” she said. “We had questions: Should we give patients more fluids – or less? Steroids or not? In my experience as a hospitalist I never had patients die every day on my shift, but that was happening with COVID.” The crisis imposed serious stresses on frontline providers, and hospitalists were concerned about personal safety and exposure risk – not just for themselves but for their families.
“The first time I worked on the COVID unit, I moved into the guest room in our home, apart from my husband and our young children,” Dr. Barnes said. “Ultimately I caught the virus, although I have since recovered.” Her experience has highlighted how existing issues of job stress and burnout in hospital medicine have been exacerbated by COVID-19. Even physicians who consider themselves healthy may have little emotional reserve to draw upon in a crisis of this magnitude.
“We are social distancing at work, wearing masks, not eating together with our colleagues – with less camaraderie and social support than we used to have,” she said. “I feel exhausted and there’s no question that my colleagues and I have sacrificed a lot to deal with the pandemic.” Add to that the second front of the COVID-19 crisis, Dr. Barnes said, which is “fighting the medical information wars, trying to correct misinformation put out there by people. Physicians who have been on the front lines of the pandemic know how demoralizing it can be to have people negate your first-hand experience.”
The situation has gotten better in Sioux Falls, Dr. Barnes said, although cases have started rising in the state again. The stress, while not gone, is reduced. For some doctors, “COVID reminded us of why we do what we do. Some of the usual bureaucratic requirements were set aside and we could focus on what our patients needed and how to take care of them.”
Taking job stress seriously
Tiffani Panek, MA, SFHM, CLHM, administrator of the division of hospital medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore, said job stress is a major issue for hospitalist groups.
“We take it seriously here, and use a survey tool to measure morale in our group annually,” she said. “So far, knock on wood, Baltimore has not been one of the big hot spots, but we’ve definitely had waves of COVID patients.”
The Bayview hospitalist group has a diversified set of leaders, including a wellness director. “They’re always checking up on our people, keeping an eye on those who are most vulnerable. One of the stressors we hadn’t thought about before was for our people who live alone. With the isolation and lockdown, they haven’t been able to socialize, so we’ve made direct outreach, asking people how they were doing,” Ms. Panek said. “People know we’ve got their back – professionally and personally. They know, if there’s something we can do to help, we will do it.”
Bayview Medical Center has COVID-specific units and non-COVID units, and has tried to rotate hospitalist assignments because more than a couple days in a row spent wearing full personal protective equipment (PPE) is exhausting, Ms. Panek said. The group also allocated a respite room just outside the biocontainment unit, with a computer and opportunities for providers to just sit and take a breather – with appropriate social distancing. “It’s not fancy, but you just have to wear a mask, not full PPE.”
The Hopkins hospitalist group’s wellness director, Catherine Washburn, MD, also a working hospitalist, said providers are exhausted, and trying to transition to the new normal is a moving target.
“It’s hard for anyone to say what our lives will look like in 6 months,” she said. “People in our group have lost family members to COVID, or postponed major life events, like weddings. We acknowledge losses together as a group, and celebrate things worth celebrating, like babies or birthdays.”
Greatest COVID caseload
Joshua Case, MD, hospitalist medical director for 16 acute care hospitals of Northwell Health serving metropolitan New York City and Long Island, said his group’s hospitalists and other staff worked incredibly hard during the surge of COVID-19 patients in New York. “Northwell likely cared for more COVID patients than any other health care system in the U.S., if not the world.
“It’s vastly different now. We went from a peak of thousands of cases per day down to about 70-90 new cases a day across our system. We’re lucky our system recognized that COVID could be an issue early on, with all of the multifaceted stressors on patient care,” Dr. Case said. “We’ve done whatever we could to give people time off, especially as the census started to come down. We freed up as many supportive mental health services as we could, working with the health system’s employee assistance program.”
Northwell gave out numbers for the psychiatry department, with clinicians available 24/7 for a confidential call, along with outside volunteers and a network of trauma psychologists. “Our system also provided emergency child care for staff, including hospitalists, wherever we could, drawing upon community resources,” Dr. Case added.
“We recognize that we’re all in the same foxhole. That’s been a helpful attitude – recognizing that it’s okay to be upset in a crisis and to have trouble dealing with what’s going on,” he said. “We need to acknowledge that some of us are suffering and try to encourage people to face it head on. For a lot of physicians, especially those who were redeployed here from other departments, it was important just to have us ask if they were doing okay.”
Brian Schroeder, MHA, FACHE, FHM, assistant vice president for hospital and emergency medicine for Atrium Health, based in Charlotte, N.C., said one of the biggest sources of stress on his staff has been the constant pace of change – whether local hospital protocols, state policies, or guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “The updating is difficult to keep up with. A lot of our physicians get worried and anxious that they’re not following the latest guidelines or correctly doing what they should be doing to care for COVID patients. One thing we’ve done to alleviate some of that fear and anxiety is through weekly huddles with our hospital teams, focusing on changes relevant to their work. We also have weekly ‘all-hands’ meetings for our 250 providers across 13 acute and four postacute facilities.”
Before COVID, it was difficult to get everyone together as one big group from hospitals up to 5 hours apart, but with the Microsoft Teams platform, they can all meet together.
“At the height of the pandemic, we’d convene weekly and share national statistics, organizational statistics, testing updates, changes to protocols,” Mr. Schroeder said. As the pace of change has slowed, these meetings were cut back to monthly. “Our physicians feel we are passing on information as soon as we get it. They know we’ll always tell them what we know.”
Sarah Richards, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, who heads the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Well-Being Task Force, formed to address staff stress in the COVID environment, said there are things that health care systems can do to help mitigate job stress and burnout. But broader issues may need to be addressed at a national level. “SHM is trying to understand work-related stress – and to identify resources that could support doctors, so they can spend more of their time doing what they enjoy most, which is taking care of patients,” she said.
“We also recognize that people have had very different experiences, depending on geography, and at the individual level stressors are experienced very differently,” Dr. Richard noted. “One of the most common stressors we’ve heard from doctors is the challenge of caring for patients who are lonely and isolated in their hospital rooms, suffering and dying in new ways. In low-incidence areas, doctors are expressing guilt because they aren’t under as much stress as their colleagues. In high-incidence areas, doctors are already experiencing posttraumatic stress disorder.”
SHM’s Well-Being Task Force is working on a tool to help normalize these stressors and encourage open conversations about mental health issues. A guide called “HM COVID Check-in Guide for Self & Peers” is designed to help hospitalists break the culture of silence around well-being and burnout during COVID-19 and how people are handling and processing the pandemic experience. It is expected to be completed later this year, Dr. Richards said. Other SHM projects and resources for staff support are also in the works.
The impact on women doctors
In a recent Journal of Hospital Medicine article entitled “Collateral Damage: How COVID-19 is Adversely Impacting Women Physicians,” hospitalist Yemisi Jones, MD, medical director of continuing medical education at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues argue that preexisting gender inequities in compensation, academic rank and leadership positions for physicians have made the COVID-19 crisis even more burdensome on female hospitalists.1
“Increased childcare and schooling obligations, coupled with disproportionate household responsibilities and an inability to work from home, will likely result in female hospitalists struggling to meet family needs while pandemic-related work responsibilities are ramping up,” they write. COVID may intensify workplace inequalities, with a lack of recognition of the undue strain that group policies place on women.
“Often women suffer in silence,” said coauthor Jennifer O’Toole, MD, MEd, director of education in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and program director of the internal medicine–pediatrics residency. “We are not always the best self-advocates, although many of us are working on that.”
When women in hospital medicine take leadership roles, these often tend to involve mutual support activities, taking care of colleagues, and promoting collaborative work environments, Dr. Jones added. The stereotypical example is the committee that organizes celebrations when group members get married or have babies.
These activities can take a lot of time, she said. “We need to pay attention to that kind of role in our groups, because it’s important to the cohesiveness of the group. But it often goes unrecognized and doesn’t translate into the currency of promotion and leadership in medicine. When women go for promotions in the future, how will what happened during the COVID crisis impact their opportunities?”
What is the answer to overcoming these systemic inequities? Start with making sure women are part of the leadership team, with responsibilities for group policies, schedules, and other important decisions. “Look at your group’s leadership – particularly the higher positions. If it’s not diverse, ask why. ‘What is it about the structure of our group?’ Make a more concerted effort in your recruitment and retention,” Dr. Jones said.
The JHM article also recommends closely monitoring the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 on female hospitalists, inquiring specifically about the needs of women in the organization, and ensuring that diversity, inclusion, and equity efforts are not suspended during the pandemic. Gender-based disparities in pay also need a closer look, and not just one time but reviewed periodically and adjusted accordingly.
Mentoring for early career women is important, but more so is sponsorship – someone in a high-level leadership role in the group sponsoring women who are rising up the career ladder, Dr. O’Toole said. “Professional women tend to be overmentored and undersponsored.”
What are the answers?
Ultimately, listening is key to try to help people get through the pandemic, Dr. Washburn said. “People become burned out when they feel leadership doesn’t understand their needs or doesn’t hear their concerns. Our group leaders all do clinical work, so they are seen as one of us. They try very hard; they have listening ears. But listening is just the first step. Next step is to work creatively to get the identified needs met.”
A few years ago, Johns Hopkins developed training in enhanced communication in health care for all hospital providers, including nurses and doctors, encouraging them to get trained in how to actively listen and address their patients’ emotional and social experiences as well as disease, Dr. Washburn explained. Learning how to listen better to patients can enhance skills at listening to colleagues, and vice versa. “We recognize the importance of better communication – for reducing sentinel events in the hospital and also for preventing staff burnout.”
Dr. Barnes also does physician coaching, and says a lot of that work is helping people achieve clarity on their core values. “Healing patients is a core identify for physicians; we want to take care of people. But other things can get in the way of that, and hospitalist groups can work at minimizing those barriers. We also need to learn, as hospitalists, that we work in a group. You need to be creative in how you do your team building, especially now, when you can no longer get together for dinner. Whatever it is, how do we bring our team back together? The biggest source of support for many hospitalists, beyond their family, is the group.”
Dr. Case said there is a longer-term need to study the root causes of burnout in hospitalists and to identify the issues that cause job stress. “What is modifiable? How can we tackle it? I see that as big part of my job every day. Being a physician is hard enough as it is. Let’s work to resolve those issues that add needlessly to the stress.”
“I think the pandemic brought a magnifying glass to how important a concern staff stress is,” Ms. Panek said. Resilience is important.
“We were working in our group on creating a culture that values trust and transparency, and then the COVID crisis hit,” she said. “But you can still keep working on those things. We would not have been as good or as positive as we were in managing this crisis without that preexisting culture to draw upon. We always said it was important. Now we know that’s true.”
Reference
1. Jones Y et al. Collateral Damage: How COVID-19 Is Adversely Impacting Women Physicians. J Hosp Med. 2020 August;15(8):507-9.
Clarissa Barnes, MD, a hospitalist at Avera McKennan Hospital in Sioux Falls, S.D., and until recently medical director of Avera’s LIGHT Program, a wellness-oriented service for doctors, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, watched the COVID-19 crisis unfold up close in her community and her hospital. Sioux Falls traced its surge of COVID patients to an outbreak at a local meatpacking plant.
“In the beginning, we didn’t know much about the virus and its communicability, although we have since gotten a better handle on that,” she said. “We had questions: Should we give patients more fluids – or less? Steroids or not? In my experience as a hospitalist I never had patients die every day on my shift, but that was happening with COVID.” The crisis imposed serious stresses on frontline providers, and hospitalists were concerned about personal safety and exposure risk – not just for themselves but for their families.
“The first time I worked on the COVID unit, I moved into the guest room in our home, apart from my husband and our young children,” Dr. Barnes said. “Ultimately I caught the virus, although I have since recovered.” Her experience has highlighted how existing issues of job stress and burnout in hospital medicine have been exacerbated by COVID-19. Even physicians who consider themselves healthy may have little emotional reserve to draw upon in a crisis of this magnitude.
“We are social distancing at work, wearing masks, not eating together with our colleagues – with less camaraderie and social support than we used to have,” she said. “I feel exhausted and there’s no question that my colleagues and I have sacrificed a lot to deal with the pandemic.” Add to that the second front of the COVID-19 crisis, Dr. Barnes said, which is “fighting the medical information wars, trying to correct misinformation put out there by people. Physicians who have been on the front lines of the pandemic know how demoralizing it can be to have people negate your first-hand experience.”
The situation has gotten better in Sioux Falls, Dr. Barnes said, although cases have started rising in the state again. The stress, while not gone, is reduced. For some doctors, “COVID reminded us of why we do what we do. Some of the usual bureaucratic requirements were set aside and we could focus on what our patients needed and how to take care of them.”
Taking job stress seriously
Tiffani Panek, MA, SFHM, CLHM, administrator of the division of hospital medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore, said job stress is a major issue for hospitalist groups.
“We take it seriously here, and use a survey tool to measure morale in our group annually,” she said. “So far, knock on wood, Baltimore has not been one of the big hot spots, but we’ve definitely had waves of COVID patients.”
The Bayview hospitalist group has a diversified set of leaders, including a wellness director. “They’re always checking up on our people, keeping an eye on those who are most vulnerable. One of the stressors we hadn’t thought about before was for our people who live alone. With the isolation and lockdown, they haven’t been able to socialize, so we’ve made direct outreach, asking people how they were doing,” Ms. Panek said. “People know we’ve got their back – professionally and personally. They know, if there’s something we can do to help, we will do it.”
Bayview Medical Center has COVID-specific units and non-COVID units, and has tried to rotate hospitalist assignments because more than a couple days in a row spent wearing full personal protective equipment (PPE) is exhausting, Ms. Panek said. The group also allocated a respite room just outside the biocontainment unit, with a computer and opportunities for providers to just sit and take a breather – with appropriate social distancing. “It’s not fancy, but you just have to wear a mask, not full PPE.”
The Hopkins hospitalist group’s wellness director, Catherine Washburn, MD, also a working hospitalist, said providers are exhausted, and trying to transition to the new normal is a moving target.
“It’s hard for anyone to say what our lives will look like in 6 months,” she said. “People in our group have lost family members to COVID, or postponed major life events, like weddings. We acknowledge losses together as a group, and celebrate things worth celebrating, like babies or birthdays.”
Greatest COVID caseload
Joshua Case, MD, hospitalist medical director for 16 acute care hospitals of Northwell Health serving metropolitan New York City and Long Island, said his group’s hospitalists and other staff worked incredibly hard during the surge of COVID-19 patients in New York. “Northwell likely cared for more COVID patients than any other health care system in the U.S., if not the world.
“It’s vastly different now. We went from a peak of thousands of cases per day down to about 70-90 new cases a day across our system. We’re lucky our system recognized that COVID could be an issue early on, with all of the multifaceted stressors on patient care,” Dr. Case said. “We’ve done whatever we could to give people time off, especially as the census started to come down. We freed up as many supportive mental health services as we could, working with the health system’s employee assistance program.”
Northwell gave out numbers for the psychiatry department, with clinicians available 24/7 for a confidential call, along with outside volunteers and a network of trauma psychologists. “Our system also provided emergency child care for staff, including hospitalists, wherever we could, drawing upon community resources,” Dr. Case added.
“We recognize that we’re all in the same foxhole. That’s been a helpful attitude – recognizing that it’s okay to be upset in a crisis and to have trouble dealing with what’s going on,” he said. “We need to acknowledge that some of us are suffering and try to encourage people to face it head on. For a lot of physicians, especially those who were redeployed here from other departments, it was important just to have us ask if they were doing okay.”
Brian Schroeder, MHA, FACHE, FHM, assistant vice president for hospital and emergency medicine for Atrium Health, based in Charlotte, N.C., said one of the biggest sources of stress on his staff has been the constant pace of change – whether local hospital protocols, state policies, or guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “The updating is difficult to keep up with. A lot of our physicians get worried and anxious that they’re not following the latest guidelines or correctly doing what they should be doing to care for COVID patients. One thing we’ve done to alleviate some of that fear and anxiety is through weekly huddles with our hospital teams, focusing on changes relevant to their work. We also have weekly ‘all-hands’ meetings for our 250 providers across 13 acute and four postacute facilities.”
Before COVID, it was difficult to get everyone together as one big group from hospitals up to 5 hours apart, but with the Microsoft Teams platform, they can all meet together.
“At the height of the pandemic, we’d convene weekly and share national statistics, organizational statistics, testing updates, changes to protocols,” Mr. Schroeder said. As the pace of change has slowed, these meetings were cut back to monthly. “Our physicians feel we are passing on information as soon as we get it. They know we’ll always tell them what we know.”
Sarah Richards, MD, assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Nebraska, Omaha, who heads the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Well-Being Task Force, formed to address staff stress in the COVID environment, said there are things that health care systems can do to help mitigate job stress and burnout. But broader issues may need to be addressed at a national level. “SHM is trying to understand work-related stress – and to identify resources that could support doctors, so they can spend more of their time doing what they enjoy most, which is taking care of patients,” she said.
“We also recognize that people have had very different experiences, depending on geography, and at the individual level stressors are experienced very differently,” Dr. Richard noted. “One of the most common stressors we’ve heard from doctors is the challenge of caring for patients who are lonely and isolated in their hospital rooms, suffering and dying in new ways. In low-incidence areas, doctors are expressing guilt because they aren’t under as much stress as their colleagues. In high-incidence areas, doctors are already experiencing posttraumatic stress disorder.”
SHM’s Well-Being Task Force is working on a tool to help normalize these stressors and encourage open conversations about mental health issues. A guide called “HM COVID Check-in Guide for Self & Peers” is designed to help hospitalists break the culture of silence around well-being and burnout during COVID-19 and how people are handling and processing the pandemic experience. It is expected to be completed later this year, Dr. Richards said. Other SHM projects and resources for staff support are also in the works.
The impact on women doctors
In a recent Journal of Hospital Medicine article entitled “Collateral Damage: How COVID-19 is Adversely Impacting Women Physicians,” hospitalist Yemisi Jones, MD, medical director of continuing medical education at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues argue that preexisting gender inequities in compensation, academic rank and leadership positions for physicians have made the COVID-19 crisis even more burdensome on female hospitalists.1
“Increased childcare and schooling obligations, coupled with disproportionate household responsibilities and an inability to work from home, will likely result in female hospitalists struggling to meet family needs while pandemic-related work responsibilities are ramping up,” they write. COVID may intensify workplace inequalities, with a lack of recognition of the undue strain that group policies place on women.
“Often women suffer in silence,” said coauthor Jennifer O’Toole, MD, MEd, director of education in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and program director of the internal medicine–pediatrics residency. “We are not always the best self-advocates, although many of us are working on that.”
When women in hospital medicine take leadership roles, these often tend to involve mutual support activities, taking care of colleagues, and promoting collaborative work environments, Dr. Jones added. The stereotypical example is the committee that organizes celebrations when group members get married or have babies.
These activities can take a lot of time, she said. “We need to pay attention to that kind of role in our groups, because it’s important to the cohesiveness of the group. But it often goes unrecognized and doesn’t translate into the currency of promotion and leadership in medicine. When women go for promotions in the future, how will what happened during the COVID crisis impact their opportunities?”
What is the answer to overcoming these systemic inequities? Start with making sure women are part of the leadership team, with responsibilities for group policies, schedules, and other important decisions. “Look at your group’s leadership – particularly the higher positions. If it’s not diverse, ask why. ‘What is it about the structure of our group?’ Make a more concerted effort in your recruitment and retention,” Dr. Jones said.
The JHM article also recommends closely monitoring the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 on female hospitalists, inquiring specifically about the needs of women in the organization, and ensuring that diversity, inclusion, and equity efforts are not suspended during the pandemic. Gender-based disparities in pay also need a closer look, and not just one time but reviewed periodically and adjusted accordingly.
Mentoring for early career women is important, but more so is sponsorship – someone in a high-level leadership role in the group sponsoring women who are rising up the career ladder, Dr. O’Toole said. “Professional women tend to be overmentored and undersponsored.”
What are the answers?
Ultimately, listening is key to try to help people get through the pandemic, Dr. Washburn said. “People become burned out when they feel leadership doesn’t understand their needs or doesn’t hear their concerns. Our group leaders all do clinical work, so they are seen as one of us. They try very hard; they have listening ears. But listening is just the first step. Next step is to work creatively to get the identified needs met.”
A few years ago, Johns Hopkins developed training in enhanced communication in health care for all hospital providers, including nurses and doctors, encouraging them to get trained in how to actively listen and address their patients’ emotional and social experiences as well as disease, Dr. Washburn explained. Learning how to listen better to patients can enhance skills at listening to colleagues, and vice versa. “We recognize the importance of better communication – for reducing sentinel events in the hospital and also for preventing staff burnout.”
Dr. Barnes also does physician coaching, and says a lot of that work is helping people achieve clarity on their core values. “Healing patients is a core identify for physicians; we want to take care of people. But other things can get in the way of that, and hospitalist groups can work at minimizing those barriers. We also need to learn, as hospitalists, that we work in a group. You need to be creative in how you do your team building, especially now, when you can no longer get together for dinner. Whatever it is, how do we bring our team back together? The biggest source of support for many hospitalists, beyond their family, is the group.”
Dr. Case said there is a longer-term need to study the root causes of burnout in hospitalists and to identify the issues that cause job stress. “What is modifiable? How can we tackle it? I see that as big part of my job every day. Being a physician is hard enough as it is. Let’s work to resolve those issues that add needlessly to the stress.”
“I think the pandemic brought a magnifying glass to how important a concern staff stress is,” Ms. Panek said. Resilience is important.
“We were working in our group on creating a culture that values trust and transparency, and then the COVID crisis hit,” she said. “But you can still keep working on those things. We would not have been as good or as positive as we were in managing this crisis without that preexisting culture to draw upon. We always said it was important. Now we know that’s true.”
Reference
1. Jones Y et al. Collateral Damage: How COVID-19 Is Adversely Impacting Women Physicians. J Hosp Med. 2020 August;15(8):507-9.
How cannabis-based therapeutics could help fight COVID inflammation
Plagued by false starts, a few dashed hopes, but with perhaps a glimmer of light on the horizon, the race to find an effective treatment for COVID-19 continues. At last count, more than 300 treatments and 200 vaccines were in preclinical or clinical development (not to mention the numerous existing agents that are being evaluated for repurposing).
There is also a renewed interest in cannabinoid therapeutics — in particular, the nonpsychoactive agent cannabidiol (CBD) and the prospect of its modulating inflammatory and other disease-associated clinical indices, including SARS-CoV-2–induced viral load, hyperinflammation, the cytokine storm, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Long hobbled by regulatory, political, and financial barriers, CBD’s potential ability to knock back COVID-19–related inflammation might just open doors that have been closed for years to CBD researchers.
Why CBD and why now?
CBD and the resulting therapeutics have been plagued by a complicated association with recreational cannabis use. It’s been just 2 years since CBD-based therapeutics moved into mainstream medicine — the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Epidiolex oral solution for the treatment of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome, and in August, the FDA approved it for tuberous sclerosis complex.
CBD’s mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, but on the basis of its role in immune responses — well described in research spanning more than two decades — it›s not surprising that cannabinoid researchers have thrown their hats into the COVID-19 drug development ring.
The anti-inflammatory potential of CBD is substantial and appears to be related to the fact that it shares 20 protein targets common to inflammation-related pathways, Jenny Wilkerson, PhD, research assistant professor at the University of Florida School of Pharmacy, Gainesville, Florida, explained to Medscape Medical News.
Among the various trials that are currently recruiting or are underway is one that is slated for completion this fall. CANDIDATE (Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients With Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19) is a randomized, controlled, double-blind study led by Brazilian researchers at the University of São Paulo. The study, which began recruitment this past August, enrolled 100 patients, 50 in the active treatment group (who received capsulated CBD 300 mg daily for 14 days plus pharmacologic therapy [antipyretics] and clinical measures) and 50 who received placebo.
The primary outcome is intended to help clarify the potential role of oral CBD for preventing COVID-19 disease progression, modifying disease-associated clinical indices, and modulating inflammatory parameters, such as the cytokine storm, according to lead investigator Jose Alexandre de Souza Crippa, MD, PhD, professor of neuropsychology at the Ribeirao Preto Medical School at the University of São Paulo in Brazil, in the description of the study on clinicaltrials.gov. Crippa declined to provide any additional information about the trial in an email to Medscape Medical News.
Calming or preventing the storm
While Crippa and colleagues wrap up their CBD trial in South America, several North American and Canadian researchers are seeking to clarify and address one of the most therapeutically challenging aspects of SARS-CoV-2 infection — the lung macrophage–orchestrated hyperinflammatory response.
Although hyperinflammation is not unique to SARS-CoV-2 infection, disease severity and COVID-19–related mortality have been linked to this rapid and prolonged surge of inflammatory cytokines (eg, interleukin 6 [IL-6], IL-10, tumor necrosis factors [TNF], and chemokines) and the cytokine storm.
“When you stimulate CB2 receptors (involved in fighting inflammation), you get a release of the same inflammatory cytokines that are involved in COVID,” Cecilia Costiniuk, MD, associate professor and researcher at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Center, Montreal, Canada, told Medscape Medical News.
“So, if you can act on this receptor, you might be able to reduce the release of those damaging cytokines that are causing ARDS, lung damage, etc,” she explained. Targeting these inflammatory mediators has been a key strategy in research aimed at reducing COVID-19 severity and related mortality, which is where CBD comes into play.
“CBD is a very powerful immune regulator. It keeps the [immune] engine on, but it doesn’t push the gas pedal, and it doesn’t push the brake completely,” Babak Baban, PhD, professor and immunologist at the Dental College of Georgia at Augusta University, told Medscape Medical News.
To explore the effectiveness of CBD in reducing hyperactivated inflammatory reactions, Baban and colleagues examined the potential of CBD to ameliorate ARDS in a murine model. The group divided wild-type male mice into sham, control, and treatment groups.
The sham group received intranasal phosphate buffered saline; the treatment and control groups received a polyriboinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly I:C) double-stranded RNA analogue (100 mcg daily for 3 days) to simulate the cytokine storm and clinical ARDS symptoms.
Following the second poly I:C dose, the treatment group received CBD 5 mg/kg intraperitoneally every other day for 6 days. The mice were sacrificed on day 8.
The study results, published in July in Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, first confirmed that the poly I:C model simulated the cytokine storm in ARDS, reducing blood oxygen saturation by as much as 10% (from ±81.6% to ±72.2%).
Intraperitoneally administered CBD appeared to reverse these ARDS-like trends. “We observed a significant improvement in severe lymphopenia, a mild decline in the ratio of neutrophils to T cells, and significant reductions in levels of [inflammatory and immune factors] IL-6, IFN-gamma [interferon gamma], and in TNF-alpha after the second CBD dose,” Baban said.
There was also a marked downregulation in infiltrating neutrophils and macrophages in the lung, leading to partial restoration of lung morphology and structure. The investigators write that this suggests “a counter inflammatory role for CBD to limit ARDS progression.”
Additional findings from a follow-up study published in mid-October “provide strong data that CBD may partially assert its beneficial and protective impact through its regulation of the apelin peptide,” wrote Baban in an email to Medscape Medical News.
“Apelin may also be a reliable biomarker for early diagnosis of ARDS in general, and in COVID-19 in particular,” he wrote.
Questions remain concerning dose response and whether CBD alone or in combination with other phytocannabinoids is more effective for treating COVID-19. Timing is likewise unclear.
Baban explained that as a result of the biphasic nature of COVID-19, the “sweet spot” appears to be just before the innate immune response progresses into an inflammation-driven response and fibrotic lung damage occurs.
But Wilkerson isn’t as convinced. She said that as with a thermostat, the endocannabinoid system needs tweaking to get it in the right place, that is, to achieve immune homeostasis. The COVID cytokine storm is highly unpredictable, she added, saying, “Right now, the timing for controlling the COVID cytokine storm is really a moving target.”
Is safety a concern?
Safety questions are expected to arise, especially in relation to COVID-19. CBD is not risk free, and one size does not fit all. Human CBD studies report gastrointestinal and somnolent effects, as well as drug-drug interactions.
Findings from a recent systematic review of randomized, controlled CBD trials support overall tolerability, suggesting that serious adverse events are rare. Such events are believed to be related to drug-drug interactions rather than to CBD itself. On the flip side, it is nonintoxicating, and there does not appear to be potential for abuse.
“It’s generally well tolerated,” Wilkerson said. “There’ve now been several clinical trials in numerous patient population settings where basically the only time you really start to have issues is where you have patients on very select agents. But this is where a pharmacist would come into play.”
Costiniuk agreed: “Just because it’s cannabis, it doesn’t mean that there’s going to be strange or unusual effects; these people [ie, those with severe COVID-19] are in the hospital and monitored very closely.”
Delving into the weeds: What’s next?
Although non-COVID-19 cannabinoid researchers have encountered regulatory roadblocks, several research groups that have had the prescience to dive in at the right time are gaining momentum.
Baban’s team has connected with one of the nation’s few academic laboratories authorized to work with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and are awaiting protocol approval so that they can reproduce their research, this time using two CBD formulations (injectable and inhaled).
If findings are positive, they will move forward quickly to meet with the FDA, Baban said, adding that the team is also collaborating with two organizations to conduct human clinical trials in hopes of pushing up timing.
The initial article caught the eye of the World Health Organization, which included it in its global literature on the coronavirus resource section.
Israeli researchers have also been quite busy. InnoCan Pharma and Tel Aviv University are collaborating to explore the potential for CBD-loaded exosomes (minute extracellular particles that mediate intracellular communication, including via innate and adaptive immune responses). The group plans to use these loaded exosomes to target and facilitate recovery of COVID-19–damaged lung cells.
From a broader perspective, the prospects for harnessing cannabinoids for immune modulation will be more thoroughly explored in a special issue of Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, which has extended its current call for papers, studies, abstracts, and conference proceedings until the end of December.
Like many of the therapeutic strategies under investigation for the treatment of COVID-19, studies in CBD may continue to raise more questions than answers.
Still, Wilkerson is optimistic. “Taken together, these studies along with countless others suggest that the complex pharmacophore of Cannabis sativa may hold therapeutic utility to treat lung inflammation, such as what is seen in a COVID-19 cytokine storm,» she told Medscape Medical News. “I’m very excited to see what comes out of the research.”
Baban, Wilkerson, and Costiniuk have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Plagued by false starts, a few dashed hopes, but with perhaps a glimmer of light on the horizon, the race to find an effective treatment for COVID-19 continues. At last count, more than 300 treatments and 200 vaccines were in preclinical or clinical development (not to mention the numerous existing agents that are being evaluated for repurposing).
There is also a renewed interest in cannabinoid therapeutics — in particular, the nonpsychoactive agent cannabidiol (CBD) and the prospect of its modulating inflammatory and other disease-associated clinical indices, including SARS-CoV-2–induced viral load, hyperinflammation, the cytokine storm, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Long hobbled by regulatory, political, and financial barriers, CBD’s potential ability to knock back COVID-19–related inflammation might just open doors that have been closed for years to CBD researchers.
Why CBD and why now?
CBD and the resulting therapeutics have been plagued by a complicated association with recreational cannabis use. It’s been just 2 years since CBD-based therapeutics moved into mainstream medicine — the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Epidiolex oral solution for the treatment of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome, and in August, the FDA approved it for tuberous sclerosis complex.
CBD’s mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, but on the basis of its role in immune responses — well described in research spanning more than two decades — it›s not surprising that cannabinoid researchers have thrown their hats into the COVID-19 drug development ring.
The anti-inflammatory potential of CBD is substantial and appears to be related to the fact that it shares 20 protein targets common to inflammation-related pathways, Jenny Wilkerson, PhD, research assistant professor at the University of Florida School of Pharmacy, Gainesville, Florida, explained to Medscape Medical News.
Among the various trials that are currently recruiting or are underway is one that is slated for completion this fall. CANDIDATE (Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients With Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19) is a randomized, controlled, double-blind study led by Brazilian researchers at the University of São Paulo. The study, which began recruitment this past August, enrolled 100 patients, 50 in the active treatment group (who received capsulated CBD 300 mg daily for 14 days plus pharmacologic therapy [antipyretics] and clinical measures) and 50 who received placebo.
The primary outcome is intended to help clarify the potential role of oral CBD for preventing COVID-19 disease progression, modifying disease-associated clinical indices, and modulating inflammatory parameters, such as the cytokine storm, according to lead investigator Jose Alexandre de Souza Crippa, MD, PhD, professor of neuropsychology at the Ribeirao Preto Medical School at the University of São Paulo in Brazil, in the description of the study on clinicaltrials.gov. Crippa declined to provide any additional information about the trial in an email to Medscape Medical News.
Calming or preventing the storm
While Crippa and colleagues wrap up their CBD trial in South America, several North American and Canadian researchers are seeking to clarify and address one of the most therapeutically challenging aspects of SARS-CoV-2 infection — the lung macrophage–orchestrated hyperinflammatory response.
Although hyperinflammation is not unique to SARS-CoV-2 infection, disease severity and COVID-19–related mortality have been linked to this rapid and prolonged surge of inflammatory cytokines (eg, interleukin 6 [IL-6], IL-10, tumor necrosis factors [TNF], and chemokines) and the cytokine storm.
“When you stimulate CB2 receptors (involved in fighting inflammation), you get a release of the same inflammatory cytokines that are involved in COVID,” Cecilia Costiniuk, MD, associate professor and researcher at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Center, Montreal, Canada, told Medscape Medical News.
“So, if you can act on this receptor, you might be able to reduce the release of those damaging cytokines that are causing ARDS, lung damage, etc,” she explained. Targeting these inflammatory mediators has been a key strategy in research aimed at reducing COVID-19 severity and related mortality, which is where CBD comes into play.
“CBD is a very powerful immune regulator. It keeps the [immune] engine on, but it doesn’t push the gas pedal, and it doesn’t push the brake completely,” Babak Baban, PhD, professor and immunologist at the Dental College of Georgia at Augusta University, told Medscape Medical News.
To explore the effectiveness of CBD in reducing hyperactivated inflammatory reactions, Baban and colleagues examined the potential of CBD to ameliorate ARDS in a murine model. The group divided wild-type male mice into sham, control, and treatment groups.
The sham group received intranasal phosphate buffered saline; the treatment and control groups received a polyriboinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly I:C) double-stranded RNA analogue (100 mcg daily for 3 days) to simulate the cytokine storm and clinical ARDS symptoms.
Following the second poly I:C dose, the treatment group received CBD 5 mg/kg intraperitoneally every other day for 6 days. The mice were sacrificed on day 8.
The study results, published in July in Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, first confirmed that the poly I:C model simulated the cytokine storm in ARDS, reducing blood oxygen saturation by as much as 10% (from ±81.6% to ±72.2%).
Intraperitoneally administered CBD appeared to reverse these ARDS-like trends. “We observed a significant improvement in severe lymphopenia, a mild decline in the ratio of neutrophils to T cells, and significant reductions in levels of [inflammatory and immune factors] IL-6, IFN-gamma [interferon gamma], and in TNF-alpha after the second CBD dose,” Baban said.
There was also a marked downregulation in infiltrating neutrophils and macrophages in the lung, leading to partial restoration of lung morphology and structure. The investigators write that this suggests “a counter inflammatory role for CBD to limit ARDS progression.”
Additional findings from a follow-up study published in mid-October “provide strong data that CBD may partially assert its beneficial and protective impact through its regulation of the apelin peptide,” wrote Baban in an email to Medscape Medical News.
“Apelin may also be a reliable biomarker for early diagnosis of ARDS in general, and in COVID-19 in particular,” he wrote.
Questions remain concerning dose response and whether CBD alone or in combination with other phytocannabinoids is more effective for treating COVID-19. Timing is likewise unclear.
Baban explained that as a result of the biphasic nature of COVID-19, the “sweet spot” appears to be just before the innate immune response progresses into an inflammation-driven response and fibrotic lung damage occurs.
But Wilkerson isn’t as convinced. She said that as with a thermostat, the endocannabinoid system needs tweaking to get it in the right place, that is, to achieve immune homeostasis. The COVID cytokine storm is highly unpredictable, she added, saying, “Right now, the timing for controlling the COVID cytokine storm is really a moving target.”
Is safety a concern?
Safety questions are expected to arise, especially in relation to COVID-19. CBD is not risk free, and one size does not fit all. Human CBD studies report gastrointestinal and somnolent effects, as well as drug-drug interactions.
Findings from a recent systematic review of randomized, controlled CBD trials support overall tolerability, suggesting that serious adverse events are rare. Such events are believed to be related to drug-drug interactions rather than to CBD itself. On the flip side, it is nonintoxicating, and there does not appear to be potential for abuse.
“It’s generally well tolerated,” Wilkerson said. “There’ve now been several clinical trials in numerous patient population settings where basically the only time you really start to have issues is where you have patients on very select agents. But this is where a pharmacist would come into play.”
Costiniuk agreed: “Just because it’s cannabis, it doesn’t mean that there’s going to be strange or unusual effects; these people [ie, those with severe COVID-19] are in the hospital and monitored very closely.”
Delving into the weeds: What’s next?
Although non-COVID-19 cannabinoid researchers have encountered regulatory roadblocks, several research groups that have had the prescience to dive in at the right time are gaining momentum.
Baban’s team has connected with one of the nation’s few academic laboratories authorized to work with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and are awaiting protocol approval so that they can reproduce their research, this time using two CBD formulations (injectable and inhaled).
If findings are positive, they will move forward quickly to meet with the FDA, Baban said, adding that the team is also collaborating with two organizations to conduct human clinical trials in hopes of pushing up timing.
The initial article caught the eye of the World Health Organization, which included it in its global literature on the coronavirus resource section.
Israeli researchers have also been quite busy. InnoCan Pharma and Tel Aviv University are collaborating to explore the potential for CBD-loaded exosomes (minute extracellular particles that mediate intracellular communication, including via innate and adaptive immune responses). The group plans to use these loaded exosomes to target and facilitate recovery of COVID-19–damaged lung cells.
From a broader perspective, the prospects for harnessing cannabinoids for immune modulation will be more thoroughly explored in a special issue of Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, which has extended its current call for papers, studies, abstracts, and conference proceedings until the end of December.
Like many of the therapeutic strategies under investigation for the treatment of COVID-19, studies in CBD may continue to raise more questions than answers.
Still, Wilkerson is optimistic. “Taken together, these studies along with countless others suggest that the complex pharmacophore of Cannabis sativa may hold therapeutic utility to treat lung inflammation, such as what is seen in a COVID-19 cytokine storm,» she told Medscape Medical News. “I’m very excited to see what comes out of the research.”
Baban, Wilkerson, and Costiniuk have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Plagued by false starts, a few dashed hopes, but with perhaps a glimmer of light on the horizon, the race to find an effective treatment for COVID-19 continues. At last count, more than 300 treatments and 200 vaccines were in preclinical or clinical development (not to mention the numerous existing agents that are being evaluated for repurposing).
There is also a renewed interest in cannabinoid therapeutics — in particular, the nonpsychoactive agent cannabidiol (CBD) and the prospect of its modulating inflammatory and other disease-associated clinical indices, including SARS-CoV-2–induced viral load, hyperinflammation, the cytokine storm, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Long hobbled by regulatory, political, and financial barriers, CBD’s potential ability to knock back COVID-19–related inflammation might just open doors that have been closed for years to CBD researchers.
Why CBD and why now?
CBD and the resulting therapeutics have been plagued by a complicated association with recreational cannabis use. It’s been just 2 years since CBD-based therapeutics moved into mainstream medicine — the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Epidiolex oral solution for the treatment of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome, and in August, the FDA approved it for tuberous sclerosis complex.
CBD’s mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, but on the basis of its role in immune responses — well described in research spanning more than two decades — it›s not surprising that cannabinoid researchers have thrown their hats into the COVID-19 drug development ring.
The anti-inflammatory potential of CBD is substantial and appears to be related to the fact that it shares 20 protein targets common to inflammation-related pathways, Jenny Wilkerson, PhD, research assistant professor at the University of Florida School of Pharmacy, Gainesville, Florida, explained to Medscape Medical News.
Among the various trials that are currently recruiting or are underway is one that is slated for completion this fall. CANDIDATE (Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients With Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19) is a randomized, controlled, double-blind study led by Brazilian researchers at the University of São Paulo. The study, which began recruitment this past August, enrolled 100 patients, 50 in the active treatment group (who received capsulated CBD 300 mg daily for 14 days plus pharmacologic therapy [antipyretics] and clinical measures) and 50 who received placebo.
The primary outcome is intended to help clarify the potential role of oral CBD for preventing COVID-19 disease progression, modifying disease-associated clinical indices, and modulating inflammatory parameters, such as the cytokine storm, according to lead investigator Jose Alexandre de Souza Crippa, MD, PhD, professor of neuropsychology at the Ribeirao Preto Medical School at the University of São Paulo in Brazil, in the description of the study on clinicaltrials.gov. Crippa declined to provide any additional information about the trial in an email to Medscape Medical News.
Calming or preventing the storm
While Crippa and colleagues wrap up their CBD trial in South America, several North American and Canadian researchers are seeking to clarify and address one of the most therapeutically challenging aspects of SARS-CoV-2 infection — the lung macrophage–orchestrated hyperinflammatory response.
Although hyperinflammation is not unique to SARS-CoV-2 infection, disease severity and COVID-19–related mortality have been linked to this rapid and prolonged surge of inflammatory cytokines (eg, interleukin 6 [IL-6], IL-10, tumor necrosis factors [TNF], and chemokines) and the cytokine storm.
“When you stimulate CB2 receptors (involved in fighting inflammation), you get a release of the same inflammatory cytokines that are involved in COVID,” Cecilia Costiniuk, MD, associate professor and researcher at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Center, Montreal, Canada, told Medscape Medical News.
“So, if you can act on this receptor, you might be able to reduce the release of those damaging cytokines that are causing ARDS, lung damage, etc,” she explained. Targeting these inflammatory mediators has been a key strategy in research aimed at reducing COVID-19 severity and related mortality, which is where CBD comes into play.
“CBD is a very powerful immune regulator. It keeps the [immune] engine on, but it doesn’t push the gas pedal, and it doesn’t push the brake completely,” Babak Baban, PhD, professor and immunologist at the Dental College of Georgia at Augusta University, told Medscape Medical News.
To explore the effectiveness of CBD in reducing hyperactivated inflammatory reactions, Baban and colleagues examined the potential of CBD to ameliorate ARDS in a murine model. The group divided wild-type male mice into sham, control, and treatment groups.
The sham group received intranasal phosphate buffered saline; the treatment and control groups received a polyriboinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly I:C) double-stranded RNA analogue (100 mcg daily for 3 days) to simulate the cytokine storm and clinical ARDS symptoms.
Following the second poly I:C dose, the treatment group received CBD 5 mg/kg intraperitoneally every other day for 6 days. The mice were sacrificed on day 8.
The study results, published in July in Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, first confirmed that the poly I:C model simulated the cytokine storm in ARDS, reducing blood oxygen saturation by as much as 10% (from ±81.6% to ±72.2%).
Intraperitoneally administered CBD appeared to reverse these ARDS-like trends. “We observed a significant improvement in severe lymphopenia, a mild decline in the ratio of neutrophils to T cells, and significant reductions in levels of [inflammatory and immune factors] IL-6, IFN-gamma [interferon gamma], and in TNF-alpha after the second CBD dose,” Baban said.
There was also a marked downregulation in infiltrating neutrophils and macrophages in the lung, leading to partial restoration of lung morphology and structure. The investigators write that this suggests “a counter inflammatory role for CBD to limit ARDS progression.”
Additional findings from a follow-up study published in mid-October “provide strong data that CBD may partially assert its beneficial and protective impact through its regulation of the apelin peptide,” wrote Baban in an email to Medscape Medical News.
“Apelin may also be a reliable biomarker for early diagnosis of ARDS in general, and in COVID-19 in particular,” he wrote.
Questions remain concerning dose response and whether CBD alone or in combination with other phytocannabinoids is more effective for treating COVID-19. Timing is likewise unclear.
Baban explained that as a result of the biphasic nature of COVID-19, the “sweet spot” appears to be just before the innate immune response progresses into an inflammation-driven response and fibrotic lung damage occurs.
But Wilkerson isn’t as convinced. She said that as with a thermostat, the endocannabinoid system needs tweaking to get it in the right place, that is, to achieve immune homeostasis. The COVID cytokine storm is highly unpredictable, she added, saying, “Right now, the timing for controlling the COVID cytokine storm is really a moving target.”
Is safety a concern?
Safety questions are expected to arise, especially in relation to COVID-19. CBD is not risk free, and one size does not fit all. Human CBD studies report gastrointestinal and somnolent effects, as well as drug-drug interactions.
Findings from a recent systematic review of randomized, controlled CBD trials support overall tolerability, suggesting that serious adverse events are rare. Such events are believed to be related to drug-drug interactions rather than to CBD itself. On the flip side, it is nonintoxicating, and there does not appear to be potential for abuse.
“It’s generally well tolerated,” Wilkerson said. “There’ve now been several clinical trials in numerous patient population settings where basically the only time you really start to have issues is where you have patients on very select agents. But this is where a pharmacist would come into play.”
Costiniuk agreed: “Just because it’s cannabis, it doesn’t mean that there’s going to be strange or unusual effects; these people [ie, those with severe COVID-19] are in the hospital and monitored very closely.”
Delving into the weeds: What’s next?
Although non-COVID-19 cannabinoid researchers have encountered regulatory roadblocks, several research groups that have had the prescience to dive in at the right time are gaining momentum.
Baban’s team has connected with one of the nation’s few academic laboratories authorized to work with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and are awaiting protocol approval so that they can reproduce their research, this time using two CBD formulations (injectable and inhaled).
If findings are positive, they will move forward quickly to meet with the FDA, Baban said, adding that the team is also collaborating with two organizations to conduct human clinical trials in hopes of pushing up timing.
The initial article caught the eye of the World Health Organization, which included it in its global literature on the coronavirus resource section.
Israeli researchers have also been quite busy. InnoCan Pharma and Tel Aviv University are collaborating to explore the potential for CBD-loaded exosomes (minute extracellular particles that mediate intracellular communication, including via innate and adaptive immune responses). The group plans to use these loaded exosomes to target and facilitate recovery of COVID-19–damaged lung cells.
From a broader perspective, the prospects for harnessing cannabinoids for immune modulation will be more thoroughly explored in a special issue of Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, which has extended its current call for papers, studies, abstracts, and conference proceedings until the end of December.
Like many of the therapeutic strategies under investigation for the treatment of COVID-19, studies in CBD may continue to raise more questions than answers.
Still, Wilkerson is optimistic. “Taken together, these studies along with countless others suggest that the complex pharmacophore of Cannabis sativa may hold therapeutic utility to treat lung inflammation, such as what is seen in a COVID-19 cytokine storm,» she told Medscape Medical News. “I’m very excited to see what comes out of the research.”
Baban, Wilkerson, and Costiniuk have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Survey finds European dermatologists unhappy with pandemic teledermatology experience
intensely, according to the findings of a survey presented at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“The results of our survey clearly show 7 out of 10 participating dermatologists declared that they were not happy with teledermatology, and most of them declared that they were not at all happy,” according to Mariano Suppa, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology and venereology, Free University of Brussels.
“It was very interesting: it was not just about the lack of a good quality of consultation, but was also related to some extent to a lack of respect from some patients, and also a lack of empathy. The majority of survey respondents felt [attacked] by their own patients because they were proposing teledermatology. So, yes, we were forced to go to teledermatology, and I think we will be again to some extent, but clearly we’re not happy about it,” he elaborated in response to a question from session chair Brigitte Dreno, MD, professor of dermatology and vice dean of the faculty of medicine at the University of Nantes (France).
The survey, conducted by the EADV communication committee, assessed the pandemic’s impact on European dermatologists’ professional practices and personal lives through 30 brief questions, with space at the end for additional open-ended comments. In the comments section, many dermatologists vented about their income loss, the disorganized response to round one of the pandemic, and most of all about teledermatology. Common complaints were that teledermatology required a huge consumption of energy and constituted a major intrusion upon the physicians’ personal lives. And then there was the common theme of unkind treatment by some patients.
The survey was sent twice in June 2020 to more than 4,800 EADV members. It was completed by 490 dermatologists from 39 countries. Dr. Suppa attributed the low response rate to physician weariness of the topic due to saturation news media coverage of the pandemic.
Sixty-nine percent of responding dermatologists were women. Fifty-two percent of participants were over age 50, 81% lived in a city, and 53% worked in a university or public hospital or clinic. Twelve percent lived alone.
Impact on professional practice
Many European dermatologists were on the front lines in dealing with the first wave of COVID-19. Twenty-eight percent worked in a COVID-19 unit. Forty-eight percent of dermatologists performed COVID-19 tests, and those who didn’t either had no patient contact or couldn’t get test kits. Thirty-five percent of dermatologists saw patients who presented with skin signs of COVID-19. Four percent of survey respondents became infected.
Seventy percent rescheduled or canceled all or most patient appointments. Clinical care was prioritized: during the peak of the pandemic, 76% of dermatologists saw only urgent cases – mostly potentially serious rashes – and dermato-oncology patients. Seventy-six percent of dermatologists performed teledermatology, although by June 60% of respondents reported seeing at least three-quarters of their patients face-to-face.
Twenty-three percent of dermatologists reported having lost most or all of their income during March through June, and another 26% lost about half.
Impact on dermatologists’ personal lives
About half of survey respondents reported feeling stressed, and a similar percentage checked the box marked ‘anxiety.’ Nine percent reported depressive symptoms, 15% mentioned feeling anger, 17% uselessness, and 2% admitted suicidal ideation. But 30% of dermatologists reported experiencing no negative psychological effects whatsoever stemming from the pandemic.
Sixteen percent of dermatologists reported drinking more alcohol during sequestration.
But respondents cited positive effects as well: a renewed appreciation of the importance of time, and enjoyment of the additional time spent with family and alone. Many dermatologists relished the opportunity to spend more time cooking, reading literature, doing research, listening to or playing music, and practicing yoga or meditation. And dermatologists took solace and pride in being members of the vital medical community.
Dr. Dreno asked if the survey revealed evidence of underdiagnosis and undertreatment of dermatologic diseases during the pandemic. Dr. Suppa replied that the survey didn’t address that issue, but it’s his personal opinion that this was no doubt the case. Roughly one-quarter of dermatologists canceled all appointments, and when dermatology clinics became filled beginning in June, he and his colleagues saw a number of cases of delayed-diagnosis advanced skin cancer.
“I think that the diseases that were really penalized were the chronic inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and also atopic dermatitis. We were doing a lot of telephone consultations for those patients at that time, and we saw in June that for those particular patients there was an unmet need in the pandemic because some of them really needed to have been seen. I think this is a lesson we should learn for the second wave that we’re unfortunately facing right now: We need to adopt restrictive measures to avoid spreading the pandemic, yes, for sure, but we need to keep in mind that there is not just COVID-19, but also other important diseases,” Dr. Suppa said.
A second EADV survey will be performed during the fall/winter wave of the pandemic.
Dr. Suppa reported having no financial conflicts regarding the EADV-funded survey.
SOURCE: Suppa M. EADV 2020. Presentation D3T03.4D
intensely, according to the findings of a survey presented at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“The results of our survey clearly show 7 out of 10 participating dermatologists declared that they were not happy with teledermatology, and most of them declared that they were not at all happy,” according to Mariano Suppa, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology and venereology, Free University of Brussels.
“It was very interesting: it was not just about the lack of a good quality of consultation, but was also related to some extent to a lack of respect from some patients, and also a lack of empathy. The majority of survey respondents felt [attacked] by their own patients because they were proposing teledermatology. So, yes, we were forced to go to teledermatology, and I think we will be again to some extent, but clearly we’re not happy about it,” he elaborated in response to a question from session chair Brigitte Dreno, MD, professor of dermatology and vice dean of the faculty of medicine at the University of Nantes (France).
The survey, conducted by the EADV communication committee, assessed the pandemic’s impact on European dermatologists’ professional practices and personal lives through 30 brief questions, with space at the end for additional open-ended comments. In the comments section, many dermatologists vented about their income loss, the disorganized response to round one of the pandemic, and most of all about teledermatology. Common complaints were that teledermatology required a huge consumption of energy and constituted a major intrusion upon the physicians’ personal lives. And then there was the common theme of unkind treatment by some patients.
The survey was sent twice in June 2020 to more than 4,800 EADV members. It was completed by 490 dermatologists from 39 countries. Dr. Suppa attributed the low response rate to physician weariness of the topic due to saturation news media coverage of the pandemic.
Sixty-nine percent of responding dermatologists were women. Fifty-two percent of participants were over age 50, 81% lived in a city, and 53% worked in a university or public hospital or clinic. Twelve percent lived alone.
Impact on professional practice
Many European dermatologists were on the front lines in dealing with the first wave of COVID-19. Twenty-eight percent worked in a COVID-19 unit. Forty-eight percent of dermatologists performed COVID-19 tests, and those who didn’t either had no patient contact or couldn’t get test kits. Thirty-five percent of dermatologists saw patients who presented with skin signs of COVID-19. Four percent of survey respondents became infected.
Seventy percent rescheduled or canceled all or most patient appointments. Clinical care was prioritized: during the peak of the pandemic, 76% of dermatologists saw only urgent cases – mostly potentially serious rashes – and dermato-oncology patients. Seventy-six percent of dermatologists performed teledermatology, although by June 60% of respondents reported seeing at least three-quarters of their patients face-to-face.
Twenty-three percent of dermatologists reported having lost most or all of their income during March through June, and another 26% lost about half.
Impact on dermatologists’ personal lives
About half of survey respondents reported feeling stressed, and a similar percentage checked the box marked ‘anxiety.’ Nine percent reported depressive symptoms, 15% mentioned feeling anger, 17% uselessness, and 2% admitted suicidal ideation. But 30% of dermatologists reported experiencing no negative psychological effects whatsoever stemming from the pandemic.
Sixteen percent of dermatologists reported drinking more alcohol during sequestration.
But respondents cited positive effects as well: a renewed appreciation of the importance of time, and enjoyment of the additional time spent with family and alone. Many dermatologists relished the opportunity to spend more time cooking, reading literature, doing research, listening to or playing music, and practicing yoga or meditation. And dermatologists took solace and pride in being members of the vital medical community.
Dr. Dreno asked if the survey revealed evidence of underdiagnosis and undertreatment of dermatologic diseases during the pandemic. Dr. Suppa replied that the survey didn’t address that issue, but it’s his personal opinion that this was no doubt the case. Roughly one-quarter of dermatologists canceled all appointments, and when dermatology clinics became filled beginning in June, he and his colleagues saw a number of cases of delayed-diagnosis advanced skin cancer.
“I think that the diseases that were really penalized were the chronic inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and also atopic dermatitis. We were doing a lot of telephone consultations for those patients at that time, and we saw in June that for those particular patients there was an unmet need in the pandemic because some of them really needed to have been seen. I think this is a lesson we should learn for the second wave that we’re unfortunately facing right now: We need to adopt restrictive measures to avoid spreading the pandemic, yes, for sure, but we need to keep in mind that there is not just COVID-19, but also other important diseases,” Dr. Suppa said.
A second EADV survey will be performed during the fall/winter wave of the pandemic.
Dr. Suppa reported having no financial conflicts regarding the EADV-funded survey.
SOURCE: Suppa M. EADV 2020. Presentation D3T03.4D
intensely, according to the findings of a survey presented at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“The results of our survey clearly show 7 out of 10 participating dermatologists declared that they were not happy with teledermatology, and most of them declared that they were not at all happy,” according to Mariano Suppa, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology and venereology, Free University of Brussels.
“It was very interesting: it was not just about the lack of a good quality of consultation, but was also related to some extent to a lack of respect from some patients, and also a lack of empathy. The majority of survey respondents felt [attacked] by their own patients because they were proposing teledermatology. So, yes, we were forced to go to teledermatology, and I think we will be again to some extent, but clearly we’re not happy about it,” he elaborated in response to a question from session chair Brigitte Dreno, MD, professor of dermatology and vice dean of the faculty of medicine at the University of Nantes (France).
The survey, conducted by the EADV communication committee, assessed the pandemic’s impact on European dermatologists’ professional practices and personal lives through 30 brief questions, with space at the end for additional open-ended comments. In the comments section, many dermatologists vented about their income loss, the disorganized response to round one of the pandemic, and most of all about teledermatology. Common complaints were that teledermatology required a huge consumption of energy and constituted a major intrusion upon the physicians’ personal lives. And then there was the common theme of unkind treatment by some patients.
The survey was sent twice in June 2020 to more than 4,800 EADV members. It was completed by 490 dermatologists from 39 countries. Dr. Suppa attributed the low response rate to physician weariness of the topic due to saturation news media coverage of the pandemic.
Sixty-nine percent of responding dermatologists were women. Fifty-two percent of participants were over age 50, 81% lived in a city, and 53% worked in a university or public hospital or clinic. Twelve percent lived alone.
Impact on professional practice
Many European dermatologists were on the front lines in dealing with the first wave of COVID-19. Twenty-eight percent worked in a COVID-19 unit. Forty-eight percent of dermatologists performed COVID-19 tests, and those who didn’t either had no patient contact or couldn’t get test kits. Thirty-five percent of dermatologists saw patients who presented with skin signs of COVID-19. Four percent of survey respondents became infected.
Seventy percent rescheduled or canceled all or most patient appointments. Clinical care was prioritized: during the peak of the pandemic, 76% of dermatologists saw only urgent cases – mostly potentially serious rashes – and dermato-oncology patients. Seventy-six percent of dermatologists performed teledermatology, although by June 60% of respondents reported seeing at least three-quarters of their patients face-to-face.
Twenty-three percent of dermatologists reported having lost most or all of their income during March through June, and another 26% lost about half.
Impact on dermatologists’ personal lives
About half of survey respondents reported feeling stressed, and a similar percentage checked the box marked ‘anxiety.’ Nine percent reported depressive symptoms, 15% mentioned feeling anger, 17% uselessness, and 2% admitted suicidal ideation. But 30% of dermatologists reported experiencing no negative psychological effects whatsoever stemming from the pandemic.
Sixteen percent of dermatologists reported drinking more alcohol during sequestration.
But respondents cited positive effects as well: a renewed appreciation of the importance of time, and enjoyment of the additional time spent with family and alone. Many dermatologists relished the opportunity to spend more time cooking, reading literature, doing research, listening to or playing music, and practicing yoga or meditation. And dermatologists took solace and pride in being members of the vital medical community.
Dr. Dreno asked if the survey revealed evidence of underdiagnosis and undertreatment of dermatologic diseases during the pandemic. Dr. Suppa replied that the survey didn’t address that issue, but it’s his personal opinion that this was no doubt the case. Roughly one-quarter of dermatologists canceled all appointments, and when dermatology clinics became filled beginning in June, he and his colleagues saw a number of cases of delayed-diagnosis advanced skin cancer.
“I think that the diseases that were really penalized were the chronic inflammatory diseases, such as psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and also atopic dermatitis. We were doing a lot of telephone consultations for those patients at that time, and we saw in June that for those particular patients there was an unmet need in the pandemic because some of them really needed to have been seen. I think this is a lesson we should learn for the second wave that we’re unfortunately facing right now: We need to adopt restrictive measures to avoid spreading the pandemic, yes, for sure, but we need to keep in mind that there is not just COVID-19, but also other important diseases,” Dr. Suppa said.
A second EADV survey will be performed during the fall/winter wave of the pandemic.
Dr. Suppa reported having no financial conflicts regarding the EADV-funded survey.
SOURCE: Suppa M. EADV 2020. Presentation D3T03.4D
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
COVID-19: U.S. sets new weekly high in children
the American Academy of Pediatrics announced Nov. 2.
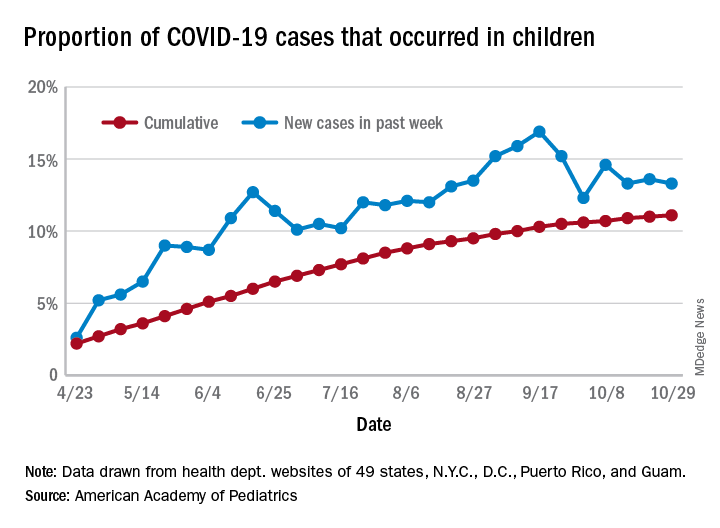
For the week, over 61,000 cases were reported in children, bringing the number of COVID-19 cases for the month of October to nearly 200,000 and the total since the start of the pandemic to over 853,000, the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly report.
“These numbers reflect a disturbing increase in cases throughout most of the United States in all populations, especially among young adults,” Yvonne Maldonado, MD, chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases, said in a separate statement. “We are entering a heightened wave of infections around the country. We would encourage family holiday gatherings to be avoided if possible, especially if there are high-risk individuals in the household.”
For the week ending Oct. 29, children represented 13.3% of all cases, possibly constituting a minitrend of stability over the past 3 weeks. For the full length of the pandemic, 11.1% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, although severe illness is much less common: 1.7% of all hospitalizations (data from 24 states and New York City) and 0.06% of all deaths (data from 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA report said.
Other data show that 1,134 per 100,000 children in the United States have been infected by the coronavirus, up from 1,053 the previous week, with state rates ranging from 221 per 100,000 in Vermont to 3,321 in North Dakota. In Wyoming, 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, the highest of any state, while New Jersey has the lowest rate at 4.9%, the AAP/CHA report showed.
In the 10 states making testing data available, children represent the lowest percentage of tests in Iowa (5.0%) and the highest in Indiana (16.9%). Iowa, however, has the highest positivity rate for children at 14.6%, along with Nevada, while West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said in the report.
These numbers, however, may not be telling the whole story. “The number of reported COVID-19 cases in children is likely an undercount because children’s symptoms are often mild and they may not be tested for every illness,” the AAP said in its statement.
“We urge policy makers to listen to doctors and public health experts rather than level baseless accusations against them. Physicians, nurses and other health care professionals have put their lives on the line to protect our communities. We can all do our part to protect them, and our communities, by wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and getting our flu immunizations,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in the AAP statement.
the American Academy of Pediatrics announced Nov. 2.

For the week, over 61,000 cases were reported in children, bringing the number of COVID-19 cases for the month of October to nearly 200,000 and the total since the start of the pandemic to over 853,000, the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly report.
“These numbers reflect a disturbing increase in cases throughout most of the United States in all populations, especially among young adults,” Yvonne Maldonado, MD, chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases, said in a separate statement. “We are entering a heightened wave of infections around the country. We would encourage family holiday gatherings to be avoided if possible, especially if there are high-risk individuals in the household.”
For the week ending Oct. 29, children represented 13.3% of all cases, possibly constituting a minitrend of stability over the past 3 weeks. For the full length of the pandemic, 11.1% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, although severe illness is much less common: 1.7% of all hospitalizations (data from 24 states and New York City) and 0.06% of all deaths (data from 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA report said.
Other data show that 1,134 per 100,000 children in the United States have been infected by the coronavirus, up from 1,053 the previous week, with state rates ranging from 221 per 100,000 in Vermont to 3,321 in North Dakota. In Wyoming, 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, the highest of any state, while New Jersey has the lowest rate at 4.9%, the AAP/CHA report showed.
In the 10 states making testing data available, children represent the lowest percentage of tests in Iowa (5.0%) and the highest in Indiana (16.9%). Iowa, however, has the highest positivity rate for children at 14.6%, along with Nevada, while West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said in the report.
These numbers, however, may not be telling the whole story. “The number of reported COVID-19 cases in children is likely an undercount because children’s symptoms are often mild and they may not be tested for every illness,” the AAP said in its statement.
“We urge policy makers to listen to doctors and public health experts rather than level baseless accusations against them. Physicians, nurses and other health care professionals have put their lives on the line to protect our communities. We can all do our part to protect them, and our communities, by wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and getting our flu immunizations,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in the AAP statement.
the American Academy of Pediatrics announced Nov. 2.

For the week, over 61,000 cases were reported in children, bringing the number of COVID-19 cases for the month of October to nearly 200,000 and the total since the start of the pandemic to over 853,000, the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly report.
“These numbers reflect a disturbing increase in cases throughout most of the United States in all populations, especially among young adults,” Yvonne Maldonado, MD, chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases, said in a separate statement. “We are entering a heightened wave of infections around the country. We would encourage family holiday gatherings to be avoided if possible, especially if there are high-risk individuals in the household.”
For the week ending Oct. 29, children represented 13.3% of all cases, possibly constituting a minitrend of stability over the past 3 weeks. For the full length of the pandemic, 11.1% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, although severe illness is much less common: 1.7% of all hospitalizations (data from 24 states and New York City) and 0.06% of all deaths (data from 42 states and New York City), the AAP and CHA report said.
Other data show that 1,134 per 100,000 children in the United States have been infected by the coronavirus, up from 1,053 the previous week, with state rates ranging from 221 per 100,000 in Vermont to 3,321 in North Dakota. In Wyoming, 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases have occurred in children, the highest of any state, while New Jersey has the lowest rate at 4.9%, the AAP/CHA report showed.
In the 10 states making testing data available, children represent the lowest percentage of tests in Iowa (5.0%) and the highest in Indiana (16.9%). Iowa, however, has the highest positivity rate for children at 14.6%, along with Nevada, while West Virginia has the lowest at 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said in the report.
These numbers, however, may not be telling the whole story. “The number of reported COVID-19 cases in children is likely an undercount because children’s symptoms are often mild and they may not be tested for every illness,” the AAP said in its statement.
“We urge policy makers to listen to doctors and public health experts rather than level baseless accusations against them. Physicians, nurses and other health care professionals have put their lives on the line to protect our communities. We can all do our part to protect them, and our communities, by wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and getting our flu immunizations,” AAP President Sally Goza, MD, said in the AAP statement.
HF an added risk in COVID-19, regardless of ejection fraction
People with a history of heart failure – no matter the type – face more complications and death than their peers without HF once hospitalized with COVID-19, a new observational study shows.
A history of HF was associated with a near doubling risk of in-hospital mortality and ICU care and more than a tripling risk of mechanical ventilation despite adjustment for 18 factors including race, obesity, diabetes, previous treatment with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors, and severity of illness.
Adverse outcomes were high regardless of whether patients had HF with a preserved, mid-range, or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (HFpEF/HFmrEF/HFrEF).
“That for me was the real zinger,” senior author Anuradha Lala, MD, said in an interview . “Because as clinicians, oftentimes, and wrongly so, we think this person has preserved ejection fraction, so they’re not needing my heart failure expertise as much as someone with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.”
In the peak of the pandemic, that may have meant triaging patients with HFpEF to a regular floor, whereas those with HFrEF were seen by the specialist team.
“What this alerted me to is to take heart failure as a diagnosis very seriously, regardless of ejection fraction, and that is very much in line with all of the emerging data about heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” said Dr. Lala, from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“Now when I see patients in the clinic, I incorporate part of our visit to talking about what they are doing to prevent COVID, which I really wasn’t doing before. It was like ‘Oh yeah, what crazy times we’re dealing with’ and then addressing their heart failure as I normally would,” she said. “But now, interwoven into every visit is: Are you wearing a mask, what’s your social distancing policy, who are you living with at home, has anyone at home or who you’ve interacted with been sick? I’m asking those questions just as a knee-jerk reaction for these patients because I know the repercussions. We have to keep in mind these are observational studies, so I can’t prove causality but these are observations that are, nonetheless, quite robust.”
Although cardiovascular disease, including HF, is recognized as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 patients, data are sparse on the clinical course and prognosis of patients with preexisting HF.
“I would have expected that there would have been a gradation of risk from the people with very low ejection fractions up into the normal range, but here it didn’t seem to matter at all. So that’s an important point that bad outcomes were independent of ejection fraction,” commented Lee Goldberg, MD, professor of medicine and chief of advanced heart failure and cardiac transplant at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The study also validated that there is no association between use of RAAS inhibitors and bad outcomes in patients with COVID-19, he said.
Although this has been demonstrated in several studies, concerns were raised early in the pandemic that ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers could facilitate infection with SARS-CoV-2 and increase the risk of severe or lethal COVID-19.
“For most clinicians that question has been put to bed, but we’re still getting patients that will ask during office visits ‘Is it safe for me to stay on?’ They still have that doubt [about] ‘Are we doing the right thing?’ ” Dr. Goldberg said.
“We can reassure them now. A lot of us are able to say there’s nothing to that, we’re very clear about this, stay on the meds. If anything, there’s data that suggest actually it may be better to be on an ACE inhibitor; that the hospitalizations were shorter and the outcomes were a little bit better.”
For the current study, published online Oct. 28 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the investigators analyzed 6,439 patients admitted for COVID-19 at one of five Mount Sinai Health System hospitals in New York between Feb. 27 and June 26. Their mean age was 65.3 years, 45% were women, and one-third were treated with RAAS inhibitors before admission.
Using ICD-9/10 codes and individual chart review, HF was identified in 422 patients (6.6%), of which 250 patients had HFpEF (≥50%), 44 had HFmrEF (41%-49%), and 128 had HFrEF (≤40%).
Patients with HFpEF were older, more frequently women with a higher body mass index and history of lung disease than patients with HFrEF, whereas those with HFmrEF fell in between.
The HFpEF group was also treated with hydroxychloroquine or macrolides and noninvasive ventilation more frequently than the other two groups, whereas antiplatelet and neurohormonal therapies were more common in the HFrEF group.
Patients with a history of HF had significantly longer hospital stays than those without HF (8 days vs. 6 days), increased need for intubation (22.8% vs. 11.9%) and ICU care (23.2% vs. 16.6%), and worse in-hospital mortality (40% vs. 24.9%).
After multivariable regression adjustment, HF persisted as an independent risk factor for ICU care (odds ratio, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.25-2.34), intubation and mechanical ventilation (OR, 3.64; 95% CI, 2.56-5.16), and in-hospital mortality (OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.27-2.78).
“I knew to expect higher rates of adverse outcomes but I didn’t expect it to be nearly a twofold increase,” Dr. Lala said. “I thought that was pretty powerful.”
No significant differences were seen across LVEF categories in length of stay, need for ICU care, intubation and mechanical ventilation, acute kidney injury, shock, thromboembolic events, arrhythmias, or 30-day readmission rates.
However, cardiogenic shock (7.8% vs. 2.3% vs. 2%) and HF-related causes for 30-day readmissions (47.1% vs. 0% vs. 8.6%) were significantly higher in patients with HFrEF than in those with HFmrEF or HFpEF.
Also, mortality was lower in those with HFmrEF (22.7%) than with HFrEF (38.3%) and HFpEF (44%). The group was small but the “results suggested that patients with HFmrEF could have a better prognosis, because they can represent a distinct and more favorable HF phenotype,” the authors wrote.
The statistical testing didn’t show much difference and the patient numbers were very small, noted Dr. Goldberg. “So they might be overreaching a little bit there.”
“To me, the take-home message is that just having the phenotype of heart failure, regardless of EF, is associated with bad outcomes and we need to be vigilant on two fronts,” he said. “We really need to be doing prevention in the folks with heart failure because if they get COVID their outcomes are not going to be as good. Second, as clinicians, if we see a patient presenting with COVID who has a history of heart failure we may want to be much more vigilant with that individual than we might otherwise be. So I think there’s something to be said for kind of risk-stratifying people in that way.”
Dr. Goldberg pointed out that the study had many “amazing strengths,” including a large, racially diverse population, direct chart review to identify HF patients, and capturing a patient’s specific HF phenotype.
Weaknesses are that it was a single-center study, so the biases of how these patients were treated are not easily controlled for, he said. “We also don’t know when the hospital system was very strained as they were making some decisions: Were the older patients who had advanced heart and lung disease ultimately less aggressively treated because they felt they wouldn’t survive?”
Dr. Lala has received personal fees from Zoll, outside the submitted work. Dr. Goldberg reported research funding with Respicardia and consulting fees from Abbott.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with a history of heart failure – no matter the type – face more complications and death than their peers without HF once hospitalized with COVID-19, a new observational study shows.
A history of HF was associated with a near doubling risk of in-hospital mortality and ICU care and more than a tripling risk of mechanical ventilation despite adjustment for 18 factors including race, obesity, diabetes, previous treatment with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors, and severity of illness.
Adverse outcomes were high regardless of whether patients had HF with a preserved, mid-range, or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (HFpEF/HFmrEF/HFrEF).
“That for me was the real zinger,” senior author Anuradha Lala, MD, said in an interview . “Because as clinicians, oftentimes, and wrongly so, we think this person has preserved ejection fraction, so they’re not needing my heart failure expertise as much as someone with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.”
In the peak of the pandemic, that may have meant triaging patients with HFpEF to a regular floor, whereas those with HFrEF were seen by the specialist team.
“What this alerted me to is to take heart failure as a diagnosis very seriously, regardless of ejection fraction, and that is very much in line with all of the emerging data about heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” said Dr. Lala, from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“Now when I see patients in the clinic, I incorporate part of our visit to talking about what they are doing to prevent COVID, which I really wasn’t doing before. It was like ‘Oh yeah, what crazy times we’re dealing with’ and then addressing their heart failure as I normally would,” she said. “But now, interwoven into every visit is: Are you wearing a mask, what’s your social distancing policy, who are you living with at home, has anyone at home or who you’ve interacted with been sick? I’m asking those questions just as a knee-jerk reaction for these patients because I know the repercussions. We have to keep in mind these are observational studies, so I can’t prove causality but these are observations that are, nonetheless, quite robust.”
Although cardiovascular disease, including HF, is recognized as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 patients, data are sparse on the clinical course and prognosis of patients with preexisting HF.
“I would have expected that there would have been a gradation of risk from the people with very low ejection fractions up into the normal range, but here it didn’t seem to matter at all. So that’s an important point that bad outcomes were independent of ejection fraction,” commented Lee Goldberg, MD, professor of medicine and chief of advanced heart failure and cardiac transplant at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The study also validated that there is no association between use of RAAS inhibitors and bad outcomes in patients with COVID-19, he said.
Although this has been demonstrated in several studies, concerns were raised early in the pandemic that ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers could facilitate infection with SARS-CoV-2 and increase the risk of severe or lethal COVID-19.
“For most clinicians that question has been put to bed, but we’re still getting patients that will ask during office visits ‘Is it safe for me to stay on?’ They still have that doubt [about] ‘Are we doing the right thing?’ ” Dr. Goldberg said.
“We can reassure them now. A lot of us are able to say there’s nothing to that, we’re very clear about this, stay on the meds. If anything, there’s data that suggest actually it may be better to be on an ACE inhibitor; that the hospitalizations were shorter and the outcomes were a little bit better.”
For the current study, published online Oct. 28 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the investigators analyzed 6,439 patients admitted for COVID-19 at one of five Mount Sinai Health System hospitals in New York between Feb. 27 and June 26. Their mean age was 65.3 years, 45% were women, and one-third were treated with RAAS inhibitors before admission.
Using ICD-9/10 codes and individual chart review, HF was identified in 422 patients (6.6%), of which 250 patients had HFpEF (≥50%), 44 had HFmrEF (41%-49%), and 128 had HFrEF (≤40%).
Patients with HFpEF were older, more frequently women with a higher body mass index and history of lung disease than patients with HFrEF, whereas those with HFmrEF fell in between.
The HFpEF group was also treated with hydroxychloroquine or macrolides and noninvasive ventilation more frequently than the other two groups, whereas antiplatelet and neurohormonal therapies were more common in the HFrEF group.
Patients with a history of HF had significantly longer hospital stays than those without HF (8 days vs. 6 days), increased need for intubation (22.8% vs. 11.9%) and ICU care (23.2% vs. 16.6%), and worse in-hospital mortality (40% vs. 24.9%).
After multivariable regression adjustment, HF persisted as an independent risk factor for ICU care (odds ratio, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.25-2.34), intubation and mechanical ventilation (OR, 3.64; 95% CI, 2.56-5.16), and in-hospital mortality (OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.27-2.78).
“I knew to expect higher rates of adverse outcomes but I didn’t expect it to be nearly a twofold increase,” Dr. Lala said. “I thought that was pretty powerful.”
No significant differences were seen across LVEF categories in length of stay, need for ICU care, intubation and mechanical ventilation, acute kidney injury, shock, thromboembolic events, arrhythmias, or 30-day readmission rates.
However, cardiogenic shock (7.8% vs. 2.3% vs. 2%) and HF-related causes for 30-day readmissions (47.1% vs. 0% vs. 8.6%) were significantly higher in patients with HFrEF than in those with HFmrEF or HFpEF.
Also, mortality was lower in those with HFmrEF (22.7%) than with HFrEF (38.3%) and HFpEF (44%). The group was small but the “results suggested that patients with HFmrEF could have a better prognosis, because they can represent a distinct and more favorable HF phenotype,” the authors wrote.
The statistical testing didn’t show much difference and the patient numbers were very small, noted Dr. Goldberg. “So they might be overreaching a little bit there.”
“To me, the take-home message is that just having the phenotype of heart failure, regardless of EF, is associated with bad outcomes and we need to be vigilant on two fronts,” he said. “We really need to be doing prevention in the folks with heart failure because if they get COVID their outcomes are not going to be as good. Second, as clinicians, if we see a patient presenting with COVID who has a history of heart failure we may want to be much more vigilant with that individual than we might otherwise be. So I think there’s something to be said for kind of risk-stratifying people in that way.”
Dr. Goldberg pointed out that the study had many “amazing strengths,” including a large, racially diverse population, direct chart review to identify HF patients, and capturing a patient’s specific HF phenotype.
Weaknesses are that it was a single-center study, so the biases of how these patients were treated are not easily controlled for, he said. “We also don’t know when the hospital system was very strained as they were making some decisions: Were the older patients who had advanced heart and lung disease ultimately less aggressively treated because they felt they wouldn’t survive?”
Dr. Lala has received personal fees from Zoll, outside the submitted work. Dr. Goldberg reported research funding with Respicardia and consulting fees from Abbott.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with a history of heart failure – no matter the type – face more complications and death than their peers without HF once hospitalized with COVID-19, a new observational study shows.
A history of HF was associated with a near doubling risk of in-hospital mortality and ICU care and more than a tripling risk of mechanical ventilation despite adjustment for 18 factors including race, obesity, diabetes, previous treatment with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors, and severity of illness.
Adverse outcomes were high regardless of whether patients had HF with a preserved, mid-range, or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (HFpEF/HFmrEF/HFrEF).
“That for me was the real zinger,” senior author Anuradha Lala, MD, said in an interview . “Because as clinicians, oftentimes, and wrongly so, we think this person has preserved ejection fraction, so they’re not needing my heart failure expertise as much as someone with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.”
In the peak of the pandemic, that may have meant triaging patients with HFpEF to a regular floor, whereas those with HFrEF were seen by the specialist team.
“What this alerted me to is to take heart failure as a diagnosis very seriously, regardless of ejection fraction, and that is very much in line with all of the emerging data about heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” said Dr. Lala, from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“Now when I see patients in the clinic, I incorporate part of our visit to talking about what they are doing to prevent COVID, which I really wasn’t doing before. It was like ‘Oh yeah, what crazy times we’re dealing with’ and then addressing their heart failure as I normally would,” she said. “But now, interwoven into every visit is: Are you wearing a mask, what’s your social distancing policy, who are you living with at home, has anyone at home or who you’ve interacted with been sick? I’m asking those questions just as a knee-jerk reaction for these patients because I know the repercussions. We have to keep in mind these are observational studies, so I can’t prove causality but these are observations that are, nonetheless, quite robust.”
Although cardiovascular disease, including HF, is recognized as a risk factor for worse outcomes in COVID-19 patients, data are sparse on the clinical course and prognosis of patients with preexisting HF.
“I would have expected that there would have been a gradation of risk from the people with very low ejection fractions up into the normal range, but here it didn’t seem to matter at all. So that’s an important point that bad outcomes were independent of ejection fraction,” commented Lee Goldberg, MD, professor of medicine and chief of advanced heart failure and cardiac transplant at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
The study also validated that there is no association between use of RAAS inhibitors and bad outcomes in patients with COVID-19, he said.
Although this has been demonstrated in several studies, concerns were raised early in the pandemic that ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers could facilitate infection with SARS-CoV-2 and increase the risk of severe or lethal COVID-19.
“For most clinicians that question has been put to bed, but we’re still getting patients that will ask during office visits ‘Is it safe for me to stay on?’ They still have that doubt [about] ‘Are we doing the right thing?’ ” Dr. Goldberg said.
“We can reassure them now. A lot of us are able to say there’s nothing to that, we’re very clear about this, stay on the meds. If anything, there’s data that suggest actually it may be better to be on an ACE inhibitor; that the hospitalizations were shorter and the outcomes were a little bit better.”
For the current study, published online Oct. 28 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the investigators analyzed 6,439 patients admitted for COVID-19 at one of five Mount Sinai Health System hospitals in New York between Feb. 27 and June 26. Their mean age was 65.3 years, 45% were women, and one-third were treated with RAAS inhibitors before admission.
Using ICD-9/10 codes and individual chart review, HF was identified in 422 patients (6.6%), of which 250 patients had HFpEF (≥50%), 44 had HFmrEF (41%-49%), and 128 had HFrEF (≤40%).
Patients with HFpEF were older, more frequently women with a higher body mass index and history of lung disease than patients with HFrEF, whereas those with HFmrEF fell in between.
The HFpEF group was also treated with hydroxychloroquine or macrolides and noninvasive ventilation more frequently than the other two groups, whereas antiplatelet and neurohormonal therapies were more common in the HFrEF group.
Patients with a history of HF had significantly longer hospital stays than those without HF (8 days vs. 6 days), increased need for intubation (22.8% vs. 11.9%) and ICU care (23.2% vs. 16.6%), and worse in-hospital mortality (40% vs. 24.9%).
After multivariable regression adjustment, HF persisted as an independent risk factor for ICU care (odds ratio, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.25-2.34), intubation and mechanical ventilation (OR, 3.64; 95% CI, 2.56-5.16), and in-hospital mortality (OR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.27-2.78).
“I knew to expect higher rates of adverse outcomes but I didn’t expect it to be nearly a twofold increase,” Dr. Lala said. “I thought that was pretty powerful.”
No significant differences were seen across LVEF categories in length of stay, need for ICU care, intubation and mechanical ventilation, acute kidney injury, shock, thromboembolic events, arrhythmias, or 30-day readmission rates.
However, cardiogenic shock (7.8% vs. 2.3% vs. 2%) and HF-related causes for 30-day readmissions (47.1% vs. 0% vs. 8.6%) were significantly higher in patients with HFrEF than in those with HFmrEF or HFpEF.
Also, mortality was lower in those with HFmrEF (22.7%) than with HFrEF (38.3%) and HFpEF (44%). The group was small but the “results suggested that patients with HFmrEF could have a better prognosis, because they can represent a distinct and more favorable HF phenotype,” the authors wrote.
The statistical testing didn’t show much difference and the patient numbers were very small, noted Dr. Goldberg. “So they might be overreaching a little bit there.”
“To me, the take-home message is that just having the phenotype of heart failure, regardless of EF, is associated with bad outcomes and we need to be vigilant on two fronts,” he said. “We really need to be doing prevention in the folks with heart failure because if they get COVID their outcomes are not going to be as good. Second, as clinicians, if we see a patient presenting with COVID who has a history of heart failure we may want to be much more vigilant with that individual than we might otherwise be. So I think there’s something to be said for kind of risk-stratifying people in that way.”
Dr. Goldberg pointed out that the study had many “amazing strengths,” including a large, racially diverse population, direct chart review to identify HF patients, and capturing a patient’s specific HF phenotype.
Weaknesses are that it was a single-center study, so the biases of how these patients were treated are not easily controlled for, he said. “We also don’t know when the hospital system was very strained as they were making some decisions: Were the older patients who had advanced heart and lung disease ultimately less aggressively treated because they felt they wouldn’t survive?”
Dr. Lala has received personal fees from Zoll, outside the submitted work. Dr. Goldberg reported research funding with Respicardia and consulting fees from Abbott.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Biologics may protect psoriasis patients against severe COVID-19
presented at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“Biologics seem to be very protective against severe, poor-prognosis COVID-19, but they do not prevent infection with the virus,” reported Giovanni Damiani, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Milan.
This apparent protective effect of biologic agents against severe and even fatal COVID-19 is all the more impressive because the psoriasis patients included in the Italian study – as is true of those elsewhere throughout the world – had relatively high rates of obesity, smoking, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, known risk factors for severe COVID-19, he added.
He presented a case-control study including 1,193 adult psoriasis patients on biologics or apremilast (Otezla) at Milan’s San Donato Hospital during the period from Feb. 21 to April 9, 2020. The control group comprised more than 10 million individuals, the entire adult population of the Lombardy region, of which Milan is the capital. This was the hardest-hit area in all of Italy during the first wave of COVID-19.
Twenty-two of the 1,193 psoriasis patients experienced confirmed COVID-19 during the study period. Seventeen were quarantined at home because their disease was mild. Five were hospitalized. But no psoriasis patients were placed in intensive care, and none died.
Psoriasis patients on biologics were significantly more likely than the general Lombardian population to test positive for COVID-19, with an unadjusted odds ratio of 3.43. They were at 9.05-fold increased risk of home quarantine for mild disease, and at 3.59-fold greater risk than controls for hospitalization for COVID-19. However, they were not at significantly increased risk of ICU admission. And while they actually had a 59% relative risk reduction for death, this didn’t achieve statistical significance.
Forty-five percent of the psoriasis patients were on an interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor, 22% were on a tumor necrosis factor–alpha inhibitor, and 20% were taking an IL-12/23 inhibitor. Of note, none of 77 patients on apremilast developed COVID-19, even though it is widely considered a less potent psoriasis therapy than the injectable monoclonal antibody biologics.
The French experience
Anne-Claire Fougerousse, MD, and her French coinvestigators conducted a study designed to address a different question: Is it safe to start psoriasis patients on biologics or older conventional systemic agents such as methotrexate during the pandemic?
She presented a French national cross-sectional study of 1,418 adult psoriasis patients on a biologic or standard systemic therapy during a snapshot in time near the peak of the first wave of the pandemic in France: the period from April 27 to May 7, 2020. The group included 1,188 psoriasis patients on maintenance therapy and 230 who had initiated systemic treatment within the past 4 months. More than one-third of the patients had at least one risk factor for severe COVID-19.
Although testing wasn’t available to confirm all cases, 54 patients developed probable COVID-19 during the study period. Only five required hospitalization. None died. The two hospitalized psoriasis patients admitted to an ICU had obesity as a risk factor for severe COVID-19, as did another of the five hospitalized patients, reported Dr. Fougerousse, a dermatologist at the Bégin Military Teaching Hospital in Saint-Mandé, France. Hospitalization for COVID-19 was required in 0.43% of the French treatment initiators, not significantly different from the 0.34% rate in patients on maintenance systemic therapy. A study limitation was the lack of a control group.
Nonetheless, the data did answer the investigators’ main question: “This is the first data showing no increased incidence of severe COVID-19 in psoriasis patients receiving systemic therapy in the treatment initiation period compared to those on maintenance therapy. This may now allow physicians to initiate conventional systemic or biologic therapy in patients with severe psoriasis on a case-by-case basis in the context of the persistent COVID-19 pandemic,” Dr. Fougerousse concluded.
Proposed mechanism of benefit
The Italian study findings that biologics boost the risk of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus in psoriasis patients while potentially protecting them against ICU admission and death are backed by a biologically plausible albeit as yet unproven mechanism of action, Dr. Damiani asserted.
He elaborated: A vast body of high-quality clinical trials data demonstrates that these targeted immunosuppressive agents are associated with modestly increased risk of viral infections, including both skin and respiratory tract infections. So there is no reason to suppose these agents would offer protection against the first phase of COVID-19, involving SARS-CoV-2 infection, nor protect against the second (pulmonary phase), whose hallmarks are dyspnea with or without hypoxia. But progression to the third phase, involving hyperinflammation and hypercoagulation – dubbed the cytokine storm – could be a different matter.
“Of particular interest was that our patients on IL-17 inhibitors displayed a really great outcome. Interleukin-17 has procoagulant and prothrombotic effects, organizes bronchoalveolar remodeling, has a profibrotic effect, induces mitochondrial dysfunction, and encourages dendritic cell migration in peribronchial lymph nodes. Therefore, by antagonizing this interleukin, we may have a better prognosis, although further studies are needed to be certain,” Dr. Damiani commented.
Publication of his preliminary findings drew the attention of a group of highly respected thought leaders in psoriasis, including James G. Krueger, MD, head of the laboratory for investigative dermatology and codirector of the center for clinical and investigative science at Rockefeller University, New York.
The Italian report prompted them to analyze data from the phase 4, double-blind, randomized ObePso-S study investigating the effects of the IL-17 inhibitor secukinumab (Cosentyx) on systemic inflammatory markers and gene expression in psoriasis patients. The investigators demonstrated that IL-17–mediated inflammation in psoriasis patients was associated with increased expression of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in lesional skin, and that treatment with secukinumab dropped ACE2 expression to levels seen in nonlesional skin. Given that ACE2 is the chief portal of entry for SARS-CoV-2 and that IL-17 exerts systemic proinflammatory effects, it’s plausible that inhibition of IL-17–mediated inflammation via dampening of ACE2 expression in noncutaneous epithelia “could prove to be advantageous in patients with psoriasis who are at risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” according to Dr. Krueger and his coinvestigators in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Dr. Damiani and Dr. Fougerousse reported having no financial conflicts regarding their studies. The secukinumab/ACE2 receptor study was funded by Novartis.
presented at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“Biologics seem to be very protective against severe, poor-prognosis COVID-19, but they do not prevent infection with the virus,” reported Giovanni Damiani, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Milan.
This apparent protective effect of biologic agents against severe and even fatal COVID-19 is all the more impressive because the psoriasis patients included in the Italian study – as is true of those elsewhere throughout the world – had relatively high rates of obesity, smoking, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, known risk factors for severe COVID-19, he added.
He presented a case-control study including 1,193 adult psoriasis patients on biologics or apremilast (Otezla) at Milan’s San Donato Hospital during the period from Feb. 21 to April 9, 2020. The control group comprised more than 10 million individuals, the entire adult population of the Lombardy region, of which Milan is the capital. This was the hardest-hit area in all of Italy during the first wave of COVID-19.
Twenty-two of the 1,193 psoriasis patients experienced confirmed COVID-19 during the study period. Seventeen were quarantined at home because their disease was mild. Five were hospitalized. But no psoriasis patients were placed in intensive care, and none died.
Psoriasis patients on biologics were significantly more likely than the general Lombardian population to test positive for COVID-19, with an unadjusted odds ratio of 3.43. They were at 9.05-fold increased risk of home quarantine for mild disease, and at 3.59-fold greater risk than controls for hospitalization for COVID-19. However, they were not at significantly increased risk of ICU admission. And while they actually had a 59% relative risk reduction for death, this didn’t achieve statistical significance.
Forty-five percent of the psoriasis patients were on an interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor, 22% were on a tumor necrosis factor–alpha inhibitor, and 20% were taking an IL-12/23 inhibitor. Of note, none of 77 patients on apremilast developed COVID-19, even though it is widely considered a less potent psoriasis therapy than the injectable monoclonal antibody biologics.
The French experience
Anne-Claire Fougerousse, MD, and her French coinvestigators conducted a study designed to address a different question: Is it safe to start psoriasis patients on biologics or older conventional systemic agents such as methotrexate during the pandemic?
She presented a French national cross-sectional study of 1,418 adult psoriasis patients on a biologic or standard systemic therapy during a snapshot in time near the peak of the first wave of the pandemic in France: the period from April 27 to May 7, 2020. The group included 1,188 psoriasis patients on maintenance therapy and 230 who had initiated systemic treatment within the past 4 months. More than one-third of the patients had at least one risk factor for severe COVID-19.
Although testing wasn’t available to confirm all cases, 54 patients developed probable COVID-19 during the study period. Only five required hospitalization. None died. The two hospitalized psoriasis patients admitted to an ICU had obesity as a risk factor for severe COVID-19, as did another of the five hospitalized patients, reported Dr. Fougerousse, a dermatologist at the Bégin Military Teaching Hospital in Saint-Mandé, France. Hospitalization for COVID-19 was required in 0.43% of the French treatment initiators, not significantly different from the 0.34% rate in patients on maintenance systemic therapy. A study limitation was the lack of a control group.
Nonetheless, the data did answer the investigators’ main question: “This is the first data showing no increased incidence of severe COVID-19 in psoriasis patients receiving systemic therapy in the treatment initiation period compared to those on maintenance therapy. This may now allow physicians to initiate conventional systemic or biologic therapy in patients with severe psoriasis on a case-by-case basis in the context of the persistent COVID-19 pandemic,” Dr. Fougerousse concluded.
Proposed mechanism of benefit
The Italian study findings that biologics boost the risk of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus in psoriasis patients while potentially protecting them against ICU admission and death are backed by a biologically plausible albeit as yet unproven mechanism of action, Dr. Damiani asserted.
He elaborated: A vast body of high-quality clinical trials data demonstrates that these targeted immunosuppressive agents are associated with modestly increased risk of viral infections, including both skin and respiratory tract infections. So there is no reason to suppose these agents would offer protection against the first phase of COVID-19, involving SARS-CoV-2 infection, nor protect against the second (pulmonary phase), whose hallmarks are dyspnea with or without hypoxia. But progression to the third phase, involving hyperinflammation and hypercoagulation – dubbed the cytokine storm – could be a different matter.
“Of particular interest was that our patients on IL-17 inhibitors displayed a really great outcome. Interleukin-17 has procoagulant and prothrombotic effects, organizes bronchoalveolar remodeling, has a profibrotic effect, induces mitochondrial dysfunction, and encourages dendritic cell migration in peribronchial lymph nodes. Therefore, by antagonizing this interleukin, we may have a better prognosis, although further studies are needed to be certain,” Dr. Damiani commented.
Publication of his preliminary findings drew the attention of a group of highly respected thought leaders in psoriasis, including James G. Krueger, MD, head of the laboratory for investigative dermatology and codirector of the center for clinical and investigative science at Rockefeller University, New York.
The Italian report prompted them to analyze data from the phase 4, double-blind, randomized ObePso-S study investigating the effects of the IL-17 inhibitor secukinumab (Cosentyx) on systemic inflammatory markers and gene expression in psoriasis patients. The investigators demonstrated that IL-17–mediated inflammation in psoriasis patients was associated with increased expression of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in lesional skin, and that treatment with secukinumab dropped ACE2 expression to levels seen in nonlesional skin. Given that ACE2 is the chief portal of entry for SARS-CoV-2 and that IL-17 exerts systemic proinflammatory effects, it’s plausible that inhibition of IL-17–mediated inflammation via dampening of ACE2 expression in noncutaneous epithelia “could prove to be advantageous in patients with psoriasis who are at risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” according to Dr. Krueger and his coinvestigators in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Dr. Damiani and Dr. Fougerousse reported having no financial conflicts regarding their studies. The secukinumab/ACE2 receptor study was funded by Novartis.
presented at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
“Biologics seem to be very protective against severe, poor-prognosis COVID-19, but they do not prevent infection with the virus,” reported Giovanni Damiani, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Milan.
This apparent protective effect of biologic agents against severe and even fatal COVID-19 is all the more impressive because the psoriasis patients included in the Italian study – as is true of those elsewhere throughout the world – had relatively high rates of obesity, smoking, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, known risk factors for severe COVID-19, he added.
He presented a case-control study including 1,193 adult psoriasis patients on biologics or apremilast (Otezla) at Milan’s San Donato Hospital during the period from Feb. 21 to April 9, 2020. The control group comprised more than 10 million individuals, the entire adult population of the Lombardy region, of which Milan is the capital. This was the hardest-hit area in all of Italy during the first wave of COVID-19.
Twenty-two of the 1,193 psoriasis patients experienced confirmed COVID-19 during the study period. Seventeen were quarantined at home because their disease was mild. Five were hospitalized. But no psoriasis patients were placed in intensive care, and none died.
Psoriasis patients on biologics were significantly more likely than the general Lombardian population to test positive for COVID-19, with an unadjusted odds ratio of 3.43. They were at 9.05-fold increased risk of home quarantine for mild disease, and at 3.59-fold greater risk than controls for hospitalization for COVID-19. However, they were not at significantly increased risk of ICU admission. And while they actually had a 59% relative risk reduction for death, this didn’t achieve statistical significance.
Forty-five percent of the psoriasis patients were on an interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitor, 22% were on a tumor necrosis factor–alpha inhibitor, and 20% were taking an IL-12/23 inhibitor. Of note, none of 77 patients on apremilast developed COVID-19, even though it is widely considered a less potent psoriasis therapy than the injectable monoclonal antibody biologics.
The French experience
Anne-Claire Fougerousse, MD, and her French coinvestigators conducted a study designed to address a different question: Is it safe to start psoriasis patients on biologics or older conventional systemic agents such as methotrexate during the pandemic?
She presented a French national cross-sectional study of 1,418 adult psoriasis patients on a biologic or standard systemic therapy during a snapshot in time near the peak of the first wave of the pandemic in France: the period from April 27 to May 7, 2020. The group included 1,188 psoriasis patients on maintenance therapy and 230 who had initiated systemic treatment within the past 4 months. More than one-third of the patients had at least one risk factor for severe COVID-19.
Although testing wasn’t available to confirm all cases, 54 patients developed probable COVID-19 during the study period. Only five required hospitalization. None died. The two hospitalized psoriasis patients admitted to an ICU had obesity as a risk factor for severe COVID-19, as did another of the five hospitalized patients, reported Dr. Fougerousse, a dermatologist at the Bégin Military Teaching Hospital in Saint-Mandé, France. Hospitalization for COVID-19 was required in 0.43% of the French treatment initiators, not significantly different from the 0.34% rate in patients on maintenance systemic therapy. A study limitation was the lack of a control group.
Nonetheless, the data did answer the investigators’ main question: “This is the first data showing no increased incidence of severe COVID-19 in psoriasis patients receiving systemic therapy in the treatment initiation period compared to those on maintenance therapy. This may now allow physicians to initiate conventional systemic or biologic therapy in patients with severe psoriasis on a case-by-case basis in the context of the persistent COVID-19 pandemic,” Dr. Fougerousse concluded.
Proposed mechanism of benefit
The Italian study findings that biologics boost the risk of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus in psoriasis patients while potentially protecting them against ICU admission and death are backed by a biologically plausible albeit as yet unproven mechanism of action, Dr. Damiani asserted.
He elaborated: A vast body of high-quality clinical trials data demonstrates that these targeted immunosuppressive agents are associated with modestly increased risk of viral infections, including both skin and respiratory tract infections. So there is no reason to suppose these agents would offer protection against the first phase of COVID-19, involving SARS-CoV-2 infection, nor protect against the second (pulmonary phase), whose hallmarks are dyspnea with or without hypoxia. But progression to the third phase, involving hyperinflammation and hypercoagulation – dubbed the cytokine storm – could be a different matter.
“Of particular interest was that our patients on IL-17 inhibitors displayed a really great outcome. Interleukin-17 has procoagulant and prothrombotic effects, organizes bronchoalveolar remodeling, has a profibrotic effect, induces mitochondrial dysfunction, and encourages dendritic cell migration in peribronchial lymph nodes. Therefore, by antagonizing this interleukin, we may have a better prognosis, although further studies are needed to be certain,” Dr. Damiani commented.
Publication of his preliminary findings drew the attention of a group of highly respected thought leaders in psoriasis, including James G. Krueger, MD, head of the laboratory for investigative dermatology and codirector of the center for clinical and investigative science at Rockefeller University, New York.
The Italian report prompted them to analyze data from the phase 4, double-blind, randomized ObePso-S study investigating the effects of the IL-17 inhibitor secukinumab (Cosentyx) on systemic inflammatory markers and gene expression in psoriasis patients. The investigators demonstrated that IL-17–mediated inflammation in psoriasis patients was associated with increased expression of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in lesional skin, and that treatment with secukinumab dropped ACE2 expression to levels seen in nonlesional skin. Given that ACE2 is the chief portal of entry for SARS-CoV-2 and that IL-17 exerts systemic proinflammatory effects, it’s plausible that inhibition of IL-17–mediated inflammation via dampening of ACE2 expression in noncutaneous epithelia “could prove to be advantageous in patients with psoriasis who are at risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” according to Dr. Krueger and his coinvestigators in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Dr. Damiani and Dr. Fougerousse reported having no financial conflicts regarding their studies. The secukinumab/ACE2 receptor study was funded by Novartis.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Updated heart failure measures add newer meds
Safety measures for lab monitoring of mineralocorticoid receptor agonist therapy, performance measures for sacubitril/valsartan, cardiac resynchronization therapy and titration of medications, and quality measures based on patient-reported outcomes are among the updates the joint task force of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have made to performance and quality measures for managing adults with heart failure.
The revisions, published online Nov. 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, update the 2011 ACC/AHA heart failure measure set, writing committee vice chair Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, said in an interview. The 2011 measure set predates the 2015 approval of the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure in adults.
Measures stress dosages, strength of evidence
“For the first time the heart failure performance measure sets also focus on not just the use of guideline-recommended medication at any dose, but on utilizing the doses that are evidence-based and guideline recommended so long as they are well tolerated,” said Dr. Fonarow, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. “The measure set now includes assessment of patients being treated with doses of medications at 50% or greater of target dose in the absence of contraindications or documented intolerance.”
The update includes seven new performance measures, two quality measures, and one structural measure. The performance measures come from the strongest recommendations – that is, a class of recommendation of 1 (strong) or 3 (no benefit or harmful, process to be avoided) – in the 2017 ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of American heart failure guideline update published in Circulation.
In addition to the 2017 update, the writing committee also reviewed existing performance measures. “Those management strategies, diagnostic testing, medications, and devices with the strongest evidence and highest level of guideline recommendations were further considered for inclusion in the performance measure set,” Dr. Fonarow said. “The measures went through extensive review by peer reviewers and approval from the organizations represented.”
Specifically, the update includes measures for monitoring serum potassium after starting mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists therapy, and cardiac resynchronization therapy for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction already on guideline-directed therapy. “This therapy can significantly improve functional capacity and outcomes in appropriately selected patients,” Dr. Fonarow said.
New and retired measures
The update adds two performance measures for titration of medications based on dose, either reaching 50% of the recommended dose for a variety of medications, including ARNI, or documenting that the dose wasn’t tolerated for other reason for not using the dose.
The new structural measure calls for facility participation in a heart failure registry. The revised measure set now consists of 18 measures in all.
The update retired one measure from the 2011 set: left ventricular ejection fraction assessment for inpatients. The committee cited its use above 97% as the reason, but LVEF in outpatients remains a measure.
The following tree measures have been revised:
- Patient self-care education has moved from performance measure to quality measure because of concerns about the accuracy of self-care education documentation and limited evidence of improved outcomes with better documentation.
- ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy for left ventricular systolic dysfunction adds ARNI therapy to align with the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA update.
- Postdischarge appointments shifts from performance to quality measure and include a 7-day limit.
Measures future research should focus on, noted Dr. Fonarow, include the use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for heart failure, including in patients without diabetes. “Since the ACC/AHA heart failure guidelines had not yet been updated to recommend these therapies they could not be included in this performance measure set,” he said.
He also said “an urgent need” exists for further research into treatments for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction along with optimal implementation strategies.
“If these ACC/AHA heart failure performance measures were applied in all settings in which patients with heart failure in the United States are being cared for, and optimal and equitable conformity with each of these measures were achieved, over 100,000 lives a year of patients with heart failure could be saved,” he said. “There’s in an urgent need to measure and improve heart failure care quality.”
Dr. Fonarow reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
SOURCE: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Nov 2;76:2527-64.
Safety measures for lab monitoring of mineralocorticoid receptor agonist therapy, performance measures for sacubitril/valsartan, cardiac resynchronization therapy and titration of medications, and quality measures based on patient-reported outcomes are among the updates the joint task force of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have made to performance and quality measures for managing adults with heart failure.
The revisions, published online Nov. 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, update the 2011 ACC/AHA heart failure measure set, writing committee vice chair Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, said in an interview. The 2011 measure set predates the 2015 approval of the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure in adults.
Measures stress dosages, strength of evidence
“For the first time the heart failure performance measure sets also focus on not just the use of guideline-recommended medication at any dose, but on utilizing the doses that are evidence-based and guideline recommended so long as they are well tolerated,” said Dr. Fonarow, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. “The measure set now includes assessment of patients being treated with doses of medications at 50% or greater of target dose in the absence of contraindications or documented intolerance.”
The update includes seven new performance measures, two quality measures, and one structural measure. The performance measures come from the strongest recommendations – that is, a class of recommendation of 1 (strong) or 3 (no benefit or harmful, process to be avoided) – in the 2017 ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of American heart failure guideline update published in Circulation.
In addition to the 2017 update, the writing committee also reviewed existing performance measures. “Those management strategies, diagnostic testing, medications, and devices with the strongest evidence and highest level of guideline recommendations were further considered for inclusion in the performance measure set,” Dr. Fonarow said. “The measures went through extensive review by peer reviewers and approval from the organizations represented.”
Specifically, the update includes measures for monitoring serum potassium after starting mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists therapy, and cardiac resynchronization therapy for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction already on guideline-directed therapy. “This therapy can significantly improve functional capacity and outcomes in appropriately selected patients,” Dr. Fonarow said.
New and retired measures
The update adds two performance measures for titration of medications based on dose, either reaching 50% of the recommended dose for a variety of medications, including ARNI, or documenting that the dose wasn’t tolerated for other reason for not using the dose.
The new structural measure calls for facility participation in a heart failure registry. The revised measure set now consists of 18 measures in all.
The update retired one measure from the 2011 set: left ventricular ejection fraction assessment for inpatients. The committee cited its use above 97% as the reason, but LVEF in outpatients remains a measure.
The following tree measures have been revised:
- Patient self-care education has moved from performance measure to quality measure because of concerns about the accuracy of self-care education documentation and limited evidence of improved outcomes with better documentation.
- ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy for left ventricular systolic dysfunction adds ARNI therapy to align with the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA update.
- Postdischarge appointments shifts from performance to quality measure and include a 7-day limit.
Measures future research should focus on, noted Dr. Fonarow, include the use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for heart failure, including in patients without diabetes. “Since the ACC/AHA heart failure guidelines had not yet been updated to recommend these therapies they could not be included in this performance measure set,” he said.
He also said “an urgent need” exists for further research into treatments for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction along with optimal implementation strategies.
“If these ACC/AHA heart failure performance measures were applied in all settings in which patients with heart failure in the United States are being cared for, and optimal and equitable conformity with each of these measures were achieved, over 100,000 lives a year of patients with heart failure could be saved,” he said. “There’s in an urgent need to measure and improve heart failure care quality.”
Dr. Fonarow reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
SOURCE: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Nov 2;76:2527-64.
Safety measures for lab monitoring of mineralocorticoid receptor agonist therapy, performance measures for sacubitril/valsartan, cardiac resynchronization therapy and titration of medications, and quality measures based on patient-reported outcomes are among the updates the joint task force of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have made to performance and quality measures for managing adults with heart failure.
The revisions, published online Nov. 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, update the 2011 ACC/AHA heart failure measure set, writing committee vice chair Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, said in an interview. The 2011 measure set predates the 2015 approval of the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure in adults.
Measures stress dosages, strength of evidence
“For the first time the heart failure performance measure sets also focus on not just the use of guideline-recommended medication at any dose, but on utilizing the doses that are evidence-based and guideline recommended so long as they are well tolerated,” said Dr. Fonarow, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. “The measure set now includes assessment of patients being treated with doses of medications at 50% or greater of target dose in the absence of contraindications or documented intolerance.”
The update includes seven new performance measures, two quality measures, and one structural measure. The performance measures come from the strongest recommendations – that is, a class of recommendation of 1 (strong) or 3 (no benefit or harmful, process to be avoided) – in the 2017 ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of American heart failure guideline update published in Circulation.
In addition to the 2017 update, the writing committee also reviewed existing performance measures. “Those management strategies, diagnostic testing, medications, and devices with the strongest evidence and highest level of guideline recommendations were further considered for inclusion in the performance measure set,” Dr. Fonarow said. “The measures went through extensive review by peer reviewers and approval from the organizations represented.”
Specifically, the update includes measures for monitoring serum potassium after starting mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists therapy, and cardiac resynchronization therapy for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction already on guideline-directed therapy. “This therapy can significantly improve functional capacity and outcomes in appropriately selected patients,” Dr. Fonarow said.
New and retired measures
The update adds two performance measures for titration of medications based on dose, either reaching 50% of the recommended dose for a variety of medications, including ARNI, or documenting that the dose wasn’t tolerated for other reason for not using the dose.
The new structural measure calls for facility participation in a heart failure registry. The revised measure set now consists of 18 measures in all.
The update retired one measure from the 2011 set: left ventricular ejection fraction assessment for inpatients. The committee cited its use above 97% as the reason, but LVEF in outpatients remains a measure.
The following tree measures have been revised:
- Patient self-care education has moved from performance measure to quality measure because of concerns about the accuracy of self-care education documentation and limited evidence of improved outcomes with better documentation.
- ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy for left ventricular systolic dysfunction adds ARNI therapy to align with the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA update.
- Postdischarge appointments shifts from performance to quality measure and include a 7-day limit.
Measures future research should focus on, noted Dr. Fonarow, include the use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for heart failure, including in patients without diabetes. “Since the ACC/AHA heart failure guidelines had not yet been updated to recommend these therapies they could not be included in this performance measure set,” he said.
He also said “an urgent need” exists for further research into treatments for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction along with optimal implementation strategies.
“If these ACC/AHA heart failure performance measures were applied in all settings in which patients with heart failure in the United States are being cared for, and optimal and equitable conformity with each of these measures were achieved, over 100,000 lives a year of patients with heart failure could be saved,” he said. “There’s in an urgent need to measure and improve heart failure care quality.”
Dr. Fonarow reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
SOURCE: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Nov 2;76:2527-64.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Health sector has spent $464 million on lobbying in 2020
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.
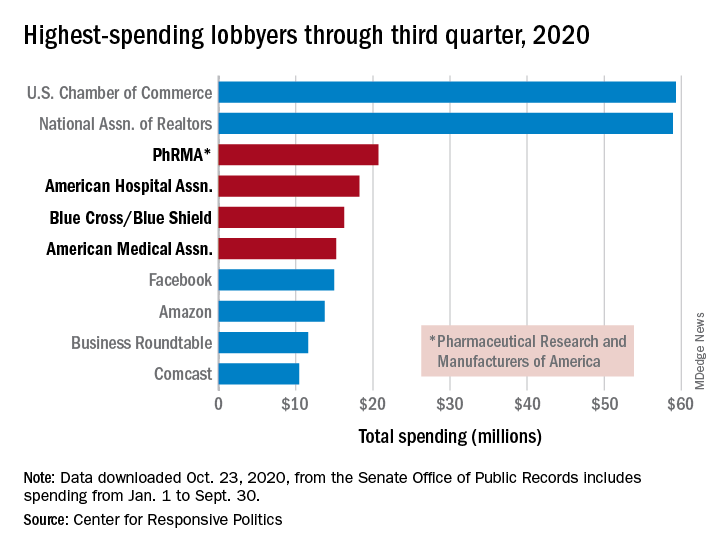
PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.

PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
, according to the Center for Responsive Politics.

PhRMA spent $20.7 million on lobbying through the end of September, good enough for third on the overall list of U.S. companies and organizations. Three other members of the health sector made the top 10: the American Hospital Association ($18.3 million), BlueCross/BlueShield ($16.3 million), and the American Medical Association ($15.2 million), the center reported.
Total spending by the health sector was $464 million from Jan. 1 to Sept. 30, topping the finance/insurance/real estate sector at $403 million, and miscellaneous business at $371 million. Miscellaneous business is the home of the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the annual leader in such spending for the last 20 years, based on data from the Senate Office of Public Records.
The largest share of health sector spending came from pharmaceuticals/health products, with a total of almost $233 million, just slightly more than the sector’s four other constituents combined: hospitals/nursing homes ($80 million), health services/HMOs ($75 million), health professionals ($67 million), and miscellaneous health ($9.5 million), the center said on OpenSecrets.org.
Taking one step down from the sector level, that $233 million made pharmaceuticals/health products the highest spending of about 100 industries in 2020, nearly doubling the efforts of electronics manufacturing and equipment ($118 million), which came a distant second. Hospitals/nursing homes was eighth on the industry list, the center noted.
Med student’s cardiac crisis a COVID-era medical mystery
Within minutes of her arrival at Community North Hospital in Indianapolis, Ramya Yeleti’s vital signs plummeted; her pulse was at 45 beats per minute and her ejection fraction was hovering near 10%. “I definitely thought there was a chance I would close my eyes and never open them again, but I only had a few seconds to process that,” she recalled. Then everything went black. Ramya fell unconscious as shock pads were positioned and a swarm of clinicians prepared to insert an Impella heart pump through a catheter into her aorta.
The third-year medical student and aspiring psychiatrist had been doing in-person neurology rotations in July when she began to experience fever and uncontrolled vomiting. Her initial thought was that she must have caught the flu from a patient.
After all, Ramya, along with her father Ram Yeleti, MD, mother Indira, and twin sister Divya, had all weathered COVID-19 in previous months and later tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The only family member who had been spared was her younger brother Rohith.
Indira suffered a severe case, requiring ICU care for 2 days but no ventilator; the others experienced mostly mild symptoms. Ramya — who was studying for her third-year board exams after classes at Marian University College of Osteopathic Medicine in Indianapolis went virtual in March — was left with lingering fatigue; however, her cough and muscle aches abated and her sense of taste and smell returned. When she started rotations, she thought her life was getting back to normal.
Ramya’s flu symptoms did not improve. A university-mandated rapid COVID test came back negative, but 2 more days of vomiting started to worry both her and her father, who is a cardiologist and chief physician executive at Community Health Network in Indianapolis. After Ramya felt some chest pain, she asked her father to listen to her heart. All sounded normal, and Ram prescribed ondansetron for her nausea.
But the antiemetic didn’t work, and by the next morning both father and daughter were convinced that they needed to head to the emergency department.
“I wanted to double-check if I was missing something about her being dehydrated,” Ram told Medscape Medical News. “Several things can cause protracted nausea, like hepatitis, appendicitis, or another infection. I feel terribly guilty I didn’t realize she had a heart condition.”
A surprising turn for the worst
Ramya’s subtle symptoms quickly gave way to the dramatic cardiac crisis that unfolded just after her arrival at Community North. “Her EKG looked absolutely horrendous, like a 75-year-old having a heart attack,” Ram said.
As a cardiologist, he knew his daughter’s situation was growing dire when he heard physicians shouting that the Impella wasn’t working and she needed extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
“At that point, I didn’t think she’d survive,” her father recalled. “We had 10 physicians in the room who worked on her for 5 hours to get her stabilized.”
“It was especially traumatic because, obviously, I knew exactly what was happening,” he added. “You can’t sugarcoat anything.”
After being connected to the heart–lung equipment, Ramya was transferred to IU Health Methodist Hospital, also in Indianapolis, where she was tested again for COVID-19. Unlike the rapid test administered just days earlier, the PCR assay came back positive.
“I knew she had acute myocarditis, but coronavirus never crossed my mind,” said Ram.
“As we were dealing with her heart, we were also dealing with this challenge: she was coming back positive for COVID-19 again,” said Roopa Rao, MD, the heart failure transplant cardiologist at IU Health who treated Ramya.
“We weren’t sure whether we were dealing with an active infection or dead virus” from her previous infection, Rao said, “so we started treating her like she had active COVID-19 and gave her remdesivir, convalescent plasma, and steroids, which was the protocol in our hospital.”
A biopsy of Ramya’s heart tissue, along with blood tests, indicated a past parvovirus infection. It’s possible that Ramya’s previous coronavirus infection made her susceptible to heart damage from a newer parvovirus infection, said Rao. Either virus, or both together, could have been responsible for the calamity.
Although it was unheard of during Ramya’s cardiac crisis in early August, evolving evidence now raises the possibility that she is one of a handful of people in the world to be reinfected with SARS-CoV-2. Also emerging are cases of COVID-related myocarditis and other extreme heart complications, particularly in young people.
“At the time, it wasn’t really clear if people could have another infection so quickly,” Rao told Medscape Medical News. “It is possible she is one of these rare individuals to have COVID-19 twice. I’m hoping at some point we will have some clarity.”
“I would favor a coinfection as probably the triggering factor for her sickness,” she said. “It may take some time, but like any other disease — and it doesn’t look like COVID will go away magically — I hope we’ll have some answers down the road.”
Another wrinkle
The next 48 hours brought astonishing news: Ramya’s heart function had rebounded to nearly normal, and her ejection fraction increased to about 45%. Heart transplantation wouldn’t be necessary, although Rao stood poised to follow through if ECMO only sustained, rather than improved, Ramya’s prognosis.
“Ramya was so sick that if she didn’t recover, the only option would be a heart transplant,” said Rao. “But we wanted to do everything to keep that heart.”
After steroid and COVID treatment, Ramya’s heart started to come back. “It didn’t make sense to me,” said Rao. “I don’t know what helped. If we hadn’t done ECMO, her heart probably wouldn’t have recovered, so I would say we have to support these patients and give them time for the heart to recover, even to the point of ECMO.”
Despite the good news, Ramya’s survival still hung in the balance. When she was disconnected from ECMO, clinicians discovered that the Impella device had caused a rare complication, damaging her mitral valve. The valve could be repaired surgically, but both Rao and Ram felt great trepidation at the prospect of cardiopulmonary bypass during the open-heart procedure.
“They would need to stop her heart and restart it, and I was concerned it would not restart,” Ram explained. “I didn’t like the idea of open-heart surgery, but my biggest fear was she was not going to survive it because of a really fresh, sick heart.”
The cardiologists’ fears did, in fact, come to pass: it took an hour to coax Ramya’s heart back at the end of surgery. But, just as the surgeon was preparing to reconnect Ramya to ECMO in desperation, “her heart recovered again,” Rao reported.
“Some things you never forget in life,” she said. “I can’t describe how everyone in the OR felt, all taking care of her. I told Ramya, ‘you are a fighter’.”
New strength
Six days would pass before Ramya woke up and learned of the astounding series of events that saved her. She knew “something was really wrong” because of the incision at the center of her chest, but learning she’d been on ECMO and the heart transplant list drove home how close to death she’d actually come.
“Most people don’t get off ECMO; they die on it,” she said. “And the chances of dying on the heart transplant list are very high. It was very strange to me that this was my story all of a sudden, when a week and a half earlier I was on rotation.”
Ongoing physical therapy over the past 3 months has transformed Ramya from a state of profound physical weakness to a place of relative strength. The now-fourth-year med student is turning 26 in November and is hungry to restart in-person rotations. Her downtime has been filled in part with researching myocarditis and collaborating with Rao on her own case study for journal publication.
But the mental trauma from her experience has girded her in ways she knows will make her stronger personally and professionally in the years ahead.
“It’s still very hard. I’m still recovering,” she acknowledged. “I described it to my therapist as an invisible wound on my brain.”
“When I came out of the hospital, I still had ECMO wounds, deep gashes on my legs that affected how fast and how long I could walk,” she said. “I felt like the same thing was going on my brain — a huge cut no one could see.”
Her intention to specialize in psychiatry has become more pressing now that Ramya has realized the impact of trauma on mental health.
“My body failing me was awful, but I could handle it,” she said. “Losing any part of my mind would have been way worse. I want to take care of that in my patients.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Within minutes of her arrival at Community North Hospital in Indianapolis, Ramya Yeleti’s vital signs plummeted; her pulse was at 45 beats per minute and her ejection fraction was hovering near 10%. “I definitely thought there was a chance I would close my eyes and never open them again, but I only had a few seconds to process that,” she recalled. Then everything went black. Ramya fell unconscious as shock pads were positioned and a swarm of clinicians prepared to insert an Impella heart pump through a catheter into her aorta.
The third-year medical student and aspiring psychiatrist had been doing in-person neurology rotations in July when she began to experience fever and uncontrolled vomiting. Her initial thought was that she must have caught the flu from a patient.
After all, Ramya, along with her father Ram Yeleti, MD, mother Indira, and twin sister Divya, had all weathered COVID-19 in previous months and later tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The only family member who had been spared was her younger brother Rohith.
Indira suffered a severe case, requiring ICU care for 2 days but no ventilator; the others experienced mostly mild symptoms. Ramya — who was studying for her third-year board exams after classes at Marian University College of Osteopathic Medicine in Indianapolis went virtual in March — was left with lingering fatigue; however, her cough and muscle aches abated and her sense of taste and smell returned. When she started rotations, she thought her life was getting back to normal.
Ramya’s flu symptoms did not improve. A university-mandated rapid COVID test came back negative, but 2 more days of vomiting started to worry both her and her father, who is a cardiologist and chief physician executive at Community Health Network in Indianapolis. After Ramya felt some chest pain, she asked her father to listen to her heart. All sounded normal, and Ram prescribed ondansetron for her nausea.
But the antiemetic didn’t work, and by the next morning both father and daughter were convinced that they needed to head to the emergency department.
“I wanted to double-check if I was missing something about her being dehydrated,” Ram told Medscape Medical News. “Several things can cause protracted nausea, like hepatitis, appendicitis, or another infection. I feel terribly guilty I didn’t realize she had a heart condition.”
A surprising turn for the worst
Ramya’s subtle symptoms quickly gave way to the dramatic cardiac crisis that unfolded just after her arrival at Community North. “Her EKG looked absolutely horrendous, like a 75-year-old having a heart attack,” Ram said.
As a cardiologist, he knew his daughter’s situation was growing dire when he heard physicians shouting that the Impella wasn’t working and she needed extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
“At that point, I didn’t think she’d survive,” her father recalled. “We had 10 physicians in the room who worked on her for 5 hours to get her stabilized.”
“It was especially traumatic because, obviously, I knew exactly what was happening,” he added. “You can’t sugarcoat anything.”
After being connected to the heart–lung equipment, Ramya was transferred to IU Health Methodist Hospital, also in Indianapolis, where she was tested again for COVID-19. Unlike the rapid test administered just days earlier, the PCR assay came back positive.
“I knew she had acute myocarditis, but coronavirus never crossed my mind,” said Ram.
“As we were dealing with her heart, we were also dealing with this challenge: she was coming back positive for COVID-19 again,” said Roopa Rao, MD, the heart failure transplant cardiologist at IU Health who treated Ramya.
“We weren’t sure whether we were dealing with an active infection or dead virus” from her previous infection, Rao said, “so we started treating her like she had active COVID-19 and gave her remdesivir, convalescent plasma, and steroids, which was the protocol in our hospital.”
A biopsy of Ramya’s heart tissue, along with blood tests, indicated a past parvovirus infection. It’s possible that Ramya’s previous coronavirus infection made her susceptible to heart damage from a newer parvovirus infection, said Rao. Either virus, or both together, could have been responsible for the calamity.
Although it was unheard of during Ramya’s cardiac crisis in early August, evolving evidence now raises the possibility that she is one of a handful of people in the world to be reinfected with SARS-CoV-2. Also emerging are cases of COVID-related myocarditis and other extreme heart complications, particularly in young people.
“At the time, it wasn’t really clear if people could have another infection so quickly,” Rao told Medscape Medical News. “It is possible she is one of these rare individuals to have COVID-19 twice. I’m hoping at some point we will have some clarity.”
“I would favor a coinfection as probably the triggering factor for her sickness,” she said. “It may take some time, but like any other disease — and it doesn’t look like COVID will go away magically — I hope we’ll have some answers down the road.”
Another wrinkle
The next 48 hours brought astonishing news: Ramya’s heart function had rebounded to nearly normal, and her ejection fraction increased to about 45%. Heart transplantation wouldn’t be necessary, although Rao stood poised to follow through if ECMO only sustained, rather than improved, Ramya’s prognosis.
“Ramya was so sick that if she didn’t recover, the only option would be a heart transplant,” said Rao. “But we wanted to do everything to keep that heart.”
After steroid and COVID treatment, Ramya’s heart started to come back. “It didn’t make sense to me,” said Rao. “I don’t know what helped. If we hadn’t done ECMO, her heart probably wouldn’t have recovered, so I would say we have to support these patients and give them time for the heart to recover, even to the point of ECMO.”
Despite the good news, Ramya’s survival still hung in the balance. When she was disconnected from ECMO, clinicians discovered that the Impella device had caused a rare complication, damaging her mitral valve. The valve could be repaired surgically, but both Rao and Ram felt great trepidation at the prospect of cardiopulmonary bypass during the open-heart procedure.
“They would need to stop her heart and restart it, and I was concerned it would not restart,” Ram explained. “I didn’t like the idea of open-heart surgery, but my biggest fear was she was not going to survive it because of a really fresh, sick heart.”
The cardiologists’ fears did, in fact, come to pass: it took an hour to coax Ramya’s heart back at the end of surgery. But, just as the surgeon was preparing to reconnect Ramya to ECMO in desperation, “her heart recovered again,” Rao reported.
“Some things you never forget in life,” she said. “I can’t describe how everyone in the OR felt, all taking care of her. I told Ramya, ‘you are a fighter’.”
New strength
Six days would pass before Ramya woke up and learned of the astounding series of events that saved her. She knew “something was really wrong” because of the incision at the center of her chest, but learning she’d been on ECMO and the heart transplant list drove home how close to death she’d actually come.
“Most people don’t get off ECMO; they die on it,” she said. “And the chances of dying on the heart transplant list are very high. It was very strange to me that this was my story all of a sudden, when a week and a half earlier I was on rotation.”
Ongoing physical therapy over the past 3 months has transformed Ramya from a state of profound physical weakness to a place of relative strength. The now-fourth-year med student is turning 26 in November and is hungry to restart in-person rotations. Her downtime has been filled in part with researching myocarditis and collaborating with Rao on her own case study for journal publication.
But the mental trauma from her experience has girded her in ways she knows will make her stronger personally and professionally in the years ahead.
“It’s still very hard. I’m still recovering,” she acknowledged. “I described it to my therapist as an invisible wound on my brain.”
“When I came out of the hospital, I still had ECMO wounds, deep gashes on my legs that affected how fast and how long I could walk,” she said. “I felt like the same thing was going on my brain — a huge cut no one could see.”
Her intention to specialize in psychiatry has become more pressing now that Ramya has realized the impact of trauma on mental health.
“My body failing me was awful, but I could handle it,” she said. “Losing any part of my mind would have been way worse. I want to take care of that in my patients.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Within minutes of her arrival at Community North Hospital in Indianapolis, Ramya Yeleti’s vital signs plummeted; her pulse was at 45 beats per minute and her ejection fraction was hovering near 10%. “I definitely thought there was a chance I would close my eyes and never open them again, but I only had a few seconds to process that,” she recalled. Then everything went black. Ramya fell unconscious as shock pads were positioned and a swarm of clinicians prepared to insert an Impella heart pump through a catheter into her aorta.
The third-year medical student and aspiring psychiatrist had been doing in-person neurology rotations in July when she began to experience fever and uncontrolled vomiting. Her initial thought was that she must have caught the flu from a patient.
After all, Ramya, along with her father Ram Yeleti, MD, mother Indira, and twin sister Divya, had all weathered COVID-19 in previous months and later tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The only family member who had been spared was her younger brother Rohith.
Indira suffered a severe case, requiring ICU care for 2 days but no ventilator; the others experienced mostly mild symptoms. Ramya — who was studying for her third-year board exams after classes at Marian University College of Osteopathic Medicine in Indianapolis went virtual in March — was left with lingering fatigue; however, her cough and muscle aches abated and her sense of taste and smell returned. When she started rotations, she thought her life was getting back to normal.
Ramya’s flu symptoms did not improve. A university-mandated rapid COVID test came back negative, but 2 more days of vomiting started to worry both her and her father, who is a cardiologist and chief physician executive at Community Health Network in Indianapolis. After Ramya felt some chest pain, she asked her father to listen to her heart. All sounded normal, and Ram prescribed ondansetron for her nausea.
But the antiemetic didn’t work, and by the next morning both father and daughter were convinced that they needed to head to the emergency department.
“I wanted to double-check if I was missing something about her being dehydrated,” Ram told Medscape Medical News. “Several things can cause protracted nausea, like hepatitis, appendicitis, or another infection. I feel terribly guilty I didn’t realize she had a heart condition.”
A surprising turn for the worst
Ramya’s subtle symptoms quickly gave way to the dramatic cardiac crisis that unfolded just after her arrival at Community North. “Her EKG looked absolutely horrendous, like a 75-year-old having a heart attack,” Ram said.
As a cardiologist, he knew his daughter’s situation was growing dire when he heard physicians shouting that the Impella wasn’t working and she needed extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
“At that point, I didn’t think she’d survive,” her father recalled. “We had 10 physicians in the room who worked on her for 5 hours to get her stabilized.”
“It was especially traumatic because, obviously, I knew exactly what was happening,” he added. “You can’t sugarcoat anything.”
After being connected to the heart–lung equipment, Ramya was transferred to IU Health Methodist Hospital, also in Indianapolis, where she was tested again for COVID-19. Unlike the rapid test administered just days earlier, the PCR assay came back positive.
“I knew she had acute myocarditis, but coronavirus never crossed my mind,” said Ram.
“As we were dealing with her heart, we were also dealing with this challenge: she was coming back positive for COVID-19 again,” said Roopa Rao, MD, the heart failure transplant cardiologist at IU Health who treated Ramya.
“We weren’t sure whether we were dealing with an active infection or dead virus” from her previous infection, Rao said, “so we started treating her like she had active COVID-19 and gave her remdesivir, convalescent plasma, and steroids, which was the protocol in our hospital.”
A biopsy of Ramya’s heart tissue, along with blood tests, indicated a past parvovirus infection. It’s possible that Ramya’s previous coronavirus infection made her susceptible to heart damage from a newer parvovirus infection, said Rao. Either virus, or both together, could have been responsible for the calamity.
Although it was unheard of during Ramya’s cardiac crisis in early August, evolving evidence now raises the possibility that she is one of a handful of people in the world to be reinfected with SARS-CoV-2. Also emerging are cases of COVID-related myocarditis and other extreme heart complications, particularly in young people.
“At the time, it wasn’t really clear if people could have another infection so quickly,” Rao told Medscape Medical News. “It is possible she is one of these rare individuals to have COVID-19 twice. I’m hoping at some point we will have some clarity.”
“I would favor a coinfection as probably the triggering factor for her sickness,” she said. “It may take some time, but like any other disease — and it doesn’t look like COVID will go away magically — I hope we’ll have some answers down the road.”
Another wrinkle
The next 48 hours brought astonishing news: Ramya’s heart function had rebounded to nearly normal, and her ejection fraction increased to about 45%. Heart transplantation wouldn’t be necessary, although Rao stood poised to follow through if ECMO only sustained, rather than improved, Ramya’s prognosis.
“Ramya was so sick that if she didn’t recover, the only option would be a heart transplant,” said Rao. “But we wanted to do everything to keep that heart.”
After steroid and COVID treatment, Ramya’s heart started to come back. “It didn’t make sense to me,” said Rao. “I don’t know what helped. If we hadn’t done ECMO, her heart probably wouldn’t have recovered, so I would say we have to support these patients and give them time for the heart to recover, even to the point of ECMO.”
Despite the good news, Ramya’s survival still hung in the balance. When she was disconnected from ECMO, clinicians discovered that the Impella device had caused a rare complication, damaging her mitral valve. The valve could be repaired surgically, but both Rao and Ram felt great trepidation at the prospect of cardiopulmonary bypass during the open-heart procedure.
“They would need to stop her heart and restart it, and I was concerned it would not restart,” Ram explained. “I didn’t like the idea of open-heart surgery, but my biggest fear was she was not going to survive it because of a really fresh, sick heart.”
The cardiologists’ fears did, in fact, come to pass: it took an hour to coax Ramya’s heart back at the end of surgery. But, just as the surgeon was preparing to reconnect Ramya to ECMO in desperation, “her heart recovered again,” Rao reported.
“Some things you never forget in life,” she said. “I can’t describe how everyone in the OR felt, all taking care of her. I told Ramya, ‘you are a fighter’.”
New strength
Six days would pass before Ramya woke up and learned of the astounding series of events that saved her. She knew “something was really wrong” because of the incision at the center of her chest, but learning she’d been on ECMO and the heart transplant list drove home how close to death she’d actually come.
“Most people don’t get off ECMO; they die on it,” she said. “And the chances of dying on the heart transplant list are very high. It was very strange to me that this was my story all of a sudden, when a week and a half earlier I was on rotation.”
Ongoing physical therapy over the past 3 months has transformed Ramya from a state of profound physical weakness to a place of relative strength. The now-fourth-year med student is turning 26 in November and is hungry to restart in-person rotations. Her downtime has been filled in part with researching myocarditis and collaborating with Rao on her own case study for journal publication.
But the mental trauma from her experience has girded her in ways she knows will make her stronger personally and professionally in the years ahead.
“It’s still very hard. I’m still recovering,” she acknowledged. “I described it to my therapist as an invisible wound on my brain.”
“When I came out of the hospital, I still had ECMO wounds, deep gashes on my legs that affected how fast and how long I could walk,” she said. “I felt like the same thing was going on my brain — a huge cut no one could see.”
Her intention to specialize in psychiatry has become more pressing now that Ramya has realized the impact of trauma on mental health.
“My body failing me was awful, but I could handle it,” she said. “Losing any part of my mind would have been way worse. I want to take care of that in my patients.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.









