User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Early cardiac rehab as effective as later start after sternotomy
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) started 2 weeks after sternotomy for a cardiac procedure was noninferior to usual care, in which CR starts 6 weeks after the procedure, with a greater improvement in 6-minute walk test outcomes, a randomized study suggests.
There was no difference in adverse events between groups, although the researchers pointed out that the study was not powered specifically for safety outcomes.
“Cardiac surgical techniques have evolved significantly over the last 60 years, leading to improved survival and shorter hospital stays,” Gordon McGregor, PhD, University of Warwick, Coventry, England, told this news organization. “However, sternal precautions and rehabilitation guidelines have not changed accordingly. There has never been a guideline based on empirical evidence to support rehabilitation professionals working with cardiac surgery patients after median sternotomy.”
“By adopting a progressive individualized approach,” he added, “cardiac surgery sternotomy patients can start cardiac rehabilitation up to 4 weeks earlier than current guidance, and thus potentially complete their recovery sooner.”
Results of the Early Initiation of Poststernotomy Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Training study were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
In the study, Dr. McGregor and colleagues randomly assigned 158 patients (mean age, 63 years; 84% men) to 8 weeks of 1-hour, twice-weekly supervised CR exercise training starting 2 weeks (early) or 6 weeks (usual care) after sternotomy.
The primary outcome was change in the 6-minute walk test distance from baseline to 10 or 14 weeks after sternotomy, respectively, and 12 months after randomization.
For usual care, training followed British standards: a warm-up with light cardiovascular and mobility exercises; continuous moderate-intensity cardiovascular exercise; a cooldown; functional exercises using resistance machines and free weights; and upper-body exercises designed to prevent sternal and leg wound pain and complications.
There are no specific outpatient CR exercise guidelines for early CR, so study participants followed an individualized exercise program for the first 2-3 weeks after surgery, starting with light mobility and moderate-intensity cardiovascular training when they could do those exercises with minimal discomfort. They then progressed to current British standards, as per usual care.
Forty patients were lost to follow-up, largely because of the pandemic; about half the participants in each group were included in the primary analysis.
Early CR was not inferior to usual care, the authors wrote. The mean change in 6-minute walk distance from baseline to completion of CR was 28 meters greater in the early group than in the usual-care group, and was achieved 4 weeks earlier in the recovery timeline.
Secondary outcomes (functional fitness and quality of life) improved in both groups and between-group differences were not statistically significant, indicating the noninferiority of early CR, the authors noted.
Safety not proven
There were more adverse events in the early group than in the usual-care group (58 vs. 46) and more serious adverse events (18 vs. 14), but fewer deaths (1 vs. 2).
Although there was no between-group difference in the likelihood of having an adverse or serious adverse event, Dr. McGregor acknowledged that the study was “not powered specifically for safety outcomes.” He added that “there is the potential to run a very large multination definitive superiority [randomized, controlled trial] with safety as the primary outcome; however, a very large sample would be required.”
Meanwhile, he said, “we can say with some degree of certainty that early CR was likely as safe as usual-care CR. In the United Kingdom, we work closely with the British Association for Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation and the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Cardiovascular Rehabilitation, who will incorporate our findings in their guidelines and training courses.”
Questions remain
Asked to comment on the study, John Larry, MD, medical director of cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center East Hospital, Columbus, said: “For those under time pressure to return to work, [early CR] could be an advantage to allow more rehab time and improved stamina prior to their return-to-work date.”
That said, he noted, “we typically delay any significant upper-body training activities for 8-10 weeks to avoid impact on healing of the sternum. Thus ... starting sooner would limit the amount of time a patient would have to engage in any upper-body resistance training. Many lose upper body strength after surgery, so this is an important part of the recovery/rehab process.”
Matthew Tomey, MD, director of the cardiac intensive care unit, Mount Sinai Morningside, New York, advised “caution” when interpreting the findings, stating that “there was no evident difference in the primary outcome measure of functional capacity by 14 weeks, and the trial was not designed to directly assess impact on either social functioning or economic productivity.”
“I would be interested to [see] more comprehensive data on safety in a larger, more diverse sample of postoperative patients,” he said, “as well as evidence to indicate clear advantage of an earlier start for patient-centered outcomes specifically after cardiac surgery.
“Perhaps the greatest challenges to full realization of the benefits of CR in practice have been gaps in referral and gaps in enrollment,” he added. “It is incumbent upon us as clinicians to counsel our patients and to provide appropriate referrals.”
The study was supported by the Medical and Life Sciences Research Fund and the Jeremy Pilcher Memorial Fund. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) started 2 weeks after sternotomy for a cardiac procedure was noninferior to usual care, in which CR starts 6 weeks after the procedure, with a greater improvement in 6-minute walk test outcomes, a randomized study suggests.
There was no difference in adverse events between groups, although the researchers pointed out that the study was not powered specifically for safety outcomes.
“Cardiac surgical techniques have evolved significantly over the last 60 years, leading to improved survival and shorter hospital stays,” Gordon McGregor, PhD, University of Warwick, Coventry, England, told this news organization. “However, sternal precautions and rehabilitation guidelines have not changed accordingly. There has never been a guideline based on empirical evidence to support rehabilitation professionals working with cardiac surgery patients after median sternotomy.”
“By adopting a progressive individualized approach,” he added, “cardiac surgery sternotomy patients can start cardiac rehabilitation up to 4 weeks earlier than current guidance, and thus potentially complete their recovery sooner.”
Results of the Early Initiation of Poststernotomy Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Training study were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
In the study, Dr. McGregor and colleagues randomly assigned 158 patients (mean age, 63 years; 84% men) to 8 weeks of 1-hour, twice-weekly supervised CR exercise training starting 2 weeks (early) or 6 weeks (usual care) after sternotomy.
The primary outcome was change in the 6-minute walk test distance from baseline to 10 or 14 weeks after sternotomy, respectively, and 12 months after randomization.
For usual care, training followed British standards: a warm-up with light cardiovascular and mobility exercises; continuous moderate-intensity cardiovascular exercise; a cooldown; functional exercises using resistance machines and free weights; and upper-body exercises designed to prevent sternal and leg wound pain and complications.
There are no specific outpatient CR exercise guidelines for early CR, so study participants followed an individualized exercise program for the first 2-3 weeks after surgery, starting with light mobility and moderate-intensity cardiovascular training when they could do those exercises with minimal discomfort. They then progressed to current British standards, as per usual care.
Forty patients were lost to follow-up, largely because of the pandemic; about half the participants in each group were included in the primary analysis.
Early CR was not inferior to usual care, the authors wrote. The mean change in 6-minute walk distance from baseline to completion of CR was 28 meters greater in the early group than in the usual-care group, and was achieved 4 weeks earlier in the recovery timeline.
Secondary outcomes (functional fitness and quality of life) improved in both groups and between-group differences were not statistically significant, indicating the noninferiority of early CR, the authors noted.
Safety not proven
There were more adverse events in the early group than in the usual-care group (58 vs. 46) and more serious adverse events (18 vs. 14), but fewer deaths (1 vs. 2).
Although there was no between-group difference in the likelihood of having an adverse or serious adverse event, Dr. McGregor acknowledged that the study was “not powered specifically for safety outcomes.” He added that “there is the potential to run a very large multination definitive superiority [randomized, controlled trial] with safety as the primary outcome; however, a very large sample would be required.”
Meanwhile, he said, “we can say with some degree of certainty that early CR was likely as safe as usual-care CR. In the United Kingdom, we work closely with the British Association for Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation and the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Cardiovascular Rehabilitation, who will incorporate our findings in their guidelines and training courses.”
Questions remain
Asked to comment on the study, John Larry, MD, medical director of cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center East Hospital, Columbus, said: “For those under time pressure to return to work, [early CR] could be an advantage to allow more rehab time and improved stamina prior to their return-to-work date.”
That said, he noted, “we typically delay any significant upper-body training activities for 8-10 weeks to avoid impact on healing of the sternum. Thus ... starting sooner would limit the amount of time a patient would have to engage in any upper-body resistance training. Many lose upper body strength after surgery, so this is an important part of the recovery/rehab process.”
Matthew Tomey, MD, director of the cardiac intensive care unit, Mount Sinai Morningside, New York, advised “caution” when interpreting the findings, stating that “there was no evident difference in the primary outcome measure of functional capacity by 14 weeks, and the trial was not designed to directly assess impact on either social functioning or economic productivity.”
“I would be interested to [see] more comprehensive data on safety in a larger, more diverse sample of postoperative patients,” he said, “as well as evidence to indicate clear advantage of an earlier start for patient-centered outcomes specifically after cardiac surgery.
“Perhaps the greatest challenges to full realization of the benefits of CR in practice have been gaps in referral and gaps in enrollment,” he added. “It is incumbent upon us as clinicians to counsel our patients and to provide appropriate referrals.”
The study was supported by the Medical and Life Sciences Research Fund and the Jeremy Pilcher Memorial Fund. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiac rehabilitation (CR) started 2 weeks after sternotomy for a cardiac procedure was noninferior to usual care, in which CR starts 6 weeks after the procedure, with a greater improvement in 6-minute walk test outcomes, a randomized study suggests.
There was no difference in adverse events between groups, although the researchers pointed out that the study was not powered specifically for safety outcomes.
“Cardiac surgical techniques have evolved significantly over the last 60 years, leading to improved survival and shorter hospital stays,” Gordon McGregor, PhD, University of Warwick, Coventry, England, told this news organization. “However, sternal precautions and rehabilitation guidelines have not changed accordingly. There has never been a guideline based on empirical evidence to support rehabilitation professionals working with cardiac surgery patients after median sternotomy.”
“By adopting a progressive individualized approach,” he added, “cardiac surgery sternotomy patients can start cardiac rehabilitation up to 4 weeks earlier than current guidance, and thus potentially complete their recovery sooner.”
Results of the Early Initiation of Poststernotomy Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Training study were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
In the study, Dr. McGregor and colleagues randomly assigned 158 patients (mean age, 63 years; 84% men) to 8 weeks of 1-hour, twice-weekly supervised CR exercise training starting 2 weeks (early) or 6 weeks (usual care) after sternotomy.
The primary outcome was change in the 6-minute walk test distance from baseline to 10 or 14 weeks after sternotomy, respectively, and 12 months after randomization.
For usual care, training followed British standards: a warm-up with light cardiovascular and mobility exercises; continuous moderate-intensity cardiovascular exercise; a cooldown; functional exercises using resistance machines and free weights; and upper-body exercises designed to prevent sternal and leg wound pain and complications.
There are no specific outpatient CR exercise guidelines for early CR, so study participants followed an individualized exercise program for the first 2-3 weeks after surgery, starting with light mobility and moderate-intensity cardiovascular training when they could do those exercises with minimal discomfort. They then progressed to current British standards, as per usual care.
Forty patients were lost to follow-up, largely because of the pandemic; about half the participants in each group were included in the primary analysis.
Early CR was not inferior to usual care, the authors wrote. The mean change in 6-minute walk distance from baseline to completion of CR was 28 meters greater in the early group than in the usual-care group, and was achieved 4 weeks earlier in the recovery timeline.
Secondary outcomes (functional fitness and quality of life) improved in both groups and between-group differences were not statistically significant, indicating the noninferiority of early CR, the authors noted.
Safety not proven
There were more adverse events in the early group than in the usual-care group (58 vs. 46) and more serious adverse events (18 vs. 14), but fewer deaths (1 vs. 2).
Although there was no between-group difference in the likelihood of having an adverse or serious adverse event, Dr. McGregor acknowledged that the study was “not powered specifically for safety outcomes.” He added that “there is the potential to run a very large multination definitive superiority [randomized, controlled trial] with safety as the primary outcome; however, a very large sample would be required.”
Meanwhile, he said, “we can say with some degree of certainty that early CR was likely as safe as usual-care CR. In the United Kingdom, we work closely with the British Association for Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation and the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Cardiovascular Rehabilitation, who will incorporate our findings in their guidelines and training courses.”
Questions remain
Asked to comment on the study, John Larry, MD, medical director of cardiology and cardiac rehabilitation at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center East Hospital, Columbus, said: “For those under time pressure to return to work, [early CR] could be an advantage to allow more rehab time and improved stamina prior to their return-to-work date.”
That said, he noted, “we typically delay any significant upper-body training activities for 8-10 weeks to avoid impact on healing of the sternum. Thus ... starting sooner would limit the amount of time a patient would have to engage in any upper-body resistance training. Many lose upper body strength after surgery, so this is an important part of the recovery/rehab process.”
Matthew Tomey, MD, director of the cardiac intensive care unit, Mount Sinai Morningside, New York, advised “caution” when interpreting the findings, stating that “there was no evident difference in the primary outcome measure of functional capacity by 14 weeks, and the trial was not designed to directly assess impact on either social functioning or economic productivity.”
“I would be interested to [see] more comprehensive data on safety in a larger, more diverse sample of postoperative patients,” he said, “as well as evidence to indicate clear advantage of an earlier start for patient-centered outcomes specifically after cardiac surgery.
“Perhaps the greatest challenges to full realization of the benefits of CR in practice have been gaps in referral and gaps in enrollment,” he added. “It is incumbent upon us as clinicians to counsel our patients and to provide appropriate referrals.”
The study was supported by the Medical and Life Sciences Research Fund and the Jeremy Pilcher Memorial Fund. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
Lawmakers argue for changes in prior authorization processes
Republican and Democratic members of the House called for changes in how insurer-run Medicare plans manage the prior authorization process, following testimony from a federal watchdog organization about improper denials of payment for care.
About 18% of payment denials in a sample examined by the Office of Inspector General (OIG) of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) either met Medicare coverage rules or the rules of the insurance plan.
As such, they should not have been denied, according to the OIG. That was the finding of an April OIG report, based on a sample of 2019 denials from large insurer-run Medicare plans.
Erin Bliss, an assistant inspector general with the OIG, appeared as a witness at a June 28 Energy and Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations hearing to discuss this investigation and other issues with prior authorization and insurer-run Medicare, also known as the Advantage plans.
Most of these payment denials of appropriate services were due to human error during manual claims-processing reviews, Ms. Bliss told the subcommittee, such as overlooking a document, and to system processing errors, such as a Medicare insurance plan failing to program or update a system correctly.
In many cases, these denials were reversed, but patient care was still disrupted and clinicians lost time chasing clearances for services that plans already had covered, Ms. Bliss said in her testimony.
The April report was not the OIG’s first look into concerns about insurer-run plans inappropriately denying care through prior authorizations. The OIG in 2018 reported that insurer-run Medicare plans overturned 75% of their own denials during 2014-2016 when patients and clinicians appealed these decisions, overturning approximately 216,000 denials each year.
‘Numerous hoops’ unnecessary for doctors, patients
Lawmakers at the hearing supported the idea of the need for prior authorization as a screening tool to prevent unneeded care.
But they chided insurance companies for their execution of this process, with clinicians and patients often frustrated by complex steps needed. Medicare Advantage plans sometimes require prior authorization for “relatively standard medical services,” said Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations Chair Diana DeGette (D-Colo.).
“Our seniors and their doctors should not be required to jump through numerous hoops to ensure coverage for straightforward and medically necessary procedures,” Rep. DeGette said.
Several lawmakers spoke at the hearing about the need for changes to prior authorization, including calling for action on a pending bill intended to compel insurers to streamline the review process. The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act of 2021 already has attracted more than 300 bipartisan sponsors. A companion Senate bill has more than 30 sponsors.
The bill’s aim is to shift this process away from faxes and phone calls while also encouraging plans to adhere to evidence-based medical guidelines in consultation with physicians. The bill calls for the establishment of an electronic prior authorization program that could issue real-time decisions.
“The result will be less administrative burden for providers and more information in the hands of patients. It will allow more patients to receive care when they need it, reducing the likelihood of additional, often more severe complications,” said Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD, (R-Ind.) who is among the active sponsors of the bill.
“In the long term, I believe it would also result in cost savings for the health care system at large by identifying problems earlier and getting them treated before their patients have more complications,” Rep. Bucshon added.
Finding ‘room for improvement’ for prior authorizations
There’s strong bipartisan support in Congress for insurer-run Medicare, which has grown by 10% per year over the last several years and has doubled since 2010, according to the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC). About 27 million people are now enrolled in these plans.
But for that reason, insurer-run Medicare may also need more careful watching, lawmakers made clear at the hearing.
“We’ve heard quite a bit of evidence today that there is room for improvement,” said Rep. Bucshon, a strong supporter of insurer-run Medicare, which can offer patients added benefits such as dental coverage.
Rep. Ann Kuster (D-N.H.) said simplifying prior authorization would reduce stress on clinicians already dealing with burnout.
“They’re just so tired of all this paperwork and red tape,” Rep. Kuster said. “In 2022 can’t we at least consider electronic prior authorization?”
At the hearing, Rep. Michael C. Burgess, MD, (R-Tex.) noted that his home state already has taken a step toward reducing the burden of prior authorization with its “gold card” program.
In 2021, a new Texas law called on the state department of insurance to develop rules to require health plans to provide an exemption from preauthorization requirements for a particular health care service if the issuer has approved, or would have approved, at least 90% of the preauthorization requests submitted by the physician or provider for that service. The law also mandates that a physician participating in a peer-to-peer review on behalf of a health benefit plan issuer must be a Texas-licensed physician who has the same or similar specialty as the physician or clinician requesting the service, according to the state insurance department.
Separately, Rep. Suzan DelBene (D-Wash.), the sponsor of the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act, told the American Medical Association in a recent interview that she expects the House Ways and Means Committee, on which she serves, to mark up her bill in July. (A mark-up is the process by which a House or Senate committee considers and often amends a bill and then sends it to the chamber’s leadership for a floor vote.)
In a statement issued about the hearing, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP) noted that there has been work in recent years toward streamlining prior authorization. AHIP said it launched the Fast Prior Authorization Technology Highway (Fast PATH) initiative in 2020 to study electronic procedures for handling these reviews.
“The findings of this study showed that ePA delivered improvements with a strong majority of experienced providers reporting faster time to patient care, fewer phone calls and faxes, better understanding of [prior authorization] requirements, and faster time to decisions,” AHIP said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Republican and Democratic members of the House called for changes in how insurer-run Medicare plans manage the prior authorization process, following testimony from a federal watchdog organization about improper denials of payment for care.
About 18% of payment denials in a sample examined by the Office of Inspector General (OIG) of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) either met Medicare coverage rules or the rules of the insurance plan.
As such, they should not have been denied, according to the OIG. That was the finding of an April OIG report, based on a sample of 2019 denials from large insurer-run Medicare plans.
Erin Bliss, an assistant inspector general with the OIG, appeared as a witness at a June 28 Energy and Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations hearing to discuss this investigation and other issues with prior authorization and insurer-run Medicare, also known as the Advantage plans.
Most of these payment denials of appropriate services were due to human error during manual claims-processing reviews, Ms. Bliss told the subcommittee, such as overlooking a document, and to system processing errors, such as a Medicare insurance plan failing to program or update a system correctly.
In many cases, these denials were reversed, but patient care was still disrupted and clinicians lost time chasing clearances for services that plans already had covered, Ms. Bliss said in her testimony.
The April report was not the OIG’s first look into concerns about insurer-run plans inappropriately denying care through prior authorizations. The OIG in 2018 reported that insurer-run Medicare plans overturned 75% of their own denials during 2014-2016 when patients and clinicians appealed these decisions, overturning approximately 216,000 denials each year.
‘Numerous hoops’ unnecessary for doctors, patients
Lawmakers at the hearing supported the idea of the need for prior authorization as a screening tool to prevent unneeded care.
But they chided insurance companies for their execution of this process, with clinicians and patients often frustrated by complex steps needed. Medicare Advantage plans sometimes require prior authorization for “relatively standard medical services,” said Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations Chair Diana DeGette (D-Colo.).
“Our seniors and their doctors should not be required to jump through numerous hoops to ensure coverage for straightforward and medically necessary procedures,” Rep. DeGette said.
Several lawmakers spoke at the hearing about the need for changes to prior authorization, including calling for action on a pending bill intended to compel insurers to streamline the review process. The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act of 2021 already has attracted more than 300 bipartisan sponsors. A companion Senate bill has more than 30 sponsors.
The bill’s aim is to shift this process away from faxes and phone calls while also encouraging plans to adhere to evidence-based medical guidelines in consultation with physicians. The bill calls for the establishment of an electronic prior authorization program that could issue real-time decisions.
“The result will be less administrative burden for providers and more information in the hands of patients. It will allow more patients to receive care when they need it, reducing the likelihood of additional, often more severe complications,” said Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD, (R-Ind.) who is among the active sponsors of the bill.
“In the long term, I believe it would also result in cost savings for the health care system at large by identifying problems earlier and getting them treated before their patients have more complications,” Rep. Bucshon added.
Finding ‘room for improvement’ for prior authorizations
There’s strong bipartisan support in Congress for insurer-run Medicare, which has grown by 10% per year over the last several years and has doubled since 2010, according to the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC). About 27 million people are now enrolled in these plans.
But for that reason, insurer-run Medicare may also need more careful watching, lawmakers made clear at the hearing.
“We’ve heard quite a bit of evidence today that there is room for improvement,” said Rep. Bucshon, a strong supporter of insurer-run Medicare, which can offer patients added benefits such as dental coverage.
Rep. Ann Kuster (D-N.H.) said simplifying prior authorization would reduce stress on clinicians already dealing with burnout.
“They’re just so tired of all this paperwork and red tape,” Rep. Kuster said. “In 2022 can’t we at least consider electronic prior authorization?”
At the hearing, Rep. Michael C. Burgess, MD, (R-Tex.) noted that his home state already has taken a step toward reducing the burden of prior authorization with its “gold card” program.
In 2021, a new Texas law called on the state department of insurance to develop rules to require health plans to provide an exemption from preauthorization requirements for a particular health care service if the issuer has approved, or would have approved, at least 90% of the preauthorization requests submitted by the physician or provider for that service. The law also mandates that a physician participating in a peer-to-peer review on behalf of a health benefit plan issuer must be a Texas-licensed physician who has the same or similar specialty as the physician or clinician requesting the service, according to the state insurance department.
Separately, Rep. Suzan DelBene (D-Wash.), the sponsor of the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act, told the American Medical Association in a recent interview that she expects the House Ways and Means Committee, on which she serves, to mark up her bill in July. (A mark-up is the process by which a House or Senate committee considers and often amends a bill and then sends it to the chamber’s leadership for a floor vote.)
In a statement issued about the hearing, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP) noted that there has been work in recent years toward streamlining prior authorization. AHIP said it launched the Fast Prior Authorization Technology Highway (Fast PATH) initiative in 2020 to study electronic procedures for handling these reviews.
“The findings of this study showed that ePA delivered improvements with a strong majority of experienced providers reporting faster time to patient care, fewer phone calls and faxes, better understanding of [prior authorization] requirements, and faster time to decisions,” AHIP said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Republican and Democratic members of the House called for changes in how insurer-run Medicare plans manage the prior authorization process, following testimony from a federal watchdog organization about improper denials of payment for care.
About 18% of payment denials in a sample examined by the Office of Inspector General (OIG) of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) either met Medicare coverage rules or the rules of the insurance plan.
As such, they should not have been denied, according to the OIG. That was the finding of an April OIG report, based on a sample of 2019 denials from large insurer-run Medicare plans.
Erin Bliss, an assistant inspector general with the OIG, appeared as a witness at a June 28 Energy and Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations hearing to discuss this investigation and other issues with prior authorization and insurer-run Medicare, also known as the Advantage plans.
Most of these payment denials of appropriate services were due to human error during manual claims-processing reviews, Ms. Bliss told the subcommittee, such as overlooking a document, and to system processing errors, such as a Medicare insurance plan failing to program or update a system correctly.
In many cases, these denials were reversed, but patient care was still disrupted and clinicians lost time chasing clearances for services that plans already had covered, Ms. Bliss said in her testimony.
The April report was not the OIG’s first look into concerns about insurer-run plans inappropriately denying care through prior authorizations. The OIG in 2018 reported that insurer-run Medicare plans overturned 75% of their own denials during 2014-2016 when patients and clinicians appealed these decisions, overturning approximately 216,000 denials each year.
‘Numerous hoops’ unnecessary for doctors, patients
Lawmakers at the hearing supported the idea of the need for prior authorization as a screening tool to prevent unneeded care.
But they chided insurance companies for their execution of this process, with clinicians and patients often frustrated by complex steps needed. Medicare Advantage plans sometimes require prior authorization for “relatively standard medical services,” said Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations Chair Diana DeGette (D-Colo.).
“Our seniors and their doctors should not be required to jump through numerous hoops to ensure coverage for straightforward and medically necessary procedures,” Rep. DeGette said.
Several lawmakers spoke at the hearing about the need for changes to prior authorization, including calling for action on a pending bill intended to compel insurers to streamline the review process. The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act of 2021 already has attracted more than 300 bipartisan sponsors. A companion Senate bill has more than 30 sponsors.
The bill’s aim is to shift this process away from faxes and phone calls while also encouraging plans to adhere to evidence-based medical guidelines in consultation with physicians. The bill calls for the establishment of an electronic prior authorization program that could issue real-time decisions.
“The result will be less administrative burden for providers and more information in the hands of patients. It will allow more patients to receive care when they need it, reducing the likelihood of additional, often more severe complications,” said Rep. Larry Bucshon, MD, (R-Ind.) who is among the active sponsors of the bill.
“In the long term, I believe it would also result in cost savings for the health care system at large by identifying problems earlier and getting them treated before their patients have more complications,” Rep. Bucshon added.
Finding ‘room for improvement’ for prior authorizations
There’s strong bipartisan support in Congress for insurer-run Medicare, which has grown by 10% per year over the last several years and has doubled since 2010, according to the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC). About 27 million people are now enrolled in these plans.
But for that reason, insurer-run Medicare may also need more careful watching, lawmakers made clear at the hearing.
“We’ve heard quite a bit of evidence today that there is room for improvement,” said Rep. Bucshon, a strong supporter of insurer-run Medicare, which can offer patients added benefits such as dental coverage.
Rep. Ann Kuster (D-N.H.) said simplifying prior authorization would reduce stress on clinicians already dealing with burnout.
“They’re just so tired of all this paperwork and red tape,” Rep. Kuster said. “In 2022 can’t we at least consider electronic prior authorization?”
At the hearing, Rep. Michael C. Burgess, MD, (R-Tex.) noted that his home state already has taken a step toward reducing the burden of prior authorization with its “gold card” program.
In 2021, a new Texas law called on the state department of insurance to develop rules to require health plans to provide an exemption from preauthorization requirements for a particular health care service if the issuer has approved, or would have approved, at least 90% of the preauthorization requests submitted by the physician or provider for that service. The law also mandates that a physician participating in a peer-to-peer review on behalf of a health benefit plan issuer must be a Texas-licensed physician who has the same or similar specialty as the physician or clinician requesting the service, according to the state insurance department.
Separately, Rep. Suzan DelBene (D-Wash.), the sponsor of the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act, told the American Medical Association in a recent interview that she expects the House Ways and Means Committee, on which she serves, to mark up her bill in July. (A mark-up is the process by which a House or Senate committee considers and often amends a bill and then sends it to the chamber’s leadership for a floor vote.)
In a statement issued about the hearing, America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP) noted that there has been work in recent years toward streamlining prior authorization. AHIP said it launched the Fast Prior Authorization Technology Highway (Fast PATH) initiative in 2020 to study electronic procedures for handling these reviews.
“The findings of this study showed that ePA delivered improvements with a strong majority of experienced providers reporting faster time to patient care, fewer phone calls and faxes, better understanding of [prior authorization] requirements, and faster time to decisions,” AHIP said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Murder of physician raises the stress level for all clinicians
As if it weren’t enough that doctors work in a profession where it’s almost more a question of when they’ll be sued than if they’ll be sued – where COVID, staff shortages, long hours, and patients frustrated over canceled procedures have caused unrelenting fatigue and stress – they now have to worry that an unhappy patient is going to buy a gun, walk into their office, and kill them.
That’s exactly what happened in Tulsa, Okla., where a patient complaining of pain after back surgery murdered his doctor and several others who happened to be in the wrong place at the wrong time.
The temptation in the aftermath of such tragedies is to think about preventive measures: Make medical facilities “hardened” targets, like schools have become, with armed guards, metal detectors, automatically locking doors, physical barriers within, security cameras, and buzzers for entry – although hardening a large medical center where members of the community routinely come and go would be challenging.
What about the enormous stress on doctors, nurses, and others in the medical workplace? Physicians who have been sued for malpractice often describe how it changes the way they interact with patients: They now size patients up and make judgments about their potential litigiousness. Will the physicians now look over their patients’ shoulders at the video feed from a security camera when they’re taking a history? Will medical professionals be forced to make snap judgments about patients’ psychological state before deciding whether to treat them?
Remember, there was a time when school shootings were unimaginable. Once one person crosses that line, others inevitably follow.
It could be a drug-seeking patient complaining of ongoing pain, angry because he can’t get a new prescription. It could be a patient whose unpaid bill was turned over to a collection agency, angry because he’s now getting calls from collectors. It could be someone who blames a physician for the loss of a loved one. It could be someone who would otherwise have filed a lawsuit, who now thinks he has a more effective option for exacting retribution.
Most of us would find it unbearable to live and work under the kind of stress faced by medical professionals today. And unfortunately, there is no short-term, systemic relief on the horizon. But there are methods of relieving at least some of the psychological burden being carried by these dedicated individuals.
For starters, the government should provide funds to improve safety and security at medical facilities. It’s sad but it’s a fact of life. The physical structure of schools, along with emergency procedures, have been changed since Columbine and Sandy Hook, and our children and their teachers undergo active shooter drills. Health care facilities will need to adopt similar strategies.
But if we don’t also support the individuals who work in health care, we’ll no longer have even partially staffed health care facilities. Hospitals and medical groups need to be conscious of the effects stress may have on them. Medical staff and administrators need to recognize changes in their colleagues’ behavior and refer those cohorts to professional stress coaches who can get them back on track.
Medical personnel should be picking up on warning signs, like irritability, depression, sudden weight gain or loss, lack of motivation and job satisfaction, obsessiveness, unusual levels of fatigue, alcohol or drug use, and, of course, avoidable medical errors.
In addition, colleagues in the medical workplace need to know each other well. They are usually the first ones to notice if something is off and may be in the best position to refer coworkers for help. Also, medical malpractice insurance carriers should consider encouraging and covering coaching sessions, because helping physicians cope with this heightened stress will prevent medical errors and the lawsuits that inevitably accompany mistakes.
This needn’t be a long-term process like ongoing psychotherapy; a few sessions with a well-trained coach may help psychologically challenged peers restore their focus and perspective. It won’t eliminate the threat any more than litigation stress coaching eliminates the threat of being sued, but it can prevent that stress from leading to avoidable errors. It also can prevent physicians’ personal lives and relationships from going off the rails and driving them out of the medical profession.
None of us can afford to ignore the impacts that these new stressors are having and simply act as if it’s business as usual. The people in the trenches need our help.
Ms. Fiore is President of Winning Focus in Murrysville, Pa. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As if it weren’t enough that doctors work in a profession where it’s almost more a question of when they’ll be sued than if they’ll be sued – where COVID, staff shortages, long hours, and patients frustrated over canceled procedures have caused unrelenting fatigue and stress – they now have to worry that an unhappy patient is going to buy a gun, walk into their office, and kill them.
That’s exactly what happened in Tulsa, Okla., where a patient complaining of pain after back surgery murdered his doctor and several others who happened to be in the wrong place at the wrong time.
The temptation in the aftermath of such tragedies is to think about preventive measures: Make medical facilities “hardened” targets, like schools have become, with armed guards, metal detectors, automatically locking doors, physical barriers within, security cameras, and buzzers for entry – although hardening a large medical center where members of the community routinely come and go would be challenging.
What about the enormous stress on doctors, nurses, and others in the medical workplace? Physicians who have been sued for malpractice often describe how it changes the way they interact with patients: They now size patients up and make judgments about their potential litigiousness. Will the physicians now look over their patients’ shoulders at the video feed from a security camera when they’re taking a history? Will medical professionals be forced to make snap judgments about patients’ psychological state before deciding whether to treat them?
Remember, there was a time when school shootings were unimaginable. Once one person crosses that line, others inevitably follow.
It could be a drug-seeking patient complaining of ongoing pain, angry because he can’t get a new prescription. It could be a patient whose unpaid bill was turned over to a collection agency, angry because he’s now getting calls from collectors. It could be someone who blames a physician for the loss of a loved one. It could be someone who would otherwise have filed a lawsuit, who now thinks he has a more effective option for exacting retribution.
Most of us would find it unbearable to live and work under the kind of stress faced by medical professionals today. And unfortunately, there is no short-term, systemic relief on the horizon. But there are methods of relieving at least some of the psychological burden being carried by these dedicated individuals.
For starters, the government should provide funds to improve safety and security at medical facilities. It’s sad but it’s a fact of life. The physical structure of schools, along with emergency procedures, have been changed since Columbine and Sandy Hook, and our children and their teachers undergo active shooter drills. Health care facilities will need to adopt similar strategies.
But if we don’t also support the individuals who work in health care, we’ll no longer have even partially staffed health care facilities. Hospitals and medical groups need to be conscious of the effects stress may have on them. Medical staff and administrators need to recognize changes in their colleagues’ behavior and refer those cohorts to professional stress coaches who can get them back on track.
Medical personnel should be picking up on warning signs, like irritability, depression, sudden weight gain or loss, lack of motivation and job satisfaction, obsessiveness, unusual levels of fatigue, alcohol or drug use, and, of course, avoidable medical errors.
In addition, colleagues in the medical workplace need to know each other well. They are usually the first ones to notice if something is off and may be in the best position to refer coworkers for help. Also, medical malpractice insurance carriers should consider encouraging and covering coaching sessions, because helping physicians cope with this heightened stress will prevent medical errors and the lawsuits that inevitably accompany mistakes.
This needn’t be a long-term process like ongoing psychotherapy; a few sessions with a well-trained coach may help psychologically challenged peers restore their focus and perspective. It won’t eliminate the threat any more than litigation stress coaching eliminates the threat of being sued, but it can prevent that stress from leading to avoidable errors. It also can prevent physicians’ personal lives and relationships from going off the rails and driving them out of the medical profession.
None of us can afford to ignore the impacts that these new stressors are having and simply act as if it’s business as usual. The people in the trenches need our help.
Ms. Fiore is President of Winning Focus in Murrysville, Pa. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As if it weren’t enough that doctors work in a profession where it’s almost more a question of when they’ll be sued than if they’ll be sued – where COVID, staff shortages, long hours, and patients frustrated over canceled procedures have caused unrelenting fatigue and stress – they now have to worry that an unhappy patient is going to buy a gun, walk into their office, and kill them.
That’s exactly what happened in Tulsa, Okla., where a patient complaining of pain after back surgery murdered his doctor and several others who happened to be in the wrong place at the wrong time.
The temptation in the aftermath of such tragedies is to think about preventive measures: Make medical facilities “hardened” targets, like schools have become, with armed guards, metal detectors, automatically locking doors, physical barriers within, security cameras, and buzzers for entry – although hardening a large medical center where members of the community routinely come and go would be challenging.
What about the enormous stress on doctors, nurses, and others in the medical workplace? Physicians who have been sued for malpractice often describe how it changes the way they interact with patients: They now size patients up and make judgments about their potential litigiousness. Will the physicians now look over their patients’ shoulders at the video feed from a security camera when they’re taking a history? Will medical professionals be forced to make snap judgments about patients’ psychological state before deciding whether to treat them?
Remember, there was a time when school shootings were unimaginable. Once one person crosses that line, others inevitably follow.
It could be a drug-seeking patient complaining of ongoing pain, angry because he can’t get a new prescription. It could be a patient whose unpaid bill was turned over to a collection agency, angry because he’s now getting calls from collectors. It could be someone who blames a physician for the loss of a loved one. It could be someone who would otherwise have filed a lawsuit, who now thinks he has a more effective option for exacting retribution.
Most of us would find it unbearable to live and work under the kind of stress faced by medical professionals today. And unfortunately, there is no short-term, systemic relief on the horizon. But there are methods of relieving at least some of the psychological burden being carried by these dedicated individuals.
For starters, the government should provide funds to improve safety and security at medical facilities. It’s sad but it’s a fact of life. The physical structure of schools, along with emergency procedures, have been changed since Columbine and Sandy Hook, and our children and their teachers undergo active shooter drills. Health care facilities will need to adopt similar strategies.
But if we don’t also support the individuals who work in health care, we’ll no longer have even partially staffed health care facilities. Hospitals and medical groups need to be conscious of the effects stress may have on them. Medical staff and administrators need to recognize changes in their colleagues’ behavior and refer those cohorts to professional stress coaches who can get them back on track.
Medical personnel should be picking up on warning signs, like irritability, depression, sudden weight gain or loss, lack of motivation and job satisfaction, obsessiveness, unusual levels of fatigue, alcohol or drug use, and, of course, avoidable medical errors.
In addition, colleagues in the medical workplace need to know each other well. They are usually the first ones to notice if something is off and may be in the best position to refer coworkers for help. Also, medical malpractice insurance carriers should consider encouraging and covering coaching sessions, because helping physicians cope with this heightened stress will prevent medical errors and the lawsuits that inevitably accompany mistakes.
This needn’t be a long-term process like ongoing psychotherapy; a few sessions with a well-trained coach may help psychologically challenged peers restore their focus and perspective. It won’t eliminate the threat any more than litigation stress coaching eliminates the threat of being sued, but it can prevent that stress from leading to avoidable errors. It also can prevent physicians’ personal lives and relationships from going off the rails and driving them out of the medical profession.
None of us can afford to ignore the impacts that these new stressors are having and simply act as if it’s business as usual. The people in the trenches need our help.
Ms. Fiore is President of Winning Focus in Murrysville, Pa. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
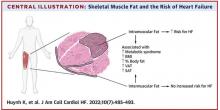
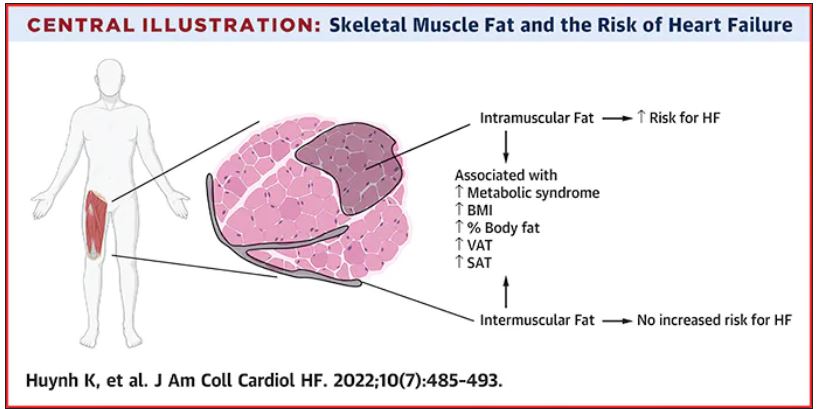
Thigh muscle fat predicts risk of developing heart failure
in a new study. The association was independent of other cardiometabolic risk factors and measures of adiposity such as body mass index.
The observation raises the possibility of new avenues of research aimed at modifying intramuscular fat levels as a strategy to reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
The study was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
The authors, led by Kevin Huynh, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, explained that obesity is a known risk for heart failure, and has been incorporated into risk calculators for heart failure.
However, obesity is a complex and heterogeneous disease with substantial regional variability of adipose deposition in body tissues, they noted. For example, variability in visceral adipose tissue and subcutaneous adipose tissue has been shown to have a differential impact on both cardiovascular risk factors and clinical cardiovascular disease outcomes.
The fat deposition around and within nonadipose tissues (termed “ectopic fat”), such as skeletal muscle, is also a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease, independent of adiposity. However, the impact of peripheral skeletal muscle fat deposition on heart failure risk is not as well studied.
The researchers noted that ectopic fat in skeletal muscle can be measured through imaging and categorized as either intermuscular or intramuscular fat according to the location of muscle fat around or within skeletal muscle, respectively.
The researchers conducted the current study to characterize the association of both intermuscular and intramuscular fat deposition with heart failure risk in a large cohort of older adults.
They used data from 2,399 individuals aged 70-79 years without heart failure at baseline who participated in the Health ABC (Health, Aging and Body Composition) study. Measures of intramuscular and intermuscular fat in the thigh were determined by CT, and the participants were followed for an average of 12 years.
During the follow-up period, there were 485 incident heart failure events. Higher sex-specific tertiles of intramuscular and intermuscular fat were each associated with heart failure risk.
After multivariable adjustment for age, sex, race, education, blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, current smoking, prevalent coronary disease, and creatinine, higher intramuscular fat, but not intermuscular fat, was significantly associated with higher risk for heart failure.
Individuals in the highest tertile of intramuscular fat had a 34% increased risk of developing heart failure, compared with those in the lowest tertile. This finding was independent of other cardiometabolic risk factors, measures of adiposity including body mass index and percent fat, muscle strength, and muscle mass.
The association was slightly attenuated when adjusted for inflammatory markers, suggesting that inflammation may be a contributor.
The association between higher intramuscular fat and heart failure appeared specific to higher risk of incident heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, but not with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
The researchers noted that skeletal muscle is a pivotal endocrine organ in addition to the role it plays in the production of mechanical power.
They pointed out that there are differences in the biology of intermuscular and intramuscular fat deposition, and that excess intramuscular fat deposition is a result of dysregulated lipid metabolism and is associated with insulin resistance (a known risk factor for the development of heart failure), inflammation, and muscle wasting conditions.
They concluded that, in patients with heart failure, alterations in skeletal muscle function are most likely affected by multiple contributors, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and neurohormonal factors. “As these factors are also implicated in the pathogenesis of heart failure, intramuscular fat deposition may indicate a biological milieu that increases the risk of heart failure.”
New approaches to reduce heart failure risk?
In an accompanying editorial, Salvatore Carbone, PhD, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the findings of the study are “exceptionally novel,” providing novel evidence that noncardiac body composition compartments, particularly intramuscular adipose tissue, can predict the risk for heart failure in a diverse population of older adults.
He called for further research to understand the mechanisms involved and to assess if this risk factor can be effectively modified to reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
Dr. Carbone reported that intramuscular adipose tissue can be influenced by dietary fat intake and can be worsened by accumulation of saturated fatty acids, which also contribute to insulin resistance.
He noted that saturated fatty acid–induced insulin resistance in the skeletal muscle appears to be mediated by proinflammatory pathways within the skeletal muscle itself, which can be reversed by monounsaturated fatty acids, like oleic acid, that can be found in the largest amount in food like olive oil, canola oil, and avocados, among others.
He added that sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors, drugs used in the treatment of diabetes that have also been shown to prevent heart failure in individuals at risk, can also improve the composition of intramuscular adipose tissue by reducing its content of saturated fatty acids and increase the content of monosaturated fatty acids.
The study results suggest that the quality of intramuscular adipose tissue might also play an important role and could be targeted by therapeutic strategies, he commented.
Dr. Carbone concluded that “studies testing novel modalities of exercise training, intentional weight loss, diet quality improvements with and without weight loss (i.e., increase of dietary monounsaturated fatty acids, such as oleic acid), as well as pharmacological anti-inflammatory strategies should be encouraged in this population to test whether the reduction in intramuscular adipose tissue or improvements of its quality can ultimately reduce the risk for heart failure in this population.”
This research was supported by the National Institute on Aging and the National Institute of Nursing Research. Dr. Huynh and Dr. Carbone disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new study. The association was independent of other cardiometabolic risk factors and measures of adiposity such as body mass index.
The observation raises the possibility of new avenues of research aimed at modifying intramuscular fat levels as a strategy to reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
The study was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
The authors, led by Kevin Huynh, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, explained that obesity is a known risk for heart failure, and has been incorporated into risk calculators for heart failure.
However, obesity is a complex and heterogeneous disease with substantial regional variability of adipose deposition in body tissues, they noted. For example, variability in visceral adipose tissue and subcutaneous adipose tissue has been shown to have a differential impact on both cardiovascular risk factors and clinical cardiovascular disease outcomes.
The fat deposition around and within nonadipose tissues (termed “ectopic fat”), such as skeletal muscle, is also a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease, independent of adiposity. However, the impact of peripheral skeletal muscle fat deposition on heart failure risk is not as well studied.
The researchers noted that ectopic fat in skeletal muscle can be measured through imaging and categorized as either intermuscular or intramuscular fat according to the location of muscle fat around or within skeletal muscle, respectively.
The researchers conducted the current study to characterize the association of both intermuscular and intramuscular fat deposition with heart failure risk in a large cohort of older adults.
They used data from 2,399 individuals aged 70-79 years without heart failure at baseline who participated in the Health ABC (Health, Aging and Body Composition) study. Measures of intramuscular and intermuscular fat in the thigh were determined by CT, and the participants were followed for an average of 12 years.
During the follow-up period, there were 485 incident heart failure events. Higher sex-specific tertiles of intramuscular and intermuscular fat were each associated with heart failure risk.
After multivariable adjustment for age, sex, race, education, blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, current smoking, prevalent coronary disease, and creatinine, higher intramuscular fat, but not intermuscular fat, was significantly associated with higher risk for heart failure.
Individuals in the highest tertile of intramuscular fat had a 34% increased risk of developing heart failure, compared with those in the lowest tertile. This finding was independent of other cardiometabolic risk factors, measures of adiposity including body mass index and percent fat, muscle strength, and muscle mass.
The association was slightly attenuated when adjusted for inflammatory markers, suggesting that inflammation may be a contributor.
The association between higher intramuscular fat and heart failure appeared specific to higher risk of incident heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, but not with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
The researchers noted that skeletal muscle is a pivotal endocrine organ in addition to the role it plays in the production of mechanical power.
They pointed out that there are differences in the biology of intermuscular and intramuscular fat deposition, and that excess intramuscular fat deposition is a result of dysregulated lipid metabolism and is associated with insulin resistance (a known risk factor for the development of heart failure), inflammation, and muscle wasting conditions.
They concluded that, in patients with heart failure, alterations in skeletal muscle function are most likely affected by multiple contributors, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and neurohormonal factors. “As these factors are also implicated in the pathogenesis of heart failure, intramuscular fat deposition may indicate a biological milieu that increases the risk of heart failure.”
New approaches to reduce heart failure risk?
In an accompanying editorial, Salvatore Carbone, PhD, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the findings of the study are “exceptionally novel,” providing novel evidence that noncardiac body composition compartments, particularly intramuscular adipose tissue, can predict the risk for heart failure in a diverse population of older adults.
He called for further research to understand the mechanisms involved and to assess if this risk factor can be effectively modified to reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
Dr. Carbone reported that intramuscular adipose tissue can be influenced by dietary fat intake and can be worsened by accumulation of saturated fatty acids, which also contribute to insulin resistance.
He noted that saturated fatty acid–induced insulin resistance in the skeletal muscle appears to be mediated by proinflammatory pathways within the skeletal muscle itself, which can be reversed by monounsaturated fatty acids, like oleic acid, that can be found in the largest amount in food like olive oil, canola oil, and avocados, among others.
He added that sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors, drugs used in the treatment of diabetes that have also been shown to prevent heart failure in individuals at risk, can also improve the composition of intramuscular adipose tissue by reducing its content of saturated fatty acids and increase the content of monosaturated fatty acids.
The study results suggest that the quality of intramuscular adipose tissue might also play an important role and could be targeted by therapeutic strategies, he commented.
Dr. Carbone concluded that “studies testing novel modalities of exercise training, intentional weight loss, diet quality improvements with and without weight loss (i.e., increase of dietary monounsaturated fatty acids, such as oleic acid), as well as pharmacological anti-inflammatory strategies should be encouraged in this population to test whether the reduction in intramuscular adipose tissue or improvements of its quality can ultimately reduce the risk for heart failure in this population.”
This research was supported by the National Institute on Aging and the National Institute of Nursing Research. Dr. Huynh and Dr. Carbone disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new study. The association was independent of other cardiometabolic risk factors and measures of adiposity such as body mass index.
The observation raises the possibility of new avenues of research aimed at modifying intramuscular fat levels as a strategy to reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
The study was published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
The authors, led by Kevin Huynh, MD, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, explained that obesity is a known risk for heart failure, and has been incorporated into risk calculators for heart failure.
However, obesity is a complex and heterogeneous disease with substantial regional variability of adipose deposition in body tissues, they noted. For example, variability in visceral adipose tissue and subcutaneous adipose tissue has been shown to have a differential impact on both cardiovascular risk factors and clinical cardiovascular disease outcomes.
The fat deposition around and within nonadipose tissues (termed “ectopic fat”), such as skeletal muscle, is also a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease, independent of adiposity. However, the impact of peripheral skeletal muscle fat deposition on heart failure risk is not as well studied.
The researchers noted that ectopic fat in skeletal muscle can be measured through imaging and categorized as either intermuscular or intramuscular fat according to the location of muscle fat around or within skeletal muscle, respectively.
The researchers conducted the current study to characterize the association of both intermuscular and intramuscular fat deposition with heart failure risk in a large cohort of older adults.
They used data from 2,399 individuals aged 70-79 years without heart failure at baseline who participated in the Health ABC (Health, Aging and Body Composition) study. Measures of intramuscular and intermuscular fat in the thigh were determined by CT, and the participants were followed for an average of 12 years.
During the follow-up period, there were 485 incident heart failure events. Higher sex-specific tertiles of intramuscular and intermuscular fat were each associated with heart failure risk.
After multivariable adjustment for age, sex, race, education, blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, current smoking, prevalent coronary disease, and creatinine, higher intramuscular fat, but not intermuscular fat, was significantly associated with higher risk for heart failure.
Individuals in the highest tertile of intramuscular fat had a 34% increased risk of developing heart failure, compared with those in the lowest tertile. This finding was independent of other cardiometabolic risk factors, measures of adiposity including body mass index and percent fat, muscle strength, and muscle mass.
The association was slightly attenuated when adjusted for inflammatory markers, suggesting that inflammation may be a contributor.
The association between higher intramuscular fat and heart failure appeared specific to higher risk of incident heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, but not with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
The researchers noted that skeletal muscle is a pivotal endocrine organ in addition to the role it plays in the production of mechanical power.
They pointed out that there are differences in the biology of intermuscular and intramuscular fat deposition, and that excess intramuscular fat deposition is a result of dysregulated lipid metabolism and is associated with insulin resistance (a known risk factor for the development of heart failure), inflammation, and muscle wasting conditions.
They concluded that, in patients with heart failure, alterations in skeletal muscle function are most likely affected by multiple contributors, including inflammation, oxidative stress, and neurohormonal factors. “As these factors are also implicated in the pathogenesis of heart failure, intramuscular fat deposition may indicate a biological milieu that increases the risk of heart failure.”
New approaches to reduce heart failure risk?
In an accompanying editorial, Salvatore Carbone, PhD, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the findings of the study are “exceptionally novel,” providing novel evidence that noncardiac body composition compartments, particularly intramuscular adipose tissue, can predict the risk for heart failure in a diverse population of older adults.
He called for further research to understand the mechanisms involved and to assess if this risk factor can be effectively modified to reduce the risk of developing heart failure.
Dr. Carbone reported that intramuscular adipose tissue can be influenced by dietary fat intake and can be worsened by accumulation of saturated fatty acids, which also contribute to insulin resistance.
He noted that saturated fatty acid–induced insulin resistance in the skeletal muscle appears to be mediated by proinflammatory pathways within the skeletal muscle itself, which can be reversed by monounsaturated fatty acids, like oleic acid, that can be found in the largest amount in food like olive oil, canola oil, and avocados, among others.
He added that sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors, drugs used in the treatment of diabetes that have also been shown to prevent heart failure in individuals at risk, can also improve the composition of intramuscular adipose tissue by reducing its content of saturated fatty acids and increase the content of monosaturated fatty acids.
The study results suggest that the quality of intramuscular adipose tissue might also play an important role and could be targeted by therapeutic strategies, he commented.
Dr. Carbone concluded that “studies testing novel modalities of exercise training, intentional weight loss, diet quality improvements with and without weight loss (i.e., increase of dietary monounsaturated fatty acids, such as oleic acid), as well as pharmacological anti-inflammatory strategies should be encouraged in this population to test whether the reduction in intramuscular adipose tissue or improvements of its quality can ultimately reduce the risk for heart failure in this population.”
This research was supported by the National Institute on Aging and the National Institute of Nursing Research. Dr. Huynh and Dr. Carbone disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: HEART FAILURE
Alabama cites Roe decision in call to ban transgender health care
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Alabama urged a federal court on June 28 to drop its block on the state’s ban on gender-affirming care for transgender youth, citing the Supreme Court’s recent decision to overturn Roe v. Wade.
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the high court ruled that abortion isn’t protected under the 14th Amendment because it’s not “deeply rooted” in the nation’s history, which he noted could be said about access to gender-affirming care as well, according to Axios.
“No one – adult or child – has a right to transitioning treatments that is deeply rooted in our Nation’s history and tradition,” he wrote in a court document.
“The State can thus regulate or prohibit those interventions for children, even if an adult wants the drugs for his child,” he wrote.
In May, a federal judge blocked part of Alabama’s Senate Bill 184, which makes it a felony for someone to “engage in or cause” certain types of medical care for transgender youths. The law, which was put in place in April, allows for criminal prosecution against doctors, parents, guardians, and anyone else who provides care to a minor. The penalties could result in up to 10 years in prison and up to $15,000 in fines.
At that time, U.S. District Judge Liles Burke issued an injunction to stop Alabama from enforcing the law and allow challenges, including one filed by the Department of Justice. Mr. Burke said the state provided “no credible evidence to show that transitioning medications are ‘experimental.’ ”
“While Defendants offer some evidence that transitioning medications pose certain risks, the uncontradicted record evidence is that at least twenty-two major medical associations in the United States endorse transitioning medications as well-established, evidence-based treatments for gender dysphoria in minors,” he wrote in the ruling.
Medical organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychological Association, and American Medical Association have urged governors to oppose legislation this year that would restrict gender-affirming medical care, saying that such laws could have negative effects on the mental health of transgender youths.
But on June 28, Mr. Marshall focused on the Constitution and what he believes the recent overturn of Roe implies.
“Just as the parental relationship does not unlock a Due Process right allowing parents to obtain medical marijuana or abortions for their children, neither does it unlock a right to transitioning treatments,” he wrote.
“The Constitution reserves to the State – not courts or medical interest groups – the authority to determine that these sterilizing interventions are too dangerous for minors,” he said.
Since the Supreme Court overturned Roe, people have expressed concerns that lawsuits could now target several rights that are protected under the 14th Amendment, including same-sex relationships, marriage equality, and access to contraceptives.
Justice Clarence Thomas, who wrote a concurring opinion to the majority decision, said the Supreme Court, “in future cases” should reconsider “substantive due process precedents” under previous landmark cases such as Griswold v. Connecticut, Lawrence v. Texas, and Obergefell v. Hodges.
At the same time, Justice Brett Kavanaugh, who also wrote a concurring opinion, said the decision to overturn Roe was only focused on abortion, saying it “does not mean the overruling of those precedents, and does not threaten or cast doubt on those precedents.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Mobile devices ‘addictive by design’: Obesity is one of many health effects
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM ENDO 2022
In the Grand Canyon, norovirus gives new meaning to ‘leave no trace’
Ain’t gastroenteritis grand?
The Grand Canyon is perhaps America’s greatest natural wonder. The mile-deep gorge of epic proportions, carved over eons by the Colorado River, elicits superlatives of the highest order from those seeing it for the first time. In the past few months, though, visitors to the Grand Canyon have been experiencing a rather more unpleasant sort of reaction: Involuntary bowel evacuation.
Since April, more than 150 river rafters and backcountry campers have fallen ill with bouts of acute gastroenteritis, likely caused by norovirus. Hey, a viral outbreak and our old friend SARS-CoV-2 isn’t involved! Hopefully it won’t get jealous. Whatever the culprit is, however, it got everywhere, as clusters of illness have popped up in unconnected parts of the park and some hikers have been restricted to a smaller portion of the park to avoid further disease spread. The majority of cases occurred in May, so it’s hoped that the outbreak is dying down, but the park remains on alert.
Now, acute gastroenteritis is certainly an unpleasant disease, but it isn’t typically a life-threatening one. There are, however, a couple of unique factors complicating this outbreak. For one, the Grand Canyon is in Arizona (duh), which can get rather hot in the summer months. Expelling waste from both ends becomes rather more dangerous when the thermometer reads over a hundred degrees, and there have been reports of multiple helicopter rescues.
That’s pretty bad, but in a way, they’re the lucky ones. How can we explain this … see, when you visit the Grand Canyon, you’re expected to follow the general rules of Leave No Trace. That means several things, but essentially, if you bring it in, you have to bring it out. Yes, that includes the various consequences of an acute gastroenteritis attack.
Forget spooky campfire stories and hungry wildlife lurking in the night, because true horror is scraping your friend’s diarrhea off the walls of the Grand Canyon into a plastic bag and stuffing it into your backpack. Probably not the sublime one-on-one Grand Canyon experience that people are expecting.
Give us a pee! ... for stem cell retrieval
Getting cells for regenerative stem cell treatment has traditionally been painful and difficult – usually they are retrieved by surgical means from bone marrow or fat tissue – but there may be an easier way.
Just pee in a cup.
Apparently, human urine contains stem cells with the potential to be used for regenerative effects. The magic ingredient? The enzyme telomerase, which “is essential for the self-renewal and potential of different types of stem cells” and is related to longevity, according to researchers at Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
They looked into how regenerative telomerase activity is for various capabilities beyond chromosomal stability, and whether these stem cells can become other kinds of cells for optimal tissue repair. Turns out they could, acting as a “distinct subpopulation” that has the ability not only to grow cells but also to morph into other cells, they said in a written statement.
Safety is also an issue. “Being able to use a patient’s own stem cells for therapy is considered advantageous because they do not induce immune responses or rejection,” said Anthony Atala, MD, a coauthor of the study published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
So less risk, easier retrieval, and great regenerative results. If this takes off, the other methods of retrieval could get flushed down the toilet.
Politicians playing the long game, literally
Before we get started with actual information, here’s a joke about politicians:
What do you call a lawyer with an IQ of 100? Your Honor.
What do you call a lawyer with an IQ of 50? Senator.
Politics is a dirty business, no doubt, so why do people do it? Is it for the prestige? Seems like everyone hates politicians, so it’s probably not that. Is it their selfless concern for the well-being of others? Probably not that either. Is it for the money? Most members of Congress have more corporate sponsors than a NASCAR driver, but we’re going to pass on that one as well.
Once again, science gives us the real answer: Longevity. Politicians live longer than the rest of us, and that longevity gap is getting wider.
Investigators looked at data from 11 industrialized countries, some of it going back to 1817, and found that politicians in the United States can expect to live about 7 years longer than the national average. The difference is around 3 years in Switzerland, 4.5 years in Germany, and 6 years in France.
“For almost all countries, politicians had similar rates of mortality to the general population in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Throughout the 20th century, differences in mortality rates widened significantly across all countries, so that politicians had an increasing survival advantage over the general population,” they said in a written statement.
Income inequality could be a factor, but the longevity gains made by politicians, which started before the 1940s, predate the rise of their earnings relative to the rest of the population, which didn’t really get going until the 1980s, the investigators noted.
Whatever the reason, we have this closing thought regarding our long-lived lawmakers: What’s the difference between a politician and a snail? One is a slimy pest that leaves a trail everywhere. The other is a snail.
Land of the free, home of obesity
In the United States, it seems, people are becoming more comfortable with obesity. TikTok and Instagram trends often try to show the world that all sizes are beautiful. There’s also the growing popularity of the dad bod.
America, it has been said, is the land of the free. We love our freedom, and we value our individualism. If an obese man orders three meals from McDonald’s just for himself, no one is going to stop him. Many Americans also have more access to the food they want at any given time, even while they are moving around a lot less because of their sedentary lifestyles.
According to a recent study cited by the New York Post, however, America is not the only country battling obesity. Egypt and Mexico, for example, also have men with higher BMIs who cherish their individualism and the right to eat what they want, Plamen Akaliyski, PhD, of University Carlos III of Madrid, and associates, said in Social Science & Medicine.
Women are not as likely to think the same way. “Men in particular think, ‘I’m an individual, don’t tell me what to do. I’m going to eat what I want,’ ” bariatric surgeon George A. Fielding, MD, said in the Post article. Dr. Fielding also noted that women are three times more likely than men to seek bariatric surgery.
Dr. Akaliyski and associates found that Asian countries such as Japan, Singapore, and South Korea – countries that value thrift, discipline, self control, and delaying gratification – have lower rates of obesity.
So yes, we can go to the drive through of a fast food restaurant whenever we want and order whatever we want, but can doesn’t always mean should.
Ain’t gastroenteritis grand?
The Grand Canyon is perhaps America’s greatest natural wonder. The mile-deep gorge of epic proportions, carved over eons by the Colorado River, elicits superlatives of the highest order from those seeing it for the first time. In the past few months, though, visitors to the Grand Canyon have been experiencing a rather more unpleasant sort of reaction: Involuntary bowel evacuation.
Since April, more than 150 river rafters and backcountry campers have fallen ill with bouts of acute gastroenteritis, likely caused by norovirus. Hey, a viral outbreak and our old friend SARS-CoV-2 isn’t involved! Hopefully it won’t get jealous. Whatever the culprit is, however, it got everywhere, as clusters of illness have popped up in unconnected parts of the park and some hikers have been restricted to a smaller portion of the park to avoid further disease spread. The majority of cases occurred in May, so it’s hoped that the outbreak is dying down, but the park remains on alert.
Now, acute gastroenteritis is certainly an unpleasant disease, but it isn’t typically a life-threatening one. There are, however, a couple of unique factors complicating this outbreak. For one, the Grand Canyon is in Arizona (duh), which can get rather hot in the summer months. Expelling waste from both ends becomes rather more dangerous when the thermometer reads over a hundred degrees, and there have been reports of multiple helicopter rescues.
That’s pretty bad, but in a way, they’re the lucky ones. How can we explain this … see, when you visit the Grand Canyon, you’re expected to follow the general rules of Leave No Trace. That means several things, but essentially, if you bring it in, you have to bring it out. Yes, that includes the various consequences of an acute gastroenteritis attack.
Forget spooky campfire stories and hungry wildlife lurking in the night, because true horror is scraping your friend’s diarrhea off the walls of the Grand Canyon into a plastic bag and stuffing it into your backpack. Probably not the sublime one-on-one Grand Canyon experience that people are expecting.
Give us a pee! ... for stem cell retrieval
Getting cells for regenerative stem cell treatment has traditionally been painful and difficult – usually they are retrieved by surgical means from bone marrow or fat tissue – but there may be an easier way.
Just pee in a cup.
Apparently, human urine contains stem cells with the potential to be used for regenerative effects. The magic ingredient? The enzyme telomerase, which “is essential for the self-renewal and potential of different types of stem cells” and is related to longevity, according to researchers at Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
They looked into how regenerative telomerase activity is for various capabilities beyond chromosomal stability, and whether these stem cells can become other kinds of cells for optimal tissue repair. Turns out they could, acting as a “distinct subpopulation” that has the ability not only to grow cells but also to morph into other cells, they said in a written statement.
Safety is also an issue. “Being able to use a patient’s own stem cells for therapy is considered advantageous because they do not induce immune responses or rejection,” said Anthony Atala, MD, a coauthor of the study published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
So less risk, easier retrieval, and great regenerative results. If this takes off, the other methods of retrieval could get flushed down the toilet.
Politicians playing the long game, literally
Before we get started with actual information, here’s a joke about politicians:
What do you call a lawyer with an IQ of 100? Your Honor.
What do you call a lawyer with an IQ of 50? Senator.
Politics is a dirty business, no doubt, so why do people do it? Is it for the prestige? Seems like everyone hates politicians, so it’s probably not that. Is it their selfless concern for the well-being of others? Probably not that either. Is it for the money? Most members of Congress have more corporate sponsors than a NASCAR driver, but we’re going to pass on that one as well.
Once again, science gives us the real answer: Longevity. Politicians live longer than the rest of us, and that longevity gap is getting wider.
Investigators looked at data from 11 industrialized countries, some of it going back to 1817, and found that politicians in the United States can expect to live about 7 years longer than the national average. The difference is around 3 years in Switzerland, 4.5 years in Germany, and 6 years in France.
“For almost all countries, politicians had similar rates of mortality to the general population in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Throughout the 20th century, differences in mortality rates widened significantly across all countries, so that politicians had an increasing survival advantage over the general population,” they said in a written statement.
Income inequality could be a factor, but the longevity gains made by politicians, which started before the 1940s, predate the rise of their earnings relative to the rest of the population, which didn’t really get going until the 1980s, the investigators noted.
Whatever the reason, we have this closing thought regarding our long-lived lawmakers: What’s the difference between a politician and a snail? One is a slimy pest that leaves a trail everywhere. The other is a snail.
Land of the free, home of obesity
In the United States, it seems, people are becoming more comfortable with obesity. TikTok and Instagram trends often try to show the world that all sizes are beautiful. There’s also the growing popularity of the dad bod.
America, it has been said, is the land of the free. We love our freedom, and we value our individualism. If an obese man orders three meals from McDonald’s just for himself, no one is going to stop him. Many Americans also have more access to the food they want at any given time, even while they are moving around a lot less because of their sedentary lifestyles.
According to a recent study cited by the New York Post, however, America is not the only country battling obesity. Egypt and Mexico, for example, also have men with higher BMIs who cherish their individualism and the right to eat what they want, Plamen Akaliyski, PhD, of University Carlos III of Madrid, and associates, said in Social Science & Medicine.
Women are not as likely to think the same way. “Men in particular think, ‘I’m an individual, don’t tell me what to do. I’m going to eat what I want,’ ” bariatric surgeon George A. Fielding, MD, said in the Post article. Dr. Fielding also noted that women are three times more likely than men to seek bariatric surgery.
Dr. Akaliyski and associates found that Asian countries such as Japan, Singapore, and South Korea – countries that value thrift, discipline, self control, and delaying gratification – have lower rates of obesity.
So yes, we can go to the drive through of a fast food restaurant whenever we want and order whatever we want, but can doesn’t always mean should.
Ain’t gastroenteritis grand?
The Grand Canyon is perhaps America’s greatest natural wonder. The mile-deep gorge of epic proportions, carved over eons by the Colorado River, elicits superlatives of the highest order from those seeing it for the first time. In the past few months, though, visitors to the Grand Canyon have been experiencing a rather more unpleasant sort of reaction: Involuntary bowel evacuation.
Since April, more than 150 river rafters and backcountry campers have fallen ill with bouts of acute gastroenteritis, likely caused by norovirus. Hey, a viral outbreak and our old friend SARS-CoV-2 isn’t involved! Hopefully it won’t get jealous. Whatever the culprit is, however, it got everywhere, as clusters of illness have popped up in unconnected parts of the park and some hikers have been restricted to a smaller portion of the park to avoid further disease spread. The majority of cases occurred in May, so it’s hoped that the outbreak is dying down, but the park remains on alert.
Now, acute gastroenteritis is certainly an unpleasant disease, but it isn’t typically a life-threatening one. There are, however, a couple of unique factors complicating this outbreak. For one, the Grand Canyon is in Arizona (duh), which can get rather hot in the summer months. Expelling waste from both ends becomes rather more dangerous when the thermometer reads over a hundred degrees, and there have been reports of multiple helicopter rescues.
That’s pretty bad, but in a way, they’re the lucky ones. How can we explain this … see, when you visit the Grand Canyon, you’re expected to follow the general rules of Leave No Trace. That means several things, but essentially, if you bring it in, you have to bring it out. Yes, that includes the various consequences of an acute gastroenteritis attack.
Forget spooky campfire stories and hungry wildlife lurking in the night, because true horror is scraping your friend’s diarrhea off the walls of the Grand Canyon into a plastic bag and stuffing it into your backpack. Probably not the sublime one-on-one Grand Canyon experience that people are expecting.
Give us a pee! ... for stem cell retrieval
Getting cells for regenerative stem cell treatment has traditionally been painful and difficult – usually they are retrieved by surgical means from bone marrow or fat tissue – but there may be an easier way.
Just pee in a cup.
Apparently, human urine contains stem cells with the potential to be used for regenerative effects. The magic ingredient? The enzyme telomerase, which “is essential for the self-renewal and potential of different types of stem cells” and is related to longevity, according to researchers at Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
They looked into how regenerative telomerase activity is for various capabilities beyond chromosomal stability, and whether these stem cells can become other kinds of cells for optimal tissue repair. Turns out they could, acting as a “distinct subpopulation” that has the ability not only to grow cells but also to morph into other cells, they said in a written statement.
Safety is also an issue. “Being able to use a patient’s own stem cells for therapy is considered advantageous because they do not induce immune responses or rejection,” said Anthony Atala, MD, a coauthor of the study published in Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
So less risk, easier retrieval, and great regenerative results. If this takes off, the other methods of retrieval could get flushed down the toilet.
Politicians playing the long game, literally
Before we get started with actual information, here’s a joke about politicians:
What do you call a lawyer with an IQ of 100? Your Honor.
What do you call a lawyer with an IQ of 50? Senator.
Politics is a dirty business, no doubt, so why do people do it? Is it for the prestige? Seems like everyone hates politicians, so it’s probably not that. Is it their selfless concern for the well-being of others? Probably not that either. Is it for the money? Most members of Congress have more corporate sponsors than a NASCAR driver, but we’re going to pass on that one as well.
Once again, science gives us the real answer: Longevity. Politicians live longer than the rest of us, and that longevity gap is getting wider.
Investigators looked at data from 11 industrialized countries, some of it going back to 1817, and found that politicians in the United States can expect to live about 7 years longer than the national average. The difference is around 3 years in Switzerland, 4.5 years in Germany, and 6 years in France.
“For almost all countries, politicians had similar rates of mortality to the general population in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Throughout the 20th century, differences in mortality rates widened significantly across all countries, so that politicians had an increasing survival advantage over the general population,” they said in a written statement.
Income inequality could be a factor, but the longevity gains made by politicians, which started before the 1940s, predate the rise of their earnings relative to the rest of the population, which didn’t really get going until the 1980s, the investigators noted.
Whatever the reason, we have this closing thought regarding our long-lived lawmakers: What’s the difference between a politician and a snail? One is a slimy pest that leaves a trail everywhere. The other is a snail.
Land of the free, home of obesity
In the United States, it seems, people are becoming more comfortable with obesity. TikTok and Instagram trends often try to show the world that all sizes are beautiful. There’s also the growing popularity of the dad bod.
America, it has been said, is the land of the free. We love our freedom, and we value our individualism. If an obese man orders three meals from McDonald’s just for himself, no one is going to stop him. Many Americans also have more access to the food they want at any given time, even while they are moving around a lot less because of their sedentary lifestyles.
According to a recent study cited by the New York Post, however, America is not the only country battling obesity. Egypt and Mexico, for example, also have men with higher BMIs who cherish their individualism and the right to eat what they want, Plamen Akaliyski, PhD, of University Carlos III of Madrid, and associates, said in Social Science & Medicine.
Women are not as likely to think the same way. “Men in particular think, ‘I’m an individual, don’t tell me what to do. I’m going to eat what I want,’ ” bariatric surgeon George A. Fielding, MD, said in the Post article. Dr. Fielding also noted that women are three times more likely than men to seek bariatric surgery.
Dr. Akaliyski and associates found that Asian countries such as Japan, Singapore, and South Korea – countries that value thrift, discipline, self control, and delaying gratification – have lower rates of obesity.
So yes, we can go to the drive through of a fast food restaurant whenever we want and order whatever we want, but can doesn’t always mean should.
Food insecurity drives poor glycemic control
People with diabetes who had a poor-quality diet and food insecurity were significantly more likely to have poor glycemic and cholesterol control than were those with a healthier diet and food security, based on data from a national study of more than 2,000 individuals.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a high-quality diet for people with diabetes (PWD) to achieve treatment goals; however, roughly 18% of PWD in the United States are food insecure and/or have a poor-quality diet, Sarah S. Casagrande, PhD, of DLH Corporation, Silver Spring, Md., and colleagues wrote in a poster presented at the annual scientific sessions of the ADA in New Orleans.
To examine the impact of food insecurity and diet quality on diabetes and lipid management, the researchers reviewed data from 2,075 adults with self-reported diabetes who completed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys between 2013 and 2018.
Diet quality was divided into quartiles based on the 2015 Healthy Eating Index. Food insecurity was assessed using a standard 10-item questionnaire including questions about running out of food and not being able to afford more, reducing meal sizes, eating less or not at all, and going hungry because of lack of money for food.
The logistic regression analysis controlled for factors including sociodemographics, health care use, smoking, diabetes medications, blood pressure medication use, cholesterol medication use, and body mass index.
Overall, 17.6% of the participants were food insecure and had a low-quality diet, 14.2% were food insecure with a high-quality diet, 33.1% were food secure with a low-quality diet, and 35.2% were food secure with a high-quality diet.
PWD in the food insecure/low-quality diet group were significantly more likely to be younger, non-Hispanic black or Hispanic, and uninsured compared to those in the food secure/high-quality diet group (P < .001 for all).
When the researchers examined glycemic control, they found that PWD in the food insecurity/low-quality diet groups were significantly more likely than were those with food security/high-quality diets to have hemoglobin A1c of at least 7.0% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.79), low HDL cholesterol (aOR, 1.69), and high triglycerides (aOR, 3.26).
PWD with food insecurity but a high-quality diet also were significantly more likely than were those with food security and a high quality diet to have A1c of at least 7.0% (aOR, 1.69), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.83), and high triglycerides (aOR, 2.44). PWD with food security but a low-quality diet were significantly more likely than was the food security/high-quality diet group to have A1c of at least 7% (aOR, 1.55).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and inability to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the researchers wrote.
However, the results were strengthened by the large, nationally representative sample and the inclusion of multiple clinical outcomes in the patient assessment, they said.
The results suggest that food insecurity had a significant impact on both glycemic control and cholesterol management independent of diet quality, the researchers noted. Based on these findings, health care providers treating PWD may wish to assess their patients’ food security status, and “interventions could address disparities in food security,” they concluded.
Food insecurity a growing problem
“With more communities being pushed into state of war, drought, and famine globally, it is important to track impact of food insecurity and low quality food on common medical conditions like diabetes in our vulnerable communities,” Romesh K. Khardori, MD, professor of medicine: endocrinology, and metabolism at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview.
Dr. Khardori, who was not involved in the study, said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
“Type of food, amount of food, and quality of food have been stressed in diabetes management for more than 100 years,” he said. “Organizations charged with recommendations, such as the ADA and American Dietetic Association, have regularly updated their recommendations,” he noted. “It was not surprising, therefore, to find food insecurity and low quality tied to poor glycemic control.”
The take-home message for clinicians is to consider the availability and quality of food that their patients are exposed to when evaluating barriers to proper glycemic control, Dr. Khardori emphasized.
However, additional research is needed to explore whether the prescription of a sufficient amount of good quality food would alleviate the adverse impact seen in the current study, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Khardori had no financial conflicts to disclose.
People with diabetes who had a poor-quality diet and food insecurity were significantly more likely to have poor glycemic and cholesterol control than were those with a healthier diet and food security, based on data from a national study of more than 2,000 individuals.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a high-quality diet for people with diabetes (PWD) to achieve treatment goals; however, roughly 18% of PWD in the United States are food insecure and/or have a poor-quality diet, Sarah S. Casagrande, PhD, of DLH Corporation, Silver Spring, Md., and colleagues wrote in a poster presented at the annual scientific sessions of the ADA in New Orleans.
To examine the impact of food insecurity and diet quality on diabetes and lipid management, the researchers reviewed data from 2,075 adults with self-reported diabetes who completed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys between 2013 and 2018.
Diet quality was divided into quartiles based on the 2015 Healthy Eating Index. Food insecurity was assessed using a standard 10-item questionnaire including questions about running out of food and not being able to afford more, reducing meal sizes, eating less or not at all, and going hungry because of lack of money for food.
The logistic regression analysis controlled for factors including sociodemographics, health care use, smoking, diabetes medications, blood pressure medication use, cholesterol medication use, and body mass index.
Overall, 17.6% of the participants were food insecure and had a low-quality diet, 14.2% were food insecure with a high-quality diet, 33.1% were food secure with a low-quality diet, and 35.2% were food secure with a high-quality diet.
PWD in the food insecure/low-quality diet group were significantly more likely to be younger, non-Hispanic black or Hispanic, and uninsured compared to those in the food secure/high-quality diet group (P < .001 for all).
When the researchers examined glycemic control, they found that PWD in the food insecurity/low-quality diet groups were significantly more likely than were those with food security/high-quality diets to have hemoglobin A1c of at least 7.0% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.79), low HDL cholesterol (aOR, 1.69), and high triglycerides (aOR, 3.26).
PWD with food insecurity but a high-quality diet also were significantly more likely than were those with food security and a high quality diet to have A1c of at least 7.0% (aOR, 1.69), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.83), and high triglycerides (aOR, 2.44). PWD with food security but a low-quality diet were significantly more likely than was the food security/high-quality diet group to have A1c of at least 7% (aOR, 1.55).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and inability to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the researchers wrote.
However, the results were strengthened by the large, nationally representative sample and the inclusion of multiple clinical outcomes in the patient assessment, they said.
The results suggest that food insecurity had a significant impact on both glycemic control and cholesterol management independent of diet quality, the researchers noted. Based on these findings, health care providers treating PWD may wish to assess their patients’ food security status, and “interventions could address disparities in food security,” they concluded.
Food insecurity a growing problem
“With more communities being pushed into state of war, drought, and famine globally, it is important to track impact of food insecurity and low quality food on common medical conditions like diabetes in our vulnerable communities,” Romesh K. Khardori, MD, professor of medicine: endocrinology, and metabolism at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview.
Dr. Khardori, who was not involved in the study, said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
“Type of food, amount of food, and quality of food have been stressed in diabetes management for more than 100 years,” he said. “Organizations charged with recommendations, such as the ADA and American Dietetic Association, have regularly updated their recommendations,” he noted. “It was not surprising, therefore, to find food insecurity and low quality tied to poor glycemic control.”
The take-home message for clinicians is to consider the availability and quality of food that their patients are exposed to when evaluating barriers to proper glycemic control, Dr. Khardori emphasized.
However, additional research is needed to explore whether the prescription of a sufficient amount of good quality food would alleviate the adverse impact seen in the current study, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Khardori had no financial conflicts to disclose.
People with diabetes who had a poor-quality diet and food insecurity were significantly more likely to have poor glycemic and cholesterol control than were those with a healthier diet and food security, based on data from a national study of more than 2,000 individuals.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a high-quality diet for people with diabetes (PWD) to achieve treatment goals; however, roughly 18% of PWD in the United States are food insecure and/or have a poor-quality diet, Sarah S. Casagrande, PhD, of DLH Corporation, Silver Spring, Md., and colleagues wrote in a poster presented at the annual scientific sessions of the ADA in New Orleans.
To examine the impact of food insecurity and diet quality on diabetes and lipid management, the researchers reviewed data from 2,075 adults with self-reported diabetes who completed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys between 2013 and 2018.
Diet quality was divided into quartiles based on the 2015 Healthy Eating Index. Food insecurity was assessed using a standard 10-item questionnaire including questions about running out of food and not being able to afford more, reducing meal sizes, eating less or not at all, and going hungry because of lack of money for food.
The logistic regression analysis controlled for factors including sociodemographics, health care use, smoking, diabetes medications, blood pressure medication use, cholesterol medication use, and body mass index.
Overall, 17.6% of the participants were food insecure and had a low-quality diet, 14.2% were food insecure with a high-quality diet, 33.1% were food secure with a low-quality diet, and 35.2% were food secure with a high-quality diet.
PWD in the food insecure/low-quality diet group were significantly more likely to be younger, non-Hispanic black or Hispanic, and uninsured compared to those in the food secure/high-quality diet group (P < .001 for all).
When the researchers examined glycemic control, they found that PWD in the food insecurity/low-quality diet groups were significantly more likely than were those with food security/high-quality diets to have hemoglobin A1c of at least 7.0% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.79), low HDL cholesterol (aOR, 1.69), and high triglycerides (aOR, 3.26).
PWD with food insecurity but a high-quality diet also were significantly more likely than were those with food security and a high quality diet to have A1c of at least 7.0% (aOR, 1.69), A1c of at least 8.0% (aOR, 1.83), and high triglycerides (aOR, 2.44). PWD with food security but a low-quality diet were significantly more likely than was the food security/high-quality diet group to have A1c of at least 7% (aOR, 1.55).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and inability to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the researchers wrote.
However, the results were strengthened by the large, nationally representative sample and the inclusion of multiple clinical outcomes in the patient assessment, they said.
The results suggest that food insecurity had a significant impact on both glycemic control and cholesterol management independent of diet quality, the researchers noted. Based on these findings, health care providers treating PWD may wish to assess their patients’ food security status, and “interventions could address disparities in food security,” they concluded.
Food insecurity a growing problem
“With more communities being pushed into state of war, drought, and famine globally, it is important to track impact of food insecurity and low quality food on common medical conditions like diabetes in our vulnerable communities,” Romesh K. Khardori, MD, professor of medicine: endocrinology, and metabolism at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview.
Dr. Khardori, who was not involved in the study, said he was not surprised by the current study findings.
“Type of food, amount of food, and quality of food have been stressed in diabetes management for more than 100 years,” he said. “Organizations charged with recommendations, such as the ADA and American Dietetic Association, have regularly updated their recommendations,” he noted. “It was not surprising, therefore, to find food insecurity and low quality tied to poor glycemic control.”
The take-home message for clinicians is to consider the availability and quality of food that their patients are exposed to when evaluating barriers to proper glycemic control, Dr. Khardori emphasized.
However, additional research is needed to explore whether the prescription of a sufficient amount of good quality food would alleviate the adverse impact seen in the current study, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The researchers and Dr. Khardori had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ADA 2022
ACC/AHA issue clinical lexicon for complications of COVID-19
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have jointly issued a comprehensive set of data standards to help clarify definitions of the cardiovascular (CV) and non-CV complications of COVID-19.
It’s the work of the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Data Standards and has been endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions.
There is increased importance to understanding the acute and long-term impact of COVID-19 on CV health, the writing group notes. Until now, however, there has not been “clarity or consensus” on definitions of CV conditions related to COVID-19, with different diagnostic terminologies being used for overlapping conditions, such as “myocardial injury,” “myocarditis,” “type Il myocardial infarction,” “stress cardiomyopathy,” and “inflammatory cardiomyopathy,” they point out.
“We, as a research community, did some things right and some things wrong surrounding the COVID pandemic,” Sandeep Das, MD, MPH, vice chair of the writing group, noted in an interview with this news organization.
“The things that we really did right is that everybody responded with enthusiasm, kind of all hands on deck with a massive crisis response, and that was fantastic,” Dr. Das said.
“However, because of the need to hurry, we didn’t structure and organize in the way that we typically would for something that was sort of a slow burn kind of problem rather than an emergency. One of the consequences of that was fragmentation of how things are collected, reported, et cetera, and that leads to confusion,” he added.
The report was published simultaneously June 23 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
A necessary but not glamorous project
The new data standards for COVID-19 will help standardize definitions and set the framework to capture and better understand how COVID-19 affects CV health.
“It wasn’t exactly a glamorous-type project but, at the same time, it’s super necessary to kind of get everybody on the same page and working together,” Dr. Das said.
Broad agreement on common vocabulary and definitions will help with efforts to pool or compare data from electronic health records, clinical registries, administrative datasets, and other databases, and determine whether these data apply to clinical practice and research endeavors, the writing group says.
They considered data elements relevant to the full range of care provided to COVID-19 patients in all care settings. Among the key items included in the document are:
- Case definitions for confirmed, probable, and suspected acute COVID-19, as well as postacute sequelae of COVID-19.
- Definitions for acute CV complications related to COVID-19, including acute myocardial injury, heart failure, shock, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications, and .
- Data elements related to COVID-19 vaccination status, comorbidities, and preexisting CV conditions.
- Definitions for postacute CV sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection and long-term CV complications of COVID-19.
- Data elements for CV mortality during acute COVID-19.
- Data elements for non-CV complications to help document severity of illness and other competing diagnoses and complications that might affect CV outcomes.
- A list of symptoms and signs related to COVID-19 and CV complications.
- Data elements for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and CV conditions.
- A discussion of advanced therapies, including , extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and end-of-life management strategies.
These data standards will be useful for researchers, registry developers, and clinicians, and they are proposed as a framework for ICD-10 code development of COVID-19–related CV conditions, the writing group says.
The standards are also of “great importance” to patients, clinicians, investigators, scientists, administrators, public health officials, policymakers, and payers, the group says.
Dr. Das said that, although there is no formal plan in place to update the document, he could see sections that might be refined.
“For example, there’s a nice long list of all the various variants, and unfortunately, I suspect that that is going to change and evolve over time,” Dr. Das told this news organization.
“We tried very hard not to include things like specifying specific treatments so we didn’t get proscriptive. We wanted to make it descriptive, so hopefully it will stand the test of time pretty well,” he added.
This research had no commercial funding. The writing group has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have jointly issued a comprehensive set of data standards to help clarify definitions of the cardiovascular (CV) and non-CV complications of COVID-19.
It’s the work of the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Data Standards and has been endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions.
There is increased importance to understanding the acute and long-term impact of COVID-19 on CV health, the writing group notes. Until now, however, there has not been “clarity or consensus” on definitions of CV conditions related to COVID-19, with different diagnostic terminologies being used for overlapping conditions, such as “myocardial injury,” “myocarditis,” “type Il myocardial infarction,” “stress cardiomyopathy,” and “inflammatory cardiomyopathy,” they point out.
“We, as a research community, did some things right and some things wrong surrounding the COVID pandemic,” Sandeep Das, MD, MPH, vice chair of the writing group, noted in an interview with this news organization.
“The things that we really did right is that everybody responded with enthusiasm, kind of all hands on deck with a massive crisis response, and that was fantastic,” Dr. Das said.
“However, because of the need to hurry, we didn’t structure and organize in the way that we typically would for something that was sort of a slow burn kind of problem rather than an emergency. One of the consequences of that was fragmentation of how things are collected, reported, et cetera, and that leads to confusion,” he added.
The report was published simultaneously June 23 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
A necessary but not glamorous project
The new data standards for COVID-19 will help standardize definitions and set the framework to capture and better understand how COVID-19 affects CV health.
“It wasn’t exactly a glamorous-type project but, at the same time, it’s super necessary to kind of get everybody on the same page and working together,” Dr. Das said.
Broad agreement on common vocabulary and definitions will help with efforts to pool or compare data from electronic health records, clinical registries, administrative datasets, and other databases, and determine whether these data apply to clinical practice and research endeavors, the writing group says.
They considered data elements relevant to the full range of care provided to COVID-19 patients in all care settings. Among the key items included in the document are:
- Case definitions for confirmed, probable, and suspected acute COVID-19, as well as postacute sequelae of COVID-19.
- Definitions for acute CV complications related to COVID-19, including acute myocardial injury, heart failure, shock, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications, and .
- Data elements related to COVID-19 vaccination status, comorbidities, and preexisting CV conditions.
- Definitions for postacute CV sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection and long-term CV complications of COVID-19.
- Data elements for CV mortality during acute COVID-19.
- Data elements for non-CV complications to help document severity of illness and other competing diagnoses and complications that might affect CV outcomes.
- A list of symptoms and signs related to COVID-19 and CV complications.
- Data elements for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and CV conditions.
- A discussion of advanced therapies, including , extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and end-of-life management strategies.
These data standards will be useful for researchers, registry developers, and clinicians, and they are proposed as a framework for ICD-10 code development of COVID-19–related CV conditions, the writing group says.
The standards are also of “great importance” to patients, clinicians, investigators, scientists, administrators, public health officials, policymakers, and payers, the group says.
Dr. Das said that, although there is no formal plan in place to update the document, he could see sections that might be refined.
“For example, there’s a nice long list of all the various variants, and unfortunately, I suspect that that is going to change and evolve over time,” Dr. Das told this news organization.
“We tried very hard not to include things like specifying specific treatments so we didn’t get proscriptive. We wanted to make it descriptive, so hopefully it will stand the test of time pretty well,” he added.
This research had no commercial funding. The writing group has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have jointly issued a comprehensive set of data standards to help clarify definitions of the cardiovascular (CV) and non-CV complications of COVID-19.
It’s the work of the ACC/AHA Task Force on Clinical Data Standards and has been endorsed by the Heart Failure Society of America and Society for Cardiac Angiography and Interventions.
There is increased importance to understanding the acute and long-term impact of COVID-19 on CV health, the writing group notes. Until now, however, there has not been “clarity or consensus” on definitions of CV conditions related to COVID-19, with different diagnostic terminologies being used for overlapping conditions, such as “myocardial injury,” “myocarditis,” “type Il myocardial infarction,” “stress cardiomyopathy,” and “inflammatory cardiomyopathy,” they point out.
“We, as a research community, did some things right and some things wrong surrounding the COVID pandemic,” Sandeep Das, MD, MPH, vice chair of the writing group, noted in an interview with this news organization.
“The things that we really did right is that everybody responded with enthusiasm, kind of all hands on deck with a massive crisis response, and that was fantastic,” Dr. Das said.
“However, because of the need to hurry, we didn’t structure and organize in the way that we typically would for something that was sort of a slow burn kind of problem rather than an emergency. One of the consequences of that was fragmentation of how things are collected, reported, et cetera, and that leads to confusion,” he added.
The report was published simultaneously June 23 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
A necessary but not glamorous project
The new data standards for COVID-19 will help standardize definitions and set the framework to capture and better understand how COVID-19 affects CV health.
“It wasn’t exactly a glamorous-type project but, at the same time, it’s super necessary to kind of get everybody on the same page and working together,” Dr. Das said.
Broad agreement on common vocabulary and definitions will help with efforts to pool or compare data from electronic health records, clinical registries, administrative datasets, and other databases, and determine whether these data apply to clinical practice and research endeavors, the writing group says.
They considered data elements relevant to the full range of care provided to COVID-19 patients in all care settings. Among the key items included in the document are:
- Case definitions for confirmed, probable, and suspected acute COVID-19, as well as postacute sequelae of COVID-19.
- Definitions for acute CV complications related to COVID-19, including acute myocardial injury, heart failure, shock, arrhythmia, thromboembolic complications, and .
- Data elements related to COVID-19 vaccination status, comorbidities, and preexisting CV conditions.
- Definitions for postacute CV sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection and long-term CV complications of COVID-19.
- Data elements for CV mortality during acute COVID-19.
- Data elements for non-CV complications to help document severity of illness and other competing diagnoses and complications that might affect CV outcomes.
- A list of symptoms and signs related to COVID-19 and CV complications.
- Data elements for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and CV conditions.
- A discussion of advanced therapies, including , extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and end-of-life management strategies.
These data standards will be useful for researchers, registry developers, and clinicians, and they are proposed as a framework for ICD-10 code development of COVID-19–related CV conditions, the writing group says.
The standards are also of “great importance” to patients, clinicians, investigators, scientists, administrators, public health officials, policymakers, and payers, the group says.
Dr. Das said that, although there is no formal plan in place to update the document, he could see sections that might be refined.
“For example, there’s a nice long list of all the various variants, and unfortunately, I suspect that that is going to change and evolve over time,” Dr. Das told this news organization.
“We tried very hard not to include things like specifying specific treatments so we didn’t get proscriptive. We wanted to make it descriptive, so hopefully it will stand the test of time pretty well,” he added.
This research had no commercial funding. The writing group has no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-carb, high-fat diet improves A1c, reduces liver fat
LONDON – A low-carbohydrate, high-fat (LCHF) diet reduced the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and despite no calorie restriction, participants with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes lost 5.8% of their body weight, according to a randomized controlled study.
“Based on these results, the LCHF diet may be recommended to people with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes,” said Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who presented the data at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“Basically, if you have fat in your liver, you will benefit from eating fat,” she said.
The LCHF diet was compared with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet more typically followed for these conditions. The low-fat diet was also found to reduce the progression of NAFLD, but to a lesser extent than the LCHF diet.
Dr. Dalby Hansen called their study one of the most extensive investigations of the LCHF diet in patients with type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease.
“Combining this [reduction in NAFLD score] with the huge weight loss, the lower HbA1c [blood sugar], the lowering of blood pressure in women, the rise in HDL levels, and reduction in triglycerides – all in all, this diet is very promising,” she said.
Stephen Harrison, MD, visiting professor, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, medical director of Pinnacle Clinical Research and president of Summit Clinical Research, San Antonio, commended Dr. Dalby Hansen on her methodology, which included before-and-after liver biopsies. “It’s a heinous effort to do paired liver biopsies in a lifestyle modification trial. That’s huge.”
“This study tells me that the way we manage patients doesn’t change – it is still lifestyle modification,” said Dr. Harrison, who was not involved with the study. “It’s eat less [rather] than more. It’s exercise and try to lose weight. In the long term, we give patients benefit, and we show that the disease has improved, and we offer something that means they can maintain a healthy life.”
He added that the relatively small and short trial was informative.
“They improved the NAFLD activity score [NAS],” he said. “I don’t know by how much. There was no change in fibrosis, but we wouldn’t expect this at 6 months.”
“It’s provocative work, and it gives us healthy information about how we can help manage our patients from a lifestyle perspective,” he concluded.
‘Do not lose weight. Eat until you are full’
In the study, 110 participants with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD, aged 18-78 years, were allocated to the LCHF diet, and 55 were allocated to the low-fat diet for 6 months.
The researchers performed liver biopsies at baseline and 6 months, which were blinded for scoring.
Participants had ongoing dietitian consultations, with follow-up visits at 3 and 6 months. Compliance was reported continuously through an online food diary platform.
The primary endpoint was change in glycemic control as measured by A1c level over 6 months. The secondary endpoints comprised the proportion of participants with changes in the NAS of at least 2 points over 6 months. Both these measures were compared between the two dietary groups.
The two groups were matched at baseline, with a mean age of 55-57 years, 58% were women, 89% with metabolic syndrome, and a mean BMI 34 kg/m2.
In baseline liver disease, F1 level fibrosis was the most common (58%), followed by hepatic steatosis (S1, 47%; S2, 32%), with a median NAS of 3, and 19% had nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The special thing about these diets was that participants were told to “not lose weight, but eat until you are full,” remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Those on the LCHF diet consumed an average of 61% energy from fat, 13% from carbohydrates, and 23% from protein, compared with the low-fat diet, which comprised an average of 29% energy from fat, 46% from carbohydrates, and 21% from protein.
“It’s a lot of fat and corresponds to a quarter of a liter of olive oil per day,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen. “They really had to change their mindset a lot, because it was difficult for them to start eating all these fats, especially since we’ve all been told for decades that it isn’t good. But we supported them, and they got into it.”
The LCHF diet was primarily comprised of unsaturated fats – for example, avocado, oil, nuts, and seeds – but also included saturated fats, such as cheese, cream, and high-fat dairy products. Participants were free to eat unsaturated and saturated fats, but Dr. Dalby Hansen and her team advised participants that “good” unsaturated fats were preferable.
“Also, this diet contained vegetables but no bread, no potatoes, no rice, and no pasta. It was low in carbohydrates, below 20%,” she added.
Improved glycemic control, reduced liver fat
“We found that the LCHF diet improved diabetes control, it reduced the fat in the liver, and, even though they’re eating as many calories as they were used to until they were full, they lost 5.8% of body weight,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen in reporting the results. Participants in the low-fat group lost only 1.8% of body weight.
However, mean calorie intake dropped in both groups, by –2.2% in the LCHF group and –8.7% in the low-fat group.
“The LCHF diet improved the primary outcome of A1c by 9.5 mmol/mol, which is similar to some anti-diabetic medications, such as DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors,” she said.
The low-fat group reduced A1c by 3.4 mmol/mol, resulting in a between-group difference of 6.1 mmol/mol.
“Upon follow-up of 3 months, after stopping the diets, on average the participants in both groups returned their HbA1c levels to nearly baseline values,” she said. Results were adjusted for weight loss and baseline values.
Both diets also improved the NAS. The proportion of participants who improved their NAS score by 2 or more points was 22% in the LCHF group versus 17% in the low-fat group (P = 0.58). Additionally, in the LCHF group, 70% of participants improved their score by 1 or more points, compared with 49% in the low-fat group and fewer in the LCHF group experienced a worsening of their score (1% vs. 23%, respectively).
One participant on LCHF had high triglycerides of 12 mmol/L after 3 months. Overall, the low-density lipoprotein increased marginally by 0.2 mmol per liter in the high-fat group, said Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Dr. Dalby Hansen noted some limitations. The findings might not be applicable in more severe NAFLD, dietary assessment relied on self-reporting, no food was provided, and participants had to cook themselves. It was also an open-label study because of the nature of the intervention.
Some hope for more sustainable dieting
Many diets are difficult to adhere to, remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen. “We thought this [diet] might be easier to comply with in the longer term, and we hope that these results might provide patients with more options.”
She added that most people who started the diet adapted and complied with it. “However, it might not be for everyone, but I think we can say that if people try, and it fits into their lives, then they go for it.”
However, “it is not about going out and eating whatever fat and how much of it you want. It’s important that you cut the carbohydrates too,” she said. “With this approach, we really saw amazing results.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen added that having various diets available, including the LCHF one, meant that as clinicians they could empower patients to take control of their metabolic health.
“We can ask them directly, ‘What would fit into their life?’” she said. “We know that one size does not fit at all, and I believe that if we could engage patients more, then they can take control of their own situation.”
Asked whether these findings were enough to change guidelines, Zobair Younossi, MD, professor and chairman, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., remarked that it was the sugar at work here.
“Dietary fat – it’s not the same as fat in the liver, and this diet has more to do with the sugar levels,” he said.
“I’m always reluctant to take results from a short-term study without long-term follow-up,” Dr. Younossi said. “I want to know will patients live longer, and long-term data are needed for this. Until I have that strong evidence that outcomes are going to change, or at least some sign that the outcome is going to change, it is too early to change any guidelines.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrison reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Younossi reports the following financial relationships: research funds and/or consultant to Abbott, Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – A low-carbohydrate, high-fat (LCHF) diet reduced the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and despite no calorie restriction, participants with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes lost 5.8% of their body weight, according to a randomized controlled study.
“Based on these results, the LCHF diet may be recommended to people with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes,” said Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who presented the data at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“Basically, if you have fat in your liver, you will benefit from eating fat,” she said.
The LCHF diet was compared with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet more typically followed for these conditions. The low-fat diet was also found to reduce the progression of NAFLD, but to a lesser extent than the LCHF diet.
Dr. Dalby Hansen called their study one of the most extensive investigations of the LCHF diet in patients with type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease.
“Combining this [reduction in NAFLD score] with the huge weight loss, the lower HbA1c [blood sugar], the lowering of blood pressure in women, the rise in HDL levels, and reduction in triglycerides – all in all, this diet is very promising,” she said.
Stephen Harrison, MD, visiting professor, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, medical director of Pinnacle Clinical Research and president of Summit Clinical Research, San Antonio, commended Dr. Dalby Hansen on her methodology, which included before-and-after liver biopsies. “It’s a heinous effort to do paired liver biopsies in a lifestyle modification trial. That’s huge.”
“This study tells me that the way we manage patients doesn’t change – it is still lifestyle modification,” said Dr. Harrison, who was not involved with the study. “It’s eat less [rather] than more. It’s exercise and try to lose weight. In the long term, we give patients benefit, and we show that the disease has improved, and we offer something that means they can maintain a healthy life.”
He added that the relatively small and short trial was informative.
“They improved the NAFLD activity score [NAS],” he said. “I don’t know by how much. There was no change in fibrosis, but we wouldn’t expect this at 6 months.”
“It’s provocative work, and it gives us healthy information about how we can help manage our patients from a lifestyle perspective,” he concluded.
‘Do not lose weight. Eat until you are full’
In the study, 110 participants with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD, aged 18-78 years, were allocated to the LCHF diet, and 55 were allocated to the low-fat diet for 6 months.
The researchers performed liver biopsies at baseline and 6 months, which were blinded for scoring.
Participants had ongoing dietitian consultations, with follow-up visits at 3 and 6 months. Compliance was reported continuously through an online food diary platform.
The primary endpoint was change in glycemic control as measured by A1c level over 6 months. The secondary endpoints comprised the proportion of participants with changes in the NAS of at least 2 points over 6 months. Both these measures were compared between the two dietary groups.
The two groups were matched at baseline, with a mean age of 55-57 years, 58% were women, 89% with metabolic syndrome, and a mean BMI 34 kg/m2.
In baseline liver disease, F1 level fibrosis was the most common (58%), followed by hepatic steatosis (S1, 47%; S2, 32%), with a median NAS of 3, and 19% had nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The special thing about these diets was that participants were told to “not lose weight, but eat until you are full,” remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Those on the LCHF diet consumed an average of 61% energy from fat, 13% from carbohydrates, and 23% from protein, compared with the low-fat diet, which comprised an average of 29% energy from fat, 46% from carbohydrates, and 21% from protein.
“It’s a lot of fat and corresponds to a quarter of a liter of olive oil per day,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen. “They really had to change their mindset a lot, because it was difficult for them to start eating all these fats, especially since we’ve all been told for decades that it isn’t good. But we supported them, and they got into it.”
The LCHF diet was primarily comprised of unsaturated fats – for example, avocado, oil, nuts, and seeds – but also included saturated fats, such as cheese, cream, and high-fat dairy products. Participants were free to eat unsaturated and saturated fats, but Dr. Dalby Hansen and her team advised participants that “good” unsaturated fats were preferable.
“Also, this diet contained vegetables but no bread, no potatoes, no rice, and no pasta. It was low in carbohydrates, below 20%,” she added.
Improved glycemic control, reduced liver fat
“We found that the LCHF diet improved diabetes control, it reduced the fat in the liver, and, even though they’re eating as many calories as they were used to until they were full, they lost 5.8% of body weight,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen in reporting the results. Participants in the low-fat group lost only 1.8% of body weight.
However, mean calorie intake dropped in both groups, by –2.2% in the LCHF group and –8.7% in the low-fat group.
“The LCHF diet improved the primary outcome of A1c by 9.5 mmol/mol, which is similar to some anti-diabetic medications, such as DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors,” she said.
The low-fat group reduced A1c by 3.4 mmol/mol, resulting in a between-group difference of 6.1 mmol/mol.
“Upon follow-up of 3 months, after stopping the diets, on average the participants in both groups returned their HbA1c levels to nearly baseline values,” she said. Results were adjusted for weight loss and baseline values.
Both diets also improved the NAS. The proportion of participants who improved their NAS score by 2 or more points was 22% in the LCHF group versus 17% in the low-fat group (P = 0.58). Additionally, in the LCHF group, 70% of participants improved their score by 1 or more points, compared with 49% in the low-fat group and fewer in the LCHF group experienced a worsening of their score (1% vs. 23%, respectively).
One participant on LCHF had high triglycerides of 12 mmol/L after 3 months. Overall, the low-density lipoprotein increased marginally by 0.2 mmol per liter in the high-fat group, said Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Dr. Dalby Hansen noted some limitations. The findings might not be applicable in more severe NAFLD, dietary assessment relied on self-reporting, no food was provided, and participants had to cook themselves. It was also an open-label study because of the nature of the intervention.
Some hope for more sustainable dieting
Many diets are difficult to adhere to, remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen. “We thought this [diet] might be easier to comply with in the longer term, and we hope that these results might provide patients with more options.”
She added that most people who started the diet adapted and complied with it. “However, it might not be for everyone, but I think we can say that if people try, and it fits into their lives, then they go for it.”
However, “it is not about going out and eating whatever fat and how much of it you want. It’s important that you cut the carbohydrates too,” she said. “With this approach, we really saw amazing results.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen added that having various diets available, including the LCHF one, meant that as clinicians they could empower patients to take control of their metabolic health.
“We can ask them directly, ‘What would fit into their life?’” she said. “We know that one size does not fit at all, and I believe that if we could engage patients more, then they can take control of their own situation.”
Asked whether these findings were enough to change guidelines, Zobair Younossi, MD, professor and chairman, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., remarked that it was the sugar at work here.
“Dietary fat – it’s not the same as fat in the liver, and this diet has more to do with the sugar levels,” he said.
“I’m always reluctant to take results from a short-term study without long-term follow-up,” Dr. Younossi said. “I want to know will patients live longer, and long-term data are needed for this. Until I have that strong evidence that outcomes are going to change, or at least some sign that the outcome is going to change, it is too early to change any guidelines.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrison reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Younossi reports the following financial relationships: research funds and/or consultant to Abbott, Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – A low-carbohydrate, high-fat (LCHF) diet reduced the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and despite no calorie restriction, participants with both NAFLD and type 2 diabetes lost 5.8% of their body weight, according to a randomized controlled study.
“Based on these results, the LCHF diet may be recommended to people with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes,” said Camilla Dalby Hansen, MD, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark, who presented the data at the International Liver Congress (ILC) 2022.
“Basically, if you have fat in your liver, you will benefit from eating fat,” she said.
The LCHF diet was compared with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet more typically followed for these conditions. The low-fat diet was also found to reduce the progression of NAFLD, but to a lesser extent than the LCHF diet.
Dr. Dalby Hansen called their study one of the most extensive investigations of the LCHF diet in patients with type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease.
“Combining this [reduction in NAFLD score] with the huge weight loss, the lower HbA1c [blood sugar], the lowering of blood pressure in women, the rise in HDL levels, and reduction in triglycerides – all in all, this diet is very promising,” she said.
Stephen Harrison, MD, visiting professor, University of Oxford, United Kingdom, medical director of Pinnacle Clinical Research and president of Summit Clinical Research, San Antonio, commended Dr. Dalby Hansen on her methodology, which included before-and-after liver biopsies. “It’s a heinous effort to do paired liver biopsies in a lifestyle modification trial. That’s huge.”
“This study tells me that the way we manage patients doesn’t change – it is still lifestyle modification,” said Dr. Harrison, who was not involved with the study. “It’s eat less [rather] than more. It’s exercise and try to lose weight. In the long term, we give patients benefit, and we show that the disease has improved, and we offer something that means they can maintain a healthy life.”
He added that the relatively small and short trial was informative.
“They improved the NAFLD activity score [NAS],” he said. “I don’t know by how much. There was no change in fibrosis, but we wouldn’t expect this at 6 months.”
“It’s provocative work, and it gives us healthy information about how we can help manage our patients from a lifestyle perspective,” he concluded.
‘Do not lose weight. Eat until you are full’
In the study, 110 participants with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD, aged 18-78 years, were allocated to the LCHF diet, and 55 were allocated to the low-fat diet for 6 months.
The researchers performed liver biopsies at baseline and 6 months, which were blinded for scoring.
Participants had ongoing dietitian consultations, with follow-up visits at 3 and 6 months. Compliance was reported continuously through an online food diary platform.
The primary endpoint was change in glycemic control as measured by A1c level over 6 months. The secondary endpoints comprised the proportion of participants with changes in the NAS of at least 2 points over 6 months. Both these measures were compared between the two dietary groups.
The two groups were matched at baseline, with a mean age of 55-57 years, 58% were women, 89% with metabolic syndrome, and a mean BMI 34 kg/m2.
In baseline liver disease, F1 level fibrosis was the most common (58%), followed by hepatic steatosis (S1, 47%; S2, 32%), with a median NAS of 3, and 19% had nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The special thing about these diets was that participants were told to “not lose weight, but eat until you are full,” remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Those on the LCHF diet consumed an average of 61% energy from fat, 13% from carbohydrates, and 23% from protein, compared with the low-fat diet, which comprised an average of 29% energy from fat, 46% from carbohydrates, and 21% from protein.
“It’s a lot of fat and corresponds to a quarter of a liter of olive oil per day,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen. “They really had to change their mindset a lot, because it was difficult for them to start eating all these fats, especially since we’ve all been told for decades that it isn’t good. But we supported them, and they got into it.”
The LCHF diet was primarily comprised of unsaturated fats – for example, avocado, oil, nuts, and seeds – but also included saturated fats, such as cheese, cream, and high-fat dairy products. Participants were free to eat unsaturated and saturated fats, but Dr. Dalby Hansen and her team advised participants that “good” unsaturated fats were preferable.
“Also, this diet contained vegetables but no bread, no potatoes, no rice, and no pasta. It was low in carbohydrates, below 20%,” she added.
Improved glycemic control, reduced liver fat
“We found that the LCHF diet improved diabetes control, it reduced the fat in the liver, and, even though they’re eating as many calories as they were used to until they were full, they lost 5.8% of body weight,” said Dr. Dalby Hansen in reporting the results. Participants in the low-fat group lost only 1.8% of body weight.
However, mean calorie intake dropped in both groups, by –2.2% in the LCHF group and –8.7% in the low-fat group.
“The LCHF diet improved the primary outcome of A1c by 9.5 mmol/mol, which is similar to some anti-diabetic medications, such as DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors,” she said.
The low-fat group reduced A1c by 3.4 mmol/mol, resulting in a between-group difference of 6.1 mmol/mol.
“Upon follow-up of 3 months, after stopping the diets, on average the participants in both groups returned their HbA1c levels to nearly baseline values,” she said. Results were adjusted for weight loss and baseline values.
Both diets also improved the NAS. The proportion of participants who improved their NAS score by 2 or more points was 22% in the LCHF group versus 17% in the low-fat group (P = 0.58). Additionally, in the LCHF group, 70% of participants improved their score by 1 or more points, compared with 49% in the low-fat group and fewer in the LCHF group experienced a worsening of their score (1% vs. 23%, respectively).
One participant on LCHF had high triglycerides of 12 mmol/L after 3 months. Overall, the low-density lipoprotein increased marginally by 0.2 mmol per liter in the high-fat group, said Dr. Dalby Hansen.
Dr. Dalby Hansen noted some limitations. The findings might not be applicable in more severe NAFLD, dietary assessment relied on self-reporting, no food was provided, and participants had to cook themselves. It was also an open-label study because of the nature of the intervention.
Some hope for more sustainable dieting
Many diets are difficult to adhere to, remarked Dr. Dalby Hansen. “We thought this [diet] might be easier to comply with in the longer term, and we hope that these results might provide patients with more options.”
She added that most people who started the diet adapted and complied with it. “However, it might not be for everyone, but I think we can say that if people try, and it fits into their lives, then they go for it.”
However, “it is not about going out and eating whatever fat and how much of it you want. It’s important that you cut the carbohydrates too,” she said. “With this approach, we really saw amazing results.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen added that having various diets available, including the LCHF one, meant that as clinicians they could empower patients to take control of their metabolic health.
“We can ask them directly, ‘What would fit into their life?’” she said. “We know that one size does not fit at all, and I believe that if we could engage patients more, then they can take control of their own situation.”
Asked whether these findings were enough to change guidelines, Zobair Younossi, MD, professor and chairman, department of medicine, Inova Fairfax Medical Campus, Falls Church, Va., remarked that it was the sugar at work here.
“Dietary fat – it’s not the same as fat in the liver, and this diet has more to do with the sugar levels,” he said.
“I’m always reluctant to take results from a short-term study without long-term follow-up,” Dr. Younossi said. “I want to know will patients live longer, and long-term data are needed for this. Until I have that strong evidence that outcomes are going to change, or at least some sign that the outcome is going to change, it is too early to change any guidelines.”
Dr. Dalby Hansen reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Harrison reported financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Younossi reports the following financial relationships: research funds and/or consultant to Abbott, Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Echosens, Genfit, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Madrigal, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ILC 2022