User login
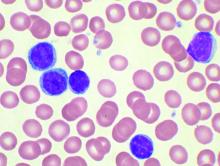
Venetoclax and obinutuzumab induces deep responses in CLL
The combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab provided high response rates and deep remissions regardless of cytogenetic risk factors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to recently reported results of a phase 1b study.
The regimen elicited high rates of undetectable minimal residual disease in peripheral blood and had an acceptable safety profile with manageable toxicities in the study reported in Blood, which included patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
“The deep remission rates we observed with venetoclax-obinutuzumab have not been reported with previously available CLL treatments, including FCR [fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab], which is currently considered the most efficacious regimen with limited-duration therapy,” wrote the investigators, led by Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute/Tennessee Oncology, Nashville.
Venetoclax-obinutuzumab combinations are meanwhile being tested in other studies – including the phase 3 CLL13 and CLL14 studies – which have enrolled previously untreated fit or unfit CLL patients, respectively.
“If the primary endpoints of these large-scale trials are met, venetoclax-obinutuzumab may become a new standard treatment option in [first-line] CLL, irrespective of clinical fitness,” Dr. Flinn and his colleagues wrote in their report.
The present phase 1b, dose-escalation study enrolled 32 patients who were previously untreated (median age, 63 years) and 46 patients who were relapsed or refractory to previous treatments (median age, 61 years).
Doses of venetoclax were escalated from 100 mg to 400 mg to determine its maximum tolerated dose when combined with obinutuzumab, the investigators wrote. Some patients received venetoclax first, while others received obinutuzumab first, for a total of 1 year of treatment.
The study confirmed favorable risk-benefit treatment used a dose of 400 mg venetoclax plus the standard dose of obinutuzumab, according to the researchers.
The overall best response rate was 95% for relapsed/refractory patients, including a 37% rate of complete response or complete response with incomplete marrow recovery. In previously untreated patients, the overall best response rate was 100%, including a 78% rate of complete responses by those criteria.
Undetectable minimal residual disease was observed in 64% of relapsed/refractory patients and 91% of previously untreated patients at 3 months after the last obinutuzumab dose, the investigators reported.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities in the study, no clinical tumor lysis syndrome, and no differences between the two schedules (venetoclax first or obinutuzumab first) in terms of adverse events, the investigators wrote.
Neutropenia was the most common serious (grade 3-4) adverse event, occurring in 58% of relapsed/refractory patients and 53% of patients treated in the first line. Grade 3-4 infections were seen in 29% and 13% of the relapsed/refractory and previously untreated patients, respectively.
There were no fatal infections among previously untreated patients, while three relapsed/refractory patients (7%) had fatal adverse events, including one case of acute respiratory failure in a patient with suspected Richter’s transformation, pneumonia in a patient with metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma, and another case of pneumonia occurring about 3 months after the last dose of venetoclax.
Genentech and AbbVie provided financial support for the study. Dr. Flinn reported receiving research funding for his institution from Genentech, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-01-896290.
The combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab provided high response rates and deep remissions regardless of cytogenetic risk factors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to recently reported results of a phase 1b study.
The regimen elicited high rates of undetectable minimal residual disease in peripheral blood and had an acceptable safety profile with manageable toxicities in the study reported in Blood, which included patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
“The deep remission rates we observed with venetoclax-obinutuzumab have not been reported with previously available CLL treatments, including FCR [fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab], which is currently considered the most efficacious regimen with limited-duration therapy,” wrote the investigators, led by Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute/Tennessee Oncology, Nashville.
Venetoclax-obinutuzumab combinations are meanwhile being tested in other studies – including the phase 3 CLL13 and CLL14 studies – which have enrolled previously untreated fit or unfit CLL patients, respectively.
“If the primary endpoints of these large-scale trials are met, venetoclax-obinutuzumab may become a new standard treatment option in [first-line] CLL, irrespective of clinical fitness,” Dr. Flinn and his colleagues wrote in their report.
The present phase 1b, dose-escalation study enrolled 32 patients who were previously untreated (median age, 63 years) and 46 patients who were relapsed or refractory to previous treatments (median age, 61 years).
Doses of venetoclax were escalated from 100 mg to 400 mg to determine its maximum tolerated dose when combined with obinutuzumab, the investigators wrote. Some patients received venetoclax first, while others received obinutuzumab first, for a total of 1 year of treatment.
The study confirmed favorable risk-benefit treatment used a dose of 400 mg venetoclax plus the standard dose of obinutuzumab, according to the researchers.
The overall best response rate was 95% for relapsed/refractory patients, including a 37% rate of complete response or complete response with incomplete marrow recovery. In previously untreated patients, the overall best response rate was 100%, including a 78% rate of complete responses by those criteria.
Undetectable minimal residual disease was observed in 64% of relapsed/refractory patients and 91% of previously untreated patients at 3 months after the last obinutuzumab dose, the investigators reported.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities in the study, no clinical tumor lysis syndrome, and no differences between the two schedules (venetoclax first or obinutuzumab first) in terms of adverse events, the investigators wrote.
Neutropenia was the most common serious (grade 3-4) adverse event, occurring in 58% of relapsed/refractory patients and 53% of patients treated in the first line. Grade 3-4 infections were seen in 29% and 13% of the relapsed/refractory and previously untreated patients, respectively.
There were no fatal infections among previously untreated patients, while three relapsed/refractory patients (7%) had fatal adverse events, including one case of acute respiratory failure in a patient with suspected Richter’s transformation, pneumonia in a patient with metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma, and another case of pneumonia occurring about 3 months after the last dose of venetoclax.
Genentech and AbbVie provided financial support for the study. Dr. Flinn reported receiving research funding for his institution from Genentech, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-01-896290.
The combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab provided high response rates and deep remissions regardless of cytogenetic risk factors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to recently reported results of a phase 1b study.
The regimen elicited high rates of undetectable minimal residual disease in peripheral blood and had an acceptable safety profile with manageable toxicities in the study reported in Blood, which included patients with previously untreated or relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
“The deep remission rates we observed with venetoclax-obinutuzumab have not been reported with previously available CLL treatments, including FCR [fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab], which is currently considered the most efficacious regimen with limited-duration therapy,” wrote the investigators, led by Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute/Tennessee Oncology, Nashville.
Venetoclax-obinutuzumab combinations are meanwhile being tested in other studies – including the phase 3 CLL13 and CLL14 studies – which have enrolled previously untreated fit or unfit CLL patients, respectively.
“If the primary endpoints of these large-scale trials are met, venetoclax-obinutuzumab may become a new standard treatment option in [first-line] CLL, irrespective of clinical fitness,” Dr. Flinn and his colleagues wrote in their report.
The present phase 1b, dose-escalation study enrolled 32 patients who were previously untreated (median age, 63 years) and 46 patients who were relapsed or refractory to previous treatments (median age, 61 years).
Doses of venetoclax were escalated from 100 mg to 400 mg to determine its maximum tolerated dose when combined with obinutuzumab, the investigators wrote. Some patients received venetoclax first, while others received obinutuzumab first, for a total of 1 year of treatment.
The study confirmed favorable risk-benefit treatment used a dose of 400 mg venetoclax plus the standard dose of obinutuzumab, according to the researchers.
The overall best response rate was 95% for relapsed/refractory patients, including a 37% rate of complete response or complete response with incomplete marrow recovery. In previously untreated patients, the overall best response rate was 100%, including a 78% rate of complete responses by those criteria.
Undetectable minimal residual disease was observed in 64% of relapsed/refractory patients and 91% of previously untreated patients at 3 months after the last obinutuzumab dose, the investigators reported.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities in the study, no clinical tumor lysis syndrome, and no differences between the two schedules (venetoclax first or obinutuzumab first) in terms of adverse events, the investigators wrote.
Neutropenia was the most common serious (grade 3-4) adverse event, occurring in 58% of relapsed/refractory patients and 53% of patients treated in the first line. Grade 3-4 infections were seen in 29% and 13% of the relapsed/refractory and previously untreated patients, respectively.
There were no fatal infections among previously untreated patients, while three relapsed/refractory patients (7%) had fatal adverse events, including one case of acute respiratory failure in a patient with suspected Richter’s transformation, pneumonia in a patient with metastatic squamous cell lung carcinoma, and another case of pneumonia occurring about 3 months after the last dose of venetoclax.
Genentech and AbbVie provided financial support for the study. Dr. Flinn reported receiving research funding for his institution from Genentech, AbbVie, and several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. Blood. 2019 Mar 12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-01-896290.
FROM BLOOD
Short telomeres predict poorer response to chemo in CLL
A telomere-length analysis tool appears to identify reliably which chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients will benefit from frontline chemotherapy, according to an analysis of 260 patients across two separate trials.
The analysis compared the use of high-throughput, single telomere–length analysis (HTSTELA) with other commonly used markers including beta-2 microglobulin, fluorescence-in-situ hybridization (FISH) cytogenetics, CD38 expression, ZAP70 expression, and IGHV mutation status. The researchers looked specifically at whether telomere length could predict response to frontline treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab (FCR)–based regimens.
“[T]elomere length is a powerful predictor of both [progression-free survival] and [overall survival] in patients treated with FCR-based therapies. In contrast, CD38 expression and beta-2 microglobulin expression were not predictive, and IGHV mutation status was only predictive of PFS (progression-free survival),” Kevin Norris, PhD, of Cardiff (Wales) University and his colleagues wrote in Leukemia.
Previous studies have shown that telomere-length analysis offers independent prognostic information in all stages of CLL. In the present study, the researchers used HTSTELA to analyze patient samples taken from two concurrent, phase 2 clinical trials of frontline FCR-based treatment – ARCTIC and ADMIRE.
The researchers divided the cohort based on a threshold of telomere dysfunction – the point at which the chromosome end-capping function is lost and there is genomic instability. Shorter telomeres are inside the fusogenic range (TL-IFR) and longer telomeres are outside fusogenic range (TL-OFR).
Patients with TL-IFR had significantly shorter PFS on FCR-based treatment (P less than .0001). They also had reduced overall survival (OS; P = .0002). In the same cohort of patients, IGHV mutation status was predictive of PFS (P = .0016), but it was not predictive for OS (P = .38), while CD38 and beta-2 microglobulin were not predictive of PFS or OS.
The researchers also looked at the value of telomere length in predicting outcomes among IGHV-mutated and -unmutated patients.
Patients with IGHV-mutated disease and TL-IFR had worse PFS and OS than did patients with TL-OFR. TL-IFR patients in this cohort were more likely to progress (hazard ratio, 4.35; P less than .0001) and more likely to die from their disease (HR, 3.81; P = .006).
“Although the number of IGHV-mutated patients with TL-IFR was relatively small (n = 16), our data suggests that telomere length can identify a subset of “bad risk” IGHV-mutated patients who do not respond well to FCR,” the researchers wrote.
Among IGHV unmutated patients, those with short telomeres had worse PFS (HR, 1.48; P = .08) and OS (HR, 2.18; P = .025) than did those with longer telomeres.
In multivariate modeling of all the potential markers, telomere length was the statistically significant dominant covariable for both PFS and OS.
The study was funded by a Bloodwise grant and the Wales Cancer Research Center. Dr. Norris and three coauthors reported that they are coinventors of patents relevant to the study and hold shares in a company set to provide telomere length testing.
SOURCE: Norris K et al. Leukemia. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0389-9.
A telomere-length analysis tool appears to identify reliably which chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients will benefit from frontline chemotherapy, according to an analysis of 260 patients across two separate trials.
The analysis compared the use of high-throughput, single telomere–length analysis (HTSTELA) with other commonly used markers including beta-2 microglobulin, fluorescence-in-situ hybridization (FISH) cytogenetics, CD38 expression, ZAP70 expression, and IGHV mutation status. The researchers looked specifically at whether telomere length could predict response to frontline treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab (FCR)–based regimens.
“[T]elomere length is a powerful predictor of both [progression-free survival] and [overall survival] in patients treated with FCR-based therapies. In contrast, CD38 expression and beta-2 microglobulin expression were not predictive, and IGHV mutation status was only predictive of PFS (progression-free survival),” Kevin Norris, PhD, of Cardiff (Wales) University and his colleagues wrote in Leukemia.
Previous studies have shown that telomere-length analysis offers independent prognostic information in all stages of CLL. In the present study, the researchers used HTSTELA to analyze patient samples taken from two concurrent, phase 2 clinical trials of frontline FCR-based treatment – ARCTIC and ADMIRE.
The researchers divided the cohort based on a threshold of telomere dysfunction – the point at which the chromosome end-capping function is lost and there is genomic instability. Shorter telomeres are inside the fusogenic range (TL-IFR) and longer telomeres are outside fusogenic range (TL-OFR).
Patients with TL-IFR had significantly shorter PFS on FCR-based treatment (P less than .0001). They also had reduced overall survival (OS; P = .0002). In the same cohort of patients, IGHV mutation status was predictive of PFS (P = .0016), but it was not predictive for OS (P = .38), while CD38 and beta-2 microglobulin were not predictive of PFS or OS.
The researchers also looked at the value of telomere length in predicting outcomes among IGHV-mutated and -unmutated patients.
Patients with IGHV-mutated disease and TL-IFR had worse PFS and OS than did patients with TL-OFR. TL-IFR patients in this cohort were more likely to progress (hazard ratio, 4.35; P less than .0001) and more likely to die from their disease (HR, 3.81; P = .006).
“Although the number of IGHV-mutated patients with TL-IFR was relatively small (n = 16), our data suggests that telomere length can identify a subset of “bad risk” IGHV-mutated patients who do not respond well to FCR,” the researchers wrote.
Among IGHV unmutated patients, those with short telomeres had worse PFS (HR, 1.48; P = .08) and OS (HR, 2.18; P = .025) than did those with longer telomeres.
In multivariate modeling of all the potential markers, telomere length was the statistically significant dominant covariable for both PFS and OS.
The study was funded by a Bloodwise grant and the Wales Cancer Research Center. Dr. Norris and three coauthors reported that they are coinventors of patents relevant to the study and hold shares in a company set to provide telomere length testing.
SOURCE: Norris K et al. Leukemia. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0389-9.
A telomere-length analysis tool appears to identify reliably which chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients will benefit from frontline chemotherapy, according to an analysis of 260 patients across two separate trials.
The analysis compared the use of high-throughput, single telomere–length analysis (HTSTELA) with other commonly used markers including beta-2 microglobulin, fluorescence-in-situ hybridization (FISH) cytogenetics, CD38 expression, ZAP70 expression, and IGHV mutation status. The researchers looked specifically at whether telomere length could predict response to frontline treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab (FCR)–based regimens.
“[T]elomere length is a powerful predictor of both [progression-free survival] and [overall survival] in patients treated with FCR-based therapies. In contrast, CD38 expression and beta-2 microglobulin expression were not predictive, and IGHV mutation status was only predictive of PFS (progression-free survival),” Kevin Norris, PhD, of Cardiff (Wales) University and his colleagues wrote in Leukemia.
Previous studies have shown that telomere-length analysis offers independent prognostic information in all stages of CLL. In the present study, the researchers used HTSTELA to analyze patient samples taken from two concurrent, phase 2 clinical trials of frontline FCR-based treatment – ARCTIC and ADMIRE.
The researchers divided the cohort based on a threshold of telomere dysfunction – the point at which the chromosome end-capping function is lost and there is genomic instability. Shorter telomeres are inside the fusogenic range (TL-IFR) and longer telomeres are outside fusogenic range (TL-OFR).
Patients with TL-IFR had significantly shorter PFS on FCR-based treatment (P less than .0001). They also had reduced overall survival (OS; P = .0002). In the same cohort of patients, IGHV mutation status was predictive of PFS (P = .0016), but it was not predictive for OS (P = .38), while CD38 and beta-2 microglobulin were not predictive of PFS or OS.
The researchers also looked at the value of telomere length in predicting outcomes among IGHV-mutated and -unmutated patients.
Patients with IGHV-mutated disease and TL-IFR had worse PFS and OS than did patients with TL-OFR. TL-IFR patients in this cohort were more likely to progress (hazard ratio, 4.35; P less than .0001) and more likely to die from their disease (HR, 3.81; P = .006).
“Although the number of IGHV-mutated patients with TL-IFR was relatively small (n = 16), our data suggests that telomere length can identify a subset of “bad risk” IGHV-mutated patients who do not respond well to FCR,” the researchers wrote.
Among IGHV unmutated patients, those with short telomeres had worse PFS (HR, 1.48; P = .08) and OS (HR, 2.18; P = .025) than did those with longer telomeres.
In multivariate modeling of all the potential markers, telomere length was the statistically significant dominant covariable for both PFS and OS.
The study was funded by a Bloodwise grant and the Wales Cancer Research Center. Dr. Norris and three coauthors reported that they are coinventors of patents relevant to the study and hold shares in a company set to provide telomere length testing.
SOURCE: Norris K et al. Leukemia. 2019 Jan 30. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0389-9.
FROM LEUKEMIA
Neurologists grappling with patients who embrace ‘stem cell tourism’
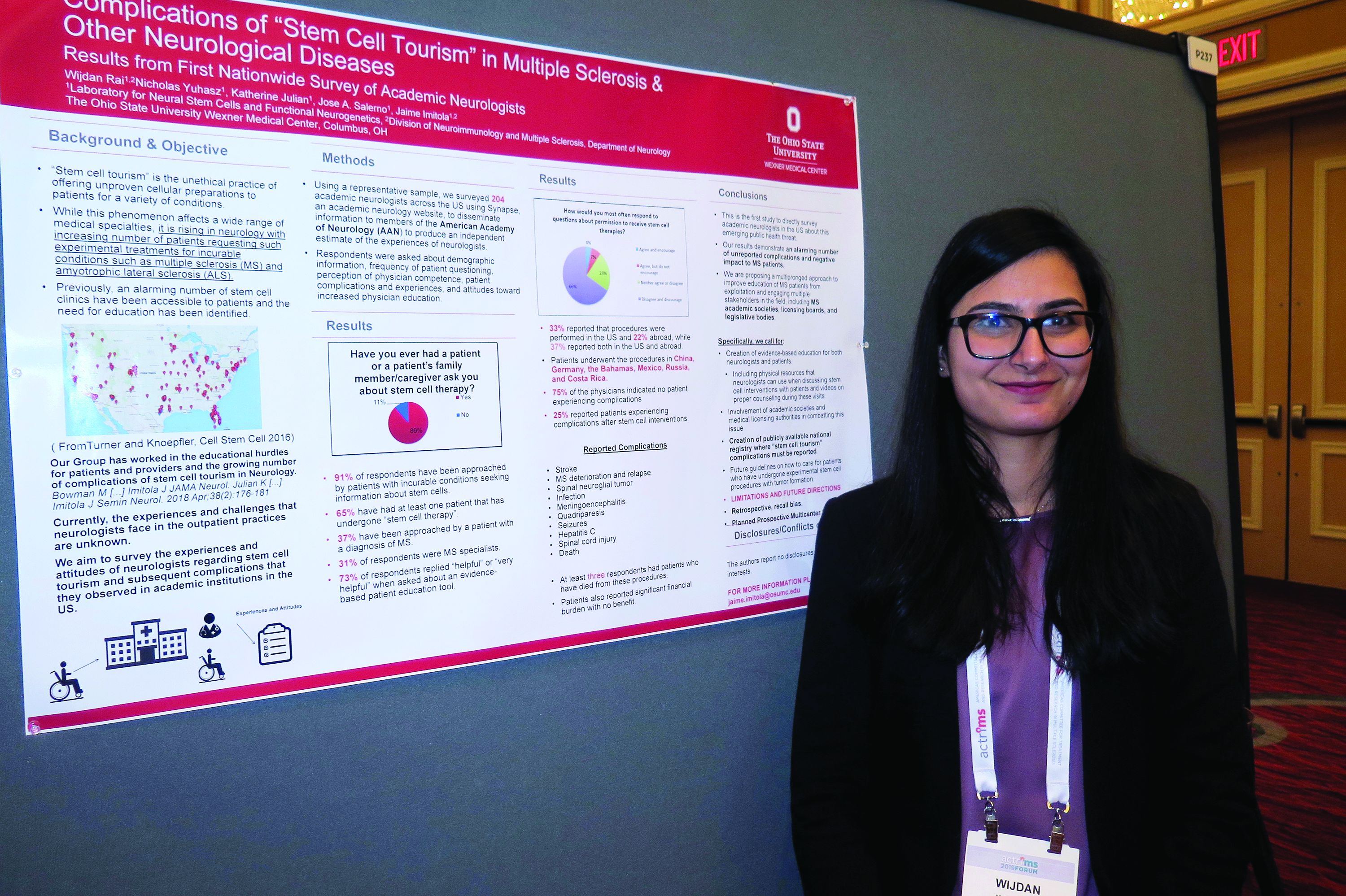
DALLAS – Stem cell tourism – the unethical practice of offering unproven cellular preparations to patients for a variety of conditions – is increasingly sought by patients with incurable conditions such as multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, results from a novel survey suggest.
In fact, most academic neurologists have been approached by patients with incurable conditions who ask them about stem cell therapy, while about two-thirds have had at least one patient who has undergone stem cell therapy.
“It’s really scary,” Wijdan Rai, MBBS, the study’s first author, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. “This is a more prevalent issue than we think, and the complication rates are higher than we think.”
According to the study’s senior author, Jaime Imitola, MD, who directs the Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Multidisciplinary Clinic and Translational Research Program at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, the results “call for the creation of a nationwide registry where neurologists can document adverse reactions to stem cell procedures and further support dedicated patient and neurologist education as we have proposed before” (See Semin Neurol. 2018; 38[2]:176-81 and JAMA Neurol. 2015;72[11]:1342-5).
In an effort to understand the experiences and attitudes of academic neurologists regarding stem cell tourism and patient-reported complications, the researchers developed a 25-question survey disseminated via Synapse, a web tool from the American Academy of Neurology. Respondents were asked about demographic information, frequency of patient questioning, perception of physician competence, patient complications and experiences, and attitudes toward increased physician education.
Dr. Rai, who is a senior neurology resident at the medical center, presented findings from 204 neurologist respondents, of whom 31% identified themselves as MS specialists. Nearly all respondents (91%) said they have been approached by patients with incurable conditions seeking information about stem cells (37% of whom had diagnosis of MS). In addition, 65% have had at least one patient that has undergone “stem cell therapy,” and 73% said it would be “helpful” or “very helpful” to have an evidence-based patient education tool on the topic. “Patients most often wanted general information,” Dr. Rai said. “However, 50% requested permission to undergo a stem cell procedure, and 31% approached their neurologist after the procedure.”
Survey respondents reported that 33% of the stem cell interventions were performed in the United States and 22% abroad, while 37% reported both in the U.S. and abroad. Patients underwent the procedures in China, Germany, the Bahamas, Mexico, Russia, and Costa Rica. Three-quarters of respondents (75%) indicated no patient experiencing complications from the stem cell interventions. However, 25% reported patients experiencing a variety of complications from the procedures, including strokes, meningoencephalitis, quadriparesis, MS deterioration, sepsis, hepatitis C, seizures, meningitis from intrathecal cell injections, infections, and spinal cord tumors. “At least three respondents had a patient who died as a direct complication from stem cell therapy,” Dr. Rai said.
In their poster, the researchers recommended a “multipronged approach to improve education of MS patients from exploitation and engaging multiple stakeholders in the field, including MS academic societies, licensing boards, and legislative bodies. Specifically, we call for creation of evidence-based education for both neurologists and patients, including physical resources that neurologists can use when discussing stem cell interventions with patients and videos on proper counseling during these visits.”
Colleagues from OSU’s Laboratory for Neural Stem Cells and Functional Neurogenetics contributed to this work. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Rai W et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2019, Poster 237.
DALLAS – Stem cell tourism – the unethical practice of offering unproven cellular preparations to patients for a variety of conditions – is increasingly sought by patients with incurable conditions such as multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, results from a novel survey suggest.
In fact, most academic neurologists have been approached by patients with incurable conditions who ask them about stem cell therapy, while about two-thirds have had at least one patient who has undergone stem cell therapy.
“It’s really scary,” Wijdan Rai, MBBS, the study’s first author, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. “This is a more prevalent issue than we think, and the complication rates are higher than we think.”
According to the study’s senior author, Jaime Imitola, MD, who directs the Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Multidisciplinary Clinic and Translational Research Program at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, the results “call for the creation of a nationwide registry where neurologists can document adverse reactions to stem cell procedures and further support dedicated patient and neurologist education as we have proposed before” (See Semin Neurol. 2018; 38[2]:176-81 and JAMA Neurol. 2015;72[11]:1342-5).
In an effort to understand the experiences and attitudes of academic neurologists regarding stem cell tourism and patient-reported complications, the researchers developed a 25-question survey disseminated via Synapse, a web tool from the American Academy of Neurology. Respondents were asked about demographic information, frequency of patient questioning, perception of physician competence, patient complications and experiences, and attitudes toward increased physician education.
Dr. Rai, who is a senior neurology resident at the medical center, presented findings from 204 neurologist respondents, of whom 31% identified themselves as MS specialists. Nearly all respondents (91%) said they have been approached by patients with incurable conditions seeking information about stem cells (37% of whom had diagnosis of MS). In addition, 65% have had at least one patient that has undergone “stem cell therapy,” and 73% said it would be “helpful” or “very helpful” to have an evidence-based patient education tool on the topic. “Patients most often wanted general information,” Dr. Rai said. “However, 50% requested permission to undergo a stem cell procedure, and 31% approached their neurologist after the procedure.”
Survey respondents reported that 33% of the stem cell interventions were performed in the United States and 22% abroad, while 37% reported both in the U.S. and abroad. Patients underwent the procedures in China, Germany, the Bahamas, Mexico, Russia, and Costa Rica. Three-quarters of respondents (75%) indicated no patient experiencing complications from the stem cell interventions. However, 25% reported patients experiencing a variety of complications from the procedures, including strokes, meningoencephalitis, quadriparesis, MS deterioration, sepsis, hepatitis C, seizures, meningitis from intrathecal cell injections, infections, and spinal cord tumors. “At least three respondents had a patient who died as a direct complication from stem cell therapy,” Dr. Rai said.
In their poster, the researchers recommended a “multipronged approach to improve education of MS patients from exploitation and engaging multiple stakeholders in the field, including MS academic societies, licensing boards, and legislative bodies. Specifically, we call for creation of evidence-based education for both neurologists and patients, including physical resources that neurologists can use when discussing stem cell interventions with patients and videos on proper counseling during these visits.”
Colleagues from OSU’s Laboratory for Neural Stem Cells and Functional Neurogenetics contributed to this work. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Rai W et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2019, Poster 237.
DALLAS – Stem cell tourism – the unethical practice of offering unproven cellular preparations to patients for a variety of conditions – is increasingly sought by patients with incurable conditions such as multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, results from a novel survey suggest.
In fact, most academic neurologists have been approached by patients with incurable conditions who ask them about stem cell therapy, while about two-thirds have had at least one patient who has undergone stem cell therapy.
“It’s really scary,” Wijdan Rai, MBBS, the study’s first author, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. “This is a more prevalent issue than we think, and the complication rates are higher than we think.”
According to the study’s senior author, Jaime Imitola, MD, who directs the Progressive Multiple Sclerosis Multidisciplinary Clinic and Translational Research Program at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, the results “call for the creation of a nationwide registry where neurologists can document adverse reactions to stem cell procedures and further support dedicated patient and neurologist education as we have proposed before” (See Semin Neurol. 2018; 38[2]:176-81 and JAMA Neurol. 2015;72[11]:1342-5).
In an effort to understand the experiences and attitudes of academic neurologists regarding stem cell tourism and patient-reported complications, the researchers developed a 25-question survey disseminated via Synapse, a web tool from the American Academy of Neurology. Respondents were asked about demographic information, frequency of patient questioning, perception of physician competence, patient complications and experiences, and attitudes toward increased physician education.
Dr. Rai, who is a senior neurology resident at the medical center, presented findings from 204 neurologist respondents, of whom 31% identified themselves as MS specialists. Nearly all respondents (91%) said they have been approached by patients with incurable conditions seeking information about stem cells (37% of whom had diagnosis of MS). In addition, 65% have had at least one patient that has undergone “stem cell therapy,” and 73% said it would be “helpful” or “very helpful” to have an evidence-based patient education tool on the topic. “Patients most often wanted general information,” Dr. Rai said. “However, 50% requested permission to undergo a stem cell procedure, and 31% approached their neurologist after the procedure.”
Survey respondents reported that 33% of the stem cell interventions were performed in the United States and 22% abroad, while 37% reported both in the U.S. and abroad. Patients underwent the procedures in China, Germany, the Bahamas, Mexico, Russia, and Costa Rica. Three-quarters of respondents (75%) indicated no patient experiencing complications from the stem cell interventions. However, 25% reported patients experiencing a variety of complications from the procedures, including strokes, meningoencephalitis, quadriparesis, MS deterioration, sepsis, hepatitis C, seizures, meningitis from intrathecal cell injections, infections, and spinal cord tumors. “At least three respondents had a patient who died as a direct complication from stem cell therapy,” Dr. Rai said.
In their poster, the researchers recommended a “multipronged approach to improve education of MS patients from exploitation and engaging multiple stakeholders in the field, including MS academic societies, licensing boards, and legislative bodies. Specifically, we call for creation of evidence-based education for both neurologists and patients, including physical resources that neurologists can use when discussing stem cell interventions with patients and videos on proper counseling during these visits.”
Colleagues from OSU’s Laboratory for Neural Stem Cells and Functional Neurogenetics contributed to this work. The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Rai W et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2019, Poster 237.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
Bendamustine-rituximab shines in frontline treatment of MCL, iNHL
Frontline treatment with patients in the BRIGHT study.
The bendamustine-rituximab (BR) regimen had superior 5-year progression-free survival rates, event-free survival, and duration of response, compared with either rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or rituximab with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). The follow-up study did not find a significant difference in overall survival, however.
While the cumulative evidence from BRIGHT and other studies supports BR as a first-line treatment option for patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the lack of an overall survival benefit indicates that the sequence of BR and R-CHOP or R-CVP “may not be critical,” Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute in Nashville, and his colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“[The] choice of regimen for the initial treatment of iNHL may be driven more by patient preferences regarding the differences in toxicity profile,” the researchers wrote.
Initial results from the BRIGHT study found that BR was noninferior to R-CHOP/R-CVP in terms of complete response rate (P = .0225 for noninferiority). The present study includes outcomes data for at least 5 years after completion of the study treatment.
For the entire study, the median follow-up was 65.0 months for patients in the BR group and 64.1 months for patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. Overall, the intention-to-treat population included 224 patients receiving BR and 223 patients receiving R-CHOP and R-CVP.
The median time to progression was not reached in either treatment group. The 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 65.5% in the BR group and 55.8% in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. The difference between these rates was significant, with a hazard ratio of 0.61 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.85; P = .0025).
Similarly, event-free survival was better in the BR group versus the R-CHOP/R-CVP group (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.46-0.84; P = .0020). Duration of response also favored the BR treatment regimen (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.47-0.92; P = .0134).
The long-term follow-up showed no significant difference in overall survival, with an HR of 1.15 for BR versus R-CHOP/R-CVP (95% CI, 0.72-1.84; P = .5461). Overall, there were 40 deaths in the BR treatment group and 32 deaths in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group.
Whether patients received maintenance rituximab did not affect the overall survival between groups. Similarly, there was no difference in overall survival by lymphoma type.
“Benefit from BR treatment did not translate to prolonged [overall survival], possibly because of the subsequent lines of therapy, including the use of BR in patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group,” the researchers wrote.
In terms of safety, the follow-up data showed no significant difference in early non–disease-related mortality between the treatment groups. However, the BRIGHT study showed higher rates of secondary malignancies in the BR group, compared with R-CHOP/R-CVP. That finding was not seen in the Study Group of Indolent Lymphomas Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (StiL NHL) 1 trial, and the authors could not provide an explanation for the increase in their research.
This study was supported by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Flinn reported receiving institutional research funding from Teva and receiving institutional research funding from or serving as a consultant to several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00605.
Frontline treatment with patients in the BRIGHT study.
The bendamustine-rituximab (BR) regimen had superior 5-year progression-free survival rates, event-free survival, and duration of response, compared with either rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or rituximab with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). The follow-up study did not find a significant difference in overall survival, however.
While the cumulative evidence from BRIGHT and other studies supports BR as a first-line treatment option for patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the lack of an overall survival benefit indicates that the sequence of BR and R-CHOP or R-CVP “may not be critical,” Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute in Nashville, and his colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“[The] choice of regimen for the initial treatment of iNHL may be driven more by patient preferences regarding the differences in toxicity profile,” the researchers wrote.
Initial results from the BRIGHT study found that BR was noninferior to R-CHOP/R-CVP in terms of complete response rate (P = .0225 for noninferiority). The present study includes outcomes data for at least 5 years after completion of the study treatment.
For the entire study, the median follow-up was 65.0 months for patients in the BR group and 64.1 months for patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. Overall, the intention-to-treat population included 224 patients receiving BR and 223 patients receiving R-CHOP and R-CVP.
The median time to progression was not reached in either treatment group. The 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 65.5% in the BR group and 55.8% in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. The difference between these rates was significant, with a hazard ratio of 0.61 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.85; P = .0025).
Similarly, event-free survival was better in the BR group versus the R-CHOP/R-CVP group (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.46-0.84; P = .0020). Duration of response also favored the BR treatment regimen (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.47-0.92; P = .0134).
The long-term follow-up showed no significant difference in overall survival, with an HR of 1.15 for BR versus R-CHOP/R-CVP (95% CI, 0.72-1.84; P = .5461). Overall, there were 40 deaths in the BR treatment group and 32 deaths in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group.
Whether patients received maintenance rituximab did not affect the overall survival between groups. Similarly, there was no difference in overall survival by lymphoma type.
“Benefit from BR treatment did not translate to prolonged [overall survival], possibly because of the subsequent lines of therapy, including the use of BR in patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group,” the researchers wrote.
In terms of safety, the follow-up data showed no significant difference in early non–disease-related mortality between the treatment groups. However, the BRIGHT study showed higher rates of secondary malignancies in the BR group, compared with R-CHOP/R-CVP. That finding was not seen in the Study Group of Indolent Lymphomas Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (StiL NHL) 1 trial, and the authors could not provide an explanation for the increase in their research.
This study was supported by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Flinn reported receiving institutional research funding from Teva and receiving institutional research funding from or serving as a consultant to several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00605.
Frontline treatment with patients in the BRIGHT study.
The bendamustine-rituximab (BR) regimen had superior 5-year progression-free survival rates, event-free survival, and duration of response, compared with either rituximab with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or rituximab with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CVP). The follow-up study did not find a significant difference in overall survival, however.
While the cumulative evidence from BRIGHT and other studies supports BR as a first-line treatment option for patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the lack of an overall survival benefit indicates that the sequence of BR and R-CHOP or R-CVP “may not be critical,” Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD, of Sarah Cannon Research Institute in Nashville, and his colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“[The] choice of regimen for the initial treatment of iNHL may be driven more by patient preferences regarding the differences in toxicity profile,” the researchers wrote.
Initial results from the BRIGHT study found that BR was noninferior to R-CHOP/R-CVP in terms of complete response rate (P = .0225 for noninferiority). The present study includes outcomes data for at least 5 years after completion of the study treatment.
For the entire study, the median follow-up was 65.0 months for patients in the BR group and 64.1 months for patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. Overall, the intention-to-treat population included 224 patients receiving BR and 223 patients receiving R-CHOP and R-CVP.
The median time to progression was not reached in either treatment group. The 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 65.5% in the BR group and 55.8% in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group. The difference between these rates was significant, with a hazard ratio of 0.61 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.85; P = .0025).
Similarly, event-free survival was better in the BR group versus the R-CHOP/R-CVP group (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.46-0.84; P = .0020). Duration of response also favored the BR treatment regimen (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.47-0.92; P = .0134).
The long-term follow-up showed no significant difference in overall survival, with an HR of 1.15 for BR versus R-CHOP/R-CVP (95% CI, 0.72-1.84; P = .5461). Overall, there were 40 deaths in the BR treatment group and 32 deaths in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group.
Whether patients received maintenance rituximab did not affect the overall survival between groups. Similarly, there was no difference in overall survival by lymphoma type.
“Benefit from BR treatment did not translate to prolonged [overall survival], possibly because of the subsequent lines of therapy, including the use of BR in patients in the R-CHOP/R-CVP group,” the researchers wrote.
In terms of safety, the follow-up data showed no significant difference in early non–disease-related mortality between the treatment groups. However, the BRIGHT study showed higher rates of secondary malignancies in the BR group, compared with R-CHOP/R-CVP. That finding was not seen in the Study Group of Indolent Lymphomas Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (StiL NHL) 1 trial, and the authors could not provide an explanation for the increase in their research.
This study was supported by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Flinn reported receiving institutional research funding from Teva and receiving institutional research funding from or serving as a consultant to several other companies.
SOURCE: Flinn IW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 27. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00605.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Analysis suggests ‘Burkitt-like lymphoma’ is a misnomer
They found that BLL-11q has a genomic and mutational profile more closely related to that of high grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) than typical Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
The researchers also found that BLL-11q has clinical, morphologic, and phenotypic features that are “more consistent” with HGBCL or DLBCL than with typical BL.
“These observations support a reconsideration of the ‘Burkitt-like’ term for these tumors,” Blanca Gonzalez-Farre, MD, of Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, and her colleagues wrote in Haematologica.
To reach this conclusion, the researchers performed copy number analysis and sequencing of B-cell lymphoma-related genes in 11 cases of BLL-11q.
The copy number analysis revealed that seven BLL-11q cases had the typical 11q gain/loss pattern, two had an 11q terminal deletion, one had two gains and two losses, and one had an 11q23.3-q25 copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity in addition to gain.
The BLL-11q cases also had frequent gains of 5q21.3-q32 and losses of 6q12.1-q21. However, they lacked the 1q gains observed in MYC-positive BL and alterations typically observed in germinal center B-cell like (GCB) DLBCL, such as gains in 2p16.1 and 7p.
Targeted sequencing of the BLL-11q cases revealed mutations typically observed in germinal center-derived lymphomas, including mutations in BTG2, DDX3X, ETS1, EP300, GNA13, CREBBP, KMT2C, EZH2, ARID1A, KMT2D, HIST1H1D, HIST1H2BC, and TMEM30A.
However, the BLL-11q cases lacked mutations in ID3, TCF3, and CCND3, which are typically observed in BL.
“In addition to the genetic differences, our BLL-11q differed clinically, morphologically, and phenotypically from conventional BL and instead showed features more consistent with HGBCL or DLBCL,” the researchers wrote.
Specifically, the BLL-11q patients were all younger than 40 years, with a median age of 15. Most presented with localized lymphadenopathy. And all had favorable treatment outcomes, remaining alive and free of disease at a median follow-up of 30 months.
All cases had a germinal center phenotype. They did not have the typical cytological features of BL, but they did have a high proliferative index, and some cases had a starry sky pattern.
The researchers said the BLL-11q cases were better classified as HGBCL not otherwise specified (n = 8), DLBCL (n = 2), and atypical BL (n = 1).
Considering these findings together, the team concluded that a more appropriate name for BLL-11q might be “aggressive B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration.”
This research was supported by Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and other organizations, as well as the government of Catalonia.
SOURCE: Gonzalez-Farre B et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207928.
They found that BLL-11q has a genomic and mutational profile more closely related to that of high grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) than typical Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
The researchers also found that BLL-11q has clinical, morphologic, and phenotypic features that are “more consistent” with HGBCL or DLBCL than with typical BL.
“These observations support a reconsideration of the ‘Burkitt-like’ term for these tumors,” Blanca Gonzalez-Farre, MD, of Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, and her colleagues wrote in Haematologica.
To reach this conclusion, the researchers performed copy number analysis and sequencing of B-cell lymphoma-related genes in 11 cases of BLL-11q.
The copy number analysis revealed that seven BLL-11q cases had the typical 11q gain/loss pattern, two had an 11q terminal deletion, one had two gains and two losses, and one had an 11q23.3-q25 copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity in addition to gain.
The BLL-11q cases also had frequent gains of 5q21.3-q32 and losses of 6q12.1-q21. However, they lacked the 1q gains observed in MYC-positive BL and alterations typically observed in germinal center B-cell like (GCB) DLBCL, such as gains in 2p16.1 and 7p.
Targeted sequencing of the BLL-11q cases revealed mutations typically observed in germinal center-derived lymphomas, including mutations in BTG2, DDX3X, ETS1, EP300, GNA13, CREBBP, KMT2C, EZH2, ARID1A, KMT2D, HIST1H1D, HIST1H2BC, and TMEM30A.
However, the BLL-11q cases lacked mutations in ID3, TCF3, and CCND3, which are typically observed in BL.
“In addition to the genetic differences, our BLL-11q differed clinically, morphologically, and phenotypically from conventional BL and instead showed features more consistent with HGBCL or DLBCL,” the researchers wrote.
Specifically, the BLL-11q patients were all younger than 40 years, with a median age of 15. Most presented with localized lymphadenopathy. And all had favorable treatment outcomes, remaining alive and free of disease at a median follow-up of 30 months.
All cases had a germinal center phenotype. They did not have the typical cytological features of BL, but they did have a high proliferative index, and some cases had a starry sky pattern.
The researchers said the BLL-11q cases were better classified as HGBCL not otherwise specified (n = 8), DLBCL (n = 2), and atypical BL (n = 1).
Considering these findings together, the team concluded that a more appropriate name for BLL-11q might be “aggressive B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration.”
This research was supported by Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and other organizations, as well as the government of Catalonia.
SOURCE: Gonzalez-Farre B et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207928.
They found that BLL-11q has a genomic and mutational profile more closely related to that of high grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) than typical Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
The researchers also found that BLL-11q has clinical, morphologic, and phenotypic features that are “more consistent” with HGBCL or DLBCL than with typical BL.
“These observations support a reconsideration of the ‘Burkitt-like’ term for these tumors,” Blanca Gonzalez-Farre, MD, of Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, and her colleagues wrote in Haematologica.
To reach this conclusion, the researchers performed copy number analysis and sequencing of B-cell lymphoma-related genes in 11 cases of BLL-11q.
The copy number analysis revealed that seven BLL-11q cases had the typical 11q gain/loss pattern, two had an 11q terminal deletion, one had two gains and two losses, and one had an 11q23.3-q25 copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity in addition to gain.
The BLL-11q cases also had frequent gains of 5q21.3-q32 and losses of 6q12.1-q21. However, they lacked the 1q gains observed in MYC-positive BL and alterations typically observed in germinal center B-cell like (GCB) DLBCL, such as gains in 2p16.1 and 7p.
Targeted sequencing of the BLL-11q cases revealed mutations typically observed in germinal center-derived lymphomas, including mutations in BTG2, DDX3X, ETS1, EP300, GNA13, CREBBP, KMT2C, EZH2, ARID1A, KMT2D, HIST1H1D, HIST1H2BC, and TMEM30A.
However, the BLL-11q cases lacked mutations in ID3, TCF3, and CCND3, which are typically observed in BL.
“In addition to the genetic differences, our BLL-11q differed clinically, morphologically, and phenotypically from conventional BL and instead showed features more consistent with HGBCL or DLBCL,” the researchers wrote.
Specifically, the BLL-11q patients were all younger than 40 years, with a median age of 15. Most presented with localized lymphadenopathy. And all had favorable treatment outcomes, remaining alive and free of disease at a median follow-up of 30 months.
All cases had a germinal center phenotype. They did not have the typical cytological features of BL, but they did have a high proliferative index, and some cases had a starry sky pattern.
The researchers said the BLL-11q cases were better classified as HGBCL not otherwise specified (n = 8), DLBCL (n = 2), and atypical BL (n = 1).
Considering these findings together, the team concluded that a more appropriate name for BLL-11q might be “aggressive B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberration.”
This research was supported by Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and other organizations, as well as the government of Catalonia.
SOURCE: Gonzalez-Farre B et al. Haematologica. 2019 Feb 7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.207928.
REPORTING FROM HAEMATOLOGICA
Gene expression signature reveals high-grade GCB DLBCL
New research suggests a gene expression signature can distinguish high-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) from other germinal center B-cell–like (GCB) DLBCLs.
Researchers identified GCB DLBCL patients with this 104-gene signature who had a “distinct mutational landscape” and inferior treatment outcomes. David W. Scott, MBChB, PhD, of the British Columbia Cancer Research Centre in Vancouver, and his colleagues described these patients in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The findings were published alongside a related editorial and a similar study from another group.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues began their study by analyzing data from 157 patients with de novo GCB DLBCL. Twenty-five of these patients had double- or triple-hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma with BCL2 translocations (HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2).
The researchers identified 104 genes that were the “most significantly differentially expressed between HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 and other GCB DLBCLs” to create their double-hit gene signature (DHITsig).
The signature divided the patients into two groups — 42 patients (27%) whose tumors were positive for the DHITsig and 115 (73%) whose tumors were negative. Notably, 22 of the 25 HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 tumors were DHITsig-positive and 3 were negative.
The DHITsig was not associated with clinical variables such as tumor volume, but it was associated with prognosis. Treatment outcomes were inferior in patients who were DHITsig-positive.
The 5-year time to progression rate was 81% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 57% in those who were positive (P less than .001). The 5-year overall survival rate was 81% and 60%, respectively (P = .001).
The researchers observed similar results in a validation cohort of 262 patients with GCB-DLBCL who received rituximab-based therapy. The 5-year overall survival rate was 76% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 49% in those who were positive (P less than .001).
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also evaluated the DHITsig in a second validation cohort of 162 patients with GCB DLBCL.
In analyzing data from all three cohorts, the researchers found that mutations in MYC, BCL2, CREBBP, EZH2Y646, DDX3X, TP53, and KMT2D were more frequent in DHITsig-positive patients and mutations in TNFAIP3, KLHL6, NFKBIE, TET2, CD58, and STAT3 were more common in DHITsig-negative patients.
Additional analyses suggested the cell of origin for DHITsig-positive tumors comes from the intermediate zone or dark zone of the germinal center.
Finally, the researchers found they could use a “clinically relevant assay” to detect the DHITsig. They added a 30-gene module to the Lymph3Cx assay to create a NanoString-based assay called DLBCL90.
The team tested DLBCL90 in 171 GCB DLBCL patients. In this group, 26% of patients were DHITsig-positive, 64% were negative, and 10% were indeterminate. The prognostic significance of the signature was maintained with the assay results, according to the researchers.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also wanted to validate the association between the DHITsig and HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2, so they tested the DLBCL90 assay in two additional groups of patients.
First, the assay was used in 88 patients who had transformed follicular lymphoma with DLBCL morphology. Eleven of the 25 DHITsig-positive tumors and 4 of the 13 DHITsig-indeterminate tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2. However, none of the 50 DHITsig-negative tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2.
The researchers then used the DLBCL90 assay on 26 HGBL tumors. Twenty-three of these were DHITsig-positive and 3 were indeterminate.
This research was supported by the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute and other organizations. The researchers reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Roche, Janssen, Celgene, and various other companies.
SOURCE: Scott DW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 20;37(3):190-201.
New research suggests a gene expression signature can distinguish high-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) from other germinal center B-cell–like (GCB) DLBCLs.
Researchers identified GCB DLBCL patients with this 104-gene signature who had a “distinct mutational landscape” and inferior treatment outcomes. David W. Scott, MBChB, PhD, of the British Columbia Cancer Research Centre in Vancouver, and his colleagues described these patients in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The findings were published alongside a related editorial and a similar study from another group.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues began their study by analyzing data from 157 patients with de novo GCB DLBCL. Twenty-five of these patients had double- or triple-hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma with BCL2 translocations (HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2).
The researchers identified 104 genes that were the “most significantly differentially expressed between HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 and other GCB DLBCLs” to create their double-hit gene signature (DHITsig).
The signature divided the patients into two groups — 42 patients (27%) whose tumors were positive for the DHITsig and 115 (73%) whose tumors were negative. Notably, 22 of the 25 HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 tumors were DHITsig-positive and 3 were negative.
The DHITsig was not associated with clinical variables such as tumor volume, but it was associated with prognosis. Treatment outcomes were inferior in patients who were DHITsig-positive.
The 5-year time to progression rate was 81% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 57% in those who were positive (P less than .001). The 5-year overall survival rate was 81% and 60%, respectively (P = .001).
The researchers observed similar results in a validation cohort of 262 patients with GCB-DLBCL who received rituximab-based therapy. The 5-year overall survival rate was 76% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 49% in those who were positive (P less than .001).
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also evaluated the DHITsig in a second validation cohort of 162 patients with GCB DLBCL.
In analyzing data from all three cohorts, the researchers found that mutations in MYC, BCL2, CREBBP, EZH2Y646, DDX3X, TP53, and KMT2D were more frequent in DHITsig-positive patients and mutations in TNFAIP3, KLHL6, NFKBIE, TET2, CD58, and STAT3 were more common in DHITsig-negative patients.
Additional analyses suggested the cell of origin for DHITsig-positive tumors comes from the intermediate zone or dark zone of the germinal center.
Finally, the researchers found they could use a “clinically relevant assay” to detect the DHITsig. They added a 30-gene module to the Lymph3Cx assay to create a NanoString-based assay called DLBCL90.
The team tested DLBCL90 in 171 GCB DLBCL patients. In this group, 26% of patients were DHITsig-positive, 64% were negative, and 10% were indeterminate. The prognostic significance of the signature was maintained with the assay results, according to the researchers.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also wanted to validate the association between the DHITsig and HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2, so they tested the DLBCL90 assay in two additional groups of patients.
First, the assay was used in 88 patients who had transformed follicular lymphoma with DLBCL morphology. Eleven of the 25 DHITsig-positive tumors and 4 of the 13 DHITsig-indeterminate tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2. However, none of the 50 DHITsig-negative tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2.
The researchers then used the DLBCL90 assay on 26 HGBL tumors. Twenty-three of these were DHITsig-positive and 3 were indeterminate.
This research was supported by the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute and other organizations. The researchers reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Roche, Janssen, Celgene, and various other companies.
SOURCE: Scott DW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 20;37(3):190-201.
New research suggests a gene expression signature can distinguish high-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) from other germinal center B-cell–like (GCB) DLBCLs.
Researchers identified GCB DLBCL patients with this 104-gene signature who had a “distinct mutational landscape” and inferior treatment outcomes. David W. Scott, MBChB, PhD, of the British Columbia Cancer Research Centre in Vancouver, and his colleagues described these patients in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
The findings were published alongside a related editorial and a similar study from another group.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues began their study by analyzing data from 157 patients with de novo GCB DLBCL. Twenty-five of these patients had double- or triple-hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma with BCL2 translocations (HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2).
The researchers identified 104 genes that were the “most significantly differentially expressed between HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 and other GCB DLBCLs” to create their double-hit gene signature (DHITsig).
The signature divided the patients into two groups — 42 patients (27%) whose tumors were positive for the DHITsig and 115 (73%) whose tumors were negative. Notably, 22 of the 25 HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2 tumors were DHITsig-positive and 3 were negative.
The DHITsig was not associated with clinical variables such as tumor volume, but it was associated with prognosis. Treatment outcomes were inferior in patients who were DHITsig-positive.
The 5-year time to progression rate was 81% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 57% in those who were positive (P less than .001). The 5-year overall survival rate was 81% and 60%, respectively (P = .001).
The researchers observed similar results in a validation cohort of 262 patients with GCB-DLBCL who received rituximab-based therapy. The 5-year overall survival rate was 76% in patients who were DHITsig-negative and 49% in those who were positive (P less than .001).
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also evaluated the DHITsig in a second validation cohort of 162 patients with GCB DLBCL.
In analyzing data from all three cohorts, the researchers found that mutations in MYC, BCL2, CREBBP, EZH2Y646, DDX3X, TP53, and KMT2D were more frequent in DHITsig-positive patients and mutations in TNFAIP3, KLHL6, NFKBIE, TET2, CD58, and STAT3 were more common in DHITsig-negative patients.
Additional analyses suggested the cell of origin for DHITsig-positive tumors comes from the intermediate zone or dark zone of the germinal center.
Finally, the researchers found they could use a “clinically relevant assay” to detect the DHITsig. They added a 30-gene module to the Lymph3Cx assay to create a NanoString-based assay called DLBCL90.
The team tested DLBCL90 in 171 GCB DLBCL patients. In this group, 26% of patients were DHITsig-positive, 64% were negative, and 10% were indeterminate. The prognostic significance of the signature was maintained with the assay results, according to the researchers.
Dr. Scott and his colleagues also wanted to validate the association between the DHITsig and HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2, so they tested the DLBCL90 assay in two additional groups of patients.
First, the assay was used in 88 patients who had transformed follicular lymphoma with DLBCL morphology. Eleven of the 25 DHITsig-positive tumors and 4 of the 13 DHITsig-indeterminate tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2. However, none of the 50 DHITsig-negative tumors were HGBL-DH/TH-BCL2.
The researchers then used the DLBCL90 assay on 26 HGBL tumors. Twenty-three of these were DHITsig-positive and 3 were indeterminate.
This research was supported by the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute and other organizations. The researchers reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Roche, Janssen, Celgene, and various other companies.
SOURCE: Scott DW et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan 20;37(3):190-201.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Priority review granted to lenalidomide for FL, MZL
The Food and Drug Administration has granted priority review to a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for lenalidomide (Revlimid).
Celgene is seeking approval for lenalidomide in combination with rituximab to treat patients with previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL) or marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
The FDA plans to make a decision on the sNDA by June 27, 2019.
The FDA aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it rather than the standard 10 months. The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The sNDA for lenalidomide is supported by the phase 3 AUGMENT study (NCT01938001) in which researchers compared rituximab plus lenalidomide to rituximab plus placebo in patients with relapsed/refractory FL or MZL.
Results from AUGMENT were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood 2018 Nov 29;132:445).
According to the ASH abstract, the trial included 358 patients who were randomized to receive rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 178) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 180).
At a median follow-up of 28.3 months, the overall response rate was 78% in the lenalidomide arm and 53% in the placebo arm (P less than .0001). The complete response rate was 34% and 18%, respectively (P = .001).
The median progression-free survival was 39.4 months in the lenalidomide arm and 14.1 months in the placebo arm. Overall survival data were not mature, but there were 16 deaths reported in the lenalidomide arm and 26 deaths in the placebo arm.
Treatment-emergent adverse events that were more common in the lenalidomide arm than the placebo arm included infections, cutaneous reactions, constipation, thrombocytopenia, and tumor flare reaction.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted priority review to a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for lenalidomide (Revlimid).
Celgene is seeking approval for lenalidomide in combination with rituximab to treat patients with previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL) or marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
The FDA plans to make a decision on the sNDA by June 27, 2019.
The FDA aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it rather than the standard 10 months. The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The sNDA for lenalidomide is supported by the phase 3 AUGMENT study (NCT01938001) in which researchers compared rituximab plus lenalidomide to rituximab plus placebo in patients with relapsed/refractory FL or MZL.
Results from AUGMENT were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood 2018 Nov 29;132:445).
According to the ASH abstract, the trial included 358 patients who were randomized to receive rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 178) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 180).
At a median follow-up of 28.3 months, the overall response rate was 78% in the lenalidomide arm and 53% in the placebo arm (P less than .0001). The complete response rate was 34% and 18%, respectively (P = .001).
The median progression-free survival was 39.4 months in the lenalidomide arm and 14.1 months in the placebo arm. Overall survival data were not mature, but there were 16 deaths reported in the lenalidomide arm and 26 deaths in the placebo arm.
Treatment-emergent adverse events that were more common in the lenalidomide arm than the placebo arm included infections, cutaneous reactions, constipation, thrombocytopenia, and tumor flare reaction.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted priority review to a supplemental new drug application (sNDA) for lenalidomide (Revlimid).
Celgene is seeking approval for lenalidomide in combination with rituximab to treat patients with previously treated follicular lymphoma (FL) or marginal zone lymphoma (MZL).
The FDA plans to make a decision on the sNDA by June 27, 2019.
The FDA aims to take action on a priority review application within 6 months of receiving it rather than the standard 10 months. The FDA grants priority review to applications for products that are expected to provide significant improvements in the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of serious conditions.
The sNDA for lenalidomide is supported by the phase 3 AUGMENT study (NCT01938001) in which researchers compared rituximab plus lenalidomide to rituximab plus placebo in patients with relapsed/refractory FL or MZL.
Results from AUGMENT were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Blood 2018 Nov 29;132:445).
According to the ASH abstract, the trial included 358 patients who were randomized to receive rituximab plus lenalidomide (n = 178) or rituximab plus placebo (n = 180).
At a median follow-up of 28.3 months, the overall response rate was 78% in the lenalidomide arm and 53% in the placebo arm (P less than .0001). The complete response rate was 34% and 18%, respectively (P = .001).
The median progression-free survival was 39.4 months in the lenalidomide arm and 14.1 months in the placebo arm. Overall survival data were not mature, but there were 16 deaths reported in the lenalidomide arm and 26 deaths in the placebo arm.
Treatment-emergent adverse events that were more common in the lenalidomide arm than the placebo arm included infections, cutaneous reactions, constipation, thrombocytopenia, and tumor flare reaction.
Don’t forget social determinants of health in minority MS patients
DALLAS – The way Lilyana Amezcua, MD, sees it, clinicians should view race and ethnicity as health disparities when assessing individuals with multiple sclerosis.
Whites are predominately affected with MS, “but we have seen changing demographics,” said Dr. Amezcua, of the University of Southern California MS Comprehensive Care and Research Group. “Why are African Americans now at higher risk ... and why do African Americans appear to have more severe disease? Is it a biological difference ... or is it because of poor access” to health care?
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Amezcua delivered a presentation entitled “Effect of Race and Ethnicity on MS Presentation and Disease Course.” She called on researchers in the field “to not just take race and ethnicity as any small variable. We need to be cognizant and use the correct methodology, depending on what [question] we want to answer. We need to better define how we ascertain race, how we ascertain ethnicity.”
Dr. Amezcua, who is also the MS fellowship program director at the Keck School of Medicine, disclosed that she receives funding from the National MS Society, the National Institutes of Health, the California Community Foundation, and Biogen.
DALLAS – The way Lilyana Amezcua, MD, sees it, clinicians should view race and ethnicity as health disparities when assessing individuals with multiple sclerosis.
Whites are predominately affected with MS, “but we have seen changing demographics,” said Dr. Amezcua, of the University of Southern California MS Comprehensive Care and Research Group. “Why are African Americans now at higher risk ... and why do African Americans appear to have more severe disease? Is it a biological difference ... or is it because of poor access” to health care?
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Amezcua delivered a presentation entitled “Effect of Race and Ethnicity on MS Presentation and Disease Course.” She called on researchers in the field “to not just take race and ethnicity as any small variable. We need to be cognizant and use the correct methodology, depending on what [question] we want to answer. We need to better define how we ascertain race, how we ascertain ethnicity.”
Dr. Amezcua, who is also the MS fellowship program director at the Keck School of Medicine, disclosed that she receives funding from the National MS Society, the National Institutes of Health, the California Community Foundation, and Biogen.
DALLAS – The way Lilyana Amezcua, MD, sees it, clinicians should view race and ethnicity as health disparities when assessing individuals with multiple sclerosis.
Whites are predominately affected with MS, “but we have seen changing demographics,” said Dr. Amezcua, of the University of Southern California MS Comprehensive Care and Research Group. “Why are African Americans now at higher risk ... and why do African Americans appear to have more severe disease? Is it a biological difference ... or is it because of poor access” to health care?
At the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Dr. Amezcua delivered a presentation entitled “Effect of Race and Ethnicity on MS Presentation and Disease Course.” She called on researchers in the field “to not just take race and ethnicity as any small variable. We need to be cognizant and use the correct methodology, depending on what [question] we want to answer. We need to better define how we ascertain race, how we ascertain ethnicity.”
Dr. Amezcua, who is also the MS fellowship program director at the Keck School of Medicine, disclosed that she receives funding from the National MS Society, the National Institutes of Health, the California Community Foundation, and Biogen.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
CSF biomarker clusters correlate with MS severity
DALLAS – Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) have elevated levels of specific clusters of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers related to astrocytes and microglia that correlated with disease severity in a blinded analysis of more than 1,000 proteins from the CSF of more than 400 patients with neuroimmunologic disease and healthy volunteers.
Previous studies have indicated that aberrant activation of astrocytes and microglia underlies disability progression in older patients with MS, but researchers have lacked biomarkers of these processes in living subjects. In a presentation at a meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Ruturaj R. Masvekar, PhD, described developing biomarkers of CNS cell–specific processes and examining how they relate to MS disability progression. Dr. Masvekar, a researcher at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and his coinvestigators used a modified DNA aptamer assay to measure proteins in the CSF of 431 patients with neuroimmunologic diseases and healthy volunteers, followed by variable cluster analysis and in vitro modeling to define 64 clusters of CSF biomarkers that relate to CNS cell types.
The study included 42 healthy donors, 20 patients with clinically isolated syndrome, 57 patients with noninflammatory neurologic disorders, 127 patients with relapsing-remitting MS, 72 patients with secondary progressive MS, and 113 patients with primary progressive MS. In a training cohort of 217 participants, the researchers assessed how biomarkers differed between the diagnostic categories. The researchers then validated the results in an independent cohort of 214 participants.
One astrocyte-related cluster (MMP7, SERPINA3, GZMA, and CLIC1) and one microglia-related cluster (DSG2 and TNFRSF25) was significantly elevated in all MS subgroups, compared with healthy controls and patients with noninflammatory neurologic disorders.
In addition, these clusters “significantly correlated with clinical measures of disability, CNS tissue destruction, and MS severity,” Dr. Masvekar said.
The microglial cluster was significantly elevated in all MS subgroups, whereas neuronal endothelial, astrocytic, and oligodendroglial biomarker clusters were elevated only in patients with progressive MS.
“Microglial activation is present in all stages of MS, while toxic astrogliosis increases with MS duration, concomitantly with neuronal and oligodendroglial degeneration,” Dr. Masvekar said. “Microglial activation and toxic astrogliosis likely partake in CNS tissue destruction and enhance MS severity.”
This study, which was recently published in Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders (2019 Feb;28:34-43), was supported by the intramural research program at NIAID.
SOURCE: Masvekar RR et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2019, Abstract 281.
DALLAS – Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) have elevated levels of specific clusters of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers related to astrocytes and microglia that correlated with disease severity in a blinded analysis of more than 1,000 proteins from the CSF of more than 400 patients with neuroimmunologic disease and healthy volunteers.
Previous studies have indicated that aberrant activation of astrocytes and microglia underlies disability progression in older patients with MS, but researchers have lacked biomarkers of these processes in living subjects. In a presentation at a meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Ruturaj R. Masvekar, PhD, described developing biomarkers of CNS cell–specific processes and examining how they relate to MS disability progression. Dr. Masvekar, a researcher at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and his coinvestigators used a modified DNA aptamer assay to measure proteins in the CSF of 431 patients with neuroimmunologic diseases and healthy volunteers, followed by variable cluster analysis and in vitro modeling to define 64 clusters of CSF biomarkers that relate to CNS cell types.
The study included 42 healthy donors, 20 patients with clinically isolated syndrome, 57 patients with noninflammatory neurologic disorders, 127 patients with relapsing-remitting MS, 72 patients with secondary progressive MS, and 113 patients with primary progressive MS. In a training cohort of 217 participants, the researchers assessed how biomarkers differed between the diagnostic categories. The researchers then validated the results in an independent cohort of 214 participants.
One astrocyte-related cluster (MMP7, SERPINA3, GZMA, and CLIC1) and one microglia-related cluster (DSG2 and TNFRSF25) was significantly elevated in all MS subgroups, compared with healthy controls and patients with noninflammatory neurologic disorders.
In addition, these clusters “significantly correlated with clinical measures of disability, CNS tissue destruction, and MS severity,” Dr. Masvekar said.
The microglial cluster was significantly elevated in all MS subgroups, whereas neuronal endothelial, astrocytic, and oligodendroglial biomarker clusters were elevated only in patients with progressive MS.
“Microglial activation is present in all stages of MS, while toxic astrogliosis increases with MS duration, concomitantly with neuronal and oligodendroglial degeneration,” Dr. Masvekar said. “Microglial activation and toxic astrogliosis likely partake in CNS tissue destruction and enhance MS severity.”
This study, which was recently published in Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders (2019 Feb;28:34-43), was supported by the intramural research program at NIAID.
SOURCE: Masvekar RR et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2019, Abstract 281.
DALLAS – Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) have elevated levels of specific clusters of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers related to astrocytes and microglia that correlated with disease severity in a blinded analysis of more than 1,000 proteins from the CSF of more than 400 patients with neuroimmunologic disease and healthy volunteers.
Previous studies have indicated that aberrant activation of astrocytes and microglia underlies disability progression in older patients with MS, but researchers have lacked biomarkers of these processes in living subjects. In a presentation at a meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis, Ruturaj R. Masvekar, PhD, described developing biomarkers of CNS cell–specific processes and examining how they relate to MS disability progression. Dr. Masvekar, a researcher at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and his coinvestigators used a modified DNA aptamer assay to measure proteins in the CSF of 431 patients with neuroimmunologic diseases and healthy volunteers, followed by variable cluster analysis and in vitro modeling to define 64 clusters of CSF biomarkers that relate to CNS cell types.
The study included 42 healthy donors, 20 patients with clinically isolated syndrome, 57 patients with noninflammatory neurologic disorders, 127 patients with relapsing-remitting MS, 72 patients with secondary progressive MS, and 113 patients with primary progressive MS. In a training cohort of 217 participants, the researchers assessed how biomarkers differed between the diagnostic categories. The researchers then validated the results in an independent cohort of 214 participants.
One astrocyte-related cluster (MMP7, SERPINA3, GZMA, and CLIC1) and one microglia-related cluster (DSG2 and TNFRSF25) was significantly elevated in all MS subgroups, compared with healthy controls and patients with noninflammatory neurologic disorders.
In addition, these clusters “significantly correlated with clinical measures of disability, CNS tissue destruction, and MS severity,” Dr. Masvekar said.
The microglial cluster was significantly elevated in all MS subgroups, whereas neuronal endothelial, astrocytic, and oligodendroglial biomarker clusters were elevated only in patients with progressive MS.
“Microglial activation is present in all stages of MS, while toxic astrogliosis increases with MS duration, concomitantly with neuronal and oligodendroglial degeneration,” Dr. Masvekar said. “Microglial activation and toxic astrogliosis likely partake in CNS tissue destruction and enhance MS severity.”
This study, which was recently published in Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders (2019 Feb;28:34-43), was supported by the intramural research program at NIAID.
SOURCE: Masvekar RR et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2019, Abstract 281.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019
Smartphone-based visual tests for MS patients show promise
DALLAS – A battery of smartphone-based tests has been developed to help detect visual pathway disturbances in MS patients and to follow them over time.
“One of the ideas is, can you design something that’s so easy to use and quick that it’s not a burden on the patient?” Randy H. Kardon, MD, PhD, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. “The other was to test a couple of different modalities. By that I mean we test visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and critical flicker fusion, which is a way of measuring the speed of conduction of nerves in the visual system.”
Dr. Kardon, professor of neuro-ophthalmology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, worked with colleagues from Aalborg University, Denmark, to study these tests and a novel measure known as the vanishing optotype on 117 patients with MS and 103 age-matched controls. They found that the tests “very nicely discriminated between normal eyes from patients that had MS,” said Dr. Kardon, director of the Iowa City VA Center for Prevention and Treatment of Visual Loss. “Furthermore, we could determine which eyes from the MS patients had previous optic neuritis and which eyes hadn’t. We’re now looking for partners to go forward with larger studies to validate it further and refine these tests even more.”
Dr. Kardon disclosed that he has received funding from the National Eye Institute, the Department of Defense, and from VA Rehabilitation Research and Development. He was also a member of the Novartis steering committee for the OCTiMS study and is a cofounder of MedFace and FaceX.
DALLAS – A battery of smartphone-based tests has been developed to help detect visual pathway disturbances in MS patients and to follow them over time.
“One of the ideas is, can you design something that’s so easy to use and quick that it’s not a burden on the patient?” Randy H. Kardon, MD, PhD, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. “The other was to test a couple of different modalities. By that I mean we test visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and critical flicker fusion, which is a way of measuring the speed of conduction of nerves in the visual system.”
Dr. Kardon, professor of neuro-ophthalmology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, worked with colleagues from Aalborg University, Denmark, to study these tests and a novel measure known as the vanishing optotype on 117 patients with MS and 103 age-matched controls. They found that the tests “very nicely discriminated between normal eyes from patients that had MS,” said Dr. Kardon, director of the Iowa City VA Center for Prevention and Treatment of Visual Loss. “Furthermore, we could determine which eyes from the MS patients had previous optic neuritis and which eyes hadn’t. We’re now looking for partners to go forward with larger studies to validate it further and refine these tests even more.”
Dr. Kardon disclosed that he has received funding from the National Eye Institute, the Department of Defense, and from VA Rehabilitation Research and Development. He was also a member of the Novartis steering committee for the OCTiMS study and is a cofounder of MedFace and FaceX.
DALLAS – A battery of smartphone-based tests has been developed to help detect visual pathway disturbances in MS patients and to follow them over time.
“One of the ideas is, can you design something that’s so easy to use and quick that it’s not a burden on the patient?” Randy H. Kardon, MD, PhD, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis. “The other was to test a couple of different modalities. By that I mean we test visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and critical flicker fusion, which is a way of measuring the speed of conduction of nerves in the visual system.”
Dr. Kardon, professor of neuro-ophthalmology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, worked with colleagues from Aalborg University, Denmark, to study these tests and a novel measure known as the vanishing optotype on 117 patients with MS and 103 age-matched controls. They found that the tests “very nicely discriminated between normal eyes from patients that had MS,” said Dr. Kardon, director of the Iowa City VA Center for Prevention and Treatment of Visual Loss. “Furthermore, we could determine which eyes from the MS patients had previous optic neuritis and which eyes hadn’t. We’re now looking for partners to go forward with larger studies to validate it further and refine these tests even more.”
Dr. Kardon disclosed that he has received funding from the National Eye Institute, the Department of Defense, and from VA Rehabilitation Research and Development. He was also a member of the Novartis steering committee for the OCTiMS study and is a cofounder of MedFace and FaceX.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2019