User login
HIV Prevention: A 3-Pronged Approach
› Screen all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A
› Prescribe tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) for pre-exposure prophylaxis for patients at high risk of acquiring HIV. A
› Offer needle and syringe exchange programs and, when appropriate, opioid substitution therapy to individuals who inject drugs. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Despite advances in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) screening and treatment over the last 30 years, HIV remains a public health concern. In the United States, after an initial decline, total HIV incidence has failed to significantly decrease in the last 25 years. More than 1.2 million people are living with HIV in the United States, and 12.8% of them (156,300) are unaware they are affected.1 Of those diagnosed with HIV, only 30% are receiving treatment and are virally suppressed.2 Due to structural inequalities and psychosocial factors, African American and Latino patients remain disproportionately affected.3 The incidence of HIV infection among men who have sex with men has increased, and the incidence of HIV infection among people who inject drugs has plateaued after years of progressive decline.4
HIV prevention strategies are highly effective, but in general are underutilized. This article reviews 3 prevention strategies that can be administered by family physicians: HIV screening, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and harm reduction.
Who and how to screen for HIV
Early identification of HIV infection generally leads to reduced transmission because diagnosis is associated with decreases in risky behavior.5,6 In addition, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is more effective when initiated early, before the development of advanced immunosuppression.7-9
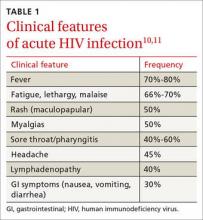
The “window period” of acute HIV infection (AHI) is the time from when the virus is transmitted to when markers of infection can be detected. Because this window period is associated with high viral transmission rates, family physicians must be familiar with symptoms of AHI (TABLE 1)10,11 and associated risk factors (eg, recent condomless sex or sharing of drug injection equipment with someone who is HIV-positive or of unknown HIV status).
Screening for HIV solely based on the presence of risk factors or clinical symptoms is not enough, however. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for HIV.12 Screening based solely on risk factors or clinical symptoms frequently leads to missed diagnoses and identification of HIV infection at more advanced stages.13,14 Both the USPSTF and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend universal opt-out screening (patients are informed that HIV screening will be performed and that they may decline testing) because such screening identifies HIV earlier and is associated with higher testing rates than opt-in screening, which requires explicit written consent and extensive pre-test counseling.
Which test to use. HIV screening with a fourth-generation antigen/antibody combination immunoassay—which detects both HIV p24 antigen and HIV antibodies—provides greater diagnostic accuracy than older tests.15 These newer tests detect HIV approximately 15 days after initial infection, reducing the window period of AHI.15,16 If you suspect a patient has AHI, consider early repeat HIV testing with a fourth-generation assay, or initial co-testing with a fourth-generation assay and a nucleic acid amplification test for HIV RNA, which makes it possible to detect infection approximately 5 days earlier than fourth-generation assays.15
Offer pre-exposure prophylaxis to high-risk patients
PrEP is the use of ART prior to HIV exposure to prevent transmission of the virus. It should be used with conventional risk reduction strategies, such as providing condoms, counseling patients about reducing risky behaviors, supporting medication adherence, and screening for and treating other sexually transmitted infections.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only one medication, Truvada (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine; TDF/FTC), for use as PrEP. Oral tenofovir-based regimens can effectively prevent HIV transmission,17-20 and strong adherence is associated with a risk reduction of 90% to 100%.17-23 The protective effect of oral PrEP is particularly strong in high-risk populations (eg, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs), where the number needed to treat to prevent one HIV infection ranges from 12 to 100, depending on the patients’ risk profile.24-26 The CDC and Department of Health and Human Services have issued guidelines for using PrEP in high-risk patients.27
Barriers to implementing PrEP. Despite being highly effective, PrEP is not routinely prescribed to high-risk patients; modeling suggests that current use of PrEP is insufficient to significantly impact the incidence of HIV.28 Demand for PrEP is high among target groups,21,29,30 but patients have expressed concerns about adverse effects31 and stigma related to ART, HIV, and being at risk for HIV.32,33 Young age, lack of social support, low perception of risk, and failure to show up for appointments are also barriers to PrEP use.28,30,34
Some physicians have expressed concern that prescribing PrEP may promote high-risk sexual behavior.35 However, because PrEP is most beneficial in individuals who already engage in high-risk sexual behavior, strategic delivery of PrEP remains an effective risk-reducing strategy.17,18,21,26,36,37 Even in instances where PrEP has been associated with higher-risk sexual behavior and higher rates of sexually transmitted infections, it still prevents as much as 100% of new HIV infections.38
Fear of drug resistance also contributes to slow implementation of PrEP. Drug resistance has been observed in clinical trials of PrEP, but it has been exceedingly rare and predominantly limited to patients who had unrecognized AHI when they started PrEP.39 Furthermore, the few cases of drug resistance attributable to PrEP pale in comparison to the large number of estimated HIV infections averted—infections that would require lifelong ART with its own associated risks of drug resistance. By decreasing HIV transmission, PrEP is expected to decrease total drug resistance.40
Cost is another obstacle. Truvada costs approximately $1,540 per month.41 However, analysis has demonstrated that PrEP is cost-effective when targeted to high-risk patients.42 Most insurance plans cover PrEP, but often require high deductibles and copays; fortunately, this financial burden for patients can be mitigated or eliminated by co-pay assistance programs. The manufacturer of Truvada offers assistance programs for both insured and uninsured patients who are candidates for PrEP; details are available at http://www.truvada.com/truvada-patient-assistance.
Stigma has historically burdened individuals who seek to protect their sexual health, including HIV-negative individuals who are candidates for PrEP. Stigma surrounding HIV may decrease ART-based HIV prevention in men who have sex with men,43 while increasing high-risk behaviors44 and all-cause mortality.45
The resources listed in TABLE 2 can help physicians overcome some of the barriers to implementing PrEP.
How to deliver PrEP
Whether HIV specialists or primary care clinicians are best suited to provide PrEP is a subject of debate. HIV specialists are most familiar with ART and routine monitoring of adherence; however, they have less access to HIV-negative patients, who are the target group for PrEP.35 Family physicians tend to work in closer proximity and maintain longitudinal relationships with PrEP target groups, but in general have less experience with ART and evaluating AHI. Some may argue that competing demands may make it impractical to take a detailed sexual history during a primary care visit.46 In truth, both HIV specialists and family physicians can be appropriately equipped to provide PrEP.
TABLE 3 outlines the steps necessary to provide a patient with PrEP.47 Assessing risk is the initial step; PrEP is beneficial for patients who have one or more risk factors for HIV infection. To be eligible for TDF/FTC, a patient must be HIV-negative, and should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and kidney disease. Because TDF/FTC treats HBV infection, candidates for PrEP who test positive for HBV should be evaluated for treatment of HBV before initiating PrEP. Candidates for PrEP who test negative for HBV infection and immunity should be vaccinated.
Candidates for PrEP should also be screened and monitored for kidney disease. TDF can cause increased serum creatinine due to tubular toxicity. A patient who has an estimated creatinine clearance <60 mL/min should not receive TDF/FTC for PrEP. If a patient’s estimated creatinine clearance falls below 60 mL/min or serum creatinine increases by 0.3 mg/dL above baseline after PrEP is started, TDF/FTC should be discontinued, and the patient should be evaluated for the underlying cause of the kidney disease.27
Before starting PrEP, candidates should be screened for HIV infection and symptoms of AHI. Strongly consider testing for sexually transmitted infections that may increase the risk of HIV transmission, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or chlamydia.
Candidates who are eligible for PrEP must be counseled on medication adverse effects, adherence strategies, and symptoms of sexually transmitted infections. To initiate PrEP, candidates may be given a one-month supply of TDF/FTC; adherence, adverse effects, and other risk-reduction strategies are assessed at an office visit 3 to 4 weeks later. Subsequent prescriptions are then dispensed as a 3-month supply, with office visits to monitor PrEP scheduled for at least once every 3 months. During these monitoring visits, evaluate the patient’s HIV status, pregnancy status, adherence, adverse effects, risk-reduction behaviors, and indications for continued PrEP. Every 6 months, renal function and sexually transmitted infection status should be reassessed.
Reducing risk of harm among patients who inject drugs
Nonsexual transmission of HIV is a route of high infectivity.48 It includes transfusion of infected blood, sharing of equipment during injection drug use, and percutaneous needle sticks. Sharing of equipment during injection drug use is estimated to account for 8% of new infections in the United States.4
Harm reduction is a collection of strategies meant to reduce complications of illicit drug use, including HIV transmission. These strategies include needle and syringe programs that provide injection drug users with sterile equipment, and opioid substitution therapy.
Needle and syringe programs decrease HIV transmission49 and risky behaviors related to injection drug use,50 but federal funding of such programs is prohibited. Opioid substitution therapy reduces the incidence of HIV,50,51 injection drug use, sharing of drug preparation and injection equipment, and drug-related behaviors associated with a high risk of HIV transmission.50,52 However, in the United States, the quality of these programs varies; a study of opioid substitution therapy delivery found that 22.8% of programs provided doses that were too low to be effective.53
FDA-approved medications for opioid substitution therapy include sublingual buprenorphine, sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets or strips (Suboxone), and oral methadone. Buprenorphine-based regimens can be provided by appropriately trained primary care clinicians; methadone requires a referral to a narcotic treatment program. TABLE 4 provides training and support resources for physicians who want to integrate opioid substitution therapy into their clinical practice.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard Moore II, MD, 250 Smith Church Road, Roanoke Rapids, NC 27870; [email protected].
1. Hall HI, An Q, Tang T, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed HIV infection--United States, 2008-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:657-662.
2. Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:1113-1117.
3. Maulsby C, Millet G, Lindsey K, et al. HIV among black men who have sex with men (MSM) in the United States: a review of the literature. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:10-25.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Estimated HIV incidence among adults and adolescents in the United States, 2007-2010, HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2012. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_hssr_vol_17_no_4.pdf. Accessed October 8, 2015.
5. Cleary PD, Van Devanter N, Rogers TF, et al. Behavior changes after notification of HIV infection. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:1586-1590.
6. Higgins DL, Galavotti C, O’Reilly KR, et al. Evidence for the effects of HIV antibody counseling and testing on risk behaviors. JAMA. 1991;266:2419-2429.
7. Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17-26.
8. Palella FJ Jr, Deloria-Knoll M, Chmiel JS, et al. Survival benefit of initiating antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected persons in different CD4 cell strata. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:620-626.
9. INSIGHT START Study Group, Lundgren JD, Babiker AG, Gordin F, et al. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in early asymptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:795-807.
10. Daar ES, Pilcher CD, Hecht FM. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of primary HIV-1 infection. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2008;3:10-15.
11. Tindall B, Barker S, Donovan B, et al. Characterization of the acute clinical illness associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:945-949.
12. Moyer V, US Preventative Services Task Force. Screening for HIV: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:51-60.
13. Jenkins T, Gardner E, Thrun M, et al. Risk-based HIV testing fails to detect the majority of HIV-infected persons in medical care settings. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33:329-333.
14. Klein D, Hurley LB, Merrill D, et al. Review of medical encounters in the 5 years before a diagnosis of HIV-1 infection: implications for early detection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;32:143-152.
15. Pandori M, Hackett J Jr, Louie B, et al. Assessment of the ability of a fourth-generation immunoassay for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody and p24 antigen to detect both acute and recent HIV infections in a high-risk setting. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2639-2642.
16. Branson BM. The future of HIV testing. J Acquir Imm Defic Syndr. 2010;55 Suppl 2:S102-S105.
17. Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599.
18. Baeten JM, Donnell D, Ndase P, et al; Partners PrEP Study Team. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention in heterosexual men and women. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:399-410.
19. Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:423-434.
20. Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2083-2090.
21. Grant RM, Anderson PL, McMahan V, et al. Uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis, sexual practices, and HIV incidence in men and transgender women who have sex with men: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:820-829.
22. Anderson PL, Glidden DV, Liu A, et al. Emtricitabine-tenofovir concentrations and pre-exposure prophylaxis efficacy in men who have sex with men. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:151ra125.
23. Henderson FL, Taylor AW, Chirwa LI, et al. Characteristics and oral PrEP adherence in the TDF2 open-label extension in Botswana. Paper presented at International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; July 1922, 2015; Vancouver, Canada.
24. Murnane PM, Celum C, Mugo N, et al. Efficacy of preexposure prophylaxis for HIV-1 prevention among high-risk heterosexuals: subgroup analyses from a randomized trial. AIDS. 2013;27:2155-2160.
25. Heffron R, Mugo N, Were E, et al. Preexposure prophylaxis is efficacious for HIV-1 prevention among women using depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for contraception. AIDS. 2014;28:2771-2776.
26. Buchbinder SP, Glidden DV, Liu AY, et al. HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in men who have sex with men and transgender women: a secondary analysis of a phase 3 randomised controlled efficacy trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:468-475.
27. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States – 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed June 18, 2015.
28. Grant RM. Scale-up of preexposure prophylaxis in San Francisco to impact HIV incidence. Abstract 25. Paper presented at Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 23-26, 2015; Seattle, WA.
29. Cohen SE, Vittinghoff E, Bacon O, et al. High interest in preexposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men at risk for HIV infection: baseline data from the US PrEP demonstration project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;68:439-448.
30. Haberer JE, Baeten JM, Campbell J, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a substudy cohort within a clinical trial of serodiscordant couples in East Africa. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001511.
31. Gilmore H, Koester K, Liu A, et al. To PrEP or not to PrEP: Perspectives from US iPrEx open label extension (OLE) participants. Abstract 440. Paper presented at 9th International Conference on HIV Treatment and Prevention Adherence; June 9, 2014; Miami Beach, FL.
32. Jain S, Gregor C, Krakower D, et al. Attitudes and interest toward HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among participants using HIV non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (NPEP). Poster Abstract 1523. Poster presented at Infectious Disease Society of America Conference; October 8-12, 2014; Philadelphia, PA.
33. van der Straten A, Stadler J, Luecke E, et al; VOICE-C Study Team, Perspectives on use of oral and vaginal antiretrovirals for HIV prevention: the VOICE-C qualitative study in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19146.
34. Corneli AL, McKenna K, Headley J, et al; FEM-PrEP Study Group. A descriptive analysis of perceptions of HIV risk and worry about acquiring HIV among FEM-PrEP participants who seroconverted in Bondo, Kenya, and Pretoria, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19152.
35. Krakower D, Ware N, Mitty JA, et al. HIV providers’ perceived barriers and facilitators to implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis in care settings: a qualitative study. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1712-1721.
36. McCormack S, Dunn DT, Desai M, et al. Pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent the acquisition of HIV-1 infection (PROUD): effectiveness results from the pilot phase of a pragmatic open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2015. [Epub ahead of print].
37. Mugwanya KK, Donnell D, Celum C, et al. Sexual behaviour of heterosexual men and women receiving antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:1021-1028.
38. Volk JE, Marcus JL, Phengrasamy T, et al. No new HIV infections with increasing use of HIV preexposure prophylaxis in a clinical practice setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1601-1603.
39. Lehman DA, Baeten JM, McCoy CO, et al. Risk of drug resistance among persons acquiring HIV within a randomized clinical trial of single- or dual-agent preexposure prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1211-1218.
40. Supervie V, Garcia-Lerma JG, Heneine W, et al. HIV, transmitted drug resistance, and the paradox of preexposure prophylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:12381-12386.
41. AIDSinfo. Cost considerations and antiretroviral therapy. AIDSinfo Web site. Available at: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/1/adult-and-adolescent-arv-guidelines/459/cost-considerations-and-antiretroviral-therapy. Accessed December 14, 2015.
42. Gomez GB, Borquez A, Case KK, et al. The cost and impact of scaling up pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness modelling studies. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001401.
43. Oldenburg CE, Perez-Brumer AG, Hatzenbuehler ML, et al. State-level structural sexual stigma and HIV prevention in a national online sample of HIV-uninfected MSM in the United States. AIDS. 2015;29:837-845.
44. Hatzenbuehler ML, O’Cleirigh C, Mayer KH, et al. Prospective associations between HIV-related stigma, transmission risk behaviors, and adverse mental health outcomes in men who have sex with men. Ann Behav Med. 2011;42:227-234.
45. Hatzenbuehler ML, Bellatorre A, Lee Y, et al. Structural stigma and all-cause mortality in sexual minority populations. Soc Sci Med. 2014;103:33-41.
46. Arnold EA, Hazelton P, Lane T, et al. A qualitative study of provider thoughts on implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in clinical settings to prevent HIV infection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40603.
47. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center. For PrEP Providers. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center Web site. Available at: http://www.med.unc.edu/ncaidstraining/prep/for-providers/for-prep-prescribers. Accessed July 7, 2015.
48. Patel P, Borkowf CB, Brook JT, et al. Estimating per-act HIV transmission risk: a systematic review. AIDS. 2014;28:1509-1519.
49. Aspinall EJ, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43:235-248.
50. MacArthur GJ, van Velzen E, Palmateer N, et al. Interventions to prevent HIV and Hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: a review of reviews to assess evidence of effectiveness. Int J Drug Policy. 2014;25:34-52.
51. MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5945.
52. Gowing L, Farrell MF, Bornemann R, et al. Oral substitution treatment of injecting opioid users for prevention of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(8):CD004145.
53. D’Aunno T, Pollack HA, Frimpong JA, et al. Evidence-based treatment for opioid disorders: a 23-year national study of methadone dose levels. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2014;47:245-250.
› Screen all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A
› Prescribe tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) for pre-exposure prophylaxis for patients at high risk of acquiring HIV. A
› Offer needle and syringe exchange programs and, when appropriate, opioid substitution therapy to individuals who inject drugs. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Despite advances in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) screening and treatment over the last 30 years, HIV remains a public health concern. In the United States, after an initial decline, total HIV incidence has failed to significantly decrease in the last 25 years. More than 1.2 million people are living with HIV in the United States, and 12.8% of them (156,300) are unaware they are affected.1 Of those diagnosed with HIV, only 30% are receiving treatment and are virally suppressed.2 Due to structural inequalities and psychosocial factors, African American and Latino patients remain disproportionately affected.3 The incidence of HIV infection among men who have sex with men has increased, and the incidence of HIV infection among people who inject drugs has plateaued after years of progressive decline.4
HIV prevention strategies are highly effective, but in general are underutilized. This article reviews 3 prevention strategies that can be administered by family physicians: HIV screening, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and harm reduction.
Who and how to screen for HIV
Early identification of HIV infection generally leads to reduced transmission because diagnosis is associated with decreases in risky behavior.5,6 In addition, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is more effective when initiated early, before the development of advanced immunosuppression.7-9
The “window period” of acute HIV infection (AHI) is the time from when the virus is transmitted to when markers of infection can be detected. Because this window period is associated with high viral transmission rates, family physicians must be familiar with symptoms of AHI (TABLE 1)10,11 and associated risk factors (eg, recent condomless sex or sharing of drug injection equipment with someone who is HIV-positive or of unknown HIV status).
Screening for HIV solely based on the presence of risk factors or clinical symptoms is not enough, however. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for HIV.12 Screening based solely on risk factors or clinical symptoms frequently leads to missed diagnoses and identification of HIV infection at more advanced stages.13,14 Both the USPSTF and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend universal opt-out screening (patients are informed that HIV screening will be performed and that they may decline testing) because such screening identifies HIV earlier and is associated with higher testing rates than opt-in screening, which requires explicit written consent and extensive pre-test counseling.
Which test to use. HIV screening with a fourth-generation antigen/antibody combination immunoassay—which detects both HIV p24 antigen and HIV antibodies—provides greater diagnostic accuracy than older tests.15 These newer tests detect HIV approximately 15 days after initial infection, reducing the window period of AHI.15,16 If you suspect a patient has AHI, consider early repeat HIV testing with a fourth-generation assay, or initial co-testing with a fourth-generation assay and a nucleic acid amplification test for HIV RNA, which makes it possible to detect infection approximately 5 days earlier than fourth-generation assays.15
Offer pre-exposure prophylaxis to high-risk patients
PrEP is the use of ART prior to HIV exposure to prevent transmission of the virus. It should be used with conventional risk reduction strategies, such as providing condoms, counseling patients about reducing risky behaviors, supporting medication adherence, and screening for and treating other sexually transmitted infections.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only one medication, Truvada (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine; TDF/FTC), for use as PrEP. Oral tenofovir-based regimens can effectively prevent HIV transmission,17-20 and strong adherence is associated with a risk reduction of 90% to 100%.17-23 The protective effect of oral PrEP is particularly strong in high-risk populations (eg, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs), where the number needed to treat to prevent one HIV infection ranges from 12 to 100, depending on the patients’ risk profile.24-26 The CDC and Department of Health and Human Services have issued guidelines for using PrEP in high-risk patients.27
Barriers to implementing PrEP. Despite being highly effective, PrEP is not routinely prescribed to high-risk patients; modeling suggests that current use of PrEP is insufficient to significantly impact the incidence of HIV.28 Demand for PrEP is high among target groups,21,29,30 but patients have expressed concerns about adverse effects31 and stigma related to ART, HIV, and being at risk for HIV.32,33 Young age, lack of social support, low perception of risk, and failure to show up for appointments are also barriers to PrEP use.28,30,34
Some physicians have expressed concern that prescribing PrEP may promote high-risk sexual behavior.35 However, because PrEP is most beneficial in individuals who already engage in high-risk sexual behavior, strategic delivery of PrEP remains an effective risk-reducing strategy.17,18,21,26,36,37 Even in instances where PrEP has been associated with higher-risk sexual behavior and higher rates of sexually transmitted infections, it still prevents as much as 100% of new HIV infections.38
Fear of drug resistance also contributes to slow implementation of PrEP. Drug resistance has been observed in clinical trials of PrEP, but it has been exceedingly rare and predominantly limited to patients who had unrecognized AHI when they started PrEP.39 Furthermore, the few cases of drug resistance attributable to PrEP pale in comparison to the large number of estimated HIV infections averted—infections that would require lifelong ART with its own associated risks of drug resistance. By decreasing HIV transmission, PrEP is expected to decrease total drug resistance.40
Cost is another obstacle. Truvada costs approximately $1,540 per month.41 However, analysis has demonstrated that PrEP is cost-effective when targeted to high-risk patients.42 Most insurance plans cover PrEP, but often require high deductibles and copays; fortunately, this financial burden for patients can be mitigated or eliminated by co-pay assistance programs. The manufacturer of Truvada offers assistance programs for both insured and uninsured patients who are candidates for PrEP; details are available at http://www.truvada.com/truvada-patient-assistance.
Stigma has historically burdened individuals who seek to protect their sexual health, including HIV-negative individuals who are candidates for PrEP. Stigma surrounding HIV may decrease ART-based HIV prevention in men who have sex with men,43 while increasing high-risk behaviors44 and all-cause mortality.45
The resources listed in TABLE 2 can help physicians overcome some of the barriers to implementing PrEP.
How to deliver PrEP
Whether HIV specialists or primary care clinicians are best suited to provide PrEP is a subject of debate. HIV specialists are most familiar with ART and routine monitoring of adherence; however, they have less access to HIV-negative patients, who are the target group for PrEP.35 Family physicians tend to work in closer proximity and maintain longitudinal relationships with PrEP target groups, but in general have less experience with ART and evaluating AHI. Some may argue that competing demands may make it impractical to take a detailed sexual history during a primary care visit.46 In truth, both HIV specialists and family physicians can be appropriately equipped to provide PrEP.
TABLE 3 outlines the steps necessary to provide a patient with PrEP.47 Assessing risk is the initial step; PrEP is beneficial for patients who have one or more risk factors for HIV infection. To be eligible for TDF/FTC, a patient must be HIV-negative, and should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and kidney disease. Because TDF/FTC treats HBV infection, candidates for PrEP who test positive for HBV should be evaluated for treatment of HBV before initiating PrEP. Candidates for PrEP who test negative for HBV infection and immunity should be vaccinated.
Candidates for PrEP should also be screened and monitored for kidney disease. TDF can cause increased serum creatinine due to tubular toxicity. A patient who has an estimated creatinine clearance <60 mL/min should not receive TDF/FTC for PrEP. If a patient’s estimated creatinine clearance falls below 60 mL/min or serum creatinine increases by 0.3 mg/dL above baseline after PrEP is started, TDF/FTC should be discontinued, and the patient should be evaluated for the underlying cause of the kidney disease.27
Before starting PrEP, candidates should be screened for HIV infection and symptoms of AHI. Strongly consider testing for sexually transmitted infections that may increase the risk of HIV transmission, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or chlamydia.
Candidates who are eligible for PrEP must be counseled on medication adverse effects, adherence strategies, and symptoms of sexually transmitted infections. To initiate PrEP, candidates may be given a one-month supply of TDF/FTC; adherence, adverse effects, and other risk-reduction strategies are assessed at an office visit 3 to 4 weeks later. Subsequent prescriptions are then dispensed as a 3-month supply, with office visits to monitor PrEP scheduled for at least once every 3 months. During these monitoring visits, evaluate the patient’s HIV status, pregnancy status, adherence, adverse effects, risk-reduction behaviors, and indications for continued PrEP. Every 6 months, renal function and sexually transmitted infection status should be reassessed.
Reducing risk of harm among patients who inject drugs
Nonsexual transmission of HIV is a route of high infectivity.48 It includes transfusion of infected blood, sharing of equipment during injection drug use, and percutaneous needle sticks. Sharing of equipment during injection drug use is estimated to account for 8% of new infections in the United States.4
Harm reduction is a collection of strategies meant to reduce complications of illicit drug use, including HIV transmission. These strategies include needle and syringe programs that provide injection drug users with sterile equipment, and opioid substitution therapy.
Needle and syringe programs decrease HIV transmission49 and risky behaviors related to injection drug use,50 but federal funding of such programs is prohibited. Opioid substitution therapy reduces the incidence of HIV,50,51 injection drug use, sharing of drug preparation and injection equipment, and drug-related behaviors associated with a high risk of HIV transmission.50,52 However, in the United States, the quality of these programs varies; a study of opioid substitution therapy delivery found that 22.8% of programs provided doses that were too low to be effective.53
FDA-approved medications for opioid substitution therapy include sublingual buprenorphine, sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets or strips (Suboxone), and oral methadone. Buprenorphine-based regimens can be provided by appropriately trained primary care clinicians; methadone requires a referral to a narcotic treatment program. TABLE 4 provides training and support resources for physicians who want to integrate opioid substitution therapy into their clinical practice.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard Moore II, MD, 250 Smith Church Road, Roanoke Rapids, NC 27870; [email protected].
› Screen all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A
› Prescribe tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) for pre-exposure prophylaxis for patients at high risk of acquiring HIV. A
› Offer needle and syringe exchange programs and, when appropriate, opioid substitution therapy to individuals who inject drugs. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Despite advances in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) screening and treatment over the last 30 years, HIV remains a public health concern. In the United States, after an initial decline, total HIV incidence has failed to significantly decrease in the last 25 years. More than 1.2 million people are living with HIV in the United States, and 12.8% of them (156,300) are unaware they are affected.1 Of those diagnosed with HIV, only 30% are receiving treatment and are virally suppressed.2 Due to structural inequalities and psychosocial factors, African American and Latino patients remain disproportionately affected.3 The incidence of HIV infection among men who have sex with men has increased, and the incidence of HIV infection among people who inject drugs has plateaued after years of progressive decline.4
HIV prevention strategies are highly effective, but in general are underutilized. This article reviews 3 prevention strategies that can be administered by family physicians: HIV screening, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and harm reduction.
Who and how to screen for HIV
Early identification of HIV infection generally leads to reduced transmission because diagnosis is associated with decreases in risky behavior.5,6 In addition, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is more effective when initiated early, before the development of advanced immunosuppression.7-9
The “window period” of acute HIV infection (AHI) is the time from when the virus is transmitted to when markers of infection can be detected. Because this window period is associated with high viral transmission rates, family physicians must be familiar with symptoms of AHI (TABLE 1)10,11 and associated risk factors (eg, recent condomless sex or sharing of drug injection equipment with someone who is HIV-positive or of unknown HIV status).
Screening for HIV solely based on the presence of risk factors or clinical symptoms is not enough, however. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for HIV.12 Screening based solely on risk factors or clinical symptoms frequently leads to missed diagnoses and identification of HIV infection at more advanced stages.13,14 Both the USPSTF and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend universal opt-out screening (patients are informed that HIV screening will be performed and that they may decline testing) because such screening identifies HIV earlier and is associated with higher testing rates than opt-in screening, which requires explicit written consent and extensive pre-test counseling.
Which test to use. HIV screening with a fourth-generation antigen/antibody combination immunoassay—which detects both HIV p24 antigen and HIV antibodies—provides greater diagnostic accuracy than older tests.15 These newer tests detect HIV approximately 15 days after initial infection, reducing the window period of AHI.15,16 If you suspect a patient has AHI, consider early repeat HIV testing with a fourth-generation assay, or initial co-testing with a fourth-generation assay and a nucleic acid amplification test for HIV RNA, which makes it possible to detect infection approximately 5 days earlier than fourth-generation assays.15
Offer pre-exposure prophylaxis to high-risk patients
PrEP is the use of ART prior to HIV exposure to prevent transmission of the virus. It should be used with conventional risk reduction strategies, such as providing condoms, counseling patients about reducing risky behaviors, supporting medication adherence, and screening for and treating other sexually transmitted infections.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only one medication, Truvada (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine; TDF/FTC), for use as PrEP. Oral tenofovir-based regimens can effectively prevent HIV transmission,17-20 and strong adherence is associated with a risk reduction of 90% to 100%.17-23 The protective effect of oral PrEP is particularly strong in high-risk populations (eg, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs), where the number needed to treat to prevent one HIV infection ranges from 12 to 100, depending on the patients’ risk profile.24-26 The CDC and Department of Health and Human Services have issued guidelines for using PrEP in high-risk patients.27
Barriers to implementing PrEP. Despite being highly effective, PrEP is not routinely prescribed to high-risk patients; modeling suggests that current use of PrEP is insufficient to significantly impact the incidence of HIV.28 Demand for PrEP is high among target groups,21,29,30 but patients have expressed concerns about adverse effects31 and stigma related to ART, HIV, and being at risk for HIV.32,33 Young age, lack of social support, low perception of risk, and failure to show up for appointments are also barriers to PrEP use.28,30,34
Some physicians have expressed concern that prescribing PrEP may promote high-risk sexual behavior.35 However, because PrEP is most beneficial in individuals who already engage in high-risk sexual behavior, strategic delivery of PrEP remains an effective risk-reducing strategy.17,18,21,26,36,37 Even in instances where PrEP has been associated with higher-risk sexual behavior and higher rates of sexually transmitted infections, it still prevents as much as 100% of new HIV infections.38
Fear of drug resistance also contributes to slow implementation of PrEP. Drug resistance has been observed in clinical trials of PrEP, but it has been exceedingly rare and predominantly limited to patients who had unrecognized AHI when they started PrEP.39 Furthermore, the few cases of drug resistance attributable to PrEP pale in comparison to the large number of estimated HIV infections averted—infections that would require lifelong ART with its own associated risks of drug resistance. By decreasing HIV transmission, PrEP is expected to decrease total drug resistance.40
Cost is another obstacle. Truvada costs approximately $1,540 per month.41 However, analysis has demonstrated that PrEP is cost-effective when targeted to high-risk patients.42 Most insurance plans cover PrEP, but often require high deductibles and copays; fortunately, this financial burden for patients can be mitigated or eliminated by co-pay assistance programs. The manufacturer of Truvada offers assistance programs for both insured and uninsured patients who are candidates for PrEP; details are available at http://www.truvada.com/truvada-patient-assistance.
Stigma has historically burdened individuals who seek to protect their sexual health, including HIV-negative individuals who are candidates for PrEP. Stigma surrounding HIV may decrease ART-based HIV prevention in men who have sex with men,43 while increasing high-risk behaviors44 and all-cause mortality.45
The resources listed in TABLE 2 can help physicians overcome some of the barriers to implementing PrEP.
How to deliver PrEP
Whether HIV specialists or primary care clinicians are best suited to provide PrEP is a subject of debate. HIV specialists are most familiar with ART and routine monitoring of adherence; however, they have less access to HIV-negative patients, who are the target group for PrEP.35 Family physicians tend to work in closer proximity and maintain longitudinal relationships with PrEP target groups, but in general have less experience with ART and evaluating AHI. Some may argue that competing demands may make it impractical to take a detailed sexual history during a primary care visit.46 In truth, both HIV specialists and family physicians can be appropriately equipped to provide PrEP.
TABLE 3 outlines the steps necessary to provide a patient with PrEP.47 Assessing risk is the initial step; PrEP is beneficial for patients who have one or more risk factors for HIV infection. To be eligible for TDF/FTC, a patient must be HIV-negative, and should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and kidney disease. Because TDF/FTC treats HBV infection, candidates for PrEP who test positive for HBV should be evaluated for treatment of HBV before initiating PrEP. Candidates for PrEP who test negative for HBV infection and immunity should be vaccinated.
Candidates for PrEP should also be screened and monitored for kidney disease. TDF can cause increased serum creatinine due to tubular toxicity. A patient who has an estimated creatinine clearance <60 mL/min should not receive TDF/FTC for PrEP. If a patient’s estimated creatinine clearance falls below 60 mL/min or serum creatinine increases by 0.3 mg/dL above baseline after PrEP is started, TDF/FTC should be discontinued, and the patient should be evaluated for the underlying cause of the kidney disease.27
Before starting PrEP, candidates should be screened for HIV infection and symptoms of AHI. Strongly consider testing for sexually transmitted infections that may increase the risk of HIV transmission, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or chlamydia.
Candidates who are eligible for PrEP must be counseled on medication adverse effects, adherence strategies, and symptoms of sexually transmitted infections. To initiate PrEP, candidates may be given a one-month supply of TDF/FTC; adherence, adverse effects, and other risk-reduction strategies are assessed at an office visit 3 to 4 weeks later. Subsequent prescriptions are then dispensed as a 3-month supply, with office visits to monitor PrEP scheduled for at least once every 3 months. During these monitoring visits, evaluate the patient’s HIV status, pregnancy status, adherence, adverse effects, risk-reduction behaviors, and indications for continued PrEP. Every 6 months, renal function and sexually transmitted infection status should be reassessed.
Reducing risk of harm among patients who inject drugs
Nonsexual transmission of HIV is a route of high infectivity.48 It includes transfusion of infected blood, sharing of equipment during injection drug use, and percutaneous needle sticks. Sharing of equipment during injection drug use is estimated to account for 8% of new infections in the United States.4
Harm reduction is a collection of strategies meant to reduce complications of illicit drug use, including HIV transmission. These strategies include needle and syringe programs that provide injection drug users with sterile equipment, and opioid substitution therapy.
Needle and syringe programs decrease HIV transmission49 and risky behaviors related to injection drug use,50 but federal funding of such programs is prohibited. Opioid substitution therapy reduces the incidence of HIV,50,51 injection drug use, sharing of drug preparation and injection equipment, and drug-related behaviors associated with a high risk of HIV transmission.50,52 However, in the United States, the quality of these programs varies; a study of opioid substitution therapy delivery found that 22.8% of programs provided doses that were too low to be effective.53
FDA-approved medications for opioid substitution therapy include sublingual buprenorphine, sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets or strips (Suboxone), and oral methadone. Buprenorphine-based regimens can be provided by appropriately trained primary care clinicians; methadone requires a referral to a narcotic treatment program. TABLE 4 provides training and support resources for physicians who want to integrate opioid substitution therapy into their clinical practice.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard Moore II, MD, 250 Smith Church Road, Roanoke Rapids, NC 27870; [email protected].
1. Hall HI, An Q, Tang T, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed HIV infection--United States, 2008-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:657-662.
2. Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:1113-1117.
3. Maulsby C, Millet G, Lindsey K, et al. HIV among black men who have sex with men (MSM) in the United States: a review of the literature. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:10-25.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Estimated HIV incidence among adults and adolescents in the United States, 2007-2010, HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2012. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_hssr_vol_17_no_4.pdf. Accessed October 8, 2015.
5. Cleary PD, Van Devanter N, Rogers TF, et al. Behavior changes after notification of HIV infection. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:1586-1590.
6. Higgins DL, Galavotti C, O’Reilly KR, et al. Evidence for the effects of HIV antibody counseling and testing on risk behaviors. JAMA. 1991;266:2419-2429.
7. Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17-26.
8. Palella FJ Jr, Deloria-Knoll M, Chmiel JS, et al. Survival benefit of initiating antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected persons in different CD4 cell strata. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:620-626.
9. INSIGHT START Study Group, Lundgren JD, Babiker AG, Gordin F, et al. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in early asymptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:795-807.
10. Daar ES, Pilcher CD, Hecht FM. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of primary HIV-1 infection. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2008;3:10-15.
11. Tindall B, Barker S, Donovan B, et al. Characterization of the acute clinical illness associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:945-949.
12. Moyer V, US Preventative Services Task Force. Screening for HIV: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:51-60.
13. Jenkins T, Gardner E, Thrun M, et al. Risk-based HIV testing fails to detect the majority of HIV-infected persons in medical care settings. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33:329-333.
14. Klein D, Hurley LB, Merrill D, et al. Review of medical encounters in the 5 years before a diagnosis of HIV-1 infection: implications for early detection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;32:143-152.
15. Pandori M, Hackett J Jr, Louie B, et al. Assessment of the ability of a fourth-generation immunoassay for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody and p24 antigen to detect both acute and recent HIV infections in a high-risk setting. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2639-2642.
16. Branson BM. The future of HIV testing. J Acquir Imm Defic Syndr. 2010;55 Suppl 2:S102-S105.
17. Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599.
18. Baeten JM, Donnell D, Ndase P, et al; Partners PrEP Study Team. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention in heterosexual men and women. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:399-410.
19. Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:423-434.
20. Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2083-2090.
21. Grant RM, Anderson PL, McMahan V, et al. Uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis, sexual practices, and HIV incidence in men and transgender women who have sex with men: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:820-829.
22. Anderson PL, Glidden DV, Liu A, et al. Emtricitabine-tenofovir concentrations and pre-exposure prophylaxis efficacy in men who have sex with men. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:151ra125.
23. Henderson FL, Taylor AW, Chirwa LI, et al. Characteristics and oral PrEP adherence in the TDF2 open-label extension in Botswana. Paper presented at International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; July 1922, 2015; Vancouver, Canada.
24. Murnane PM, Celum C, Mugo N, et al. Efficacy of preexposure prophylaxis for HIV-1 prevention among high-risk heterosexuals: subgroup analyses from a randomized trial. AIDS. 2013;27:2155-2160.
25. Heffron R, Mugo N, Were E, et al. Preexposure prophylaxis is efficacious for HIV-1 prevention among women using depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for contraception. AIDS. 2014;28:2771-2776.
26. Buchbinder SP, Glidden DV, Liu AY, et al. HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in men who have sex with men and transgender women: a secondary analysis of a phase 3 randomised controlled efficacy trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:468-475.
27. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States – 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed June 18, 2015.
28. Grant RM. Scale-up of preexposure prophylaxis in San Francisco to impact HIV incidence. Abstract 25. Paper presented at Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 23-26, 2015; Seattle, WA.
29. Cohen SE, Vittinghoff E, Bacon O, et al. High interest in preexposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men at risk for HIV infection: baseline data from the US PrEP demonstration project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;68:439-448.
30. Haberer JE, Baeten JM, Campbell J, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a substudy cohort within a clinical trial of serodiscordant couples in East Africa. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001511.
31. Gilmore H, Koester K, Liu A, et al. To PrEP or not to PrEP: Perspectives from US iPrEx open label extension (OLE) participants. Abstract 440. Paper presented at 9th International Conference on HIV Treatment and Prevention Adherence; June 9, 2014; Miami Beach, FL.
32. Jain S, Gregor C, Krakower D, et al. Attitudes and interest toward HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among participants using HIV non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (NPEP). Poster Abstract 1523. Poster presented at Infectious Disease Society of America Conference; October 8-12, 2014; Philadelphia, PA.
33. van der Straten A, Stadler J, Luecke E, et al; VOICE-C Study Team, Perspectives on use of oral and vaginal antiretrovirals for HIV prevention: the VOICE-C qualitative study in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19146.
34. Corneli AL, McKenna K, Headley J, et al; FEM-PrEP Study Group. A descriptive analysis of perceptions of HIV risk and worry about acquiring HIV among FEM-PrEP participants who seroconverted in Bondo, Kenya, and Pretoria, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19152.
35. Krakower D, Ware N, Mitty JA, et al. HIV providers’ perceived barriers and facilitators to implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis in care settings: a qualitative study. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1712-1721.
36. McCormack S, Dunn DT, Desai M, et al. Pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent the acquisition of HIV-1 infection (PROUD): effectiveness results from the pilot phase of a pragmatic open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2015. [Epub ahead of print].
37. Mugwanya KK, Donnell D, Celum C, et al. Sexual behaviour of heterosexual men and women receiving antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:1021-1028.
38. Volk JE, Marcus JL, Phengrasamy T, et al. No new HIV infections with increasing use of HIV preexposure prophylaxis in a clinical practice setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1601-1603.
39. Lehman DA, Baeten JM, McCoy CO, et al. Risk of drug resistance among persons acquiring HIV within a randomized clinical trial of single- or dual-agent preexposure prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1211-1218.
40. Supervie V, Garcia-Lerma JG, Heneine W, et al. HIV, transmitted drug resistance, and the paradox of preexposure prophylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:12381-12386.
41. AIDSinfo. Cost considerations and antiretroviral therapy. AIDSinfo Web site. Available at: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/1/adult-and-adolescent-arv-guidelines/459/cost-considerations-and-antiretroviral-therapy. Accessed December 14, 2015.
42. Gomez GB, Borquez A, Case KK, et al. The cost and impact of scaling up pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness modelling studies. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001401.
43. Oldenburg CE, Perez-Brumer AG, Hatzenbuehler ML, et al. State-level structural sexual stigma and HIV prevention in a national online sample of HIV-uninfected MSM in the United States. AIDS. 2015;29:837-845.
44. Hatzenbuehler ML, O’Cleirigh C, Mayer KH, et al. Prospective associations between HIV-related stigma, transmission risk behaviors, and adverse mental health outcomes in men who have sex with men. Ann Behav Med. 2011;42:227-234.
45. Hatzenbuehler ML, Bellatorre A, Lee Y, et al. Structural stigma and all-cause mortality in sexual minority populations. Soc Sci Med. 2014;103:33-41.
46. Arnold EA, Hazelton P, Lane T, et al. A qualitative study of provider thoughts on implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in clinical settings to prevent HIV infection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40603.
47. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center. For PrEP Providers. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center Web site. Available at: http://www.med.unc.edu/ncaidstraining/prep/for-providers/for-prep-prescribers. Accessed July 7, 2015.
48. Patel P, Borkowf CB, Brook JT, et al. Estimating per-act HIV transmission risk: a systematic review. AIDS. 2014;28:1509-1519.
49. Aspinall EJ, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43:235-248.
50. MacArthur GJ, van Velzen E, Palmateer N, et al. Interventions to prevent HIV and Hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: a review of reviews to assess evidence of effectiveness. Int J Drug Policy. 2014;25:34-52.
51. MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5945.
52. Gowing L, Farrell MF, Bornemann R, et al. Oral substitution treatment of injecting opioid users for prevention of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(8):CD004145.
53. D’Aunno T, Pollack HA, Frimpong JA, et al. Evidence-based treatment for opioid disorders: a 23-year national study of methadone dose levels. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2014;47:245-250.
1. Hall HI, An Q, Tang T, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed HIV infection--United States, 2008-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:657-662.
2. Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:1113-1117.
3. Maulsby C, Millet G, Lindsey K, et al. HIV among black men who have sex with men (MSM) in the United States: a review of the literature. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:10-25.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Estimated HIV incidence among adults and adolescents in the United States, 2007-2010, HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2012. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_hssr_vol_17_no_4.pdf. Accessed October 8, 2015.
5. Cleary PD, Van Devanter N, Rogers TF, et al. Behavior changes after notification of HIV infection. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:1586-1590.
6. Higgins DL, Galavotti C, O’Reilly KR, et al. Evidence for the effects of HIV antibody counseling and testing on risk behaviors. JAMA. 1991;266:2419-2429.
7. Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17-26.
8. Palella FJ Jr, Deloria-Knoll M, Chmiel JS, et al. Survival benefit of initiating antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected persons in different CD4 cell strata. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:620-626.
9. INSIGHT START Study Group, Lundgren JD, Babiker AG, Gordin F, et al. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in early asymptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:795-807.
10. Daar ES, Pilcher CD, Hecht FM. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of primary HIV-1 infection. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2008;3:10-15.
11. Tindall B, Barker S, Donovan B, et al. Characterization of the acute clinical illness associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:945-949.
12. Moyer V, US Preventative Services Task Force. Screening for HIV: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:51-60.
13. Jenkins T, Gardner E, Thrun M, et al. Risk-based HIV testing fails to detect the majority of HIV-infected persons in medical care settings. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33:329-333.
14. Klein D, Hurley LB, Merrill D, et al. Review of medical encounters in the 5 years before a diagnosis of HIV-1 infection: implications for early detection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;32:143-152.
15. Pandori M, Hackett J Jr, Louie B, et al. Assessment of the ability of a fourth-generation immunoassay for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody and p24 antigen to detect both acute and recent HIV infections in a high-risk setting. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2639-2642.
16. Branson BM. The future of HIV testing. J Acquir Imm Defic Syndr. 2010;55 Suppl 2:S102-S105.
17. Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599.
18. Baeten JM, Donnell D, Ndase P, et al; Partners PrEP Study Team. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention in heterosexual men and women. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:399-410.
19. Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:423-434.
20. Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2083-2090.
21. Grant RM, Anderson PL, McMahan V, et al. Uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis, sexual practices, and HIV incidence in men and transgender women who have sex with men: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:820-829.
22. Anderson PL, Glidden DV, Liu A, et al. Emtricitabine-tenofovir concentrations and pre-exposure prophylaxis efficacy in men who have sex with men. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:151ra125.
23. Henderson FL, Taylor AW, Chirwa LI, et al. Characteristics and oral PrEP adherence in the TDF2 open-label extension in Botswana. Paper presented at International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; July 1922, 2015; Vancouver, Canada.
24. Murnane PM, Celum C, Mugo N, et al. Efficacy of preexposure prophylaxis for HIV-1 prevention among high-risk heterosexuals: subgroup analyses from a randomized trial. AIDS. 2013;27:2155-2160.
25. Heffron R, Mugo N, Were E, et al. Preexposure prophylaxis is efficacious for HIV-1 prevention among women using depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for contraception. AIDS. 2014;28:2771-2776.
26. Buchbinder SP, Glidden DV, Liu AY, et al. HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in men who have sex with men and transgender women: a secondary analysis of a phase 3 randomised controlled efficacy trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:468-475.
27. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States – 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed June 18, 2015.
28. Grant RM. Scale-up of preexposure prophylaxis in San Francisco to impact HIV incidence. Abstract 25. Paper presented at Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 23-26, 2015; Seattle, WA.
29. Cohen SE, Vittinghoff E, Bacon O, et al. High interest in preexposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men at risk for HIV infection: baseline data from the US PrEP demonstration project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;68:439-448.
30. Haberer JE, Baeten JM, Campbell J, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a substudy cohort within a clinical trial of serodiscordant couples in East Africa. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001511.
31. Gilmore H, Koester K, Liu A, et al. To PrEP or not to PrEP: Perspectives from US iPrEx open label extension (OLE) participants. Abstract 440. Paper presented at 9th International Conference on HIV Treatment and Prevention Adherence; June 9, 2014; Miami Beach, FL.
32. Jain S, Gregor C, Krakower D, et al. Attitudes and interest toward HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among participants using HIV non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (NPEP). Poster Abstract 1523. Poster presented at Infectious Disease Society of America Conference; October 8-12, 2014; Philadelphia, PA.
33. van der Straten A, Stadler J, Luecke E, et al; VOICE-C Study Team, Perspectives on use of oral and vaginal antiretrovirals for HIV prevention: the VOICE-C qualitative study in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19146.
34. Corneli AL, McKenna K, Headley J, et al; FEM-PrEP Study Group. A descriptive analysis of perceptions of HIV risk and worry about acquiring HIV among FEM-PrEP participants who seroconverted in Bondo, Kenya, and Pretoria, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19152.
35. Krakower D, Ware N, Mitty JA, et al. HIV providers’ perceived barriers and facilitators to implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis in care settings: a qualitative study. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1712-1721.
36. McCormack S, Dunn DT, Desai M, et al. Pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent the acquisition of HIV-1 infection (PROUD): effectiveness results from the pilot phase of a pragmatic open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2015. [Epub ahead of print].
37. Mugwanya KK, Donnell D, Celum C, et al. Sexual behaviour of heterosexual men and women receiving antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:1021-1028.
38. Volk JE, Marcus JL, Phengrasamy T, et al. No new HIV infections with increasing use of HIV preexposure prophylaxis in a clinical practice setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1601-1603.
39. Lehman DA, Baeten JM, McCoy CO, et al. Risk of drug resistance among persons acquiring HIV within a randomized clinical trial of single- or dual-agent preexposure prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1211-1218.
40. Supervie V, Garcia-Lerma JG, Heneine W, et al. HIV, transmitted drug resistance, and the paradox of preexposure prophylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:12381-12386.
41. AIDSinfo. Cost considerations and antiretroviral therapy. AIDSinfo Web site. Available at: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/1/adult-and-adolescent-arv-guidelines/459/cost-considerations-and-antiretroviral-therapy. Accessed December 14, 2015.
42. Gomez GB, Borquez A, Case KK, et al. The cost and impact of scaling up pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness modelling studies. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001401.
43. Oldenburg CE, Perez-Brumer AG, Hatzenbuehler ML, et al. State-level structural sexual stigma and HIV prevention in a national online sample of HIV-uninfected MSM in the United States. AIDS. 2015;29:837-845.
44. Hatzenbuehler ML, O’Cleirigh C, Mayer KH, et al. Prospective associations between HIV-related stigma, transmission risk behaviors, and adverse mental health outcomes in men who have sex with men. Ann Behav Med. 2011;42:227-234.
45. Hatzenbuehler ML, Bellatorre A, Lee Y, et al. Structural stigma and all-cause mortality in sexual minority populations. Soc Sci Med. 2014;103:33-41.
46. Arnold EA, Hazelton P, Lane T, et al. A qualitative study of provider thoughts on implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in clinical settings to prevent HIV infection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40603.
47. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center. For PrEP Providers. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center Web site. Available at: http://www.med.unc.edu/ncaidstraining/prep/for-providers/for-prep-prescribers. Accessed July 7, 2015.
48. Patel P, Borkowf CB, Brook JT, et al. Estimating per-act HIV transmission risk: a systematic review. AIDS. 2014;28:1509-1519.
49. Aspinall EJ, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43:235-248.
50. MacArthur GJ, van Velzen E, Palmateer N, et al. Interventions to prevent HIV and Hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: a review of reviews to assess evidence of effectiveness. Int J Drug Policy. 2014;25:34-52.
51. MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5945.
52. Gowing L, Farrell MF, Bornemann R, et al. Oral substitution treatment of injecting opioid users for prevention of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(8):CD004145.
53. D’Aunno T, Pollack HA, Frimpong JA, et al. Evidence-based treatment for opioid disorders: a 23-year national study of methadone dose levels. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2014;47:245-250.
HIV prevention: A 3-pronged approach
› Screen all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A
› Prescribe tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) for pre-exposure prophylaxis for patients at high risk of acquiring HIV. A
› Offer needle and syringe exchange programs and, when appropriate, opioid substitution therapy to individuals who inject drugs. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Despite advances in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) screening and treatment over the last 30 years, HIV remains a public health concern. In the United States, after an initial decline, total HIV incidence has failed to significantly decrease in the last 25 years. More than 1.2 million people are living with HIV in the United States, and 12.8% of them (156,300) are unaware they are affected.1 Of those diagnosed with HIV, only 30% are receiving treatment and are virally suppressed.2 Due to structural inequalities and psychosocial factors, African American and Latino patients remain disproportionately affected.3 The incidence of HIV infection among men who have sex with men has increased, and the incidence of HIV infection among people who inject drugs has plateaued after years of progressive decline.4
HIV prevention strategies are highly effective, but in general are underutilized. This article reviews 3 prevention strategies that can be administered by family physicians: HIV screening, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and harm reduction.
Who and how to screen for HIV
Early identification of HIV infection generally leads to reduced transmission because diagnosis is associated with decreases in risky behavior.5,6 In addition, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is more effective when initiated early, before the development of advanced immunosuppression.7-9
The “window period” of acute HIV infection (AHI) is the time from when the virus is transmitted to when markers of infection can be detected. Because this window period is associated with high viral transmission rates, family physicians must be familiar with symptoms of AHI (TABLE 1)10,11 and associated risk factors (eg, recent condomless sex or sharing of drug injection equipment with someone who is HIV-positive or of unknown HIV status).
Screening for HIV solely based on the presence of risk factors or clinical symptoms is not enough, however. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for HIV.12 Screening based solely on risk factors or clinical symptoms frequently leads to missed diagnoses and identification of HIV infection at more advanced stages.13,14 Both the USPSTF and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend universal opt-out screening (patients are informed that HIV screening will be performed and that they may decline testing) because such screening identifies HIV earlier and is associated with higher testing rates than opt-in screening, which requires explicit written consent and extensive pre-test counseling.
Which test to use. HIV screening with a fourth-generation antigen/antibody combination immunoassay—which detects both HIV p24 antigen and HIV antibodies—provides greater diagnostic accuracy than older tests.15 These newer tests detect HIV approximately 15 days after initial infection, reducing the window period of AHI.15,16 If you suspect a patient has AHI, consider early repeat HIV testing with a fourth-generation assay, or initial co-testing with a fourth-generation assay and a nucleic acid amplification test for HIV RNA, which makes it possible to detect infection approximately 5 days earlier than fourth-generation assays.15
Offer pre-exposure prophylaxis to high-risk patients
PrEP is the use of ART prior to HIV exposure to prevent transmission of the virus. It should be used with conventional risk reduction strategies, such as providing condoms, counseling patients about reducing risky behaviors, supporting medication adherence, and screening for and treating other sexually transmitted infections.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only one medication, Truvada (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine; TDF/FTC), for use as PrEP. Oral tenofovir-based regimens can effectively prevent HIV transmission,17-20 and strong adherence is associated with a risk reduction of 90% to 100%.17-23 The protective effect of oral PrEP is particularly strong in high-risk populations (eg, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs), where the number needed to treat to prevent one HIV infection ranges from 12 to 100, depending on the patients’ risk profile.24-26 The CDC and Department of Health and Human Services have issued guidelines for using PrEP in high-risk patients.27
Barriers to implementing PrEP. Despite being highly effective, PrEP is not routinely prescribed to high-risk patients; modeling suggests that current use of PrEP is insufficient to significantly impact the incidence of HIV.28 Demand for PrEP is high among target groups,21,29,30 but patients have expressed concerns about adverse effects31 and stigma related to ART, HIV, and being at risk for HIV.32,33 Young age, lack of social support, low perception of risk, and failure to show up for appointments are also barriers to PrEP use.28,30,34
Some physicians have expressed concern that prescribing PrEP may promote high-risk sexual behavior.35 However, because PrEP is most beneficial in individuals who already engage in high-risk sexual behavior, strategic delivery of PrEP remains an effective risk-reducing strategy.17,18,21,26,36,37 Even in instances where PrEP has been associated with higher-risk sexual behavior and higher rates of sexually transmitted infections, it still prevents as much as 100% of new HIV infections.38
Fear of drug resistance also contributes to slow implementation of PrEP. Drug resistance has been observed in clinical trials of PrEP, but it has been exceedingly rare and predominantly limited to patients who had unrecognized AHI when they started PrEP.39 Furthermore, the few cases of drug resistance attributable to PrEP pale in comparison to the large number of estimated HIV infections averted—infections that would require lifelong ART with its own associated risks of drug resistance. By decreasing HIV transmission, PrEP is expected to decrease total drug resistance.40
Cost is another obstacle. Truvada costs approximately $1,540 per month.41 However, analysis has demonstrated that PrEP is cost-effective when targeted to high-risk patients.42 Most insurance plans cover PrEP, but often require high deductibles and copays; fortunately, this financial burden for patients can be mitigated or eliminated by co-pay assistance programs. The manufacturer of Truvada offers assistance programs for both insured and uninsured patients who are candidates for PrEP; details are available at http://www.truvada.com/truvada-patient-assistance.
Stigma has historically burdened individuals who seek to protect their sexual health, including HIV-negative individuals who are candidates for PrEP. Stigma surrounding HIV may decrease ART-based HIV prevention in men who have sex with men,43 while increasing high-risk behaviors44 and all-cause mortality.45
The resources listed in TABLE 2 can help physicians overcome some of the barriers to implementing PrEP.
How to deliver PrEP
Whether HIV specialists or primary care clinicians are best suited to provide PrEP is a subject of debate. HIV specialists are most familiar with ART and routine monitoring of adherence; however, they have less access to HIV-negative patients, who are the target group for PrEP.35 Family physicians tend to work in closer proximity and maintain longitudinal relationships with PrEP target groups, but in general have less experience with ART and evaluating AHI. Some may argue that competing demands may make it impractical to take a detailed sexual history during a primary care visit.46 In truth, both HIV specialists and family physicians can be appropriately equipped to provide PrEP.
TABLE 3 outlines the steps necessary to provide a patient with PrEP.47 Assessing risk is the initial step; PrEP is beneficial for patients who have one or more risk factors for HIV infection. To be eligible for TDF/FTC, a patient must be HIV-negative, and should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and kidney disease. Because TDF/FTC treats HBV infection, candidates for PrEP who test positive for HBV should be evaluated for treatment of HBV before initiating PrEP. Candidates for PrEP who test negative for HBV infection and immunity should be vaccinated.
Candidates for PrEP should also be screened and monitored for kidney disease. TDF can cause increased serum creatinine due to tubular toxicity. A patient who has an estimated creatinine clearance <60 mL/min should not receive TDF/FTC for PrEP. If a patient’s estimated creatinine clearance falls below 60 mL/min or serum creatinine increases by 0.3 mg/dL above baseline after PrEP is started, TDF/FTC should be discontinued, and the patient should be evaluated for the underlying cause of the kidney disease.27
Before starting PrEP, candidates should be screened for HIV infection and symptoms of AHI. Strongly consider testing for sexually transmitted infections that may increase the risk of HIV transmission, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or chlamydia.
Candidates who are eligible for PrEP must be counseled on medication adverse effects, adherence strategies, and symptoms of sexually transmitted infections. To initiate PrEP, candidates may be given a one-month supply of TDF/FTC; adherence, adverse effects, and other risk-reduction strategies are assessed at an office visit 3 to 4 weeks later. Subsequent prescriptions are then dispensed as a 3-month supply, with office visits to monitor PrEP scheduled for at least once every 3 months. During these monitoring visits, evaluate the patient’s HIV status, pregnancy status, adherence, adverse effects, risk-reduction behaviors, and indications for continued PrEP. Every 6 months, renal function and sexually transmitted infection status should be reassessed.
Reducing risk of harm among patients who inject drugs
Nonsexual transmission of HIV is a route of high infectivity.48 It includes transfusion of infected blood, sharing of equipment during injection drug use, and percutaneous needle sticks. Sharing of equipment during injection drug use is estimated to account for 8% of new infections in the United States.4
Harm reduction is a collection of strategies meant to reduce complications of illicit drug use, including HIV transmission. These strategies include needle and syringe programs that provide injection drug users with sterile equipment, and opioid substitution therapy.
Needle and syringe programs decrease HIV transmission49 and risky behaviors related to injection drug use,50 but federal funding of such programs is prohibited. Opioid substitution therapy reduces the incidence of HIV,50,51 injection drug use, sharing of drug preparation and injection equipment, and drug-related behaviors associated with a high risk of HIV transmission.50,52 However, in the United States, the quality of these programs varies; a study of opioid substitution therapy delivery found that 22.8% of programs provided doses that were too low to be effective.53
FDA-approved medications for opioid substitution therapy include sublingual buprenorphine, sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets or strips (Suboxone), and oral methadone. Buprenorphine-based regimens can be provided by appropriately trained primary care clinicians; methadone requires a referral to a narcotic treatment program. TABLE 4 provides training and support resources for physicians who want to integrate opioid substitution therapy into their clinical practice.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard Moore II, MD, 250 Smith Church Road, Roanoke Rapids, NC 27870; [email protected].
1. Hall HI, An Q, Tang T, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed HIV infection--United States, 2008-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:657-662.
2. Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:1113-1117.
3. Maulsby C, Millet G, Lindsey K, et al. HIV among black men who have sex with men (MSM) in the United States: a review of the literature. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:10-25.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Estimated HIV incidence among adults and adolescents in the United States, 2007-2010, HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2012. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_hssr_vol_17_no_4.pdf. Accessed October 8, 2015.
5. Cleary PD, Van Devanter N, Rogers TF, et al. Behavior changes after notification of HIV infection. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:1586-1590.
6. Higgins DL, Galavotti C, O’Reilly KR, et al. Evidence for the effects of HIV antibody counseling and testing on risk behaviors. JAMA. 1991;266:2419-2429.
7. Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17-26.
8. Palella FJ Jr, Deloria-Knoll M, Chmiel JS, et al. Survival benefit of initiating antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected persons in different CD4 cell strata. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:620-626.
9. INSIGHT START Study Group, Lundgren JD, Babiker AG, Gordin F, et al. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in early asymptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:795-807.
10. Daar ES, Pilcher CD, Hecht FM. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of primary HIV-1 infection. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2008;3:10-15.
11. Tindall B, Barker S, Donovan B, et al. Characterization of the acute clinical illness associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:945-949.
12. Moyer V, US Preventative Services Task Force. Screening for HIV: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:51-60.
13. Jenkins T, Gardner E, Thrun M, et al. Risk-based HIV testing fails to detect the majority of HIV-infected persons in medical care settings. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33:329-333.
14. Klein D, Hurley LB, Merrill D, et al. Review of medical encounters in the 5 years before a diagnosis of HIV-1 infection: implications for early detection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;32:143-152.
15. Pandori M, Hackett J Jr, Louie B, et al. Assessment of the ability of a fourth-generation immunoassay for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody and p24 antigen to detect both acute and recent HIV infections in a high-risk setting. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2639-2642.
16. Branson BM. The future of HIV testing. J Acquir Imm Defic Syndr. 2010;55 Suppl 2:S102-S105.
17. Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599.
18. Baeten JM, Donnell D, Ndase P, et al; Partners PrEP Study Team. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention in heterosexual men and women. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:399-410.
19. Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:423-434.
20. Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2083-2090.
21. Grant RM, Anderson PL, McMahan V, et al. Uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis, sexual practices, and HIV incidence in men and transgender women who have sex with men: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:820-829.
22. Anderson PL, Glidden DV, Liu A, et al. Emtricitabine-tenofovir concentrations and pre-exposure prophylaxis efficacy in men who have sex with men. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:151ra125.
23. Henderson FL, Taylor AW, Chirwa LI, et al. Characteristics and oral PrEP adherence in the TDF2 open-label extension in Botswana. Paper presented at International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; July 1922, 2015; Vancouver, Canada.
24. Murnane PM, Celum C, Mugo N, et al. Efficacy of preexposure prophylaxis for HIV-1 prevention among high-risk heterosexuals: subgroup analyses from a randomized trial. AIDS. 2013;27:2155-2160.
25. Heffron R, Mugo N, Were E, et al. Preexposure prophylaxis is efficacious for HIV-1 prevention among women using depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for contraception. AIDS. 2014;28:2771-2776.
26. Buchbinder SP, Glidden DV, Liu AY, et al. HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in men who have sex with men and transgender women: a secondary analysis of a phase 3 randomised controlled efficacy trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:468-475.
27. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States – 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed June 18, 2015.
28. Grant RM. Scale-up of preexposure prophylaxis in San Francisco to impact HIV incidence. Abstract 25. Paper presented at Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 23-26, 2015; Seattle, WA.
29. Cohen SE, Vittinghoff E, Bacon O, et al. High interest in preexposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men at risk for HIV infection: baseline data from the US PrEP demonstration project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;68:439-448.
30. Haberer JE, Baeten JM, Campbell J, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a substudy cohort within a clinical trial of serodiscordant couples in East Africa. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001511.
31. Gilmore H, Koester K, Liu A, et al. To PrEP or not to PrEP: Perspectives from US iPrEx open label extension (OLE) participants. Abstract 440. Paper presented at 9th International Conference on HIV Treatment and Prevention Adherence; June 9, 2014; Miami Beach, FL.
32. Jain S, Gregor C, Krakower D, et al. Attitudes and interest toward HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among participants using HIV non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (NPEP). Poster Abstract 1523. Poster presented at Infectious Disease Society of America Conference; October 8-12, 2014; Philadelphia, PA.
33. van der Straten A, Stadler J, Luecke E, et al; VOICE-C Study Team, Perspectives on use of oral and vaginal antiretrovirals for HIV prevention: the VOICE-C qualitative study in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19146.
34. Corneli AL, McKenna K, Headley J, et al; FEM-PrEP Study Group. A descriptive analysis of perceptions of HIV risk and worry about acquiring HIV among FEM-PrEP participants who seroconverted in Bondo, Kenya, and Pretoria, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19152.
35. Krakower D, Ware N, Mitty JA, et al. HIV providers’ perceived barriers and facilitators to implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis in care settings: a qualitative study. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1712-1721.
36. McCormack S, Dunn DT, Desai M, et al. Pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent the acquisition of HIV-1 infection (PROUD): effectiveness results from the pilot phase of a pragmatic open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2015. [Epub ahead of print].
37. Mugwanya KK, Donnell D, Celum C, et al. Sexual behaviour of heterosexual men and women receiving antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:1021-1028.
38. Volk JE, Marcus JL, Phengrasamy T, et al. No new HIV infections with increasing use of HIV preexposure prophylaxis in a clinical practice setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1601-1603.
39. Lehman DA, Baeten JM, McCoy CO, et al. Risk of drug resistance among persons acquiring HIV within a randomized clinical trial of single- or dual-agent preexposure prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1211-1218.
40. Supervie V, Garcia-Lerma JG, Heneine W, et al. HIV, transmitted drug resistance, and the paradox of preexposure prophylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:12381-12386.
41. AIDSinfo. Cost considerations and antiretroviral therapy. AIDSinfo Web site. Available at: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/1/adult-and-adolescent-arv-guidelines/459/cost-considerations-and-antiretroviral-therapy. Accessed December 14, 2015.
42. Gomez GB, Borquez A, Case KK, et al. The cost and impact of scaling up pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness modelling studies. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001401.
43. Oldenburg CE, Perez-Brumer AG, Hatzenbuehler ML, et al. State-level structural sexual stigma and HIV prevention in a national online sample of HIV-uninfected MSM in the United States. AIDS. 2015;29:837-845.
44. Hatzenbuehler ML, O’Cleirigh C, Mayer KH, et al. Prospective associations between HIV-related stigma, transmission risk behaviors, and adverse mental health outcomes in men who have sex with men. Ann Behav Med. 2011;42:227-234.
45. Hatzenbuehler ML, Bellatorre A, Lee Y, et al. Structural stigma and all-cause mortality in sexual minority populations. Soc Sci Med. 2014;103:33-41.
46. Arnold EA, Hazelton P, Lane T, et al. A qualitative study of provider thoughts on implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in clinical settings to prevent HIV infection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40603.
47. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center. For PrEP Providers. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center Web site. Available at: http://www.med.unc.edu/ncaidstraining/prep/for-providers/for-prep-prescribers. Accessed July 7, 2015.
48. Patel P, Borkowf CB, Brook JT, et al. Estimating per-act HIV transmission risk: a systematic review. AIDS. 2014;28:1509-1519.
49. Aspinall EJ, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43:235-248.
50. MacArthur GJ, van Velzen E, Palmateer N, et al. Interventions to prevent HIV and Hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: a review of reviews to assess evidence of effectiveness. Int J Drug Policy. 2014;25:34-52.
51. MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5945.
52. Gowing L, Farrell MF, Bornemann R, et al. Oral substitution treatment of injecting opioid users for prevention of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(8):CD004145.
53. D’Aunno T, Pollack HA, Frimpong JA, et al. Evidence-based treatment for opioid disorders: a 23-year national study of methadone dose levels. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2014;47:245-250.
› Screen all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A
› Prescribe tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) for pre-exposure prophylaxis for patients at high risk of acquiring HIV. A
› Offer needle and syringe exchange programs and, when appropriate, opioid substitution therapy to individuals who inject drugs. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Despite advances in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) screening and treatment over the last 30 years, HIV remains a public health concern. In the United States, after an initial decline, total HIV incidence has failed to significantly decrease in the last 25 years. More than 1.2 million people are living with HIV in the United States, and 12.8% of them (156,300) are unaware they are affected.1 Of those diagnosed with HIV, only 30% are receiving treatment and are virally suppressed.2 Due to structural inequalities and psychosocial factors, African American and Latino patients remain disproportionately affected.3 The incidence of HIV infection among men who have sex with men has increased, and the incidence of HIV infection among people who inject drugs has plateaued after years of progressive decline.4
HIV prevention strategies are highly effective, but in general are underutilized. This article reviews 3 prevention strategies that can be administered by family physicians: HIV screening, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and harm reduction.
Who and how to screen for HIV
Early identification of HIV infection generally leads to reduced transmission because diagnosis is associated with decreases in risky behavior.5,6 In addition, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is more effective when initiated early, before the development of advanced immunosuppression.7-9
The “window period” of acute HIV infection (AHI) is the time from when the virus is transmitted to when markers of infection can be detected. Because this window period is associated with high viral transmission rates, family physicians must be familiar with symptoms of AHI (TABLE 1)10,11 and associated risk factors (eg, recent condomless sex or sharing of drug injection equipment with someone who is HIV-positive or of unknown HIV status).
Screening for HIV solely based on the presence of risk factors or clinical symptoms is not enough, however. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for HIV.12 Screening based solely on risk factors or clinical symptoms frequently leads to missed diagnoses and identification of HIV infection at more advanced stages.13,14 Both the USPSTF and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend universal opt-out screening (patients are informed that HIV screening will be performed and that they may decline testing) because such screening identifies HIV earlier and is associated with higher testing rates than opt-in screening, which requires explicit written consent and extensive pre-test counseling.
Which test to use. HIV screening with a fourth-generation antigen/antibody combination immunoassay—which detects both HIV p24 antigen and HIV antibodies—provides greater diagnostic accuracy than older tests.15 These newer tests detect HIV approximately 15 days after initial infection, reducing the window period of AHI.15,16 If you suspect a patient has AHI, consider early repeat HIV testing with a fourth-generation assay, or initial co-testing with a fourth-generation assay and a nucleic acid amplification test for HIV RNA, which makes it possible to detect infection approximately 5 days earlier than fourth-generation assays.15
Offer pre-exposure prophylaxis to high-risk patients
PrEP is the use of ART prior to HIV exposure to prevent transmission of the virus. It should be used with conventional risk reduction strategies, such as providing condoms, counseling patients about reducing risky behaviors, supporting medication adherence, and screening for and treating other sexually transmitted infections.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only one medication, Truvada (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine; TDF/FTC), for use as PrEP. Oral tenofovir-based regimens can effectively prevent HIV transmission,17-20 and strong adherence is associated with a risk reduction of 90% to 100%.17-23 The protective effect of oral PrEP is particularly strong in high-risk populations (eg, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs), where the number needed to treat to prevent one HIV infection ranges from 12 to 100, depending on the patients’ risk profile.24-26 The CDC and Department of Health and Human Services have issued guidelines for using PrEP in high-risk patients.27
Barriers to implementing PrEP. Despite being highly effective, PrEP is not routinely prescribed to high-risk patients; modeling suggests that current use of PrEP is insufficient to significantly impact the incidence of HIV.28 Demand for PrEP is high among target groups,21,29,30 but patients have expressed concerns about adverse effects31 and stigma related to ART, HIV, and being at risk for HIV.32,33 Young age, lack of social support, low perception of risk, and failure to show up for appointments are also barriers to PrEP use.28,30,34
Some physicians have expressed concern that prescribing PrEP may promote high-risk sexual behavior.35 However, because PrEP is most beneficial in individuals who already engage in high-risk sexual behavior, strategic delivery of PrEP remains an effective risk-reducing strategy.17,18,21,26,36,37 Even in instances where PrEP has been associated with higher-risk sexual behavior and higher rates of sexually transmitted infections, it still prevents as much as 100% of new HIV infections.38
Fear of drug resistance also contributes to slow implementation of PrEP. Drug resistance has been observed in clinical trials of PrEP, but it has been exceedingly rare and predominantly limited to patients who had unrecognized AHI when they started PrEP.39 Furthermore, the few cases of drug resistance attributable to PrEP pale in comparison to the large number of estimated HIV infections averted—infections that would require lifelong ART with its own associated risks of drug resistance. By decreasing HIV transmission, PrEP is expected to decrease total drug resistance.40
Cost is another obstacle. Truvada costs approximately $1,540 per month.41 However, analysis has demonstrated that PrEP is cost-effective when targeted to high-risk patients.42 Most insurance plans cover PrEP, but often require high deductibles and copays; fortunately, this financial burden for patients can be mitigated or eliminated by co-pay assistance programs. The manufacturer of Truvada offers assistance programs for both insured and uninsured patients who are candidates for PrEP; details are available at http://www.truvada.com/truvada-patient-assistance.
Stigma has historically burdened individuals who seek to protect their sexual health, including HIV-negative individuals who are candidates for PrEP. Stigma surrounding HIV may decrease ART-based HIV prevention in men who have sex with men,43 while increasing high-risk behaviors44 and all-cause mortality.45
The resources listed in TABLE 2 can help physicians overcome some of the barriers to implementing PrEP.
How to deliver PrEP
Whether HIV specialists or primary care clinicians are best suited to provide PrEP is a subject of debate. HIV specialists are most familiar with ART and routine monitoring of adherence; however, they have less access to HIV-negative patients, who are the target group for PrEP.35 Family physicians tend to work in closer proximity and maintain longitudinal relationships with PrEP target groups, but in general have less experience with ART and evaluating AHI. Some may argue that competing demands may make it impractical to take a detailed sexual history during a primary care visit.46 In truth, both HIV specialists and family physicians can be appropriately equipped to provide PrEP.
TABLE 3 outlines the steps necessary to provide a patient with PrEP.47 Assessing risk is the initial step; PrEP is beneficial for patients who have one or more risk factors for HIV infection. To be eligible for TDF/FTC, a patient must be HIV-negative, and should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and kidney disease. Because TDF/FTC treats HBV infection, candidates for PrEP who test positive for HBV should be evaluated for treatment of HBV before initiating PrEP. Candidates for PrEP who test negative for HBV infection and immunity should be vaccinated.
Candidates for PrEP should also be screened and monitored for kidney disease. TDF can cause increased serum creatinine due to tubular toxicity. A patient who has an estimated creatinine clearance <60 mL/min should not receive TDF/FTC for PrEP. If a patient’s estimated creatinine clearance falls below 60 mL/min or serum creatinine increases by 0.3 mg/dL above baseline after PrEP is started, TDF/FTC should be discontinued, and the patient should be evaluated for the underlying cause of the kidney disease.27
Before starting PrEP, candidates should be screened for HIV infection and symptoms of AHI. Strongly consider testing for sexually transmitted infections that may increase the risk of HIV transmission, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or chlamydia.
Candidates who are eligible for PrEP must be counseled on medication adverse effects, adherence strategies, and symptoms of sexually transmitted infections. To initiate PrEP, candidates may be given a one-month supply of TDF/FTC; adherence, adverse effects, and other risk-reduction strategies are assessed at an office visit 3 to 4 weeks later. Subsequent prescriptions are then dispensed as a 3-month supply, with office visits to monitor PrEP scheduled for at least once every 3 months. During these monitoring visits, evaluate the patient’s HIV status, pregnancy status, adherence, adverse effects, risk-reduction behaviors, and indications for continued PrEP. Every 6 months, renal function and sexually transmitted infection status should be reassessed.
Reducing risk of harm among patients who inject drugs
Nonsexual transmission of HIV is a route of high infectivity.48 It includes transfusion of infected blood, sharing of equipment during injection drug use, and percutaneous needle sticks. Sharing of equipment during injection drug use is estimated to account for 8% of new infections in the United States.4
Harm reduction is a collection of strategies meant to reduce complications of illicit drug use, including HIV transmission. These strategies include needle and syringe programs that provide injection drug users with sterile equipment, and opioid substitution therapy.
Needle and syringe programs decrease HIV transmission49 and risky behaviors related to injection drug use,50 but federal funding of such programs is prohibited. Opioid substitution therapy reduces the incidence of HIV,50,51 injection drug use, sharing of drug preparation and injection equipment, and drug-related behaviors associated with a high risk of HIV transmission.50,52 However, in the United States, the quality of these programs varies; a study of opioid substitution therapy delivery found that 22.8% of programs provided doses that were too low to be effective.53
FDA-approved medications for opioid substitution therapy include sublingual buprenorphine, sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets or strips (Suboxone), and oral methadone. Buprenorphine-based regimens can be provided by appropriately trained primary care clinicians; methadone requires a referral to a narcotic treatment program. TABLE 4 provides training and support resources for physicians who want to integrate opioid substitution therapy into their clinical practice.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard Moore II, MD, 250 Smith Church Road, Roanoke Rapids, NC 27870; [email protected].
› Screen all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A
› Prescribe tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (Truvada) for pre-exposure prophylaxis for patients at high risk of acquiring HIV. A
› Offer needle and syringe exchange programs and, when appropriate, opioid substitution therapy to individuals who inject drugs. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Despite advances in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) screening and treatment over the last 30 years, HIV remains a public health concern. In the United States, after an initial decline, total HIV incidence has failed to significantly decrease in the last 25 years. More than 1.2 million people are living with HIV in the United States, and 12.8% of them (156,300) are unaware they are affected.1 Of those diagnosed with HIV, only 30% are receiving treatment and are virally suppressed.2 Due to structural inequalities and psychosocial factors, African American and Latino patients remain disproportionately affected.3 The incidence of HIV infection among men who have sex with men has increased, and the incidence of HIV infection among people who inject drugs has plateaued after years of progressive decline.4
HIV prevention strategies are highly effective, but in general are underutilized. This article reviews 3 prevention strategies that can be administered by family physicians: HIV screening, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), and harm reduction.
Who and how to screen for HIV
Early identification of HIV infection generally leads to reduced transmission because diagnosis is associated with decreases in risky behavior.5,6 In addition, antiretroviral therapy (ART) is more effective when initiated early, before the development of advanced immunosuppression.7-9
The “window period” of acute HIV infection (AHI) is the time from when the virus is transmitted to when markers of infection can be detected. Because this window period is associated with high viral transmission rates, family physicians must be familiar with symptoms of AHI (TABLE 1)10,11 and associated risk factors (eg, recent condomless sex or sharing of drug injection equipment with someone who is HIV-positive or of unknown HIV status).
Screening for HIV solely based on the presence of risk factors or clinical symptoms is not enough, however. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening all pregnant women and individuals ages 15 to 65 for HIV.12 Screening based solely on risk factors or clinical symptoms frequently leads to missed diagnoses and identification of HIV infection at more advanced stages.13,14 Both the USPSTF and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend universal opt-out screening (patients are informed that HIV screening will be performed and that they may decline testing) because such screening identifies HIV earlier and is associated with higher testing rates than opt-in screening, which requires explicit written consent and extensive pre-test counseling.
Which test to use. HIV screening with a fourth-generation antigen/antibody combination immunoassay—which detects both HIV p24 antigen and HIV antibodies—provides greater diagnostic accuracy than older tests.15 These newer tests detect HIV approximately 15 days after initial infection, reducing the window period of AHI.15,16 If you suspect a patient has AHI, consider early repeat HIV testing with a fourth-generation assay, or initial co-testing with a fourth-generation assay and a nucleic acid amplification test for HIV RNA, which makes it possible to detect infection approximately 5 days earlier than fourth-generation assays.15
Offer pre-exposure prophylaxis to high-risk patients
PrEP is the use of ART prior to HIV exposure to prevent transmission of the virus. It should be used with conventional risk reduction strategies, such as providing condoms, counseling patients about reducing risky behaviors, supporting medication adherence, and screening for and treating other sexually transmitted infections.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only one medication, Truvada (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine; TDF/FTC), for use as PrEP. Oral tenofovir-based regimens can effectively prevent HIV transmission,17-20 and strong adherence is associated with a risk reduction of 90% to 100%.17-23 The protective effect of oral PrEP is particularly strong in high-risk populations (eg, men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs), where the number needed to treat to prevent one HIV infection ranges from 12 to 100, depending on the patients’ risk profile.24-26 The CDC and Department of Health and Human Services have issued guidelines for using PrEP in high-risk patients.27
Barriers to implementing PrEP. Despite being highly effective, PrEP is not routinely prescribed to high-risk patients; modeling suggests that current use of PrEP is insufficient to significantly impact the incidence of HIV.28 Demand for PrEP is high among target groups,21,29,30 but patients have expressed concerns about adverse effects31 and stigma related to ART, HIV, and being at risk for HIV.32,33 Young age, lack of social support, low perception of risk, and failure to show up for appointments are also barriers to PrEP use.28,30,34
Some physicians have expressed concern that prescribing PrEP may promote high-risk sexual behavior.35 However, because PrEP is most beneficial in individuals who already engage in high-risk sexual behavior, strategic delivery of PrEP remains an effective risk-reducing strategy.17,18,21,26,36,37 Even in instances where PrEP has been associated with higher-risk sexual behavior and higher rates of sexually transmitted infections, it still prevents as much as 100% of new HIV infections.38
Fear of drug resistance also contributes to slow implementation of PrEP. Drug resistance has been observed in clinical trials of PrEP, but it has been exceedingly rare and predominantly limited to patients who had unrecognized AHI when they started PrEP.39 Furthermore, the few cases of drug resistance attributable to PrEP pale in comparison to the large number of estimated HIV infections averted—infections that would require lifelong ART with its own associated risks of drug resistance. By decreasing HIV transmission, PrEP is expected to decrease total drug resistance.40
Cost is another obstacle. Truvada costs approximately $1,540 per month.41 However, analysis has demonstrated that PrEP is cost-effective when targeted to high-risk patients.42 Most insurance plans cover PrEP, but often require high deductibles and copays; fortunately, this financial burden for patients can be mitigated or eliminated by co-pay assistance programs. The manufacturer of Truvada offers assistance programs for both insured and uninsured patients who are candidates for PrEP; details are available at http://www.truvada.com/truvada-patient-assistance.
Stigma has historically burdened individuals who seek to protect their sexual health, including HIV-negative individuals who are candidates for PrEP. Stigma surrounding HIV may decrease ART-based HIV prevention in men who have sex with men,43 while increasing high-risk behaviors44 and all-cause mortality.45
The resources listed in TABLE 2 can help physicians overcome some of the barriers to implementing PrEP.
How to deliver PrEP
Whether HIV specialists or primary care clinicians are best suited to provide PrEP is a subject of debate. HIV specialists are most familiar with ART and routine monitoring of adherence; however, they have less access to HIV-negative patients, who are the target group for PrEP.35 Family physicians tend to work in closer proximity and maintain longitudinal relationships with PrEP target groups, but in general have less experience with ART and evaluating AHI. Some may argue that competing demands may make it impractical to take a detailed sexual history during a primary care visit.46 In truth, both HIV specialists and family physicians can be appropriately equipped to provide PrEP.
TABLE 3 outlines the steps necessary to provide a patient with PrEP.47 Assessing risk is the initial step; PrEP is beneficial for patients who have one or more risk factors for HIV infection. To be eligible for TDF/FTC, a patient must be HIV-negative, and should be tested for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and kidney disease. Because TDF/FTC treats HBV infection, candidates for PrEP who test positive for HBV should be evaluated for treatment of HBV before initiating PrEP. Candidates for PrEP who test negative for HBV infection and immunity should be vaccinated.
Candidates for PrEP should also be screened and monitored for kidney disease. TDF can cause increased serum creatinine due to tubular toxicity. A patient who has an estimated creatinine clearance <60 mL/min should not receive TDF/FTC for PrEP. If a patient’s estimated creatinine clearance falls below 60 mL/min or serum creatinine increases by 0.3 mg/dL above baseline after PrEP is started, TDF/FTC should be discontinued, and the patient should be evaluated for the underlying cause of the kidney disease.27
Before starting PrEP, candidates should be screened for HIV infection and symptoms of AHI. Strongly consider testing for sexually transmitted infections that may increase the risk of HIV transmission, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or chlamydia.
Candidates who are eligible for PrEP must be counseled on medication adverse effects, adherence strategies, and symptoms of sexually transmitted infections. To initiate PrEP, candidates may be given a one-month supply of TDF/FTC; adherence, adverse effects, and other risk-reduction strategies are assessed at an office visit 3 to 4 weeks later. Subsequent prescriptions are then dispensed as a 3-month supply, with office visits to monitor PrEP scheduled for at least once every 3 months. During these monitoring visits, evaluate the patient’s HIV status, pregnancy status, adherence, adverse effects, risk-reduction behaviors, and indications for continued PrEP. Every 6 months, renal function and sexually transmitted infection status should be reassessed.
Reducing risk of harm among patients who inject drugs
Nonsexual transmission of HIV is a route of high infectivity.48 It includes transfusion of infected blood, sharing of equipment during injection drug use, and percutaneous needle sticks. Sharing of equipment during injection drug use is estimated to account for 8% of new infections in the United States.4
Harm reduction is a collection of strategies meant to reduce complications of illicit drug use, including HIV transmission. These strategies include needle and syringe programs that provide injection drug users with sterile equipment, and opioid substitution therapy.
Needle and syringe programs decrease HIV transmission49 and risky behaviors related to injection drug use,50 but federal funding of such programs is prohibited. Opioid substitution therapy reduces the incidence of HIV,50,51 injection drug use, sharing of drug preparation and injection equipment, and drug-related behaviors associated with a high risk of HIV transmission.50,52 However, in the United States, the quality of these programs varies; a study of opioid substitution therapy delivery found that 22.8% of programs provided doses that were too low to be effective.53
FDA-approved medications for opioid substitution therapy include sublingual buprenorphine, sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablets or strips (Suboxone), and oral methadone. Buprenorphine-based regimens can be provided by appropriately trained primary care clinicians; methadone requires a referral to a narcotic treatment program. TABLE 4 provides training and support resources for physicians who want to integrate opioid substitution therapy into their clinical practice.
CORRESPONDENCE
Richard Moore II, MD, 250 Smith Church Road, Roanoke Rapids, NC 27870; [email protected].
1. Hall HI, An Q, Tang T, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed HIV infection--United States, 2008-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:657-662.
2. Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:1113-1117.
3. Maulsby C, Millet G, Lindsey K, et al. HIV among black men who have sex with men (MSM) in the United States: a review of the literature. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:10-25.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Estimated HIV incidence among adults and adolescents in the United States, 2007-2010, HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2012. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_hssr_vol_17_no_4.pdf. Accessed October 8, 2015.
5. Cleary PD, Van Devanter N, Rogers TF, et al. Behavior changes after notification of HIV infection. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:1586-1590.
6. Higgins DL, Galavotti C, O’Reilly KR, et al. Evidence for the effects of HIV antibody counseling and testing on risk behaviors. JAMA. 1991;266:2419-2429.
7. Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17-26.
8. Palella FJ Jr, Deloria-Knoll M, Chmiel JS, et al. Survival benefit of initiating antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected persons in different CD4 cell strata. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:620-626.
9. INSIGHT START Study Group, Lundgren JD, Babiker AG, Gordin F, et al. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in early asymptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:795-807.
10. Daar ES, Pilcher CD, Hecht FM. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of primary HIV-1 infection. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2008;3:10-15.
11. Tindall B, Barker S, Donovan B, et al. Characterization of the acute clinical illness associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:945-949.
12. Moyer V, US Preventative Services Task Force. Screening for HIV: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:51-60.
13. Jenkins T, Gardner E, Thrun M, et al. Risk-based HIV testing fails to detect the majority of HIV-infected persons in medical care settings. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33:329-333.
14. Klein D, Hurley LB, Merrill D, et al. Review of medical encounters in the 5 years before a diagnosis of HIV-1 infection: implications for early detection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;32:143-152.
15. Pandori M, Hackett J Jr, Louie B, et al. Assessment of the ability of a fourth-generation immunoassay for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody and p24 antigen to detect both acute and recent HIV infections in a high-risk setting. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2639-2642.
16. Branson BM. The future of HIV testing. J Acquir Imm Defic Syndr. 2010;55 Suppl 2:S102-S105.
17. Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599.
18. Baeten JM, Donnell D, Ndase P, et al; Partners PrEP Study Team. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention in heterosexual men and women. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:399-410.
19. Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:423-434.
20. Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2083-2090.
21. Grant RM, Anderson PL, McMahan V, et al. Uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis, sexual practices, and HIV incidence in men and transgender women who have sex with men: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:820-829.
22. Anderson PL, Glidden DV, Liu A, et al. Emtricitabine-tenofovir concentrations and pre-exposure prophylaxis efficacy in men who have sex with men. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:151ra125.
23. Henderson FL, Taylor AW, Chirwa LI, et al. Characteristics and oral PrEP adherence in the TDF2 open-label extension in Botswana. Paper presented at International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; July 1922, 2015; Vancouver, Canada.
24. Murnane PM, Celum C, Mugo N, et al. Efficacy of preexposure prophylaxis for HIV-1 prevention among high-risk heterosexuals: subgroup analyses from a randomized trial. AIDS. 2013;27:2155-2160.
25. Heffron R, Mugo N, Were E, et al. Preexposure prophylaxis is efficacious for HIV-1 prevention among women using depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for contraception. AIDS. 2014;28:2771-2776.
26. Buchbinder SP, Glidden DV, Liu AY, et al. HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in men who have sex with men and transgender women: a secondary analysis of a phase 3 randomised controlled efficacy trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:468-475.
27. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States – 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed June 18, 2015.
28. Grant RM. Scale-up of preexposure prophylaxis in San Francisco to impact HIV incidence. Abstract 25. Paper presented at Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 23-26, 2015; Seattle, WA.
29. Cohen SE, Vittinghoff E, Bacon O, et al. High interest in preexposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men at risk for HIV infection: baseline data from the US PrEP demonstration project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;68:439-448.
30. Haberer JE, Baeten JM, Campbell J, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a substudy cohort within a clinical trial of serodiscordant couples in East Africa. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001511.
31. Gilmore H, Koester K, Liu A, et al. To PrEP or not to PrEP: Perspectives from US iPrEx open label extension (OLE) participants. Abstract 440. Paper presented at 9th International Conference on HIV Treatment and Prevention Adherence; June 9, 2014; Miami Beach, FL.
32. Jain S, Gregor C, Krakower D, et al. Attitudes and interest toward HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among participants using HIV non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (NPEP). Poster Abstract 1523. Poster presented at Infectious Disease Society of America Conference; October 8-12, 2014; Philadelphia, PA.
33. van der Straten A, Stadler J, Luecke E, et al; VOICE-C Study Team, Perspectives on use of oral and vaginal antiretrovirals for HIV prevention: the VOICE-C qualitative study in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19146.
34. Corneli AL, McKenna K, Headley J, et al; FEM-PrEP Study Group. A descriptive analysis of perceptions of HIV risk and worry about acquiring HIV among FEM-PrEP participants who seroconverted in Bondo, Kenya, and Pretoria, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19152.
35. Krakower D, Ware N, Mitty JA, et al. HIV providers’ perceived barriers and facilitators to implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis in care settings: a qualitative study. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1712-1721.
36. McCormack S, Dunn DT, Desai M, et al. Pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent the acquisition of HIV-1 infection (PROUD): effectiveness results from the pilot phase of a pragmatic open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2015. [Epub ahead of print].
37. Mugwanya KK, Donnell D, Celum C, et al. Sexual behaviour of heterosexual men and women receiving antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:1021-1028.
38. Volk JE, Marcus JL, Phengrasamy T, et al. No new HIV infections with increasing use of HIV preexposure prophylaxis in a clinical practice setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1601-1603.
39. Lehman DA, Baeten JM, McCoy CO, et al. Risk of drug resistance among persons acquiring HIV within a randomized clinical trial of single- or dual-agent preexposure prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1211-1218.
40. Supervie V, Garcia-Lerma JG, Heneine W, et al. HIV, transmitted drug resistance, and the paradox of preexposure prophylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:12381-12386.
41. AIDSinfo. Cost considerations and antiretroviral therapy. AIDSinfo Web site. Available at: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/1/adult-and-adolescent-arv-guidelines/459/cost-considerations-and-antiretroviral-therapy. Accessed December 14, 2015.
42. Gomez GB, Borquez A, Case KK, et al. The cost and impact of scaling up pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness modelling studies. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001401.
43. Oldenburg CE, Perez-Brumer AG, Hatzenbuehler ML, et al. State-level structural sexual stigma and HIV prevention in a national online sample of HIV-uninfected MSM in the United States. AIDS. 2015;29:837-845.
44. Hatzenbuehler ML, O’Cleirigh C, Mayer KH, et al. Prospective associations between HIV-related stigma, transmission risk behaviors, and adverse mental health outcomes in men who have sex with men. Ann Behav Med. 2011;42:227-234.
45. Hatzenbuehler ML, Bellatorre A, Lee Y, et al. Structural stigma and all-cause mortality in sexual minority populations. Soc Sci Med. 2014;103:33-41.
46. Arnold EA, Hazelton P, Lane T, et al. A qualitative study of provider thoughts on implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in clinical settings to prevent HIV infection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40603.
47. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center. For PrEP Providers. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center Web site. Available at: http://www.med.unc.edu/ncaidstraining/prep/for-providers/for-prep-prescribers. Accessed July 7, 2015.
48. Patel P, Borkowf CB, Brook JT, et al. Estimating per-act HIV transmission risk: a systematic review. AIDS. 2014;28:1509-1519.
49. Aspinall EJ, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43:235-248.
50. MacArthur GJ, van Velzen E, Palmateer N, et al. Interventions to prevent HIV and Hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: a review of reviews to assess evidence of effectiveness. Int J Drug Policy. 2014;25:34-52.
51. MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5945.
52. Gowing L, Farrell MF, Bornemann R, et al. Oral substitution treatment of injecting opioid users for prevention of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(8):CD004145.
53. D’Aunno T, Pollack HA, Frimpong JA, et al. Evidence-based treatment for opioid disorders: a 23-year national study of methadone dose levels. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2014;47:245-250.
1. Hall HI, An Q, Tang T, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed HIV infection--United States, 2008-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:657-662.
2. Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:1113-1117.
3. Maulsby C, Millet G, Lindsey K, et al. HIV among black men who have sex with men (MSM) in the United States: a review of the literature. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:10-25.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Estimated HIV incidence among adults and adolescents in the United States, 2007-2010, HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report. 2012. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/statistics_hssr_vol_17_no_4.pdf. Accessed October 8, 2015.
5. Cleary PD, Van Devanter N, Rogers TF, et al. Behavior changes after notification of HIV infection. Am J Public Health. 1991;81:1586-1590.
6. Higgins DL, Galavotti C, O’Reilly KR, et al. Evidence for the effects of HIV antibody counseling and testing on risk behaviors. JAMA. 1991;266:2419-2429.
7. Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17-26.
8. Palella FJ Jr, Deloria-Knoll M, Chmiel JS, et al. Survival benefit of initiating antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected persons in different CD4 cell strata. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:620-626.
9. INSIGHT START Study Group, Lundgren JD, Babiker AG, Gordin F, et al. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in early asymptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:795-807.
10. Daar ES, Pilcher CD, Hecht FM. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of primary HIV-1 infection. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2008;3:10-15.
11. Tindall B, Barker S, Donovan B, et al. Characterization of the acute clinical illness associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988;148:945-949.
12. Moyer V, US Preventative Services Task Force. Screening for HIV: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:51-60.
13. Jenkins T, Gardner E, Thrun M, et al. Risk-based HIV testing fails to detect the majority of HIV-infected persons in medical care settings. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33:329-333.
14. Klein D, Hurley LB, Merrill D, et al. Review of medical encounters in the 5 years before a diagnosis of HIV-1 infection: implications for early detection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;32:143-152.
15. Pandori M, Hackett J Jr, Louie B, et al. Assessment of the ability of a fourth-generation immunoassay for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody and p24 antigen to detect both acute and recent HIV infections in a high-risk setting. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:2639-2642.
16. Branson BM. The future of HIV testing. J Acquir Imm Defic Syndr. 2010;55 Suppl 2:S102-S105.
17. Grant RM, Lama JR, Anderson PL, et al; iPrEx Study Team. Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2587-2599.
18. Baeten JM, Donnell D, Ndase P, et al; Partners PrEP Study Team. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention in heterosexual men and women. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:399-410.
19. Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:423-434.
20. Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:2083-2090.
21. Grant RM, Anderson PL, McMahan V, et al. Uptake of pre-exposure prophylaxis, sexual practices, and HIV incidence in men and transgender women who have sex with men: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:820-829.
22. Anderson PL, Glidden DV, Liu A, et al. Emtricitabine-tenofovir concentrations and pre-exposure prophylaxis efficacy in men who have sex with men. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:151ra125.
23. Henderson FL, Taylor AW, Chirwa LI, et al. Characteristics and oral PrEP adherence in the TDF2 open-label extension in Botswana. Paper presented at International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; July 1922, 2015; Vancouver, Canada.
24. Murnane PM, Celum C, Mugo N, et al. Efficacy of preexposure prophylaxis for HIV-1 prevention among high-risk heterosexuals: subgroup analyses from a randomized trial. AIDS. 2013;27:2155-2160.
25. Heffron R, Mugo N, Were E, et al. Preexposure prophylaxis is efficacious for HIV-1 prevention among women using depot medroxyprogesterone acetate for contraception. AIDS. 2014;28:2771-2776.
26. Buchbinder SP, Glidden DV, Liu AY, et al. HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis in men who have sex with men and transgender women: a secondary analysis of a phase 3 randomised controlled efficacy trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:468-475.
27. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States – 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed June 18, 2015.
28. Grant RM. Scale-up of preexposure prophylaxis in San Francisco to impact HIV incidence. Abstract 25. Paper presented at Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 23-26, 2015; Seattle, WA.
29. Cohen SE, Vittinghoff E, Bacon O, et al. High interest in preexposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men at risk for HIV infection: baseline data from the US PrEP demonstration project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;68:439-448.
30. Haberer JE, Baeten JM, Campbell J, et al. Adherence to antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a substudy cohort within a clinical trial of serodiscordant couples in East Africa. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001511.
31. Gilmore H, Koester K, Liu A, et al. To PrEP or not to PrEP: Perspectives from US iPrEx open label extension (OLE) participants. Abstract 440. Paper presented at 9th International Conference on HIV Treatment and Prevention Adherence; June 9, 2014; Miami Beach, FL.
32. Jain S, Gregor C, Krakower D, et al. Attitudes and interest toward HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among participants using HIV non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis (NPEP). Poster Abstract 1523. Poster presented at Infectious Disease Society of America Conference; October 8-12, 2014; Philadelphia, PA.
33. van der Straten A, Stadler J, Luecke E, et al; VOICE-C Study Team, Perspectives on use of oral and vaginal antiretrovirals for HIV prevention: the VOICE-C qualitative study in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19146.
34. Corneli AL, McKenna K, Headley J, et al; FEM-PrEP Study Group. A descriptive analysis of perceptions of HIV risk and worry about acquiring HIV among FEM-PrEP participants who seroconverted in Bondo, Kenya, and Pretoria, South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17:19152.
35. Krakower D, Ware N, Mitty JA, et al. HIV providers’ perceived barriers and facilitators to implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis in care settings: a qualitative study. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1712-1721.
36. McCormack S, Dunn DT, Desai M, et al. Pre-exposure prophylaxis to prevent the acquisition of HIV-1 infection (PROUD): effectiveness results from the pilot phase of a pragmatic open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2015. [Epub ahead of print].
37. Mugwanya KK, Donnell D, Celum C, et al. Sexual behaviour of heterosexual men and women receiving antiretroviral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:1021-1028.
38. Volk JE, Marcus JL, Phengrasamy T, et al. No new HIV infections with increasing use of HIV preexposure prophylaxis in a clinical practice setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1601-1603.
39. Lehman DA, Baeten JM, McCoy CO, et al. Risk of drug resistance among persons acquiring HIV within a randomized clinical trial of single- or dual-agent preexposure prophylaxis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1211-1218.
40. Supervie V, Garcia-Lerma JG, Heneine W, et al. HIV, transmitted drug resistance, and the paradox of preexposure prophylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:12381-12386.
41. AIDSinfo. Cost considerations and antiretroviral therapy. AIDSinfo Web site. Available at: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines/html/1/adult-and-adolescent-arv-guidelines/459/cost-considerations-and-antiretroviral-therapy. Accessed December 14, 2015.
42. Gomez GB, Borquez A, Case KK, et al. The cost and impact of scaling up pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: a systematic review of cost-effectiveness modelling studies. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001401.
43. Oldenburg CE, Perez-Brumer AG, Hatzenbuehler ML, et al. State-level structural sexual stigma and HIV prevention in a national online sample of HIV-uninfected MSM in the United States. AIDS. 2015;29:837-845.
44. Hatzenbuehler ML, O’Cleirigh C, Mayer KH, et al. Prospective associations between HIV-related stigma, transmission risk behaviors, and adverse mental health outcomes in men who have sex with men. Ann Behav Med. 2011;42:227-234.
45. Hatzenbuehler ML, Bellatorre A, Lee Y, et al. Structural stigma and all-cause mortality in sexual minority populations. Soc Sci Med. 2014;103:33-41.
46. Arnold EA, Hazelton P, Lane T, et al. A qualitative study of provider thoughts on implementing pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in clinical settings to prevent HIV infection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40603.
47. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center. For PrEP Providers. North Carolina AIDS Training and Education Center Web site. Available at: http://www.med.unc.edu/ncaidstraining/prep/for-providers/for-prep-prescribers. Accessed July 7, 2015.
48. Patel P, Borkowf CB, Brook JT, et al. Estimating per-act HIV transmission risk: a systematic review. AIDS. 2014;28:1509-1519.
49. Aspinall EJ, Nambiar D, Goldberg DJ, et al. Are needle and syringe programmes associated with a reduction in HIV transmission among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43:235-248.
50. MacArthur GJ, van Velzen E, Palmateer N, et al. Interventions to prevent HIV and Hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: a review of reviews to assess evidence of effectiveness. Int J Drug Policy. 2014;25:34-52.
51. MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5945.
52. Gowing L, Farrell MF, Bornemann R, et al. Oral substitution treatment of injecting opioid users for prevention of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(8):CD004145.
53. D’Aunno T, Pollack HA, Frimpong JA, et al. Evidence-based treatment for opioid disorders: a 23-year national study of methadone dose levels. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2014;47:245-250.
Managing patients on antipsychotics: Your domain, too
› Evaluate patients for movement disorders before initiating or adjusting antipsychotic therapy, then weekly until the dose is stabilized. A
› Use nonpharmacologic interventions—eg, positive reinforcement, music, light exercise—as first-line therapy for neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia; consider antipsychotic therapy only if they fail. A
› Obtain a fasting glucose level before initiating or adjusting antipsychotic therapy, then at 12 weeks, and annually if the patient is taking a second-generation agent. B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
CASE 1 › Steve B is a 43-year-old patient with bipolar disorder and a history of hypertension and high cholesterol. His body mass index (BMI) is 29. During a checkup, he tells you his psychiatrist recently started him on olanzapine. He reports that the medication is working, but he’s concerned about adverse effects, and asks whether he should be monitored for signs of diabetes.
CASE 2 › Mary F, an 83-year-old with Alzheimer’s disease and a history of stable coronary artery disease, is a resident in a long-term care facility, where staff members report that she is increasingly combative. The floor nurse says Ms. F has been striking out at the nurses’ aides who attempt to dress her and asks that you prescribe an antipsychotic to “calm her down.”
If Mr. B and Ms. F were your patients, what would you do?
In 1951, the chance discovery of an anesthetic’s calming properties was the first step in the development of the medications that came to be known as antipsychotics.1 In recent years, we have seen an expansion in both the number of antipsychotic agents on the market and the scope of their use, for conditions as varied as chronic pain, dementia, nausea and vomiting, and Tourette syndrome.
While antipsychotics often are prescribed by psychiatrists or other specialists, primary care physicians are increasingly likely to be involved in the management of patients who take them—and, at times, to prescribe antipsychotic agents themselves. We developed this guide to increase awareness of safe prescribing practices and principles guiding the initiation and management of antipsychotic agents. We start with a review of the mechanism of action of first- and second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs).
In the last decade, research has called into question whether second-generation antipsychotics really are more effective than first-generation agents
First- and second-generation agents: How they work and differ
Antipsychotics act at the level of the dopaminergic pathways in the central nervous system by blocking the D2 receptors. Action on the mesolimbic pathway is thought to be responsible for their effects on schizophrenia symptoms,2 while action at receptor sites in other dopaminergic pathways leads to common adverse effects, primarily the extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) associated with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs).
The distinction between first- and second-generation agents relates to SGAs’ blockage of serotonin receptors (thought to better relieve schizophrenia symptoms) and increased specificity for the mesolimbic pathway (which reduces the action on other dopamine pathways and is less likely to produce EPS).3 These differences largely accounted for the belief that SGAs were more effective and provided the rationale for their designation as atypical antipsychotics.
Are SGAs really better?
In the last decade, research has called such claims into question. Trials such as the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness4 and Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia study,5 as well as a meta-analysis,6 found that SGAs as a class are no more effective than FGAs. That said, 2 SGAs—clozapine and olanzapine—were found to be superior to FGAs for the treatment of schizophrenia. The studies also raised doubts about SGAs’ advantages regarding tolerability, as the time to discontinuation due to intolerable adverse effects was similar for first- and second-generation drugs.4-6
Approved and off-label indications: A look at the evidence
In addition to schizophrenia, many antipsychotics have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to treat various psychiatric and nonpsychiatric conditions (TABLE 1).7 Several are approved for use in bipolar disorder, 2 are approved as adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), and one is approved for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Porphyria, tetanus, and intractable hiccups are among the nonpsychiatric conditions for which some antipsychotics are approved.7
Evidence ranging from anecdotal to randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is steadily emerging about off-label uses of antipsychotics, with risperidone, quetiapine, and olanzapine foremost among them.8,9 Use of antipsychotics in the treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPS) of dementia has become particularly widespread, with off-label use of antipsychotics more prevalent in long-term care facilities than in outpatient settings.9
NPS. Antipsychotics’ efficacy in controlling dementia-related agitation, aggression, and psychosis has consistently shown a modest but statistically significant benefit. A Cochrane review found evidence that the use of risperidone and olanzapine resulted in improvements in agitation scale scores; risperidone was linked to improved scores on a psychosis scale, as well.10 A second meta-analysis showed small but statistically significant improvements in NPS with risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole.8 Another study showed that nearly half (48%) of patients who had a positive response to risperidone relapsed when they stopped taking the drug.11
A rapidly aging population is expected to further increase the need for pharmacologic interventions to control NPS. Yet safety concerns about the use of antipsychotics in the elderly (more on this in a bit) call this practice into question.
Chronic pain. A 2008 Cochrane review analyzed the efficacy of antipsychotics for acute and chronic pain, pooling results of 11 studies of the treatment of conditions such as postherpetic neuralgia, tension headache, acute myocardial infarction (MI), and terminal cancer. Results from the pooled trials were described as mixed, although an overall statistically significant decrease in pain intensity was found.12
Polypharmacy. The simultaneous use of 2 or more antipsychotic agents is also increasingly prevalent,13 with levels exceeding 50% in one study of patients with schizophrenia.14 Because there is little data on the safety and efficacy of antipsychotic polypharmacy, this off-label approach should be considered only as a last resort.15
Off-label treatment of psychiatric conditions
GAD. In comparative effectiveness trials, quetiapine was found to be equal to both paroxetine and escitalopram for the treatment of GAD, with a favorable effect on symptoms 8 weeks after its initiation.8 Trials of other antipsychotics for the treatment of GAD have not demonstrated clear efficacy. Trifluoperazine is approved for GAD, as a short-term treatment.
MDD. Antipsychotics have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of MDD, although only quetiapine and aripiprazole are approved (and only as adjunctive treatment). Evidence supports the use of both agents, as well as risperidone, as augmentation to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and in pooled results from 5 placebo-controlled trials, quetiapine was found to be effective as monotherapy for MDD.9
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Compared with placebo, risperidone showed a 4-fold increase in the likelihood of a favorable response (number needed to treat [NNT]=4) in patients with OCD,8 but the drug remains off-label for this purpose.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). A meta-analysis of 7 studies demonstrated risperidone’s efficacy in the treatment of combat-related PTSD.9 In a large Veterans Administration study of patients with combat-related PTSD resistant to treatment with SSRIs, however, risperidone showed no benefit after 6 months of therapy.16 Antipsychotics have not been found beneficial for substance abuse, eating disorders, or insomnia.9
Identifying risk factos, monitoring for adverse effects
While FGAs carry an increased risk of EPS, SGAs increase the risk of obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. The average life expectancy of patients with schizophrenia is 2 to 3 decades lower than that of age-matched controls,17 a finding largely attributed to the increased rate of cardiovascular disease. While this can be partly explained by differences in lifestyle and access to care, the metabolic effects of SGAs are a likely contributing factor.
Because of the adverse effects of FGAs and SGAs, the American Diabetes Association and American Psychiatric Association jointly issued guidelines addressing both the type and optimal frequency of monitoring for patients on antipsychotics (TABLE 2).18,19 Following them is critical, as both the initiation of an antipsychotic agent and any change in regimen can lead to the development—or exacerbation—of a number of diseases.
Before initiating antipsychotic therapy—or the first time you see a patient like Mr. B, whose care you will be monitoring—a thorough assessment of risk factors is needed. Foremost among them are overweight or obesity, insulin resistance or diabetes, a history of heart disease, and EPS.
In some cases, preexisting conditions and the potential harm of a specific drug must be weighed in determining which antipsychotic to prescribe. When adverse effects develop after drug therapy has been initiated, decisions about further actions should be based on both the degree of the unfavorable response and the availability of other treatments—and made, as appropriate, in consultation with the specialist who prescribed the drug.
CASE 1 › You tell Mr. B that metabolic side effects like weight gain, impaired glucose tolerance, and increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol are common with SGAs like the one he is taking, and that you will monitor his fasting glucose levels to evaluate his risk for developing diabetes—starting with this visit. (Olanzapine, the drug he is taking, is 4 times more likely than an FGA to lead to diabetes.18)
You talk to him, too, about the importance of weight control and note that if his BMI increases by ≥1 point you will refer him to a nutritionist and recommend a structured exercise program. Finally, you schedule an appointment in 3 months.
Risks associated with older age and dementia
In 2010, there were 84,842 visits to US emergency departments (EDs) due to adverse drug events involving antipsychotic agents—a 110% increase since 2005. Nearly 30% of these ED visits involved patients 65 years or older.20
Among patients with dementia, use of antipsychotics has been found to dramatically increase the risk of stroke (rate ratio, 3.26 for FGAs and 5.86 for SGAs).21 The risk was greatest in the first 35 days of treatment, but persisted throughout the 175-day study period.
The rate of MI also was elevated in dementia patients (hazard ratio of 2.19 for the first 30 days of treatment, then falling to 1.15 for the first year).22 The risk of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis also rose for patients who had been on antipsychotics during the previous 24 months (odds ratio=1.32), with the highest risk within the first 90 days of treatment.23
Risk of death varies with agent and dose. Multiple studies have shown that the mortality risk associated with antipsychotics varies greatly among individual drugs, with haloperidol carrying the highest risk and quetiapine the lowest.24-26 The hazard ratio for death within the first 30 days was 3.2 for haloperidol, 1.6 for risperidone, and 1.5 for olanzapine; quetiapine had no statistically significant increase. The increased mortality risk was statistically significant only at higher doses.24
The FDA weighs in
Evidence of the elevated risk of death led the FDA to require black-box warnings on SGAs (in 2005)27 and FGAs (in 2008),28 stating that “antipsychotics are not indicated for the treatment of dementia-related psychosis.”28 More recently (in 2012), the American Geriatrics Society (AGS) published a guide on the management of NPS in patients with dementia.29 In it, the AGS acknowledges that despite FDA warnings, antipsychotics may be necessary for the treatment of NPS.
The AGS stresses the importance of nonpharmacologic interventions (eg, positive reinforcement, orientation to time and place, music, light exercise, pet therapy) as a first-line approach. If these measures fail and antipsychotics are necessary, the AGS calls for obtaining informed consent from a family member, using the lowest effective dose, and regularly attempting to wean the patient off the antipsychotic as the standard of care.28
CASE 2 › New or worsening aggressive behavior in an elderly patient with dementia requires a prompt assessment. You start with a complete medical evaluation of Ms. F, ruling out common causes of agitation such as infection, pain, constipation, and an adverse reaction to medication.
You also ask about the incidents of aggression: Does the same aide dress Ms. F daily? Does the aide introduce herself and explain what she’s about to do before attempting to dress the patient?
Next, you recommend nonpharmacologic therapies, such as calming music, participation in group activities, and pet therapy. You tell the floor nurse that if these measures fail and Ms. F’s threatening behavior continues, an antipsychotic may be considered.
Guard against abuse of antipsychotics
As antipsychotic use increases, so, too, does misuse and abuse, particularly of quetiapine. The drug has a reported street value of $3 to $8 for a 25- to 100-mg dose and is known as “quell,” “Susie-Q,” “and “baby heroin”; “Q-ball” is the name used for a combination of cocaine and quetiapine.30,31
The Drug Abuse Warning Network reported a 115% increase in ED visits related to the misuse or abuse of pharmaceuticals between 2004 and 2010.32 In 2010, 57,199 drug abuse cases—including 28,618 suicide attempts—were linked to antipsychotics.20
To optimize the benefit of antipsychotics and minimize the likelihood of abuse, ensure that every patient taking them has a clearly documented indication for an antipsychotic and a single responsible prescriber of the antipsychotic, often a psychiatrist. Your responsibilities: Schedule visits for monitoring, do a medication review to identify potential drug-drug interactions, and assess efficacy, all on a regular basis.
CASE 1 › At Mr. B’s next visit, you retest his fasting glucose (which is now 105 mg/dL) and recheck his BMI, which has climbed to 30. You tell him you will speak with his psychiatrist about his weight gain and your concern about the development of insulin resistance.
Meanwhile, you refer the patient to a nutritionist and encourage a healthy lifestyle. Because the medication has been effective, you schedule a follow-up visit in 6 weeks to see if the lifestyle interventions have been successful before consulting with the patient’s psychiatrist about a change in medication.
CASE 2 › When you return to the long-term care facility one week later, you find that Ms. F’s NPS have not abated. You realize an antipsychotic agent may be needed. Because she has a history of heart disease, however, she has a higher risk for cardiovascular events.
You meet with her son to review the benefits and risks of antipsychotic therapy, explaining that risperidone is a reasonable agent and that a low starting dose (0.25-0.5 mg) will reduce the risk. You obtain his informed consent, document your treatment goals—a decrease in threatening behavior and the ability of the staff to work with Ms. F to get her up and out of bed—and establish a plan to review in 2 weeks.
CORRESPONDENCE
Daniel DeJoseph, MD, Drexel Family Medicine, 3401 Market Street, Suite 105-B, Philadelphia, PA 19104; [email protected]
1. Shen WW. A history of antipsychotic drug development. Compr Psychiatry. 1999;40:407-414.
2. Miller R. Mechanism of action of antipsychotic drugs of different classes, refractoriness to therapeutic effects of classical neuroleptics, and individual variation in sensitivity to their actions. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7:302-314.
3. Seeman P. Atypical antipsychotics: mechanism of action. Can J Psychiatry. 2002;47:27-38.
4. Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, et al; Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) Investigators. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1209-1223.
5. Jones PB, Barnes TR, Davies L, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effect on quality of life of second- vs first-generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia Study (CUtLASS 1). Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:1079-1087.
6. Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, et al. Second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:31-41.
7. Christian R, Saavedra L, Gaynes BN, et al. Future research needs for first- and second-generation antipsychotics for children and young adults [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2012:12-EHC042-EF.
8. Maher AR, Maglione M, Bagley S, et al. Efficacy and comparative effectiveness of atypical antipsychotic medications for off-label uses in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011;306:1359-1369.
9. Maglione M, Maher AR, Hu J, et al. Off-label use of atypical antipsychotics: An update [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2011:11-EHC087-EF.
10. Ballard CG, Waite J. Atypical antipsychotics for aggression and psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(1):CD003476.
11. Devanand DP, Mintzer J, Schultz SK, et al. Relapse risk after discontinuation of risperidone in Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1497-1507.
12. Seidel S, Aigner M, Ossege M, et al. Antipsychotics for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(4):CD004844.
13. Mojtabai R, Olfson M. National trends in psychotropic medication polypharmacy in office-based psychiatry. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:26-36.
14. Faries D, Ascher-Svanum H, Zhu B, et al. Antipsychotic monotherapy and polypharmacy in the naturalistic treatment of schizophrenia with atypical antipsychotics. BMC Psychiatry. 2005;5:26.
15. Ballon J, Stroup TS. Polypharmacy for schizophrenia. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2013;26:208-213.
16. Krystal JH, Rosenheck RA, Cramer JA, et al; Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study No. 504 Group. Adjunctive risperidone treatment for antidepressant-resistant symptoms of chronic military service-related PTSD: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2011;306:493-502.
17. Institute of Medicine. Retooling for an Aging America: Building the Health Care Workforce. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences; 2008.
18. Marder SR, Essock SM, Miller AL, et al. Physical health monitoring of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:1334-1349.
19. Barrett E, Blonde L, Clement S, et al. Consensus development conference on antipsychotic drugs and obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:596-601.
20. Drug Abuse Warning Network, 2010: National Estimates of Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits. HHS Publication No. (SMA) 12-4733, DAWN Series D-38. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/2k13/DAWN2k10ED/DAWN2k10ED.htm. Accessed May 1, 2013.
21. Douglas IJ, Smeeth L. Exposure to antipsychotics and risk of stroke: self controlled case series study. BMJ. 2008;337:a1227.
22. Pariente A, Fourrier-Réglat A, Ducruet T, et al. Antipsychotic use and myocardial infarction in older patients with treated dementia. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:648-653.
23. Parker C, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Antipsychotic drugs and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control study. BMJ. 2010;341:c4245.
24. Rossom RC, Rector TS, Lederle FA, et al. Are all commonly prescribed antipsychotics associated with greater mortality in elderly male veterans with dementia? J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:1027-1034.
25. Kales HC, Kim HM, Zivin K, et al. Risk of mortality among individual antipsychotics in patients with dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:71-79.
26. Huybrechts KF, Gerhard T, Crystal S, et al. Differential risk of death in older residents in nursing homes prescribed specific antipsychotic drugs: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2012;344:e977.
27. US Food and Drug Public Health Advisory: Deaths with antipsychotics in elderly patients with behavioral disturbances. US Food and Drug Administration Web site Available at: http://1.usa.gov/1plsxPk. Accessed February 5, 2014.
28. Information for healthcare professionals: conventional antipsychotics. US Food and Drug Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/drugs/drugsafety/postmarketdrugsafetyinformationforpatientsandproviders/ucm124830.htm. Accessed February 5, 2014.
29. Guide to the management of psychotic disorders and neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in older adults. American Geriatric Society Web site. Available at: http://dementia.americangeriatrics.org/GeriPsych_index.php. Accessed April 15, 2013.
30. Bogart GT, Ott CA. Abuse of second-generation antipsychotics: What prescribers need to know. Curr Psychiatr. 2011;10:77-79.
31. Tarosoff G, Osti K. Black-market value of antipsychotics, antidepressants, and hypnotics in Las Vegas, Nevada. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:350.
32. Highlights of the 2010 Drug Abuse Warning Network (DAWN) findings on drug-related emergency department visits. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality Web site. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/2k12/DAWN096/SR096EDHighlights2010.htm. Accessed May 1, 2013.
› Evaluate patients for movement disorders before initiating or adjusting antipsychotic therapy, then weekly until the dose is stabilized. A
› Use nonpharmacologic interventions—eg, positive reinforcement, music, light exercise—as first-line therapy for neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia; consider antipsychotic therapy only if they fail. A
› Obtain a fasting glucose level before initiating or adjusting antipsychotic therapy, then at 12 weeks, and annually if the patient is taking a second-generation agent. B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
CASE 1 › Steve B is a 43-year-old patient with bipolar disorder and a history of hypertension and high cholesterol. His body mass index (BMI) is 29. During a checkup, he tells you his psychiatrist recently started him on olanzapine. He reports that the medication is working, but he’s concerned about adverse effects, and asks whether he should be monitored for signs of diabetes.
CASE 2 › Mary F, an 83-year-old with Alzheimer’s disease and a history of stable coronary artery disease, is a resident in a long-term care facility, where staff members report that she is increasingly combative. The floor nurse says Ms. F has been striking out at the nurses’ aides who attempt to dress her and asks that you prescribe an antipsychotic to “calm her down.”
If Mr. B and Ms. F were your patients, what would you do?
In 1951, the chance discovery of an anesthetic’s calming properties was the first step in the development of the medications that came to be known as antipsychotics.1 In recent years, we have seen an expansion in both the number of antipsychotic agents on the market and the scope of their use, for conditions as varied as chronic pain, dementia, nausea and vomiting, and Tourette syndrome.
While antipsychotics often are prescribed by psychiatrists or other specialists, primary care physicians are increasingly likely to be involved in the management of patients who take them—and, at times, to prescribe antipsychotic agents themselves. We developed this guide to increase awareness of safe prescribing practices and principles guiding the initiation and management of antipsychotic agents. We start with a review of the mechanism of action of first- and second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs).
In the last decade, research has called into question whether second-generation antipsychotics really are more effective than first-generation agents
First- and second-generation agents: How they work and differ
Antipsychotics act at the level of the dopaminergic pathways in the central nervous system by blocking the D2 receptors. Action on the mesolimbic pathway is thought to be responsible for their effects on schizophrenia symptoms,2 while action at receptor sites in other dopaminergic pathways leads to common adverse effects, primarily the extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) associated with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs).
The distinction between first- and second-generation agents relates to SGAs’ blockage of serotonin receptors (thought to better relieve schizophrenia symptoms) and increased specificity for the mesolimbic pathway (which reduces the action on other dopamine pathways and is less likely to produce EPS).3 These differences largely accounted for the belief that SGAs were more effective and provided the rationale for their designation as atypical antipsychotics.
Are SGAs really better?
In the last decade, research has called such claims into question. Trials such as the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness4 and Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia study,5 as well as a meta-analysis,6 found that SGAs as a class are no more effective than FGAs. That said, 2 SGAs—clozapine and olanzapine—were found to be superior to FGAs for the treatment of schizophrenia. The studies also raised doubts about SGAs’ advantages regarding tolerability, as the time to discontinuation due to intolerable adverse effects was similar for first- and second-generation drugs.4-6
Approved and off-label indications: A look at the evidence
In addition to schizophrenia, many antipsychotics have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to treat various psychiatric and nonpsychiatric conditions (TABLE 1).7 Several are approved for use in bipolar disorder, 2 are approved as adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), and one is approved for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Porphyria, tetanus, and intractable hiccups are among the nonpsychiatric conditions for which some antipsychotics are approved.7
Evidence ranging from anecdotal to randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is steadily emerging about off-label uses of antipsychotics, with risperidone, quetiapine, and olanzapine foremost among them.8,9 Use of antipsychotics in the treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPS) of dementia has become particularly widespread, with off-label use of antipsychotics more prevalent in long-term care facilities than in outpatient settings.9
NPS. Antipsychotics’ efficacy in controlling dementia-related agitation, aggression, and psychosis has consistently shown a modest but statistically significant benefit. A Cochrane review found evidence that the use of risperidone and olanzapine resulted in improvements in agitation scale scores; risperidone was linked to improved scores on a psychosis scale, as well.10 A second meta-analysis showed small but statistically significant improvements in NPS with risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole.8 Another study showed that nearly half (48%) of patients who had a positive response to risperidone relapsed when they stopped taking the drug.11
A rapidly aging population is expected to further increase the need for pharmacologic interventions to control NPS. Yet safety concerns about the use of antipsychotics in the elderly (more on this in a bit) call this practice into question.
Chronic pain. A 2008 Cochrane review analyzed the efficacy of antipsychotics for acute and chronic pain, pooling results of 11 studies of the treatment of conditions such as postherpetic neuralgia, tension headache, acute myocardial infarction (MI), and terminal cancer. Results from the pooled trials were described as mixed, although an overall statistically significant decrease in pain intensity was found.12
Polypharmacy. The simultaneous use of 2 or more antipsychotic agents is also increasingly prevalent,13 with levels exceeding 50% in one study of patients with schizophrenia.14 Because there is little data on the safety and efficacy of antipsychotic polypharmacy, this off-label approach should be considered only as a last resort.15
Off-label treatment of psychiatric conditions
GAD. In comparative effectiveness trials, quetiapine was found to be equal to both paroxetine and escitalopram for the treatment of GAD, with a favorable effect on symptoms 8 weeks after its initiation.8 Trials of other antipsychotics for the treatment of GAD have not demonstrated clear efficacy. Trifluoperazine is approved for GAD, as a short-term treatment.
MDD. Antipsychotics have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of MDD, although only quetiapine and aripiprazole are approved (and only as adjunctive treatment). Evidence supports the use of both agents, as well as risperidone, as augmentation to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and in pooled results from 5 placebo-controlled trials, quetiapine was found to be effective as monotherapy for MDD.9
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Compared with placebo, risperidone showed a 4-fold increase in the likelihood of a favorable response (number needed to treat [NNT]=4) in patients with OCD,8 but the drug remains off-label for this purpose.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). A meta-analysis of 7 studies demonstrated risperidone’s efficacy in the treatment of combat-related PTSD.9 In a large Veterans Administration study of patients with combat-related PTSD resistant to treatment with SSRIs, however, risperidone showed no benefit after 6 months of therapy.16 Antipsychotics have not been found beneficial for substance abuse, eating disorders, or insomnia.9
Identifying risk factos, monitoring for adverse effects
While FGAs carry an increased risk of EPS, SGAs increase the risk of obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. The average life expectancy of patients with schizophrenia is 2 to 3 decades lower than that of age-matched controls,17 a finding largely attributed to the increased rate of cardiovascular disease. While this can be partly explained by differences in lifestyle and access to care, the metabolic effects of SGAs are a likely contributing factor.
Because of the adverse effects of FGAs and SGAs, the American Diabetes Association and American Psychiatric Association jointly issued guidelines addressing both the type and optimal frequency of monitoring for patients on antipsychotics (TABLE 2).18,19 Following them is critical, as both the initiation of an antipsychotic agent and any change in regimen can lead to the development—or exacerbation—of a number of diseases.
Before initiating antipsychotic therapy—or the first time you see a patient like Mr. B, whose care you will be monitoring—a thorough assessment of risk factors is needed. Foremost among them are overweight or obesity, insulin resistance or diabetes, a history of heart disease, and EPS.
In some cases, preexisting conditions and the potential harm of a specific drug must be weighed in determining which antipsychotic to prescribe. When adverse effects develop after drug therapy has been initiated, decisions about further actions should be based on both the degree of the unfavorable response and the availability of other treatments—and made, as appropriate, in consultation with the specialist who prescribed the drug.
CASE 1 › You tell Mr. B that metabolic side effects like weight gain, impaired glucose tolerance, and increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol are common with SGAs like the one he is taking, and that you will monitor his fasting glucose levels to evaluate his risk for developing diabetes—starting with this visit. (Olanzapine, the drug he is taking, is 4 times more likely than an FGA to lead to diabetes.18)
You talk to him, too, about the importance of weight control and note that if his BMI increases by ≥1 point you will refer him to a nutritionist and recommend a structured exercise program. Finally, you schedule an appointment in 3 months.
Risks associated with older age and dementia
In 2010, there were 84,842 visits to US emergency departments (EDs) due to adverse drug events involving antipsychotic agents—a 110% increase since 2005. Nearly 30% of these ED visits involved patients 65 years or older.20
Among patients with dementia, use of antipsychotics has been found to dramatically increase the risk of stroke (rate ratio, 3.26 for FGAs and 5.86 for SGAs).21 The risk was greatest in the first 35 days of treatment, but persisted throughout the 175-day study period.
The rate of MI also was elevated in dementia patients (hazard ratio of 2.19 for the first 30 days of treatment, then falling to 1.15 for the first year).22 The risk of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis also rose for patients who had been on antipsychotics during the previous 24 months (odds ratio=1.32), with the highest risk within the first 90 days of treatment.23
Risk of death varies with agent and dose. Multiple studies have shown that the mortality risk associated with antipsychotics varies greatly among individual drugs, with haloperidol carrying the highest risk and quetiapine the lowest.24-26 The hazard ratio for death within the first 30 days was 3.2 for haloperidol, 1.6 for risperidone, and 1.5 for olanzapine; quetiapine had no statistically significant increase. The increased mortality risk was statistically significant only at higher doses.24
The FDA weighs in
Evidence of the elevated risk of death led the FDA to require black-box warnings on SGAs (in 2005)27 and FGAs (in 2008),28 stating that “antipsychotics are not indicated for the treatment of dementia-related psychosis.”28 More recently (in 2012), the American Geriatrics Society (AGS) published a guide on the management of NPS in patients with dementia.29 In it, the AGS acknowledges that despite FDA warnings, antipsychotics may be necessary for the treatment of NPS.
The AGS stresses the importance of nonpharmacologic interventions (eg, positive reinforcement, orientation to time and place, music, light exercise, pet therapy) as a first-line approach. If these measures fail and antipsychotics are necessary, the AGS calls for obtaining informed consent from a family member, using the lowest effective dose, and regularly attempting to wean the patient off the antipsychotic as the standard of care.28
CASE 2 › New or worsening aggressive behavior in an elderly patient with dementia requires a prompt assessment. You start with a complete medical evaluation of Ms. F, ruling out common causes of agitation such as infection, pain, constipation, and an adverse reaction to medication.
You also ask about the incidents of aggression: Does the same aide dress Ms. F daily? Does the aide introduce herself and explain what she’s about to do before attempting to dress the patient?
Next, you recommend nonpharmacologic therapies, such as calming music, participation in group activities, and pet therapy. You tell the floor nurse that if these measures fail and Ms. F’s threatening behavior continues, an antipsychotic may be considered.
Guard against abuse of antipsychotics
As antipsychotic use increases, so, too, does misuse and abuse, particularly of quetiapine. The drug has a reported street value of $3 to $8 for a 25- to 100-mg dose and is known as “quell,” “Susie-Q,” “and “baby heroin”; “Q-ball” is the name used for a combination of cocaine and quetiapine.30,31
The Drug Abuse Warning Network reported a 115% increase in ED visits related to the misuse or abuse of pharmaceuticals between 2004 and 2010.32 In 2010, 57,199 drug abuse cases—including 28,618 suicide attempts—were linked to antipsychotics.20
To optimize the benefit of antipsychotics and minimize the likelihood of abuse, ensure that every patient taking them has a clearly documented indication for an antipsychotic and a single responsible prescriber of the antipsychotic, often a psychiatrist. Your responsibilities: Schedule visits for monitoring, do a medication review to identify potential drug-drug interactions, and assess efficacy, all on a regular basis.
CASE 1 › At Mr. B’s next visit, you retest his fasting glucose (which is now 105 mg/dL) and recheck his BMI, which has climbed to 30. You tell him you will speak with his psychiatrist about his weight gain and your concern about the development of insulin resistance.
Meanwhile, you refer the patient to a nutritionist and encourage a healthy lifestyle. Because the medication has been effective, you schedule a follow-up visit in 6 weeks to see if the lifestyle interventions have been successful before consulting with the patient’s psychiatrist about a change in medication.
CASE 2 › When you return to the long-term care facility one week later, you find that Ms. F’s NPS have not abated. You realize an antipsychotic agent may be needed. Because she has a history of heart disease, however, she has a higher risk for cardiovascular events.
You meet with her son to review the benefits and risks of antipsychotic therapy, explaining that risperidone is a reasonable agent and that a low starting dose (0.25-0.5 mg) will reduce the risk. You obtain his informed consent, document your treatment goals—a decrease in threatening behavior and the ability of the staff to work with Ms. F to get her up and out of bed—and establish a plan to review in 2 weeks.
CORRESPONDENCE
Daniel DeJoseph, MD, Drexel Family Medicine, 3401 Market Street, Suite 105-B, Philadelphia, PA 19104; [email protected]
› Evaluate patients for movement disorders before initiating or adjusting antipsychotic therapy, then weekly until the dose is stabilized. A
› Use nonpharmacologic interventions—eg, positive reinforcement, music, light exercise—as first-line therapy for neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia; consider antipsychotic therapy only if they fail. A
› Obtain a fasting glucose level before initiating or adjusting antipsychotic therapy, then at 12 weeks, and annually if the patient is taking a second-generation agent. B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
CASE 1 › Steve B is a 43-year-old patient with bipolar disorder and a history of hypertension and high cholesterol. His body mass index (BMI) is 29. During a checkup, he tells you his psychiatrist recently started him on olanzapine. He reports that the medication is working, but he’s concerned about adverse effects, and asks whether he should be monitored for signs of diabetes.
CASE 2 › Mary F, an 83-year-old with Alzheimer’s disease and a history of stable coronary artery disease, is a resident in a long-term care facility, where staff members report that she is increasingly combative. The floor nurse says Ms. F has been striking out at the nurses’ aides who attempt to dress her and asks that you prescribe an antipsychotic to “calm her down.”
If Mr. B and Ms. F were your patients, what would you do?
In 1951, the chance discovery of an anesthetic’s calming properties was the first step in the development of the medications that came to be known as antipsychotics.1 In recent years, we have seen an expansion in both the number of antipsychotic agents on the market and the scope of their use, for conditions as varied as chronic pain, dementia, nausea and vomiting, and Tourette syndrome.
While antipsychotics often are prescribed by psychiatrists or other specialists, primary care physicians are increasingly likely to be involved in the management of patients who take them—and, at times, to prescribe antipsychotic agents themselves. We developed this guide to increase awareness of safe prescribing practices and principles guiding the initiation and management of antipsychotic agents. We start with a review of the mechanism of action of first- and second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs).
In the last decade, research has called into question whether second-generation antipsychotics really are more effective than first-generation agents
First- and second-generation agents: How they work and differ
Antipsychotics act at the level of the dopaminergic pathways in the central nervous system by blocking the D2 receptors. Action on the mesolimbic pathway is thought to be responsible for their effects on schizophrenia symptoms,2 while action at receptor sites in other dopaminergic pathways leads to common adverse effects, primarily the extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) associated with first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs).
The distinction between first- and second-generation agents relates to SGAs’ blockage of serotonin receptors (thought to better relieve schizophrenia symptoms) and increased specificity for the mesolimbic pathway (which reduces the action on other dopamine pathways and is less likely to produce EPS).3 These differences largely accounted for the belief that SGAs were more effective and provided the rationale for their designation as atypical antipsychotics.
Are SGAs really better?
In the last decade, research has called such claims into question. Trials such as the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness4 and Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia study,5 as well as a meta-analysis,6 found that SGAs as a class are no more effective than FGAs. That said, 2 SGAs—clozapine and olanzapine—were found to be superior to FGAs for the treatment of schizophrenia. The studies also raised doubts about SGAs’ advantages regarding tolerability, as the time to discontinuation due to intolerable adverse effects was similar for first- and second-generation drugs.4-6
Approved and off-label indications: A look at the evidence
In addition to schizophrenia, many antipsychotics have US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to treat various psychiatric and nonpsychiatric conditions (TABLE 1).7 Several are approved for use in bipolar disorder, 2 are approved as adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), and one is approved for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Porphyria, tetanus, and intractable hiccups are among the nonpsychiatric conditions for which some antipsychotics are approved.7
Evidence ranging from anecdotal to randomized controlled trials (RCTs) is steadily emerging about off-label uses of antipsychotics, with risperidone, quetiapine, and olanzapine foremost among them.8,9 Use of antipsychotics in the treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPS) of dementia has become particularly widespread, with off-label use of antipsychotics more prevalent in long-term care facilities than in outpatient settings.9
NPS. Antipsychotics’ efficacy in controlling dementia-related agitation, aggression, and psychosis has consistently shown a modest but statistically significant benefit. A Cochrane review found evidence that the use of risperidone and olanzapine resulted in improvements in agitation scale scores; risperidone was linked to improved scores on a psychosis scale, as well.10 A second meta-analysis showed small but statistically significant improvements in NPS with risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole.8 Another study showed that nearly half (48%) of patients who had a positive response to risperidone relapsed when they stopped taking the drug.11
A rapidly aging population is expected to further increase the need for pharmacologic interventions to control NPS. Yet safety concerns about the use of antipsychotics in the elderly (more on this in a bit) call this practice into question.
Chronic pain. A 2008 Cochrane review analyzed the efficacy of antipsychotics for acute and chronic pain, pooling results of 11 studies of the treatment of conditions such as postherpetic neuralgia, tension headache, acute myocardial infarction (MI), and terminal cancer. Results from the pooled trials were described as mixed, although an overall statistically significant decrease in pain intensity was found.12
Polypharmacy. The simultaneous use of 2 or more antipsychotic agents is also increasingly prevalent,13 with levels exceeding 50% in one study of patients with schizophrenia.14 Because there is little data on the safety and efficacy of antipsychotic polypharmacy, this off-label approach should be considered only as a last resort.15
Off-label treatment of psychiatric conditions
GAD. In comparative effectiveness trials, quetiapine was found to be equal to both paroxetine and escitalopram for the treatment of GAD, with a favorable effect on symptoms 8 weeks after its initiation.8 Trials of other antipsychotics for the treatment of GAD have not demonstrated clear efficacy. Trifluoperazine is approved for GAD, as a short-term treatment.
MDD. Antipsychotics have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of MDD, although only quetiapine and aripiprazole are approved (and only as adjunctive treatment). Evidence supports the use of both agents, as well as risperidone, as augmentation to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and in pooled results from 5 placebo-controlled trials, quetiapine was found to be effective as monotherapy for MDD.9
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Compared with placebo, risperidone showed a 4-fold increase in the likelihood of a favorable response (number needed to treat [NNT]=4) in patients with OCD,8 but the drug remains off-label for this purpose.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). A meta-analysis of 7 studies demonstrated risperidone’s efficacy in the treatment of combat-related PTSD.9 In a large Veterans Administration study of patients with combat-related PTSD resistant to treatment with SSRIs, however, risperidone showed no benefit after 6 months of therapy.16 Antipsychotics have not been found beneficial for substance abuse, eating disorders, or insomnia.9
Identifying risk factos, monitoring for adverse effects
While FGAs carry an increased risk of EPS, SGAs increase the risk of obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. The average life expectancy of patients with schizophrenia is 2 to 3 decades lower than that of age-matched controls,17 a finding largely attributed to the increased rate of cardiovascular disease. While this can be partly explained by differences in lifestyle and access to care, the metabolic effects of SGAs are a likely contributing factor.
Because of the adverse effects of FGAs and SGAs, the American Diabetes Association and American Psychiatric Association jointly issued guidelines addressing both the type and optimal frequency of monitoring for patients on antipsychotics (TABLE 2).18,19 Following them is critical, as both the initiation of an antipsychotic agent and any change in regimen can lead to the development—or exacerbation—of a number of diseases.
Before initiating antipsychotic therapy—or the first time you see a patient like Mr. B, whose care you will be monitoring—a thorough assessment of risk factors is needed. Foremost among them are overweight or obesity, insulin resistance or diabetes, a history of heart disease, and EPS.
In some cases, preexisting conditions and the potential harm of a specific drug must be weighed in determining which antipsychotic to prescribe. When adverse effects develop after drug therapy has been initiated, decisions about further actions should be based on both the degree of the unfavorable response and the availability of other treatments—and made, as appropriate, in consultation with the specialist who prescribed the drug.
CASE 1 › You tell Mr. B that metabolic side effects like weight gain, impaired glucose tolerance, and increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol are common with SGAs like the one he is taking, and that you will monitor his fasting glucose levels to evaluate his risk for developing diabetes—starting with this visit. (Olanzapine, the drug he is taking, is 4 times more likely than an FGA to lead to diabetes.18)
You talk to him, too, about the importance of weight control and note that if his BMI increases by ≥1 point you will refer him to a nutritionist and recommend a structured exercise program. Finally, you schedule an appointment in 3 months.
Risks associated with older age and dementia
In 2010, there were 84,842 visits to US emergency departments (EDs) due to adverse drug events involving antipsychotic agents—a 110% increase since 2005. Nearly 30% of these ED visits involved patients 65 years or older.20
Among patients with dementia, use of antipsychotics has been found to dramatically increase the risk of stroke (rate ratio, 3.26 for FGAs and 5.86 for SGAs).21 The risk was greatest in the first 35 days of treatment, but persisted throughout the 175-day study period.
The rate of MI also was elevated in dementia patients (hazard ratio of 2.19 for the first 30 days of treatment, then falling to 1.15 for the first year).22 The risk of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis also rose for patients who had been on antipsychotics during the previous 24 months (odds ratio=1.32), with the highest risk within the first 90 days of treatment.23
Risk of death varies with agent and dose. Multiple studies have shown that the mortality risk associated with antipsychotics varies greatly among individual drugs, with haloperidol carrying the highest risk and quetiapine the lowest.24-26 The hazard ratio for death within the first 30 days was 3.2 for haloperidol, 1.6 for risperidone, and 1.5 for olanzapine; quetiapine had no statistically significant increase. The increased mortality risk was statistically significant only at higher doses.24
The FDA weighs in
Evidence of the elevated risk of death led the FDA to require black-box warnings on SGAs (in 2005)27 and FGAs (in 2008),28 stating that “antipsychotics are not indicated for the treatment of dementia-related psychosis.”28 More recently (in 2012), the American Geriatrics Society (AGS) published a guide on the management of NPS in patients with dementia.29 In it, the AGS acknowledges that despite FDA warnings, antipsychotics may be necessary for the treatment of NPS.
The AGS stresses the importance of nonpharmacologic interventions (eg, positive reinforcement, orientation to time and place, music, light exercise, pet therapy) as a first-line approach. If these measures fail and antipsychotics are necessary, the AGS calls for obtaining informed consent from a family member, using the lowest effective dose, and regularly attempting to wean the patient off the antipsychotic as the standard of care.28
CASE 2 › New or worsening aggressive behavior in an elderly patient with dementia requires a prompt assessment. You start with a complete medical evaluation of Ms. F, ruling out common causes of agitation such as infection, pain, constipation, and an adverse reaction to medication.
You also ask about the incidents of aggression: Does the same aide dress Ms. F daily? Does the aide introduce herself and explain what she’s about to do before attempting to dress the patient?
Next, you recommend nonpharmacologic therapies, such as calming music, participation in group activities, and pet therapy. You tell the floor nurse that if these measures fail and Ms. F’s threatening behavior continues, an antipsychotic may be considered.
Guard against abuse of antipsychotics
As antipsychotic use increases, so, too, does misuse and abuse, particularly of quetiapine. The drug has a reported street value of $3 to $8 for a 25- to 100-mg dose and is known as “quell,” “Susie-Q,” “and “baby heroin”; “Q-ball” is the name used for a combination of cocaine and quetiapine.30,31
The Drug Abuse Warning Network reported a 115% increase in ED visits related to the misuse or abuse of pharmaceuticals between 2004 and 2010.32 In 2010, 57,199 drug abuse cases—including 28,618 suicide attempts—were linked to antipsychotics.20
To optimize the benefit of antipsychotics and minimize the likelihood of abuse, ensure that every patient taking them has a clearly documented indication for an antipsychotic and a single responsible prescriber of the antipsychotic, often a psychiatrist. Your responsibilities: Schedule visits for monitoring, do a medication review to identify potential drug-drug interactions, and assess efficacy, all on a regular basis.
CASE 1 › At Mr. B’s next visit, you retest his fasting glucose (which is now 105 mg/dL) and recheck his BMI, which has climbed to 30. You tell him you will speak with his psychiatrist about his weight gain and your concern about the development of insulin resistance.
Meanwhile, you refer the patient to a nutritionist and encourage a healthy lifestyle. Because the medication has been effective, you schedule a follow-up visit in 6 weeks to see if the lifestyle interventions have been successful before consulting with the patient’s psychiatrist about a change in medication.
CASE 2 › When you return to the long-term care facility one week later, you find that Ms. F’s NPS have not abated. You realize an antipsychotic agent may be needed. Because she has a history of heart disease, however, she has a higher risk for cardiovascular events.
You meet with her son to review the benefits and risks of antipsychotic therapy, explaining that risperidone is a reasonable agent and that a low starting dose (0.25-0.5 mg) will reduce the risk. You obtain his informed consent, document your treatment goals—a decrease in threatening behavior and the ability of the staff to work with Ms. F to get her up and out of bed—and establish a plan to review in 2 weeks.
CORRESPONDENCE
Daniel DeJoseph, MD, Drexel Family Medicine, 3401 Market Street, Suite 105-B, Philadelphia, PA 19104; [email protected]
1. Shen WW. A history of antipsychotic drug development. Compr Psychiatry. 1999;40:407-414.
2. Miller R. Mechanism of action of antipsychotic drugs of different classes, refractoriness to therapeutic effects of classical neuroleptics, and individual variation in sensitivity to their actions. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7:302-314.
3. Seeman P. Atypical antipsychotics: mechanism of action. Can J Psychiatry. 2002;47:27-38.
4. Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, et al; Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) Investigators. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1209-1223.
5. Jones PB, Barnes TR, Davies L, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effect on quality of life of second- vs first-generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia Study (CUtLASS 1). Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:1079-1087.
6. Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, et al. Second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:31-41.
7. Christian R, Saavedra L, Gaynes BN, et al. Future research needs for first- and second-generation antipsychotics for children and young adults [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2012:12-EHC042-EF.
8. Maher AR, Maglione M, Bagley S, et al. Efficacy and comparative effectiveness of atypical antipsychotic medications for off-label uses in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011;306:1359-1369.
9. Maglione M, Maher AR, Hu J, et al. Off-label use of atypical antipsychotics: An update [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2011:11-EHC087-EF.
10. Ballard CG, Waite J. Atypical antipsychotics for aggression and psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(1):CD003476.
11. Devanand DP, Mintzer J, Schultz SK, et al. Relapse risk after discontinuation of risperidone in Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1497-1507.
12. Seidel S, Aigner M, Ossege M, et al. Antipsychotics for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(4):CD004844.
13. Mojtabai R, Olfson M. National trends in psychotropic medication polypharmacy in office-based psychiatry. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:26-36.
14. Faries D, Ascher-Svanum H, Zhu B, et al. Antipsychotic monotherapy and polypharmacy in the naturalistic treatment of schizophrenia with atypical antipsychotics. BMC Psychiatry. 2005;5:26.
15. Ballon J, Stroup TS. Polypharmacy for schizophrenia. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2013;26:208-213.
16. Krystal JH, Rosenheck RA, Cramer JA, et al; Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study No. 504 Group. Adjunctive risperidone treatment for antidepressant-resistant symptoms of chronic military service-related PTSD: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2011;306:493-502.
17. Institute of Medicine. Retooling for an Aging America: Building the Health Care Workforce. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences; 2008.
18. Marder SR, Essock SM, Miller AL, et al. Physical health monitoring of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:1334-1349.
19. Barrett E, Blonde L, Clement S, et al. Consensus development conference on antipsychotic drugs and obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:596-601.
20. Drug Abuse Warning Network, 2010: National Estimates of Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits. HHS Publication No. (SMA) 12-4733, DAWN Series D-38. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/2k13/DAWN2k10ED/DAWN2k10ED.htm. Accessed May 1, 2013.
21. Douglas IJ, Smeeth L. Exposure to antipsychotics and risk of stroke: self controlled case series study. BMJ. 2008;337:a1227.
22. Pariente A, Fourrier-Réglat A, Ducruet T, et al. Antipsychotic use and myocardial infarction in older patients with treated dementia. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:648-653.
23. Parker C, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Antipsychotic drugs and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control study. BMJ. 2010;341:c4245.
24. Rossom RC, Rector TS, Lederle FA, et al. Are all commonly prescribed antipsychotics associated with greater mortality in elderly male veterans with dementia? J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:1027-1034.
25. Kales HC, Kim HM, Zivin K, et al. Risk of mortality among individual antipsychotics in patients with dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:71-79.
26. Huybrechts KF, Gerhard T, Crystal S, et al. Differential risk of death in older residents in nursing homes prescribed specific antipsychotic drugs: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2012;344:e977.
27. US Food and Drug Public Health Advisory: Deaths with antipsychotics in elderly patients with behavioral disturbances. US Food and Drug Administration Web site Available at: http://1.usa.gov/1plsxPk. Accessed February 5, 2014.
28. Information for healthcare professionals: conventional antipsychotics. US Food and Drug Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/drugs/drugsafety/postmarketdrugsafetyinformationforpatientsandproviders/ucm124830.htm. Accessed February 5, 2014.
29. Guide to the management of psychotic disorders and neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in older adults. American Geriatric Society Web site. Available at: http://dementia.americangeriatrics.org/GeriPsych_index.php. Accessed April 15, 2013.
30. Bogart GT, Ott CA. Abuse of second-generation antipsychotics: What prescribers need to know. Curr Psychiatr. 2011;10:77-79.
31. Tarosoff G, Osti K. Black-market value of antipsychotics, antidepressants, and hypnotics in Las Vegas, Nevada. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:350.
32. Highlights of the 2010 Drug Abuse Warning Network (DAWN) findings on drug-related emergency department visits. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality Web site. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/2k12/DAWN096/SR096EDHighlights2010.htm. Accessed May 1, 2013.
1. Shen WW. A history of antipsychotic drug development. Compr Psychiatry. 1999;40:407-414.
2. Miller R. Mechanism of action of antipsychotic drugs of different classes, refractoriness to therapeutic effects of classical neuroleptics, and individual variation in sensitivity to their actions. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009;7:302-314.
3. Seeman P. Atypical antipsychotics: mechanism of action. Can J Psychiatry. 2002;47:27-38.
4. Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, et al; Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) Investigators. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1209-1223.
5. Jones PB, Barnes TR, Davies L, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effect on quality of life of second- vs first-generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia Study (CUtLASS 1). Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:1079-1087.
6. Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, et al. Second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2009;373:31-41.
7. Christian R, Saavedra L, Gaynes BN, et al. Future research needs for first- and second-generation antipsychotics for children and young adults [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2012:12-EHC042-EF.
8. Maher AR, Maglione M, Bagley S, et al. Efficacy and comparative effectiveness of atypical antipsychotic medications for off-label uses in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011;306:1359-1369.
9. Maglione M, Maher AR, Hu J, et al. Off-label use of atypical antipsychotics: An update [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2011:11-EHC087-EF.
10. Ballard CG, Waite J. Atypical antipsychotics for aggression and psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(1):CD003476.
11. Devanand DP, Mintzer J, Schultz SK, et al. Relapse risk after discontinuation of risperidone in Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1497-1507.
12. Seidel S, Aigner M, Ossege M, et al. Antipsychotics for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(4):CD004844.
13. Mojtabai R, Olfson M. National trends in psychotropic medication polypharmacy in office-based psychiatry. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:26-36.
14. Faries D, Ascher-Svanum H, Zhu B, et al. Antipsychotic monotherapy and polypharmacy in the naturalistic treatment of schizophrenia with atypical antipsychotics. BMC Psychiatry. 2005;5:26.
15. Ballon J, Stroup TS. Polypharmacy for schizophrenia. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2013;26:208-213.
16. Krystal JH, Rosenheck RA, Cramer JA, et al; Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study No. 504 Group. Adjunctive risperidone treatment for antidepressant-resistant symptoms of chronic military service-related PTSD: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2011;306:493-502.
17. Institute of Medicine. Retooling for an Aging America: Building the Health Care Workforce. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences; 2008.
18. Marder SR, Essock SM, Miller AL, et al. Physical health monitoring of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:1334-1349.
19. Barrett E, Blonde L, Clement S, et al. Consensus development conference on antipsychotic drugs and obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:596-601.
20. Drug Abuse Warning Network, 2010: National Estimates of Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits. HHS Publication No. (SMA) 12-4733, DAWN Series D-38. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/2k13/DAWN2k10ED/DAWN2k10ED.htm. Accessed May 1, 2013.
21. Douglas IJ, Smeeth L. Exposure to antipsychotics and risk of stroke: self controlled case series study. BMJ. 2008;337:a1227.
22. Pariente A, Fourrier-Réglat A, Ducruet T, et al. Antipsychotic use and myocardial infarction in older patients with treated dementia. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172:648-653.
23. Parker C, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Antipsychotic drugs and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control study. BMJ. 2010;341:c4245.
24. Rossom RC, Rector TS, Lederle FA, et al. Are all commonly prescribed antipsychotics associated with greater mortality in elderly male veterans with dementia? J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:1027-1034.
25. Kales HC, Kim HM, Zivin K, et al. Risk of mortality among individual antipsychotics in patients with dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:71-79.
26. Huybrechts KF, Gerhard T, Crystal S, et al. Differential risk of death in older residents in nursing homes prescribed specific antipsychotic drugs: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2012;344:e977.
27. US Food and Drug Public Health Advisory: Deaths with antipsychotics in elderly patients with behavioral disturbances. US Food and Drug Administration Web site Available at: http://1.usa.gov/1plsxPk. Accessed February 5, 2014.
28. Information for healthcare professionals: conventional antipsychotics. US Food and Drug Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/drugs/drugsafety/postmarketdrugsafetyinformationforpatientsandproviders/ucm124830.htm. Accessed February 5, 2014.
29. Guide to the management of psychotic disorders and neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia in older adults. American Geriatric Society Web site. Available at: http://dementia.americangeriatrics.org/GeriPsych_index.php. Accessed April 15, 2013.
30. Bogart GT, Ott CA. Abuse of second-generation antipsychotics: What prescribers need to know. Curr Psychiatr. 2011;10:77-79.
31. Tarosoff G, Osti K. Black-market value of antipsychotics, antidepressants, and hypnotics in Las Vegas, Nevada. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:350.
32. Highlights of the 2010 Drug Abuse Warning Network (DAWN) findings on drug-related emergency department visits. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality Web site. Available at: http://www.samhsa.gov/data/2k12/DAWN096/SR096EDHighlights2010.htm. Accessed May 1, 2013.