User login
‘Striking’ difference in adverse events in women with Watchman LAAO
Women have more in-hospital complications than men and double the risk for major adverse events after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device, according to new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry data.
In-hospital mortality was also twofold higher among women than men and hospital stay was longer. Even after adjustment for potential confounders, these relationships still exist, Douglas Darden, MD, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
“I think this article certainly highlights – specific to a procedure that has gained more popularity and will become more commonplace in cardiovascular practice – that operators and patients need to pay more attention [to the fact] that women may be at more risk for adverse events and mortality,” senior author Jonathan Hsu, MD, also from UCSD, told this news organization.
Possible explanations for the disparities include anatomic differences between the sexes, such as smaller vessel diameter, thinner myocardial wall, and a more friable LLA in women; increased frailty; and clinician inexperience, the authors suggest.
“It could be something as simple or as specific as thinness of tissue or friability of tissue that may predispose women more than men to perforation or other risks that may put them at risk for adverse events specifically,” Dr. Hsu said.
Commenting further, he said, “I think we would be remiss not to mention the fact that part of this association may unfortunately be a disparity in care that women as a specific sex may receive,” he said.
Indeed, postimplantation women had higher adjusted odds of receiving a direct oral anticoagulant only (odds ratio, 1.07, P = .02) and warfarin only (OR, 1.12; P < .001), and lower odds of receiving clinical trial-recommended combined oral anticoagulants plus single antiplatelet therapy (OR, 0.91; P < .001).
“This article highlights the fact that in all aspects we need to pay attention that women receive as high-level, guideline-driven care as men,” Dr. Hsu said.
First author Dr. Darden pointed out in an email that women suffer disproportionately from atrial fibrillation (AFib), compared with men, with worse quality of life and higher risk for stroke. So “it’s only natural to seek further treatment in order to decrease that risk, specifically LAAO with Watchman.”
Despite the fact that women are known to be at greater risk for adverse events after invasive procedures, including AFib ablation and TAVR, little is known about sex differences with LAAO, as the LAAO clinical trials only included about 30% women, he said.
Two 2021 papers zeroing in on these sex differences produced mixed results. An American report in roughly 9,200 patients reported a higher risk for major in-hospital events in women after receipt of Watchman implants, whereas a German report found similar safety and efficacy among 387 consecutive patients, regardless of sex.
The present study involved 20,388 women and 28,969 men implanted with the Watchman device between January 2016 and June 2019 in the NCDR registry, the largest LAAO registry with adjudicated events with participation mandated for Medicare coverage.
The women were older (mean age, 76.5 vs. 75.8 years), had a higher mean CHA2DS2-VASc score (5.3 vs. 4.5), and were more likely to have a high fall risk as an indication for LAAO (39.8% vs. 33.5%).
Furthermore, women were more likely than men to have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and uncontrolled hypertension, but less likely to have congestive heart failure, diabetes, and coronary artery disease.
After multivariable adjustment, all but one of the primary outcomes was significantly worse in women versus men:
- Aborted or canceled procedure: 3.0% vs. 2.9% (OR, 1.01; P = .87)
- Any adverse event: 6.3% vs. 3.9% (OR, 1.63; P < .001)
- Major adverse event: 4.1% vs. 2.0% (OR, 2.06; P < .001)
- Hospital stay more than 1 day: 16.0% vs. 11.6% (OR, 1.46; P < .001)
- Death: 58/0.3% vs. 37/0.1% (OR, 2.01; P = .001).
The authors point out that device-related adverse events are lower than in the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL clinical trials of the Watchman, with 0.8% of patients developing a pericardial effusion requiring drainage and 1.2% having major bleeding, down from highs of 4.8% and 3.5%, respectively, in PROTECT-AF.
Although promising overall, adverse events among women were driven by higher rates of both pericardial effusion requiring draining (1.2% vs. 0.5%; P < .001) and major bleeding (1.7% vs. 0.8%; P < .001).
Commenting for this news organization John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Kentucky, expressed concern that despite its increasing popularity, the rate of serious complications appears to be increasing for the preventive procedure. “That’s peculiar because you’d expect increased experience and device iterations to decrease complications. And the NCDR data surely undercounts the real rate of adverse events because it only includes in-hospital complications.”
Based on the current data, he observed that there’s a 3% chance for a major complication overall, with the typical female Watchman patient facing a 6% chance of any adverse event and 4% risk for a major adverse event during her hospital stay alone.
“The striking difference in complications in women is a super important observation because higher upfront risk has an even more negative effect on the harm-benefit calculus of this procedure,” Dr. Mandrola said.
“Some of the increased harm in women may have been due to the slightly higher rate of comorbid conditions, but that is real-life,” he said. “Registry data like this is extremely valuable because, unlike the carefully selected randomized trial, registries reflect what is actually being done in practice.”
Dr. Hsu agreed that the absolute numbers are concerning. Nevertheless, “it doesn’t necessarily sound an alarm that our adverse events are worse in contemporary practice or that adverse events continue to increase. But, in general, it just points to the fact that there is this inherent larger risk in women, compared with men, and that we need to, first, figure out why, and second, we need to figure out how to improve.”
Strategies to mitigate procedural risk included ultrasound-guided venous access, preprocedural imaging, improved proficiency with LAAO devices, and continued development of safer devices, they note.
Despite the more generalizable nature of registry data, “the results of this study should not result in differing sex-based thresholds for LAAO implant,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s NCDR. Dr. Hsu reports financial relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Biotronik, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Biosense Webster, Altathera Pharmaceuticals, and Zoll Medical and holding equity interest in Acutus Medical and Vektor Medical outside the submitted work. Dr. Darden reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women have more in-hospital complications than men and double the risk for major adverse events after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device, according to new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry data.
In-hospital mortality was also twofold higher among women than men and hospital stay was longer. Even after adjustment for potential confounders, these relationships still exist, Douglas Darden, MD, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
“I think this article certainly highlights – specific to a procedure that has gained more popularity and will become more commonplace in cardiovascular practice – that operators and patients need to pay more attention [to the fact] that women may be at more risk for adverse events and mortality,” senior author Jonathan Hsu, MD, also from UCSD, told this news organization.
Possible explanations for the disparities include anatomic differences between the sexes, such as smaller vessel diameter, thinner myocardial wall, and a more friable LLA in women; increased frailty; and clinician inexperience, the authors suggest.
“It could be something as simple or as specific as thinness of tissue or friability of tissue that may predispose women more than men to perforation or other risks that may put them at risk for adverse events specifically,” Dr. Hsu said.
Commenting further, he said, “I think we would be remiss not to mention the fact that part of this association may unfortunately be a disparity in care that women as a specific sex may receive,” he said.
Indeed, postimplantation women had higher adjusted odds of receiving a direct oral anticoagulant only (odds ratio, 1.07, P = .02) and warfarin only (OR, 1.12; P < .001), and lower odds of receiving clinical trial-recommended combined oral anticoagulants plus single antiplatelet therapy (OR, 0.91; P < .001).
“This article highlights the fact that in all aspects we need to pay attention that women receive as high-level, guideline-driven care as men,” Dr. Hsu said.
First author Dr. Darden pointed out in an email that women suffer disproportionately from atrial fibrillation (AFib), compared with men, with worse quality of life and higher risk for stroke. So “it’s only natural to seek further treatment in order to decrease that risk, specifically LAAO with Watchman.”
Despite the fact that women are known to be at greater risk for adverse events after invasive procedures, including AFib ablation and TAVR, little is known about sex differences with LAAO, as the LAAO clinical trials only included about 30% women, he said.
Two 2021 papers zeroing in on these sex differences produced mixed results. An American report in roughly 9,200 patients reported a higher risk for major in-hospital events in women after receipt of Watchman implants, whereas a German report found similar safety and efficacy among 387 consecutive patients, regardless of sex.
The present study involved 20,388 women and 28,969 men implanted with the Watchman device between January 2016 and June 2019 in the NCDR registry, the largest LAAO registry with adjudicated events with participation mandated for Medicare coverage.
The women were older (mean age, 76.5 vs. 75.8 years), had a higher mean CHA2DS2-VASc score (5.3 vs. 4.5), and were more likely to have a high fall risk as an indication for LAAO (39.8% vs. 33.5%).
Furthermore, women were more likely than men to have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and uncontrolled hypertension, but less likely to have congestive heart failure, diabetes, and coronary artery disease.
After multivariable adjustment, all but one of the primary outcomes was significantly worse in women versus men:
- Aborted or canceled procedure: 3.0% vs. 2.9% (OR, 1.01; P = .87)
- Any adverse event: 6.3% vs. 3.9% (OR, 1.63; P < .001)
- Major adverse event: 4.1% vs. 2.0% (OR, 2.06; P < .001)
- Hospital stay more than 1 day: 16.0% vs. 11.6% (OR, 1.46; P < .001)
- Death: 58/0.3% vs. 37/0.1% (OR, 2.01; P = .001).
The authors point out that device-related adverse events are lower than in the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL clinical trials of the Watchman, with 0.8% of patients developing a pericardial effusion requiring drainage and 1.2% having major bleeding, down from highs of 4.8% and 3.5%, respectively, in PROTECT-AF.
Although promising overall, adverse events among women were driven by higher rates of both pericardial effusion requiring draining (1.2% vs. 0.5%; P < .001) and major bleeding (1.7% vs. 0.8%; P < .001).
Commenting for this news organization John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Kentucky, expressed concern that despite its increasing popularity, the rate of serious complications appears to be increasing for the preventive procedure. “That’s peculiar because you’d expect increased experience and device iterations to decrease complications. And the NCDR data surely undercounts the real rate of adverse events because it only includes in-hospital complications.”
Based on the current data, he observed that there’s a 3% chance for a major complication overall, with the typical female Watchman patient facing a 6% chance of any adverse event and 4% risk for a major adverse event during her hospital stay alone.
“The striking difference in complications in women is a super important observation because higher upfront risk has an even more negative effect on the harm-benefit calculus of this procedure,” Dr. Mandrola said.
“Some of the increased harm in women may have been due to the slightly higher rate of comorbid conditions, but that is real-life,” he said. “Registry data like this is extremely valuable because, unlike the carefully selected randomized trial, registries reflect what is actually being done in practice.”
Dr. Hsu agreed that the absolute numbers are concerning. Nevertheless, “it doesn’t necessarily sound an alarm that our adverse events are worse in contemporary practice or that adverse events continue to increase. But, in general, it just points to the fact that there is this inherent larger risk in women, compared with men, and that we need to, first, figure out why, and second, we need to figure out how to improve.”
Strategies to mitigate procedural risk included ultrasound-guided venous access, preprocedural imaging, improved proficiency with LAAO devices, and continued development of safer devices, they note.
Despite the more generalizable nature of registry data, “the results of this study should not result in differing sex-based thresholds for LAAO implant,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s NCDR. Dr. Hsu reports financial relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Biotronik, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Biosense Webster, Altathera Pharmaceuticals, and Zoll Medical and holding equity interest in Acutus Medical and Vektor Medical outside the submitted work. Dr. Darden reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women have more in-hospital complications than men and double the risk for major adverse events after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device, according to new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry data.
In-hospital mortality was also twofold higher among women than men and hospital stay was longer. Even after adjustment for potential confounders, these relationships still exist, Douglas Darden, MD, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
“I think this article certainly highlights – specific to a procedure that has gained more popularity and will become more commonplace in cardiovascular practice – that operators and patients need to pay more attention [to the fact] that women may be at more risk for adverse events and mortality,” senior author Jonathan Hsu, MD, also from UCSD, told this news organization.
Possible explanations for the disparities include anatomic differences between the sexes, such as smaller vessel diameter, thinner myocardial wall, and a more friable LLA in women; increased frailty; and clinician inexperience, the authors suggest.
“It could be something as simple or as specific as thinness of tissue or friability of tissue that may predispose women more than men to perforation or other risks that may put them at risk for adverse events specifically,” Dr. Hsu said.
Commenting further, he said, “I think we would be remiss not to mention the fact that part of this association may unfortunately be a disparity in care that women as a specific sex may receive,” he said.
Indeed, postimplantation women had higher adjusted odds of receiving a direct oral anticoagulant only (odds ratio, 1.07, P = .02) and warfarin only (OR, 1.12; P < .001), and lower odds of receiving clinical trial-recommended combined oral anticoagulants plus single antiplatelet therapy (OR, 0.91; P < .001).
“This article highlights the fact that in all aspects we need to pay attention that women receive as high-level, guideline-driven care as men,” Dr. Hsu said.
First author Dr. Darden pointed out in an email that women suffer disproportionately from atrial fibrillation (AFib), compared with men, with worse quality of life and higher risk for stroke. So “it’s only natural to seek further treatment in order to decrease that risk, specifically LAAO with Watchman.”
Despite the fact that women are known to be at greater risk for adverse events after invasive procedures, including AFib ablation and TAVR, little is known about sex differences with LAAO, as the LAAO clinical trials only included about 30% women, he said.
Two 2021 papers zeroing in on these sex differences produced mixed results. An American report in roughly 9,200 patients reported a higher risk for major in-hospital events in women after receipt of Watchman implants, whereas a German report found similar safety and efficacy among 387 consecutive patients, regardless of sex.
The present study involved 20,388 women and 28,969 men implanted with the Watchman device between January 2016 and June 2019 in the NCDR registry, the largest LAAO registry with adjudicated events with participation mandated for Medicare coverage.
The women were older (mean age, 76.5 vs. 75.8 years), had a higher mean CHA2DS2-VASc score (5.3 vs. 4.5), and were more likely to have a high fall risk as an indication for LAAO (39.8% vs. 33.5%).
Furthermore, women were more likely than men to have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and uncontrolled hypertension, but less likely to have congestive heart failure, diabetes, and coronary artery disease.
After multivariable adjustment, all but one of the primary outcomes was significantly worse in women versus men:
- Aborted or canceled procedure: 3.0% vs. 2.9% (OR, 1.01; P = .87)
- Any adverse event: 6.3% vs. 3.9% (OR, 1.63; P < .001)
- Major adverse event: 4.1% vs. 2.0% (OR, 2.06; P < .001)
- Hospital stay more than 1 day: 16.0% vs. 11.6% (OR, 1.46; P < .001)
- Death: 58/0.3% vs. 37/0.1% (OR, 2.01; P = .001).
The authors point out that device-related adverse events are lower than in the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL clinical trials of the Watchman, with 0.8% of patients developing a pericardial effusion requiring drainage and 1.2% having major bleeding, down from highs of 4.8% and 3.5%, respectively, in PROTECT-AF.
Although promising overall, adverse events among women were driven by higher rates of both pericardial effusion requiring draining (1.2% vs. 0.5%; P < .001) and major bleeding (1.7% vs. 0.8%; P < .001).
Commenting for this news organization John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Kentucky, expressed concern that despite its increasing popularity, the rate of serious complications appears to be increasing for the preventive procedure. “That’s peculiar because you’d expect increased experience and device iterations to decrease complications. And the NCDR data surely undercounts the real rate of adverse events because it only includes in-hospital complications.”
Based on the current data, he observed that there’s a 3% chance for a major complication overall, with the typical female Watchman patient facing a 6% chance of any adverse event and 4% risk for a major adverse event during her hospital stay alone.
“The striking difference in complications in women is a super important observation because higher upfront risk has an even more negative effect on the harm-benefit calculus of this procedure,” Dr. Mandrola said.
“Some of the increased harm in women may have been due to the slightly higher rate of comorbid conditions, but that is real-life,” he said. “Registry data like this is extremely valuable because, unlike the carefully selected randomized trial, registries reflect what is actually being done in practice.”
Dr. Hsu agreed that the absolute numbers are concerning. Nevertheless, “it doesn’t necessarily sound an alarm that our adverse events are worse in contemporary practice or that adverse events continue to increase. But, in general, it just points to the fact that there is this inherent larger risk in women, compared with men, and that we need to, first, figure out why, and second, we need to figure out how to improve.”
Strategies to mitigate procedural risk included ultrasound-guided venous access, preprocedural imaging, improved proficiency with LAAO devices, and continued development of safer devices, they note.
Despite the more generalizable nature of registry data, “the results of this study should not result in differing sex-based thresholds for LAAO implant,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s NCDR. Dr. Hsu reports financial relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Biotronik, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Biosense Webster, Altathera Pharmaceuticals, and Zoll Medical and holding equity interest in Acutus Medical and Vektor Medical outside the submitted work. Dr. Darden reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart doc offering ‘fountain of youth’ jailed for 6 1/2 years
Cardiologist Samirkumar J. Shah, MD, was sentenced to 78 months in prison after his conviction on two counts of federal health care fraud involving more than $13 million.
As part of his sentence, Dr. Shah, 58, of Fox Chapel, Pa., must pay $1.7 million in restitution and other penalties and undergo 3 years of supervised release after prison.
“Dr. Shah risked the health of his patients so he could make millions of dollars through unnecessary procedures, and lied and fabricated records for years to perpetuate his fraud scheme,” acting U.S. Attorney Stephen R. Kaufman said in an Aug. 5 statement from the Department of Justice.
As previously reported, Dr. Shah was convicted June 14, 2019, of submitting fraudulent claims to private and federal insurance programs between 2008 and 2013 for external counterpulsation (ECP) therapy, a lower limb compression treatment approved for patients with coronary artery disease and refractory angina.
Dr. Shah, however, advertised ECP as the “fountain of youth,” claimed it made patients “younger and smarter,” and offered the treatment for conditions such as obesity, hypertension, hypotension, diabetes, and erectile dysfunction.
Patients were required to undergo diagnostic ultrasounds as a precautionary measure prior to starting ECP, but witness testimony established that Dr. Shah did not review any of the imaging before approving new patients for ECP, placing his patients at risk for serious injury or even death, the DOJ stated.
The evidence also showed that Dr. Shah double-billed insurers, routinely submitted fabricated patient files, and made false statements concerning his practice, patient population, recording keeping, and compliance with coverage guidelines, the government said.
During the scheme, Dr. Shah submitted ECP-related claims for Medicare Part B, UPMC Health Plan, Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield, and Gateway Health Plan beneficiaries totalling more than $13 million and received reimbursement payments in excess of $3.5 million.
“Rather than upholding the oath he swore and providing care for patients who trusted him, this defendant misled patients and drained critical Medicaid funds from families who needed it,” said Attorney General Josh Shapiro. “We will not let anyone put their patients’ lives at risk for a profit.”
“Today’s sentence holds Mr. Shah accountable for his appalling actions,” said FBI Pittsburgh Special Agent in Charge Mike Nordwall. “Mr. Shah used his position as a doctor to illegally profit from a health care program paid for by taxpayers. Fraud of this magnitude will not be tolerated.”
Dr. Shah has been in custody since July 15, 2021, after skipping out on his original July 14 sentencing date. The Tribune-Review reported that Dr. Shah filed a last-minute request for a continuance, claiming he had an adverse reaction to the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination and was advised by his doctor that he needed “strict bedrest for at least 6 weeks.”
Dr. Shah reportedly turned himself after presiding U.S. District Judge David S. Cercone denied the motion and issued an arrest warrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiologist Samirkumar J. Shah, MD, was sentenced to 78 months in prison after his conviction on two counts of federal health care fraud involving more than $13 million.
As part of his sentence, Dr. Shah, 58, of Fox Chapel, Pa., must pay $1.7 million in restitution and other penalties and undergo 3 years of supervised release after prison.
“Dr. Shah risked the health of his patients so he could make millions of dollars through unnecessary procedures, and lied and fabricated records for years to perpetuate his fraud scheme,” acting U.S. Attorney Stephen R. Kaufman said in an Aug. 5 statement from the Department of Justice.
As previously reported, Dr. Shah was convicted June 14, 2019, of submitting fraudulent claims to private and federal insurance programs between 2008 and 2013 for external counterpulsation (ECP) therapy, a lower limb compression treatment approved for patients with coronary artery disease and refractory angina.
Dr. Shah, however, advertised ECP as the “fountain of youth,” claimed it made patients “younger and smarter,” and offered the treatment for conditions such as obesity, hypertension, hypotension, diabetes, and erectile dysfunction.
Patients were required to undergo diagnostic ultrasounds as a precautionary measure prior to starting ECP, but witness testimony established that Dr. Shah did not review any of the imaging before approving new patients for ECP, placing his patients at risk for serious injury or even death, the DOJ stated.
The evidence also showed that Dr. Shah double-billed insurers, routinely submitted fabricated patient files, and made false statements concerning his practice, patient population, recording keeping, and compliance with coverage guidelines, the government said.
During the scheme, Dr. Shah submitted ECP-related claims for Medicare Part B, UPMC Health Plan, Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield, and Gateway Health Plan beneficiaries totalling more than $13 million and received reimbursement payments in excess of $3.5 million.
“Rather than upholding the oath he swore and providing care for patients who trusted him, this defendant misled patients and drained critical Medicaid funds from families who needed it,” said Attorney General Josh Shapiro. “We will not let anyone put their patients’ lives at risk for a profit.”
“Today’s sentence holds Mr. Shah accountable for his appalling actions,” said FBI Pittsburgh Special Agent in Charge Mike Nordwall. “Mr. Shah used his position as a doctor to illegally profit from a health care program paid for by taxpayers. Fraud of this magnitude will not be tolerated.”
Dr. Shah has been in custody since July 15, 2021, after skipping out on his original July 14 sentencing date. The Tribune-Review reported that Dr. Shah filed a last-minute request for a continuance, claiming he had an adverse reaction to the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination and was advised by his doctor that he needed “strict bedrest for at least 6 weeks.”
Dr. Shah reportedly turned himself after presiding U.S. District Judge David S. Cercone denied the motion and issued an arrest warrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiologist Samirkumar J. Shah, MD, was sentenced to 78 months in prison after his conviction on two counts of federal health care fraud involving more than $13 million.
As part of his sentence, Dr. Shah, 58, of Fox Chapel, Pa., must pay $1.7 million in restitution and other penalties and undergo 3 years of supervised release after prison.
“Dr. Shah risked the health of his patients so he could make millions of dollars through unnecessary procedures, and lied and fabricated records for years to perpetuate his fraud scheme,” acting U.S. Attorney Stephen R. Kaufman said in an Aug. 5 statement from the Department of Justice.
As previously reported, Dr. Shah was convicted June 14, 2019, of submitting fraudulent claims to private and federal insurance programs between 2008 and 2013 for external counterpulsation (ECP) therapy, a lower limb compression treatment approved for patients with coronary artery disease and refractory angina.
Dr. Shah, however, advertised ECP as the “fountain of youth,” claimed it made patients “younger and smarter,” and offered the treatment for conditions such as obesity, hypertension, hypotension, diabetes, and erectile dysfunction.
Patients were required to undergo diagnostic ultrasounds as a precautionary measure prior to starting ECP, but witness testimony established that Dr. Shah did not review any of the imaging before approving new patients for ECP, placing his patients at risk for serious injury or even death, the DOJ stated.
The evidence also showed that Dr. Shah double-billed insurers, routinely submitted fabricated patient files, and made false statements concerning his practice, patient population, recording keeping, and compliance with coverage guidelines, the government said.
During the scheme, Dr. Shah submitted ECP-related claims for Medicare Part B, UPMC Health Plan, Highmark Blue Cross Blue Shield, and Gateway Health Plan beneficiaries totalling more than $13 million and received reimbursement payments in excess of $3.5 million.
“Rather than upholding the oath he swore and providing care for patients who trusted him, this defendant misled patients and drained critical Medicaid funds from families who needed it,” said Attorney General Josh Shapiro. “We will not let anyone put their patients’ lives at risk for a profit.”
“Today’s sentence holds Mr. Shah accountable for his appalling actions,” said FBI Pittsburgh Special Agent in Charge Mike Nordwall. “Mr. Shah used his position as a doctor to illegally profit from a health care program paid for by taxpayers. Fraud of this magnitude will not be tolerated.”
Dr. Shah has been in custody since July 15, 2021, after skipping out on his original July 14 sentencing date. The Tribune-Review reported that Dr. Shah filed a last-minute request for a continuance, claiming he had an adverse reaction to the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination and was advised by his doctor that he needed “strict bedrest for at least 6 weeks.”
Dr. Shah reportedly turned himself after presiding U.S. District Judge David S. Cercone denied the motion and issued an arrest warrant.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Despite retraction, study using fraudulent Surgisphere data still cited
A retracted study on the safety of blood pressure medications in patients with COVID-19 continues to be cited nearly a year later, new research shows.
The study in question, published on May 1, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine, showed no increased risk for in-hospital death with the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Concerns about the veracity of the Surgisphere database used for the study, however, led to a June 4 retraction and to the June 13 retraction of a second study, published in the Lancet, that focused on hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment.
Although the Surgisphere scandal caused a global reckoning of COVID-19 scientific studies, the new analysis identified 652 citations of the NEJM article as of May 31.
More than a third of the citations occurred in the first 2 months after the retraction, 54% were at least 3 months later, and 2.8% at least 6 months later. In May, 11 months after the article was retracted, it was cited 21 times, senior author Emily G. McDonald, MD, MSc, McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues reported in a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“In early May and June there were already more than 200 citations in one of the world’s leading scientific journals, so I do believe it was a highly influential article early on and had an impact on different types of studies or research taking place,” she said in an interview.
Dr. McDonald said she’s also “certain that it impacted patient care,” observing that when there are no guidelines available on how to manage patients, physicians will turn to the most recent evidence in the most reputable journals.
“In the case of ACE [inhibitors] and ARBs, although the study was based on fraudulent data, we were lucky that the overall message was in the end probably correct, but that might not have been the case for another study or dataset,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, concerns existed that ACE inhibitors and ARBs could be harmful, increasing the expression of ACE2 receptors, which the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to gain entry into cells. The first randomized trial to examine the issue, BRACE CORONA, showed no clinical benefit to interrupting use of the agents in hospitalized patients. An observational study suggested ACE inhibitors may even be protective.
Of two high-profile retractions, McDonald said they chose to bypass the hydroxychloroquine study, which had an eye-popping Altmetric attention score of 23,084, compared with 3,727 for the NEJM paper, because it may have been cited for “other” reasons. “We wanted to focus less on the politics and more on the problem of retracted work.”
The team found that researchers across the globe were citing the retracted ACE/ARB paper (18.7% in the United States, 8.1% in Italy, and 44% other countries). Most citations were used to support a statement in the main text of a study, but in nearly 3% of cases, the data were incorporated into new analyses.
Just 17.6% of the studies cited or noted the retraction. “For sure, that was surprising to us. We suspected it, but our study confirmed it,” Dr. McDonald said.
Although retracted articles can be identified by a watermark or line of text, in some cases that can be easily missed, she noted. What’s more, not all citation software points out when a study has been retracted, a fate shared by the copyediting process.
“There are a lot of mechanisms in place and, in general, what’s happening is rare but there isn’t a perfect automated system solution to absolutely prevent this from happening,” she said. “It’s still subject to human error.”
The findings also have to be taken in the context of a rapidly emerging pandemic and the unprecedented torrent of scientific papers released over the past year.
“That might have contributed to why this happened, but the takeaway message is that this can happen despite our best efforts, and we need to challenge ourselves to come up with a system solution to prevent this from happening in the future,” Dr. McDonald said. “Current mechanisms are probably capturing 95% of it, but we need to do better.”
Limitations of the present analysis are that it was limited to the single retracted study; used only a single search engine, Google Scholar, to identify the citing works; and that additional citations may have been missed, the authors noted.
McDonald and coauthor Todd C. Lee, MD, report being signatories on a public letter calling for the retraction of the Surgisphere papers. Dr. Lee also reported receiving research support from Fonds De Recherche du Quebec-Sante during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A retracted study on the safety of blood pressure medications in patients with COVID-19 continues to be cited nearly a year later, new research shows.
The study in question, published on May 1, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine, showed no increased risk for in-hospital death with the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Concerns about the veracity of the Surgisphere database used for the study, however, led to a June 4 retraction and to the June 13 retraction of a second study, published in the Lancet, that focused on hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment.
Although the Surgisphere scandal caused a global reckoning of COVID-19 scientific studies, the new analysis identified 652 citations of the NEJM article as of May 31.
More than a third of the citations occurred in the first 2 months after the retraction, 54% were at least 3 months later, and 2.8% at least 6 months later. In May, 11 months after the article was retracted, it was cited 21 times, senior author Emily G. McDonald, MD, MSc, McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues reported in a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“In early May and June there were already more than 200 citations in one of the world’s leading scientific journals, so I do believe it was a highly influential article early on and had an impact on different types of studies or research taking place,” she said in an interview.
Dr. McDonald said she’s also “certain that it impacted patient care,” observing that when there are no guidelines available on how to manage patients, physicians will turn to the most recent evidence in the most reputable journals.
“In the case of ACE [inhibitors] and ARBs, although the study was based on fraudulent data, we were lucky that the overall message was in the end probably correct, but that might not have been the case for another study or dataset,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, concerns existed that ACE inhibitors and ARBs could be harmful, increasing the expression of ACE2 receptors, which the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to gain entry into cells. The first randomized trial to examine the issue, BRACE CORONA, showed no clinical benefit to interrupting use of the agents in hospitalized patients. An observational study suggested ACE inhibitors may even be protective.
Of two high-profile retractions, McDonald said they chose to bypass the hydroxychloroquine study, which had an eye-popping Altmetric attention score of 23,084, compared with 3,727 for the NEJM paper, because it may have been cited for “other” reasons. “We wanted to focus less on the politics and more on the problem of retracted work.”
The team found that researchers across the globe were citing the retracted ACE/ARB paper (18.7% in the United States, 8.1% in Italy, and 44% other countries). Most citations were used to support a statement in the main text of a study, but in nearly 3% of cases, the data were incorporated into new analyses.
Just 17.6% of the studies cited or noted the retraction. “For sure, that was surprising to us. We suspected it, but our study confirmed it,” Dr. McDonald said.
Although retracted articles can be identified by a watermark or line of text, in some cases that can be easily missed, she noted. What’s more, not all citation software points out when a study has been retracted, a fate shared by the copyediting process.
“There are a lot of mechanisms in place and, in general, what’s happening is rare but there isn’t a perfect automated system solution to absolutely prevent this from happening,” she said. “It’s still subject to human error.”
The findings also have to be taken in the context of a rapidly emerging pandemic and the unprecedented torrent of scientific papers released over the past year.
“That might have contributed to why this happened, but the takeaway message is that this can happen despite our best efforts, and we need to challenge ourselves to come up with a system solution to prevent this from happening in the future,” Dr. McDonald said. “Current mechanisms are probably capturing 95% of it, but we need to do better.”
Limitations of the present analysis are that it was limited to the single retracted study; used only a single search engine, Google Scholar, to identify the citing works; and that additional citations may have been missed, the authors noted.
McDonald and coauthor Todd C. Lee, MD, report being signatories on a public letter calling for the retraction of the Surgisphere papers. Dr. Lee also reported receiving research support from Fonds De Recherche du Quebec-Sante during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A retracted study on the safety of blood pressure medications in patients with COVID-19 continues to be cited nearly a year later, new research shows.
The study in question, published on May 1, 2020, in the New England Journal of Medicine, showed no increased risk for in-hospital death with the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Concerns about the veracity of the Surgisphere database used for the study, however, led to a June 4 retraction and to the June 13 retraction of a second study, published in the Lancet, that focused on hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment.
Although the Surgisphere scandal caused a global reckoning of COVID-19 scientific studies, the new analysis identified 652 citations of the NEJM article as of May 31.
More than a third of the citations occurred in the first 2 months after the retraction, 54% were at least 3 months later, and 2.8% at least 6 months later. In May, 11 months after the article was retracted, it was cited 21 times, senior author Emily G. McDonald, MD, MSc, McGill University, Montreal, and colleagues reported in a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“In early May and June there were already more than 200 citations in one of the world’s leading scientific journals, so I do believe it was a highly influential article early on and had an impact on different types of studies or research taking place,” she said in an interview.
Dr. McDonald said she’s also “certain that it impacted patient care,” observing that when there are no guidelines available on how to manage patients, physicians will turn to the most recent evidence in the most reputable journals.
“In the case of ACE [inhibitors] and ARBs, although the study was based on fraudulent data, we were lucky that the overall message was in the end probably correct, but that might not have been the case for another study or dataset,” she said.
Early in the pandemic, concerns existed that ACE inhibitors and ARBs could be harmful, increasing the expression of ACE2 receptors, which the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to gain entry into cells. The first randomized trial to examine the issue, BRACE CORONA, showed no clinical benefit to interrupting use of the agents in hospitalized patients. An observational study suggested ACE inhibitors may even be protective.
Of two high-profile retractions, McDonald said they chose to bypass the hydroxychloroquine study, which had an eye-popping Altmetric attention score of 23,084, compared with 3,727 for the NEJM paper, because it may have been cited for “other” reasons. “We wanted to focus less on the politics and more on the problem of retracted work.”
The team found that researchers across the globe were citing the retracted ACE/ARB paper (18.7% in the United States, 8.1% in Italy, and 44% other countries). Most citations were used to support a statement in the main text of a study, but in nearly 3% of cases, the data were incorporated into new analyses.
Just 17.6% of the studies cited or noted the retraction. “For sure, that was surprising to us. We suspected it, but our study confirmed it,” Dr. McDonald said.
Although retracted articles can be identified by a watermark or line of text, in some cases that can be easily missed, she noted. What’s more, not all citation software points out when a study has been retracted, a fate shared by the copyediting process.
“There are a lot of mechanisms in place and, in general, what’s happening is rare but there isn’t a perfect automated system solution to absolutely prevent this from happening,” she said. “It’s still subject to human error.”
The findings also have to be taken in the context of a rapidly emerging pandemic and the unprecedented torrent of scientific papers released over the past year.
“That might have contributed to why this happened, but the takeaway message is that this can happen despite our best efforts, and we need to challenge ourselves to come up with a system solution to prevent this from happening in the future,” Dr. McDonald said. “Current mechanisms are probably capturing 95% of it, but we need to do better.”
Limitations of the present analysis are that it was limited to the single retracted study; used only a single search engine, Google Scholar, to identify the citing works; and that additional citations may have been missed, the authors noted.
McDonald and coauthor Todd C. Lee, MD, report being signatories on a public letter calling for the retraction of the Surgisphere papers. Dr. Lee also reported receiving research support from Fonds De Recherche du Quebec-Sante during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA panel balks at TriGuard 3 cerebral embolic device for TAVR
A Food and Drug Administration advisory panel struggled to muster support for marketing clearance of the TriGuard 3 (Keystone Heart) device for use during transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
The Circulatory Systems Devices Panel of the Medical Devices Advisory Committee took no vote when it met Aug. 3, but weighed evidence for a proposed indication for the device “to minimize the risk of cerebral damage by deflecting embolic debris away from the cerebral circulation” during TAVR.
“While this device may deflect some debris, the data would suggest it may also create issues,” said Keith B. Allen, MD, director of surgical research at the Mid America Heart & Lung Surgeons, Kansas City, Mo. “I am really concerned that our desire and the emotion that surrounds preventing stroke are not being supported by the data.”
TriGuard 3 received CE Mark in Europe in March 2020. It was submitted for 510(k) clearance and seeks to prove substantial equivalence to the predicate Sentinel device (Claret Medical), currently the only approved embolic protection device in the United States.
The device is designed to cover all three major aortic vessels (innominate, left carotid, and left subclavian arteries) and is delivered transfemorally through an 8F sheath, whereas the Sentinel is positioned within the branch vessels, doesn’t cover the left subclavian artery, and is introduced through the radial or brachial artery via a 6F sheath.
TriGuard 3 faced an uphill battle, however, after failing to meet the primary composite efficacy endpoint in the REFLECT phase 2 trial (P = .857), with numeric trends showing higher all-cause mortality or any stroke at 30 days (9.8% vs. 6.7%) than pooled control subjects without embolic protection.
Rates for other components of the endpoint also trended higher with the device: National Institutes of Stroke Stroke Scale score worsening 2-5 days after the procedure, cerebral ischemic lesions on MRI 2-5 days after the procedure, and total cerebral ischemic lesion volume.
The Sentinel device was approved in 2017 after it failed to meet its primary efficacy endpoint of new brain lesion volume on MRI, but death and stroke rates favored the device over control, the panel pointed out.
The sponsor provided additional analyses in the per treatment (PT) population, defined as those with complete three-vessel coverage in at least two of three procedural time points. Compared with pooled control subjects, most of the imaging endpoints favored the TriGuard 3 device, but clinical neurologic event rates continued to favor the control group.
“The data used to demonstrate efficacy are all based on the PT subpopulation of the whole population, and those have to be considered promissory data,” said John Hirshfeld, MD, emeritus professor, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “This is the group where everything went well and for us to decide that’s achievable in the general population is speculative.”
Safety data
The REFLECT trial did meet its primary safety endpoint, with a 30-day major adverse cardiovascular event rate of 15.9%, compared with a performance goal of 34.4% (P < .0001).
Although prespecified, panel members pushed back, saying that the performance goal was unacceptably high, with several members remarking they’d never heard of a trial adding 9% as a “fudge factor” to a 25% historic control rate to get to the 34% performance target.
Keystone health officials noted that REFLECT was not designed to demonstrate a significant difference in the rate of primary safety events, compared with control. Instead, its purpose was to demonstrate that TriGuard 3 did not increase the risk associated with a TAVR procedure.
The TriGuard 3 device was successfully placed and retrieved in 100% of patients, but complete coverage was not uniform, with 72% of 157 as-treated patients having complete three-vessel coverage post TAVR but 15% having no coverage.
Panel members also expressed concern over device interference during TAVR, which was reported in nearly 10% of all TriGuard patients.
The TriGuard 3 group had 11 major vascular complications, 2 directly related to the device, and 3 stage 3 acute kidney injuries, whereas neither complication occurred in the control group.
Throughout the 9-hour hearing, the panel wrestled with what was described as a highly select patient group and small patient numbers that made it difficult to interpret observed differences. The trial involved 157 TriGuard 3 patients (including 41 from the roll-in phase) and 119 control subjects pooled from phase 2 of the trial (n = 57) and from phase 1 using the early-stage TriGuard HDH device (n = 57).
Pieter Stella, MD, PhD, Utrecht (the Netherlands) Medical Center, also presented “real-world” evidence from 75 patients in the Netherlands using the latest iteration of the device available in Europe with updates to the crimper and additional training materials to prevent the device from torquing during delivery. No strokes were reported, one patient had a transient ischemic attack (TIA), and two patients had a dissection, which resolved without sequelae.
Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, University of California, San Francisco, countered that there were only three experienced operators from a single center and that the stroke incidence was physician reported, “not data we can really embrace.”
There was much debate over why enrollment in phase 2 of the RHYTHM trial was temporarily paused in February 2019, briefly restarted, and then prematurely stopped in April 2019.
FDA officials said the study was paused at the recommendation of the data monitoring committee (DMC) because rates of safety events were different between patients and control subjects and operational errors called into question the accuracy of the data being reviewed. Ultimately, both the DMC and FDA recommended study suspension.
During the public hearing, TAVR pioneer Alain Cribier, MD, University of Rouen’s Charles Nicolle Hospital, Mont-Saint-Aignan, France, said the TriGuard 3 is of interest because it can be used with minimal need for manipulation and complete coverage of the cerebral vessels that is achieved by diverting rather than capturing debris. “The rapid and exponential growth of TAVR procedures demands safe TAVR interventions and the use of cerebral protection devices is a step in this direction.”
Others took a dim view. “Given that the Sentinel device has not demonstrated benefit on clinical outcomes, there is significant concern about similar devices, such as the TriGuard 3, providing clinical benefit,” Rita Redberg, MD, Sanket Dhruva, MD, and Robin Ji, University of California, San Francisco, wrote in a letter submitted to the panel.
Commenting further, they added: “With the results from the REFLECT II trial demonstrating no evidence for clinical outcome benefit in TAVR patients, and numerically higher rates for stroke risk, mortality, bleeding risk, and other dangerous adverse complications among those treated, it is concerning and dangerous for patient safety that the TriGUARD 3 cerebral embolic protection device is being considered for FDA 510(k) clearance.”
The FDA panel members reported no financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Food and Drug Administration advisory panel struggled to muster support for marketing clearance of the TriGuard 3 (Keystone Heart) device for use during transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
The Circulatory Systems Devices Panel of the Medical Devices Advisory Committee took no vote when it met Aug. 3, but weighed evidence for a proposed indication for the device “to minimize the risk of cerebral damage by deflecting embolic debris away from the cerebral circulation” during TAVR.
“While this device may deflect some debris, the data would suggest it may also create issues,” said Keith B. Allen, MD, director of surgical research at the Mid America Heart & Lung Surgeons, Kansas City, Mo. “I am really concerned that our desire and the emotion that surrounds preventing stroke are not being supported by the data.”
TriGuard 3 received CE Mark in Europe in March 2020. It was submitted for 510(k) clearance and seeks to prove substantial equivalence to the predicate Sentinel device (Claret Medical), currently the only approved embolic protection device in the United States.
The device is designed to cover all three major aortic vessels (innominate, left carotid, and left subclavian arteries) and is delivered transfemorally through an 8F sheath, whereas the Sentinel is positioned within the branch vessels, doesn’t cover the left subclavian artery, and is introduced through the radial or brachial artery via a 6F sheath.
TriGuard 3 faced an uphill battle, however, after failing to meet the primary composite efficacy endpoint in the REFLECT phase 2 trial (P = .857), with numeric trends showing higher all-cause mortality or any stroke at 30 days (9.8% vs. 6.7%) than pooled control subjects without embolic protection.
Rates for other components of the endpoint also trended higher with the device: National Institutes of Stroke Stroke Scale score worsening 2-5 days after the procedure, cerebral ischemic lesions on MRI 2-5 days after the procedure, and total cerebral ischemic lesion volume.
The Sentinel device was approved in 2017 after it failed to meet its primary efficacy endpoint of new brain lesion volume on MRI, but death and stroke rates favored the device over control, the panel pointed out.
The sponsor provided additional analyses in the per treatment (PT) population, defined as those with complete three-vessel coverage in at least two of three procedural time points. Compared with pooled control subjects, most of the imaging endpoints favored the TriGuard 3 device, but clinical neurologic event rates continued to favor the control group.
“The data used to demonstrate efficacy are all based on the PT subpopulation of the whole population, and those have to be considered promissory data,” said John Hirshfeld, MD, emeritus professor, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “This is the group where everything went well and for us to decide that’s achievable in the general population is speculative.”
Safety data
The REFLECT trial did meet its primary safety endpoint, with a 30-day major adverse cardiovascular event rate of 15.9%, compared with a performance goal of 34.4% (P < .0001).
Although prespecified, panel members pushed back, saying that the performance goal was unacceptably high, with several members remarking they’d never heard of a trial adding 9% as a “fudge factor” to a 25% historic control rate to get to the 34% performance target.
Keystone health officials noted that REFLECT was not designed to demonstrate a significant difference in the rate of primary safety events, compared with control. Instead, its purpose was to demonstrate that TriGuard 3 did not increase the risk associated with a TAVR procedure.
The TriGuard 3 device was successfully placed and retrieved in 100% of patients, but complete coverage was not uniform, with 72% of 157 as-treated patients having complete three-vessel coverage post TAVR but 15% having no coverage.
Panel members also expressed concern over device interference during TAVR, which was reported in nearly 10% of all TriGuard patients.
The TriGuard 3 group had 11 major vascular complications, 2 directly related to the device, and 3 stage 3 acute kidney injuries, whereas neither complication occurred in the control group.
Throughout the 9-hour hearing, the panel wrestled with what was described as a highly select patient group and small patient numbers that made it difficult to interpret observed differences. The trial involved 157 TriGuard 3 patients (including 41 from the roll-in phase) and 119 control subjects pooled from phase 2 of the trial (n = 57) and from phase 1 using the early-stage TriGuard HDH device (n = 57).
Pieter Stella, MD, PhD, Utrecht (the Netherlands) Medical Center, also presented “real-world” evidence from 75 patients in the Netherlands using the latest iteration of the device available in Europe with updates to the crimper and additional training materials to prevent the device from torquing during delivery. No strokes were reported, one patient had a transient ischemic attack (TIA), and two patients had a dissection, which resolved without sequelae.
Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, University of California, San Francisco, countered that there were only three experienced operators from a single center and that the stroke incidence was physician reported, “not data we can really embrace.”
There was much debate over why enrollment in phase 2 of the RHYTHM trial was temporarily paused in February 2019, briefly restarted, and then prematurely stopped in April 2019.
FDA officials said the study was paused at the recommendation of the data monitoring committee (DMC) because rates of safety events were different between patients and control subjects and operational errors called into question the accuracy of the data being reviewed. Ultimately, both the DMC and FDA recommended study suspension.
During the public hearing, TAVR pioneer Alain Cribier, MD, University of Rouen’s Charles Nicolle Hospital, Mont-Saint-Aignan, France, said the TriGuard 3 is of interest because it can be used with minimal need for manipulation and complete coverage of the cerebral vessels that is achieved by diverting rather than capturing debris. “The rapid and exponential growth of TAVR procedures demands safe TAVR interventions and the use of cerebral protection devices is a step in this direction.”
Others took a dim view. “Given that the Sentinel device has not demonstrated benefit on clinical outcomes, there is significant concern about similar devices, such as the TriGuard 3, providing clinical benefit,” Rita Redberg, MD, Sanket Dhruva, MD, and Robin Ji, University of California, San Francisco, wrote in a letter submitted to the panel.
Commenting further, they added: “With the results from the REFLECT II trial demonstrating no evidence for clinical outcome benefit in TAVR patients, and numerically higher rates for stroke risk, mortality, bleeding risk, and other dangerous adverse complications among those treated, it is concerning and dangerous for patient safety that the TriGUARD 3 cerebral embolic protection device is being considered for FDA 510(k) clearance.”
The FDA panel members reported no financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Food and Drug Administration advisory panel struggled to muster support for marketing clearance of the TriGuard 3 (Keystone Heart) device for use during transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
The Circulatory Systems Devices Panel of the Medical Devices Advisory Committee took no vote when it met Aug. 3, but weighed evidence for a proposed indication for the device “to minimize the risk of cerebral damage by deflecting embolic debris away from the cerebral circulation” during TAVR.
“While this device may deflect some debris, the data would suggest it may also create issues,” said Keith B. Allen, MD, director of surgical research at the Mid America Heart & Lung Surgeons, Kansas City, Mo. “I am really concerned that our desire and the emotion that surrounds preventing stroke are not being supported by the data.”
TriGuard 3 received CE Mark in Europe in March 2020. It was submitted for 510(k) clearance and seeks to prove substantial equivalence to the predicate Sentinel device (Claret Medical), currently the only approved embolic protection device in the United States.
The device is designed to cover all three major aortic vessels (innominate, left carotid, and left subclavian arteries) and is delivered transfemorally through an 8F sheath, whereas the Sentinel is positioned within the branch vessels, doesn’t cover the left subclavian artery, and is introduced through the radial or brachial artery via a 6F sheath.
TriGuard 3 faced an uphill battle, however, after failing to meet the primary composite efficacy endpoint in the REFLECT phase 2 trial (P = .857), with numeric trends showing higher all-cause mortality or any stroke at 30 days (9.8% vs. 6.7%) than pooled control subjects without embolic protection.
Rates for other components of the endpoint also trended higher with the device: National Institutes of Stroke Stroke Scale score worsening 2-5 days after the procedure, cerebral ischemic lesions on MRI 2-5 days after the procedure, and total cerebral ischemic lesion volume.
The Sentinel device was approved in 2017 after it failed to meet its primary efficacy endpoint of new brain lesion volume on MRI, but death and stroke rates favored the device over control, the panel pointed out.
The sponsor provided additional analyses in the per treatment (PT) population, defined as those with complete three-vessel coverage in at least two of three procedural time points. Compared with pooled control subjects, most of the imaging endpoints favored the TriGuard 3 device, but clinical neurologic event rates continued to favor the control group.
“The data used to demonstrate efficacy are all based on the PT subpopulation of the whole population, and those have to be considered promissory data,” said John Hirshfeld, MD, emeritus professor, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “This is the group where everything went well and for us to decide that’s achievable in the general population is speculative.”
Safety data
The REFLECT trial did meet its primary safety endpoint, with a 30-day major adverse cardiovascular event rate of 15.9%, compared with a performance goal of 34.4% (P < .0001).
Although prespecified, panel members pushed back, saying that the performance goal was unacceptably high, with several members remarking they’d never heard of a trial adding 9% as a “fudge factor” to a 25% historic control rate to get to the 34% performance target.
Keystone health officials noted that REFLECT was not designed to demonstrate a significant difference in the rate of primary safety events, compared with control. Instead, its purpose was to demonstrate that TriGuard 3 did not increase the risk associated with a TAVR procedure.
The TriGuard 3 device was successfully placed and retrieved in 100% of patients, but complete coverage was not uniform, with 72% of 157 as-treated patients having complete three-vessel coverage post TAVR but 15% having no coverage.
Panel members also expressed concern over device interference during TAVR, which was reported in nearly 10% of all TriGuard patients.
The TriGuard 3 group had 11 major vascular complications, 2 directly related to the device, and 3 stage 3 acute kidney injuries, whereas neither complication occurred in the control group.
Throughout the 9-hour hearing, the panel wrestled with what was described as a highly select patient group and small patient numbers that made it difficult to interpret observed differences. The trial involved 157 TriGuard 3 patients (including 41 from the roll-in phase) and 119 control subjects pooled from phase 2 of the trial (n = 57) and from phase 1 using the early-stage TriGuard HDH device (n = 57).
Pieter Stella, MD, PhD, Utrecht (the Netherlands) Medical Center, also presented “real-world” evidence from 75 patients in the Netherlands using the latest iteration of the device available in Europe with updates to the crimper and additional training materials to prevent the device from torquing during delivery. No strokes were reported, one patient had a transient ischemic attack (TIA), and two patients had a dissection, which resolved without sequelae.
Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, professor of medicine, University of California, San Francisco, countered that there were only three experienced operators from a single center and that the stroke incidence was physician reported, “not data we can really embrace.”
There was much debate over why enrollment in phase 2 of the RHYTHM trial was temporarily paused in February 2019, briefly restarted, and then prematurely stopped in April 2019.
FDA officials said the study was paused at the recommendation of the data monitoring committee (DMC) because rates of safety events were different between patients and control subjects and operational errors called into question the accuracy of the data being reviewed. Ultimately, both the DMC and FDA recommended study suspension.
During the public hearing, TAVR pioneer Alain Cribier, MD, University of Rouen’s Charles Nicolle Hospital, Mont-Saint-Aignan, France, said the TriGuard 3 is of interest because it can be used with minimal need for manipulation and complete coverage of the cerebral vessels that is achieved by diverting rather than capturing debris. “The rapid and exponential growth of TAVR procedures demands safe TAVR interventions and the use of cerebral protection devices is a step in this direction.”
Others took a dim view. “Given that the Sentinel device has not demonstrated benefit on clinical outcomes, there is significant concern about similar devices, such as the TriGuard 3, providing clinical benefit,” Rita Redberg, MD, Sanket Dhruva, MD, and Robin Ji, University of California, San Francisco, wrote in a letter submitted to the panel.
Commenting further, they added: “With the results from the REFLECT II trial demonstrating no evidence for clinical outcome benefit in TAVR patients, and numerically higher rates for stroke risk, mortality, bleeding risk, and other dangerous adverse complications among those treated, it is concerning and dangerous for patient safety that the TriGUARD 3 cerebral embolic protection device is being considered for FDA 510(k) clearance.”
The FDA panel members reported no financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
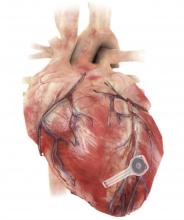
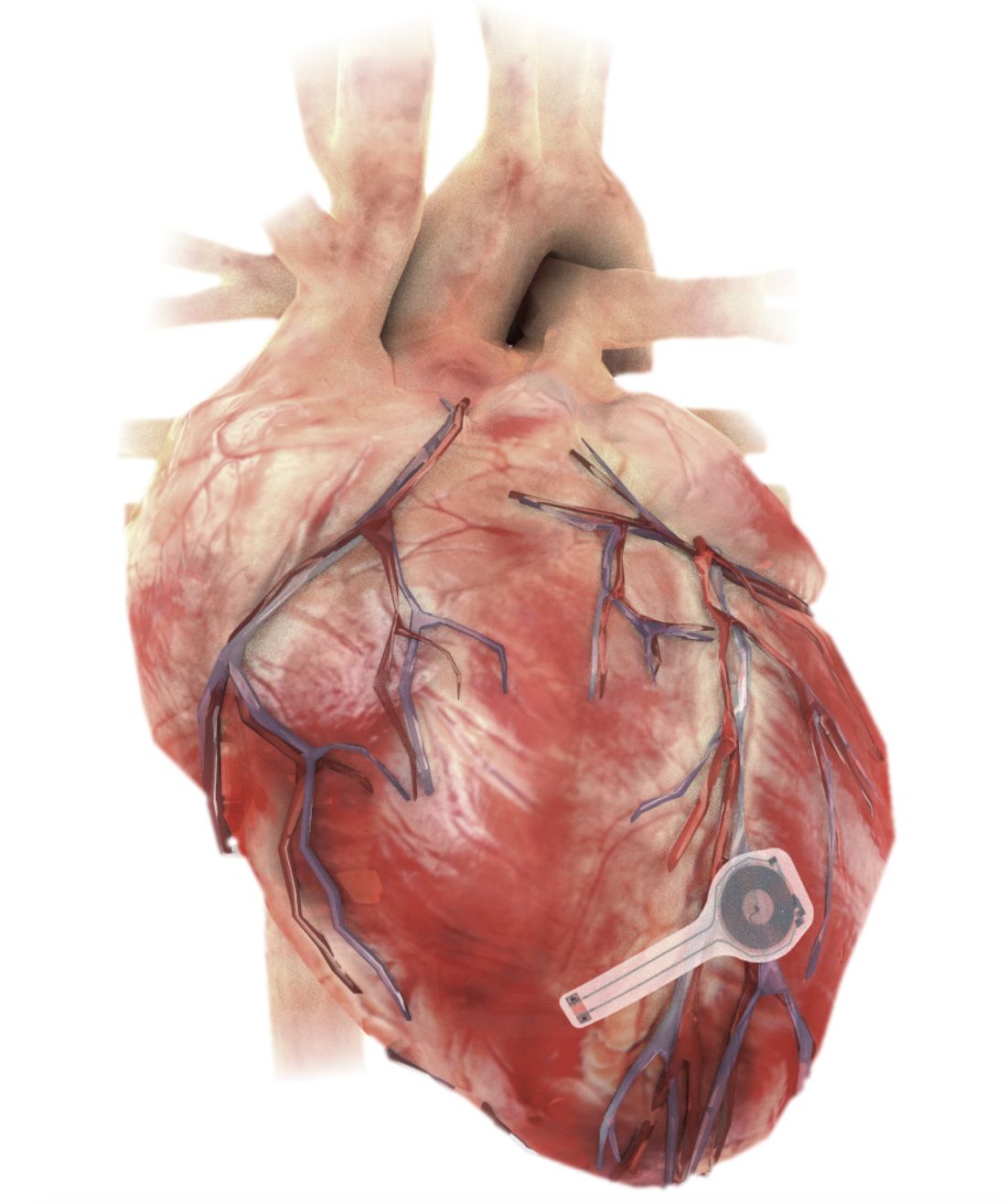
Dissolving pacemaker impressive in early research
A fully implantable, bioresorbable pacemaker has been developed that’s capable of sustaining heart rhythms in animal and human donor hearts before disappearing over 5-7 weeks.
Temporary pacing devices are frequently used after cardiac surgery but rely on bulky external generators and transcutaneous pacing leads that run the risk of becoming infected or dislodged and can damage the heart when removed if they’re enveloped in fibrotic tissue.
The experimental device is thin, powered without leads or batteries, and made of water-soluble, biocompatible materials, thereby bypassing many of the disadvantages of conventional temporary pacing devices, according to John A. Rogers, PhD, who led the device’s development and directs the Querrey Simpson Institute for Bioelectronics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
“The total material load on the body is very minimal,” he said in an interview. “The amount of silicon and magnesium in a multivitamin tablet is about 3,000 times more than the amount of those materials in our electronics. So you can think of them as a very tiny vitamin pill, in a sense, but configured with electronic functionality.”
Dr. Rogers and his team have a reputation for innovation in bioelectronic medicine, having recently constructed transient wireless devices to accelerate neuroregeneration associated with damaged peripheral nerves, to monitor critically ill neonates, and to detect early signs and symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Shortly after Dr. Rogers joined Northwestern, Rishi Arora, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at Northwestern, reached out to discuss how they could leverage wireless electronics for patients needing temporary pacing.
“It was a natural marriage,” Dr. Arora said in an interview. “Part of the reason to go into the heart was because the cardiology group here at Northwestern, especially on the electrophysiology side, has been very involved in translational research, and John also had a very strong collaboration before he came here with Igor Efimov, [PhD, of George Washington University, Washington], a giant in the field in terms of heart rhythm research.”
Dr. Arora noted that the incidence of temporary pacing after cardiac surgery is at least 10% but can reach 20%. Current devices work well in most patients, but temporary pacing with epicardial wires can cause complications and, typically, work well only for a few days after cardiac surgery. Clinically, though, several patients need postoperative pacing support for 1-2 weeks.
“So if something like this were available where you could tack it onto the surface and forget it for a week or 10 days or 2 weeks, you’d be doing those 20% of patients a huge service,” he said.
Bioresorbable scaffold déjà vu?
The philosophy of “leave nothing behind” is nothing new in cardiology, with bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) gaining initial support as a potential solution to neoatherosclerosis and late-stent thrombosis in permanent metal stents. Failure to show advantages, and safety concerns such as in-scaffold thrombosis, however, led Abbott to stop global sales of the first approved BVS and Boston Scientific to halt its BVS program in 2017.
The wireless pacemaker, however, is an electrical device, not a mechanical one, observed Dr. Rogers. “The fact that it’s not in the bloodstream greatly lowers risks and, as I mentioned before, everything is super thin, low-mass quantities of materials. So, I guess there’s a relationship there, but it’s different in a couple of very important ways.”
As Dr. Rogers, Dr. Arora, Dr. Efimov, and colleagues recently reported in Nature Biotechnology, the electronic part of the pacemaker contains three layers: A loop antenna with a bilayer tungsten-coated magnesium inductive coil, a radiofrequency PIN diode based on a monocrystalline silicon nanomembrane, and a poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) dielectric interlayer.
The electronic components rest between two encapsulation layers of PLGA to isolate the active materials from the surrounding biofluids during implantation, and connect to a pair of flexible extension electrodes that deliver the electrical stimuli to a contact pad sutured onto the heart. The entire system is about 16 mm in width and 15 mm in length, and weighs in at about 0.3 g.
The pacemaker receives power and control commands through a wireless inductive power transfer – the same technology used in implanted medical devices, smartphones, and radio-frequency identification tags – between the receiver coil in the device and a wand-shaped, external transmission coil placed on top of or within a few inches of the heart.
“Right now we’re almost at 15 inches, which I think is a very respectable distance for this particular piece of hardware, and clinically very doable,” observed Dr. Arora.
Competing considerations
Testing thus far shows effective ventricular capture across a range of frequencies in mouse and rabbit hearts and successful pacing and activation of human cardiac tissue.
In vivo tests in dogs also suggest that the system can “achieve the power necessary for operation of bioresorbable pacemakers in adult human patients,” the authors say.
Electrodes placed on the dogs’ legs showed a change in ECG signals from a narrow QRS complex (consistent with a normal rate sinus rhythm of 350-400 bpm) to a widened QRS complex with a shortened R-R interval (consistent with a paced rhythm of 400-450 bpm) – indicating successful ventricular capture.
The device successfully paced the dogs through postoperative day 4 but couldn’t provide enough energy to capture the ventricular myocardium on day 5 and failed to pace the heart on day 6, even when transmitting voltages were increased from 1 Vpp to more than 10 Vpp.
Dr. Rogers pointed out that a transient device of theirs that uses very thin films of silica provides stable intracranial pressure monitoring for traumatic brain injury recovery for 3 weeks before dissolving. The problem with the polymers used as encapsulating layers in the pacemaker is that even if they haven’t completely dissolved, there’s a finite rate of water permeation through the film.
“It turns out that’s what’s become the limiting factor, rather than the chemistry of bioresorption,” he said. “So, what we’re seeing with these devices beginning to degrade electrically in terms of performance around 5-6 days is due to that water permeation.”
Although it is not part of the current study, there’s no reason thin silica layers couldn’t be incorporated into the pacemaker to make it less water permeable, Dr. Rogers said. Still, this will have to be weighed against the competing consideration of stable operating life.
The researchers specifically chose materials that would naturally bioresorb via hydrolysis and metabolic action in the body. PLGA degrades into glycolic and lactic acid, the tungsten-coated magnesium inductive coil into Wox and Mg(OH)2, and the silicon nanomembrane radiofrequency PIN diode into Si(OH)4.
CT imaging in rat models shows the device is enveloped in fibrotic tissue and completely decouples from the heart at 4 weeks, while images of explanted devices suggest the pacemaker largely dissolves within 3 weeks and the remaining residues disappear after 12 weeks.
The researchers have started an investigational device exemption process to allow the device to be used in clinical trials, and they plan to dig deeper into the potential for fragments to form at various stages of resorption, which some imaging suggests may occur.
“Because these devices are made out of pure materials and they’re in a heterogeneous environment, both mechanically and biomechanically, the devices don’t resorb in a perfectly uniform way and, as a result, at the tail end of the process you can end up with small fragments that eventually bioresorb, but before they’re gone, they are potentially mobile within the body cavity,” Dr. Rogers said.
“We feel that because the devices aren’t in the bloodstream, the risk associated with those fragments is probably manageable but at the same time, these are the sorts of details that must be thoroughly addressed before trials in humans,” he said, adding that one solution, if needed, would be to encapsulate the entire device in a thin bioresorbable hydrogel as a containment vehicle.
Dr. Arora said they hope the pacemaker “will make patients’ lives a lot easier in the postoperative setting but, even there, I think one must remember current pacing technology in this setting is actually very good. So there’s a word of caution not to get ahead of ourselves.”
Looking forward, the excitement of this approach is not only in the immediate postop setting but in the transvenous setting, he said. “If we can get to the point where we can actually do this transvenously, that opens up a huge window of opportunity because there we’re talking about post-TAVR [transcatheter aortic valve replacement], post–myocardial infarction, etc.”
Currently, temporary transvenous pacing can be quite unreliable because of a high risk of dislodgement and infection – much higher than for surgical pacing wires, he noted.
“In terms of translatability to larger numbers of patients, the value would be huge. But again, a lot needs to be done before we can get there. But if it can get to that point, then I think you have a real therapy that could potentially be transformative,” Dr. Arora said.
Dr. Rogers reported support from the Leducq Foundation projects RHYTHM and ROI-HL121270. Dr. Arora has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A fully implantable, bioresorbable pacemaker has been developed that’s capable of sustaining heart rhythms in animal and human donor hearts before disappearing over 5-7 weeks.
Temporary pacing devices are frequently used after cardiac surgery but rely on bulky external generators and transcutaneous pacing leads that run the risk of becoming infected or dislodged and can damage the heart when removed if they’re enveloped in fibrotic tissue.
The experimental device is thin, powered without leads or batteries, and made of water-soluble, biocompatible materials, thereby bypassing many of the disadvantages of conventional temporary pacing devices, according to John A. Rogers, PhD, who led the device’s development and directs the Querrey Simpson Institute for Bioelectronics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
“The total material load on the body is very minimal,” he said in an interview. “The amount of silicon and magnesium in a multivitamin tablet is about 3,000 times more than the amount of those materials in our electronics. So you can think of them as a very tiny vitamin pill, in a sense, but configured with electronic functionality.”
Dr. Rogers and his team have a reputation for innovation in bioelectronic medicine, having recently constructed transient wireless devices to accelerate neuroregeneration associated with damaged peripheral nerves, to monitor critically ill neonates, and to detect early signs and symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Shortly after Dr. Rogers joined Northwestern, Rishi Arora, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at Northwestern, reached out to discuss how they could leverage wireless electronics for patients needing temporary pacing.
“It was a natural marriage,” Dr. Arora said in an interview. “Part of the reason to go into the heart was because the cardiology group here at Northwestern, especially on the electrophysiology side, has been very involved in translational research, and John also had a very strong collaboration before he came here with Igor Efimov, [PhD, of George Washington University, Washington], a giant in the field in terms of heart rhythm research.”
Dr. Arora noted that the incidence of temporary pacing after cardiac surgery is at least 10% but can reach 20%. Current devices work well in most patients, but temporary pacing with epicardial wires can cause complications and, typically, work well only for a few days after cardiac surgery. Clinically, though, several patients need postoperative pacing support for 1-2 weeks.
“So if something like this were available where you could tack it onto the surface and forget it for a week or 10 days or 2 weeks, you’d be doing those 20% of patients a huge service,” he said.
Bioresorbable scaffold déjà vu?
The philosophy of “leave nothing behind” is nothing new in cardiology, with bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) gaining initial support as a potential solution to neoatherosclerosis and late-stent thrombosis in permanent metal stents. Failure to show advantages, and safety concerns such as in-scaffold thrombosis, however, led Abbott to stop global sales of the first approved BVS and Boston Scientific to halt its BVS program in 2017.
The wireless pacemaker, however, is an electrical device, not a mechanical one, observed Dr. Rogers. “The fact that it’s not in the bloodstream greatly lowers risks and, as I mentioned before, everything is super thin, low-mass quantities of materials. So, I guess there’s a relationship there, but it’s different in a couple of very important ways.”
As Dr. Rogers, Dr. Arora, Dr. Efimov, and colleagues recently reported in Nature Biotechnology, the electronic part of the pacemaker contains three layers: A loop antenna with a bilayer tungsten-coated magnesium inductive coil, a radiofrequency PIN diode based on a monocrystalline silicon nanomembrane, and a poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) dielectric interlayer.
The electronic components rest between two encapsulation layers of PLGA to isolate the active materials from the surrounding biofluids during implantation, and connect to a pair of flexible extension electrodes that deliver the electrical stimuli to a contact pad sutured onto the heart. The entire system is about 16 mm in width and 15 mm in length, and weighs in at about 0.3 g.
The pacemaker receives power and control commands through a wireless inductive power transfer – the same technology used in implanted medical devices, smartphones, and radio-frequency identification tags – between the receiver coil in the device and a wand-shaped, external transmission coil placed on top of or within a few inches of the heart.
“Right now we’re almost at 15 inches, which I think is a very respectable distance for this particular piece of hardware, and clinically very doable,” observed Dr. Arora.
Competing considerations
Testing thus far shows effective ventricular capture across a range of frequencies in mouse and rabbit hearts and successful pacing and activation of human cardiac tissue.
In vivo tests in dogs also suggest that the system can “achieve the power necessary for operation of bioresorbable pacemakers in adult human patients,” the authors say.
Electrodes placed on the dogs’ legs showed a change in ECG signals from a narrow QRS complex (consistent with a normal rate sinus rhythm of 350-400 bpm) to a widened QRS complex with a shortened R-R interval (consistent with a paced rhythm of 400-450 bpm) – indicating successful ventricular capture.
The device successfully paced the dogs through postoperative day 4 but couldn’t provide enough energy to capture the ventricular myocardium on day 5 and failed to pace the heart on day 6, even when transmitting voltages were increased from 1 Vpp to more than 10 Vpp.
Dr. Rogers pointed out that a transient device of theirs that uses very thin films of silica provides stable intracranial pressure monitoring for traumatic brain injury recovery for 3 weeks before dissolving. The problem with the polymers used as encapsulating layers in the pacemaker is that even if they haven’t completely dissolved, there’s a finite rate of water permeation through the film.
“It turns out that’s what’s become the limiting factor, rather than the chemistry of bioresorption,” he said. “So, what we’re seeing with these devices beginning to degrade electrically in terms of performance around 5-6 days is due to that water permeation.”
Although it is not part of the current study, there’s no reason thin silica layers couldn’t be incorporated into the pacemaker to make it less water permeable, Dr. Rogers said. Still, this will have to be weighed against the competing consideration of stable operating life.
The researchers specifically chose materials that would naturally bioresorb via hydrolysis and metabolic action in the body. PLGA degrades into glycolic and lactic acid, the tungsten-coated magnesium inductive coil into Wox and Mg(OH)2, and the silicon nanomembrane radiofrequency PIN diode into Si(OH)4.
CT imaging in rat models shows the device is enveloped in fibrotic tissue and completely decouples from the heart at 4 weeks, while images of explanted devices suggest the pacemaker largely dissolves within 3 weeks and the remaining residues disappear after 12 weeks.
The researchers have started an investigational device exemption process to allow the device to be used in clinical trials, and they plan to dig deeper into the potential for fragments to form at various stages of resorption, which some imaging suggests may occur.
“Because these devices are made out of pure materials and they’re in a heterogeneous environment, both mechanically and biomechanically, the devices don’t resorb in a perfectly uniform way and, as a result, at the tail end of the process you can end up with small fragments that eventually bioresorb, but before they’re gone, they are potentially mobile within the body cavity,” Dr. Rogers said.
“We feel that because the devices aren’t in the bloodstream, the risk associated with those fragments is probably manageable but at the same time, these are the sorts of details that must be thoroughly addressed before trials in humans,” he said, adding that one solution, if needed, would be to encapsulate the entire device in a thin bioresorbable hydrogel as a containment vehicle.
Dr. Arora said they hope the pacemaker “will make patients’ lives a lot easier in the postoperative setting but, even there, I think one must remember current pacing technology in this setting is actually very good. So there’s a word of caution not to get ahead of ourselves.”
Looking forward, the excitement of this approach is not only in the immediate postop setting but in the transvenous setting, he said. “If we can get to the point where we can actually do this transvenously, that opens up a huge window of opportunity because there we’re talking about post-TAVR [transcatheter aortic valve replacement], post–myocardial infarction, etc.”
Currently, temporary transvenous pacing can be quite unreliable because of a high risk of dislodgement and infection – much higher than for surgical pacing wires, he noted.
“In terms of translatability to larger numbers of patients, the value would be huge. But again, a lot needs to be done before we can get there. But if it can get to that point, then I think you have a real therapy that could potentially be transformative,” Dr. Arora said.
Dr. Rogers reported support from the Leducq Foundation projects RHYTHM and ROI-HL121270. Dr. Arora has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A fully implantable, bioresorbable pacemaker has been developed that’s capable of sustaining heart rhythms in animal and human donor hearts before disappearing over 5-7 weeks.
Temporary pacing devices are frequently used after cardiac surgery but rely on bulky external generators and transcutaneous pacing leads that run the risk of becoming infected or dislodged and can damage the heart when removed if they’re enveloped in fibrotic tissue.
The experimental device is thin, powered without leads or batteries, and made of water-soluble, biocompatible materials, thereby bypassing many of the disadvantages of conventional temporary pacing devices, according to John A. Rogers, PhD, who led the device’s development and directs the Querrey Simpson Institute for Bioelectronics at Northwestern University in Chicago.
“The total material load on the body is very minimal,” he said in an interview. “The amount of silicon and magnesium in a multivitamin tablet is about 3,000 times more than the amount of those materials in our electronics. So you can think of them as a very tiny vitamin pill, in a sense, but configured with electronic functionality.”
Dr. Rogers and his team have a reputation for innovation in bioelectronic medicine, having recently constructed transient wireless devices to accelerate neuroregeneration associated with damaged peripheral nerves, to monitor critically ill neonates, and to detect early signs and symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Shortly after Dr. Rogers joined Northwestern, Rishi Arora, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at Northwestern, reached out to discuss how they could leverage wireless electronics for patients needing temporary pacing.
“It was a natural marriage,” Dr. Arora said in an interview. “Part of the reason to go into the heart was because the cardiology group here at Northwestern, especially on the electrophysiology side, has been very involved in translational research, and John also had a very strong collaboration before he came here with Igor Efimov, [PhD, of George Washington University, Washington], a giant in the field in terms of heart rhythm research.”
Dr. Arora noted that the incidence of temporary pacing after cardiac surgery is at least 10% but can reach 20%. Current devices work well in most patients, but temporary pacing with epicardial wires can cause complications and, typically, work well only for a few days after cardiac surgery. Clinically, though, several patients need postoperative pacing support for 1-2 weeks.
“So if something like this were available where you could tack it onto the surface and forget it for a week or 10 days or 2 weeks, you’d be doing those 20% of patients a huge service,” he said.
Bioresorbable scaffold déjà vu?
The philosophy of “leave nothing behind” is nothing new in cardiology, with bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) gaining initial support as a potential solution to neoatherosclerosis and late-stent thrombosis in permanent metal stents. Failure to show advantages, and safety concerns such as in-scaffold thrombosis, however, led Abbott to stop global sales of the first approved BVS and Boston Scientific to halt its BVS program in 2017.
The wireless pacemaker, however, is an electrical device, not a mechanical one, observed Dr. Rogers. “The fact that it’s not in the bloodstream greatly lowers risks and, as I mentioned before, everything is super thin, low-mass quantities of materials. So, I guess there’s a relationship there, but it’s different in a couple of very important ways.”
As Dr. Rogers, Dr. Arora, Dr. Efimov, and colleagues recently reported in Nature Biotechnology, the electronic part of the pacemaker contains three layers: A loop antenna with a bilayer tungsten-coated magnesium inductive coil, a radiofrequency PIN diode based on a monocrystalline silicon nanomembrane, and a poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) dielectric interlayer.
The electronic components rest between two encapsulation layers of PLGA to isolate the active materials from the surrounding biofluids during implantation, and connect to a pair of flexible extension electrodes that deliver the electrical stimuli to a contact pad sutured onto the heart. The entire system is about 16 mm in width and 15 mm in length, and weighs in at about 0.3 g.
The pacemaker receives power and control commands through a wireless inductive power transfer – the same technology used in implanted medical devices, smartphones, and radio-frequency identification tags – between the receiver coil in the device and a wand-shaped, external transmission coil placed on top of or within a few inches of the heart.
“Right now we’re almost at 15 inches, which I think is a very respectable distance for this particular piece of hardware, and clinically very doable,” observed Dr. Arora.
Competing considerations
Testing thus far shows effective ventricular capture across a range of frequencies in mouse and rabbit hearts and successful pacing and activation of human cardiac tissue.
In vivo tests in dogs also suggest that the system can “achieve the power necessary for operation of bioresorbable pacemakers in adult human patients,” the authors say.
Electrodes placed on the dogs’ legs showed a change in ECG signals from a narrow QRS complex (consistent with a normal rate sinus rhythm of 350-400 bpm) to a widened QRS complex with a shortened R-R interval (consistent with a paced rhythm of 400-450 bpm) – indicating successful ventricular capture.
The device successfully paced the dogs through postoperative day 4 but couldn’t provide enough energy to capture the ventricular myocardium on day 5 and failed to pace the heart on day 6, even when transmitting voltages were increased from 1 Vpp to more than 10 Vpp.
Dr. Rogers pointed out that a transient device of theirs that uses very thin films of silica provides stable intracranial pressure monitoring for traumatic brain injury recovery for 3 weeks before dissolving. The problem with the polymers used as encapsulating layers in the pacemaker is that even if they haven’t completely dissolved, there’s a finite rate of water permeation through the film.
“It turns out that’s what’s become the limiting factor, rather than the chemistry of bioresorption,” he said. “So, what we’re seeing with these devices beginning to degrade electrically in terms of performance around 5-6 days is due to that water permeation.”
Although it is not part of the current study, there’s no reason thin silica layers couldn’t be incorporated into the pacemaker to make it less water permeable, Dr. Rogers said. Still, this will have to be weighed against the competing consideration of stable operating life.
The researchers specifically chose materials that would naturally bioresorb via hydrolysis and metabolic action in the body. PLGA degrades into glycolic and lactic acid, the tungsten-coated magnesium inductive coil into Wox and Mg(OH)2, and the silicon nanomembrane radiofrequency PIN diode into Si(OH)4.
CT imaging in rat models shows the device is enveloped in fibrotic tissue and completely decouples from the heart at 4 weeks, while images of explanted devices suggest the pacemaker largely dissolves within 3 weeks and the remaining residues disappear after 12 weeks.
The researchers have started an investigational device exemption process to allow the device to be used in clinical trials, and they plan to dig deeper into the potential for fragments to form at various stages of resorption, which some imaging suggests may occur.
“Because these devices are made out of pure materials and they’re in a heterogeneous environment, both mechanically and biomechanically, the devices don’t resorb in a perfectly uniform way and, as a result, at the tail end of the process you can end up with small fragments that eventually bioresorb, but before they’re gone, they are potentially mobile within the body cavity,” Dr. Rogers said.
“We feel that because the devices aren’t in the bloodstream, the risk associated with those fragments is probably manageable but at the same time, these are the sorts of details that must be thoroughly addressed before trials in humans,” he said, adding that one solution, if needed, would be to encapsulate the entire device in a thin bioresorbable hydrogel as a containment vehicle.
Dr. Arora said they hope the pacemaker “will make patients’ lives a lot easier in the postoperative setting but, even there, I think one must remember current pacing technology in this setting is actually very good. So there’s a word of caution not to get ahead of ourselves.”
Looking forward, the excitement of this approach is not only in the immediate postop setting but in the transvenous setting, he said. “If we can get to the point where we can actually do this transvenously, that opens up a huge window of opportunity because there we’re talking about post-TAVR [transcatheter aortic valve replacement], post–myocardial infarction, etc.”
Currently, temporary transvenous pacing can be quite unreliable because of a high risk of dislodgement and infection – much higher than for surgical pacing wires, he noted.
“In terms of translatability to larger numbers of patients, the value would be huge. But again, a lot needs to be done before we can get there. But if it can get to that point, then I think you have a real therapy that could potentially be transformative,” Dr. Arora said.
Dr. Rogers reported support from the Leducq Foundation projects RHYTHM and ROI-HL121270. Dr. Arora has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five risk factors may predict thrombus on LAA occlusion implants
, itself an important risk factor for cerebrovascular events, in patients with implants for left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), new research suggests.
The identified independent predictors of DRT in the largest dedicated multicenter LAAO-DRT registry to date were presence of a hypercoagulability disorder, pericardial effusion, renal insufficiency, an implantation depth greater than 10 mm from the pulmonary ridge, and presence of nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFib).
“Unfortunately, most of them are not modifiable, like hypercoaguable disorders or nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation. But we can avoid deep implants because that’s been associated with creating a little bit of a crater or valley where the clot can form,” senior author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, said in an interview.
But most important, and “really why we wanted to do this,” he said, is that “we want to give the patient a realistic prediction of adverse events for this procedure.”
LAAO has taken off in recent years for preventing thrombus formation and stroke in patients with AFib. Predicting DRT is a priority for the LAAO field, the authors note, especially given its expansion to younger, lower-risk patients and the increasing procedural volumes.
“This is a problem, DRT, that’s been discussed a lot because this is a preventative procedure,” observed Dr. Alkhouli, professor of medicine at Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
“The actual stroke risk every year – even if you don’t take any blood thinner and you have a CHADsVASc score of 9, the highest – is 11%. So if the chance of having thrombus is close, then that’s not a good tradeoff.”
Previous studies have also identified implantation depth and nonparoxysmal AFib as risk factors for DRT. But most of them have been small, he noted, with one of the largest reporting 65 DRTs in four prospective trials.
To cast a wider net, the investigators, led by Trevor Simard, MD, also from the Mayo Clinic, invited more than 50 international sites to contribute data to the registry. Of these, 37 centers reported on 237 DRTs and 474 device-matched control subjects from the same site.
Three-fourths of patients received a first-generation Watchman or a FLEX device (Boston Scientific).
Medical regimens were similar between the DRT and control cohorts at discharge after LAA closure. Most patients were managed with single (36.3%) or dual antiplatelet therapy (26.2%) at the time of DRT diagnosis.
As reported July 19 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the timing of DRT development varied widely, with 24.9% appearing in the first 45 days, 38.8% between days 45 and 180, 16.0% between days 180 to 365, and 20.3% beyond 1 year. At last known follow-up, one-quarter of patients had DRT.
The odds ratios for DRT associated with the five identified risk factors were:
- 17.50 (95% confidence interval, 3.39-90.45) for hypercoagulability disorder
- 13.45 (95% CI, 1.46-123.52) for pericardial effusion
- 4.02 (95% CI, 1.22-13.25) for renal insufficiency
- 2.41 (95% CI, 1.57-3.69) for implantation depth >10 mm
- 1.90 (95% CI, 1.22-2.97) for nonparoxysmal AFib
The risk for a composite of death, ischemic stroke, and systemic embolization was twofold higher in the DRT cohort than in the control cohort (29.5% vs. 14.4%; hazard ratio, 2.37; 95% CI, 1.58-3.56) and driven by a higher rate of ischemic stroke (16.9% vs. 3.6%; HR, 3.49; 95% CI, 1.35-9.00).
The incidence of bleeding and intracerebral hemorrhage, however, was similar in the DRT and control cohorts.
One of the surprises of the study was that medications prescribed in the short term after LAA closure were not associated with DRT, Dr. Alkhouli said. A previous meta-analysis of 66 studies by the investigators also found that antithrombotic regimen did not explain the heterogeneity of DRT formation.
“I think we’ll have to take that with a grain of salt, because there’s so many variations in the practice, and this is observational data. But that, in my mind, brings up a mechanistic issue,” he said.
It’s often recommended “that we should put patients on blood thinners for 3 months or 6 weeks, or whatever it is, to decrease the chance of thrombus, assuming the patients will have a normal endothelialization of the device,” Dr. Alkhouli said.
“Well, we know that’s not the reality,” he continued. “We know many patients don’t endothelialize, and, even if some patients do, there may be some endothelial damage. So I think the whole mechanism of prescribing a little bit of a blood thinner to avoid that risk may be missing the point. It’s a bit more complex than that, evidenced also by the fact that three-fourths of all the DRTs happened after 45 days, when patients are typically not taking a blood thinner.”
Based on the five independent risk factors, the investigators created a clinical DRT risk score that assigned 1 point for renal insufficiency, implantation depth greater than 10 mm from the pulmonary ridge, and nonparoxysmal AFib; and 4 points for iatrogenic pericardial effusion and for hypercoagulability disorder. Low risk was categorized as 1 point and high risk as 2 or more points.
The presence of one major risk factor or two minor risk factors, for example, led to a 2.1-fold increased risk for DRT, compared with those with no DRT risk factors.
The risk score will require validation in a prospective cohort but is “a step forward in addressing DRT” and triaging patients, Dr. Alkhouli said. The findings highlight the need to avoid deep device implantation and the importance of shared decision-making with patients, especially with those at high risk.
“And third, which is most important, I think, in my mind, is that it tells us not to put a blind eye to this topic and just say with improved devices it will go away,” he said. “That’s a bit unrealistic.”
In an accompanying editorial, Oussama Wazni, MD, Walid Saliba, MD, and Ayman A. Hussein, MD, all from the Cleveland Clinic, write that “the study sheds light on this yet unresolved issue, and the observations may help with risk stratification and optimization of procedural techniques.”
Whereas many of the nonmodifiable risk factors are helpful in shared decision-making decisions, they continue, “knowledge of these risk factors may not preclude implantation in patients who are otherwise at risk of both stroke off anticoagulation and bleeding on anticoagulation.”
Dr. Wazni and colleagues acknowledge that the small number of events in the study limits statistical power for definitive conclusions and say that further studies are needed to clarify the natural history of DRTs and their management, resolution, and impact on cardiovascular events.
Practitioners should also continue to cautiously assess for LAAO clinical indications for implant, according to the editorialists, who point out that the regulatory approval language in the United States was “flexible and nonspecific.”
“As the field grows wider, enhancing LAAO safety with optimal design, implantation, and periprocedural management is critically important, yet the main focus should remain on optimal patient selection for the purpose of achieving safe and successful outcomes,” the editorialists conclude.
Dr. Alkhouli has served as a consultant for Boston Scientific. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Wazni and Dr. Hussein have received research grant support from Boston Scientific. Dr. Wazni and Dr. Saliba have been consultants for Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, itself an important risk factor for cerebrovascular events, in patients with implants for left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), new research suggests.
The identified independent predictors of DRT in the largest dedicated multicenter LAAO-DRT registry to date were presence of a hypercoagulability disorder, pericardial effusion, renal insufficiency, an implantation depth greater than 10 mm from the pulmonary ridge, and presence of nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFib).
“Unfortunately, most of them are not modifiable, like hypercoaguable disorders or nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation. But we can avoid deep implants because that’s been associated with creating a little bit of a crater or valley where the clot can form,” senior author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, said in an interview.
But most important, and “really why we wanted to do this,” he said, is that “we want to give the patient a realistic prediction of adverse events for this procedure.”
LAAO has taken off in recent years for preventing thrombus formation and stroke in patients with AFib. Predicting DRT is a priority for the LAAO field, the authors note, especially given its expansion to younger, lower-risk patients and the increasing procedural volumes.
“This is a problem, DRT, that’s been discussed a lot because this is a preventative procedure,” observed Dr. Alkhouli, professor of medicine at Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
“The actual stroke risk every year – even if you don’t take any blood thinner and you have a CHADsVASc score of 9, the highest – is 11%. So if the chance of having thrombus is close, then that’s not a good tradeoff.”
Previous studies have also identified implantation depth and nonparoxysmal AFib as risk factors for DRT. But most of them have been small, he noted, with one of the largest reporting 65 DRTs in four prospective trials.
To cast a wider net, the investigators, led by Trevor Simard, MD, also from the Mayo Clinic, invited more than 50 international sites to contribute data to the registry. Of these, 37 centers reported on 237 DRTs and 474 device-matched control subjects from the same site.
Three-fourths of patients received a first-generation Watchman or a FLEX device (Boston Scientific).
Medical regimens were similar between the DRT and control cohorts at discharge after LAA closure. Most patients were managed with single (36.3%) or dual antiplatelet therapy (26.2%) at the time of DRT diagnosis.
As reported July 19 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the timing of DRT development varied widely, with 24.9% appearing in the first 45 days, 38.8% between days 45 and 180, 16.0% between days 180 to 365, and 20.3% beyond 1 year. At last known follow-up, one-quarter of patients had DRT.
The odds ratios for DRT associated with the five identified risk factors were:
- 17.50 (95% confidence interval, 3.39-90.45) for hypercoagulability disorder
- 13.45 (95% CI, 1.46-123.52) for pericardial effusion
- 4.02 (95% CI, 1.22-13.25) for renal insufficiency
- 2.41 (95% CI, 1.57-3.69) for implantation depth >10 mm
- 1.90 (95% CI, 1.22-2.97) for nonparoxysmal AFib
The risk for a composite of death, ischemic stroke, and systemic embolization was twofold higher in the DRT cohort than in the control cohort (29.5% vs. 14.4%; hazard ratio, 2.37; 95% CI, 1.58-3.56) and driven by a higher rate of ischemic stroke (16.9% vs. 3.6%; HR, 3.49; 95% CI, 1.35-9.00).
The incidence of bleeding and intracerebral hemorrhage, however, was similar in the DRT and control cohorts.
One of the surprises of the study was that medications prescribed in the short term after LAA closure were not associated with DRT, Dr. Alkhouli said. A previous meta-analysis of 66 studies by the investigators also found that antithrombotic regimen did not explain the heterogeneity of DRT formation.
“I think we’ll have to take that with a grain of salt, because there’s so many variations in the practice, and this is observational data. But that, in my mind, brings up a mechanistic issue,” he said.
It’s often recommended “that we should put patients on blood thinners for 3 months or 6 weeks, or whatever it is, to decrease the chance of thrombus, assuming the patients will have a normal endothelialization of the device,” Dr. Alkhouli said.
“Well, we know that’s not the reality,” he continued. “We know many patients don’t endothelialize, and, even if some patients do, there may be some endothelial damage. So I think the whole mechanism of prescribing a little bit of a blood thinner to avoid that risk may be missing the point. It’s a bit more complex than that, evidenced also by the fact that three-fourths of all the DRTs happened after 45 days, when patients are typically not taking a blood thinner.”
Based on the five independent risk factors, the investigators created a clinical DRT risk score that assigned 1 point for renal insufficiency, implantation depth greater than 10 mm from the pulmonary ridge, and nonparoxysmal AFib; and 4 points for iatrogenic pericardial effusion and for hypercoagulability disorder. Low risk was categorized as 1 point and high risk as 2 or more points.
The presence of one major risk factor or two minor risk factors, for example, led to a 2.1-fold increased risk for DRT, compared with those with no DRT risk factors.
The risk score will require validation in a prospective cohort but is “a step forward in addressing DRT” and triaging patients, Dr. Alkhouli said. The findings highlight the need to avoid deep device implantation and the importance of shared decision-making with patients, especially with those at high risk.
“And third, which is most important, I think, in my mind, is that it tells us not to put a blind eye to this topic and just say with improved devices it will go away,” he said. “That’s a bit unrealistic.”
In an accompanying editorial, Oussama Wazni, MD, Walid Saliba, MD, and Ayman A. Hussein, MD, all from the Cleveland Clinic, write that “the study sheds light on this yet unresolved issue, and the observations may help with risk stratification and optimization of procedural techniques.”
Whereas many of the nonmodifiable risk factors are helpful in shared decision-making decisions, they continue, “knowledge of these risk factors may not preclude implantation in patients who are otherwise at risk of both stroke off anticoagulation and bleeding on anticoagulation.”
Dr. Wazni and colleagues acknowledge that the small number of events in the study limits statistical power for definitive conclusions and say that further studies are needed to clarify the natural history of DRTs and their management, resolution, and impact on cardiovascular events.
Practitioners should also continue to cautiously assess for LAAO clinical indications for implant, according to the editorialists, who point out that the regulatory approval language in the United States was “flexible and nonspecific.”
“As the field grows wider, enhancing LAAO safety with optimal design, implantation, and periprocedural management is critically important, yet the main focus should remain on optimal patient selection for the purpose of achieving safe and successful outcomes,” the editorialists conclude.
Dr. Alkhouli has served as a consultant for Boston Scientific. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Wazni and Dr. Hussein have received research grant support from Boston Scientific. Dr. Wazni and Dr. Saliba have been consultants for Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, itself an important risk factor for cerebrovascular events, in patients with implants for left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), new research suggests.
The identified independent predictors of DRT in the largest dedicated multicenter LAAO-DRT registry to date were presence of a hypercoagulability disorder, pericardial effusion, renal insufficiency, an implantation depth greater than 10 mm from the pulmonary ridge, and presence of nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFib).
“Unfortunately, most of them are not modifiable, like hypercoaguable disorders or nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation. But we can avoid deep implants because that’s been associated with creating a little bit of a crater or valley where the clot can form,” senior author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, said in an interview.
But most important, and “really why we wanted to do this,” he said, is that “we want to give the patient a realistic prediction of adverse events for this procedure.”
LAAO has taken off in recent years for preventing thrombus formation and stroke in patients with AFib. Predicting DRT is a priority for the LAAO field, the authors note, especially given its expansion to younger, lower-risk patients and the increasing procedural volumes.
“This is a problem, DRT, that’s been discussed a lot because this is a preventative procedure,” observed Dr. Alkhouli, professor of medicine at Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn.
“The actual stroke risk every year – even if you don’t take any blood thinner and you have a CHADsVASc score of 9, the highest – is 11%. So if the chance of having thrombus is close, then that’s not a good tradeoff.”
Previous studies have also identified implantation depth and nonparoxysmal AFib as risk factors for DRT. But most of them have been small, he noted, with one of the largest reporting 65 DRTs in four prospective trials.
To cast a wider net, the investigators, led by Trevor Simard, MD, also from the Mayo Clinic, invited more than 50 international sites to contribute data to the registry. Of these, 37 centers reported on 237 DRTs and 474 device-matched control subjects from the same site.
Three-fourths of patients received a first-generation Watchman or a FLEX device (Boston Scientific).
Medical regimens were similar between the DRT and control cohorts at discharge after LAA closure. Most patients were managed with single (36.3%) or dual antiplatelet therapy (26.2%) at the time of DRT diagnosis.
As reported July 19 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the timing of DRT development varied widely, with 24.9% appearing in the first 45 days, 38.8% between days 45 and 180, 16.0% between days 180 to 365, and 20.3% beyond 1 year. At last known follow-up, one-quarter of patients had DRT.
The odds ratios for DRT associated with the five identified risk factors were:
- 17.50 (95% confidence interval, 3.39-90.45) for hypercoagulability disorder
- 13.45 (95% CI, 1.46-123.52) for pericardial effusion
- 4.02 (95% CI, 1.22-13.25) for renal insufficiency
- 2.41 (95% CI, 1.57-3.69) for implantation depth >10 mm
- 1.90 (95% CI, 1.22-2.97) for nonparoxysmal AFib
The risk for a composite of death, ischemic stroke, and systemic embolization was twofold higher in the DRT cohort than in the control cohort (29.5% vs. 14.4%; hazard ratio, 2.37; 95% CI, 1.58-3.56) and driven by a higher rate of ischemic stroke (16.9% vs. 3.6%; HR, 3.49; 95% CI, 1.35-9.00).
The incidence of bleeding and intracerebral hemorrhage, however, was similar in the DRT and control cohorts.
One of the surprises of the study was that medications prescribed in the short term after LAA closure were not associated with DRT, Dr. Alkhouli said. A previous meta-analysis of 66 studies by the investigators also found that antithrombotic regimen did not explain the heterogeneity of DRT formation.
“I think we’ll have to take that with a grain of salt, because there’s so many variations in the practice, and this is observational data. But that, in my mind, brings up a mechanistic issue,” he said.
It’s often recommended “that we should put patients on blood thinners for 3 months or 6 weeks, or whatever it is, to decrease the chance of thrombus, assuming the patients will have a normal endothelialization of the device,” Dr. Alkhouli said.
“Well, we know that’s not the reality,” he continued. “We know many patients don’t endothelialize, and, even if some patients do, there may be some endothelial damage. So I think the whole mechanism of prescribing a little bit of a blood thinner to avoid that risk may be missing the point. It’s a bit more complex than that, evidenced also by the fact that three-fourths of all the DRTs happened after 45 days, when patients are typically not taking a blood thinner.”
Based on the five independent risk factors, the investigators created a clinical DRT risk score that assigned 1 point for renal insufficiency, implantation depth greater than 10 mm from the pulmonary ridge, and nonparoxysmal AFib; and 4 points for iatrogenic pericardial effusion and for hypercoagulability disorder. Low risk was categorized as 1 point and high risk as 2 or more points.
The presence of one major risk factor or two minor risk factors, for example, led to a 2.1-fold increased risk for DRT, compared with those with no DRT risk factors.
The risk score will require validation in a prospective cohort but is “a step forward in addressing DRT” and triaging patients, Dr. Alkhouli said. The findings highlight the need to avoid deep device implantation and the importance of shared decision-making with patients, especially with those at high risk.
“And third, which is most important, I think, in my mind, is that it tells us not to put a blind eye to this topic and just say with improved devices it will go away,” he said. “That’s a bit unrealistic.”
In an accompanying editorial, Oussama Wazni, MD, Walid Saliba, MD, and Ayman A. Hussein, MD, all from the Cleveland Clinic, write that “the study sheds light on this yet unresolved issue, and the observations may help with risk stratification and optimization of procedural techniques.”
Whereas many of the nonmodifiable risk factors are helpful in shared decision-making decisions, they continue, “knowledge of these risk factors may not preclude implantation in patients who are otherwise at risk of both stroke off anticoagulation and bleeding on anticoagulation.”
Dr. Wazni and colleagues acknowledge that the small number of events in the study limits statistical power for definitive conclusions and say that further studies are needed to clarify the natural history of DRTs and their management, resolution, and impact on cardiovascular events.
Practitioners should also continue to cautiously assess for LAAO clinical indications for implant, according to the editorialists, who point out that the regulatory approval language in the United States was “flexible and nonspecific.”
“As the field grows wider, enhancing LAAO safety with optimal design, implantation, and periprocedural management is critically important, yet the main focus should remain on optimal patient selection for the purpose of achieving safe and successful outcomes,” the editorialists conclude.
Dr. Alkhouli has served as a consultant for Boston Scientific. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Wazni and Dr. Hussein have received research grant support from Boston Scientific. Dr. Wazni and Dr. Saliba have been consultants for Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Statin safety, low muscle pain risk upheld in ‘reassuring’ study
Statins are associated with a low risk of adverse events in patients without a history of heart disease, but the potential harms are small and should not deter their use in primary prevention, a new systematic review and meta-analysis concludes.
As reported July 14 in BMJ, the analysis showed a slightly increased risk for self-reported muscle symptoms after treatment with statins but no increased risk for clinically confirmed muscle disorders. Statins were associated with liver dysfunction, renal insufficiency, and eye conditions, but not with diabetes.
“These risks are very, very small and, in fact, the adverse events we’re talking about are potentially quite mild, so if you weigh them against the benefits in terms of reduction in major cardiovascular events, the benefit-to-harm ratio is very much in favor of prescribing treatment for almost all patients,” senior author James P. Sheppard, MD, University of Oxford (England), said in an interview.
Although there’s an abundance of data showing that statins prevent recurrent cardiovascular events, their use is controversial in primary prevention, owing partly to the lower risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). The absolute benefits of statins are smaller in primary prevention than in those with existing CVD, and the benefit-to-harm balance of treatment might be less favorable, the authors note.
A 2019 review suggested that the use of statins in primary prevention may be an example of “low-value care, having little benefit and potential to cause harm,” and a meta-analysis with more than 94,000 trial participants showed statins significantly increased risks for myopathy, renal dysfunction, and hepatic dysfunction.
Nevertheless, clinical guidelines have recommended wider use of statins for primary prevention, calling on physicians to weigh the benefits and harms.
“This is a reasonable expectation but, at present, the data on the harms of treatment are much less well understood in comparison to the benefits and there’s quite a lot of debate about the extent to which statins are associated with adverse events,” Dr. Sheppard said. “So we wanted to look at this in a bit more detail.”
The investigators analyzed results from 62 randomized controlled trials with 120,456 participants (mean age, 61; 40% women) followed for a mean of 3.9 years. All but two studies enrolled participants with hyperlipidemia or dyslipidemia. Common comorbidities were diabetes (11 studies), asymptomatic atherosclerosis (nine studies), and hypertension (four studies).
Statins increased risks for self-reported muscle symptoms in 21 trials (odds ratio [OR], 1.06), liver dysfunction in 21 trials (OR, 1.33), renal insufficiency in eight trials (OR, 1.14), and cataracts or other eye-related conditions in six trials (OR, 1.23).
At the same time, statins decreased risks for myocardial infarction in 22 trials (OR, 0.72), stroke in 17 trials (OR, 0.80), and CVD death in 22 trials (OR, 0.83).
These risks translated into 15 more events of muscle symptoms, 8 more liver events, 12 more kidney events, and 14 more eye conditions per 10,000 patients treated for a year.
Statins were estimated to prevent 19 myocardial infarctions, 9 strokes, and 8 CVD deaths per 10,000 patients treated for a year.
Dr. Sheppard suggested that the inclusion of previously omitted trials and the decision to classify muscle problems as self-reported symptoms or clinically defined muscle disorders based on changes in creatine kinase might explain why they found the association with statins, whereas most systematic reviews have not.
“Some people would argue that these side effects are so small and so negligible that we shouldn’t talk about them, but the problem with doing that is if you’ve got a patient who has a preconceived idea that statins are harmful,” he added. “So having some empirical data where you can actually say: ‘Look, just 15 people out of 10,000 patients who’ve been treated for a year might experience one of those self-reported muscle symptoms,’ hopefully, will be helpful for physicians having discussions in practice.”
The analysis is “another data point indicating the overall safety and net benefit of statins for patients, even in primary prevention,” Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, ScM, chair of preventive medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
He noted that the renal insufficiency findings are difficult to interpret, given that the endpoint was defined as “any decline in renal function,” but that most will have been clinically unimportant. In general, most studies didn’t systematically look to ascertain some of adverse events but relied on participant or physician report. “Nonetheless, there is little reason to suspect bias in the collection of these data among the blinded studies.
“Although not definitive, given the study design and inclusion of very different types of studies and variable ascertainment of adverse events, the findings are reassuring that the risks of adverse events were small, and the potential adverse events identified were not very clinically significant and clearly outweighed by the important beneficial reductions in major cardiovascular events,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones.
“This study is yet another reminder of the safety of statins,” Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, a specialist in preventive cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, said in an email.
“I’m pleased to have a comprehensive study like this – a well-done, systematic review of randomized trials – to help combat the vast amounts of misinformation about statins circulating on the Internet.”
Dr. Lloyd-Jones also acknowledged the need to address misinformation, pointing out that the loss of contact with physicians and the adverse effects of the pandemic on weight and other health behaviors mean that many patients have had worsening of their cardiovascular risk factors.
“We must continue to help patients and the public understand that statins are beneficial for patients at sufficient risk for cardiovascular disease because of elevated cholesterol or their total burden of risk factors,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. “We must also be upfront about the risks of potential side effects, which are uncommon and almost always very easily managed with washout and dose reduction or switching to a different drug in the same class.”
Analyses by type of statin, however, showed few significant differences in adverse events. Rosuvastatin was associated with increased risks for self-reported muscle symptoms, renal insufficiency, diabetes, and eye conditions, whereas atorvastatin and lovastatin increased the risk for liver dysfunction.
In dose-response meta-analyses, a possible modest dose-response relationship was detected only for the effect of atorvastatin on liver dysfunction.
The current data do not support tailoring the type of statin or dosage to reduce adverse events, the authors say, although routine monitoring of liver function during treatment is probably warranted in primary prevention, given the increased risk for liver dysfunction.
To help improve adherence to statins, the investigators said, additional studies are needed to identify patient characteristics crucial to the small risks of adverse events.
Limitations of the research, they said, are that many of the analyses were underpowered to detect between-group differences, many trials had short periods of follow-up, and some trials excluded vulnerable people more likely to have adverse events, such as those with high serum creatinine.
The study was funded by a British Heart Foundation PhD Scholarship held by first author Ting Cai. Dr. Sheppard reports receiving funding from a Wellcome Trust/Royal Society Sir Henry Dale Fellowship. Disclosures for other authors are listed in the paper. Dr. Lloyd-Jones and Dr. Navar report having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Statins are associated with a low risk of adverse events in patients without a history of heart disease, but the potential harms are small and should not deter their use in primary prevention, a new systematic review and meta-analysis concludes.
As reported July 14 in BMJ, the analysis showed a slightly increased risk for self-reported muscle symptoms after treatment with statins but no increased risk for clinically confirmed muscle disorders. Statins were associated with liver dysfunction, renal insufficiency, and eye conditions, but not with diabetes.
“These risks are very, very small and, in fact, the adverse events we’re talking about are potentially quite mild, so if you weigh them against the benefits in terms of reduction in major cardiovascular events, the benefit-to-harm ratio is very much in favor of prescribing treatment for almost all patients,” senior author James P. Sheppard, MD, University of Oxford (England), said in an interview.
Although there’s an abundance of data showing that statins prevent recurrent cardiovascular events, their use is controversial in primary prevention, owing partly to the lower risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). The absolute benefits of statins are smaller in primary prevention than in those with existing CVD, and the benefit-to-harm balance of treatment might be less favorable, the authors note.
A 2019 review suggested that the use of statins in primary prevention may be an example of “low-value care, having little benefit and potential to cause harm,” and a meta-analysis with more than 94,000 trial participants showed statins significantly increased risks for myopathy, renal dysfunction, and hepatic dysfunction.
Nevertheless, clinical guidelines have recommended wider use of statins for primary prevention, calling on physicians to weigh the benefits and harms.
“This is a reasonable expectation but, at present, the data on the harms of treatment are much less well understood in comparison to the benefits and there’s quite a lot of debate about the extent to which statins are associated with adverse events,” Dr. Sheppard said. “So we wanted to look at this in a bit more detail.”
The investigators analyzed results from 62 randomized controlled trials with 120,456 participants (mean age, 61; 40% women) followed for a mean of 3.9 years. All but two studies enrolled participants with hyperlipidemia or dyslipidemia. Common comorbidities were diabetes (11 studies), asymptomatic atherosclerosis (nine studies), and hypertension (four studies).
Statins increased risks for self-reported muscle symptoms in 21 trials (odds ratio [OR], 1.06), liver dysfunction in 21 trials (OR, 1.33), renal insufficiency in eight trials (OR, 1.14), and cataracts or other eye-related conditions in six trials (OR, 1.23).
At the same time, statins decreased risks for myocardial infarction in 22 trials (OR, 0.72), stroke in 17 trials (OR, 0.80), and CVD death in 22 trials (OR, 0.83).
These risks translated into 15 more events of muscle symptoms, 8 more liver events, 12 more kidney events, and 14 more eye conditions per 10,000 patients treated for a year.
Statins were estimated to prevent 19 myocardial infarctions, 9 strokes, and 8 CVD deaths per 10,000 patients treated for a year.
Dr. Sheppard suggested that the inclusion of previously omitted trials and the decision to classify muscle problems as self-reported symptoms or clinically defined muscle disorders based on changes in creatine kinase might explain why they found the association with statins, whereas most systematic reviews have not.
“Some people would argue that these side effects are so small and so negligible that we shouldn’t talk about them, but the problem with doing that is if you’ve got a patient who has a preconceived idea that statins are harmful,” he added. “So having some empirical data where you can actually say: ‘Look, just 15 people out of 10,000 patients who’ve been treated for a year might experience one of those self-reported muscle symptoms,’ hopefully, will be helpful for physicians having discussions in practice.”
The analysis is “another data point indicating the overall safety and net benefit of statins for patients, even in primary prevention,” Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, ScM, chair of preventive medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
He noted that the renal insufficiency findings are difficult to interpret, given that the endpoint was defined as “any decline in renal function,” but that most will have been clinically unimportant. In general, most studies didn’t systematically look to ascertain some of adverse events but relied on participant or physician report. “Nonetheless, there is little reason to suspect bias in the collection of these data among the blinded studies.
“Although not definitive, given the study design and inclusion of very different types of studies and variable ascertainment of adverse events, the findings are reassuring that the risks of adverse events were small, and the potential adverse events identified were not very clinically significant and clearly outweighed by the important beneficial reductions in major cardiovascular events,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones.
“This study is yet another reminder of the safety of statins,” Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, a specialist in preventive cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, said in an email.
“I’m pleased to have a comprehensive study like this – a well-done, systematic review of randomized trials – to help combat the vast amounts of misinformation about statins circulating on the Internet.”
Dr. Lloyd-Jones also acknowledged the need to address misinformation, pointing out that the loss of contact with physicians and the adverse effects of the pandemic on weight and other health behaviors mean that many patients have had worsening of their cardiovascular risk factors.
“We must continue to help patients and the public understand that statins are beneficial for patients at sufficient risk for cardiovascular disease because of elevated cholesterol or their total burden of risk factors,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. “We must also be upfront about the risks of potential side effects, which are uncommon and almost always very easily managed with washout and dose reduction or switching to a different drug in the same class.”
Analyses by type of statin, however, showed few significant differences in adverse events. Rosuvastatin was associated with increased risks for self-reported muscle symptoms, renal insufficiency, diabetes, and eye conditions, whereas atorvastatin and lovastatin increased the risk for liver dysfunction.
In dose-response meta-analyses, a possible modest dose-response relationship was detected only for the effect of atorvastatin on liver dysfunction.
The current data do not support tailoring the type of statin or dosage to reduce adverse events, the authors say, although routine monitoring of liver function during treatment is probably warranted in primary prevention, given the increased risk for liver dysfunction.
To help improve adherence to statins, the investigators said, additional studies are needed to identify patient characteristics crucial to the small risks of adverse events.
Limitations of the research, they said, are that many of the analyses were underpowered to detect between-group differences, many trials had short periods of follow-up, and some trials excluded vulnerable people more likely to have adverse events, such as those with high serum creatinine.
The study was funded by a British Heart Foundation PhD Scholarship held by first author Ting Cai. Dr. Sheppard reports receiving funding from a Wellcome Trust/Royal Society Sir Henry Dale Fellowship. Disclosures for other authors are listed in the paper. Dr. Lloyd-Jones and Dr. Navar report having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Statins are associated with a low risk of adverse events in patients without a history of heart disease, but the potential harms are small and should not deter their use in primary prevention, a new systematic review and meta-analysis concludes.
As reported July 14 in BMJ, the analysis showed a slightly increased risk for self-reported muscle symptoms after treatment with statins but no increased risk for clinically confirmed muscle disorders. Statins were associated with liver dysfunction, renal insufficiency, and eye conditions, but not with diabetes.
“These risks are very, very small and, in fact, the adverse events we’re talking about are potentially quite mild, so if you weigh them against the benefits in terms of reduction in major cardiovascular events, the benefit-to-harm ratio is very much in favor of prescribing treatment for almost all patients,” senior author James P. Sheppard, MD, University of Oxford (England), said in an interview.
Although there’s an abundance of data showing that statins prevent recurrent cardiovascular events, their use is controversial in primary prevention, owing partly to the lower risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). The absolute benefits of statins are smaller in primary prevention than in those with existing CVD, and the benefit-to-harm balance of treatment might be less favorable, the authors note.
A 2019 review suggested that the use of statins in primary prevention may be an example of “low-value care, having little benefit and potential to cause harm,” and a meta-analysis with more than 94,000 trial participants showed statins significantly increased risks for myopathy, renal dysfunction, and hepatic dysfunction.
Nevertheless, clinical guidelines have recommended wider use of statins for primary prevention, calling on physicians to weigh the benefits and harms.
“This is a reasonable expectation but, at present, the data on the harms of treatment are much less well understood in comparison to the benefits and there’s quite a lot of debate about the extent to which statins are associated with adverse events,” Dr. Sheppard said. “So we wanted to look at this in a bit more detail.”
The investigators analyzed results from 62 randomized controlled trials with 120,456 participants (mean age, 61; 40% women) followed for a mean of 3.9 years. All but two studies enrolled participants with hyperlipidemia or dyslipidemia. Common comorbidities were diabetes (11 studies), asymptomatic atherosclerosis (nine studies), and hypertension (four studies).
Statins increased risks for self-reported muscle symptoms in 21 trials (odds ratio [OR], 1.06), liver dysfunction in 21 trials (OR, 1.33), renal insufficiency in eight trials (OR, 1.14), and cataracts or other eye-related conditions in six trials (OR, 1.23).
At the same time, statins decreased risks for myocardial infarction in 22 trials (OR, 0.72), stroke in 17 trials (OR, 0.80), and CVD death in 22 trials (OR, 0.83).
These risks translated into 15 more events of muscle symptoms, 8 more liver events, 12 more kidney events, and 14 more eye conditions per 10,000 patients treated for a year.
Statins were estimated to prevent 19 myocardial infarctions, 9 strokes, and 8 CVD deaths per 10,000 patients treated for a year.
Dr. Sheppard suggested that the inclusion of previously omitted trials and the decision to classify muscle problems as self-reported symptoms or clinically defined muscle disorders based on changes in creatine kinase might explain why they found the association with statins, whereas most systematic reviews have not.
“Some people would argue that these side effects are so small and so negligible that we shouldn’t talk about them, but the problem with doing that is if you’ve got a patient who has a preconceived idea that statins are harmful,” he added. “So having some empirical data where you can actually say: ‘Look, just 15 people out of 10,000 patients who’ve been treated for a year might experience one of those self-reported muscle symptoms,’ hopefully, will be helpful for physicians having discussions in practice.”
The analysis is “another data point indicating the overall safety and net benefit of statins for patients, even in primary prevention,” Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, ScM, chair of preventive medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
He noted that the renal insufficiency findings are difficult to interpret, given that the endpoint was defined as “any decline in renal function,” but that most will have been clinically unimportant. In general, most studies didn’t systematically look to ascertain some of adverse events but relied on participant or physician report. “Nonetheless, there is little reason to suspect bias in the collection of these data among the blinded studies.
“Although not definitive, given the study design and inclusion of very different types of studies and variable ascertainment of adverse events, the findings are reassuring that the risks of adverse events were small, and the potential adverse events identified were not very clinically significant and clearly outweighed by the important beneficial reductions in major cardiovascular events,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones.
“This study is yet another reminder of the safety of statins,” Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, a specialist in preventive cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, said in an email.
“I’m pleased to have a comprehensive study like this – a well-done, systematic review of randomized trials – to help combat the vast amounts of misinformation about statins circulating on the Internet.”
Dr. Lloyd-Jones also acknowledged the need to address misinformation, pointing out that the loss of contact with physicians and the adverse effects of the pandemic on weight and other health behaviors mean that many patients have had worsening of their cardiovascular risk factors.
“We must continue to help patients and the public understand that statins are beneficial for patients at sufficient risk for cardiovascular disease because of elevated cholesterol or their total burden of risk factors,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said. “We must also be upfront about the risks of potential side effects, which are uncommon and almost always very easily managed with washout and dose reduction or switching to a different drug in the same class.”
Analyses by type of statin, however, showed few significant differences in adverse events. Rosuvastatin was associated with increased risks for self-reported muscle symptoms, renal insufficiency, diabetes, and eye conditions, whereas atorvastatin and lovastatin increased the risk for liver dysfunction.
In dose-response meta-analyses, a possible modest dose-response relationship was detected only for the effect of atorvastatin on liver dysfunction.
The current data do not support tailoring the type of statin or dosage to reduce adverse events, the authors say, although routine monitoring of liver function during treatment is probably warranted in primary prevention, given the increased risk for liver dysfunction.
To help improve adherence to statins, the investigators said, additional studies are needed to identify patient characteristics crucial to the small risks of adverse events.
Limitations of the research, they said, are that many of the analyses were underpowered to detect between-group differences, many trials had short periods of follow-up, and some trials excluded vulnerable people more likely to have adverse events, such as those with high serum creatinine.
The study was funded by a British Heart Foundation PhD Scholarship held by first author Ting Cai. Dr. Sheppard reports receiving funding from a Wellcome Trust/Royal Society Sir Henry Dale Fellowship. Disclosures for other authors are listed in the paper. Dr. Lloyd-Jones and Dr. Navar report having no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA okays 1-month dual antiplatelet therapy for Abbott’s Xience stents
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Abbott announced on June 30.
Patients who receive stents are typically on DAPT regimens such as aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors for 6 to 12 months to prevent blood clots, but high-bleeding risk patients can experience bleeding during prolonged DAPT.
“The new FDA approval for DAPT for the XIENCE family of stents provides interventional cardiologists confidence they are delivering the best care to patients with high bleeding risk. A short DAPT duration minimizes risks for high bleeding risk patients and allows them to return to daily life sooner and with more assurance,” Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York and the global principal investigator for Abbott’s Short DAPT program (XIENCE 28 and XIENCE 90), said in a news release.
The new labeling comes on the heels of European CE Mark approval for the Xience stents with DAPT as short as 28 days, “giving Xience stents the shortest DAPT indication in the world,” the company noted.
Results of the XIENCE 28 trial were used to support the new CE Mark DAPT indication. The trial showed no increase in death of myocardial infarction between 1 and 6 months and a significantly lower risk for severe bleeding with the Xience stent and 1-month DAPT, compared with 6-month DAPT in more than 1,600 high-bleeding risk patients.
The XIENCE 90 trial involving more than 2,000 high-bleeding risk patients reported no difference in death or MI between 3 and 12 months with Xience and 3-month DAPT versus 12-month DAPT.
Abbott scored a second win, also announcing FDA and CE Mark approval of its next-generation Xience Skypoint stent in high-bleeding risk patients with 1-month DAPT.
“XIENCE Skypoint is easier to place and allows physicians to treat larger blood vessels through improved stent expansion that can open clogged vessels more effectively,” the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Abbott announced on June 30.
Patients who receive stents are typically on DAPT regimens such as aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors for 6 to 12 months to prevent blood clots, but high-bleeding risk patients can experience bleeding during prolonged DAPT.
“The new FDA approval for DAPT for the XIENCE family of stents provides interventional cardiologists confidence they are delivering the best care to patients with high bleeding risk. A short DAPT duration minimizes risks for high bleeding risk patients and allows them to return to daily life sooner and with more assurance,” Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York and the global principal investigator for Abbott’s Short DAPT program (XIENCE 28 and XIENCE 90), said in a news release.
The new labeling comes on the heels of European CE Mark approval for the Xience stents with DAPT as short as 28 days, “giving Xience stents the shortest DAPT indication in the world,” the company noted.
Results of the XIENCE 28 trial were used to support the new CE Mark DAPT indication. The trial showed no increase in death of myocardial infarction between 1 and 6 months and a significantly lower risk for severe bleeding with the Xience stent and 1-month DAPT, compared with 6-month DAPT in more than 1,600 high-bleeding risk patients.
The XIENCE 90 trial involving more than 2,000 high-bleeding risk patients reported no difference in death or MI between 3 and 12 months with Xience and 3-month DAPT versus 12-month DAPT.
Abbott scored a second win, also announcing FDA and CE Mark approval of its next-generation Xience Skypoint stent in high-bleeding risk patients with 1-month DAPT.
“XIENCE Skypoint is easier to place and allows physicians to treat larger blood vessels through improved stent expansion that can open clogged vessels more effectively,” the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Abbott announced on June 30.
Patients who receive stents are typically on DAPT regimens such as aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors for 6 to 12 months to prevent blood clots, but high-bleeding risk patients can experience bleeding during prolonged DAPT.
“The new FDA approval for DAPT for the XIENCE family of stents provides interventional cardiologists confidence they are delivering the best care to patients with high bleeding risk. A short DAPT duration minimizes risks for high bleeding risk patients and allows them to return to daily life sooner and with more assurance,” Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York and the global principal investigator for Abbott’s Short DAPT program (XIENCE 28 and XIENCE 90), said in a news release.
The new labeling comes on the heels of European CE Mark approval for the Xience stents with DAPT as short as 28 days, “giving Xience stents the shortest DAPT indication in the world,” the company noted.
Results of the XIENCE 28 trial were used to support the new CE Mark DAPT indication. The trial showed no increase in death of myocardial infarction between 1 and 6 months and a significantly lower risk for severe bleeding with the Xience stent and 1-month DAPT, compared with 6-month DAPT in more than 1,600 high-bleeding risk patients.
The XIENCE 90 trial involving more than 2,000 high-bleeding risk patients reported no difference in death or MI between 3 and 12 months with Xience and 3-month DAPT versus 12-month DAPT.
Abbott scored a second win, also announcing FDA and CE Mark approval of its next-generation Xience Skypoint stent in high-bleeding risk patients with 1-month DAPT.
“XIENCE Skypoint is easier to place and allows physicians to treat larger blood vessels through improved stent expansion that can open clogged vessels more effectively,” the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Reversal agents curb DOAC-related bleeding but deaths still high
Agents that reverse the effect of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are highly effective in patients with severe bleeding, but mortality rates remain high despite their use, a meta-analysis shows.
Effective hemostasis was achieved in 78.5% of patients treated with a reversal agent, whereas failure to achieve hemostasis was associated with more than a threefold higher relative risk for death (relative risk, 3.63; 95% confidence interval, 2.56-5.16).
“This has implications in practice because it emphasizes the need for achieving effective hemostasis, if not with only one agent, trying other agents or treatment modalities, because it is a strong predictor of survival,” lead author Antonio Gómez-Outes, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
The bad news, he said, is that the mortality rate was still significant, at 17.7%, and approximately half of patients with DOAC-related severe intracranial bleeding survived with long-term moderate/severe disability.
“The lesson is to prevent these bleeding events because once they appear, even if you give an antidote, the outcome is poor, particularly for intracranial bleeding,” said Dr. Gómez-Outes, division of pharmacology and clinical drug evaluation, Spanish Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices, Madrid.
To put this in context, mortality rates were close to 50% after intracranial bleeding a decade ago when there were no antidotes or reversal agents, he observed. “So to some extent, patient care has improved, and the outcome has improved, but there is a long road to improve regarding disability.”
More than 100,000 DOAC-related major bleeding cases occur each year in the United States and European Union, Dr. Gómez-Outes said, and about half are severe enough to require hospitalization and potentially the use of a reversal agent. These include idarucizumab (Praxbind) for dabigatran reversal and prothombin complex concentrates (4CCC) or andexanet alpha (Andexxa) for reversal of direct factor Xa inhibitors like rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban.
As reported in the June 22 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the meta-analysis comprised 4,735 patients (mean age, 77 years; 57% male) with severe DOAC-related bleeding who received 4PCC (n = 2,688), idarucizumab (n = 1,111), or andexanet (n = 936) in 60 studies between January 2010 and December 2020.
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) was the most common reason for use of a DOAC (82%), followed by venous thromboembolism (14%). Rivaroxaban was used in 36%, apixaban in 32%, dabigatran in 31%, and edoxaban in 1%.
The index bleeding event was intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) in 55%. Anticoagulation was restarted in 57% of patients an average of 11 days after admission.
Mortality rates were 20.2% in patients with ICH and 15.4% in those with extracranial bleeding. There were no differences in death rates by reversal agent used, type of study, risk for bias, or study sponsorship in meta-regression analysis.
Rebleeding occurred in 13.2% of patients; 82.0% of these events were described as an ICH, and 78.0% occurred after anticoagulation was restarted.
The overall rate of thromboembolism was 4.6%. The risk was particularly high with andexanet, at 10.7%, and relatively low with idarucizumab (3.8%) and 4PCC (4.3%), the authors note.
“Our meta-analysis suggests specific reversal with andexanet is not superior to unspecific reversal with 4PCC, and that’s good news because many centers, in many countries, have no access to specific antidotes that are more costly,” Dr. Gómez-Outes said. “4PCC is an effective and relatively safe drug, so it’s still a good option for these patients.”
Labeling for andexanet includes a warning for thromboembolic events, but in the absence of direct comparisons, the findings should be interpreted with caution, he added. Further insights are expected from an ongoing randomized trial of andexanet and standard of care in 900 patients who present with acute ICH less than 15 hours after taking an oral factor Xa inhibitor. The preliminary completion date is set for 2023.
“The meta-analysis raises awareness about the rates of mortality and thromboembolism after reversal agent administration, although understanding the implications of these data is challenging,” Christopher Granger, MD, and Sean P. Pokomey, MD, MBA, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., say in an accompanying editorial.
The fact that failure to achieve hemostasis was associated with death is expected and might be related to the way hemostasis was defined, rather than the actual failure of the hemostatic treatments, they suggest. “The prothrombotic effects of each agent, including andexanet, need to be better understood, as clinicians work toward including reversal agents into algorithms for bleeding management.”
Effective hemostasis was defined in the studies through various methods as: “Excellent/good” using the Sarode and ANNEXA-4 scales; “yes” in the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis Scale; and with other scales and through clinical judgment.
Although the size of the meta-analysis dwarfs previous reviews, the editorialists and authors point out that 47 of the 60 studies were retrospective, only two had control groups, and 45 had a high risk for bias.
In general, there was also poor reporting of key clinical data, such as postbleeding anticoagulation management, and a limitation of the mortality analysis is that it was based in selected patients with effective hemostasis assessed within 48 hours, which may not capture early deaths, the authors note.
“The morbidity and mortality from ischemic strokes as a result of undertreatment of stroke prevention in patients with AFib continue to dwarf the bleeding related mortality among patients with AFib and on DOACs, and thus the number one priority is to treat nearly all patients with AFib with a DOAC,” Dr. Granger and Dr. Pokomey conclude. “The availability of reversal agents for DOACs should provide reassurance, with another tool in our armamentarium, to providers to prescribe OACs for stroke prevention.”
No funding/grant support was received to conduct the study. Coauthor Ramón Lecumberri has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. All other authors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Granger has received research and consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, Janssen, Boston Scientific, Apple, AstraZeneca, Novartis, AbbVie, Biomed, CeleCor, GSK, Novartis, Medtronic, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Philips, Rho, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Pokomey has received modest consulting support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen, and Zoll; modest research support from Gilead, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Janssen; and significant research support from the FDA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Agents that reverse the effect of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are highly effective in patients with severe bleeding, but mortality rates remain high despite their use, a meta-analysis shows.
Effective hemostasis was achieved in 78.5% of patients treated with a reversal agent, whereas failure to achieve hemostasis was associated with more than a threefold higher relative risk for death (relative risk, 3.63; 95% confidence interval, 2.56-5.16).
“This has implications in practice because it emphasizes the need for achieving effective hemostasis, if not with only one agent, trying other agents or treatment modalities, because it is a strong predictor of survival,” lead author Antonio Gómez-Outes, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
The bad news, he said, is that the mortality rate was still significant, at 17.7%, and approximately half of patients with DOAC-related severe intracranial bleeding survived with long-term moderate/severe disability.
“The lesson is to prevent these bleeding events because once they appear, even if you give an antidote, the outcome is poor, particularly for intracranial bleeding,” said Dr. Gómez-Outes, division of pharmacology and clinical drug evaluation, Spanish Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices, Madrid.
To put this in context, mortality rates were close to 50% after intracranial bleeding a decade ago when there were no antidotes or reversal agents, he observed. “So to some extent, patient care has improved, and the outcome has improved, but there is a long road to improve regarding disability.”
More than 100,000 DOAC-related major bleeding cases occur each year in the United States and European Union, Dr. Gómez-Outes said, and about half are severe enough to require hospitalization and potentially the use of a reversal agent. These include idarucizumab (Praxbind) for dabigatran reversal and prothombin complex concentrates (4CCC) or andexanet alpha (Andexxa) for reversal of direct factor Xa inhibitors like rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban.
As reported in the June 22 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the meta-analysis comprised 4,735 patients (mean age, 77 years; 57% male) with severe DOAC-related bleeding who received 4PCC (n = 2,688), idarucizumab (n = 1,111), or andexanet (n = 936) in 60 studies between January 2010 and December 2020.
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) was the most common reason for use of a DOAC (82%), followed by venous thromboembolism (14%). Rivaroxaban was used in 36%, apixaban in 32%, dabigatran in 31%, and edoxaban in 1%.
The index bleeding event was intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) in 55%. Anticoagulation was restarted in 57% of patients an average of 11 days after admission.
Mortality rates were 20.2% in patients with ICH and 15.4% in those with extracranial bleeding. There were no differences in death rates by reversal agent used, type of study, risk for bias, or study sponsorship in meta-regression analysis.
Rebleeding occurred in 13.2% of patients; 82.0% of these events were described as an ICH, and 78.0% occurred after anticoagulation was restarted.
The overall rate of thromboembolism was 4.6%. The risk was particularly high with andexanet, at 10.7%, and relatively low with idarucizumab (3.8%) and 4PCC (4.3%), the authors note.
“Our meta-analysis suggests specific reversal with andexanet is not superior to unspecific reversal with 4PCC, and that’s good news because many centers, in many countries, have no access to specific antidotes that are more costly,” Dr. Gómez-Outes said. “4PCC is an effective and relatively safe drug, so it’s still a good option for these patients.”
Labeling for andexanet includes a warning for thromboembolic events, but in the absence of direct comparisons, the findings should be interpreted with caution, he added. Further insights are expected from an ongoing randomized trial of andexanet and standard of care in 900 patients who present with acute ICH less than 15 hours after taking an oral factor Xa inhibitor. The preliminary completion date is set for 2023.
“The meta-analysis raises awareness about the rates of mortality and thromboembolism after reversal agent administration, although understanding the implications of these data is challenging,” Christopher Granger, MD, and Sean P. Pokomey, MD, MBA, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., say in an accompanying editorial.
The fact that failure to achieve hemostasis was associated with death is expected and might be related to the way hemostasis was defined, rather than the actual failure of the hemostatic treatments, they suggest. “The prothrombotic effects of each agent, including andexanet, need to be better understood, as clinicians work toward including reversal agents into algorithms for bleeding management.”
Effective hemostasis was defined in the studies through various methods as: “Excellent/good” using the Sarode and ANNEXA-4 scales; “yes” in the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis Scale; and with other scales and through clinical judgment.
Although the size of the meta-analysis dwarfs previous reviews, the editorialists and authors point out that 47 of the 60 studies were retrospective, only two had control groups, and 45 had a high risk for bias.
In general, there was also poor reporting of key clinical data, such as postbleeding anticoagulation management, and a limitation of the mortality analysis is that it was based in selected patients with effective hemostasis assessed within 48 hours, which may not capture early deaths, the authors note.
“The morbidity and mortality from ischemic strokes as a result of undertreatment of stroke prevention in patients with AFib continue to dwarf the bleeding related mortality among patients with AFib and on DOACs, and thus the number one priority is to treat nearly all patients with AFib with a DOAC,” Dr. Granger and Dr. Pokomey conclude. “The availability of reversal agents for DOACs should provide reassurance, with another tool in our armamentarium, to providers to prescribe OACs for stroke prevention.”
No funding/grant support was received to conduct the study. Coauthor Ramón Lecumberri has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. All other authors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Granger has received research and consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, Janssen, Boston Scientific, Apple, AstraZeneca, Novartis, AbbVie, Biomed, CeleCor, GSK, Novartis, Medtronic, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Philips, Rho, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Pokomey has received modest consulting support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen, and Zoll; modest research support from Gilead, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Janssen; and significant research support from the FDA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Agents that reverse the effect of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are highly effective in patients with severe bleeding, but mortality rates remain high despite their use, a meta-analysis shows.
Effective hemostasis was achieved in 78.5% of patients treated with a reversal agent, whereas failure to achieve hemostasis was associated with more than a threefold higher relative risk for death (relative risk, 3.63; 95% confidence interval, 2.56-5.16).
“This has implications in practice because it emphasizes the need for achieving effective hemostasis, if not with only one agent, trying other agents or treatment modalities, because it is a strong predictor of survival,” lead author Antonio Gómez-Outes, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
The bad news, he said, is that the mortality rate was still significant, at 17.7%, and approximately half of patients with DOAC-related severe intracranial bleeding survived with long-term moderate/severe disability.
“The lesson is to prevent these bleeding events because once they appear, even if you give an antidote, the outcome is poor, particularly for intracranial bleeding,” said Dr. Gómez-Outes, division of pharmacology and clinical drug evaluation, Spanish Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices, Madrid.
To put this in context, mortality rates were close to 50% after intracranial bleeding a decade ago when there were no antidotes or reversal agents, he observed. “So to some extent, patient care has improved, and the outcome has improved, but there is a long road to improve regarding disability.”
More than 100,000 DOAC-related major bleeding cases occur each year in the United States and European Union, Dr. Gómez-Outes said, and about half are severe enough to require hospitalization and potentially the use of a reversal agent. These include idarucizumab (Praxbind) for dabigatran reversal and prothombin complex concentrates (4CCC) or andexanet alpha (Andexxa) for reversal of direct factor Xa inhibitors like rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban.
As reported in the June 22 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, the meta-analysis comprised 4,735 patients (mean age, 77 years; 57% male) with severe DOAC-related bleeding who received 4PCC (n = 2,688), idarucizumab (n = 1,111), or andexanet (n = 936) in 60 studies between January 2010 and December 2020.
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) was the most common reason for use of a DOAC (82%), followed by venous thromboembolism (14%). Rivaroxaban was used in 36%, apixaban in 32%, dabigatran in 31%, and edoxaban in 1%.
The index bleeding event was intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) in 55%. Anticoagulation was restarted in 57% of patients an average of 11 days after admission.
Mortality rates were 20.2% in patients with ICH and 15.4% in those with extracranial bleeding. There were no differences in death rates by reversal agent used, type of study, risk for bias, or study sponsorship in meta-regression analysis.
Rebleeding occurred in 13.2% of patients; 82.0% of these events were described as an ICH, and 78.0% occurred after anticoagulation was restarted.
The overall rate of thromboembolism was 4.6%. The risk was particularly high with andexanet, at 10.7%, and relatively low with idarucizumab (3.8%) and 4PCC (4.3%), the authors note.
“Our meta-analysis suggests specific reversal with andexanet is not superior to unspecific reversal with 4PCC, and that’s good news because many centers, in many countries, have no access to specific antidotes that are more costly,” Dr. Gómez-Outes said. “4PCC is an effective and relatively safe drug, so it’s still a good option for these patients.”
Labeling for andexanet includes a warning for thromboembolic events, but in the absence of direct comparisons, the findings should be interpreted with caution, he added. Further insights are expected from an ongoing randomized trial of andexanet and standard of care in 900 patients who present with acute ICH less than 15 hours after taking an oral factor Xa inhibitor. The preliminary completion date is set for 2023.
“The meta-analysis raises awareness about the rates of mortality and thromboembolism after reversal agent administration, although understanding the implications of these data is challenging,” Christopher Granger, MD, and Sean P. Pokomey, MD, MBA, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., say in an accompanying editorial.
The fact that failure to achieve hemostasis was associated with death is expected and might be related to the way hemostasis was defined, rather than the actual failure of the hemostatic treatments, they suggest. “The prothrombotic effects of each agent, including andexanet, need to be better understood, as clinicians work toward including reversal agents into algorithms for bleeding management.”
Effective hemostasis was defined in the studies through various methods as: “Excellent/good” using the Sarode and ANNEXA-4 scales; “yes” in the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis Scale; and with other scales and through clinical judgment.
Although the size of the meta-analysis dwarfs previous reviews, the editorialists and authors point out that 47 of the 60 studies were retrospective, only two had control groups, and 45 had a high risk for bias.
In general, there was also poor reporting of key clinical data, such as postbleeding anticoagulation management, and a limitation of the mortality analysis is that it was based in selected patients with effective hemostasis assessed within 48 hours, which may not capture early deaths, the authors note.
“The morbidity and mortality from ischemic strokes as a result of undertreatment of stroke prevention in patients with AFib continue to dwarf the bleeding related mortality among patients with AFib and on DOACs, and thus the number one priority is to treat nearly all patients with AFib with a DOAC,” Dr. Granger and Dr. Pokomey conclude. “The availability of reversal agents for DOACs should provide reassurance, with another tool in our armamentarium, to providers to prescribe OACs for stroke prevention.”
No funding/grant support was received to conduct the study. Coauthor Ramón Lecumberri has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. All other authors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Granger has received research and consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, Janssen, Boston Scientific, Apple, AstraZeneca, Novartis, AbbVie, Biomed, CeleCor, GSK, Novartis, Medtronic, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Philips, Rho, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Pokomey has received modest consulting support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen, and Zoll; modest research support from Gilead, Boston Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Janssen; and significant research support from the FDA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First risk score to predict bleeding risk after TAVR
(TAVR).
“Despite the TAVR iterations, we recognize that bleeding remains a very important and perhaps also neglected issue. Indeed, no specifically developed standard algorithm existed before this to assess bleeding risk post-TAVR,” lead author Eliano Pio Navarese, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Although bleeding rates can be as high as 9% at 30 days and between 3% and 11% in the first year, only a few studies have applied existing scores to TAVR patients, he noted.
The PREDICT-TAVR score includes six common variables and can be calculated by hand using a simple nomogram or a web-based calculator, with a dedicated website in the works, said Dr. Navarese, Nicolaus Copernicus University and SIRO MEDICINE Network, Bydgoszcz, Poland, and the University of Alberta, Edmonton.
A strength of the score is that machine-learning methods were used and the choice of variables optimized through recursive feature elimination and cross validation to remove the weakest variables, he said. Artificial intelligence, including use of random forest, naïve Bayes, and logistic regression classifiers, was also applied to the algorithms and the results cross-checked with standard multivariate analysis.
“It was a tremendous effort in terms of the analytics conducted,” Dr. Navarese said. “This is not a simple score but the integration of the most sophisticated machine learning methods and algorithms.”
Details are published in the June 14 issue of JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The six variables used to calculate 30-day bleeding risk after TAVR and the points assigned to each are:
- blood hemoglobin (0-10 points)
- serum iron concentration (0-5 points)
- common femoral artery diameter (0-3 points)
- (0-3 points)
- dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT; 0-2 points)
- oral anticoagulation therapy (0-2 points)
The six items were selected among 104 baseline variables from 5,185 consecutive patients undergoing transfemoral TAVR in the prospective RISPEVA (Registro Italiano GISE sull’Impianto di Valvola Aortica Percutanea) registry between March 2012 and December 2019, then validated in 5,043 patients in the prospective POL-TAVI (Polish Registry of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) between January 2013 and December 2019.
In the derivation cohort, 216 patients (4.2%) experienced bleeding events at 1 year, with 169 events (78%) occurring during the first 30 days.
PREDICT-TAVR exhibited high discriminatory power for bleeding events at 30 days, as reflected by an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.80 (95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.83). Internal validation by optimism bootstrap-corrected AUC was consistent at 0.79 (95% CI, 0.75-0.83).
PREDICT-TAVR also outperformed scores not developed for TAVR, such as the PARIS score for patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (AUC, 0.69) and the well-validated HAS-BLED for patients receiving anticoagulation (AUC, 0.58; P < .001 for both).
In the validation cohort, the AUC for bleeding complications at 30 days was 0.78 (95% CI, 0.72-0.82) versus an AUC of 0.68 for PARIS and 0.66 for HAS-BLED.
A HAS-BLED score of 4 predicted a higher rate of severe bleeding and mortality in the year after transfemoral TAVR in the 2018 Japanese OCEAN-TAVI study.
Bleeding events by risk categories
Risk score quartiles identified as low risk were 8 points or less, as moderate risk were 8 to less than 10 points, as high risk were 10 to less than 12 points, and as very-high-risk score were above 12 points.
In the derivation cohort, 30-day bleeding events across quartiles were 0.8%, 1.1%, 2.5%, and 8.5%, respectively (overall P < .001).
Compared with the lowest quartile, bleeding risk was numerically higher for the second quartile (odds ratio, 1.75) and significantly higher in the third (OR, 2.0) and fourth (OR, 2.49) quartiles (P < .001 for both).
A landmark cumulative-event analysis showed a significantly greater risk of bleeding for the two highest quartiles up to 30 days; however, these differences were no longer significant from 30 days to 1 year, likely because of a limited number of events, the authors suggest. Similar results were seen in the validation cohort.
The number of patients in the high- and very-high-risk groups isn’t trivial, and bleeding rates reached as high as 12.6% in the highest quartile, Dr. Navarese observed. Guidelines recommend DAPT for 3 to 6 months after TAVR; however, emerging data, including a recent meta-analysis, suggest monotherapy may be a very good option.
“So, if you had a high bleeding risk and are considering postprocedural DAPT or anticoagulation, I would think twice rather than administering dual antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulation for a long time, or at least, I would consider the impact of this score on this choice,” he said.
Subgroup analyses showed AUCs ranging from 0.77 to 0.81 for subgroups such as age older than 80 years, diabetes, obesity, female sex, previous PCI, and New York Heart Association class III or IV.
Serum iron showed the highest AUC in the primary PREDICT-TAVR model; however, should iron levels be unavailable, a simplified score modeled without iron levels retained predictive power, yielding AUCs for 30-day bleeding of 0.78 in the derivation cohort and 0.75 in the validation cohort.
“PREDICT-TAVR score can impact clinical practice, not only selecting the optimal thrombotic regimen in certain high bleeding-risk populations but also to treat pre-TAVR anemia and iron deficiencies, which may affect outcomes,” Dr. Navarese said. “Of course, future prospective biological and clinical investigations are needed to elucidate the score and the role of the score’s treatable risk traits in reducing post-TAVR bleeding complications.”
Commenting for this news organization, Sunil Rao, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., said anemia is a covariant in many risk models for bleeding and vascular complications in PCI and acute coronary syndrome, but hemoglobin and iron levels are collinear.
“The problem I think is when you throw hemoglobin and iron in the same model, just by play of chance, one variable can knock out the other one,” he said. “So I don’t know necessarily if we need to start measuring iron on everyone. We certainly should be measuring hemoglobin, which I think most people will have, and if a patient has pre-existing anemia, that should be a red flag for us.”
Age and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score did not reach statistical significance in the model – likely reflecting the high-/extremely-high-risk patient population with an average STS score of 7.7 and average age of 82 years – but may become more important as TAVR is applied more widely, Dr. Rao and Zachary Wegermann, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, write in an accompanying editorial.
They also point out that the study was limited by a low rate of bleeding events, and, importantly, the score can’t distinguish between minor or major bleeding.
“It’s worth trying to repeat the analyses in lower-risk patients because we may find other covariates that are important,” Dr. Rao said in an interview. “The other thing we need to get to is probably being a little bit more sophisticated. The variables included in these models are the ones that are measured; they’re also the ones that are clinically apparent.”
“But there’s a whole area of genomic medicine, proteomic medicine, metabolomic medicine that, as it starts developing and becomes more and more sophisticated, my suspicion is that we’re going to get even more precise and accurate about patients’ risk, and it’s going to become more individualized, rather than just measuring variables like age and lab values,” he said.
In the meantime, having variables documented in the electronic health record, with hard stops deployed if variables aren’t measured, is “a step in the right direction,” he added.
Dr. Navarese has received research grants from Abbott, Amgen, and Medtronic and received lecture fees and honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Pfizer, and Sanofi-Regeneron, outside the submitted work. Dr. Rao and Dr. Wegermann report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(TAVR).
“Despite the TAVR iterations, we recognize that bleeding remains a very important and perhaps also neglected issue. Indeed, no specifically developed standard algorithm existed before this to assess bleeding risk post-TAVR,” lead author Eliano Pio Navarese, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Although bleeding rates can be as high as 9% at 30 days and between 3% and 11% in the first year, only a few studies have applied existing scores to TAVR patients, he noted.
The PREDICT-TAVR score includes six common variables and can be calculated by hand using a simple nomogram or a web-based calculator, with a dedicated website in the works, said Dr. Navarese, Nicolaus Copernicus University and SIRO MEDICINE Network, Bydgoszcz, Poland, and the University of Alberta, Edmonton.
A strength of the score is that machine-learning methods were used and the choice of variables optimized through recursive feature elimination and cross validation to remove the weakest variables, he said. Artificial intelligence, including use of random forest, naïve Bayes, and logistic regression classifiers, was also applied to the algorithms and the results cross-checked with standard multivariate analysis.
“It was a tremendous effort in terms of the analytics conducted,” Dr. Navarese said. “This is not a simple score but the integration of the most sophisticated machine learning methods and algorithms.”
Details are published in the June 14 issue of JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The six variables used to calculate 30-day bleeding risk after TAVR and the points assigned to each are:
- blood hemoglobin (0-10 points)
- serum iron concentration (0-5 points)
- common femoral artery diameter (0-3 points)
- (0-3 points)
- dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT; 0-2 points)
- oral anticoagulation therapy (0-2 points)
The six items were selected among 104 baseline variables from 5,185 consecutive patients undergoing transfemoral TAVR in the prospective RISPEVA (Registro Italiano GISE sull’Impianto di Valvola Aortica Percutanea) registry between March 2012 and December 2019, then validated in 5,043 patients in the prospective POL-TAVI (Polish Registry of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) between January 2013 and December 2019.
In the derivation cohort, 216 patients (4.2%) experienced bleeding events at 1 year, with 169 events (78%) occurring during the first 30 days.
PREDICT-TAVR exhibited high discriminatory power for bleeding events at 30 days, as reflected by an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.80 (95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.83). Internal validation by optimism bootstrap-corrected AUC was consistent at 0.79 (95% CI, 0.75-0.83).
PREDICT-TAVR also outperformed scores not developed for TAVR, such as the PARIS score for patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (AUC, 0.69) and the well-validated HAS-BLED for patients receiving anticoagulation (AUC, 0.58; P < .001 for both).
In the validation cohort, the AUC for bleeding complications at 30 days was 0.78 (95% CI, 0.72-0.82) versus an AUC of 0.68 for PARIS and 0.66 for HAS-BLED.
A HAS-BLED score of 4 predicted a higher rate of severe bleeding and mortality in the year after transfemoral TAVR in the 2018 Japanese OCEAN-TAVI study.
Bleeding events by risk categories
Risk score quartiles identified as low risk were 8 points or less, as moderate risk were 8 to less than 10 points, as high risk were 10 to less than 12 points, and as very-high-risk score were above 12 points.
In the derivation cohort, 30-day bleeding events across quartiles were 0.8%, 1.1%, 2.5%, and 8.5%, respectively (overall P < .001).
Compared with the lowest quartile, bleeding risk was numerically higher for the second quartile (odds ratio, 1.75) and significantly higher in the third (OR, 2.0) and fourth (OR, 2.49) quartiles (P < .001 for both).
A landmark cumulative-event analysis showed a significantly greater risk of bleeding for the two highest quartiles up to 30 days; however, these differences were no longer significant from 30 days to 1 year, likely because of a limited number of events, the authors suggest. Similar results were seen in the validation cohort.
The number of patients in the high- and very-high-risk groups isn’t trivial, and bleeding rates reached as high as 12.6% in the highest quartile, Dr. Navarese observed. Guidelines recommend DAPT for 3 to 6 months after TAVR; however, emerging data, including a recent meta-analysis, suggest monotherapy may be a very good option.
“So, if you had a high bleeding risk and are considering postprocedural DAPT or anticoagulation, I would think twice rather than administering dual antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulation for a long time, or at least, I would consider the impact of this score on this choice,” he said.
Subgroup analyses showed AUCs ranging from 0.77 to 0.81 for subgroups such as age older than 80 years, diabetes, obesity, female sex, previous PCI, and New York Heart Association class III or IV.
Serum iron showed the highest AUC in the primary PREDICT-TAVR model; however, should iron levels be unavailable, a simplified score modeled without iron levels retained predictive power, yielding AUCs for 30-day bleeding of 0.78 in the derivation cohort and 0.75 in the validation cohort.
“PREDICT-TAVR score can impact clinical practice, not only selecting the optimal thrombotic regimen in certain high bleeding-risk populations but also to treat pre-TAVR anemia and iron deficiencies, which may affect outcomes,” Dr. Navarese said. “Of course, future prospective biological and clinical investigations are needed to elucidate the score and the role of the score’s treatable risk traits in reducing post-TAVR bleeding complications.”
Commenting for this news organization, Sunil Rao, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., said anemia is a covariant in many risk models for bleeding and vascular complications in PCI and acute coronary syndrome, but hemoglobin and iron levels are collinear.
“The problem I think is when you throw hemoglobin and iron in the same model, just by play of chance, one variable can knock out the other one,” he said. “So I don’t know necessarily if we need to start measuring iron on everyone. We certainly should be measuring hemoglobin, which I think most people will have, and if a patient has pre-existing anemia, that should be a red flag for us.”
Age and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score did not reach statistical significance in the model – likely reflecting the high-/extremely-high-risk patient population with an average STS score of 7.7 and average age of 82 years – but may become more important as TAVR is applied more widely, Dr. Rao and Zachary Wegermann, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, write in an accompanying editorial.
They also point out that the study was limited by a low rate of bleeding events, and, importantly, the score can’t distinguish between minor or major bleeding.
“It’s worth trying to repeat the analyses in lower-risk patients because we may find other covariates that are important,” Dr. Rao said in an interview. “The other thing we need to get to is probably being a little bit more sophisticated. The variables included in these models are the ones that are measured; they’re also the ones that are clinically apparent.”
“But there’s a whole area of genomic medicine, proteomic medicine, metabolomic medicine that, as it starts developing and becomes more and more sophisticated, my suspicion is that we’re going to get even more precise and accurate about patients’ risk, and it’s going to become more individualized, rather than just measuring variables like age and lab values,” he said.
In the meantime, having variables documented in the electronic health record, with hard stops deployed if variables aren’t measured, is “a step in the right direction,” he added.
Dr. Navarese has received research grants from Abbott, Amgen, and Medtronic and received lecture fees and honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Pfizer, and Sanofi-Regeneron, outside the submitted work. Dr. Rao and Dr. Wegermann report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(TAVR).
“Despite the TAVR iterations, we recognize that bleeding remains a very important and perhaps also neglected issue. Indeed, no specifically developed standard algorithm existed before this to assess bleeding risk post-TAVR,” lead author Eliano Pio Navarese, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Although bleeding rates can be as high as 9% at 30 days and between 3% and 11% in the first year, only a few studies have applied existing scores to TAVR patients, he noted.
The PREDICT-TAVR score includes six common variables and can be calculated by hand using a simple nomogram or a web-based calculator, with a dedicated website in the works, said Dr. Navarese, Nicolaus Copernicus University and SIRO MEDICINE Network, Bydgoszcz, Poland, and the University of Alberta, Edmonton.
A strength of the score is that machine-learning methods were used and the choice of variables optimized through recursive feature elimination and cross validation to remove the weakest variables, he said. Artificial intelligence, including use of random forest, naïve Bayes, and logistic regression classifiers, was also applied to the algorithms and the results cross-checked with standard multivariate analysis.
“It was a tremendous effort in terms of the analytics conducted,” Dr. Navarese said. “This is not a simple score but the integration of the most sophisticated machine learning methods and algorithms.”
Details are published in the June 14 issue of JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The six variables used to calculate 30-day bleeding risk after TAVR and the points assigned to each are:
- blood hemoglobin (0-10 points)
- serum iron concentration (0-5 points)
- common femoral artery diameter (0-3 points)
- (0-3 points)
- dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT; 0-2 points)
- oral anticoagulation therapy (0-2 points)
The six items were selected among 104 baseline variables from 5,185 consecutive patients undergoing transfemoral TAVR in the prospective RISPEVA (Registro Italiano GISE sull’Impianto di Valvola Aortica Percutanea) registry between March 2012 and December 2019, then validated in 5,043 patients in the prospective POL-TAVI (Polish Registry of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) between January 2013 and December 2019.
In the derivation cohort, 216 patients (4.2%) experienced bleeding events at 1 year, with 169 events (78%) occurring during the first 30 days.
PREDICT-TAVR exhibited high discriminatory power for bleeding events at 30 days, as reflected by an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.80 (95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.83). Internal validation by optimism bootstrap-corrected AUC was consistent at 0.79 (95% CI, 0.75-0.83).
PREDICT-TAVR also outperformed scores not developed for TAVR, such as the PARIS score for patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (AUC, 0.69) and the well-validated HAS-BLED for patients receiving anticoagulation (AUC, 0.58; P < .001 for both).
In the validation cohort, the AUC for bleeding complications at 30 days was 0.78 (95% CI, 0.72-0.82) versus an AUC of 0.68 for PARIS and 0.66 for HAS-BLED.
A HAS-BLED score of 4 predicted a higher rate of severe bleeding and mortality in the year after transfemoral TAVR in the 2018 Japanese OCEAN-TAVI study.
Bleeding events by risk categories
Risk score quartiles identified as low risk were 8 points or less, as moderate risk were 8 to less than 10 points, as high risk were 10 to less than 12 points, and as very-high-risk score were above 12 points.
In the derivation cohort, 30-day bleeding events across quartiles were 0.8%, 1.1%, 2.5%, and 8.5%, respectively (overall P < .001).
Compared with the lowest quartile, bleeding risk was numerically higher for the second quartile (odds ratio, 1.75) and significantly higher in the third (OR, 2.0) and fourth (OR, 2.49) quartiles (P < .001 for both).
A landmark cumulative-event analysis showed a significantly greater risk of bleeding for the two highest quartiles up to 30 days; however, these differences were no longer significant from 30 days to 1 year, likely because of a limited number of events, the authors suggest. Similar results were seen in the validation cohort.
The number of patients in the high- and very-high-risk groups isn’t trivial, and bleeding rates reached as high as 12.6% in the highest quartile, Dr. Navarese observed. Guidelines recommend DAPT for 3 to 6 months after TAVR; however, emerging data, including a recent meta-analysis, suggest monotherapy may be a very good option.
“So, if you had a high bleeding risk and are considering postprocedural DAPT or anticoagulation, I would think twice rather than administering dual antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulation for a long time, or at least, I would consider the impact of this score on this choice,” he said.
Subgroup analyses showed AUCs ranging from 0.77 to 0.81 for subgroups such as age older than 80 years, diabetes, obesity, female sex, previous PCI, and New York Heart Association class III or IV.
Serum iron showed the highest AUC in the primary PREDICT-TAVR model; however, should iron levels be unavailable, a simplified score modeled without iron levels retained predictive power, yielding AUCs for 30-day bleeding of 0.78 in the derivation cohort and 0.75 in the validation cohort.
“PREDICT-TAVR score can impact clinical practice, not only selecting the optimal thrombotic regimen in certain high bleeding-risk populations but also to treat pre-TAVR anemia and iron deficiencies, which may affect outcomes,” Dr. Navarese said. “Of course, future prospective biological and clinical investigations are needed to elucidate the score and the role of the score’s treatable risk traits in reducing post-TAVR bleeding complications.”
Commenting for this news organization, Sunil Rao, MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., said anemia is a covariant in many risk models for bleeding and vascular complications in PCI and acute coronary syndrome, but hemoglobin and iron levels are collinear.
“The problem I think is when you throw hemoglobin and iron in the same model, just by play of chance, one variable can knock out the other one,” he said. “So I don’t know necessarily if we need to start measuring iron on everyone. We certainly should be measuring hemoglobin, which I think most people will have, and if a patient has pre-existing anemia, that should be a red flag for us.”
Age and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score did not reach statistical significance in the model – likely reflecting the high-/extremely-high-risk patient population with an average STS score of 7.7 and average age of 82 years – but may become more important as TAVR is applied more widely, Dr. Rao and Zachary Wegermann, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, write in an accompanying editorial.
They also point out that the study was limited by a low rate of bleeding events, and, importantly, the score can’t distinguish between minor or major bleeding.
“It’s worth trying to repeat the analyses in lower-risk patients because we may find other covariates that are important,” Dr. Rao said in an interview. “The other thing we need to get to is probably being a little bit more sophisticated. The variables included in these models are the ones that are measured; they’re also the ones that are clinically apparent.”
“But there’s a whole area of genomic medicine, proteomic medicine, metabolomic medicine that, as it starts developing and becomes more and more sophisticated, my suspicion is that we’re going to get even more precise and accurate about patients’ risk, and it’s going to become more individualized, rather than just measuring variables like age and lab values,” he said.
In the meantime, having variables documented in the electronic health record, with hard stops deployed if variables aren’t measured, is “a step in the right direction,” he added.
Dr. Navarese has received research grants from Abbott, Amgen, and Medtronic and received lecture fees and honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Pfizer, and Sanofi-Regeneron, outside the submitted work. Dr. Rao and Dr. Wegermann report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.