User login
Fresh data confirm healthy plant foods link to lower diabetes risk
A scientific analysis of metabolites from plant-based-diets – especially those rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables – may in the future yield clues as to how such eating patterns lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, finds a new study of more than 8,000 people.
The research looked at healthy, unhealthy, and overall plant-based diets, but only metabolic profiles for the healthy and overall plant-based diets showed an inverse relationship with type 2 diabetes.
A primarily “unhealthy” plant-based diet was one including mainly refined grains (e.g., white bread and pasta), fruit juices, potatoes, sugar-sweetened beverages, and sweets/desserts.
“Individual metabolites from consumption of polyphenol-rich plant foods like fruits, vegetables, coffee, and legumes are all closely linked to healthy plant-based diet and lower risk of diabetes,” lead author Frank Hu, MD, said in a press release.
Dr. Hu, of the department of nutrition at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues reported their findings in Diabetologia.
High-throughput profiling of the metabolome
Given that an individual’s metabolic profile reflects their diet, there is a growing trend in nutritional research to use a technique called high-throughput metabolomics to profile biological samples.
The team conducted an analysis of blood plasma samples and dietary intake using food frequency questionnaires of 10,684 participants from three prospective cohorts (Nurses’ Health Study, Nurses’ Health Study II, and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study). Participants were predominantly White and middle-aged (mean age 54 years), with a mean body mass index of 25.6 kg/m2.
Metabolite profile scores were generated from the blood samples, taken in the 1980s and 1990s, and matched to any cases of incident type 2 diabetes reported during follow-up, which ended in 2016-2017.
The team looked at three different plant-based diets – by definition, higher in plant foods and lower in animal foods – and further categorized them according to the actual foods consumed, to generate an overall plant diet index (PDI), a healthy PDI, or an unhealthy PDI.
In all, 8,827 participants completed the study, and 270 cases of diabetes were reported.
Multi-metabolite profiles were composed of 55 metabolites for the overall PDI, 93 metabolites for healthy PDI, and 75 metabolites for unhealthy PDI.
The findings are that metabolomics can be harnessed and “the identified metabolic profiles could be used to assess adherence to ... plant-based diets as part of type 2 diabetes prevention ... and provide new insights for future investigation,” the researchers concluded.
One coauthor received research support from the California Walnut Commission and Swiss ReManagement; another reported being a scientific consultant to LayerIV. The other authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A scientific analysis of metabolites from plant-based-diets – especially those rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables – may in the future yield clues as to how such eating patterns lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, finds a new study of more than 8,000 people.
The research looked at healthy, unhealthy, and overall plant-based diets, but only metabolic profiles for the healthy and overall plant-based diets showed an inverse relationship with type 2 diabetes.
A primarily “unhealthy” plant-based diet was one including mainly refined grains (e.g., white bread and pasta), fruit juices, potatoes, sugar-sweetened beverages, and sweets/desserts.
“Individual metabolites from consumption of polyphenol-rich plant foods like fruits, vegetables, coffee, and legumes are all closely linked to healthy plant-based diet and lower risk of diabetes,” lead author Frank Hu, MD, said in a press release.
Dr. Hu, of the department of nutrition at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues reported their findings in Diabetologia.
High-throughput profiling of the metabolome
Given that an individual’s metabolic profile reflects their diet, there is a growing trend in nutritional research to use a technique called high-throughput metabolomics to profile biological samples.
The team conducted an analysis of blood plasma samples and dietary intake using food frequency questionnaires of 10,684 participants from three prospective cohorts (Nurses’ Health Study, Nurses’ Health Study II, and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study). Participants were predominantly White and middle-aged (mean age 54 years), with a mean body mass index of 25.6 kg/m2.
Metabolite profile scores were generated from the blood samples, taken in the 1980s and 1990s, and matched to any cases of incident type 2 diabetes reported during follow-up, which ended in 2016-2017.
The team looked at three different plant-based diets – by definition, higher in plant foods and lower in animal foods – and further categorized them according to the actual foods consumed, to generate an overall plant diet index (PDI), a healthy PDI, or an unhealthy PDI.
In all, 8,827 participants completed the study, and 270 cases of diabetes were reported.
Multi-metabolite profiles were composed of 55 metabolites for the overall PDI, 93 metabolites for healthy PDI, and 75 metabolites for unhealthy PDI.
The findings are that metabolomics can be harnessed and “the identified metabolic profiles could be used to assess adherence to ... plant-based diets as part of type 2 diabetes prevention ... and provide new insights for future investigation,” the researchers concluded.
One coauthor received research support from the California Walnut Commission and Swiss ReManagement; another reported being a scientific consultant to LayerIV. The other authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A scientific analysis of metabolites from plant-based-diets – especially those rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables – may in the future yield clues as to how such eating patterns lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, finds a new study of more than 8,000 people.
The research looked at healthy, unhealthy, and overall plant-based diets, but only metabolic profiles for the healthy and overall plant-based diets showed an inverse relationship with type 2 diabetes.
A primarily “unhealthy” plant-based diet was one including mainly refined grains (e.g., white bread and pasta), fruit juices, potatoes, sugar-sweetened beverages, and sweets/desserts.
“Individual metabolites from consumption of polyphenol-rich plant foods like fruits, vegetables, coffee, and legumes are all closely linked to healthy plant-based diet and lower risk of diabetes,” lead author Frank Hu, MD, said in a press release.
Dr. Hu, of the department of nutrition at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues reported their findings in Diabetologia.
High-throughput profiling of the metabolome
Given that an individual’s metabolic profile reflects their diet, there is a growing trend in nutritional research to use a technique called high-throughput metabolomics to profile biological samples.
The team conducted an analysis of blood plasma samples and dietary intake using food frequency questionnaires of 10,684 participants from three prospective cohorts (Nurses’ Health Study, Nurses’ Health Study II, and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study). Participants were predominantly White and middle-aged (mean age 54 years), with a mean body mass index of 25.6 kg/m2.
Metabolite profile scores were generated from the blood samples, taken in the 1980s and 1990s, and matched to any cases of incident type 2 diabetes reported during follow-up, which ended in 2016-2017.
The team looked at three different plant-based diets – by definition, higher in plant foods and lower in animal foods – and further categorized them according to the actual foods consumed, to generate an overall plant diet index (PDI), a healthy PDI, or an unhealthy PDI.
In all, 8,827 participants completed the study, and 270 cases of diabetes were reported.
Multi-metabolite profiles were composed of 55 metabolites for the overall PDI, 93 metabolites for healthy PDI, and 75 metabolites for unhealthy PDI.
The findings are that metabolomics can be harnessed and “the identified metabolic profiles could be used to assess adherence to ... plant-based diets as part of type 2 diabetes prevention ... and provide new insights for future investigation,” the researchers concluded.
One coauthor received research support from the California Walnut Commission and Swiss ReManagement; another reported being a scientific consultant to LayerIV. The other authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETOLOGIA
Children with RMDs not at high risk for severe COVID-19, study finds
The of short-term COVID-19 outcomes in this patient group to date.
In the study, only 1 in 15 (7%) children and young people (younger than 19 years) with RMDs and COVID-19 were hospitalized, and even then, they experienced only mild symptoms; 4 of 5 of those hospitalized did not require supplemental oxygen or ventilatory support.
The study also found that those with severe systemic RMDs and obesity were more likely to be hospitalized than children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Treatment with biologics, such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, did not appear to be associated with more severe COVID-19; however, the study found that children and young people with obesity (body mass index ≥ 30) were more likely to be hospitalized, although only 6% of patients in this study had a BMI in this category. Three patients died – two from areas of lower resources who were diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) at approximately the same time they were diagnosed with COVID-19, and one with a preexisting autoinflammatory syndrome who was being treated with low-dose glucocorticoids and methotrexate.
Published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the study was led by Kimme L. Hyrich, MD, PhD, and Lianne Kearsley-Fleet, PhD, both from the University of Manchester (England). Dr. Hyrich is also a consultant rheumatologist at Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
In an interview, Dr. Hyrich explained that overall these data are reassuring and show that the majority of children and young people with RMDs are not at high risk of severe COVID-19.
“Many parents and families with children who have RMDs have lived with great fear over the pandemic about whether or not their children are at an increased risk of severe COVID-19,” said Dr. Hyrich. “Many are immunosuppressed or take other immunomodulatory medications. This has also had a great impact on schooling and children’s well-being.”
In the study, children with SLE, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), or vasculitis were more likely to have severe COVID-19. “[This] is not surprising given the typically greater systemic involvement and need for more aggressive immunosuppressive therapy than the majority of individuals with JIA,” the researchers wrote.
Dr. Hyrich added: “There may be times when children are on particularly high doses of immunosuppression or their disease is particularly active, when they may need more protection, and rheumatology teams can advise parents and young people about this.”
Studies such as those by Zimmerman and Curtis and Viner and colleagues have found that generally, children with no underlying disease are less susceptible to symptomatic COVID-19 and that reports of death are rare. Findings show that the younger the child, the less likely they will be symptomatic.
Adult data suggest a higher risk of COVID-related death among patients with arthritis, lupus, or psoriasis. A recent systematic review of the literature suggested that increased risk of COVID-related death only applies to subgroups of people with RMDs.
However, whether children and young people with RMDs are likely to have more severe COVID-19 and whether there is additional risk attributable to either their underlying disease or its therapy remain unknown. The goal of the study by Dr. Hyrich and colleagues was to address these questions.
The global analysis aimed to describe characteristics of those children and young people (younger than 19 years) with preexisting RMDs who also had COVID-19; to describe outcomes following COVID-19; and to identify characteristics associated with more severe COVID-19 outcomes.
Data were drawn from the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology COVID-19 Registry, the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry, and the CARRA-sponsored COVID-19 Global Paediatric Rheumatology Database.
Demographic information included primary RMD diagnosis; RMD disease activity (remission, low, moderate, high, or unknown); RMD treatments, including glucocorticoid use and which disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) the patient was taking at the time of COVID-19; and comorbidities (none, ocular inflammation, interstitial lung disease, asthma, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, renal disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and heart disease).
With respect to COVID-19, information collected included diagnosis date, whether the case was presumptive or confirmed, clinical symptoms, hospitalization and/or death because of COVID-19, and whether the patient stopped receiving rheumatic therapies.
Rheumatology diagnoses were categorized into four groups: JIA; SLE, MCTD, vasculitis, or other RMD; autoinflammatory syndromes; and “other,” including chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, sarcoidosis, or ocular inflammation.
Of the 607 children and young people with reported SARS-CoV-2 infection from 25 different countries (464 from the EULAR COVID-19 Registry), 499 (82%) cases were polymerase chain reaction confirmed, and 399 (66%) patients were female (median age, 14 years). Most (62%) had JIA: 37%, polyarticular JIA; 30%, oligoarticular JIA; 12%, enthesitis-related JIA; 9%, systemic JIA; 4%, psoriatic JIA; and 9%, JIA of unknown subcategory. Furthermore, 13% of patients had autoinflammatory syndromes, 8% with SLE or MCTD, 3% with vasculitis, and 2% with inflammatory myopathy.
No associations were seen between DMARD treatment (conventional-synthetic, biologic/targeted-synthetic, or combination therapy), compared with no DMARD treatment, glucocorticoid use, and hospitalization.
Owing to substantial differences in reporting of race and ethnicity between data sources, the researchers were unable to analyze whether Black, Asian, and minority ethnic groups with pediatric RMDs are at higher risk of COVID-19–related death, compared with those of White ethnicity, as has been reported for the general population.
The study also did not account for variants of SARS-CoV-2 other than to note that data were collected prior to the spread of the Omicron variant. Also, the registries did not capture vaccination status (though very few children had received vaccines at the time of data collection) or information on long COVID or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
Dr. Hyrich and Dr. Kearsley-Fleet have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The of short-term COVID-19 outcomes in this patient group to date.
In the study, only 1 in 15 (7%) children and young people (younger than 19 years) with RMDs and COVID-19 were hospitalized, and even then, they experienced only mild symptoms; 4 of 5 of those hospitalized did not require supplemental oxygen or ventilatory support.
The study also found that those with severe systemic RMDs and obesity were more likely to be hospitalized than children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Treatment with biologics, such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, did not appear to be associated with more severe COVID-19; however, the study found that children and young people with obesity (body mass index ≥ 30) were more likely to be hospitalized, although only 6% of patients in this study had a BMI in this category. Three patients died – two from areas of lower resources who were diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) at approximately the same time they were diagnosed with COVID-19, and one with a preexisting autoinflammatory syndrome who was being treated with low-dose glucocorticoids and methotrexate.
Published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the study was led by Kimme L. Hyrich, MD, PhD, and Lianne Kearsley-Fleet, PhD, both from the University of Manchester (England). Dr. Hyrich is also a consultant rheumatologist at Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
In an interview, Dr. Hyrich explained that overall these data are reassuring and show that the majority of children and young people with RMDs are not at high risk of severe COVID-19.
“Many parents and families with children who have RMDs have lived with great fear over the pandemic about whether or not their children are at an increased risk of severe COVID-19,” said Dr. Hyrich. “Many are immunosuppressed or take other immunomodulatory medications. This has also had a great impact on schooling and children’s well-being.”
In the study, children with SLE, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), or vasculitis were more likely to have severe COVID-19. “[This] is not surprising given the typically greater systemic involvement and need for more aggressive immunosuppressive therapy than the majority of individuals with JIA,” the researchers wrote.
Dr. Hyrich added: “There may be times when children are on particularly high doses of immunosuppression or their disease is particularly active, when they may need more protection, and rheumatology teams can advise parents and young people about this.”
Studies such as those by Zimmerman and Curtis and Viner and colleagues have found that generally, children with no underlying disease are less susceptible to symptomatic COVID-19 and that reports of death are rare. Findings show that the younger the child, the less likely they will be symptomatic.
Adult data suggest a higher risk of COVID-related death among patients with arthritis, lupus, or psoriasis. A recent systematic review of the literature suggested that increased risk of COVID-related death only applies to subgroups of people with RMDs.
However, whether children and young people with RMDs are likely to have more severe COVID-19 and whether there is additional risk attributable to either their underlying disease or its therapy remain unknown. The goal of the study by Dr. Hyrich and colleagues was to address these questions.
The global analysis aimed to describe characteristics of those children and young people (younger than 19 years) with preexisting RMDs who also had COVID-19; to describe outcomes following COVID-19; and to identify characteristics associated with more severe COVID-19 outcomes.
Data were drawn from the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology COVID-19 Registry, the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry, and the CARRA-sponsored COVID-19 Global Paediatric Rheumatology Database.
Demographic information included primary RMD diagnosis; RMD disease activity (remission, low, moderate, high, or unknown); RMD treatments, including glucocorticoid use and which disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) the patient was taking at the time of COVID-19; and comorbidities (none, ocular inflammation, interstitial lung disease, asthma, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, renal disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and heart disease).
With respect to COVID-19, information collected included diagnosis date, whether the case was presumptive or confirmed, clinical symptoms, hospitalization and/or death because of COVID-19, and whether the patient stopped receiving rheumatic therapies.
Rheumatology diagnoses were categorized into four groups: JIA; SLE, MCTD, vasculitis, or other RMD; autoinflammatory syndromes; and “other,” including chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, sarcoidosis, or ocular inflammation.
Of the 607 children and young people with reported SARS-CoV-2 infection from 25 different countries (464 from the EULAR COVID-19 Registry), 499 (82%) cases were polymerase chain reaction confirmed, and 399 (66%) patients were female (median age, 14 years). Most (62%) had JIA: 37%, polyarticular JIA; 30%, oligoarticular JIA; 12%, enthesitis-related JIA; 9%, systemic JIA; 4%, psoriatic JIA; and 9%, JIA of unknown subcategory. Furthermore, 13% of patients had autoinflammatory syndromes, 8% with SLE or MCTD, 3% with vasculitis, and 2% with inflammatory myopathy.
No associations were seen between DMARD treatment (conventional-synthetic, biologic/targeted-synthetic, or combination therapy), compared with no DMARD treatment, glucocorticoid use, and hospitalization.
Owing to substantial differences in reporting of race and ethnicity between data sources, the researchers were unable to analyze whether Black, Asian, and minority ethnic groups with pediatric RMDs are at higher risk of COVID-19–related death, compared with those of White ethnicity, as has been reported for the general population.
The study also did not account for variants of SARS-CoV-2 other than to note that data were collected prior to the spread of the Omicron variant. Also, the registries did not capture vaccination status (though very few children had received vaccines at the time of data collection) or information on long COVID or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
Dr. Hyrich and Dr. Kearsley-Fleet have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The of short-term COVID-19 outcomes in this patient group to date.
In the study, only 1 in 15 (7%) children and young people (younger than 19 years) with RMDs and COVID-19 were hospitalized, and even then, they experienced only mild symptoms; 4 of 5 of those hospitalized did not require supplemental oxygen or ventilatory support.
The study also found that those with severe systemic RMDs and obesity were more likely to be hospitalized than children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Treatment with biologics, such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, did not appear to be associated with more severe COVID-19; however, the study found that children and young people with obesity (body mass index ≥ 30) were more likely to be hospitalized, although only 6% of patients in this study had a BMI in this category. Three patients died – two from areas of lower resources who were diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) at approximately the same time they were diagnosed with COVID-19, and one with a preexisting autoinflammatory syndrome who was being treated with low-dose glucocorticoids and methotrexate.
Published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the study was led by Kimme L. Hyrich, MD, PhD, and Lianne Kearsley-Fleet, PhD, both from the University of Manchester (England). Dr. Hyrich is also a consultant rheumatologist at Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
In an interview, Dr. Hyrich explained that overall these data are reassuring and show that the majority of children and young people with RMDs are not at high risk of severe COVID-19.
“Many parents and families with children who have RMDs have lived with great fear over the pandemic about whether or not their children are at an increased risk of severe COVID-19,” said Dr. Hyrich. “Many are immunosuppressed or take other immunomodulatory medications. This has also had a great impact on schooling and children’s well-being.”
In the study, children with SLE, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), or vasculitis were more likely to have severe COVID-19. “[This] is not surprising given the typically greater systemic involvement and need for more aggressive immunosuppressive therapy than the majority of individuals with JIA,” the researchers wrote.
Dr. Hyrich added: “There may be times when children are on particularly high doses of immunosuppression or their disease is particularly active, when they may need more protection, and rheumatology teams can advise parents and young people about this.”
Studies such as those by Zimmerman and Curtis and Viner and colleagues have found that generally, children with no underlying disease are less susceptible to symptomatic COVID-19 and that reports of death are rare. Findings show that the younger the child, the less likely they will be symptomatic.
Adult data suggest a higher risk of COVID-related death among patients with arthritis, lupus, or psoriasis. A recent systematic review of the literature suggested that increased risk of COVID-related death only applies to subgroups of people with RMDs.
However, whether children and young people with RMDs are likely to have more severe COVID-19 and whether there is additional risk attributable to either their underlying disease or its therapy remain unknown. The goal of the study by Dr. Hyrich and colleagues was to address these questions.
The global analysis aimed to describe characteristics of those children and young people (younger than 19 years) with preexisting RMDs who also had COVID-19; to describe outcomes following COVID-19; and to identify characteristics associated with more severe COVID-19 outcomes.
Data were drawn from the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology COVID-19 Registry, the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry, and the CARRA-sponsored COVID-19 Global Paediatric Rheumatology Database.
Demographic information included primary RMD diagnosis; RMD disease activity (remission, low, moderate, high, or unknown); RMD treatments, including glucocorticoid use and which disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) the patient was taking at the time of COVID-19; and comorbidities (none, ocular inflammation, interstitial lung disease, asthma, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, renal disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and heart disease).
With respect to COVID-19, information collected included diagnosis date, whether the case was presumptive or confirmed, clinical symptoms, hospitalization and/or death because of COVID-19, and whether the patient stopped receiving rheumatic therapies.
Rheumatology diagnoses were categorized into four groups: JIA; SLE, MCTD, vasculitis, or other RMD; autoinflammatory syndromes; and “other,” including chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, sarcoidosis, or ocular inflammation.
Of the 607 children and young people with reported SARS-CoV-2 infection from 25 different countries (464 from the EULAR COVID-19 Registry), 499 (82%) cases were polymerase chain reaction confirmed, and 399 (66%) patients were female (median age, 14 years). Most (62%) had JIA: 37%, polyarticular JIA; 30%, oligoarticular JIA; 12%, enthesitis-related JIA; 9%, systemic JIA; 4%, psoriatic JIA; and 9%, JIA of unknown subcategory. Furthermore, 13% of patients had autoinflammatory syndromes, 8% with SLE or MCTD, 3% with vasculitis, and 2% with inflammatory myopathy.
No associations were seen between DMARD treatment (conventional-synthetic, biologic/targeted-synthetic, or combination therapy), compared with no DMARD treatment, glucocorticoid use, and hospitalization.
Owing to substantial differences in reporting of race and ethnicity between data sources, the researchers were unable to analyze whether Black, Asian, and minority ethnic groups with pediatric RMDs are at higher risk of COVID-19–related death, compared with those of White ethnicity, as has been reported for the general population.
The study also did not account for variants of SARS-CoV-2 other than to note that data were collected prior to the spread of the Omicron variant. Also, the registries did not capture vaccination status (though very few children had received vaccines at the time of data collection) or information on long COVID or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
Dr. Hyrich and Dr. Kearsley-Fleet have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Different variants may cause different long COVID symptoms: Study
Long COVID symptoms may differ depending on which SARS-CoV-2 variant is behind a person’s infection, a new study shows.
The data from Italy compared long COVID symptoms reported by patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 from March to December 2020 (when the original, or “Wuhan,” variant was dominant) with those reported by patients infected from January to April 2021 (B.1.1.7-, or Alpha variant-dominant). It showed a substantial change in the pattern of neurological and cognitive/emotional problems – the latter mostly seen with the Alpha variant.
Infectious disease specialist Michele Spinicci, MD, from the University of Florence and Careggi University Hospital, Italy, led the work. “Many of the symptoms reported in this study have been measured [before], but this is the first time they have been linked to different COVID-19 variants,” he told this news organization. “Findings in patients with long COVID were focused on neurological and psychological difficulties.”
However, he pointed out that much remains to be understood about long COVID in terms of symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
“Long COVID is a huge area that involves many different fields of medicine, so there is not one single piece of advice to give on management. There’s lots to consider when evaluating a long COVID patient,” he said.
Results showed that when the Alpha variant was the dominant variant, the prevalence of myalgia (10%), dyspnea (42%), brain fog/mental confusion (17%), and anxiety/depression (13%) significantly increased relative to the wild-type (original, Wuhan) variant, while anosmia (2%), dysgeusia (4%), and impaired hearing (1%) were less common.
When the wild-type (original, Wuhan) variant was dominant, fatigue (37%), insomnia (16%), dysgeusia (11%), and impaired hearing (5%) were all more common than with the Alpha variant. Dyspnea (33%), brain fog (10%), myalgia (4%), and anxiety/depression (6%) were less common.
Overall, 76% of the patients in the trial reported at least one persistent symptom, while the most common reported symptoms were dyspnea (37%) and chronic fatigue (36%), followed by insomnia (16%), visual disorders (13%), and brain fog (13%).
The findings come from an early-release abstract that will be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) 2022, in Lisbon, Portugal, in a few weeks’ time.
‘The take-home point’
Michael A. Horberg, MD, associate medical director, Kaiser Permanente – Mid-Atlantic Permanente Medical Group, Rockville, Maryland, has recently presented data on symptoms seen with long COVID in over 28,000 people, as reported by this news organization, at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2022. These people were infected with the wild-type virus.
Commenting on the study by Dr. Spinicci, he said: “The issue is that as we go along the COVID lifespan from acute to long COVID, what prompts patients to seek medical attention may change. If symptoms are not severe or were not well publicized previously, patients may not see the need to seek care or evaluation. As such, it doesn’t surprise me to find these changes over time, independent of any potential biological activity of the virus or its consequences.”
Dr. Horberg noted that their own study results are consistent with those of Dr. Spinicci et al. from March to December 2020 (original, Wuhan variant). “To me, the take-home point is long COVID is real, and physicians need to be on the lookout for it. However, not all symptoms are due to long COVID, and we need to keep the time course of symptoms during evaluation of such patients.”
Also providing comment on the findings was Debby Bogaert, MD, chair of Pediatric Medicine, University of Edinburgh. Reflecting on whether the symptoms were due to long COVID or another underlying disease, she said: “The number of patients with ongoing symptoms is very high, therefore [it is] unlikely that all of this is re-emergence of underlying or previous health problems. The type of symptoms reported are also as reported by other cohorts, so not unexpected. And irrespective of the root cause, they require care.”
Dr. Bogaert also noted that the data reiterate that COVID-19 is a new disease, and that “new variants might show shifting clinical pictures, not only regarding severity and symptoms of acute disease, but possibly also regarding sequela,” and that this, “underlines the importance of ongoing surveillance of variants, and ongoing evaluation of the acute and long-term clinical picture accompanying these, to ensure we adapt our public health approaches, clinical treatment plans, and long-term follow-up when and where needed.”
Dr. Bogaert stressed that only by keeping track of the changes in symptoms both acute and long-term – by patients and doctors – would the best patient care be provided.
“Patients need to know so they can report these back to their doctors, and doctors need to know over time that the picture of sequela might shift, so sequela are recognized early, and these patients receive the appropriate follow-up treatment,” she said. These shifting patterns might also apply to community patients as well as those hospitalized with COVID-19.
Study details
The retrospective, observational study included 428 patients, 59% men, with a mean age of 64 years, who had been treated at the Careggi University Hospital’s post-COVID outpatient service between June 2020 and June 2021, when the original form of SARS-CoV-2, and later the Alpha variant, were circulating, with some overlap.
All patients had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and discharged 4-12 weeks prior to attending the outpatient post-COVID service. They were asked to complete a questionnaire on persistent symptoms at the median of 53 days after being discharged from the hospital. In addition, data on medical history, microbiological and clinical COVID-19 course, self-reported symptoms (at the point of the follow-up visit), and patient demographics were obtained from electronic medical records.
Newer variants being studied
Upon analysis of long COVID symptoms according to treatment given during the acute phase using multivariate analysis, increasing oxygen support (odds ratio, 1.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-1.8), use of immunosuppressant drugs (OR, 6.4; 95% CI, 1.5-28), and female sex (OR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.1-2.9) were associated with a higher risk for long COVID symptoms, while patients with type 2 diabetes (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.2-0.7) had a lower risk of developing long COVID symptoms.
When asked whether the increased anxiety and depression seen with the Alpha variant might be also linked to the fact that people are living through hard times, with lockdowns, economic difficulties, possible illness, and even fatalities among family and friends due to COVID, Dr. Spinicci pointed out that “it’s a preliminary study, and there are lots of factors that we didn’t explore. It’s difficult to arrive at definite conclusions about long COVID because so much remains unknown. There are lots of external and environmental factors in the general population that might contribute to these findings.”
Dr. Spinicci has continued to enroll patients from later periods of the pandemic, including patients who were infected with the Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2.
“We’re interested in finding out if these other variants are also associated with different phenotypes of long COVID. This study is part of our follow-up program here in the hospital where lots of different specialties are following patients for 20 months,” he said.
Dr. Horberg noted that one criticism of this study is that it was unclear whether the researchers accounted for pre-existing conditions. “They note the co-morbidities in the table 1, but don’t say how they accounted for that in their analyses. We found a lot of what patients were calling ‘long COVID’ were exacerbations of co-morbidities but not a new condition.”
Dr. Spinicci and his coauthors acknowledged that the study was observational. And, as such, it does not prove cause and effect, and they could not confirm which variant of the virus caused the infection in different patients, which may limit the conclusions that can be drawn.
“Future research should focus on the potential impacts of variants of concern and vaccination status on ongoing symptoms,” Spinicci said.
Early release of an abstract will be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) 2022, in Lisbon, Portugal, April 23-26, 2022. Abstract 02768.
Dr. Spinicci and Dr. Horberg have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bogaert declared that she is on the program committee of ECCMID; she has been a member of SIGN/NICE COVID-19 rapid guideline: managing the long-term effects of COVID-19; and she is involved in multiple ongoing COVID-related studies, both acute and long-term sequela (funding MRC, CSO, ZonMw).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID symptoms may differ depending on which SARS-CoV-2 variant is behind a person’s infection, a new study shows.
The data from Italy compared long COVID symptoms reported by patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 from March to December 2020 (when the original, or “Wuhan,” variant was dominant) with those reported by patients infected from January to April 2021 (B.1.1.7-, or Alpha variant-dominant). It showed a substantial change in the pattern of neurological and cognitive/emotional problems – the latter mostly seen with the Alpha variant.
Infectious disease specialist Michele Spinicci, MD, from the University of Florence and Careggi University Hospital, Italy, led the work. “Many of the symptoms reported in this study have been measured [before], but this is the first time they have been linked to different COVID-19 variants,” he told this news organization. “Findings in patients with long COVID were focused on neurological and psychological difficulties.”
However, he pointed out that much remains to be understood about long COVID in terms of symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
“Long COVID is a huge area that involves many different fields of medicine, so there is not one single piece of advice to give on management. There’s lots to consider when evaluating a long COVID patient,” he said.
Results showed that when the Alpha variant was the dominant variant, the prevalence of myalgia (10%), dyspnea (42%), brain fog/mental confusion (17%), and anxiety/depression (13%) significantly increased relative to the wild-type (original, Wuhan) variant, while anosmia (2%), dysgeusia (4%), and impaired hearing (1%) were less common.
When the wild-type (original, Wuhan) variant was dominant, fatigue (37%), insomnia (16%), dysgeusia (11%), and impaired hearing (5%) were all more common than with the Alpha variant. Dyspnea (33%), brain fog (10%), myalgia (4%), and anxiety/depression (6%) were less common.
Overall, 76% of the patients in the trial reported at least one persistent symptom, while the most common reported symptoms were dyspnea (37%) and chronic fatigue (36%), followed by insomnia (16%), visual disorders (13%), and brain fog (13%).
The findings come from an early-release abstract that will be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) 2022, in Lisbon, Portugal, in a few weeks’ time.
‘The take-home point’
Michael A. Horberg, MD, associate medical director, Kaiser Permanente – Mid-Atlantic Permanente Medical Group, Rockville, Maryland, has recently presented data on symptoms seen with long COVID in over 28,000 people, as reported by this news organization, at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2022. These people were infected with the wild-type virus.
Commenting on the study by Dr. Spinicci, he said: “The issue is that as we go along the COVID lifespan from acute to long COVID, what prompts patients to seek medical attention may change. If symptoms are not severe or were not well publicized previously, patients may not see the need to seek care or evaluation. As such, it doesn’t surprise me to find these changes over time, independent of any potential biological activity of the virus or its consequences.”
Dr. Horberg noted that their own study results are consistent with those of Dr. Spinicci et al. from March to December 2020 (original, Wuhan variant). “To me, the take-home point is long COVID is real, and physicians need to be on the lookout for it. However, not all symptoms are due to long COVID, and we need to keep the time course of symptoms during evaluation of such patients.”
Also providing comment on the findings was Debby Bogaert, MD, chair of Pediatric Medicine, University of Edinburgh. Reflecting on whether the symptoms were due to long COVID or another underlying disease, she said: “The number of patients with ongoing symptoms is very high, therefore [it is] unlikely that all of this is re-emergence of underlying or previous health problems. The type of symptoms reported are also as reported by other cohorts, so not unexpected. And irrespective of the root cause, they require care.”
Dr. Bogaert also noted that the data reiterate that COVID-19 is a new disease, and that “new variants might show shifting clinical pictures, not only regarding severity and symptoms of acute disease, but possibly also regarding sequela,” and that this, “underlines the importance of ongoing surveillance of variants, and ongoing evaluation of the acute and long-term clinical picture accompanying these, to ensure we adapt our public health approaches, clinical treatment plans, and long-term follow-up when and where needed.”
Dr. Bogaert stressed that only by keeping track of the changes in symptoms both acute and long-term – by patients and doctors – would the best patient care be provided.
“Patients need to know so they can report these back to their doctors, and doctors need to know over time that the picture of sequela might shift, so sequela are recognized early, and these patients receive the appropriate follow-up treatment,” she said. These shifting patterns might also apply to community patients as well as those hospitalized with COVID-19.
Study details
The retrospective, observational study included 428 patients, 59% men, with a mean age of 64 years, who had been treated at the Careggi University Hospital’s post-COVID outpatient service between June 2020 and June 2021, when the original form of SARS-CoV-2, and later the Alpha variant, were circulating, with some overlap.
All patients had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and discharged 4-12 weeks prior to attending the outpatient post-COVID service. They were asked to complete a questionnaire on persistent symptoms at the median of 53 days after being discharged from the hospital. In addition, data on medical history, microbiological and clinical COVID-19 course, self-reported symptoms (at the point of the follow-up visit), and patient demographics were obtained from electronic medical records.
Newer variants being studied
Upon analysis of long COVID symptoms according to treatment given during the acute phase using multivariate analysis, increasing oxygen support (odds ratio, 1.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-1.8), use of immunosuppressant drugs (OR, 6.4; 95% CI, 1.5-28), and female sex (OR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.1-2.9) were associated with a higher risk for long COVID symptoms, while patients with type 2 diabetes (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.2-0.7) had a lower risk of developing long COVID symptoms.
When asked whether the increased anxiety and depression seen with the Alpha variant might be also linked to the fact that people are living through hard times, with lockdowns, economic difficulties, possible illness, and even fatalities among family and friends due to COVID, Dr. Spinicci pointed out that “it’s a preliminary study, and there are lots of factors that we didn’t explore. It’s difficult to arrive at definite conclusions about long COVID because so much remains unknown. There are lots of external and environmental factors in the general population that might contribute to these findings.”
Dr. Spinicci has continued to enroll patients from later periods of the pandemic, including patients who were infected with the Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2.
“We’re interested in finding out if these other variants are also associated with different phenotypes of long COVID. This study is part of our follow-up program here in the hospital where lots of different specialties are following patients for 20 months,” he said.
Dr. Horberg noted that one criticism of this study is that it was unclear whether the researchers accounted for pre-existing conditions. “They note the co-morbidities in the table 1, but don’t say how they accounted for that in their analyses. We found a lot of what patients were calling ‘long COVID’ were exacerbations of co-morbidities but not a new condition.”
Dr. Spinicci and his coauthors acknowledged that the study was observational. And, as such, it does not prove cause and effect, and they could not confirm which variant of the virus caused the infection in different patients, which may limit the conclusions that can be drawn.
“Future research should focus on the potential impacts of variants of concern and vaccination status on ongoing symptoms,” Spinicci said.
Early release of an abstract will be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) 2022, in Lisbon, Portugal, April 23-26, 2022. Abstract 02768.
Dr. Spinicci and Dr. Horberg have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bogaert declared that she is on the program committee of ECCMID; she has been a member of SIGN/NICE COVID-19 rapid guideline: managing the long-term effects of COVID-19; and she is involved in multiple ongoing COVID-related studies, both acute and long-term sequela (funding MRC, CSO, ZonMw).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID symptoms may differ depending on which SARS-CoV-2 variant is behind a person’s infection, a new study shows.
The data from Italy compared long COVID symptoms reported by patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 from March to December 2020 (when the original, or “Wuhan,” variant was dominant) with those reported by patients infected from January to April 2021 (B.1.1.7-, or Alpha variant-dominant). It showed a substantial change in the pattern of neurological and cognitive/emotional problems – the latter mostly seen with the Alpha variant.
Infectious disease specialist Michele Spinicci, MD, from the University of Florence and Careggi University Hospital, Italy, led the work. “Many of the symptoms reported in this study have been measured [before], but this is the first time they have been linked to different COVID-19 variants,” he told this news organization. “Findings in patients with long COVID were focused on neurological and psychological difficulties.”
However, he pointed out that much remains to be understood about long COVID in terms of symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
“Long COVID is a huge area that involves many different fields of medicine, so there is not one single piece of advice to give on management. There’s lots to consider when evaluating a long COVID patient,” he said.
Results showed that when the Alpha variant was the dominant variant, the prevalence of myalgia (10%), dyspnea (42%), brain fog/mental confusion (17%), and anxiety/depression (13%) significantly increased relative to the wild-type (original, Wuhan) variant, while anosmia (2%), dysgeusia (4%), and impaired hearing (1%) were less common.
When the wild-type (original, Wuhan) variant was dominant, fatigue (37%), insomnia (16%), dysgeusia (11%), and impaired hearing (5%) were all more common than with the Alpha variant. Dyspnea (33%), brain fog (10%), myalgia (4%), and anxiety/depression (6%) were less common.
Overall, 76% of the patients in the trial reported at least one persistent symptom, while the most common reported symptoms were dyspnea (37%) and chronic fatigue (36%), followed by insomnia (16%), visual disorders (13%), and brain fog (13%).
The findings come from an early-release abstract that will be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) 2022, in Lisbon, Portugal, in a few weeks’ time.
‘The take-home point’
Michael A. Horberg, MD, associate medical director, Kaiser Permanente – Mid-Atlantic Permanente Medical Group, Rockville, Maryland, has recently presented data on symptoms seen with long COVID in over 28,000 people, as reported by this news organization, at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2022. These people were infected with the wild-type virus.
Commenting on the study by Dr. Spinicci, he said: “The issue is that as we go along the COVID lifespan from acute to long COVID, what prompts patients to seek medical attention may change. If symptoms are not severe or were not well publicized previously, patients may not see the need to seek care or evaluation. As such, it doesn’t surprise me to find these changes over time, independent of any potential biological activity of the virus or its consequences.”
Dr. Horberg noted that their own study results are consistent with those of Dr. Spinicci et al. from March to December 2020 (original, Wuhan variant). “To me, the take-home point is long COVID is real, and physicians need to be on the lookout for it. However, not all symptoms are due to long COVID, and we need to keep the time course of symptoms during evaluation of such patients.”
Also providing comment on the findings was Debby Bogaert, MD, chair of Pediatric Medicine, University of Edinburgh. Reflecting on whether the symptoms were due to long COVID or another underlying disease, she said: “The number of patients with ongoing symptoms is very high, therefore [it is] unlikely that all of this is re-emergence of underlying or previous health problems. The type of symptoms reported are also as reported by other cohorts, so not unexpected. And irrespective of the root cause, they require care.”
Dr. Bogaert also noted that the data reiterate that COVID-19 is a new disease, and that “new variants might show shifting clinical pictures, not only regarding severity and symptoms of acute disease, but possibly also regarding sequela,” and that this, “underlines the importance of ongoing surveillance of variants, and ongoing evaluation of the acute and long-term clinical picture accompanying these, to ensure we adapt our public health approaches, clinical treatment plans, and long-term follow-up when and where needed.”
Dr. Bogaert stressed that only by keeping track of the changes in symptoms both acute and long-term – by patients and doctors – would the best patient care be provided.
“Patients need to know so they can report these back to their doctors, and doctors need to know over time that the picture of sequela might shift, so sequela are recognized early, and these patients receive the appropriate follow-up treatment,” she said. These shifting patterns might also apply to community patients as well as those hospitalized with COVID-19.
Study details
The retrospective, observational study included 428 patients, 59% men, with a mean age of 64 years, who had been treated at the Careggi University Hospital’s post-COVID outpatient service between June 2020 and June 2021, when the original form of SARS-CoV-2, and later the Alpha variant, were circulating, with some overlap.
All patients had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and discharged 4-12 weeks prior to attending the outpatient post-COVID service. They were asked to complete a questionnaire on persistent symptoms at the median of 53 days after being discharged from the hospital. In addition, data on medical history, microbiological and clinical COVID-19 course, self-reported symptoms (at the point of the follow-up visit), and patient demographics were obtained from electronic medical records.
Newer variants being studied
Upon analysis of long COVID symptoms according to treatment given during the acute phase using multivariate analysis, increasing oxygen support (odds ratio, 1.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-1.8), use of immunosuppressant drugs (OR, 6.4; 95% CI, 1.5-28), and female sex (OR, 1.8; 95% CI, 1.1-2.9) were associated with a higher risk for long COVID symptoms, while patients with type 2 diabetes (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.2-0.7) had a lower risk of developing long COVID symptoms.
When asked whether the increased anxiety and depression seen with the Alpha variant might be also linked to the fact that people are living through hard times, with lockdowns, economic difficulties, possible illness, and even fatalities among family and friends due to COVID, Dr. Spinicci pointed out that “it’s a preliminary study, and there are lots of factors that we didn’t explore. It’s difficult to arrive at definite conclusions about long COVID because so much remains unknown. There are lots of external and environmental factors in the general population that might contribute to these findings.”
Dr. Spinicci has continued to enroll patients from later periods of the pandemic, including patients who were infected with the Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2.
“We’re interested in finding out if these other variants are also associated with different phenotypes of long COVID. This study is part of our follow-up program here in the hospital where lots of different specialties are following patients for 20 months,” he said.
Dr. Horberg noted that one criticism of this study is that it was unclear whether the researchers accounted for pre-existing conditions. “They note the co-morbidities in the table 1, but don’t say how they accounted for that in their analyses. We found a lot of what patients were calling ‘long COVID’ were exacerbations of co-morbidities but not a new condition.”
Dr. Spinicci and his coauthors acknowledged that the study was observational. And, as such, it does not prove cause and effect, and they could not confirm which variant of the virus caused the infection in different patients, which may limit the conclusions that can be drawn.
“Future research should focus on the potential impacts of variants of concern and vaccination status on ongoing symptoms,” Spinicci said.
Early release of an abstract will be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) 2022, in Lisbon, Portugal, April 23-26, 2022. Abstract 02768.
Dr. Spinicci and Dr. Horberg have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bogaert declared that she is on the program committee of ECCMID; she has been a member of SIGN/NICE COVID-19 rapid guideline: managing the long-term effects of COVID-19; and she is involved in multiple ongoing COVID-related studies, both acute and long-term sequela (funding MRC, CSO, ZonMw).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CROI 2022
Inside insulin (Part 2): Approaching a cure for type 1 diabetes?
Editor’s note: This is the second in a two-part series commemorating the 100-year anniversary of the first use of insulin in humans. Part 1 of this series examined the rivalry behind the discovery and use of insulin.
One hundred years ago, teenager Leonard Thompson was the first patient with type 1 diabetes to be successfully treated with insulin, granting him a reprieve from what was a certain death sentence at the time.
Since then, research has gathered pace. In the century since insulin’s discovery and first use, recombinant DNA technology has allowed for the engineering of the insulin molecule, providing numerous short- and long-acting analog versions. At the same time, technological leaps in automated insulin delivery and monitoring of blood glucose ensure more time with glucose in range and fewer life-threatening complications for those with type 1 diabetes fortunate enough to have access to the technology.
In spite of these advancements, there is still scope for further evolution of disease management, with the holy grail being the transplant of stem cell–derived islet cells capable of making insulin, ideally encased in some kind of protective device so that immunosuppression is not required.
Indeed, it is not unreasonable to “hope that type 1 diabetes will be a curable disease in the next 100 years,” said Elizabeth Stephens, MD, an endocrinologist who has type 1 diabetes and practices in Portland, Ore.
Type 1 diabetes: The past 100 years
The epidemiology of type 1 diabetes has shifted considerably since 1922. A century ago, given that average life expectancy in the United States was around 54 years, it was pretty much the only type of diabetes that doctors encountered. “There was some type 2 diabetes about in heavier people, but the focus was on type 1 diabetes,” noted Dr. Stephens.
Originally called juvenile diabetes because it was thought to only occur in children, “now 50% of people are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes ... over [the age of] 20,” explained Dr. Stephens.
In the United States, around 1.4 million adults 20 years and older, and 187,000 children younger than 20, have the disease, according to data from the National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This total represents an increase of nearly 30% from 2017.
Over the years, theories as to the cause, or trigger, for type 1 diabetes “have included cow’s milk and [viral] infections,” said Dr. Stephens. “Most likely, there’s a genetic predisposition and some type of exposure, which creates the perfect storm to trigger disease.”
There are hints that COVID-19 might be precipitating type 1 diabetes in some people. Recently, the CDC found SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes (all types) among youth, but not other acute respiratory infections. And two further studies from different parts of the world have recently identified an increase in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in children since the COVID-19 pandemic began, but the reasons remain unclear.
The global CoviDiab registry has also been established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes.
The million-dollar question: Is COVID-19 itself is propagating type 1 diabetes or unmasking a predisposition to the disease sooner? The latter might be associated with a lower type 1 diabetes rate in the future, said Partha Kar, MBBS, OBE, national specialty advisor, diabetes, for National Health Service England.
“Right now, we don’t know the answer. Whichever way you look at it, it is likely there will be a rise in cases, and in countries where insulin is not freely available, healthcare systems need to have supply ready because insulin is lifesaving in type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Kar emphasized.
CGMs and automated insulin delivery: A ‘godsend’
A huge change has also been seen, most notably in the past 15 to 20 years, in the technological advancements that can help those with type 1 diabetes live an easier life.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and automated ways of delivering insulin, such as smart pens and insulin pumps, have made the daily life of a person with type 1 diabetes in the Western world considerably more comfortable.
CGMs provide a constant stream of data to an app, often wirelessly in sync with the insulin pump. However, on a global level, they are only available to a lucky few.
In England, pending National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) approval, any CGM should be available to all eligible patients with type 1 diabetes within the NHS from April 2022, Dr. Kar pointed out. In the United States, CGMs are often unaffordable and access is mostly dependent on a person’s health insurance.
Kersten Hall, PhD, a scientist and U.K.-based medical historian who recently wrote a book, “Insulin, the Crooked Timber” (Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2022) uncovering the lesser-known story behind the discovery of insulin, was diagnosed with adult-onset type 1 diabetes at the age of 41. Dr. Hall had always found the finger-prick blood glucose test to be a chore but now has a CGM.
“It’s a total game changer for me: a godsend. I can’t sing its praises enough,” he said. “All it involves is the swipe of the phone and this provides a reading which tells me if my glucose is too low, so I eat something, or too high, so I might [go for] a run.”
Brewing insulin at scale
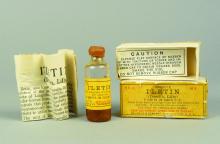
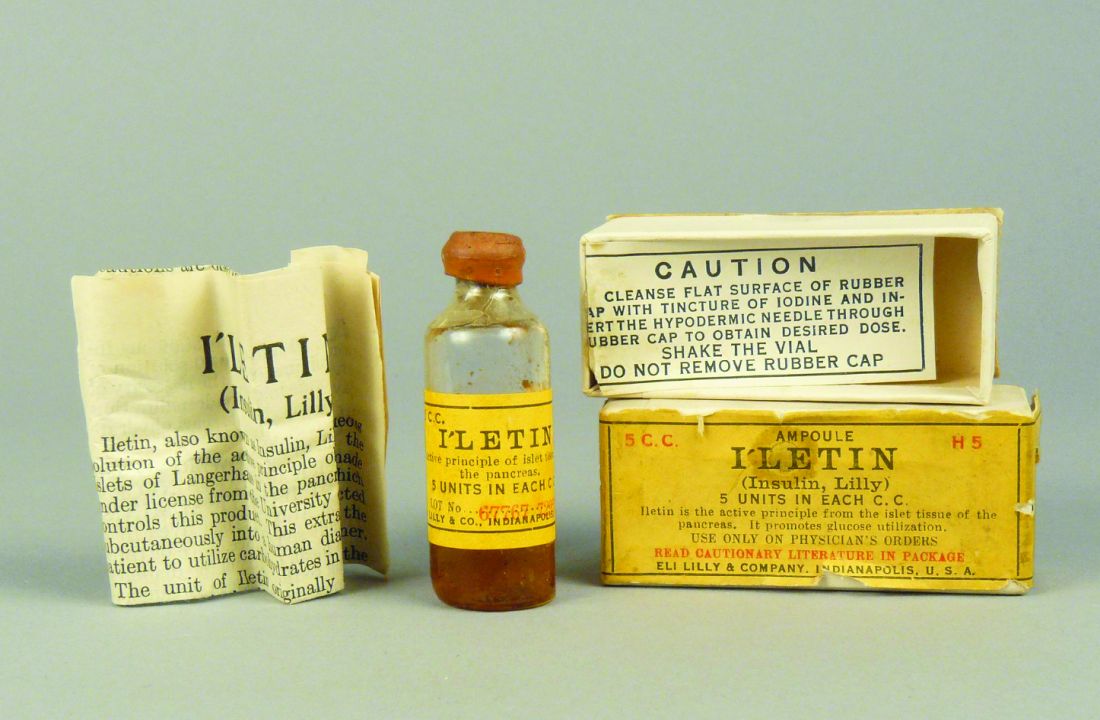
As described by Dr. Hall in his book, the journey from treating Mr. Thompson in 1922 to treating the masses began when biochemist James Collip, MD, PhD, discovered a means of purifying the animal pancreas extracts used to treat the teenager.
But production at scale presented a further challenge. This was overcome in 1924 when Eli Lilly drew on a technique used in the beer brewing process – where pH guides bitterness – to purify and manufacture large amounts of insulin.
By 1936, a range of slower-acting cattle and pig-derived insulins, the first produced by Novo Nordisk Pharmaceuticals, were developed.
However, it took 8,000 lb (approximately 3,600 kg) of pancreas glands from 23,500 animals to make 1 lb (0.5 kg) of insulin, so a more efficient process was badly needed.
Dr. Hall, who is a molecular biologist as well as an author, explains that the use of recombinant DNA technology to produce human insulin, as done by Genentech in the late 70s, was a key development in the story of modern insulin products. Genentech then provided synthetic human insulin for Eli Lilly to conduct clinical trials.
Human insulin most closely resembles porcine insulin structure and function, differing by only one amino acid, while human insulin differs from bovine insulin by three amino acid residues. This synthetic human insulin eliminated the allergies that the animal-derived products sometimes caused.
In the early 1980s, Eli Lilly produced Humulin, the first biosynthetic (made in Escherichia coli, hence the term, “bio”) human insulin.
This technology eventually “allowed for the alteration of specific amino acids in the sequence of the insulin protein to make insulin analogs [synthetic versions grown in E. coli and genetically altered for various properties] that act faster, or more slowly, than normal human insulin. By using the slow- and fast-acting insulins in combination, a patient can control their blood sugar levels with a much greater degree of finesse and precision,” Dr. Hall explained.
Today, a whole range of insulins are available, including ultra–rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, long-acting, ultra–long-acting, and even inhaled insulin, although the latter is expensive, has been associated with side effects, and is less commonly used, according to Dr. Stephens.
Oral insulin formulations are even in the early stages of development, with candidate drugs by Generex and from the Oralis project.
“With insulin therapy, we try to reproduce the normal physiology of the healthy body and pancreas,” Dr. Stephens explained.
Insulin analogs are only made by three companies (Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi), and they are generally much more expensive than nonanalog human insulin. In the United Kingdom through the NHS, they cost twice as much.
In the United States today, one of the biggest barriers to proper care of type 1 diabetes is the cost of insulin, which can limit access. With the market controlled by these three large companies, the average cost of a unit of insulin in the United States, according to RAND research, was $98.17 in January 2021, compared with $7.52 in the United Kingdom and $12.00 in Canada.
Several U.S. states have enacted legislation capping insulin copayments to at, or under, $100 a month. But the federal Build Back Better Framework Act – which would cap copayments for insulin at $35 – currently hangs in the balance.
Alongside these moves, in 2020 the Food and Drug Administration approved the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin for type 1 diabetes (and insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes) in children and adults, called Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals).
Biosimilars (essentially generic versions of branded insulins) are expected to be less expensive than branded analogs, but the indications so far are that they will only be around 20% cheaper.
“I totally fail to understand how the richest country in the world still has a debate about price caps, and we are looking at biosimilar markets to change the debate. This makes no sense to me at all,” stressed Dr. Kar. “For lifesaving drugs, they should be funded by the state.”
Insulin also remains unaffordable for many in numerous low- and middle-income countries, where most patients pay out-of-pocket for medicines. Globally, there are estimated to be around 30 million people who need insulin but cannot afford it.
How near to a cure in the coming decades?
Looking ahead to the coming years, if not the next 100, Dr. Stephens highlighted two important aspects of care.
First, the use of a CGM device in combination with an insulin pump (also known as a closed-loop system or artificial pancreas), where the CGM effectively tells the insulin pump how much insulin to automatically dispense, should revolutionize care.
A number of such closed-loop systems have recently been approved in both the United States, including systems from Medtronic and Omnipod, and Europe.
“I wear one of these and it’s been a life changer for me, but it doesn’t suit everyone because the technology can be cumbersome, but with time, hopefully things will become smaller and more accurate in insulin delivery,” Dr. Stephens added.
The second advance of interest is the development and transplantation of cells that produce insulin.
Dr. Stephens explained that someone living with type 1 diabetes has a lot to think about, not least, doing the math related to insulin requirement. “If we just had cells from a pancreas that could be transplanted and would do that for us, then it would be a total game changer.”
To date, Vertex Pharmaceuticals has successfully treated one patient – who had lived with type 1 diabetes for about 40 years and had recurrent episodes of severe hypoglycemia – with an infusion of stem cell–derived differentiated islet cells into his liver. The procedure resulted in near reversal of type 1 diabetes, with his insulin dose reduced from 34 to 3 units, and his hemoglobin A1c falling from 8.6% to 7.2%.
And although the patient, Brian Shelton, still needs to take immunosuppressive agents to prevent rejection of the stem cell–derived islets, “it’s a whole new life,” he recently told the New York Times.
Another company called ViaCyte is also working on a similar approach.
Whether this is a cure for type 1 diabetes is still debatable, said Anne Peters, MD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “Is it true? In a word, no. But we are part of the way there, which is much closer than we were 6 months ago.”
There are also ongoing clinical trials of therapeutic interventions to prevent or delay the trajectory from presymptomatic to clinical type 1 diabetes. The most advanced is the anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody teplizumab (Tzield, Provention Bio), which was rejected by the FDA in July 2021, but has since been refiled. The company expects to hear from the agency by the end of March 2022 as to whether the resubmission has been accepted.
Diabetes specialist nurses/educators keep it human
Dr. Hall said he concurs with the late eminent U.K. diabetes specialist Robert Tattersall’s observation on what he considers one of the most important advances in the management and treatment of type 1 diabetes: the human touch.
Referring to Dr. Tattersall’s book, “Diabetes: A Biography,” Dr. Hall quoted: “If asked what innovation had made the most difference to their lives in the 1980s, patients with type 1 diabetes in England would unhesitatingly have chosen not human insulin, but the spread of diabetes specialist nurses ... these people (mainly women) did more in the last two decades of the 20th century to improve the standard of diabetes care than any other innovation or drug.”
In the United States, diabetes specialist nurses were called diabetes educators until recently, when the name changed to certified diabetes care and education specialist.
“Above all, they have humanized the service and given the patient a say in the otherwise unequal relationship with all-powerful doctors,” concluded Dr. Hall, again quoting Dr. Tattersall.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Editor’s note: This is the second in a two-part series commemorating the 100-year anniversary of the first use of insulin in humans. Part 1 of this series examined the rivalry behind the discovery and use of insulin.
One hundred years ago, teenager Leonard Thompson was the first patient with type 1 diabetes to be successfully treated with insulin, granting him a reprieve from what was a certain death sentence at the time.
Since then, research has gathered pace. In the century since insulin’s discovery and first use, recombinant DNA technology has allowed for the engineering of the insulin molecule, providing numerous short- and long-acting analog versions. At the same time, technological leaps in automated insulin delivery and monitoring of blood glucose ensure more time with glucose in range and fewer life-threatening complications for those with type 1 diabetes fortunate enough to have access to the technology.
In spite of these advancements, there is still scope for further evolution of disease management, with the holy grail being the transplant of stem cell–derived islet cells capable of making insulin, ideally encased in some kind of protective device so that immunosuppression is not required.
Indeed, it is not unreasonable to “hope that type 1 diabetes will be a curable disease in the next 100 years,” said Elizabeth Stephens, MD, an endocrinologist who has type 1 diabetes and practices in Portland, Ore.
Type 1 diabetes: The past 100 years
The epidemiology of type 1 diabetes has shifted considerably since 1922. A century ago, given that average life expectancy in the United States was around 54 years, it was pretty much the only type of diabetes that doctors encountered. “There was some type 2 diabetes about in heavier people, but the focus was on type 1 diabetes,” noted Dr. Stephens.
Originally called juvenile diabetes because it was thought to only occur in children, “now 50% of people are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes ... over [the age of] 20,” explained Dr. Stephens.
In the United States, around 1.4 million adults 20 years and older, and 187,000 children younger than 20, have the disease, according to data from the National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This total represents an increase of nearly 30% from 2017.
Over the years, theories as to the cause, or trigger, for type 1 diabetes “have included cow’s milk and [viral] infections,” said Dr. Stephens. “Most likely, there’s a genetic predisposition and some type of exposure, which creates the perfect storm to trigger disease.”
There are hints that COVID-19 might be precipitating type 1 diabetes in some people. Recently, the CDC found SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes (all types) among youth, but not other acute respiratory infections. And two further studies from different parts of the world have recently identified an increase in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in children since the COVID-19 pandemic began, but the reasons remain unclear.
The global CoviDiab registry has also been established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes.
The million-dollar question: Is COVID-19 itself is propagating type 1 diabetes or unmasking a predisposition to the disease sooner? The latter might be associated with a lower type 1 diabetes rate in the future, said Partha Kar, MBBS, OBE, national specialty advisor, diabetes, for National Health Service England.
“Right now, we don’t know the answer. Whichever way you look at it, it is likely there will be a rise in cases, and in countries where insulin is not freely available, healthcare systems need to have supply ready because insulin is lifesaving in type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Kar emphasized.
CGMs and automated insulin delivery: A ‘godsend’
A huge change has also been seen, most notably in the past 15 to 20 years, in the technological advancements that can help those with type 1 diabetes live an easier life.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and automated ways of delivering insulin, such as smart pens and insulin pumps, have made the daily life of a person with type 1 diabetes in the Western world considerably more comfortable.
CGMs provide a constant stream of data to an app, often wirelessly in sync with the insulin pump. However, on a global level, they are only available to a lucky few.
In England, pending National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) approval, any CGM should be available to all eligible patients with type 1 diabetes within the NHS from April 2022, Dr. Kar pointed out. In the United States, CGMs are often unaffordable and access is mostly dependent on a person’s health insurance.
Kersten Hall, PhD, a scientist and U.K.-based medical historian who recently wrote a book, “Insulin, the Crooked Timber” (Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2022) uncovering the lesser-known story behind the discovery of insulin, was diagnosed with adult-onset type 1 diabetes at the age of 41. Dr. Hall had always found the finger-prick blood glucose test to be a chore but now has a CGM.
“It’s a total game changer for me: a godsend. I can’t sing its praises enough,” he said. “All it involves is the swipe of the phone and this provides a reading which tells me if my glucose is too low, so I eat something, or too high, so I might [go for] a run.”
Brewing insulin at scale
As described by Dr. Hall in his book, the journey from treating Mr. Thompson in 1922 to treating the masses began when biochemist James Collip, MD, PhD, discovered a means of purifying the animal pancreas extracts used to treat the teenager.
But production at scale presented a further challenge. This was overcome in 1924 when Eli Lilly drew on a technique used in the beer brewing process – where pH guides bitterness – to purify and manufacture large amounts of insulin.
By 1936, a range of slower-acting cattle and pig-derived insulins, the first produced by Novo Nordisk Pharmaceuticals, were developed.
However, it took 8,000 lb (approximately 3,600 kg) of pancreas glands from 23,500 animals to make 1 lb (0.5 kg) of insulin, so a more efficient process was badly needed.
Dr. Hall, who is a molecular biologist as well as an author, explains that the use of recombinant DNA technology to produce human insulin, as done by Genentech in the late 70s, was a key development in the story of modern insulin products. Genentech then provided synthetic human insulin for Eli Lilly to conduct clinical trials.
Human insulin most closely resembles porcine insulin structure and function, differing by only one amino acid, while human insulin differs from bovine insulin by three amino acid residues. This synthetic human insulin eliminated the allergies that the animal-derived products sometimes caused.
In the early 1980s, Eli Lilly produced Humulin, the first biosynthetic (made in Escherichia coli, hence the term, “bio”) human insulin.
This technology eventually “allowed for the alteration of specific amino acids in the sequence of the insulin protein to make insulin analogs [synthetic versions grown in E. coli and genetically altered for various properties] that act faster, or more slowly, than normal human insulin. By using the slow- and fast-acting insulins in combination, a patient can control their blood sugar levels with a much greater degree of finesse and precision,” Dr. Hall explained.
Today, a whole range of insulins are available, including ultra–rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, long-acting, ultra–long-acting, and even inhaled insulin, although the latter is expensive, has been associated with side effects, and is less commonly used, according to Dr. Stephens.
Oral insulin formulations are even in the early stages of development, with candidate drugs by Generex and from the Oralis project.
“With insulin therapy, we try to reproduce the normal physiology of the healthy body and pancreas,” Dr. Stephens explained.
Insulin analogs are only made by three companies (Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi), and they are generally much more expensive than nonanalog human insulin. In the United Kingdom through the NHS, they cost twice as much.
In the United States today, one of the biggest barriers to proper care of type 1 diabetes is the cost of insulin, which can limit access. With the market controlled by these three large companies, the average cost of a unit of insulin in the United States, according to RAND research, was $98.17 in January 2021, compared with $7.52 in the United Kingdom and $12.00 in Canada.
Several U.S. states have enacted legislation capping insulin copayments to at, or under, $100 a month. But the federal Build Back Better Framework Act – which would cap copayments for insulin at $35 – currently hangs in the balance.
Alongside these moves, in 2020 the Food and Drug Administration approved the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin for type 1 diabetes (and insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes) in children and adults, called Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals).
Biosimilars (essentially generic versions of branded insulins) are expected to be less expensive than branded analogs, but the indications so far are that they will only be around 20% cheaper.
“I totally fail to understand how the richest country in the world still has a debate about price caps, and we are looking at biosimilar markets to change the debate. This makes no sense to me at all,” stressed Dr. Kar. “For lifesaving drugs, they should be funded by the state.”
Insulin also remains unaffordable for many in numerous low- and middle-income countries, where most patients pay out-of-pocket for medicines. Globally, there are estimated to be around 30 million people who need insulin but cannot afford it.
How near to a cure in the coming decades?
Looking ahead to the coming years, if not the next 100, Dr. Stephens highlighted two important aspects of care.
First, the use of a CGM device in combination with an insulin pump (also known as a closed-loop system or artificial pancreas), where the CGM effectively tells the insulin pump how much insulin to automatically dispense, should revolutionize care.
A number of such closed-loop systems have recently been approved in both the United States, including systems from Medtronic and Omnipod, and Europe.
“I wear one of these and it’s been a life changer for me, but it doesn’t suit everyone because the technology can be cumbersome, but with time, hopefully things will become smaller and more accurate in insulin delivery,” Dr. Stephens added.
The second advance of interest is the development and transplantation of cells that produce insulin.
Dr. Stephens explained that someone living with type 1 diabetes has a lot to think about, not least, doing the math related to insulin requirement. “If we just had cells from a pancreas that could be transplanted and would do that for us, then it would be a total game changer.”
To date, Vertex Pharmaceuticals has successfully treated one patient – who had lived with type 1 diabetes for about 40 years and had recurrent episodes of severe hypoglycemia – with an infusion of stem cell–derived differentiated islet cells into his liver. The procedure resulted in near reversal of type 1 diabetes, with his insulin dose reduced from 34 to 3 units, and his hemoglobin A1c falling from 8.6% to 7.2%.
And although the patient, Brian Shelton, still needs to take immunosuppressive agents to prevent rejection of the stem cell–derived islets, “it’s a whole new life,” he recently told the New York Times.
Another company called ViaCyte is also working on a similar approach.
Whether this is a cure for type 1 diabetes is still debatable, said Anne Peters, MD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “Is it true? In a word, no. But we are part of the way there, which is much closer than we were 6 months ago.”
There are also ongoing clinical trials of therapeutic interventions to prevent or delay the trajectory from presymptomatic to clinical type 1 diabetes. The most advanced is the anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody teplizumab (Tzield, Provention Bio), which was rejected by the FDA in July 2021, but has since been refiled. The company expects to hear from the agency by the end of March 2022 as to whether the resubmission has been accepted.
Diabetes specialist nurses/educators keep it human
Dr. Hall said he concurs with the late eminent U.K. diabetes specialist Robert Tattersall’s observation on what he considers one of the most important advances in the management and treatment of type 1 diabetes: the human touch.
Referring to Dr. Tattersall’s book, “Diabetes: A Biography,” Dr. Hall quoted: “If asked what innovation had made the most difference to their lives in the 1980s, patients with type 1 diabetes in England would unhesitatingly have chosen not human insulin, but the spread of diabetes specialist nurses ... these people (mainly women) did more in the last two decades of the 20th century to improve the standard of diabetes care than any other innovation or drug.”
In the United States, diabetes specialist nurses were called diabetes educators until recently, when the name changed to certified diabetes care and education specialist.
“Above all, they have humanized the service and given the patient a say in the otherwise unequal relationship with all-powerful doctors,” concluded Dr. Hall, again quoting Dr. Tattersall.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Editor’s note: This is the second in a two-part series commemorating the 100-year anniversary of the first use of insulin in humans. Part 1 of this series examined the rivalry behind the discovery and use of insulin.
One hundred years ago, teenager Leonard Thompson was the first patient with type 1 diabetes to be successfully treated with insulin, granting him a reprieve from what was a certain death sentence at the time.
Since then, research has gathered pace. In the century since insulin’s discovery and first use, recombinant DNA technology has allowed for the engineering of the insulin molecule, providing numerous short- and long-acting analog versions. At the same time, technological leaps in automated insulin delivery and monitoring of blood glucose ensure more time with glucose in range and fewer life-threatening complications for those with type 1 diabetes fortunate enough to have access to the technology.
In spite of these advancements, there is still scope for further evolution of disease management, with the holy grail being the transplant of stem cell–derived islet cells capable of making insulin, ideally encased in some kind of protective device so that immunosuppression is not required.
Indeed, it is not unreasonable to “hope that type 1 diabetes will be a curable disease in the next 100 years,” said Elizabeth Stephens, MD, an endocrinologist who has type 1 diabetes and practices in Portland, Ore.
Type 1 diabetes: The past 100 years
The epidemiology of type 1 diabetes has shifted considerably since 1922. A century ago, given that average life expectancy in the United States was around 54 years, it was pretty much the only type of diabetes that doctors encountered. “There was some type 2 diabetes about in heavier people, but the focus was on type 1 diabetes,” noted Dr. Stephens.
Originally called juvenile diabetes because it was thought to only occur in children, “now 50% of people are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes ... over [the age of] 20,” explained Dr. Stephens.
In the United States, around 1.4 million adults 20 years and older, and 187,000 children younger than 20, have the disease, according to data from the National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020 by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This total represents an increase of nearly 30% from 2017.
Over the years, theories as to the cause, or trigger, for type 1 diabetes “have included cow’s milk and [viral] infections,” said Dr. Stephens. “Most likely, there’s a genetic predisposition and some type of exposure, which creates the perfect storm to trigger disease.”
There are hints that COVID-19 might be precipitating type 1 diabetes in some people. Recently, the CDC found SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes (all types) among youth, but not other acute respiratory infections. And two further studies from different parts of the world have recently identified an increase in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in children since the COVID-19 pandemic began, but the reasons remain unclear.
The global CoviDiab registry has also been established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes.
The million-dollar question: Is COVID-19 itself is propagating type 1 diabetes or unmasking a predisposition to the disease sooner? The latter might be associated with a lower type 1 diabetes rate in the future, said Partha Kar, MBBS, OBE, national specialty advisor, diabetes, for National Health Service England.
“Right now, we don’t know the answer. Whichever way you look at it, it is likely there will be a rise in cases, and in countries where insulin is not freely available, healthcare systems need to have supply ready because insulin is lifesaving in type 1 diabetes,” Dr. Kar emphasized.
CGMs and automated insulin delivery: A ‘godsend’
A huge change has also been seen, most notably in the past 15 to 20 years, in the technological advancements that can help those with type 1 diabetes live an easier life.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and automated ways of delivering insulin, such as smart pens and insulin pumps, have made the daily life of a person with type 1 diabetes in the Western world considerably more comfortable.
CGMs provide a constant stream of data to an app, often wirelessly in sync with the insulin pump. However, on a global level, they are only available to a lucky few.
In England, pending National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) approval, any CGM should be available to all eligible patients with type 1 diabetes within the NHS from April 2022, Dr. Kar pointed out. In the United States, CGMs are often unaffordable and access is mostly dependent on a person’s health insurance.
Kersten Hall, PhD, a scientist and U.K.-based medical historian who recently wrote a book, “Insulin, the Crooked Timber” (Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2022) uncovering the lesser-known story behind the discovery of insulin, was diagnosed with adult-onset type 1 diabetes at the age of 41. Dr. Hall had always found the finger-prick blood glucose test to be a chore but now has a CGM.
“It’s a total game changer for me: a godsend. I can’t sing its praises enough,” he said. “All it involves is the swipe of the phone and this provides a reading which tells me if my glucose is too low, so I eat something, or too high, so I might [go for] a run.”
Brewing insulin at scale
As described by Dr. Hall in his book, the journey from treating Mr. Thompson in 1922 to treating the masses began when biochemist James Collip, MD, PhD, discovered a means of purifying the animal pancreas extracts used to treat the teenager.
But production at scale presented a further challenge. This was overcome in 1924 when Eli Lilly drew on a technique used in the beer brewing process – where pH guides bitterness – to purify and manufacture large amounts of insulin.
By 1936, a range of slower-acting cattle and pig-derived insulins, the first produced by Novo Nordisk Pharmaceuticals, were developed.
However, it took 8,000 lb (approximately 3,600 kg) of pancreas glands from 23,500 animals to make 1 lb (0.5 kg) of insulin, so a more efficient process was badly needed.
Dr. Hall, who is a molecular biologist as well as an author, explains that the use of recombinant DNA technology to produce human insulin, as done by Genentech in the late 70s, was a key development in the story of modern insulin products. Genentech then provided synthetic human insulin for Eli Lilly to conduct clinical trials.
Human insulin most closely resembles porcine insulin structure and function, differing by only one amino acid, while human insulin differs from bovine insulin by three amino acid residues. This synthetic human insulin eliminated the allergies that the animal-derived products sometimes caused.
In the early 1980s, Eli Lilly produced Humulin, the first biosynthetic (made in Escherichia coli, hence the term, “bio”) human insulin.
This technology eventually “allowed for the alteration of specific amino acids in the sequence of the insulin protein to make insulin analogs [synthetic versions grown in E. coli and genetically altered for various properties] that act faster, or more slowly, than normal human insulin. By using the slow- and fast-acting insulins in combination, a patient can control their blood sugar levels with a much greater degree of finesse and precision,” Dr. Hall explained.
Today, a whole range of insulins are available, including ultra–rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, long-acting, ultra–long-acting, and even inhaled insulin, although the latter is expensive, has been associated with side effects, and is less commonly used, according to Dr. Stephens.
Oral insulin formulations are even in the early stages of development, with candidate drugs by Generex and from the Oralis project.
“With insulin therapy, we try to reproduce the normal physiology of the healthy body and pancreas,” Dr. Stephens explained.
Insulin analogs are only made by three companies (Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi), and they are generally much more expensive than nonanalog human insulin. In the United Kingdom through the NHS, they cost twice as much.
In the United States today, one of the biggest barriers to proper care of type 1 diabetes is the cost of insulin, which can limit access. With the market controlled by these three large companies, the average cost of a unit of insulin in the United States, according to RAND research, was $98.17 in January 2021, compared with $7.52 in the United Kingdom and $12.00 in Canada.
Several U.S. states have enacted legislation capping insulin copayments to at, or under, $100 a month. But the federal Build Back Better Framework Act – which would cap copayments for insulin at $35 – currently hangs in the balance.
Alongside these moves, in 2020 the Food and Drug Administration approved the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin for type 1 diabetes (and insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes) in children and adults, called Semglee (Mylan Pharmaceuticals).
Biosimilars (essentially generic versions of branded insulins) are expected to be less expensive than branded analogs, but the indications so far are that they will only be around 20% cheaper.
“I totally fail to understand how the richest country in the world still has a debate about price caps, and we are looking at biosimilar markets to change the debate. This makes no sense to me at all,” stressed Dr. Kar. “For lifesaving drugs, they should be funded by the state.”
Insulin also remains unaffordable for many in numerous low- and middle-income countries, where most patients pay out-of-pocket for medicines. Globally, there are estimated to be around 30 million people who need insulin but cannot afford it.
How near to a cure in the coming decades?
Looking ahead to the coming years, if not the next 100, Dr. Stephens highlighted two important aspects of care.
First, the use of a CGM device in combination with an insulin pump (also known as a closed-loop system or artificial pancreas), where the CGM effectively tells the insulin pump how much insulin to automatically dispense, should revolutionize care.
A number of such closed-loop systems have recently been approved in both the United States, including systems from Medtronic and Omnipod, and Europe.
“I wear one of these and it’s been a life changer for me, but it doesn’t suit everyone because the technology can be cumbersome, but with time, hopefully things will become smaller and more accurate in insulin delivery,” Dr. Stephens added.
The second advance of interest is the development and transplantation of cells that produce insulin.
Dr. Stephens explained that someone living with type 1 diabetes has a lot to think about, not least, doing the math related to insulin requirement. “If we just had cells from a pancreas that could be transplanted and would do that for us, then it would be a total game changer.”
To date, Vertex Pharmaceuticals has successfully treated one patient – who had lived with type 1 diabetes for about 40 years and had recurrent episodes of severe hypoglycemia – with an infusion of stem cell–derived differentiated islet cells into his liver. The procedure resulted in near reversal of type 1 diabetes, with his insulin dose reduced from 34 to 3 units, and his hemoglobin A1c falling from 8.6% to 7.2%.
And although the patient, Brian Shelton, still needs to take immunosuppressive agents to prevent rejection of the stem cell–derived islets, “it’s a whole new life,” he recently told the New York Times.
Another company called ViaCyte is also working on a similar approach.
Whether this is a cure for type 1 diabetes is still debatable, said Anne Peters, MD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “Is it true? In a word, no. But we are part of the way there, which is much closer than we were 6 months ago.”
There are also ongoing clinical trials of therapeutic interventions to prevent or delay the trajectory from presymptomatic to clinical type 1 diabetes. The most advanced is the anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody teplizumab (Tzield, Provention Bio), which was rejected by the FDA in July 2021, but has since been refiled. The company expects to hear from the agency by the end of March 2022 as to whether the resubmission has been accepted.
Diabetes specialist nurses/educators keep it human
Dr. Hall said he concurs with the late eminent U.K. diabetes specialist Robert Tattersall’s observation on what he considers one of the most important advances in the management and treatment of type 1 diabetes: the human touch.
Referring to Dr. Tattersall’s book, “Diabetes: A Biography,” Dr. Hall quoted: “If asked what innovation had made the most difference to their lives in the 1980s, patients with type 1 diabetes in England would unhesitatingly have chosen not human insulin, but the spread of diabetes specialist nurses ... these people (mainly women) did more in the last two decades of the 20th century to improve the standard of diabetes care than any other innovation or drug.”
In the United States, diabetes specialist nurses were called diabetes educators until recently, when the name changed to certified diabetes care and education specialist.
“Above all, they have humanized the service and given the patient a say in the otherwise unequal relationship with all-powerful doctors,” concluded Dr. Hall, again quoting Dr. Tattersall.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The battle of egos behind the life-saving discovery of insulin
Leonard Thompson’s father was so desperate to save his 14-year-old child from certain death due to diabetes that, on Jan. 11, 1922, he took him to Toronto General Hospital to receive what is arguably the first dose of insulin given to a human. From an anticipated life expectancy of weeks – months at best – Thompson lived for an astonishing further 13 years, eventually dying from pneumonia unrelated to diabetes.
By all accounts, the story is a centenary celebration of a remarkable discovery. Insulin has changed what was once a death sentence to a near-normal life expectancy for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes over the past 100 years.
But behind the life-changing success of the discovery – and the Nobel Prize that went with it – lies a tale blighted by disputed claims, twisted truths, and likely injustices between the scientists involved, as they each vied for an honored place in medical history.
Kersten Hall, PhD, honorary fellow, religion and history of science, at the University of Leeds, England, has scoured archives and personal records held at the University of Toronto to uncover the personal stories behind insulin’s discovery.
Despite the wranglings, Dr. Hall asserts: “There’s a distinction between the science and the scientists. Scientists are wonderfully flawed and complex human beings with all their glorious virtues and vices, as we all are. It’s no surprise that they get greedy, jealous, and insecure.”
At death’s door: Diabetes before the 1920s
Prior to insulin’s discovery in 1921, a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes placed someone at death’s door, with nothing but starvation – albeit a slightly slower death – to mitigate a fast-approaching departure from this world. At that time, most diabetes cases would have been type 1 diabetes because, with less obesogenic diets and shorter lifespans, people were much less likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
Nowadays, it is widely recognized that the prevalence of type 2 diabetes is on a steep upward curve, but so too is type 1 diabetes. In the United States alone, there are 1.5 million people diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, a number expected to rise to around 5 million by 2050, according to JDRF, the type 1 diabetes advocacy organization.
Interestingly, 100 years since the first treated patient, life-long insulin remains the only real effective therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes. Once pancreatic beta cells have ceased to function and insulin production has stopped, insulin replacement is the only way to keep blood glucose levels within the recommended range (A1c ≤ 48 mmol/mol [6.5%]), according to the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), as well as numerous diabetes organizations, including the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
Preliminary clinical trials have looked at stem cell transplantation, prematurely dubbed as a “cure” for type 1 diabetes, as an alternative to insulin therapy. The procedure involves transplanting stem cell–derived cells, which become functional beta cells when infused into humans, but requires immunosuppression, as reported by this news organization.
Today, the life expectancy of people with type 1 diabetes treated with insulin is close to those without the disease, although this is dependent on how tightly blood glucose is controlled. Some studies show life expectancy of those with type 1 diabetes is around 8-12 years lower than the general population but varies depending on where a person lives.
In some lower-income countries, many with type 1 diabetes still die prematurely either because they are undiagnosed or cannot access insulin. The high cost of insulin in the United States is well publicized, as featured in numerous articles by this news organization, and numerous patients in the United States have died because they cannot afford insulin.
Without insulin, young Leonard Thompson would have been lucky to have reached his 15th birthday.
“Such patients were cachectic and thin and would have weighed around 40-50 pounds (18-23 kg), which is very low for an older child. Survival was short and lasted weeks or months usually,” said Elizabeth Stephens, MD, an endocrinologist in Portland, Ore.
“The discovery of insulin was really a miracle because without it diabetes patients were facing certain death. Even nowadays, if people don’t get their insulin because they can’t afford it or for whatever reason, they can still die,” Dr. Stephens stressed.
Antidiabetic effects of pancreatic extract limited
Back in 1869, Paul Langerhans, MD, discovered pancreatic islet cells, or islets of Langerhans, as a medical student. Researchers tried to produce extracts that lowered blood glucose but they were too toxic for patient use.
In 1908, as detailed in his recent book, Insulin – the Crooked Timber, Dr. Hall also refers to the fact that a German researcher, Georg Zuelzer, MD, demonstrated in six patients that pancreatic extracts could reduce urinary levels of glucose and ketones, and that in one case, the treatment woke the patient from a coma. Dr. Zuelzer had purified the extract with alcohol but patients still experienced convulsions and coma; in fact, they were experiencing hypoglycemic shock, but Dr. Zuelzer had not identified it as such.
“He thought his preparation was full of impurities – and that’s the irony. He had in his hands an insulin prep that was so clean and so potent that it sent the test animals into hypoglycemic shock,” Dr. Hall pointed out.
By 1921, two young researchers, Frederick G. Banting, MD, a practicing medical doctor in Toronto, together with a final year physiology student at the University of Toronto, Charles H. Best, MD, DSc, collaborated on the instruction of Dr. Best’s superior, John James Rickard Macleod, MBChB, professor of physiology at the University of Toronto, to make pancreatic extracts, first from dogs and then from cattle.
Over the months prior to treating Thompson, working together in the laboratory, Dr. Banting and Dr. Best prepared the pancreatic extract from cattle and tested it on dogs with diabetes.
Then, in what amounted to a phase 1 trial of its day, with an “n of one,” a frail and close-to-death Thompson was given 15 cc of pancreatic extract at Toronto General Hospital in January 1922. His blood glucose level dropped by 25%, but unfortunately, his body still produced ketones, indicating the antidiabetic effect was limited. He also experienced an adverse reaction at the injection site with an accumulation of abscesses.
So despite success with isolating the extract and administering it to Thompson, the product remained tainted with impurities.
At this point, colleague James Collip, MD, PhD, came to the rescue. He used his skills as a biochemist to purify the pancreatic extract enough to eliminate impurities.
When Thompson was treated 2 weeks later with the purified extract, he experienced a more positive outcome. Gone was the injection site reaction, gone were the high blood glucose levels, and Thompson “became brighter, more active, looked better, and said he felt stronger,” according to a publication describing the treatment.
Dr. Collip also determined that by over-purifying the product, the animals he experimented on could overreact and experience convulsions, coma, and death due to hypoglycemia from too much insulin.
Fighting talk
Recalling an excerpt from Dr. Banting’s diary, Dr. Hall said that Dr. Banting had a mercurial temper and testified to his loss of patience with Dr. Collip when the chemist refused to share his formula of purification. His diary reads: “I grabbed him in one hand by the overcoat ... and almost lifting him I sat him down hard on the chair ... I remember telling him that it was a good job he was so much smaller – otherwise I would ‘knock hell out of him.’ ”
According to Dr. Hall, in 1923, when Dr. Banting and Dr. Macleod were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine, Dr. Best resented being excluded, and despite Dr. Banting’s sharing half his prize money with Dr. Best, animosity prevailed.
At one point, before leaving on a plane for a wartime mission to the United Kingdom, Dr. Banting noted that if he didn’t make it back alive, “and they give my [professorial] chair to that son-of-a-bitch Best, I’ll never rest in my grave.” In a cruel twist of fate, Dr. Banting’s plane crashed and all aboard died.
The Nobel Prize had also been a source of rivalry between Dr. Banting and his boss, Dr. Macleod. In late 1921, while presenting the findings from animal models at the American Physiological Society conference, Dr. Banting’s nerves got the better of him and Dr. Macleod took over at the podium to finish the talk. Dr. Banting perceived this as his boss stealing the limelight.
Only a few months later, at the Association of American Physicians annual conference, Dr. Macleod played to an audience for a second time by making the first formal announcement of the discovery to the scientific community. Notably, Dr. Banting was absent.
The Nobel Prize or a poisoned chalice?
Awarded annually for physics, chemistry, medicine/physiology, literature, peace, and economics, Nobel Prizes are usually considered the holy grail of achievement. In 1895, funds for the prizes were bequeathed by Alfred Nobel in his last will and testament, with each prize worth around $40,000 at the time (approximately $1,000,000 in today’s value).
Writing in 2001 in the journal Diabetes Voice, Professor Sir George Alberti, DPhil, BM BCh, former president of the UK Royal College of Physicians, summarized the burden that accompanies the Nobel Prize: “I personally believe that such prizes and awards do more harm than good and should be abolished. Many a scientist has gone to their grave feeling deeply aggrieved because they were not awarded a Nobel Prize.”
Such high stakes surround the prize that, in the case of insulin, the course of its discovery meant courtesies and truth were swept aside in hot pursuit of fame. After Dr. Macleod died in 1935 and Dr. Banting died in 1941, Dr. Best took the opportunity to try to revise history. There was the small obstacle of Dr. Collip, but Dr. Best managed to play down Dr. Collip’s contribution by focusing on the eureka moment as being the first insulin dose administered, despite the fact that a more complete recovery without side effects was later achieved only with Dr. Collip’s help.
Despite exclusion from the Nobel Prize, Dr. Best nevertheless became recognized as the “go-to-guy” for the discovery of insulin, said Dr. Hall. When Dr. Best spoke about the discovery of insulin at the New York Diabetes Association meeting in 1946, he was introduced as a speaker whose reputation was already so great that he did “not require much of an introduction.”
“And when a new research institute was opened in Toronto in 1953, it was named in his honor. The opening address, by Sir Henry Dale of the UK Medical Research Council, sang Best’s praises to the rafters, much to the disgruntlement of Best’s former colleague, James Collip, who was sitting in the audience,” Dr. Hall pointed out.
Both Dr. Hall and Dr. Stephens live with type 1 diabetes and have benefited from the efforts of Dr. Banting, Dr. Best, Dr. Collip, Dr. Zuelzer, and Dr. Macleod.
“The discovery of insulin was a miracle, it has allowed people to survive,” said Dr. Stephens. “Few medicines can reverse a death sentence like insulin can. It’s easy to forget how it was when insulin wasn’t there – and it wasn’t that long ago.”
Dr. Hall reflects that scientific progress and discovery are often portrayed as being the result of towering geniuses standing on each other’s shoulders.
“But I think that when German philosopher Immanuel Kant remarked that ‘Out of the crooked timber of humanity, no straight thing can ever be made,’ he offered us a much more accurate picture of how science works. And I think that there’s perhaps no more powerful example of this than the story of insulin,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Leonard Thompson’s father was so desperate to save his 14-year-old child from certain death due to diabetes that, on Jan. 11, 1922, he took him to Toronto General Hospital to receive what is arguably the first dose of insulin given to a human. From an anticipated life expectancy of weeks – months at best – Thompson lived for an astonishing further 13 years, eventually dying from pneumonia unrelated to diabetes.
By all accounts, the story is a centenary celebration of a remarkable discovery. Insulin has changed what was once a death sentence to a near-normal life expectancy for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes over the past 100 years.
But behind the life-changing success of the discovery – and the Nobel Prize that went with it – lies a tale blighted by disputed claims, twisted truths, and likely injustices between the scientists involved, as they each vied for an honored place in medical history.
Kersten Hall, PhD, honorary fellow, religion and history of science, at the University of Leeds, England, has scoured archives and personal records held at the University of Toronto to uncover the personal stories behind insulin’s discovery.
Despite the wranglings, Dr. Hall asserts: “There’s a distinction between the science and the scientists. Scientists are wonderfully flawed and complex human beings with all their glorious virtues and vices, as we all are. It’s no surprise that they get greedy, jealous, and insecure.”
At death’s door: Diabetes before the 1920s
Prior to insulin’s discovery in 1921, a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes placed someone at death’s door, with nothing but starvation – albeit a slightly slower death – to mitigate a fast-approaching departure from this world. At that time, most diabetes cases would have been type 1 diabetes because, with less obesogenic diets and shorter lifespans, people were much less likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
Nowadays, it is widely recognized that the prevalence of type 2 diabetes is on a steep upward curve, but so too is type 1 diabetes. In the United States alone, there are 1.5 million people diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, a number expected to rise to around 5 million by 2050, according to JDRF, the type 1 diabetes advocacy organization.
Interestingly, 100 years since the first treated patient, life-long insulin remains the only real effective therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes. Once pancreatic beta cells have ceased to function and insulin production has stopped, insulin replacement is the only way to keep blood glucose levels within the recommended range (A1c ≤ 48 mmol/mol [6.5%]), according to the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), as well as numerous diabetes organizations, including the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
Preliminary clinical trials have looked at stem cell transplantation, prematurely dubbed as a “cure” for type 1 diabetes, as an alternative to insulin therapy. The procedure involves transplanting stem cell–derived cells, which become functional beta cells when infused into humans, but requires immunosuppression, as reported by this news organization.
Today, the life expectancy of people with type 1 diabetes treated with insulin is close to those without the disease, although this is dependent on how tightly blood glucose is controlled. Some studies show life expectancy of those with type 1 diabetes is around 8-12 years lower than the general population but varies depending on where a person lives.
In some lower-income countries, many with type 1 diabetes still die prematurely either because they are undiagnosed or cannot access insulin. The high cost of insulin in the United States is well publicized, as featured in numerous articles by this news organization, and numerous patients in the United States have died because they cannot afford insulin.
Without insulin, young Leonard Thompson would have been lucky to have reached his 15th birthday.
“Such patients were cachectic and thin and would have weighed around 40-50 pounds (18-23 kg), which is very low for an older child. Survival was short and lasted weeks or months usually,” said Elizabeth Stephens, MD, an endocrinologist in Portland, Ore.
“The discovery of insulin was really a miracle because without it diabetes patients were facing certain death. Even nowadays, if people don’t get their insulin because they can’t afford it or for whatever reason, they can still die,” Dr. Stephens stressed.
Antidiabetic effects of pancreatic extract limited
Back in 1869, Paul Langerhans, MD, discovered pancreatic islet cells, or islets of Langerhans, as a medical student. Researchers tried to produce extracts that lowered blood glucose but they were too toxic for patient use.
In 1908, as detailed in his recent book, Insulin – the Crooked Timber, Dr. Hall also refers to the fact that a German researcher, Georg Zuelzer, MD, demonstrated in six patients that pancreatic extracts could reduce urinary levels of glucose and ketones, and that in one case, the treatment woke the patient from a coma. Dr. Zuelzer had purified the extract with alcohol but patients still experienced convulsions and coma; in fact, they were experiencing hypoglycemic shock, but Dr. Zuelzer had not identified it as such.
“He thought his preparation was full of impurities – and that’s the irony. He had in his hands an insulin prep that was so clean and so potent that it sent the test animals into hypoglycemic shock,” Dr. Hall pointed out.
By 1921, two young researchers, Frederick G. Banting, MD, a practicing medical doctor in Toronto, together with a final year physiology student at the University of Toronto, Charles H. Best, MD, DSc, collaborated on the instruction of Dr. Best’s superior, John James Rickard Macleod, MBChB, professor of physiology at the University of Toronto, to make pancreatic extracts, first from dogs and then from cattle.
Over the months prior to treating Thompson, working together in the laboratory, Dr. Banting and Dr. Best prepared the pancreatic extract from cattle and tested it on dogs with diabetes.
Then, in what amounted to a phase 1 trial of its day, with an “n of one,” a frail and close-to-death Thompson was given 15 cc of pancreatic extract at Toronto General Hospital in January 1922. His blood glucose level dropped by 25%, but unfortunately, his body still produced ketones, indicating the antidiabetic effect was limited. He also experienced an adverse reaction at the injection site with an accumulation of abscesses.
So despite success with isolating the extract and administering it to Thompson, the product remained tainted with impurities.
At this point, colleague James Collip, MD, PhD, came to the rescue. He used his skills as a biochemist to purify the pancreatic extract enough to eliminate impurities.
When Thompson was treated 2 weeks later with the purified extract, he experienced a more positive outcome. Gone was the injection site reaction, gone were the high blood glucose levels, and Thompson “became brighter, more active, looked better, and said he felt stronger,” according to a publication describing the treatment.
Dr. Collip also determined that by over-purifying the product, the animals he experimented on could overreact and experience convulsions, coma, and death due to hypoglycemia from too much insulin.
Fighting talk
Recalling an excerpt from Dr. Banting’s diary, Dr. Hall said that Dr. Banting had a mercurial temper and testified to his loss of patience with Dr. Collip when the chemist refused to share his formula of purification. His diary reads: “I grabbed him in one hand by the overcoat ... and almost lifting him I sat him down hard on the chair ... I remember telling him that it was a good job he was so much smaller – otherwise I would ‘knock hell out of him.’ ”
According to Dr. Hall, in 1923, when Dr. Banting and Dr. Macleod were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine, Dr. Best resented being excluded, and despite Dr. Banting’s sharing half his prize money with Dr. Best, animosity prevailed.
At one point, before leaving on a plane for a wartime mission to the United Kingdom, Dr. Banting noted that if he didn’t make it back alive, “and they give my [professorial] chair to that son-of-a-bitch Best, I’ll never rest in my grave.” In a cruel twist of fate, Dr. Banting’s plane crashed and all aboard died.
The Nobel Prize had also been a source of rivalry between Dr. Banting and his boss, Dr. Macleod. In late 1921, while presenting the findings from animal models at the American Physiological Society conference, Dr. Banting’s nerves got the better of him and Dr. Macleod took over at the podium to finish the talk. Dr. Banting perceived this as his boss stealing the limelight.
Only a few months later, at the Association of American Physicians annual conference, Dr. Macleod played to an audience for a second time by making the first formal announcement of the discovery to the scientific community. Notably, Dr. Banting was absent.
The Nobel Prize or a poisoned chalice?
Awarded annually for physics, chemistry, medicine/physiology, literature, peace, and economics, Nobel Prizes are usually considered the holy grail of achievement. In 1895, funds for the prizes were bequeathed by Alfred Nobel in his last will and testament, with each prize worth around $40,000 at the time (approximately $1,000,000 in today’s value).
Writing in 2001 in the journal Diabetes Voice, Professor Sir George Alberti, DPhil, BM BCh, former president of the UK Royal College of Physicians, summarized the burden that accompanies the Nobel Prize: “I personally believe that such prizes and awards do more harm than good and should be abolished. Many a scientist has gone to their grave feeling deeply aggrieved because they were not awarded a Nobel Prize.”
Such high stakes surround the prize that, in the case of insulin, the course of its discovery meant courtesies and truth were swept aside in hot pursuit of fame. After Dr. Macleod died in 1935 and Dr. Banting died in 1941, Dr. Best took the opportunity to try to revise history. There was the small obstacle of Dr. Collip, but Dr. Best managed to play down Dr. Collip’s contribution by focusing on the eureka moment as being the first insulin dose administered, despite the fact that a more complete recovery without side effects was later achieved only with Dr. Collip’s help.
Despite exclusion from the Nobel Prize, Dr. Best nevertheless became recognized as the “go-to-guy” for the discovery of insulin, said Dr. Hall. When Dr. Best spoke about the discovery of insulin at the New York Diabetes Association meeting in 1946, he was introduced as a speaker whose reputation was already so great that he did “not require much of an introduction.”
“And when a new research institute was opened in Toronto in 1953, it was named in his honor. The opening address, by Sir Henry Dale of the UK Medical Research Council, sang Best’s praises to the rafters, much to the disgruntlement of Best’s former colleague, James Collip, who was sitting in the audience,” Dr. Hall pointed out.
Both Dr. Hall and Dr. Stephens live with type 1 diabetes and have benefited from the efforts of Dr. Banting, Dr. Best, Dr. Collip, Dr. Zuelzer, and Dr. Macleod.
“The discovery of insulin was a miracle, it has allowed people to survive,” said Dr. Stephens. “Few medicines can reverse a death sentence like insulin can. It’s easy to forget how it was when insulin wasn’t there – and it wasn’t that long ago.”
Dr. Hall reflects that scientific progress and discovery are often portrayed as being the result of towering geniuses standing on each other’s shoulders.
“But I think that when German philosopher Immanuel Kant remarked that ‘Out of the crooked timber of humanity, no straight thing can ever be made,’ he offered us a much more accurate picture of how science works. And I think that there’s perhaps no more powerful example of this than the story of insulin,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Leonard Thompson’s father was so desperate to save his 14-year-old child from certain death due to diabetes that, on Jan. 11, 1922, he took him to Toronto General Hospital to receive what is arguably the first dose of insulin given to a human. From an anticipated life expectancy of weeks – months at best – Thompson lived for an astonishing further 13 years, eventually dying from pneumonia unrelated to diabetes.
By all accounts, the story is a centenary celebration of a remarkable discovery. Insulin has changed what was once a death sentence to a near-normal life expectancy for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes over the past 100 years.
But behind the life-changing success of the discovery – and the Nobel Prize that went with it – lies a tale blighted by disputed claims, twisted truths, and likely injustices between the scientists involved, as they each vied for an honored place in medical history.
Kersten Hall, PhD, honorary fellow, religion and history of science, at the University of Leeds, England, has scoured archives and personal records held at the University of Toronto to uncover the personal stories behind insulin’s discovery.
Despite the wranglings, Dr. Hall asserts: “There’s a distinction between the science and the scientists. Scientists are wonderfully flawed and complex human beings with all their glorious virtues and vices, as we all are. It’s no surprise that they get greedy, jealous, and insecure.”
At death’s door: Diabetes before the 1920s
Prior to insulin’s discovery in 1921, a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes placed someone at death’s door, with nothing but starvation – albeit a slightly slower death – to mitigate a fast-approaching departure from this world. At that time, most diabetes cases would have been type 1 diabetes because, with less obesogenic diets and shorter lifespans, people were much less likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
Nowadays, it is widely recognized that the prevalence of type 2 diabetes is on a steep upward curve, but so too is type 1 diabetes. In the United States alone, there are 1.5 million people diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, a number expected to rise to around 5 million by 2050, according to JDRF, the type 1 diabetes advocacy organization.
Interestingly, 100 years since the first treated patient, life-long insulin remains the only real effective therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes. Once pancreatic beta cells have ceased to function and insulin production has stopped, insulin replacement is the only way to keep blood glucose levels within the recommended range (A1c ≤ 48 mmol/mol [6.5%]), according to the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), as well as numerous diabetes organizations, including the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
Preliminary clinical trials have looked at stem cell transplantation, prematurely dubbed as a “cure” for type 1 diabetes, as an alternative to insulin therapy. The procedure involves transplanting stem cell–derived cells, which become functional beta cells when infused into humans, but requires immunosuppression, as reported by this news organization.
Today, the life expectancy of people with type 1 diabetes treated with insulin is close to those without the disease, although this is dependent on how tightly blood glucose is controlled. Some studies show life expectancy of those with type 1 diabetes is around 8-12 years lower than the general population but varies depending on where a person lives.
In some lower-income countries, many with type 1 diabetes still die prematurely either because they are undiagnosed or cannot access insulin. The high cost of insulin in the United States is well publicized, as featured in numerous articles by this news organization, and numerous patients in the United States have died because they cannot afford insulin.
Without insulin, young Leonard Thompson would have been lucky to have reached his 15th birthday.
“Such patients were cachectic and thin and would have weighed around 40-50 pounds (18-23 kg), which is very low for an older child. Survival was short and lasted weeks or months usually,” said Elizabeth Stephens, MD, an endocrinologist in Portland, Ore.
“The discovery of insulin was really a miracle because without it diabetes patients were facing certain death. Even nowadays, if people don’t get their insulin because they can’t afford it or for whatever reason, they can still die,” Dr. Stephens stressed.
Antidiabetic effects of pancreatic extract limited
Back in 1869, Paul Langerhans, MD, discovered pancreatic islet cells, or islets of Langerhans, as a medical student. Researchers tried to produce extracts that lowered blood glucose but they were too toxic for patient use.
In 1908, as detailed in his recent book, Insulin – the Crooked Timber, Dr. Hall also refers to the fact that a German researcher, Georg Zuelzer, MD, demonstrated in six patients that pancreatic extracts could reduce urinary levels of glucose and ketones, and that in one case, the treatment woke the patient from a coma. Dr. Zuelzer had purified the extract with alcohol but patients still experienced convulsions and coma; in fact, they were experiencing hypoglycemic shock, but Dr. Zuelzer had not identified it as such.
“He thought his preparation was full of impurities – and that’s the irony. He had in his hands an insulin prep that was so clean and so potent that it sent the test animals into hypoglycemic shock,” Dr. Hall pointed out.
By 1921, two young researchers, Frederick G. Banting, MD, a practicing medical doctor in Toronto, together with a final year physiology student at the University of Toronto, Charles H. Best, MD, DSc, collaborated on the instruction of Dr. Best’s superior, John James Rickard Macleod, MBChB, professor of physiology at the University of Toronto, to make pancreatic extracts, first from dogs and then from cattle.
Over the months prior to treating Thompson, working together in the laboratory, Dr. Banting and Dr. Best prepared the pancreatic extract from cattle and tested it on dogs with diabetes.
Then, in what amounted to a phase 1 trial of its day, with an “n of one,” a frail and close-to-death Thompson was given 15 cc of pancreatic extract at Toronto General Hospital in January 1922. His blood glucose level dropped by 25%, but unfortunately, his body still produced ketones, indicating the antidiabetic effect was limited. He also experienced an adverse reaction at the injection site with an accumulation of abscesses.
So despite success with isolating the extract and administering it to Thompson, the product remained tainted with impurities.
At this point, colleague James Collip, MD, PhD, came to the rescue. He used his skills as a biochemist to purify the pancreatic extract enough to eliminate impurities.
When Thompson was treated 2 weeks later with the purified extract, he experienced a more positive outcome. Gone was the injection site reaction, gone were the high blood glucose levels, and Thompson “became brighter, more active, looked better, and said he felt stronger,” according to a publication describing the treatment.
Dr. Collip also determined that by over-purifying the product, the animals he experimented on could overreact and experience convulsions, coma, and death due to hypoglycemia from too much insulin.
Fighting talk
Recalling an excerpt from Dr. Banting’s diary, Dr. Hall said that Dr. Banting had a mercurial temper and testified to his loss of patience with Dr. Collip when the chemist refused to share his formula of purification. His diary reads: “I grabbed him in one hand by the overcoat ... and almost lifting him I sat him down hard on the chair ... I remember telling him that it was a good job he was so much smaller – otherwise I would ‘knock hell out of him.’ ”
According to Dr. Hall, in 1923, when Dr. Banting and Dr. Macleod were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine, Dr. Best resented being excluded, and despite Dr. Banting’s sharing half his prize money with Dr. Best, animosity prevailed.
At one point, before leaving on a plane for a wartime mission to the United Kingdom, Dr. Banting noted that if he didn’t make it back alive, “and they give my [professorial] chair to that son-of-a-bitch Best, I’ll never rest in my grave.” In a cruel twist of fate, Dr. Banting’s plane crashed and all aboard died.
The Nobel Prize had also been a source of rivalry between Dr. Banting and his boss, Dr. Macleod. In late 1921, while presenting the findings from animal models at the American Physiological Society conference, Dr. Banting’s nerves got the better of him and Dr. Macleod took over at the podium to finish the talk. Dr. Banting perceived this as his boss stealing the limelight.
Only a few months later, at the Association of American Physicians annual conference, Dr. Macleod played to an audience for a second time by making the first formal announcement of the discovery to the scientific community. Notably, Dr. Banting was absent.
The Nobel Prize or a poisoned chalice?
Awarded annually for physics, chemistry, medicine/physiology, literature, peace, and economics, Nobel Prizes are usually considered the holy grail of achievement. In 1895, funds for the prizes were bequeathed by Alfred Nobel in his last will and testament, with each prize worth around $40,000 at the time (approximately $1,000,000 in today’s value).
Writing in 2001 in the journal Diabetes Voice, Professor Sir George Alberti, DPhil, BM BCh, former president of the UK Royal College of Physicians, summarized the burden that accompanies the Nobel Prize: “I personally believe that such prizes and awards do more harm than good and should be abolished. Many a scientist has gone to their grave feeling deeply aggrieved because they were not awarded a Nobel Prize.”
Such high stakes surround the prize that, in the case of insulin, the course of its discovery meant courtesies and truth were swept aside in hot pursuit of fame. After Dr. Macleod died in 1935 and Dr. Banting died in 1941, Dr. Best took the opportunity to try to revise history. There was the small obstacle of Dr. Collip, but Dr. Best managed to play down Dr. Collip’s contribution by focusing on the eureka moment as being the first insulin dose administered, despite the fact that a more complete recovery without side effects was later achieved only with Dr. Collip’s help.
Despite exclusion from the Nobel Prize, Dr. Best nevertheless became recognized as the “go-to-guy” for the discovery of insulin, said Dr. Hall. When Dr. Best spoke about the discovery of insulin at the New York Diabetes Association meeting in 1946, he was introduced as a speaker whose reputation was already so great that he did “not require much of an introduction.”
“And when a new research institute was opened in Toronto in 1953, it was named in his honor. The opening address, by Sir Henry Dale of the UK Medical Research Council, sang Best’s praises to the rafters, much to the disgruntlement of Best’s former colleague, James Collip, who was sitting in the audience,” Dr. Hall pointed out.
Both Dr. Hall and Dr. Stephens live with type 1 diabetes and have benefited from the efforts of Dr. Banting, Dr. Best, Dr. Collip, Dr. Zuelzer, and Dr. Macleod.
“The discovery of insulin was a miracle, it has allowed people to survive,” said Dr. Stephens. “Few medicines can reverse a death sentence like insulin can. It’s easy to forget how it was when insulin wasn’t there – and it wasn’t that long ago.”
Dr. Hall reflects that scientific progress and discovery are often portrayed as being the result of towering geniuses standing on each other’s shoulders.
“But I think that when German philosopher Immanuel Kant remarked that ‘Out of the crooked timber of humanity, no straight thing can ever be made,’ he offered us a much more accurate picture of how science works. And I think that there’s perhaps no more powerful example of this than the story of insulin,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Referrals to gender clinics in Sweden drop after media coverage
Media coverage of transgender health care judged to be “negative” was associated with a drop of around 30% in referral rates to gender identity clinics in Sweden among young people under age 19, a new study indicates.
Malin Indremo, MS, from the department of neuroscience, Uppsala (Sweden) University, and colleagues explored the effect of the documentaries, “The Trans Train and Teenage Girls,” which they explain was a “Swedish public service television show” representing “investigative journalism.” The two-part documentary series was aired in Sweden in April 2019 and October 2019, respectively, and is now available in English on YouTube.
In their article, published online in JAMA Network Open, the authors said they consider “The Trans Train” programs to be “negative” media coverage because the “documentaries addressed the distinct increase among adolescents referred to gender identity clinics in recent years. Two young adults who regretted their transition and parents of transgender individuals who questioned the clinics’ assessments of their children were interviewed, and concerns were raised about whether gender-confirming treatments are based on sufficient scientific evidence.”
The programs, they suggest, may have influenced and jeopardized young transgender individuals’ access to transgender-specific health care.
Stella O’Malley, a U.K.-based psychotherapist specializing in transgender care and executive director of Genspect, an international organization that provides support to the parents of young people who are questioning their gender, expressed her disappointment with the study’s conclusions.
“I’m really surprised and disappointed that the researchers believe that negative coverage is the reason for a drop in referrals when it is more accurate to say that the information provided by ‘The Trans Train’ documentaries was concerning and suggests that further critical analysis and a review needs to be carried out on the clinics in question,” she said in an interview.
Ms. O’Malley herself made a documentary for Channel 4 in the United Kingdom, broadcast in 2018, called: “Trans Kids: It’s Time to Talk.”
Rapidly increasing numbers of youth, especially girls, question gender
As Ms. Indremo and coauthors explained – and as has been widely reported by this news organization – “the number of referrals to gender identity clinics have rapidly increased worldwide” in recent years, and this “has been especially prominent in adolescents and young adults.”
In addition, they acknowledged, “there has been a shift in gender ratio, with a preponderance toward individuals who were assigned female at birth (AFAB).”
This was the topic of “The Trans Train” programs, and in fact, following their broadcast, Ms. Indremo and colleagues noted that “an intense debate in national media [in Sweden] arose from the documentaries.”
Their research aimed to explore the association between both “positive” and “negative” media coverage and the number of referrals to gender identity clinics for young people (under aged 19) respectively. Data from the six gender clinics in Sweden were included between January 2017 and December 2019.
In the period studied, the clinics received 1,784 referrals, including 613 referrals in 2017, 663 referrals in 2018, and 508 referrals in 2019.
From the age-specific data that included 1,674 referrals, 359 individuals (21.4%) were younger than 13 years and 1,315 individuals (78.6%) were aged 13-18 years. From the assigned sex-specific data that included 1,435 referrals, 1,034 individuals (72.1%) were AFAB and 401 individuals (27.9%) were assigned male at birth (AMAB). Information on sex assigned at birth was lacking from one clinic, which was excluded from the analysis.
When they examined data for the 3 months following the airing of the first part of “The Trans Train” documentary series (in April 2019), they found that referrals to gender clinics fell by 25.4% overall, compared with the 3 months before part 1 was screened. Specifically, they fell by 25.3% for young people aged 13-18 years and by 32.2% for those born female.
In the extended analyses of 6 months following part 1, a decrease of total referrals by 30.7% was observed, while referrals for AFAB individuals decreased by 37.4% and referrals for individuals aged 13-18 years decreased by 27.7%. A decrease of referrals by 41.7% for children aged younger than 13 years was observed in the 6-month analysis, as well as a decrease of 8.2% among AMAB individuals.
“The Trans Train” documentaries, Ms. Indremo and colleagues said, “were criticized for being negatively biased and giving an oversimplified picture of transgender health care.”
Did the nature of the trans train documentaries influence referrals?
In an invited commentary published in JAMA Network Open, Ken C. Pang, PhD, from the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Melbourne, and colleagues noted: “Although the mechanisms underlying this decrease [in referrals] were not formally explored in their study, the authors reasonably speculated that both parents and referring health professionals may have been less likely to support a child or adolescent’s attendance at a specialist pediatric gender clinic following the documentaries.”
Dr. Pang and colleagues went on to say it is “the ... responsibility of media organizations in ensuring that stories depicting health care for transgender and gender diverse (TGD) young people are fair, balanced, nuanced, and accurate.”
Often, media reports have “fallen short of these standards and lacked the voices of TGD young people who have benefited from gender-affirming care or the perspectives of health professionals with expertise in providing such care,” they added.
“For example, some [media reports] have suggested that the growing number of referrals to such clinics is not owing to greater awareness of gender diversity and empowerment of TGD young people but is instead being driven by other factors such as peer influence, while others have warned that the use of gender-affirming hormonal interventions in TGD young people represents an undue risk,” they continue.
Ms. Indremo and colleagues didn’t see any drop-in referrals after the second part of the series, aired in October 2019, but they say this was likely because referrals were “already lowered” by the airing of the first part of the documentaries.
Nor did they see an increase in referrals following what they say was a “positive” media event in the form of a story about a professional Swedish handball player who announced the decision to quit his career to seek care for gender dysphoria.
“One may assume that a single news event is not significant enough to influence referral counts,” they suggested, noting also that Sweden represents “a society where there is already a relatively high level of awareness of gender identity issues.”
“Our results point to a differential association of media attention depending on the tone of the media content,” they observed.
Dr. Pang and coauthors noted it would be “helpful to examine whether similar media coverage in other countries has been associated with similar decreases in referral numbers and whether particular types of media stories are more prone to having this association.”
Parents and doctors debate treatment of gender dysphoria
In Sweden, custodians’ permission as well as custodians’ help is needed for minors to access care for gender dysphoria, said Ms. Indremo and coauthors. “It is possible that the content of the documentaries contributed to a higher custodian barrier to having their children referred for assessment, believing it may not be in the best interest of their child. This would highly impact young transgender individuals’ possibilities to access care.”
They also acknowledge that health care practitioners who refer young people to specialist clinics might also have been influenced by the documentaries, noting “some commentators argued that all treatments for gender dysphoria be stopped, and that ‘all health care given at the gender identity clinics was an experiment lacking scientific basis.’ ”
In April 2021, Angela Sämfjord, MD, child and adolescent psychiatrist at Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden, who started a child and adolescent clinic – the Lundstrom Gender Clinic – told this news organization she had reevaluated her approach even prior to “The Trans Train” documentaries and had resigned in 2018 because of her own fears about the lack of evidence for hormonal and surgical treatments of youth with gender dysphoria.
Following the debate that ensued after the airing of “The Trans Train” programs, the Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare published new recommendations in March 2021, which reflected a significant change in direction for the evaluation of gender dysphoria in minors, emphasizing the requirement for a thorough mental health assessment.
And in May 2021, Karolinska Children’s Hospital, which houses one of the leading gender identity clinics in Sweden, announced it would stop the routine medical treatment of children with gender dysphoria under the age of 18, which meant a total ban on the prescribing of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to minors. Such treatment could henceforth only be carried out within the setting of a clinical trial approved by the EPM (Ethical Review Agency/Swedish Institutional Review Board), it said.
The remaining five gender identity clinics in Sweden decided upon their own rules, but in general, they have become much more cautious regarding medical treatment of minors within the past year. Also, there is a desire in Sweden to reduce the number of gender identity clinics for minors from the current six to perhaps a maximum of three nationwide.
However, neither Ms. Indremo and colleagues nor Dr. Pang and colleagues mentioned the subsequent change to the Swedish NBHW recommendations on evaluation of gender dysphoria in minors in JAMA articles.
New NBHW recommendations about medical treatment of gender dysphoria with puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones for minors were due to be issued in 2021 but have been delayed.
Debate in other countries
Sweden is not alone in discussing this issue. In 2020, Finland became the first country in the world to issue new guidelines that concluded there is a lack of quality evidence to support the use of hormonal interventions in adolescents with gender dysphoria.
This issue has been hotly debated in the United Kingdom – not least with the Keira Bell court case and two National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence evidence reviews concluding there is a lack of data to support the use of puberty-blocking agents and “cross-sex” hormones in youth with gender dysphoria.
And a number of U.S. states are attempting to outlaw the medical and surgical treatment of gender dysphoria in minors. Even health care professionals who have been treating young people with gender dysphoria for years – some of whom are transgender themselves – have started to speak out and are questioning what they call “sloppy care” given to many such youth.
Indeed, a recent survey shows that detransitioners – individuals who suffer from gender dysphoria, transition to the opposite sex but then regret their decision and detransition – are getting short shrift when it comes to care, with over half of the 100 surveyed saying they feel they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting to transition.
And new draft standards of care for treating people with gender dysphoria by the World Professional Association for Transgender Health have drawn criticism from experts.
‘First do no harm’
In their conclusion, Dr. Pang and coauthors said that, with respect to the media coverage of young people with gender dysphoria, “who are, after all, one of the most vulnerable subgroups within our society, perhaps our media should recall one of the core tenets of health care and ensure their stories ‘first, do no harm.’”
However, in a commentary recently published in Child and Adolescent Mental Health, Alison Clayton, MBBS, from the University of Melbourne, and coauthors again pointed out that evidence reviews of the use of puberty blockers in young people with gender dysphoria show “there is very low certainty of the benefits of puberty blockers, an unknown risk of harm, and there is need for more rigorous research.”
“The clinically prudent thing to do, if we aim to ‘first, do no harm,’ is to proceed with extreme caution, especially given the rapidly rising case numbers and novel gender dysphoria presentations,” Clayton and colleagues concluded.
Ms. Indremo and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pang reported being a member of the Australian Professional Association for Trans Health and its research committee. One commentary coauthor has reported being a member of WPATH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Media coverage of transgender health care judged to be “negative” was associated with a drop of around 30% in referral rates to gender identity clinics in Sweden among young people under age 19, a new study indicates.
Malin Indremo, MS, from the department of neuroscience, Uppsala (Sweden) University, and colleagues explored the effect of the documentaries, “The Trans Train and Teenage Girls,” which they explain was a “Swedish public service television show” representing “investigative journalism.” The two-part documentary series was aired in Sweden in April 2019 and October 2019, respectively, and is now available in English on YouTube.
In their article, published online in JAMA Network Open, the authors said they consider “The Trans Train” programs to be “negative” media coverage because the “documentaries addressed the distinct increase among adolescents referred to gender identity clinics in recent years. Two young adults who regretted their transition and parents of transgender individuals who questioned the clinics’ assessments of their children were interviewed, and concerns were raised about whether gender-confirming treatments are based on sufficient scientific evidence.”
The programs, they suggest, may have influenced and jeopardized young transgender individuals’ access to transgender-specific health care.
Stella O’Malley, a U.K.-based psychotherapist specializing in transgender care and executive director of Genspect, an international organization that provides support to the parents of young people who are questioning their gender, expressed her disappointment with the study’s conclusions.
“I’m really surprised and disappointed that the researchers believe that negative coverage is the reason for a drop in referrals when it is more accurate to say that the information provided by ‘The Trans Train’ documentaries was concerning and suggests that further critical analysis and a review needs to be carried out on the clinics in question,” she said in an interview.
Ms. O’Malley herself made a documentary for Channel 4 in the United Kingdom, broadcast in 2018, called: “Trans Kids: It’s Time to Talk.”
Rapidly increasing numbers of youth, especially girls, question gender
As Ms. Indremo and coauthors explained – and as has been widely reported by this news organization – “the number of referrals to gender identity clinics have rapidly increased worldwide” in recent years, and this “has been especially prominent in adolescents and young adults.”
In addition, they acknowledged, “there has been a shift in gender ratio, with a preponderance toward individuals who were assigned female at birth (AFAB).”
This was the topic of “The Trans Train” programs, and in fact, following their broadcast, Ms. Indremo and colleagues noted that “an intense debate in national media [in Sweden] arose from the documentaries.”
Their research aimed to explore the association between both “positive” and “negative” media coverage and the number of referrals to gender identity clinics for young people (under aged 19) respectively. Data from the six gender clinics in Sweden were included between January 2017 and December 2019.
In the period studied, the clinics received 1,784 referrals, including 613 referrals in 2017, 663 referrals in 2018, and 508 referrals in 2019.
From the age-specific data that included 1,674 referrals, 359 individuals (21.4%) were younger than 13 years and 1,315 individuals (78.6%) were aged 13-18 years. From the assigned sex-specific data that included 1,435 referrals, 1,034 individuals (72.1%) were AFAB and 401 individuals (27.9%) were assigned male at birth (AMAB). Information on sex assigned at birth was lacking from one clinic, which was excluded from the analysis.
When they examined data for the 3 months following the airing of the first part of “The Trans Train” documentary series (in April 2019), they found that referrals to gender clinics fell by 25.4% overall, compared with the 3 months before part 1 was screened. Specifically, they fell by 25.3% for young people aged 13-18 years and by 32.2% for those born female.
In the extended analyses of 6 months following part 1, a decrease of total referrals by 30.7% was observed, while referrals for AFAB individuals decreased by 37.4% and referrals for individuals aged 13-18 years decreased by 27.7%. A decrease of referrals by 41.7% for children aged younger than 13 years was observed in the 6-month analysis, as well as a decrease of 8.2% among AMAB individuals.
“The Trans Train” documentaries, Ms. Indremo and colleagues said, “were criticized for being negatively biased and giving an oversimplified picture of transgender health care.”
Did the nature of the trans train documentaries influence referrals?
In an invited commentary published in JAMA Network Open, Ken C. Pang, PhD, from the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Melbourne, and colleagues noted: “Although the mechanisms underlying this decrease [in referrals] were not formally explored in their study, the authors reasonably speculated that both parents and referring health professionals may have been less likely to support a child or adolescent’s attendance at a specialist pediatric gender clinic following the documentaries.”
Dr. Pang and colleagues went on to say it is “the ... responsibility of media organizations in ensuring that stories depicting health care for transgender and gender diverse (TGD) young people are fair, balanced, nuanced, and accurate.”
Often, media reports have “fallen short of these standards and lacked the voices of TGD young people who have benefited from gender-affirming care or the perspectives of health professionals with expertise in providing such care,” they added.
“For example, some [media reports] have suggested that the growing number of referrals to such clinics is not owing to greater awareness of gender diversity and empowerment of TGD young people but is instead being driven by other factors such as peer influence, while others have warned that the use of gender-affirming hormonal interventions in TGD young people represents an undue risk,” they continue.
Ms. Indremo and colleagues didn’t see any drop-in referrals after the second part of the series, aired in October 2019, but they say this was likely because referrals were “already lowered” by the airing of the first part of the documentaries.
Nor did they see an increase in referrals following what they say was a “positive” media event in the form of a story about a professional Swedish handball player who announced the decision to quit his career to seek care for gender dysphoria.
“One may assume that a single news event is not significant enough to influence referral counts,” they suggested, noting also that Sweden represents “a society where there is already a relatively high level of awareness of gender identity issues.”
“Our results point to a differential association of media attention depending on the tone of the media content,” they observed.
Dr. Pang and coauthors noted it would be “helpful to examine whether similar media coverage in other countries has been associated with similar decreases in referral numbers and whether particular types of media stories are more prone to having this association.”
Parents and doctors debate treatment of gender dysphoria
In Sweden, custodians’ permission as well as custodians’ help is needed for minors to access care for gender dysphoria, said Ms. Indremo and coauthors. “It is possible that the content of the documentaries contributed to a higher custodian barrier to having their children referred for assessment, believing it may not be in the best interest of their child. This would highly impact young transgender individuals’ possibilities to access care.”
They also acknowledge that health care practitioners who refer young people to specialist clinics might also have been influenced by the documentaries, noting “some commentators argued that all treatments for gender dysphoria be stopped, and that ‘all health care given at the gender identity clinics was an experiment lacking scientific basis.’ ”
In April 2021, Angela Sämfjord, MD, child and adolescent psychiatrist at Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden, who started a child and adolescent clinic – the Lundstrom Gender Clinic – told this news organization she had reevaluated her approach even prior to “The Trans Train” documentaries and had resigned in 2018 because of her own fears about the lack of evidence for hormonal and surgical treatments of youth with gender dysphoria.
Following the debate that ensued after the airing of “The Trans Train” programs, the Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare published new recommendations in March 2021, which reflected a significant change in direction for the evaluation of gender dysphoria in minors, emphasizing the requirement for a thorough mental health assessment.
And in May 2021, Karolinska Children’s Hospital, which houses one of the leading gender identity clinics in Sweden, announced it would stop the routine medical treatment of children with gender dysphoria under the age of 18, which meant a total ban on the prescribing of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to minors. Such treatment could henceforth only be carried out within the setting of a clinical trial approved by the EPM (Ethical Review Agency/Swedish Institutional Review Board), it said.
The remaining five gender identity clinics in Sweden decided upon their own rules, but in general, they have become much more cautious regarding medical treatment of minors within the past year. Also, there is a desire in Sweden to reduce the number of gender identity clinics for minors from the current six to perhaps a maximum of three nationwide.
However, neither Ms. Indremo and colleagues nor Dr. Pang and colleagues mentioned the subsequent change to the Swedish NBHW recommendations on evaluation of gender dysphoria in minors in JAMA articles.
New NBHW recommendations about medical treatment of gender dysphoria with puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones for minors were due to be issued in 2021 but have been delayed.
Debate in other countries
Sweden is not alone in discussing this issue. In 2020, Finland became the first country in the world to issue new guidelines that concluded there is a lack of quality evidence to support the use of hormonal interventions in adolescents with gender dysphoria.
This issue has been hotly debated in the United Kingdom – not least with the Keira Bell court case and two National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence evidence reviews concluding there is a lack of data to support the use of puberty-blocking agents and “cross-sex” hormones in youth with gender dysphoria.
And a number of U.S. states are attempting to outlaw the medical and surgical treatment of gender dysphoria in minors. Even health care professionals who have been treating young people with gender dysphoria for years – some of whom are transgender themselves – have started to speak out and are questioning what they call “sloppy care” given to many such youth.
Indeed, a recent survey shows that detransitioners – individuals who suffer from gender dysphoria, transition to the opposite sex but then regret their decision and detransition – are getting short shrift when it comes to care, with over half of the 100 surveyed saying they feel they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting to transition.
And new draft standards of care for treating people with gender dysphoria by the World Professional Association for Transgender Health have drawn criticism from experts.
‘First do no harm’
In their conclusion, Dr. Pang and coauthors said that, with respect to the media coverage of young people with gender dysphoria, “who are, after all, one of the most vulnerable subgroups within our society, perhaps our media should recall one of the core tenets of health care and ensure their stories ‘first, do no harm.’”
However, in a commentary recently published in Child and Adolescent Mental Health, Alison Clayton, MBBS, from the University of Melbourne, and coauthors again pointed out that evidence reviews of the use of puberty blockers in young people with gender dysphoria show “there is very low certainty of the benefits of puberty blockers, an unknown risk of harm, and there is need for more rigorous research.”
“The clinically prudent thing to do, if we aim to ‘first, do no harm,’ is to proceed with extreme caution, especially given the rapidly rising case numbers and novel gender dysphoria presentations,” Clayton and colleagues concluded.
Ms. Indremo and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pang reported being a member of the Australian Professional Association for Trans Health and its research committee. One commentary coauthor has reported being a member of WPATH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Media coverage of transgender health care judged to be “negative” was associated with a drop of around 30% in referral rates to gender identity clinics in Sweden among young people under age 19, a new study indicates.
Malin Indremo, MS, from the department of neuroscience, Uppsala (Sweden) University, and colleagues explored the effect of the documentaries, “The Trans Train and Teenage Girls,” which they explain was a “Swedish public service television show” representing “investigative journalism.” The two-part documentary series was aired in Sweden in April 2019 and October 2019, respectively, and is now available in English on YouTube.
In their article, published online in JAMA Network Open, the authors said they consider “The Trans Train” programs to be “negative” media coverage because the “documentaries addressed the distinct increase among adolescents referred to gender identity clinics in recent years. Two young adults who regretted their transition and parents of transgender individuals who questioned the clinics’ assessments of their children were interviewed, and concerns were raised about whether gender-confirming treatments are based on sufficient scientific evidence.”
The programs, they suggest, may have influenced and jeopardized young transgender individuals’ access to transgender-specific health care.
Stella O’Malley, a U.K.-based psychotherapist specializing in transgender care and executive director of Genspect, an international organization that provides support to the parents of young people who are questioning their gender, expressed her disappointment with the study’s conclusions.
“I’m really surprised and disappointed that the researchers believe that negative coverage is the reason for a drop in referrals when it is more accurate to say that the information provided by ‘The Trans Train’ documentaries was concerning and suggests that further critical analysis and a review needs to be carried out on the clinics in question,” she said in an interview.
Ms. O’Malley herself made a documentary for Channel 4 in the United Kingdom, broadcast in 2018, called: “Trans Kids: It’s Time to Talk.”
Rapidly increasing numbers of youth, especially girls, question gender
As Ms. Indremo and coauthors explained – and as has been widely reported by this news organization – “the number of referrals to gender identity clinics have rapidly increased worldwide” in recent years, and this “has been especially prominent in adolescents and young adults.”
In addition, they acknowledged, “there has been a shift in gender ratio, with a preponderance toward individuals who were assigned female at birth (AFAB).”
This was the topic of “The Trans Train” programs, and in fact, following their broadcast, Ms. Indremo and colleagues noted that “an intense debate in national media [in Sweden] arose from the documentaries.”
Their research aimed to explore the association between both “positive” and “negative” media coverage and the number of referrals to gender identity clinics for young people (under aged 19) respectively. Data from the six gender clinics in Sweden were included between January 2017 and December 2019.
In the period studied, the clinics received 1,784 referrals, including 613 referrals in 2017, 663 referrals in 2018, and 508 referrals in 2019.
From the age-specific data that included 1,674 referrals, 359 individuals (21.4%) were younger than 13 years and 1,315 individuals (78.6%) were aged 13-18 years. From the assigned sex-specific data that included 1,435 referrals, 1,034 individuals (72.1%) were AFAB and 401 individuals (27.9%) were assigned male at birth (AMAB). Information on sex assigned at birth was lacking from one clinic, which was excluded from the analysis.
When they examined data for the 3 months following the airing of the first part of “The Trans Train” documentary series (in April 2019), they found that referrals to gender clinics fell by 25.4% overall, compared with the 3 months before part 1 was screened. Specifically, they fell by 25.3% for young people aged 13-18 years and by 32.2% for those born female.
In the extended analyses of 6 months following part 1, a decrease of total referrals by 30.7% was observed, while referrals for AFAB individuals decreased by 37.4% and referrals for individuals aged 13-18 years decreased by 27.7%. A decrease of referrals by 41.7% for children aged younger than 13 years was observed in the 6-month analysis, as well as a decrease of 8.2% among AMAB individuals.
“The Trans Train” documentaries, Ms. Indremo and colleagues said, “were criticized for being negatively biased and giving an oversimplified picture of transgender health care.”
Did the nature of the trans train documentaries influence referrals?
In an invited commentary published in JAMA Network Open, Ken C. Pang, PhD, from the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute, Melbourne, and colleagues noted: “Although the mechanisms underlying this decrease [in referrals] were not formally explored in their study, the authors reasonably speculated that both parents and referring health professionals may have been less likely to support a child or adolescent’s attendance at a specialist pediatric gender clinic following the documentaries.”
Dr. Pang and colleagues went on to say it is “the ... responsibility of media organizations in ensuring that stories depicting health care for transgender and gender diverse (TGD) young people are fair, balanced, nuanced, and accurate.”
Often, media reports have “fallen short of these standards and lacked the voices of TGD young people who have benefited from gender-affirming care or the perspectives of health professionals with expertise in providing such care,” they added.
“For example, some [media reports] have suggested that the growing number of referrals to such clinics is not owing to greater awareness of gender diversity and empowerment of TGD young people but is instead being driven by other factors such as peer influence, while others have warned that the use of gender-affirming hormonal interventions in TGD young people represents an undue risk,” they continue.
Ms. Indremo and colleagues didn’t see any drop-in referrals after the second part of the series, aired in October 2019, but they say this was likely because referrals were “already lowered” by the airing of the first part of the documentaries.
Nor did they see an increase in referrals following what they say was a “positive” media event in the form of a story about a professional Swedish handball player who announced the decision to quit his career to seek care for gender dysphoria.
“One may assume that a single news event is not significant enough to influence referral counts,” they suggested, noting also that Sweden represents “a society where there is already a relatively high level of awareness of gender identity issues.”
“Our results point to a differential association of media attention depending on the tone of the media content,” they observed.
Dr. Pang and coauthors noted it would be “helpful to examine whether similar media coverage in other countries has been associated with similar decreases in referral numbers and whether particular types of media stories are more prone to having this association.”
Parents and doctors debate treatment of gender dysphoria
In Sweden, custodians’ permission as well as custodians’ help is needed for minors to access care for gender dysphoria, said Ms. Indremo and coauthors. “It is possible that the content of the documentaries contributed to a higher custodian barrier to having their children referred for assessment, believing it may not be in the best interest of their child. This would highly impact young transgender individuals’ possibilities to access care.”
They also acknowledge that health care practitioners who refer young people to specialist clinics might also have been influenced by the documentaries, noting “some commentators argued that all treatments for gender dysphoria be stopped, and that ‘all health care given at the gender identity clinics was an experiment lacking scientific basis.’ ”
In April 2021, Angela Sämfjord, MD, child and adolescent psychiatrist at Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden, who started a child and adolescent clinic – the Lundstrom Gender Clinic – told this news organization she had reevaluated her approach even prior to “The Trans Train” documentaries and had resigned in 2018 because of her own fears about the lack of evidence for hormonal and surgical treatments of youth with gender dysphoria.
Following the debate that ensued after the airing of “The Trans Train” programs, the Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare published new recommendations in March 2021, which reflected a significant change in direction for the evaluation of gender dysphoria in minors, emphasizing the requirement for a thorough mental health assessment.
And in May 2021, Karolinska Children’s Hospital, which houses one of the leading gender identity clinics in Sweden, announced it would stop the routine medical treatment of children with gender dysphoria under the age of 18, which meant a total ban on the prescribing of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones to minors. Such treatment could henceforth only be carried out within the setting of a clinical trial approved by the EPM (Ethical Review Agency/Swedish Institutional Review Board), it said.
The remaining five gender identity clinics in Sweden decided upon their own rules, but in general, they have become much more cautious regarding medical treatment of minors within the past year. Also, there is a desire in Sweden to reduce the number of gender identity clinics for minors from the current six to perhaps a maximum of three nationwide.
However, neither Ms. Indremo and colleagues nor Dr. Pang and colleagues mentioned the subsequent change to the Swedish NBHW recommendations on evaluation of gender dysphoria in minors in JAMA articles.
New NBHW recommendations about medical treatment of gender dysphoria with puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones for minors were due to be issued in 2021 but have been delayed.
Debate in other countries
Sweden is not alone in discussing this issue. In 2020, Finland became the first country in the world to issue new guidelines that concluded there is a lack of quality evidence to support the use of hormonal interventions in adolescents with gender dysphoria.
This issue has been hotly debated in the United Kingdom – not least with the Keira Bell court case and two National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence evidence reviews concluding there is a lack of data to support the use of puberty-blocking agents and “cross-sex” hormones in youth with gender dysphoria.
And a number of U.S. states are attempting to outlaw the medical and surgical treatment of gender dysphoria in minors. Even health care professionals who have been treating young people with gender dysphoria for years – some of whom are transgender themselves – have started to speak out and are questioning what they call “sloppy care” given to many such youth.
Indeed, a recent survey shows that detransitioners – individuals who suffer from gender dysphoria, transition to the opposite sex but then regret their decision and detransition – are getting short shrift when it comes to care, with over half of the 100 surveyed saying they feel they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting to transition.
And new draft standards of care for treating people with gender dysphoria by the World Professional Association for Transgender Health have drawn criticism from experts.
‘First do no harm’
In their conclusion, Dr. Pang and coauthors said that, with respect to the media coverage of young people with gender dysphoria, “who are, after all, one of the most vulnerable subgroups within our society, perhaps our media should recall one of the core tenets of health care and ensure their stories ‘first, do no harm.’”
However, in a commentary recently published in Child and Adolescent Mental Health, Alison Clayton, MBBS, from the University of Melbourne, and coauthors again pointed out that evidence reviews of the use of puberty blockers in young people with gender dysphoria show “there is very low certainty of the benefits of puberty blockers, an unknown risk of harm, and there is need for more rigorous research.”
“The clinically prudent thing to do, if we aim to ‘first, do no harm,’ is to proceed with extreme caution, especially given the rapidly rising case numbers and novel gender dysphoria presentations,” Clayton and colleagues concluded.
Ms. Indremo and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Pang reported being a member of the Australian Professional Association for Trans Health and its research committee. One commentary coauthor has reported being a member of WPATH.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
WPATH draft on gender dysphoria ‘skewed and misses urgent issues’
New draft guidance from the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) is raising serious concerns among professionals caring for people with gender dysphoria, prompting claims that WPATH is an organization “captured by activists.”
Experts in adolescent and child psychology, as well as pediatric health, have expressed dismay that the WPATH Standards of Care (SOC) 8 appear to miss some of the most urgent issues in the field of transgender medicine and are considered to express a radical and unreserved leaning towards “gender-affirmation.”
The WPATH SOC 8 document is available for view and comment until Dec. 16 until 11.59 PM EST, after which time revisions will be made and the final version published.
Despite repeated attempts by this news organization to seek clarification on certain aspects of the guidance from members of the WPATH SOC 8 committee, requests were declined “until the guidance is finalized.”
According to the WPATH website, the SOC 8 aims to provide “clinical guidance for health professionals to assist transgender and gender diverse people with safe and effective pathways” to manage their gender dysphoria and potentially transition.
Such pathways may relate to primary care, gynecologic and urologic care, reproductive options, voice and communication therapy, mental health services, and hormonal or surgical treatments, among others.
WPATH adds that it was felt necessary to revise the existing SOC 7 (published in 2012) because of recent “globally unprecedented increase and visibility of transgender and gender-diverse people seeking support and gender-affirming medical treatment.”
Gender-affirming medical treatment means different things at different ages. In the case of kids with gender dysphoria who have not yet entered puberty associated with their birth sex, this might include prescribing so-called “puberty blockers” to delay natural puberty – gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogs that are licensed for use in precocious puberty in children. Such agents have not been licensed for use in children with gender dysphoria, however, so any use for this purpose is off-label.
Following puberty blockade – or in cases where adolescents have already undergone natural puberty – the next step is to begin cross-sex hormones. So, for a female patient who wants to transition to male (FTM), that would be lifelong testosterone, and for a male who wants to be female (MTF), it involves lifelong estrogen. Again, use of such hormones in transgender individuals is entirely off-label.
Just last month, two of America’s leading experts on transgender medicine, both psychologists – including one who is transgender – told this news organization they were concerned that the quality of the evaluations of youth with gender dysphoria are being stifled by activists who are worried that open discussions will further stigmatize trans individuals.
They subsequently wrote an op-ed on the topic entitled, “The mental health establishment is failing trans kids,” which was finally published in the Washington Post on Nov. 24, after numerous other mainstream U.S. media outlets had rejected it.
New SOC 8 ‘is not evidence based,’ should not be new ‘gold standard’
One expert says the draft SOC 8 lacks balance and does not address certain issues, while paying undue attention to others that detract from real questions facing the field of transgender medicine, both in the United States and around the world.
Julia Mason, MD, is a pediatrician based in Gresham, Oregon, with a special interest in children and adolescents experiencing gender dysphoria. “The SOC 8 shows us that WPATH remains captured by activists,” she asserts.
Dr. Mason questions the integrity of WPATH based on what she has read in the draft SOC 8.
“We need a serious organization to take a sober look at the evidence, and that is why we have established the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine [SEGM],” she noted. “This is what we do – we are looking at all of the evidence.”
Dr. Mason is a clinical advisor to SEGM, an organization set-up to evaluate current interventions and evidence on gender dysphoria.
The pediatrician has particular concerns regarding the child and adolescent chapters in the draft SOC 8. The adolescent chapter states: “Guidelines are meant to provide a gold standard based on the available evidence at this moment of time.”
Dr. Mason disputes this assertion. “This document should not be the new gold standard going forward, primarily because it is not evidence based.”
In an interview, Dr. Mason explained that WPATH say they used the “Delphi consensus process” to determine their recommendations, but “this process is designed for use with a panel of experts when evidence is lacking. I would say they didn’t have a panel of experts. They largely had a panel of activists, with a few experts.”
There is no mention, for example, of England’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) evidence reviews on puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones from earlier this year. These reviews determined that no studies have compared cross-sex hormones or puberty blockers with a control group and all follow-up periods for cross-sex hormones were relatively short.
This disappoints Dr. Mason: “These are significant; they are important documents.”
And much of the evidence quoted comes from the well-known and often-quoted “Dutch-protocol” study of 2011, in which the children studied were much younger at the time of their gender dysphoria, compared with the many adolescents who make up the current surge in presentation at gender clinics worldwide, she adds.
Rapid-onset GD: adolescents presenting late with little history
Dr. Mason also stresses that the SOC 8 does not address the most urgent issues in transgender medicine today, mainly because it does not address rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD): “This is the dilemma of the 21st century; it’s new.”
ROGD – a term first coined in 2018 by researcher Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, now president of the Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR) – refers to the phenomena of adolescents expressing a desire to transition from their birth sex after little or no apparent previous indication.
However, the SOC 8 does make reference to aspects of adolescent development that might impact their decision-making processes around gender identity during teen years. The chapter on adolescents reads: “... adolescence is also often associated with increased risk-taking behaviors. Along with these notable changes ... individuation from parents ... [there is] often a heightened focus on peer relationships, which can be both positive and detrimental.”
The guidance goes on to point out that “it is critical to understand how all of these aspects of development may impact the decision-making for a given young person within their specific cultural context.”
Desistance and detransitioning not adequately addressed
Dr. Mason also says there is little mention “about detransitioning in this SOC [8], and ‘gender dysphoria’ and ‘trans’ are terms that are not defined.”
Likewise, there is no mention of desistance, she highlights, which is when individuals naturally resolve their dysphoria around their birth sex as they grow older.
The most recent published data seen by this news organization relates to a study from March 2021 that showed nearly 88% of boys who struggled with gender identity in childhood (approximate mean age 8 years and follow-up at approximate mean age 20 years) desisted. It reads: “Of the 139 participants, 17 (12.2%) were classified as ‘persisters’ and the remaining 122 (87.8%) were classified as desisters.”
“Most children with gender dysphoria will desist and lose their concept of themselves as being the opposite gender,” Dr. Mason explains. “This is the safest path for a child – desistance.”
“Transition can turn a healthy young person into a lifelong medical patient and has significant health risks,” she emphasizes, stressing that transition has not been shown to decrease the probability of suicide, or attempts at suicide, despite myriad claims saying otherwise.
“Before we were routinely transitioning kids at school, the vast majority of children grew out of their gender dysphoria. This history is not recognized at all in these SOC [8],” she maintains.
Ken Zucker, PhD, CPsych, an author of the study of desistance in boys, says the terms desistence and persistence of gender dysphoria have caused some consternation in certain circles.
An editor of the Archives of Sexual Behavior and professor in the department of psychiatry, University of Toronto, Dr. Zucker has published widely on the topic.
He told this news organization: “The terms persistence and desistance have become verboten among the WPATH cognoscenti. Perhaps the contributors to SOC 8 have come up with alternative descriptors.”
“The term ‘desistance’ is particularly annoying to some of the gender-affirming clinicians, because they don’t believe that desistance is bona fide,” Dr. Zucker points out.
“The desistance resisters are like anti-vaxxers – nothing one can provide as evidence for the efficacy of vaccines is sufficient. There will always be a new objection.”
Other mental health issues, in particular ADHD and autism
It is also widely acknowledged that there is a higher rate of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric diagnoses in individuals with gender dysphoria. For example, one 2020 study found that transgender people were three to six times as likely to be autistic as cisgender people (those whose gender is aligned with their birth sex).
Statement one in the chapter on adolescents in draft WPATH SOC 8 does give a nod to this, pointing out that health professionals working with gender diverse adolescents “should receive training and develop expertise in autism spectrum disorders and other neurodiversity conditions.”
It also notes that in some cases “a more extended assessment process may be useful, such as for youth with more complex presentations (e.g., complicated mental health histories, co-occurring autism spectrum characteristics in particular) and an absence of experienced childhood gender incongruence.”
However, Dr. Mason stresses that underlying mental health issues are central to addressing how to manage a significant number of these patients.
“If a young person has ADHD or autism, they are not ready to make decisions about the rest of their life at age 18. Even a neurotypical young person is still developing their frontal cortex in their early 20s, and it takes longer for those with ADHD or on the autism spectrum.”
She firmly believes that the guidance does not give sufficient consideration to comorbidities in people over the age of 18.
According to their [SOC 8] guidelines, “once someone is 18 they are ready for anything,” says Dr. Mason.
Offering some explanation for the increased prevalence of ADHD and autism in those with gender dysphoria, Dr. Mason notes that children can have “hyperfocus” and those with autism will fixate on a particular area of interest. “If a child is unhappy in their life, and this can be more likely if someone is neuro-atypical, then it is likely that the individual might go online and find this one solution [for example, a transgender identity] that seems to fix everything.”
Perceptions of femininity and masculinity can also be extra challenging for a child with autism, Dr. Mason says. “It is relatively easy for an autistic girl to feel like she should be a boy because the rules of femininity are composed of nonverbal, subtle behaviors that can be difficult to pick up on,” she points out. “An autistic child who isn’t particularly good at nonverbal communication might not pick up on these and thus feel they are not very ‘female.’”
“There’s a whole lot of grass-is-greener-type thinking. Girls think boys have an easier life, and boys think girls have an easier life. I know some detransitioners who have spoken eloquently about realizing their mistake on this,” she adds.
Other parts of the SOC 8 that Dr. Mason disagrees with include the recommendation in the adolescent chapter that 14-year-olds are mature enough to start cross-sex hormones, that is, giving testosterone to a female who wants to transition to male or estrogen to a male who wishes to transition to female. “I think that’s far too young,” she asserts.
And she points out that the document states 17-year-olds are ready for genital reassignment surgery. Again, she believes this is far too young.
“Also, the SOC 8 document does not clarify who is appropriate for surgery. Whenever surgery is discussed, it becomes very vague,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New draft guidance from the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) is raising serious concerns among professionals caring for people with gender dysphoria, prompting claims that WPATH is an organization “captured by activists.”
Experts in adolescent and child psychology, as well as pediatric health, have expressed dismay that the WPATH Standards of Care (SOC) 8 appear to miss some of the most urgent issues in the field of transgender medicine and are considered to express a radical and unreserved leaning towards “gender-affirmation.”
The WPATH SOC 8 document is available for view and comment until Dec. 16 until 11.59 PM EST, after which time revisions will be made and the final version published.
Despite repeated attempts by this news organization to seek clarification on certain aspects of the guidance from members of the WPATH SOC 8 committee, requests were declined “until the guidance is finalized.”
According to the WPATH website, the SOC 8 aims to provide “clinical guidance for health professionals to assist transgender and gender diverse people with safe and effective pathways” to manage their gender dysphoria and potentially transition.
Such pathways may relate to primary care, gynecologic and urologic care, reproductive options, voice and communication therapy, mental health services, and hormonal or surgical treatments, among others.
WPATH adds that it was felt necessary to revise the existing SOC 7 (published in 2012) because of recent “globally unprecedented increase and visibility of transgender and gender-diverse people seeking support and gender-affirming medical treatment.”
Gender-affirming medical treatment means different things at different ages. In the case of kids with gender dysphoria who have not yet entered puberty associated with their birth sex, this might include prescribing so-called “puberty blockers” to delay natural puberty – gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogs that are licensed for use in precocious puberty in children. Such agents have not been licensed for use in children with gender dysphoria, however, so any use for this purpose is off-label.
Following puberty blockade – or in cases where adolescents have already undergone natural puberty – the next step is to begin cross-sex hormones. So, for a female patient who wants to transition to male (FTM), that would be lifelong testosterone, and for a male who wants to be female (MTF), it involves lifelong estrogen. Again, use of such hormones in transgender individuals is entirely off-label.
Just last month, two of America’s leading experts on transgender medicine, both psychologists – including one who is transgender – told this news organization they were concerned that the quality of the evaluations of youth with gender dysphoria are being stifled by activists who are worried that open discussions will further stigmatize trans individuals.
They subsequently wrote an op-ed on the topic entitled, “The mental health establishment is failing trans kids,” which was finally published in the Washington Post on Nov. 24, after numerous other mainstream U.S. media outlets had rejected it.
New SOC 8 ‘is not evidence based,’ should not be new ‘gold standard’
One expert says the draft SOC 8 lacks balance and does not address certain issues, while paying undue attention to others that detract from real questions facing the field of transgender medicine, both in the United States and around the world.
Julia Mason, MD, is a pediatrician based in Gresham, Oregon, with a special interest in children and adolescents experiencing gender dysphoria. “The SOC 8 shows us that WPATH remains captured by activists,” she asserts.
Dr. Mason questions the integrity of WPATH based on what she has read in the draft SOC 8.
“We need a serious organization to take a sober look at the evidence, and that is why we have established the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine [SEGM],” she noted. “This is what we do – we are looking at all of the evidence.”
Dr. Mason is a clinical advisor to SEGM, an organization set-up to evaluate current interventions and evidence on gender dysphoria.
The pediatrician has particular concerns regarding the child and adolescent chapters in the draft SOC 8. The adolescent chapter states: “Guidelines are meant to provide a gold standard based on the available evidence at this moment of time.”
Dr. Mason disputes this assertion. “This document should not be the new gold standard going forward, primarily because it is not evidence based.”
In an interview, Dr. Mason explained that WPATH say they used the “Delphi consensus process” to determine their recommendations, but “this process is designed for use with a panel of experts when evidence is lacking. I would say they didn’t have a panel of experts. They largely had a panel of activists, with a few experts.”
There is no mention, for example, of England’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) evidence reviews on puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones from earlier this year. These reviews determined that no studies have compared cross-sex hormones or puberty blockers with a control group and all follow-up periods for cross-sex hormones were relatively short.
This disappoints Dr. Mason: “These are significant; they are important documents.”
And much of the evidence quoted comes from the well-known and often-quoted “Dutch-protocol” study of 2011, in which the children studied were much younger at the time of their gender dysphoria, compared with the many adolescents who make up the current surge in presentation at gender clinics worldwide, she adds.
Rapid-onset GD: adolescents presenting late with little history
Dr. Mason also stresses that the SOC 8 does not address the most urgent issues in transgender medicine today, mainly because it does not address rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD): “This is the dilemma of the 21st century; it’s new.”
ROGD – a term first coined in 2018 by researcher Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, now president of the Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR) – refers to the phenomena of adolescents expressing a desire to transition from their birth sex after little or no apparent previous indication.
However, the SOC 8 does make reference to aspects of adolescent development that might impact their decision-making processes around gender identity during teen years. The chapter on adolescents reads: “... adolescence is also often associated with increased risk-taking behaviors. Along with these notable changes ... individuation from parents ... [there is] often a heightened focus on peer relationships, which can be both positive and detrimental.”
The guidance goes on to point out that “it is critical to understand how all of these aspects of development may impact the decision-making for a given young person within their specific cultural context.”
Desistance and detransitioning not adequately addressed
Dr. Mason also says there is little mention “about detransitioning in this SOC [8], and ‘gender dysphoria’ and ‘trans’ are terms that are not defined.”
Likewise, there is no mention of desistance, she highlights, which is when individuals naturally resolve their dysphoria around their birth sex as they grow older.
The most recent published data seen by this news organization relates to a study from March 2021 that showed nearly 88% of boys who struggled with gender identity in childhood (approximate mean age 8 years and follow-up at approximate mean age 20 years) desisted. It reads: “Of the 139 participants, 17 (12.2%) were classified as ‘persisters’ and the remaining 122 (87.8%) were classified as desisters.”
“Most children with gender dysphoria will desist and lose their concept of themselves as being the opposite gender,” Dr. Mason explains. “This is the safest path for a child – desistance.”
“Transition can turn a healthy young person into a lifelong medical patient and has significant health risks,” she emphasizes, stressing that transition has not been shown to decrease the probability of suicide, or attempts at suicide, despite myriad claims saying otherwise.
“Before we were routinely transitioning kids at school, the vast majority of children grew out of their gender dysphoria. This history is not recognized at all in these SOC [8],” she maintains.
Ken Zucker, PhD, CPsych, an author of the study of desistance in boys, says the terms desistence and persistence of gender dysphoria have caused some consternation in certain circles.
An editor of the Archives of Sexual Behavior and professor in the department of psychiatry, University of Toronto, Dr. Zucker has published widely on the topic.
He told this news organization: “The terms persistence and desistance have become verboten among the WPATH cognoscenti. Perhaps the contributors to SOC 8 have come up with alternative descriptors.”
“The term ‘desistance’ is particularly annoying to some of the gender-affirming clinicians, because they don’t believe that desistance is bona fide,” Dr. Zucker points out.
“The desistance resisters are like anti-vaxxers – nothing one can provide as evidence for the efficacy of vaccines is sufficient. There will always be a new objection.”
Other mental health issues, in particular ADHD and autism
It is also widely acknowledged that there is a higher rate of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric diagnoses in individuals with gender dysphoria. For example, one 2020 study found that transgender people were three to six times as likely to be autistic as cisgender people (those whose gender is aligned with their birth sex).
Statement one in the chapter on adolescents in draft WPATH SOC 8 does give a nod to this, pointing out that health professionals working with gender diverse adolescents “should receive training and develop expertise in autism spectrum disorders and other neurodiversity conditions.”
It also notes that in some cases “a more extended assessment process may be useful, such as for youth with more complex presentations (e.g., complicated mental health histories, co-occurring autism spectrum characteristics in particular) and an absence of experienced childhood gender incongruence.”
However, Dr. Mason stresses that underlying mental health issues are central to addressing how to manage a significant number of these patients.
“If a young person has ADHD or autism, they are not ready to make decisions about the rest of their life at age 18. Even a neurotypical young person is still developing their frontal cortex in their early 20s, and it takes longer for those with ADHD or on the autism spectrum.”
She firmly believes that the guidance does not give sufficient consideration to comorbidities in people over the age of 18.
According to their [SOC 8] guidelines, “once someone is 18 they are ready for anything,” says Dr. Mason.
Offering some explanation for the increased prevalence of ADHD and autism in those with gender dysphoria, Dr. Mason notes that children can have “hyperfocus” and those with autism will fixate on a particular area of interest. “If a child is unhappy in their life, and this can be more likely if someone is neuro-atypical, then it is likely that the individual might go online and find this one solution [for example, a transgender identity] that seems to fix everything.”
Perceptions of femininity and masculinity can also be extra challenging for a child with autism, Dr. Mason says. “It is relatively easy for an autistic girl to feel like she should be a boy because the rules of femininity are composed of nonverbal, subtle behaviors that can be difficult to pick up on,” she points out. “An autistic child who isn’t particularly good at nonverbal communication might not pick up on these and thus feel they are not very ‘female.’”
“There’s a whole lot of grass-is-greener-type thinking. Girls think boys have an easier life, and boys think girls have an easier life. I know some detransitioners who have spoken eloquently about realizing their mistake on this,” she adds.
Other parts of the SOC 8 that Dr. Mason disagrees with include the recommendation in the adolescent chapter that 14-year-olds are mature enough to start cross-sex hormones, that is, giving testosterone to a female who wants to transition to male or estrogen to a male who wishes to transition to female. “I think that’s far too young,” she asserts.
And she points out that the document states 17-year-olds are ready for genital reassignment surgery. Again, she believes this is far too young.
“Also, the SOC 8 document does not clarify who is appropriate for surgery. Whenever surgery is discussed, it becomes very vague,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New draft guidance from the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) is raising serious concerns among professionals caring for people with gender dysphoria, prompting claims that WPATH is an organization “captured by activists.”
Experts in adolescent and child psychology, as well as pediatric health, have expressed dismay that the WPATH Standards of Care (SOC) 8 appear to miss some of the most urgent issues in the field of transgender medicine and are considered to express a radical and unreserved leaning towards “gender-affirmation.”
The WPATH SOC 8 document is available for view and comment until Dec. 16 until 11.59 PM EST, after which time revisions will be made and the final version published.
Despite repeated attempts by this news organization to seek clarification on certain aspects of the guidance from members of the WPATH SOC 8 committee, requests were declined “until the guidance is finalized.”
According to the WPATH website, the SOC 8 aims to provide “clinical guidance for health professionals to assist transgender and gender diverse people with safe and effective pathways” to manage their gender dysphoria and potentially transition.
Such pathways may relate to primary care, gynecologic and urologic care, reproductive options, voice and communication therapy, mental health services, and hormonal or surgical treatments, among others.
WPATH adds that it was felt necessary to revise the existing SOC 7 (published in 2012) because of recent “globally unprecedented increase and visibility of transgender and gender-diverse people seeking support and gender-affirming medical treatment.”
Gender-affirming medical treatment means different things at different ages. In the case of kids with gender dysphoria who have not yet entered puberty associated with their birth sex, this might include prescribing so-called “puberty blockers” to delay natural puberty – gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogs that are licensed for use in precocious puberty in children. Such agents have not been licensed for use in children with gender dysphoria, however, so any use for this purpose is off-label.
Following puberty blockade – or in cases where adolescents have already undergone natural puberty – the next step is to begin cross-sex hormones. So, for a female patient who wants to transition to male (FTM), that would be lifelong testosterone, and for a male who wants to be female (MTF), it involves lifelong estrogen. Again, use of such hormones in transgender individuals is entirely off-label.
Just last month, two of America’s leading experts on transgender medicine, both psychologists – including one who is transgender – told this news organization they were concerned that the quality of the evaluations of youth with gender dysphoria are being stifled by activists who are worried that open discussions will further stigmatize trans individuals.
They subsequently wrote an op-ed on the topic entitled, “The mental health establishment is failing trans kids,” which was finally published in the Washington Post on Nov. 24, after numerous other mainstream U.S. media outlets had rejected it.
New SOC 8 ‘is not evidence based,’ should not be new ‘gold standard’
One expert says the draft SOC 8 lacks balance and does not address certain issues, while paying undue attention to others that detract from real questions facing the field of transgender medicine, both in the United States and around the world.
Julia Mason, MD, is a pediatrician based in Gresham, Oregon, with a special interest in children and adolescents experiencing gender dysphoria. “The SOC 8 shows us that WPATH remains captured by activists,” she asserts.
Dr. Mason questions the integrity of WPATH based on what she has read in the draft SOC 8.
“We need a serious organization to take a sober look at the evidence, and that is why we have established the Society for Evidence-Based Gender Medicine [SEGM],” she noted. “This is what we do – we are looking at all of the evidence.”
Dr. Mason is a clinical advisor to SEGM, an organization set-up to evaluate current interventions and evidence on gender dysphoria.
The pediatrician has particular concerns regarding the child and adolescent chapters in the draft SOC 8. The adolescent chapter states: “Guidelines are meant to provide a gold standard based on the available evidence at this moment of time.”
Dr. Mason disputes this assertion. “This document should not be the new gold standard going forward, primarily because it is not evidence based.”
In an interview, Dr. Mason explained that WPATH say they used the “Delphi consensus process” to determine their recommendations, but “this process is designed for use with a panel of experts when evidence is lacking. I would say they didn’t have a panel of experts. They largely had a panel of activists, with a few experts.”
There is no mention, for example, of England’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) evidence reviews on puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones from earlier this year. These reviews determined that no studies have compared cross-sex hormones or puberty blockers with a control group and all follow-up periods for cross-sex hormones were relatively short.
This disappoints Dr. Mason: “These are significant; they are important documents.”
And much of the evidence quoted comes from the well-known and often-quoted “Dutch-protocol” study of 2011, in which the children studied were much younger at the time of their gender dysphoria, compared with the many adolescents who make up the current surge in presentation at gender clinics worldwide, she adds.
Rapid-onset GD: adolescents presenting late with little history
Dr. Mason also stresses that the SOC 8 does not address the most urgent issues in transgender medicine today, mainly because it does not address rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD): “This is the dilemma of the 21st century; it’s new.”
ROGD – a term first coined in 2018 by researcher Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, now president of the Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR) – refers to the phenomena of adolescents expressing a desire to transition from their birth sex after little or no apparent previous indication.
However, the SOC 8 does make reference to aspects of adolescent development that might impact their decision-making processes around gender identity during teen years. The chapter on adolescents reads: “... adolescence is also often associated with increased risk-taking behaviors. Along with these notable changes ... individuation from parents ... [there is] often a heightened focus on peer relationships, which can be both positive and detrimental.”
The guidance goes on to point out that “it is critical to understand how all of these aspects of development may impact the decision-making for a given young person within their specific cultural context.”
Desistance and detransitioning not adequately addressed
Dr. Mason also says there is little mention “about detransitioning in this SOC [8], and ‘gender dysphoria’ and ‘trans’ are terms that are not defined.”
Likewise, there is no mention of desistance, she highlights, which is when individuals naturally resolve their dysphoria around their birth sex as they grow older.
The most recent published data seen by this news organization relates to a study from March 2021 that showed nearly 88% of boys who struggled with gender identity in childhood (approximate mean age 8 years and follow-up at approximate mean age 20 years) desisted. It reads: “Of the 139 participants, 17 (12.2%) were classified as ‘persisters’ and the remaining 122 (87.8%) were classified as desisters.”
“Most children with gender dysphoria will desist and lose their concept of themselves as being the opposite gender,” Dr. Mason explains. “This is the safest path for a child – desistance.”
“Transition can turn a healthy young person into a lifelong medical patient and has significant health risks,” she emphasizes, stressing that transition has not been shown to decrease the probability of suicide, or attempts at suicide, despite myriad claims saying otherwise.
“Before we were routinely transitioning kids at school, the vast majority of children grew out of their gender dysphoria. This history is not recognized at all in these SOC [8],” she maintains.
Ken Zucker, PhD, CPsych, an author of the study of desistance in boys, says the terms desistence and persistence of gender dysphoria have caused some consternation in certain circles.
An editor of the Archives of Sexual Behavior and professor in the department of psychiatry, University of Toronto, Dr. Zucker has published widely on the topic.
He told this news organization: “The terms persistence and desistance have become verboten among the WPATH cognoscenti. Perhaps the contributors to SOC 8 have come up with alternative descriptors.”
“The term ‘desistance’ is particularly annoying to some of the gender-affirming clinicians, because they don’t believe that desistance is bona fide,” Dr. Zucker points out.
“The desistance resisters are like anti-vaxxers – nothing one can provide as evidence for the efficacy of vaccines is sufficient. There will always be a new objection.”
Other mental health issues, in particular ADHD and autism
It is also widely acknowledged that there is a higher rate of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric diagnoses in individuals with gender dysphoria. For example, one 2020 study found that transgender people were three to six times as likely to be autistic as cisgender people (those whose gender is aligned with their birth sex).
Statement one in the chapter on adolescents in draft WPATH SOC 8 does give a nod to this, pointing out that health professionals working with gender diverse adolescents “should receive training and develop expertise in autism spectrum disorders and other neurodiversity conditions.”
It also notes that in some cases “a more extended assessment process may be useful, such as for youth with more complex presentations (e.g., complicated mental health histories, co-occurring autism spectrum characteristics in particular) and an absence of experienced childhood gender incongruence.”
However, Dr. Mason stresses that underlying mental health issues are central to addressing how to manage a significant number of these patients.
“If a young person has ADHD or autism, they are not ready to make decisions about the rest of their life at age 18. Even a neurotypical young person is still developing their frontal cortex in their early 20s, and it takes longer for those with ADHD or on the autism spectrum.”
She firmly believes that the guidance does not give sufficient consideration to comorbidities in people over the age of 18.
According to their [SOC 8] guidelines, “once someone is 18 they are ready for anything,” says Dr. Mason.
Offering some explanation for the increased prevalence of ADHD and autism in those with gender dysphoria, Dr. Mason notes that children can have “hyperfocus” and those with autism will fixate on a particular area of interest. “If a child is unhappy in their life, and this can be more likely if someone is neuro-atypical, then it is likely that the individual might go online and find this one solution [for example, a transgender identity] that seems to fix everything.”
Perceptions of femininity and masculinity can also be extra challenging for a child with autism, Dr. Mason says. “It is relatively easy for an autistic girl to feel like she should be a boy because the rules of femininity are composed of nonverbal, subtle behaviors that can be difficult to pick up on,” she points out. “An autistic child who isn’t particularly good at nonverbal communication might not pick up on these and thus feel they are not very ‘female.’”
“There’s a whole lot of grass-is-greener-type thinking. Girls think boys have an easier life, and boys think girls have an easier life. I know some detransitioners who have spoken eloquently about realizing their mistake on this,” she adds.
Other parts of the SOC 8 that Dr. Mason disagrees with include the recommendation in the adolescent chapter that 14-year-olds are mature enough to start cross-sex hormones, that is, giving testosterone to a female who wants to transition to male or estrogen to a male who wishes to transition to female. “I think that’s far too young,” she asserts.
And she points out that the document states 17-year-olds are ready for genital reassignment surgery. Again, she believes this is far too young.
“Also, the SOC 8 document does not clarify who is appropriate for surgery. Whenever surgery is discussed, it becomes very vague,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Top’ surgery for trans youth: Advance or dangerous medicine?
Is the gender-affirmative treatment approach an example of “medicine continuing on its progressive march of improving human life” or “a manifestation of dangerous medicine that ... will cause more harm than benefit to vulnerable youths?” wonders an Australian psychiatrist in a newly published letter that addresses the controversial procedure of masculinizing chest surgery – a double mastectomy – in young people with gender dysphoria (GD).
Alison Clayton, MBBS, explores the evidence for masculinizing chest surgery and looks back at examples of “dangerous medicine” in the past century while looking forward, wondering how future medics will retrospectively view gender affirmative treatment, especially so-called “top” or masculinizing chest surgery, which is in actual fact a double mastectomy, in a letter published Nov. 22 in the Archives of Sexual Behavior.
“It is surprising that clinicians and researchers claim chest surgery for GD youth is an evidence-based intervention, rather than acknowledging it is an experimental treatment that requires more rigorous and human research ethics committee [HREC] approved research,” she writes.
“The medical profession needs to consider whether, in its championing of the gender-affirmative approach for GD youth, it is also acting brashly and making mistakes that will negatively impact some young people for the rest of their lives,” she continues.
Ms. Clayton, after many years of experience as a psychiatrist, has recently returned to postgraduate research into the history of 20th-century psychiatry at the School of Historical and Philosophical Studies, University of Melbourne.
Meanwhile, the authors of a viewpoint published online Dec. 1 in JAMA Surgery, agree with Ms. Clayton on the issue of a lack of long-term studies on which to base decisions, particularly when it comes to insurance coverage for gender surgeries in the United States.
Nnenaya Agochukwu-Mmonu, MD, and colleagues recommend use of the coverage with evidence development (CED) approach, which would, they say, provide a “rigorous evidence base for gender-affirming interventions and surgery while simultaneously allowing access and provisional coverage for these services.”
Threefold increase in gender-affirming surgeries in past decade
There has been a threefold rise in the rate of gender-affirming surgeries in the United States in the past decade, which can be attributed to increased recognition of gender dysphoria, decreasing social stigma toward these individuals, greater clinical experience, and expanding insurance coverage, according to Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu, of the department of urology, NYU School of Medicine, and coauthors.
Ms. Clayton meanwhile notes that of the increasing number of adolescents being referred for treatment for gender dysphoria in the Western world, most were born female and many have “a history of psychiatric illness or neurodevelopmental disorders.”
Many of these youngsters also show a “high demand” for surgical removal of breasts, she adds, noting that this operation is being undertaken as routine treatment in patients as young as 13, with some clinicians arguing that “this surgery is an evidence-based intervention that improves mental health outcomes, and that it is discriminatory for it not to be available.”
She also notes that “chest dysphoria” is “a recently created term meaning discomfort with one’s breasts.” The term “breast” is therefore largely absent in publications talking about this surgery as it “may cause distress for transgender males,” to quote one source, Ms. Clayton says, and “this seems part of a broader pattern of removing this term from clinical language,” according to another article on the subject.
Ms. Clayton also says, “There are only a handful of published studies focusing on the potential benefits of masculinizing chest surgery,” and notes that these mostly report on surgery for individuals younger than 21 years old.
Significant methodological flaws in existing research
One study of 14 postsurgical youth (nine of whom were under 18 years) found that “all reported high aesthetic satisfaction and most self-reported low complication rates and improvement in mood.”
Another cross-sectional retrospective survey looked at 68 postsurgical transmasculine youth (72% of the eligible postsurgical population); 49% had surgery when younger than age 18, with the youngest being age 13 and the oldest age 24. At the time of the survey, only 14% of participants were more than 2 years postsurgery. The postsurgical participants were found to have reduced chest dysphoria (the outcome) compared with a convenience and nonmatched comparison sample of nonsurgical transmasculine youth.
And a 2021 qualitative study of 30 transmale youth – about half of whom had undergone chest surgery – concluded that the postsurgical cohort experienced “tremendous” benefits in chest dysphoria and a range of psychological outcomes.
On this particular study, Ms. Clayton notes that “in my opinion, they did not provide enough detail for the reader to make an informed judgment regarding this latter claim.”
She goes on to discuss genital surgery, sometimes called full gender-affirming surgery (or “bottom surgery”), and says proponents of these operations point out that the main objections to them in minors is to “surgical sterilization, and people get super worked up about that ... it is a barrier we have to overcome, and I think we are going to.”
Ms. Clayton asserts that it seems “this barrier is already being overcome, as it has been reported that in the United States, genital surgery is being undertaken on gender dysphoric minors as young as 15 years old.”
Reflecting on the available evidence, Ms. Clayton highlights the significant methodological flaws that limit the extent to which surgery can be linked to short-term improved mental health outcomes and adds that information on long-term outcomes and rates of regret is unavailable.
She also asserts that the research fails to assess “a role for psychological interventions which could be utilized, as a least-harm intervention, until maturity is reached.”
Historical examples of experimental medicine
Ms. Clayton goes on to draw parallels with experimental medicine performed on homosexuals in the 20th century, highlighting the medical and surgical interventions, which included metrazol convulsive therapy, chemical castration with estrogens, surgical castration, clitoridectomy, brain operations, and aversive electrotherapy.
She also refers to the historical practice of hormonal treatment for “tall girls” and “short boys” between the 1960s and 1980s. Hormones were given to young people who did not have any medical reason underpinning their stature but were distressed, and society considered their height to have a negative social impact.
“With the encouragement of physicians and school nurses, enthusiastic media promotion, and pharmaceutical companies’ advertising, parents sought hormonal interventions,” she writes, adding that, at the time the hormones were considered safe, but long-term adverse effects emerged, including impaired fertility and increased risk of cancers.
“This seems another part of the story of medicine acting to reinforce society’s sex stereotypes, and for some patients it came at disastrous personal cost,” writes Ms. Clayton.
The gender-affirming approach is based on endorsing the adolescent’s stated gender identity with minimal questioning and “that they should be supported to undertake social transition, medical transition, masculinizing chest surgery, and, some also argue, genital surgery,” she writes.
Objectors to this approach pinpoint the “limited and low-quality evidence base for the benefits” but also “the irreversible and long-term adverse impacts of these treatments on fertility and sexual function, as well as on bone, brain, and cardiovascular functioning.”
Current studies of gender-affirming surgeries lack standardization
In their viewpoint, Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu and colleagues state that use of a CED would not only help provide an evidence base but would also ensure better-informed policy access and coverage decisions to help standardize approaches to gender surgery in the United States.
Currently, they note, “Studies examining the mental health benefit for patients undergoing gender-affirming surgeries include measures that lack standardization, evaluate different interventions (that is, surgeries are rarely done with concurrent hormone administration), include dissimilar patient populations, and use different study designs.”
This difference in study design leads to variation in reported outcomes. Although many studies have shown benefit, others report that patients have unrealistic expectations or experience regret, Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu and coauthors conclude.
CED provides an option that would enable informed decisions. “It allows the deliberate use of innovative therapies, explicit integration of transgender and nonbinary patient input, and ongoing systematic evaluation aimed to identify specific patient groups who would or would not benefit from their use.”
This leads back to Ms. Clayton’s central question around whether the gender-affirmative approach is a medical advance or dangerous medicine.
“Why are these experimental interventions, with inherent risks and scarce, low-quality evidence for benefits being implemented outside HREC-regulated clinical trial settings?’” she wonders.
Ms. Clayton has declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is the gender-affirmative treatment approach an example of “medicine continuing on its progressive march of improving human life” or “a manifestation of dangerous medicine that ... will cause more harm than benefit to vulnerable youths?” wonders an Australian psychiatrist in a newly published letter that addresses the controversial procedure of masculinizing chest surgery – a double mastectomy – in young people with gender dysphoria (GD).
Alison Clayton, MBBS, explores the evidence for masculinizing chest surgery and looks back at examples of “dangerous medicine” in the past century while looking forward, wondering how future medics will retrospectively view gender affirmative treatment, especially so-called “top” or masculinizing chest surgery, which is in actual fact a double mastectomy, in a letter published Nov. 22 in the Archives of Sexual Behavior.
“It is surprising that clinicians and researchers claim chest surgery for GD youth is an evidence-based intervention, rather than acknowledging it is an experimental treatment that requires more rigorous and human research ethics committee [HREC] approved research,” she writes.
“The medical profession needs to consider whether, in its championing of the gender-affirmative approach for GD youth, it is also acting brashly and making mistakes that will negatively impact some young people for the rest of their lives,” she continues.
Ms. Clayton, after many years of experience as a psychiatrist, has recently returned to postgraduate research into the history of 20th-century psychiatry at the School of Historical and Philosophical Studies, University of Melbourne.
Meanwhile, the authors of a viewpoint published online Dec. 1 in JAMA Surgery, agree with Ms. Clayton on the issue of a lack of long-term studies on which to base decisions, particularly when it comes to insurance coverage for gender surgeries in the United States.
Nnenaya Agochukwu-Mmonu, MD, and colleagues recommend use of the coverage with evidence development (CED) approach, which would, they say, provide a “rigorous evidence base for gender-affirming interventions and surgery while simultaneously allowing access and provisional coverage for these services.”
Threefold increase in gender-affirming surgeries in past decade
There has been a threefold rise in the rate of gender-affirming surgeries in the United States in the past decade, which can be attributed to increased recognition of gender dysphoria, decreasing social stigma toward these individuals, greater clinical experience, and expanding insurance coverage, according to Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu, of the department of urology, NYU School of Medicine, and coauthors.
Ms. Clayton meanwhile notes that of the increasing number of adolescents being referred for treatment for gender dysphoria in the Western world, most were born female and many have “a history of psychiatric illness or neurodevelopmental disorders.”
Many of these youngsters also show a “high demand” for surgical removal of breasts, she adds, noting that this operation is being undertaken as routine treatment in patients as young as 13, with some clinicians arguing that “this surgery is an evidence-based intervention that improves mental health outcomes, and that it is discriminatory for it not to be available.”
She also notes that “chest dysphoria” is “a recently created term meaning discomfort with one’s breasts.” The term “breast” is therefore largely absent in publications talking about this surgery as it “may cause distress for transgender males,” to quote one source, Ms. Clayton says, and “this seems part of a broader pattern of removing this term from clinical language,” according to another article on the subject.
Ms. Clayton also says, “There are only a handful of published studies focusing on the potential benefits of masculinizing chest surgery,” and notes that these mostly report on surgery for individuals younger than 21 years old.
Significant methodological flaws in existing research
One study of 14 postsurgical youth (nine of whom were under 18 years) found that “all reported high aesthetic satisfaction and most self-reported low complication rates and improvement in mood.”
Another cross-sectional retrospective survey looked at 68 postsurgical transmasculine youth (72% of the eligible postsurgical population); 49% had surgery when younger than age 18, with the youngest being age 13 and the oldest age 24. At the time of the survey, only 14% of participants were more than 2 years postsurgery. The postsurgical participants were found to have reduced chest dysphoria (the outcome) compared with a convenience and nonmatched comparison sample of nonsurgical transmasculine youth.
And a 2021 qualitative study of 30 transmale youth – about half of whom had undergone chest surgery – concluded that the postsurgical cohort experienced “tremendous” benefits in chest dysphoria and a range of psychological outcomes.
On this particular study, Ms. Clayton notes that “in my opinion, they did not provide enough detail for the reader to make an informed judgment regarding this latter claim.”
She goes on to discuss genital surgery, sometimes called full gender-affirming surgery (or “bottom surgery”), and says proponents of these operations point out that the main objections to them in minors is to “surgical sterilization, and people get super worked up about that ... it is a barrier we have to overcome, and I think we are going to.”
Ms. Clayton asserts that it seems “this barrier is already being overcome, as it has been reported that in the United States, genital surgery is being undertaken on gender dysphoric minors as young as 15 years old.”
Reflecting on the available evidence, Ms. Clayton highlights the significant methodological flaws that limit the extent to which surgery can be linked to short-term improved mental health outcomes and adds that information on long-term outcomes and rates of regret is unavailable.
She also asserts that the research fails to assess “a role for psychological interventions which could be utilized, as a least-harm intervention, until maturity is reached.”
Historical examples of experimental medicine
Ms. Clayton goes on to draw parallels with experimental medicine performed on homosexuals in the 20th century, highlighting the medical and surgical interventions, which included metrazol convulsive therapy, chemical castration with estrogens, surgical castration, clitoridectomy, brain operations, and aversive electrotherapy.
She also refers to the historical practice of hormonal treatment for “tall girls” and “short boys” between the 1960s and 1980s. Hormones were given to young people who did not have any medical reason underpinning their stature but were distressed, and society considered their height to have a negative social impact.
“With the encouragement of physicians and school nurses, enthusiastic media promotion, and pharmaceutical companies’ advertising, parents sought hormonal interventions,” she writes, adding that, at the time the hormones were considered safe, but long-term adverse effects emerged, including impaired fertility and increased risk of cancers.
“This seems another part of the story of medicine acting to reinforce society’s sex stereotypes, and for some patients it came at disastrous personal cost,” writes Ms. Clayton.
The gender-affirming approach is based on endorsing the adolescent’s stated gender identity with minimal questioning and “that they should be supported to undertake social transition, medical transition, masculinizing chest surgery, and, some also argue, genital surgery,” she writes.
Objectors to this approach pinpoint the “limited and low-quality evidence base for the benefits” but also “the irreversible and long-term adverse impacts of these treatments on fertility and sexual function, as well as on bone, brain, and cardiovascular functioning.”
Current studies of gender-affirming surgeries lack standardization
In their viewpoint, Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu and colleagues state that use of a CED would not only help provide an evidence base but would also ensure better-informed policy access and coverage decisions to help standardize approaches to gender surgery in the United States.
Currently, they note, “Studies examining the mental health benefit for patients undergoing gender-affirming surgeries include measures that lack standardization, evaluate different interventions (that is, surgeries are rarely done with concurrent hormone administration), include dissimilar patient populations, and use different study designs.”
This difference in study design leads to variation in reported outcomes. Although many studies have shown benefit, others report that patients have unrealistic expectations or experience regret, Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu and coauthors conclude.
CED provides an option that would enable informed decisions. “It allows the deliberate use of innovative therapies, explicit integration of transgender and nonbinary patient input, and ongoing systematic evaluation aimed to identify specific patient groups who would or would not benefit from their use.”
This leads back to Ms. Clayton’s central question around whether the gender-affirmative approach is a medical advance or dangerous medicine.
“Why are these experimental interventions, with inherent risks and scarce, low-quality evidence for benefits being implemented outside HREC-regulated clinical trial settings?’” she wonders.
Ms. Clayton has declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is the gender-affirmative treatment approach an example of “medicine continuing on its progressive march of improving human life” or “a manifestation of dangerous medicine that ... will cause more harm than benefit to vulnerable youths?” wonders an Australian psychiatrist in a newly published letter that addresses the controversial procedure of masculinizing chest surgery – a double mastectomy – in young people with gender dysphoria (GD).
Alison Clayton, MBBS, explores the evidence for masculinizing chest surgery and looks back at examples of “dangerous medicine” in the past century while looking forward, wondering how future medics will retrospectively view gender affirmative treatment, especially so-called “top” or masculinizing chest surgery, which is in actual fact a double mastectomy, in a letter published Nov. 22 in the Archives of Sexual Behavior.
“It is surprising that clinicians and researchers claim chest surgery for GD youth is an evidence-based intervention, rather than acknowledging it is an experimental treatment that requires more rigorous and human research ethics committee [HREC] approved research,” she writes.
“The medical profession needs to consider whether, in its championing of the gender-affirmative approach for GD youth, it is also acting brashly and making mistakes that will negatively impact some young people for the rest of their lives,” she continues.
Ms. Clayton, after many years of experience as a psychiatrist, has recently returned to postgraduate research into the history of 20th-century psychiatry at the School of Historical and Philosophical Studies, University of Melbourne.
Meanwhile, the authors of a viewpoint published online Dec. 1 in JAMA Surgery, agree with Ms. Clayton on the issue of a lack of long-term studies on which to base decisions, particularly when it comes to insurance coverage for gender surgeries in the United States.
Nnenaya Agochukwu-Mmonu, MD, and colleagues recommend use of the coverage with evidence development (CED) approach, which would, they say, provide a “rigorous evidence base for gender-affirming interventions and surgery while simultaneously allowing access and provisional coverage for these services.”
Threefold increase in gender-affirming surgeries in past decade
There has been a threefold rise in the rate of gender-affirming surgeries in the United States in the past decade, which can be attributed to increased recognition of gender dysphoria, decreasing social stigma toward these individuals, greater clinical experience, and expanding insurance coverage, according to Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu, of the department of urology, NYU School of Medicine, and coauthors.
Ms. Clayton meanwhile notes that of the increasing number of adolescents being referred for treatment for gender dysphoria in the Western world, most were born female and many have “a history of psychiatric illness or neurodevelopmental disorders.”
Many of these youngsters also show a “high demand” for surgical removal of breasts, she adds, noting that this operation is being undertaken as routine treatment in patients as young as 13, with some clinicians arguing that “this surgery is an evidence-based intervention that improves mental health outcomes, and that it is discriminatory for it not to be available.”
She also notes that “chest dysphoria” is “a recently created term meaning discomfort with one’s breasts.” The term “breast” is therefore largely absent in publications talking about this surgery as it “may cause distress for transgender males,” to quote one source, Ms. Clayton says, and “this seems part of a broader pattern of removing this term from clinical language,” according to another article on the subject.
Ms. Clayton also says, “There are only a handful of published studies focusing on the potential benefits of masculinizing chest surgery,” and notes that these mostly report on surgery for individuals younger than 21 years old.
Significant methodological flaws in existing research
One study of 14 postsurgical youth (nine of whom were under 18 years) found that “all reported high aesthetic satisfaction and most self-reported low complication rates and improvement in mood.”
Another cross-sectional retrospective survey looked at 68 postsurgical transmasculine youth (72% of the eligible postsurgical population); 49% had surgery when younger than age 18, with the youngest being age 13 and the oldest age 24. At the time of the survey, only 14% of participants were more than 2 years postsurgery. The postsurgical participants were found to have reduced chest dysphoria (the outcome) compared with a convenience and nonmatched comparison sample of nonsurgical transmasculine youth.
And a 2021 qualitative study of 30 transmale youth – about half of whom had undergone chest surgery – concluded that the postsurgical cohort experienced “tremendous” benefits in chest dysphoria and a range of psychological outcomes.
On this particular study, Ms. Clayton notes that “in my opinion, they did not provide enough detail for the reader to make an informed judgment regarding this latter claim.”
She goes on to discuss genital surgery, sometimes called full gender-affirming surgery (or “bottom surgery”), and says proponents of these operations point out that the main objections to them in minors is to “surgical sterilization, and people get super worked up about that ... it is a barrier we have to overcome, and I think we are going to.”
Ms. Clayton asserts that it seems “this barrier is already being overcome, as it has been reported that in the United States, genital surgery is being undertaken on gender dysphoric minors as young as 15 years old.”
Reflecting on the available evidence, Ms. Clayton highlights the significant methodological flaws that limit the extent to which surgery can be linked to short-term improved mental health outcomes and adds that information on long-term outcomes and rates of regret is unavailable.
She also asserts that the research fails to assess “a role for psychological interventions which could be utilized, as a least-harm intervention, until maturity is reached.”
Historical examples of experimental medicine
Ms. Clayton goes on to draw parallels with experimental medicine performed on homosexuals in the 20th century, highlighting the medical and surgical interventions, which included metrazol convulsive therapy, chemical castration with estrogens, surgical castration, clitoridectomy, brain operations, and aversive electrotherapy.
She also refers to the historical practice of hormonal treatment for “tall girls” and “short boys” between the 1960s and 1980s. Hormones were given to young people who did not have any medical reason underpinning their stature but were distressed, and society considered their height to have a negative social impact.
“With the encouragement of physicians and school nurses, enthusiastic media promotion, and pharmaceutical companies’ advertising, parents sought hormonal interventions,” she writes, adding that, at the time the hormones were considered safe, but long-term adverse effects emerged, including impaired fertility and increased risk of cancers.
“This seems another part of the story of medicine acting to reinforce society’s sex stereotypes, and for some patients it came at disastrous personal cost,” writes Ms. Clayton.
The gender-affirming approach is based on endorsing the adolescent’s stated gender identity with minimal questioning and “that they should be supported to undertake social transition, medical transition, masculinizing chest surgery, and, some also argue, genital surgery,” she writes.
Objectors to this approach pinpoint the “limited and low-quality evidence base for the benefits” but also “the irreversible and long-term adverse impacts of these treatments on fertility and sexual function, as well as on bone, brain, and cardiovascular functioning.”
Current studies of gender-affirming surgeries lack standardization
In their viewpoint, Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu and colleagues state that use of a CED would not only help provide an evidence base but would also ensure better-informed policy access and coverage decisions to help standardize approaches to gender surgery in the United States.
Currently, they note, “Studies examining the mental health benefit for patients undergoing gender-affirming surgeries include measures that lack standardization, evaluate different interventions (that is, surgeries are rarely done with concurrent hormone administration), include dissimilar patient populations, and use different study designs.”
This difference in study design leads to variation in reported outcomes. Although many studies have shown benefit, others report that patients have unrealistic expectations or experience regret, Dr. Agochukwu-Mmonu and coauthors conclude.
CED provides an option that would enable informed decisions. “It allows the deliberate use of innovative therapies, explicit integration of transgender and nonbinary patient input, and ongoing systematic evaluation aimed to identify specific patient groups who would or would not benefit from their use.”
This leads back to Ms. Clayton’s central question around whether the gender-affirmative approach is a medical advance or dangerous medicine.
“Why are these experimental interventions, with inherent risks and scarce, low-quality evidence for benefits being implemented outside HREC-regulated clinical trial settings?’” she wonders.
Ms. Clayton has declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
Patient risk, not disease duration, key to timing biologics in IBD
The decision to initiate biologics early in the treatment of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) should be based on complication risk, not on the assumption that earlier treatment produces better results, new research suggests.
Results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials show that “the proportional biologic/placebo treatment effect on remission and response to biologics was not influenced by disease duration in UC or CD patients,” the investigators note.
“Patients with Crohn’s disease treated with biologics early on show over 40% remission rate, compared [with] around 30% for those with disease of 20 years or more,” study investigator Shomron Ben-Horin, MD, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Israel, told this news organization.
The rates of remission with both biologics and placebo were higher for patients with short-duration CD compared with patients with disease of longer duration. However, for patients with UC, the remission rates with both biologics and placebo were similar regardless of disease duration.
“Our findings support the use of biologics in patients with Crohn’s disease early after diagnosis, if they are at high risk of disease progression and complications, but not just to achieve better efficacy,” Dr. Ben-Horin said.
The meta-analysis was published online in Gastroenterology.
Getting the timing right
Dr. Ben-Horin led the research with an international group of investigators who assessed individual data from 6,168 patients with CD and 3,227 patients with UC. The patients were participants in 25 placebo-controlled trials.
For patients with CD, the odds ratio of achieving remission with biologics in comparison with placebo was 1.47 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.15) for short-duration disease (≤18 months), which was not so different from the odds ratio for longer-duration disease (>18 months) (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.19-1.72).
“These results remained similar when tested for other disease duration cutoffs or when accounting for individual patients’ characteristics, such as whether patients were previously exposed to biologics or not,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
For patients with UC, the OR for remission with biologics in comparison with placebo was 1.82 (95% CI, 1.12-2.97) for those with short-duration disease and 2.21 (95% CI, 1.79-2.72) for those with long-duration disease.
What the optimal timing is for using biologics for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes both CD and UC, and whether all patients with these conditions need them are very pertinent questions, said Dr. Ben-Horin.
About a decade ago, the treatment of IBD changed. At that time, patients were initially treated with immunomodulators or steroids; biologics were used only if those treatments failed. More recently, a top-down approach has been followed, in which biologics are brought in at the beginning of the treatment protocol, said Dr. Ben-Horin.
This top-down approach has been widely adopted to prevent complications, such as intestinal strictures, bowel obstruction, or fistulas, which can increase the odds that patients with CD will require surgery, he added.
Although treatment with biologics was more effective when initiated earlier than later, data to support this were limited, prompting the investigators to conduct the current review.
“A substantial fraction of patients with Crohn’s disease may be better off with biologics first if they are at a high risk of complications: for example, smokers, patients with extensive disease, or those with perianal fistula. But this may not be necessarily true for those with a low risk of complications,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
For patients with UC, “the lack of better efficacy with biologics in short-duration disease forces us to rethink our protocols of an early start of biologics,” he added.
Possible reasons for the early response
The reasons for the higher response to both placebo and biologics for patients with early CD are unknown.
“It may be that there is plasticity in Crohn’s disease early in the course of disease, where the tissue is more amenable to return to normal whether the patient is on placebo or treatment,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
He suspects that the more likely explanation is that the placebo response is higher in patients with CD of short duration.
“When we looked at levels of C-reactive protein, this was reduced by biologics at similar magnitude in early- and late-disease patients,” Dr. Ben-Horin said. He noted that more studies are needed to better understand disease dynamics with these conditions.
Commenting on the findings, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, from Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, noted that they “absolutely support earlier intervention for moderate-severe Crohn’s disease from diagnosis, rather than waiting for transmural progression that will make disease more refractory to any mechanism of action.”
“Unfortunately, the average duration of disease in biologic trials is often close to 10 years, which implies a more refractory population,” Dr. Hanauer said.
“Furthermore, in the United States, clinicians and patients are hampered by inability to gain third-party authorization for biologics or advanced oral agents, such as JAK inhibitors or S1P modulators, until failure of so-called conventional agents despite labeling indication for moderate-severe disease,” he added.
Dr. Ben-Horin has received consultancy and/or advisory board fees from AbbVie, Novartis, Schering-Plough, Janssen, Celltrion, GSK, Pfizer, Galmed, and Takeda and research support from AbbVie, Janssen, Celltrion, Galmed, and Takeda. Dr. Hanauer is a consultant and speaker for AbbVie, Janssen, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The decision to initiate biologics early in the treatment of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) should be based on complication risk, not on the assumption that earlier treatment produces better results, new research suggests.
Results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials show that “the proportional biologic/placebo treatment effect on remission and response to biologics was not influenced by disease duration in UC or CD patients,” the investigators note.
“Patients with Crohn’s disease treated with biologics early on show over 40% remission rate, compared [with] around 30% for those with disease of 20 years or more,” study investigator Shomron Ben-Horin, MD, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Israel, told this news organization.
The rates of remission with both biologics and placebo were higher for patients with short-duration CD compared with patients with disease of longer duration. However, for patients with UC, the remission rates with both biologics and placebo were similar regardless of disease duration.
“Our findings support the use of biologics in patients with Crohn’s disease early after diagnosis, if they are at high risk of disease progression and complications, but not just to achieve better efficacy,” Dr. Ben-Horin said.
The meta-analysis was published online in Gastroenterology.
Getting the timing right
Dr. Ben-Horin led the research with an international group of investigators who assessed individual data from 6,168 patients with CD and 3,227 patients with UC. The patients were participants in 25 placebo-controlled trials.
For patients with CD, the odds ratio of achieving remission with biologics in comparison with placebo was 1.47 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.15) for short-duration disease (≤18 months), which was not so different from the odds ratio for longer-duration disease (>18 months) (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.19-1.72).
“These results remained similar when tested for other disease duration cutoffs or when accounting for individual patients’ characteristics, such as whether patients were previously exposed to biologics or not,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
For patients with UC, the OR for remission with biologics in comparison with placebo was 1.82 (95% CI, 1.12-2.97) for those with short-duration disease and 2.21 (95% CI, 1.79-2.72) for those with long-duration disease.
What the optimal timing is for using biologics for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes both CD and UC, and whether all patients with these conditions need them are very pertinent questions, said Dr. Ben-Horin.
About a decade ago, the treatment of IBD changed. At that time, patients were initially treated with immunomodulators or steroids; biologics were used only if those treatments failed. More recently, a top-down approach has been followed, in which biologics are brought in at the beginning of the treatment protocol, said Dr. Ben-Horin.
This top-down approach has been widely adopted to prevent complications, such as intestinal strictures, bowel obstruction, or fistulas, which can increase the odds that patients with CD will require surgery, he added.
Although treatment with biologics was more effective when initiated earlier than later, data to support this were limited, prompting the investigators to conduct the current review.
“A substantial fraction of patients with Crohn’s disease may be better off with biologics first if they are at a high risk of complications: for example, smokers, patients with extensive disease, or those with perianal fistula. But this may not be necessarily true for those with a low risk of complications,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
For patients with UC, “the lack of better efficacy with biologics in short-duration disease forces us to rethink our protocols of an early start of biologics,” he added.
Possible reasons for the early response
The reasons for the higher response to both placebo and biologics for patients with early CD are unknown.
“It may be that there is plasticity in Crohn’s disease early in the course of disease, where the tissue is more amenable to return to normal whether the patient is on placebo or treatment,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
He suspects that the more likely explanation is that the placebo response is higher in patients with CD of short duration.
“When we looked at levels of C-reactive protein, this was reduced by biologics at similar magnitude in early- and late-disease patients,” Dr. Ben-Horin said. He noted that more studies are needed to better understand disease dynamics with these conditions.
Commenting on the findings, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, from Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, noted that they “absolutely support earlier intervention for moderate-severe Crohn’s disease from diagnosis, rather than waiting for transmural progression that will make disease more refractory to any mechanism of action.”
“Unfortunately, the average duration of disease in biologic trials is often close to 10 years, which implies a more refractory population,” Dr. Hanauer said.
“Furthermore, in the United States, clinicians and patients are hampered by inability to gain third-party authorization for biologics or advanced oral agents, such as JAK inhibitors or S1P modulators, until failure of so-called conventional agents despite labeling indication for moderate-severe disease,” he added.
Dr. Ben-Horin has received consultancy and/or advisory board fees from AbbVie, Novartis, Schering-Plough, Janssen, Celltrion, GSK, Pfizer, Galmed, and Takeda and research support from AbbVie, Janssen, Celltrion, Galmed, and Takeda. Dr. Hanauer is a consultant and speaker for AbbVie, Janssen, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The decision to initiate biologics early in the treatment of Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) should be based on complication risk, not on the assumption that earlier treatment produces better results, new research suggests.
Results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials show that “the proportional biologic/placebo treatment effect on remission and response to biologics was not influenced by disease duration in UC or CD patients,” the investigators note.
“Patients with Crohn’s disease treated with biologics early on show over 40% remission rate, compared [with] around 30% for those with disease of 20 years or more,” study investigator Shomron Ben-Horin, MD, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Israel, told this news organization.
The rates of remission with both biologics and placebo were higher for patients with short-duration CD compared with patients with disease of longer duration. However, for patients with UC, the remission rates with both biologics and placebo were similar regardless of disease duration.
“Our findings support the use of biologics in patients with Crohn’s disease early after diagnosis, if they are at high risk of disease progression and complications, but not just to achieve better efficacy,” Dr. Ben-Horin said.
The meta-analysis was published online in Gastroenterology.
Getting the timing right
Dr. Ben-Horin led the research with an international group of investigators who assessed individual data from 6,168 patients with CD and 3,227 patients with UC. The patients were participants in 25 placebo-controlled trials.
For patients with CD, the odds ratio of achieving remission with biologics in comparison with placebo was 1.47 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.15) for short-duration disease (≤18 months), which was not so different from the odds ratio for longer-duration disease (>18 months) (OR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.19-1.72).
“These results remained similar when tested for other disease duration cutoffs or when accounting for individual patients’ characteristics, such as whether patients were previously exposed to biologics or not,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
For patients with UC, the OR for remission with biologics in comparison with placebo was 1.82 (95% CI, 1.12-2.97) for those with short-duration disease and 2.21 (95% CI, 1.79-2.72) for those with long-duration disease.
What the optimal timing is for using biologics for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes both CD and UC, and whether all patients with these conditions need them are very pertinent questions, said Dr. Ben-Horin.
About a decade ago, the treatment of IBD changed. At that time, patients were initially treated with immunomodulators or steroids; biologics were used only if those treatments failed. More recently, a top-down approach has been followed, in which biologics are brought in at the beginning of the treatment protocol, said Dr. Ben-Horin.
This top-down approach has been widely adopted to prevent complications, such as intestinal strictures, bowel obstruction, or fistulas, which can increase the odds that patients with CD will require surgery, he added.
Although treatment with biologics was more effective when initiated earlier than later, data to support this were limited, prompting the investigators to conduct the current review.
“A substantial fraction of patients with Crohn’s disease may be better off with biologics first if they are at a high risk of complications: for example, smokers, patients with extensive disease, or those with perianal fistula. But this may not be necessarily true for those with a low risk of complications,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
For patients with UC, “the lack of better efficacy with biologics in short-duration disease forces us to rethink our protocols of an early start of biologics,” he added.
Possible reasons for the early response
The reasons for the higher response to both placebo and biologics for patients with early CD are unknown.
“It may be that there is plasticity in Crohn’s disease early in the course of disease, where the tissue is more amenable to return to normal whether the patient is on placebo or treatment,” said Dr. Ben-Horin.
He suspects that the more likely explanation is that the placebo response is higher in patients with CD of short duration.
“When we looked at levels of C-reactive protein, this was reduced by biologics at similar magnitude in early- and late-disease patients,” Dr. Ben-Horin said. He noted that more studies are needed to better understand disease dynamics with these conditions.
Commenting on the findings, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, from Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, noted that they “absolutely support earlier intervention for moderate-severe Crohn’s disease from diagnosis, rather than waiting for transmural progression that will make disease more refractory to any mechanism of action.”
“Unfortunately, the average duration of disease in biologic trials is often close to 10 years, which implies a more refractory population,” Dr. Hanauer said.
“Furthermore, in the United States, clinicians and patients are hampered by inability to gain third-party authorization for biologics or advanced oral agents, such as JAK inhibitors or S1P modulators, until failure of so-called conventional agents despite labeling indication for moderate-severe disease,” he added.
Dr. Ben-Horin has received consultancy and/or advisory board fees from AbbVie, Novartis, Schering-Plough, Janssen, Celltrion, GSK, Pfizer, Galmed, and Takeda and research support from AbbVie, Janssen, Celltrion, Galmed, and Takeda. Dr. Hanauer is a consultant and speaker for AbbVie, Janssen, and Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Newly discovered vascular barrier in the brain may explain IBD-related anxiety, depression
A newly discovered vascular brain barrier that blocks the passage of inflammatory molecules triggered by gut bacteria may be why patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are at increased risk for certain mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression, early research suggests.
The discovery, which was based on a preclinical model, could lead to new therapeutic targets that could have applications for both gastrointestinal and psychiatric conditions, investigators note.
The research team, which was led by immunologist Maria Rescigno, PhD, and neuroscientist Simona Lodato, PhD, both from Humanitas University, Milan, notes that the barrier resides in the choroid plexus, a region of the brain that is involved in filtering cerebrospinal fluid. The researchers found that the region closes in response to inflammatory molecules produced in reaction to the presence of intestinal bacteria in patients with gut disorders.
Dr. Lodato said in an interview that the brain’s choroid plexus vascular barrier, along with another barrier between the gut and liver, known as the gut vascular barrier, appear to control the movement of molecules along the gut-brain axis.
“We show that in addition to the epithelial barrier in the choroid plexus, there is a functional vascular barrier that only becomes evident in blocking entry of various inflammatory molecules under conditions of systemic inflammation,” Dr. Lodato said.
“This interruption of the gut-brain interaction has developed to protect the brain from inflammation. Why this happens is not yet known, but it is likely to prevent epileptic seizures and imbalanced neuronal activity,” added Dr. Rescigno.
The study was published online October 22 in Science.
The gut a root cause of mental illness?
Nearly 40% of patients with IBD also experience depression and anxiety. It was once thought that these conditions arose because of patients’ difficulties in coping with their disease, said Dr. Rescigno.
“People with these disorders conventionally thought to be caused by an imbalance in the brain may actually find the root cause is located in the intestine. This is the first time these symptoms have been associated with the choroid plexus vascular brain barrier and its closure,” she noted.
Dr. Rescigno added that subtle, rather than overt, inflammation may be all that’s required for closure of the choroid plexus and the subsequent effects on mental health.
In 2015, Dr. Rescigno’s group first described the gut vascular barrier that protects the systemic circulation from gut bacteria or associated bacteria-derived molecules. During intestinal inflammation, such as occurs in IBD, this barrier is compromised and becomes more permeable. This allows microbes to pass across the epithelium of the gut barrier and enter the systemic circulation, including the liver and spleen, explained Dr. Rescigno.
Dr. Rescigno and Dr. Lodato then explored whether this systemic inflammatory condition was connected to the brain along a gut-brain axis and found that it was.
The researchers tested the hypothesis that central nervous system symptoms may be due to vascular changes at the interface between the gut or the brain and elsewhere in the body.
“We set out to test whether opening of the gut vascular barrier would allow gut bacteria to trigger the release of inflammatory molecules that spread to more distant areas, possibly leading to a deficiency of certain nutrients and precipitating mental disorders,” they said.
An experimental preclinical model of the choroid plexus vascular barrier closure led to anxiety-like behavior, as well as short-term memory loss. That this behavior occurred independently of inflammation suggested that it was likely a response to closure itself, they note.
In the noninflammatory state, the epithelium of the choroid plexus filters molecules. Those that are ≤70 kDa are allowed to pass through to the brain. However, the investigators found that during systemic inflammation, this filtration stops, and the blood capillaries of the choroid plexus prevent entry of inflammatory molecules such as cytokines.
Dr. Lodato speculated that when the vascular barrier of the choroid plexus shuts off during the systemic inflammatory state, it responds by bathing the brain in cerebrospinal fluid.
“When the choroid plexus closes, like a door slamming shut, then communication between the brain and the rest of the body is halted. This means that the brain is deprived of certain nutrients and other beneficial molecules that usually enter via the cerebrospinal fluid or enriched of potentially dangerous ones, as drainage could also be affected,” she said.
If confirmed in further studies, these results may open the way to new interventions.
‘A significant leap forward’
Commenting on the findings, David T. Rubin, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, noted that the study’s results represent “a significant leap forward” and that it highlights “another important cost to uncontrolled gut inflammation that is the potential for worsened mental health disorders.”
Dr. Rubin, whose research involves measuring metabolites of the dietary amino acid tryptophan, including melatonin and serotonin, in patients with IBD, added that the findings offer a possible explanation for the association of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis with anxiety and depressive disorders.
“There was a belief that the association was in the opposite direction, that the mental health disorder was causing or worsening the gut inflammation, but this has been disavowed,” Dr. Rubin said.
“Most recently, the recognition that the major sources of serotonin and other metabolites of tryptophan that come from the gut microbiome has led to the hypothesis that the inflamed bowel and dysbiotic gut biome may in fact be driving the mental health disorders due to the effect of neurotransmitter imbalance,” he added. Dr. Rubin also suggested that the shutdown of the choroid plexus vascular barrier may contribute to this imbalance but that this needs additional study.
“This further supports my ongoing contention that the gut really is the center of the universe,” said Dr. Rubin.
Also commenting on the findings, Miguel Rigueiro, MD, professor in the department of medicine in the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said, “There’s an implication that anxiety and depression and other behavioral health disorders may be explained by this mechanism. If that is the case, there may be a way to target medications against the choroid plexus and potentially treat depression or anxiety.”
This prospect was echoed by Dr. Rubin, who said, “The clinical implication is that treatment of gut inflammation may restore a balance to the neurotransmitters and resolve anxiety or depressive disorders.”
To identify new therapeutic targets, investigators will study the regions and circuits of the brain that are more susceptible to this closure of the choroid plexus, said Dr. Lodato.
“If these regions are associated with depression or other psychosocial disorders, then this new understanding around the choroid plexus vascular barrier might eventually have implications for helping treat such disorders,” she noted.
Reflecting a general shift from a brain-centric view of some psychosocial disorders to an intestinal-centric one, Dr. Lodato added, “The brain cannot be considered in isolation. It is part of a much larger body, and we need to think this way.”
Dr. Rescigno, Dr. Lodato, and Dr. Rubin report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rigueiro has served on advisory boards and as consultant for AbbVie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, Miraca Labs, Amgen, Celgene, Seres, Allergan, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, TARGET Pharma Solutions, ALFASIGMA, SpA, and Bristol-Meyer Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A newly discovered vascular brain barrier that blocks the passage of inflammatory molecules triggered by gut bacteria may be why patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are at increased risk for certain mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression, early research suggests.
The discovery, which was based on a preclinical model, could lead to new therapeutic targets that could have applications for both gastrointestinal and psychiatric conditions, investigators note.
The research team, which was led by immunologist Maria Rescigno, PhD, and neuroscientist Simona Lodato, PhD, both from Humanitas University, Milan, notes that the barrier resides in the choroid plexus, a region of the brain that is involved in filtering cerebrospinal fluid. The researchers found that the region closes in response to inflammatory molecules produced in reaction to the presence of intestinal bacteria in patients with gut disorders.
Dr. Lodato said in an interview that the brain’s choroid plexus vascular barrier, along with another barrier between the gut and liver, known as the gut vascular barrier, appear to control the movement of molecules along the gut-brain axis.
“We show that in addition to the epithelial barrier in the choroid plexus, there is a functional vascular barrier that only becomes evident in blocking entry of various inflammatory molecules under conditions of systemic inflammation,” Dr. Lodato said.
“This interruption of the gut-brain interaction has developed to protect the brain from inflammation. Why this happens is not yet known, but it is likely to prevent epileptic seizures and imbalanced neuronal activity,” added Dr. Rescigno.
The study was published online October 22 in Science.
The gut a root cause of mental illness?
Nearly 40% of patients with IBD also experience depression and anxiety. It was once thought that these conditions arose because of patients’ difficulties in coping with their disease, said Dr. Rescigno.
“People with these disorders conventionally thought to be caused by an imbalance in the brain may actually find the root cause is located in the intestine. This is the first time these symptoms have been associated with the choroid plexus vascular brain barrier and its closure,” she noted.
Dr. Rescigno added that subtle, rather than overt, inflammation may be all that’s required for closure of the choroid plexus and the subsequent effects on mental health.
In 2015, Dr. Rescigno’s group first described the gut vascular barrier that protects the systemic circulation from gut bacteria or associated bacteria-derived molecules. During intestinal inflammation, such as occurs in IBD, this barrier is compromised and becomes more permeable. This allows microbes to pass across the epithelium of the gut barrier and enter the systemic circulation, including the liver and spleen, explained Dr. Rescigno.
Dr. Rescigno and Dr. Lodato then explored whether this systemic inflammatory condition was connected to the brain along a gut-brain axis and found that it was.
The researchers tested the hypothesis that central nervous system symptoms may be due to vascular changes at the interface between the gut or the brain and elsewhere in the body.
“We set out to test whether opening of the gut vascular barrier would allow gut bacteria to trigger the release of inflammatory molecules that spread to more distant areas, possibly leading to a deficiency of certain nutrients and precipitating mental disorders,” they said.
An experimental preclinical model of the choroid plexus vascular barrier closure led to anxiety-like behavior, as well as short-term memory loss. That this behavior occurred independently of inflammation suggested that it was likely a response to closure itself, they note.
In the noninflammatory state, the epithelium of the choroid plexus filters molecules. Those that are ≤70 kDa are allowed to pass through to the brain. However, the investigators found that during systemic inflammation, this filtration stops, and the blood capillaries of the choroid plexus prevent entry of inflammatory molecules such as cytokines.
Dr. Lodato speculated that when the vascular barrier of the choroid plexus shuts off during the systemic inflammatory state, it responds by bathing the brain in cerebrospinal fluid.
“When the choroid plexus closes, like a door slamming shut, then communication between the brain and the rest of the body is halted. This means that the brain is deprived of certain nutrients and other beneficial molecules that usually enter via the cerebrospinal fluid or enriched of potentially dangerous ones, as drainage could also be affected,” she said.
If confirmed in further studies, these results may open the way to new interventions.
‘A significant leap forward’
Commenting on the findings, David T. Rubin, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, noted that the study’s results represent “a significant leap forward” and that it highlights “another important cost to uncontrolled gut inflammation that is the potential for worsened mental health disorders.”
Dr. Rubin, whose research involves measuring metabolites of the dietary amino acid tryptophan, including melatonin and serotonin, in patients with IBD, added that the findings offer a possible explanation for the association of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis with anxiety and depressive disorders.
“There was a belief that the association was in the opposite direction, that the mental health disorder was causing or worsening the gut inflammation, but this has been disavowed,” Dr. Rubin said.
“Most recently, the recognition that the major sources of serotonin and other metabolites of tryptophan that come from the gut microbiome has led to the hypothesis that the inflamed bowel and dysbiotic gut biome may in fact be driving the mental health disorders due to the effect of neurotransmitter imbalance,” he added. Dr. Rubin also suggested that the shutdown of the choroid plexus vascular barrier may contribute to this imbalance but that this needs additional study.
“This further supports my ongoing contention that the gut really is the center of the universe,” said Dr. Rubin.
Also commenting on the findings, Miguel Rigueiro, MD, professor in the department of medicine in the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said, “There’s an implication that anxiety and depression and other behavioral health disorders may be explained by this mechanism. If that is the case, there may be a way to target medications against the choroid plexus and potentially treat depression or anxiety.”
This prospect was echoed by Dr. Rubin, who said, “The clinical implication is that treatment of gut inflammation may restore a balance to the neurotransmitters and resolve anxiety or depressive disorders.”
To identify new therapeutic targets, investigators will study the regions and circuits of the brain that are more susceptible to this closure of the choroid plexus, said Dr. Lodato.
“If these regions are associated with depression or other psychosocial disorders, then this new understanding around the choroid plexus vascular barrier might eventually have implications for helping treat such disorders,” she noted.
Reflecting a general shift from a brain-centric view of some psychosocial disorders to an intestinal-centric one, Dr. Lodato added, “The brain cannot be considered in isolation. It is part of a much larger body, and we need to think this way.”
Dr. Rescigno, Dr. Lodato, and Dr. Rubin report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rigueiro has served on advisory boards and as consultant for AbbVie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, Miraca Labs, Amgen, Celgene, Seres, Allergan, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, TARGET Pharma Solutions, ALFASIGMA, SpA, and Bristol-Meyer Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A newly discovered vascular brain barrier that blocks the passage of inflammatory molecules triggered by gut bacteria may be why patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are at increased risk for certain mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression, early research suggests.
The discovery, which was based on a preclinical model, could lead to new therapeutic targets that could have applications for both gastrointestinal and psychiatric conditions, investigators note.
The research team, which was led by immunologist Maria Rescigno, PhD, and neuroscientist Simona Lodato, PhD, both from Humanitas University, Milan, notes that the barrier resides in the choroid plexus, a region of the brain that is involved in filtering cerebrospinal fluid. The researchers found that the region closes in response to inflammatory molecules produced in reaction to the presence of intestinal bacteria in patients with gut disorders.
Dr. Lodato said in an interview that the brain’s choroid plexus vascular barrier, along with another barrier between the gut and liver, known as the gut vascular barrier, appear to control the movement of molecules along the gut-brain axis.
“We show that in addition to the epithelial barrier in the choroid plexus, there is a functional vascular barrier that only becomes evident in blocking entry of various inflammatory molecules under conditions of systemic inflammation,” Dr. Lodato said.
“This interruption of the gut-brain interaction has developed to protect the brain from inflammation. Why this happens is not yet known, but it is likely to prevent epileptic seizures and imbalanced neuronal activity,” added Dr. Rescigno.
The study was published online October 22 in Science.
The gut a root cause of mental illness?
Nearly 40% of patients with IBD also experience depression and anxiety. It was once thought that these conditions arose because of patients’ difficulties in coping with their disease, said Dr. Rescigno.
“People with these disorders conventionally thought to be caused by an imbalance in the brain may actually find the root cause is located in the intestine. This is the first time these symptoms have been associated with the choroid plexus vascular brain barrier and its closure,” she noted.
Dr. Rescigno added that subtle, rather than overt, inflammation may be all that’s required for closure of the choroid plexus and the subsequent effects on mental health.
In 2015, Dr. Rescigno’s group first described the gut vascular barrier that protects the systemic circulation from gut bacteria or associated bacteria-derived molecules. During intestinal inflammation, such as occurs in IBD, this barrier is compromised and becomes more permeable. This allows microbes to pass across the epithelium of the gut barrier and enter the systemic circulation, including the liver and spleen, explained Dr. Rescigno.
Dr. Rescigno and Dr. Lodato then explored whether this systemic inflammatory condition was connected to the brain along a gut-brain axis and found that it was.
The researchers tested the hypothesis that central nervous system symptoms may be due to vascular changes at the interface between the gut or the brain and elsewhere in the body.
“We set out to test whether opening of the gut vascular barrier would allow gut bacteria to trigger the release of inflammatory molecules that spread to more distant areas, possibly leading to a deficiency of certain nutrients and precipitating mental disorders,” they said.
An experimental preclinical model of the choroid plexus vascular barrier closure led to anxiety-like behavior, as well as short-term memory loss. That this behavior occurred independently of inflammation suggested that it was likely a response to closure itself, they note.
In the noninflammatory state, the epithelium of the choroid plexus filters molecules. Those that are ≤70 kDa are allowed to pass through to the brain. However, the investigators found that during systemic inflammation, this filtration stops, and the blood capillaries of the choroid plexus prevent entry of inflammatory molecules such as cytokines.
Dr. Lodato speculated that when the vascular barrier of the choroid plexus shuts off during the systemic inflammatory state, it responds by bathing the brain in cerebrospinal fluid.
“When the choroid plexus closes, like a door slamming shut, then communication between the brain and the rest of the body is halted. This means that the brain is deprived of certain nutrients and other beneficial molecules that usually enter via the cerebrospinal fluid or enriched of potentially dangerous ones, as drainage could also be affected,” she said.
If confirmed in further studies, these results may open the way to new interventions.
‘A significant leap forward’
Commenting on the findings, David T. Rubin, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, noted that the study’s results represent “a significant leap forward” and that it highlights “another important cost to uncontrolled gut inflammation that is the potential for worsened mental health disorders.”
Dr. Rubin, whose research involves measuring metabolites of the dietary amino acid tryptophan, including melatonin and serotonin, in patients with IBD, added that the findings offer a possible explanation for the association of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis with anxiety and depressive disorders.
“There was a belief that the association was in the opposite direction, that the mental health disorder was causing or worsening the gut inflammation, but this has been disavowed,” Dr. Rubin said.
“Most recently, the recognition that the major sources of serotonin and other metabolites of tryptophan that come from the gut microbiome has led to the hypothesis that the inflamed bowel and dysbiotic gut biome may in fact be driving the mental health disorders due to the effect of neurotransmitter imbalance,” he added. Dr. Rubin also suggested that the shutdown of the choroid plexus vascular barrier may contribute to this imbalance but that this needs additional study.
“This further supports my ongoing contention that the gut really is the center of the universe,” said Dr. Rubin.
Also commenting on the findings, Miguel Rigueiro, MD, professor in the department of medicine in the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said, “There’s an implication that anxiety and depression and other behavioral health disorders may be explained by this mechanism. If that is the case, there may be a way to target medications against the choroid plexus and potentially treat depression or anxiety.”
This prospect was echoed by Dr. Rubin, who said, “The clinical implication is that treatment of gut inflammation may restore a balance to the neurotransmitters and resolve anxiety or depressive disorders.”
To identify new therapeutic targets, investigators will study the regions and circuits of the brain that are more susceptible to this closure of the choroid plexus, said Dr. Lodato.
“If these regions are associated with depression or other psychosocial disorders, then this new understanding around the choroid plexus vascular barrier might eventually have implications for helping treat such disorders,” she noted.
Reflecting a general shift from a brain-centric view of some psychosocial disorders to an intestinal-centric one, Dr. Lodato added, “The brain cannot be considered in isolation. It is part of a much larger body, and we need to think this way.”
Dr. Rescigno, Dr. Lodato, and Dr. Rubin report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Rigueiro has served on advisory boards and as consultant for AbbVie, Janssen, UCB, Takeda, Pfizer, Miraca Labs, Amgen, Celgene, Seres, Allergan, Genentech, Gilead, Salix, Prometheus, Lilly, TARGET Pharma Solutions, ALFASIGMA, SpA, and Bristol-Meyer Squibb.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE