User login
AGA Guideline: Transient elastography in liver fibrosis, most used and most accurate
Vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) can accurately diagnose cirrhosis in most patients with chronic liver disease, particularly those with chronic hepatitis B or C, states a new guideline from the AGA Institute, published in the May issue of Gastroenterology (doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.017).
However, magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is somewhat more accurate for detecting cirrhosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, wrote Joseph K. Lim, MD, AGAF, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., with his associates from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the AGA. VCTE is convenient but performs unevenly in some liver conditions and is especially unreliable in patients with acute hepatitis, alcohol abuse, food intake within 2-3 hours, congestive heart failure, or extrahepatic cholestasis, the guideline notes. Yet, VCTE remains the most common imaging tool for diagnosing fibrosis in the United States, and the guideline addresses “focused, clinically relevant questions” to guide its use.
When possible, clinicians should use VCTE instead of noninvasive serum tests for cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C, the guideline asserts. In pooled analyses of 62 studies, VCTE detected about 89% of cirrhosis cases (95% confidence interval, 84%-92%), Fibrosis-4 test (FIB-4) detected 87% (95% CI, 74%-94%), and aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) detected 77% (95% CI, 73%-81%). The specificity of VCTE (91%) also equaled or exceeded that of FIB-4 (91%) or APRI (78%), the guideline noted.
For chronic hepatitis C, MRE had “poorer specificity with higher false-positive rates, suggesting poorer diagnostic performance,” compared with VCTE. Lower cost and lower point-of-care availability make VCTE “an attractive solution compared to MRE,” the guideline adds. It conditionally recommends VCTE cutoffs of 12.5 kPa for cirrhosis and 9.5 kPa for advanced (F3-F4) liver fibrosis after patients have a sustained virologic response to therapy. The 9.5-kPa cutoff would misclassify only 1% of low-risk patients and 7% of high-risk patients, but noncirrhotic patients (less than 9.5 kPa) may reasonably choose to continue specialty care if they prioritize avoiding “the small risk” of hepatocellular carcinoma over the “inconvenience and risks of continued laboratory and fibrosis testing.”
For chronic hepatitis B, the guideline conditionally recommends VCTE with an 11.0-kPa cutoff over APRI or FIB-4. In a pooled analysis of 28 studies, VCTE detected cirrhosis with a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 85%, compared with 66% and 74%, respectively, for APRI, and 87% and 65%, respectively, for FIB-4. However, the overall diagnostic performance of VCTE resembled that of the serum tests, and clinicians should interpret VCTE in the context of other clinical cirrhosis data, the guideline states.
Among 17 studies of VCTE cutoffs in hepatitis B, an 11.0-kPa threshold diagnosed cirrhosis with a sensitivity of 81% and a specificity of 83%. This cutoff would miss cirrhosis in less than 1% of low-risk patients and about 5% of high-risk patients and would yield false positives in 10%-15% of patients. Thus, its cutoff minimizes false negatives, reflecting “a judgment that the harm of missing cirrhosis is greater than the harm of over diagnosis,” the authors write.
For chronic alcoholic liver disease, the AGA conditionally recommends VCTE with a cirrhosis cutoff of 12.5 kPa. In pooled analyses, this value had a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 71%. For suspected compensated cirrhosis, the guideline conditionally suggests a 19.5-kPa cutoff when assessing the need for esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) to identify high-risk esophageal varices. Patients who fall below this cutoff can reasonably pursue screening endoscopy if they are concerned about the small risk of acute variceal hemorrhage, the guideline adds.
The guideline also conditionally recommends a 17-kPa cutoff to detect clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with suspected chronic liver disease who are undergoing elective nonhepatic surgeries. This cutoff will miss about 0.1% of very low-risk patients, 0.8% of low-risk patients, and 7% of high-risk patients. Because the failure to detect portal hypertension contributes to operative morbidity and mortality, higher-risk patients might “reasonably” pursue screening endoscopy even if their kPa is below the cutoff, the guideline states.
The guideline made no recommendation about VCTE versus APRI or FIB-4 in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), citing “unacceptable bias” in 12 studies that excluded obese patients, used per-protocol rather than intention-to-diagnose analyses, and ignored “unsuccessful or inadequate” liver stiffness measurements, which are relatively common in NAFLD, the guideline notes. It conditionally recommends MRE over VCTE in high-risk adults with NAFLD, including those who are older, diabetic, or obese (especially with central adiposity) or who have alanine levels more than twice the upper limit of normal. However, it cites insufficient evidence to extend this recommendation to low-risk patients who only have imaging evidence of fatty liver.
Overall, the guideline focuses on “routine clinical management issues, and [does] not address comparisons with proprietary serum fibrosis assays, other emerging imaging-based fibrosis assessment techniques, or combinations of more than one noninvasive fibrosis test,” the authors note. They also limited VCTE cutoffs to single thresholds that prioritized sensitivity over specificity. “Additional studies are needed to further define the role of VCTE, MRE, and emerging diagnostic studies in the assessment of liver fibrosis, for which a significant unmet medical need remains, particularly in conditions such as NAFLD/[nonalcoholic steatohepatitis],” they add. “In particular, defining the implications for serial liver stiffness measurements over time on management decisions is of great interest.”
Dr. Muir has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, and Merck. Dr. Lim has served as a consultant for Bristol Myers-Squibb, Gilead, Merck, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Flamm has served as a consultant or received research support from Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Salix Pharmaceuticals, and Intercept Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Dieterich has presented lectures for Gilead and Merck products. The rest of the authors disclosed no conflicts related to the content of this guideline.
Vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) can accurately diagnose cirrhosis in most patients with chronic liver disease, particularly those with chronic hepatitis B or C, states a new guideline from the AGA Institute, published in the May issue of Gastroenterology (doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.017).
However, magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is somewhat more accurate for detecting cirrhosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, wrote Joseph K. Lim, MD, AGAF, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., with his associates from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the AGA. VCTE is convenient but performs unevenly in some liver conditions and is especially unreliable in patients with acute hepatitis, alcohol abuse, food intake within 2-3 hours, congestive heart failure, or extrahepatic cholestasis, the guideline notes. Yet, VCTE remains the most common imaging tool for diagnosing fibrosis in the United States, and the guideline addresses “focused, clinically relevant questions” to guide its use.
When possible, clinicians should use VCTE instead of noninvasive serum tests for cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C, the guideline asserts. In pooled analyses of 62 studies, VCTE detected about 89% of cirrhosis cases (95% confidence interval, 84%-92%), Fibrosis-4 test (FIB-4) detected 87% (95% CI, 74%-94%), and aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) detected 77% (95% CI, 73%-81%). The specificity of VCTE (91%) also equaled or exceeded that of FIB-4 (91%) or APRI (78%), the guideline noted.
For chronic hepatitis C, MRE had “poorer specificity with higher false-positive rates, suggesting poorer diagnostic performance,” compared with VCTE. Lower cost and lower point-of-care availability make VCTE “an attractive solution compared to MRE,” the guideline adds. It conditionally recommends VCTE cutoffs of 12.5 kPa for cirrhosis and 9.5 kPa for advanced (F3-F4) liver fibrosis after patients have a sustained virologic response to therapy. The 9.5-kPa cutoff would misclassify only 1% of low-risk patients and 7% of high-risk patients, but noncirrhotic patients (less than 9.5 kPa) may reasonably choose to continue specialty care if they prioritize avoiding “the small risk” of hepatocellular carcinoma over the “inconvenience and risks of continued laboratory and fibrosis testing.”
For chronic hepatitis B, the guideline conditionally recommends VCTE with an 11.0-kPa cutoff over APRI or FIB-4. In a pooled analysis of 28 studies, VCTE detected cirrhosis with a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 85%, compared with 66% and 74%, respectively, for APRI, and 87% and 65%, respectively, for FIB-4. However, the overall diagnostic performance of VCTE resembled that of the serum tests, and clinicians should interpret VCTE in the context of other clinical cirrhosis data, the guideline states.
Among 17 studies of VCTE cutoffs in hepatitis B, an 11.0-kPa threshold diagnosed cirrhosis with a sensitivity of 81% and a specificity of 83%. This cutoff would miss cirrhosis in less than 1% of low-risk patients and about 5% of high-risk patients and would yield false positives in 10%-15% of patients. Thus, its cutoff minimizes false negatives, reflecting “a judgment that the harm of missing cirrhosis is greater than the harm of over diagnosis,” the authors write.
For chronic alcoholic liver disease, the AGA conditionally recommends VCTE with a cirrhosis cutoff of 12.5 kPa. In pooled analyses, this value had a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 71%. For suspected compensated cirrhosis, the guideline conditionally suggests a 19.5-kPa cutoff when assessing the need for esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) to identify high-risk esophageal varices. Patients who fall below this cutoff can reasonably pursue screening endoscopy if they are concerned about the small risk of acute variceal hemorrhage, the guideline adds.
The guideline also conditionally recommends a 17-kPa cutoff to detect clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with suspected chronic liver disease who are undergoing elective nonhepatic surgeries. This cutoff will miss about 0.1% of very low-risk patients, 0.8% of low-risk patients, and 7% of high-risk patients. Because the failure to detect portal hypertension contributes to operative morbidity and mortality, higher-risk patients might “reasonably” pursue screening endoscopy even if their kPa is below the cutoff, the guideline states.
The guideline made no recommendation about VCTE versus APRI or FIB-4 in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), citing “unacceptable bias” in 12 studies that excluded obese patients, used per-protocol rather than intention-to-diagnose analyses, and ignored “unsuccessful or inadequate” liver stiffness measurements, which are relatively common in NAFLD, the guideline notes. It conditionally recommends MRE over VCTE in high-risk adults with NAFLD, including those who are older, diabetic, or obese (especially with central adiposity) or who have alanine levels more than twice the upper limit of normal. However, it cites insufficient evidence to extend this recommendation to low-risk patients who only have imaging evidence of fatty liver.
Overall, the guideline focuses on “routine clinical management issues, and [does] not address comparisons with proprietary serum fibrosis assays, other emerging imaging-based fibrosis assessment techniques, or combinations of more than one noninvasive fibrosis test,” the authors note. They also limited VCTE cutoffs to single thresholds that prioritized sensitivity over specificity. “Additional studies are needed to further define the role of VCTE, MRE, and emerging diagnostic studies in the assessment of liver fibrosis, for which a significant unmet medical need remains, particularly in conditions such as NAFLD/[nonalcoholic steatohepatitis],” they add. “In particular, defining the implications for serial liver stiffness measurements over time on management decisions is of great interest.”
Dr. Muir has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, and Merck. Dr. Lim has served as a consultant for Bristol Myers-Squibb, Gilead, Merck, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Flamm has served as a consultant or received research support from Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Salix Pharmaceuticals, and Intercept Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Dieterich has presented lectures for Gilead and Merck products. The rest of the authors disclosed no conflicts related to the content of this guideline.
Vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) can accurately diagnose cirrhosis in most patients with chronic liver disease, particularly those with chronic hepatitis B or C, states a new guideline from the AGA Institute, published in the May issue of Gastroenterology (doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.017).
However, magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is somewhat more accurate for detecting cirrhosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, wrote Joseph K. Lim, MD, AGAF, of Yale University in New Haven, Conn., with his associates from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the AGA. VCTE is convenient but performs unevenly in some liver conditions and is especially unreliable in patients with acute hepatitis, alcohol abuse, food intake within 2-3 hours, congestive heart failure, or extrahepatic cholestasis, the guideline notes. Yet, VCTE remains the most common imaging tool for diagnosing fibrosis in the United States, and the guideline addresses “focused, clinically relevant questions” to guide its use.
When possible, clinicians should use VCTE instead of noninvasive serum tests for cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C, the guideline asserts. In pooled analyses of 62 studies, VCTE detected about 89% of cirrhosis cases (95% confidence interval, 84%-92%), Fibrosis-4 test (FIB-4) detected 87% (95% CI, 74%-94%), and aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) detected 77% (95% CI, 73%-81%). The specificity of VCTE (91%) also equaled or exceeded that of FIB-4 (91%) or APRI (78%), the guideline noted.
For chronic hepatitis C, MRE had “poorer specificity with higher false-positive rates, suggesting poorer diagnostic performance,” compared with VCTE. Lower cost and lower point-of-care availability make VCTE “an attractive solution compared to MRE,” the guideline adds. It conditionally recommends VCTE cutoffs of 12.5 kPa for cirrhosis and 9.5 kPa for advanced (F3-F4) liver fibrosis after patients have a sustained virologic response to therapy. The 9.5-kPa cutoff would misclassify only 1% of low-risk patients and 7% of high-risk patients, but noncirrhotic patients (less than 9.5 kPa) may reasonably choose to continue specialty care if they prioritize avoiding “the small risk” of hepatocellular carcinoma over the “inconvenience and risks of continued laboratory and fibrosis testing.”
For chronic hepatitis B, the guideline conditionally recommends VCTE with an 11.0-kPa cutoff over APRI or FIB-4. In a pooled analysis of 28 studies, VCTE detected cirrhosis with a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 85%, compared with 66% and 74%, respectively, for APRI, and 87% and 65%, respectively, for FIB-4. However, the overall diagnostic performance of VCTE resembled that of the serum tests, and clinicians should interpret VCTE in the context of other clinical cirrhosis data, the guideline states.
Among 17 studies of VCTE cutoffs in hepatitis B, an 11.0-kPa threshold diagnosed cirrhosis with a sensitivity of 81% and a specificity of 83%. This cutoff would miss cirrhosis in less than 1% of low-risk patients and about 5% of high-risk patients and would yield false positives in 10%-15% of patients. Thus, its cutoff minimizes false negatives, reflecting “a judgment that the harm of missing cirrhosis is greater than the harm of over diagnosis,” the authors write.
For chronic alcoholic liver disease, the AGA conditionally recommends VCTE with a cirrhosis cutoff of 12.5 kPa. In pooled analyses, this value had a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 71%. For suspected compensated cirrhosis, the guideline conditionally suggests a 19.5-kPa cutoff when assessing the need for esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) to identify high-risk esophageal varices. Patients who fall below this cutoff can reasonably pursue screening endoscopy if they are concerned about the small risk of acute variceal hemorrhage, the guideline adds.
The guideline also conditionally recommends a 17-kPa cutoff to detect clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with suspected chronic liver disease who are undergoing elective nonhepatic surgeries. This cutoff will miss about 0.1% of very low-risk patients, 0.8% of low-risk patients, and 7% of high-risk patients. Because the failure to detect portal hypertension contributes to operative morbidity and mortality, higher-risk patients might “reasonably” pursue screening endoscopy even if their kPa is below the cutoff, the guideline states.
The guideline made no recommendation about VCTE versus APRI or FIB-4 in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), citing “unacceptable bias” in 12 studies that excluded obese patients, used per-protocol rather than intention-to-diagnose analyses, and ignored “unsuccessful or inadequate” liver stiffness measurements, which are relatively common in NAFLD, the guideline notes. It conditionally recommends MRE over VCTE in high-risk adults with NAFLD, including those who are older, diabetic, or obese (especially with central adiposity) or who have alanine levels more than twice the upper limit of normal. However, it cites insufficient evidence to extend this recommendation to low-risk patients who only have imaging evidence of fatty liver.
Overall, the guideline focuses on “routine clinical management issues, and [does] not address comparisons with proprietary serum fibrosis assays, other emerging imaging-based fibrosis assessment techniques, or combinations of more than one noninvasive fibrosis test,” the authors note. They also limited VCTE cutoffs to single thresholds that prioritized sensitivity over specificity. “Additional studies are needed to further define the role of VCTE, MRE, and emerging diagnostic studies in the assessment of liver fibrosis, for which a significant unmet medical need remains, particularly in conditions such as NAFLD/[nonalcoholic steatohepatitis],” they add. “In particular, defining the implications for serial liver stiffness measurements over time on management decisions is of great interest.”
Dr. Muir has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, and Merck. Dr. Lim has served as a consultant for Bristol Myers-Squibb, Gilead, Merck, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Flamm has served as a consultant or received research support from Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Salix Pharmaceuticals, and Intercept Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Dieterich has presented lectures for Gilead and Merck products. The rest of the authors disclosed no conflicts related to the content of this guideline.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Acne, rosacea prescriptions cost more when prescribed by dermatologists
PORTLAND, ORE. – Dermatologists have plenty of room to improve when it comes to choosing cost-effective medications for acne or rosacea, based on the results of a large retrospective analysis of Medicare claims data.
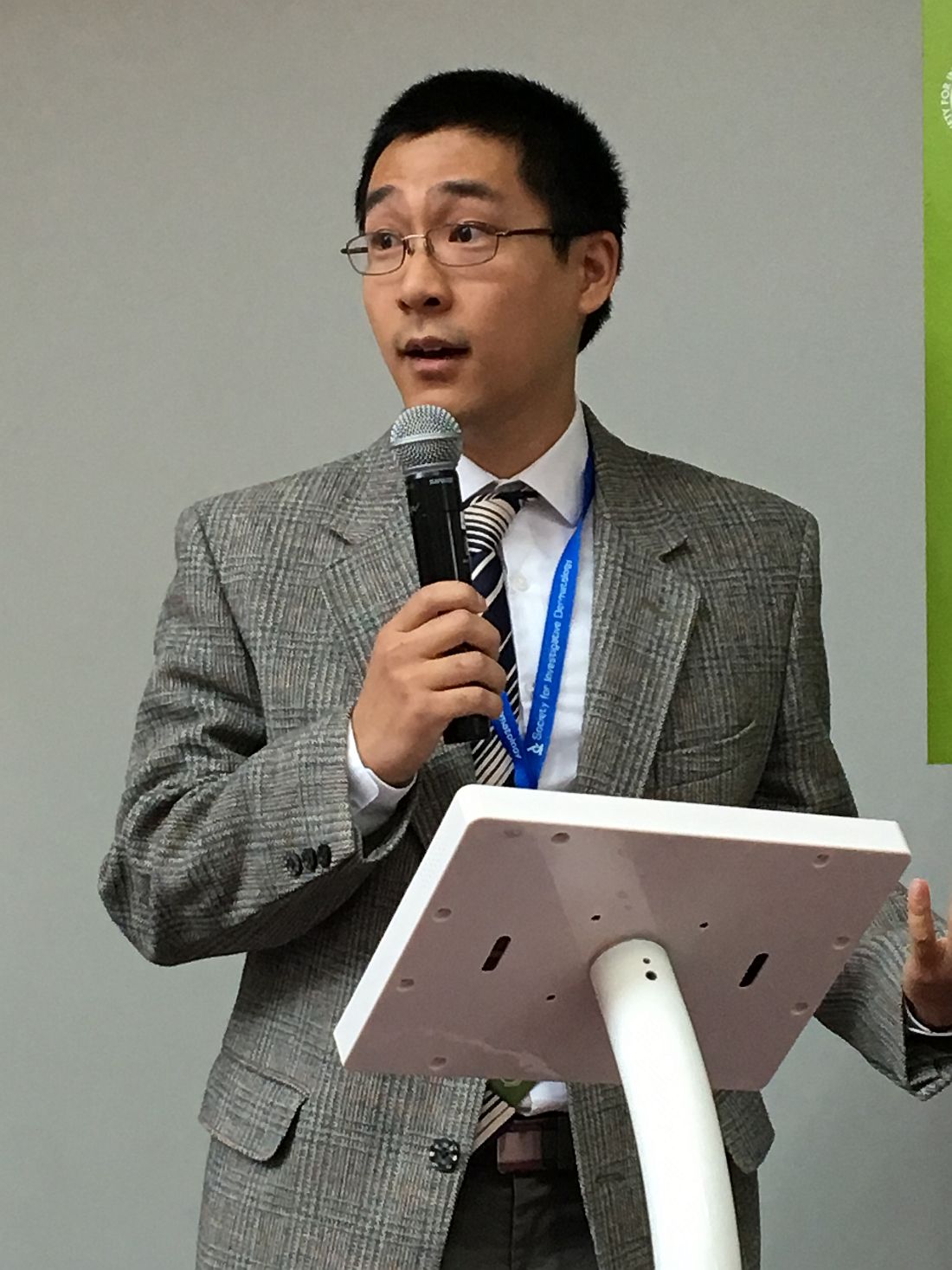
Patients with acne or rosacea consistently paid more for topical retinoids, topical antibiotics, and oral tetracyclines when the prescriber was a dermatologist instead of a family or internal medicine physician, Myron Zhang reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
“There is a large potential for reducing expenditures on health care for patients with acne and rosacea by choosing more generics and less expensive options within drug classes,” said Mr. Zhang, a medical student at the Ohio State University, Columbus, who conducted the study with colleagues there and at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Treating acne and rosacea falls under the purview of both primary and specialty outpatient care, but, researchers had not broken down costs of prescriptions for these conditions by provider type. To help fill that gap, Mr. Zhang and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed all Medicare drug claims for topical retinoids, topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, and oral tetracycline-class antibiotics used to treat acne and rosacea in the United States in 2008 and 2010.
Medicare claims for these prescriptions added up to $65 million in 2008 and $74 million in 2004, Mr. Zhang said. Although most generics either dropped in cost or rose by small amounts in that 2-year span, many brand name prescriptions rose by between 30% and 70%. “Specialist prescriptions were associated with higher brand name usage, a greater variety of medications, and higher costs,” Mr. Zhang said.
Patients paid an average of about $2-$3 more for a topical retinoid, $3-$4 more for oral tetracycline, and $1 more for a topical antibiotic prescribed by a specialist instead of a primary care physician.
This finding might indicate that dermatologists are more comfortable prescribing a greater variety of medications for acne and rosacea, such as tazarotene, azelaic acid, and sulfacetamide, while primary care physicians might stick to a narrower range of medicines, Mr. Zhang said. However, the prescribing behavior of dermatologists could also reflect “external factors,” such as increased contact with representatives from pharmaceutical companies, he added.
“As always, prescription costs need to be weighed against patient preference, compliance, and quality of care,” he said. “More outcomes research is needed to understand the comparative efficacy of generic and brand name treatments.”
The study included both rosacea and acne so that the researchers could capture the total costs of medications such as tretinoin, which is used to treat both conditions. Approximately 80% of topical retinoid prescriptions were for tretinoin, about 50% of topical antibiotic prescriptions were for metronidazole, while about 27% were for clindamycin. About half of oral antibiotic prescriptions were for tetracycline, while about 40% were for minocycline.
Mr. Zhang reported having no conflicts of interest.
PORTLAND, ORE. – Dermatologists have plenty of room to improve when it comes to choosing cost-effective medications for acne or rosacea, based on the results of a large retrospective analysis of Medicare claims data.
Patients with acne or rosacea consistently paid more for topical retinoids, topical antibiotics, and oral tetracyclines when the prescriber was a dermatologist instead of a family or internal medicine physician, Myron Zhang reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
“There is a large potential for reducing expenditures on health care for patients with acne and rosacea by choosing more generics and less expensive options within drug classes,” said Mr. Zhang, a medical student at the Ohio State University, Columbus, who conducted the study with colleagues there and at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Treating acne and rosacea falls under the purview of both primary and specialty outpatient care, but, researchers had not broken down costs of prescriptions for these conditions by provider type. To help fill that gap, Mr. Zhang and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed all Medicare drug claims for topical retinoids, topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, and oral tetracycline-class antibiotics used to treat acne and rosacea in the United States in 2008 and 2010.
Medicare claims for these prescriptions added up to $65 million in 2008 and $74 million in 2004, Mr. Zhang said. Although most generics either dropped in cost or rose by small amounts in that 2-year span, many brand name prescriptions rose by between 30% and 70%. “Specialist prescriptions were associated with higher brand name usage, a greater variety of medications, and higher costs,” Mr. Zhang said.
Patients paid an average of about $2-$3 more for a topical retinoid, $3-$4 more for oral tetracycline, and $1 more for a topical antibiotic prescribed by a specialist instead of a primary care physician.
This finding might indicate that dermatologists are more comfortable prescribing a greater variety of medications for acne and rosacea, such as tazarotene, azelaic acid, and sulfacetamide, while primary care physicians might stick to a narrower range of medicines, Mr. Zhang said. However, the prescribing behavior of dermatologists could also reflect “external factors,” such as increased contact with representatives from pharmaceutical companies, he added.
“As always, prescription costs need to be weighed against patient preference, compliance, and quality of care,” he said. “More outcomes research is needed to understand the comparative efficacy of generic and brand name treatments.”
The study included both rosacea and acne so that the researchers could capture the total costs of medications such as tretinoin, which is used to treat both conditions. Approximately 80% of topical retinoid prescriptions were for tretinoin, about 50% of topical antibiotic prescriptions were for metronidazole, while about 27% were for clindamycin. About half of oral antibiotic prescriptions were for tetracycline, while about 40% were for minocycline.
Mr. Zhang reported having no conflicts of interest.
PORTLAND, ORE. – Dermatologists have plenty of room to improve when it comes to choosing cost-effective medications for acne or rosacea, based on the results of a large retrospective analysis of Medicare claims data.
Patients with acne or rosacea consistently paid more for topical retinoids, topical antibiotics, and oral tetracyclines when the prescriber was a dermatologist instead of a family or internal medicine physician, Myron Zhang reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
“There is a large potential for reducing expenditures on health care for patients with acne and rosacea by choosing more generics and less expensive options within drug classes,” said Mr. Zhang, a medical student at the Ohio State University, Columbus, who conducted the study with colleagues there and at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Treating acne and rosacea falls under the purview of both primary and specialty outpatient care, but, researchers had not broken down costs of prescriptions for these conditions by provider type. To help fill that gap, Mr. Zhang and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed all Medicare drug claims for topical retinoids, topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, and oral tetracycline-class antibiotics used to treat acne and rosacea in the United States in 2008 and 2010.
Medicare claims for these prescriptions added up to $65 million in 2008 and $74 million in 2004, Mr. Zhang said. Although most generics either dropped in cost or rose by small amounts in that 2-year span, many brand name prescriptions rose by between 30% and 70%. “Specialist prescriptions were associated with higher brand name usage, a greater variety of medications, and higher costs,” Mr. Zhang said.
Patients paid an average of about $2-$3 more for a topical retinoid, $3-$4 more for oral tetracycline, and $1 more for a topical antibiotic prescribed by a specialist instead of a primary care physician.
This finding might indicate that dermatologists are more comfortable prescribing a greater variety of medications for acne and rosacea, such as tazarotene, azelaic acid, and sulfacetamide, while primary care physicians might stick to a narrower range of medicines, Mr. Zhang said. However, the prescribing behavior of dermatologists could also reflect “external factors,” such as increased contact with representatives from pharmaceutical companies, he added.
“As always, prescription costs need to be weighed against patient preference, compliance, and quality of care,” he said. “More outcomes research is needed to understand the comparative efficacy of generic and brand name treatments.”
The study included both rosacea and acne so that the researchers could capture the total costs of medications such as tretinoin, which is used to treat both conditions. Approximately 80% of topical retinoid prescriptions were for tretinoin, about 50% of topical antibiotic prescriptions were for metronidazole, while about 27% were for clindamycin. About half of oral antibiotic prescriptions were for tetracycline, while about 40% were for minocycline.
Mr. Zhang reported having no conflicts of interest.
At SID 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients paid an average of $2-$3 more for a topical retinoid, $3-$4 more for an oral tetracycline-class antibiotic, and $1 more for a topical antibiotic prescribed by a dermatologist, compared with prescriptions from a primary care physician.
Data source: A retrospective analysis of Medicare prescription claims for oral antibiotics, topical antibiotics, and topical retinoids for acne and rosacea in 2008 and 2010.
Disclosures: Mr. Zhang reported having no conflicts of interest.
Vitamin D3 supplementation beat placebo in atopic dermatitis trial
PORTLAND – Short-term daily oral supplementation with 5000 IU of vitamin D3 was safe and significantly outperformed placebo for lessening the signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis (AD), according to the results of a randomized, double-blind trial of 65 patients with moderate to severe disease.
At week 12, average improvements on the Scoring Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index (standard deviation, 11.1 points) were 21.2 points in the vitamin D3 group and 13.9 points (standard deviation, 12.3 points) in the placebo group (P = .02), Karen Sanchez-Armendariz, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology. “Vitamin D3 should be considered a valuable adjuvant in the treatment of AD, especially in patients with relapses,” she said.
Past studies have reported an inverse relationship between 25(OH)D (vitamin D) serum levels and the severity of AD, noted Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz, who is with the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City. This finding makes sense, as vitamin D3 induces the topical production of antimicrobial peptides, which have direct antimicrobial activity and induce a host response characterized by cytokine release, chemotaxis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and re-epithelialization, she added.
Consequently, 25(OH)D deficiency has been posited as a culprit in the pathophysiology of AD. However, scientific and endocrine societies have published differing recommendations about safe and optimal doses for vitamin D3 supplementation, while experts have noted that 5000 IU per day is needed to achieve an increase of 10 ng 25(OH)D per mL serum (J Am Board Fam Med. 2014 Jul-Aug;27[4]:495-509).
For the study, therefore, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz and her associates evaluated this dose as adjuvant therapy in patients with moderate to severe AD despite topical hydrocortisone aceponate, soap substitute, and emollient. Patients continued this usual care and received either a cellulose capsule placebo or 5000 IU oral vitamin D3 per day. Based on previously recommended cutoff values, the researchers considered serum 25(OH)D levels sufficient if they exceeded 30 ng per mL, insufficient if they were between 20 and 30 ng per mL, and deficient if they were less than 20 ng per mL (J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26[3]:455-7).
At baseline, the placebo and intervention groups resembled each other in terms of baseline levels of 25(OH)D, calcium, and phosphorus, pruritus, and scores on SCORAD and the six-area Total Body Severity Assessment. A total of 59% of patients had insufficient serum 25(OH)D, and 39% were deficient.
Patients in both groups improved on the Total Body Severity Assessment, but the extent of improvement did not statistically differ between groups, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz reported. Supplementation did significantly increase serum 25(OH)D levels, which at week 12 averaged 58.3 ng per mL (SD, 18.5 ng per mL), compared with 22.2 (SD, 7.6 ng per mL) with placebo (P less than .001).
Interestingly, at week 12, all patients in the vitamin D3 group achieved serum 25(OH)D levels of at least 30 ng per mL, as did 41% of patients in the placebo arm. Patients in both groups who achieved this “sufficient” serum 25(OH)D level averaged a nearly 21-point improvement on the SCORAD (SD, 11.1 points), compared with 7.5 points (SD, 9.9 points) among patients who remained deficient, and 17.4 points (SD, 12.7 points) among patients who remained insufficient (P = .004 for difference among groups; P = .02 for difference between sufficient and insufficient groups).
An analysis of variance confirmed this finding, showing that, regardless of treatment group, patients whose final serum 25(OH)D level was at least 20 ng per mL scored an average of 20 points on the SCORAD, compared with 38 points for patients whose 25(OH)D level remained below 20 ng per mL. Patients whose final 25(OH)D level exceeded 20 ng per mL had fivefold greater odds of having a SCORAD below 25 than did patients with lower serum 25(OH)D levels (odds ratio, 5.1; 95% confidence interval, 1.2-22.6; P = .03).
The investigators identified no adverse effects of vitamin D3 supplementation, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz said. “Attaining 25(OH)D levels above 20 ng per mL in addition to baseline therapy reduced the SCORAD of patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis,” she added. Clinicians should consider vitamin D3 deficiency and supplementation in patients with relapsing or refractory AD, she emphasized.
Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz reported no external funding sources and no conflicts of interest.
PORTLAND – Short-term daily oral supplementation with 5000 IU of vitamin D3 was safe and significantly outperformed placebo for lessening the signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis (AD), according to the results of a randomized, double-blind trial of 65 patients with moderate to severe disease.
At week 12, average improvements on the Scoring Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index (standard deviation, 11.1 points) were 21.2 points in the vitamin D3 group and 13.9 points (standard deviation, 12.3 points) in the placebo group (P = .02), Karen Sanchez-Armendariz, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology. “Vitamin D3 should be considered a valuable adjuvant in the treatment of AD, especially in patients with relapses,” she said.
Past studies have reported an inverse relationship between 25(OH)D (vitamin D) serum levels and the severity of AD, noted Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz, who is with the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City. This finding makes sense, as vitamin D3 induces the topical production of antimicrobial peptides, which have direct antimicrobial activity and induce a host response characterized by cytokine release, chemotaxis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and re-epithelialization, she added.
Consequently, 25(OH)D deficiency has been posited as a culprit in the pathophysiology of AD. However, scientific and endocrine societies have published differing recommendations about safe and optimal doses for vitamin D3 supplementation, while experts have noted that 5000 IU per day is needed to achieve an increase of 10 ng 25(OH)D per mL serum (J Am Board Fam Med. 2014 Jul-Aug;27[4]:495-509).
For the study, therefore, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz and her associates evaluated this dose as adjuvant therapy in patients with moderate to severe AD despite topical hydrocortisone aceponate, soap substitute, and emollient. Patients continued this usual care and received either a cellulose capsule placebo or 5000 IU oral vitamin D3 per day. Based on previously recommended cutoff values, the researchers considered serum 25(OH)D levels sufficient if they exceeded 30 ng per mL, insufficient if they were between 20 and 30 ng per mL, and deficient if they were less than 20 ng per mL (J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26[3]:455-7).
At baseline, the placebo and intervention groups resembled each other in terms of baseline levels of 25(OH)D, calcium, and phosphorus, pruritus, and scores on SCORAD and the six-area Total Body Severity Assessment. A total of 59% of patients had insufficient serum 25(OH)D, and 39% were deficient.
Patients in both groups improved on the Total Body Severity Assessment, but the extent of improvement did not statistically differ between groups, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz reported. Supplementation did significantly increase serum 25(OH)D levels, which at week 12 averaged 58.3 ng per mL (SD, 18.5 ng per mL), compared with 22.2 (SD, 7.6 ng per mL) with placebo (P less than .001).
Interestingly, at week 12, all patients in the vitamin D3 group achieved serum 25(OH)D levels of at least 30 ng per mL, as did 41% of patients in the placebo arm. Patients in both groups who achieved this “sufficient” serum 25(OH)D level averaged a nearly 21-point improvement on the SCORAD (SD, 11.1 points), compared with 7.5 points (SD, 9.9 points) among patients who remained deficient, and 17.4 points (SD, 12.7 points) among patients who remained insufficient (P = .004 for difference among groups; P = .02 for difference between sufficient and insufficient groups).
An analysis of variance confirmed this finding, showing that, regardless of treatment group, patients whose final serum 25(OH)D level was at least 20 ng per mL scored an average of 20 points on the SCORAD, compared with 38 points for patients whose 25(OH)D level remained below 20 ng per mL. Patients whose final 25(OH)D level exceeded 20 ng per mL had fivefold greater odds of having a SCORAD below 25 than did patients with lower serum 25(OH)D levels (odds ratio, 5.1; 95% confidence interval, 1.2-22.6; P = .03).
The investigators identified no adverse effects of vitamin D3 supplementation, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz said. “Attaining 25(OH)D levels above 20 ng per mL in addition to baseline therapy reduced the SCORAD of patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis,” she added. Clinicians should consider vitamin D3 deficiency and supplementation in patients with relapsing or refractory AD, she emphasized.
Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz reported no external funding sources and no conflicts of interest.
PORTLAND – Short-term daily oral supplementation with 5000 IU of vitamin D3 was safe and significantly outperformed placebo for lessening the signs and symptoms of atopic dermatitis (AD), according to the results of a randomized, double-blind trial of 65 patients with moderate to severe disease.
At week 12, average improvements on the Scoring Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD) index (standard deviation, 11.1 points) were 21.2 points in the vitamin D3 group and 13.9 points (standard deviation, 12.3 points) in the placebo group (P = .02), Karen Sanchez-Armendariz, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology. “Vitamin D3 should be considered a valuable adjuvant in the treatment of AD, especially in patients with relapses,” she said.
Past studies have reported an inverse relationship between 25(OH)D (vitamin D) serum levels and the severity of AD, noted Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz, who is with the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City. This finding makes sense, as vitamin D3 induces the topical production of antimicrobial peptides, which have direct antimicrobial activity and induce a host response characterized by cytokine release, chemotaxis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and re-epithelialization, she added.
Consequently, 25(OH)D deficiency has been posited as a culprit in the pathophysiology of AD. However, scientific and endocrine societies have published differing recommendations about safe and optimal doses for vitamin D3 supplementation, while experts have noted that 5000 IU per day is needed to achieve an increase of 10 ng 25(OH)D per mL serum (J Am Board Fam Med. 2014 Jul-Aug;27[4]:495-509).
For the study, therefore, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz and her associates evaluated this dose as adjuvant therapy in patients with moderate to severe AD despite topical hydrocortisone aceponate, soap substitute, and emollient. Patients continued this usual care and received either a cellulose capsule placebo or 5000 IU oral vitamin D3 per day. Based on previously recommended cutoff values, the researchers considered serum 25(OH)D levels sufficient if they exceeded 30 ng per mL, insufficient if they were between 20 and 30 ng per mL, and deficient if they were less than 20 ng per mL (J Bone Miner Res. 2011 Mar;26[3]:455-7).
At baseline, the placebo and intervention groups resembled each other in terms of baseline levels of 25(OH)D, calcium, and phosphorus, pruritus, and scores on SCORAD and the six-area Total Body Severity Assessment. A total of 59% of patients had insufficient serum 25(OH)D, and 39% were deficient.
Patients in both groups improved on the Total Body Severity Assessment, but the extent of improvement did not statistically differ between groups, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz reported. Supplementation did significantly increase serum 25(OH)D levels, which at week 12 averaged 58.3 ng per mL (SD, 18.5 ng per mL), compared with 22.2 (SD, 7.6 ng per mL) with placebo (P less than .001).
Interestingly, at week 12, all patients in the vitamin D3 group achieved serum 25(OH)D levels of at least 30 ng per mL, as did 41% of patients in the placebo arm. Patients in both groups who achieved this “sufficient” serum 25(OH)D level averaged a nearly 21-point improvement on the SCORAD (SD, 11.1 points), compared with 7.5 points (SD, 9.9 points) among patients who remained deficient, and 17.4 points (SD, 12.7 points) among patients who remained insufficient (P = .004 for difference among groups; P = .02 for difference between sufficient and insufficient groups).
An analysis of variance confirmed this finding, showing that, regardless of treatment group, patients whose final serum 25(OH)D level was at least 20 ng per mL scored an average of 20 points on the SCORAD, compared with 38 points for patients whose 25(OH)D level remained below 20 ng per mL. Patients whose final 25(OH)D level exceeded 20 ng per mL had fivefold greater odds of having a SCORAD below 25 than did patients with lower serum 25(OH)D levels (odds ratio, 5.1; 95% confidence interval, 1.2-22.6; P = .03).
The investigators identified no adverse effects of vitamin D3 supplementation, Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz said. “Attaining 25(OH)D levels above 20 ng per mL in addition to baseline therapy reduced the SCORAD of patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis,” she added. Clinicians should consider vitamin D3 deficiency and supplementation in patients with relapsing or refractory AD, she emphasized.
Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz reported no external funding sources and no conflicts of interest.
Key clinical point:
Major finding: At week 12, average improvements on the SCORAD index were 21.2 points with vitamin D3 and 13.9 points (SD, 12.3 points) with placebo (P = .02).
Data source: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of 65 patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis despite usual therapy with topical steroids, soap substitute, and topical emollient.
Disclosures: Dr. Sanchez-Armendariz did not acknowledge external funding sources. She reported having no conflicts of interest.
Truncal vagotomy might help delay Parkinson’s disease
Patients who were followed for more than 5 years after truncal vagotomy had about a 40% lower risk of being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with matched population controls, according to the results of a cohort registry study.
Selective vagotomy did not decrease the risk of Parkinson’s disease (PD), however, reported Bojing Liu of Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and her associates. The findings, which reflect those from a prior Danish study, “provide preliminary and indirect support” for the idea that Lewy pathology in PD begins in peripheral nerves and spreads to the central nervous system through “prion-like mechanisms,” they added.
The findings reflect a prior registry study that found a 15% decrease in the risk of PD compared with the general population more than 5 years after truncal vagotomy (Ann Neurol. 2015 Oct. 78[4];522-9). “This Danish study, however, did not differentiate truncal from selective vagotomy and thus might have underestimated the association of truncal vagotomy with PD,” the researchers said.
Another study found that truncal vagotomy exhibited a nonsignificant protective effect overall and an insignificantly increased risk of PD more than 20 years after surgery (Neurology Today 2015 Dec 3;15[23]:27-30). Likewise, the current study yielded “stronger evidence for PD risk reduction more than 5 or 10 years after truncal vagotomy,” and the protective effect appeared to weaken with longer follow-up, the investigators noted. If PD started at multiple sites within the peripheral nervous system, “even truncal vagotomy may delay, rather than eliminate, the risk for PD,” they emphasized. “Indeed, abnormal alpha-synuclein accumulation has been found throughout the digestive tract of patients with PD with descending pattern of density, and even in the submandibular gland in patients with preclinical PD.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Parkinson Research Foundation in Sweden, the Karolinska Institutet, the Swedish Society for Medical Research, the Stockholm County Council, and Karolinska Institutet–NIH Doctoral Partnership Program in Neuroscience. The investigators had no relevant disclosures.
The current study provides an independent dataset suggesting that truncal vagotomy may be protective in Parkinson’s disease. Therefore, the time has come to seriously consider the implications of these findings.
Could it be true that alpha-synuclein misfolding in PD may originate in the autonomic nerve terminals of the gastrointestinal tract? For the moment, more research is needed. One may consider studying the effects of vagotomy in patients with mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 gene (LRRK2), which dramatically increases the risk of developing neurodegenerative parkinsonism. Some of these mutations have a penetrance of up to 80% in the very elderly. However, it is largely unknown whether alpha-synuclein aggregates are present in gastrointestinal nerve endings of these patients. At this stage, we have insufficient knowledge to propose vagotomy as a putative treatment for PD. Although vagotomy will likely never become a widespread treatment for PD, strategies to prevent alpha-synuclein misfolding in the gastrointestinal tract may be proposed, because nerve terminals are reachable by oral therapeutic interventions.
Per Borghammer, MD, PhD, is in the department of nuclear medicine and PET Centre, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark. Clement Hamani, MD, PhD, is at the division of neurosurgery, Toronto Western Hospital, University of Toronto, and the department of neuroimaging, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute, Toronto. They reported no conflicts of interest. These comments are excerpted from their editorial (Neurology. 2017 Apr 26. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003969).
The current study provides an independent dataset suggesting that truncal vagotomy may be protective in Parkinson’s disease. Therefore, the time has come to seriously consider the implications of these findings.
Could it be true that alpha-synuclein misfolding in PD may originate in the autonomic nerve terminals of the gastrointestinal tract? For the moment, more research is needed. One may consider studying the effects of vagotomy in patients with mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 gene (LRRK2), which dramatically increases the risk of developing neurodegenerative parkinsonism. Some of these mutations have a penetrance of up to 80% in the very elderly. However, it is largely unknown whether alpha-synuclein aggregates are present in gastrointestinal nerve endings of these patients. At this stage, we have insufficient knowledge to propose vagotomy as a putative treatment for PD. Although vagotomy will likely never become a widespread treatment for PD, strategies to prevent alpha-synuclein misfolding in the gastrointestinal tract may be proposed, because nerve terminals are reachable by oral therapeutic interventions.
Per Borghammer, MD, PhD, is in the department of nuclear medicine and PET Centre, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark. Clement Hamani, MD, PhD, is at the division of neurosurgery, Toronto Western Hospital, University of Toronto, and the department of neuroimaging, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute, Toronto. They reported no conflicts of interest. These comments are excerpted from their editorial (Neurology. 2017 Apr 26. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003969).
The current study provides an independent dataset suggesting that truncal vagotomy may be protective in Parkinson’s disease. Therefore, the time has come to seriously consider the implications of these findings.
Could it be true that alpha-synuclein misfolding in PD may originate in the autonomic nerve terminals of the gastrointestinal tract? For the moment, more research is needed. One may consider studying the effects of vagotomy in patients with mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 gene (LRRK2), which dramatically increases the risk of developing neurodegenerative parkinsonism. Some of these mutations have a penetrance of up to 80% in the very elderly. However, it is largely unknown whether alpha-synuclein aggregates are present in gastrointestinal nerve endings of these patients. At this stage, we have insufficient knowledge to propose vagotomy as a putative treatment for PD. Although vagotomy will likely never become a widespread treatment for PD, strategies to prevent alpha-synuclein misfolding in the gastrointestinal tract may be proposed, because nerve terminals are reachable by oral therapeutic interventions.
Per Borghammer, MD, PhD, is in the department of nuclear medicine and PET Centre, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark. Clement Hamani, MD, PhD, is at the division of neurosurgery, Toronto Western Hospital, University of Toronto, and the department of neuroimaging, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute, Toronto. They reported no conflicts of interest. These comments are excerpted from their editorial (Neurology. 2017 Apr 26. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003969).
Patients who were followed for more than 5 years after truncal vagotomy had about a 40% lower risk of being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with matched population controls, according to the results of a cohort registry study.
Selective vagotomy did not decrease the risk of Parkinson’s disease (PD), however, reported Bojing Liu of Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and her associates. The findings, which reflect those from a prior Danish study, “provide preliminary and indirect support” for the idea that Lewy pathology in PD begins in peripheral nerves and spreads to the central nervous system through “prion-like mechanisms,” they added.
The findings reflect a prior registry study that found a 15% decrease in the risk of PD compared with the general population more than 5 years after truncal vagotomy (Ann Neurol. 2015 Oct. 78[4];522-9). “This Danish study, however, did not differentiate truncal from selective vagotomy and thus might have underestimated the association of truncal vagotomy with PD,” the researchers said.
Another study found that truncal vagotomy exhibited a nonsignificant protective effect overall and an insignificantly increased risk of PD more than 20 years after surgery (Neurology Today 2015 Dec 3;15[23]:27-30). Likewise, the current study yielded “stronger evidence for PD risk reduction more than 5 or 10 years after truncal vagotomy,” and the protective effect appeared to weaken with longer follow-up, the investigators noted. If PD started at multiple sites within the peripheral nervous system, “even truncal vagotomy may delay, rather than eliminate, the risk for PD,” they emphasized. “Indeed, abnormal alpha-synuclein accumulation has been found throughout the digestive tract of patients with PD with descending pattern of density, and even in the submandibular gland in patients with preclinical PD.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Parkinson Research Foundation in Sweden, the Karolinska Institutet, the Swedish Society for Medical Research, the Stockholm County Council, and Karolinska Institutet–NIH Doctoral Partnership Program in Neuroscience. The investigators had no relevant disclosures.
Patients who were followed for more than 5 years after truncal vagotomy had about a 40% lower risk of being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with matched population controls, according to the results of a cohort registry study.
Selective vagotomy did not decrease the risk of Parkinson’s disease (PD), however, reported Bojing Liu of Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, and her associates. The findings, which reflect those from a prior Danish study, “provide preliminary and indirect support” for the idea that Lewy pathology in PD begins in peripheral nerves and spreads to the central nervous system through “prion-like mechanisms,” they added.
The findings reflect a prior registry study that found a 15% decrease in the risk of PD compared with the general population more than 5 years after truncal vagotomy (Ann Neurol. 2015 Oct. 78[4];522-9). “This Danish study, however, did not differentiate truncal from selective vagotomy and thus might have underestimated the association of truncal vagotomy with PD,” the researchers said.
Another study found that truncal vagotomy exhibited a nonsignificant protective effect overall and an insignificantly increased risk of PD more than 20 years after surgery (Neurology Today 2015 Dec 3;15[23]:27-30). Likewise, the current study yielded “stronger evidence for PD risk reduction more than 5 or 10 years after truncal vagotomy,” and the protective effect appeared to weaken with longer follow-up, the investigators noted. If PD started at multiple sites within the peripheral nervous system, “even truncal vagotomy may delay, rather than eliminate, the risk for PD,” they emphasized. “Indeed, abnormal alpha-synuclein accumulation has been found throughout the digestive tract of patients with PD with descending pattern of density, and even in the submandibular gland in patients with preclinical PD.”
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Parkinson Research Foundation in Sweden, the Karolinska Institutet, the Swedish Society for Medical Research, the Stockholm County Council, and Karolinska Institutet–NIH Doctoral Partnership Program in Neuroscience. The investigators had no relevant disclosures.
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Compared with controls, patients who underwent truncal vagotomy were at decreased risk of Parkinson’s disease after more than 5 years (hazard ratio, 0.59, 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.93). Selective vagotomy did not show this association.
Data source: A matched cohort study of 9,430 vagotomized patients (3,445 truncal, 5,978 selective, 7 unknown) between 1970 and 2010, and 377,200 population controls matched by age and sex.
Disclosures: The Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Parkinson Research Foundation in Sweden, the Karolinska Institutet, the Swedish Society for Medical Research, the Stockholm County Council, and Karolinska Institutet–NIH Doctoral Partnership Program in Neuroscience funded the study. The investigators had no relevant disclosures.
VIDEO: Study confirms uneven access to liver cancer treatment at VA hospitals
Only 25% of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients with potentially curable (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A) hepatocellular carcinoma received resection, transplantation, or ablative therapy, according to the results of a national retrospective cohort study published in the June issue of Gastroenterology (doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.040).
Furthermore, 13% of the fittest (ECOG performance status 1-2) patients received no active treatment for their hepatocellular carcinoma, Marina Serper, MD, of Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, and Tamar H. Taddei, MD, of VA New York Harbor Health Care System, Brooklyn, New York, wrote with their associates in Gastroenterology.
Source: American Gastroenterological Association
“Delivery of curative therapies conferred the highest survival benefit, and notable geographic and specialist variation was observed in the delivery of active treatment,” they added. “Future studies should further evaluate modifiable health system and provider-specific barriers to delivering high quality, multidisciplinary care in hepatocellular carcinoma [in order] to optimize patient outcomes.”
Hepatocellular carcinoma ranks second worldwide and fifth in the United States as a cause of cancer mortality. Gastroenterologists, hepatologists, medical oncologists, or surgeons may take primary responsibility for treatment in community settings, but little is known about how provider and health system factors affect outcomes or the likelihood of receiving active treatments, such as liver transplantation, resection, ablative or transarterial therapy, sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy, or radiation. Accordingly, the researchers reviewed medical records and demographic data from all 3,988 U.S. patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma between 2008 and 2010 who received care at 128 Veterans Affairs centers. Patients were followed through the end of 2014. Data were from the Veterans Outcomes and Costs Associated with Liver Disease (VOCAL) cohort study (Gastroenterology. 2017 Mar 7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.040).
After diagnosis, most (54%) patients only underwent transarterial palliative therapy, and 24% received no cancer treatment, the researchers reported. Being treated at an academically affiliated VA hospital nearly doubled the odds of receiving active therapy (odds ratio, 1.97; 95% confidence interval, 1.6 to 2.4; P less than .001), even after the researchers controlled for race, Charlson-Deyo comorbidity, and presenting Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage. Evaluation by multiple specialists also significantly increased the odds of active treatment (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.15 to 2.21; P = .005), but review by a multidisciplinary tumor board did not (OR, 1.19; P = .1).
Receipt of active therapy also varied significantly by region. Compared with patients in the Northeastern United States, those in the mid-South were significantly less likely to receive active therapy (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.44-0.85). Patients in the Southeast, Central, and Western United States also were less likely to receive active treatment than were those in the Northeast, but 95% CIs for these hazard ratios were nonsignificant. Virtual tumor boards could help overcome diagnostic and treatment delays, but costs, care coordination, patient factors, and compensation issues are major barriers against implementation, the investigators noted.
Overall survival was associated with active treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, including liver transplantation (hazard ratio, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.16-0.31), liver resection (HR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.28-0.52), ablative therapy (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.52-0.76), and transarterial therapy (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.74-0.92). Reduced mortality was associated with seeing a hepatologist (HR, 0.7), medical oncologist (HR, 0.82), or surgeon (HR, 0.79) within 30 days of diagnosis (P less than .001 for each). Undergoing review by a multidisciplinary tumor board was associated with significantly reduced mortality (HR, 0.83; P less than .001), said the researchers.
“Findings from the VOCAL cohort of predominantly older males with significant medical comorbidities are important in light of the aging U.S. population and a nearly 70% expected increase in cancer among older adults,” they wrote. Together, the results indicate that access to multidisciplinary and expert care “is critical for optimizing treatment choices and for maximizing survival, but that such access is non-uniform,” they noted. “Detailed national VA clinical and administrative data are a unique resource that may be tapped to facilitate development of a parsimonious set of evidence-based, patient-centered, liver cancer–specific quality measures,” they emphasized. Quality measures based on timeliness, receipt of appropriate care, survival, or patient-reported outcomes “could be applicable both within and outside the VA system.”
The study was funded by unrestricted grants from Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals and the VA HIV, Hepatitis and Public Health Pathogens Programs. The investigators had no conflicts.
The treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be challenging because of the presence of underlying chronic liver disease and cirrhosis in the majority of patients. The study by Dr. Serper and colleagues evaluated the care of patients diagnosed with HCC in the Veterans Affairs (VA) system between 2008 and 2010. There are important aspects of this study worth highlighting.
First, 36% of patients presented with early-stage HCC and clearly had a better overall survival. This highlights the need for surveillance of patients with cirrhosis not only in the VA but also in other health systems. Second, only a minority of patients with early-stage HCC received curative interventions. In order to improve outcomes, patients with early stage disease should receive appropriate curative interventions. Third, gastroenterologists saw a large number of patients with HCC in the VA system, but, unfortunately, this led to less receipt of active therapy and a trend for a worse all-cause mortality, compared with hepatologists and other specialties. It is critical that gastroenterologists refer patients to specialties more adept at treating HCC in order to achieve better outcomes.
Lastly, only 34% of patients with HCC were managed via a multidisciplinary tumor conference. Importantly, these patients had an increased probability of receipt of active treatment and a 17% reduction in all-cause mortality. Our group has shown that a multidisciplinary approach to treating HCC improves overall survival. It is critical that medical centers develop a multidisciplinary treatment approach to HCC.
Jorge A. Marrero, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and medical director for liver transplantation at UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas. He has no conflicts of interest to report regarding this manuscript or commentary.
The treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be challenging because of the presence of underlying chronic liver disease and cirrhosis in the majority of patients. The study by Dr. Serper and colleagues evaluated the care of patients diagnosed with HCC in the Veterans Affairs (VA) system between 2008 and 2010. There are important aspects of this study worth highlighting.
First, 36% of patients presented with early-stage HCC and clearly had a better overall survival. This highlights the need for surveillance of patients with cirrhosis not only in the VA but also in other health systems. Second, only a minority of patients with early-stage HCC received curative interventions. In order to improve outcomes, patients with early stage disease should receive appropriate curative interventions. Third, gastroenterologists saw a large number of patients with HCC in the VA system, but, unfortunately, this led to less receipt of active therapy and a trend for a worse all-cause mortality, compared with hepatologists and other specialties. It is critical that gastroenterologists refer patients to specialties more adept at treating HCC in order to achieve better outcomes.
Lastly, only 34% of patients with HCC were managed via a multidisciplinary tumor conference. Importantly, these patients had an increased probability of receipt of active treatment and a 17% reduction in all-cause mortality. Our group has shown that a multidisciplinary approach to treating HCC improves overall survival. It is critical that medical centers develop a multidisciplinary treatment approach to HCC.
Jorge A. Marrero, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and medical director for liver transplantation at UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas. He has no conflicts of interest to report regarding this manuscript or commentary.
The treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) can be challenging because of the presence of underlying chronic liver disease and cirrhosis in the majority of patients. The study by Dr. Serper and colleagues evaluated the care of patients diagnosed with HCC in the Veterans Affairs (VA) system between 2008 and 2010. There are important aspects of this study worth highlighting.
First, 36% of patients presented with early-stage HCC and clearly had a better overall survival. This highlights the need for surveillance of patients with cirrhosis not only in the VA but also in other health systems. Second, only a minority of patients with early-stage HCC received curative interventions. In order to improve outcomes, patients with early stage disease should receive appropriate curative interventions. Third, gastroenterologists saw a large number of patients with HCC in the VA system, but, unfortunately, this led to less receipt of active therapy and a trend for a worse all-cause mortality, compared with hepatologists and other specialties. It is critical that gastroenterologists refer patients to specialties more adept at treating HCC in order to achieve better outcomes.
Lastly, only 34% of patients with HCC were managed via a multidisciplinary tumor conference. Importantly, these patients had an increased probability of receipt of active treatment and a 17% reduction in all-cause mortality. Our group has shown that a multidisciplinary approach to treating HCC improves overall survival. It is critical that medical centers develop a multidisciplinary treatment approach to HCC.
Jorge A. Marrero, MD, MS, AGAF, is professor of medicine and medical director for liver transplantation at UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas. He has no conflicts of interest to report regarding this manuscript or commentary.
Only 25% of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients with potentially curable (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A) hepatocellular carcinoma received resection, transplantation, or ablative therapy, according to the results of a national retrospective cohort study published in the June issue of Gastroenterology (doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.040).
Furthermore, 13% of the fittest (ECOG performance status 1-2) patients received no active treatment for their hepatocellular carcinoma, Marina Serper, MD, of Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, and Tamar H. Taddei, MD, of VA New York Harbor Health Care System, Brooklyn, New York, wrote with their associates in Gastroenterology.
Source: American Gastroenterological Association
“Delivery of curative therapies conferred the highest survival benefit, and notable geographic and specialist variation was observed in the delivery of active treatment,” they added. “Future studies should further evaluate modifiable health system and provider-specific barriers to delivering high quality, multidisciplinary care in hepatocellular carcinoma [in order] to optimize patient outcomes.”
Hepatocellular carcinoma ranks second worldwide and fifth in the United States as a cause of cancer mortality. Gastroenterologists, hepatologists, medical oncologists, or surgeons may take primary responsibility for treatment in community settings, but little is known about how provider and health system factors affect outcomes or the likelihood of receiving active treatments, such as liver transplantation, resection, ablative or transarterial therapy, sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy, or radiation. Accordingly, the researchers reviewed medical records and demographic data from all 3,988 U.S. patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma between 2008 and 2010 who received care at 128 Veterans Affairs centers. Patients were followed through the end of 2014. Data were from the Veterans Outcomes and Costs Associated with Liver Disease (VOCAL) cohort study (Gastroenterology. 2017 Mar 7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.040).
After diagnosis, most (54%) patients only underwent transarterial palliative therapy, and 24% received no cancer treatment, the researchers reported. Being treated at an academically affiliated VA hospital nearly doubled the odds of receiving active therapy (odds ratio, 1.97; 95% confidence interval, 1.6 to 2.4; P less than .001), even after the researchers controlled for race, Charlson-Deyo comorbidity, and presenting Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage. Evaluation by multiple specialists also significantly increased the odds of active treatment (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.15 to 2.21; P = .005), but review by a multidisciplinary tumor board did not (OR, 1.19; P = .1).
Receipt of active therapy also varied significantly by region. Compared with patients in the Northeastern United States, those in the mid-South were significantly less likely to receive active therapy (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.44-0.85). Patients in the Southeast, Central, and Western United States also were less likely to receive active treatment than were those in the Northeast, but 95% CIs for these hazard ratios were nonsignificant. Virtual tumor boards could help overcome diagnostic and treatment delays, but costs, care coordination, patient factors, and compensation issues are major barriers against implementation, the investigators noted.
Overall survival was associated with active treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, including liver transplantation (hazard ratio, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.16-0.31), liver resection (HR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.28-0.52), ablative therapy (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.52-0.76), and transarterial therapy (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.74-0.92). Reduced mortality was associated with seeing a hepatologist (HR, 0.7), medical oncologist (HR, 0.82), or surgeon (HR, 0.79) within 30 days of diagnosis (P less than .001 for each). Undergoing review by a multidisciplinary tumor board was associated with significantly reduced mortality (HR, 0.83; P less than .001), said the researchers.
“Findings from the VOCAL cohort of predominantly older males with significant medical comorbidities are important in light of the aging U.S. population and a nearly 70% expected increase in cancer among older adults,” they wrote. Together, the results indicate that access to multidisciplinary and expert care “is critical for optimizing treatment choices and for maximizing survival, but that such access is non-uniform,” they noted. “Detailed national VA clinical and administrative data are a unique resource that may be tapped to facilitate development of a parsimonious set of evidence-based, patient-centered, liver cancer–specific quality measures,” they emphasized. Quality measures based on timeliness, receipt of appropriate care, survival, or patient-reported outcomes “could be applicable both within and outside the VA system.”
The study was funded by unrestricted grants from Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals and the VA HIV, Hepatitis and Public Health Pathogens Programs. The investigators had no conflicts.
Only 25% of Veterans Affairs (VA) patients with potentially curable (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A) hepatocellular carcinoma received resection, transplantation, or ablative therapy, according to the results of a national retrospective cohort study published in the June issue of Gastroenterology (doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.040).
Furthermore, 13% of the fittest (ECOG performance status 1-2) patients received no active treatment for their hepatocellular carcinoma, Marina Serper, MD, of Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, and Tamar H. Taddei, MD, of VA New York Harbor Health Care System, Brooklyn, New York, wrote with their associates in Gastroenterology.
Source: American Gastroenterological Association
“Delivery of curative therapies conferred the highest survival benefit, and notable geographic and specialist variation was observed in the delivery of active treatment,” they added. “Future studies should further evaluate modifiable health system and provider-specific barriers to delivering high quality, multidisciplinary care in hepatocellular carcinoma [in order] to optimize patient outcomes.”
Hepatocellular carcinoma ranks second worldwide and fifth in the United States as a cause of cancer mortality. Gastroenterologists, hepatologists, medical oncologists, or surgeons may take primary responsibility for treatment in community settings, but little is known about how provider and health system factors affect outcomes or the likelihood of receiving active treatments, such as liver transplantation, resection, ablative or transarterial therapy, sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy, or radiation. Accordingly, the researchers reviewed medical records and demographic data from all 3,988 U.S. patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma between 2008 and 2010 who received care at 128 Veterans Affairs centers. Patients were followed through the end of 2014. Data were from the Veterans Outcomes and Costs Associated with Liver Disease (VOCAL) cohort study (Gastroenterology. 2017 Mar 7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.040).
After diagnosis, most (54%) patients only underwent transarterial palliative therapy, and 24% received no cancer treatment, the researchers reported. Being treated at an academically affiliated VA hospital nearly doubled the odds of receiving active therapy (odds ratio, 1.97; 95% confidence interval, 1.6 to 2.4; P less than .001), even after the researchers controlled for race, Charlson-Deyo comorbidity, and presenting Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage. Evaluation by multiple specialists also significantly increased the odds of active treatment (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.15 to 2.21; P = .005), but review by a multidisciplinary tumor board did not (OR, 1.19; P = .1).
Receipt of active therapy also varied significantly by region. Compared with patients in the Northeastern United States, those in the mid-South were significantly less likely to receive active therapy (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.44-0.85). Patients in the Southeast, Central, and Western United States also were less likely to receive active treatment than were those in the Northeast, but 95% CIs for these hazard ratios were nonsignificant. Virtual tumor boards could help overcome diagnostic and treatment delays, but costs, care coordination, patient factors, and compensation issues are major barriers against implementation, the investigators noted.
Overall survival was associated with active treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, including liver transplantation (hazard ratio, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.16-0.31), liver resection (HR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.28-0.52), ablative therapy (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.52-0.76), and transarterial therapy (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.74-0.92). Reduced mortality was associated with seeing a hepatologist (HR, 0.7), medical oncologist (HR, 0.82), or surgeon (HR, 0.79) within 30 days of diagnosis (P less than .001 for each). Undergoing review by a multidisciplinary tumor board was associated with significantly reduced mortality (HR, 0.83; P less than .001), said the researchers.
“Findings from the VOCAL cohort of predominantly older males with significant medical comorbidities are important in light of the aging U.S. population and a nearly 70% expected increase in cancer among older adults,” they wrote. Together, the results indicate that access to multidisciplinary and expert care “is critical for optimizing treatment choices and for maximizing survival, but that such access is non-uniform,” they noted. “Detailed national VA clinical and administrative data are a unique resource that may be tapped to facilitate development of a parsimonious set of evidence-based, patient-centered, liver cancer–specific quality measures,” they emphasized. Quality measures based on timeliness, receipt of appropriate care, survival, or patient-reported outcomes “could be applicable both within and outside the VA system.”
The study was funded by unrestricted grants from Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals and the VA HIV, Hepatitis and Public Health Pathogens Programs. The investigators had no conflicts.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Key clinical point: Undertreatment of hepatocellular carcinoma was common within the Veterans Affairs system, and varied by geographic region.
Major finding: Only 25% of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A patients received potentially curative therapies. Those in the mid-South were significantly less likely to receive active treatment than were those in the Northeast (HR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.44-0.85). In an adjusted model, treatment at an academically affiliated VA hospital nearly doubled the odds of receiving active therapy (odds ratio, 1.97; P less than .001).
Data source: A national, retrospective cohort study of all 3,988 patients who were diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma between 2008 and 2010 and received care through Veterans Affairs.
Disclosures: The study was funded by unrestricted grants from Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals and the VA HIV, Hepatitis and Public Health Pathogens Programs. The investigators had no conflicts.
Study underscores antipsoriatic effect of gastric bypass surgery
Gastric bypass surgery was associated with more than a 50% drop in baseline rates of psoriasis, and with about a 70% decrease in the incidence of psoriatic arthritis, investigators reported.
In contrast, gastric banding did not appear to affect baselines rates of either of these autoimmune conditions, Alexander Egeberg, MD, of Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Hellerup, Denmark, and associates reported in JAMA Surgery. “Although speculative, these findings may be the result of post-operative differences in weight loss and nutrient uptake, as well as differences in the postsurgical secretion of a number of gut hormones, including [glucagon-like peptide-1],” they wrote.
Psoriasis strongly correlates with obesity, and weight loss appears to mitigate psoriatic symptoms, the investigators noted. Previously, small studies and case series indicated that bariatric surgery might induce remission of psoriasis. To further investigate this possibility, Dr. Egeberg and his associates conducted a longitudinal cohort study of all 12,364 patients who underwent gastric bypass surgery and all 1,071 patients who underwent gastric banding in Denmark between 1997 and 2012 (JAMA Surg. 2017;152:344-349). No patient had psoriasis symptoms at the start of the study. A total of 272 (2%) gastric bypass patients developed psoriasis before their surgery, while only 0.5% did so afterward. In contrast, gastric banding was not tied to a significant change in the incidence of psoriasis – the preoperative rate was 0.5%, and the postoperative rate was 0.4%. Similarly, respective rates of psoriatic arthritis were 0.5% and 0.1% before and after gastric bypass, but were 0.3% and 0.6% before and after gastric banding. Additionally, respective rates of severe psoriasis were 0.8% and 0% before and after gastric bypass, but were about 0.2% and 0.5% before and after gastric banding.
After adjusting for age, sex, alcohol abuse, socioeconomic status, smoking, and diabetes status, gastric bypass was associated with about a 48% drop in the incidence of any type of psoriasis (P = .004), with about a 56% drop in the rate of severe psoriasis (P = .02), and with about a 71% drop in the rate of psoriatic arthritis (P = .01). In contrast, neither crude nor adjusted models linked gastric banding to a decrease in the incidence of psoriasis, severe psoriasis, or psoriatic arthritis, the researchers said.
Gastric banding is “a purely restrictive procedure,” while gastric bypass – especially Roux-en-Y bypass – diverts nutrients to the distal small intestine, where enteroendocrine cells secrete GLP-1, the researchers wrote.
“These postoperative hormonal changes may, in addition to the weight loss, be important for the antipsoriatic effect of gastric bypass,” they added. “Both gastric bypass and gastric banding have been shown to lead to sustained weight loss, suggesting that the observed differences in our study might be caused by factors other than weight loss.”
An unrestricted research grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the work. Dr. Egeberg disclosed ties to Pfizer and Eli Lilly. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to these and several other pharmaceutical companies.
Gastric bypass surgery was associated with more than a 50% drop in baseline rates of psoriasis, and with about a 70% decrease in the incidence of psoriatic arthritis, investigators reported.
In contrast, gastric banding did not appear to affect baselines rates of either of these autoimmune conditions, Alexander Egeberg, MD, of Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Hellerup, Denmark, and associates reported in JAMA Surgery. “Although speculative, these findings may be the result of post-operative differences in weight loss and nutrient uptake, as well as differences in the postsurgical secretion of a number of gut hormones, including [glucagon-like peptide-1],” they wrote.
Psoriasis strongly correlates with obesity, and weight loss appears to mitigate psoriatic symptoms, the investigators noted. Previously, small studies and case series indicated that bariatric surgery might induce remission of psoriasis. To further investigate this possibility, Dr. Egeberg and his associates conducted a longitudinal cohort study of all 12,364 patients who underwent gastric bypass surgery and all 1,071 patients who underwent gastric banding in Denmark between 1997 and 2012 (JAMA Surg. 2017;152:344-349). No patient had psoriasis symptoms at the start of the study. A total of 272 (2%) gastric bypass patients developed psoriasis before their surgery, while only 0.5% did so afterward. In contrast, gastric banding was not tied to a significant change in the incidence of psoriasis – the preoperative rate was 0.5%, and the postoperative rate was 0.4%. Similarly, respective rates of psoriatic arthritis were 0.5% and 0.1% before and after gastric bypass, but were 0.3% and 0.6% before and after gastric banding. Additionally, respective rates of severe psoriasis were 0.8% and 0% before and after gastric bypass, but were about 0.2% and 0.5% before and after gastric banding.
After adjusting for age, sex, alcohol abuse, socioeconomic status, smoking, and diabetes status, gastric bypass was associated with about a 48% drop in the incidence of any type of psoriasis (P = .004), with about a 56% drop in the rate of severe psoriasis (P = .02), and with about a 71% drop in the rate of psoriatic arthritis (P = .01). In contrast, neither crude nor adjusted models linked gastric banding to a decrease in the incidence of psoriasis, severe psoriasis, or psoriatic arthritis, the researchers said.
Gastric banding is “a purely restrictive procedure,” while gastric bypass – especially Roux-en-Y bypass – diverts nutrients to the distal small intestine, where enteroendocrine cells secrete GLP-1, the researchers wrote.
“These postoperative hormonal changes may, in addition to the weight loss, be important for the antipsoriatic effect of gastric bypass,” they added. “Both gastric bypass and gastric banding have been shown to lead to sustained weight loss, suggesting that the observed differences in our study might be caused by factors other than weight loss.”
An unrestricted research grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the work. Dr. Egeberg disclosed ties to Pfizer and Eli Lilly. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to these and several other pharmaceutical companies.
Gastric bypass surgery was associated with more than a 50% drop in baseline rates of psoriasis, and with about a 70% decrease in the incidence of psoriatic arthritis, investigators reported.
In contrast, gastric banding did not appear to affect baselines rates of either of these autoimmune conditions, Alexander Egeberg, MD, of Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Hellerup, Denmark, and associates reported in JAMA Surgery. “Although speculative, these findings may be the result of post-operative differences in weight loss and nutrient uptake, as well as differences in the postsurgical secretion of a number of gut hormones, including [glucagon-like peptide-1],” they wrote.
Psoriasis strongly correlates with obesity, and weight loss appears to mitigate psoriatic symptoms, the investigators noted. Previously, small studies and case series indicated that bariatric surgery might induce remission of psoriasis. To further investigate this possibility, Dr. Egeberg and his associates conducted a longitudinal cohort study of all 12,364 patients who underwent gastric bypass surgery and all 1,071 patients who underwent gastric banding in Denmark between 1997 and 2012 (JAMA Surg. 2017;152:344-349). No patient had psoriasis symptoms at the start of the study. A total of 272 (2%) gastric bypass patients developed psoriasis before their surgery, while only 0.5% did so afterward. In contrast, gastric banding was not tied to a significant change in the incidence of psoriasis – the preoperative rate was 0.5%, and the postoperative rate was 0.4%. Similarly, respective rates of psoriatic arthritis were 0.5% and 0.1% before and after gastric bypass, but were 0.3% and 0.6% before and after gastric banding. Additionally, respective rates of severe psoriasis were 0.8% and 0% before and after gastric bypass, but were about 0.2% and 0.5% before and after gastric banding.
After adjusting for age, sex, alcohol abuse, socioeconomic status, smoking, and diabetes status, gastric bypass was associated with about a 48% drop in the incidence of any type of psoriasis (P = .004), with about a 56% drop in the rate of severe psoriasis (P = .02), and with about a 71% drop in the rate of psoriatic arthritis (P = .01). In contrast, neither crude nor adjusted models linked gastric banding to a decrease in the incidence of psoriasis, severe psoriasis, or psoriatic arthritis, the researchers said.
Gastric banding is “a purely restrictive procedure,” while gastric bypass – especially Roux-en-Y bypass – diverts nutrients to the distal small intestine, where enteroendocrine cells secrete GLP-1, the researchers wrote.
“These postoperative hormonal changes may, in addition to the weight loss, be important for the antipsoriatic effect of gastric bypass,” they added. “Both gastric bypass and gastric banding have been shown to lead to sustained weight loss, suggesting that the observed differences in our study might be caused by factors other than weight loss.”
An unrestricted research grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the work. Dr. Egeberg disclosed ties to Pfizer and Eli Lilly. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to these and several other pharmaceutical companies.
Key clinical point: Gastric bypass, but not gastric banding, was associated with significant drops in rates of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Major finding: In an adjusted model, gastric bypass was associated with about a 48% drop in the incidence of any type of psoriasis, with a 56% drop in the rate of severe psoriasis, and with a 71% drop in the rate of psoriatic arthritis.
Data source: A population-based cohort study of 12,364 gastric bypass patients and 1,071 gastric banding patients.
Disclosures: An unrestricted research grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the work. Dr. Egeberg disclosed ties to Pfizer and Eli Lilly. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to these and several other pharmaceutical companies. The other coinvestigators reported having no ties to industry.
Secukinumab beat etanercept in 52-week psoriasis quality of life analysis
Compared with etanercept, secukinumab was associated with significantly faster and greater improvements in skin-specific quality of life among adults with moderate to severe psoriasis, according to a pooled analysis of data from the randomized, multicenter phase III ERASURE and FIXTURE trials.
The findings confirm the clinical superiority of secukinumab and extend prior head-to-head comparisons of this IL-17A inhibitor and etanercept, said Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of the University of Connecticut in Farmington, Conn.
ERASURE and FIXTURE compared secukinumab (weekly for 4 weeks, then once-monthly) with etanercept (twice weekly for 12 weeks, then once-weekly) and placebo. Both secukinumab doses outperformed etanercept and placebo based on coprimary endpoints of PASI 75 and the proportion of patients who were clear or almost clear on a 5-point modified investigator’s global assessment (N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371[4]:326-38). A subsequent analysis showed that the clinical superiority of secukinumab held up at 52 weeks (J Dermatolog Treat. 2016;27[1]:1).
Because health-related quality of life is of increasing interest in psoriasis, Dr. Strober and his associates analyzed ERASURE and FIXTURE data on the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), a 10-item assessment of daily activities, leisure, personal relationships, symptoms and feelings, treatment, and work or school. Their analysis included 572 patients who received 300 mg secukinumab, 572 patients who received 150 mg secukinumab, and 326 patients who received 50 mg etanercept.
Baseline DLQI scores were similar among treatment groups. By week 4, significantly more secukinumab than etanercept recipients reported DLQI scores of 0 or 1 (DLQI 0/1), indicating that psoriasis was not impairing their quality of life (P < .05). This difference remained significant through week 52 at the 300-mg dose. The 150-mg dose significantly outperformed etanercept by week 8, and the difference remained significant through week 48.
In all, 81% of patients who received 300 mg secukinumab reported DLQI 0/1 at week 24, compared with 71% of those who received 150 mg secukinumab and 55% of those who received etanercept (P < .001 for each comparison with etanercept).
Among patients with complete data available, 86% of 300-mg secukinumab recipients achieved DLQI 0/1 at week 24, maintained this response through 52 weeks, and achieved a 90%-100% reduction in PASI total score at week 24. That was true of only 75% of etanercept recipients (P = .02, compared with 300 mg secukinumab) and 79% of 150-mg secukinumab recipients (P = .4, compared with etanercept).
In an adjusted model, patients who received 300 mg secukinumab were 1.9 times more likely to reach DLQI 0/1 than those who received etanercept (95% confidence interval, 1.6-2.3). Median time to response to both doses of secukinumab was 12 weeks, versus 24 weeks for etanercept (P < .0001).
This analysis offers “a robust, longer-term head-to-head comparison” of how secukinumab and etanercept affect quality of life in psoriasis, the researchers wrote. “Future research should consider replicating this evaluation using real-world long-term data and including other aspects of patient-centered outcomes, such as work productivity and psoriasis-related symptoms.”
Novartis funded ERASURE and FIXTURE. Dr. Strober reported financial ties to AbbVie, Amgen, Novartis, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
Compared with etanercept, secukinumab was associated with significantly faster and greater improvements in skin-specific quality of life among adults with moderate to severe psoriasis, according to a pooled analysis of data from the randomized, multicenter phase III ERASURE and FIXTURE trials.
The findings confirm the clinical superiority of secukinumab and extend prior head-to-head comparisons of this IL-17A inhibitor and etanercept, said Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of the University of Connecticut in Farmington, Conn.
ERASURE and FIXTURE compared secukinumab (weekly for 4 weeks, then once-monthly) with etanercept (twice weekly for 12 weeks, then once-weekly) and placebo. Both secukinumab doses outperformed etanercept and placebo based on coprimary endpoints of PASI 75 and the proportion of patients who were clear or almost clear on a 5-point modified investigator’s global assessment (N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371[4]:326-38). A subsequent analysis showed that the clinical superiority of secukinumab held up at 52 weeks (J Dermatolog Treat. 2016;27[1]:1).
Because health-related quality of life is of increasing interest in psoriasis, Dr. Strober and his associates analyzed ERASURE and FIXTURE data on the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), a 10-item assessment of daily activities, leisure, personal relationships, symptoms and feelings, treatment, and work or school. Their analysis included 572 patients who received 300 mg secukinumab, 572 patients who received 150 mg secukinumab, and 326 patients who received 50 mg etanercept.
Baseline DLQI scores were similar among treatment groups. By week 4, significantly more secukinumab than etanercept recipients reported DLQI scores of 0 or 1 (DLQI 0/1), indicating that psoriasis was not impairing their quality of life (P < .05). This difference remained significant through week 52 at the 300-mg dose. The 150-mg dose significantly outperformed etanercept by week 8, and the difference remained significant through week 48.
In all, 81% of patients who received 300 mg secukinumab reported DLQI 0/1 at week 24, compared with 71% of those who received 150 mg secukinumab and 55% of those who received etanercept (P < .001 for each comparison with etanercept).
Among patients with complete data available, 86% of 300-mg secukinumab recipients achieved DLQI 0/1 at week 24, maintained this response through 52 weeks, and achieved a 90%-100% reduction in PASI total score at week 24. That was true of only 75% of etanercept recipients (P = .02, compared with 300 mg secukinumab) and 79% of 150-mg secukinumab recipients (P = .4, compared with etanercept).
In an adjusted model, patients who received 300 mg secukinumab were 1.9 times more likely to reach DLQI 0/1 than those who received etanercept (95% confidence interval, 1.6-2.3). Median time to response to both doses of secukinumab was 12 weeks, versus 24 weeks for etanercept (P < .0001).
This analysis offers “a robust, longer-term head-to-head comparison” of how secukinumab and etanercept affect quality of life in psoriasis, the researchers wrote. “Future research should consider replicating this evaluation using real-world long-term data and including other aspects of patient-centered outcomes, such as work productivity and psoriasis-related symptoms.”
Novartis funded ERASURE and FIXTURE. Dr. Strober reported financial ties to AbbVie, Amgen, Novartis, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
Compared with etanercept, secukinumab was associated with significantly faster and greater improvements in skin-specific quality of life among adults with moderate to severe psoriasis, according to a pooled analysis of data from the randomized, multicenter phase III ERASURE and FIXTURE trials.
The findings confirm the clinical superiority of secukinumab and extend prior head-to-head comparisons of this IL-17A inhibitor and etanercept, said Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of the University of Connecticut in Farmington, Conn.
ERASURE and FIXTURE compared secukinumab (weekly for 4 weeks, then once-monthly) with etanercept (twice weekly for 12 weeks, then once-weekly) and placebo. Both secukinumab doses outperformed etanercept and placebo based on coprimary endpoints of PASI 75 and the proportion of patients who were clear or almost clear on a 5-point modified investigator’s global assessment (N Engl J Med. 2014 Jul 24;371[4]:326-38). A subsequent analysis showed that the clinical superiority of secukinumab held up at 52 weeks (J Dermatolog Treat. 2016;27[1]:1).
Because health-related quality of life is of increasing interest in psoriasis, Dr. Strober and his associates analyzed ERASURE and FIXTURE data on the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), a 10-item assessment of daily activities, leisure, personal relationships, symptoms and feelings, treatment, and work or school. Their analysis included 572 patients who received 300 mg secukinumab, 572 patients who received 150 mg secukinumab, and 326 patients who received 50 mg etanercept.
Baseline DLQI scores were similar among treatment groups. By week 4, significantly more secukinumab than etanercept recipients reported DLQI scores of 0 or 1 (DLQI 0/1), indicating that psoriasis was not impairing their quality of life (P < .05). This difference remained significant through week 52 at the 300-mg dose. The 150-mg dose significantly outperformed etanercept by week 8, and the difference remained significant through week 48.
In all, 81% of patients who received 300 mg secukinumab reported DLQI 0/1 at week 24, compared with 71% of those who received 150 mg secukinumab and 55% of those who received etanercept (P < .001 for each comparison with etanercept).
Among patients with complete data available, 86% of 300-mg secukinumab recipients achieved DLQI 0/1 at week 24, maintained this response through 52 weeks, and achieved a 90%-100% reduction in PASI total score at week 24. That was true of only 75% of etanercept recipients (P = .02, compared with 300 mg secukinumab) and 79% of 150-mg secukinumab recipients (P = .4, compared with etanercept).
In an adjusted model, patients who received 300 mg secukinumab were 1.9 times more likely to reach DLQI 0/1 than those who received etanercept (95% confidence interval, 1.6-2.3). Median time to response to both doses of secukinumab was 12 weeks, versus 24 weeks for etanercept (P < .0001).
This analysis offers “a robust, longer-term head-to-head comparison” of how secukinumab and etanercept affect quality of life in psoriasis, the researchers wrote. “Future research should consider replicating this evaluation using real-world long-term data and including other aspects of patient-centered outcomes, such as work productivity and psoriasis-related symptoms.”
Novartis funded ERASURE and FIXTURE. Dr. Strober reported financial ties to AbbVie, Amgen, Novartis, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Secukinumab was associated with faster and greater improvements in self-reported quality of life, compared with etanercept, in adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
Major finding: In all, 81% of patients who received 300 mg secukinumab reported DLQI 0/1 at week 24, compared with 71% of those who received 150 mg secukinumab and 55% of those who received etanercept (P < .001 for each comparison with etanercept).
Data source: A pooled analysis of the randomized, multicenter, phase III ERASURE and FIXTURE trials.
Disclosures: Novartis funded ERASURE and FIXTURE. Dr. Strober reported financial ties to AbbVie, Amgen, Novartis, and several other pharmaceutical companies.
Transplantation plus VRD tops VRD alone in myeloma
Adding high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation to two cycles of bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRD) significantly improved progression-free survival in adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to new analyses from the multicenter, randomized, phase III IFM 2009 Study.
Median PFS was 50 months in the transplantation group, versus 36 months when patients only received five cycles of VRD for consolidation (adjusted hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.65; 95% confidence interval, 0.53 to 0.80; P less than .001), reported Michel Attal, MD, of Institut Universitaire du Cancer de Toulouse-Oncopole in Toulouse, France, and his associates. “Transplantation was also associated with a higher rate of complete response, a lower rate of minimal residual disease detection, and a longer median time to progression,” they wrote (N Engl J Med. 2017 April 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1611750).
Transplantation did not improve 4-year overall survival (81% with transplantation plus VRD and 82% with VRD only), perhaps because VRD-only patients had the option of salvage transplantation if their disease progressed, the investigators said. In addition, grade 3 or 4 neutropenias were significantly more common with transplantation than otherwise (92% versus 47%), as were grade 3 or 4 gastrointestinal disorders (28% versus 7%) and infections (20% versus 9%). However, the groups did not significantly differ in terms of treatment-related deaths, second primary cancers, thromboembolic events, or peripheral neuropathy.
Before the advent of immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors, several randomized trials showed that the benefits of high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplantation outperformed conventional chemotherapy in multiple myeloma. For IFM 2009, 700 newly diagnosed patients aged up to 65 years received three 21-day cycles of VRD induction: bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 on days 1, 4, 8, and 11; lenalidomide 25 mg on days 1-14; and dexamethasone 20 mg on days 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 11, and 12. Consolidation consisted of either five more VRD cycles with dexamethasone reduced to 10 mg/day, or high-dose (200 mg/m2) melphalan plus transplantation followed by two VRD cycles with the reduced dexamethasone dose. Both arms received 1 year of lenalidomide maintenance (10 mg/day for 3 months, followed by 15/mg day, depending on side effects).
Transplantation was associated with a significantly higher likelihood of complete response (59% versus 48%; P = .03) and undetectable minimal residual disease (79% versus 65%; P less than .001). Undetectable minimal residual disease, in turn, predicted longer PFS (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.30; P = .001). In contrast, age, sex, isotype of the monoclonal component, International Staging System disease stage, and cytogenetic risk profile did not significantly affect PFS among transplant patients.
The PFS benefit of transplantation “must be weighed against the increased risk of toxic effects associated with high-dose chemotherapy plus transplantation, especially since we found that later transplantation might be as effective as early transplantation in securing long- term survival,” the researchers said. “Our results suggest that the use of a combination therapy that incorporates newer proteasome inhibitors, next-generation immunomodulatory drugs, and potent monoclonal antibodies along with transplantation tailored according to minimal residual disease detection could further improve outcomes among adults up to 65 years of age who have multiple myeloma.”
Celgene, Janssen, the French Ministry of Health Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique, and the French National Research Agency funded the study. Dr. Attal had no conflicts. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Celgene, Janssen, and several other pharmaceutical companies. Two coinvestigators disclosed ownership or founder roles in OncoPep, one of whom disclosed patent licensure to OncoPep for a multipeptide vaccine. The other investigators had no conflicts.
In the IFM 2009 trial, the planned treatments were realistic. The combination of immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors is associated with high response rates similar to those achieved with transplantation, whereas previous trials had used less effective chemotherapy regimens as comparators.
[Transplantation] resulted in a deeper and longer initial treatment response than did nontransplantation. However, the benefits of transplantation were more modest than some might have hoped, and it did not appear to be curative.
A question remains as to whether all patients with multiple myeloma should undergo immediate autologous stem-cell transplantation, since the use of delayed transplantation resulted in similar overall survival, with some patients not needing transplantation to date. The observed lack of a survival benefit for early transplantation was consistent with previous results that suggested salvage transplantation is an equalizer in this regard.
Charles A. Schiffer, MD, and Jeffrey A. Zonder, MD, are with Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University, Detroit, Mich. Dr. Zonder is a member of the editorial advisory board of Hematology News. Their comments were taken from an editorial (N Engl J Med. 2017 April 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1700453).
In the IFM 2009 trial, the planned treatments were realistic. The combination of immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors is associated with high response rates similar to those achieved with transplantation, whereas previous trials had used less effective chemotherapy regimens as comparators.
[Transplantation] resulted in a deeper and longer initial treatment response than did nontransplantation. However, the benefits of transplantation were more modest than some might have hoped, and it did not appear to be curative.
A question remains as to whether all patients with multiple myeloma should undergo immediate autologous stem-cell transplantation, since the use of delayed transplantation resulted in similar overall survival, with some patients not needing transplantation to date. The observed lack of a survival benefit for early transplantation was consistent with previous results that suggested salvage transplantation is an equalizer in this regard.
Charles A. Schiffer, MD, and Jeffrey A. Zonder, MD, are with Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University, Detroit, Mich. Dr. Zonder is a member of the editorial advisory board of Hematology News. Their comments were taken from an editorial (N Engl J Med. 2017 April 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1700453).
In the IFM 2009 trial, the planned treatments were realistic. The combination of immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors is associated with high response rates similar to those achieved with transplantation, whereas previous trials had used less effective chemotherapy regimens as comparators.
[Transplantation] resulted in a deeper and longer initial treatment response than did nontransplantation. However, the benefits of transplantation were more modest than some might have hoped, and it did not appear to be curative.
A question remains as to whether all patients with multiple myeloma should undergo immediate autologous stem-cell transplantation, since the use of delayed transplantation resulted in similar overall survival, with some patients not needing transplantation to date. The observed lack of a survival benefit for early transplantation was consistent with previous results that suggested salvage transplantation is an equalizer in this regard.
Charles A. Schiffer, MD, and Jeffrey A. Zonder, MD, are with Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University, Detroit, Mich. Dr. Zonder is a member of the editorial advisory board of Hematology News. Their comments were taken from an editorial (N Engl J Med. 2017 April 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1700453).
Adding high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation to two cycles of bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRD) significantly improved progression-free survival in adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to new analyses from the multicenter, randomized, phase III IFM 2009 Study.
Median PFS was 50 months in the transplantation group, versus 36 months when patients only received five cycles of VRD for consolidation (adjusted hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.65; 95% confidence interval, 0.53 to 0.80; P less than .001), reported Michel Attal, MD, of Institut Universitaire du Cancer de Toulouse-Oncopole in Toulouse, France, and his associates. “Transplantation was also associated with a higher rate of complete response, a lower rate of minimal residual disease detection, and a longer median time to progression,” they wrote (N Engl J Med. 2017 April 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1611750).
Transplantation did not improve 4-year overall survival (81% with transplantation plus VRD and 82% with VRD only), perhaps because VRD-only patients had the option of salvage transplantation if their disease progressed, the investigators said. In addition, grade 3 or 4 neutropenias were significantly more common with transplantation than otherwise (92% versus 47%), as were grade 3 or 4 gastrointestinal disorders (28% versus 7%) and infections (20% versus 9%). However, the groups did not significantly differ in terms of treatment-related deaths, second primary cancers, thromboembolic events, or peripheral neuropathy.
Before the advent of immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors, several randomized trials showed that the benefits of high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplantation outperformed conventional chemotherapy in multiple myeloma. For IFM 2009, 700 newly diagnosed patients aged up to 65 years received three 21-day cycles of VRD induction: bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 on days 1, 4, 8, and 11; lenalidomide 25 mg on days 1-14; and dexamethasone 20 mg on days 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 11, and 12. Consolidation consisted of either five more VRD cycles with dexamethasone reduced to 10 mg/day, or high-dose (200 mg/m2) melphalan plus transplantation followed by two VRD cycles with the reduced dexamethasone dose. Both arms received 1 year of lenalidomide maintenance (10 mg/day for 3 months, followed by 15/mg day, depending on side effects).
Transplantation was associated with a significantly higher likelihood of complete response (59% versus 48%; P = .03) and undetectable minimal residual disease (79% versus 65%; P less than .001). Undetectable minimal residual disease, in turn, predicted longer PFS (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.30; P = .001). In contrast, age, sex, isotype of the monoclonal component, International Staging System disease stage, and cytogenetic risk profile did not significantly affect PFS among transplant patients.
The PFS benefit of transplantation “must be weighed against the increased risk of toxic effects associated with high-dose chemotherapy plus transplantation, especially since we found that later transplantation might be as effective as early transplantation in securing long- term survival,” the researchers said. “Our results suggest that the use of a combination therapy that incorporates newer proteasome inhibitors, next-generation immunomodulatory drugs, and potent monoclonal antibodies along with transplantation tailored according to minimal residual disease detection could further improve outcomes among adults up to 65 years of age who have multiple myeloma.”
Celgene, Janssen, the French Ministry of Health Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique, and the French National Research Agency funded the study. Dr. Attal had no conflicts. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Celgene, Janssen, and several other pharmaceutical companies. Two coinvestigators disclosed ownership or founder roles in OncoPep, one of whom disclosed patent licensure to OncoPep for a multipeptide vaccine. The other investigators had no conflicts.
Adding high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation to two cycles of bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRD) significantly improved progression-free survival in adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to new analyses from the multicenter, randomized, phase III IFM 2009 Study.
Median PFS was 50 months in the transplantation group, versus 36 months when patients only received five cycles of VRD for consolidation (adjusted hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.65; 95% confidence interval, 0.53 to 0.80; P less than .001), reported Michel Attal, MD, of Institut Universitaire du Cancer de Toulouse-Oncopole in Toulouse, France, and his associates. “Transplantation was also associated with a higher rate of complete response, a lower rate of minimal residual disease detection, and a longer median time to progression,” they wrote (N Engl J Med. 2017 April 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1611750).
Transplantation did not improve 4-year overall survival (81% with transplantation plus VRD and 82% with VRD only), perhaps because VRD-only patients had the option of salvage transplantation if their disease progressed, the investigators said. In addition, grade 3 or 4 neutropenias were significantly more common with transplantation than otherwise (92% versus 47%), as were grade 3 or 4 gastrointestinal disorders (28% versus 7%) and infections (20% versus 9%). However, the groups did not significantly differ in terms of treatment-related deaths, second primary cancers, thromboembolic events, or peripheral neuropathy.
Before the advent of immunomodulatory drugs and proteasome inhibitors, several randomized trials showed that the benefits of high-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell transplantation outperformed conventional chemotherapy in multiple myeloma. For IFM 2009, 700 newly diagnosed patients aged up to 65 years received three 21-day cycles of VRD induction: bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 on days 1, 4, 8, and 11; lenalidomide 25 mg on days 1-14; and dexamethasone 20 mg on days 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 11, and 12. Consolidation consisted of either five more VRD cycles with dexamethasone reduced to 10 mg/day, or high-dose (200 mg/m2) melphalan plus transplantation followed by two VRD cycles with the reduced dexamethasone dose. Both arms received 1 year of lenalidomide maintenance (10 mg/day for 3 months, followed by 15/mg day, depending on side effects).
Transplantation was associated with a significantly higher likelihood of complete response (59% versus 48%; P = .03) and undetectable minimal residual disease (79% versus 65%; P less than .001). Undetectable minimal residual disease, in turn, predicted longer PFS (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.30; P = .001). In contrast, age, sex, isotype of the monoclonal component, International Staging System disease stage, and cytogenetic risk profile did not significantly affect PFS among transplant patients.
The PFS benefit of transplantation “must be weighed against the increased risk of toxic effects associated with high-dose chemotherapy plus transplantation, especially since we found that later transplantation might be as effective as early transplantation in securing long- term survival,” the researchers said. “Our results suggest that the use of a combination therapy that incorporates newer proteasome inhibitors, next-generation immunomodulatory drugs, and potent monoclonal antibodies along with transplantation tailored according to minimal residual disease detection could further improve outcomes among adults up to 65 years of age who have multiple myeloma.”
Celgene, Janssen, the French Ministry of Health Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique, and the French National Research Agency funded the study. Dr. Attal had no conflicts. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Celgene, Janssen, and several other pharmaceutical companies. Two coinvestigators disclosed ownership or founder roles in OncoPep, one of whom disclosed patent licensure to OncoPep for a multipeptide vaccine. The other investigators had no conflicts.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: High-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation plus bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRD) outperformed consolidation with VRD only in adults with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
Major finding: Median progression-free survival was 50 months with transplantation plus VRD and 36 months with VRD only (adjusted hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.65; P less than .001).
Data source: A randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase III trial of 700 patients with multiple myeloma.
Disclosures: Celgene, Janssen, the French Ministry of Health Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique, and the French National Research Agency funded the study. Dr. Attal had no conflicts. Nine coinvestigators disclosed ties to Celgene, Janssen, and several other pharmaceutical companies. Two coinvestigators disclosed ownership or founder roles in OncoPep, one of whom disclosed patent licensure to OncoPep for a multipeptide vaccine. The other investigators had no conflicts.
Cell sheet transplantation improves ischemic cardiomyopathy at 1 year
For patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM), transplanting sheets of autologous myoblasts onto the epicardial surface was safe and led to “marked” improvements in functional and laboratory measures, investigators reported.
However, cell sheet transplantation was much less effective for patients with dilated cardiomyopathy in this phase I trial, wrote Shigeru Miyagawa, MD, PhD, of Osaka (Japan) University, and his associates in the Journal of the American Heart Association. The findings merit additional follow-up in larger clinical studies, the investigators asserted.
Heart failure remains life threatening even with the best approved treatments. Previously, the researchers transplanted scaffold-free sheets of autologous myoblasts derived from skeletal muscle into small and large animals with heart failure and found that this approach healed severely damaged myocardium. Transplantation caused secreted cytokines to induce native regeneration through paracrine effects, Dr. Miyagawa noted in a prior review article (BioMed Research International. 2013. doi: 10.1155/2013/583912).
To evaluate this approach in humans, the researchers transplanted 15 patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and 12 patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Patients were 20-75 years old, had ejection fractions under 35% and New York Heart Association (NYHA) classifications of II or more, and were responding inadequately to standard treatment with a beta-blocker or ACE inhibitor and an angiotensin receptor blocker. The sole intervention was transplantation of the cell sheet over the left ventricular-free wall during left thoracotomy (J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Apr 5. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003918). There were no major procedure-related complications during follow-up, the researchers said. For patients with ICM, NYHA classifications dropped significantly at 6 months, from 2.9 at baseline to 2.1 at 6 months and 1.9 at 1 year. Six-Minute Walk Test scores improved significantly, from 416 m at baseline to 475 m at 6 months to 484 m at 1 year. Transplantation also led to significant drops in serum brain natriuretic peptide levels (baseline average, 308 pg/mL; 6 months, 191 pg/mL; 1 year, 182 pg/mL). Additionally, ICM patients improved significantly on measures of pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, pulmonary vein resistance, and left ventricular wall stress.
In contrast, DCM patients did not significantly improve based on the 6-Minute Walk Test, NYHA classification, or brain natriuretic peptide serum levels. Of 12, 3 progressed to NYHA functional class IV by 1-year follow-up and there were five cardiac deaths. There were no cardiac deaths in the ICM group. “It has been reported that regeneration mechanisms in cell sheet mainly depend on angiogenesis induced by secreted cytokines, so cell-sheet implantation may be more suitable for ICM patients, compared with DCM patients, considering pathophysiological aspects,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by grants from Regenerative Medicine for Clinical Application, Health and Labor Sciences Research, and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. The investigators disclosed laboratory funding from Terumo for cooperative research in cell sheet.
For patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM), transplanting sheets of autologous myoblasts onto the epicardial surface was safe and led to “marked” improvements in functional and laboratory measures, investigators reported.
However, cell sheet transplantation was much less effective for patients with dilated cardiomyopathy in this phase I trial, wrote Shigeru Miyagawa, MD, PhD, of Osaka (Japan) University, and his associates in the Journal of the American Heart Association. The findings merit additional follow-up in larger clinical studies, the investigators asserted.
Heart failure remains life threatening even with the best approved treatments. Previously, the researchers transplanted scaffold-free sheets of autologous myoblasts derived from skeletal muscle into small and large animals with heart failure and found that this approach healed severely damaged myocardium. Transplantation caused secreted cytokines to induce native regeneration through paracrine effects, Dr. Miyagawa noted in a prior review article (BioMed Research International. 2013. doi: 10.1155/2013/583912).
To evaluate this approach in humans, the researchers transplanted 15 patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and 12 patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Patients were 20-75 years old, had ejection fractions under 35% and New York Heart Association (NYHA) classifications of II or more, and were responding inadequately to standard treatment with a beta-blocker or ACE inhibitor and an angiotensin receptor blocker. The sole intervention was transplantation of the cell sheet over the left ventricular-free wall during left thoracotomy (J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Apr 5. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003918). There were no major procedure-related complications during follow-up, the researchers said. For patients with ICM, NYHA classifications dropped significantly at 6 months, from 2.9 at baseline to 2.1 at 6 months and 1.9 at 1 year. Six-Minute Walk Test scores improved significantly, from 416 m at baseline to 475 m at 6 months to 484 m at 1 year. Transplantation also led to significant drops in serum brain natriuretic peptide levels (baseline average, 308 pg/mL; 6 months, 191 pg/mL; 1 year, 182 pg/mL). Additionally, ICM patients improved significantly on measures of pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, pulmonary vein resistance, and left ventricular wall stress.
In contrast, DCM patients did not significantly improve based on the 6-Minute Walk Test, NYHA classification, or brain natriuretic peptide serum levels. Of 12, 3 progressed to NYHA functional class IV by 1-year follow-up and there were five cardiac deaths. There were no cardiac deaths in the ICM group. “It has been reported that regeneration mechanisms in cell sheet mainly depend on angiogenesis induced by secreted cytokines, so cell-sheet implantation may be more suitable for ICM patients, compared with DCM patients, considering pathophysiological aspects,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by grants from Regenerative Medicine for Clinical Application, Health and Labor Sciences Research, and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. The investigators disclosed laboratory funding from Terumo for cooperative research in cell sheet.
For patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM), transplanting sheets of autologous myoblasts onto the epicardial surface was safe and led to “marked” improvements in functional and laboratory measures, investigators reported.
However, cell sheet transplantation was much less effective for patients with dilated cardiomyopathy in this phase I trial, wrote Shigeru Miyagawa, MD, PhD, of Osaka (Japan) University, and his associates in the Journal of the American Heart Association. The findings merit additional follow-up in larger clinical studies, the investigators asserted.
Heart failure remains life threatening even with the best approved treatments. Previously, the researchers transplanted scaffold-free sheets of autologous myoblasts derived from skeletal muscle into small and large animals with heart failure and found that this approach healed severely damaged myocardium. Transplantation caused secreted cytokines to induce native regeneration through paracrine effects, Dr. Miyagawa noted in a prior review article (BioMed Research International. 2013. doi: 10.1155/2013/583912).
To evaluate this approach in humans, the researchers transplanted 15 patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and 12 patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Patients were 20-75 years old, had ejection fractions under 35% and New York Heart Association (NYHA) classifications of II or more, and were responding inadequately to standard treatment with a beta-blocker or ACE inhibitor and an angiotensin receptor blocker. The sole intervention was transplantation of the cell sheet over the left ventricular-free wall during left thoracotomy (J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Apr 5. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003918). There were no major procedure-related complications during follow-up, the researchers said. For patients with ICM, NYHA classifications dropped significantly at 6 months, from 2.9 at baseline to 2.1 at 6 months and 1.9 at 1 year. Six-Minute Walk Test scores improved significantly, from 416 m at baseline to 475 m at 6 months to 484 m at 1 year. Transplantation also led to significant drops in serum brain natriuretic peptide levels (baseline average, 308 pg/mL; 6 months, 191 pg/mL; 1 year, 182 pg/mL). Additionally, ICM patients improved significantly on measures of pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, pulmonary vein resistance, and left ventricular wall stress.
In contrast, DCM patients did not significantly improve based on the 6-Minute Walk Test, NYHA classification, or brain natriuretic peptide serum levels. Of 12, 3 progressed to NYHA functional class IV by 1-year follow-up and there were five cardiac deaths. There were no cardiac deaths in the ICM group. “It has been reported that regeneration mechanisms in cell sheet mainly depend on angiogenesis induced by secreted cytokines, so cell-sheet implantation may be more suitable for ICM patients, compared with DCM patients, considering pathophysiological aspects,” the researchers wrote.
The study was funded by grants from Regenerative Medicine for Clinical Application, Health and Labor Sciences Research, and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. The investigators disclosed laboratory funding from Terumo for cooperative research in cell sheet.
Key clinical point: Transplanting a sheet of autologous myoblasts onto the epicardial surface was safe and was associated with functional and symptomatic improvements in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Major finding: Patients improved significantly on the 6-Minute Walk Test, New York Heart Classification, and on measures of brain natriuretic peptide, pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, pulmonary vein resistance, and left ventricular wall stress. These effects did not extend to patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.
Data source: A phase I trial of 27 patients with ischemic or dilated cardiomyopathy.
Disclosures: The study was funded by grants from Regenerative Medicine for Clinical Application, Health and Labor Sciences Research, and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development. The investigators disclosed laboratory funding from Terumo for cooperative research in cell sheet.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy induces mutational, molecular shifts in ovarian cancers
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Treatment of high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas with platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy led to significant changes in the expression of genes encoding “canonical” cell cycle and DNA damage pathways, said Rebecca C. Arend, MD.
Analyses of cell-free (plasma) DNA also revealed mutations that matched those in tumor specimens obtained before and after platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Dr. Arend reported at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. “Understanding the effect of chemotherapy on gene expression profiles may help guide therapy, and plasma cfDNA could provide a noninvasive approach for monitoring tumor mutations,” said Dr. Arend of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma is genetically heterogeneous, and chemotherapy further alters gene expression profiles and causes molecular derangement, Dr. Arend noted. “Neoadjuvant chemotherapy provides a unique opportunity to evaluate biospecimens before and afterward,” she added.
Both gene expression and mutational profiles have been used to characterize HGSC, but researchers lack solid methods to evaluate tumor heterogeneity and clonal evolution. To begin filling this gap, Dr. Arend and her associates analyzed plasma and tumor specimens from 19 patients with stage 3 or 4 high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma before and after they underwent three to six cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Biopsies yielded the baseline tumor specimens, and follow-up specimens were obtained during interval debulking.
The investigators used the NanoString PanCancer 770 gene pathway panel, the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis tool, and nSolver Analysis software to assess changes in gene expression. To quantify mutations, they performed longitudinal next-generation sequencing of 50 genes in tumor and plasma specimens with a 50-gene Ion Torrent panel.
After neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the most up-regulated genes included NR4A1 and NR4A3, which regulate cellular proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, and SFRP2, which promotes resistance to chemotherapy by modulating Wnt signaling, Dr. Arend said. The most down-regulated genes included E2F1, which helps mediate the cell cycle and the activity of tumor suppressor genes, and BRCA2, the tumor suppressor gene that encodes a DNA repair protein.
Pathway analysis confirmed that the cell cycle pathway was most up-regulated after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and that the DNA damage repair pathway was the most downregulated, Dr. Arend reported. Within the DNA damage repair pathway, no gene was significantly up-regulated, while RAD51C, BRCA1, BRCA2, and the FA core complex genes were down-regulated.
Next-generation sequencing of baseline plasma cfDNA identified 57 mutations, of which 6 persisted after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In contrast, of 38 mutations in tumor at baseline, 33 persisted after chemotherapy.
Only 15 of the 38 mutations in tumor also appeared in cfDNA before treatment. At the time of interval debulking, tumor specimens yielded 36 mutations, of which 11 were detected in cfDNA.
At baseline and after treatment, all patients had TP53 mutations either tumor alone, or in both tumor and plasma. Among four patients whose cancer recurred, three had mutations in cfDNA that were previously detected in tumor. Implicated genes included PIK3CA, TP53, KIT, and KDR.
Overall, the study suggests that gene expression profiling of ovarian HGSC tumor tissue taken at interval debulking could someday help guide treatment decisions after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Dr. Arend said. “To be able to use cfDNA as liquid biopsy, more studies like this one, which match tumor and cfDNA from multiple time points, are needed,” she added.
Dr. Arend cited no funding sources and reported having no conflicts of interest.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Treatment of high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas with platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy led to significant changes in the expression of genes encoding “canonical” cell cycle and DNA damage pathways, said Rebecca C. Arend, MD.
Analyses of cell-free (plasma) DNA also revealed mutations that matched those in tumor specimens obtained before and after platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Dr. Arend reported at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. “Understanding the effect of chemotherapy on gene expression profiles may help guide therapy, and plasma cfDNA could provide a noninvasive approach for monitoring tumor mutations,” said Dr. Arend of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma is genetically heterogeneous, and chemotherapy further alters gene expression profiles and causes molecular derangement, Dr. Arend noted. “Neoadjuvant chemotherapy provides a unique opportunity to evaluate biospecimens before and afterward,” she added.
Both gene expression and mutational profiles have been used to characterize HGSC, but researchers lack solid methods to evaluate tumor heterogeneity and clonal evolution. To begin filling this gap, Dr. Arend and her associates analyzed plasma and tumor specimens from 19 patients with stage 3 or 4 high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma before and after they underwent three to six cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Biopsies yielded the baseline tumor specimens, and follow-up specimens were obtained during interval debulking.
The investigators used the NanoString PanCancer 770 gene pathway panel, the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis tool, and nSolver Analysis software to assess changes in gene expression. To quantify mutations, they performed longitudinal next-generation sequencing of 50 genes in tumor and plasma specimens with a 50-gene Ion Torrent panel.
After neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the most up-regulated genes included NR4A1 and NR4A3, which regulate cellular proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, and SFRP2, which promotes resistance to chemotherapy by modulating Wnt signaling, Dr. Arend said. The most down-regulated genes included E2F1, which helps mediate the cell cycle and the activity of tumor suppressor genes, and BRCA2, the tumor suppressor gene that encodes a DNA repair protein.
Pathway analysis confirmed that the cell cycle pathway was most up-regulated after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and that the DNA damage repair pathway was the most downregulated, Dr. Arend reported. Within the DNA damage repair pathway, no gene was significantly up-regulated, while RAD51C, BRCA1, BRCA2, and the FA core complex genes were down-regulated.
Next-generation sequencing of baseline plasma cfDNA identified 57 mutations, of which 6 persisted after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In contrast, of 38 mutations in tumor at baseline, 33 persisted after chemotherapy.
Only 15 of the 38 mutations in tumor also appeared in cfDNA before treatment. At the time of interval debulking, tumor specimens yielded 36 mutations, of which 11 were detected in cfDNA.
At baseline and after treatment, all patients had TP53 mutations either tumor alone, or in both tumor and plasma. Among four patients whose cancer recurred, three had mutations in cfDNA that were previously detected in tumor. Implicated genes included PIK3CA, TP53, KIT, and KDR.
Overall, the study suggests that gene expression profiling of ovarian HGSC tumor tissue taken at interval debulking could someday help guide treatment decisions after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Dr. Arend said. “To be able to use cfDNA as liquid biopsy, more studies like this one, which match tumor and cfDNA from multiple time points, are needed,” she added.
Dr. Arend cited no funding sources and reported having no conflicts of interest.
NATIONAL HARBOR, MD. – Treatment of high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas with platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy led to significant changes in the expression of genes encoding “canonical” cell cycle and DNA damage pathways, said Rebecca C. Arend, MD.
Analyses of cell-free (plasma) DNA also revealed mutations that matched those in tumor specimens obtained before and after platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Dr. Arend reported at the annual meeting of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology. “Understanding the effect of chemotherapy on gene expression profiles may help guide therapy, and plasma cfDNA could provide a noninvasive approach for monitoring tumor mutations,” said Dr. Arend of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma is genetically heterogeneous, and chemotherapy further alters gene expression profiles and causes molecular derangement, Dr. Arend noted. “Neoadjuvant chemotherapy provides a unique opportunity to evaluate biospecimens before and afterward,” she added.
Both gene expression and mutational profiles have been used to characterize HGSC, but researchers lack solid methods to evaluate tumor heterogeneity and clonal evolution. To begin filling this gap, Dr. Arend and her associates analyzed plasma and tumor specimens from 19 patients with stage 3 or 4 high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma before and after they underwent three to six cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Biopsies yielded the baseline tumor specimens, and follow-up specimens were obtained during interval debulking.
The investigators used the NanoString PanCancer 770 gene pathway panel, the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis tool, and nSolver Analysis software to assess changes in gene expression. To quantify mutations, they performed longitudinal next-generation sequencing of 50 genes in tumor and plasma specimens with a 50-gene Ion Torrent panel.
After neoadjuvant chemotherapy, the most up-regulated genes included NR4A1 and NR4A3, which regulate cellular proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, and SFRP2, which promotes resistance to chemotherapy by modulating Wnt signaling, Dr. Arend said. The most down-regulated genes included E2F1, which helps mediate the cell cycle and the activity of tumor suppressor genes, and BRCA2, the tumor suppressor gene that encodes a DNA repair protein.
Pathway analysis confirmed that the cell cycle pathway was most up-regulated after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and that the DNA damage repair pathway was the most downregulated, Dr. Arend reported. Within the DNA damage repair pathway, no gene was significantly up-regulated, while RAD51C, BRCA1, BRCA2, and the FA core complex genes were down-regulated.
Next-generation sequencing of baseline plasma cfDNA identified 57 mutations, of which 6 persisted after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. In contrast, of 38 mutations in tumor at baseline, 33 persisted after chemotherapy.
Only 15 of the 38 mutations in tumor also appeared in cfDNA before treatment. At the time of interval debulking, tumor specimens yielded 36 mutations, of which 11 were detected in cfDNA.
At baseline and after treatment, all patients had TP53 mutations either tumor alone, or in both tumor and plasma. Among four patients whose cancer recurred, three had mutations in cfDNA that were previously detected in tumor. Implicated genes included PIK3CA, TP53, KIT, and KDR.
Overall, the study suggests that gene expression profiling of ovarian HGSC tumor tissue taken at interval debulking could someday help guide treatment decisions after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Dr. Arend said. “To be able to use cfDNA as liquid biopsy, more studies like this one, which match tumor and cfDNA from multiple time points, are needed,” she added.
Dr. Arend cited no funding sources and reported having no conflicts of interest.
Key clinical point. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy was associated with changes in gene expression and associated pathways in high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas. Some mutations in tumors were also present in plasma cell-free DNA.
Major finding: Pathway analysis confirmed that the cell cycle and apoptosis pathway was the most up-regulated after neoadjuvant chemotherapy, while the DNA damage repair pathway was the most down-regulated. Among 38 baseline mutations in tumor specimens, 15 of 38 appeared in plasma cell-free DNA. At interval debulking, tumor specimens yielded 36 mutations, of which 11 were detected in cfDNA.
Data source: Gene expression profiling, pathway analysis, and next-generation sequencing of 19 patients with high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas.
Disclosures: Dr. Arend cited no funding sources and reported having no conflicts of interest.