User login
A primer on cannabis for cosmeceuticals: The endocannabinoid system
In the United States, 31 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam have legalized medical marijuana, which is also permitted for recreational use in 9 states, as well as in the District of Columbia. However, marijuana, derived from Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, is regulated as a schedule I drug in the United States at the federal level. (Some believe that the federal status may change in the coming year as a result of the Democratic Party’s takeover in the House of Representatives.1)
Cannabis species contain hundreds of various substances, of which the cannabinoids are the most studied. More than 113 biologically active chemical compounds are found within the class of cannabinoids and their derivatives,2 which have been used for centuries in natural medicine.3 The legal status of marijuana has long hampered scientific research of cannabinoids. Nevertheless, the number of studies focusing on the therapeutic potential of these compounds has steadily risen as the legal landscape of marijuana has evolved.
Findings over the last 20 years have shown that cannabinoids present in C. sativa exhibit anti-inflammatory activity and suppress the proliferation of multiple tumorigenic cell lines, some of which are moderated through cannabinoid (CB) receptors.4 In addition to anti-inflammatory properties, .3 Recent research has demonstrated that CB receptors are present in human skin.4
The endocannabinoid system has emerged as an intriguing area of research, as we’ve come to learn about its convoluted role in human anatomy and health. It features a pervasive network of endogenous ligands, enzymes, and receptors, which exogenous substances (including phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids) can activate.5 Data from recent studies indicate that the endocannabinoid system plays a significant role in cutaneous homeostasis, as it regulates proliferation, differentiation, and inflammatory mediator release.5 Further, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pruritus, and wound healing have been identified in recent research as cutaneous concerns in which the use of cannabinoids may be of benefit.6,7 We must also consider reports that cannabinoids can slow human hair growth and that some constituents may spur the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines.8,9This column will briefly address potential confusion over the psychoactive aspects of cannabis, which are related to particular constituents of cannabis and specific CB receptors, and focus on the endocannabinoid system.
Psychoactive or not?
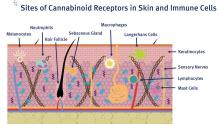
C. sativa confers biological activity through its influence on the G-protein-coupled receptor types CB1 and CB2,10 which pervade human skin epithelium.11 CB1 receptors are found in greatest supply in the central nervous system, especially the basal ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex, where their activation yields psychoactivity.2,5,12,13 Stimulation of CB1 receptors in the skin – where they are present in differentiated keratinocytes, hair follicle cells, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons14 – diminishes pain and pruritus, controls keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, inhibits hair follicle growth, and regulates the release of damage-induced keratins and inflammatory mediators to maintain cutaneous homeostasis.11,14,15
CB2 receptors are expressed in the immune system, particularly monocytes, macrophages, as well as B and T cells, and in peripheral tissues including the spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, bone, and, notably, the skin.2,16 Stimulation of CB2 receptors in the skin – where they are found in keratinocytes, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons – fosters sebum production, regulates pain sensation, hinders keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, and suppresses cutaneous inflammatory responses.14,15
The best known, or most notorious, component of exogenous cannabinoids is delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta9-THC or simply THC), which is a natural psychoactive constituent in marijuana.3 In fact, of the five primary cannabinoids derived from marijuana, including cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and THC, only THC imparts psychoactive effects.17
CBD is thought to exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities.18 THC has been found to have the capacity to induce cancer cell apoptosis and block angiogenesis,19 and is thought to have immunomodulatory potential, partly acting through the G-protein-coupled CB1 and CB2 receptors but also yielding effects not related to these receptors.20In a 2014 survey of medical cannabis users, a statistically significant preference for C. indica (which contains higher CBD and lower THC levels) was observed for pain management, sedation, and sleep, while C. sativa was associated with euphoria and improving energy.21
The endocannabinoid system and skin health
The endogenous cannabinoid or endocannabinoid system includes cannabinoid receptors, associated endogenous ligands (such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide [anandamide or AEA], 2-arachidonoyl glycerol [2-AG], and N-palmitoylethanolamide [PEA], a fatty acid amide that enhances AEA activity),2 and enzymes involved in endocannabinoid production and decay.11,15,22,23 Research in recent years appears to support the notion that the endocannabinoid system plays an important role in skin health, as its dysregulation has been linked to atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, and skin cancer. Data indicate that exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids influence the endocannabinoid system through cannabinoid receptors, transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), and peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). Río et al. suggest that the dynamism of the endocannabinoid system buttresses the targeting of multiple endpoints for therapeutic success with cannabinoids rather than the one-disease-one-target approach.24 Endogenous cannabinoids, such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, are now thought to be significant mediators in the skin.3 Further, endocannabinoids have been shown to deliver analgesia to the skin, at the spinal and supraspinal levels.25
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Tubaro et al. used the Croton oil mouse ear dermatitis assay to study the in vivo topical anti-inflammatory effects of seven phytocannabinoids and their related cannabivarins (nonpsychoactive cannabinoids). They found that anti-inflammatory activity was derived from the involvement of the cannabinoid receptors as well as the inflammatory endpoints that the phytocannabinoids targeted.26
In 2013, Gaffal et al. explored the anti-inflammatory activity of topical THC in dinitrofluorobenzene-mediated allergic contact dermatitis independent of CB1/2 receptors by using wild-type and CB1/2 receptor-deficient mice. The researchers found that topically applied THC reduced contact allergic ear edema and myeloid immune cell infiltration in both groups of mice. They concluded that such a decline in inflammation resulted from mitigating the keratinocyte-derived proinflammatory mediators that direct myeloid immune cell infiltration independent of CB1/2 receptors, and positions cannabinoids well for future use in treating inflammatory cutaneous conditions.20
Literature reviews
In a 2018 literature review on the uses of cannabinoids for cutaneous disorders, Eagleston et al. determined that preclinical data on cannabinoids reveal the potential to treat acne, allergic contact dermatitis, asteatotic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, Kaposi sarcoma, pruritus, psoriasis, skin cancer, and the skin symptoms of systemic sclerosis. They caution, though, that more preclinical work is necessary along with randomized, controlled trials with sufficiently large sample sizes to establish the safety and efficacy of cannabinoids to treat skin conditions.27
A literature review by Marks and Friedman published later that year on the therapeutic potential of phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids in managing skin disorders revealed the same findings regarding the cutaneous conditions associated with these compounds. The authors noted, though, that while the preponderance of articles highlight the efficacy of cannabinoids in treating inflammatory and neoplastic cutaneous conditions, some reports indicate proinflammatory and proneoplastic activities of cannabinoids. Like Eagleston et al., they call for additional studies.28
Conclusion
As in many botanical agents that I cover in this column, cannabis is associated with numerous medical benefits. I am encouraged to see expanding legalization of medical marijuana and increased research into its reputedly broad potential to improve human health. Anecdotally, I have heard stunning reports from patients about amelioration of joint and back pain as well as relief from other inflammatory symptoms. Discovery and elucidation of the endogenous cannabinoid system is a recent development. Research on its functions and roles in cutaneous health has followed suit and is steadily increasing. Particular skin conditions for which cannabis and cannabinoids may be indicated will be the focus of the next column.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems LLC. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Higdon J. Why 2019 could be marijuana’s biggest year yet. Politico Magazine. Jan 21, 2019.
2. Singh D et al. Clin Dermatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):399-419.
3. Kupczyk P et al. Exp Dermatol. 2009 Aug;18(8):669-79.
4. Wilkinson JD et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Feb;45(2):87-92.
5. Milando R et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 April;20(2):167-80.
6. Robinson E et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Dec 1;17(12):1273-8.
7. Mounessa JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jul;77(1):188-90.
8. Liszewski W et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77(3):e87-e88.
9. Telek A et al. FASEB J. 2007 Nov;21(13):3534-41.
10. Wollenberg A et al. Br J Dermatol. 2014 Jul;170 Suppl 1:7-11.
11. Ramot Y et al. PeerJ. 2013 Feb 19;1:e40.
12. Schlicker E et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):565-72.
13. Christie MJ et al. Nature. 2001 Mar 29;410(6828):527-30.
14. Ibid.
15. Bíró T et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(8):411-20.
16. Pacher P et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):389-462.
17. Shalaby M et al. Pract Dermatol. 2018 Jan;68-70.
18. Chelliah MP et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35(4):e224-e227.
19. Glodde N et al. Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;138:35-40.
20. Gaffal E et al. Allergy. 2013 Aug;68(8):994-1000.
21. Pearce DD et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2014 Oct;20(10):787:91.
22. Leonti M et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15;79(12):1815-26.
23. Trusler AR et al. Dermatitis. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):22-32.
24. Río CD et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;157:122-133.
25. Chuquilin M et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Feb;74(2):197-212.
26. Tubaro A et al. Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):816-9.
27. Eagleston LRM et al. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jun 15;24(6).
28. Marks DH et al. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018 Nov;23(6):1-5.
In the United States, 31 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam have legalized medical marijuana, which is also permitted for recreational use in 9 states, as well as in the District of Columbia. However, marijuana, derived from Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, is regulated as a schedule I drug in the United States at the federal level. (Some believe that the federal status may change in the coming year as a result of the Democratic Party’s takeover in the House of Representatives.1)
Cannabis species contain hundreds of various substances, of which the cannabinoids are the most studied. More than 113 biologically active chemical compounds are found within the class of cannabinoids and their derivatives,2 which have been used for centuries in natural medicine.3 The legal status of marijuana has long hampered scientific research of cannabinoids. Nevertheless, the number of studies focusing on the therapeutic potential of these compounds has steadily risen as the legal landscape of marijuana has evolved.
Findings over the last 20 years have shown that cannabinoids present in C. sativa exhibit anti-inflammatory activity and suppress the proliferation of multiple tumorigenic cell lines, some of which are moderated through cannabinoid (CB) receptors.4 In addition to anti-inflammatory properties, .3 Recent research has demonstrated that CB receptors are present in human skin.4
The endocannabinoid system has emerged as an intriguing area of research, as we’ve come to learn about its convoluted role in human anatomy and health. It features a pervasive network of endogenous ligands, enzymes, and receptors, which exogenous substances (including phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids) can activate.5 Data from recent studies indicate that the endocannabinoid system plays a significant role in cutaneous homeostasis, as it regulates proliferation, differentiation, and inflammatory mediator release.5 Further, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pruritus, and wound healing have been identified in recent research as cutaneous concerns in which the use of cannabinoids may be of benefit.6,7 We must also consider reports that cannabinoids can slow human hair growth and that some constituents may spur the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines.8,9This column will briefly address potential confusion over the psychoactive aspects of cannabis, which are related to particular constituents of cannabis and specific CB receptors, and focus on the endocannabinoid system.
Psychoactive or not?
C. sativa confers biological activity through its influence on the G-protein-coupled receptor types CB1 and CB2,10 which pervade human skin epithelium.11 CB1 receptors are found in greatest supply in the central nervous system, especially the basal ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex, where their activation yields psychoactivity.2,5,12,13 Stimulation of CB1 receptors in the skin – where they are present in differentiated keratinocytes, hair follicle cells, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons14 – diminishes pain and pruritus, controls keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, inhibits hair follicle growth, and regulates the release of damage-induced keratins and inflammatory mediators to maintain cutaneous homeostasis.11,14,15
CB2 receptors are expressed in the immune system, particularly monocytes, macrophages, as well as B and T cells, and in peripheral tissues including the spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, bone, and, notably, the skin.2,16 Stimulation of CB2 receptors in the skin – where they are found in keratinocytes, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons – fosters sebum production, regulates pain sensation, hinders keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, and suppresses cutaneous inflammatory responses.14,15
The best known, or most notorious, component of exogenous cannabinoids is delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta9-THC or simply THC), which is a natural psychoactive constituent in marijuana.3 In fact, of the five primary cannabinoids derived from marijuana, including cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and THC, only THC imparts psychoactive effects.17
CBD is thought to exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities.18 THC has been found to have the capacity to induce cancer cell apoptosis and block angiogenesis,19 and is thought to have immunomodulatory potential, partly acting through the G-protein-coupled CB1 and CB2 receptors but also yielding effects not related to these receptors.20In a 2014 survey of medical cannabis users, a statistically significant preference for C. indica (which contains higher CBD and lower THC levels) was observed for pain management, sedation, and sleep, while C. sativa was associated with euphoria and improving energy.21
The endocannabinoid system and skin health
The endogenous cannabinoid or endocannabinoid system includes cannabinoid receptors, associated endogenous ligands (such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide [anandamide or AEA], 2-arachidonoyl glycerol [2-AG], and N-palmitoylethanolamide [PEA], a fatty acid amide that enhances AEA activity),2 and enzymes involved in endocannabinoid production and decay.11,15,22,23 Research in recent years appears to support the notion that the endocannabinoid system plays an important role in skin health, as its dysregulation has been linked to atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, and skin cancer. Data indicate that exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids influence the endocannabinoid system through cannabinoid receptors, transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), and peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). Río et al. suggest that the dynamism of the endocannabinoid system buttresses the targeting of multiple endpoints for therapeutic success with cannabinoids rather than the one-disease-one-target approach.24 Endogenous cannabinoids, such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, are now thought to be significant mediators in the skin.3 Further, endocannabinoids have been shown to deliver analgesia to the skin, at the spinal and supraspinal levels.25
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Tubaro et al. used the Croton oil mouse ear dermatitis assay to study the in vivo topical anti-inflammatory effects of seven phytocannabinoids and their related cannabivarins (nonpsychoactive cannabinoids). They found that anti-inflammatory activity was derived from the involvement of the cannabinoid receptors as well as the inflammatory endpoints that the phytocannabinoids targeted.26
In 2013, Gaffal et al. explored the anti-inflammatory activity of topical THC in dinitrofluorobenzene-mediated allergic contact dermatitis independent of CB1/2 receptors by using wild-type and CB1/2 receptor-deficient mice. The researchers found that topically applied THC reduced contact allergic ear edema and myeloid immune cell infiltration in both groups of mice. They concluded that such a decline in inflammation resulted from mitigating the keratinocyte-derived proinflammatory mediators that direct myeloid immune cell infiltration independent of CB1/2 receptors, and positions cannabinoids well for future use in treating inflammatory cutaneous conditions.20
Literature reviews
In a 2018 literature review on the uses of cannabinoids for cutaneous disorders, Eagleston et al. determined that preclinical data on cannabinoids reveal the potential to treat acne, allergic contact dermatitis, asteatotic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, Kaposi sarcoma, pruritus, psoriasis, skin cancer, and the skin symptoms of systemic sclerosis. They caution, though, that more preclinical work is necessary along with randomized, controlled trials with sufficiently large sample sizes to establish the safety and efficacy of cannabinoids to treat skin conditions.27
A literature review by Marks and Friedman published later that year on the therapeutic potential of phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids in managing skin disorders revealed the same findings regarding the cutaneous conditions associated with these compounds. The authors noted, though, that while the preponderance of articles highlight the efficacy of cannabinoids in treating inflammatory and neoplastic cutaneous conditions, some reports indicate proinflammatory and proneoplastic activities of cannabinoids. Like Eagleston et al., they call for additional studies.28
Conclusion
As in many botanical agents that I cover in this column, cannabis is associated with numerous medical benefits. I am encouraged to see expanding legalization of medical marijuana and increased research into its reputedly broad potential to improve human health. Anecdotally, I have heard stunning reports from patients about amelioration of joint and back pain as well as relief from other inflammatory symptoms. Discovery and elucidation of the endogenous cannabinoid system is a recent development. Research on its functions and roles in cutaneous health has followed suit and is steadily increasing. Particular skin conditions for which cannabis and cannabinoids may be indicated will be the focus of the next column.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems LLC. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Higdon J. Why 2019 could be marijuana’s biggest year yet. Politico Magazine. Jan 21, 2019.
2. Singh D et al. Clin Dermatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):399-419.
3. Kupczyk P et al. Exp Dermatol. 2009 Aug;18(8):669-79.
4. Wilkinson JD et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Feb;45(2):87-92.
5. Milando R et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 April;20(2):167-80.
6. Robinson E et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Dec 1;17(12):1273-8.
7. Mounessa JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jul;77(1):188-90.
8. Liszewski W et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77(3):e87-e88.
9. Telek A et al. FASEB J. 2007 Nov;21(13):3534-41.
10. Wollenberg A et al. Br J Dermatol. 2014 Jul;170 Suppl 1:7-11.
11. Ramot Y et al. PeerJ. 2013 Feb 19;1:e40.
12. Schlicker E et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):565-72.
13. Christie MJ et al. Nature. 2001 Mar 29;410(6828):527-30.
14. Ibid.
15. Bíró T et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(8):411-20.
16. Pacher P et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):389-462.
17. Shalaby M et al. Pract Dermatol. 2018 Jan;68-70.
18. Chelliah MP et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35(4):e224-e227.
19. Glodde N et al. Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;138:35-40.
20. Gaffal E et al. Allergy. 2013 Aug;68(8):994-1000.
21. Pearce DD et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2014 Oct;20(10):787:91.
22. Leonti M et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15;79(12):1815-26.
23. Trusler AR et al. Dermatitis. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):22-32.
24. Río CD et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;157:122-133.
25. Chuquilin M et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Feb;74(2):197-212.
26. Tubaro A et al. Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):816-9.
27. Eagleston LRM et al. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jun 15;24(6).
28. Marks DH et al. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018 Nov;23(6):1-5.
In the United States, 31 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam have legalized medical marijuana, which is also permitted for recreational use in 9 states, as well as in the District of Columbia. However, marijuana, derived from Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, is regulated as a schedule I drug in the United States at the federal level. (Some believe that the federal status may change in the coming year as a result of the Democratic Party’s takeover in the House of Representatives.1)
Cannabis species contain hundreds of various substances, of which the cannabinoids are the most studied. More than 113 biologically active chemical compounds are found within the class of cannabinoids and their derivatives,2 which have been used for centuries in natural medicine.3 The legal status of marijuana has long hampered scientific research of cannabinoids. Nevertheless, the number of studies focusing on the therapeutic potential of these compounds has steadily risen as the legal landscape of marijuana has evolved.
Findings over the last 20 years have shown that cannabinoids present in C. sativa exhibit anti-inflammatory activity and suppress the proliferation of multiple tumorigenic cell lines, some of which are moderated through cannabinoid (CB) receptors.4 In addition to anti-inflammatory properties, .3 Recent research has demonstrated that CB receptors are present in human skin.4
The endocannabinoid system has emerged as an intriguing area of research, as we’ve come to learn about its convoluted role in human anatomy and health. It features a pervasive network of endogenous ligands, enzymes, and receptors, which exogenous substances (including phytocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoids) can activate.5 Data from recent studies indicate that the endocannabinoid system plays a significant role in cutaneous homeostasis, as it regulates proliferation, differentiation, and inflammatory mediator release.5 Further, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pruritus, and wound healing have been identified in recent research as cutaneous concerns in which the use of cannabinoids may be of benefit.6,7 We must also consider reports that cannabinoids can slow human hair growth and that some constituents may spur the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines.8,9This column will briefly address potential confusion over the psychoactive aspects of cannabis, which are related to particular constituents of cannabis and specific CB receptors, and focus on the endocannabinoid system.
Psychoactive or not?
C. sativa confers biological activity through its influence on the G-protein-coupled receptor types CB1 and CB2,10 which pervade human skin epithelium.11 CB1 receptors are found in greatest supply in the central nervous system, especially the basal ganglia, cerebellum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex, where their activation yields psychoactivity.2,5,12,13 Stimulation of CB1 receptors in the skin – where they are present in differentiated keratinocytes, hair follicle cells, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons14 – diminishes pain and pruritus, controls keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, inhibits hair follicle growth, and regulates the release of damage-induced keratins and inflammatory mediators to maintain cutaneous homeostasis.11,14,15
CB2 receptors are expressed in the immune system, particularly monocytes, macrophages, as well as B and T cells, and in peripheral tissues including the spleen, tonsils, thymus gland, bone, and, notably, the skin.2,16 Stimulation of CB2 receptors in the skin – where they are found in keratinocytes, immune cells, sebaceous glands, and sensory neurons – fosters sebum production, regulates pain sensation, hinders keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation, and suppresses cutaneous inflammatory responses.14,15
The best known, or most notorious, component of exogenous cannabinoids is delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta9-THC or simply THC), which is a natural psychoactive constituent in marijuana.3 In fact, of the five primary cannabinoids derived from marijuana, including cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and THC, only THC imparts psychoactive effects.17
CBD is thought to exhibit anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities.18 THC has been found to have the capacity to induce cancer cell apoptosis and block angiogenesis,19 and is thought to have immunomodulatory potential, partly acting through the G-protein-coupled CB1 and CB2 receptors but also yielding effects not related to these receptors.20In a 2014 survey of medical cannabis users, a statistically significant preference for C. indica (which contains higher CBD and lower THC levels) was observed for pain management, sedation, and sleep, while C. sativa was associated with euphoria and improving energy.21
The endocannabinoid system and skin health
The endogenous cannabinoid or endocannabinoid system includes cannabinoid receptors, associated endogenous ligands (such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide [anandamide or AEA], 2-arachidonoyl glycerol [2-AG], and N-palmitoylethanolamide [PEA], a fatty acid amide that enhances AEA activity),2 and enzymes involved in endocannabinoid production and decay.11,15,22,23 Research in recent years appears to support the notion that the endocannabinoid system plays an important role in skin health, as its dysregulation has been linked to atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, and skin cancer. Data indicate that exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids influence the endocannabinoid system through cannabinoid receptors, transient receptor potential channels (TRPs), and peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). Río et al. suggest that the dynamism of the endocannabinoid system buttresses the targeting of multiple endpoints for therapeutic success with cannabinoids rather than the one-disease-one-target approach.24 Endogenous cannabinoids, such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, are now thought to be significant mediators in the skin.3 Further, endocannabinoids have been shown to deliver analgesia to the skin, at the spinal and supraspinal levels.25
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Tubaro et al. used the Croton oil mouse ear dermatitis assay to study the in vivo topical anti-inflammatory effects of seven phytocannabinoids and their related cannabivarins (nonpsychoactive cannabinoids). They found that anti-inflammatory activity was derived from the involvement of the cannabinoid receptors as well as the inflammatory endpoints that the phytocannabinoids targeted.26
In 2013, Gaffal et al. explored the anti-inflammatory activity of topical THC in dinitrofluorobenzene-mediated allergic contact dermatitis independent of CB1/2 receptors by using wild-type and CB1/2 receptor-deficient mice. The researchers found that topically applied THC reduced contact allergic ear edema and myeloid immune cell infiltration in both groups of mice. They concluded that such a decline in inflammation resulted from mitigating the keratinocyte-derived proinflammatory mediators that direct myeloid immune cell infiltration independent of CB1/2 receptors, and positions cannabinoids well for future use in treating inflammatory cutaneous conditions.20
Literature reviews
In a 2018 literature review on the uses of cannabinoids for cutaneous disorders, Eagleston et al. determined that preclinical data on cannabinoids reveal the potential to treat acne, allergic contact dermatitis, asteatotic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, Kaposi sarcoma, pruritus, psoriasis, skin cancer, and the skin symptoms of systemic sclerosis. They caution, though, that more preclinical work is necessary along with randomized, controlled trials with sufficiently large sample sizes to establish the safety and efficacy of cannabinoids to treat skin conditions.27
A literature review by Marks and Friedman published later that year on the therapeutic potential of phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids in managing skin disorders revealed the same findings regarding the cutaneous conditions associated with these compounds. The authors noted, though, that while the preponderance of articles highlight the efficacy of cannabinoids in treating inflammatory and neoplastic cutaneous conditions, some reports indicate proinflammatory and proneoplastic activities of cannabinoids. Like Eagleston et al., they call for additional studies.28
Conclusion
As in many botanical agents that I cover in this column, cannabis is associated with numerous medical benefits. I am encouraged to see expanding legalization of medical marijuana and increased research into its reputedly broad potential to improve human health. Anecdotally, I have heard stunning reports from patients about amelioration of joint and back pain as well as relief from other inflammatory symptoms. Discovery and elucidation of the endogenous cannabinoid system is a recent development. Research on its functions and roles in cutaneous health has followed suit and is steadily increasing. Particular skin conditions for which cannabis and cannabinoids may be indicated will be the focus of the next column.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann wrote two textbooks: “Cosmetic Dermatology: Principles and Practice” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002), and “Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients” (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2014), and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers, “The Skin Type Solution” (New York: Bantam Dell, 2006). Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Evolus, Galderma, and Revance. She is the founder and CEO of Skin Type Solutions Franchise Systems LLC. Write to her at [email protected]
References
1. Higdon J. Why 2019 could be marijuana’s biggest year yet. Politico Magazine. Jan 21, 2019.
2. Singh D et al. Clin Dermatol. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):399-419.
3. Kupczyk P et al. Exp Dermatol. 2009 Aug;18(8):669-79.
4. Wilkinson JD et al. J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Feb;45(2):87-92.
5. Milando R et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019 April;20(2):167-80.
6. Robinson E et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 Dec 1;17(12):1273-8.
7. Mounessa JS et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Jul;77(1):188-90.
8. Liszewski W et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Sep;77(3):e87-e88.
9. Telek A et al. FASEB J. 2007 Nov;21(13):3534-41.
10. Wollenberg A et al. Br J Dermatol. 2014 Jul;170 Suppl 1:7-11.
11. Ramot Y et al. PeerJ. 2013 Feb 19;1:e40.
12. Schlicker E et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001 Nov;22(11):565-72.
13. Christie MJ et al. Nature. 2001 Mar 29;410(6828):527-30.
14. Ibid.
15. Bíró T et al. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(8):411-20.
16. Pacher P et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2006 Sep;58(3):389-462.
17. Shalaby M et al. Pract Dermatol. 2018 Jan;68-70.
18. Chelliah MP et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35(4):e224-e227.
19. Glodde N et al. Life Sci. 2015 Oct 1;138:35-40.
20. Gaffal E et al. Allergy. 2013 Aug;68(8):994-1000.
21. Pearce DD et al. J Altern Complement Med. 2014 Oct;20(10):787:91.
22. Leonti M et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15;79(12):1815-26.
23. Trusler AR et al. Dermatitis. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):22-32.
24. Río CD et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;157:122-133.
25. Chuquilin M et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Feb;74(2):197-212.
26. Tubaro A et al. Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):816-9.
27. Eagleston LRM et al. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jun 15;24(6).
28. Marks DH et al. Skin Therapy Lett. 2018 Nov;23(6):1-5.
Dr. Douglas Paauw gives updates on antihypertensives, statins, SGLT2 inhibitors
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Paauw, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, began by discussing some of the issues that occurred with antihypertensive drugs in the past year. These included the link between hydrochlorothiazide use and the increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancers, the recalls of many drug lots of angiotensin II receptor blockers, and a study that found an increased risk of lung cancer in people who were taking ACE inhibitors.
He then described the findings of studies that examined the links between statins and muscle pain and other new research on these drugs.
He also warned physicians to be particularity cautious about prescribing sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors to certain kinds of patients.
Dr. Paauw concluded by explaining why clarithromycin is his most hated drug.
Dr. Paauw is also the Rathmann Family Foundation Endowed Chair for Patient-Centered Clinical Education and the medicine clerkship director at the University of Washington.
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Paauw, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, began by discussing some of the issues that occurred with antihypertensive drugs in the past year. These included the link between hydrochlorothiazide use and the increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancers, the recalls of many drug lots of angiotensin II receptor blockers, and a study that found an increased risk of lung cancer in people who were taking ACE inhibitors.
He then described the findings of studies that examined the links between statins and muscle pain and other new research on these drugs.
He also warned physicians to be particularity cautious about prescribing sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors to certain kinds of patients.
Dr. Paauw concluded by explaining why clarithromycin is his most hated drug.
Dr. Paauw is also the Rathmann Family Foundation Endowed Chair for Patient-Centered Clinical Education and the medicine clerkship director at the University of Washington.
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Paauw, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, began by discussing some of the issues that occurred with antihypertensive drugs in the past year. These included the link between hydrochlorothiazide use and the increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancers, the recalls of many drug lots of angiotensin II receptor blockers, and a study that found an increased risk of lung cancer in people who were taking ACE inhibitors.
He then described the findings of studies that examined the links between statins and muscle pain and other new research on these drugs.
He also warned physicians to be particularity cautious about prescribing sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors to certain kinds of patients.
Dr. Paauw concluded by explaining why clarithromycin is his most hated drug.
Dr. Paauw is also the Rathmann Family Foundation Endowed Chair for Patient-Centered Clinical Education and the medicine clerkship director at the University of Washington.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019
Study highlights lack of data on transgender leukemia patients
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Researchers have shown they can identify transgender leukemia patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches, but some transgender patients may be overlooked with this method.
The researchers’ work also highlights how little we know about transgender patients with leukemia and other cancers.
Alison Alpert, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, and her colleagues conducted this research and presented their findings in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
“There’s almost no data about transgender people with cancer ... in terms of prevalence or anything else,” Dr. Alpert noted. “And because we don’t know which patients with cancer are transgender, we can’t begin to answer any of the other big questions for patients.”
Specifically, it’s unclear what kinds of cancer transgender patients have, if there are health disparities among transgender patients, if it is safe to continue hormone therapy during cancer treatment, and if it is possible to do transition-related surgeries in the context of cancer care.
With this in mind, Dr. Alpert and her colleagues set out to identify transgender patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches. The team analyzed data on patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes enrolled in five Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) trials.
Of the 1,748 patients analyzed, six (0.3%) had a gender-karyotype mismatch. Five patients had a 46,XY karyotype and identified as female, and one patient had a 46,XX karyotype and identified as male.
“Some transgender patients have their gender identity accurately reflected in the electronic medical record, [but] some transgender patients probably don’t,” Dr. Alpert noted. “So we identified some, but probably not all, and probably not even most, transgender patients with leukemia in this cohort.”
All six of the transgender patients identified had AML, and all were white. They ranged in age from 18 to 57 years. Four patients had achieved a complete response to therapy, and two had refractory disease.
Four patients, including one who was refractory, were still alive at last follow-up. The remaining two patients, including one who had achieved a complete response, had died.
The transgender patients identified in this analysis represent a very small percentage of the population studied, Dr. Alpert noted. Therefore, the researchers could not draw any conclusions about transgender patients with AML.
“Mostly, what we did was, we pointed out how little information we have,” Dr. Alpert said. “Oncologists don’t routinely collect gender identity information, and this information doesn’t exist in cooperative group databases either.”
“But going forward, what probably really needs to happen is that oncologists need to ask their patients whether they are transgender or not. And then, ideally, consent forms for large cooperative groups like SWOG would include gender identity data, and then we would be able to answer some of our other questions and better counsel our patients.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues are hoping to gain insights regarding transgender patients with lymphoma as well. The researchers are analyzing the lymphoma database at the University of Rochester Medical Center, which includes about 2,200 patients.
The team is attempting to identify transgender lymphoma patients using gender-karyotype mismatch as well as other methods, including assessing patients’ medication and surgical histories, determining whether patients have any aliases, and looking for the word “transgender” in patient charts.
“Given that the country is finally starting to talk about transgender patients, their health disparities, and their needs and experiences, it’s really time that we start collecting this data,” Dr. Alpert said.
“[I]f we are able to start to collect this data, it can help us build relationships with our patients, improve their care and outcomes, and, hopefully, be able to better counsel them about hormones and surgery.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Researchers have shown they can identify transgender leukemia patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches, but some transgender patients may be overlooked with this method.
The researchers’ work also highlights how little we know about transgender patients with leukemia and other cancers.
Alison Alpert, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, and her colleagues conducted this research and presented their findings in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
“There’s almost no data about transgender people with cancer ... in terms of prevalence or anything else,” Dr. Alpert noted. “And because we don’t know which patients with cancer are transgender, we can’t begin to answer any of the other big questions for patients.”
Specifically, it’s unclear what kinds of cancer transgender patients have, if there are health disparities among transgender patients, if it is safe to continue hormone therapy during cancer treatment, and if it is possible to do transition-related surgeries in the context of cancer care.
With this in mind, Dr. Alpert and her colleagues set out to identify transgender patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches. The team analyzed data on patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes enrolled in five Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) trials.
Of the 1,748 patients analyzed, six (0.3%) had a gender-karyotype mismatch. Five patients had a 46,XY karyotype and identified as female, and one patient had a 46,XX karyotype and identified as male.
“Some transgender patients have their gender identity accurately reflected in the electronic medical record, [but] some transgender patients probably don’t,” Dr. Alpert noted. “So we identified some, but probably not all, and probably not even most, transgender patients with leukemia in this cohort.”
All six of the transgender patients identified had AML, and all were white. They ranged in age from 18 to 57 years. Four patients had achieved a complete response to therapy, and two had refractory disease.
Four patients, including one who was refractory, were still alive at last follow-up. The remaining two patients, including one who had achieved a complete response, had died.
The transgender patients identified in this analysis represent a very small percentage of the population studied, Dr. Alpert noted. Therefore, the researchers could not draw any conclusions about transgender patients with AML.
“Mostly, what we did was, we pointed out how little information we have,” Dr. Alpert said. “Oncologists don’t routinely collect gender identity information, and this information doesn’t exist in cooperative group databases either.”
“But going forward, what probably really needs to happen is that oncologists need to ask their patients whether they are transgender or not. And then, ideally, consent forms for large cooperative groups like SWOG would include gender identity data, and then we would be able to answer some of our other questions and better counsel our patients.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues are hoping to gain insights regarding transgender patients with lymphoma as well. The researchers are analyzing the lymphoma database at the University of Rochester Medical Center, which includes about 2,200 patients.
The team is attempting to identify transgender lymphoma patients using gender-karyotype mismatch as well as other methods, including assessing patients’ medication and surgical histories, determining whether patients have any aliases, and looking for the word “transgender” in patient charts.
“Given that the country is finally starting to talk about transgender patients, their health disparities, and their needs and experiences, it’s really time that we start collecting this data,” Dr. Alpert said.
“[I]f we are able to start to collect this data, it can help us build relationships with our patients, improve their care and outcomes, and, hopefully, be able to better counsel them about hormones and surgery.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Researchers have shown they can identify transgender leukemia patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches, but some transgender patients may be overlooked with this method.
The researchers’ work also highlights how little we know about transgender patients with leukemia and other cancers.
Alison Alpert, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center, and her colleagues conducted this research and presented their findings in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
“There’s almost no data about transgender people with cancer ... in terms of prevalence or anything else,” Dr. Alpert noted. “And because we don’t know which patients with cancer are transgender, we can’t begin to answer any of the other big questions for patients.”
Specifically, it’s unclear what kinds of cancer transgender patients have, if there are health disparities among transgender patients, if it is safe to continue hormone therapy during cancer treatment, and if it is possible to do transition-related surgeries in the context of cancer care.
With this in mind, Dr. Alpert and her colleagues set out to identify transgender patients by detecting gender-karyotype mismatches. The team analyzed data on patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndromes enrolled in five Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) trials.
Of the 1,748 patients analyzed, six (0.3%) had a gender-karyotype mismatch. Five patients had a 46,XY karyotype and identified as female, and one patient had a 46,XX karyotype and identified as male.
“Some transgender patients have their gender identity accurately reflected in the electronic medical record, [but] some transgender patients probably don’t,” Dr. Alpert noted. “So we identified some, but probably not all, and probably not even most, transgender patients with leukemia in this cohort.”
All six of the transgender patients identified had AML, and all were white. They ranged in age from 18 to 57 years. Four patients had achieved a complete response to therapy, and two had refractory disease.
Four patients, including one who was refractory, were still alive at last follow-up. The remaining two patients, including one who had achieved a complete response, had died.
The transgender patients identified in this analysis represent a very small percentage of the population studied, Dr. Alpert noted. Therefore, the researchers could not draw any conclusions about transgender patients with AML.
“Mostly, what we did was, we pointed out how little information we have,” Dr. Alpert said. “Oncologists don’t routinely collect gender identity information, and this information doesn’t exist in cooperative group databases either.”
“But going forward, what probably really needs to happen is that oncologists need to ask their patients whether they are transgender or not. And then, ideally, consent forms for large cooperative groups like SWOG would include gender identity data, and then we would be able to answer some of our other questions and better counsel our patients.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues are hoping to gain insights regarding transgender patients with lymphoma as well. The researchers are analyzing the lymphoma database at the University of Rochester Medical Center, which includes about 2,200 patients.
The team is attempting to identify transgender lymphoma patients using gender-karyotype mismatch as well as other methods, including assessing patients’ medication and surgical histories, determining whether patients have any aliases, and looking for the word “transgender” in patient charts.
“Given that the country is finally starting to talk about transgender patients, their health disparities, and their needs and experiences, it’s really time that we start collecting this data,” Dr. Alpert said.
“[I]f we are able to start to collect this data, it can help us build relationships with our patients, improve their care and outcomes, and, hopefully, be able to better counsel them about hormones and surgery.”
Dr. Alpert and her colleagues did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM ALF 2019
ALF 2019 showcases evolving treatment of AML
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The evolving treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was highlighted at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
In a video interview, Martin Tallman, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, discussed several meeting presentations on the treatment of AML.
In his presentation, Craig Jordan, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained how the combination of venetoclax and azacitidine appears to target leukemic stem cells in AML.
Courtney DiNardo, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, presented information on novel agents for AML, including antibody-drug conjugates; bispecific therapies; checkpoint inhibitors; and inhibitors of IDH1/2, MCL1, and MDM2.
Richard Larson, MD, of the University of Chicago, explored the possibility of an individualized approach to postremission therapy in AML.
Frederick Appelbaum, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, showed that various maintenance therapies given after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have not proven beneficial for AML patients.
Richard Jones, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, presented data showing that post-HSCT cyclophosphamide has made haploidentical transplants safer and more effective for AML patients.
And James Ferrara, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, detailed research showing that biomarkers of graft-versus-host disease can predict nonrelapse mortality after HSCT.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The evolving treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was highlighted at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
In a video interview, Martin Tallman, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, discussed several meeting presentations on the treatment of AML.
In his presentation, Craig Jordan, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained how the combination of venetoclax and azacitidine appears to target leukemic stem cells in AML.
Courtney DiNardo, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, presented information on novel agents for AML, including antibody-drug conjugates; bispecific therapies; checkpoint inhibitors; and inhibitors of IDH1/2, MCL1, and MDM2.
Richard Larson, MD, of the University of Chicago, explored the possibility of an individualized approach to postremission therapy in AML.
Frederick Appelbaum, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, showed that various maintenance therapies given after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have not proven beneficial for AML patients.
Richard Jones, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, presented data showing that post-HSCT cyclophosphamide has made haploidentical transplants safer and more effective for AML patients.
And James Ferrara, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, detailed research showing that biomarkers of graft-versus-host disease can predict nonrelapse mortality after HSCT.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The evolving treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was highlighted at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
In a video interview, Martin Tallman, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, discussed several meeting presentations on the treatment of AML.
In his presentation, Craig Jordan, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained how the combination of venetoclax and azacitidine appears to target leukemic stem cells in AML.
Courtney DiNardo, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, presented information on novel agents for AML, including antibody-drug conjugates; bispecific therapies; checkpoint inhibitors; and inhibitors of IDH1/2, MCL1, and MDM2.
Richard Larson, MD, of the University of Chicago, explored the possibility of an individualized approach to postremission therapy in AML.
Frederick Appelbaum, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, showed that various maintenance therapies given after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have not proven beneficial for AML patients.
Richard Jones, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore, presented data showing that post-HSCT cyclophosphamide has made haploidentical transplants safer and more effective for AML patients.
And James Ferrara, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, detailed research showing that biomarkers of graft-versus-host disease can predict nonrelapse mortality after HSCT.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM ALF 2019
Back to the drawing board for MPN combo
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The combination of ruxolitinib and decitabine will not proceed to a phase 3 trial in patients with accelerated or blast phase myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).
The combination demonstrated activity and tolerability in a phase 2 trial, but outcomes were not optimal, according to Raajit K. Rampal, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“[P]erhaps the outcomes might be favorable compared to standard induction chemotherapy regimens,” Dr. Rampal said. “Nonetheless, it’s clear that we still have a lot of work to do, and the outcomes are not optimal in these patients.”
However, Dr. Rampal and his colleagues are investigating the possibility of combining ruxolitinib and decitabine with other agents to treat patients with accelerated or blast phase MPNs.
Dr. Rampal and his colleagues presented results from the phase 2 trial in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
The trial (NCT02076191) enrolled 25 patients, 10 with accelerated phase MPN (10%-19% blasts) and 15 with blast phase MPN (at least 20% blasts). The patients’ median age was 71 years.
Patients had a median disease duration of 72.9 months. Six patients (25%) had received prior ruxolitinib, and two (8.3%) had received prior decitabine.
Treatment and safety
For the first cycle, patients received decitabine at 20 mg/m2 per day on days 8-12 and ruxolitinib at 25 mg twice a day on days 1-35. For subsequent cycles, patients received the same dose of decitabine on days 1-5 and ruxolitinib at 10 mg twice a day on days 6-28. Patients were treated until progression, withdrawal, or unacceptable toxicity.
“The adverse events we saw in this study were typical for this population, including fevers, mostly neutropenic fevers, as well as anemia and thrombocytopenia,” Dr. Rampal said.
Nonhematologic adverse events (AEs) included fatigue, abdominal pain, pneumonia, diarrhea, dizziness, and constipation. Hematologic AEs included anemia, neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Response and survival
Eighteen patients were evaluable for response. Four patients were not evaluable because they withdrew from the study due to secondary AEs and completed one cycle of therapy or less, two patients did not have circulating blasts at baseline, and one patient refused further treatment.
Among the evaluable patients, nine (50%) achieved a partial response, including four patients with accelerated phase MPN and five with blast phase MPN.
Two patients (11.1%), one with accelerated phase MPN and one with blast phase MPN, achieved a complete response with incomplete count recovery.
The remaining seven patients (38.9%), five with blast phase MPN and two with accelerated phase MPN, did not respond.
The median overall survival was 7.6 months for the entire cohort, 9.7 months for patients with blast phase MPN, and 5.8 months for patients with accelerated phase MPN.
Based on these results, Dr. Rampal and his colleagues theorized that ruxolitinib plus decitabine might be improved by the addition of other agents. The researchers are currently investigating this possibility.
“The work for this trial really came out of preclinical work in the laboratory where we combined these drugs and saw efficacy in murine models,” Dr. Rampal said. “So we’re going back to the drawing board and looking at those again to see, ‘Can we come up with new rational combinations?’ ”
Dr. Rampal and his colleagues reported having no conflicts of interest. Their study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Cancer Institute, and Incyte Corporation.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The combination of ruxolitinib and decitabine will not proceed to a phase 3 trial in patients with accelerated or blast phase myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).
The combination demonstrated activity and tolerability in a phase 2 trial, but outcomes were not optimal, according to Raajit K. Rampal, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“[P]erhaps the outcomes might be favorable compared to standard induction chemotherapy regimens,” Dr. Rampal said. “Nonetheless, it’s clear that we still have a lot of work to do, and the outcomes are not optimal in these patients.”
However, Dr. Rampal and his colleagues are investigating the possibility of combining ruxolitinib and decitabine with other agents to treat patients with accelerated or blast phase MPNs.
Dr. Rampal and his colleagues presented results from the phase 2 trial in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
The trial (NCT02076191) enrolled 25 patients, 10 with accelerated phase MPN (10%-19% blasts) and 15 with blast phase MPN (at least 20% blasts). The patients’ median age was 71 years.
Patients had a median disease duration of 72.9 months. Six patients (25%) had received prior ruxolitinib, and two (8.3%) had received prior decitabine.
Treatment and safety
For the first cycle, patients received decitabine at 20 mg/m2 per day on days 8-12 and ruxolitinib at 25 mg twice a day on days 1-35. For subsequent cycles, patients received the same dose of decitabine on days 1-5 and ruxolitinib at 10 mg twice a day on days 6-28. Patients were treated until progression, withdrawal, or unacceptable toxicity.
“The adverse events we saw in this study were typical for this population, including fevers, mostly neutropenic fevers, as well as anemia and thrombocytopenia,” Dr. Rampal said.
Nonhematologic adverse events (AEs) included fatigue, abdominal pain, pneumonia, diarrhea, dizziness, and constipation. Hematologic AEs included anemia, neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Response and survival
Eighteen patients were evaluable for response. Four patients were not evaluable because they withdrew from the study due to secondary AEs and completed one cycle of therapy or less, two patients did not have circulating blasts at baseline, and one patient refused further treatment.
Among the evaluable patients, nine (50%) achieved a partial response, including four patients with accelerated phase MPN and five with blast phase MPN.
Two patients (11.1%), one with accelerated phase MPN and one with blast phase MPN, achieved a complete response with incomplete count recovery.
The remaining seven patients (38.9%), five with blast phase MPN and two with accelerated phase MPN, did not respond.
The median overall survival was 7.6 months for the entire cohort, 9.7 months for patients with blast phase MPN, and 5.8 months for patients with accelerated phase MPN.
Based on these results, Dr. Rampal and his colleagues theorized that ruxolitinib plus decitabine might be improved by the addition of other agents. The researchers are currently investigating this possibility.
“The work for this trial really came out of preclinical work in the laboratory where we combined these drugs and saw efficacy in murine models,” Dr. Rampal said. “So we’re going back to the drawing board and looking at those again to see, ‘Can we come up with new rational combinations?’ ”
Dr. Rampal and his colleagues reported having no conflicts of interest. Their study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Cancer Institute, and Incyte Corporation.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – The combination of ruxolitinib and decitabine will not proceed to a phase 3 trial in patients with accelerated or blast phase myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs).
The combination demonstrated activity and tolerability in a phase 2 trial, but outcomes were not optimal, according to Raajit K. Rampal, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“[P]erhaps the outcomes might be favorable compared to standard induction chemotherapy regimens,” Dr. Rampal said. “Nonetheless, it’s clear that we still have a lot of work to do, and the outcomes are not optimal in these patients.”
However, Dr. Rampal and his colleagues are investigating the possibility of combining ruxolitinib and decitabine with other agents to treat patients with accelerated or blast phase MPNs.
Dr. Rampal and his colleagues presented results from the phase 2 trial in a poster at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
The trial (NCT02076191) enrolled 25 patients, 10 with accelerated phase MPN (10%-19% blasts) and 15 with blast phase MPN (at least 20% blasts). The patients’ median age was 71 years.
Patients had a median disease duration of 72.9 months. Six patients (25%) had received prior ruxolitinib, and two (8.3%) had received prior decitabine.
Treatment and safety
For the first cycle, patients received decitabine at 20 mg/m2 per day on days 8-12 and ruxolitinib at 25 mg twice a day on days 1-35. For subsequent cycles, patients received the same dose of decitabine on days 1-5 and ruxolitinib at 10 mg twice a day on days 6-28. Patients were treated until progression, withdrawal, or unacceptable toxicity.
“The adverse events we saw in this study were typical for this population, including fevers, mostly neutropenic fevers, as well as anemia and thrombocytopenia,” Dr. Rampal said.
Nonhematologic adverse events (AEs) included fatigue, abdominal pain, pneumonia, diarrhea, dizziness, and constipation. Hematologic AEs included anemia, neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia.
Response and survival
Eighteen patients were evaluable for response. Four patients were not evaluable because they withdrew from the study due to secondary AEs and completed one cycle of therapy or less, two patients did not have circulating blasts at baseline, and one patient refused further treatment.
Among the evaluable patients, nine (50%) achieved a partial response, including four patients with accelerated phase MPN and five with blast phase MPN.
Two patients (11.1%), one with accelerated phase MPN and one with blast phase MPN, achieved a complete response with incomplete count recovery.
The remaining seven patients (38.9%), five with blast phase MPN and two with accelerated phase MPN, did not respond.
The median overall survival was 7.6 months for the entire cohort, 9.7 months for patients with blast phase MPN, and 5.8 months for patients with accelerated phase MPN.
Based on these results, Dr. Rampal and his colleagues theorized that ruxolitinib plus decitabine might be improved by the addition of other agents. The researchers are currently investigating this possibility.
“The work for this trial really came out of preclinical work in the laboratory where we combined these drugs and saw efficacy in murine models,” Dr. Rampal said. “So we’re going back to the drawing board and looking at those again to see, ‘Can we come up with new rational combinations?’ ”
Dr. Rampal and his colleagues reported having no conflicts of interest. Their study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Cancer Institute, and Incyte Corporation.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is held by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM ALF 2019
Physicians discuss bringing cultural humility to medicine
PHILADELPHIA – during a panel discussion moderated by Sarah Candler, MD, an internist in Houston.
Dr. Candler, former chair, Council of Resident and Fellow Members, Board of Regents, American College of Physicians, began the discussion by asking Dr. DeLisser, to describe his role in teaching medical students about the social determinants of health, at the annual Internal Medicine meeting of the ACP.
Dr. DeLisser, associate dean for professionalism and humanism at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said he focuses on a number of issues, including social medicine, cultural competency, and cultural humility.
“We look at health care disparities and try to do a lot of innovation around service learning that will bring our students into the community, one to learn about these determinants but more importantly to be able to see how these issues can be addressed both on a provider level but also on a more structural systemic level,” he noted.
Dr. Poorman, an internist at the University of Washington, later discussed the importance of practicing cultural humility as it related to her experience providing care to migrant workers while she was a medical school student.
Dr. Candler, an internist in Houston, concluded the discussion by describing some of the ACP’s newest resources designed to address the social determinants of health for specific groups of patients.
The full panel discussion was recorded as a video.
PHILADELPHIA – during a panel discussion moderated by Sarah Candler, MD, an internist in Houston.
Dr. Candler, former chair, Council of Resident and Fellow Members, Board of Regents, American College of Physicians, began the discussion by asking Dr. DeLisser, to describe his role in teaching medical students about the social determinants of health, at the annual Internal Medicine meeting of the ACP.
Dr. DeLisser, associate dean for professionalism and humanism at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said he focuses on a number of issues, including social medicine, cultural competency, and cultural humility.
“We look at health care disparities and try to do a lot of innovation around service learning that will bring our students into the community, one to learn about these determinants but more importantly to be able to see how these issues can be addressed both on a provider level but also on a more structural systemic level,” he noted.
Dr. Poorman, an internist at the University of Washington, later discussed the importance of practicing cultural humility as it related to her experience providing care to migrant workers while she was a medical school student.
Dr. Candler, an internist in Houston, concluded the discussion by describing some of the ACP’s newest resources designed to address the social determinants of health for specific groups of patients.
The full panel discussion was recorded as a video.
PHILADELPHIA – during a panel discussion moderated by Sarah Candler, MD, an internist in Houston.
Dr. Candler, former chair, Council of Resident and Fellow Members, Board of Regents, American College of Physicians, began the discussion by asking Dr. DeLisser, to describe his role in teaching medical students about the social determinants of health, at the annual Internal Medicine meeting of the ACP.
Dr. DeLisser, associate dean for professionalism and humanism at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said he focuses on a number of issues, including social medicine, cultural competency, and cultural humility.
“We look at health care disparities and try to do a lot of innovation around service learning that will bring our students into the community, one to learn about these determinants but more importantly to be able to see how these issues can be addressed both on a provider level but also on a more structural systemic level,” he noted.
Dr. Poorman, an internist at the University of Washington, later discussed the importance of practicing cultural humility as it related to her experience providing care to migrant workers while she was a medical school student.
Dr. Candler, an internist in Houston, concluded the discussion by describing some of the ACP’s newest resources designed to address the social determinants of health for specific groups of patients.
The full panel discussion was recorded as a video.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019
ACP governmental affairs leaders discuss ACA, Title X
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview conducted during the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.

Robert B. Doherty, the ACP’s senior vice president, governmental affairs and public policy, and Shari M. Erickson, the organization’s vice president of governmental affairs and medical practice, addressed the future of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), cuts to the funding of Title X clinics, and the National Rifle Association’s urging of Congress to vote against the Violence Against Women Reauthorization Act.
“We’re very, very concerned by a decision by a Texas judge that, if upheld on appeal, would gut the entire ACA and the decision by the administration not to defend any part of the ACA,” said Mr. Doherty.
Ms. Erikson later discussed a final rule released by the administration that she said “significantly impacts access to care for women,” particularly for those in low-income and underserved areas who may be seen by clinics that receive Title X funding.
She also addressed the rule’s effects on federally qualified health centers and other health clinics near Title X–funded clinics that are forced to close.
On a positive note, Mr. Doherty noted that the ACP is supporting legislation that has been introduced in the House to stabilize the current insurance markets.
Mr. Doherty and Ms. Erikson concluded by discussing an ACP initiative focused on reducing administrative burden for ACP members.
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview conducted during the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.

Robert B. Doherty, the ACP’s senior vice president, governmental affairs and public policy, and Shari M. Erickson, the organization’s vice president of governmental affairs and medical practice, addressed the future of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), cuts to the funding of Title X clinics, and the National Rifle Association’s urging of Congress to vote against the Violence Against Women Reauthorization Act.
“We’re very, very concerned by a decision by a Texas judge that, if upheld on appeal, would gut the entire ACA and the decision by the administration not to defend any part of the ACA,” said Mr. Doherty.
Ms. Erikson later discussed a final rule released by the administration that she said “significantly impacts access to care for women,” particularly for those in low-income and underserved areas who may be seen by clinics that receive Title X funding.
She also addressed the rule’s effects on federally qualified health centers and other health clinics near Title X–funded clinics that are forced to close.
On a positive note, Mr. Doherty noted that the ACP is supporting legislation that has been introduced in the House to stabilize the current insurance markets.
Mr. Doherty and Ms. Erikson concluded by discussing an ACP initiative focused on reducing administrative burden for ACP members.
PHILADELPHIA – in a video interview conducted during the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.

Robert B. Doherty, the ACP’s senior vice president, governmental affairs and public policy, and Shari M. Erickson, the organization’s vice president of governmental affairs and medical practice, addressed the future of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), cuts to the funding of Title X clinics, and the National Rifle Association’s urging of Congress to vote against the Violence Against Women Reauthorization Act.
“We’re very, very concerned by a decision by a Texas judge that, if upheld on appeal, would gut the entire ACA and the decision by the administration not to defend any part of the ACA,” said Mr. Doherty.
Ms. Erikson later discussed a final rule released by the administration that she said “significantly impacts access to care for women,” particularly for those in low-income and underserved areas who may be seen by clinics that receive Title X funding.
She also addressed the rule’s effects on federally qualified health centers and other health clinics near Title X–funded clinics that are forced to close.
On a positive note, Mr. Doherty noted that the ACP is supporting legislation that has been introduced in the House to stabilize the current insurance markets.
Mr. Doherty and Ms. Erikson concluded by discussing an ACP initiative focused on reducing administrative burden for ACP members.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019
Role of Diet in Treating Skin Conditions



Volunteerism: How and why to do it, according to Dr. Eileen Barrett
PHILADELPHIA –
“I think what we get out of it is the feeling of our commitment to our sense of purpose and mission, and you just feel great when you’re giving, and then you meet these really remarkable people who do really, really remarkable things. ... It’s tremendously inspiring,” Dr. Barrett said in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. She is a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and serves on the ACP Board of Regents.
In addition, Dr. Barrett has done disaster relief work in West Africa, provided patient care to refugees in a hospital on the Thailand side of the Thailand-Myanmar border, and even helped bring organization to a public radio station in rural New Mexico.
She also described some opportunities available to internists who are trying to get their feet wet in volunteering that are available through the organizations, Health Volunteers Overseas and the Maven Project.
PHILADELPHIA –
“I think what we get out of it is the feeling of our commitment to our sense of purpose and mission, and you just feel great when you’re giving, and then you meet these really remarkable people who do really, really remarkable things. ... It’s tremendously inspiring,” Dr. Barrett said in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. She is a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and serves on the ACP Board of Regents.
In addition, Dr. Barrett has done disaster relief work in West Africa, provided patient care to refugees in a hospital on the Thailand side of the Thailand-Myanmar border, and even helped bring organization to a public radio station in rural New Mexico.
She also described some opportunities available to internists who are trying to get their feet wet in volunteering that are available through the organizations, Health Volunteers Overseas and the Maven Project.
PHILADELPHIA –
“I think what we get out of it is the feeling of our commitment to our sense of purpose and mission, and you just feel great when you’re giving, and then you meet these really remarkable people who do really, really remarkable things. ... It’s tremendously inspiring,” Dr. Barrett said in a video interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. She is a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and serves on the ACP Board of Regents.
In addition, Dr. Barrett has done disaster relief work in West Africa, provided patient care to refugees in a hospital on the Thailand side of the Thailand-Myanmar border, and even helped bring organization to a public radio station in rural New Mexico.
She also described some opportunities available to internists who are trying to get their feet wet in volunteering that are available through the organizations, Health Volunteers Overseas and the Maven Project.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019
Creating CAR T-cell therapies for T-cell malignancies
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Preclinical research has revealed workarounds that may make chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy feasible for patients with T-cell malignancies.
Researchers have found that using allogeneic cells for CAR T-cell therapy can eliminate contamination by malignant T cells, and editing those allogeneic T cells to delete the target antigen and the T-cell receptor alpha chain (TRAC) can prevent fratricide and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Additionally, an interleukin-7 molecule called NT-I7 has been shown to enhance CAR T-cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumor killing in a mouse model of a T-cell malignancy.
John F. DiPersio, MD, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, described this work in a presentation at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
Obstacles to development
“The primary obstacle for targeting T-cell malignancies with a T cell is that all of the targets that are on the [malignant] T cells are also expressed on the normal T cells,” Dr. DiPersio said. “So when you put a CAR into a normal T cell, it just kills itself. It’s called fratricide.”
A second issue that has limited development is that the phenotype of the malignant T cell in the blood is similar to a normal T cell, so they can’t be separated, he explained.
“So if you were to do anything to a normal T cell, you would also be doing it, in theory, to the malignant T cell – in theory, making it resistant to therapy,” he said.
A third obstacle, which has been seen in patients with B-cell malignancies as well, is the inability to harvest enough T cells to generate effective CAR T-cell therapy.
And a fourth obstacle is that T cells from patients with malignancies may not function normally because they have been exposed to prior therapies.
Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues believe these obstacles can be overcome by creating CAR T-cell therapies using T cells derived from healthy donors or cord blood, using gene editing to remove the target antigen and TRAC, and using NT-I7 to enhance the efficacy of these universal, “off-the-shelf” CAR T cells.
The researchers have tested these theories, and achieved successes, in preclinical models. The team is now planning a clinical trial in patients at Washington University. Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues also created a company called WUGEN that will develop the universal CAR T-cell therapies if the initial proof-of-principle trial proves successful.
UCART7
One of the universal CAR T-cell therapies Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues have tested is UCART7, which targets CD7. Dr. DiPersio noted that CD7 is expressed on 98% of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias (T-ALLs), 24% of acute myeloid leukemias, natural killer (NK) cells, and T cells.
The researchers created UCART7 by using CRISPR/Cas9 to delete CD7 and TRAC from allogeneic T cells and following this with lentiviral transduction with a third-generation CD7-CAR. The team found a way to delete both TRAC and CD7 in a single day with 95% efficiency, Dr. DiPersio noted.
“Knocking out CD7 doesn’t seem to have any impact on the expansion or trafficking of these T cells in vivo,” Dr. DiPersio said. “So we think that deleting that target in a normal T cell will not affect its overall ability to kill a target when we put a CAR into those T cells.”
In fact, the researchers’ experiments showed that UCART7 can kill T-ALL cells in vitro and target primary T-ALL in vivo without inducing GVHD (Leukemia. 2018 Sep;32[9]:1970-83.)
UCART2 and NT-I7
Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues have also tested UCART2, an allogeneic CAR T-cell therapy in which CD2 and TRAC are deleted. The therapy targets CD2 because this antigen is expressed on T-ALL and other T-cell and NK-cell malignancies. Experiments showed that UCART2 targets T-cell malignancies, including T-ALL and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, in vitro.
The researchers also tested UCART2 in a mouse model of Sézary syndrome. In these experiments, UCART2 was combined with NT-I7.
NT-I7 enhanced the proliferation, persistence, and tumor killing ability of UCART2. Sézary mice that received UCART2 and NT-I7 had “virtually no tumor burden,” according to researchers, and survived longer than mice treated with UCART2 alone (Blood. 2018;132:340).
Dr. DiPersio noted that there was no cytokine release syndrome because these were immunodeficient mice. However, cytokine release syndrome may be a side effect of NT-I7 in patients as NT-I7 induces rapid expansion of CAR T cells.
Dr. DiPersio reported ownership and investment in WUGEN and Magenta Therapeutics. He also has relationships with Cellworks Group, Tioma Therapeutics, RiverVest Venture Partners, Bioline, Asterias Biotherapeutics, Amphivena Therapeutics, Bluebird Bio, Celgene, Incyte, NeoImuneTech, and MacroGenics.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Preclinical research has revealed workarounds that may make chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy feasible for patients with T-cell malignancies.
Researchers have found that using allogeneic cells for CAR T-cell therapy can eliminate contamination by malignant T cells, and editing those allogeneic T cells to delete the target antigen and the T-cell receptor alpha chain (TRAC) can prevent fratricide and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Additionally, an interleukin-7 molecule called NT-I7 has been shown to enhance CAR T-cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumor killing in a mouse model of a T-cell malignancy.
John F. DiPersio, MD, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, described this work in a presentation at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
Obstacles to development
“The primary obstacle for targeting T-cell malignancies with a T cell is that all of the targets that are on the [malignant] T cells are also expressed on the normal T cells,” Dr. DiPersio said. “So when you put a CAR into a normal T cell, it just kills itself. It’s called fratricide.”
A second issue that has limited development is that the phenotype of the malignant T cell in the blood is similar to a normal T cell, so they can’t be separated, he explained.
“So if you were to do anything to a normal T cell, you would also be doing it, in theory, to the malignant T cell – in theory, making it resistant to therapy,” he said.
A third obstacle, which has been seen in patients with B-cell malignancies as well, is the inability to harvest enough T cells to generate effective CAR T-cell therapy.
And a fourth obstacle is that T cells from patients with malignancies may not function normally because they have been exposed to prior therapies.
Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues believe these obstacles can be overcome by creating CAR T-cell therapies using T cells derived from healthy donors or cord blood, using gene editing to remove the target antigen and TRAC, and using NT-I7 to enhance the efficacy of these universal, “off-the-shelf” CAR T cells.
The researchers have tested these theories, and achieved successes, in preclinical models. The team is now planning a clinical trial in patients at Washington University. Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues also created a company called WUGEN that will develop the universal CAR T-cell therapies if the initial proof-of-principle trial proves successful.
UCART7
One of the universal CAR T-cell therapies Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues have tested is UCART7, which targets CD7. Dr. DiPersio noted that CD7 is expressed on 98% of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias (T-ALLs), 24% of acute myeloid leukemias, natural killer (NK) cells, and T cells.
The researchers created UCART7 by using CRISPR/Cas9 to delete CD7 and TRAC from allogeneic T cells and following this with lentiviral transduction with a third-generation CD7-CAR. The team found a way to delete both TRAC and CD7 in a single day with 95% efficiency, Dr. DiPersio noted.
“Knocking out CD7 doesn’t seem to have any impact on the expansion or trafficking of these T cells in vivo,” Dr. DiPersio said. “So we think that deleting that target in a normal T cell will not affect its overall ability to kill a target when we put a CAR into those T cells.”
In fact, the researchers’ experiments showed that UCART7 can kill T-ALL cells in vitro and target primary T-ALL in vivo without inducing GVHD (Leukemia. 2018 Sep;32[9]:1970-83.)
UCART2 and NT-I7
Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues have also tested UCART2, an allogeneic CAR T-cell therapy in which CD2 and TRAC are deleted. The therapy targets CD2 because this antigen is expressed on T-ALL and other T-cell and NK-cell malignancies. Experiments showed that UCART2 targets T-cell malignancies, including T-ALL and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, in vitro.
The researchers also tested UCART2 in a mouse model of Sézary syndrome. In these experiments, UCART2 was combined with NT-I7.
NT-I7 enhanced the proliferation, persistence, and tumor killing ability of UCART2. Sézary mice that received UCART2 and NT-I7 had “virtually no tumor burden,” according to researchers, and survived longer than mice treated with UCART2 alone (Blood. 2018;132:340).
Dr. DiPersio noted that there was no cytokine release syndrome because these were immunodeficient mice. However, cytokine release syndrome may be a side effect of NT-I7 in patients as NT-I7 induces rapid expansion of CAR T cells.
Dr. DiPersio reported ownership and investment in WUGEN and Magenta Therapeutics. He also has relationships with Cellworks Group, Tioma Therapeutics, RiverVest Venture Partners, Bioline, Asterias Biotherapeutics, Amphivena Therapeutics, Bluebird Bio, Celgene, Incyte, NeoImuneTech, and MacroGenics.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
NEWPORT BEACH, CALIF. – Preclinical research has revealed workarounds that may make chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy feasible for patients with T-cell malignancies.
Researchers have found that using allogeneic cells for CAR T-cell therapy can eliminate contamination by malignant T cells, and editing those allogeneic T cells to delete the target antigen and the T-cell receptor alpha chain (TRAC) can prevent fratricide and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Additionally, an interleukin-7 molecule called NT-I7 has been shown to enhance CAR T-cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumor killing in a mouse model of a T-cell malignancy.
John F. DiPersio, MD, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, described this work in a presentation at the Acute Leukemia Forum of Hemedicus.
Obstacles to development
“The primary obstacle for targeting T-cell malignancies with a T cell is that all of the targets that are on the [malignant] T cells are also expressed on the normal T cells,” Dr. DiPersio said. “So when you put a CAR into a normal T cell, it just kills itself. It’s called fratricide.”
A second issue that has limited development is that the phenotype of the malignant T cell in the blood is similar to a normal T cell, so they can’t be separated, he explained.
“So if you were to do anything to a normal T cell, you would also be doing it, in theory, to the malignant T cell – in theory, making it resistant to therapy,” he said.
A third obstacle, which has been seen in patients with B-cell malignancies as well, is the inability to harvest enough T cells to generate effective CAR T-cell therapy.
And a fourth obstacle is that T cells from patients with malignancies may not function normally because they have been exposed to prior therapies.
Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues believe these obstacles can be overcome by creating CAR T-cell therapies using T cells derived from healthy donors or cord blood, using gene editing to remove the target antigen and TRAC, and using NT-I7 to enhance the efficacy of these universal, “off-the-shelf” CAR T cells.
The researchers have tested these theories, and achieved successes, in preclinical models. The team is now planning a clinical trial in patients at Washington University. Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues also created a company called WUGEN that will develop the universal CAR T-cell therapies if the initial proof-of-principle trial proves successful.
UCART7
One of the universal CAR T-cell therapies Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues have tested is UCART7, which targets CD7. Dr. DiPersio noted that CD7 is expressed on 98% of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias (T-ALLs), 24% of acute myeloid leukemias, natural killer (NK) cells, and T cells.
The researchers created UCART7 by using CRISPR/Cas9 to delete CD7 and TRAC from allogeneic T cells and following this with lentiviral transduction with a third-generation CD7-CAR. The team found a way to delete both TRAC and CD7 in a single day with 95% efficiency, Dr. DiPersio noted.
“Knocking out CD7 doesn’t seem to have any impact on the expansion or trafficking of these T cells in vivo,” Dr. DiPersio said. “So we think that deleting that target in a normal T cell will not affect its overall ability to kill a target when we put a CAR into those T cells.”
In fact, the researchers’ experiments showed that UCART7 can kill T-ALL cells in vitro and target primary T-ALL in vivo without inducing GVHD (Leukemia. 2018 Sep;32[9]:1970-83.)
UCART2 and NT-I7
Dr. DiPersio and his colleagues have also tested UCART2, an allogeneic CAR T-cell therapy in which CD2 and TRAC are deleted. The therapy targets CD2 because this antigen is expressed on T-ALL and other T-cell and NK-cell malignancies. Experiments showed that UCART2 targets T-cell malignancies, including T-ALL and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, in vitro.
The researchers also tested UCART2 in a mouse model of Sézary syndrome. In these experiments, UCART2 was combined with NT-I7.
NT-I7 enhanced the proliferation, persistence, and tumor killing ability of UCART2. Sézary mice that received UCART2 and NT-I7 had “virtually no tumor burden,” according to researchers, and survived longer than mice treated with UCART2 alone (Blood. 2018;132:340).
Dr. DiPersio noted that there was no cytokine release syndrome because these were immunodeficient mice. However, cytokine release syndrome may be a side effect of NT-I7 in patients as NT-I7 induces rapid expansion of CAR T cells.
Dr. DiPersio reported ownership and investment in WUGEN and Magenta Therapeutics. He also has relationships with Cellworks Group, Tioma Therapeutics, RiverVest Venture Partners, Bioline, Asterias Biotherapeutics, Amphivena Therapeutics, Bluebird Bio, Celgene, Incyte, NeoImuneTech, and MacroGenics.
The Acute Leukemia Forum is organized by Hemedicus, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ALF 2019