User login
Commentary: Concerning PsA treatments and comorbidities, March 2023
With regard to advanced targeted therapies, there is concern about the side effects of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, especially in patients with comorbidities. To address safety concerns with upadacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, Burmester and colleagues conducted an integrated safety analysis of 12 phase 3 trials that included 6991 patients (PsA n = 907; rheumatoid arthritis [RA] n = 3209; ankylosing spondylitis n = 182; and atopic dermatitis n = 2693) who received upadacitinib (15 or 30 mg once daily). Some trials included active comparators; therefore, safety among 1008 patients (RA n = 579; PsA n = 429) who received 40-mg adalimumab every other week and 314 patients with RA who received methotrexate were compared with those treated with upadacitinib. Overall, patients with PsA receiving 15-mg upadacitinib once daily had acceptable rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE; 244.8/100 patient-years [PY]), serious TEAE (11.1/100 PY), TEAE leading to discontinuation (5.4/100 PY), and death (0.8/100 PY). Patients with PsA treated with upadacitinib had higher rates of herpes zoster, nonmelanoma skin cancer, and elevations in creatine phosphokinase when compared with patients treated with adalimumab. Although these results are reassuring to clinicians treating PsA, continued surveillance regarding the risks for venous thrombosis, cardiovascular events, and cancer are required.
In a post hoc analysis of 10 clinical trials that included patients with PsA (n = 783) and psoriasis (n = 3663) who received tofacitinib, Kristensen and colleagues reported that the risk for major adverse cardiac events was higher among patients with PsA and a high 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk vs patients with a low ASCVD risk. The incidence of cancer was highest in patients with PsA and an intermediate 10-year ASCVD risk. Although these studies are reassuring, the assessment and risk stratification of adverse events with JAK inhibitors and therapies in PsA will require longer-term comparative clinical trials as well as an evaluation of observational data from disease registries.
Comorbidities also have an impact on treatment persistence in PsA. Tillett and colleagues conducted a retrospective study including 9057 patients with plaque psoriasis alone or with concomitant PsA who received either ustekinumab or conventional systemic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. They demonstrated that among patients receiving ustekinumab, those with concomitant PsA had a higher comorbidity burden, including diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, and a shorter time to ustekinumab discontinuation when compared with those with psoriasis alone. Secondary failure of advanced therapies is increasingly noted in the management of psoriatic disease. Female sex, depression, previous exposure to biologics, and the presence of comorbidities are important risk factors. Comprehensive management of psoriatic disease should include appropriate management of comorbidities for better long-term treatment persistence and outcomes.
With regard to advanced targeted therapies, there is concern about the side effects of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, especially in patients with comorbidities. To address safety concerns with upadacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, Burmester and colleagues conducted an integrated safety analysis of 12 phase 3 trials that included 6991 patients (PsA n = 907; rheumatoid arthritis [RA] n = 3209; ankylosing spondylitis n = 182; and atopic dermatitis n = 2693) who received upadacitinib (15 or 30 mg once daily). Some trials included active comparators; therefore, safety among 1008 patients (RA n = 579; PsA n = 429) who received 40-mg adalimumab every other week and 314 patients with RA who received methotrexate were compared with those treated with upadacitinib. Overall, patients with PsA receiving 15-mg upadacitinib once daily had acceptable rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE; 244.8/100 patient-years [PY]), serious TEAE (11.1/100 PY), TEAE leading to discontinuation (5.4/100 PY), and death (0.8/100 PY). Patients with PsA treated with upadacitinib had higher rates of herpes zoster, nonmelanoma skin cancer, and elevations in creatine phosphokinase when compared with patients treated with adalimumab. Although these results are reassuring to clinicians treating PsA, continued surveillance regarding the risks for venous thrombosis, cardiovascular events, and cancer are required.
In a post hoc analysis of 10 clinical trials that included patients with PsA (n = 783) and psoriasis (n = 3663) who received tofacitinib, Kristensen and colleagues reported that the risk for major adverse cardiac events was higher among patients with PsA and a high 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk vs patients with a low ASCVD risk. The incidence of cancer was highest in patients with PsA and an intermediate 10-year ASCVD risk. Although these studies are reassuring, the assessment and risk stratification of adverse events with JAK inhibitors and therapies in PsA will require longer-term comparative clinical trials as well as an evaluation of observational data from disease registries.
Comorbidities also have an impact on treatment persistence in PsA. Tillett and colleagues conducted a retrospective study including 9057 patients with plaque psoriasis alone or with concomitant PsA who received either ustekinumab or conventional systemic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. They demonstrated that among patients receiving ustekinumab, those with concomitant PsA had a higher comorbidity burden, including diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, and a shorter time to ustekinumab discontinuation when compared with those with psoriasis alone. Secondary failure of advanced therapies is increasingly noted in the management of psoriatic disease. Female sex, depression, previous exposure to biologics, and the presence of comorbidities are important risk factors. Comprehensive management of psoriatic disease should include appropriate management of comorbidities for better long-term treatment persistence and outcomes.
With regard to advanced targeted therapies, there is concern about the side effects of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, especially in patients with comorbidities. To address safety concerns with upadacitinib, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, Burmester and colleagues conducted an integrated safety analysis of 12 phase 3 trials that included 6991 patients (PsA n = 907; rheumatoid arthritis [RA] n = 3209; ankylosing spondylitis n = 182; and atopic dermatitis n = 2693) who received upadacitinib (15 or 30 mg once daily). Some trials included active comparators; therefore, safety among 1008 patients (RA n = 579; PsA n = 429) who received 40-mg adalimumab every other week and 314 patients with RA who received methotrexate were compared with those treated with upadacitinib. Overall, patients with PsA receiving 15-mg upadacitinib once daily had acceptable rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE; 244.8/100 patient-years [PY]), serious TEAE (11.1/100 PY), TEAE leading to discontinuation (5.4/100 PY), and death (0.8/100 PY). Patients with PsA treated with upadacitinib had higher rates of herpes zoster, nonmelanoma skin cancer, and elevations in creatine phosphokinase when compared with patients treated with adalimumab. Although these results are reassuring to clinicians treating PsA, continued surveillance regarding the risks for venous thrombosis, cardiovascular events, and cancer are required.
In a post hoc analysis of 10 clinical trials that included patients with PsA (n = 783) and psoriasis (n = 3663) who received tofacitinib, Kristensen and colleagues reported that the risk for major adverse cardiac events was higher among patients with PsA and a high 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk vs patients with a low ASCVD risk. The incidence of cancer was highest in patients with PsA and an intermediate 10-year ASCVD risk. Although these studies are reassuring, the assessment and risk stratification of adverse events with JAK inhibitors and therapies in PsA will require longer-term comparative clinical trials as well as an evaluation of observational data from disease registries.
Comorbidities also have an impact on treatment persistence in PsA. Tillett and colleagues conducted a retrospective study including 9057 patients with plaque psoriasis alone or with concomitant PsA who received either ustekinumab or conventional systemic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. They demonstrated that among patients receiving ustekinumab, those with concomitant PsA had a higher comorbidity burden, including diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, and a shorter time to ustekinumab discontinuation when compared with those with psoriasis alone. Secondary failure of advanced therapies is increasingly noted in the management of psoriatic disease. Female sex, depression, previous exposure to biologics, and the presence of comorbidities are important risk factors. Comprehensive management of psoriatic disease should include appropriate management of comorbidities for better long-term treatment persistence and outcomes.
Non-Surgical Treatment of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding From Fibroids: A New Paradigm
GnRH antagonists with estrogen/progesterone are promising new uterine-sparing options for treating uterine fibroids. Two experts review data from two recent clinical trials to bring you up to speed on the benefits and risks of this treatment approach.
After reading this short article, you have an opportunity to earn 1.0 CME credits.
GnRH antagonists with estrogen/progesterone are promising new uterine-sparing options for treating uterine fibroids. Two experts review data from two recent clinical trials to bring you up to speed on the benefits and risks of this treatment approach.
After reading this short article, you have an opportunity to earn 1.0 CME credits.
GnRH antagonists with estrogen/progesterone are promising new uterine-sparing options for treating uterine fibroids. Two experts review data from two recent clinical trials to bring you up to speed on the benefits and risks of this treatment approach.
After reading this short article, you have an opportunity to earn 1.0 CME credits.
The Cognition Self-Assessment Rating Scale for patients with schizophrenia
Cognition represents the most important function of the human brain and the essence of the mind. Cognitive functions such as memory, learning, comprehension, processing speed, attention, planning, and problem-solving are the best indicators of the status of brain health.
Many psychiatric brain disorders are associated with cognitive impairments. Decades of extensive research have documented that the most severe cognitive deficits occur in schizophrenia. No wonder Emil Kraepelin coined the term “dementia praecox,” which means premature dementia (in youth)1 for this neuropsychiatric brain disorder. This condition was later renamed schizophrenia by Eugen Bleuler,2 who regarded it primarily as a thought disorder, with splitting of associations (not split personality, as misinterpreted by many in the public). Interestingly, a century ago both of those early masters of psychiatry de-emphasized psychotic symptoms (delusions and hallucinations), regarding them as “supplemental symptoms.”3 Yet for the next 100 years, clinicians overemphasized psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia and overlooked the more disabling cognitive impairment and negative symptoms, referred to as Bleuler’s 4 A’s—Associations disruption, Ambivalence, Affect pathology, and Avolition—symptoms that persist even after the psychotic symptoms are successfully treated.3
Most contemporary researchers regard cognitive impairment as the “core” feature of schizophrenia.4 The justification of this view is that cognitive deficits are detected in childhood and early adolescence (by age 13),5 long before the appearance of psychotic symptoms, and many studies have confirmed that cognitive deficits are the primary cause of functional disability and unemployment of patients with schizophrenia. Cognitive dysfunction is also found in milder forms in the parents and siblings of patients with schizophrenia,6 and is thus considered an “endophenotype” of the illness.
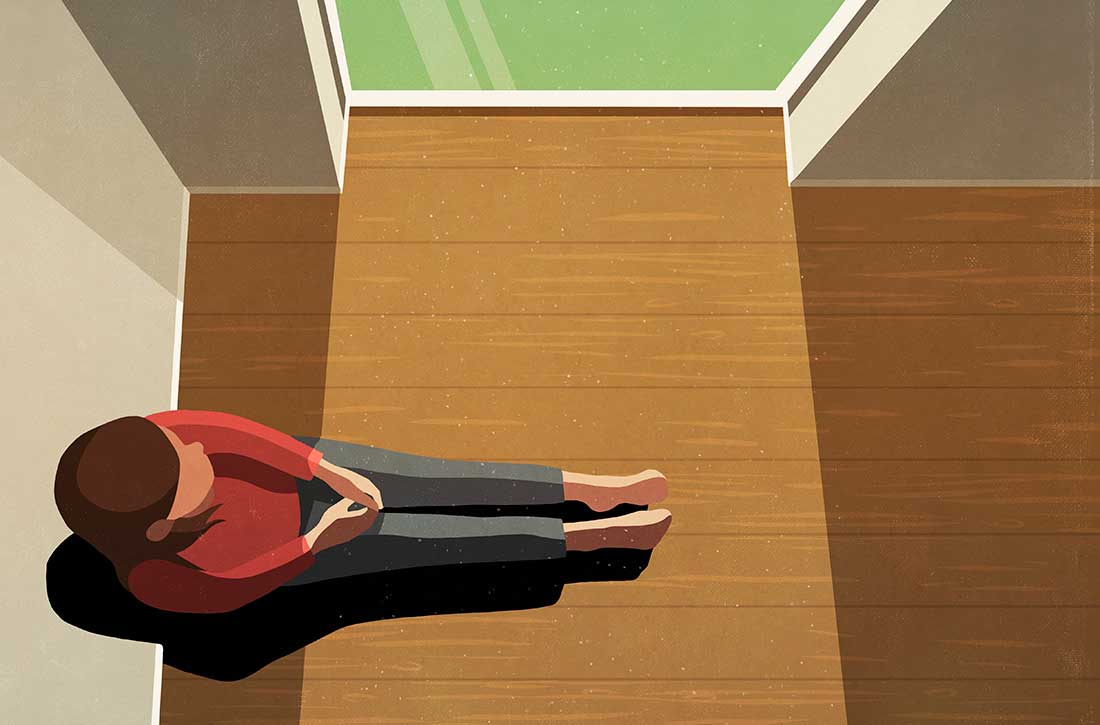
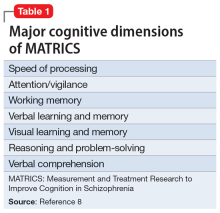
Because of its centrality, cognition has emerged as a major focus of schizophrenia research over the past 20 years. Multiple stakeholders (academic investigators, the National Institute of Mental Health, and the FDA) have collaborated to develop a standard measurement for cognition in schizophrenia. The project culminated in what was labeled MATRICS (Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia).7 The MATRICS settled on a battery of 7 major cognitive functions that are often impaired in individuals with schizophrenia (Table 18). Most contemporary researchers have adopted MATRICS in their studies, which facilitates replication to confirm research findings.
Measuring cognition in patients with schizophrenia is extremely important, as critical as measuring fasting glucose in patients with diabetes or blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Measuring the extent of impairment or nonimpairment across various cognitive tests can help with vocational rehabilitation, to place a patient in a job consistent with their level of cognitive functioning. In addition, once medications are developed and approved for cognitive impairments in schizophrenia, measuring cognition will be necessary to gauge the degree of improvement.
Currently, few psychiatric practitioners measure cognition in their patients. This is perplexing because cognitive measurement is important for confirming the diagnosis of schizophrenia in first-episode psychosis, or distinguishing it from other psychotic disorders (such as drug-induced psychosis, brief reactive psychosis, or delusional disorders) that do not have severe cognitive deficits.
The scores of various cognitive functions in individuals with schizophrenia range from .75 to 2.0 SD below the performance of the general population (matched for age and gender).9 This translates to dismally low percentiles of 2% and 24%. It is essential that all clinicians measure cognition in every patient with psychotic symptoms. It can be argued that cognition should even be measured in other psychiatric patients because cognitive deficits have been well documented in bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and other disorders, albeit not as severe as in schizophrenia, and these deficits usually correlate with the patient’s vocational and social functioning.
Continue to: So how is cognition measured...
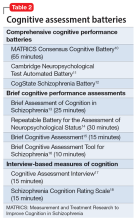
So how is cognition measured, and can clinicians incorporate cognitive batteries in their practices? The most logical answer is to refer the patient to a board-certified neuropsychologist. These specialists are well-trained in assessing cognitive functions, and their evaluations generally are covered by health insurance. They use various validated cognitive batteries. Table 210-18 lists the currently recognized cognitive assessments and how much time they require. Psychiatrists can have nurses or medical assistants administer a brief cognitive test.
C-SARS: A self-rated cognition scale
Patient self-rating can provide psychiatric clinicians with valuable information, and is a time-saver. The widely used Patient Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9)19 is an excellent example of a self-rating scale for depression that enables patients to recognize and rate their depressive symptoms. It immediately informs the clinician how depressed their patient is and whether the severity of the depression has improved from the previous visit, which can indicate whether the prescribed medication is working. Based on the PHQ-9, which I regularly use—and recognizing that there is no cognition counterpart and that almost all clinicians could use a practical method of measuring their patients’ cognitive function—I developed an instrument called the Cognition Self-Assessment Rating Scale (C-SARS) (Table 3). The C-SARS can be completed online at https://curesz.org/csars/ and patients will be emailed the results within a minute. The C-SARS can be completed by the patient (with the help of their family or caregiver, if necessary, who observe the patient’s daily functioning, which corresponds to their cognition). The main purpose of the C-SARS is to inform the clinician about serious cognitive dysfunction in their patients, which should instigate a referral for formal neurocognitive assessment by a neuropsychology expert.

The items on the C-SARS reflect how well the patient is performing routine daily functions, each of which correlates with one of the cognitive domains of the MATRICS battery. Table 3 shows the 12 items in the C-SARS, their scoring, and their clinical implications (ie, when the results require referral for formal neurocognitive testing). In the future, when the FDA approves medications for addressing cognitive impairment (and several molecules are currently undergoing clinical trials), clinicians will be able to gauge a patient’s response to such treatments using the C-SARS and formal testing as needed. It may take several weeks to detect a significant reversal of cognitive deficits, but doing so would address a major unmet need in schizophrenia and may speed up vocational rehabilitation. The C-SARS also contains 2 items related to social cognition (items 11 and 12), which is also impaired in schizophrenia.20 Future medications that improve social cognition in addition to neurocognition may also lead to improved social functioning among patients with schizophrenia.
In conclusion, the C-SARS, which needs to be validated in controlled studies, is the first cognition self-rating scale for schizophrenia and may be useful for other major psychiatric disorders. It will be a substantial time-saver for clinicians and will facilitate the routine incorporation of the cognitive assessment of patients with psychotic symptoms to help with the differential diagnosis of schizophrenia vs other psychotic disorders. Measuring cognitive functions is a vital step towards the valid diagnosis and treatment of this major clinical challenge in schizophrenia and improving patient outcomes in this serious psychiatric brain syndrome, in which up to 98% of patients have cognitive impairment across several domains.21
1. Kraepelin E. Dementia Praecox and Paraphrenia. Barth; 1904.
2. Bleuler E. Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias. International Universities Press; 1950.
3. Nasrallah HA, Smeltzer DJ. Contemporary Diagnosis and Management of the Patient with Schizophrenia. Handbooks in Health Care Company; 2011.
4. Kahn RS, Keefe RSE. Schizophrenia is a cognitive illness: time for a change in focus. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(10):1107-1112.
5. van Oel CJ, Sitskoorn MM, Cremer MPM, et al. School performance as a premorbid marker for schizophrenia: a twin study. Schizophr Bull. 2002;28(3):401-414.
6. Jameson KG, Nasrallah HA, Northern TG, et al. Executive function in first-degree relatives of persons with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of controlled studies. Asian J Psychiatry 2011;4(2):96-99.
7. Marder SR, Fenton W. Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia: NIMH MATRICS initiative to support the development of agents for improving cognition in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):5-9.
8. Neuchterlein KH, Barch DM, Gold JM, et al. Identification of separable cognitive factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):29-39.
9. Heinrich RW, Zakzanis KK. Neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of the evidence. Neuropsychology. 1998;12(3):426-445.
10. Nuechterlein KH, Green MF. MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB). 3rd ed. MATRICS Assessment Inc.; 2016.
11. Robins TW, James M, Owen AM, et al. Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB): a factor analytic study of a large sample of normal elderly volunteers. Dementia. 1994;5(5):266-281.
12. Pietrzak RH, Olver J, Norman T, et al. A comparison of the CogState Schizophrenia Battery and the Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia (MATRICS) battery in assessing cognitive impairment in chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2009;31(7):848-859.
13. Keefe RSE, Goldberg TE, Harvey PD, et al. The Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia: reliability, sensitivity and comparison with a standard neurocognitive battery. Schizophr Res. 2004;68(2-3):283-297.
14. Randolph C, Tierney MC, Mohr E, et al. The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS): preliminary clinical validity. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1998;20(3):310-319.
15. Velligan DI, DiCocco M, Bow-Thomas CC, et al. A brief cognitive assessment for use with schizophrenia patients in community clinics. Schizophr Res. 2004;71(2-3):272-283.
16. Huford IM, Marder SR, Keefe RSE, et al. A brief cognitive assessment tool for schizophrenia: construction of a tool for clinicians. Schizophr Bull. 2011;37(3):538-545.
17. Ventura J, Reise SP, Keefe RSE, et al. The Cognitive Assessment Interview (CAI): reliability and validity of a brief interview-based measure of cognition. Schizophr Bull. 2013;39(3):583-591.
18. Keefe RSE, Poe M, Walker TM, et al. The Schizophrenia Cognition Rating Scale: an interview-based assessment and its relationship to cognition, real-world functioning, and functional capacity. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(3):426-432.
19. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen Intern Med. 2001;16(9):606-613.
20. Green MF, Horan WP, Lee J. Nonsocial and social cognition in schizophrenia: current evidence and future directions. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):146-161.
21. Keefe RS, Eesley CE, Poe MP. Defining a cognitive function decrement in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57(6):688-691.
Cognition represents the most important function of the human brain and the essence of the mind. Cognitive functions such as memory, learning, comprehension, processing speed, attention, planning, and problem-solving are the best indicators of the status of brain health.
Many psychiatric brain disorders are associated with cognitive impairments. Decades of extensive research have documented that the most severe cognitive deficits occur in schizophrenia. No wonder Emil Kraepelin coined the term “dementia praecox,” which means premature dementia (in youth)1 for this neuropsychiatric brain disorder. This condition was later renamed schizophrenia by Eugen Bleuler,2 who regarded it primarily as a thought disorder, with splitting of associations (not split personality, as misinterpreted by many in the public). Interestingly, a century ago both of those early masters of psychiatry de-emphasized psychotic symptoms (delusions and hallucinations), regarding them as “supplemental symptoms.”3 Yet for the next 100 years, clinicians overemphasized psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia and overlooked the more disabling cognitive impairment and negative symptoms, referred to as Bleuler’s 4 A’s—Associations disruption, Ambivalence, Affect pathology, and Avolition—symptoms that persist even after the psychotic symptoms are successfully treated.3
Most contemporary researchers regard cognitive impairment as the “core” feature of schizophrenia.4 The justification of this view is that cognitive deficits are detected in childhood and early adolescence (by age 13),5 long before the appearance of psychotic symptoms, and many studies have confirmed that cognitive deficits are the primary cause of functional disability and unemployment of patients with schizophrenia. Cognitive dysfunction is also found in milder forms in the parents and siblings of patients with schizophrenia,6 and is thus considered an “endophenotype” of the illness.
Because of its centrality, cognition has emerged as a major focus of schizophrenia research over the past 20 years. Multiple stakeholders (academic investigators, the National Institute of Mental Health, and the FDA) have collaborated to develop a standard measurement for cognition in schizophrenia. The project culminated in what was labeled MATRICS (Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia).7 The MATRICS settled on a battery of 7 major cognitive functions that are often impaired in individuals with schizophrenia (Table 18). Most contemporary researchers have adopted MATRICS in their studies, which facilitates replication to confirm research findings.
Measuring cognition in patients with schizophrenia is extremely important, as critical as measuring fasting glucose in patients with diabetes or blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Measuring the extent of impairment or nonimpairment across various cognitive tests can help with vocational rehabilitation, to place a patient in a job consistent with their level of cognitive functioning. In addition, once medications are developed and approved for cognitive impairments in schizophrenia, measuring cognition will be necessary to gauge the degree of improvement.
Currently, few psychiatric practitioners measure cognition in their patients. This is perplexing because cognitive measurement is important for confirming the diagnosis of schizophrenia in first-episode psychosis, or distinguishing it from other psychotic disorders (such as drug-induced psychosis, brief reactive psychosis, or delusional disorders) that do not have severe cognitive deficits.
The scores of various cognitive functions in individuals with schizophrenia range from .75 to 2.0 SD below the performance of the general population (matched for age and gender).9 This translates to dismally low percentiles of 2% and 24%. It is essential that all clinicians measure cognition in every patient with psychotic symptoms. It can be argued that cognition should even be measured in other psychiatric patients because cognitive deficits have been well documented in bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and other disorders, albeit not as severe as in schizophrenia, and these deficits usually correlate with the patient’s vocational and social functioning.
Continue to: So how is cognition measured...
So how is cognition measured, and can clinicians incorporate cognitive batteries in their practices? The most logical answer is to refer the patient to a board-certified neuropsychologist. These specialists are well-trained in assessing cognitive functions, and their evaluations generally are covered by health insurance. They use various validated cognitive batteries. Table 210-18 lists the currently recognized cognitive assessments and how much time they require. Psychiatrists can have nurses or medical assistants administer a brief cognitive test.
C-SARS: A self-rated cognition scale
Patient self-rating can provide psychiatric clinicians with valuable information, and is a time-saver. The widely used Patient Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9)19 is an excellent example of a self-rating scale for depression that enables patients to recognize and rate their depressive symptoms. It immediately informs the clinician how depressed their patient is and whether the severity of the depression has improved from the previous visit, which can indicate whether the prescribed medication is working. Based on the PHQ-9, which I regularly use—and recognizing that there is no cognition counterpart and that almost all clinicians could use a practical method of measuring their patients’ cognitive function—I developed an instrument called the Cognition Self-Assessment Rating Scale (C-SARS) (Table 3). The C-SARS can be completed online at https://curesz.org/csars/ and patients will be emailed the results within a minute. The C-SARS can be completed by the patient (with the help of their family or caregiver, if necessary, who observe the patient’s daily functioning, which corresponds to their cognition). The main purpose of the C-SARS is to inform the clinician about serious cognitive dysfunction in their patients, which should instigate a referral for formal neurocognitive assessment by a neuropsychology expert.

The items on the C-SARS reflect how well the patient is performing routine daily functions, each of which correlates with one of the cognitive domains of the MATRICS battery. Table 3 shows the 12 items in the C-SARS, their scoring, and their clinical implications (ie, when the results require referral for formal neurocognitive testing). In the future, when the FDA approves medications for addressing cognitive impairment (and several molecules are currently undergoing clinical trials), clinicians will be able to gauge a patient’s response to such treatments using the C-SARS and formal testing as needed. It may take several weeks to detect a significant reversal of cognitive deficits, but doing so would address a major unmet need in schizophrenia and may speed up vocational rehabilitation. The C-SARS also contains 2 items related to social cognition (items 11 and 12), which is also impaired in schizophrenia.20 Future medications that improve social cognition in addition to neurocognition may also lead to improved social functioning among patients with schizophrenia.
In conclusion, the C-SARS, which needs to be validated in controlled studies, is the first cognition self-rating scale for schizophrenia and may be useful for other major psychiatric disorders. It will be a substantial time-saver for clinicians and will facilitate the routine incorporation of the cognitive assessment of patients with psychotic symptoms to help with the differential diagnosis of schizophrenia vs other psychotic disorders. Measuring cognitive functions is a vital step towards the valid diagnosis and treatment of this major clinical challenge in schizophrenia and improving patient outcomes in this serious psychiatric brain syndrome, in which up to 98% of patients have cognitive impairment across several domains.21
Cognition represents the most important function of the human brain and the essence of the mind. Cognitive functions such as memory, learning, comprehension, processing speed, attention, planning, and problem-solving are the best indicators of the status of brain health.
Many psychiatric brain disorders are associated with cognitive impairments. Decades of extensive research have documented that the most severe cognitive deficits occur in schizophrenia. No wonder Emil Kraepelin coined the term “dementia praecox,” which means premature dementia (in youth)1 for this neuropsychiatric brain disorder. This condition was later renamed schizophrenia by Eugen Bleuler,2 who regarded it primarily as a thought disorder, with splitting of associations (not split personality, as misinterpreted by many in the public). Interestingly, a century ago both of those early masters of psychiatry de-emphasized psychotic symptoms (delusions and hallucinations), regarding them as “supplemental symptoms.”3 Yet for the next 100 years, clinicians overemphasized psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia and overlooked the more disabling cognitive impairment and negative symptoms, referred to as Bleuler’s 4 A’s—Associations disruption, Ambivalence, Affect pathology, and Avolition—symptoms that persist even after the psychotic symptoms are successfully treated.3
Most contemporary researchers regard cognitive impairment as the “core” feature of schizophrenia.4 The justification of this view is that cognitive deficits are detected in childhood and early adolescence (by age 13),5 long before the appearance of psychotic symptoms, and many studies have confirmed that cognitive deficits are the primary cause of functional disability and unemployment of patients with schizophrenia. Cognitive dysfunction is also found in milder forms in the parents and siblings of patients with schizophrenia,6 and is thus considered an “endophenotype” of the illness.
Because of its centrality, cognition has emerged as a major focus of schizophrenia research over the past 20 years. Multiple stakeholders (academic investigators, the National Institute of Mental Health, and the FDA) have collaborated to develop a standard measurement for cognition in schizophrenia. The project culminated in what was labeled MATRICS (Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia).7 The MATRICS settled on a battery of 7 major cognitive functions that are often impaired in individuals with schizophrenia (Table 18). Most contemporary researchers have adopted MATRICS in their studies, which facilitates replication to confirm research findings.
Measuring cognition in patients with schizophrenia is extremely important, as critical as measuring fasting glucose in patients with diabetes or blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Measuring the extent of impairment or nonimpairment across various cognitive tests can help with vocational rehabilitation, to place a patient in a job consistent with their level of cognitive functioning. In addition, once medications are developed and approved for cognitive impairments in schizophrenia, measuring cognition will be necessary to gauge the degree of improvement.
Currently, few psychiatric practitioners measure cognition in their patients. This is perplexing because cognitive measurement is important for confirming the diagnosis of schizophrenia in first-episode psychosis, or distinguishing it from other psychotic disorders (such as drug-induced psychosis, brief reactive psychosis, or delusional disorders) that do not have severe cognitive deficits.
The scores of various cognitive functions in individuals with schizophrenia range from .75 to 2.0 SD below the performance of the general population (matched for age and gender).9 This translates to dismally low percentiles of 2% and 24%. It is essential that all clinicians measure cognition in every patient with psychotic symptoms. It can be argued that cognition should even be measured in other psychiatric patients because cognitive deficits have been well documented in bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and other disorders, albeit not as severe as in schizophrenia, and these deficits usually correlate with the patient’s vocational and social functioning.
Continue to: So how is cognition measured...
So how is cognition measured, and can clinicians incorporate cognitive batteries in their practices? The most logical answer is to refer the patient to a board-certified neuropsychologist. These specialists are well-trained in assessing cognitive functions, and their evaluations generally are covered by health insurance. They use various validated cognitive batteries. Table 210-18 lists the currently recognized cognitive assessments and how much time they require. Psychiatrists can have nurses or medical assistants administer a brief cognitive test.
C-SARS: A self-rated cognition scale
Patient self-rating can provide psychiatric clinicians with valuable information, and is a time-saver. The widely used Patient Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9)19 is an excellent example of a self-rating scale for depression that enables patients to recognize and rate their depressive symptoms. It immediately informs the clinician how depressed their patient is and whether the severity of the depression has improved from the previous visit, which can indicate whether the prescribed medication is working. Based on the PHQ-9, which I regularly use—and recognizing that there is no cognition counterpart and that almost all clinicians could use a practical method of measuring their patients’ cognitive function—I developed an instrument called the Cognition Self-Assessment Rating Scale (C-SARS) (Table 3). The C-SARS can be completed online at https://curesz.org/csars/ and patients will be emailed the results within a minute. The C-SARS can be completed by the patient (with the help of their family or caregiver, if necessary, who observe the patient’s daily functioning, which corresponds to their cognition). The main purpose of the C-SARS is to inform the clinician about serious cognitive dysfunction in their patients, which should instigate a referral for formal neurocognitive assessment by a neuropsychology expert.

The items on the C-SARS reflect how well the patient is performing routine daily functions, each of which correlates with one of the cognitive domains of the MATRICS battery. Table 3 shows the 12 items in the C-SARS, their scoring, and their clinical implications (ie, when the results require referral for formal neurocognitive testing). In the future, when the FDA approves medications for addressing cognitive impairment (and several molecules are currently undergoing clinical trials), clinicians will be able to gauge a patient’s response to such treatments using the C-SARS and formal testing as needed. It may take several weeks to detect a significant reversal of cognitive deficits, but doing so would address a major unmet need in schizophrenia and may speed up vocational rehabilitation. The C-SARS also contains 2 items related to social cognition (items 11 and 12), which is also impaired in schizophrenia.20 Future medications that improve social cognition in addition to neurocognition may also lead to improved social functioning among patients with schizophrenia.
In conclusion, the C-SARS, which needs to be validated in controlled studies, is the first cognition self-rating scale for schizophrenia and may be useful for other major psychiatric disorders. It will be a substantial time-saver for clinicians and will facilitate the routine incorporation of the cognitive assessment of patients with psychotic symptoms to help with the differential diagnosis of schizophrenia vs other psychotic disorders. Measuring cognitive functions is a vital step towards the valid diagnosis and treatment of this major clinical challenge in schizophrenia and improving patient outcomes in this serious psychiatric brain syndrome, in which up to 98% of patients have cognitive impairment across several domains.21
1. Kraepelin E. Dementia Praecox and Paraphrenia. Barth; 1904.
2. Bleuler E. Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias. International Universities Press; 1950.
3. Nasrallah HA, Smeltzer DJ. Contemporary Diagnosis and Management of the Patient with Schizophrenia. Handbooks in Health Care Company; 2011.
4. Kahn RS, Keefe RSE. Schizophrenia is a cognitive illness: time for a change in focus. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(10):1107-1112.
5. van Oel CJ, Sitskoorn MM, Cremer MPM, et al. School performance as a premorbid marker for schizophrenia: a twin study. Schizophr Bull. 2002;28(3):401-414.
6. Jameson KG, Nasrallah HA, Northern TG, et al. Executive function in first-degree relatives of persons with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of controlled studies. Asian J Psychiatry 2011;4(2):96-99.
7. Marder SR, Fenton W. Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia: NIMH MATRICS initiative to support the development of agents for improving cognition in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):5-9.
8. Neuchterlein KH, Barch DM, Gold JM, et al. Identification of separable cognitive factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):29-39.
9. Heinrich RW, Zakzanis KK. Neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of the evidence. Neuropsychology. 1998;12(3):426-445.
10. Nuechterlein KH, Green MF. MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB). 3rd ed. MATRICS Assessment Inc.; 2016.
11. Robins TW, James M, Owen AM, et al. Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB): a factor analytic study of a large sample of normal elderly volunteers. Dementia. 1994;5(5):266-281.
12. Pietrzak RH, Olver J, Norman T, et al. A comparison of the CogState Schizophrenia Battery and the Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia (MATRICS) battery in assessing cognitive impairment in chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2009;31(7):848-859.
13. Keefe RSE, Goldberg TE, Harvey PD, et al. The Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia: reliability, sensitivity and comparison with a standard neurocognitive battery. Schizophr Res. 2004;68(2-3):283-297.
14. Randolph C, Tierney MC, Mohr E, et al. The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS): preliminary clinical validity. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1998;20(3):310-319.
15. Velligan DI, DiCocco M, Bow-Thomas CC, et al. A brief cognitive assessment for use with schizophrenia patients in community clinics. Schizophr Res. 2004;71(2-3):272-283.
16. Huford IM, Marder SR, Keefe RSE, et al. A brief cognitive assessment tool for schizophrenia: construction of a tool for clinicians. Schizophr Bull. 2011;37(3):538-545.
17. Ventura J, Reise SP, Keefe RSE, et al. The Cognitive Assessment Interview (CAI): reliability and validity of a brief interview-based measure of cognition. Schizophr Bull. 2013;39(3):583-591.
18. Keefe RSE, Poe M, Walker TM, et al. The Schizophrenia Cognition Rating Scale: an interview-based assessment and its relationship to cognition, real-world functioning, and functional capacity. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(3):426-432.
19. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen Intern Med. 2001;16(9):606-613.
20. Green MF, Horan WP, Lee J. Nonsocial and social cognition in schizophrenia: current evidence and future directions. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):146-161.
21. Keefe RS, Eesley CE, Poe MP. Defining a cognitive function decrement in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57(6):688-691.
1. Kraepelin E. Dementia Praecox and Paraphrenia. Barth; 1904.
2. Bleuler E. Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias. International Universities Press; 1950.
3. Nasrallah HA, Smeltzer DJ. Contemporary Diagnosis and Management of the Patient with Schizophrenia. Handbooks in Health Care Company; 2011.
4. Kahn RS, Keefe RSE. Schizophrenia is a cognitive illness: time for a change in focus. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(10):1107-1112.
5. van Oel CJ, Sitskoorn MM, Cremer MPM, et al. School performance as a premorbid marker for schizophrenia: a twin study. Schizophr Bull. 2002;28(3):401-414.
6. Jameson KG, Nasrallah HA, Northern TG, et al. Executive function in first-degree relatives of persons with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of controlled studies. Asian J Psychiatry 2011;4(2):96-99.
7. Marder SR, Fenton W. Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia: NIMH MATRICS initiative to support the development of agents for improving cognition in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):5-9.
8. Neuchterlein KH, Barch DM, Gold JM, et al. Identification of separable cognitive factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):29-39.
9. Heinrich RW, Zakzanis KK. Neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of the evidence. Neuropsychology. 1998;12(3):426-445.
10. Nuechterlein KH, Green MF. MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB). 3rd ed. MATRICS Assessment Inc.; 2016.
11. Robins TW, James M, Owen AM, et al. Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB): a factor analytic study of a large sample of normal elderly volunteers. Dementia. 1994;5(5):266-281.
12. Pietrzak RH, Olver J, Norman T, et al. A comparison of the CogState Schizophrenia Battery and the Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia (MATRICS) battery in assessing cognitive impairment in chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2009;31(7):848-859.
13. Keefe RSE, Goldberg TE, Harvey PD, et al. The Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia: reliability, sensitivity and comparison with a standard neurocognitive battery. Schizophr Res. 2004;68(2-3):283-297.
14. Randolph C, Tierney MC, Mohr E, et al. The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS): preliminary clinical validity. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1998;20(3):310-319.
15. Velligan DI, DiCocco M, Bow-Thomas CC, et al. A brief cognitive assessment for use with schizophrenia patients in community clinics. Schizophr Res. 2004;71(2-3):272-283.
16. Huford IM, Marder SR, Keefe RSE, et al. A brief cognitive assessment tool for schizophrenia: construction of a tool for clinicians. Schizophr Bull. 2011;37(3):538-545.
17. Ventura J, Reise SP, Keefe RSE, et al. The Cognitive Assessment Interview (CAI): reliability and validity of a brief interview-based measure of cognition. Schizophr Bull. 2013;39(3):583-591.
18. Keefe RSE, Poe M, Walker TM, et al. The Schizophrenia Cognition Rating Scale: an interview-based assessment and its relationship to cognition, real-world functioning, and functional capacity. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163(3):426-432.
19. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen Intern Med. 2001;16(9):606-613.
20. Green MF, Horan WP, Lee J. Nonsocial and social cognition in schizophrenia: current evidence and future directions. World Psychiatry. 2019;18(2):146-161.
21. Keefe RS, Eesley CE, Poe MP. Defining a cognitive function decrement in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57(6):688-691.
Violaceous Nodules on the Leg in a Patient with HIV
The Diagnosis: Plasmablastic Lymphoma
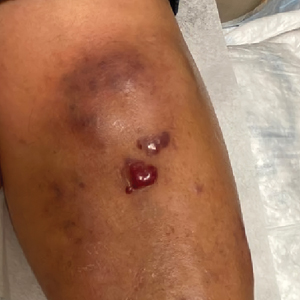
A punch biopsy of one of the leg nodules with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed sheets of medium to large cells with plasmacytic differentiation (Figure, A and B). Immunohistochemistry showed CD79, epithelial membrane antigen, multiple myeloma 1, and CD138 positivity, as well as CD-19 negativity and positive staining on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (Figure, C). Ki-67 stained greater than 90% of the neoplastic cells. Neoplastic cells were found to be λ restricted on κ and λ immunohistochemistry. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD3, and CD20 stains were negative. Subsequent fluorescent in situ hybridization was positive for MYC/immunoglobulin heavy chain (MYC/IGH) rearrangement t(8;14), confirming a diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL).
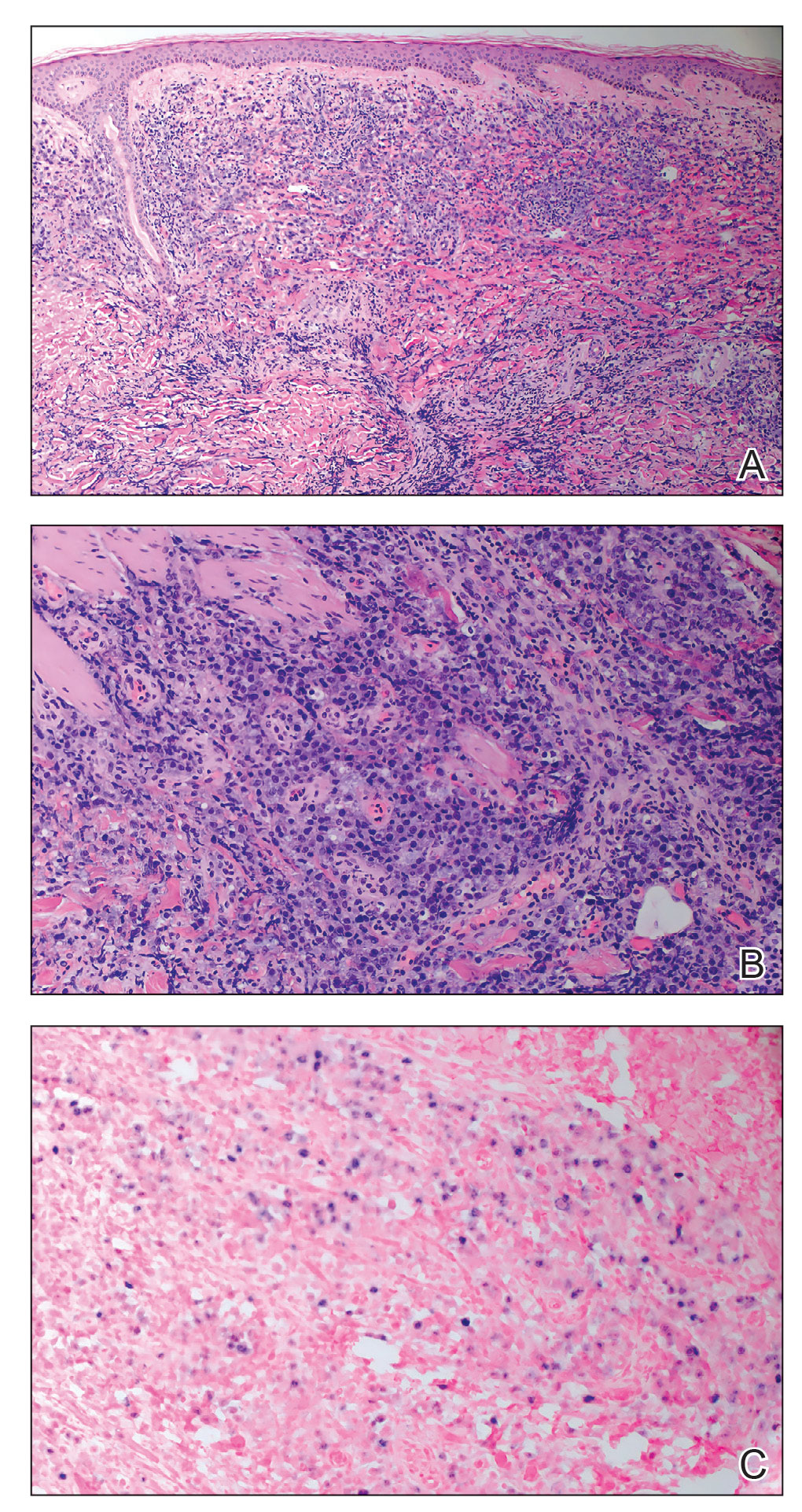
A bone marrow biopsy revealed normocellular bone marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis and no morphologic, immunophenotypic, or fluorescent in situ hybridization evidence of plasmablastic lymphoma or other pathology in the bone marrow. Our patient was started on hyper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin hydrochloride, dexamethasone) chemotherapy and was doing well with plans for a fourth course of chemotherapy. There is no standardized treatment course for cutaneous PBL, though excision with adjunctive chemotherapy treatment commonly has been reported in the literature.1
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare and aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with EBV infection that compromises approximately 2% to 3% of all HIV-related lymphomas.1,2 It frequently is associated with immunosuppression in patients with HIV or in transplant recipients on immunosuppression; however, it has been reported in immunocompetent individuals such as elderly patients.2 Plasmablastic lymphoma most commonly presents on the buccal mucosa but also can affect the gastrointestinal tract and occasionally has cutaneous manifestations.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations of PBL range from erythematous infiltrated plaques to ulcerated nodules presenting in an array of colors from flesh colored to violaceous.2 Primary cutaneous lesions can be seen on the legs, as in our patient.
Histopathologic examination reveals sheets of plasmablasts or large cells with eccentric nuclei and abundant basophilic cytoplasm.1 Plasmablastic lymphoma frequently is positive for mature B-cell markers such as CD38, CD138, multiple myeloma 1, and B lymphocyte–induced maturation protein 1.2,3 Uncommonly, PBL expresses paired box protein Pax-5 and CD20 markers.3 Although pathogenesis is poorly understood, it has been speculated that EBV infection is a common pathogenic factor. Epstein-Barr virus positivity has been noted in 60% of cases.2
Plasmablastic lymphoma and other malignant plasma cell processes such as plasmablastic myeloma (PBM) are morphologically similar. Proliferation of plasmablasts with rare plasmacytic cells is common in PBL, while plasmacytic cells are predominant in PBM. MYC rearrangement/ immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement t(8;14) was used to differentiate PBL from PBM in our patient; however, more cases of PBM with MYC/IGH rearrangement t(8;14) have been reported, making it an unreliable differentiating factor.4 A detailed clinical, pathologic, and genetic survey remains necessary for confirmatory diagnosis of PBL. Compared to other malignant plasma cell processes, PBL more commonly is seen in immunocompromised patients or those with HIV, such as our patient. Additionally, EBV testing is more likely to be positive in patients with PBL, further supporting this diagnosis in our patient.4
Presentations of bacillary angiomatosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and cutaneous lymphoma may be clinically similar; therefore, careful immunohistopathologic differentiation is necessary. Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative disorder that develops from HHV-8 infection and commonly is associated with HIV. It presents as painless vascular lesions in a range of colors with typical progression from patch to plaque to nodules, frequently on the lower extremities. Histologically, admixtures of bland spindle cells, slitlike small vessel proliferation, and lymphocytic infiltration are typical. Neoplastic vessels lack basement membrane zones, resulting in microhemorrhages and hemosiderin deposition. Neoplastic vessels label with CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers in addition to HHV-8 antibodies, which is highly specific for Kaposi sarcoma and differentiates it from PBL.5
Bacillary angiomatosis is an infectious neovascular proliferation characterized by papular lesions that may resemble the lesions of PBL. Mixed cell infiltration in inflammatory cells with clumping of granular material is characteristic. Under Warthin-Starry staining, the granular material is abundant in gram-negative rods representing Bartonella species, which is the implicated infectious agent in bacillary angiomatosis.
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is the most common CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder and also may present with exophytic nodules. The etiology of LyP remains unknown, but it is suspected that overexpression of CD30 plays a role. Lymphomatoid papulosis presents as red-violaceous papules and nodules in various stages of healing. Although variable histology among types of LyP exists, CD30+ T-cell lymphocytes remain the hallmark of LyP. Type A LyP, which accounts for 80% of LyP cases, reveals CD4+ and CD30+ cells scattered among neutrophils, eosinophils, and small lymphocytes.5 Lymphomatoid papulosis typically is self-healing, recurrent, and carries an excellent prognosis.
Plasmablastic lymphoma remains a rare and aggressive type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that can have primary cutaneous manifestations. It is prudent to consider PBL in the differential diagnosis of nodular lower extremity lesions, especially in immunosuppressed patients.
- Jambusaria A, Shafer D, Wu H, et al. Cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:676-678.
- Marques SA, Abbade LP, Guiotoku MM, et al. Primary cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma revealing clinically unsuspected HIV infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:507-509.
- Bhatt R, Desai DS. Plasmablastic lymphoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532975/
- Morris A, Monohan G. Plasmablastic myeloma versus plasmablastic lymphoma: different yet related diseases. Hematol Transfus Int J. 2018;6:25-28. doi:10.15406/htij.2018.06.00146
- Prieto-Torres L, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Onaindia A, et al. CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies. Haematologica. 2019;104:226-235.
The Diagnosis: Plasmablastic Lymphoma
A punch biopsy of one of the leg nodules with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed sheets of medium to large cells with plasmacytic differentiation (Figure, A and B). Immunohistochemistry showed CD79, epithelial membrane antigen, multiple myeloma 1, and CD138 positivity, as well as CD-19 negativity and positive staining on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (Figure, C). Ki-67 stained greater than 90% of the neoplastic cells. Neoplastic cells were found to be λ restricted on κ and λ immunohistochemistry. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD3, and CD20 stains were negative. Subsequent fluorescent in situ hybridization was positive for MYC/immunoglobulin heavy chain (MYC/IGH) rearrangement t(8;14), confirming a diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL).

A bone marrow biopsy revealed normocellular bone marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis and no morphologic, immunophenotypic, or fluorescent in situ hybridization evidence of plasmablastic lymphoma or other pathology in the bone marrow. Our patient was started on hyper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin hydrochloride, dexamethasone) chemotherapy and was doing well with plans for a fourth course of chemotherapy. There is no standardized treatment course for cutaneous PBL, though excision with adjunctive chemotherapy treatment commonly has been reported in the literature.1
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare and aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with EBV infection that compromises approximately 2% to 3% of all HIV-related lymphomas.1,2 It frequently is associated with immunosuppression in patients with HIV or in transplant recipients on immunosuppression; however, it has been reported in immunocompetent individuals such as elderly patients.2 Plasmablastic lymphoma most commonly presents on the buccal mucosa but also can affect the gastrointestinal tract and occasionally has cutaneous manifestations.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations of PBL range from erythematous infiltrated plaques to ulcerated nodules presenting in an array of colors from flesh colored to violaceous.2 Primary cutaneous lesions can be seen on the legs, as in our patient.
Histopathologic examination reveals sheets of plasmablasts or large cells with eccentric nuclei and abundant basophilic cytoplasm.1 Plasmablastic lymphoma frequently is positive for mature B-cell markers such as CD38, CD138, multiple myeloma 1, and B lymphocyte–induced maturation protein 1.2,3 Uncommonly, PBL expresses paired box protein Pax-5 and CD20 markers.3 Although pathogenesis is poorly understood, it has been speculated that EBV infection is a common pathogenic factor. Epstein-Barr virus positivity has been noted in 60% of cases.2
Plasmablastic lymphoma and other malignant plasma cell processes such as plasmablastic myeloma (PBM) are morphologically similar. Proliferation of plasmablasts with rare plasmacytic cells is common in PBL, while plasmacytic cells are predominant in PBM. MYC rearrangement/ immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement t(8;14) was used to differentiate PBL from PBM in our patient; however, more cases of PBM with MYC/IGH rearrangement t(8;14) have been reported, making it an unreliable differentiating factor.4 A detailed clinical, pathologic, and genetic survey remains necessary for confirmatory diagnosis of PBL. Compared to other malignant plasma cell processes, PBL more commonly is seen in immunocompromised patients or those with HIV, such as our patient. Additionally, EBV testing is more likely to be positive in patients with PBL, further supporting this diagnosis in our patient.4
Presentations of bacillary angiomatosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and cutaneous lymphoma may be clinically similar; therefore, careful immunohistopathologic differentiation is necessary. Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative disorder that develops from HHV-8 infection and commonly is associated with HIV. It presents as painless vascular lesions in a range of colors with typical progression from patch to plaque to nodules, frequently on the lower extremities. Histologically, admixtures of bland spindle cells, slitlike small vessel proliferation, and lymphocytic infiltration are typical. Neoplastic vessels lack basement membrane zones, resulting in microhemorrhages and hemosiderin deposition. Neoplastic vessels label with CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers in addition to HHV-8 antibodies, which is highly specific for Kaposi sarcoma and differentiates it from PBL.5
Bacillary angiomatosis is an infectious neovascular proliferation characterized by papular lesions that may resemble the lesions of PBL. Mixed cell infiltration in inflammatory cells with clumping of granular material is characteristic. Under Warthin-Starry staining, the granular material is abundant in gram-negative rods representing Bartonella species, which is the implicated infectious agent in bacillary angiomatosis.
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is the most common CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder and also may present with exophytic nodules. The etiology of LyP remains unknown, but it is suspected that overexpression of CD30 plays a role. Lymphomatoid papulosis presents as red-violaceous papules and nodules in various stages of healing. Although variable histology among types of LyP exists, CD30+ T-cell lymphocytes remain the hallmark of LyP. Type A LyP, which accounts for 80% of LyP cases, reveals CD4+ and CD30+ cells scattered among neutrophils, eosinophils, and small lymphocytes.5 Lymphomatoid papulosis typically is self-healing, recurrent, and carries an excellent prognosis.
Plasmablastic lymphoma remains a rare and aggressive type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that can have primary cutaneous manifestations. It is prudent to consider PBL in the differential diagnosis of nodular lower extremity lesions, especially in immunosuppressed patients.
The Diagnosis: Plasmablastic Lymphoma
A punch biopsy of one of the leg nodules with hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed sheets of medium to large cells with plasmacytic differentiation (Figure, A and B). Immunohistochemistry showed CD79, epithelial membrane antigen, multiple myeloma 1, and CD138 positivity, as well as CD-19 negativity and positive staining on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (Figure, C). Ki-67 stained greater than 90% of the neoplastic cells. Neoplastic cells were found to be λ restricted on κ and λ immunohistochemistry. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), CD3, and CD20 stains were negative. Subsequent fluorescent in situ hybridization was positive for MYC/immunoglobulin heavy chain (MYC/IGH) rearrangement t(8;14), confirming a diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL).

A bone marrow biopsy revealed normocellular bone marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis and no morphologic, immunophenotypic, or fluorescent in situ hybridization evidence of plasmablastic lymphoma or other pathology in the bone marrow. Our patient was started on hyper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin hydrochloride, dexamethasone) chemotherapy and was doing well with plans for a fourth course of chemotherapy. There is no standardized treatment course for cutaneous PBL, though excision with adjunctive chemotherapy treatment commonly has been reported in the literature.1
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare and aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with EBV infection that compromises approximately 2% to 3% of all HIV-related lymphomas.1,2 It frequently is associated with immunosuppression in patients with HIV or in transplant recipients on immunosuppression; however, it has been reported in immunocompetent individuals such as elderly patients.2 Plasmablastic lymphoma most commonly presents on the buccal mucosa but also can affect the gastrointestinal tract and occasionally has cutaneous manifestations.1,2 Cutaneous manifestations of PBL range from erythematous infiltrated plaques to ulcerated nodules presenting in an array of colors from flesh colored to violaceous.2 Primary cutaneous lesions can be seen on the legs, as in our patient.
Histopathologic examination reveals sheets of plasmablasts or large cells with eccentric nuclei and abundant basophilic cytoplasm.1 Plasmablastic lymphoma frequently is positive for mature B-cell markers such as CD38, CD138, multiple myeloma 1, and B lymphocyte–induced maturation protein 1.2,3 Uncommonly, PBL expresses paired box protein Pax-5 and CD20 markers.3 Although pathogenesis is poorly understood, it has been speculated that EBV infection is a common pathogenic factor. Epstein-Barr virus positivity has been noted in 60% of cases.2
Plasmablastic lymphoma and other malignant plasma cell processes such as plasmablastic myeloma (PBM) are morphologically similar. Proliferation of plasmablasts with rare plasmacytic cells is common in PBL, while plasmacytic cells are predominant in PBM. MYC rearrangement/ immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement t(8;14) was used to differentiate PBL from PBM in our patient; however, more cases of PBM with MYC/IGH rearrangement t(8;14) have been reported, making it an unreliable differentiating factor.4 A detailed clinical, pathologic, and genetic survey remains necessary for confirmatory diagnosis of PBL. Compared to other malignant plasma cell processes, PBL more commonly is seen in immunocompromised patients or those with HIV, such as our patient. Additionally, EBV testing is more likely to be positive in patients with PBL, further supporting this diagnosis in our patient.4
Presentations of bacillary angiomatosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and cutaneous lymphoma may be clinically similar; therefore, careful immunohistopathologic differentiation is necessary. Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative disorder that develops from HHV-8 infection and commonly is associated with HIV. It presents as painless vascular lesions in a range of colors with typical progression from patch to plaque to nodules, frequently on the lower extremities. Histologically, admixtures of bland spindle cells, slitlike small vessel proliferation, and lymphocytic infiltration are typical. Neoplastic vessels lack basement membrane zones, resulting in microhemorrhages and hemosiderin deposition. Neoplastic vessels label with CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers in addition to HHV-8 antibodies, which is highly specific for Kaposi sarcoma and differentiates it from PBL.5
Bacillary angiomatosis is an infectious neovascular proliferation characterized by papular lesions that may resemble the lesions of PBL. Mixed cell infiltration in inflammatory cells with clumping of granular material is characteristic. Under Warthin-Starry staining, the granular material is abundant in gram-negative rods representing Bartonella species, which is the implicated infectious agent in bacillary angiomatosis.
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is the most common CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder and also may present with exophytic nodules. The etiology of LyP remains unknown, but it is suspected that overexpression of CD30 plays a role. Lymphomatoid papulosis presents as red-violaceous papules and nodules in various stages of healing. Although variable histology among types of LyP exists, CD30+ T-cell lymphocytes remain the hallmark of LyP. Type A LyP, which accounts for 80% of LyP cases, reveals CD4+ and CD30+ cells scattered among neutrophils, eosinophils, and small lymphocytes.5 Lymphomatoid papulosis typically is self-healing, recurrent, and carries an excellent prognosis.
Plasmablastic lymphoma remains a rare and aggressive type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that can have primary cutaneous manifestations. It is prudent to consider PBL in the differential diagnosis of nodular lower extremity lesions, especially in immunosuppressed patients.
- Jambusaria A, Shafer D, Wu H, et al. Cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:676-678.
- Marques SA, Abbade LP, Guiotoku MM, et al. Primary cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma revealing clinically unsuspected HIV infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:507-509.
- Bhatt R, Desai DS. Plasmablastic lymphoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532975/
- Morris A, Monohan G. Plasmablastic myeloma versus plasmablastic lymphoma: different yet related diseases. Hematol Transfus Int J. 2018;6:25-28. doi:10.15406/htij.2018.06.00146
- Prieto-Torres L, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Onaindia A, et al. CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies. Haematologica. 2019;104:226-235.
- Jambusaria A, Shafer D, Wu H, et al. Cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:676-678.
- Marques SA, Abbade LP, Guiotoku MM, et al. Primary cutaneous plasmablastic lymphoma revealing clinically unsuspected HIV infection. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:507-509.
- Bhatt R, Desai DS. Plasmablastic lymphoma. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532975/
- Morris A, Monohan G. Plasmablastic myeloma versus plasmablastic lymphoma: different yet related diseases. Hematol Transfus Int J. 2018;6:25-28. doi:10.15406/htij.2018.06.00146
- Prieto-Torres L, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Onaindia A, et al. CD30-positive primary cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular alterations and targeted therapies. Haematologica. 2019;104:226-235.
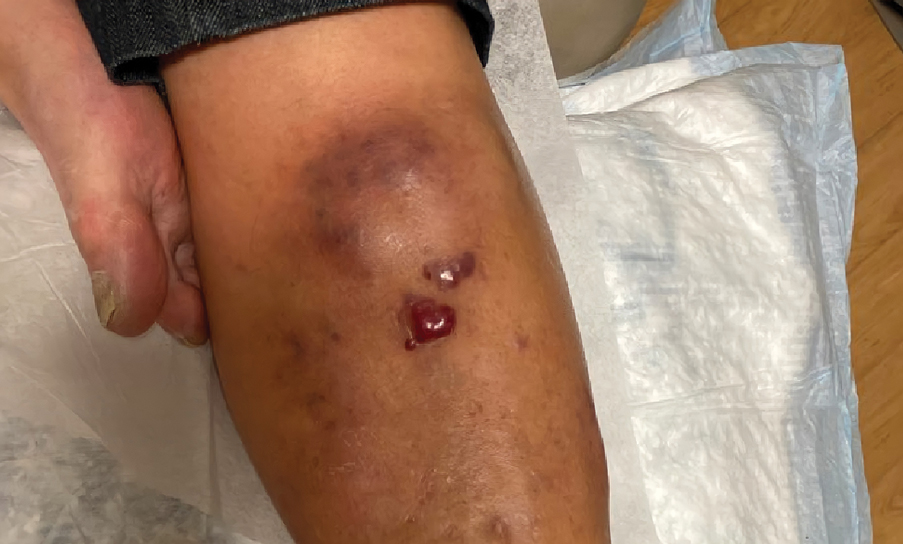
A 67-year-old man with long-standing hepatitis B virus and HIV managed with chronic antiretroviral therapy presented to an urgent care facility with worsening erythema and edema of the legs of 2 weeks’ duration. He was prescribed a 7-day course of cephalexin for presumed cellulitis. Two months later, he developed nodules on the lower extremities. He was seen by podiatry and prescribed a course of amoxicillin–clavulanic acid for presumed infection. Despite 2 courses of antibiotics, his symptoms progressed. The nodules expanded in number and some developed ulceration. Three months into his clinical course, he presented to our dermatology clinic. Physical examination revealed two 2- to 3-cm, violaceous, exophytic, tender nodules. He reported tactile allodynia of the lower extremities and denied fever, chills, night sweats, or weight loss. He also denied exposure to infectious or chemical agents and reported no recent travel. The patient was chronically taking lisinopril/hydrochlorothiazide, escitalopram, elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide, bupropion, and aspirin with no recent changes. A complete hematologic and biochemical survey largely was unremarkable. His HIV viral load was undetectable with a CD4 count greater than 400/mm3 (reference range, 490–1436/mm3). Lactate dehydrogenase was elevated at 568 IU/L (reference range, 135–225 IU/L). The lower leg lesions were biopsied for confirmatory diagnosis.
Visual hallucinations: Differentiating psychiatric and neurologic causes
A visual hallucination is a visual percept experienced when awake that is not elicited by an external stimulus. Historically, hallucinations have been synonymous with psychiatric disease, most notably schizophrenia; however, over recent decades, hallucinations have been categorized based on their underlying etiology as psychodynamic (primary psychiatric), psychophysiologic (primary neurologic/structural), and psychobiochemical (neurotransmitter dysfunction).1 Presently, visual hallucinations are known to be caused by a wide variety of primary psychiatric, neurologic, ophthalmologic, and chemically-mediated conditions. Despite these causes, clinically differentiating the characteristics and qualities of visual hallucinations is often a lesser-known skillset among clinicians. The utility of this skillset is important for the clinician’s ability to differentiate the expected and unexpected characteristics of visual hallucinations in patients with both known and unknown neuropsychiatric conditions.
Though many primary psychiatric and neurologic conditions have been associated with and/or known to cause visual hallucinations, this review focuses on the following grouped causes:
- Primary psychiatric causes: psychiatric disorders with psychotic features and delirium; and
- Primary neurologic causes: neurodegenerative disease/dementias, seizure disorders, migraine disorders, vision loss, peduncular hallucinosis, and hypnagogic/hypnopompic phenomena.
Because the accepted definition of visual hallucinations excludes visual percepts elicited by external stimuli, drug-induced hallucinations would not qualify for either of these categories. Additionally, most studies reporting on the effects of drug-induced hallucinations did not control for underlying comorbid psychiatric conditions, dementia, or delirium, and thus the results cannot be attributed to the drug alone, nor is it possible to identify reliable trends in the properties of the hallucinations.2 The goals of this review are to characterize visual hallucinations experienced as a result of primary psychiatric and primary neurologic conditions and describe key grouping and differentiating features to help guide the diagnosis.
Visual hallucinations in the general population
A review of 6 studies (N = 42,519) reported that the prevalence of visual hallucinations in the general population is 7.3%.3 The prevalence decreases to 6% when visual hallucinations arising from physical illness or drug/chemical consumption are excluded. The prevalence of visual hallucinations in the general population has been associated with comorbid anxiety, stress, bereavement, and psychotic pathology.4,5 Regarding the age of occurrence of visual hallucinations in the general population, there appears to be a bimodal distribution.3 One peak appears in later adolescence and early adulthood, which corresponds with higher rates of psychosis, and another peak occurs late in life, which corresponds to a higher prevalence of neurodegenerative conditions and visual impairment.
Primary psychiatric causes
Most studies of visual hallucinations in primary psychiatric conditions have specifically evaluated patients with schizophrenia and mood disorders with psychotic features.6,7 In a review of 29 studies (N = 5,873) that specifically examined visual hallucinations in individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia, Waters et al3 found a wide range of reported prevalence (4% to 65%) and a weighted mean prevalence of 27%. In contrast, the prevalence of auditory hallucinations in these participants ranged from 25% to 86%, with a weighted mean of 59%.3
Hallucinations are a known but less common symptom of mood disorders that present with psychotic features.8 Waters et al3 also examined the prevalence of visual and auditory hallucinations in mood disorders (including mania, bipolar disorder, and depression) reported in 12 studies (N = 2,892).3 They found the prevalence of visual hallucinations in patients with mood disorders ranged from 6% to 27%, with a weighted mean of 15%, compared to the weighted mean of 28% who experienced auditory hallucinations. Visual hallucinations in primary psychiatric conditions are associated with more severe disease, longer hospitalizations, and poorer prognoses.9-11
Visual hallucinations of psychosis
In patients with psychotic symptoms, the characteristics of the visually hallucinated entity as well as the cognitive and emotional perception of the hallucinations are notably different than in patients with other, nonpsychiatric causes of visual hallucations.3
Continue to: Content and perceived physical properties
Content and perceived physical properties. Hallucinated entities are most often perceived as solid, 3-dimensional, well-detailed, life-sized people, animals, and objects (often fire) or events existing in the real world.3 The entity is almost always perceived as real, with accurate form and color, fine edges, and shadow; is often out of reach of the perceiver; and can be stationary or moving within the physical properties of the external environment.3
Timing and triggers. The temporal properties vary widely. Hallucinations can last from seconds to minutes and occur at any time of day, though by definition, they must occur while the individual is awake.3 Visual hallucinations in psychosis are more common during times of acute stress, strong emotions, and tiredness.3
Patient reaction and belief. Because of realistic qualities of the visual hallucination and the perception that it is real, patients commonly attempt to participate in some activity in relation to the hallucination, such as moving away from or attempting to interact with it.3 Additionally, patients usually perceive the hallucinated entity as uncontrollable, and are surprised when the entity appears or disappears. Though the content of the hallucination is usually impersonal, the meaning the patient attributes to the presence of the hallucinated entity is usually perceived as very personal and often requiring action. The hallucination may represent a harbinger, sign, or omen, and is often interpreted religiously or spiritually and accompanied by comorbid delusions.3
Visual hallucinations of delirium
Delirium is a syndrome of altered mentation—most notably consciousness, attention, and orientation—that occurs as a result of ≥1 metabolic, infectious, drug-induced, or other medical conditions and often manifests as an acute secondary psychotic illness.12 Multiple patient and environmental characteristics have been identified as risk factors for developing delirium, including multiple and/or severe medical illnesses, preexisting dementia, depression, advanced age, polypharmacy, having an indwelling urinary catheter, impaired sight or hearing, and low albumin levels.13-15 The development of delirium is significantly and positively associated with regular alcohol use, benzodiazepine withdrawal, and angiotensin receptor blocker and dopamine receptor agonist usage.15 Approximately 40% of patients with delirium have symptoms of psychosis, and in contrast to the hallucinations experienced by patients with schizophrenia, visual hallucinations are the most common type of hallucinations seen in delirium (27%).13 In a 2021 review that included 602 patients with delirium, Tachibana et al15 found that approximately 26% experienced hallucinations, 92% of which were visual hallucinations.
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Because of the limited attention and cognitive function of patients with delirium, less is known about the content of their visual hallucinations. However, much like those with primary psychotic symptoms, patients with delirium often report seeing complex, normal-sized, concrete entities, most commonly people. Tachibana et al15 found that the hallucinated person is more often a stranger than a familiar person, but (rarely) may be an ethereal being such as a devil or ghost. The next most common visually hallucinated entities were creatures, most frequently insects and animals. Other common hallucinations were visions of events or objects, such as fires, falling ceilings, or water. Similar to those with primary psychotic illness such as schizophrenia, patients with delirium often experience emotional distress, anxiety, fear, and confusion in response to the hallucinated person, object, and/or event.15
Continue to: Primary neurologic causes
Primary neurologic causes
Visual hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases
Patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), or Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) commonly experience hallucinations as a feature of their condition. However, the true cause of these hallucinations often cannot be directly attributed to any specific pathophysiology because these patients often have multiple coexisting risk factors, such as advanced age, major depressive disorder, use of neuroactive medications, and co-occurring somatic illness. Though the prevalence of visual hallucinations varies widely between studies, with 15% to 40% reported in patients with PD, the prevalence roughly doubles in patients with PD-associated dementia (30% to 60%), and is reported by 60% to 90% of those with DLB.16-18 Hallucinations are generally thought to be less common in Alzheimer disease; such patients most commonly experience visual hallucinations, although the reported prevalence ranges widely (4% to 59%).19,20 Notably, similarly to hallucinations experienced in patients with delirium, and in contrast to those with psychosis, visual hallucinations are more common than auditory hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases.20 Hallucinations are not common in individuals with CJD but are a key defining feature of the He
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Similar to the visual hallucinations experienced by patients with psychosis or delirium, those experienced in patients with PD, DLB, or CJD are often complex, most commonly of people, followed by animals and objects. The presence of “passage hallucinations”—in which a person or animal is seen in a patient’s peripheral vision, but passes out of their visual field before the entity can be directly visualized—is common.20 Those with PD also commonly have visual hallucinations in which the form of an object appears distorted (dysmorphopsia) or the color of an object appears distorted (metachromatopsia), though these would better be classified as illusions because a real object is being perceived with distortion.22
Hallucinations are more common in the evening and at night. “Presence hallucinations” are a common type of hallucination that cannot be directly related to a specific sensory modality such as vision, though they are commonly described by patients with PD as a seen or perceived image (usually a person) that is not directly in the individual’s visual field.17 These presence hallucinations are often described as being behind the patient or in a visualized scene of what was about to happen. Before developing the dementia and myoclonus also seen in sporadic CJD, patients with the Heidenhain variant of CJD describe illusions such as metachromatopsia, dysmorphia, and micropsia that eventually develop into frank visual hallucinations, which have been poorly reported in medical literature.22,23 There are no generalizable trends in the temporal nature of visual hallucinations in patients with neurodegenerative diseases. In most cases of visual hallucinations in patients with PD and dementia, insight relating to the perception varies widely based on the patient’s cognitive status. Subsequently, patients’ reactions to the hallucinations also vary widely.
Visual hallucinations in epileptic seizures
Occipital lobe epilepsies represent 1% to 4.6% of all epilepsies; however, these represent 20% to 30% of benign childhood partial epilepsies.24,25 These are commonly associated with various types of visual hallucinations depending upon the location of the seizure onset within the occipital lobe. These are referred to as visual auras.26 Visual auras are classified into simple visual hallucinations, complex visual hallucinations, visual illusions, and ictal amaurosis (hemifield blindness or complete blindness).
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Simple visual hallucinations are often described as brief, stereotypical flashing lights of various shapes and colors. These images may flicker, change shape, or take on a geometric or irregular pattern. Appearances can be repetitive and stereotyped, are often reported as moving horizontally from the periphery to the center of the visual field, and can spread to the entire visual field. Most often, these hallucinations occur for 5 to 30 seconds, and have no discernible provoking factors. Complex visual hallucinations consist of formed images of animals, people, or elaborate scenes. These are believed to reflect activation of a larger area of cortex in the temporo-parieto-occipital region, which is the visual association cortex. Very rarely, occipital lobe seizures can manifest with ictal amaurosis.24
Continue to: Simple visual auras...
Simple visual auras have a very high localizing value to the occipital lobe. The primary visual cortex (Brodmann area 17) is situated in the banks of calcarine fissure and activation of this region produces these simple hallucinations. If the hallucinations are consistently lateralized, the seizures are very likely to be coming from the contralateral occipital lobe.
Visual hallucinations in brain tumors
In general, a tumor anywhere along the optic path can produce visual hallucinations; however, the exact causal mechanism of the hallucinations is unknown. Moreover, tumors in different locations—namely the occipital lobes, temporal lobes, and frontal lobes—appear to produce visual hallucinations with substantially different characteristics.27-29 Further complicating the search for the mechanism of these hallucinations is the fact that tumors are epileptogenic. In addition, 36% to 48% of patients with brain tumors have mood symptoms (depression/mania), and 22% to 24% have psychotic symptoms (delusions/hallucinations); these symptoms are considerably location-dependent.30-32
Content and associated signs/symptoms. There are some grouped symptoms and/or hallucination characteristics associated with cerebral tumors in different lobes of the brain, though these symptoms are not specific. The visual hallucinations associated with brain tumors are typically confined to the field of vision that corresponds to the location of the tumor. Additionally, many such patients have a baseline visual field defect to some extent due to the tumor location.
In patients with occipital lobe tumors, visual hallucinations closely resemble those experienced in occipital lobe seizures, specifically bright flashes of light in colorful simple and complex shapes. Interestingly, those with occipital lobe tumors report xanthopsia, a form of chromatopsia in which objects in their field of view appear abnormally colored a yellowish shade.26,27
In patients with temporal lobe tumors, more complex visual hallucinations of people, objects, and events occurring around them are often accompanied by auditory hallucinations, olfactory hallucinations, and/or anosmia.28In those with frontal lobe tumors, similar complex visual hallucinations of people, objects, and events are seen, and olfactory hallucinations and/or anosmia are often experienced. However, these patients often have a lower likelihood of experiencing auditory hallucinations, and a higher likelihood of developing personality changes and depression than other psychotic symptoms. The visual hallucinations experienced in those with frontal lobe tumors are more likely to have violent content.29
Continue to: Visual hallucinations in migraine with aura
Visual hallucinations in migraine with aura
The estimated prevalence of migraine in the general population is 15% to 29%; 31% of those with migraine experience auras.33-35 Approximately 99% of those with migraine auras experience some type of associated visual phenomena.33,36 The pathophysiology of migraine is believed to be related to spreading cortical depression, in which a slowly propagating wave of neuroelectric depolarization travels over the cortex, followed by a depression of normal brain activity. Visual aura is thought to occur due to the resulting changes in cortical activity in the visual cortex; however, the exact electrophysiology of visual migraine aura is not entirely known.37,38 Though most patients with visual migraine aura experience simple visual hallucinations, complex hallucinations have been reported in the (very rare) cases of migraine coma and familial hemiplegic migraine.39
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The most common hallucinated entities reported by patients with migraine with aura are zigzag, flashing/sparkling, black and white curved figure(s) in the center of the visual field, commonly called a scintillating phosphene or scintillating scotoma.36 The perceived entity is often singular and gradually moves from the center to the periphery of the visual field. These visual hallucinations appear in front of all other objects in the visual field and do not interact with the environment or observer, or resemble or morph into any real-world objects, though they may change in contour, size, and color. The scintillating nature of the hallucination often resolves within minutes, usually leaving a scotoma, or area of vision loss, in the area, with resolution back to baseline vision within 1 hour. The straight, zigzag, and usually black-and-white nature of the scintillating phosphenes of migraine are in notable contrast to the colorful, often circular visual hallucinations experienced in patients with occipital lobe seizures.25
Visual hallucinations in peduncular hallucinosis
Peduncular hallucinosis is a syndrome of predominantly dreamlike visual hallucinations that occurs in the setting of lesions in the midbrain and/or thalamus.40 A recent review of the lesion etiology found that approximately 63% are caused by focal infarction and approximately 15% are caused by mass lesions; subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage, and demyelination cause approximately 5% of cases each.40 Additionally, a review of the affected brainstem anatomy showed almost all lesions were found in the paramedian reticular formations of the midbrain and pons, with the vast majority of lesions affecting or adjacent to the oculomotor and raphe nuclei of the midbrain.39 Due to the commonly involved visual pathway, some researchers have suggested these hallucinations may be the result of a release phenomenon.39
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The visual hallucinations of peduncular hallucinosis usually start 1 to 5 days after the causal lesion forms, last several minutes to hours, and most stop after 1 to 3 weeks; however, cases of hallucinations lasting for years have been reported. These hallucinations have a diurnal pattern of usually appearing while the patient is resting in the evening and/or preparing for sleep. The characteristics of visual hallucinations vary widely from simple distortions in how real objects appear to colorful and vivid hallucinated events and people who can interact with the observer. The content of the visual hallucinations often changes in nature during the hallucination, or from one hallucination to the next. The hallucinated entities can be worldly or extraterrestrial. Once these patients fall asleep, they often have equally vivid and unusual dreams, with content similar to their visual hallucinations. Due to the anatomical involvement of the nigrostriatal pathway and oculomotor nuclei, co-occurring parkinsonism, ataxia, and oculomotor nerve palsy are common and can be a key clinical feature in establishing the diagnosis. Though patients with peduncular hallucinations commonly fear their hallucinations, they often eventually gain insight, which eases their anxiety.39
Other causes
Visual hallucinations in visual impairment
Visual hallucinations are a diagnostic requirement for Charles Bonnet syndrome, in which individuals with vision loss experience visual hallucinations in the corresponding field of vision loss.41 A lesion at any point in the visual pathway that produces visual loss can lead to Charles Bonnet syndrome; however, age-related macular degeneration is the most common cause.42 The hallucinations of Charles Bonnet syndrome are believed to be a release phenomenon, given the defective visual pathway and resultant dysfunction in visual processing. The prevalence of Charles Bonnet syndrome ranges widely by study. Larger studies report a prevalence of 11% to 27% in patients with age-related macular degeneration, depending on the severity of vision loss.43,44 Because there are many causes of Charles Bonnet syndrome, and because a recent study found that only 15% of patients with this syndrome told their eye care clinician and that 21% had not reported their hallucinatory symptoms to anyone, the true prevalence is unknown.42 Though the onset of visual hallucinations correlates with the onset of vision loss, there appears to be no association between the nature or complexity of the hallucinations and the severity or progression of the patient’s vision loss.45 Some studies have reported either the onset of or a higher frequency of visual hallucinations at a time of visual recovery (for example, treatment or exudative age-related macular degeneration), which suggests that hallucinations may be triggered by fluctuations in visual acuity.46,47 Additional risk factors for experiencing visual hallucinations in the setting of visual pathway deficit include a history of stroke, social isolation, poor cognitive function, poor lighting, and age ≥65.
Continue to: Content and associated signs/symptoms
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The visual hallucinations of patients with Charles Bonnet syndrome appear almost exclusively in the defective visual field. Images tend to be complex, colored, with moving parts, and appear in front of the patient. The hallucinations are usually of familiar or normal-appearing people or mundane objects, and as such, the patient often does not realize the hallucinated entity is not real. In patients without comorbid psychiatric disease, visual hallucinations are not accompanied by any other types of hallucinations. The most commonly hallucinated entities are people, followed by simple visual hallucinations of geometric patterns, and then by faces (natural or cartoon-like) and inanimate objects. Hallucinations most commonly occur daily or weekly, and upon waking. These hallucinations most often last several minutes, though they can last just a few seconds or for hours. Hallucinations are usually emotionally neutral, but most patients report feeling confused by their appearance and having a fear of underlying psychiatric disease. They often gain insight to the unreal nature of the hallucinations after counseling.48
Visual hallucinations at the sleep/wake interface
Hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations are fleeting perceptual experiences that occur while an individual is falling asleep or waking, respectively.49 Because by definition visual hallucinations occur while the individual is fully awake, categorizing hallucination-like experiences such as hypnagogia and hypnopompia is difficult, especially since these are similar to other states in which alterations in perception are expected (namely a dream state). They are commonly associated with sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, cataplexy, and sleep paralysis.50,51 In a study of 13,057 individuals in the general population, Ohayon et al4 found the overall prevalence of hypnagogic or hypnopompic hallucinations was 24.8% (5.3% visual) and 6.6% (1.5% visual), respectively. Approximately one-third of participants reported having experienced ≥1 hallucinatory experience in their lifetime, regardless of being asleep or awake.4 There was a higher prevalence of hypnagogic/hypnopompic experiences among those who also reported daytime hallucinations or other psychotic features.
Content and associated signs/symptoms. Unfortunately, because of the frequent co-occurrence of sleep disorders and psychiatric conditions, as well as the general paucity of research, it is difficult to characterize the visual phenomenology of hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations. Some evidence suggests the nature of the perception of the objects hallucinated is substantially impacted by the presence of preexisting psychotic symptoms. Insight into the reality of these hallucinations also depends upon the presence of comorbid psychiatric disease. Hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations are often described as complex, colorful, vivid, and dream-like, as if the patient was in a “half sleep” state.52 They are usually described as highly detailed events involving people and/or animals, though they may be grotesque in nature. Perceived entities are often described as undergoing a transformation or being mobile in their environment. Rarely do these perceptions invoke emotion or change the patient’s beliefs. Hypnagogia/hypnopompia also often have an auditory or haptic component to them. Visual phenomena can either appear to take place within an alternative background environment or appear superimposed on the patient’s actual physical environment.
How to determine the cause
In many of the studies cited in this review, the participants had a considerable amount of psychiatric comorbidity, which makes it difficult to discriminate between pure neurologic and pure psychiatric causes of hallucinations. Though the visual content of the hallucinations (people, objects, shapes, lights) can help clinicians broadly differentiate causes, many other characteristics of both the hallucinations and the patient can help determine the cause (Table3,4,12-39,41-52). The most useful characteristics for discerning the etiology of an individual’s visual hallucinations are the patient’s age, the visual field in which the hallucination occurs, and the complexity/simplicity of the hallucination.
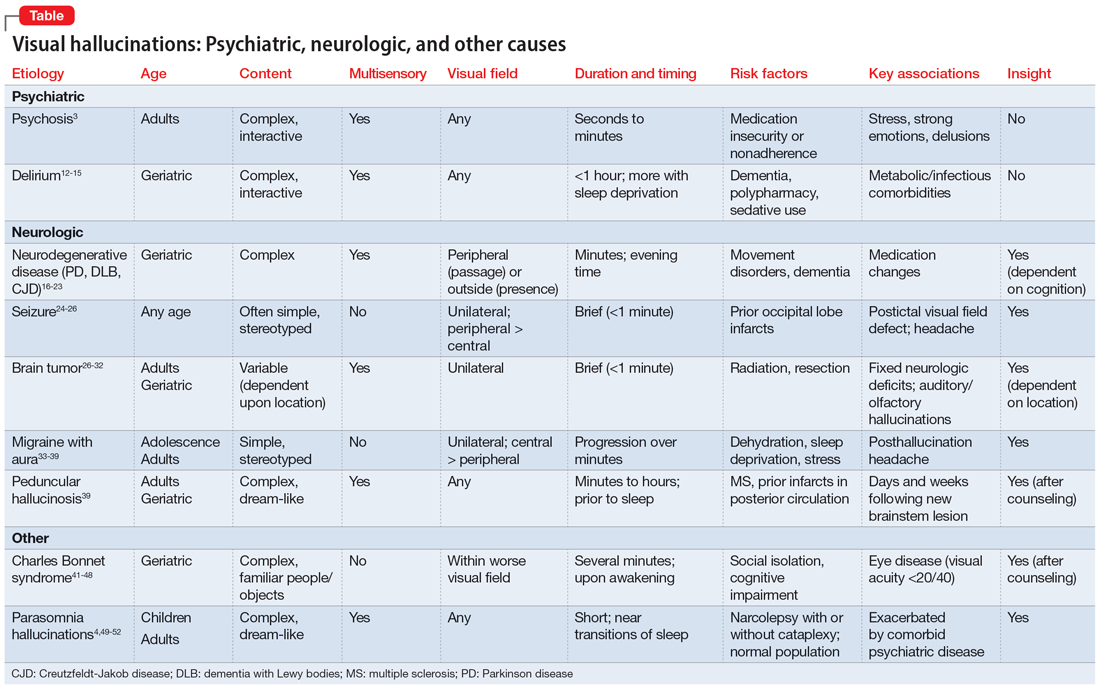
Patient age. Hallucinations associated with primary psychosis decrease with age. The average age of onset of migraine with aura is 21. Occipital lobe seizures occur in early childhood to age 40, but most commonly occur in the second decade.32,36 No trend in age can be reliably determined in individuals who experience hypnagogia/hypnopompia. In contrast, other potential causes of visual hallucinations, such as delirium, neurodegenerative disease, eye disease, and peduncular hallucinosis, are more commonly associated with advanced age.
Continue to: The visual field(s)
The visual field(s) in which the hallucination occurs can help differentiate possible causes in patients with seizure, brain tumor, migraine, or visual impairment. In patients with psychosis, delirium, peduncular hallucinosis, or hypnagogia/hypnopompia, hallucinations can occur in any visual field. Those with neurodegenerative disease, particularly PD, commonly describe seeing so-called passage hallucinations and presence hallucinations, which occur outside of the patient’s direct vision. Visual hallucinations associated with seizure are often unilateral (homonymous left or right hemifield), and contralateral to the affected neurologic structures in the visual neural pathway; they start in the left or right peripheral vision and gradually move to the central visual field. In hallucinations experienced by patients with brain tumors, the hallucinated entities typically appear on the visual field contralateral to the underlying tumor. Visual hallucinations seen in migraine often include a figure that moves from central vision to more lateral in the visual field. The visual hallucinations seen in eye disease (namely Charles Bonnet syndrome) are almost exclusively perceived in the visual fields affected by decreased visual acuity, though non-side-locked visual hallucinations are common in patients with age-related macular degeneration.
Content and complexity. The visual hallucinations perceived in those with psychosis, delirium, neurodegenerative disease, and sleep disorders are generally complex. These hallucinations tend to be of people, animals, scenes, or faces and include color and associated sound, with moving parts and interactivity with either the patient or the environment. These are in contrast to the simple visual hallucinations of visual cortex seizures, brain tumors, and migraine aura, which are often reported as brightly colored or black/white lights, flashes, and shapes, with or without associated auditory, olfactory, or somatic sensation. Furthermore, hallucinations due to seizure and brain tumor (also likely due to seizure) are often of brightly colored shapes and lights with curved edges, while patients with migraine more commonly report singular sparkling black/white objects with straight lines.
Bottom Line
Though there are no features known to be specific to only 1 cause of visual hallucinations, some characteristics of both the patient and the hallucinations can help direct the diagnostic differential. The most useful characteristics are the patient’s age, the visual field in which the hallucination occurs, and the complexity/ simplicity of the hallucination.
Related Resources
- Wang J, Patel D, Francois D. Elaborate hallucinations, but is it a psychotic disorder? Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):46-50. doi:10.12788/cp.0091
- O’Brien J, Taylor JP, Ballard C, et al. Visual hallucinations in neurological and ophthalmological disease: pathophysiology and management. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020; 91(5):512-519. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2019-322702
1. Asaad G, Shapiro B. Hallucinations: theoretical and clinical overview. Am J Psychiatry. 1987;143(9):1088-1097.
2. Taam MA, Boissieu P, Taam RA, et al. Drug-induced hallucination: a case/non-case study in the French Pharmacovigilance Database. Article in French. Eur J Psychiatry. 2015;29(1):21-31.
3. Waters F, Collerton D, Ffytche DH, et al. Visual hallucinations in the psychosis spectrum and comparative information from neurodegenerative disorders and disease. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40(Suppl 4):S233-S245.
4. Ohayon MM. Prevalence of hallucinations and their pathological associations in the general population. Psychiatry Res. 2000;97(2-3):153-164.
5. Rees WD. The hallucinations of widowhood. Br Med J. 1971;4(5778):37-41.
6. Delespaul P, deVries M, van Os J. Determinants of occurrence and recovery from hallucinations in daily life. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2002;37(3):97-104.
7. Gauntlett-Gilbert J, Kuipers E. Phenomenology of visual hallucinations in psychiatric conditions. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2003;191(3):203-205.
8. Goodwin FK, Jamison KR. Manic Depressive Illness. Oxford University Press, Inc.; 1999.
9. Mueser KT, Bellack AS, Brady EU. Hallucinations in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1990;82(1):26-29.
10. McCabe MS, Fowler RC, Cadoret RJ, et al. Symptom differences in schizophrenia with good and bad prognosis. Am J Psychiatry. 1972;128(10):1239-1243.
11. Baethge C, Baldessarini RJ, Freudenthal K, et al. Hallucinations in bipolar disorder: characteristics and comparison to unipolar depression and schizophrenia. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(2):136-145.
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
13. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-333.
14. Webster R, Holroyd S. Prevalence of psychotic symptoms in delirium. Psychosomatics. 2000;41(6):519-522.
15. Tachibana M, Inada T, Ichida M, et al. Factors affecting hallucinations in patients with delirium. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13005. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-92578-1
16. Fenelon G, Mahieux F, Huon R, et al. Hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 4):733-745.
17. Papapetropoulos S, Argyriou AA, Ellul J. Factors associated with drug-induced visual hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2005;252(10):1223-1228.
18. Williams DR, Warren JD, Lees AJ. Using the presence of visual hallucinations to differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(6):652-655.
19. Linszen MMJ, Lemstra AW, Dauwan M, et al. Understanding hallucinations in probable Alzheimer’s disease: very low prevalence rates in a tertiary memory clinic. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2018;10:358-362.
20. Burghaus L, Eggers C, Timmermann L, et al. Hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012;18(2):149-159.
21. Brar HK, Vaddigiri V, Scicutella A. Of illusions, hallucinations, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (Heidenhain’s variant). J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005;17(1):124-126.
22. Sasaki C, Yokoi K, Takahashi H, et al. Visual illusions in Parkinson’s disease: an interview survey of symptomatology. Psychogeriatrics. 2022;22(1):28-48.
23. Kropp S, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Finkenstaedt M, et al. The Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol. 1999;56(1):55-61.
24. Taylor I, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF. Occipital epilepsies: identification of specific and newly recognized syndromes. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 4):753-769.
25. Caraballo R, Cersosimo R, Medina C, et al. Panayiotopoulos-type benign childhood occipital epilepsy: a prospective study. Neurology. 2000;5(8):1096-1100.
26. Chowdhury FA, Silva R, Whatley B, et al. Localisation in focal epilepsy: a practical guide. Practical Neurol. 2021;21(6):481-491.
27. Horrax G, Putnam TJ. Distortions of the visual fields in cases of brain tumour: the field defects and hallucinations produced by tumours of the occipital lobe. Brain. 1932;55(4):499-523.
28. Cushing H. Distortions of the visual fields in cases of brain tumor (6th paper): the field defects produced by temporal lobe lesions. Brain. 1922;44(4):341-396.
29. Fornazzari L, Farcnik K, Smith I, et al. Violent visual hallucinations and aggression in frontal lobe dysfunction: clinical manifestations of deep orbitofrontal foci. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1992;4(1):42-44.
30. Madhusoodanan S, Opler MGA, Moise D, et al. Brain tumor location and psychiatric symptoms: is there an association? A meta-analysis of published cases studies. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010;10(10):1529-1536.
31. Madhusoodanan S, Sinha A, Moise D. Brain tumors and psychiatric manifestations: a review and analysis. Poster presented at: The American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry Annual Meeting; March 10-13; 2006; San Juan, Puerto Rico.
32. Madhusoodanan S, Danan D, Moise D. Psychiatric manifestations of brain tumors/gliomas. Rivistica Medica. 2007;13(4):209-215.
33. Kirchmann M. Migraine with aura: new understanding from clinical epidemiological studies. Curr Opin Neurol. 2006;19:286-293.
34. Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine: current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):257-270.
35. Waters WE, O’Connor PJ. Prevalence of migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975;38(6):613-616.
36. Russell MB, Olesen J. A nosographic analysis of the migraine aura in a general population. Brain. 1996;119(Pt 2):355-361.
37. Cozzolino O, Marchese M, Trovato F, et al. Understanding spreading depression from headache to sudden unexpected death. Front Neurol. 2018;9:19.
38. Hadjikhani N, Sanchez del Rio M, Wu O, et al. Mechanisms of migraine aura revealed by functional MRI in human visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(8):4687-4692.
39. Manford M, Andermann F. Complex visual hallucinations. Clinical and neurobiological insights. Brain. 1998;121(Pt 10):1819-1840.
40. Galetta KM, Prasad S. Historical trends in the diagnosis of peduncular hallucinosis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38(4):438-441.
41. Schadlu AP, Schadlu R, Shepherd JB III. Charles Bonnet syndrome: a review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009;20(3):219-222.
42. Vukicevic M, Fitzmaurice K. Butterflies and black lace patterns: the prevalence and characteristics of Charles Bonnet hallucinations in an Australian population. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;36(7):659-665.
43. Teunisse RJ, Cruysberg JR, Verbeek A, et al. The Charles Bonnet syndrome: a large prospective study in the Netherlands. A study of the prevalence of the Charles Bonnet syndrome and associated factors in 500 patients attending the University Department of Ophthalmology at Nijmegen. Br J Psychiatry. 1995;166(2):254-257.
44. Holroyd S, Rabins PV, Finkelstein D, et al. Visual hallucination in patients with macular degeneration. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149(12):1701-1706.
45. Khan JC, Shahid H, Thurlby DA, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome in age-related macular degeneration: the nature and frequency of images in subjects with end-stage disease. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2008;15(3):202-208.
46. Cohen SY, Bulik A, Tadayoni R, et al. Visual hallucinations and Charles Bonnet syndrome after photodynamic therapy for age related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003;87(8):977-979.
47. Meyer CH, Mennel S, Horle S, et al. Visual hallucinations after intravitreal injection of bevacizumab in vascular age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143(1):169-170.
48. Jan T, Del Castillo J. Visual hallucinations: Charles Bonnet syndrome. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(6):544-547. doi:10.5811/westjem.2012.7.12891
49. Foulkes D, Vogel G. Mental activity at sleep onset. J Abnorm Psychol. 1965;70:231-243.
50. Mitler MM, Hajdukovic R, Erman M, et al. Narcolepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1990;7(1):93-118.
51. Nishino S. Clinical and neurobiological aspects of narcolepsy. Sleep Med. 2007;8(4):373-399.
52. Schultz SK, Miller DD, Oliver SE, et al. The life course of schizophrenia: age and symptom dimensions. Schizophr Res. 1997;23(1):15-23.
A visual hallucination is a visual percept experienced when awake that is not elicited by an external stimulus. Historically, hallucinations have been synonymous with psychiatric disease, most notably schizophrenia; however, over recent decades, hallucinations have been categorized based on their underlying etiology as psychodynamic (primary psychiatric), psychophysiologic (primary neurologic/structural), and psychobiochemical (neurotransmitter dysfunction).1 Presently, visual hallucinations are known to be caused by a wide variety of primary psychiatric, neurologic, ophthalmologic, and chemically-mediated conditions. Despite these causes, clinically differentiating the characteristics and qualities of visual hallucinations is often a lesser-known skillset among clinicians. The utility of this skillset is important for the clinician’s ability to differentiate the expected and unexpected characteristics of visual hallucinations in patients with both known and unknown neuropsychiatric conditions.
Though many primary psychiatric and neurologic conditions have been associated with and/or known to cause visual hallucinations, this review focuses on the following grouped causes:
- Primary psychiatric causes: psychiatric disorders with psychotic features and delirium; and
- Primary neurologic causes: neurodegenerative disease/dementias, seizure disorders, migraine disorders, vision loss, peduncular hallucinosis, and hypnagogic/hypnopompic phenomena.
Because the accepted definition of visual hallucinations excludes visual percepts elicited by external stimuli, drug-induced hallucinations would not qualify for either of these categories. Additionally, most studies reporting on the effects of drug-induced hallucinations did not control for underlying comorbid psychiatric conditions, dementia, or delirium, and thus the results cannot be attributed to the drug alone, nor is it possible to identify reliable trends in the properties of the hallucinations.2 The goals of this review are to characterize visual hallucinations experienced as a result of primary psychiatric and primary neurologic conditions and describe key grouping and differentiating features to help guide the diagnosis.
Visual hallucinations in the general population
A review of 6 studies (N = 42,519) reported that the prevalence of visual hallucinations in the general population is 7.3%.3 The prevalence decreases to 6% when visual hallucinations arising from physical illness or drug/chemical consumption are excluded. The prevalence of visual hallucinations in the general population has been associated with comorbid anxiety, stress, bereavement, and psychotic pathology.4,5 Regarding the age of occurrence of visual hallucinations in the general population, there appears to be a bimodal distribution.3 One peak appears in later adolescence and early adulthood, which corresponds with higher rates of psychosis, and another peak occurs late in life, which corresponds to a higher prevalence of neurodegenerative conditions and visual impairment.
Primary psychiatric causes
Most studies of visual hallucinations in primary psychiatric conditions have specifically evaluated patients with schizophrenia and mood disorders with psychotic features.6,7 In a review of 29 studies (N = 5,873) that specifically examined visual hallucinations in individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia, Waters et al3 found a wide range of reported prevalence (4% to 65%) and a weighted mean prevalence of 27%. In contrast, the prevalence of auditory hallucinations in these participants ranged from 25% to 86%, with a weighted mean of 59%.3
Hallucinations are a known but less common symptom of mood disorders that present with psychotic features.8 Waters et al3 also examined the prevalence of visual and auditory hallucinations in mood disorders (including mania, bipolar disorder, and depression) reported in 12 studies (N = 2,892).3 They found the prevalence of visual hallucinations in patients with mood disorders ranged from 6% to 27%, with a weighted mean of 15%, compared to the weighted mean of 28% who experienced auditory hallucinations. Visual hallucinations in primary psychiatric conditions are associated with more severe disease, longer hospitalizations, and poorer prognoses.9-11
Visual hallucinations of psychosis
In patients with psychotic symptoms, the characteristics of the visually hallucinated entity as well as the cognitive and emotional perception of the hallucinations are notably different than in patients with other, nonpsychiatric causes of visual hallucations.3
Continue to: Content and perceived physical properties
Content and perceived physical properties. Hallucinated entities are most often perceived as solid, 3-dimensional, well-detailed, life-sized people, animals, and objects (often fire) or events existing in the real world.3 The entity is almost always perceived as real, with accurate form and color, fine edges, and shadow; is often out of reach of the perceiver; and can be stationary or moving within the physical properties of the external environment.3
Timing and triggers. The temporal properties vary widely. Hallucinations can last from seconds to minutes and occur at any time of day, though by definition, they must occur while the individual is awake.3 Visual hallucinations in psychosis are more common during times of acute stress, strong emotions, and tiredness.3
Patient reaction and belief. Because of realistic qualities of the visual hallucination and the perception that it is real, patients commonly attempt to participate in some activity in relation to the hallucination, such as moving away from or attempting to interact with it.3 Additionally, patients usually perceive the hallucinated entity as uncontrollable, and are surprised when the entity appears or disappears. Though the content of the hallucination is usually impersonal, the meaning the patient attributes to the presence of the hallucinated entity is usually perceived as very personal and often requiring action. The hallucination may represent a harbinger, sign, or omen, and is often interpreted religiously or spiritually and accompanied by comorbid delusions.3
Visual hallucinations of delirium
Delirium is a syndrome of altered mentation—most notably consciousness, attention, and orientation—that occurs as a result of ≥1 metabolic, infectious, drug-induced, or other medical conditions and often manifests as an acute secondary psychotic illness.12 Multiple patient and environmental characteristics have been identified as risk factors for developing delirium, including multiple and/or severe medical illnesses, preexisting dementia, depression, advanced age, polypharmacy, having an indwelling urinary catheter, impaired sight or hearing, and low albumin levels.13-15 The development of delirium is significantly and positively associated with regular alcohol use, benzodiazepine withdrawal, and angiotensin receptor blocker and dopamine receptor agonist usage.15 Approximately 40% of patients with delirium have symptoms of psychosis, and in contrast to the hallucinations experienced by patients with schizophrenia, visual hallucinations are the most common type of hallucinations seen in delirium (27%).13 In a 2021 review that included 602 patients with delirium, Tachibana et al15 found that approximately 26% experienced hallucinations, 92% of which were visual hallucinations.
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Because of the limited attention and cognitive function of patients with delirium, less is known about the content of their visual hallucinations. However, much like those with primary psychotic symptoms, patients with delirium often report seeing complex, normal-sized, concrete entities, most commonly people. Tachibana et al15 found that the hallucinated person is more often a stranger than a familiar person, but (rarely) may be an ethereal being such as a devil or ghost. The next most common visually hallucinated entities were creatures, most frequently insects and animals. Other common hallucinations were visions of events or objects, such as fires, falling ceilings, or water. Similar to those with primary psychotic illness such as schizophrenia, patients with delirium often experience emotional distress, anxiety, fear, and confusion in response to the hallucinated person, object, and/or event.15
Continue to: Primary neurologic causes
Primary neurologic causes
Visual hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases
Patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), or Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) commonly experience hallucinations as a feature of their condition. However, the true cause of these hallucinations often cannot be directly attributed to any specific pathophysiology because these patients often have multiple coexisting risk factors, such as advanced age, major depressive disorder, use of neuroactive medications, and co-occurring somatic illness. Though the prevalence of visual hallucinations varies widely between studies, with 15% to 40% reported in patients with PD, the prevalence roughly doubles in patients with PD-associated dementia (30% to 60%), and is reported by 60% to 90% of those with DLB.16-18 Hallucinations are generally thought to be less common in Alzheimer disease; such patients most commonly experience visual hallucinations, although the reported prevalence ranges widely (4% to 59%).19,20 Notably, similarly to hallucinations experienced in patients with delirium, and in contrast to those with psychosis, visual hallucinations are more common than auditory hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases.20 Hallucinations are not common in individuals with CJD but are a key defining feature of the He
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Similar to the visual hallucinations experienced by patients with psychosis or delirium, those experienced in patients with PD, DLB, or CJD are often complex, most commonly of people, followed by animals and objects. The presence of “passage hallucinations”—in which a person or animal is seen in a patient’s peripheral vision, but passes out of their visual field before the entity can be directly visualized—is common.20 Those with PD also commonly have visual hallucinations in which the form of an object appears distorted (dysmorphopsia) or the color of an object appears distorted (metachromatopsia), though these would better be classified as illusions because a real object is being perceived with distortion.22
Hallucinations are more common in the evening and at night. “Presence hallucinations” are a common type of hallucination that cannot be directly related to a specific sensory modality such as vision, though they are commonly described by patients with PD as a seen or perceived image (usually a person) that is not directly in the individual’s visual field.17 These presence hallucinations are often described as being behind the patient or in a visualized scene of what was about to happen. Before developing the dementia and myoclonus also seen in sporadic CJD, patients with the Heidenhain variant of CJD describe illusions such as metachromatopsia, dysmorphia, and micropsia that eventually develop into frank visual hallucinations, which have been poorly reported in medical literature.22,23 There are no generalizable trends in the temporal nature of visual hallucinations in patients with neurodegenerative diseases. In most cases of visual hallucinations in patients with PD and dementia, insight relating to the perception varies widely based on the patient’s cognitive status. Subsequently, patients’ reactions to the hallucinations also vary widely.
Visual hallucinations in epileptic seizures
Occipital lobe epilepsies represent 1% to 4.6% of all epilepsies; however, these represent 20% to 30% of benign childhood partial epilepsies.24,25 These are commonly associated with various types of visual hallucinations depending upon the location of the seizure onset within the occipital lobe. These are referred to as visual auras.26 Visual auras are classified into simple visual hallucinations, complex visual hallucinations, visual illusions, and ictal amaurosis (hemifield blindness or complete blindness).
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Simple visual hallucinations are often described as brief, stereotypical flashing lights of various shapes and colors. These images may flicker, change shape, or take on a geometric or irregular pattern. Appearances can be repetitive and stereotyped, are often reported as moving horizontally from the periphery to the center of the visual field, and can spread to the entire visual field. Most often, these hallucinations occur for 5 to 30 seconds, and have no discernible provoking factors. Complex visual hallucinations consist of formed images of animals, people, or elaborate scenes. These are believed to reflect activation of a larger area of cortex in the temporo-parieto-occipital region, which is the visual association cortex. Very rarely, occipital lobe seizures can manifest with ictal amaurosis.24
Continue to: Simple visual auras...
Simple visual auras have a very high localizing value to the occipital lobe. The primary visual cortex (Brodmann area 17) is situated in the banks of calcarine fissure and activation of this region produces these simple hallucinations. If the hallucinations are consistently lateralized, the seizures are very likely to be coming from the contralateral occipital lobe.
Visual hallucinations in brain tumors
In general, a tumor anywhere along the optic path can produce visual hallucinations; however, the exact causal mechanism of the hallucinations is unknown. Moreover, tumors in different locations—namely the occipital lobes, temporal lobes, and frontal lobes—appear to produce visual hallucinations with substantially different characteristics.27-29 Further complicating the search for the mechanism of these hallucinations is the fact that tumors are epileptogenic. In addition, 36% to 48% of patients with brain tumors have mood symptoms (depression/mania), and 22% to 24% have psychotic symptoms (delusions/hallucinations); these symptoms are considerably location-dependent.30-32
Content and associated signs/symptoms. There are some grouped symptoms and/or hallucination characteristics associated with cerebral tumors in different lobes of the brain, though these symptoms are not specific. The visual hallucinations associated with brain tumors are typically confined to the field of vision that corresponds to the location of the tumor. Additionally, many such patients have a baseline visual field defect to some extent due to the tumor location.
In patients with occipital lobe tumors, visual hallucinations closely resemble those experienced in occipital lobe seizures, specifically bright flashes of light in colorful simple and complex shapes. Interestingly, those with occipital lobe tumors report xanthopsia, a form of chromatopsia in which objects in their field of view appear abnormally colored a yellowish shade.26,27
In patients with temporal lobe tumors, more complex visual hallucinations of people, objects, and events occurring around them are often accompanied by auditory hallucinations, olfactory hallucinations, and/or anosmia.28In those with frontal lobe tumors, similar complex visual hallucinations of people, objects, and events are seen, and olfactory hallucinations and/or anosmia are often experienced. However, these patients often have a lower likelihood of experiencing auditory hallucinations, and a higher likelihood of developing personality changes and depression than other psychotic symptoms. The visual hallucinations experienced in those with frontal lobe tumors are more likely to have violent content.29
Continue to: Visual hallucinations in migraine with aura
Visual hallucinations in migraine with aura
The estimated prevalence of migraine in the general population is 15% to 29%; 31% of those with migraine experience auras.33-35 Approximately 99% of those with migraine auras experience some type of associated visual phenomena.33,36 The pathophysiology of migraine is believed to be related to spreading cortical depression, in which a slowly propagating wave of neuroelectric depolarization travels over the cortex, followed by a depression of normal brain activity. Visual aura is thought to occur due to the resulting changes in cortical activity in the visual cortex; however, the exact electrophysiology of visual migraine aura is not entirely known.37,38 Though most patients with visual migraine aura experience simple visual hallucinations, complex hallucinations have been reported in the (very rare) cases of migraine coma and familial hemiplegic migraine.39
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The most common hallucinated entities reported by patients with migraine with aura are zigzag, flashing/sparkling, black and white curved figure(s) in the center of the visual field, commonly called a scintillating phosphene or scintillating scotoma.36 The perceived entity is often singular and gradually moves from the center to the periphery of the visual field. These visual hallucinations appear in front of all other objects in the visual field and do not interact with the environment or observer, or resemble or morph into any real-world objects, though they may change in contour, size, and color. The scintillating nature of the hallucination often resolves within minutes, usually leaving a scotoma, or area of vision loss, in the area, with resolution back to baseline vision within 1 hour. The straight, zigzag, and usually black-and-white nature of the scintillating phosphenes of migraine are in notable contrast to the colorful, often circular visual hallucinations experienced in patients with occipital lobe seizures.25
Visual hallucinations in peduncular hallucinosis
Peduncular hallucinosis is a syndrome of predominantly dreamlike visual hallucinations that occurs in the setting of lesions in the midbrain and/or thalamus.40 A recent review of the lesion etiology found that approximately 63% are caused by focal infarction and approximately 15% are caused by mass lesions; subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage, and demyelination cause approximately 5% of cases each.40 Additionally, a review of the affected brainstem anatomy showed almost all lesions were found in the paramedian reticular formations of the midbrain and pons, with the vast majority of lesions affecting or adjacent to the oculomotor and raphe nuclei of the midbrain.39 Due to the commonly involved visual pathway, some researchers have suggested these hallucinations may be the result of a release phenomenon.39
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The visual hallucinations of peduncular hallucinosis usually start 1 to 5 days after the causal lesion forms, last several minutes to hours, and most stop after 1 to 3 weeks; however, cases of hallucinations lasting for years have been reported. These hallucinations have a diurnal pattern of usually appearing while the patient is resting in the evening and/or preparing for sleep. The characteristics of visual hallucinations vary widely from simple distortions in how real objects appear to colorful and vivid hallucinated events and people who can interact with the observer. The content of the visual hallucinations often changes in nature during the hallucination, or from one hallucination to the next. The hallucinated entities can be worldly or extraterrestrial. Once these patients fall asleep, they often have equally vivid and unusual dreams, with content similar to their visual hallucinations. Due to the anatomical involvement of the nigrostriatal pathway and oculomotor nuclei, co-occurring parkinsonism, ataxia, and oculomotor nerve palsy are common and can be a key clinical feature in establishing the diagnosis. Though patients with peduncular hallucinations commonly fear their hallucinations, they often eventually gain insight, which eases their anxiety.39
Other causes
Visual hallucinations in visual impairment
Visual hallucinations are a diagnostic requirement for Charles Bonnet syndrome, in which individuals with vision loss experience visual hallucinations in the corresponding field of vision loss.41 A lesion at any point in the visual pathway that produces visual loss can lead to Charles Bonnet syndrome; however, age-related macular degeneration is the most common cause.42 The hallucinations of Charles Bonnet syndrome are believed to be a release phenomenon, given the defective visual pathway and resultant dysfunction in visual processing. The prevalence of Charles Bonnet syndrome ranges widely by study. Larger studies report a prevalence of 11% to 27% in patients with age-related macular degeneration, depending on the severity of vision loss.43,44 Because there are many causes of Charles Bonnet syndrome, and because a recent study found that only 15% of patients with this syndrome told their eye care clinician and that 21% had not reported their hallucinatory symptoms to anyone, the true prevalence is unknown.42 Though the onset of visual hallucinations correlates with the onset of vision loss, there appears to be no association between the nature or complexity of the hallucinations and the severity or progression of the patient’s vision loss.45 Some studies have reported either the onset of or a higher frequency of visual hallucinations at a time of visual recovery (for example, treatment or exudative age-related macular degeneration), which suggests that hallucinations may be triggered by fluctuations in visual acuity.46,47 Additional risk factors for experiencing visual hallucinations in the setting of visual pathway deficit include a history of stroke, social isolation, poor cognitive function, poor lighting, and age ≥65.
Continue to: Content and associated signs/symptoms
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The visual hallucinations of patients with Charles Bonnet syndrome appear almost exclusively in the defective visual field. Images tend to be complex, colored, with moving parts, and appear in front of the patient. The hallucinations are usually of familiar or normal-appearing people or mundane objects, and as such, the patient often does not realize the hallucinated entity is not real. In patients without comorbid psychiatric disease, visual hallucinations are not accompanied by any other types of hallucinations. The most commonly hallucinated entities are people, followed by simple visual hallucinations of geometric patterns, and then by faces (natural or cartoon-like) and inanimate objects. Hallucinations most commonly occur daily or weekly, and upon waking. These hallucinations most often last several minutes, though they can last just a few seconds or for hours. Hallucinations are usually emotionally neutral, but most patients report feeling confused by their appearance and having a fear of underlying psychiatric disease. They often gain insight to the unreal nature of the hallucinations after counseling.48
Visual hallucinations at the sleep/wake interface
Hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations are fleeting perceptual experiences that occur while an individual is falling asleep or waking, respectively.49 Because by definition visual hallucinations occur while the individual is fully awake, categorizing hallucination-like experiences such as hypnagogia and hypnopompia is difficult, especially since these are similar to other states in which alterations in perception are expected (namely a dream state). They are commonly associated with sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, cataplexy, and sleep paralysis.50,51 In a study of 13,057 individuals in the general population, Ohayon et al4 found the overall prevalence of hypnagogic or hypnopompic hallucinations was 24.8% (5.3% visual) and 6.6% (1.5% visual), respectively. Approximately one-third of participants reported having experienced ≥1 hallucinatory experience in their lifetime, regardless of being asleep or awake.4 There was a higher prevalence of hypnagogic/hypnopompic experiences among those who also reported daytime hallucinations or other psychotic features.
Content and associated signs/symptoms. Unfortunately, because of the frequent co-occurrence of sleep disorders and psychiatric conditions, as well as the general paucity of research, it is difficult to characterize the visual phenomenology of hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations. Some evidence suggests the nature of the perception of the objects hallucinated is substantially impacted by the presence of preexisting psychotic symptoms. Insight into the reality of these hallucinations also depends upon the presence of comorbid psychiatric disease. Hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations are often described as complex, colorful, vivid, and dream-like, as if the patient was in a “half sleep” state.52 They are usually described as highly detailed events involving people and/or animals, though they may be grotesque in nature. Perceived entities are often described as undergoing a transformation or being mobile in their environment. Rarely do these perceptions invoke emotion or change the patient’s beliefs. Hypnagogia/hypnopompia also often have an auditory or haptic component to them. Visual phenomena can either appear to take place within an alternative background environment or appear superimposed on the patient’s actual physical environment.
How to determine the cause
In many of the studies cited in this review, the participants had a considerable amount of psychiatric comorbidity, which makes it difficult to discriminate between pure neurologic and pure psychiatric causes of hallucinations. Though the visual content of the hallucinations (people, objects, shapes, lights) can help clinicians broadly differentiate causes, many other characteristics of both the hallucinations and the patient can help determine the cause (Table3,4,12-39,41-52). The most useful characteristics for discerning the etiology of an individual’s visual hallucinations are the patient’s age, the visual field in which the hallucination occurs, and the complexity/simplicity of the hallucination.

Patient age. Hallucinations associated with primary psychosis decrease with age. The average age of onset of migraine with aura is 21. Occipital lobe seizures occur in early childhood to age 40, but most commonly occur in the second decade.32,36 No trend in age can be reliably determined in individuals who experience hypnagogia/hypnopompia. In contrast, other potential causes of visual hallucinations, such as delirium, neurodegenerative disease, eye disease, and peduncular hallucinosis, are more commonly associated with advanced age.
Continue to: The visual field(s)
The visual field(s) in which the hallucination occurs can help differentiate possible causes in patients with seizure, brain tumor, migraine, or visual impairment. In patients with psychosis, delirium, peduncular hallucinosis, or hypnagogia/hypnopompia, hallucinations can occur in any visual field. Those with neurodegenerative disease, particularly PD, commonly describe seeing so-called passage hallucinations and presence hallucinations, which occur outside of the patient’s direct vision. Visual hallucinations associated with seizure are often unilateral (homonymous left or right hemifield), and contralateral to the affected neurologic structures in the visual neural pathway; they start in the left or right peripheral vision and gradually move to the central visual field. In hallucinations experienced by patients with brain tumors, the hallucinated entities typically appear on the visual field contralateral to the underlying tumor. Visual hallucinations seen in migraine often include a figure that moves from central vision to more lateral in the visual field. The visual hallucinations seen in eye disease (namely Charles Bonnet syndrome) are almost exclusively perceived in the visual fields affected by decreased visual acuity, though non-side-locked visual hallucinations are common in patients with age-related macular degeneration.
Content and complexity. The visual hallucinations perceived in those with psychosis, delirium, neurodegenerative disease, and sleep disorders are generally complex. These hallucinations tend to be of people, animals, scenes, or faces and include color and associated sound, with moving parts and interactivity with either the patient or the environment. These are in contrast to the simple visual hallucinations of visual cortex seizures, brain tumors, and migraine aura, which are often reported as brightly colored or black/white lights, flashes, and shapes, with or without associated auditory, olfactory, or somatic sensation. Furthermore, hallucinations due to seizure and brain tumor (also likely due to seizure) are often of brightly colored shapes and lights with curved edges, while patients with migraine more commonly report singular sparkling black/white objects with straight lines.
Bottom Line
Though there are no features known to be specific to only 1 cause of visual hallucinations, some characteristics of both the patient and the hallucinations can help direct the diagnostic differential. The most useful characteristics are the patient’s age, the visual field in which the hallucination occurs, and the complexity/ simplicity of the hallucination.
Related Resources
- Wang J, Patel D, Francois D. Elaborate hallucinations, but is it a psychotic disorder? Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):46-50. doi:10.12788/cp.0091
- O’Brien J, Taylor JP, Ballard C, et al. Visual hallucinations in neurological and ophthalmological disease: pathophysiology and management. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020; 91(5):512-519. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2019-322702
A visual hallucination is a visual percept experienced when awake that is not elicited by an external stimulus. Historically, hallucinations have been synonymous with psychiatric disease, most notably schizophrenia; however, over recent decades, hallucinations have been categorized based on their underlying etiology as psychodynamic (primary psychiatric), psychophysiologic (primary neurologic/structural), and psychobiochemical (neurotransmitter dysfunction).1 Presently, visual hallucinations are known to be caused by a wide variety of primary psychiatric, neurologic, ophthalmologic, and chemically-mediated conditions. Despite these causes, clinically differentiating the characteristics and qualities of visual hallucinations is often a lesser-known skillset among clinicians. The utility of this skillset is important for the clinician’s ability to differentiate the expected and unexpected characteristics of visual hallucinations in patients with both known and unknown neuropsychiatric conditions.
Though many primary psychiatric and neurologic conditions have been associated with and/or known to cause visual hallucinations, this review focuses on the following grouped causes:
- Primary psychiatric causes: psychiatric disorders with psychotic features and delirium; and
- Primary neurologic causes: neurodegenerative disease/dementias, seizure disorders, migraine disorders, vision loss, peduncular hallucinosis, and hypnagogic/hypnopompic phenomena.
Because the accepted definition of visual hallucinations excludes visual percepts elicited by external stimuli, drug-induced hallucinations would not qualify for either of these categories. Additionally, most studies reporting on the effects of drug-induced hallucinations did not control for underlying comorbid psychiatric conditions, dementia, or delirium, and thus the results cannot be attributed to the drug alone, nor is it possible to identify reliable trends in the properties of the hallucinations.2 The goals of this review are to characterize visual hallucinations experienced as a result of primary psychiatric and primary neurologic conditions and describe key grouping and differentiating features to help guide the diagnosis.
Visual hallucinations in the general population
A review of 6 studies (N = 42,519) reported that the prevalence of visual hallucinations in the general population is 7.3%.3 The prevalence decreases to 6% when visual hallucinations arising from physical illness or drug/chemical consumption are excluded. The prevalence of visual hallucinations in the general population has been associated with comorbid anxiety, stress, bereavement, and psychotic pathology.4,5 Regarding the age of occurrence of visual hallucinations in the general population, there appears to be a bimodal distribution.3 One peak appears in later adolescence and early adulthood, which corresponds with higher rates of psychosis, and another peak occurs late in life, which corresponds to a higher prevalence of neurodegenerative conditions and visual impairment.
Primary psychiatric causes
Most studies of visual hallucinations in primary psychiatric conditions have specifically evaluated patients with schizophrenia and mood disorders with psychotic features.6,7 In a review of 29 studies (N = 5,873) that specifically examined visual hallucinations in individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia, Waters et al3 found a wide range of reported prevalence (4% to 65%) and a weighted mean prevalence of 27%. In contrast, the prevalence of auditory hallucinations in these participants ranged from 25% to 86%, with a weighted mean of 59%.3
Hallucinations are a known but less common symptom of mood disorders that present with psychotic features.8 Waters et al3 also examined the prevalence of visual and auditory hallucinations in mood disorders (including mania, bipolar disorder, and depression) reported in 12 studies (N = 2,892).3 They found the prevalence of visual hallucinations in patients with mood disorders ranged from 6% to 27%, with a weighted mean of 15%, compared to the weighted mean of 28% who experienced auditory hallucinations. Visual hallucinations in primary psychiatric conditions are associated with more severe disease, longer hospitalizations, and poorer prognoses.9-11
Visual hallucinations of psychosis
In patients with psychotic symptoms, the characteristics of the visually hallucinated entity as well as the cognitive and emotional perception of the hallucinations are notably different than in patients with other, nonpsychiatric causes of visual hallucations.3
Continue to: Content and perceived physical properties
Content and perceived physical properties. Hallucinated entities are most often perceived as solid, 3-dimensional, well-detailed, life-sized people, animals, and objects (often fire) or events existing in the real world.3 The entity is almost always perceived as real, with accurate form and color, fine edges, and shadow; is often out of reach of the perceiver; and can be stationary or moving within the physical properties of the external environment.3
Timing and triggers. The temporal properties vary widely. Hallucinations can last from seconds to minutes and occur at any time of day, though by definition, they must occur while the individual is awake.3 Visual hallucinations in psychosis are more common during times of acute stress, strong emotions, and tiredness.3
Patient reaction and belief. Because of realistic qualities of the visual hallucination and the perception that it is real, patients commonly attempt to participate in some activity in relation to the hallucination, such as moving away from or attempting to interact with it.3 Additionally, patients usually perceive the hallucinated entity as uncontrollable, and are surprised when the entity appears or disappears. Though the content of the hallucination is usually impersonal, the meaning the patient attributes to the presence of the hallucinated entity is usually perceived as very personal and often requiring action. The hallucination may represent a harbinger, sign, or omen, and is often interpreted religiously or spiritually and accompanied by comorbid delusions.3
Visual hallucinations of delirium
Delirium is a syndrome of altered mentation—most notably consciousness, attention, and orientation—that occurs as a result of ≥1 metabolic, infectious, drug-induced, or other medical conditions and often manifests as an acute secondary psychotic illness.12 Multiple patient and environmental characteristics have been identified as risk factors for developing delirium, including multiple and/or severe medical illnesses, preexisting dementia, depression, advanced age, polypharmacy, having an indwelling urinary catheter, impaired sight or hearing, and low albumin levels.13-15 The development of delirium is significantly and positively associated with regular alcohol use, benzodiazepine withdrawal, and angiotensin receptor blocker and dopamine receptor agonist usage.15 Approximately 40% of patients with delirium have symptoms of psychosis, and in contrast to the hallucinations experienced by patients with schizophrenia, visual hallucinations are the most common type of hallucinations seen in delirium (27%).13 In a 2021 review that included 602 patients with delirium, Tachibana et al15 found that approximately 26% experienced hallucinations, 92% of which were visual hallucinations.
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Because of the limited attention and cognitive function of patients with delirium, less is known about the content of their visual hallucinations. However, much like those with primary psychotic symptoms, patients with delirium often report seeing complex, normal-sized, concrete entities, most commonly people. Tachibana et al15 found that the hallucinated person is more often a stranger than a familiar person, but (rarely) may be an ethereal being such as a devil or ghost. The next most common visually hallucinated entities were creatures, most frequently insects and animals. Other common hallucinations were visions of events or objects, such as fires, falling ceilings, or water. Similar to those with primary psychotic illness such as schizophrenia, patients with delirium often experience emotional distress, anxiety, fear, and confusion in response to the hallucinated person, object, and/or event.15
Continue to: Primary neurologic causes
Primary neurologic causes
Visual hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases
Patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), or Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) commonly experience hallucinations as a feature of their condition. However, the true cause of these hallucinations often cannot be directly attributed to any specific pathophysiology because these patients often have multiple coexisting risk factors, such as advanced age, major depressive disorder, use of neuroactive medications, and co-occurring somatic illness. Though the prevalence of visual hallucinations varies widely between studies, with 15% to 40% reported in patients with PD, the prevalence roughly doubles in patients with PD-associated dementia (30% to 60%), and is reported by 60% to 90% of those with DLB.16-18 Hallucinations are generally thought to be less common in Alzheimer disease; such patients most commonly experience visual hallucinations, although the reported prevalence ranges widely (4% to 59%).19,20 Notably, similarly to hallucinations experienced in patients with delirium, and in contrast to those with psychosis, visual hallucinations are more common than auditory hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases.20 Hallucinations are not common in individuals with CJD but are a key defining feature of the He
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Similar to the visual hallucinations experienced by patients with psychosis or delirium, those experienced in patients with PD, DLB, or CJD are often complex, most commonly of people, followed by animals and objects. The presence of “passage hallucinations”—in which a person or animal is seen in a patient’s peripheral vision, but passes out of their visual field before the entity can be directly visualized—is common.20 Those with PD also commonly have visual hallucinations in which the form of an object appears distorted (dysmorphopsia) or the color of an object appears distorted (metachromatopsia), though these would better be classified as illusions because a real object is being perceived with distortion.22
Hallucinations are more common in the evening and at night. “Presence hallucinations” are a common type of hallucination that cannot be directly related to a specific sensory modality such as vision, though they are commonly described by patients with PD as a seen or perceived image (usually a person) that is not directly in the individual’s visual field.17 These presence hallucinations are often described as being behind the patient or in a visualized scene of what was about to happen. Before developing the dementia and myoclonus also seen in sporadic CJD, patients with the Heidenhain variant of CJD describe illusions such as metachromatopsia, dysmorphia, and micropsia that eventually develop into frank visual hallucinations, which have been poorly reported in medical literature.22,23 There are no generalizable trends in the temporal nature of visual hallucinations in patients with neurodegenerative diseases. In most cases of visual hallucinations in patients with PD and dementia, insight relating to the perception varies widely based on the patient’s cognitive status. Subsequently, patients’ reactions to the hallucinations also vary widely.
Visual hallucinations in epileptic seizures
Occipital lobe epilepsies represent 1% to 4.6% of all epilepsies; however, these represent 20% to 30% of benign childhood partial epilepsies.24,25 These are commonly associated with various types of visual hallucinations depending upon the location of the seizure onset within the occipital lobe. These are referred to as visual auras.26 Visual auras are classified into simple visual hallucinations, complex visual hallucinations, visual illusions, and ictal amaurosis (hemifield blindness or complete blindness).
Content, perceived physical properties, and reaction. Simple visual hallucinations are often described as brief, stereotypical flashing lights of various shapes and colors. These images may flicker, change shape, or take on a geometric or irregular pattern. Appearances can be repetitive and stereotyped, are often reported as moving horizontally from the periphery to the center of the visual field, and can spread to the entire visual field. Most often, these hallucinations occur for 5 to 30 seconds, and have no discernible provoking factors. Complex visual hallucinations consist of formed images of animals, people, or elaborate scenes. These are believed to reflect activation of a larger area of cortex in the temporo-parieto-occipital region, which is the visual association cortex. Very rarely, occipital lobe seizures can manifest with ictal amaurosis.24
Continue to: Simple visual auras...
Simple visual auras have a very high localizing value to the occipital lobe. The primary visual cortex (Brodmann area 17) is situated in the banks of calcarine fissure and activation of this region produces these simple hallucinations. If the hallucinations are consistently lateralized, the seizures are very likely to be coming from the contralateral occipital lobe.
Visual hallucinations in brain tumors
In general, a tumor anywhere along the optic path can produce visual hallucinations; however, the exact causal mechanism of the hallucinations is unknown. Moreover, tumors in different locations—namely the occipital lobes, temporal lobes, and frontal lobes—appear to produce visual hallucinations with substantially different characteristics.27-29 Further complicating the search for the mechanism of these hallucinations is the fact that tumors are epileptogenic. In addition, 36% to 48% of patients with brain tumors have mood symptoms (depression/mania), and 22% to 24% have psychotic symptoms (delusions/hallucinations); these symptoms are considerably location-dependent.30-32
Content and associated signs/symptoms. There are some grouped symptoms and/or hallucination characteristics associated with cerebral tumors in different lobes of the brain, though these symptoms are not specific. The visual hallucinations associated with brain tumors are typically confined to the field of vision that corresponds to the location of the tumor. Additionally, many such patients have a baseline visual field defect to some extent due to the tumor location.
In patients with occipital lobe tumors, visual hallucinations closely resemble those experienced in occipital lobe seizures, specifically bright flashes of light in colorful simple and complex shapes. Interestingly, those with occipital lobe tumors report xanthopsia, a form of chromatopsia in which objects in their field of view appear abnormally colored a yellowish shade.26,27
In patients with temporal lobe tumors, more complex visual hallucinations of people, objects, and events occurring around them are often accompanied by auditory hallucinations, olfactory hallucinations, and/or anosmia.28In those with frontal lobe tumors, similar complex visual hallucinations of people, objects, and events are seen, and olfactory hallucinations and/or anosmia are often experienced. However, these patients often have a lower likelihood of experiencing auditory hallucinations, and a higher likelihood of developing personality changes and depression than other psychotic symptoms. The visual hallucinations experienced in those with frontal lobe tumors are more likely to have violent content.29
Continue to: Visual hallucinations in migraine with aura
Visual hallucinations in migraine with aura
The estimated prevalence of migraine in the general population is 15% to 29%; 31% of those with migraine experience auras.33-35 Approximately 99% of those with migraine auras experience some type of associated visual phenomena.33,36 The pathophysiology of migraine is believed to be related to spreading cortical depression, in which a slowly propagating wave of neuroelectric depolarization travels over the cortex, followed by a depression of normal brain activity. Visual aura is thought to occur due to the resulting changes in cortical activity in the visual cortex; however, the exact electrophysiology of visual migraine aura is not entirely known.37,38 Though most patients with visual migraine aura experience simple visual hallucinations, complex hallucinations have been reported in the (very rare) cases of migraine coma and familial hemiplegic migraine.39
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The most common hallucinated entities reported by patients with migraine with aura are zigzag, flashing/sparkling, black and white curved figure(s) in the center of the visual field, commonly called a scintillating phosphene or scintillating scotoma.36 The perceived entity is often singular and gradually moves from the center to the periphery of the visual field. These visual hallucinations appear in front of all other objects in the visual field and do not interact with the environment or observer, or resemble or morph into any real-world objects, though they may change in contour, size, and color. The scintillating nature of the hallucination often resolves within minutes, usually leaving a scotoma, or area of vision loss, in the area, with resolution back to baseline vision within 1 hour. The straight, zigzag, and usually black-and-white nature of the scintillating phosphenes of migraine are in notable contrast to the colorful, often circular visual hallucinations experienced in patients with occipital lobe seizures.25
Visual hallucinations in peduncular hallucinosis
Peduncular hallucinosis is a syndrome of predominantly dreamlike visual hallucinations that occurs in the setting of lesions in the midbrain and/or thalamus.40 A recent review of the lesion etiology found that approximately 63% are caused by focal infarction and approximately 15% are caused by mass lesions; subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage, and demyelination cause approximately 5% of cases each.40 Additionally, a review of the affected brainstem anatomy showed almost all lesions were found in the paramedian reticular formations of the midbrain and pons, with the vast majority of lesions affecting or adjacent to the oculomotor and raphe nuclei of the midbrain.39 Due to the commonly involved visual pathway, some researchers have suggested these hallucinations may be the result of a release phenomenon.39
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The visual hallucinations of peduncular hallucinosis usually start 1 to 5 days after the causal lesion forms, last several minutes to hours, and most stop after 1 to 3 weeks; however, cases of hallucinations lasting for years have been reported. These hallucinations have a diurnal pattern of usually appearing while the patient is resting in the evening and/or preparing for sleep. The characteristics of visual hallucinations vary widely from simple distortions in how real objects appear to colorful and vivid hallucinated events and people who can interact with the observer. The content of the visual hallucinations often changes in nature during the hallucination, or from one hallucination to the next. The hallucinated entities can be worldly or extraterrestrial. Once these patients fall asleep, they often have equally vivid and unusual dreams, with content similar to their visual hallucinations. Due to the anatomical involvement of the nigrostriatal pathway and oculomotor nuclei, co-occurring parkinsonism, ataxia, and oculomotor nerve palsy are common and can be a key clinical feature in establishing the diagnosis. Though patients with peduncular hallucinations commonly fear their hallucinations, they often eventually gain insight, which eases their anxiety.39
Other causes
Visual hallucinations in visual impairment
Visual hallucinations are a diagnostic requirement for Charles Bonnet syndrome, in which individuals with vision loss experience visual hallucinations in the corresponding field of vision loss.41 A lesion at any point in the visual pathway that produces visual loss can lead to Charles Bonnet syndrome; however, age-related macular degeneration is the most common cause.42 The hallucinations of Charles Bonnet syndrome are believed to be a release phenomenon, given the defective visual pathway and resultant dysfunction in visual processing. The prevalence of Charles Bonnet syndrome ranges widely by study. Larger studies report a prevalence of 11% to 27% in patients with age-related macular degeneration, depending on the severity of vision loss.43,44 Because there are many causes of Charles Bonnet syndrome, and because a recent study found that only 15% of patients with this syndrome told their eye care clinician and that 21% had not reported their hallucinatory symptoms to anyone, the true prevalence is unknown.42 Though the onset of visual hallucinations correlates with the onset of vision loss, there appears to be no association between the nature or complexity of the hallucinations and the severity or progression of the patient’s vision loss.45 Some studies have reported either the onset of or a higher frequency of visual hallucinations at a time of visual recovery (for example, treatment or exudative age-related macular degeneration), which suggests that hallucinations may be triggered by fluctuations in visual acuity.46,47 Additional risk factors for experiencing visual hallucinations in the setting of visual pathway deficit include a history of stroke, social isolation, poor cognitive function, poor lighting, and age ≥65.
Continue to: Content and associated signs/symptoms
Content and associated signs/symptoms. The visual hallucinations of patients with Charles Bonnet syndrome appear almost exclusively in the defective visual field. Images tend to be complex, colored, with moving parts, and appear in front of the patient. The hallucinations are usually of familiar or normal-appearing people or mundane objects, and as such, the patient often does not realize the hallucinated entity is not real. In patients without comorbid psychiatric disease, visual hallucinations are not accompanied by any other types of hallucinations. The most commonly hallucinated entities are people, followed by simple visual hallucinations of geometric patterns, and then by faces (natural or cartoon-like) and inanimate objects. Hallucinations most commonly occur daily or weekly, and upon waking. These hallucinations most often last several minutes, though they can last just a few seconds or for hours. Hallucinations are usually emotionally neutral, but most patients report feeling confused by their appearance and having a fear of underlying psychiatric disease. They often gain insight to the unreal nature of the hallucinations after counseling.48
Visual hallucinations at the sleep/wake interface
Hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations are fleeting perceptual experiences that occur while an individual is falling asleep or waking, respectively.49 Because by definition visual hallucinations occur while the individual is fully awake, categorizing hallucination-like experiences such as hypnagogia and hypnopompia is difficult, especially since these are similar to other states in which alterations in perception are expected (namely a dream state). They are commonly associated with sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, cataplexy, and sleep paralysis.50,51 In a study of 13,057 individuals in the general population, Ohayon et al4 found the overall prevalence of hypnagogic or hypnopompic hallucinations was 24.8% (5.3% visual) and 6.6% (1.5% visual), respectively. Approximately one-third of participants reported having experienced ≥1 hallucinatory experience in their lifetime, regardless of being asleep or awake.4 There was a higher prevalence of hypnagogic/hypnopompic experiences among those who also reported daytime hallucinations or other psychotic features.
Content and associated signs/symptoms. Unfortunately, because of the frequent co-occurrence of sleep disorders and psychiatric conditions, as well as the general paucity of research, it is difficult to characterize the visual phenomenology of hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations. Some evidence suggests the nature of the perception of the objects hallucinated is substantially impacted by the presence of preexisting psychotic symptoms. Insight into the reality of these hallucinations also depends upon the presence of comorbid psychiatric disease. Hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations are often described as complex, colorful, vivid, and dream-like, as if the patient was in a “half sleep” state.52 They are usually described as highly detailed events involving people and/or animals, though they may be grotesque in nature. Perceived entities are often described as undergoing a transformation or being mobile in their environment. Rarely do these perceptions invoke emotion or change the patient’s beliefs. Hypnagogia/hypnopompia also often have an auditory or haptic component to them. Visual phenomena can either appear to take place within an alternative background environment or appear superimposed on the patient’s actual physical environment.
How to determine the cause
In many of the studies cited in this review, the participants had a considerable amount of psychiatric comorbidity, which makes it difficult to discriminate between pure neurologic and pure psychiatric causes of hallucinations. Though the visual content of the hallucinations (people, objects, shapes, lights) can help clinicians broadly differentiate causes, many other characteristics of both the hallucinations and the patient can help determine the cause (Table3,4,12-39,41-52). The most useful characteristics for discerning the etiology of an individual’s visual hallucinations are the patient’s age, the visual field in which the hallucination occurs, and the complexity/simplicity of the hallucination.

Patient age. Hallucinations associated with primary psychosis decrease with age. The average age of onset of migraine with aura is 21. Occipital lobe seizures occur in early childhood to age 40, but most commonly occur in the second decade.32,36 No trend in age can be reliably determined in individuals who experience hypnagogia/hypnopompia. In contrast, other potential causes of visual hallucinations, such as delirium, neurodegenerative disease, eye disease, and peduncular hallucinosis, are more commonly associated with advanced age.
Continue to: The visual field(s)
The visual field(s) in which the hallucination occurs can help differentiate possible causes in patients with seizure, brain tumor, migraine, or visual impairment. In patients with psychosis, delirium, peduncular hallucinosis, or hypnagogia/hypnopompia, hallucinations can occur in any visual field. Those with neurodegenerative disease, particularly PD, commonly describe seeing so-called passage hallucinations and presence hallucinations, which occur outside of the patient’s direct vision. Visual hallucinations associated with seizure are often unilateral (homonymous left or right hemifield), and contralateral to the affected neurologic structures in the visual neural pathway; they start in the left or right peripheral vision and gradually move to the central visual field. In hallucinations experienced by patients with brain tumors, the hallucinated entities typically appear on the visual field contralateral to the underlying tumor. Visual hallucinations seen in migraine often include a figure that moves from central vision to more lateral in the visual field. The visual hallucinations seen in eye disease (namely Charles Bonnet syndrome) are almost exclusively perceived in the visual fields affected by decreased visual acuity, though non-side-locked visual hallucinations are common in patients with age-related macular degeneration.
Content and complexity. The visual hallucinations perceived in those with psychosis, delirium, neurodegenerative disease, and sleep disorders are generally complex. These hallucinations tend to be of people, animals, scenes, or faces and include color and associated sound, with moving parts and interactivity with either the patient or the environment. These are in contrast to the simple visual hallucinations of visual cortex seizures, brain tumors, and migraine aura, which are often reported as brightly colored or black/white lights, flashes, and shapes, with or without associated auditory, olfactory, or somatic sensation. Furthermore, hallucinations due to seizure and brain tumor (also likely due to seizure) are often of brightly colored shapes and lights with curved edges, while patients with migraine more commonly report singular sparkling black/white objects with straight lines.
Bottom Line
Though there are no features known to be specific to only 1 cause of visual hallucinations, some characteristics of both the patient and the hallucinations can help direct the diagnostic differential. The most useful characteristics are the patient’s age, the visual field in which the hallucination occurs, and the complexity/ simplicity of the hallucination.
Related Resources
- Wang J, Patel D, Francois D. Elaborate hallucinations, but is it a psychotic disorder? Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):46-50. doi:10.12788/cp.0091
- O’Brien J, Taylor JP, Ballard C, et al. Visual hallucinations in neurological and ophthalmological disease: pathophysiology and management. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020; 91(5):512-519. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2019-322702
1. Asaad G, Shapiro B. Hallucinations: theoretical and clinical overview. Am J Psychiatry. 1987;143(9):1088-1097.
2. Taam MA, Boissieu P, Taam RA, et al. Drug-induced hallucination: a case/non-case study in the French Pharmacovigilance Database. Article in French. Eur J Psychiatry. 2015;29(1):21-31.
3. Waters F, Collerton D, Ffytche DH, et al. Visual hallucinations in the psychosis spectrum and comparative information from neurodegenerative disorders and disease. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40(Suppl 4):S233-S245.
4. Ohayon MM. Prevalence of hallucinations and their pathological associations in the general population. Psychiatry Res. 2000;97(2-3):153-164.
5. Rees WD. The hallucinations of widowhood. Br Med J. 1971;4(5778):37-41.
6. Delespaul P, deVries M, van Os J. Determinants of occurrence and recovery from hallucinations in daily life. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2002;37(3):97-104.
7. Gauntlett-Gilbert J, Kuipers E. Phenomenology of visual hallucinations in psychiatric conditions. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2003;191(3):203-205.
8. Goodwin FK, Jamison KR. Manic Depressive Illness. Oxford University Press, Inc.; 1999.
9. Mueser KT, Bellack AS, Brady EU. Hallucinations in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1990;82(1):26-29.
10. McCabe MS, Fowler RC, Cadoret RJ, et al. Symptom differences in schizophrenia with good and bad prognosis. Am J Psychiatry. 1972;128(10):1239-1243.
11. Baethge C, Baldessarini RJ, Freudenthal K, et al. Hallucinations in bipolar disorder: characteristics and comparison to unipolar depression and schizophrenia. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(2):136-145.
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
13. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-333.
14. Webster R, Holroyd S. Prevalence of psychotic symptoms in delirium. Psychosomatics. 2000;41(6):519-522.
15. Tachibana M, Inada T, Ichida M, et al. Factors affecting hallucinations in patients with delirium. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13005. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-92578-1
16. Fenelon G, Mahieux F, Huon R, et al. Hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 4):733-745.
17. Papapetropoulos S, Argyriou AA, Ellul J. Factors associated with drug-induced visual hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2005;252(10):1223-1228.
18. Williams DR, Warren JD, Lees AJ. Using the presence of visual hallucinations to differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(6):652-655.
19. Linszen MMJ, Lemstra AW, Dauwan M, et al. Understanding hallucinations in probable Alzheimer’s disease: very low prevalence rates in a tertiary memory clinic. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2018;10:358-362.
20. Burghaus L, Eggers C, Timmermann L, et al. Hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012;18(2):149-159.
21. Brar HK, Vaddigiri V, Scicutella A. Of illusions, hallucinations, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (Heidenhain’s variant). J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005;17(1):124-126.
22. Sasaki C, Yokoi K, Takahashi H, et al. Visual illusions in Parkinson’s disease: an interview survey of symptomatology. Psychogeriatrics. 2022;22(1):28-48.
23. Kropp S, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Finkenstaedt M, et al. The Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol. 1999;56(1):55-61.
24. Taylor I, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF. Occipital epilepsies: identification of specific and newly recognized syndromes. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 4):753-769.
25. Caraballo R, Cersosimo R, Medina C, et al. Panayiotopoulos-type benign childhood occipital epilepsy: a prospective study. Neurology. 2000;5(8):1096-1100.
26. Chowdhury FA, Silva R, Whatley B, et al. Localisation in focal epilepsy: a practical guide. Practical Neurol. 2021;21(6):481-491.
27. Horrax G, Putnam TJ. Distortions of the visual fields in cases of brain tumour: the field defects and hallucinations produced by tumours of the occipital lobe. Brain. 1932;55(4):499-523.
28. Cushing H. Distortions of the visual fields in cases of brain tumor (6th paper): the field defects produced by temporal lobe lesions. Brain. 1922;44(4):341-396.
29. Fornazzari L, Farcnik K, Smith I, et al. Violent visual hallucinations and aggression in frontal lobe dysfunction: clinical manifestations of deep orbitofrontal foci. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1992;4(1):42-44.
30. Madhusoodanan S, Opler MGA, Moise D, et al. Brain tumor location and psychiatric symptoms: is there an association? A meta-analysis of published cases studies. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010;10(10):1529-1536.
31. Madhusoodanan S, Sinha A, Moise D. Brain tumors and psychiatric manifestations: a review and analysis. Poster presented at: The American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry Annual Meeting; March 10-13; 2006; San Juan, Puerto Rico.
32. Madhusoodanan S, Danan D, Moise D. Psychiatric manifestations of brain tumors/gliomas. Rivistica Medica. 2007;13(4):209-215.
33. Kirchmann M. Migraine with aura: new understanding from clinical epidemiological studies. Curr Opin Neurol. 2006;19:286-293.
34. Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine: current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):257-270.
35. Waters WE, O’Connor PJ. Prevalence of migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975;38(6):613-616.
36. Russell MB, Olesen J. A nosographic analysis of the migraine aura in a general population. Brain. 1996;119(Pt 2):355-361.
37. Cozzolino O, Marchese M, Trovato F, et al. Understanding spreading depression from headache to sudden unexpected death. Front Neurol. 2018;9:19.
38. Hadjikhani N, Sanchez del Rio M, Wu O, et al. Mechanisms of migraine aura revealed by functional MRI in human visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(8):4687-4692.
39. Manford M, Andermann F. Complex visual hallucinations. Clinical and neurobiological insights. Brain. 1998;121(Pt 10):1819-1840.
40. Galetta KM, Prasad S. Historical trends in the diagnosis of peduncular hallucinosis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38(4):438-441.
41. Schadlu AP, Schadlu R, Shepherd JB III. Charles Bonnet syndrome: a review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009;20(3):219-222.
42. Vukicevic M, Fitzmaurice K. Butterflies and black lace patterns: the prevalence and characteristics of Charles Bonnet hallucinations in an Australian population. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;36(7):659-665.
43. Teunisse RJ, Cruysberg JR, Verbeek A, et al. The Charles Bonnet syndrome: a large prospective study in the Netherlands. A study of the prevalence of the Charles Bonnet syndrome and associated factors in 500 patients attending the University Department of Ophthalmology at Nijmegen. Br J Psychiatry. 1995;166(2):254-257.
44. Holroyd S, Rabins PV, Finkelstein D, et al. Visual hallucination in patients with macular degeneration. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149(12):1701-1706.
45. Khan JC, Shahid H, Thurlby DA, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome in age-related macular degeneration: the nature and frequency of images in subjects with end-stage disease. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2008;15(3):202-208.
46. Cohen SY, Bulik A, Tadayoni R, et al. Visual hallucinations and Charles Bonnet syndrome after photodynamic therapy for age related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003;87(8):977-979.
47. Meyer CH, Mennel S, Horle S, et al. Visual hallucinations after intravitreal injection of bevacizumab in vascular age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143(1):169-170.
48. Jan T, Del Castillo J. Visual hallucinations: Charles Bonnet syndrome. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(6):544-547. doi:10.5811/westjem.2012.7.12891
49. Foulkes D, Vogel G. Mental activity at sleep onset. J Abnorm Psychol. 1965;70:231-243.
50. Mitler MM, Hajdukovic R, Erman M, et al. Narcolepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1990;7(1):93-118.
51. Nishino S. Clinical and neurobiological aspects of narcolepsy. Sleep Med. 2007;8(4):373-399.
52. Schultz SK, Miller DD, Oliver SE, et al. The life course of schizophrenia: age and symptom dimensions. Schizophr Res. 1997;23(1):15-23.
1. Asaad G, Shapiro B. Hallucinations: theoretical and clinical overview. Am J Psychiatry. 1987;143(9):1088-1097.
2. Taam MA, Boissieu P, Taam RA, et al. Drug-induced hallucination: a case/non-case study in the French Pharmacovigilance Database. Article in French. Eur J Psychiatry. 2015;29(1):21-31.
3. Waters F, Collerton D, Ffytche DH, et al. Visual hallucinations in the psychosis spectrum and comparative information from neurodegenerative disorders and disease. Schizophr Bull. 2014;40(Suppl 4):S233-S245.
4. Ohayon MM. Prevalence of hallucinations and their pathological associations in the general population. Psychiatry Res. 2000;97(2-3):153-164.
5. Rees WD. The hallucinations of widowhood. Br Med J. 1971;4(5778):37-41.
6. Delespaul P, deVries M, van Os J. Determinants of occurrence and recovery from hallucinations in daily life. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2002;37(3):97-104.
7. Gauntlett-Gilbert J, Kuipers E. Phenomenology of visual hallucinations in psychiatric conditions. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2003;191(3):203-205.
8. Goodwin FK, Jamison KR. Manic Depressive Illness. Oxford University Press, Inc.; 1999.
9. Mueser KT, Bellack AS, Brady EU. Hallucinations in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1990;82(1):26-29.
10. McCabe MS, Fowler RC, Cadoret RJ, et al. Symptom differences in schizophrenia with good and bad prognosis. Am J Psychiatry. 1972;128(10):1239-1243.
11. Baethge C, Baldessarini RJ, Freudenthal K, et al. Hallucinations in bipolar disorder: characteristics and comparison to unipolar depression and schizophrenia. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(2):136-145.
12. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
13. Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL. Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2014;43(3):326-333.
14. Webster R, Holroyd S. Prevalence of psychotic symptoms in delirium. Psychosomatics. 2000;41(6):519-522.
15. Tachibana M, Inada T, Ichida M, et al. Factors affecting hallucinations in patients with delirium. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13005. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-92578-1
16. Fenelon G, Mahieux F, Huon R, et al. Hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 4):733-745.
17. Papapetropoulos S, Argyriou AA, Ellul J. Factors associated with drug-induced visual hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2005;252(10):1223-1228.
18. Williams DR, Warren JD, Lees AJ. Using the presence of visual hallucinations to differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(6):652-655.
19. Linszen MMJ, Lemstra AW, Dauwan M, et al. Understanding hallucinations in probable Alzheimer’s disease: very low prevalence rates in a tertiary memory clinic. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2018;10:358-362.
20. Burghaus L, Eggers C, Timmermann L, et al. Hallucinations in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012;18(2):149-159.
21. Brar HK, Vaddigiri V, Scicutella A. Of illusions, hallucinations, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (Heidenhain’s variant). J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2005;17(1):124-126.
22. Sasaki C, Yokoi K, Takahashi H, et al. Visual illusions in Parkinson’s disease: an interview survey of symptomatology. Psychogeriatrics. 2022;22(1):28-48.
23. Kropp S, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Finkenstaedt M, et al. The Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol. 1999;56(1):55-61.
24. Taylor I, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF. Occipital epilepsies: identification of specific and newly recognized syndromes. Brain. 2003;126(Pt 4):753-769.
25. Caraballo R, Cersosimo R, Medina C, et al. Panayiotopoulos-type benign childhood occipital epilepsy: a prospective study. Neurology. 2000;5(8):1096-1100.
26. Chowdhury FA, Silva R, Whatley B, et al. Localisation in focal epilepsy: a practical guide. Practical Neurol. 2021;21(6):481-491.
27. Horrax G, Putnam TJ. Distortions of the visual fields in cases of brain tumour: the field defects and hallucinations produced by tumours of the occipital lobe. Brain. 1932;55(4):499-523.
28. Cushing H. Distortions of the visual fields in cases of brain tumor (6th paper): the field defects produced by temporal lobe lesions. Brain. 1922;44(4):341-396.
29. Fornazzari L, Farcnik K, Smith I, et al. Violent visual hallucinations and aggression in frontal lobe dysfunction: clinical manifestations of deep orbitofrontal foci. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1992;4(1):42-44.
30. Madhusoodanan S, Opler MGA, Moise D, et al. Brain tumor location and psychiatric symptoms: is there an association? A meta-analysis of published cases studies. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010;10(10):1529-1536.
31. Madhusoodanan S, Sinha A, Moise D. Brain tumors and psychiatric manifestations: a review and analysis. Poster presented at: The American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry Annual Meeting; March 10-13; 2006; San Juan, Puerto Rico.
32. Madhusoodanan S, Danan D, Moise D. Psychiatric manifestations of brain tumors/gliomas. Rivistica Medica. 2007;13(4):209-215.
33. Kirchmann M. Migraine with aura: new understanding from clinical epidemiological studies. Curr Opin Neurol. 2006;19:286-293.
34. Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine: current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):257-270.
35. Waters WE, O’Connor PJ. Prevalence of migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975;38(6):613-616.
36. Russell MB, Olesen J. A nosographic analysis of the migraine aura in a general population. Brain. 1996;119(Pt 2):355-361.
37. Cozzolino O, Marchese M, Trovato F, et al. Understanding spreading depression from headache to sudden unexpected death. Front Neurol. 2018;9:19.
38. Hadjikhani N, Sanchez del Rio M, Wu O, et al. Mechanisms of migraine aura revealed by functional MRI in human visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(8):4687-4692.
39. Manford M, Andermann F. Complex visual hallucinations. Clinical and neurobiological insights. Brain. 1998;121(Pt 10):1819-1840.
40. Galetta KM, Prasad S. Historical trends in the diagnosis of peduncular hallucinosis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38(4):438-441.
41. Schadlu AP, Schadlu R, Shepherd JB III. Charles Bonnet syndrome: a review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2009;20(3):219-222.
42. Vukicevic M, Fitzmaurice K. Butterflies and black lace patterns: the prevalence and characteristics of Charles Bonnet hallucinations in an Australian population. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;36(7):659-665.
43. Teunisse RJ, Cruysberg JR, Verbeek A, et al. The Charles Bonnet syndrome: a large prospective study in the Netherlands. A study of the prevalence of the Charles Bonnet syndrome and associated factors in 500 patients attending the University Department of Ophthalmology at Nijmegen. Br J Psychiatry. 1995;166(2):254-257.
44. Holroyd S, Rabins PV, Finkelstein D, et al. Visual hallucination in patients with macular degeneration. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149(12):1701-1706.
45. Khan JC, Shahid H, Thurlby DA, et al. Charles Bonnet syndrome in age-related macular degeneration: the nature and frequency of images in subjects with end-stage disease. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2008;15(3):202-208.
46. Cohen SY, Bulik A, Tadayoni R, et al. Visual hallucinations and Charles Bonnet syndrome after photodynamic therapy for age related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003;87(8):977-979.
47. Meyer CH, Mennel S, Horle S, et al. Visual hallucinations after intravitreal injection of bevacizumab in vascular age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143(1):169-170.
48. Jan T, Del Castillo J. Visual hallucinations: Charles Bonnet syndrome. West J Emerg Med. 2012;13(6):544-547. doi:10.5811/westjem.2012.7.12891
49. Foulkes D, Vogel G. Mental activity at sleep onset. J Abnorm Psychol. 1965;70:231-243.
50. Mitler MM, Hajdukovic R, Erman M, et al. Narcolepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1990;7(1):93-118.
51. Nishino S. Clinical and neurobiological aspects of narcolepsy. Sleep Med. 2007;8(4):373-399.
52. Schultz SK, Miller DD, Oliver SE, et al. The life course of schizophrenia: age and symptom dimensions. Schizophr Res. 1997;23(1):15-23.
Iron deficiency in psychiatric patients
Nutritional deficiencies are one of the many causes of or contributors to symptoms in patients with psychiatric disorders. In this article, we discuss the prevalence of iron deficiency and its link to poor mental health, and how proper treatment may improve psychiatric symptoms. We also offer suggestions for how and when to test for and treat iron deficiency in psychiatric patients.
A common condition
Iron deficiency is the most common mineral deficiency in the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 25% of the global population is anemic and nearly one-half of those cases are the result of iron deficiency.1 While the WHO has published guidelines defining iron deficiency as it relates to ferritin levels (<15 ug/L in adults and <12 ug/L in children), this estimate might be low.2,3 Mei et al2 found that hemoglobin and soluble transferrin receptors can be used to determine iron-deficient erythropoiesis, which indicates a physiological definition of iron deficiency. According to a study of children and nonpregnant women by Mei et al,2 children with ferritin levels <20 ug/L and women with ferritin levels <25 ug/L should be considered iron-deficient. If replicated, this study suggests the prevalence of iron deficiency is higher than currently estimated.2 Overall, an estimated 1.2 billion people worldwide have iron-deficiency anemia.4 Additionally, patients can be iron deficient without being anemic, a condition thought to be at least twice as common.4
Essential for brain function
Research shows the importance of iron to proper brain function.5 Iron deficiency in pregnant women is associated with significant neuropsychological impairments in neonates. Rodent studies have demonstrated the importance of iron and the effects of iron deficiency on the hippocampus, corpus striatum, and production of monoamines.5 Specifically, iron is a necessary cofactor in the enzymes tryptophan hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase, which produce serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. In rodent studies, monoamine deficits secondary to iron deficiency persist into adulthood even with iron supplementation, which highlights the importance of preventing iron deficiency during pregnancy and early life.5 While most research has focused on the impact of iron deficiency in infancy and early childhood, iron deficiency has an ongoing impact into adulthood, even if treated.6
Iron deficiency and psychiatric symptoms
Current research suggests an association between iron deficiency or low ferritin levels and psychiatric disorders, specifically depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. In a web survey of 11,876 adults, Hidese et al7 found an association between a self-reported history of iron deficiency anemia and a self-reported history of depression. Another study of 528 municipal employees found an association between low serum ferritin concentrations and a high prevalence of depressive symptoms among men; no statistically significant association was detected in women.8 In an analysis of the Taiwan National Health Insurance Database from 2000 to 2012, Lee et al9 found a statistically significant increased risk of anxiety disorders, depression, sleep disorders, and psychotic disorders in patients with iron deficiency anemia after controlling for multiple confounders. Xu et al10 used quantitative susceptibility mapping to assess the iron status in certain regions of the brain of 30 patients with first-episode psychosis. They found lower levels of iron in the bilateral substantia nigra, left red nucleus, and left thalamus compared to healthy controls.10 Kim et al11 found an association between iron deficiency and more severe negative symptoms in 121 patients with first-episode psychosis, which supports the hypothesis that iron deficiency may alter dopamine transmission in the brain.
Iron deficiency has been associated with psychopathology across the lifespan. In a population-based study in Taiwan, Chen et al12 found an association between iron deficiency anemia and psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents, including mood disorders, autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and developmental disorders. At the other end of the age spectrum, in a survey of 1,875 older adults in England, Stewart et al13 found an association between low ferritin levels (<45 ng/mL) and depressive symptoms after adjusting for demographic factors and overall health status.
In addition to specific psychiatric disorders and symptoms, iron deficiency is often associated with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue.14 Fatigue is a symptom of numerous psychiatric disorders and is included in the DSM diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.15
Iron supplementation might improve psychiatric symptoms
Some evidence suggests that using iron supplementation to treat iron deficiency can improve psychiatric symptoms. In a 2013 systematic literature review of 10 studies, Greig et al16 found a link between low iron status and poor cognition, poor mental health scores, and fatigue among women of childbearing age. In this review, 7 studies demonstrated improvement in cognition and 3 demonstrated improvement in mental health with iron supplementation.16 In a 2021 prospective study, 19 children and adolescents age 6 to 15 who had serum ferritin levels <30 ng/mL were treated with oral iron supplementation for 12 weeks.17 Participants showed significant improvements in sleep quality, depressive symptoms, and general mood as assessed via the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale, and Profile of Mood States (POMS) questionnaires, respectively.17 A randomized controlled trial of 219 female soldiers who were given iron supplementation or placebo for 8 weeks during basic combat training found that compared to placebo, iron supplementation led to improvements in mood as measured by the POMS questionnaire.18 Lastly, in a 2016 observational study of 412 adult psychiatric patients, Kassir19 found most patients (81%) had iron deficiency, defined as a transferrin saturation coefficient <30% or serum ferritin <100 ng/mL. Although these cutoffs are not considered standard and thus may have overrepresented the percentage of patients considered iron-deficient, more than one-half of patients considered iron-deficient in this study experienced a reduction or elimination of psychiatric symptoms following treatment with iron supplementation and/or psychotropic medications.19
Continue to: Individuals with iron deficiency...
Individuals with iron deficiency without anemia also may see improvement in psychiatric symptoms with iron treatment. In a 2018 systematic review, Houston et al20 evaluated iron supplementation in 1,170 adults who were iron-deficient but not anemic. They found that in these patients, fatigue significantly improved but physical capacity did not.20 Additionally, 2 other studies found iron treatment improved fatigue in nonanemic women.21,22 In a 2016 systematic review, Pratt et al23 concluded, “There is emerging evidence that … nonanemic iron deficiency … is a disease in its own right, deserving of further research in the development of strategies for detection and treatment.” Al-Naseem et al24 suggested severity distinguishes iron deficiency with and without anemia.
Your role in assessing and treating iron deficiency
Testing for and treating iron deficiency generally is not a part of routine psychiatric practice. This might be due to apathy given the pervasiveness of iron deficiency, a belief that iron deficiency should be managed by primary care physicians, or a lack of familiarity with how to treat it and the benefits of such treatment for psychiatric patients. However, assessing for and treating iron deficiency in psychiatric patients is important, especially for individuals who are highly susceptible to inadequate iron levels. People at risk for iron deficiency include pregnant women, infants, young children, women with heavy menstrual bleeding, frequent blood donors, patients with cancer, individuals who have gastrointestinal (GI) surgeries or disorders, and those with heart failure.25
Assessment. Iron status can be assessed through an iron studies panel. Because a patient can have iron deficiency without anemia, a complete blood count (CBC) alone does not suffice.26 The iron panel includes serum iron, serum ferritin, serum transferrin or total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), and calculated transferrin saturation (TSAT), which is the ratio of serum iron to TIBC.
Iron deficiency is diagnosed if ferritin is <30 ng/mL, regardless of the hemoglobin concentration or underlying condition, and confirmed by a low TSAT.26 In most guidelines, the cutoff value for TSAT for iron deficiency is <20%. Because the TSAT can be influenced by iron supplements or iron-rich foods, wait several hours to obtain blood after a patient takes an oral iron supplement or eats iron-rich foods. If desired, clinicians can use either ferritin or TSAT alone to diagnose iron deficiency. However, because ferritin can be falsely normal in inflammatory conditions such as obesity and infection, a TSAT may be needed to confirm iron deficiency if there is a high clinical suspicion despite a normal ferritin level.26
Treatment. If iron deficiency is confirmed, instruct your patient to follow up with their primary care physician or the appropriate specialist to evaluate for any underlying etiologies.
Continue to: Iron deficiency should be treated...
Iron deficiency should be treated with supplementation because diet alone is insufficient for replenishing iron stores. Iron replacement can be oral or IV. Oral replacement is effective, safe, inexpensive, easy to obtain, and easy to administer.27 Oral replacement is recommended for adults whose anemia is not severe or who do not have a comorbid condition such as pregnancy, inflammatory bowel conditions, gastric surgery, or chronic kidney disease. When anemia is severe or a patient has one of these comorbid conditions, IV is the preferred method of replacement.27 In these cases, defer treatment to the patient’s primary care physician or specialist.
There are no clear recommendations on the amount of iron per dose to prescribe.27 The maximum amount of oral iron that can be absorbed is approximately 25 mg/d of elemental iron. A 325 mg ferrous sulfate tablet contains 65 mg of elemental iron, of which approximately 25 mg is absorbed and utilized.27
Emerging evidence suggests that excessive iron dosing may reduce iron absorption and increase adverse effects. In a study of 54 nonanemic young women with iron deficiency who were given iron supplementation, Moretti et al28 found that a large oral dose of iron taken in the morning increased hepcidin, which decreased the absorption of iron taken later for up to 48 hours. They found that 40 to 80 mg of elemental iron given on alternate days may maximize the fractional iron absorbed, increase dosage efficacy, reduce GI exposure to unabsorbed iron, and improve patients’ ability to tolerate iron supplementation.28
Adverse effects from iron supplements occur in up to 70% of patients.27 These can include metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea, epigastric pain, constipation, and dark stools.27 Using a liquid form may help reduce adverse effects because it can be more easily titrated.27 Tell patients to avoid enteric-coated or sustained-release iron capsules because these are poorly absorbed. Be cautious when prescribing iron supplementation to older adults because these patients tend to have more adverse effects, especially constipation, as well as reduced absorption, and may ultimately need IV treatment. Iron should not be taken with food, calcium supplements, antacids, coffee, tea, or milk.27
The amount of iron present, cost, and adverse effects vary by supplement. The Table27,29-33 provides more information on available forms of iron. Many forms of iron supplementation are available over-the-counter, and most are equally effective.27 Advise patients to use iron products that have been tested by an independent company, such as ConsumerLab.com. Such companies evaluate products to see if they contain the amount of iron listed on the product’s label; for contamination with lead, cadmium, or arsenic; and for the product’s ability to break apart for absorption.34
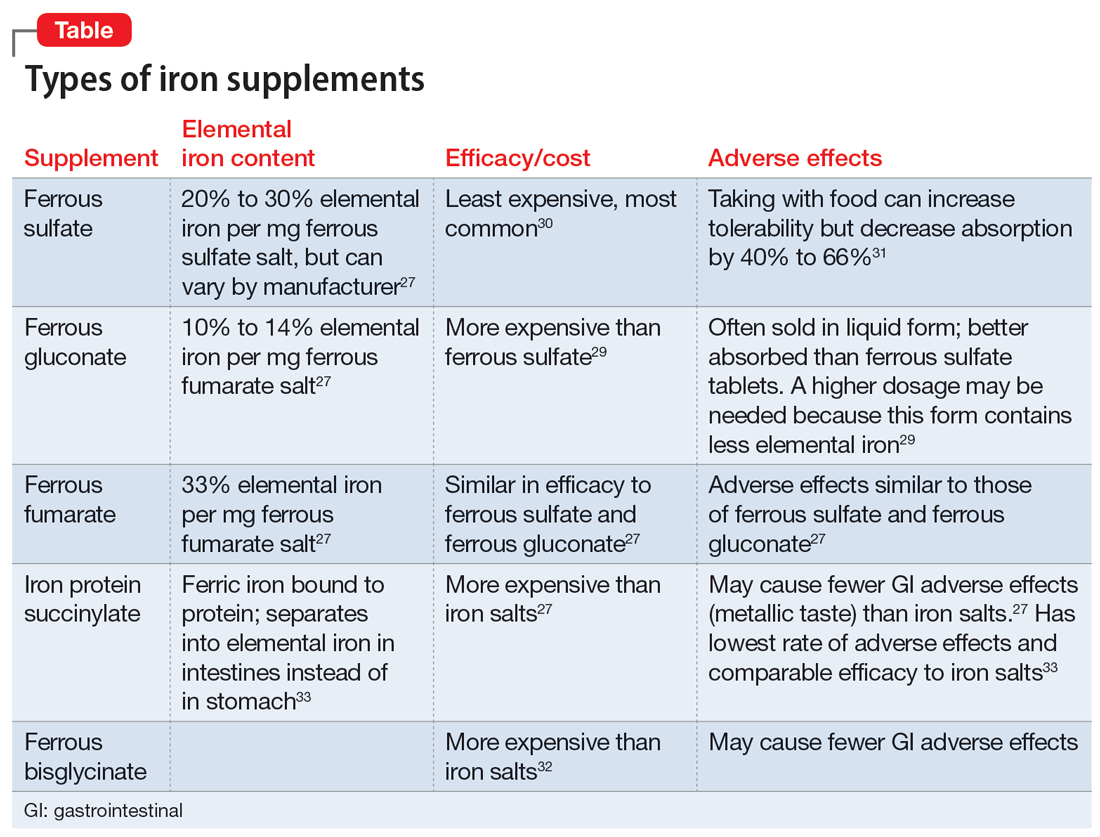
Six to 8 weeks of treatment with oral iron supplementation may be necessary before anemia is fully resolved, and it may take up to 6 months for iron stores to be repleted.27 If a patient cannot tolerate an iron supplement, reducing the dose or taking it with meals may help prevent adverse effects, but also will reduce absorption. Auerbach27 recommends assessing tolerability and rechecking the patient’s CBC 2 weeks after starting oral iron replacement, while also checking hemoglobin and the reticulocyte count to see if the patient is responding to treatment. An analysis of 5 studies found that a hemoglobin measurement on Day 14 that shows an increase ≥1.0 g/dL from baseline predicts longer-term and sustained treatment response to continued oral therapy.35 There is no clear consensus for target ferritin levels, but we suggest aiming for a ferritin level >100 ug/L based on recommendations for the treatment of restless legs syndrome.36 We recommend ongoing monitoring every 4 to 6 weeks.
Bottom Line
Iron deficiency is common and can cause or contribute to psychiatric symptoms and disorders. Consider screening patients for iron deficiency and treating it with oral supplementation in individuals without any comorbidities, or referring them to their primary care physician or specialist.
Related Resources
- Berthou C, Iliou JP, Barba D. Iron, neuro-bioavailability and depression. EJHaem. 2021;3(1):263-275.
1. McLean E, Cogswell M, Egli I, et al. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993-2005. Public Health Nutr. 2009;12(4):444-454.
2. Mei Z, Addo OY, Jefferds ME, et al. Physiologically based serum ferritin thresholds for iron deficiency in children and non-pregnant women: a US National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) serial cross-sectional study. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(8):e572-e582.
3. Snozek CLH, Spears GM, Porco AB, et al. Updated ferritin reference intervals for the Roche Elecsys® immunoassay. Clin Biochem. 2021;87:100-103. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.11.006
4. Camaschella C. Iron deficiency. Blood. 2019;133(1):30-39. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-05-815944
5. Lozoff B, Georgieff MK. Iron deficiency and brain development. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2006;13(3):158-165.
6. Shah HE, Bhawnani N, Ethirajulu A, et al. Iron deficiency-induced changes in the hippocampus, corpus striatum, and monoamines levels that lead to anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and psychotic disorders. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18138.
7. Hidese S, Saito K, Asano S, et al. Association between iron-deficiency anemia and depression: a web-based Japanese investigation. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018;72(7):513-521.
8. Yi S, Nanri A, Poudel-Tandukar K, et al. Association between serum ferritin concentrations and depressive symptoms in Japanese municipal employees. Psychiatry Res. 2011;189(3):368-372.
9. Lee HS, Chao HH, Huang WT, et al. Psychiatric disorders risk in patients with iron deficiency anemia and association with iron supplementation medications: a nationwide database analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20(1):216.
10. Xu M, Guo Y, Cheng J, et al. Brain iron assessment in patients with first-episode schizophrenia using quantitative susceptibility mapping. Neuroimage Clin. 2021;31:102736.
11. Kim SW, Stewart R, Park WY, et al. Latent iron deficiency as a marker of negative symptoms in patients with first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Nutrients. 2018;10(11):1707.
12. Chen MH, Su TP, Chen YS, et al. Association between psychiatric disorders and iron deficiency anemia among children and adolescents: a nationwide population-based study. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:161.
13. Stewart R, Hirani V. Relationship between depressive symptoms, anemia, and iron status in older residents from a national survey population. Psychosom Med. 2012;74(2):208-213.
14. Hanif N. Anwer F. Chronic iron deficiency. Updated September 10, 2022. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560876/
15.
16. Greig AJ, Patterson AJ, Collins CE, et al. Iron deficiency, cognition, mental health and fatigue in women of childbearing age: a systematic review. J Nutr Sci. 2013;2:e14.
17. Mikami K, Akama F, Kimoto K, et al. Iron supplementation for hypoferritinemia-related psychological symptoms in children and adolescents. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89(2):203-211.
18. McClung JP, Karl JP, Cable SJ, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of iron supplementation in female soldiers during military training: effects on iron status, physical performance, and mood. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(1):124-131.
19. Kassir A. Iron deficiency: a diagnostic and therapeutic perspective in psychiatry. Article in French. Encephale. 2017;43(1):85-89.
20. Houston BL, Hurrie D, Graham J, et al. Efficacy of iron supplementation on fatigue and physical capacity in non-anaemic iron-deficient adults: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2018;8(4):e019240. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019240
21. Krayenbuehl PA, Battegay E, Breymann C, et al. Intravenous iron for the treatment of fatigue in nonanemic, premenopausal women with low serum ferritin concentration. Blood. 2011;118(12):3222-3227. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-04-346304
22. Vaucher P, Druais PL, Waldvogel S, et al. Effect of iron supplementation on fatigue in nonanemic menstruating women with low ferritin: a randomized controlled trial. CMAJ. 2012;184(11):1247-1254. doi:10.1503/cmaj.110950
23. Pratt JJ, Khan KS. Non-anaemic iron deficiency - a disease looking for recognition of diagnosis: a systematic review. Eur J Haematol. 2016;96(6):618-628. doi:10.1111/ejh.12645
24. Al-Naseem A, Sallam A, Choudhury S, et al. Iron deficiency without anaemia: a diagnosis that matters. Clin Med (Lond). 2021;21(2):107-113. doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0582
25. National Institute of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Iron. Fact sheet for health professionals. Updated April 5, 2022. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/
26. Auerbach M. Causes and diagnosis of iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/causes-and-diagnosis-of-iron-deficiency-and-iron-deficiency-anemia-in-adults
27. Auerbach M. Treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-iron-deficiency-anemia-in-adults
28. Moretti D, Goede JS, Zeder C, et al. Oral iron supplements increase hepcidin and decrease iron absorption from daily or twice-daily doses in iron-depleted young women. Blood. 2015;126(17):1981-1989.
29. Cooperman T. Iron supplements review (iron pills, liquids and chews). ConsumerLab.com. Published January 31, 2022. Updated December 19, 2022. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://www.consumerlab.com/reviews/iron-supplements-review/iron/
30. Okam MM, Koch TA, Tran MH. Iron deficiency anemia treatment response to oral iron therapy: a pooled analysis of five randomized controlled trials. Haematologica. 2016;101(1):e6-e7.
31. Silber MH. Management of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 10, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-restless-legs-syndrome-and-periodic-limb-movement-disorder-in-adults
32. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The nutrition source: iron. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/iron/
33. Little DR. Ambulatory management of common forms of anemia. Am Fam Physician. 1999;59(6):1598-1604.
34. Blood modifiers. In: Drug Facts and Comparisons. Facts and Comparisons. 1998:238-257.
35. Cancelo-Hidalgo MJ, Castelo-Branco C, Palacios S, et al. Tolerability of different oral iron supplements: a systematic review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29(4):291-303.
36. Francés AM, Martínez-Bujanda JL. Efficacy and tolerability of oral iron protein succinylate: a systematic review of three decades of research. Curr Med Res Opinion. 2020;36(4):613-623. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1716702
Nutritional deficiencies are one of the many causes of or contributors to symptoms in patients with psychiatric disorders. In this article, we discuss the prevalence of iron deficiency and its link to poor mental health, and how proper treatment may improve psychiatric symptoms. We also offer suggestions for how and when to test for and treat iron deficiency in psychiatric patients.
A common condition
Iron deficiency is the most common mineral deficiency in the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 25% of the global population is anemic and nearly one-half of those cases are the result of iron deficiency.1 While the WHO has published guidelines defining iron deficiency as it relates to ferritin levels (<15 ug/L in adults and <12 ug/L in children), this estimate might be low.2,3 Mei et al2 found that hemoglobin and soluble transferrin receptors can be used to determine iron-deficient erythropoiesis, which indicates a physiological definition of iron deficiency. According to a study of children and nonpregnant women by Mei et al,2 children with ferritin levels <20 ug/L and women with ferritin levels <25 ug/L should be considered iron-deficient. If replicated, this study suggests the prevalence of iron deficiency is higher than currently estimated.2 Overall, an estimated 1.2 billion people worldwide have iron-deficiency anemia.4 Additionally, patients can be iron deficient without being anemic, a condition thought to be at least twice as common.4
Essential for brain function
Research shows the importance of iron to proper brain function.5 Iron deficiency in pregnant women is associated with significant neuropsychological impairments in neonates. Rodent studies have demonstrated the importance of iron and the effects of iron deficiency on the hippocampus, corpus striatum, and production of monoamines.5 Specifically, iron is a necessary cofactor in the enzymes tryptophan hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase, which produce serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. In rodent studies, monoamine deficits secondary to iron deficiency persist into adulthood even with iron supplementation, which highlights the importance of preventing iron deficiency during pregnancy and early life.5 While most research has focused on the impact of iron deficiency in infancy and early childhood, iron deficiency has an ongoing impact into adulthood, even if treated.6
Iron deficiency and psychiatric symptoms
Current research suggests an association between iron deficiency or low ferritin levels and psychiatric disorders, specifically depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. In a web survey of 11,876 adults, Hidese et al7 found an association between a self-reported history of iron deficiency anemia and a self-reported history of depression. Another study of 528 municipal employees found an association between low serum ferritin concentrations and a high prevalence of depressive symptoms among men; no statistically significant association was detected in women.8 In an analysis of the Taiwan National Health Insurance Database from 2000 to 2012, Lee et al9 found a statistically significant increased risk of anxiety disorders, depression, sleep disorders, and psychotic disorders in patients with iron deficiency anemia after controlling for multiple confounders. Xu et al10 used quantitative susceptibility mapping to assess the iron status in certain regions of the brain of 30 patients with first-episode psychosis. They found lower levels of iron in the bilateral substantia nigra, left red nucleus, and left thalamus compared to healthy controls.10 Kim et al11 found an association between iron deficiency and more severe negative symptoms in 121 patients with first-episode psychosis, which supports the hypothesis that iron deficiency may alter dopamine transmission in the brain.
Iron deficiency has been associated with psychopathology across the lifespan. In a population-based study in Taiwan, Chen et al12 found an association between iron deficiency anemia and psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents, including mood disorders, autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and developmental disorders. At the other end of the age spectrum, in a survey of 1,875 older adults in England, Stewart et al13 found an association between low ferritin levels (<45 ng/mL) and depressive symptoms after adjusting for demographic factors and overall health status.
In addition to specific psychiatric disorders and symptoms, iron deficiency is often associated with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue.14 Fatigue is a symptom of numerous psychiatric disorders and is included in the DSM diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.15
Iron supplementation might improve psychiatric symptoms
Some evidence suggests that using iron supplementation to treat iron deficiency can improve psychiatric symptoms. In a 2013 systematic literature review of 10 studies, Greig et al16 found a link between low iron status and poor cognition, poor mental health scores, and fatigue among women of childbearing age. In this review, 7 studies demonstrated improvement in cognition and 3 demonstrated improvement in mental health with iron supplementation.16 In a 2021 prospective study, 19 children and adolescents age 6 to 15 who had serum ferritin levels <30 ng/mL were treated with oral iron supplementation for 12 weeks.17 Participants showed significant improvements in sleep quality, depressive symptoms, and general mood as assessed via the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale, and Profile of Mood States (POMS) questionnaires, respectively.17 A randomized controlled trial of 219 female soldiers who were given iron supplementation or placebo for 8 weeks during basic combat training found that compared to placebo, iron supplementation led to improvements in mood as measured by the POMS questionnaire.18 Lastly, in a 2016 observational study of 412 adult psychiatric patients, Kassir19 found most patients (81%) had iron deficiency, defined as a transferrin saturation coefficient <30% or serum ferritin <100 ng/mL. Although these cutoffs are not considered standard and thus may have overrepresented the percentage of patients considered iron-deficient, more than one-half of patients considered iron-deficient in this study experienced a reduction or elimination of psychiatric symptoms following treatment with iron supplementation and/or psychotropic medications.19
Continue to: Individuals with iron deficiency...
Individuals with iron deficiency without anemia also may see improvement in psychiatric symptoms with iron treatment. In a 2018 systematic review, Houston et al20 evaluated iron supplementation in 1,170 adults who were iron-deficient but not anemic. They found that in these patients, fatigue significantly improved but physical capacity did not.20 Additionally, 2 other studies found iron treatment improved fatigue in nonanemic women.21,22 In a 2016 systematic review, Pratt et al23 concluded, “There is emerging evidence that … nonanemic iron deficiency … is a disease in its own right, deserving of further research in the development of strategies for detection and treatment.” Al-Naseem et al24 suggested severity distinguishes iron deficiency with and without anemia.
Your role in assessing and treating iron deficiency
Testing for and treating iron deficiency generally is not a part of routine psychiatric practice. This might be due to apathy given the pervasiveness of iron deficiency, a belief that iron deficiency should be managed by primary care physicians, or a lack of familiarity with how to treat it and the benefits of such treatment for psychiatric patients. However, assessing for and treating iron deficiency in psychiatric patients is important, especially for individuals who are highly susceptible to inadequate iron levels. People at risk for iron deficiency include pregnant women, infants, young children, women with heavy menstrual bleeding, frequent blood donors, patients with cancer, individuals who have gastrointestinal (GI) surgeries or disorders, and those with heart failure.25
Assessment. Iron status can be assessed through an iron studies panel. Because a patient can have iron deficiency without anemia, a complete blood count (CBC) alone does not suffice.26 The iron panel includes serum iron, serum ferritin, serum transferrin or total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), and calculated transferrin saturation (TSAT), which is the ratio of serum iron to TIBC.
Iron deficiency is diagnosed if ferritin is <30 ng/mL, regardless of the hemoglobin concentration or underlying condition, and confirmed by a low TSAT.26 In most guidelines, the cutoff value for TSAT for iron deficiency is <20%. Because the TSAT can be influenced by iron supplements or iron-rich foods, wait several hours to obtain blood after a patient takes an oral iron supplement or eats iron-rich foods. If desired, clinicians can use either ferritin or TSAT alone to diagnose iron deficiency. However, because ferritin can be falsely normal in inflammatory conditions such as obesity and infection, a TSAT may be needed to confirm iron deficiency if there is a high clinical suspicion despite a normal ferritin level.26
Treatment. If iron deficiency is confirmed, instruct your patient to follow up with their primary care physician or the appropriate specialist to evaluate for any underlying etiologies.
Continue to: Iron deficiency should be treated...
Iron deficiency should be treated with supplementation because diet alone is insufficient for replenishing iron stores. Iron replacement can be oral or IV. Oral replacement is effective, safe, inexpensive, easy to obtain, and easy to administer.27 Oral replacement is recommended for adults whose anemia is not severe or who do not have a comorbid condition such as pregnancy, inflammatory bowel conditions, gastric surgery, or chronic kidney disease. When anemia is severe or a patient has one of these comorbid conditions, IV is the preferred method of replacement.27 In these cases, defer treatment to the patient’s primary care physician or specialist.
There are no clear recommendations on the amount of iron per dose to prescribe.27 The maximum amount of oral iron that can be absorbed is approximately 25 mg/d of elemental iron. A 325 mg ferrous sulfate tablet contains 65 mg of elemental iron, of which approximately 25 mg is absorbed and utilized.27
Emerging evidence suggests that excessive iron dosing may reduce iron absorption and increase adverse effects. In a study of 54 nonanemic young women with iron deficiency who were given iron supplementation, Moretti et al28 found that a large oral dose of iron taken in the morning increased hepcidin, which decreased the absorption of iron taken later for up to 48 hours. They found that 40 to 80 mg of elemental iron given on alternate days may maximize the fractional iron absorbed, increase dosage efficacy, reduce GI exposure to unabsorbed iron, and improve patients’ ability to tolerate iron supplementation.28
Adverse effects from iron supplements occur in up to 70% of patients.27 These can include metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea, epigastric pain, constipation, and dark stools.27 Using a liquid form may help reduce adverse effects because it can be more easily titrated.27 Tell patients to avoid enteric-coated or sustained-release iron capsules because these are poorly absorbed. Be cautious when prescribing iron supplementation to older adults because these patients tend to have more adverse effects, especially constipation, as well as reduced absorption, and may ultimately need IV treatment. Iron should not be taken with food, calcium supplements, antacids, coffee, tea, or milk.27
The amount of iron present, cost, and adverse effects vary by supplement. The Table27,29-33 provides more information on available forms of iron. Many forms of iron supplementation are available over-the-counter, and most are equally effective.27 Advise patients to use iron products that have been tested by an independent company, such as ConsumerLab.com. Such companies evaluate products to see if they contain the amount of iron listed on the product’s label; for contamination with lead, cadmium, or arsenic; and for the product’s ability to break apart for absorption.34

Six to 8 weeks of treatment with oral iron supplementation may be necessary before anemia is fully resolved, and it may take up to 6 months for iron stores to be repleted.27 If a patient cannot tolerate an iron supplement, reducing the dose or taking it with meals may help prevent adverse effects, but also will reduce absorption. Auerbach27 recommends assessing tolerability and rechecking the patient’s CBC 2 weeks after starting oral iron replacement, while also checking hemoglobin and the reticulocyte count to see if the patient is responding to treatment. An analysis of 5 studies found that a hemoglobin measurement on Day 14 that shows an increase ≥1.0 g/dL from baseline predicts longer-term and sustained treatment response to continued oral therapy.35 There is no clear consensus for target ferritin levels, but we suggest aiming for a ferritin level >100 ug/L based on recommendations for the treatment of restless legs syndrome.36 We recommend ongoing monitoring every 4 to 6 weeks.
Bottom Line
Iron deficiency is common and can cause or contribute to psychiatric symptoms and disorders. Consider screening patients for iron deficiency and treating it with oral supplementation in individuals without any comorbidities, or referring them to their primary care physician or specialist.
Related Resources
- Berthou C, Iliou JP, Barba D. Iron, neuro-bioavailability and depression. EJHaem. 2021;3(1):263-275.
Nutritional deficiencies are one of the many causes of or contributors to symptoms in patients with psychiatric disorders. In this article, we discuss the prevalence of iron deficiency and its link to poor mental health, and how proper treatment may improve psychiatric symptoms. We also offer suggestions for how and when to test for and treat iron deficiency in psychiatric patients.
A common condition
Iron deficiency is the most common mineral deficiency in the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 25% of the global population is anemic and nearly one-half of those cases are the result of iron deficiency.1 While the WHO has published guidelines defining iron deficiency as it relates to ferritin levels (<15 ug/L in adults and <12 ug/L in children), this estimate might be low.2,3 Mei et al2 found that hemoglobin and soluble transferrin receptors can be used to determine iron-deficient erythropoiesis, which indicates a physiological definition of iron deficiency. According to a study of children and nonpregnant women by Mei et al,2 children with ferritin levels <20 ug/L and women with ferritin levels <25 ug/L should be considered iron-deficient. If replicated, this study suggests the prevalence of iron deficiency is higher than currently estimated.2 Overall, an estimated 1.2 billion people worldwide have iron-deficiency anemia.4 Additionally, patients can be iron deficient without being anemic, a condition thought to be at least twice as common.4
Essential for brain function
Research shows the importance of iron to proper brain function.5 Iron deficiency in pregnant women is associated with significant neuropsychological impairments in neonates. Rodent studies have demonstrated the importance of iron and the effects of iron deficiency on the hippocampus, corpus striatum, and production of monoamines.5 Specifically, iron is a necessary cofactor in the enzymes tryptophan hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase, which produce serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. In rodent studies, monoamine deficits secondary to iron deficiency persist into adulthood even with iron supplementation, which highlights the importance of preventing iron deficiency during pregnancy and early life.5 While most research has focused on the impact of iron deficiency in infancy and early childhood, iron deficiency has an ongoing impact into adulthood, even if treated.6
Iron deficiency and psychiatric symptoms
Current research suggests an association between iron deficiency or low ferritin levels and psychiatric disorders, specifically depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. In a web survey of 11,876 adults, Hidese et al7 found an association between a self-reported history of iron deficiency anemia and a self-reported history of depression. Another study of 528 municipal employees found an association between low serum ferritin concentrations and a high prevalence of depressive symptoms among men; no statistically significant association was detected in women.8 In an analysis of the Taiwan National Health Insurance Database from 2000 to 2012, Lee et al9 found a statistically significant increased risk of anxiety disorders, depression, sleep disorders, and psychotic disorders in patients with iron deficiency anemia after controlling for multiple confounders. Xu et al10 used quantitative susceptibility mapping to assess the iron status in certain regions of the brain of 30 patients with first-episode psychosis. They found lower levels of iron in the bilateral substantia nigra, left red nucleus, and left thalamus compared to healthy controls.10 Kim et al11 found an association between iron deficiency and more severe negative symptoms in 121 patients with first-episode psychosis, which supports the hypothesis that iron deficiency may alter dopamine transmission in the brain.
Iron deficiency has been associated with psychopathology across the lifespan. In a population-based study in Taiwan, Chen et al12 found an association between iron deficiency anemia and psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents, including mood disorders, autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and developmental disorders. At the other end of the age spectrum, in a survey of 1,875 older adults in England, Stewart et al13 found an association between low ferritin levels (<45 ng/mL) and depressive symptoms after adjusting for demographic factors and overall health status.
In addition to specific psychiatric disorders and symptoms, iron deficiency is often associated with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue.14 Fatigue is a symptom of numerous psychiatric disorders and is included in the DSM diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder.15
Iron supplementation might improve psychiatric symptoms
Some evidence suggests that using iron supplementation to treat iron deficiency can improve psychiatric symptoms. In a 2013 systematic literature review of 10 studies, Greig et al16 found a link between low iron status and poor cognition, poor mental health scores, and fatigue among women of childbearing age. In this review, 7 studies demonstrated improvement in cognition and 3 demonstrated improvement in mental health with iron supplementation.16 In a 2021 prospective study, 19 children and adolescents age 6 to 15 who had serum ferritin levels <30 ng/mL were treated with oral iron supplementation for 12 weeks.17 Participants showed significant improvements in sleep quality, depressive symptoms, and general mood as assessed via the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale, and Profile of Mood States (POMS) questionnaires, respectively.17 A randomized controlled trial of 219 female soldiers who were given iron supplementation or placebo for 8 weeks during basic combat training found that compared to placebo, iron supplementation led to improvements in mood as measured by the POMS questionnaire.18 Lastly, in a 2016 observational study of 412 adult psychiatric patients, Kassir19 found most patients (81%) had iron deficiency, defined as a transferrin saturation coefficient <30% or serum ferritin <100 ng/mL. Although these cutoffs are not considered standard and thus may have overrepresented the percentage of patients considered iron-deficient, more than one-half of patients considered iron-deficient in this study experienced a reduction or elimination of psychiatric symptoms following treatment with iron supplementation and/or psychotropic medications.19
Continue to: Individuals with iron deficiency...
Individuals with iron deficiency without anemia also may see improvement in psychiatric symptoms with iron treatment. In a 2018 systematic review, Houston et al20 evaluated iron supplementation in 1,170 adults who were iron-deficient but not anemic. They found that in these patients, fatigue significantly improved but physical capacity did not.20 Additionally, 2 other studies found iron treatment improved fatigue in nonanemic women.21,22 In a 2016 systematic review, Pratt et al23 concluded, “There is emerging evidence that … nonanemic iron deficiency … is a disease in its own right, deserving of further research in the development of strategies for detection and treatment.” Al-Naseem et al24 suggested severity distinguishes iron deficiency with and without anemia.
Your role in assessing and treating iron deficiency
Testing for and treating iron deficiency generally is not a part of routine psychiatric practice. This might be due to apathy given the pervasiveness of iron deficiency, a belief that iron deficiency should be managed by primary care physicians, or a lack of familiarity with how to treat it and the benefits of such treatment for psychiatric patients. However, assessing for and treating iron deficiency in psychiatric patients is important, especially for individuals who are highly susceptible to inadequate iron levels. People at risk for iron deficiency include pregnant women, infants, young children, women with heavy menstrual bleeding, frequent blood donors, patients with cancer, individuals who have gastrointestinal (GI) surgeries or disorders, and those with heart failure.25
Assessment. Iron status can be assessed through an iron studies panel. Because a patient can have iron deficiency without anemia, a complete blood count (CBC) alone does not suffice.26 The iron panel includes serum iron, serum ferritin, serum transferrin or total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), and calculated transferrin saturation (TSAT), which is the ratio of serum iron to TIBC.
Iron deficiency is diagnosed if ferritin is <30 ng/mL, regardless of the hemoglobin concentration or underlying condition, and confirmed by a low TSAT.26 In most guidelines, the cutoff value for TSAT for iron deficiency is <20%. Because the TSAT can be influenced by iron supplements or iron-rich foods, wait several hours to obtain blood after a patient takes an oral iron supplement or eats iron-rich foods. If desired, clinicians can use either ferritin or TSAT alone to diagnose iron deficiency. However, because ferritin can be falsely normal in inflammatory conditions such as obesity and infection, a TSAT may be needed to confirm iron deficiency if there is a high clinical suspicion despite a normal ferritin level.26
Treatment. If iron deficiency is confirmed, instruct your patient to follow up with their primary care physician or the appropriate specialist to evaluate for any underlying etiologies.
Continue to: Iron deficiency should be treated...
Iron deficiency should be treated with supplementation because diet alone is insufficient for replenishing iron stores. Iron replacement can be oral or IV. Oral replacement is effective, safe, inexpensive, easy to obtain, and easy to administer.27 Oral replacement is recommended for adults whose anemia is not severe or who do not have a comorbid condition such as pregnancy, inflammatory bowel conditions, gastric surgery, or chronic kidney disease. When anemia is severe or a patient has one of these comorbid conditions, IV is the preferred method of replacement.27 In these cases, defer treatment to the patient’s primary care physician or specialist.
There are no clear recommendations on the amount of iron per dose to prescribe.27 The maximum amount of oral iron that can be absorbed is approximately 25 mg/d of elemental iron. A 325 mg ferrous sulfate tablet contains 65 mg of elemental iron, of which approximately 25 mg is absorbed and utilized.27
Emerging evidence suggests that excessive iron dosing may reduce iron absorption and increase adverse effects. In a study of 54 nonanemic young women with iron deficiency who were given iron supplementation, Moretti et al28 found that a large oral dose of iron taken in the morning increased hepcidin, which decreased the absorption of iron taken later for up to 48 hours. They found that 40 to 80 mg of elemental iron given on alternate days may maximize the fractional iron absorbed, increase dosage efficacy, reduce GI exposure to unabsorbed iron, and improve patients’ ability to tolerate iron supplementation.28
Adverse effects from iron supplements occur in up to 70% of patients.27 These can include metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea, epigastric pain, constipation, and dark stools.27 Using a liquid form may help reduce adverse effects because it can be more easily titrated.27 Tell patients to avoid enteric-coated or sustained-release iron capsules because these are poorly absorbed. Be cautious when prescribing iron supplementation to older adults because these patients tend to have more adverse effects, especially constipation, as well as reduced absorption, and may ultimately need IV treatment. Iron should not be taken with food, calcium supplements, antacids, coffee, tea, or milk.27
The amount of iron present, cost, and adverse effects vary by supplement. The Table27,29-33 provides more information on available forms of iron. Many forms of iron supplementation are available over-the-counter, and most are equally effective.27 Advise patients to use iron products that have been tested by an independent company, such as ConsumerLab.com. Such companies evaluate products to see if they contain the amount of iron listed on the product’s label; for contamination with lead, cadmium, or arsenic; and for the product’s ability to break apart for absorption.34

Six to 8 weeks of treatment with oral iron supplementation may be necessary before anemia is fully resolved, and it may take up to 6 months for iron stores to be repleted.27 If a patient cannot tolerate an iron supplement, reducing the dose or taking it with meals may help prevent adverse effects, but also will reduce absorption. Auerbach27 recommends assessing tolerability and rechecking the patient’s CBC 2 weeks after starting oral iron replacement, while also checking hemoglobin and the reticulocyte count to see if the patient is responding to treatment. An analysis of 5 studies found that a hemoglobin measurement on Day 14 that shows an increase ≥1.0 g/dL from baseline predicts longer-term and sustained treatment response to continued oral therapy.35 There is no clear consensus for target ferritin levels, but we suggest aiming for a ferritin level >100 ug/L based on recommendations for the treatment of restless legs syndrome.36 We recommend ongoing monitoring every 4 to 6 weeks.
Bottom Line
Iron deficiency is common and can cause or contribute to psychiatric symptoms and disorders. Consider screening patients for iron deficiency and treating it with oral supplementation in individuals without any comorbidities, or referring them to their primary care physician or specialist.
Related Resources
- Berthou C, Iliou JP, Barba D. Iron, neuro-bioavailability and depression. EJHaem. 2021;3(1):263-275.
1. McLean E, Cogswell M, Egli I, et al. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993-2005. Public Health Nutr. 2009;12(4):444-454.
2. Mei Z, Addo OY, Jefferds ME, et al. Physiologically based serum ferritin thresholds for iron deficiency in children and non-pregnant women: a US National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) serial cross-sectional study. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(8):e572-e582.
3. Snozek CLH, Spears GM, Porco AB, et al. Updated ferritin reference intervals for the Roche Elecsys® immunoassay. Clin Biochem. 2021;87:100-103. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.11.006
4. Camaschella C. Iron deficiency. Blood. 2019;133(1):30-39. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-05-815944
5. Lozoff B, Georgieff MK. Iron deficiency and brain development. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2006;13(3):158-165.
6. Shah HE, Bhawnani N, Ethirajulu A, et al. Iron deficiency-induced changes in the hippocampus, corpus striatum, and monoamines levels that lead to anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and psychotic disorders. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18138.
7. Hidese S, Saito K, Asano S, et al. Association between iron-deficiency anemia and depression: a web-based Japanese investigation. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018;72(7):513-521.
8. Yi S, Nanri A, Poudel-Tandukar K, et al. Association between serum ferritin concentrations and depressive symptoms in Japanese municipal employees. Psychiatry Res. 2011;189(3):368-372.
9. Lee HS, Chao HH, Huang WT, et al. Psychiatric disorders risk in patients with iron deficiency anemia and association with iron supplementation medications: a nationwide database analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20(1):216.
10. Xu M, Guo Y, Cheng J, et al. Brain iron assessment in patients with first-episode schizophrenia using quantitative susceptibility mapping. Neuroimage Clin. 2021;31:102736.
11. Kim SW, Stewart R, Park WY, et al. Latent iron deficiency as a marker of negative symptoms in patients with first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Nutrients. 2018;10(11):1707.
12. Chen MH, Su TP, Chen YS, et al. Association between psychiatric disorders and iron deficiency anemia among children and adolescents: a nationwide population-based study. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:161.
13. Stewart R, Hirani V. Relationship between depressive symptoms, anemia, and iron status in older residents from a national survey population. Psychosom Med. 2012;74(2):208-213.
14. Hanif N. Anwer F. Chronic iron deficiency. Updated September 10, 2022. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560876/
15.
16. Greig AJ, Patterson AJ, Collins CE, et al. Iron deficiency, cognition, mental health and fatigue in women of childbearing age: a systematic review. J Nutr Sci. 2013;2:e14.
17. Mikami K, Akama F, Kimoto K, et al. Iron supplementation for hypoferritinemia-related psychological symptoms in children and adolescents. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89(2):203-211.
18. McClung JP, Karl JP, Cable SJ, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of iron supplementation in female soldiers during military training: effects on iron status, physical performance, and mood. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(1):124-131.
19. Kassir A. Iron deficiency: a diagnostic and therapeutic perspective in psychiatry. Article in French. Encephale. 2017;43(1):85-89.
20. Houston BL, Hurrie D, Graham J, et al. Efficacy of iron supplementation on fatigue and physical capacity in non-anaemic iron-deficient adults: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2018;8(4):e019240. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019240
21. Krayenbuehl PA, Battegay E, Breymann C, et al. Intravenous iron for the treatment of fatigue in nonanemic, premenopausal women with low serum ferritin concentration. Blood. 2011;118(12):3222-3227. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-04-346304
22. Vaucher P, Druais PL, Waldvogel S, et al. Effect of iron supplementation on fatigue in nonanemic menstruating women with low ferritin: a randomized controlled trial. CMAJ. 2012;184(11):1247-1254. doi:10.1503/cmaj.110950
23. Pratt JJ, Khan KS. Non-anaemic iron deficiency - a disease looking for recognition of diagnosis: a systematic review. Eur J Haematol. 2016;96(6):618-628. doi:10.1111/ejh.12645
24. Al-Naseem A, Sallam A, Choudhury S, et al. Iron deficiency without anaemia: a diagnosis that matters. Clin Med (Lond). 2021;21(2):107-113. doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0582
25. National Institute of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Iron. Fact sheet for health professionals. Updated April 5, 2022. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/
26. Auerbach M. Causes and diagnosis of iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/causes-and-diagnosis-of-iron-deficiency-and-iron-deficiency-anemia-in-adults
27. Auerbach M. Treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-iron-deficiency-anemia-in-adults
28. Moretti D, Goede JS, Zeder C, et al. Oral iron supplements increase hepcidin and decrease iron absorption from daily or twice-daily doses in iron-depleted young women. Blood. 2015;126(17):1981-1989.
29. Cooperman T. Iron supplements review (iron pills, liquids and chews). ConsumerLab.com. Published January 31, 2022. Updated December 19, 2022. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://www.consumerlab.com/reviews/iron-supplements-review/iron/
30. Okam MM, Koch TA, Tran MH. Iron deficiency anemia treatment response to oral iron therapy: a pooled analysis of five randomized controlled trials. Haematologica. 2016;101(1):e6-e7.
31. Silber MH. Management of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 10, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-restless-legs-syndrome-and-periodic-limb-movement-disorder-in-adults
32. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The nutrition source: iron. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/iron/
33. Little DR. Ambulatory management of common forms of anemia. Am Fam Physician. 1999;59(6):1598-1604.
34. Blood modifiers. In: Drug Facts and Comparisons. Facts and Comparisons. 1998:238-257.
35. Cancelo-Hidalgo MJ, Castelo-Branco C, Palacios S, et al. Tolerability of different oral iron supplements: a systematic review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29(4):291-303.
36. Francés AM, Martínez-Bujanda JL. Efficacy and tolerability of oral iron protein succinylate: a systematic review of three decades of research. Curr Med Res Opinion. 2020;36(4):613-623. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1716702
1. McLean E, Cogswell M, Egli I, et al. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993-2005. Public Health Nutr. 2009;12(4):444-454.
2. Mei Z, Addo OY, Jefferds ME, et al. Physiologically based serum ferritin thresholds for iron deficiency in children and non-pregnant women: a US National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) serial cross-sectional study. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(8):e572-e582.
3. Snozek CLH, Spears GM, Porco AB, et al. Updated ferritin reference intervals for the Roche Elecsys® immunoassay. Clin Biochem. 2021;87:100-103. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.11.006
4. Camaschella C. Iron deficiency. Blood. 2019;133(1):30-39. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-05-815944
5. Lozoff B, Georgieff MK. Iron deficiency and brain development. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2006;13(3):158-165.
6. Shah HE, Bhawnani N, Ethirajulu A, et al. Iron deficiency-induced changes in the hippocampus, corpus striatum, and monoamines levels that lead to anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and psychotic disorders. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18138.
7. Hidese S, Saito K, Asano S, et al. Association between iron-deficiency anemia and depression: a web-based Japanese investigation. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2018;72(7):513-521.
8. Yi S, Nanri A, Poudel-Tandukar K, et al. Association between serum ferritin concentrations and depressive symptoms in Japanese municipal employees. Psychiatry Res. 2011;189(3):368-372.
9. Lee HS, Chao HH, Huang WT, et al. Psychiatric disorders risk in patients with iron deficiency anemia and association with iron supplementation medications: a nationwide database analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20(1):216.
10. Xu M, Guo Y, Cheng J, et al. Brain iron assessment in patients with first-episode schizophrenia using quantitative susceptibility mapping. Neuroimage Clin. 2021;31:102736.
11. Kim SW, Stewart R, Park WY, et al. Latent iron deficiency as a marker of negative symptoms in patients with first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Nutrients. 2018;10(11):1707.
12. Chen MH, Su TP, Chen YS, et al. Association between psychiatric disorders and iron deficiency anemia among children and adolescents: a nationwide population-based study. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:161.
13. Stewart R, Hirani V. Relationship between depressive symptoms, anemia, and iron status in older residents from a national survey population. Psychosom Med. 2012;74(2):208-213.
14. Hanif N. Anwer F. Chronic iron deficiency. Updated September 10, 2022. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560876/
15.
16. Greig AJ, Patterson AJ, Collins CE, et al. Iron deficiency, cognition, mental health and fatigue in women of childbearing age: a systematic review. J Nutr Sci. 2013;2:e14.
17. Mikami K, Akama F, Kimoto K, et al. Iron supplementation for hypoferritinemia-related psychological symptoms in children and adolescents. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89(2):203-211.
18. McClung JP, Karl JP, Cable SJ, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of iron supplementation in female soldiers during military training: effects on iron status, physical performance, and mood. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(1):124-131.
19. Kassir A. Iron deficiency: a diagnostic and therapeutic perspective in psychiatry. Article in French. Encephale. 2017;43(1):85-89.
20. Houston BL, Hurrie D, Graham J, et al. Efficacy of iron supplementation on fatigue and physical capacity in non-anaemic iron-deficient adults: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2018;8(4):e019240. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019240
21. Krayenbuehl PA, Battegay E, Breymann C, et al. Intravenous iron for the treatment of fatigue in nonanemic, premenopausal women with low serum ferritin concentration. Blood. 2011;118(12):3222-3227. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-04-346304
22. Vaucher P, Druais PL, Waldvogel S, et al. Effect of iron supplementation on fatigue in nonanemic menstruating women with low ferritin: a randomized controlled trial. CMAJ. 2012;184(11):1247-1254. doi:10.1503/cmaj.110950
23. Pratt JJ, Khan KS. Non-anaemic iron deficiency - a disease looking for recognition of diagnosis: a systematic review. Eur J Haematol. 2016;96(6):618-628. doi:10.1111/ejh.12645
24. Al-Naseem A, Sallam A, Choudhury S, et al. Iron deficiency without anaemia: a diagnosis that matters. Clin Med (Lond). 2021;21(2):107-113. doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0582
25. National Institute of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Iron. Fact sheet for health professionals. Updated April 5, 2022. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/
26. Auerbach M. Causes and diagnosis of iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/causes-and-diagnosis-of-iron-deficiency-and-iron-deficiency-anemia-in-adults
27. Auerbach M. Treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-iron-deficiency-anemia-in-adults
28. Moretti D, Goede JS, Zeder C, et al. Oral iron supplements increase hepcidin and decrease iron absorption from daily or twice-daily doses in iron-depleted young women. Blood. 2015;126(17):1981-1989.
29. Cooperman T. Iron supplements review (iron pills, liquids and chews). ConsumerLab.com. Published January 31, 2022. Updated December 19, 2022. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://www.consumerlab.com/reviews/iron-supplements-review/iron/
30. Okam MM, Koch TA, Tran MH. Iron deficiency anemia treatment response to oral iron therapy: a pooled analysis of five randomized controlled trials. Haematologica. 2016;101(1):e6-e7.
31. Silber MH. Management of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder in adults. UpToDate. Accessed July 10, 2022. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-restless-legs-syndrome-and-periodic-limb-movement-disorder-in-adults
32. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The nutrition source: iron. Accessed January 31, 2023. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/iron/
33. Little DR. Ambulatory management of common forms of anemia. Am Fam Physician. 1999;59(6):1598-1604.
34. Blood modifiers. In: Drug Facts and Comparisons. Facts and Comparisons. 1998:238-257.
35. Cancelo-Hidalgo MJ, Castelo-Branco C, Palacios S, et al. Tolerability of different oral iron supplements: a systematic review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29(4):291-303.
36. Francés AM, Martínez-Bujanda JL. Efficacy and tolerability of oral iron protein succinylate: a systematic review of three decades of research. Curr Med Res Opinion. 2020;36(4):613-623. doi:10.1080/03007995.2020.1716702
Co-occurring psychogenic nonepileptic seizures and possible true seizures
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) are a physical manifestation of a psychological disturbance. They are characterized by episodes of altered subjective experience and movements that can resemble epilepsy, syncope, or other paroxysmal disorders, but are not caused by neuronal hypersynchronization or other epileptic semiology.
Patients with PNES may present to multiple clinicians and hospitals for assessment. Access to outside hospital records can be limited, which can lead to redundant testing and increased health care costs and burden. Additionally, repeat presentations can increase stigmatization of the patient and delay or prevent appropriate therapeutic management, which might exacerbate a patient’s underlying psychiatric condition and could be dangerous in a patient with a co-occurring true seizure disorder. Though obtaining and reviewing external medical records can be cumbersome, doing so may prevent unnecessary testing, guide medical treatment, and strengthen the patient-doctor therapeutic alliance.
In this article, I discuss our treatment team’s management of a patient with PNES who, based on our careful review of records from previous hospitalizations, may have had a co-occurring true seizure disorder.
Case report
Ms. M, age 31, has a medical history of anxiety, depression, first-degree atrioventricular block, type 2 diabetes, and PNES. She presented to the ED with witnessed seizure activity at home.
According to collateral information, earlier that day Ms. M said she felt like she was seizing and began mumbling, but returned to baseline within a few minutes. Later, she demonstrated intermittent upper and lower extremity shaking for more than 1 hour. At one point, Ms. M appeared to be not breathing. However, upon initiation of chest compressions, she began gasping for air and immediately returned to baseline.
In the ED, Ms. M demonstrated multiple seizure-like episodes every 5 minutes, each lasting 5 to 10 seconds. These episodes were described as thrashing of the bilateral limbs and head crossing midline with eyes closed. No urinary incontinence or tongue biting was observed. Following each episode, Ms. M was unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli but intermittently opened her eyes. Laboratory test results were notable for an elevated serum lactate and positive for cannabinoids on urine drug screen.
Ms. M expressed frustration when told that her seizures were psychogenic. She was adamant that she had a true seizure disorder, demanded testing, and threatened to leave against medical advice without it. She said her brother had epilepsy, and thus she knew how seizures present. The interview was complicated by Ms. M’s mistrust and Cluster B personality disorder traits, such as splitting staff into “good and bad.” Ultimately, she was able to be reassured and did not leave the hospital.
Continue to: The treatment team...
The treatment team reviewed external records from 2 hospitals, Hospital A and Hospital B. These records showed well-documented inpatient and outpatient Psychiatry and Neurology diagnoses of PNES and other conversion disorders. Her medications included
Ms. M’s first lifetime documented seizure occurred in May 2020, when she woke up with tongue biting, extremity shaking (laterality was unclear), and urinary incontinence followed by fatigue. She did not go to the hospital after this first episode. In June 2020, she presented and was admitted to Hospital A after similar seizure-like activity. While admitted and monitored on continuous EEG (cEEG), she had numerous events consistent with a nonepileptic etiology without a postictal state. A brain MRI was unremarkable, and Ms. M was diagnosed with PNES.
She presented to Hospital B in October 2020 reporting seizure-like activity. Hospital B reviewed Hospital A’s brain MRI and found right temporal lobe cortical dysplasia that was not noted in Hospital A’s MRI read. Ms. M again underwent cEEG while at Hospital B and had 2 recorded nonepileptic events. Interestingly, the cEEG demonstrated
Ms. M documented 3 seizure-like events between October and December 2020. She documented activity with and without full-body convulsions, some with laterality, some with loss of consciousness, and some preceded by an aura of impending doom. Ms. M was referred to psychotherapy and instructed to continue topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours for seizure prophylaxis.
Ms. M presented to Hospital B again in March 2022 reporting seizure-like activity. A brain MRI found cortical dysplasia in the right temporal lobe, consistent with the MRI at Hospital A in June 2020. cEEG was also repeated at Hospital B and was unremarkable. Oxcarbazepine 300 mg every 12 hours was added to Ms. M’s medications.
Ultimately, based on an external record review, our team (at Hospital C) concluded Ms. M had a possible true seizure co-occurrence with PNES. To avoid redundant testing, we did not repeat imaging or cEEG. Instead, we increased the patient’s oxcarbazepine to 450 mg every 12 hours, for both its effectiveness in temporal seizures and its mood-stabilizing properties. Moreover, in collecting our own data to draw a conclusion by a thorough record review, we gained Ms. M’s trust and strengthened the therapeutic alliance. She was agreeable to forgo more testing and continue outpatient follow-up with our hospital’s Neurology team.
Take-home points
Although PNES and true seizure disorder may not frequently co-occur, this case highlights the importance of clinician due diligence when evaluating a potential psychogenic illness, both for patient safety and clinician liability. By trusting our patients and drawing our own data-based conclusions, we can cultivate a safer and more satisfactory patient-clinician experience in the context of psychosomatic disorders.
1. Bajestan SN, LaFrance WC Jr. Clinical approaches to psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2016;14(4):422-431. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160020
2. Dickson JM, Dudhill H, Shewan J, et al. Cross-sectional study of the hospital management of adult patients with a suspected seizure (EPIC2). BMJ Open. 2017;7(7):e015696. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015696
3. Kutlubaev MA, Xu Y, Hackett ML, et al. Dual diagnosis of epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: systematic review and meta-analysis of frequency, correlates, and outcomes. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;89:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.10.010
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) are a physical manifestation of a psychological disturbance. They are characterized by episodes of altered subjective experience and movements that can resemble epilepsy, syncope, or other paroxysmal disorders, but are not caused by neuronal hypersynchronization or other epileptic semiology.
Patients with PNES may present to multiple clinicians and hospitals for assessment. Access to outside hospital records can be limited, which can lead to redundant testing and increased health care costs and burden. Additionally, repeat presentations can increase stigmatization of the patient and delay or prevent appropriate therapeutic management, which might exacerbate a patient’s underlying psychiatric condition and could be dangerous in a patient with a co-occurring true seizure disorder. Though obtaining and reviewing external medical records can be cumbersome, doing so may prevent unnecessary testing, guide medical treatment, and strengthen the patient-doctor therapeutic alliance.
In this article, I discuss our treatment team’s management of a patient with PNES who, based on our careful review of records from previous hospitalizations, may have had a co-occurring true seizure disorder.
Case report
Ms. M, age 31, has a medical history of anxiety, depression, first-degree atrioventricular block, type 2 diabetes, and PNES. She presented to the ED with witnessed seizure activity at home.
According to collateral information, earlier that day Ms. M said she felt like she was seizing and began mumbling, but returned to baseline within a few minutes. Later, she demonstrated intermittent upper and lower extremity shaking for more than 1 hour. At one point, Ms. M appeared to be not breathing. However, upon initiation of chest compressions, she began gasping for air and immediately returned to baseline.
In the ED, Ms. M demonstrated multiple seizure-like episodes every 5 minutes, each lasting 5 to 10 seconds. These episodes were described as thrashing of the bilateral limbs and head crossing midline with eyes closed. No urinary incontinence or tongue biting was observed. Following each episode, Ms. M was unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli but intermittently opened her eyes. Laboratory test results were notable for an elevated serum lactate and positive for cannabinoids on urine drug screen.
Ms. M expressed frustration when told that her seizures were psychogenic. She was adamant that she had a true seizure disorder, demanded testing, and threatened to leave against medical advice without it. She said her brother had epilepsy, and thus she knew how seizures present. The interview was complicated by Ms. M’s mistrust and Cluster B personality disorder traits, such as splitting staff into “good and bad.” Ultimately, she was able to be reassured and did not leave the hospital.
Continue to: The treatment team...
The treatment team reviewed external records from 2 hospitals, Hospital A and Hospital B. These records showed well-documented inpatient and outpatient Psychiatry and Neurology diagnoses of PNES and other conversion disorders. Her medications included
Ms. M’s first lifetime documented seizure occurred in May 2020, when she woke up with tongue biting, extremity shaking (laterality was unclear), and urinary incontinence followed by fatigue. She did not go to the hospital after this first episode. In June 2020, she presented and was admitted to Hospital A after similar seizure-like activity. While admitted and monitored on continuous EEG (cEEG), she had numerous events consistent with a nonepileptic etiology without a postictal state. A brain MRI was unremarkable, and Ms. M was diagnosed with PNES.
She presented to Hospital B in October 2020 reporting seizure-like activity. Hospital B reviewed Hospital A’s brain MRI and found right temporal lobe cortical dysplasia that was not noted in Hospital A’s MRI read. Ms. M again underwent cEEG while at Hospital B and had 2 recorded nonepileptic events. Interestingly, the cEEG demonstrated
Ms. M documented 3 seizure-like events between October and December 2020. She documented activity with and without full-body convulsions, some with laterality, some with loss of consciousness, and some preceded by an aura of impending doom. Ms. M was referred to psychotherapy and instructed to continue topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours for seizure prophylaxis.
Ms. M presented to Hospital B again in March 2022 reporting seizure-like activity. A brain MRI found cortical dysplasia in the right temporal lobe, consistent with the MRI at Hospital A in June 2020. cEEG was also repeated at Hospital B and was unremarkable. Oxcarbazepine 300 mg every 12 hours was added to Ms. M’s medications.
Ultimately, based on an external record review, our team (at Hospital C) concluded Ms. M had a possible true seizure co-occurrence with PNES. To avoid redundant testing, we did not repeat imaging or cEEG. Instead, we increased the patient’s oxcarbazepine to 450 mg every 12 hours, for both its effectiveness in temporal seizures and its mood-stabilizing properties. Moreover, in collecting our own data to draw a conclusion by a thorough record review, we gained Ms. M’s trust and strengthened the therapeutic alliance. She was agreeable to forgo more testing and continue outpatient follow-up with our hospital’s Neurology team.
Take-home points
Although PNES and true seizure disorder may not frequently co-occur, this case highlights the importance of clinician due diligence when evaluating a potential psychogenic illness, both for patient safety and clinician liability. By trusting our patients and drawing our own data-based conclusions, we can cultivate a safer and more satisfactory patient-clinician experience in the context of psychosomatic disorders.
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) are a physical manifestation of a psychological disturbance. They are characterized by episodes of altered subjective experience and movements that can resemble epilepsy, syncope, or other paroxysmal disorders, but are not caused by neuronal hypersynchronization or other epileptic semiology.
Patients with PNES may present to multiple clinicians and hospitals for assessment. Access to outside hospital records can be limited, which can lead to redundant testing and increased health care costs and burden. Additionally, repeat presentations can increase stigmatization of the patient and delay or prevent appropriate therapeutic management, which might exacerbate a patient’s underlying psychiatric condition and could be dangerous in a patient with a co-occurring true seizure disorder. Though obtaining and reviewing external medical records can be cumbersome, doing so may prevent unnecessary testing, guide medical treatment, and strengthen the patient-doctor therapeutic alliance.
In this article, I discuss our treatment team’s management of a patient with PNES who, based on our careful review of records from previous hospitalizations, may have had a co-occurring true seizure disorder.
Case report
Ms. M, age 31, has a medical history of anxiety, depression, first-degree atrioventricular block, type 2 diabetes, and PNES. She presented to the ED with witnessed seizure activity at home.
According to collateral information, earlier that day Ms. M said she felt like she was seizing and began mumbling, but returned to baseline within a few minutes. Later, she demonstrated intermittent upper and lower extremity shaking for more than 1 hour. At one point, Ms. M appeared to be not breathing. However, upon initiation of chest compressions, she began gasping for air and immediately returned to baseline.
In the ED, Ms. M demonstrated multiple seizure-like episodes every 5 minutes, each lasting 5 to 10 seconds. These episodes were described as thrashing of the bilateral limbs and head crossing midline with eyes closed. No urinary incontinence or tongue biting was observed. Following each episode, Ms. M was unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli but intermittently opened her eyes. Laboratory test results were notable for an elevated serum lactate and positive for cannabinoids on urine drug screen.
Ms. M expressed frustration when told that her seizures were psychogenic. She was adamant that she had a true seizure disorder, demanded testing, and threatened to leave against medical advice without it. She said her brother had epilepsy, and thus she knew how seizures present. The interview was complicated by Ms. M’s mistrust and Cluster B personality disorder traits, such as splitting staff into “good and bad.” Ultimately, she was able to be reassured and did not leave the hospital.
Continue to: The treatment team...
The treatment team reviewed external records from 2 hospitals, Hospital A and Hospital B. These records showed well-documented inpatient and outpatient Psychiatry and Neurology diagnoses of PNES and other conversion disorders. Her medications included
Ms. M’s first lifetime documented seizure occurred in May 2020, when she woke up with tongue biting, extremity shaking (laterality was unclear), and urinary incontinence followed by fatigue. She did not go to the hospital after this first episode. In June 2020, she presented and was admitted to Hospital A after similar seizure-like activity. While admitted and monitored on continuous EEG (cEEG), she had numerous events consistent with a nonepileptic etiology without a postictal state. A brain MRI was unremarkable, and Ms. M was diagnosed with PNES.
She presented to Hospital B in October 2020 reporting seizure-like activity. Hospital B reviewed Hospital A’s brain MRI and found right temporal lobe cortical dysplasia that was not noted in Hospital A’s MRI read. Ms. M again underwent cEEG while at Hospital B and had 2 recorded nonepileptic events. Interestingly, the cEEG demonstrated
Ms. M documented 3 seizure-like events between October and December 2020. She documented activity with and without full-body convulsions, some with laterality, some with loss of consciousness, and some preceded by an aura of impending doom. Ms. M was referred to psychotherapy and instructed to continue topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours for seizure prophylaxis.
Ms. M presented to Hospital B again in March 2022 reporting seizure-like activity. A brain MRI found cortical dysplasia in the right temporal lobe, consistent with the MRI at Hospital A in June 2020. cEEG was also repeated at Hospital B and was unremarkable. Oxcarbazepine 300 mg every 12 hours was added to Ms. M’s medications.
Ultimately, based on an external record review, our team (at Hospital C) concluded Ms. M had a possible true seizure co-occurrence with PNES. To avoid redundant testing, we did not repeat imaging or cEEG. Instead, we increased the patient’s oxcarbazepine to 450 mg every 12 hours, for both its effectiveness in temporal seizures and its mood-stabilizing properties. Moreover, in collecting our own data to draw a conclusion by a thorough record review, we gained Ms. M’s trust and strengthened the therapeutic alliance. She was agreeable to forgo more testing and continue outpatient follow-up with our hospital’s Neurology team.
Take-home points
Although PNES and true seizure disorder may not frequently co-occur, this case highlights the importance of clinician due diligence when evaluating a potential psychogenic illness, both for patient safety and clinician liability. By trusting our patients and drawing our own data-based conclusions, we can cultivate a safer and more satisfactory patient-clinician experience in the context of psychosomatic disorders.
1. Bajestan SN, LaFrance WC Jr. Clinical approaches to psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2016;14(4):422-431. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160020
2. Dickson JM, Dudhill H, Shewan J, et al. Cross-sectional study of the hospital management of adult patients with a suspected seizure (EPIC2). BMJ Open. 2017;7(7):e015696. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015696
3. Kutlubaev MA, Xu Y, Hackett ML, et al. Dual diagnosis of epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: systematic review and meta-analysis of frequency, correlates, and outcomes. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;89:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.10.010
1. Bajestan SN, LaFrance WC Jr. Clinical approaches to psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Focus (Am Psychiatr Publ). 2016;14(4):422-431. doi:10.1176/appi.focus.20160020
2. Dickson JM, Dudhill H, Shewan J, et al. Cross-sectional study of the hospital management of adult patients with a suspected seizure (EPIC2). BMJ Open. 2017;7(7):e015696. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015696
3. Kutlubaev MA, Xu Y, Hackett ML, et al. Dual diagnosis of epilepsy and psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: systematic review and meta-analysis of frequency, correlates, and outcomes. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;89:70-78. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.10.010
Reimagining psychiatric assessment and interventions as procedures
Many psychiatric physicians lament the dearth of procedures in psychiatry compared to other medical specialties such as surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, or radiology. The few procedures in psychiatry include electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, and vagus nerve stimulation, which are restricted to a small number of sites and not available for most psychiatric practitioners. This lack of tangible/physical procedures should not be surprising because psychiatry deals with disorders of the mind, which are invisible.
However, when one closely examines what psychiatrists do in daily practice to heal our patients, most of what we do actually qualifies as “procedures” although no hardware, machines, or gadgets are involved. Treating psychiatric brain disorders (aka mental illness) requires exquisite skills and expertise, just like medical specialties that use machines to measure or treat various body organs.
It’s time to relabel psychiatric interventions as procedures designed to improve anomalous thoughts, affect, emotions, cognition, and behavior. After giving it some thought (and with a bit of tongue in cheek), I came up with the following list of “psychiatric procedures”:
- Psychosocial exploratory laparotomy: The comprehensive psychiatric assessment and mental status exam.
- Chemotherapy: Oral or injective pharmacotherapeutic intervention.
- Psychoplastic repair: Neuroplasticity, including neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and dendritic spine regeneration, have been shown to be associated with both psychotherapy and psychotropic medications.1,2
- Suicidectomy: Extracting the lethal urge to die by suicide.
- Anger debridement: Removing the irritability and destructive anger outbursts frequently associated with various psychopathologies.
- Anxiety ablation: Eliminating the noxious emotional state of anxiety and frightening panic attacks.
- Empathy infusion: Enabling patients to become more understanding of other people and bolstering their impaired “theory of mind.”
- Personality transplant: Replacing a maladaptive personality with a healthier one (eg, using dialectical behavior therapy for borderline personality disorder).
- Cognitive LASIK: To improve insight, analogous to how ophthalmologic LASIK improves sight.
- Mental embolectomy: Removing a blockage to repair rigid attitudes and develop “open-mindedness.”
- Behavioral dilation and curettage (D&C): To rid patients of negative attributes such as impulsivity or reckless behavior.
- Psychotherapeutic anesthesia: Numbing emotional pain or severe grief reaction.
- Social anastomosis: Helping patients who are schizoid or isolative via group therapy, an effective interpersonal and social procedure.
- Psychotherapeutic stent: To open the vessels of narrow-mindedness.
- Cortico-psychological resuscitation (CPR): For patients experiencing stress-induced behavioral arrhythmias or emotional infarction.
- Immunotherapy: Using various neuroprotective psychotropic medications with anti-inflammatory properties or employing evidence-based psychotherapy such as cognitive-behavior therapy (aka neuropsychotherapy), which have been shown to reduce inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein and cytokines.3
- Psychotherapy: A neuromodulation procedure for a variety of psychiatric disorders.4
- Neurobiological facelift: It is well established that neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and dendritic spine sprouting are significantly increased with both neuroprotective psychotropic medications (antidepressants, lithium, valproate, and second-generationantipsychotics5) as well as with psychotherapy. There is growing evidence of “premature brain aging” in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression, with shrinkage in the volume of the cortex and subcortical regions, especially the hippocampus. Psychiatric biopsychosocial intervention rebuilds those brain regions by stimulating and replenishing the neuropil and neurogenic regions (dentate gyrus and subventricular zone). This is like performing virtual plastic surgery on a wrinkled brain and its sagging mind. MRI scans before and after ECT show a remarkable ≥10% increase in the volume of the hippocampus and amygdala, which translates to billions of new neurons, glia, and synapses.6
Reinventing psychiatric therapies as procedures may elicit sarcasm from skeptics, but when you think about it, it is justified. Excising depression is like excising a tumor, not with a scalpel, but virtually. Stabilizing the broken brain and mind after a psychotic episode (aka brain attack) is like stabilizing the heart after a myocardial infarction (aka heart attack). Just because the mind is virtual doesn’t mean it is not “real and tangible.” A desktop computer is visible, but the software that brings it to life is invisible. Healing the human mind requires multiple medical interventions by psychiatrists in hospitals and clinics, just like surgeons and endoscopists or cardiologists. Mental health care is as much procedural as other medical and surgical specialties.
One more thing: the validated clinical rating scales for various psychiatric brain disorders (eg, the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale for schizophrenia, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale for depression, Young Mania Rating Scale for bipolar mania, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale for anxiety, Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale for obsessive-compulsive disorder) are actual measurement procedures for the severity of the illness, just as a sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure and its improvement with treatment. There are also multiple cognitive test batteries to measure cognitive impairment.7
Finally, unlike psychiatric reimbursement, which is tethered to time, procedures are compensated more generously, irrespective of the time involved. The complexities of diagnosing and treating psychiatric brain disorders that dangerously disrupt thoughts, feelings, behavior, and cognition are just as intricate and demanding as the diagnosis and treatment of general medical and surgical conditions. They should all be equally appreciated as vital life-saving procedures for the human body, brain, and mind.
1. Nasrallah HA, Hopkins T, Pixley SK. Differential effects of antipsychotic and antidepressant drugs on neurogenic regions in rats. Brain Res. 2010;1354:23-29.
2. Tomasino B, Fabbro F. Increases in the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and decreases the rostral prefrontal cortex activation after-8 weeks of focused attention based mindfulness meditation. Brain Cogn. 2016;102:46-54.
3. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
4. Nasrallah HA. Optimal psychiatric treatment: Target the brain and avoid the body. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(12):3-6.
5. Chen AT, Nasrallah HA. Neuroprotective effects of the second generation antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2019;208:1-7.
6. Gryglewski G, Lanzenberger R, Silberbauer LR, et al. Meta-analysis of brain structural changes after electroconvulsive therapy in depression. Brain Stimul. 2021;14(4):927-937.
7. Nasrallah HA. The Cognition Self-Assessment Rating Scale for patients with schizophrenia. Current Psychiatry. 2023;22(3):30-34.
Many psychiatric physicians lament the dearth of procedures in psychiatry compared to other medical specialties such as surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, or radiology. The few procedures in psychiatry include electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, and vagus nerve stimulation, which are restricted to a small number of sites and not available for most psychiatric practitioners. This lack of tangible/physical procedures should not be surprising because psychiatry deals with disorders of the mind, which are invisible.
However, when one closely examines what psychiatrists do in daily practice to heal our patients, most of what we do actually qualifies as “procedures” although no hardware, machines, or gadgets are involved. Treating psychiatric brain disorders (aka mental illness) requires exquisite skills and expertise, just like medical specialties that use machines to measure or treat various body organs.
It’s time to relabel psychiatric interventions as procedures designed to improve anomalous thoughts, affect, emotions, cognition, and behavior. After giving it some thought (and with a bit of tongue in cheek), I came up with the following list of “psychiatric procedures”:
- Psychosocial exploratory laparotomy: The comprehensive psychiatric assessment and mental status exam.
- Chemotherapy: Oral or injective pharmacotherapeutic intervention.
- Psychoplastic repair: Neuroplasticity, including neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and dendritic spine regeneration, have been shown to be associated with both psychotherapy and psychotropic medications.1,2
- Suicidectomy: Extracting the lethal urge to die by suicide.
- Anger debridement: Removing the irritability and destructive anger outbursts frequently associated with various psychopathologies.
- Anxiety ablation: Eliminating the noxious emotional state of anxiety and frightening panic attacks.
- Empathy infusion: Enabling patients to become more understanding of other people and bolstering their impaired “theory of mind.”
- Personality transplant: Replacing a maladaptive personality with a healthier one (eg, using dialectical behavior therapy for borderline personality disorder).
- Cognitive LASIK: To improve insight, analogous to how ophthalmologic LASIK improves sight.
- Mental embolectomy: Removing a blockage to repair rigid attitudes and develop “open-mindedness.”
- Behavioral dilation and curettage (D&C): To rid patients of negative attributes such as impulsivity or reckless behavior.
- Psychotherapeutic anesthesia: Numbing emotional pain or severe grief reaction.
- Social anastomosis: Helping patients who are schizoid or isolative via group therapy, an effective interpersonal and social procedure.
- Psychotherapeutic stent: To open the vessels of narrow-mindedness.
- Cortico-psychological resuscitation (CPR): For patients experiencing stress-induced behavioral arrhythmias or emotional infarction.
- Immunotherapy: Using various neuroprotective psychotropic medications with anti-inflammatory properties or employing evidence-based psychotherapy such as cognitive-behavior therapy (aka neuropsychotherapy), which have been shown to reduce inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein and cytokines.3
- Psychotherapy: A neuromodulation procedure for a variety of psychiatric disorders.4
- Neurobiological facelift: It is well established that neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and dendritic spine sprouting are significantly increased with both neuroprotective psychotropic medications (antidepressants, lithium, valproate, and second-generationantipsychotics5) as well as with psychotherapy. There is growing evidence of “premature brain aging” in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression, with shrinkage in the volume of the cortex and subcortical regions, especially the hippocampus. Psychiatric biopsychosocial intervention rebuilds those brain regions by stimulating and replenishing the neuropil and neurogenic regions (dentate gyrus and subventricular zone). This is like performing virtual plastic surgery on a wrinkled brain and its sagging mind. MRI scans before and after ECT show a remarkable ≥10% increase in the volume of the hippocampus and amygdala, which translates to billions of new neurons, glia, and synapses.6
Reinventing psychiatric therapies as procedures may elicit sarcasm from skeptics, but when you think about it, it is justified. Excising depression is like excising a tumor, not with a scalpel, but virtually. Stabilizing the broken brain and mind after a psychotic episode (aka brain attack) is like stabilizing the heart after a myocardial infarction (aka heart attack). Just because the mind is virtual doesn’t mean it is not “real and tangible.” A desktop computer is visible, but the software that brings it to life is invisible. Healing the human mind requires multiple medical interventions by psychiatrists in hospitals and clinics, just like surgeons and endoscopists or cardiologists. Mental health care is as much procedural as other medical and surgical specialties.
One more thing: the validated clinical rating scales for various psychiatric brain disorders (eg, the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale for schizophrenia, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale for depression, Young Mania Rating Scale for bipolar mania, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale for anxiety, Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale for obsessive-compulsive disorder) are actual measurement procedures for the severity of the illness, just as a sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure and its improvement with treatment. There are also multiple cognitive test batteries to measure cognitive impairment.7
Finally, unlike psychiatric reimbursement, which is tethered to time, procedures are compensated more generously, irrespective of the time involved. The complexities of diagnosing and treating psychiatric brain disorders that dangerously disrupt thoughts, feelings, behavior, and cognition are just as intricate and demanding as the diagnosis and treatment of general medical and surgical conditions. They should all be equally appreciated as vital life-saving procedures for the human body, brain, and mind.
Many psychiatric physicians lament the dearth of procedures in psychiatry compared to other medical specialties such as surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, or radiology. The few procedures in psychiatry include electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, and vagus nerve stimulation, which are restricted to a small number of sites and not available for most psychiatric practitioners. This lack of tangible/physical procedures should not be surprising because psychiatry deals with disorders of the mind, which are invisible.
However, when one closely examines what psychiatrists do in daily practice to heal our patients, most of what we do actually qualifies as “procedures” although no hardware, machines, or gadgets are involved. Treating psychiatric brain disorders (aka mental illness) requires exquisite skills and expertise, just like medical specialties that use machines to measure or treat various body organs.
It’s time to relabel psychiatric interventions as procedures designed to improve anomalous thoughts, affect, emotions, cognition, and behavior. After giving it some thought (and with a bit of tongue in cheek), I came up with the following list of “psychiatric procedures”:
- Psychosocial exploratory laparotomy: The comprehensive psychiatric assessment and mental status exam.
- Chemotherapy: Oral or injective pharmacotherapeutic intervention.
- Psychoplastic repair: Neuroplasticity, including neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and dendritic spine regeneration, have been shown to be associated with both psychotherapy and psychotropic medications.1,2
- Suicidectomy: Extracting the lethal urge to die by suicide.
- Anger debridement: Removing the irritability and destructive anger outbursts frequently associated with various psychopathologies.
- Anxiety ablation: Eliminating the noxious emotional state of anxiety and frightening panic attacks.
- Empathy infusion: Enabling patients to become more understanding of other people and bolstering their impaired “theory of mind.”
- Personality transplant: Replacing a maladaptive personality with a healthier one (eg, using dialectical behavior therapy for borderline personality disorder).
- Cognitive LASIK: To improve insight, analogous to how ophthalmologic LASIK improves sight.
- Mental embolectomy: Removing a blockage to repair rigid attitudes and develop “open-mindedness.”
- Behavioral dilation and curettage (D&C): To rid patients of negative attributes such as impulsivity or reckless behavior.
- Psychotherapeutic anesthesia: Numbing emotional pain or severe grief reaction.
- Social anastomosis: Helping patients who are schizoid or isolative via group therapy, an effective interpersonal and social procedure.
- Psychotherapeutic stent: To open the vessels of narrow-mindedness.
- Cortico-psychological resuscitation (CPR): For patients experiencing stress-induced behavioral arrhythmias or emotional infarction.
- Immunotherapy: Using various neuroprotective psychotropic medications with anti-inflammatory properties or employing evidence-based psychotherapy such as cognitive-behavior therapy (aka neuropsychotherapy), which have been shown to reduce inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein and cytokines.3
- Psychotherapy: A neuromodulation procedure for a variety of psychiatric disorders.4
- Neurobiological facelift: It is well established that neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and dendritic spine sprouting are significantly increased with both neuroprotective psychotropic medications (antidepressants, lithium, valproate, and second-generationantipsychotics5) as well as with psychotherapy. There is growing evidence of “premature brain aging” in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression, with shrinkage in the volume of the cortex and subcortical regions, especially the hippocampus. Psychiatric biopsychosocial intervention rebuilds those brain regions by stimulating and replenishing the neuropil and neurogenic regions (dentate gyrus and subventricular zone). This is like performing virtual plastic surgery on a wrinkled brain and its sagging mind. MRI scans before and after ECT show a remarkable ≥10% increase in the volume of the hippocampus and amygdala, which translates to billions of new neurons, glia, and synapses.6
Reinventing psychiatric therapies as procedures may elicit sarcasm from skeptics, but when you think about it, it is justified. Excising depression is like excising a tumor, not with a scalpel, but virtually. Stabilizing the broken brain and mind after a psychotic episode (aka brain attack) is like stabilizing the heart after a myocardial infarction (aka heart attack). Just because the mind is virtual doesn’t mean it is not “real and tangible.” A desktop computer is visible, but the software that brings it to life is invisible. Healing the human mind requires multiple medical interventions by psychiatrists in hospitals and clinics, just like surgeons and endoscopists or cardiologists. Mental health care is as much procedural as other medical and surgical specialties.
One more thing: the validated clinical rating scales for various psychiatric brain disorders (eg, the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale for schizophrenia, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale for depression, Young Mania Rating Scale for bipolar mania, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale for anxiety, Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale for obsessive-compulsive disorder) are actual measurement procedures for the severity of the illness, just as a sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure and its improvement with treatment. There are also multiple cognitive test batteries to measure cognitive impairment.7
Finally, unlike psychiatric reimbursement, which is tethered to time, procedures are compensated more generously, irrespective of the time involved. The complexities of diagnosing and treating psychiatric brain disorders that dangerously disrupt thoughts, feelings, behavior, and cognition are just as intricate and demanding as the diagnosis and treatment of general medical and surgical conditions. They should all be equally appreciated as vital life-saving procedures for the human body, brain, and mind.
1. Nasrallah HA, Hopkins T, Pixley SK. Differential effects of antipsychotic and antidepressant drugs on neurogenic regions in rats. Brain Res. 2010;1354:23-29.
2. Tomasino B, Fabbro F. Increases in the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and decreases the rostral prefrontal cortex activation after-8 weeks of focused attention based mindfulness meditation. Brain Cogn. 2016;102:46-54.
3. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
4. Nasrallah HA. Optimal psychiatric treatment: Target the brain and avoid the body. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(12):3-6.
5. Chen AT, Nasrallah HA. Neuroprotective effects of the second generation antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2019;208:1-7.
6. Gryglewski G, Lanzenberger R, Silberbauer LR, et al. Meta-analysis of brain structural changes after electroconvulsive therapy in depression. Brain Stimul. 2021;14(4):927-937.
7. Nasrallah HA. The Cognition Self-Assessment Rating Scale for patients with schizophrenia. Current Psychiatry. 2023;22(3):30-34.
1. Nasrallah HA, Hopkins T, Pixley SK. Differential effects of antipsychotic and antidepressant drugs on neurogenic regions in rats. Brain Res. 2010;1354:23-29.
2. Tomasino B, Fabbro F. Increases in the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and decreases the rostral prefrontal cortex activation after-8 weeks of focused attention based mindfulness meditation. Brain Cogn. 2016;102:46-54.
3. Nasrallah HA. Repositioning psychotherapy as a neurobiological intervention. Current Psychiatry. 2013;12(12):18-19.
4. Nasrallah HA. Optimal psychiatric treatment: Target the brain and avoid the body. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(12):3-6.
5. Chen AT, Nasrallah HA. Neuroprotective effects of the second generation antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2019;208:1-7.
6. Gryglewski G, Lanzenberger R, Silberbauer LR, et al. Meta-analysis of brain structural changes after electroconvulsive therapy in depression. Brain Stimul. 2021;14(4):927-937.
7. Nasrallah HA. The Cognition Self-Assessment Rating Scale for patients with schizophrenia. Current Psychiatry. 2023;22(3):30-34.
Psychoactive supplements: What to tell patients
Mr. D, age 41, presents to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and suspected intoxication. His medical history includes alcohol use disorder and spinal injury. Upon initial examination, he is confused, disorganized, and agitated. He receives IM lorazepam 4 mg to manage his agitation. His laboratory workup includes a negative screening for blood alcohol, slightly elevated creatine kinase, and urine toxicology positive for barbiturates and opioids. During re-evaluation by the consulting psychiatrist the following morning, Mr. D is alert, oriented, and calm with an organized thought process. He does not appear to be in withdrawal from any substances and tells the psychiatrist that he takes butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine as needed for migraines. Mr. D says that 3 days before he came to the ED, he also began taking a supplement called phenibut that he purchased online for “well-being and sleep.”
Natural substances have been used throughout history as medicinal agents, sacred substances in religious rituals, and for recreational purposes.1 Supplement use in the United States is prevalent, with 57.6% of adults age ≥20 reporting supplement use in the past 30 days.2 Between 2000 and 2017, US poison control centers recorded a 74.1% increase in calls involving exposure to natural psychoactive substances, mostly driven by cases involving marijuana in adults and adolescents.3 Like synthetic drugs, herbal supplements may have psychoactive properties, including sedative, stimulant, psychedelic, euphoric, or anticholinergic effects. The variety and unregulated nature of supplements makes managing patients who use supplements particularly challenging.
Why patients use supplements
People may use supplements to treat or prevent vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, iron, calcium). Other reasons may include for promoting wellness in various disease states, for weight loss, for recreational use or misuse, or for overall well-being. In the mental health realm, patients report using supplements to treat depression, anxiety, insomnia, memory, or for vague indications such as “mood support.”4,5
Patients may view supplements as appealing alternatives to prescription medications because they are widely accessible, may be purchased over-the-counter, are inexpensive, and represent a “natural” treatment option.6 For these reasons, they may also falsely perceive supplements as categorically safe.1 People with psychiatric diagnoses may choose such alternative treatments due to a history of adverse effects or treatment failure with traditional psychiatric medications, mistrust of the health care or pharmaceutical industry, or based on the recommendations of others.7
Regulation, safety, and efficacy of dietary supplements
In the US, dietary supplements are regulated more like food products than medications. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the FDA regulates the quality, safety, and labeling of supplements using Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.8 The Federal Trade Commission monitors advertisements and marketing. Despite some regulations, dietary supplements may be adulterated or contaminated, contain unknown or toxic ingredients, have inconsistent potencies, or be sold at toxic doses.9 Importantly, supplements are not required to be evaluated for clinical efficacy. As a result, it is not known if most supplements are effective in treating the conditions for which they are promoted, mainly due to a lack of financial incentive for manufacturers to conduct large, high-quality trials.5
Further complicating matters is the inconsistent labeling of supplements or similar products that are easily obtainable via the internet. These products might be marketed as nutritional supplements or nootropics, which often are referred to as “cognitive enhancers” or “smart drugs.” New psychoactive substances (NPS) are drugs of misuse or abuse developed to imitate illicit drugs or controlled drug substances.10 They are sometimes referred to as “herbal highs” or “legal highs.”11 Supplements may also be labeled as performance- or image-enhancing agents and may include medications marketed to promote weight loss. This includes herbal substances (Table12-19) and medications associated with neuropsychiatric adverse effects that may be easily accessible online without a prescription.12,20
The growing popularity of the internet and social media plays an important role in the availability of supplements and nonregulated substances and may contribute to misleading claims of efficacy and safety. While many herbal supplements are available in pharmacies or supplement stores, NPS are usually sold through anonymous, low-risk means either via traditional online vendors or the deep web (parts of the internet that are not indexed via search engines). Strategies to circumvent regulation and legislative control include labeling NPS as research chemicals, fertilizers, incense, bath salts, or other identifiers and marketing them as “not for human consumption.”21 Manufacturers frequently change the chemical structures of NPS, which allows these products to exist within a legal gray area due to the lag time between when a new compound hits the market and when it is categorized as a regulated substance.10
Continue to: Another category of "supplements"...
Another category of “supplements” includes medications that are not FDA-approved but are approved for therapeutic use in other countries and readily available in the US via online sources. Such medications include phenibut, a glutamic acid derivative that functions as a gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptor agonist in the brain, spinal cord, and autonomic nervous system. Phenibut was developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s, and outside of the US it is prescribed for anxiolysis and other psychiatric indications.22 In the US, phenibut may be used as a nootropic or as a dietary supplement to treat anxiety, sleep problems, and other psychiatric disorders.22 It may also be used recreationally to induce euphoria. Chronic phenibut use results in tolerance and abrupt discontinuation may mimic benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms.13,22
Educating patients about supplements
One of the most critical steps in assessing a patient’s supplement use is to directly ask them about their use of herbal or over-the-counter products. Research has consistently shown that patients are unlikely to disclose supplement use unless they are specifically asked.23,24
Additional strategies include25,26:
- Approach patients without judgment; ask open-ended questions to determine their motivations for using supplements.
- Explain the difference between supplements medically necessary to treat vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium) and those without robust clinical evidence.
- Counsel patients that many supplements with psychoactive properties, if indicated, are generally meant to be used short-term and not as substitutes for prescription medications.
- Educate patients that supplements have limited evidence regarding their safety and efficacy, but like prescription medications, supplements may cause organ damage, adverse effects, and drug-drug interactions.
- Remind patients that commonly used nutritional supplements/dietary aids, including protein or workout supplements, may contain potentially harmful ingredients.
- Utilize evidence-based resources such as the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database14 or the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (https://www.nccih.nih.gov) to review levels of evidence and educate patients.
- When toxicity or withdrawal is suspected, reach out to local poison control centers for guidance.
- For a patient with a potential supplement-related substance use disorder, urine drug screens may be of limited utility and evidence is often sparse; clinicians may need to rely on primary literature such as case reports to guide management.
- If patients wish to continue taking a supplement, recommend they purchase supplements from manufacturers that have achieved the US Pharmacopeia (USP) verification mark. Products with the USP mark undergo quality assurance measures to ensure the product contains the ingredients listed on the label in the declared potency and amounts, does not contain harmful levels of contaminants, will be metabolized in the body within a specified amount of time, and has been produced in keeping with FDA Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.
CASE CONTINUED
In the ED, the consulting psychiatry team discusses Mr. D’s use of phenibut with him, and asks if he uses any additional supplements or nonprescription medications. Mr. D discloses he has been anxious and having trouble sleeping, and a friend recommended phenibut as a safe, natural alternative to medication. The team explains to Mr. D that phenibut’s efficacy has not been studied in the US and that based on available evidence, it is likely unsafe. It may have serious adverse effects, drug-drug interactions, and is potentially addictive.
Mr. D says he was unaware of these risks and agrees to stop taking phenibut. The treatment team discharges him from the ED with a referral for outpatient psychiatric services to address his anxiety and insomnia.
Related Resources
- Tillman B. The hidden dangers of supplements: a case of substance-induced psychosis. Current Psychiatry. 2020; 19(7):e7-e8. doi:10.12788/cp.0018
- McQueen CE. Herb–drug interactions: caution patients when changing supplements. Current Psychiatry. 2017; 16(6):38-41.
Drug Brand Names
Butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine • Fioricet with Codeine
1. Graziano S, Orsolini L, Rotolo MC, et al. Herbal highs: review on psychoactive effects and neuropharmacology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):750-761.
2. Mishra S, Stierman B, Gahche JJ, et al. Dietary supplement use among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2021;(399):1-8.
3. O’Neill-Dee C, Spiller HA, Casavant MJ, et al. Natural psychoactive substance-related exposures reported to United States poison control centers, 2000-2017. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020;58(8):813-820.
4. Gray DC, Rutledge CM. Herbal supplements in primary care: patient perceptions, motivations, and effects on use. Holist Nurs Pract. 2013;27(1):6-12.
5. Wu K, Messamore E. Reimagining roles of dietary supplements in psychiatric care. AMA J Ethics. 2022;24(5):E437-E442.
6. Snyder FJ, Dundas ML, Kirkpatrick C, et al. Use and safety perceptions regarding herbal supplements: a study of older persons in southeast Idaho. J Nutr Elder. 2009;28(1):81-95.
7. Schulz P, Hede V. Alternative and complementary approaches in psychiatry: beliefs versus evidence. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20(3):207-214.
8. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, Pub L 103-417, 103rd Cong (1993-1994).
9. Starr RR. Too little, too late: ineffective regulation of dietary supplements in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(3):478-485.
10. New psychoactive substances. Alcohol and Drug Foundation. November 10, 2021. Updated November 28, 2022. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/new-psychoactive-substances/
11. Shafi A, Berry AJ, Sumnall H, et al. New psychoactive substances: a review and updates. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320967197.
12. Bersani FS, Coviello M, Imperatori C, et al. Adverse psychiatric effects associated with herbal weight-loss products. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:120679.
13. IBM Micromedex POISINDEX® System. IBM Watson Health. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://www.micromedexsolutions.com
14. Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. Therapeutic Research Center. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com
15. Savage KM, Stough CK, Byrne GJ, et al. Kava for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (K-GAD): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:493.
16. Swogger MT, Smith KE, Garcia-Romeu A, et al. Understanding kratom use: a guide for healthcare providers. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:801855.
17. Modabbernia A, Akhondzadeh S. Saffron, passionflower, valerian and sage for mental health. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2013;36(1):85-91.
18. Coffeen U, Pellicer F. Salvia divinorum: from recreational hallucinogenic use to analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. J Pain Res. 2019;12:1069-1076.
19. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. Valerian Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Updated March 15, 2013. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Valerian-HealthProfessional
20. An H, Sohn H, Chung S. Phentermine, sibutramine and affective disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(1):7-12.
21. Miliano C, Margiani G, Fattore L, et al. Sales and advertising channels of new psychoactive substances (NPS): internet, social networks, and smartphone apps. Brain Sci. 2018;8(7):123.
22. Hardman MI, Sprung J, Weingarten TN. Acute phenibut withdrawal: a comprehensive literature review and illustrative case report. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019;19(2):125-129.
23. Guzman JR, Paterniti DA, Liu Y, et al. Factors related to disclosure and nondisclosure of dietary supplements in primary care, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine. J Fam Med Dis Prev. 2019;5(4):10.23937/2469-5793/1510109.
24. Foley H, Steel A, Cramer H, et al. Disclosure of complementary medicine use to medical providers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1573.
25. Aldridge Young C. ‘No miracle cures’: counseling patients about dietary supplements. Pharmacy Today. 2014;February:35.
26. United States Pharmacopeia. USP Verified Mark. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://www.usp.org/verification-services/verified-mark
Mr. D, age 41, presents to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and suspected intoxication. His medical history includes alcohol use disorder and spinal injury. Upon initial examination, he is confused, disorganized, and agitated. He receives IM lorazepam 4 mg to manage his agitation. His laboratory workup includes a negative screening for blood alcohol, slightly elevated creatine kinase, and urine toxicology positive for barbiturates and opioids. During re-evaluation by the consulting psychiatrist the following morning, Mr. D is alert, oriented, and calm with an organized thought process. He does not appear to be in withdrawal from any substances and tells the psychiatrist that he takes butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine as needed for migraines. Mr. D says that 3 days before he came to the ED, he also began taking a supplement called phenibut that he purchased online for “well-being and sleep.”
Natural substances have been used throughout history as medicinal agents, sacred substances in religious rituals, and for recreational purposes.1 Supplement use in the United States is prevalent, with 57.6% of adults age ≥20 reporting supplement use in the past 30 days.2 Between 2000 and 2017, US poison control centers recorded a 74.1% increase in calls involving exposure to natural psychoactive substances, mostly driven by cases involving marijuana in adults and adolescents.3 Like synthetic drugs, herbal supplements may have psychoactive properties, including sedative, stimulant, psychedelic, euphoric, or anticholinergic effects. The variety and unregulated nature of supplements makes managing patients who use supplements particularly challenging.
Why patients use supplements
People may use supplements to treat or prevent vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, iron, calcium). Other reasons may include for promoting wellness in various disease states, for weight loss, for recreational use or misuse, or for overall well-being. In the mental health realm, patients report using supplements to treat depression, anxiety, insomnia, memory, or for vague indications such as “mood support.”4,5
Patients may view supplements as appealing alternatives to prescription medications because they are widely accessible, may be purchased over-the-counter, are inexpensive, and represent a “natural” treatment option.6 For these reasons, they may also falsely perceive supplements as categorically safe.1 People with psychiatric diagnoses may choose such alternative treatments due to a history of adverse effects or treatment failure with traditional psychiatric medications, mistrust of the health care or pharmaceutical industry, or based on the recommendations of others.7
Regulation, safety, and efficacy of dietary supplements
In the US, dietary supplements are regulated more like food products than medications. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the FDA regulates the quality, safety, and labeling of supplements using Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.8 The Federal Trade Commission monitors advertisements and marketing. Despite some regulations, dietary supplements may be adulterated or contaminated, contain unknown or toxic ingredients, have inconsistent potencies, or be sold at toxic doses.9 Importantly, supplements are not required to be evaluated for clinical efficacy. As a result, it is not known if most supplements are effective in treating the conditions for which they are promoted, mainly due to a lack of financial incentive for manufacturers to conduct large, high-quality trials.5
Further complicating matters is the inconsistent labeling of supplements or similar products that are easily obtainable via the internet. These products might be marketed as nutritional supplements or nootropics, which often are referred to as “cognitive enhancers” or “smart drugs.” New psychoactive substances (NPS) are drugs of misuse or abuse developed to imitate illicit drugs or controlled drug substances.10 They are sometimes referred to as “herbal highs” or “legal highs.”11 Supplements may also be labeled as performance- or image-enhancing agents and may include medications marketed to promote weight loss. This includes herbal substances (Table12-19) and medications associated with neuropsychiatric adverse effects that may be easily accessible online without a prescription.12,20

The growing popularity of the internet and social media plays an important role in the availability of supplements and nonregulated substances and may contribute to misleading claims of efficacy and safety. While many herbal supplements are available in pharmacies or supplement stores, NPS are usually sold through anonymous, low-risk means either via traditional online vendors or the deep web (parts of the internet that are not indexed via search engines). Strategies to circumvent regulation and legislative control include labeling NPS as research chemicals, fertilizers, incense, bath salts, or other identifiers and marketing them as “not for human consumption.”21 Manufacturers frequently change the chemical structures of NPS, which allows these products to exist within a legal gray area due to the lag time between when a new compound hits the market and when it is categorized as a regulated substance.10
Continue to: Another category of "supplements"...
Another category of “supplements” includes medications that are not FDA-approved but are approved for therapeutic use in other countries and readily available in the US via online sources. Such medications include phenibut, a glutamic acid derivative that functions as a gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptor agonist in the brain, spinal cord, and autonomic nervous system. Phenibut was developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s, and outside of the US it is prescribed for anxiolysis and other psychiatric indications.22 In the US, phenibut may be used as a nootropic or as a dietary supplement to treat anxiety, sleep problems, and other psychiatric disorders.22 It may also be used recreationally to induce euphoria. Chronic phenibut use results in tolerance and abrupt discontinuation may mimic benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms.13,22
Educating patients about supplements
One of the most critical steps in assessing a patient’s supplement use is to directly ask them about their use of herbal or over-the-counter products. Research has consistently shown that patients are unlikely to disclose supplement use unless they are specifically asked.23,24
Additional strategies include25,26:
- Approach patients without judgment; ask open-ended questions to determine their motivations for using supplements.
- Explain the difference between supplements medically necessary to treat vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium) and those without robust clinical evidence.
- Counsel patients that many supplements with psychoactive properties, if indicated, are generally meant to be used short-term and not as substitutes for prescription medications.
- Educate patients that supplements have limited evidence regarding their safety and efficacy, but like prescription medications, supplements may cause organ damage, adverse effects, and drug-drug interactions.
- Remind patients that commonly used nutritional supplements/dietary aids, including protein or workout supplements, may contain potentially harmful ingredients.
- Utilize evidence-based resources such as the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database14 or the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (https://www.nccih.nih.gov) to review levels of evidence and educate patients.
- When toxicity or withdrawal is suspected, reach out to local poison control centers for guidance.
- For a patient with a potential supplement-related substance use disorder, urine drug screens may be of limited utility and evidence is often sparse; clinicians may need to rely on primary literature such as case reports to guide management.
- If patients wish to continue taking a supplement, recommend they purchase supplements from manufacturers that have achieved the US Pharmacopeia (USP) verification mark. Products with the USP mark undergo quality assurance measures to ensure the product contains the ingredients listed on the label in the declared potency and amounts, does not contain harmful levels of contaminants, will be metabolized in the body within a specified amount of time, and has been produced in keeping with FDA Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.
CASE CONTINUED
In the ED, the consulting psychiatry team discusses Mr. D’s use of phenibut with him, and asks if he uses any additional supplements or nonprescription medications. Mr. D discloses he has been anxious and having trouble sleeping, and a friend recommended phenibut as a safe, natural alternative to medication. The team explains to Mr. D that phenibut’s efficacy has not been studied in the US and that based on available evidence, it is likely unsafe. It may have serious adverse effects, drug-drug interactions, and is potentially addictive.
Mr. D says he was unaware of these risks and agrees to stop taking phenibut. The treatment team discharges him from the ED with a referral for outpatient psychiatric services to address his anxiety and insomnia.
Related Resources
- Tillman B. The hidden dangers of supplements: a case of substance-induced psychosis. Current Psychiatry. 2020; 19(7):e7-e8. doi:10.12788/cp.0018
- McQueen CE. Herb–drug interactions: caution patients when changing supplements. Current Psychiatry. 2017; 16(6):38-41.
Drug Brand Names
Butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine • Fioricet with Codeine
Mr. D, age 41, presents to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and suspected intoxication. His medical history includes alcohol use disorder and spinal injury. Upon initial examination, he is confused, disorganized, and agitated. He receives IM lorazepam 4 mg to manage his agitation. His laboratory workup includes a negative screening for blood alcohol, slightly elevated creatine kinase, and urine toxicology positive for barbiturates and opioids. During re-evaluation by the consulting psychiatrist the following morning, Mr. D is alert, oriented, and calm with an organized thought process. He does not appear to be in withdrawal from any substances and tells the psychiatrist that he takes butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine as needed for migraines. Mr. D says that 3 days before he came to the ED, he also began taking a supplement called phenibut that he purchased online for “well-being and sleep.”
Natural substances have been used throughout history as medicinal agents, sacred substances in religious rituals, and for recreational purposes.1 Supplement use in the United States is prevalent, with 57.6% of adults age ≥20 reporting supplement use in the past 30 days.2 Between 2000 and 2017, US poison control centers recorded a 74.1% increase in calls involving exposure to natural psychoactive substances, mostly driven by cases involving marijuana in adults and adolescents.3 Like synthetic drugs, herbal supplements may have psychoactive properties, including sedative, stimulant, psychedelic, euphoric, or anticholinergic effects. The variety and unregulated nature of supplements makes managing patients who use supplements particularly challenging.
Why patients use supplements
People may use supplements to treat or prevent vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, iron, calcium). Other reasons may include for promoting wellness in various disease states, for weight loss, for recreational use or misuse, or for overall well-being. In the mental health realm, patients report using supplements to treat depression, anxiety, insomnia, memory, or for vague indications such as “mood support.”4,5
Patients may view supplements as appealing alternatives to prescription medications because they are widely accessible, may be purchased over-the-counter, are inexpensive, and represent a “natural” treatment option.6 For these reasons, they may also falsely perceive supplements as categorically safe.1 People with psychiatric diagnoses may choose such alternative treatments due to a history of adverse effects or treatment failure with traditional psychiatric medications, mistrust of the health care or pharmaceutical industry, or based on the recommendations of others.7
Regulation, safety, and efficacy of dietary supplements
In the US, dietary supplements are regulated more like food products than medications. Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, the FDA regulates the quality, safety, and labeling of supplements using Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.8 The Federal Trade Commission monitors advertisements and marketing. Despite some regulations, dietary supplements may be adulterated or contaminated, contain unknown or toxic ingredients, have inconsistent potencies, or be sold at toxic doses.9 Importantly, supplements are not required to be evaluated for clinical efficacy. As a result, it is not known if most supplements are effective in treating the conditions for which they are promoted, mainly due to a lack of financial incentive for manufacturers to conduct large, high-quality trials.5
Further complicating matters is the inconsistent labeling of supplements or similar products that are easily obtainable via the internet. These products might be marketed as nutritional supplements or nootropics, which often are referred to as “cognitive enhancers” or “smart drugs.” New psychoactive substances (NPS) are drugs of misuse or abuse developed to imitate illicit drugs or controlled drug substances.10 They are sometimes referred to as “herbal highs” or “legal highs.”11 Supplements may also be labeled as performance- or image-enhancing agents and may include medications marketed to promote weight loss. This includes herbal substances (Table12-19) and medications associated with neuropsychiatric adverse effects that may be easily accessible online without a prescription.12,20

The growing popularity of the internet and social media plays an important role in the availability of supplements and nonregulated substances and may contribute to misleading claims of efficacy and safety. While many herbal supplements are available in pharmacies or supplement stores, NPS are usually sold through anonymous, low-risk means either via traditional online vendors or the deep web (parts of the internet that are not indexed via search engines). Strategies to circumvent regulation and legislative control include labeling NPS as research chemicals, fertilizers, incense, bath salts, or other identifiers and marketing them as “not for human consumption.”21 Manufacturers frequently change the chemical structures of NPS, which allows these products to exist within a legal gray area due to the lag time between when a new compound hits the market and when it is categorized as a regulated substance.10
Continue to: Another category of "supplements"...
Another category of “supplements” includes medications that are not FDA-approved but are approved for therapeutic use in other countries and readily available in the US via online sources. Such medications include phenibut, a glutamic acid derivative that functions as a gamma-aminobutyric acid-B receptor agonist in the brain, spinal cord, and autonomic nervous system. Phenibut was developed in the Soviet Union in the 1960s, and outside of the US it is prescribed for anxiolysis and other psychiatric indications.22 In the US, phenibut may be used as a nootropic or as a dietary supplement to treat anxiety, sleep problems, and other psychiatric disorders.22 It may also be used recreationally to induce euphoria. Chronic phenibut use results in tolerance and abrupt discontinuation may mimic benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms.13,22
Educating patients about supplements
One of the most critical steps in assessing a patient’s supplement use is to directly ask them about their use of herbal or over-the-counter products. Research has consistently shown that patients are unlikely to disclose supplement use unless they are specifically asked.23,24
Additional strategies include25,26:
- Approach patients without judgment; ask open-ended questions to determine their motivations for using supplements.
- Explain the difference between supplements medically necessary to treat vitamin deficiencies (eg, vitamin D, calcium, magnesium) and those without robust clinical evidence.
- Counsel patients that many supplements with psychoactive properties, if indicated, are generally meant to be used short-term and not as substitutes for prescription medications.
- Educate patients that supplements have limited evidence regarding their safety and efficacy, but like prescription medications, supplements may cause organ damage, adverse effects, and drug-drug interactions.
- Remind patients that commonly used nutritional supplements/dietary aids, including protein or workout supplements, may contain potentially harmful ingredients.
- Utilize evidence-based resources such as the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database14 or the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (https://www.nccih.nih.gov) to review levels of evidence and educate patients.
- When toxicity or withdrawal is suspected, reach out to local poison control centers for guidance.
- For a patient with a potential supplement-related substance use disorder, urine drug screens may be of limited utility and evidence is often sparse; clinicians may need to rely on primary literature such as case reports to guide management.
- If patients wish to continue taking a supplement, recommend they purchase supplements from manufacturers that have achieved the US Pharmacopeia (USP) verification mark. Products with the USP mark undergo quality assurance measures to ensure the product contains the ingredients listed on the label in the declared potency and amounts, does not contain harmful levels of contaminants, will be metabolized in the body within a specified amount of time, and has been produced in keeping with FDA Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations.
CASE CONTINUED
In the ED, the consulting psychiatry team discusses Mr. D’s use of phenibut with him, and asks if he uses any additional supplements or nonprescription medications. Mr. D discloses he has been anxious and having trouble sleeping, and a friend recommended phenibut as a safe, natural alternative to medication. The team explains to Mr. D that phenibut’s efficacy has not been studied in the US and that based on available evidence, it is likely unsafe. It may have serious adverse effects, drug-drug interactions, and is potentially addictive.
Mr. D says he was unaware of these risks and agrees to stop taking phenibut. The treatment team discharges him from the ED with a referral for outpatient psychiatric services to address his anxiety and insomnia.
Related Resources
- Tillman B. The hidden dangers of supplements: a case of substance-induced psychosis. Current Psychiatry. 2020; 19(7):e7-e8. doi:10.12788/cp.0018
- McQueen CE. Herb–drug interactions: caution patients when changing supplements. Current Psychiatry. 2017; 16(6):38-41.
Drug Brand Names
Butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine/codeine • Fioricet with Codeine
1. Graziano S, Orsolini L, Rotolo MC, et al. Herbal highs: review on psychoactive effects and neuropharmacology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):750-761.
2. Mishra S, Stierman B, Gahche JJ, et al. Dietary supplement use among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2021;(399):1-8.
3. O’Neill-Dee C, Spiller HA, Casavant MJ, et al. Natural psychoactive substance-related exposures reported to United States poison control centers, 2000-2017. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020;58(8):813-820.
4. Gray DC, Rutledge CM. Herbal supplements in primary care: patient perceptions, motivations, and effects on use. Holist Nurs Pract. 2013;27(1):6-12.
5. Wu K, Messamore E. Reimagining roles of dietary supplements in psychiatric care. AMA J Ethics. 2022;24(5):E437-E442.
6. Snyder FJ, Dundas ML, Kirkpatrick C, et al. Use and safety perceptions regarding herbal supplements: a study of older persons in southeast Idaho. J Nutr Elder. 2009;28(1):81-95.
7. Schulz P, Hede V. Alternative and complementary approaches in psychiatry: beliefs versus evidence. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20(3):207-214.
8. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, Pub L 103-417, 103rd Cong (1993-1994).
9. Starr RR. Too little, too late: ineffective regulation of dietary supplements in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(3):478-485.
10. New psychoactive substances. Alcohol and Drug Foundation. November 10, 2021. Updated November 28, 2022. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/new-psychoactive-substances/
11. Shafi A, Berry AJ, Sumnall H, et al. New psychoactive substances: a review and updates. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320967197.
12. Bersani FS, Coviello M, Imperatori C, et al. Adverse psychiatric effects associated with herbal weight-loss products. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:120679.
13. IBM Micromedex POISINDEX® System. IBM Watson Health. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://www.micromedexsolutions.com
14. Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. Therapeutic Research Center. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com
15. Savage KM, Stough CK, Byrne GJ, et al. Kava for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (K-GAD): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:493.
16. Swogger MT, Smith KE, Garcia-Romeu A, et al. Understanding kratom use: a guide for healthcare providers. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:801855.
17. Modabbernia A, Akhondzadeh S. Saffron, passionflower, valerian and sage for mental health. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2013;36(1):85-91.
18. Coffeen U, Pellicer F. Salvia divinorum: from recreational hallucinogenic use to analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. J Pain Res. 2019;12:1069-1076.
19. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. Valerian Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Updated March 15, 2013. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Valerian-HealthProfessional
20. An H, Sohn H, Chung S. Phentermine, sibutramine and affective disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(1):7-12.
21. Miliano C, Margiani G, Fattore L, et al. Sales and advertising channels of new psychoactive substances (NPS): internet, social networks, and smartphone apps. Brain Sci. 2018;8(7):123.
22. Hardman MI, Sprung J, Weingarten TN. Acute phenibut withdrawal: a comprehensive literature review and illustrative case report. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019;19(2):125-129.
23. Guzman JR, Paterniti DA, Liu Y, et al. Factors related to disclosure and nondisclosure of dietary supplements in primary care, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine. J Fam Med Dis Prev. 2019;5(4):10.23937/2469-5793/1510109.
24. Foley H, Steel A, Cramer H, et al. Disclosure of complementary medicine use to medical providers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1573.
25. Aldridge Young C. ‘No miracle cures’: counseling patients about dietary supplements. Pharmacy Today. 2014;February:35.
26. United States Pharmacopeia. USP Verified Mark. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://www.usp.org/verification-services/verified-mark
1. Graziano S, Orsolini L, Rotolo MC, et al. Herbal highs: review on psychoactive effects and neuropharmacology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(5):750-761.
2. Mishra S, Stierman B, Gahche JJ, et al. Dietary supplement use among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2021;(399):1-8.
3. O’Neill-Dee C, Spiller HA, Casavant MJ, et al. Natural psychoactive substance-related exposures reported to United States poison control centers, 2000-2017. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020;58(8):813-820.
4. Gray DC, Rutledge CM. Herbal supplements in primary care: patient perceptions, motivations, and effects on use. Holist Nurs Pract. 2013;27(1):6-12.
5. Wu K, Messamore E. Reimagining roles of dietary supplements in psychiatric care. AMA J Ethics. 2022;24(5):E437-E442.
6. Snyder FJ, Dundas ML, Kirkpatrick C, et al. Use and safety perceptions regarding herbal supplements: a study of older persons in southeast Idaho. J Nutr Elder. 2009;28(1):81-95.
7. Schulz P, Hede V. Alternative and complementary approaches in psychiatry: beliefs versus evidence. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2018;20(3):207-214.
8. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, Pub L 103-417, 103rd Cong (1993-1994).
9. Starr RR. Too little, too late: ineffective regulation of dietary supplements in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(3):478-485.
10. New psychoactive substances. Alcohol and Drug Foundation. November 10, 2021. Updated November 28, 2022. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/new-psychoactive-substances/
11. Shafi A, Berry AJ, Sumnall H, et al. New psychoactive substances: a review and updates. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320967197.
12. Bersani FS, Coviello M, Imperatori C, et al. Adverse psychiatric effects associated with herbal weight-loss products. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:120679.
13. IBM Micromedex POISINDEX® System. IBM Watson Health. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://www.micromedexsolutions.com
14. Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. Therapeutic Research Center. Accessed October 3, 2022. https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com
15. Savage KM, Stough CK, Byrne GJ, et al. Kava for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (K-GAD): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:493.
16. Swogger MT, Smith KE, Garcia-Romeu A, et al. Understanding kratom use: a guide for healthcare providers. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:801855.
17. Modabbernia A, Akhondzadeh S. Saffron, passionflower, valerian and sage for mental health. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2013;36(1):85-91.
18. Coffeen U, Pellicer F. Salvia divinorum: from recreational hallucinogenic use to analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. J Pain Res. 2019;12:1069-1076.
19. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. Valerian Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Updated March 15, 2013. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Valerian-HealthProfessional
20. An H, Sohn H, Chung S. Phentermine, sibutramine and affective disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2013;11(1):7-12.
21. Miliano C, Margiani G, Fattore L, et al. Sales and advertising channels of new psychoactive substances (NPS): internet, social networks, and smartphone apps. Brain Sci. 2018;8(7):123.
22. Hardman MI, Sprung J, Weingarten TN. Acute phenibut withdrawal: a comprehensive literature review and illustrative case report. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019;19(2):125-129.
23. Guzman JR, Paterniti DA, Liu Y, et al. Factors related to disclosure and nondisclosure of dietary supplements in primary care, integrative medicine, and naturopathic medicine. J Fam Med Dis Prev. 2019;5(4):10.23937/2469-5793/1510109.
24. Foley H, Steel A, Cramer H, et al. Disclosure of complementary medicine use to medical providers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1573.
25. Aldridge Young C. ‘No miracle cures’: counseling patients about dietary supplements. Pharmacy Today. 2014;February:35.
26. United States Pharmacopeia. USP Verified Mark. Accessed January 25, 2023. https://www.usp.org/verification-services/verified-mark
Increased anxiety and depression after menstruation
CASE Increased anxiety and depression
Ms. C, age 29, has bipolar II disorder (BD II) and generalized anxiety disorder. She presents to her outpatient psychiatrist seeking relief from chronic and significant dips in her mood from Day 5 to Day 15 of her menstrual cycle. During this time, she says she experiences increased anxiety, insomnia, frequent tearfulness, and intermittent suicidal ideation.
Ms. C meticulously charts her menstrual cycle using a smartphone app and reports having a regular 28-day cycle. She says she has experienced this worsening of symptoms since the onset of menarche, but her mood generally stabilizes after Day 14 of her cycle–around the time of ovulation–and remains euthymic throughout the premenstrual period.
HISTORY Depression and a change in medication
Ms. C has a history of major depressive episodes and has experienced hypomanic episodes that lasted 1 to 2 weeks and were associated with an elevated mood, high energy, rapid speech, and increased self-confidence. Ms. C says she has chronically high anxiety associated with trouble sleeping, difficulty focusing, restlessness, and muscle tension. When she was receiving care from previous psychiatrists, treatment with lithium, quetiapine, lamotrigine, sertraline, and fluoxetine was not successful, and Ms. C said she had severe anxiety when she tried sertraline and fluoxetine. After several months of substantial mood instability and high anxiety, Ms. C responded well to pregabalin 100 mg 3 times a day, lurasidone 60 mg/d at bedtime, and gabapentin 500 mg/d at bedtime. Over the last 4 months, she reports that her overall mood has been even, and she has been coping well with her anxiety.
Ms. C is married with no children. She uses condoms for birth control. She previously tried taking a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive, but stopped because she said it made her feel very depressed. Ms. C reports no history of substance use. She is employed, says she has many positive relationships, and does not have a social history suggestive of a personality disorder.
[polldaddy:11818926]
The author’s observations
Many women report worsening of mood during the premenstrual period (luteal phase). Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) involves symptoms that develop during the luteal phase and end shortly after menstruation; this condition impacts ≤5% of women.1 The etiology of PMDD appears to involve contributions from genetics, hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, allopregnanolone (a progesterone metabolite), brain-derived neurotrophic factor, brain structural and functional differences, and hypothalamic pathways.2
Researchers have postulated that the precipitous decline in the levels of progesterone and allopregnanolone in the luteal phase may contribute to the mood symptoms of PMDD.2 Allopregnanolone is a modulator of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA-A) receptors and may exert anxiolytic and sedative effects. Women who experience PMDD may be less sensitive to the effects of allopregnanolone.3 Additionally, early luteal phase levels of estrogen may predict late luteal phase symptoms of PMDD.4 The mechanism involved may be estrogen’s effect on the serotonin system. The HPA axis may also be involved in the etiology of PMDD because patients with this condition appear to have a blunted cortisol response in reaction to stress.5 Research also has implicated immune activation and inflammation in the etiology of PMDD.6
A PMDD diagnosis should be distinguished from a premenstrual exacerbation of an underlying psychiatric condition, which occurs when a patient has an untreated primary mood or anxiety disorder that worsens during the premenstrual period. PMDD is differentiated from premenstrual syndrome by the severity of symptoms.2 The recommended first-line treatment of PMDD is an SSRI, but if an SSRI does not work, is not tolerated, or is not preferred for any other reason, recommended alternatives include combined hormone oral contraceptive pills, dutasteride, gabapentin, or various supplements.7,8 PMDD has been widely studied and is treated by both psychiatrists and gynecologists. In addition, some women report experiencing mood instability around ovulation. Kiesner9 found that 13% of women studied showed an increased negative mood state midcycle, rather than during the premenstrual period.
Continue to: Postmenstrual syndrome
Postmenstrual syndrome
Postmenstrual mood symptoms are atypical. Postmenstrual syndrome is not listed in DSM-5 or formally recognized as a medical diagnosis. Peer-reviewed research or literature on the condition is scarce to nonexistent. However, it has been discussed by physicians in articles in the lay press. One gynecologist and reproductive endocrinologist estimated that approximately 10% of women experience significant physical and emotional symptoms postmenstruation.10 An internist and women’s health specialist suggested that the cause of postmenstrual syndrome might be a surge in levels of estrogen and testosterone and may be associated with insulin resistance and polycystic ovarian syndrome, while another possible contribution could be iron deficiency caused by loss of blood from menstruation.11
TREATMENT Recommending an oral contraceptive
Ms. C’s psychiatrist does not prescribe an SSRI because he is concerned it would destabilize her BD II. The patient also had negative experiences in her past 2 trials of SSRIs.
Because the psychiatrist believes it is prudent to optimize the dosages of a patient’s current medication before starting a new medication or intervention, he considers increasing Ms. C’s dosage of lurasidone or pregabalin. The rationale for optimizing Ms. C’s current medication regimen is that greater overall mood stability would likely result in less severe postmenstrual mood symptoms. However, Ms. C does not want to increase her dosage of either medication because she is concerned about adverse effects.
Ms. C’s psychiatrist discusses the case with 2 gynecologist/obstetrician colleagues. One suggests the patient try a progesterone-only oral contraceptive and the other suggests a trial of Prometrium (a progesterone capsule used to treat endometrial hyperplasia and secondary amenorrhea). Both suggestions are based on the theory that Ms. C may be sensitive to levels of progesterone, which are low during the follicular phase and rise after ovulation; neither recommendation is evidence-based. A low level of allopregnanolone may lead to less GABAergic activity and consequently greater mood dysregulation. Some women are particularly sensitive to low levels of allopregnanolone in the follicular phase, which might lead to postmenstrual mood symptoms. Additionally, Ms. C’s previous treatment with a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive may have decreased her level of allopregnanolone.12 Ultimately, Ms. C’s psychiatrist suggests that she take a progesterone-only oral contraceptive.
The author’s observations
Guidance on how to treat Ms. C’s postmenstrual symptoms came from research on how to treat PMDD in patients who have BD. In a review of managing PMDD in women with BD, Sepede et al13 presented a treatment algorithm that recommends a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive as first-line treatment in euthymic patients who are already receiving an optimal dose of mood stabilizers. Sepede et al13 expressed caution about using SSRIs due to the risk of inducing mood changes, but recommended SSRIs for patients with comorbid PMDD and BD who experience a depressive episode.
Another question is which type of oral contraceptive is most effective for treating PMDD. The combined oral contraceptive drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol has the most evidence for efficacy.14 Combined oral contraceptives carry risks of venous thromboembolism, hypertension, stroke, migraines, and liver complications, and are possibly associated with certain types of cancer, such as breast and cervical cancer.15 Their use is contraindicated in patients with a history of these conditions and for women age >35 who smoke ≥15 cigarettes/d.
The limited research that has examined the efficacy of progestin-only oral contraceptives for treating PMDD has been inconclusive.16 However, progesterone-only oral contraceptives are associated with less overall risk than combined oral contraceptives, and many women opt to use progesterone-only oral contraceptives due to concerns about possible adverse effects of the combined formulations. A substantial drawback of progesterone-only oral contraceptives is they must be taken at the same time every day, and if a dose is taken late, these agents may lose their efficacy in preventing pregnancy (and a backup birth control method must be used17). Additionally, drospirenone, a progestin that is a component of many oral contraceptives, has antimineralocorticoid properties and is contraindicated in patients with kidney or adrenal gland insufficiency or liver disease. As was the case when Ms. C initially took a combined contraceptive, hormonal contraceptives can sometimes cause mood dysregulation.
Continue to: OUTCOME Improved symptoms
OUTCOME Improved symptoms
Ms. C meets with her gynecologist, who prescribes norethindrone, a progestin-only oral contraceptive. Since taking norethindrone, Ms. C reports a dramatic improvement in the mood symptoms she experiences during the postmenstrual period.
Bottom Line
Some women may experience mood symptoms during the postmenstrual period that are similar to the symptoms experienced by patients who have premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). This phenomenon has been described as postmenstrual syndrome, and though evidence is lacking, treating it similarly to PMDD may be effective.
Related Resources
- Ray P, Mandal N, Sinha VK. Change of symptoms of schizophrenia across phases of menstrual cycle. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2020;23(1):113-122. doi:10.1007/s00737-019-0952-4
- Raffi ER, Freeman MP. The etiology of premenstrual dysphoric disorder: 5 interwoven pieces. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9):20-28.
Drug Brand Names
Drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol • Yasmin
Dutasteride • Avodart
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Lamotrigine • Lamictal
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lurasidone • Latuda
Norethindrone • Aygestin
Pregabalin • Lyrica
Progesterone • Prometrium
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Sertraline • Zoloft
1. Epperson CN, Steiner M, Hartlage SA, et al. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: evidence for a new category for DSM-5. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169(5):465-475.
2. Raffi ER, Freeman MP. The etiology of premenstrual dysphoric disorder: 5 interwoven pieces. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9):20-28.
3. Timby E, Bäckström T, Nyberg S, et al. Women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder have altered sensitivity to allopregnanolone over the menstrual cycle compared to controls--a pilot study. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016;233(11):2109-2117.
4. Yen JY, Lin HC, Lin PC, et al. Early- and late-luteal-phase estrogen and progesterone levels of women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(22):4352.
5. Huang Y, Zhou R, Wu M, et al. Premenstrual syndrome is associated with blunted cortisol reactivity to the TSST. Stress. 2015;18(2):160-168.
6. Hantsoo L, Epperson CN. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: epidemiology and treatment. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17(11):87.
7. Tiranini L, Nappi RE. Recent advances in understanding/management of premenstrual dysphoric disorder/premenstrual syndrome. Faculty Rev. 2022:11:(11). doi:10.12703/r/11-11
8. Raffi ER. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9). Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/145089/somatic-disorders/premenstrual-dysphoric-disorder
9. Kiesner J. One woman’s low is another woman’s high: paradoxical effects of the menstrual cycle. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011;36(1):68-76.
10. Alnuweiri T. Feel low after your period? Postmenstrual syndrome could be the reason. Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.wellandgood.com/pms-after-period/
11. Sharkey L. Everything you need to know about post-menstrual syndrome. Healthline. Published April 28, 2020. Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.healthline.com/health/post-menstrual-syndrome
12. Santoru F, Berretti R, Locci A, et al. Decreased allopregnanolone induced by hormonal contraceptives is associated with a reduction in social behavior and sexual motivation in female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014;231(17):3351-3364.
13. Sepede G, Brunetti M, Di Giannantonio M. Comorbid premenstrual dysphoric disorder in women with bipolar disorder: management challenges. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treatment. 2020;16:415-426.
14. Rapkin AJ, Korotkaya Y, Taylor KC. Contraception counseling for women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD): current perspectives. Open Access J Contraception. 2019;10:27-39. doi:10.2147/OAJC.S183193
15. Roe AH, Bartz DA, Douglas PS. Combined estrogen-progestin contraception: side effects and health concerns. UpToDate. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/combined-estrogen-progestin-contraception-side-effects-and-health-concerns
16. Ford O, Lethaby A, Roberts H, et al. Progesterone for premenstrual syndrome. Cochrane Database Sys Rev. 2012;3:CD003415. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003415.pub4
17. Kaunitz AM. Contraception: progestin-only pills (POPs). UpToDate. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/contraception-progestin-only-pills-pops
CASE Increased anxiety and depression
Ms. C, age 29, has bipolar II disorder (BD II) and generalized anxiety disorder. She presents to her outpatient psychiatrist seeking relief from chronic and significant dips in her mood from Day 5 to Day 15 of her menstrual cycle. During this time, she says she experiences increased anxiety, insomnia, frequent tearfulness, and intermittent suicidal ideation.
Ms. C meticulously charts her menstrual cycle using a smartphone app and reports having a regular 28-day cycle. She says she has experienced this worsening of symptoms since the onset of menarche, but her mood generally stabilizes after Day 14 of her cycle–around the time of ovulation–and remains euthymic throughout the premenstrual period.
HISTORY Depression and a change in medication
Ms. C has a history of major depressive episodes and has experienced hypomanic episodes that lasted 1 to 2 weeks and were associated with an elevated mood, high energy, rapid speech, and increased self-confidence. Ms. C says she has chronically high anxiety associated with trouble sleeping, difficulty focusing, restlessness, and muscle tension. When she was receiving care from previous psychiatrists, treatment with lithium, quetiapine, lamotrigine, sertraline, and fluoxetine was not successful, and Ms. C said she had severe anxiety when she tried sertraline and fluoxetine. After several months of substantial mood instability and high anxiety, Ms. C responded well to pregabalin 100 mg 3 times a day, lurasidone 60 mg/d at bedtime, and gabapentin 500 mg/d at bedtime. Over the last 4 months, she reports that her overall mood has been even, and she has been coping well with her anxiety.
Ms. C is married with no children. She uses condoms for birth control. She previously tried taking a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive, but stopped because she said it made her feel very depressed. Ms. C reports no history of substance use. She is employed, says she has many positive relationships, and does not have a social history suggestive of a personality disorder.
[polldaddy:11818926]
The author’s observations
Many women report worsening of mood during the premenstrual period (luteal phase). Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) involves symptoms that develop during the luteal phase and end shortly after menstruation; this condition impacts ≤5% of women.1 The etiology of PMDD appears to involve contributions from genetics, hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, allopregnanolone (a progesterone metabolite), brain-derived neurotrophic factor, brain structural and functional differences, and hypothalamic pathways.2
Researchers have postulated that the precipitous decline in the levels of progesterone and allopregnanolone in the luteal phase may contribute to the mood symptoms of PMDD.2 Allopregnanolone is a modulator of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA-A) receptors and may exert anxiolytic and sedative effects. Women who experience PMDD may be less sensitive to the effects of allopregnanolone.3 Additionally, early luteal phase levels of estrogen may predict late luteal phase symptoms of PMDD.4 The mechanism involved may be estrogen’s effect on the serotonin system. The HPA axis may also be involved in the etiology of PMDD because patients with this condition appear to have a blunted cortisol response in reaction to stress.5 Research also has implicated immune activation and inflammation in the etiology of PMDD.6
A PMDD diagnosis should be distinguished from a premenstrual exacerbation of an underlying psychiatric condition, which occurs when a patient has an untreated primary mood or anxiety disorder that worsens during the premenstrual period. PMDD is differentiated from premenstrual syndrome by the severity of symptoms.2 The recommended first-line treatment of PMDD is an SSRI, but if an SSRI does not work, is not tolerated, or is not preferred for any other reason, recommended alternatives include combined hormone oral contraceptive pills, dutasteride, gabapentin, or various supplements.7,8 PMDD has been widely studied and is treated by both psychiatrists and gynecologists. In addition, some women report experiencing mood instability around ovulation. Kiesner9 found that 13% of women studied showed an increased negative mood state midcycle, rather than during the premenstrual period.
Continue to: Postmenstrual syndrome
Postmenstrual syndrome
Postmenstrual mood symptoms are atypical. Postmenstrual syndrome is not listed in DSM-5 or formally recognized as a medical diagnosis. Peer-reviewed research or literature on the condition is scarce to nonexistent. However, it has been discussed by physicians in articles in the lay press. One gynecologist and reproductive endocrinologist estimated that approximately 10% of women experience significant physical and emotional symptoms postmenstruation.10 An internist and women’s health specialist suggested that the cause of postmenstrual syndrome might be a surge in levels of estrogen and testosterone and may be associated with insulin resistance and polycystic ovarian syndrome, while another possible contribution could be iron deficiency caused by loss of blood from menstruation.11
TREATMENT Recommending an oral contraceptive
Ms. C’s psychiatrist does not prescribe an SSRI because he is concerned it would destabilize her BD II. The patient also had negative experiences in her past 2 trials of SSRIs.
Because the psychiatrist believes it is prudent to optimize the dosages of a patient’s current medication before starting a new medication or intervention, he considers increasing Ms. C’s dosage of lurasidone or pregabalin. The rationale for optimizing Ms. C’s current medication regimen is that greater overall mood stability would likely result in less severe postmenstrual mood symptoms. However, Ms. C does not want to increase her dosage of either medication because she is concerned about adverse effects.
Ms. C’s psychiatrist discusses the case with 2 gynecologist/obstetrician colleagues. One suggests the patient try a progesterone-only oral contraceptive and the other suggests a trial of Prometrium (a progesterone capsule used to treat endometrial hyperplasia and secondary amenorrhea). Both suggestions are based on the theory that Ms. C may be sensitive to levels of progesterone, which are low during the follicular phase and rise after ovulation; neither recommendation is evidence-based. A low level of allopregnanolone may lead to less GABAergic activity and consequently greater mood dysregulation. Some women are particularly sensitive to low levels of allopregnanolone in the follicular phase, which might lead to postmenstrual mood symptoms. Additionally, Ms. C’s previous treatment with a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive may have decreased her level of allopregnanolone.12 Ultimately, Ms. C’s psychiatrist suggests that she take a progesterone-only oral contraceptive.
The author’s observations
Guidance on how to treat Ms. C’s postmenstrual symptoms came from research on how to treat PMDD in patients who have BD. In a review of managing PMDD in women with BD, Sepede et al13 presented a treatment algorithm that recommends a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive as first-line treatment in euthymic patients who are already receiving an optimal dose of mood stabilizers. Sepede et al13 expressed caution about using SSRIs due to the risk of inducing mood changes, but recommended SSRIs for patients with comorbid PMDD and BD who experience a depressive episode.
Another question is which type of oral contraceptive is most effective for treating PMDD. The combined oral contraceptive drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol has the most evidence for efficacy.14 Combined oral contraceptives carry risks of venous thromboembolism, hypertension, stroke, migraines, and liver complications, and are possibly associated with certain types of cancer, such as breast and cervical cancer.15 Their use is contraindicated in patients with a history of these conditions and for women age >35 who smoke ≥15 cigarettes/d.
The limited research that has examined the efficacy of progestin-only oral contraceptives for treating PMDD has been inconclusive.16 However, progesterone-only oral contraceptives are associated with less overall risk than combined oral contraceptives, and many women opt to use progesterone-only oral contraceptives due to concerns about possible adverse effects of the combined formulations. A substantial drawback of progesterone-only oral contraceptives is they must be taken at the same time every day, and if a dose is taken late, these agents may lose their efficacy in preventing pregnancy (and a backup birth control method must be used17). Additionally, drospirenone, a progestin that is a component of many oral contraceptives, has antimineralocorticoid properties and is contraindicated in patients with kidney or adrenal gland insufficiency or liver disease. As was the case when Ms. C initially took a combined contraceptive, hormonal contraceptives can sometimes cause mood dysregulation.
Continue to: OUTCOME Improved symptoms
OUTCOME Improved symptoms
Ms. C meets with her gynecologist, who prescribes norethindrone, a progestin-only oral contraceptive. Since taking norethindrone, Ms. C reports a dramatic improvement in the mood symptoms she experiences during the postmenstrual period.
Bottom Line
Some women may experience mood symptoms during the postmenstrual period that are similar to the symptoms experienced by patients who have premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). This phenomenon has been described as postmenstrual syndrome, and though evidence is lacking, treating it similarly to PMDD may be effective.
Related Resources
- Ray P, Mandal N, Sinha VK. Change of symptoms of schizophrenia across phases of menstrual cycle. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2020;23(1):113-122. doi:10.1007/s00737-019-0952-4
- Raffi ER, Freeman MP. The etiology of premenstrual dysphoric disorder: 5 interwoven pieces. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9):20-28.
Drug Brand Names
Drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol • Yasmin
Dutasteride • Avodart
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Lamotrigine • Lamictal
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lurasidone • Latuda
Norethindrone • Aygestin
Pregabalin • Lyrica
Progesterone • Prometrium
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Sertraline • Zoloft
CASE Increased anxiety and depression
Ms. C, age 29, has bipolar II disorder (BD II) and generalized anxiety disorder. She presents to her outpatient psychiatrist seeking relief from chronic and significant dips in her mood from Day 5 to Day 15 of her menstrual cycle. During this time, she says she experiences increased anxiety, insomnia, frequent tearfulness, and intermittent suicidal ideation.
Ms. C meticulously charts her menstrual cycle using a smartphone app and reports having a regular 28-day cycle. She says she has experienced this worsening of symptoms since the onset of menarche, but her mood generally stabilizes after Day 14 of her cycle–around the time of ovulation–and remains euthymic throughout the premenstrual period.
HISTORY Depression and a change in medication
Ms. C has a history of major depressive episodes and has experienced hypomanic episodes that lasted 1 to 2 weeks and were associated with an elevated mood, high energy, rapid speech, and increased self-confidence. Ms. C says she has chronically high anxiety associated with trouble sleeping, difficulty focusing, restlessness, and muscle tension. When she was receiving care from previous psychiatrists, treatment with lithium, quetiapine, lamotrigine, sertraline, and fluoxetine was not successful, and Ms. C said she had severe anxiety when she tried sertraline and fluoxetine. After several months of substantial mood instability and high anxiety, Ms. C responded well to pregabalin 100 mg 3 times a day, lurasidone 60 mg/d at bedtime, and gabapentin 500 mg/d at bedtime. Over the last 4 months, she reports that her overall mood has been even, and she has been coping well with her anxiety.
Ms. C is married with no children. She uses condoms for birth control. She previously tried taking a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive, but stopped because she said it made her feel very depressed. Ms. C reports no history of substance use. She is employed, says she has many positive relationships, and does not have a social history suggestive of a personality disorder.
[polldaddy:11818926]
The author’s observations
Many women report worsening of mood during the premenstrual period (luteal phase). Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) involves symptoms that develop during the luteal phase and end shortly after menstruation; this condition impacts ≤5% of women.1 The etiology of PMDD appears to involve contributions from genetics, hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, allopregnanolone (a progesterone metabolite), brain-derived neurotrophic factor, brain structural and functional differences, and hypothalamic pathways.2
Researchers have postulated that the precipitous decline in the levels of progesterone and allopregnanolone in the luteal phase may contribute to the mood symptoms of PMDD.2 Allopregnanolone is a modulator of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA-A) receptors and may exert anxiolytic and sedative effects. Women who experience PMDD may be less sensitive to the effects of allopregnanolone.3 Additionally, early luteal phase levels of estrogen may predict late luteal phase symptoms of PMDD.4 The mechanism involved may be estrogen’s effect on the serotonin system. The HPA axis may also be involved in the etiology of PMDD because patients with this condition appear to have a blunted cortisol response in reaction to stress.5 Research also has implicated immune activation and inflammation in the etiology of PMDD.6
A PMDD diagnosis should be distinguished from a premenstrual exacerbation of an underlying psychiatric condition, which occurs when a patient has an untreated primary mood or anxiety disorder that worsens during the premenstrual period. PMDD is differentiated from premenstrual syndrome by the severity of symptoms.2 The recommended first-line treatment of PMDD is an SSRI, but if an SSRI does not work, is not tolerated, or is not preferred for any other reason, recommended alternatives include combined hormone oral contraceptive pills, dutasteride, gabapentin, or various supplements.7,8 PMDD has been widely studied and is treated by both psychiatrists and gynecologists. In addition, some women report experiencing mood instability around ovulation. Kiesner9 found that 13% of women studied showed an increased negative mood state midcycle, rather than during the premenstrual period.
Continue to: Postmenstrual syndrome
Postmenstrual syndrome
Postmenstrual mood symptoms are atypical. Postmenstrual syndrome is not listed in DSM-5 or formally recognized as a medical diagnosis. Peer-reviewed research or literature on the condition is scarce to nonexistent. However, it has been discussed by physicians in articles in the lay press. One gynecologist and reproductive endocrinologist estimated that approximately 10% of women experience significant physical and emotional symptoms postmenstruation.10 An internist and women’s health specialist suggested that the cause of postmenstrual syndrome might be a surge in levels of estrogen and testosterone and may be associated with insulin resistance and polycystic ovarian syndrome, while another possible contribution could be iron deficiency caused by loss of blood from menstruation.11
TREATMENT Recommending an oral contraceptive
Ms. C’s psychiatrist does not prescribe an SSRI because he is concerned it would destabilize her BD II. The patient also had negative experiences in her past 2 trials of SSRIs.
Because the psychiatrist believes it is prudent to optimize the dosages of a patient’s current medication before starting a new medication or intervention, he considers increasing Ms. C’s dosage of lurasidone or pregabalin. The rationale for optimizing Ms. C’s current medication regimen is that greater overall mood stability would likely result in less severe postmenstrual mood symptoms. However, Ms. C does not want to increase her dosage of either medication because she is concerned about adverse effects.
Ms. C’s psychiatrist discusses the case with 2 gynecologist/obstetrician colleagues. One suggests the patient try a progesterone-only oral contraceptive and the other suggests a trial of Prometrium (a progesterone capsule used to treat endometrial hyperplasia and secondary amenorrhea). Both suggestions are based on the theory that Ms. C may be sensitive to levels of progesterone, which are low during the follicular phase and rise after ovulation; neither recommendation is evidence-based. A low level of allopregnanolone may lead to less GABAergic activity and consequently greater mood dysregulation. Some women are particularly sensitive to low levels of allopregnanolone in the follicular phase, which might lead to postmenstrual mood symptoms. Additionally, Ms. C’s previous treatment with a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive may have decreased her level of allopregnanolone.12 Ultimately, Ms. C’s psychiatrist suggests that she take a progesterone-only oral contraceptive.
The author’s observations
Guidance on how to treat Ms. C’s postmenstrual symptoms came from research on how to treat PMDD in patients who have BD. In a review of managing PMDD in women with BD, Sepede et al13 presented a treatment algorithm that recommends a combined estrogen/progestin oral contraceptive as first-line treatment in euthymic patients who are already receiving an optimal dose of mood stabilizers. Sepede et al13 expressed caution about using SSRIs due to the risk of inducing mood changes, but recommended SSRIs for patients with comorbid PMDD and BD who experience a depressive episode.
Another question is which type of oral contraceptive is most effective for treating PMDD. The combined oral contraceptive drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol has the most evidence for efficacy.14 Combined oral contraceptives carry risks of venous thromboembolism, hypertension, stroke, migraines, and liver complications, and are possibly associated with certain types of cancer, such as breast and cervical cancer.15 Their use is contraindicated in patients with a history of these conditions and for women age >35 who smoke ≥15 cigarettes/d.
The limited research that has examined the efficacy of progestin-only oral contraceptives for treating PMDD has been inconclusive.16 However, progesterone-only oral contraceptives are associated with less overall risk than combined oral contraceptives, and many women opt to use progesterone-only oral contraceptives due to concerns about possible adverse effects of the combined formulations. A substantial drawback of progesterone-only oral contraceptives is they must be taken at the same time every day, and if a dose is taken late, these agents may lose their efficacy in preventing pregnancy (and a backup birth control method must be used17). Additionally, drospirenone, a progestin that is a component of many oral contraceptives, has antimineralocorticoid properties and is contraindicated in patients with kidney or adrenal gland insufficiency or liver disease. As was the case when Ms. C initially took a combined contraceptive, hormonal contraceptives can sometimes cause mood dysregulation.
Continue to: OUTCOME Improved symptoms
OUTCOME Improved symptoms
Ms. C meets with her gynecologist, who prescribes norethindrone, a progestin-only oral contraceptive. Since taking norethindrone, Ms. C reports a dramatic improvement in the mood symptoms she experiences during the postmenstrual period.
Bottom Line
Some women may experience mood symptoms during the postmenstrual period that are similar to the symptoms experienced by patients who have premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). This phenomenon has been described as postmenstrual syndrome, and though evidence is lacking, treating it similarly to PMDD may be effective.
Related Resources
- Ray P, Mandal N, Sinha VK. Change of symptoms of schizophrenia across phases of menstrual cycle. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2020;23(1):113-122. doi:10.1007/s00737-019-0952-4
- Raffi ER, Freeman MP. The etiology of premenstrual dysphoric disorder: 5 interwoven pieces. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9):20-28.
Drug Brand Names
Drospirenone/ethinyl estradiol • Yasmin
Dutasteride • Avodart
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Gabapentin • Neurontin
Lamotrigine • Lamictal
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Lurasidone • Latuda
Norethindrone • Aygestin
Pregabalin • Lyrica
Progesterone • Prometrium
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Sertraline • Zoloft
1. Epperson CN, Steiner M, Hartlage SA, et al. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: evidence for a new category for DSM-5. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169(5):465-475.
2. Raffi ER, Freeman MP. The etiology of premenstrual dysphoric disorder: 5 interwoven pieces. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9):20-28.
3. Timby E, Bäckström T, Nyberg S, et al. Women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder have altered sensitivity to allopregnanolone over the menstrual cycle compared to controls--a pilot study. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016;233(11):2109-2117.
4. Yen JY, Lin HC, Lin PC, et al. Early- and late-luteal-phase estrogen and progesterone levels of women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(22):4352.
5. Huang Y, Zhou R, Wu M, et al. Premenstrual syndrome is associated with blunted cortisol reactivity to the TSST. Stress. 2015;18(2):160-168.
6. Hantsoo L, Epperson CN. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: epidemiology and treatment. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17(11):87.
7. Tiranini L, Nappi RE. Recent advances in understanding/management of premenstrual dysphoric disorder/premenstrual syndrome. Faculty Rev. 2022:11:(11). doi:10.12703/r/11-11
8. Raffi ER. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9). Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/145089/somatic-disorders/premenstrual-dysphoric-disorder
9. Kiesner J. One woman’s low is another woman’s high: paradoxical effects of the menstrual cycle. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011;36(1):68-76.
10. Alnuweiri T. Feel low after your period? Postmenstrual syndrome could be the reason. Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.wellandgood.com/pms-after-period/
11. Sharkey L. Everything you need to know about post-menstrual syndrome. Healthline. Published April 28, 2020. Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.healthline.com/health/post-menstrual-syndrome
12. Santoru F, Berretti R, Locci A, et al. Decreased allopregnanolone induced by hormonal contraceptives is associated with a reduction in social behavior and sexual motivation in female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014;231(17):3351-3364.
13. Sepede G, Brunetti M, Di Giannantonio M. Comorbid premenstrual dysphoric disorder in women with bipolar disorder: management challenges. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treatment. 2020;16:415-426.
14. Rapkin AJ, Korotkaya Y, Taylor KC. Contraception counseling for women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD): current perspectives. Open Access J Contraception. 2019;10:27-39. doi:10.2147/OAJC.S183193
15. Roe AH, Bartz DA, Douglas PS. Combined estrogen-progestin contraception: side effects and health concerns. UpToDate. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/combined-estrogen-progestin-contraception-side-effects-and-health-concerns
16. Ford O, Lethaby A, Roberts H, et al. Progesterone for premenstrual syndrome. Cochrane Database Sys Rev. 2012;3:CD003415. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003415.pub4
17. Kaunitz AM. Contraception: progestin-only pills (POPs). UpToDate. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/contraception-progestin-only-pills-pops
1. Epperson CN, Steiner M, Hartlage SA, et al. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: evidence for a new category for DSM-5. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169(5):465-475.
2. Raffi ER, Freeman MP. The etiology of premenstrual dysphoric disorder: 5 interwoven pieces. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9):20-28.
3. Timby E, Bäckström T, Nyberg S, et al. Women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder have altered sensitivity to allopregnanolone over the menstrual cycle compared to controls--a pilot study. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016;233(11):2109-2117.
4. Yen JY, Lin HC, Lin PC, et al. Early- and late-luteal-phase estrogen and progesterone levels of women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(22):4352.
5. Huang Y, Zhou R, Wu M, et al. Premenstrual syndrome is associated with blunted cortisol reactivity to the TSST. Stress. 2015;18(2):160-168.
6. Hantsoo L, Epperson CN. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: epidemiology and treatment. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17(11):87.
7. Tiranini L, Nappi RE. Recent advances in understanding/management of premenstrual dysphoric disorder/premenstrual syndrome. Faculty Rev. 2022:11:(11). doi:10.12703/r/11-11
8. Raffi ER. Premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(9). Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/145089/somatic-disorders/premenstrual-dysphoric-disorder
9. Kiesner J. One woman’s low is another woman’s high: paradoxical effects of the menstrual cycle. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011;36(1):68-76.
10. Alnuweiri T. Feel low after your period? Postmenstrual syndrome could be the reason. Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.wellandgood.com/pms-after-period/
11. Sharkey L. Everything you need to know about post-menstrual syndrome. Healthline. Published April 28, 2020. Accessed January 30, 2023. https://www.healthline.com/health/post-menstrual-syndrome
12. Santoru F, Berretti R, Locci A, et al. Decreased allopregnanolone induced by hormonal contraceptives is associated with a reduction in social behavior and sexual motivation in female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014;231(17):3351-3364.
13. Sepede G, Brunetti M, Di Giannantonio M. Comorbid premenstrual dysphoric disorder in women with bipolar disorder: management challenges. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treatment. 2020;16:415-426.
14. Rapkin AJ, Korotkaya Y, Taylor KC. Contraception counseling for women with premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD): current perspectives. Open Access J Contraception. 2019;10:27-39. doi:10.2147/OAJC.S183193
15. Roe AH, Bartz DA, Douglas PS. Combined estrogen-progestin contraception: side effects and health concerns. UpToDate. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/combined-estrogen-progestin-contraception-side-effects-and-health-concerns
16. Ford O, Lethaby A, Roberts H, et al. Progesterone for premenstrual syndrome. Cochrane Database Sys Rev. 2012;3:CD003415. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003415.pub4
17. Kaunitz AM. Contraception: progestin-only pills (POPs). UpToDate. Accessed February 1, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/contraception-progestin-only-pills-pops