User login
At-home births rose during the pandemic, CDC reports
More women gave birth at home in America last year, continuing a pandemic trend and reaching the highest level in decades, according to figures released by the CDC.
The report said that almost 52,000 births occurred at home in 2021, out of 4 million total births in the country. This was an increase of 12% from 2020. The figure rose by 22% in 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, over 2019.
There were several possible reasons for the increase in home births. Infection rates and hospitalizations were high. Vaccinations were not available or were not widely used, and many people avoided going to hospitals or the doctor, said Elizabeth Gregory, the report’s lead author.
Also, some women didn’t have health insurance, lived far from a medical facility, or could not get to a hospital fast enough. About 25% of home births are not planned, the Associated Press reported.
Increases in home births occurred across all races, but home births were less common among Hispanics.
The AP reported that home births are riskier than hospital births, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The organization advises against home births for women carrying multiple babies or who have previously had a cesarean section.
“Hospitals and accredited birth centers are the safest places to give birth, because although serious complications associated with labor and delivery are rare, they can be catastrophic,” said Jeffrey Ecker, M.D., chief of obstetrics and gynecology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More women gave birth at home in America last year, continuing a pandemic trend and reaching the highest level in decades, according to figures released by the CDC.
The report said that almost 52,000 births occurred at home in 2021, out of 4 million total births in the country. This was an increase of 12% from 2020. The figure rose by 22% in 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, over 2019.
There were several possible reasons for the increase in home births. Infection rates and hospitalizations were high. Vaccinations were not available or were not widely used, and many people avoided going to hospitals or the doctor, said Elizabeth Gregory, the report’s lead author.
Also, some women didn’t have health insurance, lived far from a medical facility, or could not get to a hospital fast enough. About 25% of home births are not planned, the Associated Press reported.
Increases in home births occurred across all races, but home births were less common among Hispanics.
The AP reported that home births are riskier than hospital births, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The organization advises against home births for women carrying multiple babies or who have previously had a cesarean section.
“Hospitals and accredited birth centers are the safest places to give birth, because although serious complications associated with labor and delivery are rare, they can be catastrophic,” said Jeffrey Ecker, M.D., chief of obstetrics and gynecology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More women gave birth at home in America last year, continuing a pandemic trend and reaching the highest level in decades, according to figures released by the CDC.
The report said that almost 52,000 births occurred at home in 2021, out of 4 million total births in the country. This was an increase of 12% from 2020. The figure rose by 22% in 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic hit, over 2019.
There were several possible reasons for the increase in home births. Infection rates and hospitalizations were high. Vaccinations were not available or were not widely used, and many people avoided going to hospitals or the doctor, said Elizabeth Gregory, the report’s lead author.
Also, some women didn’t have health insurance, lived far from a medical facility, or could not get to a hospital fast enough. About 25% of home births are not planned, the Associated Press reported.
Increases in home births occurred across all races, but home births were less common among Hispanics.
The AP reported that home births are riskier than hospital births, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The organization advises against home births for women carrying multiple babies or who have previously had a cesarean section.
“Hospitals and accredited birth centers are the safest places to give birth, because although serious complications associated with labor and delivery are rare, they can be catastrophic,” said Jeffrey Ecker, M.D., chief of obstetrics and gynecology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
An FP’s guide to identifying—and treating—postpartum depression
THE CASE
Alex T,* a 23-year-old first-time mom, presented to the family medicine office for her baby’s 2-week appointment. When asked how she was doing, she began to cry. She said, “I feel crazy” and indicated that she was feeling down and overwhelmed, and was struggling to bond with the baby. She filled out an Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, a standard postpartum depression (PPD) screen; her score, 15 out of 30, was suggestive of depression. Ms. T had been coming to the practice for the past 3 years and had no significant physical or mental health history. She and the baby did not live with the baby’s father, and his degree of presence in their lives varied.
●
* The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity.
PPD, traditionally defined as depression in the postpartum period for as long as a year after childbirth, is a common, underdiagnosed outcome of both normal and complicated pregnancies.1 Peripartum depression, which includes PPD and depression during pregnancy, occurs in approximately 10% of pregnancies.2,3 When depression first appears in the postpartum period, most women develop symptoms in the first month after delivery (54% of cases) or in the next 2 to 4 months (40%).4
The most significant risk factor for PPD is previous depression, peripartum or otherwise.1,4-6 Other common risk factors include major life events or stressors during or after pregnancy, domestic violence, poor social support, and preterm birth or an infant admission to the neonatal intensive care unit.1,7 Women with a self-perceived negative birth experience are also likely to experience PPD.8 PPD can be associated with significant morbidity and mortality, with suicide a more common cause of maternal mortality than either hemorrhage or hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.9
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to improving patient outcomes. Women with PPD initiate breastfeeding at lower rates and continue for shorter durations.10 PPD also affects maternal–infant bonding; may adversely affect an infant’s social, cognitive, and language development; and may lead to attachment disorders of infancy.11,12 In severe cases, it can lead to failure to thrive or infanticide.11
When to screen. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends clinicians screen for depression in pregnant and postpartum women (Grade Ba) and for women at increased risk, provide or refer to counseling interventions (Grade Ba).13,14 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends screening at least once in the postpartum period.15 Repeat screening at follow-up in the later postpartum period increases the likelihood of diagnosis.16 Screening for PPD as part of well-child care improves maternal outcomes, and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends screening at the 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month visits.11,17 These screens are separately billable. Family physicians are uniquely suited to screening at both well-child and postpartum visits, as many women share a medical home with their child, and those who do not are equally willing to receive medical advice from their child’s physician.18
Continue to: Is it "the blues" or something else? Diagnosing PPD
Is it “the blues” or something else? Diagnosing PPD
Many new mothers experience postpartum blues, which manifest as tearfulness, insomnia, irritability, and anxiety. The postpartum blues, however, don’t meet the criteria for major depressive disorder and typically resolve within 14 days of delivery.19-21 On the other end of the spectrum is postpartum psychosis, which is severe and rare, and can also affect new mothers.
Screening for PPD. The most commonly used screening tool for PPD is the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS 10), a free 10-item instrument scored out of 30 possible points, with any score ≥ 13 suggesting PPD.22 The EPDS 10 has a sensitivity of 74% and specificity of 97% for the diagnosis of PPD.23 Other screening options include the Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI-II) and the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9). The 21-item BDI-II takes longer to perform and is less sensitive (57%) than the EPDS.1 The PHQ-9, which asks about some symptoms common to the postpartum period (including sleep changes), is less specific than the EPDS (sensitivity, 75%; specificity, 90%).1 The EPDS also includes screening questions about anxiety.1
A positive depression screen, or any positive response to a question on suicidal ideation, should be followed up for confirmation using the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th Edition (DSM-5) criteria for major depressive disorder with peripartum onset.24 Women with PPD should also be asked about current or prior symptoms of bipolar disorder or mania.25 Up to 67% of women with bipolar disorder may relapse postpartum, and they also have an elevated risk of postpartum psychosis.26 The Mood Disorder Questionnaire is a useful tool if a concern for bipolar depression arises.27
Refer any woman in whom bipolar depression is a concern to a clinician experienced with its management. The presence of auditory or visual hallucinations should also be assessed as indicators of postpartum psychosis. Active suicidal or homicidal ideation and postpartum psychosis all require emergent psychiatric care.21,22 Intimate partner violence may also exist or escalate in the postpartum period and may exacerbate PPD. Both ACOG and the USPSTF recommend screening postpartum women for intimate partner violence.28,29
Also consider possible medical causes of PPD symptoms. Hypothyroidism in the postpartum period may manifest with some similar symptoms to PPD and is commonly underdiagnosed.22,30 Women with postpartum anemia and low ferritin stores also have a higher likelihood of PPD (odds ratio, 1.7-4.64), and postpartum iron supplementation may reduce this risk (number needed to treat = 4 in at least 1 randomized controlled trial).31 When anemia is present, ensure that it is properly treated.
Continue to: Steps you can take to manage pPD
Steps you can take to manage pPD
Refer any woman who has PPD to a qualified therapist whenever possible. Generally, the psychological recommendations for treatment of PPD are very similar to recommendations for general treatment of depression. Psychotherapy on its own is considered a first-line treatment for mild-to-moderate PPD, and medication plus psychotherapy is considered first-line treatment for severe PPD.32 (Worth noting: It may also be useful to offer counseling to a patient who appears distressed, even if she does not fully meet all DSM-5 criteria.)
Of the psychotherapy options, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is supported by the most evidence. There is also evidence for the use of interpersonal therapy (IPT), especially in higher socioeconomic status populations.33 Key therapeutic targets in IPT are increasing behavioral engagement (eg, reaching out to friends), decreasing negative self-talk (eg, “I am a bad mother”), and negotiating roles and support (eg, both mom’s and family members’ expectations of new motherhood). There is mixed evidence for recommending exercise as a treatment for PPD.32,34 However, as exercise is a low-risk intervention, you may choose to make that recommendation to patients. Additionally, including partners/support people in treatment/visits for PPD has been shown to increase positive outcomes.35
When medication is considered, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are most commonly used. Research indicates that SSRIs are significantly more effective than placebo for treatment of women with PPD.36 Sertraline, in particular, has shown to be both effective in treating PPD and safe in lactation.37,38 Dosing and duration of therapy are equivalent to treatment of major depression outside the perinatal period. Consult a trusted source on medications in lactation before prescribing any antidepressant to a breastfeeding mother. One resource is the National Institutes of Health drugs and lactation database (LactMed; www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501922/), which provides detailed information on the levels of medications in breastmilk and their potential effects on an infant.
Women with severe, refractory PPD may require hospitalization. Additional treatment options for women with severe, refractory PPD include electroconvulsive therapy or the new medication brexanolone, which is administered as a 60-hour continuous infusion.39,40
THE CASE
Further conversation with Ms. T revealed that she met the criteria for PPD (major depressive disorder with peripartum onset). She denied suicidal or homicidal ideation and was not experiencing any symptoms of psychosis. A complete blood count was drawn and showed no anemia, and her thyroid-stimulating hormone level was within normal limits. She had a good support network at home, with both her mom and sister taking shifts to help her get some extra rest and allow her to attend medical appointments. She said there was no domestic violence.
Ms. T was introduced to the clinic’s embedded counselor, who scheduled a follow-up appointment within the week to start CBT. After a discussion of risks and benefits, Ms. T also started a low dose of sertraline once daily. At follow-up postpartum visits, she reported significant improvement in her mood. She and her physician decided to taper her SSRI medication at 3 months postpartum. Screens for depression at her infant’s 4- and 6-month well-child visits in the office were reassuringly negative.
a There is high certainty that the net benefit is moderate, or there is moderate certainty that the net benefit is moderate to substantial.
CORRESPONDENCE
Katherine Buck, PhD, JPS Family Health Center, 1500 South Main Street, 4th Floor, Fort Worth, TX 76110; [email protected]
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 757: Screening for perinatal depression. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:e208-e212. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002927
2. Banti S, Mauri M, Oppo A, et al. From the third month of pregnancy to 1 year postpartum. Prevalence, incidence, recurrence, and new onset of depression. Results from the Perinatal Depression–Research & Screening Unit study. Compr Psychiatry. 2011;52:343-351. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2010.08.003
3. Dietz PM, Williams SB, Callaghan WM, et al. Clinically identified maternal depression before, during, and after pregnancies ending in live births. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164):1515-1520. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06111893
4. Altemus M, Neeb CC, Davis A, et al. Phenotypic differences between pregnancy-onset and postpartum-onset major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73:e1485-e1491. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m07693
5. Wilson LM, Reid AJ, Midmer DK, et al. Antenatal psychosocial risk factors associated with adverse postpartum family outcomes. CMAJ. 1996;154:785-799.
6. Robertson E, Grace S, Wallington T, et al. Antenatal risk factors for postpartum depression: a synthesis of recent literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2004;26:289-295. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2004.02.006
7. Beck CT. Predictors of postpartum depression: an update. Nurs Res. 2001;50:275-285. doi: 10.1097/00006199-200109000-00004
8. Bell AF, E Andersson. The birth experience and women’s postnatal depression: a systematic review. Midwifery. 2016;39:112-123. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2016.04.014
9. Palladino CL, Singh V, Campbell J, et al. Homicide and suicide during the perinatal period: findings from the National Violent Death Reporting System. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:1056-1063. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823294da
10. Ko JY, Rockhill KM, Tong VT, et al. Trends in postpartum depressive symptoms — 27 States, 2004, 2008, and 2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:153-158. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6606a1
11. Rafferty J, Mattson G, Earls MF, et al. Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal depression into pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2019;143:e20183260. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3260
12. Lovejoy MC, Graczyk PA, O’Hare E, et al. Maternal depression and parenting behavior: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2000;20:561-592. doi: 10.1016/s0272-7358(98)00100-7
13. Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Interventions to prevent perinatal depression: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019;321:580-587. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0007
14. Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for depression in adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2016;315:380-387. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18392
15. ACOG. Screening for perinatal depression. 2018. Accessed October 5, 2022. www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2018/11/screening-for-perinatal-depression
16. Yawn BP, Bertram S, Kurland M, et al. Repeated depression screening during the first postpartum year. Ann Fam Med. 2015;13:228-234. doi: 10.1370/afm.1777
17. van der Zee-van den Berg AI, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Groothuis-Oudshoorn CGM, et al. Post-up study: postpartum depression screening in well-child care and maternal outcomes. Pediatrics. 2017;140:e20170110. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-0110
18. Rosener SE, Barr WB, Frayne DJ, et al. Interconception care for mothers during well-child visits with family physicians: an IMPLICIT Network study. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14:350-355. doi: 10.1370/afm.1933
19. Nonacs R, Cohen LS. Postpartum mood disorders: diagnosis and treatment guidelines. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59(suppl 2):34-40.
20. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 736: Optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002633
21. Langan R, Goodbred AJ. Identification and management of peripartum depression. Am Fam Physician. 2016;93:852-858.
22. Sharma V, Sharma P. Postpartum depression: diagnostic and treatment issues. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2012;34:436-442. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)35240-9
23. Owara AH, Carabin H, Reese J, et al. Summary diagnostic validity of commonly used maternal major depression disorder case finding instruments in the United States: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;205:335-343. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.08.014
24. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Washington D.C.: 2013:160.
25. Mandelli L, Souery D, Bartova L, et al. Bipolar II disorder as a risk factor for postpartum depression. J Affect Disord. 2016;204:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.025
26. ACOG Practice Bulletin: Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists number 92, April 2008 (replaces practice bulletin number 87, November 2007). Use of psychiatric medications during pregnancy and lactation. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:1001-1020. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31816fd910
27. Hirschfeld RM, Williams JB, Spitzer RL, et al. Development and validation of a screening instrument for bipolar spectrum disorder: the Mood Disorder Questionnaire. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1873-1875. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.157.11.1873
28. Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence, elder abuse, and abuse of vulnerable adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Final Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2018;320:1678-1687. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14741
29. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 518: Intimate partner violence. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119:412-417. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e318249ff74
30. Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 223. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e261-e274. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003893
31. Wassef A, Nguyen QD, St-André M. Anaemia and depletion of iron stores as risk factors for postpartum depression: a literature review. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 2019;40:19-28. doi: 10.1080/0167482X.2018.1427725
32. Hirst KP, Moutier CY. Postpartum major depression. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:926-933.
33. Nillni YI, Mehralizade A, Mayer L, et al. Treatment of depression, anxiety, and trauma-related disorders during the perinatal period: a systematic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018;66:136-148. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2018.06.004
34. Daley AJ, Macarthur C, Winter H. The role of exercise in treating postpartum depression: a review of the literature. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2007;52:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jmwh.2006.08.017
35. Misri S, Kostaras X, Fox D, et al. The impact of partner support in the treatment of postpartum depression. Can J Psychiatry. 2000;45:554-558. doi: 10.1177/070674370004500607
36. Molyneaux E, Howard LM, McGeown HR, et al. Antidepressant treatment for postnatal depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;CD002018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002018.pub2
37. Pinheiro E, Bogen DL, Hoxha D, et al. Sertraline and breastfeeding: review and meta-analysis. Arch Women Ment Health. 2015;18:139-146. doi: 10.1007/s00737-015-0499-y
38. Hantsoo L, Ward-O’Brien D, Czarkowski KA, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of sertraline for postpartum depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014;231:939-948. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3316-1
39. Rundgren S, Brus O, Båve U, et al. Improvement of postpartum depression and psychosis after electroconvulsive therapy: a population-based study with a matched comparison group. J Affect Disord. 2018;235:258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.04.043
40. Meltzer-Brody S, Colquhoun H, Riesenberg R, et al. Brexanolone injection in post-partum depression: two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2018;392:1058-1070. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31551-4
THE CASE
Alex T,* a 23-year-old first-time mom, presented to the family medicine office for her baby’s 2-week appointment. When asked how she was doing, she began to cry. She said, “I feel crazy” and indicated that she was feeling down and overwhelmed, and was struggling to bond with the baby. She filled out an Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, a standard postpartum depression (PPD) screen; her score, 15 out of 30, was suggestive of depression. Ms. T had been coming to the practice for the past 3 years and had no significant physical or mental health history. She and the baby did not live with the baby’s father, and his degree of presence in their lives varied.
●
* The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity.
PPD, traditionally defined as depression in the postpartum period for as long as a year after childbirth, is a common, underdiagnosed outcome of both normal and complicated pregnancies.1 Peripartum depression, which includes PPD and depression during pregnancy, occurs in approximately 10% of pregnancies.2,3 When depression first appears in the postpartum period, most women develop symptoms in the first month after delivery (54% of cases) or in the next 2 to 4 months (40%).4
The most significant risk factor for PPD is previous depression, peripartum or otherwise.1,4-6 Other common risk factors include major life events or stressors during or after pregnancy, domestic violence, poor social support, and preterm birth or an infant admission to the neonatal intensive care unit.1,7 Women with a self-perceived negative birth experience are also likely to experience PPD.8 PPD can be associated with significant morbidity and mortality, with suicide a more common cause of maternal mortality than either hemorrhage or hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.9
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to improving patient outcomes. Women with PPD initiate breastfeeding at lower rates and continue for shorter durations.10 PPD also affects maternal–infant bonding; may adversely affect an infant’s social, cognitive, and language development; and may lead to attachment disorders of infancy.11,12 In severe cases, it can lead to failure to thrive or infanticide.11
When to screen. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends clinicians screen for depression in pregnant and postpartum women (Grade Ba) and for women at increased risk, provide or refer to counseling interventions (Grade Ba).13,14 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends screening at least once in the postpartum period.15 Repeat screening at follow-up in the later postpartum period increases the likelihood of diagnosis.16 Screening for PPD as part of well-child care improves maternal outcomes, and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends screening at the 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month visits.11,17 These screens are separately billable. Family physicians are uniquely suited to screening at both well-child and postpartum visits, as many women share a medical home with their child, and those who do not are equally willing to receive medical advice from their child’s physician.18
Continue to: Is it "the blues" or something else? Diagnosing PPD
Is it “the blues” or something else? Diagnosing PPD
Many new mothers experience postpartum blues, which manifest as tearfulness, insomnia, irritability, and anxiety. The postpartum blues, however, don’t meet the criteria for major depressive disorder and typically resolve within 14 days of delivery.19-21 On the other end of the spectrum is postpartum psychosis, which is severe and rare, and can also affect new mothers.
Screening for PPD. The most commonly used screening tool for PPD is the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS 10), a free 10-item instrument scored out of 30 possible points, with any score ≥ 13 suggesting PPD.22 The EPDS 10 has a sensitivity of 74% and specificity of 97% for the diagnosis of PPD.23 Other screening options include the Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI-II) and the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9). The 21-item BDI-II takes longer to perform and is less sensitive (57%) than the EPDS.1 The PHQ-9, which asks about some symptoms common to the postpartum period (including sleep changes), is less specific than the EPDS (sensitivity, 75%; specificity, 90%).1 The EPDS also includes screening questions about anxiety.1
A positive depression screen, or any positive response to a question on suicidal ideation, should be followed up for confirmation using the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th Edition (DSM-5) criteria for major depressive disorder with peripartum onset.24 Women with PPD should also be asked about current or prior symptoms of bipolar disorder or mania.25 Up to 67% of women with bipolar disorder may relapse postpartum, and they also have an elevated risk of postpartum psychosis.26 The Mood Disorder Questionnaire is a useful tool if a concern for bipolar depression arises.27
Refer any woman in whom bipolar depression is a concern to a clinician experienced with its management. The presence of auditory or visual hallucinations should also be assessed as indicators of postpartum psychosis. Active suicidal or homicidal ideation and postpartum psychosis all require emergent psychiatric care.21,22 Intimate partner violence may also exist or escalate in the postpartum period and may exacerbate PPD. Both ACOG and the USPSTF recommend screening postpartum women for intimate partner violence.28,29
Also consider possible medical causes of PPD symptoms. Hypothyroidism in the postpartum period may manifest with some similar symptoms to PPD and is commonly underdiagnosed.22,30 Women with postpartum anemia and low ferritin stores also have a higher likelihood of PPD (odds ratio, 1.7-4.64), and postpartum iron supplementation may reduce this risk (number needed to treat = 4 in at least 1 randomized controlled trial).31 When anemia is present, ensure that it is properly treated.
Continue to: Steps you can take to manage pPD
Steps you can take to manage pPD
Refer any woman who has PPD to a qualified therapist whenever possible. Generally, the psychological recommendations for treatment of PPD are very similar to recommendations for general treatment of depression. Psychotherapy on its own is considered a first-line treatment for mild-to-moderate PPD, and medication plus psychotherapy is considered first-line treatment for severe PPD.32 (Worth noting: It may also be useful to offer counseling to a patient who appears distressed, even if she does not fully meet all DSM-5 criteria.)
Of the psychotherapy options, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is supported by the most evidence. There is also evidence for the use of interpersonal therapy (IPT), especially in higher socioeconomic status populations.33 Key therapeutic targets in IPT are increasing behavioral engagement (eg, reaching out to friends), decreasing negative self-talk (eg, “I am a bad mother”), and negotiating roles and support (eg, both mom’s and family members’ expectations of new motherhood). There is mixed evidence for recommending exercise as a treatment for PPD.32,34 However, as exercise is a low-risk intervention, you may choose to make that recommendation to patients. Additionally, including partners/support people in treatment/visits for PPD has been shown to increase positive outcomes.35
When medication is considered, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are most commonly used. Research indicates that SSRIs are significantly more effective than placebo for treatment of women with PPD.36 Sertraline, in particular, has shown to be both effective in treating PPD and safe in lactation.37,38 Dosing and duration of therapy are equivalent to treatment of major depression outside the perinatal period. Consult a trusted source on medications in lactation before prescribing any antidepressant to a breastfeeding mother. One resource is the National Institutes of Health drugs and lactation database (LactMed; www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501922/), which provides detailed information on the levels of medications in breastmilk and their potential effects on an infant.
Women with severe, refractory PPD may require hospitalization. Additional treatment options for women with severe, refractory PPD include electroconvulsive therapy or the new medication brexanolone, which is administered as a 60-hour continuous infusion.39,40
THE CASE
Further conversation with Ms. T revealed that she met the criteria for PPD (major depressive disorder with peripartum onset). She denied suicidal or homicidal ideation and was not experiencing any symptoms of psychosis. A complete blood count was drawn and showed no anemia, and her thyroid-stimulating hormone level was within normal limits. She had a good support network at home, with both her mom and sister taking shifts to help her get some extra rest and allow her to attend medical appointments. She said there was no domestic violence.
Ms. T was introduced to the clinic’s embedded counselor, who scheduled a follow-up appointment within the week to start CBT. After a discussion of risks and benefits, Ms. T also started a low dose of sertraline once daily. At follow-up postpartum visits, she reported significant improvement in her mood. She and her physician decided to taper her SSRI medication at 3 months postpartum. Screens for depression at her infant’s 4- and 6-month well-child visits in the office were reassuringly negative.
a There is high certainty that the net benefit is moderate, or there is moderate certainty that the net benefit is moderate to substantial.
CORRESPONDENCE
Katherine Buck, PhD, JPS Family Health Center, 1500 South Main Street, 4th Floor, Fort Worth, TX 76110; [email protected]
THE CASE
Alex T,* a 23-year-old first-time mom, presented to the family medicine office for her baby’s 2-week appointment. When asked how she was doing, she began to cry. She said, “I feel crazy” and indicated that she was feeling down and overwhelmed, and was struggling to bond with the baby. She filled out an Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale, a standard postpartum depression (PPD) screen; her score, 15 out of 30, was suggestive of depression. Ms. T had been coming to the practice for the past 3 years and had no significant physical or mental health history. She and the baby did not live with the baby’s father, and his degree of presence in their lives varied.
●
* The patient’s name has been changed to protect her identity.
PPD, traditionally defined as depression in the postpartum period for as long as a year after childbirth, is a common, underdiagnosed outcome of both normal and complicated pregnancies.1 Peripartum depression, which includes PPD and depression during pregnancy, occurs in approximately 10% of pregnancies.2,3 When depression first appears in the postpartum period, most women develop symptoms in the first month after delivery (54% of cases) or in the next 2 to 4 months (40%).4
The most significant risk factor for PPD is previous depression, peripartum or otherwise.1,4-6 Other common risk factors include major life events or stressors during or after pregnancy, domestic violence, poor social support, and preterm birth or an infant admission to the neonatal intensive care unit.1,7 Women with a self-perceived negative birth experience are also likely to experience PPD.8 PPD can be associated with significant morbidity and mortality, with suicide a more common cause of maternal mortality than either hemorrhage or hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.9
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to improving patient outcomes. Women with PPD initiate breastfeeding at lower rates and continue for shorter durations.10 PPD also affects maternal–infant bonding; may adversely affect an infant’s social, cognitive, and language development; and may lead to attachment disorders of infancy.11,12 In severe cases, it can lead to failure to thrive or infanticide.11
When to screen. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends clinicians screen for depression in pregnant and postpartum women (Grade Ba) and for women at increased risk, provide or refer to counseling interventions (Grade Ba).13,14 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends screening at least once in the postpartum period.15 Repeat screening at follow-up in the later postpartum period increases the likelihood of diagnosis.16 Screening for PPD as part of well-child care improves maternal outcomes, and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends screening at the 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month visits.11,17 These screens are separately billable. Family physicians are uniquely suited to screening at both well-child and postpartum visits, as many women share a medical home with their child, and those who do not are equally willing to receive medical advice from their child’s physician.18
Continue to: Is it "the blues" or something else? Diagnosing PPD
Is it “the blues” or something else? Diagnosing PPD
Many new mothers experience postpartum blues, which manifest as tearfulness, insomnia, irritability, and anxiety. The postpartum blues, however, don’t meet the criteria for major depressive disorder and typically resolve within 14 days of delivery.19-21 On the other end of the spectrum is postpartum psychosis, which is severe and rare, and can also affect new mothers.
Screening for PPD. The most commonly used screening tool for PPD is the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS 10), a free 10-item instrument scored out of 30 possible points, with any score ≥ 13 suggesting PPD.22 The EPDS 10 has a sensitivity of 74% and specificity of 97% for the diagnosis of PPD.23 Other screening options include the Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI-II) and the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9). The 21-item BDI-II takes longer to perform and is less sensitive (57%) than the EPDS.1 The PHQ-9, which asks about some symptoms common to the postpartum period (including sleep changes), is less specific than the EPDS (sensitivity, 75%; specificity, 90%).1 The EPDS also includes screening questions about anxiety.1
A positive depression screen, or any positive response to a question on suicidal ideation, should be followed up for confirmation using the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th Edition (DSM-5) criteria for major depressive disorder with peripartum onset.24 Women with PPD should also be asked about current or prior symptoms of bipolar disorder or mania.25 Up to 67% of women with bipolar disorder may relapse postpartum, and they also have an elevated risk of postpartum psychosis.26 The Mood Disorder Questionnaire is a useful tool if a concern for bipolar depression arises.27
Refer any woman in whom bipolar depression is a concern to a clinician experienced with its management. The presence of auditory or visual hallucinations should also be assessed as indicators of postpartum psychosis. Active suicidal or homicidal ideation and postpartum psychosis all require emergent psychiatric care.21,22 Intimate partner violence may also exist or escalate in the postpartum period and may exacerbate PPD. Both ACOG and the USPSTF recommend screening postpartum women for intimate partner violence.28,29
Also consider possible medical causes of PPD symptoms. Hypothyroidism in the postpartum period may manifest with some similar symptoms to PPD and is commonly underdiagnosed.22,30 Women with postpartum anemia and low ferritin stores also have a higher likelihood of PPD (odds ratio, 1.7-4.64), and postpartum iron supplementation may reduce this risk (number needed to treat = 4 in at least 1 randomized controlled trial).31 When anemia is present, ensure that it is properly treated.
Continue to: Steps you can take to manage pPD
Steps you can take to manage pPD
Refer any woman who has PPD to a qualified therapist whenever possible. Generally, the psychological recommendations for treatment of PPD are very similar to recommendations for general treatment of depression. Psychotherapy on its own is considered a first-line treatment for mild-to-moderate PPD, and medication plus psychotherapy is considered first-line treatment for severe PPD.32 (Worth noting: It may also be useful to offer counseling to a patient who appears distressed, even if she does not fully meet all DSM-5 criteria.)
Of the psychotherapy options, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is supported by the most evidence. There is also evidence for the use of interpersonal therapy (IPT), especially in higher socioeconomic status populations.33 Key therapeutic targets in IPT are increasing behavioral engagement (eg, reaching out to friends), decreasing negative self-talk (eg, “I am a bad mother”), and negotiating roles and support (eg, both mom’s and family members’ expectations of new motherhood). There is mixed evidence for recommending exercise as a treatment for PPD.32,34 However, as exercise is a low-risk intervention, you may choose to make that recommendation to patients. Additionally, including partners/support people in treatment/visits for PPD has been shown to increase positive outcomes.35
When medication is considered, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are most commonly used. Research indicates that SSRIs are significantly more effective than placebo for treatment of women with PPD.36 Sertraline, in particular, has shown to be both effective in treating PPD and safe in lactation.37,38 Dosing and duration of therapy are equivalent to treatment of major depression outside the perinatal period. Consult a trusted source on medications in lactation before prescribing any antidepressant to a breastfeeding mother. One resource is the National Institutes of Health drugs and lactation database (LactMed; www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501922/), which provides detailed information on the levels of medications in breastmilk and their potential effects on an infant.
Women with severe, refractory PPD may require hospitalization. Additional treatment options for women with severe, refractory PPD include electroconvulsive therapy or the new medication brexanolone, which is administered as a 60-hour continuous infusion.39,40
THE CASE
Further conversation with Ms. T revealed that she met the criteria for PPD (major depressive disorder with peripartum onset). She denied suicidal or homicidal ideation and was not experiencing any symptoms of psychosis. A complete blood count was drawn and showed no anemia, and her thyroid-stimulating hormone level was within normal limits. She had a good support network at home, with both her mom and sister taking shifts to help her get some extra rest and allow her to attend medical appointments. She said there was no domestic violence.
Ms. T was introduced to the clinic’s embedded counselor, who scheduled a follow-up appointment within the week to start CBT. After a discussion of risks and benefits, Ms. T also started a low dose of sertraline once daily. At follow-up postpartum visits, she reported significant improvement in her mood. She and her physician decided to taper her SSRI medication at 3 months postpartum. Screens for depression at her infant’s 4- and 6-month well-child visits in the office were reassuringly negative.
a There is high certainty that the net benefit is moderate, or there is moderate certainty that the net benefit is moderate to substantial.
CORRESPONDENCE
Katherine Buck, PhD, JPS Family Health Center, 1500 South Main Street, 4th Floor, Fort Worth, TX 76110; [email protected]
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 757: Screening for perinatal depression. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:e208-e212. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002927
2. Banti S, Mauri M, Oppo A, et al. From the third month of pregnancy to 1 year postpartum. Prevalence, incidence, recurrence, and new onset of depression. Results from the Perinatal Depression–Research & Screening Unit study. Compr Psychiatry. 2011;52:343-351. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2010.08.003
3. Dietz PM, Williams SB, Callaghan WM, et al. Clinically identified maternal depression before, during, and after pregnancies ending in live births. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164):1515-1520. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06111893
4. Altemus M, Neeb CC, Davis A, et al. Phenotypic differences between pregnancy-onset and postpartum-onset major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73:e1485-e1491. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m07693
5. Wilson LM, Reid AJ, Midmer DK, et al. Antenatal psychosocial risk factors associated with adverse postpartum family outcomes. CMAJ. 1996;154:785-799.
6. Robertson E, Grace S, Wallington T, et al. Antenatal risk factors for postpartum depression: a synthesis of recent literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2004;26:289-295. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2004.02.006
7. Beck CT. Predictors of postpartum depression: an update. Nurs Res. 2001;50:275-285. doi: 10.1097/00006199-200109000-00004
8. Bell AF, E Andersson. The birth experience and women’s postnatal depression: a systematic review. Midwifery. 2016;39:112-123. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2016.04.014
9. Palladino CL, Singh V, Campbell J, et al. Homicide and suicide during the perinatal period: findings from the National Violent Death Reporting System. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:1056-1063. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823294da
10. Ko JY, Rockhill KM, Tong VT, et al. Trends in postpartum depressive symptoms — 27 States, 2004, 2008, and 2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:153-158. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6606a1
11. Rafferty J, Mattson G, Earls MF, et al. Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal depression into pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2019;143:e20183260. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3260
12. Lovejoy MC, Graczyk PA, O’Hare E, et al. Maternal depression and parenting behavior: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2000;20:561-592. doi: 10.1016/s0272-7358(98)00100-7
13. Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Interventions to prevent perinatal depression: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019;321:580-587. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0007
14. Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for depression in adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2016;315:380-387. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18392
15. ACOG. Screening for perinatal depression. 2018. Accessed October 5, 2022. www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2018/11/screening-for-perinatal-depression
16. Yawn BP, Bertram S, Kurland M, et al. Repeated depression screening during the first postpartum year. Ann Fam Med. 2015;13:228-234. doi: 10.1370/afm.1777
17. van der Zee-van den Berg AI, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Groothuis-Oudshoorn CGM, et al. Post-up study: postpartum depression screening in well-child care and maternal outcomes. Pediatrics. 2017;140:e20170110. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-0110
18. Rosener SE, Barr WB, Frayne DJ, et al. Interconception care for mothers during well-child visits with family physicians: an IMPLICIT Network study. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14:350-355. doi: 10.1370/afm.1933
19. Nonacs R, Cohen LS. Postpartum mood disorders: diagnosis and treatment guidelines. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59(suppl 2):34-40.
20. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 736: Optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002633
21. Langan R, Goodbred AJ. Identification and management of peripartum depression. Am Fam Physician. 2016;93:852-858.
22. Sharma V, Sharma P. Postpartum depression: diagnostic and treatment issues. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2012;34:436-442. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)35240-9
23. Owara AH, Carabin H, Reese J, et al. Summary diagnostic validity of commonly used maternal major depression disorder case finding instruments in the United States: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;205:335-343. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.08.014
24. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Washington D.C.: 2013:160.
25. Mandelli L, Souery D, Bartova L, et al. Bipolar II disorder as a risk factor for postpartum depression. J Affect Disord. 2016;204:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.025
26. ACOG Practice Bulletin: Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists number 92, April 2008 (replaces practice bulletin number 87, November 2007). Use of psychiatric medications during pregnancy and lactation. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:1001-1020. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31816fd910
27. Hirschfeld RM, Williams JB, Spitzer RL, et al. Development and validation of a screening instrument for bipolar spectrum disorder: the Mood Disorder Questionnaire. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1873-1875. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.157.11.1873
28. Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence, elder abuse, and abuse of vulnerable adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Final Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2018;320:1678-1687. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14741
29. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 518: Intimate partner violence. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119:412-417. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e318249ff74
30. Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 223. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e261-e274. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003893
31. Wassef A, Nguyen QD, St-André M. Anaemia and depletion of iron stores as risk factors for postpartum depression: a literature review. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 2019;40:19-28. doi: 10.1080/0167482X.2018.1427725
32. Hirst KP, Moutier CY. Postpartum major depression. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:926-933.
33. Nillni YI, Mehralizade A, Mayer L, et al. Treatment of depression, anxiety, and trauma-related disorders during the perinatal period: a systematic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018;66:136-148. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2018.06.004
34. Daley AJ, Macarthur C, Winter H. The role of exercise in treating postpartum depression: a review of the literature. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2007;52:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jmwh.2006.08.017
35. Misri S, Kostaras X, Fox D, et al. The impact of partner support in the treatment of postpartum depression. Can J Psychiatry. 2000;45:554-558. doi: 10.1177/070674370004500607
36. Molyneaux E, Howard LM, McGeown HR, et al. Antidepressant treatment for postnatal depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;CD002018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002018.pub2
37. Pinheiro E, Bogen DL, Hoxha D, et al. Sertraline and breastfeeding: review and meta-analysis. Arch Women Ment Health. 2015;18:139-146. doi: 10.1007/s00737-015-0499-y
38. Hantsoo L, Ward-O’Brien D, Czarkowski KA, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of sertraline for postpartum depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014;231:939-948. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3316-1
39. Rundgren S, Brus O, Båve U, et al. Improvement of postpartum depression and psychosis after electroconvulsive therapy: a population-based study with a matched comparison group. J Affect Disord. 2018;235:258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.04.043
40. Meltzer-Brody S, Colquhoun H, Riesenberg R, et al. Brexanolone injection in post-partum depression: two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2018;392:1058-1070. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31551-4
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 757: Screening for perinatal depression. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:e208-e212. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002927
2. Banti S, Mauri M, Oppo A, et al. From the third month of pregnancy to 1 year postpartum. Prevalence, incidence, recurrence, and new onset of depression. Results from the Perinatal Depression–Research & Screening Unit study. Compr Psychiatry. 2011;52:343-351. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2010.08.003
3. Dietz PM, Williams SB, Callaghan WM, et al. Clinically identified maternal depression before, during, and after pregnancies ending in live births. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164):1515-1520. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.06111893
4. Altemus M, Neeb CC, Davis A, et al. Phenotypic differences between pregnancy-onset and postpartum-onset major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73:e1485-e1491. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m07693
5. Wilson LM, Reid AJ, Midmer DK, et al. Antenatal psychosocial risk factors associated with adverse postpartum family outcomes. CMAJ. 1996;154:785-799.
6. Robertson E, Grace S, Wallington T, et al. Antenatal risk factors for postpartum depression: a synthesis of recent literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2004;26:289-295. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2004.02.006
7. Beck CT. Predictors of postpartum depression: an update. Nurs Res. 2001;50:275-285. doi: 10.1097/00006199-200109000-00004
8. Bell AF, E Andersson. The birth experience and women’s postnatal depression: a systematic review. Midwifery. 2016;39:112-123. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2016.04.014
9. Palladino CL, Singh V, Campbell J, et al. Homicide and suicide during the perinatal period: findings from the National Violent Death Reporting System. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:1056-1063. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823294da
10. Ko JY, Rockhill KM, Tong VT, et al. Trends in postpartum depressive symptoms — 27 States, 2004, 2008, and 2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66:153-158. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6606a1
11. Rafferty J, Mattson G, Earls MF, et al. Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal depression into pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2019;143:e20183260. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3260
12. Lovejoy MC, Graczyk PA, O’Hare E, et al. Maternal depression and parenting behavior: a meta-analytic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2000;20:561-592. doi: 10.1016/s0272-7358(98)00100-7
13. Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Interventions to prevent perinatal depression: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019;321:580-587. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0007
14. Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for depression in adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2016;315:380-387. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18392
15. ACOG. Screening for perinatal depression. 2018. Accessed October 5, 2022. www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2018/11/screening-for-perinatal-depression
16. Yawn BP, Bertram S, Kurland M, et al. Repeated depression screening during the first postpartum year. Ann Fam Med. 2015;13:228-234. doi: 10.1370/afm.1777
17. van der Zee-van den Berg AI, Boere-Boonekamp MM, Groothuis-Oudshoorn CGM, et al. Post-up study: postpartum depression screening in well-child care and maternal outcomes. Pediatrics. 2017;140:e20170110. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-0110
18. Rosener SE, Barr WB, Frayne DJ, et al. Interconception care for mothers during well-child visits with family physicians: an IMPLICIT Network study. Ann Fam Med. 2016;14:350-355. doi: 10.1370/afm.1933
19. Nonacs R, Cohen LS. Postpartum mood disorders: diagnosis and treatment guidelines. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59(suppl 2):34-40.
20. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 736: Optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002633
21. Langan R, Goodbred AJ. Identification and management of peripartum depression. Am Fam Physician. 2016;93:852-858.
22. Sharma V, Sharma P. Postpartum depression: diagnostic and treatment issues. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2012;34:436-442. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(16)35240-9
23. Owara AH, Carabin H, Reese J, et al. Summary diagnostic validity of commonly used maternal major depression disorder case finding instruments in the United States: a meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;205:335-343. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.08.014
24. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Washington D.C.: 2013:160.
25. Mandelli L, Souery D, Bartova L, et al. Bipolar II disorder as a risk factor for postpartum depression. J Affect Disord. 2016;204:54-58. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.025
26. ACOG Practice Bulletin: Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists number 92, April 2008 (replaces practice bulletin number 87, November 2007). Use of psychiatric medications during pregnancy and lactation. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:1001-1020. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31816fd910
27. Hirschfeld RM, Williams JB, Spitzer RL, et al. Development and validation of a screening instrument for bipolar spectrum disorder: the Mood Disorder Questionnaire. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1873-1875. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.157.11.1873
28. Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence, elder abuse, and abuse of vulnerable adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Final Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2018;320:1678-1687. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14741
29. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 518: Intimate partner violence. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119:412-417. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e318249ff74
30. Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 223. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:e261-e274. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003893
31. Wassef A, Nguyen QD, St-André M. Anaemia and depletion of iron stores as risk factors for postpartum depression: a literature review. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol. 2019;40:19-28. doi: 10.1080/0167482X.2018.1427725
32. Hirst KP, Moutier CY. Postpartum major depression. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:926-933.
33. Nillni YI, Mehralizade A, Mayer L, et al. Treatment of depression, anxiety, and trauma-related disorders during the perinatal period: a systematic review. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018;66:136-148. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2018.06.004
34. Daley AJ, Macarthur C, Winter H. The role of exercise in treating postpartum depression: a review of the literature. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2007;52:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jmwh.2006.08.017
35. Misri S, Kostaras X, Fox D, et al. The impact of partner support in the treatment of postpartum depression. Can J Psychiatry. 2000;45:554-558. doi: 10.1177/070674370004500607
36. Molyneaux E, Howard LM, McGeown HR, et al. Antidepressant treatment for postnatal depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;CD002018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002018.pub2
37. Pinheiro E, Bogen DL, Hoxha D, et al. Sertraline and breastfeeding: review and meta-analysis. Arch Women Ment Health. 2015;18:139-146. doi: 10.1007/s00737-015-0499-y
38. Hantsoo L, Ward-O’Brien D, Czarkowski KA, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of sertraline for postpartum depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014;231:939-948. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3316-1
39. Rundgren S, Brus O, Båve U, et al. Improvement of postpartum depression and psychosis after electroconvulsive therapy: a population-based study with a matched comparison group. J Affect Disord. 2018;235:258-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.04.043
40. Meltzer-Brody S, Colquhoun H, Riesenberg R, et al. Brexanolone injection in post-partum depression: two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2018;392:1058-1070. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31551-4
Her child was stillborn at 39 weeks. She blames a system that doesn’t always listen to mothers
The day before doctors had scheduled Amanda Duffy to give birth, the baby jolted her awake with a kick.
A few hours later, on that bright Sunday in November 2014, she leaned back on a park bench to watch her 19-month-old son Rogen enjoy his final day of being an only child. In that moment of calm, she realized that the kick that morning was the last time she had felt the baby move.
She told herself not to worry. She had heard that babies can slow down toward the end of a pregnancy and remembered reading that sugary snacks and cold fluids can stimulate a baby’s movement. When she got back to the family’s home in suburban Minneapolis, she drank a large glass of ice water and grabbed a few Tootsie Rolls off the kitchen counter.
But something about seeing her husband, Chris, lace up his shoes to leave for a run prompted her to blurt out, “I haven’t felt the baby kick.”
Chris called Amanda’s doctor, and they headed to the hospital to be checked. Once there, a nurse maneuvered a fetal monitor around Amanda’s belly. When she had trouble locating a heartbeat, she remarked that the baby must be tucked in tight. The doctor walked into the room, turned the screen away from Amanda and Chris and began searching. She was sorry, Amanda remembers her telling them, but she could not find a heartbeat.
Amanda let out a guttural scream. She said the doctor quickly performed an internal exam, which detected faint heart activity, then rushed Amanda into an emergency cesarean section.
She woke up to the sound of doctors talking to Chris. She listened but couldn’t bring herself to face the news. Her doctor told her she needed to open her eyes.
Amanda, then 31, couldn’t fathom that her daughter had died. She said her doctors had never discussed stillbirth with her. It was not mentioned in any of the pregnancy materials she had read. She didn’t even know that stillbirth was a possibility.
But every year more than 20,000 pregnancies in the United States end in stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more. That number has exceeded infant mortality every year for the last 10 years. It’s 15 times the number of babies who, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, died of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, in 2020.
The deaths are not inevitable. One study found that nearly one in four U.S. stillbirths may be preventable. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, that research shows, the figure jumps to nearly half. Thousands more babies could potentially be delivered safely every year.
But federal agencies have not prioritized critical stillbirth-focused studies that could lead to fewer deaths. Nearly two decades ago, both the CDC and the National Institutes of Health launched key stillbirth tracking and research studies, but the agencies ended those projects within about a decade. The CDC never analyzed some of the data that was collected.
Unlike with SIDS, a leading cause of infant death, federal officials have failed to launch a national campaign to reduce the risk of stillbirth or adequately raise awareness about it. Placental exams and autopsies, which can sometimes explain why stillbirths happened, are underutilized, in part because parents are not counseled on their benefits.
Federal agencies, state health departments, hospitals and doctors have also done a poor job of educating expectant parents about stillbirth or diligently counseling on fetal movement, despite research showing that patients who have had a stillbirth are more likely to have experienced abnormal fetal movements, including decreased activity. Neither the CDC nor the NIH have consistently promoted guidance telling those who are pregnant to be aware of their babies’ movement in the womb as a way to possibly reduce their risk of stillbirth.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the nation’s leading obstetrics organization, has been slow to update its own guidance to doctors on managing a stillbirth. In 2009, ACOG issued a set of guidelines that included a single paragraph regarding fetal movement. Those guidelines weren’t significantly updated for another 11 years.
Perhaps it’s no surprise that federal goals for reducing stillbirths keep moving in the wrong direction. In 2005, the U.S. stillbirth rate was 6.2 per 1,000 live births. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, in an effort to eliminate health disparities and establish a target that was “better than the best racial or ethnic group rate,” set a goal of reducing it to 4.1 for 2010. When that wasn’t met, federal officials changed their approach and set what they called more “science-based” and “realistic” goals, raising the 2020 target to 5.6. The U.S. still fell short. The 2030 goal of 5.7 was so attainable that it was met before the decade started. The 2020 rate, the most current according to the CDC, is 5.74.
By comparison, other wealthy countries have implemented national action plans to prevent stillbirth through awareness, research and care. Among other approaches, those countries have focused on increasing education around stillbirth and the importance of a baby’s movements, reducing rates of smoking and identifying fetuses that grow too slowly in the womb.
The efforts have paid off. The Netherlands, for instance, has reduced its rate of stillbirths at 28 weeks or later by more than half, from 5.2 in 2000 to 2.3 in 2019, according to a study published last year in The Lancet.
Dr. Bob Silver, chair of the obstetrics/gynecology department at University of Utah Health and a leading stillbirth expert, coauthored the study that estimated nearly one in four stillbirths are potentially preventable, a figure he referred to as conservative. He called on federal agencies to declare stillbirth reduction a priority the same way they have done for premature birth and maternal mortality.
“I’d like to see us say we really want to reduce the rate of stillbirth and raise awareness and try to do all of the reasonable things that may contribute to reducing stillbirths that other countries have done,” Silver said.
The lack of comprehensive attention and action has contributed to a stillbirth crisis, shrouded in an acceptance that some babies just die. Compounding the tragedy is a stigma and guilt so crushing that the first words some mothers utter when their lifeless babies are placed in their arms are “I’m sorry.”
In the hospital room, Amanda Duffy finally opened her eyes. She named her daughter Reese Christine, the name she had picked out for her before they found out she had died. She was 8 pounds, 3 ounces and 20 1/2 inches long and was born with her umbilical cord wrapped tightly around her neck twice. The baby was still warm when the nurse placed her in Amanda’s arms. Amanda was struck by how lovely her daughter was. Rosy skin. Chris’ red hair. Rogen’s chubby cheeks.
As Amanda held Reese, Chris hunched over the toilet, vomiting. Later that night, as he lay next to Amanda on the hospital bed, he held his daughter. He hadn’t initially wanted to see her. He worried she would be disfigured or, worse, that she would be beautiful and he would fall apart when he couldn’t take her home.
The nurses taught Amanda and Chris how to grieve and love simultaneously. One nurse told Amanda how cute Reese was and asked if she could hold her. Another placed ice packs in Reese’s swaddle to preserve her body so Amanda could keep holding her. Amanda asked the nurses to tuck cotton balls soaked in an orange scent into Reese’s blanket so the smell would trigger the memory of her daughter. And just as if Reese had been born alive, the nurses took pictures and made prints of her hands and feet.
“I felt such a deep, abiding love for her,” Amanda said. “And I was so proud to be her mom.”
On the way home from the hospital, Amanda broke down at the sight of Reese’s empty car seat. The next few weeks passed in a sleep-filled fog punctuated by intense periods of crying. The smell of oranges wrecked her. Her breast milk coming in was agonizing, physically and emotionally. She wore sports bras stuffed with ice packs to ease the pain and dry up her milk supply. While Rogen was at day care, she sobbed in his bed.
In the months that followed, Amanda and Chris searched for answers and wondered whether their medical team had missed warning signs. Late at night, Amanda turned to Google to find information about stillbirths. She mailed her medical records to a doctor who studies stillbirths, who she said told her that Reese’s death could have been prevented. They briefly discussed legal action against her doctors, but she said a lawyer told her it would be difficult to sue.
Amanda and Chris pinpointed her last two months of pregnancy as the time things started to go wrong. She had been diagnosed with polyhydramnios, meaning there was excess amniotic fluid in the womb. Her doctor had scheduled additional weekly testing.
One of those ultrasounds revealed problems with the blood flow in the umbilical cord. Reese’s cord also appeared to be wrapped around her neck, Amanda said later, but was told that was less of a concern, since it occurs in about 20% of normal deliveries. At another appointment, Amanda’s medical records show, Reese failed the portion of a test that measures fetal breathing movements.
At 37 weeks, Amanda told one of the midwives the baby’s movements felt different, but, she said, the midwife told her that it was common for movements to feel weaker with polyhydramnios. At that point, Amanda felt her baby was safer outside than inside and, her medical records show, she asked to schedule a C-section.
Despite voicing concerns about a change in the baby’s movement and asking to deliver earlier, Amanda said she and her husband were told by her midwife she couldn’t deliver for another two weeks. The doctor “continues to advise 39wks,” her medical records show. Waiting until 39 weeks is usually based on a guideline that deliveries should not happen before then unless a medical condition specifically warrants it, because early delivery can lead to complications.
Amanda would have to wait until 39 weeks and one day because, she said, her doctors didn’t typically do elective deliveries on weekends. Amanda was disappointed but said she trusted her team of doctors and midwives.
“I’m not a pushy person,” she said. “My husband is not a pushy person. That was out of our comfort zone to be, like, ‘What are we waiting for?’ But really what we wanted them to say was ‘We should deliver you.’”
Amanda’s final appointment was a maximum 30-minute-long ultrasound that combined a number of assessments to check amniotic fluid, fetal muscle tone, breathing and body movement. After 29 minutes of inactivity, Amanda said, the baby moved a hand. In the parking lot, Amanda called her mother, crying in relief. Four more days, she told her.
Less than 24 hours before the scheduled C-section, Reese was stillborn.
Four months after her death, Amanda, then a career advisor at the University of Minnesota, and Chris, a public relations specialist, wrote a letter to the University of Minnesota Medical Center, where Amanda had given birth to her dead daughter. They said they had “no ill feelings” toward anyone, but “it pains us to know that her death could’ve been prevented if we would have been sent to labor and delivery following that ultrasound.”
They noted that though they were told that Reese had passed the final ultrasound where she took 29 minutes to move, they had since come to believe that she had failed because, according to national standards, at least three movements were required. They also blamed a strict adherence to the 39-week guideline. And they encouraged the hospital staff to read more on umbilical cord accidents and acute polyhydramnios, which they later learned carries an increased stillbirth risk.
The positive feelings they had from speaking up were replaced by dismay when the hospital responded with a three-paragraph letter, signed by seven doctors and eight nurses. They said they had reexamined each medical decision in her case and concluded they had made “the best decisions medically possible.” They expressed their sympathy and said it was “so very heartwarming that you are trying to turn your tragic loss into something that will benefit others.”
Amanda felt dismissed by the medical team all over again. She didn’t expect them to admit fault, but she said she hoped that they would at least learn from Reese’s death to do things differently in the future. She was angry, and hurt, and knew that she would need to find a new doctor.
A spokesperson for the University of Minnesota Medical School told ProPublica she could not comment on individual patient cases and did not respond to questions about general protocols. “We share the physicians’ condolences,” she wrote, adding that the doctors and the university “are dedicated to delivering high quality, accessible and inclusive health care.”
For many expectant parents, it’s hard to muster the courage to call a doctor about something they’re not even sure is a problem.
“Moms self-censor a lot. No one wants to be that mom that all the doctors are rolling their eyes at because she’s freaking out over nothing,” said Samantha Banerjee, executive director of PUSH for Empowered Pregnancy, a nonprofit based in New York state that works to prevent stillbirths. Banerjee’s daughter, Alana, was stillborn two days before her due date.
In addition to raising awareness that stillbirths can happen even in low-risk pregnancies, PUSH teaches pregnant people how to advocate for themselves. The volunteers advise them to put their requests in writing and not to spend time drinking juice or lying on their side if they are worried about their baby’s lack of movement. In the majority of cases, a call or visit to the hospital reassures them.
But, the group tells parents, if their baby is in distress, calling their doctor can save their life.
Debbie Haine Vijayvergiya is fighting another narrative: that stillbirths are a rare fluke that “just happen.” When her daughter Autumn Joy was born without a heartbeat in 2011, Haine Vijayvergiya said, her doctor told her having a stillborn baby was as rare as being struck by lightning.
She believed him, but then she looked up the odds of a lightning strike and found they are less than one in a million – and most people survive. In 2020, according to the CDC, there was one stillbirth for about every 175 births.
“I’ve spoken to more women than I can count that said, ‘I raised the red flag, and I was sent home. I was told to eat a piece of cake and have some orange juice and lay on my left side,’ only to wake up the next day and their baby is not alive,” said Haine Vijayvergiya, a New Jersey mother and maternal health advocate.
She has fought for more than a decade to pass stillbirth legislation as her daughter’s legacy. Her current undertaking is her most ambitious. The federal Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education (SHINE) for Autumn Act, named after her daughter, would authorize $9 million a year for five years in federal funding for research, better data collection and training for fetal autopsies. But it is currently sitting in the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions.
Not all stillbirths are preventable, and medical experts agree more research is needed to determine who is most at risk and which babies can potentially be saved. Complicating matters is the wide range of risk factors, including hypertension and diabetes, smoking, obesity, being pregnant with multiples, being 35 or older and having had a previous stillbirth.
ProPublica reported this summer on how the U.S. botched the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant people, who faced an increased risk for stillbirth if they were unvaccinated and contracted the virus, especially during the Delta wave.
Doctors often work to balance the risk of stillbirth with other dangers, particularly an increased chance of being admitted to neonatal intensive care units or even death of the baby if it is born too early. ACOG and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine have issued guidance to try to slow a rise in elective deliveries before 39 weeks and the potential harm that can result. The Joint Commission, a national accrediting organization, began evaluating hospitals in 2010 based on that standard.
A 2019 study found that the risks of stillbirth slightly increased after the rule went into effect, but fewer infants died after birth. Other studies have not found an effect on stillbirths.
Last year, the obstetric groups updated their guidance to allow doctors to consider an early delivery if a woman has anxiety and a history of stillbirth, writing that a previous stillbirth “may” warrant an early delivery for patients who understand and accept the risks. For those who have previously had a stillbirth, one modeling analysis found that 38 weeks is the optimal timing of delivery, considering the increased risk of another stillbirth.
“A woman who has had a previous stillbirth at 37 weeks – one could argue that it’s cruel and unusual punishment to make her go to 39 weeks with her next pregnancy, although that is the current recommendation,” said Dr. Neil Mandsager, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Iowa and a medical advisor to a stillbirth prevention nonprofit.
At or after 40 weeks, the risk of stillbirth increases, especially for women 35 or older. Their risk, research shows, is doubled from 39 weeks to 40 and is more than six times as high at 42 weeks. In 2019 and 2020, a combined 1,200 stillbirths occurred between 40 and 42 weeks, according to the most recent CDC data.
Deciding when a patient should deliver entails weighing the risks to the mother and the infant against a possible stillbirth as the pregnancy continues, said Dr. Mark Turrentine, chair of ACOG’s Clinical Consensus Committee-Obstetrics, which helped create the guidance on managing a stillbirth. He said ACOG has addressed stillbirth in other documents and extensively in its 2021 guidance on fetal surveillance and testing, which is done to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
ACOG said it routinely reviewed its guidance on management of stillbirth but was unable to make significant updates “due to the lack of new, evidence-based research.” While prevention is a great concern to ACOG, Turrentine said it’s difficult to know how many stillbirths are preventable.
He said it’s standard practice for doctors to ask about fetal movement, and ACOG updated its guidance after new research became available. Doctors also need to include patients in decision-making and tailor care to them, he said, whether that›s using aspirin in patients at high risk of preeclampsia – a serious high blood pressure condition during pregnancy – or ordering additional tests.
After Reese’s death, Amanda and Chris Duffy wanted to get pregnant again. They sought out an obstetrician-gynecologist who would educate and listen to them. They set up several consultations until they found Dr. Emily Hawes-Van Pelt, who was recommended by another family who had had a stillbirth.
Hawes-Van Pelt cried with Amanda and Chris at their first meeting.
“I told her I was scared to be involved,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “It’s such a tricky subsequent pregnancy because there’s so much worry and anxiety about the horrible, awful thing happening again.”
Amanda’s fear of delivering another dead baby led to an all-consuming anxiety, but Hawes-Van Pelt supported her when she asked for additional monitoring, testing and an early delivery.
When Hawes-Van Pelt switched practices midway through Amanda’s pregnancy, Amanda followed her. But the new hospital pushed back on the early delivery.
“We intervene early for poorly controlled diabetes,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “We intervene early for all sorts of medical issues. Anxiety and prior stillbirth are two medical issues that we can intervene earlier for.”
Hawes-Van Pelt said she learned a lot from caring for Amanda, who made her reevaluate some of her own assumptions around stillbirths.
“I had a horrible fear of scaring women unnecessarily, and then realized that I was just not preparing women or educating them because of my own fears around it,” she said. “If you can carry a human being in your body and birth that human being and take care of it, you can hear those words.”
The hospital eventually agreed to let Hawes-Van Pelt schedule Amanda for a 37-week C-section. But after Amanda was again diagnosed with polyhydramnios, she went in for a C-section even earlier. She gave birth in 2015 to a healthy boy she and Chris named Rhett. Two years later, Amanda and Hawes-Van Pelt followed the same pregnancy plan, and she delivered a girl named Maeda Reese. Amanda chose the name because, when said quickly, it sounds like “made of Reese.”
Federal agencies, national organizations and state and city officials have mobilized in recent years to address maternal mortality, when mothers die during pregnancy, at delivery or soon after childbirth. They have focused on improving data collection, passing legislation and creating awareness campaigns that encourage medical professionals and others to listen when women say something doesn›t feel right.
In 2017, ProPublica and NPR documented the U.S. maternal mortality crisis, including alarming racial disparities.
According to CDC data, Black women face nearly three times the risk of maternal mortality. They also are more than twice – and in some states close to three times – as likely to have a stillbirth than white women, meaning not only are Black mothers dying at a disproportionate rate, so are their babies.
Janet Petersen, a state senator from Iowa, said it gives her hope to see how the country has turned its attention to maternal mortality and disparities in health care. She simply cannot understand why stillbirth isn’t being met with the same urgency.
In 2020, the CDC reported 861 mothers died either while pregnant or within six weeks of giving birth. That same year, 20,854 babies were stillborn.
Stillbirth, Petersen said, is a missing piece of the puzzle. Research shows the likelihood of severe maternal complications was more than four times higher for pregnancies that ended in stillbirths, and mothers who died within six weeks of delivery were more likely to have had a stillbirth.
“We see it over and over again that stillbirth is one of the maternal health care issues that continuously gets ignored,” said Petersen, a Democrat.
Petersen was a young legislator in 2003 when her daughter Grace was born still. Devastated, she thought of her grandmother, who lost a baby to stillbirth in 1920, just a few weeks before women got the right to vote.
“I was laying in my hospital bed thinking, ‘How could this still be happening in our country?’” Petersen recalled. “And it seemed, from the medical perspective, that, well, stillbirth happens. We can’t do anything to prevent them.”
Over the next few months, Petersen heard from other mothers who had lost their babies and wanted to spark change. As an elected official, Petersen was in a position to do that. In 2004, she introduced legislation that required the Iowa Department of Public Health to create a stillbirths work group, later securing funding through the CDC to create a stillbirth registry.
But the CDC didn’t renew the funding and never analyzed the data from the registry, though a CDC spokesperson said the Iowa Department of Public Health examined the data. Officials from the department did not respond to requests for comment.
Petersen and her fellow mothers pivoted. After hearing how researchers in Norway were able to increase awareness around fetal movement, they co-founded a nonprofit aimed at doing the same in the U.S.
The group, Healthy Birth Day, created colorful “Count the Kicks” pamphlets – and later an app – teaching pregnant people how to track a baby’s movements and establish what is normal for them. Monitoring a baby’s movements is the earliest and sometimes only indication that something may be wrong, said Emily Price, chief executive officer of Healthy Birth Day. One of the organization’s main messages is for pregnant people to speak up and clinicians to listen.
“Unfortunately, there are still doctors who brush women off or send them home when they come in with a complaint of a change in their baby’s movements,” Price said. “And babies are dying because of it.”
One Indiana county, which recorded 65 stillbirths from 2017 through 2019, reported that 74% had either some chance or a good chance of prevention, according to St. Joseph County Department of Health’s Fetal Infant Mortality Review program. For mothers who experienced decreased fetal movement in the few hours or days before the stillbirth, that estimate jumped to 90%.
Although there is not a scientific consensus that kick counting can prevent stillbirths, national groups, including ACOG, recommend that medical professionals encourage their patients to be aware of fetal movement patterns. ACOG also advises medical professionals to be attentive to a mother’s concerns about reduced movement and address them “in a systematic way.”
One complaint the CDC hears too often, an agency spokesperson said, is that pregnant people and those who gave birth recently find that their concerns are dismissed or ignored. “Listening and taking the concerns of pregnant and recently pregnant people seriously,” she said, “is a simple, yet powerful action to prevent serious health complications and even death.”
The CDC, she said, is “very interested” in expanding its research on stillbirth, which is “a crucial part of the development of any awareness or prevention campaigns.” In addition to working to improve its stillbirth data quality, the agency has funded some pilot programs at the city and state level to better track stillbirths, survey people who have had a stillbirth and research risk factors and causes. The Iowa registry, she said, led the CDC to fund different research projects in Arkansas and Massachusetts, which are ongoing.
In 2009, the CDC acknowledged that fetal mortality remained a “major, but often overlooked, public health problem.” Officials wrote that much of the public health concern had been focused on infant mortality “in part due to lesser awareness of the magnitude of fetal mortality, its causes, and prevention strategies.”
But little has changed over the past 13 years. Echoing its earlier message, the CDC this year declared that “much work remains” and that “stillbirth is not often viewed as a public health issue, so increased awareness is key.”
A spokesperson for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, which is part of the NIH, said the agency has continually funded research on stillbirths, even after one of its key studies ended. The agency, she said, also supports research on conditions that increase the risk of stillbirth.
As a scientific research institute, it does not issue clinical guidelines or recommendations, she said, though it did launch the Safe to Sleep campaign in 1994, two decades after Congress put it in charge of SIDS federal research efforts. That campaign, which educates parents and caregivers on ways to reduce the risk of SIDS, highlights recommendations issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics. She said the agency will continue to collaborate with organizations that raise awareness about stillbirth and other pregnancy complications “to amplify their messages and efforts.”
“NICHD continues to support research on the prevention, causes, frequency, and risk factors of stillbirth,” the spokesperson said in an email. “Our commitment to enhancing understanding of stillbirth and improving outcomes focuses on building the scientific knowledge base.”
But getting laws on the books that could raise awareness around stillbirth – even when they don’t require additional funding – has been a struggle. Petersen and Price are pushing Congress to pass legislation that would add stillbirth research and prevention to the list of activities approved for federal maternal health dollars.
Though the bill doesn’t ask for any additional funding, it has not yet passed.
In addition, the SHINE for Autumn Act breezed through the House of Representatives in December 2021. After Haine Vijayvergiya, the New Jersey mother who has championed it, secured bipartisan support from U.S. Sens. Cory Booker, D-N.J., and Marco Rubio, R-Fla., she thought the most comprehensive stillbirth legislation in U.S. history would finally become law.
Neither bill has sparked controversy.
But months after press releases announced the SHINE legislation and referred to the U.S. stillbirth rate as “unacceptable,” lawmakers and the families they represent are running out of time as this session of Congress prepares to adjourn.
“From the day that the bill was introduced into the Senate,” Haine Vijayvergiya said, “approximately 13,000 babies have been born still.”
Last month, on a brilliant fall day much like the one when Reese was stillborn, Amanda Duffy bent down to kiss her son Rogen’s head before they walked on stage.
She wore a soft blue T-shirt tucked into her jeans that read “Be courageous.” The message was as much for her as it was for the crowd on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., many of them like her, mothers who didn’t know stillbirth happened until it happened to them. Since Reese’s death, she has coached doctors and nurses on improving care for patients who have suffered pregnancy loss. Among her many suggestions, she tells them their first words when a concerned patient reaches out should be “I’m so glad you called.”
A few hundred people had gathered for The Big PUSH to End Preventable Stillbirth, billed as the first-ever march on the issue. As part of an art installation, Amanda wrote a note to Reese: “You’re pretty magical & for that I’m grateful. You’re a change maker and you are so very loved. Love, Mama.” Before she slipped the folded paper into a sea of more than 20,000 baby hats, Rogen added his own message: “Hope you are having a good time – Rogen.”
Reese would have turned 8 this month.
Before Amanda spoke, she took a deep breath and silenced her nerves. She walked onto the stage and called on Congress to pass the stillbirth legislation before it. She didn’t ask. She demanded.
“It’s time to empower pregnant people and their care providers with information that leads to prevention,” she insisted.
With the afternoon sun bearing down, Amanda and Rogen disappeared into the crowd of families marching toward the Capitol. Many carried signs. Some pushed empty strollers. Amanda was still wearing the orange-scented oil she had rubbed on her wrists that morning.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published
The day before doctors had scheduled Amanda Duffy to give birth, the baby jolted her awake with a kick.
A few hours later, on that bright Sunday in November 2014, she leaned back on a park bench to watch her 19-month-old son Rogen enjoy his final day of being an only child. In that moment of calm, she realized that the kick that morning was the last time she had felt the baby move.
She told herself not to worry. She had heard that babies can slow down toward the end of a pregnancy and remembered reading that sugary snacks and cold fluids can stimulate a baby’s movement. When she got back to the family’s home in suburban Minneapolis, she drank a large glass of ice water and grabbed a few Tootsie Rolls off the kitchen counter.
But something about seeing her husband, Chris, lace up his shoes to leave for a run prompted her to blurt out, “I haven’t felt the baby kick.”
Chris called Amanda’s doctor, and they headed to the hospital to be checked. Once there, a nurse maneuvered a fetal monitor around Amanda’s belly. When she had trouble locating a heartbeat, she remarked that the baby must be tucked in tight. The doctor walked into the room, turned the screen away from Amanda and Chris and began searching. She was sorry, Amanda remembers her telling them, but she could not find a heartbeat.
Amanda let out a guttural scream. She said the doctor quickly performed an internal exam, which detected faint heart activity, then rushed Amanda into an emergency cesarean section.
She woke up to the sound of doctors talking to Chris. She listened but couldn’t bring herself to face the news. Her doctor told her she needed to open her eyes.
Amanda, then 31, couldn’t fathom that her daughter had died. She said her doctors had never discussed stillbirth with her. It was not mentioned in any of the pregnancy materials she had read. She didn’t even know that stillbirth was a possibility.
But every year more than 20,000 pregnancies in the United States end in stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more. That number has exceeded infant mortality every year for the last 10 years. It’s 15 times the number of babies who, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, died of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, in 2020.
The deaths are not inevitable. One study found that nearly one in four U.S. stillbirths may be preventable. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, that research shows, the figure jumps to nearly half. Thousands more babies could potentially be delivered safely every year.
But federal agencies have not prioritized critical stillbirth-focused studies that could lead to fewer deaths. Nearly two decades ago, both the CDC and the National Institutes of Health launched key stillbirth tracking and research studies, but the agencies ended those projects within about a decade. The CDC never analyzed some of the data that was collected.
Unlike with SIDS, a leading cause of infant death, federal officials have failed to launch a national campaign to reduce the risk of stillbirth or adequately raise awareness about it. Placental exams and autopsies, which can sometimes explain why stillbirths happened, are underutilized, in part because parents are not counseled on their benefits.
Federal agencies, state health departments, hospitals and doctors have also done a poor job of educating expectant parents about stillbirth or diligently counseling on fetal movement, despite research showing that patients who have had a stillbirth are more likely to have experienced abnormal fetal movements, including decreased activity. Neither the CDC nor the NIH have consistently promoted guidance telling those who are pregnant to be aware of their babies’ movement in the womb as a way to possibly reduce their risk of stillbirth.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the nation’s leading obstetrics organization, has been slow to update its own guidance to doctors on managing a stillbirth. In 2009, ACOG issued a set of guidelines that included a single paragraph regarding fetal movement. Those guidelines weren’t significantly updated for another 11 years.
Perhaps it’s no surprise that federal goals for reducing stillbirths keep moving in the wrong direction. In 2005, the U.S. stillbirth rate was 6.2 per 1,000 live births. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, in an effort to eliminate health disparities and establish a target that was “better than the best racial or ethnic group rate,” set a goal of reducing it to 4.1 for 2010. When that wasn’t met, federal officials changed their approach and set what they called more “science-based” and “realistic” goals, raising the 2020 target to 5.6. The U.S. still fell short. The 2030 goal of 5.7 was so attainable that it was met before the decade started. The 2020 rate, the most current according to the CDC, is 5.74.
By comparison, other wealthy countries have implemented national action plans to prevent stillbirth through awareness, research and care. Among other approaches, those countries have focused on increasing education around stillbirth and the importance of a baby’s movements, reducing rates of smoking and identifying fetuses that grow too slowly in the womb.
The efforts have paid off. The Netherlands, for instance, has reduced its rate of stillbirths at 28 weeks or later by more than half, from 5.2 in 2000 to 2.3 in 2019, according to a study published last year in The Lancet.
Dr. Bob Silver, chair of the obstetrics/gynecology department at University of Utah Health and a leading stillbirth expert, coauthored the study that estimated nearly one in four stillbirths are potentially preventable, a figure he referred to as conservative. He called on federal agencies to declare stillbirth reduction a priority the same way they have done for premature birth and maternal mortality.
“I’d like to see us say we really want to reduce the rate of stillbirth and raise awareness and try to do all of the reasonable things that may contribute to reducing stillbirths that other countries have done,” Silver said.
The lack of comprehensive attention and action has contributed to a stillbirth crisis, shrouded in an acceptance that some babies just die. Compounding the tragedy is a stigma and guilt so crushing that the first words some mothers utter when their lifeless babies are placed in their arms are “I’m sorry.”
In the hospital room, Amanda Duffy finally opened her eyes. She named her daughter Reese Christine, the name she had picked out for her before they found out she had died. She was 8 pounds, 3 ounces and 20 1/2 inches long and was born with her umbilical cord wrapped tightly around her neck twice. The baby was still warm when the nurse placed her in Amanda’s arms. Amanda was struck by how lovely her daughter was. Rosy skin. Chris’ red hair. Rogen’s chubby cheeks.
As Amanda held Reese, Chris hunched over the toilet, vomiting. Later that night, as he lay next to Amanda on the hospital bed, he held his daughter. He hadn’t initially wanted to see her. He worried she would be disfigured or, worse, that she would be beautiful and he would fall apart when he couldn’t take her home.
The nurses taught Amanda and Chris how to grieve and love simultaneously. One nurse told Amanda how cute Reese was and asked if she could hold her. Another placed ice packs in Reese’s swaddle to preserve her body so Amanda could keep holding her. Amanda asked the nurses to tuck cotton balls soaked in an orange scent into Reese’s blanket so the smell would trigger the memory of her daughter. And just as if Reese had been born alive, the nurses took pictures and made prints of her hands and feet.
“I felt such a deep, abiding love for her,” Amanda said. “And I was so proud to be her mom.”
On the way home from the hospital, Amanda broke down at the sight of Reese’s empty car seat. The next few weeks passed in a sleep-filled fog punctuated by intense periods of crying. The smell of oranges wrecked her. Her breast milk coming in was agonizing, physically and emotionally. She wore sports bras stuffed with ice packs to ease the pain and dry up her milk supply. While Rogen was at day care, she sobbed in his bed.
In the months that followed, Amanda and Chris searched for answers and wondered whether their medical team had missed warning signs. Late at night, Amanda turned to Google to find information about stillbirths. She mailed her medical records to a doctor who studies stillbirths, who she said told her that Reese’s death could have been prevented. They briefly discussed legal action against her doctors, but she said a lawyer told her it would be difficult to sue.
Amanda and Chris pinpointed her last two months of pregnancy as the time things started to go wrong. She had been diagnosed with polyhydramnios, meaning there was excess amniotic fluid in the womb. Her doctor had scheduled additional weekly testing.
One of those ultrasounds revealed problems with the blood flow in the umbilical cord. Reese’s cord also appeared to be wrapped around her neck, Amanda said later, but was told that was less of a concern, since it occurs in about 20% of normal deliveries. At another appointment, Amanda’s medical records show, Reese failed the portion of a test that measures fetal breathing movements.
At 37 weeks, Amanda told one of the midwives the baby’s movements felt different, but, she said, the midwife told her that it was common for movements to feel weaker with polyhydramnios. At that point, Amanda felt her baby was safer outside than inside and, her medical records show, she asked to schedule a C-section.
Despite voicing concerns about a change in the baby’s movement and asking to deliver earlier, Amanda said she and her husband were told by her midwife she couldn’t deliver for another two weeks. The doctor “continues to advise 39wks,” her medical records show. Waiting until 39 weeks is usually based on a guideline that deliveries should not happen before then unless a medical condition specifically warrants it, because early delivery can lead to complications.
Amanda would have to wait until 39 weeks and one day because, she said, her doctors didn’t typically do elective deliveries on weekends. Amanda was disappointed but said she trusted her team of doctors and midwives.
“I’m not a pushy person,” she said. “My husband is not a pushy person. That was out of our comfort zone to be, like, ‘What are we waiting for?’ But really what we wanted them to say was ‘We should deliver you.’”
Amanda’s final appointment was a maximum 30-minute-long ultrasound that combined a number of assessments to check amniotic fluid, fetal muscle tone, breathing and body movement. After 29 minutes of inactivity, Amanda said, the baby moved a hand. In the parking lot, Amanda called her mother, crying in relief. Four more days, she told her.
Less than 24 hours before the scheduled C-section, Reese was stillborn.
Four months after her death, Amanda, then a career advisor at the University of Minnesota, and Chris, a public relations specialist, wrote a letter to the University of Minnesota Medical Center, where Amanda had given birth to her dead daughter. They said they had “no ill feelings” toward anyone, but “it pains us to know that her death could’ve been prevented if we would have been sent to labor and delivery following that ultrasound.”
They noted that though they were told that Reese had passed the final ultrasound where she took 29 minutes to move, they had since come to believe that she had failed because, according to national standards, at least three movements were required. They also blamed a strict adherence to the 39-week guideline. And they encouraged the hospital staff to read more on umbilical cord accidents and acute polyhydramnios, which they later learned carries an increased stillbirth risk.
The positive feelings they had from speaking up were replaced by dismay when the hospital responded with a three-paragraph letter, signed by seven doctors and eight nurses. They said they had reexamined each medical decision in her case and concluded they had made “the best decisions medically possible.” They expressed their sympathy and said it was “so very heartwarming that you are trying to turn your tragic loss into something that will benefit others.”
Amanda felt dismissed by the medical team all over again. She didn’t expect them to admit fault, but she said she hoped that they would at least learn from Reese’s death to do things differently in the future. She was angry, and hurt, and knew that she would need to find a new doctor.
A spokesperson for the University of Minnesota Medical School told ProPublica she could not comment on individual patient cases and did not respond to questions about general protocols. “We share the physicians’ condolences,” she wrote, adding that the doctors and the university “are dedicated to delivering high quality, accessible and inclusive health care.”
For many expectant parents, it’s hard to muster the courage to call a doctor about something they’re not even sure is a problem.
“Moms self-censor a lot. No one wants to be that mom that all the doctors are rolling their eyes at because she’s freaking out over nothing,” said Samantha Banerjee, executive director of PUSH for Empowered Pregnancy, a nonprofit based in New York state that works to prevent stillbirths. Banerjee’s daughter, Alana, was stillborn two days before her due date.
In addition to raising awareness that stillbirths can happen even in low-risk pregnancies, PUSH teaches pregnant people how to advocate for themselves. The volunteers advise them to put their requests in writing and not to spend time drinking juice or lying on their side if they are worried about their baby’s lack of movement. In the majority of cases, a call or visit to the hospital reassures them.
But, the group tells parents, if their baby is in distress, calling their doctor can save their life.
Debbie Haine Vijayvergiya is fighting another narrative: that stillbirths are a rare fluke that “just happen.” When her daughter Autumn Joy was born without a heartbeat in 2011, Haine Vijayvergiya said, her doctor told her having a stillborn baby was as rare as being struck by lightning.
She believed him, but then she looked up the odds of a lightning strike and found they are less than one in a million – and most people survive. In 2020, according to the CDC, there was one stillbirth for about every 175 births.
“I’ve spoken to more women than I can count that said, ‘I raised the red flag, and I was sent home. I was told to eat a piece of cake and have some orange juice and lay on my left side,’ only to wake up the next day and their baby is not alive,” said Haine Vijayvergiya, a New Jersey mother and maternal health advocate.
She has fought for more than a decade to pass stillbirth legislation as her daughter’s legacy. Her current undertaking is her most ambitious. The federal Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education (SHINE) for Autumn Act, named after her daughter, would authorize $9 million a year for five years in federal funding for research, better data collection and training for fetal autopsies. But it is currently sitting in the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions.
Not all stillbirths are preventable, and medical experts agree more research is needed to determine who is most at risk and which babies can potentially be saved. Complicating matters is the wide range of risk factors, including hypertension and diabetes, smoking, obesity, being pregnant with multiples, being 35 or older and having had a previous stillbirth.
ProPublica reported this summer on how the U.S. botched the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant people, who faced an increased risk for stillbirth if they were unvaccinated and contracted the virus, especially during the Delta wave.
Doctors often work to balance the risk of stillbirth with other dangers, particularly an increased chance of being admitted to neonatal intensive care units or even death of the baby if it is born too early. ACOG and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine have issued guidance to try to slow a rise in elective deliveries before 39 weeks and the potential harm that can result. The Joint Commission, a national accrediting organization, began evaluating hospitals in 2010 based on that standard.
A 2019 study found that the risks of stillbirth slightly increased after the rule went into effect, but fewer infants died after birth. Other studies have not found an effect on stillbirths.
Last year, the obstetric groups updated their guidance to allow doctors to consider an early delivery if a woman has anxiety and a history of stillbirth, writing that a previous stillbirth “may” warrant an early delivery for patients who understand and accept the risks. For those who have previously had a stillbirth, one modeling analysis found that 38 weeks is the optimal timing of delivery, considering the increased risk of another stillbirth.
“A woman who has had a previous stillbirth at 37 weeks – one could argue that it’s cruel and unusual punishment to make her go to 39 weeks with her next pregnancy, although that is the current recommendation,” said Dr. Neil Mandsager, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Iowa and a medical advisor to a stillbirth prevention nonprofit.
At or after 40 weeks, the risk of stillbirth increases, especially for women 35 or older. Their risk, research shows, is doubled from 39 weeks to 40 and is more than six times as high at 42 weeks. In 2019 and 2020, a combined 1,200 stillbirths occurred between 40 and 42 weeks, according to the most recent CDC data.
Deciding when a patient should deliver entails weighing the risks to the mother and the infant against a possible stillbirth as the pregnancy continues, said Dr. Mark Turrentine, chair of ACOG’s Clinical Consensus Committee-Obstetrics, which helped create the guidance on managing a stillbirth. He said ACOG has addressed stillbirth in other documents and extensively in its 2021 guidance on fetal surveillance and testing, which is done to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
ACOG said it routinely reviewed its guidance on management of stillbirth but was unable to make significant updates “due to the lack of new, evidence-based research.” While prevention is a great concern to ACOG, Turrentine said it’s difficult to know how many stillbirths are preventable.
He said it’s standard practice for doctors to ask about fetal movement, and ACOG updated its guidance after new research became available. Doctors also need to include patients in decision-making and tailor care to them, he said, whether that›s using aspirin in patients at high risk of preeclampsia – a serious high blood pressure condition during pregnancy – or ordering additional tests.
After Reese’s death, Amanda and Chris Duffy wanted to get pregnant again. They sought out an obstetrician-gynecologist who would educate and listen to them. They set up several consultations until they found Dr. Emily Hawes-Van Pelt, who was recommended by another family who had had a stillbirth.
Hawes-Van Pelt cried with Amanda and Chris at their first meeting.
“I told her I was scared to be involved,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “It’s such a tricky subsequent pregnancy because there’s so much worry and anxiety about the horrible, awful thing happening again.”
Amanda’s fear of delivering another dead baby led to an all-consuming anxiety, but Hawes-Van Pelt supported her when she asked for additional monitoring, testing and an early delivery.
When Hawes-Van Pelt switched practices midway through Amanda’s pregnancy, Amanda followed her. But the new hospital pushed back on the early delivery.
“We intervene early for poorly controlled diabetes,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “We intervene early for all sorts of medical issues. Anxiety and prior stillbirth are two medical issues that we can intervene earlier for.”
Hawes-Van Pelt said she learned a lot from caring for Amanda, who made her reevaluate some of her own assumptions around stillbirths.
“I had a horrible fear of scaring women unnecessarily, and then realized that I was just not preparing women or educating them because of my own fears around it,” she said. “If you can carry a human being in your body and birth that human being and take care of it, you can hear those words.”
The hospital eventually agreed to let Hawes-Van Pelt schedule Amanda for a 37-week C-section. But after Amanda was again diagnosed with polyhydramnios, she went in for a C-section even earlier. She gave birth in 2015 to a healthy boy she and Chris named Rhett. Two years later, Amanda and Hawes-Van Pelt followed the same pregnancy plan, and she delivered a girl named Maeda Reese. Amanda chose the name because, when said quickly, it sounds like “made of Reese.”
Federal agencies, national organizations and state and city officials have mobilized in recent years to address maternal mortality, when mothers die during pregnancy, at delivery or soon after childbirth. They have focused on improving data collection, passing legislation and creating awareness campaigns that encourage medical professionals and others to listen when women say something doesn›t feel right.
In 2017, ProPublica and NPR documented the U.S. maternal mortality crisis, including alarming racial disparities.
According to CDC data, Black women face nearly three times the risk of maternal mortality. They also are more than twice – and in some states close to three times – as likely to have a stillbirth than white women, meaning not only are Black mothers dying at a disproportionate rate, so are their babies.
Janet Petersen, a state senator from Iowa, said it gives her hope to see how the country has turned its attention to maternal mortality and disparities in health care. She simply cannot understand why stillbirth isn’t being met with the same urgency.
In 2020, the CDC reported 861 mothers died either while pregnant or within six weeks of giving birth. That same year, 20,854 babies were stillborn.
Stillbirth, Petersen said, is a missing piece of the puzzle. Research shows the likelihood of severe maternal complications was more than four times higher for pregnancies that ended in stillbirths, and mothers who died within six weeks of delivery were more likely to have had a stillbirth.
“We see it over and over again that stillbirth is one of the maternal health care issues that continuously gets ignored,” said Petersen, a Democrat.
Petersen was a young legislator in 2003 when her daughter Grace was born still. Devastated, she thought of her grandmother, who lost a baby to stillbirth in 1920, just a few weeks before women got the right to vote.
“I was laying in my hospital bed thinking, ‘How could this still be happening in our country?’” Petersen recalled. “And it seemed, from the medical perspective, that, well, stillbirth happens. We can’t do anything to prevent them.”
Over the next few months, Petersen heard from other mothers who had lost their babies and wanted to spark change. As an elected official, Petersen was in a position to do that. In 2004, she introduced legislation that required the Iowa Department of Public Health to create a stillbirths work group, later securing funding through the CDC to create a stillbirth registry.
But the CDC didn’t renew the funding and never analyzed the data from the registry, though a CDC spokesperson said the Iowa Department of Public Health examined the data. Officials from the department did not respond to requests for comment.
Petersen and her fellow mothers pivoted. After hearing how researchers in Norway were able to increase awareness around fetal movement, they co-founded a nonprofit aimed at doing the same in the U.S.
The group, Healthy Birth Day, created colorful “Count the Kicks” pamphlets – and later an app – teaching pregnant people how to track a baby’s movements and establish what is normal for them. Monitoring a baby’s movements is the earliest and sometimes only indication that something may be wrong, said Emily Price, chief executive officer of Healthy Birth Day. One of the organization’s main messages is for pregnant people to speak up and clinicians to listen.
“Unfortunately, there are still doctors who brush women off or send them home when they come in with a complaint of a change in their baby’s movements,” Price said. “And babies are dying because of it.”
One Indiana county, which recorded 65 stillbirths from 2017 through 2019, reported that 74% had either some chance or a good chance of prevention, according to St. Joseph County Department of Health’s Fetal Infant Mortality Review program. For mothers who experienced decreased fetal movement in the few hours or days before the stillbirth, that estimate jumped to 90%.
Although there is not a scientific consensus that kick counting can prevent stillbirths, national groups, including ACOG, recommend that medical professionals encourage their patients to be aware of fetal movement patterns. ACOG also advises medical professionals to be attentive to a mother’s concerns about reduced movement and address them “in a systematic way.”
One complaint the CDC hears too often, an agency spokesperson said, is that pregnant people and those who gave birth recently find that their concerns are dismissed or ignored. “Listening and taking the concerns of pregnant and recently pregnant people seriously,” she said, “is a simple, yet powerful action to prevent serious health complications and even death.”
The CDC, she said, is “very interested” in expanding its research on stillbirth, which is “a crucial part of the development of any awareness or prevention campaigns.” In addition to working to improve its stillbirth data quality, the agency has funded some pilot programs at the city and state level to better track stillbirths, survey people who have had a stillbirth and research risk factors and causes. The Iowa registry, she said, led the CDC to fund different research projects in Arkansas and Massachusetts, which are ongoing.
In 2009, the CDC acknowledged that fetal mortality remained a “major, but often overlooked, public health problem.” Officials wrote that much of the public health concern had been focused on infant mortality “in part due to lesser awareness of the magnitude of fetal mortality, its causes, and prevention strategies.”
But little has changed over the past 13 years. Echoing its earlier message, the CDC this year declared that “much work remains” and that “stillbirth is not often viewed as a public health issue, so increased awareness is key.”
A spokesperson for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, which is part of the NIH, said the agency has continually funded research on stillbirths, even after one of its key studies ended. The agency, she said, also supports research on conditions that increase the risk of stillbirth.
As a scientific research institute, it does not issue clinical guidelines or recommendations, she said, though it did launch the Safe to Sleep campaign in 1994, two decades after Congress put it in charge of SIDS federal research efforts. That campaign, which educates parents and caregivers on ways to reduce the risk of SIDS, highlights recommendations issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics. She said the agency will continue to collaborate with organizations that raise awareness about stillbirth and other pregnancy complications “to amplify their messages and efforts.”
“NICHD continues to support research on the prevention, causes, frequency, and risk factors of stillbirth,” the spokesperson said in an email. “Our commitment to enhancing understanding of stillbirth and improving outcomes focuses on building the scientific knowledge base.”
But getting laws on the books that could raise awareness around stillbirth – even when they don’t require additional funding – has been a struggle. Petersen and Price are pushing Congress to pass legislation that would add stillbirth research and prevention to the list of activities approved for federal maternal health dollars.
Though the bill doesn’t ask for any additional funding, it has not yet passed.
In addition, the SHINE for Autumn Act breezed through the House of Representatives in December 2021. After Haine Vijayvergiya, the New Jersey mother who has championed it, secured bipartisan support from U.S. Sens. Cory Booker, D-N.J., and Marco Rubio, R-Fla., she thought the most comprehensive stillbirth legislation in U.S. history would finally become law.
Neither bill has sparked controversy.
But months after press releases announced the SHINE legislation and referred to the U.S. stillbirth rate as “unacceptable,” lawmakers and the families they represent are running out of time as this session of Congress prepares to adjourn.
“From the day that the bill was introduced into the Senate,” Haine Vijayvergiya said, “approximately 13,000 babies have been born still.”
Last month, on a brilliant fall day much like the one when Reese was stillborn, Amanda Duffy bent down to kiss her son Rogen’s head before they walked on stage.
She wore a soft blue T-shirt tucked into her jeans that read “Be courageous.” The message was as much for her as it was for the crowd on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., many of them like her, mothers who didn’t know stillbirth happened until it happened to them. Since Reese’s death, she has coached doctors and nurses on improving care for patients who have suffered pregnancy loss. Among her many suggestions, she tells them their first words when a concerned patient reaches out should be “I’m so glad you called.”
A few hundred people had gathered for The Big PUSH to End Preventable Stillbirth, billed as the first-ever march on the issue. As part of an art installation, Amanda wrote a note to Reese: “You’re pretty magical & for that I’m grateful. You’re a change maker and you are so very loved. Love, Mama.” Before she slipped the folded paper into a sea of more than 20,000 baby hats, Rogen added his own message: “Hope you are having a good time – Rogen.”
Reese would have turned 8 this month.
Before Amanda spoke, she took a deep breath and silenced her nerves. She walked onto the stage and called on Congress to pass the stillbirth legislation before it. She didn’t ask. She demanded.
“It’s time to empower pregnant people and their care providers with information that leads to prevention,” she insisted.
With the afternoon sun bearing down, Amanda and Rogen disappeared into the crowd of families marching toward the Capitol. Many carried signs. Some pushed empty strollers. Amanda was still wearing the orange-scented oil she had rubbed on her wrists that morning.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published
The day before doctors had scheduled Amanda Duffy to give birth, the baby jolted her awake with a kick.
A few hours later, on that bright Sunday in November 2014, she leaned back on a park bench to watch her 19-month-old son Rogen enjoy his final day of being an only child. In that moment of calm, she realized that the kick that morning was the last time she had felt the baby move.
She told herself not to worry. She had heard that babies can slow down toward the end of a pregnancy and remembered reading that sugary snacks and cold fluids can stimulate a baby’s movement. When she got back to the family’s home in suburban Minneapolis, she drank a large glass of ice water and grabbed a few Tootsie Rolls off the kitchen counter.
But something about seeing her husband, Chris, lace up his shoes to leave for a run prompted her to blurt out, “I haven’t felt the baby kick.”
Chris called Amanda’s doctor, and they headed to the hospital to be checked. Once there, a nurse maneuvered a fetal monitor around Amanda’s belly. When she had trouble locating a heartbeat, she remarked that the baby must be tucked in tight. The doctor walked into the room, turned the screen away from Amanda and Chris and began searching. She was sorry, Amanda remembers her telling them, but she could not find a heartbeat.
Amanda let out a guttural scream. She said the doctor quickly performed an internal exam, which detected faint heart activity, then rushed Amanda into an emergency cesarean section.
She woke up to the sound of doctors talking to Chris. She listened but couldn’t bring herself to face the news. Her doctor told her she needed to open her eyes.
Amanda, then 31, couldn’t fathom that her daughter had died. She said her doctors had never discussed stillbirth with her. It was not mentioned in any of the pregnancy materials she had read. She didn’t even know that stillbirth was a possibility.
But every year more than 20,000 pregnancies in the United States end in stillbirth, the death of an expected child at 20 weeks or more. That number has exceeded infant mortality every year for the last 10 years. It’s 15 times the number of babies who, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, died of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, in 2020.
The deaths are not inevitable. One study found that nearly one in four U.S. stillbirths may be preventable. For pregnancies that last 37 weeks or more, that research shows, the figure jumps to nearly half. Thousands more babies could potentially be delivered safely every year.
But federal agencies have not prioritized critical stillbirth-focused studies that could lead to fewer deaths. Nearly two decades ago, both the CDC and the National Institutes of Health launched key stillbirth tracking and research studies, but the agencies ended those projects within about a decade. The CDC never analyzed some of the data that was collected.
Unlike with SIDS, a leading cause of infant death, federal officials have failed to launch a national campaign to reduce the risk of stillbirth or adequately raise awareness about it. Placental exams and autopsies, which can sometimes explain why stillbirths happened, are underutilized, in part because parents are not counseled on their benefits.
Federal agencies, state health departments, hospitals and doctors have also done a poor job of educating expectant parents about stillbirth or diligently counseling on fetal movement, despite research showing that patients who have had a stillbirth are more likely to have experienced abnormal fetal movements, including decreased activity. Neither the CDC nor the NIH have consistently promoted guidance telling those who are pregnant to be aware of their babies’ movement in the womb as a way to possibly reduce their risk of stillbirth.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the nation’s leading obstetrics organization, has been slow to update its own guidance to doctors on managing a stillbirth. In 2009, ACOG issued a set of guidelines that included a single paragraph regarding fetal movement. Those guidelines weren’t significantly updated for another 11 years.
Perhaps it’s no surprise that federal goals for reducing stillbirths keep moving in the wrong direction. In 2005, the U.S. stillbirth rate was 6.2 per 1,000 live births. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, in an effort to eliminate health disparities and establish a target that was “better than the best racial or ethnic group rate,” set a goal of reducing it to 4.1 for 2010. When that wasn’t met, federal officials changed their approach and set what they called more “science-based” and “realistic” goals, raising the 2020 target to 5.6. The U.S. still fell short. The 2030 goal of 5.7 was so attainable that it was met before the decade started. The 2020 rate, the most current according to the CDC, is 5.74.
By comparison, other wealthy countries have implemented national action plans to prevent stillbirth through awareness, research and care. Among other approaches, those countries have focused on increasing education around stillbirth and the importance of a baby’s movements, reducing rates of smoking and identifying fetuses that grow too slowly in the womb.
The efforts have paid off. The Netherlands, for instance, has reduced its rate of stillbirths at 28 weeks or later by more than half, from 5.2 in 2000 to 2.3 in 2019, according to a study published last year in The Lancet.
Dr. Bob Silver, chair of the obstetrics/gynecology department at University of Utah Health and a leading stillbirth expert, coauthored the study that estimated nearly one in four stillbirths are potentially preventable, a figure he referred to as conservative. He called on federal agencies to declare stillbirth reduction a priority the same way they have done for premature birth and maternal mortality.
“I’d like to see us say we really want to reduce the rate of stillbirth and raise awareness and try to do all of the reasonable things that may contribute to reducing stillbirths that other countries have done,” Silver said.
The lack of comprehensive attention and action has contributed to a stillbirth crisis, shrouded in an acceptance that some babies just die. Compounding the tragedy is a stigma and guilt so crushing that the first words some mothers utter when their lifeless babies are placed in their arms are “I’m sorry.”
In the hospital room, Amanda Duffy finally opened her eyes. She named her daughter Reese Christine, the name she had picked out for her before they found out she had died. She was 8 pounds, 3 ounces and 20 1/2 inches long and was born with her umbilical cord wrapped tightly around her neck twice. The baby was still warm when the nurse placed her in Amanda’s arms. Amanda was struck by how lovely her daughter was. Rosy skin. Chris’ red hair. Rogen’s chubby cheeks.
As Amanda held Reese, Chris hunched over the toilet, vomiting. Later that night, as he lay next to Amanda on the hospital bed, he held his daughter. He hadn’t initially wanted to see her. He worried she would be disfigured or, worse, that she would be beautiful and he would fall apart when he couldn’t take her home.
The nurses taught Amanda and Chris how to grieve and love simultaneously. One nurse told Amanda how cute Reese was and asked if she could hold her. Another placed ice packs in Reese’s swaddle to preserve her body so Amanda could keep holding her. Amanda asked the nurses to tuck cotton balls soaked in an orange scent into Reese’s blanket so the smell would trigger the memory of her daughter. And just as if Reese had been born alive, the nurses took pictures and made prints of her hands and feet.
“I felt such a deep, abiding love for her,” Amanda said. “And I was so proud to be her mom.”
On the way home from the hospital, Amanda broke down at the sight of Reese’s empty car seat. The next few weeks passed in a sleep-filled fog punctuated by intense periods of crying. The smell of oranges wrecked her. Her breast milk coming in was agonizing, physically and emotionally. She wore sports bras stuffed with ice packs to ease the pain and dry up her milk supply. While Rogen was at day care, she sobbed in his bed.
In the months that followed, Amanda and Chris searched for answers and wondered whether their medical team had missed warning signs. Late at night, Amanda turned to Google to find information about stillbirths. She mailed her medical records to a doctor who studies stillbirths, who she said told her that Reese’s death could have been prevented. They briefly discussed legal action against her doctors, but she said a lawyer told her it would be difficult to sue.
Amanda and Chris pinpointed her last two months of pregnancy as the time things started to go wrong. She had been diagnosed with polyhydramnios, meaning there was excess amniotic fluid in the womb. Her doctor had scheduled additional weekly testing.
One of those ultrasounds revealed problems with the blood flow in the umbilical cord. Reese’s cord also appeared to be wrapped around her neck, Amanda said later, but was told that was less of a concern, since it occurs in about 20% of normal deliveries. At another appointment, Amanda’s medical records show, Reese failed the portion of a test that measures fetal breathing movements.
At 37 weeks, Amanda told one of the midwives the baby’s movements felt different, but, she said, the midwife told her that it was common for movements to feel weaker with polyhydramnios. At that point, Amanda felt her baby was safer outside than inside and, her medical records show, she asked to schedule a C-section.
Despite voicing concerns about a change in the baby’s movement and asking to deliver earlier, Amanda said she and her husband were told by her midwife she couldn’t deliver for another two weeks. The doctor “continues to advise 39wks,” her medical records show. Waiting until 39 weeks is usually based on a guideline that deliveries should not happen before then unless a medical condition specifically warrants it, because early delivery can lead to complications.
Amanda would have to wait until 39 weeks and one day because, she said, her doctors didn’t typically do elective deliveries on weekends. Amanda was disappointed but said she trusted her team of doctors and midwives.
“I’m not a pushy person,” she said. “My husband is not a pushy person. That was out of our comfort zone to be, like, ‘What are we waiting for?’ But really what we wanted them to say was ‘We should deliver you.’”
Amanda’s final appointment was a maximum 30-minute-long ultrasound that combined a number of assessments to check amniotic fluid, fetal muscle tone, breathing and body movement. After 29 minutes of inactivity, Amanda said, the baby moved a hand. In the parking lot, Amanda called her mother, crying in relief. Four more days, she told her.
Less than 24 hours before the scheduled C-section, Reese was stillborn.
Four months after her death, Amanda, then a career advisor at the University of Minnesota, and Chris, a public relations specialist, wrote a letter to the University of Minnesota Medical Center, where Amanda had given birth to her dead daughter. They said they had “no ill feelings” toward anyone, but “it pains us to know that her death could’ve been prevented if we would have been sent to labor and delivery following that ultrasound.”
They noted that though they were told that Reese had passed the final ultrasound where she took 29 minutes to move, they had since come to believe that she had failed because, according to national standards, at least three movements were required. They also blamed a strict adherence to the 39-week guideline. And they encouraged the hospital staff to read more on umbilical cord accidents and acute polyhydramnios, which they later learned carries an increased stillbirth risk.
The positive feelings they had from speaking up were replaced by dismay when the hospital responded with a three-paragraph letter, signed by seven doctors and eight nurses. They said they had reexamined each medical decision in her case and concluded they had made “the best decisions medically possible.” They expressed their sympathy and said it was “so very heartwarming that you are trying to turn your tragic loss into something that will benefit others.”
Amanda felt dismissed by the medical team all over again. She didn’t expect them to admit fault, but she said she hoped that they would at least learn from Reese’s death to do things differently in the future. She was angry, and hurt, and knew that she would need to find a new doctor.
A spokesperson for the University of Minnesota Medical School told ProPublica she could not comment on individual patient cases and did not respond to questions about general protocols. “We share the physicians’ condolences,” she wrote, adding that the doctors and the university “are dedicated to delivering high quality, accessible and inclusive health care.”
For many expectant parents, it’s hard to muster the courage to call a doctor about something they’re not even sure is a problem.
“Moms self-censor a lot. No one wants to be that mom that all the doctors are rolling their eyes at because she’s freaking out over nothing,” said Samantha Banerjee, executive director of PUSH for Empowered Pregnancy, a nonprofit based in New York state that works to prevent stillbirths. Banerjee’s daughter, Alana, was stillborn two days before her due date.
In addition to raising awareness that stillbirths can happen even in low-risk pregnancies, PUSH teaches pregnant people how to advocate for themselves. The volunteers advise them to put their requests in writing and not to spend time drinking juice or lying on their side if they are worried about their baby’s lack of movement. In the majority of cases, a call or visit to the hospital reassures them.
But, the group tells parents, if their baby is in distress, calling their doctor can save their life.
Debbie Haine Vijayvergiya is fighting another narrative: that stillbirths are a rare fluke that “just happen.” When her daughter Autumn Joy was born without a heartbeat in 2011, Haine Vijayvergiya said, her doctor told her having a stillborn baby was as rare as being struck by lightning.
She believed him, but then she looked up the odds of a lightning strike and found they are less than one in a million – and most people survive. In 2020, according to the CDC, there was one stillbirth for about every 175 births.
“I’ve spoken to more women than I can count that said, ‘I raised the red flag, and I was sent home. I was told to eat a piece of cake and have some orange juice and lay on my left side,’ only to wake up the next day and their baby is not alive,” said Haine Vijayvergiya, a New Jersey mother and maternal health advocate.
She has fought for more than a decade to pass stillbirth legislation as her daughter’s legacy. Her current undertaking is her most ambitious. The federal Stillbirth Health Improvement and Education (SHINE) for Autumn Act, named after her daughter, would authorize $9 million a year for five years in federal funding for research, better data collection and training for fetal autopsies. But it is currently sitting in the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions.
Not all stillbirths are preventable, and medical experts agree more research is needed to determine who is most at risk and which babies can potentially be saved. Complicating matters is the wide range of risk factors, including hypertension and diabetes, smoking, obesity, being pregnant with multiples, being 35 or older and having had a previous stillbirth.
ProPublica reported this summer on how the U.S. botched the rollout of COVID-19 vaccines for pregnant people, who faced an increased risk for stillbirth if they were unvaccinated and contracted the virus, especially during the Delta wave.
Doctors often work to balance the risk of stillbirth with other dangers, particularly an increased chance of being admitted to neonatal intensive care units or even death of the baby if it is born too early. ACOG and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine have issued guidance to try to slow a rise in elective deliveries before 39 weeks and the potential harm that can result. The Joint Commission, a national accrediting organization, began evaluating hospitals in 2010 based on that standard.
A 2019 study found that the risks of stillbirth slightly increased after the rule went into effect, but fewer infants died after birth. Other studies have not found an effect on stillbirths.
Last year, the obstetric groups updated their guidance to allow doctors to consider an early delivery if a woman has anxiety and a history of stillbirth, writing that a previous stillbirth “may” warrant an early delivery for patients who understand and accept the risks. For those who have previously had a stillbirth, one modeling analysis found that 38 weeks is the optimal timing of delivery, considering the increased risk of another stillbirth.
“A woman who has had a previous stillbirth at 37 weeks – one could argue that it’s cruel and unusual punishment to make her go to 39 weeks with her next pregnancy, although that is the current recommendation,” said Dr. Neil Mandsager, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist in Iowa and a medical advisor to a stillbirth prevention nonprofit.
At or after 40 weeks, the risk of stillbirth increases, especially for women 35 or older. Their risk, research shows, is doubled from 39 weeks to 40 and is more than six times as high at 42 weeks. In 2019 and 2020, a combined 1,200 stillbirths occurred between 40 and 42 weeks, according to the most recent CDC data.
Deciding when a patient should deliver entails weighing the risks to the mother and the infant against a possible stillbirth as the pregnancy continues, said Dr. Mark Turrentine, chair of ACOG’s Clinical Consensus Committee-Obstetrics, which helped create the guidance on managing a stillbirth. He said ACOG has addressed stillbirth in other documents and extensively in its 2021 guidance on fetal surveillance and testing, which is done to reduce the risk of stillbirth.
ACOG said it routinely reviewed its guidance on management of stillbirth but was unable to make significant updates “due to the lack of new, evidence-based research.” While prevention is a great concern to ACOG, Turrentine said it’s difficult to know how many stillbirths are preventable.
He said it’s standard practice for doctors to ask about fetal movement, and ACOG updated its guidance after new research became available. Doctors also need to include patients in decision-making and tailor care to them, he said, whether that›s using aspirin in patients at high risk of preeclampsia – a serious high blood pressure condition during pregnancy – or ordering additional tests.
After Reese’s death, Amanda and Chris Duffy wanted to get pregnant again. They sought out an obstetrician-gynecologist who would educate and listen to them. They set up several consultations until they found Dr. Emily Hawes-Van Pelt, who was recommended by another family who had had a stillbirth.
Hawes-Van Pelt cried with Amanda and Chris at their first meeting.
“I told her I was scared to be involved,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “It’s such a tricky subsequent pregnancy because there’s so much worry and anxiety about the horrible, awful thing happening again.”
Amanda’s fear of delivering another dead baby led to an all-consuming anxiety, but Hawes-Van Pelt supported her when she asked for additional monitoring, testing and an early delivery.
When Hawes-Van Pelt switched practices midway through Amanda’s pregnancy, Amanda followed her. But the new hospital pushed back on the early delivery.
“We intervene early for poorly controlled diabetes,” Hawes-Van Pelt said. “We intervene early for all sorts of medical issues. Anxiety and prior stillbirth are two medical issues that we can intervene earlier for.”
Hawes-Van Pelt said she learned a lot from caring for Amanda, who made her reevaluate some of her own assumptions around stillbirths.
“I had a horrible fear of scaring women unnecessarily, and then realized that I was just not preparing women or educating them because of my own fears around it,” she said. “If you can carry a human being in your body and birth that human being and take care of it, you can hear those words.”
The hospital eventually agreed to let Hawes-Van Pelt schedule Amanda for a 37-week C-section. But after Amanda was again diagnosed with polyhydramnios, she went in for a C-section even earlier. She gave birth in 2015 to a healthy boy she and Chris named Rhett. Two years later, Amanda and Hawes-Van Pelt followed the same pregnancy plan, and she delivered a girl named Maeda Reese. Amanda chose the name because, when said quickly, it sounds like “made of Reese.”
Federal agencies, national organizations and state and city officials have mobilized in recent years to address maternal mortality, when mothers die during pregnancy, at delivery or soon after childbirth. They have focused on improving data collection, passing legislation and creating awareness campaigns that encourage medical professionals and others to listen when women say something doesn›t feel right.
In 2017, ProPublica and NPR documented the U.S. maternal mortality crisis, including alarming racial disparities.
According to CDC data, Black women face nearly three times the risk of maternal mortality. They also are more than twice – and in some states close to three times – as likely to have a stillbirth than white women, meaning not only are Black mothers dying at a disproportionate rate, so are their babies.
Janet Petersen, a state senator from Iowa, said it gives her hope to see how the country has turned its attention to maternal mortality and disparities in health care. She simply cannot understand why stillbirth isn’t being met with the same urgency.
In 2020, the CDC reported 861 mothers died either while pregnant or within six weeks of giving birth. That same year, 20,854 babies were stillborn.
Stillbirth, Petersen said, is a missing piece of the puzzle. Research shows the likelihood of severe maternal complications was more than four times higher for pregnancies that ended in stillbirths, and mothers who died within six weeks of delivery were more likely to have had a stillbirth.
“We see it over and over again that stillbirth is one of the maternal health care issues that continuously gets ignored,” said Petersen, a Democrat.
Petersen was a young legislator in 2003 when her daughter Grace was born still. Devastated, she thought of her grandmother, who lost a baby to stillbirth in 1920, just a few weeks before women got the right to vote.
“I was laying in my hospital bed thinking, ‘How could this still be happening in our country?’” Petersen recalled. “And it seemed, from the medical perspective, that, well, stillbirth happens. We can’t do anything to prevent them.”
Over the next few months, Petersen heard from other mothers who had lost their babies and wanted to spark change. As an elected official, Petersen was in a position to do that. In 2004, she introduced legislation that required the Iowa Department of Public Health to create a stillbirths work group, later securing funding through the CDC to create a stillbirth registry.
But the CDC didn’t renew the funding and never analyzed the data from the registry, though a CDC spokesperson said the Iowa Department of Public Health examined the data. Officials from the department did not respond to requests for comment.
Petersen and her fellow mothers pivoted. After hearing how researchers in Norway were able to increase awareness around fetal movement, they co-founded a nonprofit aimed at doing the same in the U.S.
The group, Healthy Birth Day, created colorful “Count the Kicks” pamphlets – and later an app – teaching pregnant people how to track a baby’s movements and establish what is normal for them. Monitoring a baby’s movements is the earliest and sometimes only indication that something may be wrong, said Emily Price, chief executive officer of Healthy Birth Day. One of the organization’s main messages is for pregnant people to speak up and clinicians to listen.
“Unfortunately, there are still doctors who brush women off or send them home when they come in with a complaint of a change in their baby’s movements,” Price said. “And babies are dying because of it.”
One Indiana county, which recorded 65 stillbirths from 2017 through 2019, reported that 74% had either some chance or a good chance of prevention, according to St. Joseph County Department of Health’s Fetal Infant Mortality Review program. For mothers who experienced decreased fetal movement in the few hours or days before the stillbirth, that estimate jumped to 90%.
Although there is not a scientific consensus that kick counting can prevent stillbirths, national groups, including ACOG, recommend that medical professionals encourage their patients to be aware of fetal movement patterns. ACOG also advises medical professionals to be attentive to a mother’s concerns about reduced movement and address them “in a systematic way.”
One complaint the CDC hears too often, an agency spokesperson said, is that pregnant people and those who gave birth recently find that their concerns are dismissed or ignored. “Listening and taking the concerns of pregnant and recently pregnant people seriously,” she said, “is a simple, yet powerful action to prevent serious health complications and even death.”
The CDC, she said, is “very interested” in expanding its research on stillbirth, which is “a crucial part of the development of any awareness or prevention campaigns.” In addition to working to improve its stillbirth data quality, the agency has funded some pilot programs at the city and state level to better track stillbirths, survey people who have had a stillbirth and research risk factors and causes. The Iowa registry, she said, led the CDC to fund different research projects in Arkansas and Massachusetts, which are ongoing.
In 2009, the CDC acknowledged that fetal mortality remained a “major, but often overlooked, public health problem.” Officials wrote that much of the public health concern had been focused on infant mortality “in part due to lesser awareness of the magnitude of fetal mortality, its causes, and prevention strategies.”
But little has changed over the past 13 years. Echoing its earlier message, the CDC this year declared that “much work remains” and that “stillbirth is not often viewed as a public health issue, so increased awareness is key.”
A spokesperson for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, which is part of the NIH, said the agency has continually funded research on stillbirths, even after one of its key studies ended. The agency, she said, also supports research on conditions that increase the risk of stillbirth.
As a scientific research institute, it does not issue clinical guidelines or recommendations, she said, though it did launch the Safe to Sleep campaign in 1994, two decades after Congress put it in charge of SIDS federal research efforts. That campaign, which educates parents and caregivers on ways to reduce the risk of SIDS, highlights recommendations issued by the American Academy of Pediatrics. She said the agency will continue to collaborate with organizations that raise awareness about stillbirth and other pregnancy complications “to amplify their messages and efforts.”
“NICHD continues to support research on the prevention, causes, frequency, and risk factors of stillbirth,” the spokesperson said in an email. “Our commitment to enhancing understanding of stillbirth and improving outcomes focuses on building the scientific knowledge base.”
But getting laws on the books that could raise awareness around stillbirth – even when they don’t require additional funding – has been a struggle. Petersen and Price are pushing Congress to pass legislation that would add stillbirth research and prevention to the list of activities approved for federal maternal health dollars.
Though the bill doesn’t ask for any additional funding, it has not yet passed.
In addition, the SHINE for Autumn Act breezed through the House of Representatives in December 2021. After Haine Vijayvergiya, the New Jersey mother who has championed it, secured bipartisan support from U.S. Sens. Cory Booker, D-N.J., and Marco Rubio, R-Fla., she thought the most comprehensive stillbirth legislation in U.S. history would finally become law.
Neither bill has sparked controversy.
But months after press releases announced the SHINE legislation and referred to the U.S. stillbirth rate as “unacceptable,” lawmakers and the families they represent are running out of time as this session of Congress prepares to adjourn.
“From the day that the bill was introduced into the Senate,” Haine Vijayvergiya said, “approximately 13,000 babies have been born still.”
Last month, on a brilliant fall day much like the one when Reese was stillborn, Amanda Duffy bent down to kiss her son Rogen’s head before they walked on stage.
She wore a soft blue T-shirt tucked into her jeans that read “Be courageous.” The message was as much for her as it was for the crowd on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., many of them like her, mothers who didn’t know stillbirth happened until it happened to them. Since Reese’s death, she has coached doctors and nurses on improving care for patients who have suffered pregnancy loss. Among her many suggestions, she tells them their first words when a concerned patient reaches out should be “I’m so glad you called.”
A few hundred people had gathered for The Big PUSH to End Preventable Stillbirth, billed as the first-ever march on the issue. As part of an art installation, Amanda wrote a note to Reese: “You’re pretty magical & for that I’m grateful. You’re a change maker and you are so very loved. Love, Mama.” Before she slipped the folded paper into a sea of more than 20,000 baby hats, Rogen added his own message: “Hope you are having a good time – Rogen.”
Reese would have turned 8 this month.
Before Amanda spoke, she took a deep breath and silenced her nerves. She walked onto the stage and called on Congress to pass the stillbirth legislation before it. She didn’t ask. She demanded.
“It’s time to empower pregnant people and their care providers with information that leads to prevention,” she insisted.
With the afternoon sun bearing down, Amanda and Rogen disappeared into the crowd of families marching toward the Capitol. Many carried signs. Some pushed empty strollers. Amanda was still wearing the orange-scented oil she had rubbed on her wrists that morning.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published
Update on high-grade vulvar interepithelial neoplasia
Vulvar squamous cell carcinomas (VSCC) comprise approximately 90% of all vulvar malignancies. Unlike cervical SCC, which are predominantly human papilloma virus (HPV) positive, only a minority of VSCC are HPV positive – on the order of 15%-25% of cases. Most cases occur in the setting of lichen sclerosus and are HPV negative.
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory dermatitis typically involving the anogenital area, which in some cases can become seriously distorted (e.g. atrophy of the labia minora, clitoral phimosis, and introital stenosis). Although most cases are diagnosed in postmenopausal women, LS can affect women of any age. The true prevalence of lichen sclerosus is unknown. Recent studies have shown a prevalence of 1 in 60; among older women, it can even be as high as 1 in 30. While lichen sclerosus is a pruriginous condition, it is often asymptomatic. It is not considered a premalignant condition. The diagnosis is clinical; however, suspicious lesions (erosions/ulcerations, hyperkeratosis, pigmented areas, ecchymosis, warty or papular lesions), particularly when recalcitrant to adequate first-line therapy, should be biopsied.
VSCC arises from precursor lesions or high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease nomenclature classifies high-grade VIN into high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and differentiated VIN (dVIN). Most patients with high-grade VIN are diagnosed with HSIL or usual type VIN. A preponderance of these lesions (75%-85%) are HPV positive, predominantly HPV 16. Vulvar HSIL (vHSIL) lesions affect younger women. The lesions tend to be multifocal and extensive. On the other hand, dVIN typically affects older women and commonly develops as a solitary lesion. While dVIN accounts for only a small subset of patients with high-grade VIN, these lesions are HPV negative and associated with lichen sclerosus.
Both disease entities, vHSIL and dVIN, are increasing in incidence. There is a higher risk and shortened period of progression to cancer in patients with dVIN compared to HSIL. The cancer risk of vHSIL is relatively low. The 10-year cumulative VSCC risk reported in the literature is 10.3%; 9.7% for vHSIL and 50% for dVIN. Patients with vHSIL could benefit from less aggressive treatment modalities.
Patients present with a constellation of signs such as itching, pain, burning, bleeding, and discharge. Chronic symptoms portend HPV-independent lesions associated with lichen sclerosus while episodic signs are suggestive of HPV-positive lesions.
The recurrence risk of high-grade VIN is 46%-70%. Risk factors for recurrence include age greater than 50, immunosuppression, metasynchronous HSIL, and multifocal lesions. Recurrences occur in up to 50% of women who have undergone surgery. For those who undergo surgical treatment for high-grade VIN, recurrence is more common in the setting of positive margins, underlying lichen sclerosis, persistent HPV infection, and immunosuppression.
Management of high-grade VIN is determined by the lesion characteristics, patient characteristics, and medical expertise. Given the risk of progression of high-grade VIN to cancer and risk of underlying cancer, surgical therapy is typically recommended. The treatment of choice is surgical excision in cases of dVIN. Surgical treatments include CO2 laser ablation, wide local excision, and vulvectomy. Women who undergo surgical treatment for vHSIL have about a 50% chance of the condition recurring 1 year later, irrespective of whether treatment is by surgical excision or laser vaporization.
Since surgery can be associated with disfigurement and sexual dysfunction, alternatives to surgery should be considered in cases of vHSIL. The potential for effect on sexual function should be part of preoperative counseling and treatment. Women treated for VIN often experience increased inhibition of sexual excitement and increased inhibition of orgasm. One study found that in women undergoing vulvar excision for VIN, the impairment was found to be psychological in nature. Overall, the studies of sexual effect from treatment of VIN have found that women do not return to their pretreatment sexual function. However, the optimal management of vHSIL has not been determined. Nonsurgical options include topical therapies (imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil, cidofovir, and interferon) and nonpharmacologic treatments, such as photodynamic therapy.
Imiquimod, a topical immune modulator, is the most studied pharmacologic treatment of vHSIL. The drug induces secretion of cytokines, creating an immune response that clears the HPV infection. Imiquimod is safe and well tolerated. The clinical response rate varies between 35% and 81%. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of imiquimod and the treatment was found to be noninferior to surgery. Adverse events differed, with local pain following surgical treatment and local pruritus and erythema associated with imiquimod use. Some patients did not respond to imiquimod; it was thought by the authors of the study that specific immunological factors affect the clinical response.
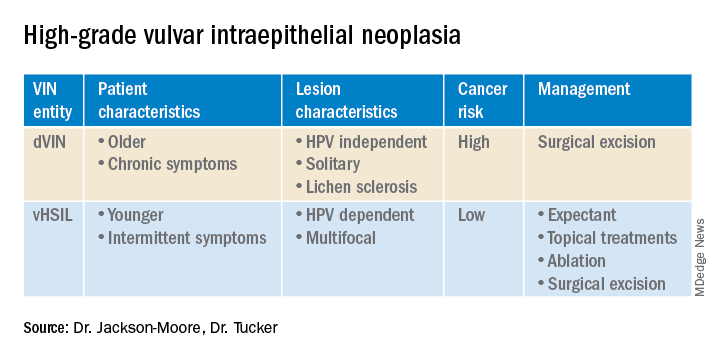
In conclusion, high-grade VIN is a heterogeneous disease made up of two distinct disease entities with rising incidence. In contrast to dVIN, the cancer risk is low for patients with vHSIL. Treatment should be driven by the clinical characteristics of the vulvar lesions, patients’ preferences, sexual activity, and compliance. Future directions include risk stratification of patients with vHSIL who are most likely to benefit from topical treatments, thus reducing overtreatment. Molecular biomarkers that could identify dVIN at an early stage are needed.
Dr. Jackson-Moore is associate professor in gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
Cendejas BR et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar;212(3):291-7.
Lebreton M et al. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2020 Nov;49(9):101801.
Thuijs NB et al. Int J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;148(1):90-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33198. .
Trutnovsky G et al. Lancet. 2022 May 7;399(10337):1790-8. Erratum in: Lancet. 2022 Oct 8;400(10359):1194.
Vulvar squamous cell carcinomas (VSCC) comprise approximately 90% of all vulvar malignancies. Unlike cervical SCC, which are predominantly human papilloma virus (HPV) positive, only a minority of VSCC are HPV positive – on the order of 15%-25% of cases. Most cases occur in the setting of lichen sclerosus and are HPV negative.
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory dermatitis typically involving the anogenital area, which in some cases can become seriously distorted (e.g. atrophy of the labia minora, clitoral phimosis, and introital stenosis). Although most cases are diagnosed in postmenopausal women, LS can affect women of any age. The true prevalence of lichen sclerosus is unknown. Recent studies have shown a prevalence of 1 in 60; among older women, it can even be as high as 1 in 30. While lichen sclerosus is a pruriginous condition, it is often asymptomatic. It is not considered a premalignant condition. The diagnosis is clinical; however, suspicious lesions (erosions/ulcerations, hyperkeratosis, pigmented areas, ecchymosis, warty or papular lesions), particularly when recalcitrant to adequate first-line therapy, should be biopsied.
VSCC arises from precursor lesions or high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease nomenclature classifies high-grade VIN into high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and differentiated VIN (dVIN). Most patients with high-grade VIN are diagnosed with HSIL or usual type VIN. A preponderance of these lesions (75%-85%) are HPV positive, predominantly HPV 16. Vulvar HSIL (vHSIL) lesions affect younger women. The lesions tend to be multifocal and extensive. On the other hand, dVIN typically affects older women and commonly develops as a solitary lesion. While dVIN accounts for only a small subset of patients with high-grade VIN, these lesions are HPV negative and associated with lichen sclerosus.
Both disease entities, vHSIL and dVIN, are increasing in incidence. There is a higher risk and shortened period of progression to cancer in patients with dVIN compared to HSIL. The cancer risk of vHSIL is relatively low. The 10-year cumulative VSCC risk reported in the literature is 10.3%; 9.7% for vHSIL and 50% for dVIN. Patients with vHSIL could benefit from less aggressive treatment modalities.
Patients present with a constellation of signs such as itching, pain, burning, bleeding, and discharge. Chronic symptoms portend HPV-independent lesions associated with lichen sclerosus while episodic signs are suggestive of HPV-positive lesions.
The recurrence risk of high-grade VIN is 46%-70%. Risk factors for recurrence include age greater than 50, immunosuppression, metasynchronous HSIL, and multifocal lesions. Recurrences occur in up to 50% of women who have undergone surgery. For those who undergo surgical treatment for high-grade VIN, recurrence is more common in the setting of positive margins, underlying lichen sclerosis, persistent HPV infection, and immunosuppression.
Management of high-grade VIN is determined by the lesion characteristics, patient characteristics, and medical expertise. Given the risk of progression of high-grade VIN to cancer and risk of underlying cancer, surgical therapy is typically recommended. The treatment of choice is surgical excision in cases of dVIN. Surgical treatments include CO2 laser ablation, wide local excision, and vulvectomy. Women who undergo surgical treatment for vHSIL have about a 50% chance of the condition recurring 1 year later, irrespective of whether treatment is by surgical excision or laser vaporization.
Since surgery can be associated with disfigurement and sexual dysfunction, alternatives to surgery should be considered in cases of vHSIL. The potential for effect on sexual function should be part of preoperative counseling and treatment. Women treated for VIN often experience increased inhibition of sexual excitement and increased inhibition of orgasm. One study found that in women undergoing vulvar excision for VIN, the impairment was found to be psychological in nature. Overall, the studies of sexual effect from treatment of VIN have found that women do not return to their pretreatment sexual function. However, the optimal management of vHSIL has not been determined. Nonsurgical options include topical therapies (imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil, cidofovir, and interferon) and nonpharmacologic treatments, such as photodynamic therapy.
Imiquimod, a topical immune modulator, is the most studied pharmacologic treatment of vHSIL. The drug induces secretion of cytokines, creating an immune response that clears the HPV infection. Imiquimod is safe and well tolerated. The clinical response rate varies between 35% and 81%. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of imiquimod and the treatment was found to be noninferior to surgery. Adverse events differed, with local pain following surgical treatment and local pruritus and erythema associated with imiquimod use. Some patients did not respond to imiquimod; it was thought by the authors of the study that specific immunological factors affect the clinical response.

In conclusion, high-grade VIN is a heterogeneous disease made up of two distinct disease entities with rising incidence. In contrast to dVIN, the cancer risk is low for patients with vHSIL. Treatment should be driven by the clinical characteristics of the vulvar lesions, patients’ preferences, sexual activity, and compliance. Future directions include risk stratification of patients with vHSIL who are most likely to benefit from topical treatments, thus reducing overtreatment. Molecular biomarkers that could identify dVIN at an early stage are needed.
Dr. Jackson-Moore is associate professor in gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
Cendejas BR et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar;212(3):291-7.
Lebreton M et al. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2020 Nov;49(9):101801.
Thuijs NB et al. Int J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;148(1):90-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33198. .
Trutnovsky G et al. Lancet. 2022 May 7;399(10337):1790-8. Erratum in: Lancet. 2022 Oct 8;400(10359):1194.
Vulvar squamous cell carcinomas (VSCC) comprise approximately 90% of all vulvar malignancies. Unlike cervical SCC, which are predominantly human papilloma virus (HPV) positive, only a minority of VSCC are HPV positive – on the order of 15%-25% of cases. Most cases occur in the setting of lichen sclerosus and are HPV negative.
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory dermatitis typically involving the anogenital area, which in some cases can become seriously distorted (e.g. atrophy of the labia minora, clitoral phimosis, and introital stenosis). Although most cases are diagnosed in postmenopausal women, LS can affect women of any age. The true prevalence of lichen sclerosus is unknown. Recent studies have shown a prevalence of 1 in 60; among older women, it can even be as high as 1 in 30. While lichen sclerosus is a pruriginous condition, it is often asymptomatic. It is not considered a premalignant condition. The diagnosis is clinical; however, suspicious lesions (erosions/ulcerations, hyperkeratosis, pigmented areas, ecchymosis, warty or papular lesions), particularly when recalcitrant to adequate first-line therapy, should be biopsied.
VSCC arises from precursor lesions or high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease nomenclature classifies high-grade VIN into high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and differentiated VIN (dVIN). Most patients with high-grade VIN are diagnosed with HSIL or usual type VIN. A preponderance of these lesions (75%-85%) are HPV positive, predominantly HPV 16. Vulvar HSIL (vHSIL) lesions affect younger women. The lesions tend to be multifocal and extensive. On the other hand, dVIN typically affects older women and commonly develops as a solitary lesion. While dVIN accounts for only a small subset of patients with high-grade VIN, these lesions are HPV negative and associated with lichen sclerosus.
Both disease entities, vHSIL and dVIN, are increasing in incidence. There is a higher risk and shortened period of progression to cancer in patients with dVIN compared to HSIL. The cancer risk of vHSIL is relatively low. The 10-year cumulative VSCC risk reported in the literature is 10.3%; 9.7% for vHSIL and 50% for dVIN. Patients with vHSIL could benefit from less aggressive treatment modalities.
Patients present with a constellation of signs such as itching, pain, burning, bleeding, and discharge. Chronic symptoms portend HPV-independent lesions associated with lichen sclerosus while episodic signs are suggestive of HPV-positive lesions.
The recurrence risk of high-grade VIN is 46%-70%. Risk factors for recurrence include age greater than 50, immunosuppression, metasynchronous HSIL, and multifocal lesions. Recurrences occur in up to 50% of women who have undergone surgery. For those who undergo surgical treatment for high-grade VIN, recurrence is more common in the setting of positive margins, underlying lichen sclerosis, persistent HPV infection, and immunosuppression.
Management of high-grade VIN is determined by the lesion characteristics, patient characteristics, and medical expertise. Given the risk of progression of high-grade VIN to cancer and risk of underlying cancer, surgical therapy is typically recommended. The treatment of choice is surgical excision in cases of dVIN. Surgical treatments include CO2 laser ablation, wide local excision, and vulvectomy. Women who undergo surgical treatment for vHSIL have about a 50% chance of the condition recurring 1 year later, irrespective of whether treatment is by surgical excision or laser vaporization.
Since surgery can be associated with disfigurement and sexual dysfunction, alternatives to surgery should be considered in cases of vHSIL. The potential for effect on sexual function should be part of preoperative counseling and treatment. Women treated for VIN often experience increased inhibition of sexual excitement and increased inhibition of orgasm. One study found that in women undergoing vulvar excision for VIN, the impairment was found to be psychological in nature. Overall, the studies of sexual effect from treatment of VIN have found that women do not return to their pretreatment sexual function. However, the optimal management of vHSIL has not been determined. Nonsurgical options include topical therapies (imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil, cidofovir, and interferon) and nonpharmacologic treatments, such as photodynamic therapy.
Imiquimod, a topical immune modulator, is the most studied pharmacologic treatment of vHSIL. The drug induces secretion of cytokines, creating an immune response that clears the HPV infection. Imiquimod is safe and well tolerated. The clinical response rate varies between 35% and 81%. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of imiquimod and the treatment was found to be noninferior to surgery. Adverse events differed, with local pain following surgical treatment and local pruritus and erythema associated with imiquimod use. Some patients did not respond to imiquimod; it was thought by the authors of the study that specific immunological factors affect the clinical response.

In conclusion, high-grade VIN is a heterogeneous disease made up of two distinct disease entities with rising incidence. In contrast to dVIN, the cancer risk is low for patients with vHSIL. Treatment should be driven by the clinical characteristics of the vulvar lesions, patients’ preferences, sexual activity, and compliance. Future directions include risk stratification of patients with vHSIL who are most likely to benefit from topical treatments, thus reducing overtreatment. Molecular biomarkers that could identify dVIN at an early stage are needed.
Dr. Jackson-Moore is associate professor in gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
Cendejas BR et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar;212(3):291-7.
Lebreton M et al. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2020 Nov;49(9):101801.
Thuijs NB et al. Int J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;148(1):90-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33198. .
Trutnovsky G et al. Lancet. 2022 May 7;399(10337):1790-8. Erratum in: Lancet. 2022 Oct 8;400(10359):1194.
Postpartum posttraumatic stress disorder: An underestimated reality?
PAU, FRANCE – Postpartum posttraumatic stress disorder tends to get worse over the months following the birth of a child. Therefore, it’s necessary to screen for it as early on as possible and to ensure that women who are affected are given the proper treatment. This was the message delivered during the Infogyn 2022 conference by Ludivine Franchitto, MD, a child psychiatrist at Toulouse University Hospital, France. Because postpartum PTSD is still not fully recognized, treatment remains inadequate and poorly documented.
Impact on the caregivers as well
“The situation is the same as what we saw with postpartum depression. The debate went on for 20 years before its existence was formally declared,” Dr. Franchitto noted. But for her, the important thing is not knowing whether a traumatic stress state may be experienced by the mother who had complications during pregnancy or delivery. Instead, it’s about focusing on the repercussions for the child.
During her presentation, Dr. Franchitto also pointed out that it’s necessary to recognize that caregivers who work in maternity wards may also be negatively impacted, as they routinely see the complications that women have during pregnancy and delivery. These workers may also develop a PTSD state, requiring support so that they can properly carry out their duties.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-V), posttraumatic stress disorder arises after exposure to actual (or threatened) death, serious injury, or sexual violence. Individuals who have witnessed a traumatic event in person or who have experienced repeated (or extreme) exposure to aversive details of traumatic events may also develop PTSD.
Dr. Franchitto mentioned some of the criteria needed to make the diagnosis. “Intrusive distressing memories of the event, recurrent distressing dreams related to the event, persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the traumatic event, or negative alterations in cognitions and mood associated with the traumatic event. And the duration of the disturbance is more than 1 month.” There may also be marked alterations in arousal and reactivity associated with the traumatic event (for example, irritable behavior, loss of awareness of present surroundings).
Prevalent in 18% of women in high-risk groups
According to the studies, there is a wide variability of PTSD rates. If referring only to traumatic symptoms (for example, depressive syndrome, suicidal ideation, hyperreactivity, and persistent avoidance), the rate could reach up to 40%. A 2016 meta-analysis of 59 studies found that the prevalence of childbirth-related PTSD was 5.9%.
The authors distinguished two groups of women: those without complications during pregnancy or during delivery and those with severe complications related to the pregnancy, a fear of giving birth, a difficult delivery, an emergency C-section, a baby born prematurely with birth defects, etc. Their analysis showed PTSD rates of 4% and 18.5%, respectively.
Surprisingly, the major risk factor for PTSD turned out to be uncontrollable vomiting during pregnancy (seen in 40% of postpartum PTSD cases). The birth of a baby with birth defects was the second risk factor (35%), and the third, a history of violence in the mother’s childhood (34%). Women who experienced depression during the delivery were also at higher risk.
Other risk factors identified were lack of communication with the health care team, lack of consent, lack of support from the medical staff, and a long labor. Conversely, a sense of control and the support of a partner play a protective role.
Early screening
“If the symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder aren’t treated after delivery, they tend to get worse over the period of 1 to 6 months following the child’s birth,” Dr. Franchitto indicated. This is why it’s necessary to screen for it as early as possible – in particular, by having the women fill out the City Birth Trauma Scale questionnaire – and provide proper treatment accordingly. When seeking to limit the effects of stress, early intervention by a psychologist may be beneficial.
Psychotherapy is the recommended first-line treatment for PTSD, especially cognitive behavioral therapy and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing therapy. This approach aims to limit the mental and behavioral avoidance that prevents the traumatic memory from being integrated and processed as a regular memory.
The consequences that the mother’s PTSD state has on the child are well documented. “Children whose mothers had PTSD during pregnancy have a lower birth weight and a shorter breast-feeding duration,” Dr. Franchitto reported. With respect to the quality of the mother-child relationship and the long-term development of the child, “the studies have highly conflicting findings.”
At the end of the presentation, Professor Israël Nisand, MD, an ob.gyn. at the American Hospital of Paris and the former president of the National College of French Gynecologists and Obstetricians, made the following comment: “I often think that we underestimate the consequences that the mother’s posttraumatic stress has on the child postpartum.” He added, “Postpartum posttraumatic stress disorder is a reality. Yet it isn’t screened for, let alone treated, even though it has serious consequences for the child.”
Dr. Franchitto also brought up the impact on members of the health care staff, the “second victims” of the traumatic events that occur while caring for the women in the maternity ward. “The estimated prevalence of PTSD symptoms among midwives is 22.9%,” which could lead to “a loss of confidence and a desire to leave the profession.”
Providing psychoeducation to health care staff
Dr. Franchitto believes that it’s essential to also protect caregivers who work in maternity wards. “It’s important to have the support of colleagues” – in particular, of team leaders – “and to share one’s experiences,” as long as one knows how to recognize the symptoms of posttraumatic stress through one’s emotions and is able to verbalize them.
She went on to say that providing psychoeducation to health care staff is therefore to be encouraged, as is “simulation-based training, for learning how to manage problematic situations.”
This content was originally published on Medscape French edition. A translated version appeared on Medscape.com.
PAU, FRANCE – Postpartum posttraumatic stress disorder tends to get worse over the months following the birth of a child. Therefore, it’s necessary to screen for it as early on as possible and to ensure that women who are affected are given the proper treatment. This was the message delivered during the Infogyn 2022 conference by Ludivine Franchitto, MD, a child psychiatrist at Toulouse University Hospital, France. Because postpartum PTSD is still not fully recognized, treatment remains inadequate and poorly documented.
Impact on the caregivers as well
“The situation is the same as what we saw with postpartum depression. The debate went on for 20 years before its existence was formally declared,” Dr. Franchitto noted. But for her, the important thing is not knowing whether a traumatic stress state may be experienced by the mother who had complications during pregnancy or delivery. Instead, it’s about focusing on the repercussions for the child.
During her presentation, Dr. Franchitto also pointed out that it’s necessary to recognize that caregivers who work in maternity wards may also be negatively impacted, as they routinely see the complications that women have during pregnancy and delivery. These workers may also develop a PTSD state, requiring support so that they can properly carry out their duties.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-V), posttraumatic stress disorder arises after exposure to actual (or threatened) death, serious injury, or sexual violence. Individuals who have witnessed a traumatic event in person or who have experienced repeated (or extreme) exposure to aversive details of traumatic events may also develop PTSD.
Dr. Franchitto mentioned some of the criteria needed to make the diagnosis. “Intrusive distressing memories of the event, recurrent distressing dreams related to the event, persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the traumatic event, or negative alterations in cognitions and mood associated with the traumatic event. And the duration of the disturbance is more than 1 month.” There may also be marked alterations in arousal and reactivity associated with the traumatic event (for example, irritable behavior, loss of awareness of present surroundings).
Prevalent in 18% of women in high-risk groups
According to the studies, there is a wide variability of PTSD rates. If referring only to traumatic symptoms (for example, depressive syndrome, suicidal ideation, hyperreactivity, and persistent avoidance), the rate could reach up to 40%. A 2016 meta-analysis of 59 studies found that the prevalence of childbirth-related PTSD was 5.9%.
The authors distinguished two groups of women: those without complications during pregnancy or during delivery and those with severe complications related to the pregnancy, a fear of giving birth, a difficult delivery, an emergency C-section, a baby born prematurely with birth defects, etc. Their analysis showed PTSD rates of 4% and 18.5%, respectively.
Surprisingly, the major risk factor for PTSD turned out to be uncontrollable vomiting during pregnancy (seen in 40% of postpartum PTSD cases). The birth of a baby with birth defects was the second risk factor (35%), and the third, a history of violence in the mother’s childhood (34%). Women who experienced depression during the delivery were also at higher risk.
Other risk factors identified were lack of communication with the health care team, lack of consent, lack of support from the medical staff, and a long labor. Conversely, a sense of control and the support of a partner play a protective role.
Early screening
“If the symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder aren’t treated after delivery, they tend to get worse over the period of 1 to 6 months following the child’s birth,” Dr. Franchitto indicated. This is why it’s necessary to screen for it as early as possible – in particular, by having the women fill out the City Birth Trauma Scale questionnaire – and provide proper treatment accordingly. When seeking to limit the effects of stress, early intervention by a psychologist may be beneficial.
Psychotherapy is the recommended first-line treatment for PTSD, especially cognitive behavioral therapy and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing therapy. This approach aims to limit the mental and behavioral avoidance that prevents the traumatic memory from being integrated and processed as a regular memory.
The consequences that the mother’s PTSD state has on the child are well documented. “Children whose mothers had PTSD during pregnancy have a lower birth weight and a shorter breast-feeding duration,” Dr. Franchitto reported. With respect to the quality of the mother-child relationship and the long-term development of the child, “the studies have highly conflicting findings.”
At the end of the presentation, Professor Israël Nisand, MD, an ob.gyn. at the American Hospital of Paris and the former president of the National College of French Gynecologists and Obstetricians, made the following comment: “I often think that we underestimate the consequences that the mother’s posttraumatic stress has on the child postpartum.” He added, “Postpartum posttraumatic stress disorder is a reality. Yet it isn’t screened for, let alone treated, even though it has serious consequences for the child.”
Dr. Franchitto also brought up the impact on members of the health care staff, the “second victims” of the traumatic events that occur while caring for the women in the maternity ward. “The estimated prevalence of PTSD symptoms among midwives is 22.9%,” which could lead to “a loss of confidence and a desire to leave the profession.”
Providing psychoeducation to health care staff
Dr. Franchitto believes that it’s essential to also protect caregivers who work in maternity wards. “It’s important to have the support of colleagues” – in particular, of team leaders – “and to share one’s experiences,” as long as one knows how to recognize the symptoms of posttraumatic stress through one’s emotions and is able to verbalize them.
She went on to say that providing psychoeducation to health care staff is therefore to be encouraged, as is “simulation-based training, for learning how to manage problematic situations.”
This content was originally published on Medscape French edition. A translated version appeared on Medscape.com.
PAU, FRANCE – Postpartum posttraumatic stress disorder tends to get worse over the months following the birth of a child. Therefore, it’s necessary to screen for it as early on as possible and to ensure that women who are affected are given the proper treatment. This was the message delivered during the Infogyn 2022 conference by Ludivine Franchitto, MD, a child psychiatrist at Toulouse University Hospital, France. Because postpartum PTSD is still not fully recognized, treatment remains inadequate and poorly documented.
Impact on the caregivers as well
“The situation is the same as what we saw with postpartum depression. The debate went on for 20 years before its existence was formally declared,” Dr. Franchitto noted. But for her, the important thing is not knowing whether a traumatic stress state may be experienced by the mother who had complications during pregnancy or delivery. Instead, it’s about focusing on the repercussions for the child.
During her presentation, Dr. Franchitto also pointed out that it’s necessary to recognize that caregivers who work in maternity wards may also be negatively impacted, as they routinely see the complications that women have during pregnancy and delivery. These workers may also develop a PTSD state, requiring support so that they can properly carry out their duties.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-V), posttraumatic stress disorder arises after exposure to actual (or threatened) death, serious injury, or sexual violence. Individuals who have witnessed a traumatic event in person or who have experienced repeated (or extreme) exposure to aversive details of traumatic events may also develop PTSD.
Dr. Franchitto mentioned some of the criteria needed to make the diagnosis. “Intrusive distressing memories of the event, recurrent distressing dreams related to the event, persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the traumatic event, or negative alterations in cognitions and mood associated with the traumatic event. And the duration of the disturbance is more than 1 month.” There may also be marked alterations in arousal and reactivity associated with the traumatic event (for example, irritable behavior, loss of awareness of present surroundings).
Prevalent in 18% of women in high-risk groups
According to the studies, there is a wide variability of PTSD rates. If referring only to traumatic symptoms (for example, depressive syndrome, suicidal ideation, hyperreactivity, and persistent avoidance), the rate could reach up to 40%. A 2016 meta-analysis of 59 studies found that the prevalence of childbirth-related PTSD was 5.9%.
The authors distinguished two groups of women: those without complications during pregnancy or during delivery and those with severe complications related to the pregnancy, a fear of giving birth, a difficult delivery, an emergency C-section, a baby born prematurely with birth defects, etc. Their analysis showed PTSD rates of 4% and 18.5%, respectively.
Surprisingly, the major risk factor for PTSD turned out to be uncontrollable vomiting during pregnancy (seen in 40% of postpartum PTSD cases). The birth of a baby with birth defects was the second risk factor (35%), and the third, a history of violence in the mother’s childhood (34%). Women who experienced depression during the delivery were also at higher risk.
Other risk factors identified were lack of communication with the health care team, lack of consent, lack of support from the medical staff, and a long labor. Conversely, a sense of control and the support of a partner play a protective role.
Early screening
“If the symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder aren’t treated after delivery, they tend to get worse over the period of 1 to 6 months following the child’s birth,” Dr. Franchitto indicated. This is why it’s necessary to screen for it as early as possible – in particular, by having the women fill out the City Birth Trauma Scale questionnaire – and provide proper treatment accordingly. When seeking to limit the effects of stress, early intervention by a psychologist may be beneficial.
Psychotherapy is the recommended first-line treatment for PTSD, especially cognitive behavioral therapy and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing therapy. This approach aims to limit the mental and behavioral avoidance that prevents the traumatic memory from being integrated and processed as a regular memory.
The consequences that the mother’s PTSD state has on the child are well documented. “Children whose mothers had PTSD during pregnancy have a lower birth weight and a shorter breast-feeding duration,” Dr. Franchitto reported. With respect to the quality of the mother-child relationship and the long-term development of the child, “the studies have highly conflicting findings.”
At the end of the presentation, Professor Israël Nisand, MD, an ob.gyn. at the American Hospital of Paris and the former president of the National College of French Gynecologists and Obstetricians, made the following comment: “I often think that we underestimate the consequences that the mother’s posttraumatic stress has on the child postpartum.” He added, “Postpartum posttraumatic stress disorder is a reality. Yet it isn’t screened for, let alone treated, even though it has serious consequences for the child.”
Dr. Franchitto also brought up the impact on members of the health care staff, the “second victims” of the traumatic events that occur while caring for the women in the maternity ward. “The estimated prevalence of PTSD symptoms among midwives is 22.9%,” which could lead to “a loss of confidence and a desire to leave the profession.”
Providing psychoeducation to health care staff
Dr. Franchitto believes that it’s essential to also protect caregivers who work in maternity wards. “It’s important to have the support of colleagues” – in particular, of team leaders – “and to share one’s experiences,” as long as one knows how to recognize the symptoms of posttraumatic stress through one’s emotions and is able to verbalize them.
She went on to say that providing psychoeducation to health care staff is therefore to be encouraged, as is “simulation-based training, for learning how to manage problematic situations.”
This content was originally published on Medscape French edition. A translated version appeared on Medscape.com.
Meditation equal to first-line medication for anxiety
“I would encourage clinicians to list meditation training as one possible treatment option for patients who are diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Doctors should feel comfortable recommending in-person, group-based meditation classes,” study investigator Elizabeth A. Hoge, MD, director, Anxiety Disorders Research Program, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Screening recommended
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, panic disorder, and agoraphobia, are the most common type of mental disorder, affecting an estimated 301 million people worldwide. Owing to their high prevalence, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for anxiety disorders.
Effective treatments for anxiety disorders include medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy. However, not all patients have access to these interventions, respond to them, or are comfortable seeking care in a psychiatric setting.
Mindfulness meditation, which has risen in popularity in recent years, may help people experiencing intrusive, anxious thoughts. “By practicing mindfulness meditation, people learn not to be overwhelmed by those thoughts,” said Dr. Hoge.
The study included 276 adult patients with an anxiety disorder, mostly generalized anxiety or social anxiety. The mean age of the study population was 33 years; 75% were women, 59% were White, 15% were Black, and 20% were Asian.
Researchers randomly assigned 136 patients to receive MBSR and 140 to receive the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor escitalopram, a first-line medication for treating anxiety disorders.
The MBSR intervention included a weekly 2.5-hour class and a day-long weekend class. Participants also completed daily 45-minute guided meditation sessions at home. They learned mindfulness meditation exercises, including breath awareness, body scanning, and mindful movement.
Those in the escitalopram group initially received 10 mg of the oral drug daily. The dose was increased to 20 mg daily at week 2 if well tolerated.
The primary outcome was the score on the Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) scale for anxiety, assessed by clinicians blinded to treatment allocation. This instrument measures overall symptom severity on a scale from 1 (not at all ill) to 7 (most extremely ill) and can be used to assess different types of anxiety disorders, said Dr. Hoge.
Among the 208 participants who completed the study, the baseline mean CGI-S score was 4.44 for MBSR and 4.51 for escitalopram. At week 8, on the CGI-S scale, the MBSR group’s score improved by a mean of 1.35 points, and the escitalopram group’s score improved by 1.43 points (difference of –0.07; 95% CI, –0.38 to 0.23; P = .65).
The lower end of the confidence interval (–0.38) was smaller than the prespecified noninferiority margin of –0.495, indicating noninferiority of MBSR, compared with escitalopram.
Remarkable results
“What was remarkable was that the medication worked great, like it always does, but the meditation also worked great; we saw about a 30% drop in symptoms for both groups,” said Dr. Hoge. “That helps us know that meditation, and in particular mindfulness meditation, could be useful as a first-line treatment for patients with anxiety disorders.”
The patient-reported outcome of the Overall Anxiety Severity and Impairment Scale also showed no significant group differences. “It’s important to have the self-reports, because that gives us two ways to look at the information,” said Dr. Hoge.
Anecdotally, participants noted that the meditation helped with their personal relationships and with being “kinder to themselves,” said Dr. Hoge. “In meditation, there’s an implicit teaching to be accepting and nonjudgmental towards your own thoughts, and that teaches people to be more self-compassionate.”
Just over 78% of patients in the escitalopram group had at least one treatment-related adverse event (AE), which included sleep disturbances, nausea, fatigue, and headache, compared with 15.4% in the MBSR group.
The most common AE in the meditation group was anxiety, which is “counterintuitive” but represents “a momentary anxiety,” said Dr. Hoge. “People who are meditating have feelings come up that maybe they didn’t pay attention to before. This gives them an opportunity to process through those emotions.”
Fatigue was the next most common AE for meditators, which “makes sense,” since they’re putting away their phones and not being stimulated, said Dr. Hoge.
MBSR was delivered in person, which limits extrapolation to mindfulness apps or programs delivered over the internet. Dr. Hoge believes apps would likely be less effective because they don’t have the face-to-face component, instructors available for consultation, or fellow participants contributing group support.
But online classes might work if “the exact same class,” including all its components, is moved online, she said.
MBSR is available in all major U.S. cities, doesn’t require finding a therapist, and is available outside a mental health environment – for example, at yoga centers and some places of employment. Anyone can learn MBSR, although it takes time and commitment, said Dr. Hoge.
A time-tested intervention
Commenting on the study, psychiatrist Gregory Scott Brown, MD, affiliate faculty, University of Texas Dell Medical School, and author of “The Self-Healing Mind: An Essential Five-Step Practice for Overcoming Anxiety and Depression and Revitalizing Your Life,” said the results aren’t surprising inasmuch as mindfulness, including spirituality, breath work, and meditation, is a “time-tested and evidence-based” intervention.
“I’m encouraged by the fact studies like this are now being conducted and there’s more evidence that supports these mindfulness-based interventions, so they can start to make their way into standard-of-care treatments.” he said.
He noted that mindfulness can produce “long-term, sustainable improvements” and that the 45-minute daily home exercise included in the study “is not a huge time commitment when you talk about benefits you can potentially glean from incorporating that time.”
Because most study participants were women and “men are anxious too,” Dr. Brown said he would like to see the study replicated “with a more diverse pool of participants.”
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Hoge and Dr. Brown have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“I would encourage clinicians to list meditation training as one possible treatment option for patients who are diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Doctors should feel comfortable recommending in-person, group-based meditation classes,” study investigator Elizabeth A. Hoge, MD, director, Anxiety Disorders Research Program, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Screening recommended
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, panic disorder, and agoraphobia, are the most common type of mental disorder, affecting an estimated 301 million people worldwide. Owing to their high prevalence, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for anxiety disorders.
Effective treatments for anxiety disorders include medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy. However, not all patients have access to these interventions, respond to them, or are comfortable seeking care in a psychiatric setting.
Mindfulness meditation, which has risen in popularity in recent years, may help people experiencing intrusive, anxious thoughts. “By practicing mindfulness meditation, people learn not to be overwhelmed by those thoughts,” said Dr. Hoge.
The study included 276 adult patients with an anxiety disorder, mostly generalized anxiety or social anxiety. The mean age of the study population was 33 years; 75% were women, 59% were White, 15% were Black, and 20% were Asian.
Researchers randomly assigned 136 patients to receive MBSR and 140 to receive the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor escitalopram, a first-line medication for treating anxiety disorders.
The MBSR intervention included a weekly 2.5-hour class and a day-long weekend class. Participants also completed daily 45-minute guided meditation sessions at home. They learned mindfulness meditation exercises, including breath awareness, body scanning, and mindful movement.
Those in the escitalopram group initially received 10 mg of the oral drug daily. The dose was increased to 20 mg daily at week 2 if well tolerated.
The primary outcome was the score on the Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) scale for anxiety, assessed by clinicians blinded to treatment allocation. This instrument measures overall symptom severity on a scale from 1 (not at all ill) to 7 (most extremely ill) and can be used to assess different types of anxiety disorders, said Dr. Hoge.
Among the 208 participants who completed the study, the baseline mean CGI-S score was 4.44 for MBSR and 4.51 for escitalopram. At week 8, on the CGI-S scale, the MBSR group’s score improved by a mean of 1.35 points, and the escitalopram group’s score improved by 1.43 points (difference of –0.07; 95% CI, –0.38 to 0.23; P = .65).
The lower end of the confidence interval (–0.38) was smaller than the prespecified noninferiority margin of –0.495, indicating noninferiority of MBSR, compared with escitalopram.
Remarkable results
“What was remarkable was that the medication worked great, like it always does, but the meditation also worked great; we saw about a 30% drop in symptoms for both groups,” said Dr. Hoge. “That helps us know that meditation, and in particular mindfulness meditation, could be useful as a first-line treatment for patients with anxiety disorders.”
The patient-reported outcome of the Overall Anxiety Severity and Impairment Scale also showed no significant group differences. “It’s important to have the self-reports, because that gives us two ways to look at the information,” said Dr. Hoge.
Anecdotally, participants noted that the meditation helped with their personal relationships and with being “kinder to themselves,” said Dr. Hoge. “In meditation, there’s an implicit teaching to be accepting and nonjudgmental towards your own thoughts, and that teaches people to be more self-compassionate.”
Just over 78% of patients in the escitalopram group had at least one treatment-related adverse event (AE), which included sleep disturbances, nausea, fatigue, and headache, compared with 15.4% in the MBSR group.
The most common AE in the meditation group was anxiety, which is “counterintuitive” but represents “a momentary anxiety,” said Dr. Hoge. “People who are meditating have feelings come up that maybe they didn’t pay attention to before. This gives them an opportunity to process through those emotions.”
Fatigue was the next most common AE for meditators, which “makes sense,” since they’re putting away their phones and not being stimulated, said Dr. Hoge.
MBSR was delivered in person, which limits extrapolation to mindfulness apps or programs delivered over the internet. Dr. Hoge believes apps would likely be less effective because they don’t have the face-to-face component, instructors available for consultation, or fellow participants contributing group support.
But online classes might work if “the exact same class,” including all its components, is moved online, she said.
MBSR is available in all major U.S. cities, doesn’t require finding a therapist, and is available outside a mental health environment – for example, at yoga centers and some places of employment. Anyone can learn MBSR, although it takes time and commitment, said Dr. Hoge.
A time-tested intervention
Commenting on the study, psychiatrist Gregory Scott Brown, MD, affiliate faculty, University of Texas Dell Medical School, and author of “The Self-Healing Mind: An Essential Five-Step Practice for Overcoming Anxiety and Depression and Revitalizing Your Life,” said the results aren’t surprising inasmuch as mindfulness, including spirituality, breath work, and meditation, is a “time-tested and evidence-based” intervention.
“I’m encouraged by the fact studies like this are now being conducted and there’s more evidence that supports these mindfulness-based interventions, so they can start to make their way into standard-of-care treatments.” he said.
He noted that mindfulness can produce “long-term, sustainable improvements” and that the 45-minute daily home exercise included in the study “is not a huge time commitment when you talk about benefits you can potentially glean from incorporating that time.”
Because most study participants were women and “men are anxious too,” Dr. Brown said he would like to see the study replicated “with a more diverse pool of participants.”
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Hoge and Dr. Brown have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“I would encourage clinicians to list meditation training as one possible treatment option for patients who are diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Doctors should feel comfortable recommending in-person, group-based meditation classes,” study investigator Elizabeth A. Hoge, MD, director, Anxiety Disorders Research Program, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Screening recommended
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, panic disorder, and agoraphobia, are the most common type of mental disorder, affecting an estimated 301 million people worldwide. Owing to their high prevalence, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for anxiety disorders.
Effective treatments for anxiety disorders include medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy. However, not all patients have access to these interventions, respond to them, or are comfortable seeking care in a psychiatric setting.
Mindfulness meditation, which has risen in popularity in recent years, may help people experiencing intrusive, anxious thoughts. “By practicing mindfulness meditation, people learn not to be overwhelmed by those thoughts,” said Dr. Hoge.
The study included 276 adult patients with an anxiety disorder, mostly generalized anxiety or social anxiety. The mean age of the study population was 33 years; 75% were women, 59% were White, 15% were Black, and 20% were Asian.
Researchers randomly assigned 136 patients to receive MBSR and 140 to receive the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor escitalopram, a first-line medication for treating anxiety disorders.
The MBSR intervention included a weekly 2.5-hour class and a day-long weekend class. Participants also completed daily 45-minute guided meditation sessions at home. They learned mindfulness meditation exercises, including breath awareness, body scanning, and mindful movement.
Those in the escitalopram group initially received 10 mg of the oral drug daily. The dose was increased to 20 mg daily at week 2 if well tolerated.
The primary outcome was the score on the Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) scale for anxiety, assessed by clinicians blinded to treatment allocation. This instrument measures overall symptom severity on a scale from 1 (not at all ill) to 7 (most extremely ill) and can be used to assess different types of anxiety disorders, said Dr. Hoge.
Among the 208 participants who completed the study, the baseline mean CGI-S score was 4.44 for MBSR and 4.51 for escitalopram. At week 8, on the CGI-S scale, the MBSR group’s score improved by a mean of 1.35 points, and the escitalopram group’s score improved by 1.43 points (difference of –0.07; 95% CI, –0.38 to 0.23; P = .65).
The lower end of the confidence interval (–0.38) was smaller than the prespecified noninferiority margin of –0.495, indicating noninferiority of MBSR, compared with escitalopram.
Remarkable results
“What was remarkable was that the medication worked great, like it always does, but the meditation also worked great; we saw about a 30% drop in symptoms for both groups,” said Dr. Hoge. “That helps us know that meditation, and in particular mindfulness meditation, could be useful as a first-line treatment for patients with anxiety disorders.”
The patient-reported outcome of the Overall Anxiety Severity and Impairment Scale also showed no significant group differences. “It’s important to have the self-reports, because that gives us two ways to look at the information,” said Dr. Hoge.
Anecdotally, participants noted that the meditation helped with their personal relationships and with being “kinder to themselves,” said Dr. Hoge. “In meditation, there’s an implicit teaching to be accepting and nonjudgmental towards your own thoughts, and that teaches people to be more self-compassionate.”
Just over 78% of patients in the escitalopram group had at least one treatment-related adverse event (AE), which included sleep disturbances, nausea, fatigue, and headache, compared with 15.4% in the MBSR group.
The most common AE in the meditation group was anxiety, which is “counterintuitive” but represents “a momentary anxiety,” said Dr. Hoge. “People who are meditating have feelings come up that maybe they didn’t pay attention to before. This gives them an opportunity to process through those emotions.”
Fatigue was the next most common AE for meditators, which “makes sense,” since they’re putting away their phones and not being stimulated, said Dr. Hoge.
MBSR was delivered in person, which limits extrapolation to mindfulness apps or programs delivered over the internet. Dr. Hoge believes apps would likely be less effective because they don’t have the face-to-face component, instructors available for consultation, or fellow participants contributing group support.
But online classes might work if “the exact same class,” including all its components, is moved online, she said.
MBSR is available in all major U.S. cities, doesn’t require finding a therapist, and is available outside a mental health environment – for example, at yoga centers and some places of employment. Anyone can learn MBSR, although it takes time and commitment, said Dr. Hoge.
A time-tested intervention
Commenting on the study, psychiatrist Gregory Scott Brown, MD, affiliate faculty, University of Texas Dell Medical School, and author of “The Self-Healing Mind: An Essential Five-Step Practice for Overcoming Anxiety and Depression and Revitalizing Your Life,” said the results aren’t surprising inasmuch as mindfulness, including spirituality, breath work, and meditation, is a “time-tested and evidence-based” intervention.
“I’m encouraged by the fact studies like this are now being conducted and there’s more evidence that supports these mindfulness-based interventions, so they can start to make their way into standard-of-care treatments.” he said.
He noted that mindfulness can produce “long-term, sustainable improvements” and that the 45-minute daily home exercise included in the study “is not a huge time commitment when you talk about benefits you can potentially glean from incorporating that time.”
Because most study participants were women and “men are anxious too,” Dr. Brown said he would like to see the study replicated “with a more diverse pool of participants.”
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Hoge and Dr. Brown have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
NSAIDs for spondyloarthritis may affect time to conception
PHILADELPHIA – Women with spondyloarthritis (SpA) who are desiring pregnancy may want to consider decreasing use or discontinuing use (with supervision) of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs before conception, new data suggest.
Researchers have found a connection between NSAID use and age and a significantly longer time to conception among women with spondyloarthritis. Sabrina Hamroun, MMed, with the rheumatology department at the University Hospital Cochin, Paris, presented the findings during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
SpA commonly affects women of childbearing age, but data are sparse regarding the effects of disease on fertility.
Patients in the study were taken from the French multicenter cohort GR2 from 2015 to June 2021.
Among the 207 patients with SpA in the cohort, 88 were selected for analysis of time to conception. Of these, 56 patients (63.6%) had a clinical pregnancy during follow-up.
Subfertility group took an average of 16 months to get pregnant
Subfertility was observed in 40 (45.4%) of the women, with an average time to conception of 16.1 months. A woman was considered subfertile if her time to conception was more than 12 months or if she did not become pregnant.
The average preconception Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index score was 2.9 (+/- 2.1), the authors noted. The average age of the participants was 32 years.
Twenty-three patients were treated with NSAIDs, eight with corticosteroids, 12 with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and 61 with biologics.
Researchers adjusted for factors including age, body mass index, disease duration and severity, smoking, form of SpA (axial, peripheral, or both), and medication in the preconception period.
They found significant associations between longer time to conception and age (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-1.40; P < .001), and a much higher hazard ratio with the use of NSAIDs during preconception (HR, 3.01; 95% CI, 2.15-3.85; P = .01).
Some data unavailable
Ms. Hamroun acknowledged that no data were available on the frequency of sexual intercourse or quality of life, factors that could affect time to conception. Women were asked when they discontinued contraceptive use and actively began trying to become pregnant.
She stated that information on the dose of NSAIDs used by the patients was incomplete, noting, “We were therefore unable to adjust the results of our statistical analyses on the dose used by patients.”
Additionally, because the study participants were patients at tertiary centers in France and had more severe disease, the results may not be generalizable to all women of childbearing age. Patients with less severe SpA are often managed in outpatient settings in France, she said.
When asked about alternatives to NSAIDs, Ms. Hamroun said that anti–tumor necrosis factor agents with low placental passage may be a good alternative “if a woman with long-standing difficulties to conceive needs a regular use of NSAIDs to control disease activity, in the absence of any other cause of subfertility.”
The patient’s age must also be considered, she noted.
“A therapeutic switch may be favored in a woman over 35 years of age, for example, whose fertility is already impaired by age,” Ms. Hamroun said.
As for the mechanism that might explain the effects of NSAIDs on conception, Ms. Hamroun said that prostaglandins are essential to ovulation and embryo implantation and explained that NSAIDs may work against ovulation and result in poor implantation (miscarriage) by blocking prostaglandins.
She pointed out that her results are in line with the ACR’s recommendation to discontinue NSAID use during the preconception period in women with SpA who are having difficulty conceiving.
Control before conception is important
Sinead Maguire, MD, a clinical and research fellow in the Spondylitis Program at Toronto (Ont.) Western Hospital who was not part of the study, said the study highlights the importance of optimizing disease control before conception.
“There are a number of things rheumatologists can do to support our SpA patients when they are trying to conceive,” she told this news organization. “One of the most important issues to address is ensuring their SpA is in remission and continues to remain so. For that reason, if a woman is requiring regular NSAIDs for symptom control, the results of this study might encourage me to consider a biologic agent sooner to ensure remission.”
She urged women who want to become pregnant to discuss medications with their rheumatologist before trying to conceive.
“It is very exciting to see studies such as this so that rheumatologists can provide answers to our patients’ questions with evidence-based advice,” she said.
Ms. Hamroun and several coauthors had no disclosures. Other coauthors disclosed relationships with companies including Merck/MSD, Novartis, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and/or UCB. Dr. Maguire reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – Women with spondyloarthritis (SpA) who are desiring pregnancy may want to consider decreasing use or discontinuing use (with supervision) of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs before conception, new data suggest.
Researchers have found a connection between NSAID use and age and a significantly longer time to conception among women with spondyloarthritis. Sabrina Hamroun, MMed, with the rheumatology department at the University Hospital Cochin, Paris, presented the findings during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
SpA commonly affects women of childbearing age, but data are sparse regarding the effects of disease on fertility.
Patients in the study were taken from the French multicenter cohort GR2 from 2015 to June 2021.
Among the 207 patients with SpA in the cohort, 88 were selected for analysis of time to conception. Of these, 56 patients (63.6%) had a clinical pregnancy during follow-up.
Subfertility group took an average of 16 months to get pregnant
Subfertility was observed in 40 (45.4%) of the women, with an average time to conception of 16.1 months. A woman was considered subfertile if her time to conception was more than 12 months or if she did not become pregnant.
The average preconception Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index score was 2.9 (+/- 2.1), the authors noted. The average age of the participants was 32 years.
Twenty-three patients were treated with NSAIDs, eight with corticosteroids, 12 with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and 61 with biologics.
Researchers adjusted for factors including age, body mass index, disease duration and severity, smoking, form of SpA (axial, peripheral, or both), and medication in the preconception period.
They found significant associations between longer time to conception and age (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-1.40; P < .001), and a much higher hazard ratio with the use of NSAIDs during preconception (HR, 3.01; 95% CI, 2.15-3.85; P = .01).
Some data unavailable
Ms. Hamroun acknowledged that no data were available on the frequency of sexual intercourse or quality of life, factors that could affect time to conception. Women were asked when they discontinued contraceptive use and actively began trying to become pregnant.
She stated that information on the dose of NSAIDs used by the patients was incomplete, noting, “We were therefore unable to adjust the results of our statistical analyses on the dose used by patients.”
Additionally, because the study participants were patients at tertiary centers in France and had more severe disease, the results may not be generalizable to all women of childbearing age. Patients with less severe SpA are often managed in outpatient settings in France, she said.
When asked about alternatives to NSAIDs, Ms. Hamroun said that anti–tumor necrosis factor agents with low placental passage may be a good alternative “if a woman with long-standing difficulties to conceive needs a regular use of NSAIDs to control disease activity, in the absence of any other cause of subfertility.”
The patient’s age must also be considered, she noted.
“A therapeutic switch may be favored in a woman over 35 years of age, for example, whose fertility is already impaired by age,” Ms. Hamroun said.
As for the mechanism that might explain the effects of NSAIDs on conception, Ms. Hamroun said that prostaglandins are essential to ovulation and embryo implantation and explained that NSAIDs may work against ovulation and result in poor implantation (miscarriage) by blocking prostaglandins.
She pointed out that her results are in line with the ACR’s recommendation to discontinue NSAID use during the preconception period in women with SpA who are having difficulty conceiving.
Control before conception is important
Sinead Maguire, MD, a clinical and research fellow in the Spondylitis Program at Toronto (Ont.) Western Hospital who was not part of the study, said the study highlights the importance of optimizing disease control before conception.
“There are a number of things rheumatologists can do to support our SpA patients when they are trying to conceive,” she told this news organization. “One of the most important issues to address is ensuring their SpA is in remission and continues to remain so. For that reason, if a woman is requiring regular NSAIDs for symptom control, the results of this study might encourage me to consider a biologic agent sooner to ensure remission.”
She urged women who want to become pregnant to discuss medications with their rheumatologist before trying to conceive.
“It is very exciting to see studies such as this so that rheumatologists can provide answers to our patients’ questions with evidence-based advice,” she said.
Ms. Hamroun and several coauthors had no disclosures. Other coauthors disclosed relationships with companies including Merck/MSD, Novartis, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and/or UCB. Dr. Maguire reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA – Women with spondyloarthritis (SpA) who are desiring pregnancy may want to consider decreasing use or discontinuing use (with supervision) of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs before conception, new data suggest.
Researchers have found a connection between NSAID use and age and a significantly longer time to conception among women with spondyloarthritis. Sabrina Hamroun, MMed, with the rheumatology department at the University Hospital Cochin, Paris, presented the findings during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
SpA commonly affects women of childbearing age, but data are sparse regarding the effects of disease on fertility.
Patients in the study were taken from the French multicenter cohort GR2 from 2015 to June 2021.
Among the 207 patients with SpA in the cohort, 88 were selected for analysis of time to conception. Of these, 56 patients (63.6%) had a clinical pregnancy during follow-up.
Subfertility group took an average of 16 months to get pregnant
Subfertility was observed in 40 (45.4%) of the women, with an average time to conception of 16.1 months. A woman was considered subfertile if her time to conception was more than 12 months or if she did not become pregnant.
The average preconception Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index score was 2.9 (+/- 2.1), the authors noted. The average age of the participants was 32 years.
Twenty-three patients were treated with NSAIDs, eight with corticosteroids, 12 with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and 61 with biologics.
Researchers adjusted for factors including age, body mass index, disease duration and severity, smoking, form of SpA (axial, peripheral, or both), and medication in the preconception period.
They found significant associations between longer time to conception and age (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-1.40; P < .001), and a much higher hazard ratio with the use of NSAIDs during preconception (HR, 3.01; 95% CI, 2.15-3.85; P = .01).
Some data unavailable
Ms. Hamroun acknowledged that no data were available on the frequency of sexual intercourse or quality of life, factors that could affect time to conception. Women were asked when they discontinued contraceptive use and actively began trying to become pregnant.
She stated that information on the dose of NSAIDs used by the patients was incomplete, noting, “We were therefore unable to adjust the results of our statistical analyses on the dose used by patients.”
Additionally, because the study participants were patients at tertiary centers in France and had more severe disease, the results may not be generalizable to all women of childbearing age. Patients with less severe SpA are often managed in outpatient settings in France, she said.
When asked about alternatives to NSAIDs, Ms. Hamroun said that anti–tumor necrosis factor agents with low placental passage may be a good alternative “if a woman with long-standing difficulties to conceive needs a regular use of NSAIDs to control disease activity, in the absence of any other cause of subfertility.”
The patient’s age must also be considered, she noted.
“A therapeutic switch may be favored in a woman over 35 years of age, for example, whose fertility is already impaired by age,” Ms. Hamroun said.
As for the mechanism that might explain the effects of NSAIDs on conception, Ms. Hamroun said that prostaglandins are essential to ovulation and embryo implantation and explained that NSAIDs may work against ovulation and result in poor implantation (miscarriage) by blocking prostaglandins.
She pointed out that her results are in line with the ACR’s recommendation to discontinue NSAID use during the preconception period in women with SpA who are having difficulty conceiving.
Control before conception is important
Sinead Maguire, MD, a clinical and research fellow in the Spondylitis Program at Toronto (Ont.) Western Hospital who was not part of the study, said the study highlights the importance of optimizing disease control before conception.
“There are a number of things rheumatologists can do to support our SpA patients when they are trying to conceive,” she told this news organization. “One of the most important issues to address is ensuring their SpA is in remission and continues to remain so. For that reason, if a woman is requiring regular NSAIDs for symptom control, the results of this study might encourage me to consider a biologic agent sooner to ensure remission.”
She urged women who want to become pregnant to discuss medications with their rheumatologist before trying to conceive.
“It is very exciting to see studies such as this so that rheumatologists can provide answers to our patients’ questions with evidence-based advice,” she said.
Ms. Hamroun and several coauthors had no disclosures. Other coauthors disclosed relationships with companies including Merck/MSD, Novartis, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and/or UCB. Dr. Maguire reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2022
Analysis affirms that giving birth protects against endometrial cancer
Compared with having no children, the risk reduction for endometrial cancer was 21% with having one child, 38% with having two, and 51% with having three, Gunn-Helen Moen, MSc, PhD, a research fellow at the University of Queensland Institute for Molecular Bioscience in St. Lucia, Australia, and the senior author of the study, said in an email.
In the United States, the prevalence of endometrial cancer is 25.7 per 100,000 women per year, with a lifetime risk of 2.8%.
Multiple observational studies have linked giving birth to risk of endometrial cancer. For the new study, Dr. Moen and her team assessed various risk factors related to ovulation and reproductive function using Mendelian randomization, an epidemiological technique that deploys genetic variants to detect cause-and-effect relationships between potentially modifiable risk factors and health outcomes in observational data.
The researcher published their findings in BMC Medicine.
Leverage genetic data
The study used detailed genetic and health data from the UK Biobank, a databank with more than half a million participants. Genetic variants related to some of the risk factors were used to assess whether the variants make people more likely to develop endometrial cancer.
Genomewide significant single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to number of live births, age at menopause and menarche, and body mass index (BMI) had been identified in previous studies, the researchers reported. They conducted genomewide association analyses of the databank to identify SNPs associated with years ovulating, years using the contraceptive pill, and age at last live birth.
The MR analysis showed a potential causal effect for the number of live births (inverse variance–weighted odds ratio, 0.537) and number of years ovulating (IVW OR, 1.051), in addition to known risk factors of BMI, age at menarche, and age at menopause.
A further multivariable MR analysis showed that number of births had a negative causal effect on endometrial cancer risk (OR, 0.783), independent of the causal effect of known risk factors such as BMI, age at menarche and age at menopause.
Reported limitations included being unable to perform MR analyses on some factors, such as oral contraceptive use, because of a lack of valid genetic instruments. The researchers could not perform an age adjustment at diagnosis because of a lack of data.
In addition, the genetic data came exclusively from White women of European ancestry.
‘A personal choice’
Other investigators have hypothesized that the protective effect of childbirth may be caused by shedding of malignant and premalignant endometrial cells during and after childbirth and exposure to high levels of progesterone in late stages of pregnancy, the research team noted.
Dr. Moen said, based on the results, physicians might consider number of childbirths in assessing a patient’s risk of endometrial cancer.
However, Britton Trabert, MSPH, MS, PhD, an epidemiologist and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said it’s unlikely the findings will affect clinical practice given that they “largely replicate well-characterized endometrial cancer risk associations.”
“Pregnancy and childbirth are a personal choice and is not largely regarded as a modifiable factor for cancer prevention,” said Dr. Trabert, who was not involved in the study.
The study’s investigators reported funding from the governments of Australia, Norway and the United Kingdom and the British Heart Foundation. No financial conflicts of interest were reported. Dr. Trabert reported no relevant financial interests.
Compared with having no children, the risk reduction for endometrial cancer was 21% with having one child, 38% with having two, and 51% with having three, Gunn-Helen Moen, MSc, PhD, a research fellow at the University of Queensland Institute for Molecular Bioscience in St. Lucia, Australia, and the senior author of the study, said in an email.
In the United States, the prevalence of endometrial cancer is 25.7 per 100,000 women per year, with a lifetime risk of 2.8%.
Multiple observational studies have linked giving birth to risk of endometrial cancer. For the new study, Dr. Moen and her team assessed various risk factors related to ovulation and reproductive function using Mendelian randomization, an epidemiological technique that deploys genetic variants to detect cause-and-effect relationships between potentially modifiable risk factors and health outcomes in observational data.
The researcher published their findings in BMC Medicine.
Leverage genetic data
The study used detailed genetic and health data from the UK Biobank, a databank with more than half a million participants. Genetic variants related to some of the risk factors were used to assess whether the variants make people more likely to develop endometrial cancer.
Genomewide significant single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to number of live births, age at menopause and menarche, and body mass index (BMI) had been identified in previous studies, the researchers reported. They conducted genomewide association analyses of the databank to identify SNPs associated with years ovulating, years using the contraceptive pill, and age at last live birth.
The MR analysis showed a potential causal effect for the number of live births (inverse variance–weighted odds ratio, 0.537) and number of years ovulating (IVW OR, 1.051), in addition to known risk factors of BMI, age at menarche, and age at menopause.
A further multivariable MR analysis showed that number of births had a negative causal effect on endometrial cancer risk (OR, 0.783), independent of the causal effect of known risk factors such as BMI, age at menarche and age at menopause.
Reported limitations included being unable to perform MR analyses on some factors, such as oral contraceptive use, because of a lack of valid genetic instruments. The researchers could not perform an age adjustment at diagnosis because of a lack of data.
In addition, the genetic data came exclusively from White women of European ancestry.
‘A personal choice’
Other investigators have hypothesized that the protective effect of childbirth may be caused by shedding of malignant and premalignant endometrial cells during and after childbirth and exposure to high levels of progesterone in late stages of pregnancy, the research team noted.
Dr. Moen said, based on the results, physicians might consider number of childbirths in assessing a patient’s risk of endometrial cancer.
However, Britton Trabert, MSPH, MS, PhD, an epidemiologist and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said it’s unlikely the findings will affect clinical practice given that they “largely replicate well-characterized endometrial cancer risk associations.”
“Pregnancy and childbirth are a personal choice and is not largely regarded as a modifiable factor for cancer prevention,” said Dr. Trabert, who was not involved in the study.
The study’s investigators reported funding from the governments of Australia, Norway and the United Kingdom and the British Heart Foundation. No financial conflicts of interest were reported. Dr. Trabert reported no relevant financial interests.
Compared with having no children, the risk reduction for endometrial cancer was 21% with having one child, 38% with having two, and 51% with having three, Gunn-Helen Moen, MSc, PhD, a research fellow at the University of Queensland Institute for Molecular Bioscience in St. Lucia, Australia, and the senior author of the study, said in an email.
In the United States, the prevalence of endometrial cancer is 25.7 per 100,000 women per year, with a lifetime risk of 2.8%.
Multiple observational studies have linked giving birth to risk of endometrial cancer. For the new study, Dr. Moen and her team assessed various risk factors related to ovulation and reproductive function using Mendelian randomization, an epidemiological technique that deploys genetic variants to detect cause-and-effect relationships between potentially modifiable risk factors and health outcomes in observational data.
The researcher published their findings in BMC Medicine.
Leverage genetic data
The study used detailed genetic and health data from the UK Biobank, a databank with more than half a million participants. Genetic variants related to some of the risk factors were used to assess whether the variants make people more likely to develop endometrial cancer.
Genomewide significant single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to number of live births, age at menopause and menarche, and body mass index (BMI) had been identified in previous studies, the researchers reported. They conducted genomewide association analyses of the databank to identify SNPs associated with years ovulating, years using the contraceptive pill, and age at last live birth.
The MR analysis showed a potential causal effect for the number of live births (inverse variance–weighted odds ratio, 0.537) and number of years ovulating (IVW OR, 1.051), in addition to known risk factors of BMI, age at menarche, and age at menopause.
A further multivariable MR analysis showed that number of births had a negative causal effect on endometrial cancer risk (OR, 0.783), independent of the causal effect of known risk factors such as BMI, age at menarche and age at menopause.
Reported limitations included being unable to perform MR analyses on some factors, such as oral contraceptive use, because of a lack of valid genetic instruments. The researchers could not perform an age adjustment at diagnosis because of a lack of data.
In addition, the genetic data came exclusively from White women of European ancestry.
‘A personal choice’
Other investigators have hypothesized that the protective effect of childbirth may be caused by shedding of malignant and premalignant endometrial cells during and after childbirth and exposure to high levels of progesterone in late stages of pregnancy, the research team noted.
Dr. Moen said, based on the results, physicians might consider number of childbirths in assessing a patient’s risk of endometrial cancer.
However, Britton Trabert, MSPH, MS, PhD, an epidemiologist and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said it’s unlikely the findings will affect clinical practice given that they “largely replicate well-characterized endometrial cancer risk associations.”
“Pregnancy and childbirth are a personal choice and is not largely regarded as a modifiable factor for cancer prevention,” said Dr. Trabert, who was not involved in the study.
The study’s investigators reported funding from the governments of Australia, Norway and the United Kingdom and the British Heart Foundation. No financial conflicts of interest were reported. Dr. Trabert reported no relevant financial interests.
FROM BMC MEDICINE
The clitoris steps into the spotlight with major scientific discovery
The patients of Jill Krapf, MD, are often too embarrassed to tell her about discomfort in their clitoris.
“I ask all of my patients about clitoral pain, and it is often the first time they have ever been asked about this,” says Dr. Krapf, the associate director of the Center for Vulvovaginal Disorders, a private clinic in Washington and New York.
Dr. Krapf is an ob.gyn. who specializes in female sexual pain that involves the pelvis, vagina, and vulva.
Many of the conditions Dr. Krapf treats don’t have outward symptoms that appear abnormal, but internally, there are damaged or irritated nerves that can result in hypersensitivity, unwanted arousal, or pain.
“Most recent research indicates that even a herniated disk or tear in the spine can lead to clitoral or vulvar symptoms, just like sciatica pain that shoots down the leg is related to issues in the spine,” Dr. Krapf says.
Dr. Krapf was excited to read of a new discovery: Dr. Krapf and other doctors are hopeful that the attention to the clitoris will spark more interest and comprehensive education among people in their field. They also hope it will empower patients to seek medical help if they are having issues with their clitoris.
“Female sexual health has historically been underfunded, especially compared with male sexual health, like erectile dysfunction,” Dr. Krapf says. “Optimizing vulvar and vaginal health is not only necessary for sexual well-being.”
Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming care, led the study, which was presented at the Sexual Medicine Society of North America conference in October. Dr. Peters says he hopes that the new information decreases stigma that the clitoris is not worthy of the same medical attention that other organs of the body receive.
When the clitoris doesn’t properly function, there can be harm to a person’s physical and mental health. Paying attention to discomfort in the clitoris, and seeking medical attention, can help catch and prevent some urinary and vaginal infections.
“The fact that it took until 2022 for someone to do this work speaks to how little attention the clitoris has received,” says Dr. Peters, an assistant professor of surgery at the Oregon Health and Science University School of Medicine, Portland.
What’s inside?
Dr. Peters and his colleagues completed the study by taking clitoral nerve tissue from seven adult transgender men who had received gender-affirming genital surgery. The tissues were dyed and magnified 1,000 times under a microscope so the researchers could count nerve fibers.
Dr. Peters says the finding is important because many surgeries take place in the groin region – like hip replacements, episiotomies during childbirth, and pelvic mesh procedures – and the revived attention to the clitoris may help health care providers know where nerves are so that injuries from medical mistakes are prevented.
“Nerves are at risk of damage if it’s not understood where they are at all times,” he says.
Dr. Peters hopes the new finding will help create new surgical techniques for nerve repair and offer insight for gender-affirming phalloplasty, which is the surgical construction of a penis often for transmasculine people.
Ownership of the body part
When it comes to the clitoris, no one type of doctor has specialized in the sex organ.
Urologists, gynecologists, plastic surgeons, and sex therapists all address potential problems that can arise with the clitoris and its surrounding body parts. But specialists like Dr. Krapf are few and far between.
It wasn’t until 2005 that Australian urologist Helen O’Connell found that the clitoris is filled with erectile and non-erectile tissues that are often hidden in anatomy drawings by fat and bone. And it wasn’t until the early 2000s that researchers began delving in earnest into the anatomy of the clitoris and how it functions.
And a 2018 study showed that if more doctors examined the clitoris, they could identify issues like adhesions or infections in the area, most of which can be treated without surgery.
A body part built for pleasure
Randi Levinson, a sex, marriage, and family therapist in Los Angeles, sees patients who have less sensation in the clitoris or pain while having sex, many of whom have recently given birth or are going through menopause.
Women often become embarrassed when they can’t orgasm, or have less sensation in the clitoris, but tend to avoid seeking medical advice, she says. Normalizing discussions about women’s pleasure and the vast anatomy that supports it may help some of her patients.
“The more normal it is to talk about and explore women’s pleasure, the less shame women will have when getting help when they aren’t experiencing pleasure,” Ms. Levinson says. “I have many ... clients who experience pain and discomfort with sex [after pregnancy] and no longer feel pleasure and are concerned that something is wrong with them.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The patients of Jill Krapf, MD, are often too embarrassed to tell her about discomfort in their clitoris.
“I ask all of my patients about clitoral pain, and it is often the first time they have ever been asked about this,” says Dr. Krapf, the associate director of the Center for Vulvovaginal Disorders, a private clinic in Washington and New York.
Dr. Krapf is an ob.gyn. who specializes in female sexual pain that involves the pelvis, vagina, and vulva.
Many of the conditions Dr. Krapf treats don’t have outward symptoms that appear abnormal, but internally, there are damaged or irritated nerves that can result in hypersensitivity, unwanted arousal, or pain.
“Most recent research indicates that even a herniated disk or tear in the spine can lead to clitoral or vulvar symptoms, just like sciatica pain that shoots down the leg is related to issues in the spine,” Dr. Krapf says.
Dr. Krapf was excited to read of a new discovery: Dr. Krapf and other doctors are hopeful that the attention to the clitoris will spark more interest and comprehensive education among people in their field. They also hope it will empower patients to seek medical help if they are having issues with their clitoris.
“Female sexual health has historically been underfunded, especially compared with male sexual health, like erectile dysfunction,” Dr. Krapf says. “Optimizing vulvar and vaginal health is not only necessary for sexual well-being.”
Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming care, led the study, which was presented at the Sexual Medicine Society of North America conference in October. Dr. Peters says he hopes that the new information decreases stigma that the clitoris is not worthy of the same medical attention that other organs of the body receive.
When the clitoris doesn’t properly function, there can be harm to a person’s physical and mental health. Paying attention to discomfort in the clitoris, and seeking medical attention, can help catch and prevent some urinary and vaginal infections.
“The fact that it took until 2022 for someone to do this work speaks to how little attention the clitoris has received,” says Dr. Peters, an assistant professor of surgery at the Oregon Health and Science University School of Medicine, Portland.
What’s inside?
Dr. Peters and his colleagues completed the study by taking clitoral nerve tissue from seven adult transgender men who had received gender-affirming genital surgery. The tissues were dyed and magnified 1,000 times under a microscope so the researchers could count nerve fibers.
Dr. Peters says the finding is important because many surgeries take place in the groin region – like hip replacements, episiotomies during childbirth, and pelvic mesh procedures – and the revived attention to the clitoris may help health care providers know where nerves are so that injuries from medical mistakes are prevented.
“Nerves are at risk of damage if it’s not understood where they are at all times,” he says.
Dr. Peters hopes the new finding will help create new surgical techniques for nerve repair and offer insight for gender-affirming phalloplasty, which is the surgical construction of a penis often for transmasculine people.
Ownership of the body part
When it comes to the clitoris, no one type of doctor has specialized in the sex organ.
Urologists, gynecologists, plastic surgeons, and sex therapists all address potential problems that can arise with the clitoris and its surrounding body parts. But specialists like Dr. Krapf are few and far between.
It wasn’t until 2005 that Australian urologist Helen O’Connell found that the clitoris is filled with erectile and non-erectile tissues that are often hidden in anatomy drawings by fat and bone. And it wasn’t until the early 2000s that researchers began delving in earnest into the anatomy of the clitoris and how it functions.
And a 2018 study showed that if more doctors examined the clitoris, they could identify issues like adhesions or infections in the area, most of which can be treated without surgery.
A body part built for pleasure
Randi Levinson, a sex, marriage, and family therapist in Los Angeles, sees patients who have less sensation in the clitoris or pain while having sex, many of whom have recently given birth or are going through menopause.
Women often become embarrassed when they can’t orgasm, or have less sensation in the clitoris, but tend to avoid seeking medical advice, she says. Normalizing discussions about women’s pleasure and the vast anatomy that supports it may help some of her patients.
“The more normal it is to talk about and explore women’s pleasure, the less shame women will have when getting help when they aren’t experiencing pleasure,” Ms. Levinson says. “I have many ... clients who experience pain and discomfort with sex [after pregnancy] and no longer feel pleasure and are concerned that something is wrong with them.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The patients of Jill Krapf, MD, are often too embarrassed to tell her about discomfort in their clitoris.
“I ask all of my patients about clitoral pain, and it is often the first time they have ever been asked about this,” says Dr. Krapf, the associate director of the Center for Vulvovaginal Disorders, a private clinic in Washington and New York.
Dr. Krapf is an ob.gyn. who specializes in female sexual pain that involves the pelvis, vagina, and vulva.
Many of the conditions Dr. Krapf treats don’t have outward symptoms that appear abnormal, but internally, there are damaged or irritated nerves that can result in hypersensitivity, unwanted arousal, or pain.
“Most recent research indicates that even a herniated disk or tear in the spine can lead to clitoral or vulvar symptoms, just like sciatica pain that shoots down the leg is related to issues in the spine,” Dr. Krapf says.
Dr. Krapf was excited to read of a new discovery: Dr. Krapf and other doctors are hopeful that the attention to the clitoris will spark more interest and comprehensive education among people in their field. They also hope it will empower patients to seek medical help if they are having issues with their clitoris.
“Female sexual health has historically been underfunded, especially compared with male sexual health, like erectile dysfunction,” Dr. Krapf says. “Optimizing vulvar and vaginal health is not only necessary for sexual well-being.”
Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming care, led the study, which was presented at the Sexual Medicine Society of North America conference in October. Dr. Peters says he hopes that the new information decreases stigma that the clitoris is not worthy of the same medical attention that other organs of the body receive.
When the clitoris doesn’t properly function, there can be harm to a person’s physical and mental health. Paying attention to discomfort in the clitoris, and seeking medical attention, can help catch and prevent some urinary and vaginal infections.
“The fact that it took until 2022 for someone to do this work speaks to how little attention the clitoris has received,” says Dr. Peters, an assistant professor of surgery at the Oregon Health and Science University School of Medicine, Portland.
What’s inside?
Dr. Peters and his colleagues completed the study by taking clitoral nerve tissue from seven adult transgender men who had received gender-affirming genital surgery. The tissues were dyed and magnified 1,000 times under a microscope so the researchers could count nerve fibers.
Dr. Peters says the finding is important because many surgeries take place in the groin region – like hip replacements, episiotomies during childbirth, and pelvic mesh procedures – and the revived attention to the clitoris may help health care providers know where nerves are so that injuries from medical mistakes are prevented.
“Nerves are at risk of damage if it’s not understood where they are at all times,” he says.
Dr. Peters hopes the new finding will help create new surgical techniques for nerve repair and offer insight for gender-affirming phalloplasty, which is the surgical construction of a penis often for transmasculine people.
Ownership of the body part
When it comes to the clitoris, no one type of doctor has specialized in the sex organ.
Urologists, gynecologists, plastic surgeons, and sex therapists all address potential problems that can arise with the clitoris and its surrounding body parts. But specialists like Dr. Krapf are few and far between.
It wasn’t until 2005 that Australian urologist Helen O’Connell found that the clitoris is filled with erectile and non-erectile tissues that are often hidden in anatomy drawings by fat and bone. And it wasn’t until the early 2000s that researchers began delving in earnest into the anatomy of the clitoris and how it functions.
And a 2018 study showed that if more doctors examined the clitoris, they could identify issues like adhesions or infections in the area, most of which can be treated without surgery.
A body part built for pleasure
Randi Levinson, a sex, marriage, and family therapist in Los Angeles, sees patients who have less sensation in the clitoris or pain while having sex, many of whom have recently given birth or are going through menopause.
Women often become embarrassed when they can’t orgasm, or have less sensation in the clitoris, but tend to avoid seeking medical advice, she says. Normalizing discussions about women’s pleasure and the vast anatomy that supports it may help some of her patients.
“The more normal it is to talk about and explore women’s pleasure, the less shame women will have when getting help when they aren’t experiencing pleasure,” Ms. Levinson says. “I have many ... clients who experience pain and discomfort with sex [after pregnancy] and no longer feel pleasure and are concerned that something is wrong with them.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Test strips ID fetal tissue in vaginal blood
A rapid test strip can accurately identify embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal blood at the bedside, say authors of a paper published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The strip, called the ROM Plus test, can detect alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) to identify the presence of the tissue, researchers say.
A positive test could help diagnose miscarriage and rule out ectopic pregnancy.
The ROM Plus test was originally created for diagnosing rupture of amniotic membranes and has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This study describes an off-label use of the test.
Lead author Michelle Volovsky, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, N.Y., said that in the current legal climate for abortion care, the test could have an additional use for women having vaginal bleeding.
“This test could be used as evidence to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred, and hence, a D&C (dilation and curettage) procedure in that case is not an induced abortion of a viable pregnancy,” Dr. Volovsky said.
Women in study
Three groups of reproductive-age women (totaling 90) were included in the study.
One was a negative control group consisting of nonpregnant women undergoing D&C or experiencing vaginal bleeding (n = 23). The positive control group of women had confirmed intrauterine pregnancy undergoing D&C (n = 31), and the third group was a study group of pregnant women with first-trimester bleeding (n = 36). Twelve women in the study group had confirmed ectopic pregnancies.
High sensitivity and specificity
Overall, 47 women had confirmed embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal or uterine blood samples. The test strip was accurately positive in 45 of those 47 cases for a test sensitivity of 95.7%. The other 43 had confirmed absence of embryonic or fetal tissue in their vaginal or uterine blood samples.
The test had high specificity as well. “In the absence of embryonic or fetal tissue, such as vaginal blood sampled in cases of ectopic pregnancy, threatened or complete miscarriage, or nonpregnant individuals, the test strip had a specificity of 97.7% for obtaining a negative result,” the authors wrote.
The researchers noted that the high sensitivity and specificity were seen as all tests were performed in real-time, common clinical scenarios encountered in a high-volume, urban ob.gyn. unit.
First-trimester bleeding can be common
First-trimester bleeding occurs in 20%-40% of pregnancies and results in almost 500,000 emergency department visits in the United States every year, the authors wrote.
The most common causes include threatened miscarriage, but more serious etiologies include ectopic pregnancy.
Because criteria often are not met for ectopic pregnancy, many women are told they have a pregnancy of unknown location, which can lead to extensive and expensive follow-up.
“The current study was designed to offer a simple diagnostic alternative that does not require the use of an automated laboratory analyzer,” the authors wrote.
The test could be used by patients with confirmed intrauterine pregnancies at home – a highly desirable feature for people hesitant to come into medical offices or who live in remote areas, they noted.
Questions about test’s use
Lauren Thaxton, MD, assistant professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin, told this publication she sees the ease of use by patients at home as the biggest benefit of the test strips.
She said she’s not sure they would add much benefit otherwise because “we already have a pretty great way of identifying pregnancy tissue by floating the products of conception.”
She said the traditional “floating products” method is very inexpensive, involving a pan and strainer, and may be more comprehensive in that it can determine whether a miscarriage is finished.
She also wonders whether in the current legal climate of abortion laws, the test could be used not only to prove that an abortion didn’t happen but used as evidence the opposite way to criminalize abortion.
It’s unfortunate that we are evaluating new technology as ‘could this cause more harm than good?’ But I think it would be wrong not to recognize the long history of criminalization of abortion as well as the current reproductive health and policy climate,” Dr. Thaxton said.
Coauthors Amir Mor, MD, PhD, and Hugh Taylor, MD, hold U.S. patent rights related to the methods described in this article. Coauthor David Seifer, MD, received payment from the Women’s Integrated Network and Rutgers Medical School. In this article the authors describe off-label use of the ROM Plus test kit, produced by Laborie USA. This device was used to test vaginal blood for the presence of embryonic or fetal products. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Thaxton reports no relevant financial relationships.
A rapid test strip can accurately identify embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal blood at the bedside, say authors of a paper published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The strip, called the ROM Plus test, can detect alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) to identify the presence of the tissue, researchers say.
A positive test could help diagnose miscarriage and rule out ectopic pregnancy.
The ROM Plus test was originally created for diagnosing rupture of amniotic membranes and has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This study describes an off-label use of the test.
Lead author Michelle Volovsky, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, N.Y., said that in the current legal climate for abortion care, the test could have an additional use for women having vaginal bleeding.
“This test could be used as evidence to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred, and hence, a D&C (dilation and curettage) procedure in that case is not an induced abortion of a viable pregnancy,” Dr. Volovsky said.
Women in study
Three groups of reproductive-age women (totaling 90) were included in the study.
One was a negative control group consisting of nonpregnant women undergoing D&C or experiencing vaginal bleeding (n = 23). The positive control group of women had confirmed intrauterine pregnancy undergoing D&C (n = 31), and the third group was a study group of pregnant women with first-trimester bleeding (n = 36). Twelve women in the study group had confirmed ectopic pregnancies.
High sensitivity and specificity
Overall, 47 women had confirmed embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal or uterine blood samples. The test strip was accurately positive in 45 of those 47 cases for a test sensitivity of 95.7%. The other 43 had confirmed absence of embryonic or fetal tissue in their vaginal or uterine blood samples.
The test had high specificity as well. “In the absence of embryonic or fetal tissue, such as vaginal blood sampled in cases of ectopic pregnancy, threatened or complete miscarriage, or nonpregnant individuals, the test strip had a specificity of 97.7% for obtaining a negative result,” the authors wrote.
The researchers noted that the high sensitivity and specificity were seen as all tests were performed in real-time, common clinical scenarios encountered in a high-volume, urban ob.gyn. unit.
First-trimester bleeding can be common
First-trimester bleeding occurs in 20%-40% of pregnancies and results in almost 500,000 emergency department visits in the United States every year, the authors wrote.
The most common causes include threatened miscarriage, but more serious etiologies include ectopic pregnancy.
Because criteria often are not met for ectopic pregnancy, many women are told they have a pregnancy of unknown location, which can lead to extensive and expensive follow-up.
“The current study was designed to offer a simple diagnostic alternative that does not require the use of an automated laboratory analyzer,” the authors wrote.
The test could be used by patients with confirmed intrauterine pregnancies at home – a highly desirable feature for people hesitant to come into medical offices or who live in remote areas, they noted.
Questions about test’s use
Lauren Thaxton, MD, assistant professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin, told this publication she sees the ease of use by patients at home as the biggest benefit of the test strips.
She said she’s not sure they would add much benefit otherwise because “we already have a pretty great way of identifying pregnancy tissue by floating the products of conception.”
She said the traditional “floating products” method is very inexpensive, involving a pan and strainer, and may be more comprehensive in that it can determine whether a miscarriage is finished.
She also wonders whether in the current legal climate of abortion laws, the test could be used not only to prove that an abortion didn’t happen but used as evidence the opposite way to criminalize abortion.
It’s unfortunate that we are evaluating new technology as ‘could this cause more harm than good?’ But I think it would be wrong not to recognize the long history of criminalization of abortion as well as the current reproductive health and policy climate,” Dr. Thaxton said.
Coauthors Amir Mor, MD, PhD, and Hugh Taylor, MD, hold U.S. patent rights related to the methods described in this article. Coauthor David Seifer, MD, received payment from the Women’s Integrated Network and Rutgers Medical School. In this article the authors describe off-label use of the ROM Plus test kit, produced by Laborie USA. This device was used to test vaginal blood for the presence of embryonic or fetal products. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Thaxton reports no relevant financial relationships.
A rapid test strip can accurately identify embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal blood at the bedside, say authors of a paper published in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The strip, called the ROM Plus test, can detect alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) to identify the presence of the tissue, researchers say.
A positive test could help diagnose miscarriage and rule out ectopic pregnancy.
The ROM Plus test was originally created for diagnosing rupture of amniotic membranes and has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This study describes an off-label use of the test.
Lead author Michelle Volovsky, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, N.Y., said that in the current legal climate for abortion care, the test could have an additional use for women having vaginal bleeding.
“This test could be used as evidence to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred, and hence, a D&C (dilation and curettage) procedure in that case is not an induced abortion of a viable pregnancy,” Dr. Volovsky said.
Women in study
Three groups of reproductive-age women (totaling 90) were included in the study.
One was a negative control group consisting of nonpregnant women undergoing D&C or experiencing vaginal bleeding (n = 23). The positive control group of women had confirmed intrauterine pregnancy undergoing D&C (n = 31), and the third group was a study group of pregnant women with first-trimester bleeding (n = 36). Twelve women in the study group had confirmed ectopic pregnancies.
High sensitivity and specificity
Overall, 47 women had confirmed embryonic or fetal tissue in vaginal or uterine blood samples. The test strip was accurately positive in 45 of those 47 cases for a test sensitivity of 95.7%. The other 43 had confirmed absence of embryonic or fetal tissue in their vaginal or uterine blood samples.
The test had high specificity as well. “In the absence of embryonic or fetal tissue, such as vaginal blood sampled in cases of ectopic pregnancy, threatened or complete miscarriage, or nonpregnant individuals, the test strip had a specificity of 97.7% for obtaining a negative result,” the authors wrote.
The researchers noted that the high sensitivity and specificity were seen as all tests were performed in real-time, common clinical scenarios encountered in a high-volume, urban ob.gyn. unit.
First-trimester bleeding can be common
First-trimester bleeding occurs in 20%-40% of pregnancies and results in almost 500,000 emergency department visits in the United States every year, the authors wrote.
The most common causes include threatened miscarriage, but more serious etiologies include ectopic pregnancy.
Because criteria often are not met for ectopic pregnancy, many women are told they have a pregnancy of unknown location, which can lead to extensive and expensive follow-up.
“The current study was designed to offer a simple diagnostic alternative that does not require the use of an automated laboratory analyzer,” the authors wrote.
The test could be used by patients with confirmed intrauterine pregnancies at home – a highly desirable feature for people hesitant to come into medical offices or who live in remote areas, they noted.
Questions about test’s use
Lauren Thaxton, MD, assistant professor in the department of women’s health at the University of Texas at Austin, told this publication she sees the ease of use by patients at home as the biggest benefit of the test strips.
She said she’s not sure they would add much benefit otherwise because “we already have a pretty great way of identifying pregnancy tissue by floating the products of conception.”
She said the traditional “floating products” method is very inexpensive, involving a pan and strainer, and may be more comprehensive in that it can determine whether a miscarriage is finished.
She also wonders whether in the current legal climate of abortion laws, the test could be used not only to prove that an abortion didn’t happen but used as evidence the opposite way to criminalize abortion.
It’s unfortunate that we are evaluating new technology as ‘could this cause more harm than good?’ But I think it would be wrong not to recognize the long history of criminalization of abortion as well as the current reproductive health and policy climate,” Dr. Thaxton said.
Coauthors Amir Mor, MD, PhD, and Hugh Taylor, MD, hold U.S. patent rights related to the methods described in this article. Coauthor David Seifer, MD, received payment from the Women’s Integrated Network and Rutgers Medical School. In this article the authors describe off-label use of the ROM Plus test kit, produced by Laborie USA. This device was used to test vaginal blood for the presence of embryonic or fetal products. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Thaxton reports no relevant financial relationships.
FROM OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY










