User login
Biosimilars face barriers to broader acceptance
BOSTON – For rheumatologists, the primary selling points of biosimilar agents are their presumed efficacy and safety, and their promised cost savings, compared with the reference product, an original biologic agent.
But market forces, patient worries, and provider concerns threaten to file off at least some of biosimilars’ presumed competitive edge, says a rheumatologist involved in the development of biosimilars to treat rheumatic diseases.
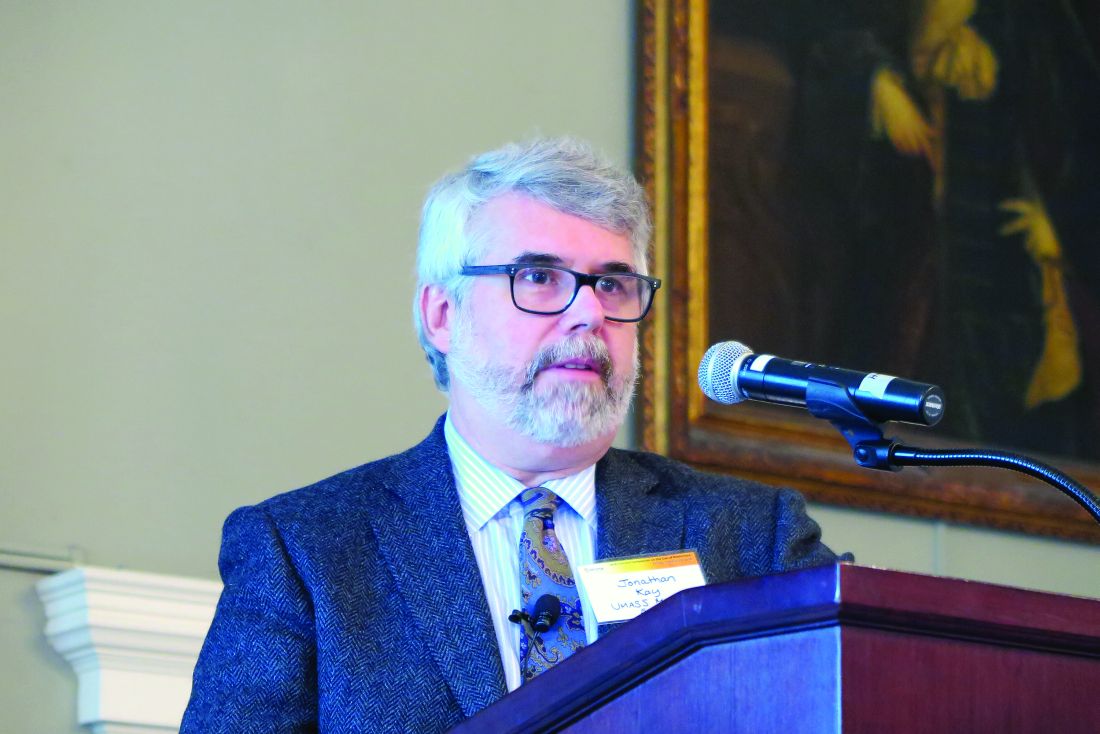
“The availability of lower-priced biosimilars, if they’re truly lower priced, should decrease the cost of treating patients; if they’re not lower cost, then this advantage is not holding true,” said Jonathan Kay, MD, professor of medicine at UMass Memorial Medical Center in Worcester.
But the world is far from perfect, and there are a host of educational, financial, and societal barriers to more widespread acceptance of these agents, he said.
Misperceptions
A common concern among patients and uninformed providers is that biosimilars are the same as biomimics – cheap, usually foreign-made knockoffs of existing drugs that have not undergone regulatory scrutiny and may be neither effective nor safe.
“Biomimics scare patients and scare physicians,” he said, “and misunderstanding of the regulatory approval process, or lack of understanding of the regulatory review or approval process, also intimidates individuals about biosimilars.”
Acceptance of biosimilars is also hampered by a lack of long-term, real-world efficacy and safety data. This is due, in part, to the “inverted pyramid” nature of the biosimilar development and approval process, which starts with myriad analytical, chemical, and functional characterization studies; nonclinical studies; and pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analyses, but only one or two clinical trials. In contrast, the development process for innovator biologics starts with molecular characterization, then moves through the traditional drug development stages of laboratory and preclinical studies, phase I and II trials, and finally phase III registration trials and post-marketing studies.
Because most of the drug development for biosimilars happens behind the scenes, patients and their physicians are often leery about the finished product, no matter how rigorously it was developed. Similarly, there is a paucity of data on long-term immunogenicity of biosimilars, Dr. Kay noted.
Extrapolating about extrapolation
The idea of extrapolation of indications for biosimilars is also an alien concept to many. Simply put, if a reference product is approved for rheumatoid arthritis and has additional indications for treatment of psoriatic arthritis, the approved biosimilar to the original can be extrapolated to be effective against the same indications, even if it has only been tested against one of the indications.
“We have a tremendous amount of clinical experience not only in randomized, controlled clinical trials but also years of marketing experience showing that the reference product is effective and safe for each of the indications for which it’s been approved, and knowing that the biosimilar is essentially like another [manufacturing] run of the reference product allows us to extrapolate indications. But until you become comfortable with accepting that concept, it is certainly a barrier to biosimilars,” he said.
Patients are also scared by the issue of interchangeability, which would allow pharmacists to substitute one product for another without approval of either the patient or the prescribing physician. However, there are currently no biosimilar agents approved as interchangeable by the Food and Drug Administration.
What cost savings?
In the United States, the price of marketed biosimilars has been only 15% lower than that of the reference product, Dr. Kay noted, and multiple discount programs and rebates offered by marketers of the reference product make it difficult to figure out the actual costs of the drugs to payers and whether biosimilars are actually any cheaper.
Additionally, clinicians may be reluctant to adopt biosimilars because of a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services billing quirk that currently offers only a single “J” code with a blended reimbursement for all biosimilar agents of a reference product, regardless of cost differences.
Nordic competition model
Dr. Kay pointed to the Norwegian Tender System as a model for using biosimilars to drive down drug costs.
The Norwegian Drug Procurement Cooperation (LIS) annually procures drugs for all publicly funded hospitals, which ensures that prices offered to hospitals for patent-protected medicines are lower than those offered for distribution to wholesalers or pharmacies. Under this system, cost is the driving factor, assuming that drugs in a similar class have similar efficacy and safety, he said.
In 2015, when Norway was purchasing infliximab, it chose Remsima, the biosimilar, over the reference product Remicade, resulting in a 69% cost saving.
The potential interchangeability of Remsima and Remicade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and chronic plaque psoriasis is currently being explored in the NOR-SWITCH trial.
Dr. Kay disclosed receiving institutional grants from AbbVie, Genentech, Roche Laboratories, and UCB, and serving as a consultant for those companies.
BOSTON – For rheumatologists, the primary selling points of biosimilar agents are their presumed efficacy and safety, and their promised cost savings, compared with the reference product, an original biologic agent.
But market forces, patient worries, and provider concerns threaten to file off at least some of biosimilars’ presumed competitive edge, says a rheumatologist involved in the development of biosimilars to treat rheumatic diseases.
“The availability of lower-priced biosimilars, if they’re truly lower priced, should decrease the cost of treating patients; if they’re not lower cost, then this advantage is not holding true,” said Jonathan Kay, MD, professor of medicine at UMass Memorial Medical Center in Worcester.
But the world is far from perfect, and there are a host of educational, financial, and societal barriers to more widespread acceptance of these agents, he said.
Misperceptions
A common concern among patients and uninformed providers is that biosimilars are the same as biomimics – cheap, usually foreign-made knockoffs of existing drugs that have not undergone regulatory scrutiny and may be neither effective nor safe.
“Biomimics scare patients and scare physicians,” he said, “and misunderstanding of the regulatory approval process, or lack of understanding of the regulatory review or approval process, also intimidates individuals about biosimilars.”
Acceptance of biosimilars is also hampered by a lack of long-term, real-world efficacy and safety data. This is due, in part, to the “inverted pyramid” nature of the biosimilar development and approval process, which starts with myriad analytical, chemical, and functional characterization studies; nonclinical studies; and pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analyses, but only one or two clinical trials. In contrast, the development process for innovator biologics starts with molecular characterization, then moves through the traditional drug development stages of laboratory and preclinical studies, phase I and II trials, and finally phase III registration trials and post-marketing studies.
Because most of the drug development for biosimilars happens behind the scenes, patients and their physicians are often leery about the finished product, no matter how rigorously it was developed. Similarly, there is a paucity of data on long-term immunogenicity of biosimilars, Dr. Kay noted.
Extrapolating about extrapolation
The idea of extrapolation of indications for biosimilars is also an alien concept to many. Simply put, if a reference product is approved for rheumatoid arthritis and has additional indications for treatment of psoriatic arthritis, the approved biosimilar to the original can be extrapolated to be effective against the same indications, even if it has only been tested against one of the indications.
“We have a tremendous amount of clinical experience not only in randomized, controlled clinical trials but also years of marketing experience showing that the reference product is effective and safe for each of the indications for which it’s been approved, and knowing that the biosimilar is essentially like another [manufacturing] run of the reference product allows us to extrapolate indications. But until you become comfortable with accepting that concept, it is certainly a barrier to biosimilars,” he said.
Patients are also scared by the issue of interchangeability, which would allow pharmacists to substitute one product for another without approval of either the patient or the prescribing physician. However, there are currently no biosimilar agents approved as interchangeable by the Food and Drug Administration.
What cost savings?
In the United States, the price of marketed biosimilars has been only 15% lower than that of the reference product, Dr. Kay noted, and multiple discount programs and rebates offered by marketers of the reference product make it difficult to figure out the actual costs of the drugs to payers and whether biosimilars are actually any cheaper.
Additionally, clinicians may be reluctant to adopt biosimilars because of a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services billing quirk that currently offers only a single “J” code with a blended reimbursement for all biosimilar agents of a reference product, regardless of cost differences.
Nordic competition model
Dr. Kay pointed to the Norwegian Tender System as a model for using biosimilars to drive down drug costs.
The Norwegian Drug Procurement Cooperation (LIS) annually procures drugs for all publicly funded hospitals, which ensures that prices offered to hospitals for patent-protected medicines are lower than those offered for distribution to wholesalers or pharmacies. Under this system, cost is the driving factor, assuming that drugs in a similar class have similar efficacy and safety, he said.
In 2015, when Norway was purchasing infliximab, it chose Remsima, the biosimilar, over the reference product Remicade, resulting in a 69% cost saving.
The potential interchangeability of Remsima and Remicade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and chronic plaque psoriasis is currently being explored in the NOR-SWITCH trial.
Dr. Kay disclosed receiving institutional grants from AbbVie, Genentech, Roche Laboratories, and UCB, and serving as a consultant for those companies.
BOSTON – For rheumatologists, the primary selling points of biosimilar agents are their presumed efficacy and safety, and their promised cost savings, compared with the reference product, an original biologic agent.
But market forces, patient worries, and provider concerns threaten to file off at least some of biosimilars’ presumed competitive edge, says a rheumatologist involved in the development of biosimilars to treat rheumatic diseases.
“The availability of lower-priced biosimilars, if they’re truly lower priced, should decrease the cost of treating patients; if they’re not lower cost, then this advantage is not holding true,” said Jonathan Kay, MD, professor of medicine at UMass Memorial Medical Center in Worcester.
But the world is far from perfect, and there are a host of educational, financial, and societal barriers to more widespread acceptance of these agents, he said.
Misperceptions
A common concern among patients and uninformed providers is that biosimilars are the same as biomimics – cheap, usually foreign-made knockoffs of existing drugs that have not undergone regulatory scrutiny and may be neither effective nor safe.
“Biomimics scare patients and scare physicians,” he said, “and misunderstanding of the regulatory approval process, or lack of understanding of the regulatory review or approval process, also intimidates individuals about biosimilars.”
Acceptance of biosimilars is also hampered by a lack of long-term, real-world efficacy and safety data. This is due, in part, to the “inverted pyramid” nature of the biosimilar development and approval process, which starts with myriad analytical, chemical, and functional characterization studies; nonclinical studies; and pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analyses, but only one or two clinical trials. In contrast, the development process for innovator biologics starts with molecular characterization, then moves through the traditional drug development stages of laboratory and preclinical studies, phase I and II trials, and finally phase III registration trials and post-marketing studies.
Because most of the drug development for biosimilars happens behind the scenes, patients and their physicians are often leery about the finished product, no matter how rigorously it was developed. Similarly, there is a paucity of data on long-term immunogenicity of biosimilars, Dr. Kay noted.
Extrapolating about extrapolation
The idea of extrapolation of indications for biosimilars is also an alien concept to many. Simply put, if a reference product is approved for rheumatoid arthritis and has additional indications for treatment of psoriatic arthritis, the approved biosimilar to the original can be extrapolated to be effective against the same indications, even if it has only been tested against one of the indications.
“We have a tremendous amount of clinical experience not only in randomized, controlled clinical trials but also years of marketing experience showing that the reference product is effective and safe for each of the indications for which it’s been approved, and knowing that the biosimilar is essentially like another [manufacturing] run of the reference product allows us to extrapolate indications. But until you become comfortable with accepting that concept, it is certainly a barrier to biosimilars,” he said.
Patients are also scared by the issue of interchangeability, which would allow pharmacists to substitute one product for another without approval of either the patient or the prescribing physician. However, there are currently no biosimilar agents approved as interchangeable by the Food and Drug Administration.
What cost savings?
In the United States, the price of marketed biosimilars has been only 15% lower than that of the reference product, Dr. Kay noted, and multiple discount programs and rebates offered by marketers of the reference product make it difficult to figure out the actual costs of the drugs to payers and whether biosimilars are actually any cheaper.
Additionally, clinicians may be reluctant to adopt biosimilars because of a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services billing quirk that currently offers only a single “J” code with a blended reimbursement for all biosimilar agents of a reference product, regardless of cost differences.
Nordic competition model
Dr. Kay pointed to the Norwegian Tender System as a model for using biosimilars to drive down drug costs.
The Norwegian Drug Procurement Cooperation (LIS) annually procures drugs for all publicly funded hospitals, which ensures that prices offered to hospitals for patent-protected medicines are lower than those offered for distribution to wholesalers or pharmacies. Under this system, cost is the driving factor, assuming that drugs in a similar class have similar efficacy and safety, he said.
In 2015, when Norway was purchasing infliximab, it chose Remsima, the biosimilar, over the reference product Remicade, resulting in a 69% cost saving.
The potential interchangeability of Remsima and Remicade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and chronic plaque psoriasis is currently being explored in the NOR-SWITCH trial.
Dr. Kay disclosed receiving institutional grants from AbbVie, Genentech, Roche Laboratories, and UCB, and serving as a consultant for those companies.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A BIOSIMILARS IN RHEUMATOLOGY SYMPOSIUM
Intravitreal sirolimus proves effective in reducing noninfectious uveitis inflammation
Intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg or 880 mcg administered on days 1, 60, and 120, was shown to significantly improve ocular inflammation with preservation of best-corrected visual acuity in patients with noninfectious uveitis of the posterior segment, a phase III study has shown.
In the multinational SAKURA (Study Assessing Double-masked Uveitis Treatment) study, 346 study eyes were analyzed in this randomly assigned, double-masked, actively controlled study. In the study arm given intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg, 22.8% (P = .025) met the primary endpoint of no vitreous haze (VH) at month 5 in the study eye without the aid of rescue therapy. In the group given intravitreal sirolimus 880 mcg, 16.4% (P = .182) met the primary endpoint, compared with 10.3% of active controls who were given 44 mcg intravitreal sirolimus.
For the secondary outcome, 52.6% (P = .008) of the intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg arm had VH scores of 0 or a 0.5+ response rate at month 5. In the intravitreal sirolimus 880 mcg, 43.1% (P = .228) achieved a VH score of 0 or a 0.5+ response rate, compared with 35% of the 44 mcg active control group. Mean best-corrected visual acuity was maintained throughout the study in each study arm, with 76.9% of those who received corticosteroids at baseline in the 440 mcg study arm successfully tapering them to 5 mg per day or less by month 5, and 66.7% of those receiving corticosteroids in the 880 mcg group doing so. This was in comparison with 63.6% of those using corticosteroids in the active control group. Adverse events were similar across the study, and all doses were well tolerated. The study was funded by Santen.
Read the full study in Ophthalmology (2016;23[11]:2413-23).
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
Intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg or 880 mcg administered on days 1, 60, and 120, was shown to significantly improve ocular inflammation with preservation of best-corrected visual acuity in patients with noninfectious uveitis of the posterior segment, a phase III study has shown.
In the multinational SAKURA (Study Assessing Double-masked Uveitis Treatment) study, 346 study eyes were analyzed in this randomly assigned, double-masked, actively controlled study. In the study arm given intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg, 22.8% (P = .025) met the primary endpoint of no vitreous haze (VH) at month 5 in the study eye without the aid of rescue therapy. In the group given intravitreal sirolimus 880 mcg, 16.4% (P = .182) met the primary endpoint, compared with 10.3% of active controls who were given 44 mcg intravitreal sirolimus.
For the secondary outcome, 52.6% (P = .008) of the intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg arm had VH scores of 0 or a 0.5+ response rate at month 5. In the intravitreal sirolimus 880 mcg, 43.1% (P = .228) achieved a VH score of 0 or a 0.5+ response rate, compared with 35% of the 44 mcg active control group. Mean best-corrected visual acuity was maintained throughout the study in each study arm, with 76.9% of those who received corticosteroids at baseline in the 440 mcg study arm successfully tapering them to 5 mg per day or less by month 5, and 66.7% of those receiving corticosteroids in the 880 mcg group doing so. This was in comparison with 63.6% of those using corticosteroids in the active control group. Adverse events were similar across the study, and all doses were well tolerated. The study was funded by Santen.
Read the full study in Ophthalmology (2016;23[11]:2413-23).
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
Intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg or 880 mcg administered on days 1, 60, and 120, was shown to significantly improve ocular inflammation with preservation of best-corrected visual acuity in patients with noninfectious uveitis of the posterior segment, a phase III study has shown.
In the multinational SAKURA (Study Assessing Double-masked Uveitis Treatment) study, 346 study eyes were analyzed in this randomly assigned, double-masked, actively controlled study. In the study arm given intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg, 22.8% (P = .025) met the primary endpoint of no vitreous haze (VH) at month 5 in the study eye without the aid of rescue therapy. In the group given intravitreal sirolimus 880 mcg, 16.4% (P = .182) met the primary endpoint, compared with 10.3% of active controls who were given 44 mcg intravitreal sirolimus.
For the secondary outcome, 52.6% (P = .008) of the intravitreal sirolimus 440 mcg arm had VH scores of 0 or a 0.5+ response rate at month 5. In the intravitreal sirolimus 880 mcg, 43.1% (P = .228) achieved a VH score of 0 or a 0.5+ response rate, compared with 35% of the 44 mcg active control group. Mean best-corrected visual acuity was maintained throughout the study in each study arm, with 76.9% of those who received corticosteroids at baseline in the 440 mcg study arm successfully tapering them to 5 mg per day or less by month 5, and 66.7% of those receiving corticosteroids in the 880 mcg group doing so. This was in comparison with 63.6% of those using corticosteroids in the active control group. Adverse events were similar across the study, and all doses were well tolerated. The study was funded by Santen.
Read the full study in Ophthalmology (2016;23[11]:2413-23).
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
TNF inhibitors’ effect on ankylosing spondylitis progression may be greatest after 6 years
The benefits of treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors in reducing spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis became most evident 6-8 years after the biologic therapy was initiated, according to findings from a prospective observational cohort study.
The study enrolled 210 consecutive patients from the Groningen Leeuwarden AS (GLAS) cohort who initiated treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors during 2004-2012 and who received baseline and biannual radiographs over the 8-year follow-up.
In patients with complete modified Stoke AS Spine Score (mSASSS) data over 8 years of follow-up, the estimated mean spinal radiographic progression was 2.3 points during the first 2 years of treatment and then declined steadily to 1.4 in years 2-4, 1.0 in years 4-6 and 0.8 in years 6-8. This decrease was seen even after adjusting for baseline mSASSS, the presence of syndesmophytes, sex, HLA-B27 status, age, symptom duration, smoking duration, body mass index, disease activity, and NSAID use.
Patients with longer follow-up also showed more use of NSAIDs, higher C-reactive protein levels, and more spinal radiographic damage at baseline. There were, however, significant improvements in all disease activity measures as soon as patients began treatment, and patients also showed a rapid decrease in NSAID use over time, said Fiona Maas of the University Medical Center Groningen (Netherlands) and her associates.
Multiple studies have been conducted into the impact of TNF-alpha inhibitors on spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis, but the results have been subject to some debate, the investigators noted.
“It is known that radiographic progression in AS is overall slow and highly variable between patients,” they wrote. “Therefore, differences in patient numbers at the different time points during follow-up can affect the outcome measure of interest, in this case radiographic progression.”
In this study, researchers saw a straightforward linear progression of disease in the first 4 years after treatment was initiated but a deflection from linear progression in years 6 and 8.
“These results may refer to a delayed effect of TNF-alpha inhibitors on radiographic progression and support the TNF brake hypothesis,” they wrote, suggesting that the long-term inhibition of inflammation with TNF-alpha inhibitors diminishes new bone formation over time in patients with longstanding disease.
The GLAS cohort was supported Pfizer. Four authors declared research grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies including Pfizer. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
The benefits of treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors in reducing spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis became most evident 6-8 years after the biologic therapy was initiated, according to findings from a prospective observational cohort study.
The study enrolled 210 consecutive patients from the Groningen Leeuwarden AS (GLAS) cohort who initiated treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors during 2004-2012 and who received baseline and biannual radiographs over the 8-year follow-up.
In patients with complete modified Stoke AS Spine Score (mSASSS) data over 8 years of follow-up, the estimated mean spinal radiographic progression was 2.3 points during the first 2 years of treatment and then declined steadily to 1.4 in years 2-4, 1.0 in years 4-6 and 0.8 in years 6-8. This decrease was seen even after adjusting for baseline mSASSS, the presence of syndesmophytes, sex, HLA-B27 status, age, symptom duration, smoking duration, body mass index, disease activity, and NSAID use.
Patients with longer follow-up also showed more use of NSAIDs, higher C-reactive protein levels, and more spinal radiographic damage at baseline. There were, however, significant improvements in all disease activity measures as soon as patients began treatment, and patients also showed a rapid decrease in NSAID use over time, said Fiona Maas of the University Medical Center Groningen (Netherlands) and her associates.
Multiple studies have been conducted into the impact of TNF-alpha inhibitors on spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis, but the results have been subject to some debate, the investigators noted.
“It is known that radiographic progression in AS is overall slow and highly variable between patients,” they wrote. “Therefore, differences in patient numbers at the different time points during follow-up can affect the outcome measure of interest, in this case radiographic progression.”
In this study, researchers saw a straightforward linear progression of disease in the first 4 years after treatment was initiated but a deflection from linear progression in years 6 and 8.
“These results may refer to a delayed effect of TNF-alpha inhibitors on radiographic progression and support the TNF brake hypothesis,” they wrote, suggesting that the long-term inhibition of inflammation with TNF-alpha inhibitors diminishes new bone formation over time in patients with longstanding disease.
The GLAS cohort was supported Pfizer. Four authors declared research grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies including Pfizer. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
The benefits of treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors in reducing spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis became most evident 6-8 years after the biologic therapy was initiated, according to findings from a prospective observational cohort study.
The study enrolled 210 consecutive patients from the Groningen Leeuwarden AS (GLAS) cohort who initiated treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors during 2004-2012 and who received baseline and biannual radiographs over the 8-year follow-up.
In patients with complete modified Stoke AS Spine Score (mSASSS) data over 8 years of follow-up, the estimated mean spinal radiographic progression was 2.3 points during the first 2 years of treatment and then declined steadily to 1.4 in years 2-4, 1.0 in years 4-6 and 0.8 in years 6-8. This decrease was seen even after adjusting for baseline mSASSS, the presence of syndesmophytes, sex, HLA-B27 status, age, symptom duration, smoking duration, body mass index, disease activity, and NSAID use.
Patients with longer follow-up also showed more use of NSAIDs, higher C-reactive protein levels, and more spinal radiographic damage at baseline. There were, however, significant improvements in all disease activity measures as soon as patients began treatment, and patients also showed a rapid decrease in NSAID use over time, said Fiona Maas of the University Medical Center Groningen (Netherlands) and her associates.
Multiple studies have been conducted into the impact of TNF-alpha inhibitors on spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis, but the results have been subject to some debate, the investigators noted.
“It is known that radiographic progression in AS is overall slow and highly variable between patients,” they wrote. “Therefore, differences in patient numbers at the different time points during follow-up can affect the outcome measure of interest, in this case radiographic progression.”
In this study, researchers saw a straightforward linear progression of disease in the first 4 years after treatment was initiated but a deflection from linear progression in years 6 and 8.
“These results may refer to a delayed effect of TNF-alpha inhibitors on radiographic progression and support the TNF brake hypothesis,” they wrote, suggesting that the long-term inhibition of inflammation with TNF-alpha inhibitors diminishes new bone formation over time in patients with longstanding disease.
The GLAS cohort was supported Pfizer. Four authors declared research grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies including Pfizer. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Key clinical point: The .
Major finding: Spinal radiographic progression rates on the modified Stoke AS Spine Score in ankylosing spondylitis patients treated with TNF-alpha inhibitors dropped from 2.3 during the first 2 years of treatment to 0.8 in years 6-8 after treatment initiation.
Data source: The Groningen Leeuwarden AS (GLAS) prospective observational cohort study involving 210 patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Disclosures: The GLAS cohort was supported by Pfizer. Four authors declared research grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
Severe joint pain in adults with arthritis continues to rise
The prevalence of severe joint pain among adults with diagnosed arthritis continues to increase, researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in the Oct. 7 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In 2014, more than one-fourth of adults with arthritis had severe joint pain. That is about 14.6 million Americans with severe joint pain, a significant increase from 2002 when there were an estimated 10.5 million adults with severe joint pain, according to Kamil E. Barbour, PhD, and his associates from the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (MMWR. 2016 Oct 7;65[39]:1052-6).
Severe joint pain was also more prevalent among patients with overall fair or poor health who were obese or had heart disease, diabetes, or serious psychological distress, the investigators reported.
The investigators defined people with arthritis as those who had “been told by a doctor or other health professional” that they have some form of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, lupus, or fibromyalgia. Severe joint pain was defined as a response of 7 or higher on a scale of 0-10 for rating joint pain on average over the past 30 days.
Recently, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services released its National Pain Strategy, the nation’s first broad, federal effort aimed at developing strategies to reduce the burden of pain among Americans. The initiatives major objectives are to take steps to reduce barriers to pain care, and to increase patient knowledge of treatment options and risks, Dr. Barbour and his associates wrote.
“Health care providers and public health practitioners can begin to implement the recommendations [from the National Pain Strategy] and improve pain care among adults with arthritis and [severe joint pain] by prioritizing self-management education and appropriate physical activity interventions as effective nonpharmacologic ways to reduce pain and improve health outcomes,” the researchers added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
The prevalence of severe joint pain among adults with diagnosed arthritis continues to increase, researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in the Oct. 7 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In 2014, more than one-fourth of adults with arthritis had severe joint pain. That is about 14.6 million Americans with severe joint pain, a significant increase from 2002 when there were an estimated 10.5 million adults with severe joint pain, according to Kamil E. Barbour, PhD, and his associates from the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (MMWR. 2016 Oct 7;65[39]:1052-6).
Severe joint pain was also more prevalent among patients with overall fair or poor health who were obese or had heart disease, diabetes, or serious psychological distress, the investigators reported.
The investigators defined people with arthritis as those who had “been told by a doctor or other health professional” that they have some form of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, lupus, or fibromyalgia. Severe joint pain was defined as a response of 7 or higher on a scale of 0-10 for rating joint pain on average over the past 30 days.
Recently, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services released its National Pain Strategy, the nation’s first broad, federal effort aimed at developing strategies to reduce the burden of pain among Americans. The initiatives major objectives are to take steps to reduce barriers to pain care, and to increase patient knowledge of treatment options and risks, Dr. Barbour and his associates wrote.
“Health care providers and public health practitioners can begin to implement the recommendations [from the National Pain Strategy] and improve pain care among adults with arthritis and [severe joint pain] by prioritizing self-management education and appropriate physical activity interventions as effective nonpharmacologic ways to reduce pain and improve health outcomes,” the researchers added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
The prevalence of severe joint pain among adults with diagnosed arthritis continues to increase, researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported in the Oct. 7 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In 2014, more than one-fourth of adults with arthritis had severe joint pain. That is about 14.6 million Americans with severe joint pain, a significant increase from 2002 when there were an estimated 10.5 million adults with severe joint pain, according to Kamil E. Barbour, PhD, and his associates from the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (MMWR. 2016 Oct 7;65[39]:1052-6).
Severe joint pain was also more prevalent among patients with overall fair or poor health who were obese or had heart disease, diabetes, or serious psychological distress, the investigators reported.
The investigators defined people with arthritis as those who had “been told by a doctor or other health professional” that they have some form of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, lupus, or fibromyalgia. Severe joint pain was defined as a response of 7 or higher on a scale of 0-10 for rating joint pain on average over the past 30 days.
Recently, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services released its National Pain Strategy, the nation’s first broad, federal effort aimed at developing strategies to reduce the burden of pain among Americans. The initiatives major objectives are to take steps to reduce barriers to pain care, and to increase patient knowledge of treatment options and risks, Dr. Barbour and his associates wrote.
“Health care providers and public health practitioners can begin to implement the recommendations [from the National Pain Strategy] and improve pain care among adults with arthritis and [severe joint pain] by prioritizing self-management education and appropriate physical activity interventions as effective nonpharmacologic ways to reduce pain and improve health outcomes,” the researchers added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
FROM MMWR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The estimated number of U.S. adults with severe joint pain rose from 10.5 million in 2002 to 14.6 million in 2014.
Data source: Analysis of data from the National Health Interview Survey in 2002, 2003, 2006, 2009, and 2014.
Disclosures: The authors are federal government employees and have no financial disclosures.
Most children with JIA get different diagnosis as adults
Two-thirds of children diagnosed with juvenile idiopathic arthritis are classified later as having a different form of arthritis as adults, with 72% of them requiring disease-modifying medication and 13% forced into retirement, according to a cross-sectional analysis of a registry database.
But among patients with inactive disease, more than one-third are off medication, and the majority have either no or very mild disabilities, reported Filipa Oliveira-Ramos, MD, of Hospital de Santa Maria, Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte, Lisbon, and her colleagues (RMD Open 2016;2:e000304. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000304).
The team used data from the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register database to discern how rheumatic disease classifications evolve as people with JIA grow into adulthood. The analysis comprised 426 patients and examined fulfillment of adult classification criteria, function as assessed by the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), clinical disease characteristics as assessed by the Juvenile Arthritis Damage Index–articular (JADI-A) and Juvenile Arthritis Damage Index–extra-articular (JADI-E), and disease activity.
The patients were a mean of 34 years old at the time of the last visit entered into the database. The patients’ mean disease duration was 22.5 years, including 80% with at least 10 years and 24% with more than 30 years.
All had been diagnosed with JIA, at a mean age of about 10 years. Disease categories were persistent oligoarthritis (19%), extended oligoarthritis (14%), rheumatoid factor–positive polyarthritis (17%), rheumatoid factor–negative polyarthritis (18%), systemic disease (10%), enthesitis-related arthritis (19%), psoriatic arthritis (3%), and undifferentiated arthritis (1%).
A total of 72% of patients were still employed, although 13% had retired because of disease-related disability. Most (67%) still had active disease, and 72% were taking a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug.
JIA had evolved into numerous new diagnoses, the team observed. Most patients with systemic-onset JIA (92%) were classified as having adult Still’s disease – more than half (58%) with persistent systemic features and about 42% with predominately polyarticular involvement.
The majority of patients with RF-positive polyarthritis (96%) and of those with RF-negative polyarthritis as children (57%) fulfilled the adult criteria for rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients who had persistent oligoarthritis as children were, as adults, most likely be classified with spondyloarthritis (35%), although 59% remained unclassifiable.
Most of the patients with extended oligoarthritis as children were later classified as having either rheumatoid arthritis (39%) or spondyloarthritis (26%). Most patients with juvenile enthesitis-related arthritis were also reclassified as having spondyloarthritis (95%).
All of those with childhood psoriatic arthritis retained that classification as adults.
A smaller portion of patients (21%) were unclassified as adults, the investigators said. Most of these patients had RF-negative polyarticular or oligoarticular classifications as children.
In a series of multivariate analyses, the team found a number of significant associations with adult outcomes. After adjustment for International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) category, inactive adult disease was associated with shorter disease duration, less delay in diagnosis, a lower HAQ score, and less exposure to corticosteroids. A higher HAQ score was associated with a longer disease duration and exposure to biologics, while a lower HAQ was associated with the persistence of systemic disease features.
Higher JADI-A scores were associated with disability-related retirement, longer disease duration, and past or current use of biologics.
Another series of multivariate models assessed outcomes associated with inactive disease. Patients who were older at disease onset were more likely to have inactive disease as adults. A positive test for anticitrullinated protein antibodies decreased the likelihood of disease inactivity by 93%.
Finally, the investigators evaluated associations with function and clinical characteristics. Younger age at disease onset was associated with higher HAQ and JADI scores in adulthood. Patients with RF-positive polyarthritis and systemic-onset JIA were more likely to have worse JADI-A and JADI-E scores, compared with patients who had persistent oligoarthritis. Corticosteroid exposure was also predictive of worse extra-articular scores on the JADI.
“Understanding the way these juvenile diseases progress could add useful information for the ongoing discussion of a new classification capable of better unifying the language between pediatric and adult care,” the authors concluded.
None of the authors had financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @alz_gal
This is an important article in that it highlights one of the fundamental flaws of the juvenile idiopathic arthritis classification.
The manifestations of the rheumatic diseases often evolve over time. There may be psoriasis before arthritis, but there also may be arthritis before psoriasis. Similarly, children with an ultimate diagnosis of Crohn’s disease may first present to the rheumatologist with arthritis.
The definition of JIA requires only the onset of arthritis lasting more than 3 weeks before 16 years of age with the exclusion of other obvious cause. A careful reading of the subclassification criteria quickly reveals that many children are “unclassifiable” because of family history or other factors.
The present study makes it clear that by the time they reach adulthood, a significant number of individuals who were told they had JIA will, in fact, meet criteria for a different classification. This would be of only casual interest were it not for the fact that these children will have previously been entered into databases about the natural history of JIA with erroneous classifications.
More worrisome is that fact that some will have been included in therapeutic trials with erroneous classifications as well. The pediatric rheumatology community would do well to recognize the urgent need for a reassessment of the classification criteria and nomenclature to better reflect the diversity of causes of childhood arthritis.
Thomas Lehman, MD, is chief of pediatric rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York. He has no relevant disclosures.
This is an important article in that it highlights one of the fundamental flaws of the juvenile idiopathic arthritis classification.
The manifestations of the rheumatic diseases often evolve over time. There may be psoriasis before arthritis, but there also may be arthritis before psoriasis. Similarly, children with an ultimate diagnosis of Crohn’s disease may first present to the rheumatologist with arthritis.
The definition of JIA requires only the onset of arthritis lasting more than 3 weeks before 16 years of age with the exclusion of other obvious cause. A careful reading of the subclassification criteria quickly reveals that many children are “unclassifiable” because of family history or other factors.
The present study makes it clear that by the time they reach adulthood, a significant number of individuals who were told they had JIA will, in fact, meet criteria for a different classification. This would be of only casual interest were it not for the fact that these children will have previously been entered into databases about the natural history of JIA with erroneous classifications.
More worrisome is that fact that some will have been included in therapeutic trials with erroneous classifications as well. The pediatric rheumatology community would do well to recognize the urgent need for a reassessment of the classification criteria and nomenclature to better reflect the diversity of causes of childhood arthritis.
Thomas Lehman, MD, is chief of pediatric rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York. He has no relevant disclosures.
This is an important article in that it highlights one of the fundamental flaws of the juvenile idiopathic arthritis classification.
The manifestations of the rheumatic diseases often evolve over time. There may be psoriasis before arthritis, but there also may be arthritis before psoriasis. Similarly, children with an ultimate diagnosis of Crohn’s disease may first present to the rheumatologist with arthritis.
The definition of JIA requires only the onset of arthritis lasting more than 3 weeks before 16 years of age with the exclusion of other obvious cause. A careful reading of the subclassification criteria quickly reveals that many children are “unclassifiable” because of family history or other factors.
The present study makes it clear that by the time they reach adulthood, a significant number of individuals who were told they had JIA will, in fact, meet criteria for a different classification. This would be of only casual interest were it not for the fact that these children will have previously been entered into databases about the natural history of JIA with erroneous classifications.
More worrisome is that fact that some will have been included in therapeutic trials with erroneous classifications as well. The pediatric rheumatology community would do well to recognize the urgent need for a reassessment of the classification criteria and nomenclature to better reflect the diversity of causes of childhood arthritis.
Thomas Lehman, MD, is chief of pediatric rheumatology at the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York. He has no relevant disclosures.
Two-thirds of children diagnosed with juvenile idiopathic arthritis are classified later as having a different form of arthritis as adults, with 72% of them requiring disease-modifying medication and 13% forced into retirement, according to a cross-sectional analysis of a registry database.
But among patients with inactive disease, more than one-third are off medication, and the majority have either no or very mild disabilities, reported Filipa Oliveira-Ramos, MD, of Hospital de Santa Maria, Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte, Lisbon, and her colleagues (RMD Open 2016;2:e000304. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000304).
The team used data from the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register database to discern how rheumatic disease classifications evolve as people with JIA grow into adulthood. The analysis comprised 426 patients and examined fulfillment of adult classification criteria, function as assessed by the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), clinical disease characteristics as assessed by the Juvenile Arthritis Damage Index–articular (JADI-A) and Juvenile Arthritis Damage Index–extra-articular (JADI-E), and disease activity.
The patients were a mean of 34 years old at the time of the last visit entered into the database. The patients’ mean disease duration was 22.5 years, including 80% with at least 10 years and 24% with more than 30 years.
All had been diagnosed with JIA, at a mean age of about 10 years. Disease categories were persistent oligoarthritis (19%), extended oligoarthritis (14%), rheumatoid factor–positive polyarthritis (17%), rheumatoid factor–negative polyarthritis (18%), systemic disease (10%), enthesitis-related arthritis (19%), psoriatic arthritis (3%), and undifferentiated arthritis (1%).
A total of 72% of patients were still employed, although 13% had retired because of disease-related disability. Most (67%) still had active disease, and 72% were taking a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug.
JIA had evolved into numerous new diagnoses, the team observed. Most patients with systemic-onset JIA (92%) were classified as having adult Still’s disease – more than half (58%) with persistent systemic features and about 42% with predominately polyarticular involvement.
The majority of patients with RF-positive polyarthritis (96%) and of those with RF-negative polyarthritis as children (57%) fulfilled the adult criteria for rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients who had persistent oligoarthritis as children were, as adults, most likely be classified with spondyloarthritis (35%), although 59% remained unclassifiable.
Most of the patients with extended oligoarthritis as children were later classified as having either rheumatoid arthritis (39%) or spondyloarthritis (26%). Most patients with juvenile enthesitis-related arthritis were also reclassified as having spondyloarthritis (95%).
All of those with childhood psoriatic arthritis retained that classification as adults.
A smaller portion of patients (21%) were unclassified as adults, the investigators said. Most of these patients had RF-negative polyarticular or oligoarticular classifications as children.
In a series of multivariate analyses, the team found a number of significant associations with adult outcomes. After adjustment for International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) category, inactive adult disease was associated with shorter disease duration, less delay in diagnosis, a lower HAQ score, and less exposure to corticosteroids. A higher HAQ score was associated with a longer disease duration and exposure to biologics, while a lower HAQ was associated with the persistence of systemic disease features.
Higher JADI-A scores were associated with disability-related retirement, longer disease duration, and past or current use of biologics.
Another series of multivariate models assessed outcomes associated with inactive disease. Patients who were older at disease onset were more likely to have inactive disease as adults. A positive test for anticitrullinated protein antibodies decreased the likelihood of disease inactivity by 93%.
Finally, the investigators evaluated associations with function and clinical characteristics. Younger age at disease onset was associated with higher HAQ and JADI scores in adulthood. Patients with RF-positive polyarthritis and systemic-onset JIA were more likely to have worse JADI-A and JADI-E scores, compared with patients who had persistent oligoarthritis. Corticosteroid exposure was also predictive of worse extra-articular scores on the JADI.
“Understanding the way these juvenile diseases progress could add useful information for the ongoing discussion of a new classification capable of better unifying the language between pediatric and adult care,” the authors concluded.
None of the authors had financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @alz_gal
Two-thirds of children diagnosed with juvenile idiopathic arthritis are classified later as having a different form of arthritis as adults, with 72% of them requiring disease-modifying medication and 13% forced into retirement, according to a cross-sectional analysis of a registry database.
But among patients with inactive disease, more than one-third are off medication, and the majority have either no or very mild disabilities, reported Filipa Oliveira-Ramos, MD, of Hospital de Santa Maria, Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte, Lisbon, and her colleagues (RMD Open 2016;2:e000304. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000304).
The team used data from the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register database to discern how rheumatic disease classifications evolve as people with JIA grow into adulthood. The analysis comprised 426 patients and examined fulfillment of adult classification criteria, function as assessed by the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), clinical disease characteristics as assessed by the Juvenile Arthritis Damage Index–articular (JADI-A) and Juvenile Arthritis Damage Index–extra-articular (JADI-E), and disease activity.
The patients were a mean of 34 years old at the time of the last visit entered into the database. The patients’ mean disease duration was 22.5 years, including 80% with at least 10 years and 24% with more than 30 years.
All had been diagnosed with JIA, at a mean age of about 10 years. Disease categories were persistent oligoarthritis (19%), extended oligoarthritis (14%), rheumatoid factor–positive polyarthritis (17%), rheumatoid factor–negative polyarthritis (18%), systemic disease (10%), enthesitis-related arthritis (19%), psoriatic arthritis (3%), and undifferentiated arthritis (1%).
A total of 72% of patients were still employed, although 13% had retired because of disease-related disability. Most (67%) still had active disease, and 72% were taking a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug.
JIA had evolved into numerous new diagnoses, the team observed. Most patients with systemic-onset JIA (92%) were classified as having adult Still’s disease – more than half (58%) with persistent systemic features and about 42% with predominately polyarticular involvement.
The majority of patients with RF-positive polyarthritis (96%) and of those with RF-negative polyarthritis as children (57%) fulfilled the adult criteria for rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients who had persistent oligoarthritis as children were, as adults, most likely be classified with spondyloarthritis (35%), although 59% remained unclassifiable.
Most of the patients with extended oligoarthritis as children were later classified as having either rheumatoid arthritis (39%) or spondyloarthritis (26%). Most patients with juvenile enthesitis-related arthritis were also reclassified as having spondyloarthritis (95%).
All of those with childhood psoriatic arthritis retained that classification as adults.
A smaller portion of patients (21%) were unclassified as adults, the investigators said. Most of these patients had RF-negative polyarticular or oligoarticular classifications as children.
In a series of multivariate analyses, the team found a number of significant associations with adult outcomes. After adjustment for International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) category, inactive adult disease was associated with shorter disease duration, less delay in diagnosis, a lower HAQ score, and less exposure to corticosteroids. A higher HAQ score was associated with a longer disease duration and exposure to biologics, while a lower HAQ was associated with the persistence of systemic disease features.
Higher JADI-A scores were associated with disability-related retirement, longer disease duration, and past or current use of biologics.
Another series of multivariate models assessed outcomes associated with inactive disease. Patients who were older at disease onset were more likely to have inactive disease as adults. A positive test for anticitrullinated protein antibodies decreased the likelihood of disease inactivity by 93%.
Finally, the investigators evaluated associations with function and clinical characteristics. Younger age at disease onset was associated with higher HAQ and JADI scores in adulthood. Patients with RF-positive polyarthritis and systemic-onset JIA were more likely to have worse JADI-A and JADI-E scores, compared with patients who had persistent oligoarthritis. Corticosteroid exposure was also predictive of worse extra-articular scores on the JADI.
“Understanding the way these juvenile diseases progress could add useful information for the ongoing discussion of a new classification capable of better unifying the language between pediatric and adult care,” the authors concluded.
None of the authors had financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @alz_gal
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The childhood diagnosis of JIA is reclassified to another form of arthritis in two-thirds of patients in adulthood.
Data source: The Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register.
Disclosures: None of the authors had financial disclosures.
FDA approves biosimilar adalimumab
There are “no clinically meaningful differences” between Amgen’s biosimilar adalimumab (Amjevita) and AbbVie’s branded product Humira, the Food and Drug Administration noted it its Sept. 23 announcement of Amjevita’s approval.
Although Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) is expected to cost less than Humira, Amgen has not released price information or a launch date pending ongoing litigation with AbbVie over intellectual property rights, an Amgen spokeswoman said.
The products carry an identical black box warning of tuberculosis and other serious infections, as well as lymphoma and other malignancies “reported in children and adolescent patients treated with [tumor necrosis factor] blockers including adalimumab.” As with Humira, “the most common expected adverse reactions with Amjevita are infections and injection site reactions,” the FDA said. Both products are approved in 20 mg/0.4 mL and 40 mg/0.8 mL prefilled injections, but Humira also has a 10 mg/0.2 mL option.
Amjevita was unanimously recommended for approval by an FDA review panel in July. Although “the biosimilar pathway is still a new frontier,” it’s likely to “enhance access to treatment for patients with serious medical conditions,” Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the agency statement.
The approval follows the FDA’s approval of biosimilar infliximab (Inflectra) in April 2016 and biosimilar etanercept (Erelzi) in August 2016. Inflectra has not hit the U.S. market yet, but the European experience with biosimilar infliximab – generally positive – may give an indication of how Amjevita will fare in the United States. It’s perhaps a third or more less expensive than the original product (Remicade) and often used for new starts. There is uncertainty, however, about switching patients already established on Remicade, especially when it’s forced by cost issues.
Interchangeability is a concern in the United States as well. The FDA is working on the issue but has not yet released guidance, and the agency was careful to note in its statement that Amjevita was “approved as a biosimilar, not as an interchangeable product.” Biosimilar adalimumab, meanwhile, is under review in Europe, according to an Amgen statement.
The FDA approved Amjevita after reviewing structural and functional characteristics, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics data, clinical immunogenicity data, and other clinical safety and effectiveness data that demonstrated similarity to Humira, including two phase III trials for plaque psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis.
An AbbVie spokesperson said the company “anticipated Amgen’s product would be approved,” but noted the ongoing litigation.
There are “no clinically meaningful differences” between Amgen’s biosimilar adalimumab (Amjevita) and AbbVie’s branded product Humira, the Food and Drug Administration noted it its Sept. 23 announcement of Amjevita’s approval.
Although Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) is expected to cost less than Humira, Amgen has not released price information or a launch date pending ongoing litigation with AbbVie over intellectual property rights, an Amgen spokeswoman said.
The products carry an identical black box warning of tuberculosis and other serious infections, as well as lymphoma and other malignancies “reported in children and adolescent patients treated with [tumor necrosis factor] blockers including adalimumab.” As with Humira, “the most common expected adverse reactions with Amjevita are infections and injection site reactions,” the FDA said. Both products are approved in 20 mg/0.4 mL and 40 mg/0.8 mL prefilled injections, but Humira also has a 10 mg/0.2 mL option.
Amjevita was unanimously recommended for approval by an FDA review panel in July. Although “the biosimilar pathway is still a new frontier,” it’s likely to “enhance access to treatment for patients with serious medical conditions,” Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the agency statement.
The approval follows the FDA’s approval of biosimilar infliximab (Inflectra) in April 2016 and biosimilar etanercept (Erelzi) in August 2016. Inflectra has not hit the U.S. market yet, but the European experience with biosimilar infliximab – generally positive – may give an indication of how Amjevita will fare in the United States. It’s perhaps a third or more less expensive than the original product (Remicade) and often used for new starts. There is uncertainty, however, about switching patients already established on Remicade, especially when it’s forced by cost issues.
Interchangeability is a concern in the United States as well. The FDA is working on the issue but has not yet released guidance, and the agency was careful to note in its statement that Amjevita was “approved as a biosimilar, not as an interchangeable product.” Biosimilar adalimumab, meanwhile, is under review in Europe, according to an Amgen statement.
The FDA approved Amjevita after reviewing structural and functional characteristics, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics data, clinical immunogenicity data, and other clinical safety and effectiveness data that demonstrated similarity to Humira, including two phase III trials for plaque psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis.
An AbbVie spokesperson said the company “anticipated Amgen’s product would be approved,” but noted the ongoing litigation.
There are “no clinically meaningful differences” between Amgen’s biosimilar adalimumab (Amjevita) and AbbVie’s branded product Humira, the Food and Drug Administration noted it its Sept. 23 announcement of Amjevita’s approval.
Although Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) is expected to cost less than Humira, Amgen has not released price information or a launch date pending ongoing litigation with AbbVie over intellectual property rights, an Amgen spokeswoman said.
The products carry an identical black box warning of tuberculosis and other serious infections, as well as lymphoma and other malignancies “reported in children and adolescent patients treated with [tumor necrosis factor] blockers including adalimumab.” As with Humira, “the most common expected adverse reactions with Amjevita are infections and injection site reactions,” the FDA said. Both products are approved in 20 mg/0.4 mL and 40 mg/0.8 mL prefilled injections, but Humira also has a 10 mg/0.2 mL option.
Amjevita was unanimously recommended for approval by an FDA review panel in July. Although “the biosimilar pathway is still a new frontier,” it’s likely to “enhance access to treatment for patients with serious medical conditions,” Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the agency statement.
The approval follows the FDA’s approval of biosimilar infliximab (Inflectra) in April 2016 and biosimilar etanercept (Erelzi) in August 2016. Inflectra has not hit the U.S. market yet, but the European experience with biosimilar infliximab – generally positive – may give an indication of how Amjevita will fare in the United States. It’s perhaps a third or more less expensive than the original product (Remicade) and often used for new starts. There is uncertainty, however, about switching patients already established on Remicade, especially when it’s forced by cost issues.
Interchangeability is a concern in the United States as well. The FDA is working on the issue but has not yet released guidance, and the agency was careful to note in its statement that Amjevita was “approved as a biosimilar, not as an interchangeable product.” Biosimilar adalimumab, meanwhile, is under review in Europe, according to an Amgen statement.
The FDA approved Amjevita after reviewing structural and functional characteristics, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics data, clinical immunogenicity data, and other clinical safety and effectiveness data that demonstrated similarity to Humira, including two phase III trials for plaque psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis.
An AbbVie spokesperson said the company “anticipated Amgen’s product would be approved,” but noted the ongoing litigation.
Some psoriasis patients benefit from switching anti-TNF agents
Psoriasis patients may have more success with a second tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist after failure with a first, report Paul S. Yamauchi, MD, PhD, and coauthors.
Investigators analyzed 15 studies evaluating the efficacy of switching TNF antagonists after primary or secondary failure. Response rates at 24 weeks for a second antagonist were 30%-74% for a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score, and 20%-70% for achieving a Physician Global Assessment score of 0/1. Mean improvements in Dermatology Life Quality Index ranged from –3.5 to –13, Dr. Yamauchi and colleagues reported.
Patients who experienced secondary failure with initial treatment generally achieved better responses than those with primary failure, the authors said.
Though response rates to a second anti-TNF agent were lower than for a first, “a substantial proportion of patients in every study achieved treatment success,” they added.
Read the full article in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Psoriasis patients may have more success with a second tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist after failure with a first, report Paul S. Yamauchi, MD, PhD, and coauthors.
Investigators analyzed 15 studies evaluating the efficacy of switching TNF antagonists after primary or secondary failure. Response rates at 24 weeks for a second antagonist were 30%-74% for a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score, and 20%-70% for achieving a Physician Global Assessment score of 0/1. Mean improvements in Dermatology Life Quality Index ranged from –3.5 to –13, Dr. Yamauchi and colleagues reported.
Patients who experienced secondary failure with initial treatment generally achieved better responses than those with primary failure, the authors said.
Though response rates to a second anti-TNF agent were lower than for a first, “a substantial proportion of patients in every study achieved treatment success,” they added.
Read the full article in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Psoriasis patients may have more success with a second tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist after failure with a first, report Paul S. Yamauchi, MD, PhD, and coauthors.
Investigators analyzed 15 studies evaluating the efficacy of switching TNF antagonists after primary or secondary failure. Response rates at 24 weeks for a second antagonist were 30%-74% for a 75% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score, and 20%-70% for achieving a Physician Global Assessment score of 0/1. Mean improvements in Dermatology Life Quality Index ranged from –3.5 to –13, Dr. Yamauchi and colleagues reported.
Patients who experienced secondary failure with initial treatment generally achieved better responses than those with primary failure, the authors said.
Though response rates to a second anti-TNF agent were lower than for a first, “a substantial proportion of patients in every study achieved treatment success,” they added.
Read the full article in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Biosimilar version of etanercept gains FDA approval
A biosimilar of etanercept received clearance for marketing from the Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 30 for all of the inflammatory disease indications held by the reference originator etanercept product, Enbrel, according to an announcement from the agency.
Approval for all of Enbrel’s indications – rheumatoid arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis – was initially met with skepticism by members of the agency’s Arthritis Advisory Committee at a meeting in July because the biosimilar was compared against Enbrel in patients with plaque psoriasis only, but eventually all panel members voted to recommend approval.
The approval allows the biosimilar etanercept, called etanercept-szzs, to be marketed as a biosimilar only, not as an interchangeable product. The FDA has not yet developed guidance for manufacturers to follow to get approval for interchangeability, which means that a biosimilar “may be substituted for the reference product by a pharmacist without the intervention of the health care provider who prescribed the reference product,” according to the agency.
“We carefully evaluate the structural and functional characteristics of these complex molecules. Patients and providers can have confidence that there are no clinically meaningful differences in safety and efficacy from the reference product,” Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the agency’s announcement.
Etanercept-szzs will be marketed by Sandoz as Erelzi. Erelzi’s prescribing information can be found here. The biosimilar is currently undergoing review with the European Medicines Agency.
A biosimilar of etanercept received clearance for marketing from the Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 30 for all of the inflammatory disease indications held by the reference originator etanercept product, Enbrel, according to an announcement from the agency.
Approval for all of Enbrel’s indications – rheumatoid arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis – was initially met with skepticism by members of the agency’s Arthritis Advisory Committee at a meeting in July because the biosimilar was compared against Enbrel in patients with plaque psoriasis only, but eventually all panel members voted to recommend approval.
The approval allows the biosimilar etanercept, called etanercept-szzs, to be marketed as a biosimilar only, not as an interchangeable product. The FDA has not yet developed guidance for manufacturers to follow to get approval for interchangeability, which means that a biosimilar “may be substituted for the reference product by a pharmacist without the intervention of the health care provider who prescribed the reference product,” according to the agency.
“We carefully evaluate the structural and functional characteristics of these complex molecules. Patients and providers can have confidence that there are no clinically meaningful differences in safety and efficacy from the reference product,” Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the agency’s announcement.
Etanercept-szzs will be marketed by Sandoz as Erelzi. Erelzi’s prescribing information can be found here. The biosimilar is currently undergoing review with the European Medicines Agency.
A biosimilar of etanercept received clearance for marketing from the Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 30 for all of the inflammatory disease indications held by the reference originator etanercept product, Enbrel, according to an announcement from the agency.
Approval for all of Enbrel’s indications – rheumatoid arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis – was initially met with skepticism by members of the agency’s Arthritis Advisory Committee at a meeting in July because the biosimilar was compared against Enbrel in patients with plaque psoriasis only, but eventually all panel members voted to recommend approval.
The approval allows the biosimilar etanercept, called etanercept-szzs, to be marketed as a biosimilar only, not as an interchangeable product. The FDA has not yet developed guidance for manufacturers to follow to get approval for interchangeability, which means that a biosimilar “may be substituted for the reference product by a pharmacist without the intervention of the health care provider who prescribed the reference product,” according to the agency.
“We carefully evaluate the structural and functional characteristics of these complex molecules. Patients and providers can have confidence that there are no clinically meaningful differences in safety and efficacy from the reference product,” Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the agency’s announcement.
Etanercept-szzs will be marketed by Sandoz as Erelzi. Erelzi’s prescribing information can be found here. The biosimilar is currently undergoing review with the European Medicines Agency.
Ixekizumab improved psoriatic arthritis in patients who had not taken biologics
Two different doses of the humanized monoclonal antibody ixekizumab improved signs and symptoms of active psoriatic arthritis in a phase III manufacturer-sponsored trial of patients who had not taken a biologic drug before.
The agent selectively binds and neutralizes interleukin (IL)-17A, which promotes joint inflammation and damage via several mechanisms. So the study findings support the view that IL-17A is a key cytokine in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis and an appropriate therapeutic target, said Philip J. Mease, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Swedish Medical Center and the University of Washington, Seattle, and his associates.
They are performing the ongoing, 3-year, randomized, double-blind trial (SPIRIT-P1) comparing responses with an 80-mg dose of ixekizumab every 2 weeks (103 patients), an 80-mg dose every 4 weeks (107 patients), a 40-mg dose of adalimumab (Humira) every 2 weeks (101 patients, active control group), and matching placebo (106 patients, placebo-control group). Each of the two ixekizumab arms received a starting dose of 160 mg given as two injections at week 0. This report presented the findings after the initial 24-week, double-blind treatment period of the trial.
The study participants are adults with active psoriatic arthritis who had never been treated with biologic agents and who continued taking their usual doses of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, oral corticosteroids, opiates, and/or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs/Cox-2 inhibitors during the study. The mean patient age was 49.5 years. Of the 382 who completed this portion of the study, 57 showed an inadequate response and required rescue medication, including 10 on the lower dose of ixekizumab, 11 on the higher dose of ixekizumab, 9 taking adalimumab, and 27 taking placebo.
The primary efficacy endpoint, ACR20 response at week 24, was met by 62.1% of the higher-dose ixekizumab group, 57.9% of the lower-dose ixekizumab group, and 57.4% of the adalimumab group, all of which were significantly greater than the 30.2% rate in the placebo group. Both doses of the study drug as well as the active control drug also improved secondary endpoints: reducing mean levels of disease activity as measured by the 28-joint Disease Activity Score using on C-reactive protein, improving patient-reported physical function on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, and improving disease-related physical health as measured by the SF-36, the investigators said (Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Aug 23. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209709).
In addition, the progression of structural joint damage, as assessed on radiographs of bone erosions and joint-space narrowing in the hands and feet, was significantly less with the three active treatments than with placebo. Among patients with the most extensive disease, a significantly greater percentage achieved Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75 level of improvement with the three active treatments than with placebo. And among patients with nail involvement, mean improvements in Nail Psoriasis Severity Index scores were significantly higher with the three active treatments than with placebo.
Adverse effects included grade 1 and 2 neutropenia, herpes zoster involving the eyelid, gastroenteritis, esophageal candidiasis, and depression-related symptoms. All infections resolved with treatment, and none required discontinuation of the study drug.
This study was funded and sponsored by Eli Lilly, maker of ixekizumab. Dr. Mease reported receiving grants, personal fees, and other support from Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Merck, Novartis, and Corrona. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Two different doses of the humanized monoclonal antibody ixekizumab improved signs and symptoms of active psoriatic arthritis in a phase III manufacturer-sponsored trial of patients who had not taken a biologic drug before.
The agent selectively binds and neutralizes interleukin (IL)-17A, which promotes joint inflammation and damage via several mechanisms. So the study findings support the view that IL-17A is a key cytokine in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis and an appropriate therapeutic target, said Philip J. Mease, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Swedish Medical Center and the University of Washington, Seattle, and his associates.
They are performing the ongoing, 3-year, randomized, double-blind trial (SPIRIT-P1) comparing responses with an 80-mg dose of ixekizumab every 2 weeks (103 patients), an 80-mg dose every 4 weeks (107 patients), a 40-mg dose of adalimumab (Humira) every 2 weeks (101 patients, active control group), and matching placebo (106 patients, placebo-control group). Each of the two ixekizumab arms received a starting dose of 160 mg given as two injections at week 0. This report presented the findings after the initial 24-week, double-blind treatment period of the trial.
The study participants are adults with active psoriatic arthritis who had never been treated with biologic agents and who continued taking their usual doses of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, oral corticosteroids, opiates, and/or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs/Cox-2 inhibitors during the study. The mean patient age was 49.5 years. Of the 382 who completed this portion of the study, 57 showed an inadequate response and required rescue medication, including 10 on the lower dose of ixekizumab, 11 on the higher dose of ixekizumab, 9 taking adalimumab, and 27 taking placebo.
The primary efficacy endpoint, ACR20 response at week 24, was met by 62.1% of the higher-dose ixekizumab group, 57.9% of the lower-dose ixekizumab group, and 57.4% of the adalimumab group, all of which were significantly greater than the 30.2% rate in the placebo group. Both doses of the study drug as well as the active control drug also improved secondary endpoints: reducing mean levels of disease activity as measured by the 28-joint Disease Activity Score using on C-reactive protein, improving patient-reported physical function on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, and improving disease-related physical health as measured by the SF-36, the investigators said (Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Aug 23. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209709).
In addition, the progression of structural joint damage, as assessed on radiographs of bone erosions and joint-space narrowing in the hands and feet, was significantly less with the three active treatments than with placebo. Among patients with the most extensive disease, a significantly greater percentage achieved Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75 level of improvement with the three active treatments than with placebo. And among patients with nail involvement, mean improvements in Nail Psoriasis Severity Index scores were significantly higher with the three active treatments than with placebo.
Adverse effects included grade 1 and 2 neutropenia, herpes zoster involving the eyelid, gastroenteritis, esophageal candidiasis, and depression-related symptoms. All infections resolved with treatment, and none required discontinuation of the study drug.
This study was funded and sponsored by Eli Lilly, maker of ixekizumab. Dr. Mease reported receiving grants, personal fees, and other support from Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Merck, Novartis, and Corrona. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Two different doses of the humanized monoclonal antibody ixekizumab improved signs and symptoms of active psoriatic arthritis in a phase III manufacturer-sponsored trial of patients who had not taken a biologic drug before.
The agent selectively binds and neutralizes interleukin (IL)-17A, which promotes joint inflammation and damage via several mechanisms. So the study findings support the view that IL-17A is a key cytokine in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis and an appropriate therapeutic target, said Philip J. Mease, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Swedish Medical Center and the University of Washington, Seattle, and his associates.
They are performing the ongoing, 3-year, randomized, double-blind trial (SPIRIT-P1) comparing responses with an 80-mg dose of ixekizumab every 2 weeks (103 patients), an 80-mg dose every 4 weeks (107 patients), a 40-mg dose of adalimumab (Humira) every 2 weeks (101 patients, active control group), and matching placebo (106 patients, placebo-control group). Each of the two ixekizumab arms received a starting dose of 160 mg given as two injections at week 0. This report presented the findings after the initial 24-week, double-blind treatment period of the trial.
The study participants are adults with active psoriatic arthritis who had never been treated with biologic agents and who continued taking their usual doses of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, oral corticosteroids, opiates, and/or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs/Cox-2 inhibitors during the study. The mean patient age was 49.5 years. Of the 382 who completed this portion of the study, 57 showed an inadequate response and required rescue medication, including 10 on the lower dose of ixekizumab, 11 on the higher dose of ixekizumab, 9 taking adalimumab, and 27 taking placebo.
The primary efficacy endpoint, ACR20 response at week 24, was met by 62.1% of the higher-dose ixekizumab group, 57.9% of the lower-dose ixekizumab group, and 57.4% of the adalimumab group, all of which were significantly greater than the 30.2% rate in the placebo group. Both doses of the study drug as well as the active control drug also improved secondary endpoints: reducing mean levels of disease activity as measured by the 28-joint Disease Activity Score using on C-reactive protein, improving patient-reported physical function on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, and improving disease-related physical health as measured by the SF-36, the investigators said (Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Aug 23. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209709).
In addition, the progression of structural joint damage, as assessed on radiographs of bone erosions and joint-space narrowing in the hands and feet, was significantly less with the three active treatments than with placebo. Among patients with the most extensive disease, a significantly greater percentage achieved Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75 level of improvement with the three active treatments than with placebo. And among patients with nail involvement, mean improvements in Nail Psoriasis Severity Index scores were significantly higher with the three active treatments than with placebo.
Adverse effects included grade 1 and 2 neutropenia, herpes zoster involving the eyelid, gastroenteritis, esophageal candidiasis, and depression-related symptoms. All infections resolved with treatment, and none required discontinuation of the study drug.
This study was funded and sponsored by Eli Lilly, maker of ixekizumab. Dr. Mease reported receiving grants, personal fees, and other support from Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Merck, Novartis, and Corrona. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Key clinical point: Ixekizumab improved signs and symptoms of active psoriatic arthritis in a phase III manufacturer-sponsored trial of patients who had not taken biologics before.
Major finding: The primary endpoint, ACR20 response at week 24, was met by 62.1% of the lower-dose ixekizumab group, 57.9% of the higher-dose ixekizumab group, and 57.4% of the adalimumab group, which was significantly greater than the 30.2% rate in the placebo group.
Data source: A randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active treatment-controlled clinical trial involving 417 adults naive to biologic therapy.
Disclosures: This study was funded and sponsored by Eli Lilly, maker of ixekizumab. Dr. Mease reported receiving grants, personal fees, and other support from Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Merck, Novartis, and Corrona. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Psoriasis cardiovascular risk parallels type 2 diabetes
Psoriasis increased the measures of coronary artery calcium at a level similar to that seen in type 2 diabetes mellitus, independent of cardiovascular disease risk factors, based on data from a trio of cross-sectional studies including 387 adults. .
“Psoriasis and type 2 diabetes share similar cardiovascular risk profiles, which may predispose patients to developing coronary atherosclerosis at a relatively young age,” wrote Bobbak Mansouri, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas and his associates (JAMA Dermatol. 2016. [doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.2907]).
The researchers compared coronary artery calcium (CAC) levels in patients with psoriasis, patients with type 2 diabetes, and healthy controls. CAC has become an accepted measure of atherosclerosis and “the cornerstone for screening the risk of future cardiac events and improving cardiovascular risk stratification beyond traditional risk factors, especially in higher-risk groups,” according to the investigators. The average age of the patients was 52 years, 50% were female, and at least 92% were white.
The researchers used a hierarchical Tobit regression analysis to determine the association between disease and CAC level, as measured by the Agatston score. After controlling for confounding variables, including cardiovascular risk factors (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting blood glucose, systolic blood pressure, and tobacco use), the association with CAC was similar in psoriasis patients and type 2 diabetes patients (Tobit regression ratio [TRR], 0.89 and 0.79, respectively).
In a logistic multivariate regression analysis, patients with either psoriasis or type 2 diabetes were approximately twice as likely to have evidence of CAC as were healthy controls (odds ratio, 2.35 and 2.18, respectively), and psoriasis remained independently associated with the presence of CAC.
“When we added use of systemic or biological therapy to the models, the TRR and OR increased; however, these analyses were exploratory,” wrote Dr. Mansouri and his associates.
The study was limited by factors including the cross-sectional design and lack of diversity in the patient population, the investigators noted. However, the results suggest that “CAC assessment may be considered in patients with psoriasis who have two or more traditional cardiovascular risk factors given the high prevalence of CAC observed in this study,” they said.
Dr. Mansouri disclosed serving on an advisory board and receiving an honorarium from Celgene, maker of the psoriasis drug apremilast (Otezl). Study coauthors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
Psoriasis increased the measures of coronary artery calcium at a level similar to that seen in type 2 diabetes mellitus, independent of cardiovascular disease risk factors, based on data from a trio of cross-sectional studies including 387 adults. .
“Psoriasis and type 2 diabetes share similar cardiovascular risk profiles, which may predispose patients to developing coronary atherosclerosis at a relatively young age,” wrote Bobbak Mansouri, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas and his associates (JAMA Dermatol. 2016. [doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.2907]).
The researchers compared coronary artery calcium (CAC) levels in patients with psoriasis, patients with type 2 diabetes, and healthy controls. CAC has become an accepted measure of atherosclerosis and “the cornerstone for screening the risk of future cardiac events and improving cardiovascular risk stratification beyond traditional risk factors, especially in higher-risk groups,” according to the investigators. The average age of the patients was 52 years, 50% were female, and at least 92% were white.
The researchers used a hierarchical Tobit regression analysis to determine the association between disease and CAC level, as measured by the Agatston score. After controlling for confounding variables, including cardiovascular risk factors (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting blood glucose, systolic blood pressure, and tobacco use), the association with CAC was similar in psoriasis patients and type 2 diabetes patients (Tobit regression ratio [TRR], 0.89 and 0.79, respectively).
In a logistic multivariate regression analysis, patients with either psoriasis or type 2 diabetes were approximately twice as likely to have evidence of CAC as were healthy controls (odds ratio, 2.35 and 2.18, respectively), and psoriasis remained independently associated with the presence of CAC.
“When we added use of systemic or biological therapy to the models, the TRR and OR increased; however, these analyses were exploratory,” wrote Dr. Mansouri and his associates.
The study was limited by factors including the cross-sectional design and lack of diversity in the patient population, the investigators noted. However, the results suggest that “CAC assessment may be considered in patients with psoriasis who have two or more traditional cardiovascular risk factors given the high prevalence of CAC observed in this study,” they said.
Dr. Mansouri disclosed serving on an advisory board and receiving an honorarium from Celgene, maker of the psoriasis drug apremilast (Otezl). Study coauthors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
Psoriasis increased the measures of coronary artery calcium at a level similar to that seen in type 2 diabetes mellitus, independent of cardiovascular disease risk factors, based on data from a trio of cross-sectional studies including 387 adults. .
“Psoriasis and type 2 diabetes share similar cardiovascular risk profiles, which may predispose patients to developing coronary atherosclerosis at a relatively young age,” wrote Bobbak Mansouri, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas and his associates (JAMA Dermatol. 2016. [doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.2907]).
The researchers compared coronary artery calcium (CAC) levels in patients with psoriasis, patients with type 2 diabetes, and healthy controls. CAC has become an accepted measure of atherosclerosis and “the cornerstone for screening the risk of future cardiac events and improving cardiovascular risk stratification beyond traditional risk factors, especially in higher-risk groups,” according to the investigators. The average age of the patients was 52 years, 50% were female, and at least 92% were white.
The researchers used a hierarchical Tobit regression analysis to determine the association between disease and CAC level, as measured by the Agatston score. After controlling for confounding variables, including cardiovascular risk factors (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting blood glucose, systolic blood pressure, and tobacco use), the association with CAC was similar in psoriasis patients and type 2 diabetes patients (Tobit regression ratio [TRR], 0.89 and 0.79, respectively).
In a logistic multivariate regression analysis, patients with either psoriasis or type 2 diabetes were approximately twice as likely to have evidence of CAC as were healthy controls (odds ratio, 2.35 and 2.18, respectively), and psoriasis remained independently associated with the presence of CAC.
“When we added use of systemic or biological therapy to the models, the TRR and OR increased; however, these analyses were exploratory,” wrote Dr. Mansouri and his associates.
The study was limited by factors including the cross-sectional design and lack of diversity in the patient population, the investigators noted. However, the results suggest that “CAC assessment may be considered in patients with psoriasis who have two or more traditional cardiovascular risk factors given the high prevalence of CAC observed in this study,” they said.
Dr. Mansouri disclosed serving on an advisory board and receiving an honorarium from Celgene, maker of the psoriasis drug apremilast (Otezl). Study coauthors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Psoriasis patients have increased coronary artery calcium levels similar to those seen in type 2 diabetes patients, suggesting subclinical atherosclerosis.
Major finding: Psoriasis patients were more than twice as likely (odds ratio, 2.35) to have evidence of coronary artery calcium, compared with healthy controls.
Data source: A set of three single-center, cross-sectional studies totaling 387 adults and including individuals with psoriasis or type 2 diabetes, and healthy controls.
Disclosures: Dr. Mansouri disclosed serving on an advisory board and receiving an honorarium from Celgene, maker of the psoriasis drug apremilast (Otezl). Study coauthors disclosed financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies.