User login
A GI society update on MOC reform
Our work was suspended when ABIM announced the creation of a new longitudinal assessment option for maintenance of certification across all specialties.
GI society leaders are in touch with ABIM. Here’s an update on what we know:
- • The ABIM Board of Directors committed to evolve its program to provide a longitudinal assessment option for Maintenance of Certification (MOC), offering a self-paced pathway for physicians to acquire and demonstrate ongoing knowledge. The traditional, long-form assessment will also remain an option, as some physicians have expressed a preference for a point-in-time exam taken less frequently.
Our next steps include seeking clarity from ABIM including:
1. The milestones in the process to create the new pathway.
2. When the new pathway will be available to diplomates.
3. Consideration and integration of the GI societies’ principles in the development of the new pathway for recertification, including:
a. MOC needs to be simpler, less intrusive and less expensive.
b. We continue to support alternatives to the high-stakes, every-10-year recertification exam.
c. We do not support single source or time-limited assessments, as they do not represent the current realities of medicine in the digital age.
d. We support the concept that, for the many diplomates who specialize within certain areas of gastroenterology and hepatology, MOC should not include high-stakes assessments of areas in which the diplomate may not practice.
e. We support the principles of lifelong learning, as evidenced by ongoing CME activities, rather than lifelong testing.
4. The role the GI societies, as representatives for thousands of U.S. members who are ABIM diplomates, play in the creation and implementation of the new pathway.
AASLD, ACG, AGA and ASGE want to be fully informed and fully respected partners in an endeavor that touches upon one of the toughest challenges facing our members and the single issue we hear about most often requesting our help.
We will continue to update our members as we learn the answers to these questions from ABIM.
Together, our first priority on the MOC issue remains ensuring that GI diplomates have a pathway for recertification that meets your needs.
Our work was suspended when ABIM announced the creation of a new longitudinal assessment option for maintenance of certification across all specialties.
GI society leaders are in touch with ABIM. Here’s an update on what we know:
- • The ABIM Board of Directors committed to evolve its program to provide a longitudinal assessment option for Maintenance of Certification (MOC), offering a self-paced pathway for physicians to acquire and demonstrate ongoing knowledge. The traditional, long-form assessment will also remain an option, as some physicians have expressed a preference for a point-in-time exam taken less frequently.
Our next steps include seeking clarity from ABIM including:
1. The milestones in the process to create the new pathway.
2. When the new pathway will be available to diplomates.
3. Consideration and integration of the GI societies’ principles in the development of the new pathway for recertification, including:
a. MOC needs to be simpler, less intrusive and less expensive.
b. We continue to support alternatives to the high-stakes, every-10-year recertification exam.
c. We do not support single source or time-limited assessments, as they do not represent the current realities of medicine in the digital age.
d. We support the concept that, for the many diplomates who specialize within certain areas of gastroenterology and hepatology, MOC should not include high-stakes assessments of areas in which the diplomate may not practice.
e. We support the principles of lifelong learning, as evidenced by ongoing CME activities, rather than lifelong testing.
4. The role the GI societies, as representatives for thousands of U.S. members who are ABIM diplomates, play in the creation and implementation of the new pathway.
AASLD, ACG, AGA and ASGE want to be fully informed and fully respected partners in an endeavor that touches upon one of the toughest challenges facing our members and the single issue we hear about most often requesting our help.
We will continue to update our members as we learn the answers to these questions from ABIM.
Together, our first priority on the MOC issue remains ensuring that GI diplomates have a pathway for recertification that meets your needs.
Our work was suspended when ABIM announced the creation of a new longitudinal assessment option for maintenance of certification across all specialties.
GI society leaders are in touch with ABIM. Here’s an update on what we know:
- • The ABIM Board of Directors committed to evolve its program to provide a longitudinal assessment option for Maintenance of Certification (MOC), offering a self-paced pathway for physicians to acquire and demonstrate ongoing knowledge. The traditional, long-form assessment will also remain an option, as some physicians have expressed a preference for a point-in-time exam taken less frequently.
Our next steps include seeking clarity from ABIM including:
1. The milestones in the process to create the new pathway.
2. When the new pathway will be available to diplomates.
3. Consideration and integration of the GI societies’ principles in the development of the new pathway for recertification, including:
a. MOC needs to be simpler, less intrusive and less expensive.
b. We continue to support alternatives to the high-stakes, every-10-year recertification exam.
c. We do not support single source or time-limited assessments, as they do not represent the current realities of medicine in the digital age.
d. We support the concept that, for the many diplomates who specialize within certain areas of gastroenterology and hepatology, MOC should not include high-stakes assessments of areas in which the diplomate may not practice.
e. We support the principles of lifelong learning, as evidenced by ongoing CME activities, rather than lifelong testing.
4. The role the GI societies, as representatives for thousands of U.S. members who are ABIM diplomates, play in the creation and implementation of the new pathway.
AASLD, ACG, AGA and ASGE want to be fully informed and fully respected partners in an endeavor that touches upon one of the toughest challenges facing our members and the single issue we hear about most often requesting our help.
We will continue to update our members as we learn the answers to these questions from ABIM.
Together, our first priority on the MOC issue remains ensuring that GI diplomates have a pathway for recertification that meets your needs.
Dr. Anil Rustgi and Dr. Raymond DuBois elected to National Academy of Medicine
Anil Rustgi, MD, AGAF, and Raymond DuBois, MD, PhD, AGAF, were elected to the National Academy of Medicine, considered one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine and recognizes individuals who have demonstrated outstanding professional achievement and commitment to service.
Share your congratulations with both Dr. Rustgi and Dr. DuBois on the AGA Community.
Dr. Rustgi is recognized for illuminating the importance of GI cancers, genomics, and genetics and demonstrating that p120-catenin, part of the adherens junctions, is a tumor suppressor gene in cancers and the first to link p120-catenin to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) in tumor metastasis, advancing therapeutic opportunities.
Dr. Rustgi is Irving Professor of Medicine and director of the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center, and associate dean of oncology, department of medicine, Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons at Columbia University, New York.
Dr. DuBois is recognized for discovering the critical and mechanistic role of prostaglandins (PGs)/cyclooxygenase in colon cancer and its malignant progression, elucidating the role of PGs in the tumor microenvironment, and spearheading the now common use of drugs for human cancer prevention that target the PG pathway, like aspirin and other NSAIDs.
Dr. DuBois is dean of the College of Medicine, and professor of biochemistry and medicine at The Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
Anil Rustgi, MD, AGAF, and Raymond DuBois, MD, PhD, AGAF, were elected to the National Academy of Medicine, considered one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine and recognizes individuals who have demonstrated outstanding professional achievement and commitment to service.
Share your congratulations with both Dr. Rustgi and Dr. DuBois on the AGA Community.
Dr. Rustgi is recognized for illuminating the importance of GI cancers, genomics, and genetics and demonstrating that p120-catenin, part of the adherens junctions, is a tumor suppressor gene in cancers and the first to link p120-catenin to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) in tumor metastasis, advancing therapeutic opportunities.
Dr. Rustgi is Irving Professor of Medicine and director of the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center, and associate dean of oncology, department of medicine, Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons at Columbia University, New York.
Dr. DuBois is recognized for discovering the critical and mechanistic role of prostaglandins (PGs)/cyclooxygenase in colon cancer and its malignant progression, elucidating the role of PGs in the tumor microenvironment, and spearheading the now common use of drugs for human cancer prevention that target the PG pathway, like aspirin and other NSAIDs.
Dr. DuBois is dean of the College of Medicine, and professor of biochemistry and medicine at The Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
Anil Rustgi, MD, AGAF, and Raymond DuBois, MD, PhD, AGAF, were elected to the National Academy of Medicine, considered one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine and recognizes individuals who have demonstrated outstanding professional achievement and commitment to service.
Share your congratulations with both Dr. Rustgi and Dr. DuBois on the AGA Community.
Dr. Rustgi is recognized for illuminating the importance of GI cancers, genomics, and genetics and demonstrating that p120-catenin, part of the adherens junctions, is a tumor suppressor gene in cancers and the first to link p120-catenin to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) in tumor metastasis, advancing therapeutic opportunities.
Dr. Rustgi is Irving Professor of Medicine and director of the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center, and associate dean of oncology, department of medicine, Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons at Columbia University, New York.
Dr. DuBois is recognized for discovering the critical and mechanistic role of prostaglandins (PGs)/cyclooxygenase in colon cancer and its malignant progression, elucidating the role of PGs in the tumor microenvironment, and spearheading the now common use of drugs for human cancer prevention that target the PG pathway, like aspirin and other NSAIDs.
Dr. DuBois is dean of the College of Medicine, and professor of biochemistry and medicine at The Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
Top AGA Community patient cases
Physicians with difficult patient scenarios regularly bring their questions to the AGA Community (https://community.gastro.org) to seek advice from colleagues about therapy and disease management options, best practices, and diagnoses. In case you missed it, here are the most popular clinical discussions shared in the forum recently:
1. Severe lower GI bleed (http://ow.ly/iTrS30pOKaP) – A 15-year-old male patient was sent to the ER with severe lower GI bleed after a general physical exam revealed he was experiencing hypotension and tachycardia. The GI community discusses diagnostic possibilities for severe lower GI bleed at such young age and management options.
2. Refractory nausea and vomiting in a transgender patient (http://ow.ly/Di9C30pOKbq) – In this case of a 45-year-old transgender male-to-female patient, the community deliberates on several clinical issues, including a non-binary gender option on patient identification forms, treatment options for the patient and if hormonal therapy is contributing to GI symptoms.
3. Multidisciplinary guidelines (http://ow.ly/BtUK30pOKC8) – Are multidisciplinary guidelines with related specialty societies “the need of the hour” or too rare and short-lived for the effort?
Also in the forum: The AGA Clinical Practice Updates Committee is soliciting topics for future clinical expert review and commentaries commissioned by AGA. Share your ideas with the GI community (http://ow.ly/siV930pOJS1).
Access these clinical cases and more discussions at https://community.gastro.org/discussions.
Physicians with difficult patient scenarios regularly bring their questions to the AGA Community (https://community.gastro.org) to seek advice from colleagues about therapy and disease management options, best practices, and diagnoses. In case you missed it, here are the most popular clinical discussions shared in the forum recently:
1. Severe lower GI bleed (http://ow.ly/iTrS30pOKaP) – A 15-year-old male patient was sent to the ER with severe lower GI bleed after a general physical exam revealed he was experiencing hypotension and tachycardia. The GI community discusses diagnostic possibilities for severe lower GI bleed at such young age and management options.
2. Refractory nausea and vomiting in a transgender patient (http://ow.ly/Di9C30pOKbq) – In this case of a 45-year-old transgender male-to-female patient, the community deliberates on several clinical issues, including a non-binary gender option on patient identification forms, treatment options for the patient and if hormonal therapy is contributing to GI symptoms.
3. Multidisciplinary guidelines (http://ow.ly/BtUK30pOKC8) – Are multidisciplinary guidelines with related specialty societies “the need of the hour” or too rare and short-lived for the effort?
Also in the forum: The AGA Clinical Practice Updates Committee is soliciting topics for future clinical expert review and commentaries commissioned by AGA. Share your ideas with the GI community (http://ow.ly/siV930pOJS1).
Access these clinical cases and more discussions at https://community.gastro.org/discussions.
Physicians with difficult patient scenarios regularly bring their questions to the AGA Community (https://community.gastro.org) to seek advice from colleagues about therapy and disease management options, best practices, and diagnoses. In case you missed it, here are the most popular clinical discussions shared in the forum recently:
1. Severe lower GI bleed (http://ow.ly/iTrS30pOKaP) – A 15-year-old male patient was sent to the ER with severe lower GI bleed after a general physical exam revealed he was experiencing hypotension and tachycardia. The GI community discusses diagnostic possibilities for severe lower GI bleed at such young age and management options.
2. Refractory nausea and vomiting in a transgender patient (http://ow.ly/Di9C30pOKbq) – In this case of a 45-year-old transgender male-to-female patient, the community deliberates on several clinical issues, including a non-binary gender option on patient identification forms, treatment options for the patient and if hormonal therapy is contributing to GI symptoms.
3. Multidisciplinary guidelines (http://ow.ly/BtUK30pOKC8) – Are multidisciplinary guidelines with related specialty societies “the need of the hour” or too rare and short-lived for the effort?
Also in the forum: The AGA Clinical Practice Updates Committee is soliciting topics for future clinical expert review and commentaries commissioned by AGA. Share your ideas with the GI community (http://ow.ly/siV930pOJS1).
Access these clinical cases and more discussions at https://community.gastro.org/discussions.
Meet Donald Payne, Jr. – A staunch advocate for increasing access to colorectal cancer screening
Rep. Donald Payne Jr., D-N.J., has been representing the 10th congressional district of New Jersey which includes the Newark area and the thriving life-sciences community in the region since 2012. Rep. Payne Jr. ran to serve in the seat that his father, the late Rep.
Donald M. Payne, D-N.J., held for eleven terms until his untimely death in March 2012. The elder Payne succumbed to colon cancer 1 month after his initial diagnosis, and Rep. Payne Jr. has made it his personal mission since assuming his father’s seat to increase awareness of colorectal cancer screenings. In fact, shortly after entering office, Rep. Payne Jr. wrote an op-ed with AGA member Carla Ginsburg, MD, MPH, AGAF, on the importance of screening, relaying in deeply personal terms the cost of not getting screened.
Rep. Payne Jr. also made it a top priority to push national awareness of colon cancer screening beyond the halls of Congress. To that end, Rep. Payne Jr. successfully lobbied the Obama administration in 2014 to designate March as National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month – the first colorectal cancer presidential proclamation in over than a decade. The presidential proclamation was subsequently reissued in both 2015 and 2016 by the Obama administration and in 2018 and 2019 by the Trump administration. Additionally, Rep. Payne Jr. introduces a resolution in the House of Representatives every year to designate March as National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month in an effort to further promote awareness and educational activities of colorectal cancer screening in the chamber.
Most importantly, Rep. Payne Jr. is the lead champion of legislative efforts in the House to increase access to colorectal cancer screenings. Specifically, Rep. Payne Jr. is the lead sponsor of H.R. 1570, the Removing Barriers to Colorectal Cancer Screening Act, legislation that has been one of AGA’s top policy priorities. The legislation, which enjoys broad bipartisan support with over 300 cosponsors in the House, would correct the Medicare beneficiary coinsurance issue when a screening colonoscopy becomes therapeutic. He also is a strong supporter of biomedical research funding, noting in an op-ed with former Rep. Charlie Dent, R-Pa., that “scientists need stable, consistent, and robust funding to ensure that we can continue ... breakthroughs for the colorectal cancer community and beyond.”
AGA looks forward to continuing to work with Rep. Payne Jr. and his office in the 116th Congress on these critical issues and on policies affecting our patients and the field of gastroenterology.
Rep. Donald Payne Jr., D-N.J., has been representing the 10th congressional district of New Jersey which includes the Newark area and the thriving life-sciences community in the region since 2012. Rep. Payne Jr. ran to serve in the seat that his father, the late Rep.
Donald M. Payne, D-N.J., held for eleven terms until his untimely death in March 2012. The elder Payne succumbed to colon cancer 1 month after his initial diagnosis, and Rep. Payne Jr. has made it his personal mission since assuming his father’s seat to increase awareness of colorectal cancer screenings. In fact, shortly after entering office, Rep. Payne Jr. wrote an op-ed with AGA member Carla Ginsburg, MD, MPH, AGAF, on the importance of screening, relaying in deeply personal terms the cost of not getting screened.
Rep. Payne Jr. also made it a top priority to push national awareness of colon cancer screening beyond the halls of Congress. To that end, Rep. Payne Jr. successfully lobbied the Obama administration in 2014 to designate March as National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month – the first colorectal cancer presidential proclamation in over than a decade. The presidential proclamation was subsequently reissued in both 2015 and 2016 by the Obama administration and in 2018 and 2019 by the Trump administration. Additionally, Rep. Payne Jr. introduces a resolution in the House of Representatives every year to designate March as National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month in an effort to further promote awareness and educational activities of colorectal cancer screening in the chamber.
Most importantly, Rep. Payne Jr. is the lead champion of legislative efforts in the House to increase access to colorectal cancer screenings. Specifically, Rep. Payne Jr. is the lead sponsor of H.R. 1570, the Removing Barriers to Colorectal Cancer Screening Act, legislation that has been one of AGA’s top policy priorities. The legislation, which enjoys broad bipartisan support with over 300 cosponsors in the House, would correct the Medicare beneficiary coinsurance issue when a screening colonoscopy becomes therapeutic. He also is a strong supporter of biomedical research funding, noting in an op-ed with former Rep. Charlie Dent, R-Pa., that “scientists need stable, consistent, and robust funding to ensure that we can continue ... breakthroughs for the colorectal cancer community and beyond.”
AGA looks forward to continuing to work with Rep. Payne Jr. and his office in the 116th Congress on these critical issues and on policies affecting our patients and the field of gastroenterology.
Rep. Donald Payne Jr., D-N.J., has been representing the 10th congressional district of New Jersey which includes the Newark area and the thriving life-sciences community in the region since 2012. Rep. Payne Jr. ran to serve in the seat that his father, the late Rep.
Donald M. Payne, D-N.J., held for eleven terms until his untimely death in March 2012. The elder Payne succumbed to colon cancer 1 month after his initial diagnosis, and Rep. Payne Jr. has made it his personal mission since assuming his father’s seat to increase awareness of colorectal cancer screenings. In fact, shortly after entering office, Rep. Payne Jr. wrote an op-ed with AGA member Carla Ginsburg, MD, MPH, AGAF, on the importance of screening, relaying in deeply personal terms the cost of not getting screened.
Rep. Payne Jr. also made it a top priority to push national awareness of colon cancer screening beyond the halls of Congress. To that end, Rep. Payne Jr. successfully lobbied the Obama administration in 2014 to designate March as National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month – the first colorectal cancer presidential proclamation in over than a decade. The presidential proclamation was subsequently reissued in both 2015 and 2016 by the Obama administration and in 2018 and 2019 by the Trump administration. Additionally, Rep. Payne Jr. introduces a resolution in the House of Representatives every year to designate March as National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month in an effort to further promote awareness and educational activities of colorectal cancer screening in the chamber.
Most importantly, Rep. Payne Jr. is the lead champion of legislative efforts in the House to increase access to colorectal cancer screenings. Specifically, Rep. Payne Jr. is the lead sponsor of H.R. 1570, the Removing Barriers to Colorectal Cancer Screening Act, legislation that has been one of AGA’s top policy priorities. The legislation, which enjoys broad bipartisan support with over 300 cosponsors in the House, would correct the Medicare beneficiary coinsurance issue when a screening colonoscopy becomes therapeutic. He also is a strong supporter of biomedical research funding, noting in an op-ed with former Rep. Charlie Dent, R-Pa., that “scientists need stable, consistent, and robust funding to ensure that we can continue ... breakthroughs for the colorectal cancer community and beyond.”
AGA looks forward to continuing to work with Rep. Payne Jr. and his office in the 116th Congress on these critical issues and on policies affecting our patients and the field of gastroenterology.
CHEST 2020 Honor Lectures and Award Nominations
Each year, CHEST honors physicians and others who are making significant or meritorious contributions to chest medicine. All honorees are recognized for advancing work in specific areas of chest medicine, mentorship, and training, furthering the work of CHEST, and more.
If you believe you have a colleague who should be recognized for their distinguished work, please submit a nomination. Those selected for an annual award and honor lecture will be featured at CHEST 2020 in Chicago.
Deadline: Monday, January 6, 2020
Questions? Please contact Emily Petraglia, Manager, Volunteer Engagement ([email protected]).
The following awards are now open for nominations:
Annual Awards
College Medalist Award
Distinguished Service AwardMaster FCCP
Honor and Memorial Lectures
Edward C. Rosenow III, MD, Master FCCP/Master Teacher Endowed Honor Lecture.
Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical CareMurray Kornfeld Memorial Founders Award
Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyPasquale Ciaglia Memorial Lecture in Interventional MedicineMargaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical VentilationThomas L. Petty, MD, Master FCCP Endowed Memorial Lecture
Educator Awards
Early Career Clinician Educator
Master Clinician Educator
Each year, CHEST honors physicians and others who are making significant or meritorious contributions to chest medicine. All honorees are recognized for advancing work in specific areas of chest medicine, mentorship, and training, furthering the work of CHEST, and more.
If you believe you have a colleague who should be recognized for their distinguished work, please submit a nomination. Those selected for an annual award and honor lecture will be featured at CHEST 2020 in Chicago.
Deadline: Monday, January 6, 2020
Questions? Please contact Emily Petraglia, Manager, Volunteer Engagement ([email protected]).
The following awards are now open for nominations:
Annual Awards
College Medalist Award
Distinguished Service AwardMaster FCCP
Honor and Memorial Lectures
Edward C. Rosenow III, MD, Master FCCP/Master Teacher Endowed Honor Lecture.
Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical CareMurray Kornfeld Memorial Founders Award
Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyPasquale Ciaglia Memorial Lecture in Interventional MedicineMargaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical VentilationThomas L. Petty, MD, Master FCCP Endowed Memorial Lecture
Educator Awards
Early Career Clinician Educator
Master Clinician Educator
Each year, CHEST honors physicians and others who are making significant or meritorious contributions to chest medicine. All honorees are recognized for advancing work in specific areas of chest medicine, mentorship, and training, furthering the work of CHEST, and more.
If you believe you have a colleague who should be recognized for their distinguished work, please submit a nomination. Those selected for an annual award and honor lecture will be featured at CHEST 2020 in Chicago.
Deadline: Monday, January 6, 2020
Questions? Please contact Emily Petraglia, Manager, Volunteer Engagement ([email protected]).
The following awards are now open for nominations:
Annual Awards
College Medalist Award
Distinguished Service AwardMaster FCCP
Honor and Memorial Lectures
Edward C. Rosenow III, MD, Master FCCP/Master Teacher Endowed Honor Lecture.
Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical CareMurray Kornfeld Memorial Founders Award
Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyPasquale Ciaglia Memorial Lecture in Interventional MedicineMargaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical VentilationThomas L. Petty, MD, Master FCCP Endowed Memorial Lecture
Educator Awards
Early Career Clinician Educator
Master Clinician Educator
November is National Diabetes Month
November is National Diabetes Month, which gives SVS members the perfect opportunity to further educate their patients and loved ones with the SVS Foundation Patient flier on diabetes and vascular disease. These are available in both English and Spanish and can be downloaded instantly. You may also send patients and referrers to our Diabetes and Vascular Disease page. This holds several resources that might be useful for education purposes. Spread awareness and education using the many resources the SVS has to offer.
November is National Diabetes Month, which gives SVS members the perfect opportunity to further educate their patients and loved ones with the SVS Foundation Patient flier on diabetes and vascular disease. These are available in both English and Spanish and can be downloaded instantly. You may also send patients and referrers to our Diabetes and Vascular Disease page. This holds several resources that might be useful for education purposes. Spread awareness and education using the many resources the SVS has to offer.
November is National Diabetes Month, which gives SVS members the perfect opportunity to further educate their patients and loved ones with the SVS Foundation Patient flier on diabetes and vascular disease. These are available in both English and Spanish and can be downloaded instantly. You may also send patients and referrers to our Diabetes and Vascular Disease page. This holds several resources that might be useful for education purposes. Spread awareness and education using the many resources the SVS has to offer.
Find Support on SVSConnect
SVSConnect gives members an opportunity to share tough cases, discuss new breakthroughs in the industry and/or seek trusty advice from other professionals. Currently a post about Peer Support through the new SVS Member Support Program is one of the many discussions that users are engaging in. This post kicks off a series of discussion posts by the SVS Wellness Task Force, in collaboration with SurgeonMasters, that will focus on improving surgeons’ well-being, practice performance and patient outcomes. It is recommended that all who access SVSConnect on their mobile device download the app. This is the most user-friendly way to access the community and is an easy download. Follow the steps on this PDF to download the app. Reach out to [email protected] with any questions.
SVSConnect gives members an opportunity to share tough cases, discuss new breakthroughs in the industry and/or seek trusty advice from other professionals. Currently a post about Peer Support through the new SVS Member Support Program is one of the many discussions that users are engaging in. This post kicks off a series of discussion posts by the SVS Wellness Task Force, in collaboration with SurgeonMasters, that will focus on improving surgeons’ well-being, practice performance and patient outcomes. It is recommended that all who access SVSConnect on their mobile device download the app. This is the most user-friendly way to access the community and is an easy download. Follow the steps on this PDF to download the app. Reach out to [email protected] with any questions.
SVSConnect gives members an opportunity to share tough cases, discuss new breakthroughs in the industry and/or seek trusty advice from other professionals. Currently a post about Peer Support through the new SVS Member Support Program is one of the many discussions that users are engaging in. This post kicks off a series of discussion posts by the SVS Wellness Task Force, in collaboration with SurgeonMasters, that will focus on improving surgeons’ well-being, practice performance and patient outcomes. It is recommended that all who access SVSConnect on their mobile device download the app. This is the most user-friendly way to access the community and is an easy download. Follow the steps on this PDF to download the app. Reach out to [email protected] with any questions.
Submit Your Abstract For VAM 2020
Abstracts and videos for the 2020 Vascular Annual Meeting will be accepted now through January 15. The submission process may be completed on a smartphone or tablet computer. The Video Committee encourages submissions in areas such as dialysis access, lower extremity revascularization, surgical bypass procedures, venous interventions, management of adverse events and more. Read more and begin the submission process here.
Abstracts and videos for the 2020 Vascular Annual Meeting will be accepted now through January 15. The submission process may be completed on a smartphone or tablet computer. The Video Committee encourages submissions in areas such as dialysis access, lower extremity revascularization, surgical bypass procedures, venous interventions, management of adverse events and more. Read more and begin the submission process here.
Abstracts and videos for the 2020 Vascular Annual Meeting will be accepted now through January 15. The submission process may be completed on a smartphone or tablet computer. The Video Committee encourages submissions in areas such as dialysis access, lower extremity revascularization, surgical bypass procedures, venous interventions, management of adverse events and more. Read more and begin the submission process here.
Environmental Scan: Drivers of social, political and environmental change
We are living through an era of rapidly accelerated social, political, and environmental change. Spiraling costs of medical care, consumer activism around health care delivery, an aging population, and growing evidence of climate change are just some of the big currents of change. These trends are national and global in scope, and as such, far beyond any one profession or sector to shape or control. It remains for the medical profession to understand the currents of the time and adapt in order to thrive in the future.
Regulatory environment in flux
Hospitals and clinicians continue to struggle with a regulatory framework designed to improve higher quality of care yet may be creating additional barriers to access and efficiency. The passionate debate about health care costs and coverage is ongoing at the national level and appears to be a central issue on the minds of voters. Although the outcome of the debate cannot be foreseen, it will be left to the medical profession to maintain standards of care. Although the Affordable Care Act may not be repealed, the federal government’s role may diminish as policy is likely to be made by state politicians and bureaucrats.1 As a result, organizations operating in multiple states may find it difficult to develop organization-wide business strategies. And with the shift to value-based reimbursement and issues related to data breaches regarding private patient health care information, many health care professionals will need better support and documentation tools to remain compliant. This puts a large burden on medical organizations to invest even more in information technology, data management systems, and a wide range of training up and down the organizational chart. Keeping up with the needs of physicians for secure data management will be costly but critical.
Patients will feel climate change
Environmental factors affecting the air we breathe are of primary concern for patients with a broad range of cardiorespiratory conditions.2 Healthy but vulnerable infants, children, pregnant women, and the elderly may also feel the effects.3 Air pollution, increased levels of pollen and ground-level ozone, and wildfire smoke are all tied to climate change and all can have a direct impact on the patients seen by chest physicians.4 Individuals exposed to these environmental conditions may experience diminished lung function, resulting in increased hospital admissions.
Keeping up with the latest research on probable health impacts of these environmental trends will be on the agenda of most chest physicians.5 Professional societies will need to prepare to serve the educational needs of members in this regard. Continuing education content on these topics will be needed. The field will respond with new diagnostic tools and new treatments.6 Climate change may be a global-level phenomenon, but for many chest physicians, it means treating increasing numbers of patients affected by pulmonary disease.
Mind the generation gap
The population in the United States is primarily under the age of 65 years (84%), but the number of older citizens is on the rise. In 2016, there were 49.2 million people age 65 or older, and this number is projected to almost double to 98 million in 2060. The 85-and-over population is projected to more than double from 6.4 million in 2016 to 14.6 million in 2040 (a 129% increase).7
The medical needs of the aging population are already part of most medical institution’s planning but the current uncertainty in the health insurance market and the potential changes in Medicare coverage, not to mention the well-documented upcoming physician shortage, are complicating the planning process.8 Almost all acknowledge the “graying” of the population, but current approaches may not be sufficient given the projected the scale of the problems such as major increases in patients with chronic illnesses and the need for upscaling long-term geriatric care.
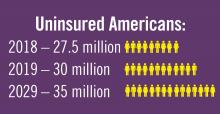
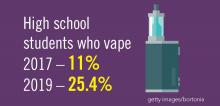
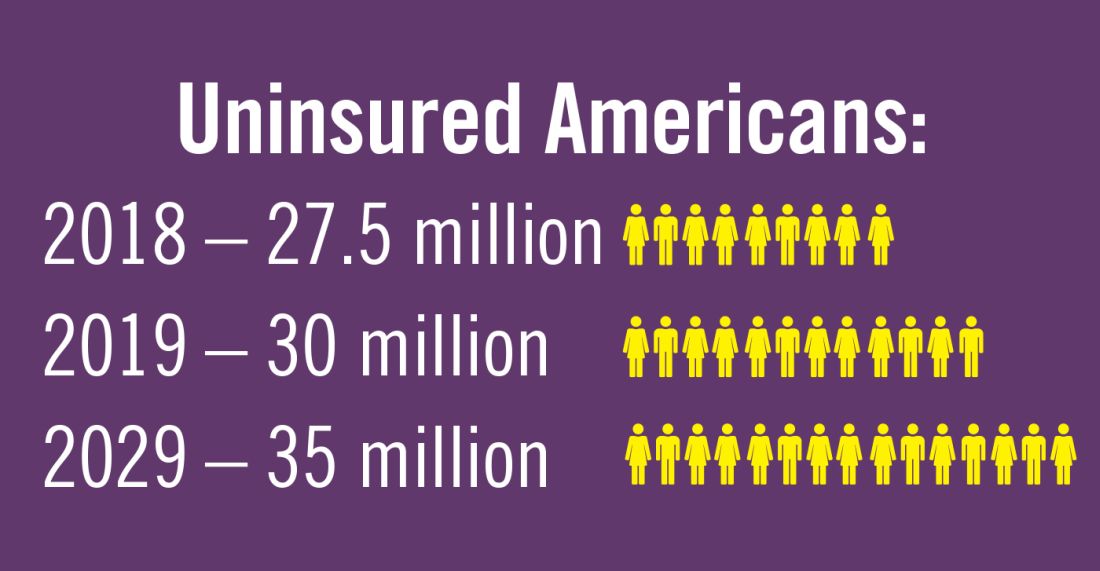
Planning for treating a growing elderly population shouldn’t mean ignoring some trends appearing among the younger population. E-cigarette use among middle- and high-school students may be creating millions of future patients with lung damage and nicotine addictions.9 Government intervention in this smoking epidemic is lagging behind the rapid spread of this unhealthy habit among young people.10 In 2019, health coverage of adults has begun to decline again after a decade of gains, and the possibility of this becoming a long-term trend has to be considered in planning for their treatment.11,12
References
1. Statistica. “Affordable Care Act - Statistics & Facts,” Matej Mikulic. 2019 Aug 14.
2. American Public Health Association and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2018). Climate Change Decreases the Quality of the Air We Breathe. Accessed 2019 Oct 7.
3. JAMA. 2019 Aug 13;322(6):546-56. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10255.
4. Lelieveld J et al. Cardiovascular disease burden from ambient air pollution in Europe reassessed using novel hazard ratio functions. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(20); 1590-6. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz135
5. European Respiratory Society. CME Online: Air pollution and respiratory health. 2018 Jun 21.
6. Environmental Protection Agency. “Particle Pollution and Your Patients’ Health,” Continuing Education for Particle Pollution Course. 2019 May 13.
7. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Administration on Aging. 2017 Profile of Older Americans. Accessed 2019 Oct 7.
8. Association of American Medical Colleges. Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projection from 2017 to 2032. 2019 Apr.
9. Miech R et al. Trends in Adolescent Vaping, 2017-2019. N Eng J Med. 2019 Sep 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1910739
10. Ned Sharpless, MD, Food and Drug Administration Acting Commissioner. “How the FDA is Regulating E-Cigarettes,” 2019 Sep 10.
11. Congressional Budget Office. Federal Subsidies for Health Insurance Coverage for People Under Age 65: 2019 to 2029. Washington D;C.: GPO, 2029
12. Galewitz P. “Breaking a 10-year streak, the number of uninsured Americans rises.” Internal Medicine News, 2019 Sep 11.
Note: Background research performed by Avenue M Group.
CHEST Inspiration is a collection of programmatic initiatives developed by the American College of Chest Physicians leadership and aimed at stimulating and encouraging innovation within the association. One of the components of CHEST Inspiration is the Environmental Scan, a series of articles focusing on the internal and external environmental factors that bear on success currently and in the future. See “Envisioning the Future: The CHEST Environmental Scan,” CHEST Physician, June 2019, p. 44, for an introduction to the series.
We are living through an era of rapidly accelerated social, political, and environmental change. Spiraling costs of medical care, consumer activism around health care delivery, an aging population, and growing evidence of climate change are just some of the big currents of change. These trends are national and global in scope, and as such, far beyond any one profession or sector to shape or control. It remains for the medical profession to understand the currents of the time and adapt in order to thrive in the future.
Regulatory environment in flux
Hospitals and clinicians continue to struggle with a regulatory framework designed to improve higher quality of care yet may be creating additional barriers to access and efficiency. The passionate debate about health care costs and coverage is ongoing at the national level and appears to be a central issue on the minds of voters. Although the outcome of the debate cannot be foreseen, it will be left to the medical profession to maintain standards of care. Although the Affordable Care Act may not be repealed, the federal government’s role may diminish as policy is likely to be made by state politicians and bureaucrats.1 As a result, organizations operating in multiple states may find it difficult to develop organization-wide business strategies. And with the shift to value-based reimbursement and issues related to data breaches regarding private patient health care information, many health care professionals will need better support and documentation tools to remain compliant. This puts a large burden on medical organizations to invest even more in information technology, data management systems, and a wide range of training up and down the organizational chart. Keeping up with the needs of physicians for secure data management will be costly but critical.
Patients will feel climate change
Environmental factors affecting the air we breathe are of primary concern for patients with a broad range of cardiorespiratory conditions.2 Healthy but vulnerable infants, children, pregnant women, and the elderly may also feel the effects.3 Air pollution, increased levels of pollen and ground-level ozone, and wildfire smoke are all tied to climate change and all can have a direct impact on the patients seen by chest physicians.4 Individuals exposed to these environmental conditions may experience diminished lung function, resulting in increased hospital admissions.
Keeping up with the latest research on probable health impacts of these environmental trends will be on the agenda of most chest physicians.5 Professional societies will need to prepare to serve the educational needs of members in this regard. Continuing education content on these topics will be needed. The field will respond with new diagnostic tools and new treatments.6 Climate change may be a global-level phenomenon, but for many chest physicians, it means treating increasing numbers of patients affected by pulmonary disease.
Mind the generation gap
The population in the United States is primarily under the age of 65 years (84%), but the number of older citizens is on the rise. In 2016, there were 49.2 million people age 65 or older, and this number is projected to almost double to 98 million in 2060. The 85-and-over population is projected to more than double from 6.4 million in 2016 to 14.6 million in 2040 (a 129% increase).7
The medical needs of the aging population are already part of most medical institution’s planning but the current uncertainty in the health insurance market and the potential changes in Medicare coverage, not to mention the well-documented upcoming physician shortage, are complicating the planning process.8 Almost all acknowledge the “graying” of the population, but current approaches may not be sufficient given the projected the scale of the problems such as major increases in patients with chronic illnesses and the need for upscaling long-term geriatric care.
Planning for treating a growing elderly population shouldn’t mean ignoring some trends appearing among the younger population. E-cigarette use among middle- and high-school students may be creating millions of future patients with lung damage and nicotine addictions.9 Government intervention in this smoking epidemic is lagging behind the rapid spread of this unhealthy habit among young people.10 In 2019, health coverage of adults has begun to decline again after a decade of gains, and the possibility of this becoming a long-term trend has to be considered in planning for their treatment.11,12
References
1. Statistica. “Affordable Care Act - Statistics & Facts,” Matej Mikulic. 2019 Aug 14.
2. American Public Health Association and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2018). Climate Change Decreases the Quality of the Air We Breathe. Accessed 2019 Oct 7.
3. JAMA. 2019 Aug 13;322(6):546-56. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10255.
4. Lelieveld J et al. Cardiovascular disease burden from ambient air pollution in Europe reassessed using novel hazard ratio functions. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(20); 1590-6. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz135
5. European Respiratory Society. CME Online: Air pollution and respiratory health. 2018 Jun 21.
6. Environmental Protection Agency. “Particle Pollution and Your Patients’ Health,” Continuing Education for Particle Pollution Course. 2019 May 13.
7. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Administration on Aging. 2017 Profile of Older Americans. Accessed 2019 Oct 7.
8. Association of American Medical Colleges. Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projection from 2017 to 2032. 2019 Apr.
9. Miech R et al. Trends in Adolescent Vaping, 2017-2019. N Eng J Med. 2019 Sep 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1910739
10. Ned Sharpless, MD, Food and Drug Administration Acting Commissioner. “How the FDA is Regulating E-Cigarettes,” 2019 Sep 10.
11. Congressional Budget Office. Federal Subsidies for Health Insurance Coverage for People Under Age 65: 2019 to 2029. Washington D;C.: GPO, 2029
12. Galewitz P. “Breaking a 10-year streak, the number of uninsured Americans rises.” Internal Medicine News, 2019 Sep 11.
Note: Background research performed by Avenue M Group.
CHEST Inspiration is a collection of programmatic initiatives developed by the American College of Chest Physicians leadership and aimed at stimulating and encouraging innovation within the association. One of the components of CHEST Inspiration is the Environmental Scan, a series of articles focusing on the internal and external environmental factors that bear on success currently and in the future. See “Envisioning the Future: The CHEST Environmental Scan,” CHEST Physician, June 2019, p. 44, for an introduction to the series.
We are living through an era of rapidly accelerated social, political, and environmental change. Spiraling costs of medical care, consumer activism around health care delivery, an aging population, and growing evidence of climate change are just some of the big currents of change. These trends are national and global in scope, and as such, far beyond any one profession or sector to shape or control. It remains for the medical profession to understand the currents of the time and adapt in order to thrive in the future.
Regulatory environment in flux
Hospitals and clinicians continue to struggle with a regulatory framework designed to improve higher quality of care yet may be creating additional barriers to access and efficiency. The passionate debate about health care costs and coverage is ongoing at the national level and appears to be a central issue on the minds of voters. Although the outcome of the debate cannot be foreseen, it will be left to the medical profession to maintain standards of care. Although the Affordable Care Act may not be repealed, the federal government’s role may diminish as policy is likely to be made by state politicians and bureaucrats.1 As a result, organizations operating in multiple states may find it difficult to develop organization-wide business strategies. And with the shift to value-based reimbursement and issues related to data breaches regarding private patient health care information, many health care professionals will need better support and documentation tools to remain compliant. This puts a large burden on medical organizations to invest even more in information technology, data management systems, and a wide range of training up and down the organizational chart. Keeping up with the needs of physicians for secure data management will be costly but critical.
Patients will feel climate change
Environmental factors affecting the air we breathe are of primary concern for patients with a broad range of cardiorespiratory conditions.2 Healthy but vulnerable infants, children, pregnant women, and the elderly may also feel the effects.3 Air pollution, increased levels of pollen and ground-level ozone, and wildfire smoke are all tied to climate change and all can have a direct impact on the patients seen by chest physicians.4 Individuals exposed to these environmental conditions may experience diminished lung function, resulting in increased hospital admissions.
Keeping up with the latest research on probable health impacts of these environmental trends will be on the agenda of most chest physicians.5 Professional societies will need to prepare to serve the educational needs of members in this regard. Continuing education content on these topics will be needed. The field will respond with new diagnostic tools and new treatments.6 Climate change may be a global-level phenomenon, but for many chest physicians, it means treating increasing numbers of patients affected by pulmonary disease.
Mind the generation gap
The population in the United States is primarily under the age of 65 years (84%), but the number of older citizens is on the rise. In 2016, there were 49.2 million people age 65 or older, and this number is projected to almost double to 98 million in 2060. The 85-and-over population is projected to more than double from 6.4 million in 2016 to 14.6 million in 2040 (a 129% increase).7
The medical needs of the aging population are already part of most medical institution’s planning but the current uncertainty in the health insurance market and the potential changes in Medicare coverage, not to mention the well-documented upcoming physician shortage, are complicating the planning process.8 Almost all acknowledge the “graying” of the population, but current approaches may not be sufficient given the projected the scale of the problems such as major increases in patients with chronic illnesses and the need for upscaling long-term geriatric care.
Planning for treating a growing elderly population shouldn’t mean ignoring some trends appearing among the younger population. E-cigarette use among middle- and high-school students may be creating millions of future patients with lung damage and nicotine addictions.9 Government intervention in this smoking epidemic is lagging behind the rapid spread of this unhealthy habit among young people.10 In 2019, health coverage of adults has begun to decline again after a decade of gains, and the possibility of this becoming a long-term trend has to be considered in planning for their treatment.11,12
References
1. Statistica. “Affordable Care Act - Statistics & Facts,” Matej Mikulic. 2019 Aug 14.
2. American Public Health Association and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2018). Climate Change Decreases the Quality of the Air We Breathe. Accessed 2019 Oct 7.
3. JAMA. 2019 Aug 13;322(6):546-56. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10255.
4. Lelieveld J et al. Cardiovascular disease burden from ambient air pollution in Europe reassessed using novel hazard ratio functions. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(20); 1590-6. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz135
5. European Respiratory Society. CME Online: Air pollution and respiratory health. 2018 Jun 21.
6. Environmental Protection Agency. “Particle Pollution and Your Patients’ Health,” Continuing Education for Particle Pollution Course. 2019 May 13.
7. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Administration on Aging. 2017 Profile of Older Americans. Accessed 2019 Oct 7.
8. Association of American Medical Colleges. Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projection from 2017 to 2032. 2019 Apr.
9. Miech R et al. Trends in Adolescent Vaping, 2017-2019. N Eng J Med. 2019 Sep 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1910739
10. Ned Sharpless, MD, Food and Drug Administration Acting Commissioner. “How the FDA is Regulating E-Cigarettes,” 2019 Sep 10.
11. Congressional Budget Office. Federal Subsidies for Health Insurance Coverage for People Under Age 65: 2019 to 2029. Washington D;C.: GPO, 2029
12. Galewitz P. “Breaking a 10-year streak, the number of uninsured Americans rises.” Internal Medicine News, 2019 Sep 11.
Note: Background research performed by Avenue M Group.
CHEST Inspiration is a collection of programmatic initiatives developed by the American College of Chest Physicians leadership and aimed at stimulating and encouraging innovation within the association. One of the components of CHEST Inspiration is the Environmental Scan, a series of articles focusing on the internal and external environmental factors that bear on success currently and in the future. See “Envisioning the Future: The CHEST Environmental Scan,” CHEST Physician, June 2019, p. 44, for an introduction to the series.
How to carve out a career as an educator during fellowship
Editor’s Note - As CHEST has just awarded the designation of Distinguished CHEST Educator (DCE) to 173 honorees at CHEST 2019 in New Orleans, this blog reminds fellows to start early to pursue a clinician educator role throughout their career.
While fellowship training is a time to continue building the foundation of expert clinical knowledge, it also offers an opportunity to start assembling a portfolio as a clinician educator. It takes time to compile educational scholarship and to establish a reputation within the communities of both teachers and learners, so it pays to get a head start. Moreover, it also takes time to master techniques for effective teaching to become that outstanding educator that you once looked up to as a medical student or resident. Below are some things that I found helpful in jump-starting that path during fellowship training.
Find a Capable Mentor
As with any sort of career planning, mentorship is key. Mentorship can open doors to expand your network and introduce opportunities for scholarship activities. Find a mentor who shares similar views and values with something that you feel passionate about. If you are planning on starting a scholarly project, make sure that your mentor has the background suited to help you maximize the experience and offer you the tools needed to achieve that end.
Determine What You Are Passionate About
Medical education is a vast field. Try to find something in medical education that is meaningful to you, whether it be in undergraduate medical education or graduate medical education or something else altogether. You want to be able to set yourself up for success, so the work has to be worthwhile.
Seek Out Opportunities to Teach
There are always opportunities to teach whether it entails precepting medical students on patient interviews or going over pulmonary/critical care topics at resident noon conferences. What I have found is that active participation in teaching opportunities tends to open a cascade of doors to more teaching opportunities.
Look for Opportunities to Be Involved in Educational Committees
Medical education, much like medicine, is a highly changing field. Leadership in medical education is always looking for resident/fellow representatives to bring new life and perspective to educational initiatives. Most of these opportunities do not require too much of a time commitment, and most committees often meet on a once-monthly basis. However, it connects you with faculty who are part of the leadership who can guide and help set you up for future success in medical education. During residency, I was able to take part in the intern curriculum committee to advise the direction of intern report. Now as a fellow, I’ve been able to meet many faculty and fellows with similar interests as mine in the CHEST Trainee Work Group.
Engage in Scholarly Activities
It is one thing to have a portfolio detailing teaching experiences, but it is another thing to have demonstrated published works in the space of medical education. It shows long-term promise as a clinician educator, and it shows leadership potential in advancing the field. It doesn’t take much to produce publications in medical education—there are always journals who look for trainees to contribute to the field whether it be an editorial or systematic review or innovative ideas.
About the Author
Justin K. Lui, MD, is a graduate of Boston University School of Medicine. He completed an internal medicine residency and chief residency at the University of Massachusetts Medical School. He is currently a second-year pulmonary and critical care medicine fellow at Boston University School of Medicine.
Reprinted from CHEST’s Thought Leader’s Blog, July 2019. This post is part of Our Life as a Fellow blog post series and includes “fellow life lessons” from current trainees in leadership with CHEST.
Editor’s Note - As CHEST has just awarded the designation of Distinguished CHEST Educator (DCE) to 173 honorees at CHEST 2019 in New Orleans, this blog reminds fellows to start early to pursue a clinician educator role throughout their career.
While fellowship training is a time to continue building the foundation of expert clinical knowledge, it also offers an opportunity to start assembling a portfolio as a clinician educator. It takes time to compile educational scholarship and to establish a reputation within the communities of both teachers and learners, so it pays to get a head start. Moreover, it also takes time to master techniques for effective teaching to become that outstanding educator that you once looked up to as a medical student or resident. Below are some things that I found helpful in jump-starting that path during fellowship training.
Find a Capable Mentor
As with any sort of career planning, mentorship is key. Mentorship can open doors to expand your network and introduce opportunities for scholarship activities. Find a mentor who shares similar views and values with something that you feel passionate about. If you are planning on starting a scholarly project, make sure that your mentor has the background suited to help you maximize the experience and offer you the tools needed to achieve that end.
Determine What You Are Passionate About
Medical education is a vast field. Try to find something in medical education that is meaningful to you, whether it be in undergraduate medical education or graduate medical education or something else altogether. You want to be able to set yourself up for success, so the work has to be worthwhile.
Seek Out Opportunities to Teach
There are always opportunities to teach whether it entails precepting medical students on patient interviews or going over pulmonary/critical care topics at resident noon conferences. What I have found is that active participation in teaching opportunities tends to open a cascade of doors to more teaching opportunities.
Look for Opportunities to Be Involved in Educational Committees
Medical education, much like medicine, is a highly changing field. Leadership in medical education is always looking for resident/fellow representatives to bring new life and perspective to educational initiatives. Most of these opportunities do not require too much of a time commitment, and most committees often meet on a once-monthly basis. However, it connects you with faculty who are part of the leadership who can guide and help set you up for future success in medical education. During residency, I was able to take part in the intern curriculum committee to advise the direction of intern report. Now as a fellow, I’ve been able to meet many faculty and fellows with similar interests as mine in the CHEST Trainee Work Group.
Engage in Scholarly Activities
It is one thing to have a portfolio detailing teaching experiences, but it is another thing to have demonstrated published works in the space of medical education. It shows long-term promise as a clinician educator, and it shows leadership potential in advancing the field. It doesn’t take much to produce publications in medical education—there are always journals who look for trainees to contribute to the field whether it be an editorial or systematic review or innovative ideas.
About the Author
Justin K. Lui, MD, is a graduate of Boston University School of Medicine. He completed an internal medicine residency and chief residency at the University of Massachusetts Medical School. He is currently a second-year pulmonary and critical care medicine fellow at Boston University School of Medicine.
Reprinted from CHEST’s Thought Leader’s Blog, July 2019. This post is part of Our Life as a Fellow blog post series and includes “fellow life lessons” from current trainees in leadership with CHEST.
Editor’s Note - As CHEST has just awarded the designation of Distinguished CHEST Educator (DCE) to 173 honorees at CHEST 2019 in New Orleans, this blog reminds fellows to start early to pursue a clinician educator role throughout their career.
While fellowship training is a time to continue building the foundation of expert clinical knowledge, it also offers an opportunity to start assembling a portfolio as a clinician educator. It takes time to compile educational scholarship and to establish a reputation within the communities of both teachers and learners, so it pays to get a head start. Moreover, it also takes time to master techniques for effective teaching to become that outstanding educator that you once looked up to as a medical student or resident. Below are some things that I found helpful in jump-starting that path during fellowship training.
Find a Capable Mentor
As with any sort of career planning, mentorship is key. Mentorship can open doors to expand your network and introduce opportunities for scholarship activities. Find a mentor who shares similar views and values with something that you feel passionate about. If you are planning on starting a scholarly project, make sure that your mentor has the background suited to help you maximize the experience and offer you the tools needed to achieve that end.
Determine What You Are Passionate About
Medical education is a vast field. Try to find something in medical education that is meaningful to you, whether it be in undergraduate medical education or graduate medical education or something else altogether. You want to be able to set yourself up for success, so the work has to be worthwhile.
Seek Out Opportunities to Teach
There are always opportunities to teach whether it entails precepting medical students on patient interviews or going over pulmonary/critical care topics at resident noon conferences. What I have found is that active participation in teaching opportunities tends to open a cascade of doors to more teaching opportunities.
Look for Opportunities to Be Involved in Educational Committees
Medical education, much like medicine, is a highly changing field. Leadership in medical education is always looking for resident/fellow representatives to bring new life and perspective to educational initiatives. Most of these opportunities do not require too much of a time commitment, and most committees often meet on a once-monthly basis. However, it connects you with faculty who are part of the leadership who can guide and help set you up for future success in medical education. During residency, I was able to take part in the intern curriculum committee to advise the direction of intern report. Now as a fellow, I’ve been able to meet many faculty and fellows with similar interests as mine in the CHEST Trainee Work Group.
Engage in Scholarly Activities
It is one thing to have a portfolio detailing teaching experiences, but it is another thing to have demonstrated published works in the space of medical education. It shows long-term promise as a clinician educator, and it shows leadership potential in advancing the field. It doesn’t take much to produce publications in medical education—there are always journals who look for trainees to contribute to the field whether it be an editorial or systematic review or innovative ideas.
About the Author
Justin K. Lui, MD, is a graduate of Boston University School of Medicine. He completed an internal medicine residency and chief residency at the University of Massachusetts Medical School. He is currently a second-year pulmonary and critical care medicine fellow at Boston University School of Medicine.
Reprinted from CHEST’s Thought Leader’s Blog, July 2019. This post is part of Our Life as a Fellow blog post series and includes “fellow life lessons” from current trainees in leadership with CHEST.