User login
Evidence builds for bariatric surgery’s role in cancer prevention
LAS VEGAS – The ability of bariatric surgery and substantial subsequent weight loss to cut the incidence of a variety of obesity-related cancers and other malignancies received further confirmation in results from two studies reported at a meeting presented by the Obesity Society and the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.
In one study, 2,107 adults enrolled in the Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS-2) study showed a statistically significant halving of the cancer incidence during 7 years of follow-up in patients who underwent bariatric surgery and had a reduction of at least 20% in their presurgical body mass index (BMI), compared with patients in the study who underwent bariatric surgery but lost less weight, reported Andrea M. Stroud, MD, a bariatric surgeon at the Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
In the second study, analysis of about 1.7 million hospitalized U.S. patients in the National Inpatient Sample showed that the incidence of an obesity-related cancer was 21% higher in more than 1.4 million obese individuals (BMI, 35 kg/m2 or greater) with no history of bariatric surgery, compared with nearly 247,000 people in the same database with a history of both obesity and bariatric surgery, said Juliana Henrique, MD, a bariatric surgeon at the Cleveland Clinic Florida in Weston.
The study reported by Dr. Henrique focused specifically on the 13 cancer types identified by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as having an incidence that links with overweight and obesity (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66[39]:1052-8), whereas the study presented by Dr. Stroud included all incident cancers during follow-up, but which were predominantly obesity related, with breast cancer – an obesity-related malignancy – having the highest incidence. Overall, 40% of all U.S. cancers in 2014 were obesity related, according to the CDC’s report.
“A number of studies have shown decreases in cancer rates after bariatric surgery, especially female cancers like breast and ovarian,” commented John Scott, MD, director of metabolic and bariatric surgery for Prism Health–Upstate in Greenville, S.C. “These two reports build on that.”
The evidence for weight loss after bariatric surgery as a means to cut the risk of a first or recurrent cancer has become strong enough for some patients to see cancer prophylaxis as a prime reason to undergo the procedure, said surgeons at the meeting.
Bariatric surgery and subsequent weight loss “is a substantial preventive factor for cancer, especially in patients who have obesity and diabetes,” commented Theresa LaMasters, MD, a bariatric surgeon in West Des Moines, Iowa. “It might not just be weight loss. It’s likely a multifactorial effect, including reduced inflammation after bariatric surgery, but weight loss is a component” of the effect, Dr. LaMasters said in an interview. It is now common for her to see patients seeking bariatric surgery because of a family or personal history of cancer. “Patients are trying to reduce their future risk” for cancer with bariatric surgery, she added.
The LABS-2 study enrolled 2,458 patients who were part of the first LABS cohort, LABS-1, but followed them longer term. The data Dr. Stroud reported came from 2,107 of the LABS-2 patients without a history of cancer, no cancer diagnosed in the first year after bariatric surgery, and longer-term follow-up of 7 years. About three-quarters of the patients underwent gastric bypass, with the rest undergoing laparoscopic gastric band placement. Nearly half of those included had diabetes. Their average BMI was 45-50 kg/m2.
Dr. Stroud and associates ran an analysis that divided the populations into tertiles based on percentage of baseline body mass lost at 12 months after surgery and cancer-free survival during the 7 years after the 12-month follow-up. The incidence of cancer was 51% lower in patients who lost 20%-34% of their BMI, compared with those who lost less than 20%, a statistically significant difference, and patients who lost 35% or more of their BMI had a 31% reduced cancer rate, compared with those who lost less than 20%, a difference that was not statistically significant, Dr. Stroud reported. The patients who lost less weight after surgery mostly underwent gastric banding, whereas those who lost more mostly underwent gastric bypass.
The analysis reported by Dr. Henrique used data collected in the U.S. National Inpatient Sample during 2010-2014, which totaled more than 7 million patients hospitalized for cancer, including 1,423,367 with a history of obesity and 246,668 with obesity who had undergone bariatric surgery. Those without bariatric surgery had a 21% higher rate of developing obesity-related cancers after adjustment for many baseline demographic and clinical features, Dr. Henrique said. The cancer protection after bariatric surgery was especially notable in the subset of patients in the sample with a genetic predisposition to developing cancer.
LABS-1 and LABS-2 were funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Stroud and Dr. Henrique had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Stroud AM et al. Obesity Week, Abstract A107; Henrique J et al. Obesity Week, Abstract A108.
LAS VEGAS – The ability of bariatric surgery and substantial subsequent weight loss to cut the incidence of a variety of obesity-related cancers and other malignancies received further confirmation in results from two studies reported at a meeting presented by the Obesity Society and the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.
In one study, 2,107 adults enrolled in the Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS-2) study showed a statistically significant halving of the cancer incidence during 7 years of follow-up in patients who underwent bariatric surgery and had a reduction of at least 20% in their presurgical body mass index (BMI), compared with patients in the study who underwent bariatric surgery but lost less weight, reported Andrea M. Stroud, MD, a bariatric surgeon at the Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
In the second study, analysis of about 1.7 million hospitalized U.S. patients in the National Inpatient Sample showed that the incidence of an obesity-related cancer was 21% higher in more than 1.4 million obese individuals (BMI, 35 kg/m2 or greater) with no history of bariatric surgery, compared with nearly 247,000 people in the same database with a history of both obesity and bariatric surgery, said Juliana Henrique, MD, a bariatric surgeon at the Cleveland Clinic Florida in Weston.
The study reported by Dr. Henrique focused specifically on the 13 cancer types identified by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as having an incidence that links with overweight and obesity (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66[39]:1052-8), whereas the study presented by Dr. Stroud included all incident cancers during follow-up, but which were predominantly obesity related, with breast cancer – an obesity-related malignancy – having the highest incidence. Overall, 40% of all U.S. cancers in 2014 were obesity related, according to the CDC’s report.
“A number of studies have shown decreases in cancer rates after bariatric surgery, especially female cancers like breast and ovarian,” commented John Scott, MD, director of metabolic and bariatric surgery for Prism Health–Upstate in Greenville, S.C. “These two reports build on that.”
The evidence for weight loss after bariatric surgery as a means to cut the risk of a first or recurrent cancer has become strong enough for some patients to see cancer prophylaxis as a prime reason to undergo the procedure, said surgeons at the meeting.
Bariatric surgery and subsequent weight loss “is a substantial preventive factor for cancer, especially in patients who have obesity and diabetes,” commented Theresa LaMasters, MD, a bariatric surgeon in West Des Moines, Iowa. “It might not just be weight loss. It’s likely a multifactorial effect, including reduced inflammation after bariatric surgery, but weight loss is a component” of the effect, Dr. LaMasters said in an interview. It is now common for her to see patients seeking bariatric surgery because of a family or personal history of cancer. “Patients are trying to reduce their future risk” for cancer with bariatric surgery, she added.
The LABS-2 study enrolled 2,458 patients who were part of the first LABS cohort, LABS-1, but followed them longer term. The data Dr. Stroud reported came from 2,107 of the LABS-2 patients without a history of cancer, no cancer diagnosed in the first year after bariatric surgery, and longer-term follow-up of 7 years. About three-quarters of the patients underwent gastric bypass, with the rest undergoing laparoscopic gastric band placement. Nearly half of those included had diabetes. Their average BMI was 45-50 kg/m2.
Dr. Stroud and associates ran an analysis that divided the populations into tertiles based on percentage of baseline body mass lost at 12 months after surgery and cancer-free survival during the 7 years after the 12-month follow-up. The incidence of cancer was 51% lower in patients who lost 20%-34% of their BMI, compared with those who lost less than 20%, a statistically significant difference, and patients who lost 35% or more of their BMI had a 31% reduced cancer rate, compared with those who lost less than 20%, a difference that was not statistically significant, Dr. Stroud reported. The patients who lost less weight after surgery mostly underwent gastric banding, whereas those who lost more mostly underwent gastric bypass.
The analysis reported by Dr. Henrique used data collected in the U.S. National Inpatient Sample during 2010-2014, which totaled more than 7 million patients hospitalized for cancer, including 1,423,367 with a history of obesity and 246,668 with obesity who had undergone bariatric surgery. Those without bariatric surgery had a 21% higher rate of developing obesity-related cancers after adjustment for many baseline demographic and clinical features, Dr. Henrique said. The cancer protection after bariatric surgery was especially notable in the subset of patients in the sample with a genetic predisposition to developing cancer.
LABS-1 and LABS-2 were funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Stroud and Dr. Henrique had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Stroud AM et al. Obesity Week, Abstract A107; Henrique J et al. Obesity Week, Abstract A108.
LAS VEGAS – The ability of bariatric surgery and substantial subsequent weight loss to cut the incidence of a variety of obesity-related cancers and other malignancies received further confirmation in results from two studies reported at a meeting presented by the Obesity Society and the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.
In one study, 2,107 adults enrolled in the Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS-2) study showed a statistically significant halving of the cancer incidence during 7 years of follow-up in patients who underwent bariatric surgery and had a reduction of at least 20% in their presurgical body mass index (BMI), compared with patients in the study who underwent bariatric surgery but lost less weight, reported Andrea M. Stroud, MD, a bariatric surgeon at the Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
In the second study, analysis of about 1.7 million hospitalized U.S. patients in the National Inpatient Sample showed that the incidence of an obesity-related cancer was 21% higher in more than 1.4 million obese individuals (BMI, 35 kg/m2 or greater) with no history of bariatric surgery, compared with nearly 247,000 people in the same database with a history of both obesity and bariatric surgery, said Juliana Henrique, MD, a bariatric surgeon at the Cleveland Clinic Florida in Weston.
The study reported by Dr. Henrique focused specifically on the 13 cancer types identified by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as having an incidence that links with overweight and obesity (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66[39]:1052-8), whereas the study presented by Dr. Stroud included all incident cancers during follow-up, but which were predominantly obesity related, with breast cancer – an obesity-related malignancy – having the highest incidence. Overall, 40% of all U.S. cancers in 2014 were obesity related, according to the CDC’s report.
“A number of studies have shown decreases in cancer rates after bariatric surgery, especially female cancers like breast and ovarian,” commented John Scott, MD, director of metabolic and bariatric surgery for Prism Health–Upstate in Greenville, S.C. “These two reports build on that.”
The evidence for weight loss after bariatric surgery as a means to cut the risk of a first or recurrent cancer has become strong enough for some patients to see cancer prophylaxis as a prime reason to undergo the procedure, said surgeons at the meeting.
Bariatric surgery and subsequent weight loss “is a substantial preventive factor for cancer, especially in patients who have obesity and diabetes,” commented Theresa LaMasters, MD, a bariatric surgeon in West Des Moines, Iowa. “It might not just be weight loss. It’s likely a multifactorial effect, including reduced inflammation after bariatric surgery, but weight loss is a component” of the effect, Dr. LaMasters said in an interview. It is now common for her to see patients seeking bariatric surgery because of a family or personal history of cancer. “Patients are trying to reduce their future risk” for cancer with bariatric surgery, she added.
The LABS-2 study enrolled 2,458 patients who were part of the first LABS cohort, LABS-1, but followed them longer term. The data Dr. Stroud reported came from 2,107 of the LABS-2 patients without a history of cancer, no cancer diagnosed in the first year after bariatric surgery, and longer-term follow-up of 7 years. About three-quarters of the patients underwent gastric bypass, with the rest undergoing laparoscopic gastric band placement. Nearly half of those included had diabetes. Their average BMI was 45-50 kg/m2.
Dr. Stroud and associates ran an analysis that divided the populations into tertiles based on percentage of baseline body mass lost at 12 months after surgery and cancer-free survival during the 7 years after the 12-month follow-up. The incidence of cancer was 51% lower in patients who lost 20%-34% of their BMI, compared with those who lost less than 20%, a statistically significant difference, and patients who lost 35% or more of their BMI had a 31% reduced cancer rate, compared with those who lost less than 20%, a difference that was not statistically significant, Dr. Stroud reported. The patients who lost less weight after surgery mostly underwent gastric banding, whereas those who lost more mostly underwent gastric bypass.
The analysis reported by Dr. Henrique used data collected in the U.S. National Inpatient Sample during 2010-2014, which totaled more than 7 million patients hospitalized for cancer, including 1,423,367 with a history of obesity and 246,668 with obesity who had undergone bariatric surgery. Those without bariatric surgery had a 21% higher rate of developing obesity-related cancers after adjustment for many baseline demographic and clinical features, Dr. Henrique said. The cancer protection after bariatric surgery was especially notable in the subset of patients in the sample with a genetic predisposition to developing cancer.
LABS-1 and LABS-2 were funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Stroud and Dr. Henrique had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Stroud AM et al. Obesity Week, Abstract A107; Henrique J et al. Obesity Week, Abstract A108.
REPORTING FROM OBESITY WEEK 2019
Pelvic insufficiency fractures are common after chemoradiotherapy for cervical cancer
CHICAGO – Radiation therapy for cervical cancer resulted in pelvic insufficiency fractures more frequently than previously thought, and many fractures were slow to heal, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America.
“Pelvic insufficiency fractures had a prevalence of 38% on MRI follow-up” after chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer, said Alina Dragan, MD. This figure is more than double the previously reported prevalence of about 14%.
Dr. Dragan, a radiology resident at London North West Healthcare, National Health Service Trust, and coinvestigators also tracked the natural history of these fractures over time, to fill a knowledge gap about whether, and at what rate, these pelvic insufficiency fractures healed.
In the single-center retrospective study, the investigators found that just 14% of sacral fractures healed during the period of observation. For acetabular and pubic fractures, roughly one in three fractures had healed by the last MRI scan. About a third of all fractures remained stable across scans, while just over 10% of fractures were either fluctuant or worsened.
The study included 115 women with locally advanced cervical cancer who were treated with radical or adjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy over a 5-year period, and had MRI scans performed in-house; the follow-up protocol had patients receiving scans at 3, 12, and 24 months post treatment. From an initial pool of 197 patients, those who had previously had pelvic radiation or were receiving palliative treatment, as well as those with incomplete imaging follow-up and those with metal implants or prostheses that could affect radiation therapy delivery or imaging quality were excluded.
The chemoradiotherapy protocol involved five doses of weekly cisplatin at 400 mg/m2 of body surface area, as well as high–dose rate cervix brachytherapy. In practice, all but six participants received these treatments. Patients also received external beam radiotherapy with or without a simultaneous integrated boost to target affected lymph nodes, as clinically indicated.
The fractures were graded as mild, moderate, or severe by the interpreting radiologist according to the course of the fracture line and corresponding bone edema.
Patients were aged a median of 54 years, and 64 (56%) were postmenopausal. Most patients (n = 84; 73%) had never used tobacco. Participants’ median body mass index was 26 kg/m2.
Most patients (n = 73; 64%) were International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage 2b, and almost half (n = 55; 48%) had pelvic nodal involvement.
Patients were followed for a median of 12 months, with patients receiving a median of two MRIs curing that period. In all, 105 fractures were identified in 44 patients. A median of two fractures were identified among the group of patients who had pelvic insufficiency fractures.
The fractures were graded as mild, moderate, or severe by the interpreting radiologist according to the course of the fracture line and corresponding bone edema. In this schema, 41% of identified fractures were considered mild, while 32% were moderate and 12% were severe.
Although just over two-thirds of fractures (70%) were identified within 6 months of beginning surveillance, a quarter were not identified until 9-13 months post therapy, and 5% were found after more than 13 months.
Sacral fractures accounted for 72% of those identified, in keeping with previous findings, said Dr. Dragan. Acetabular and pubic fractures made up 16% and 10% of fractures, respectively. One fracture was seen at the ilium and one at the ischium.
Dr. Dragan and colleagues turned to multivariable analysis to look for risk factors for pelvic insufficiency fractures in this cohort of cervical cancer patients. Younger patients had a hazard ratio of 0.30 for fracture, compared with those over the age of 50 years (P less than .01). Similarly, being menopausal carried a hazard ratio of 2.25 for fracture. Higher radiation doses to the sacrum also boosted fracture risk (HR, 2.00; P = .03). Neither sacral volume and slope nor the receipt of simultaneous integrated boost were associated with increased fracture risk.
Dr. Dragan reported that she had no relevant conflicts of interest. She reported no outside sources of funding.
SOURCE: Dragan A et al. RSNA 2019, Presentation SSE25-03.
CHICAGO – Radiation therapy for cervical cancer resulted in pelvic insufficiency fractures more frequently than previously thought, and many fractures were slow to heal, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America.
“Pelvic insufficiency fractures had a prevalence of 38% on MRI follow-up” after chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer, said Alina Dragan, MD. This figure is more than double the previously reported prevalence of about 14%.
Dr. Dragan, a radiology resident at London North West Healthcare, National Health Service Trust, and coinvestigators also tracked the natural history of these fractures over time, to fill a knowledge gap about whether, and at what rate, these pelvic insufficiency fractures healed.
In the single-center retrospective study, the investigators found that just 14% of sacral fractures healed during the period of observation. For acetabular and pubic fractures, roughly one in three fractures had healed by the last MRI scan. About a third of all fractures remained stable across scans, while just over 10% of fractures were either fluctuant or worsened.
The study included 115 women with locally advanced cervical cancer who were treated with radical or adjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy over a 5-year period, and had MRI scans performed in-house; the follow-up protocol had patients receiving scans at 3, 12, and 24 months post treatment. From an initial pool of 197 patients, those who had previously had pelvic radiation or were receiving palliative treatment, as well as those with incomplete imaging follow-up and those with metal implants or prostheses that could affect radiation therapy delivery or imaging quality were excluded.
The chemoradiotherapy protocol involved five doses of weekly cisplatin at 400 mg/m2 of body surface area, as well as high–dose rate cervix brachytherapy. In practice, all but six participants received these treatments. Patients also received external beam radiotherapy with or without a simultaneous integrated boost to target affected lymph nodes, as clinically indicated.
The fractures were graded as mild, moderate, or severe by the interpreting radiologist according to the course of the fracture line and corresponding bone edema.
Patients were aged a median of 54 years, and 64 (56%) were postmenopausal. Most patients (n = 84; 73%) had never used tobacco. Participants’ median body mass index was 26 kg/m2.
Most patients (n = 73; 64%) were International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage 2b, and almost half (n = 55; 48%) had pelvic nodal involvement.
Patients were followed for a median of 12 months, with patients receiving a median of two MRIs curing that period. In all, 105 fractures were identified in 44 patients. A median of two fractures were identified among the group of patients who had pelvic insufficiency fractures.
The fractures were graded as mild, moderate, or severe by the interpreting radiologist according to the course of the fracture line and corresponding bone edema. In this schema, 41% of identified fractures were considered mild, while 32% were moderate and 12% were severe.
Although just over two-thirds of fractures (70%) were identified within 6 months of beginning surveillance, a quarter were not identified until 9-13 months post therapy, and 5% were found after more than 13 months.
Sacral fractures accounted for 72% of those identified, in keeping with previous findings, said Dr. Dragan. Acetabular and pubic fractures made up 16% and 10% of fractures, respectively. One fracture was seen at the ilium and one at the ischium.
Dr. Dragan and colleagues turned to multivariable analysis to look for risk factors for pelvic insufficiency fractures in this cohort of cervical cancer patients. Younger patients had a hazard ratio of 0.30 for fracture, compared with those over the age of 50 years (P less than .01). Similarly, being menopausal carried a hazard ratio of 2.25 for fracture. Higher radiation doses to the sacrum also boosted fracture risk (HR, 2.00; P = .03). Neither sacral volume and slope nor the receipt of simultaneous integrated boost were associated with increased fracture risk.
Dr. Dragan reported that she had no relevant conflicts of interest. She reported no outside sources of funding.
SOURCE: Dragan A et al. RSNA 2019, Presentation SSE25-03.
CHICAGO – Radiation therapy for cervical cancer resulted in pelvic insufficiency fractures more frequently than previously thought, and many fractures were slow to heal, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America.
“Pelvic insufficiency fractures had a prevalence of 38% on MRI follow-up” after chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer, said Alina Dragan, MD. This figure is more than double the previously reported prevalence of about 14%.
Dr. Dragan, a radiology resident at London North West Healthcare, National Health Service Trust, and coinvestigators also tracked the natural history of these fractures over time, to fill a knowledge gap about whether, and at what rate, these pelvic insufficiency fractures healed.
In the single-center retrospective study, the investigators found that just 14% of sacral fractures healed during the period of observation. For acetabular and pubic fractures, roughly one in three fractures had healed by the last MRI scan. About a third of all fractures remained stable across scans, while just over 10% of fractures were either fluctuant or worsened.
The study included 115 women with locally advanced cervical cancer who were treated with radical or adjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy over a 5-year period, and had MRI scans performed in-house; the follow-up protocol had patients receiving scans at 3, 12, and 24 months post treatment. From an initial pool of 197 patients, those who had previously had pelvic radiation or were receiving palliative treatment, as well as those with incomplete imaging follow-up and those with metal implants or prostheses that could affect radiation therapy delivery or imaging quality were excluded.
The chemoradiotherapy protocol involved five doses of weekly cisplatin at 400 mg/m2 of body surface area, as well as high–dose rate cervix brachytherapy. In practice, all but six participants received these treatments. Patients also received external beam radiotherapy with or without a simultaneous integrated boost to target affected lymph nodes, as clinically indicated.
The fractures were graded as mild, moderate, or severe by the interpreting radiologist according to the course of the fracture line and corresponding bone edema.
Patients were aged a median of 54 years, and 64 (56%) were postmenopausal. Most patients (n = 84; 73%) had never used tobacco. Participants’ median body mass index was 26 kg/m2.
Most patients (n = 73; 64%) were International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage 2b, and almost half (n = 55; 48%) had pelvic nodal involvement.
Patients were followed for a median of 12 months, with patients receiving a median of two MRIs curing that period. In all, 105 fractures were identified in 44 patients. A median of two fractures were identified among the group of patients who had pelvic insufficiency fractures.
The fractures were graded as mild, moderate, or severe by the interpreting radiologist according to the course of the fracture line and corresponding bone edema. In this schema, 41% of identified fractures were considered mild, while 32% were moderate and 12% were severe.
Although just over two-thirds of fractures (70%) were identified within 6 months of beginning surveillance, a quarter were not identified until 9-13 months post therapy, and 5% were found after more than 13 months.
Sacral fractures accounted for 72% of those identified, in keeping with previous findings, said Dr. Dragan. Acetabular and pubic fractures made up 16% and 10% of fractures, respectively. One fracture was seen at the ilium and one at the ischium.
Dr. Dragan and colleagues turned to multivariable analysis to look for risk factors for pelvic insufficiency fractures in this cohort of cervical cancer patients. Younger patients had a hazard ratio of 0.30 for fracture, compared with those over the age of 50 years (P less than .01). Similarly, being menopausal carried a hazard ratio of 2.25 for fracture. Higher radiation doses to the sacrum also boosted fracture risk (HR, 2.00; P = .03). Neither sacral volume and slope nor the receipt of simultaneous integrated boost were associated with increased fracture risk.
Dr. Dragan reported that she had no relevant conflicts of interest. She reported no outside sources of funding.
SOURCE: Dragan A et al. RSNA 2019, Presentation SSE25-03.
REPORTING FROM RSNA 2019
QoL good for MGMT-methylated glioblastoma patients with lomustine-temozolide
In addition to offering an overall survival benefit for patients with MGMT-methylated glioblastoma, the combination of lomustine and temozolomide did not impair health-related quality of life (HRQOL) compared with temozolomide alone, investigators report.
Among 129 patients with newly-diagnosed glioblastoma with methylation of the MGMT promoter, there were no significant differences in any items on the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) quality of life questionnaire core-30 and the EORTC brain cancer module (BN20) between patients who received oral combined lomustine and temozolomide or temozolomide alone, reported Johannes Weller, MD, of University Hospital Bonn, Germany, and colleagues.
Although the combination was associated with slightly lower scores on the Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE), the differences were not clinically significant, the investigators asserted.
“The absence of systematic and clinically relevant changes in HRQOL and neurocognitive function combined with the survival benefit of lomustine-temozolomide versus temozolomide alone suggests that a long-term net clinical benefit exists for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylation of the MGMT promoter and supports the use of lomustine-temozolomide as a treatment option for these patients,” they wrote. The report is in The Lancet Oncology.
The investigators previously reported that median overall survival was improved from 31.4 months with temozolomide to 48.1 months with lomustine-temozolomide, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for death with the combination of 0.60 (P = .0492).
In the current report, Dr. Weller and associates looked at the secondary endpoints of HRQOL as measured by the EORTC scales, and at neurocognitive function as assessed by the MMSE and a neurocognitive test battery (NOA-07) that include Trail Making Test A and B (TMT-A and B), working memory tests, and tests for word and semantic verbal fluency.
The modified intention-to-treat analysis included all patients who received at least one dose of study chemotherapy. The analysis included data on 63 patients randomly assigned to receive standard oral temozolomide, consisting of 75 mg/m² daily during radiotherapy plus six 4-week courses of temozolomide at doses ranging from 150 to 200 mg/m² on days 1-5, every 4 weeks; and 66 patients assigned to receive oral combined lomustine consisting of a 100 mg/m² dose on day 1, plus temozolomide 100 to 200 mg/m² on days 2-6 for six cycles of 6 weeks each.
After a median follow-up of 19.4 months for the HRQOL endpoint, there were no significant differences between the groups in decline from baselines in Karnofsky Performance Score, global health, physical functioning, cognitive functioning, social functioning, or communication deficit.
As noted before, however, there were small but significant differences between the groups favoring temozolomide on the MMSE, after a median follow-up for this measure of 15.3 months. The authors noted that the differences “were not significant when adjusted for multiple testing and were also not clinically relevant, because even over the time course of 4 years the differences between the groups would only add up to 1.76/30 points and clinically significant results would require a difference of more than 3/30 points.”
There were also no significant differences between the groups in any item of the neurocognitive test, they added.
The investigators acknowledged that the trial was limited by its relatively small size, and that after 3.5 years of follow-up about half of all the expected HRQOL forms were missing, which might lead to reporting bias.
“Overall, we conclude that the addition of lomustine to temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed MGMT-methylated glioblastoma is associated with a clear long-term net clinical benefit and our data provide a good rationale for the trial regimen as a treatment option for these patients. Nevertheless, changes in HRQOL during the first year after beginning treatment needs further exploration in future studies,” Dr. Weller and colleagues wrote.
The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research funded the study. Dr. Weller reported having no conflict of interest. Several coauthors reported relationships with industry outside the submitted work.
SOURCE: Weller J et al. Lancet Oncol. Sept 2. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30502-9.
In addition to offering an overall survival benefit for patients with MGMT-methylated glioblastoma, the combination of lomustine and temozolomide did not impair health-related quality of life (HRQOL) compared with temozolomide alone, investigators report.
Among 129 patients with newly-diagnosed glioblastoma with methylation of the MGMT promoter, there were no significant differences in any items on the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) quality of life questionnaire core-30 and the EORTC brain cancer module (BN20) between patients who received oral combined lomustine and temozolomide or temozolomide alone, reported Johannes Weller, MD, of University Hospital Bonn, Germany, and colleagues.
Although the combination was associated with slightly lower scores on the Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE), the differences were not clinically significant, the investigators asserted.
“The absence of systematic and clinically relevant changes in HRQOL and neurocognitive function combined with the survival benefit of lomustine-temozolomide versus temozolomide alone suggests that a long-term net clinical benefit exists for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylation of the MGMT promoter and supports the use of lomustine-temozolomide as a treatment option for these patients,” they wrote. The report is in The Lancet Oncology.
The investigators previously reported that median overall survival was improved from 31.4 months with temozolomide to 48.1 months with lomustine-temozolomide, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for death with the combination of 0.60 (P = .0492).
In the current report, Dr. Weller and associates looked at the secondary endpoints of HRQOL as measured by the EORTC scales, and at neurocognitive function as assessed by the MMSE and a neurocognitive test battery (NOA-07) that include Trail Making Test A and B (TMT-A and B), working memory tests, and tests for word and semantic verbal fluency.
The modified intention-to-treat analysis included all patients who received at least one dose of study chemotherapy. The analysis included data on 63 patients randomly assigned to receive standard oral temozolomide, consisting of 75 mg/m² daily during radiotherapy plus six 4-week courses of temozolomide at doses ranging from 150 to 200 mg/m² on days 1-5, every 4 weeks; and 66 patients assigned to receive oral combined lomustine consisting of a 100 mg/m² dose on day 1, plus temozolomide 100 to 200 mg/m² on days 2-6 for six cycles of 6 weeks each.
After a median follow-up of 19.4 months for the HRQOL endpoint, there were no significant differences between the groups in decline from baselines in Karnofsky Performance Score, global health, physical functioning, cognitive functioning, social functioning, or communication deficit.
As noted before, however, there were small but significant differences between the groups favoring temozolomide on the MMSE, after a median follow-up for this measure of 15.3 months. The authors noted that the differences “were not significant when adjusted for multiple testing and were also not clinically relevant, because even over the time course of 4 years the differences between the groups would only add up to 1.76/30 points and clinically significant results would require a difference of more than 3/30 points.”
There were also no significant differences between the groups in any item of the neurocognitive test, they added.
The investigators acknowledged that the trial was limited by its relatively small size, and that after 3.5 years of follow-up about half of all the expected HRQOL forms were missing, which might lead to reporting bias.
“Overall, we conclude that the addition of lomustine to temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed MGMT-methylated glioblastoma is associated with a clear long-term net clinical benefit and our data provide a good rationale for the trial regimen as a treatment option for these patients. Nevertheless, changes in HRQOL during the first year after beginning treatment needs further exploration in future studies,” Dr. Weller and colleagues wrote.
The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research funded the study. Dr. Weller reported having no conflict of interest. Several coauthors reported relationships with industry outside the submitted work.
SOURCE: Weller J et al. Lancet Oncol. Sept 2. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30502-9.
In addition to offering an overall survival benefit for patients with MGMT-methylated glioblastoma, the combination of lomustine and temozolomide did not impair health-related quality of life (HRQOL) compared with temozolomide alone, investigators report.
Among 129 patients with newly-diagnosed glioblastoma with methylation of the MGMT promoter, there were no significant differences in any items on the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) quality of life questionnaire core-30 and the EORTC brain cancer module (BN20) between patients who received oral combined lomustine and temozolomide or temozolomide alone, reported Johannes Weller, MD, of University Hospital Bonn, Germany, and colleagues.
Although the combination was associated with slightly lower scores on the Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE), the differences were not clinically significant, the investigators asserted.
“The absence of systematic and clinically relevant changes in HRQOL and neurocognitive function combined with the survival benefit of lomustine-temozolomide versus temozolomide alone suggests that a long-term net clinical benefit exists for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylation of the MGMT promoter and supports the use of lomustine-temozolomide as a treatment option for these patients,” they wrote. The report is in The Lancet Oncology.
The investigators previously reported that median overall survival was improved from 31.4 months with temozolomide to 48.1 months with lomustine-temozolomide, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for death with the combination of 0.60 (P = .0492).
In the current report, Dr. Weller and associates looked at the secondary endpoints of HRQOL as measured by the EORTC scales, and at neurocognitive function as assessed by the MMSE and a neurocognitive test battery (NOA-07) that include Trail Making Test A and B (TMT-A and B), working memory tests, and tests for word and semantic verbal fluency.
The modified intention-to-treat analysis included all patients who received at least one dose of study chemotherapy. The analysis included data on 63 patients randomly assigned to receive standard oral temozolomide, consisting of 75 mg/m² daily during radiotherapy plus six 4-week courses of temozolomide at doses ranging from 150 to 200 mg/m² on days 1-5, every 4 weeks; and 66 patients assigned to receive oral combined lomustine consisting of a 100 mg/m² dose on day 1, plus temozolomide 100 to 200 mg/m² on days 2-6 for six cycles of 6 weeks each.
After a median follow-up of 19.4 months for the HRQOL endpoint, there were no significant differences between the groups in decline from baselines in Karnofsky Performance Score, global health, physical functioning, cognitive functioning, social functioning, or communication deficit.
As noted before, however, there were small but significant differences between the groups favoring temozolomide on the MMSE, after a median follow-up for this measure of 15.3 months. The authors noted that the differences “were not significant when adjusted for multiple testing and were also not clinically relevant, because even over the time course of 4 years the differences between the groups would only add up to 1.76/30 points and clinically significant results would require a difference of more than 3/30 points.”
There were also no significant differences between the groups in any item of the neurocognitive test, they added.
The investigators acknowledged that the trial was limited by its relatively small size, and that after 3.5 years of follow-up about half of all the expected HRQOL forms were missing, which might lead to reporting bias.
“Overall, we conclude that the addition of lomustine to temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed MGMT-methylated glioblastoma is associated with a clear long-term net clinical benefit and our data provide a good rationale for the trial regimen as a treatment option for these patients. Nevertheless, changes in HRQOL during the first year after beginning treatment needs further exploration in future studies,” Dr. Weller and colleagues wrote.
The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research funded the study. Dr. Weller reported having no conflict of interest. Several coauthors reported relationships with industry outside the submitted work.
SOURCE: Weller J et al. Lancet Oncol. Sept 2. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30502-9.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY
New evidence informs discussions on FL treatment and breast screening
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent studies that reinforce prior diagnostic and treatment preferences among many oncologists and will certainly influence the discussions we all will have with our patients in the coming weeks and months.
Rituximab maintenance in follicular lymphoma
The largest trial addressing the role of maintenance CD20-targeted antibody therapy was the Primary Rituximab and Maintenance (PRIMA) phase 3, intergroup study in 1,018 advanced follicular lymphoma patients with an initial response to induction chemoimmunotherapy. The induction regimen could be either of three commonly used regimens plus rituximab. Importantly, none of the induction regimens included bendamustine.
Patients were randomized to 2 years of rituximab maintenance or observation. Prior interim analyses at 3 and 6 years showed improvements for the rituximab maintenance patients in progression-free survival and other secondary endpoints, but no improvement in overall survival. Emmanuel Bachy, MD, PhD, and colleagues published the final survival data after 9 years of follow-up, including a final safety analysis (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;37[31]:2815-24).
Among the 607 patients consenting to extended follow-up, median progression-free survival was 10.5 years with rituximab maintenance, compared with 4.1 years for observation (hazard ratio, 0.61; P less than .001). There were more patients with progression-free survival at 3 years, complete response or unconfirmed complete response at 2 years, longer time to next antilymphoma treatment, and later time to next chemotherapy. But the 10-year overall survival was similar in the two groups, as were the quality of life ratings.
In all, 503 patients experienced disease progression. Overall survival after progression was shorter in the rituximab maintenance arm versus the observation arm. Among the approximately 4% of patients experiencing transformation from follicular lymphoma to a more aggressive histology, there was no difference observed in time to transformation. Results were independent of the induction regimen received, response to induction, Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index score, and other clinical factors.
In the safety analysis, there were more grade 3-4 adverse events among the rituximab maintenance patients – primarily cytopenia and infections – more serious adverse events, and more adverse events overall. Fatal adverse events were low in both groups (1.6 vs. 0.6%).
How these results influence practice
Many years ago, a senior mentor of mine taught that “progression-free survival is an important endpoint since the quality of life for patients is generally superior before relapse than afterwards.”
With that mantra playing in my mind and with the reality that discussions about relapse and subsequent treatment are never easy, the results of PRIMA seem straightforward: Rituximab maintenance is beneficial, despite the absence of an overall survival benefit, in a disease with multiple options for subsequent therapy and a long natural history. In this 9-year, final analysis of PRIMA, rituximab maintenance seems to have achieved its goals of deepening responses with low (but not inconsequential) toxicity and delaying substantially those difficult conversations with patients about how to proceed after relapse.
The influence of the final analysis of PRIMA, however, may be more complicated that it would initially seem. Bendamustine-containing regimens were not employed, are commonly used now, and some studies with bendamustine have suggested higher nonrelapse mortality with rituximab maintenance.
Low-grade adverse events take on greater importance for patients on long-term therapy than they do for patients receiving abbreviated treatment, and with noncurative treatment, the higher adverse event profile with 2 years of rituximab maintenance needs to be taken seriously. Induction and maintenance regimens involving rituximab alone, lenalidomide, or obinutuzumab may be preferred for some patients. For all of those reasons, the discussion about rituximab with advanced follicular lymphoma patients remains a long one, demanding detailed descriptions of risks, benefits, limitations of the data, and multiple modern day alternatives to the treatments employed in PRIMA.
Supplemental MRI for dense breast tissue
In the DENSE trial, investigators assigned 40,373 women with extremely dense breast tissue and negative results on screening mammography to be offered either supplemental MRI or mammography screening every other year only. The women were 50-75 years old and were enrolled in the Dutch population-based digital mammography screening program. The primary outcome was the difference in the number of cancers that developed in the 2-year interval between mammograms (N Engl J Med 2019;381:2091-102).
The interval cancer rate was 2.5 per 1,000 screenings among 4,783 women in the “MRI-invitation” group (41% of whom did not actually agree to have an MRI), and 5 per 1,000 in the 32,312 women in the “mammography-only” group, a difference of 2.5 per 1,000 screenings (P less than .001).
Of the 20 interval cancers diagnosed in the MRI-invitation group, 4 were diagnosed in the 59% of women who had undergone MRI (0.8 per 1,000 screenings). The remaining 16 were diagnosed in those who had declined an MRI (4.9 per 1,000 screenings) – virtually identical to the rate of interval cancers in the group that was not invited to have an MRI. This speaks against nonrandom allocation of patients between the mammography-only and the supplemental MRI groups.
Although supplemental MRI was associated with a cancer-detection rate of 16.5 per 1,000 screenings, there was a false positive rate of 8.0% (79.8 per 1,000 screenings). Of the women who underwent a breast biopsy after MRI, 73.7% did not have cancer. Among the women who had MRI-detected cancers, in general, the malignancies diagnosed were smaller, more likely node negative, better differentiated, and more often hormone receptor–positive, compared with those in the mammography-only group.
At the next screening mammogram, the cancer detection rate was lower in the MRI-screened group (2 per 1,000 screenings) than in the MRI–“offered but declined” (7.1 per 1,000 screenings) or mammogram-only groups (6 per 1,000 screenings).
How these results influence practice
American physicians are obligated to inform women with dense breast tissue about the limitations (for them) of conventional mammography, an unquantified, but elevated, risk of breast cancer in women with dense breast tissue, and the fact that there are no universally accepted recommended subsequent steps those women should take.
One side benefit of the requirement to disclose information about breast density, however, is that disclosure can prompt discussions about breast cancer risk reduction – an important discussion with multiple possible health-maintaining interventions.
The DENSE trial is very important news, with potential for even more value in future years. It is finite (2 years of study, with only one MRI scan mandated), narrow (Vopara or BI-RADs breast density grade 4 only), and oligo-institutional (eight participating centers in the Netherlands). Still, it provides randomized, rigorously gathered and analyzed data where there were previously none. Importantly, it answers the question, “So what can I do now, doctor?”
I have some concerns about whether we, as a medical community, have the discipline to restrict application of supplemental MRI screening beyond the population that was studied in the Netherlands. Will we be able to restrain ourselves from ordering MRI scans in women with heterogeneously dense – but not extremely dense – breasts? Will we truly manage patients whose MRI scans had BI-RADs readings of less than 4 in the rigorous, but conservative, fashion employed in the trial? Would we miss fewer significant cancers and subject fewer patients to potential expense and harm with annual mammography, instead of the biennial screening performed in the Netherlands? Does tomo-synthesis improve the interpretation of screening mammograms so much that the interval cancer rate is a lot closer to the rate obtained with supplemental MRI scans? Is the expense of MRI scanning, with the resultant subsequent tests and procedures, justified by the reduction in detecting relatively favorable breast cancers that may not materially impact overall survival?
The DENSE study promises to be a “gift that keeps on giving” as the investigators continue to assess a number of factors including: the value of ongoing supplemental MRI scans (compared with the one-time-only screening reported here); whether there will be a reduction in the advanced cancers and subsequent mortality benefit; the extent of over diagnosis, costs, and impact on quality-of-life; and the applicability of artificial intelligence techniques to reduce false positive MRI results.
While the study may not be practice changing in the United States at the present time, it may be just that as subsequent analyses emerge.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent studies that reinforce prior diagnostic and treatment preferences among many oncologists and will certainly influence the discussions we all will have with our patients in the coming weeks and months.
Rituximab maintenance in follicular lymphoma
The largest trial addressing the role of maintenance CD20-targeted antibody therapy was the Primary Rituximab and Maintenance (PRIMA) phase 3, intergroup study in 1,018 advanced follicular lymphoma patients with an initial response to induction chemoimmunotherapy. The induction regimen could be either of three commonly used regimens plus rituximab. Importantly, none of the induction regimens included bendamustine.
Patients were randomized to 2 years of rituximab maintenance or observation. Prior interim analyses at 3 and 6 years showed improvements for the rituximab maintenance patients in progression-free survival and other secondary endpoints, but no improvement in overall survival. Emmanuel Bachy, MD, PhD, and colleagues published the final survival data after 9 years of follow-up, including a final safety analysis (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;37[31]:2815-24).
Among the 607 patients consenting to extended follow-up, median progression-free survival was 10.5 years with rituximab maintenance, compared with 4.1 years for observation (hazard ratio, 0.61; P less than .001). There were more patients with progression-free survival at 3 years, complete response or unconfirmed complete response at 2 years, longer time to next antilymphoma treatment, and later time to next chemotherapy. But the 10-year overall survival was similar in the two groups, as were the quality of life ratings.
In all, 503 patients experienced disease progression. Overall survival after progression was shorter in the rituximab maintenance arm versus the observation arm. Among the approximately 4% of patients experiencing transformation from follicular lymphoma to a more aggressive histology, there was no difference observed in time to transformation. Results were independent of the induction regimen received, response to induction, Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index score, and other clinical factors.
In the safety analysis, there were more grade 3-4 adverse events among the rituximab maintenance patients – primarily cytopenia and infections – more serious adverse events, and more adverse events overall. Fatal adverse events were low in both groups (1.6 vs. 0.6%).
How these results influence practice
Many years ago, a senior mentor of mine taught that “progression-free survival is an important endpoint since the quality of life for patients is generally superior before relapse than afterwards.”
With that mantra playing in my mind and with the reality that discussions about relapse and subsequent treatment are never easy, the results of PRIMA seem straightforward: Rituximab maintenance is beneficial, despite the absence of an overall survival benefit, in a disease with multiple options for subsequent therapy and a long natural history. In this 9-year, final analysis of PRIMA, rituximab maintenance seems to have achieved its goals of deepening responses with low (but not inconsequential) toxicity and delaying substantially those difficult conversations with patients about how to proceed after relapse.
The influence of the final analysis of PRIMA, however, may be more complicated that it would initially seem. Bendamustine-containing regimens were not employed, are commonly used now, and some studies with bendamustine have suggested higher nonrelapse mortality with rituximab maintenance.
Low-grade adverse events take on greater importance for patients on long-term therapy than they do for patients receiving abbreviated treatment, and with noncurative treatment, the higher adverse event profile with 2 years of rituximab maintenance needs to be taken seriously. Induction and maintenance regimens involving rituximab alone, lenalidomide, or obinutuzumab may be preferred for some patients. For all of those reasons, the discussion about rituximab with advanced follicular lymphoma patients remains a long one, demanding detailed descriptions of risks, benefits, limitations of the data, and multiple modern day alternatives to the treatments employed in PRIMA.
Supplemental MRI for dense breast tissue
In the DENSE trial, investigators assigned 40,373 women with extremely dense breast tissue and negative results on screening mammography to be offered either supplemental MRI or mammography screening every other year only. The women were 50-75 years old and were enrolled in the Dutch population-based digital mammography screening program. The primary outcome was the difference in the number of cancers that developed in the 2-year interval between mammograms (N Engl J Med 2019;381:2091-102).
The interval cancer rate was 2.5 per 1,000 screenings among 4,783 women in the “MRI-invitation” group (41% of whom did not actually agree to have an MRI), and 5 per 1,000 in the 32,312 women in the “mammography-only” group, a difference of 2.5 per 1,000 screenings (P less than .001).
Of the 20 interval cancers diagnosed in the MRI-invitation group, 4 were diagnosed in the 59% of women who had undergone MRI (0.8 per 1,000 screenings). The remaining 16 were diagnosed in those who had declined an MRI (4.9 per 1,000 screenings) – virtually identical to the rate of interval cancers in the group that was not invited to have an MRI. This speaks against nonrandom allocation of patients between the mammography-only and the supplemental MRI groups.
Although supplemental MRI was associated with a cancer-detection rate of 16.5 per 1,000 screenings, there was a false positive rate of 8.0% (79.8 per 1,000 screenings). Of the women who underwent a breast biopsy after MRI, 73.7% did not have cancer. Among the women who had MRI-detected cancers, in general, the malignancies diagnosed were smaller, more likely node negative, better differentiated, and more often hormone receptor–positive, compared with those in the mammography-only group.
At the next screening mammogram, the cancer detection rate was lower in the MRI-screened group (2 per 1,000 screenings) than in the MRI–“offered but declined” (7.1 per 1,000 screenings) or mammogram-only groups (6 per 1,000 screenings).
How these results influence practice
American physicians are obligated to inform women with dense breast tissue about the limitations (for them) of conventional mammography, an unquantified, but elevated, risk of breast cancer in women with dense breast tissue, and the fact that there are no universally accepted recommended subsequent steps those women should take.
One side benefit of the requirement to disclose information about breast density, however, is that disclosure can prompt discussions about breast cancer risk reduction – an important discussion with multiple possible health-maintaining interventions.
The DENSE trial is very important news, with potential for even more value in future years. It is finite (2 years of study, with only one MRI scan mandated), narrow (Vopara or BI-RADs breast density grade 4 only), and oligo-institutional (eight participating centers in the Netherlands). Still, it provides randomized, rigorously gathered and analyzed data where there were previously none. Importantly, it answers the question, “So what can I do now, doctor?”
I have some concerns about whether we, as a medical community, have the discipline to restrict application of supplemental MRI screening beyond the population that was studied in the Netherlands. Will we be able to restrain ourselves from ordering MRI scans in women with heterogeneously dense – but not extremely dense – breasts? Will we truly manage patients whose MRI scans had BI-RADs readings of less than 4 in the rigorous, but conservative, fashion employed in the trial? Would we miss fewer significant cancers and subject fewer patients to potential expense and harm with annual mammography, instead of the biennial screening performed in the Netherlands? Does tomo-synthesis improve the interpretation of screening mammograms so much that the interval cancer rate is a lot closer to the rate obtained with supplemental MRI scans? Is the expense of MRI scanning, with the resultant subsequent tests and procedures, justified by the reduction in detecting relatively favorable breast cancers that may not materially impact overall survival?
The DENSE study promises to be a “gift that keeps on giving” as the investigators continue to assess a number of factors including: the value of ongoing supplemental MRI scans (compared with the one-time-only screening reported here); whether there will be a reduction in the advanced cancers and subsequent mortality benefit; the extent of over diagnosis, costs, and impact on quality-of-life; and the applicability of artificial intelligence techniques to reduce false positive MRI results.
While the study may not be practice changing in the United States at the present time, it may be just that as subsequent analyses emerge.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent studies that reinforce prior diagnostic and treatment preferences among many oncologists and will certainly influence the discussions we all will have with our patients in the coming weeks and months.
Rituximab maintenance in follicular lymphoma
The largest trial addressing the role of maintenance CD20-targeted antibody therapy was the Primary Rituximab and Maintenance (PRIMA) phase 3, intergroup study in 1,018 advanced follicular lymphoma patients with an initial response to induction chemoimmunotherapy. The induction regimen could be either of three commonly used regimens plus rituximab. Importantly, none of the induction regimens included bendamustine.
Patients were randomized to 2 years of rituximab maintenance or observation. Prior interim analyses at 3 and 6 years showed improvements for the rituximab maintenance patients in progression-free survival and other secondary endpoints, but no improvement in overall survival. Emmanuel Bachy, MD, PhD, and colleagues published the final survival data after 9 years of follow-up, including a final safety analysis (J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;37[31]:2815-24).
Among the 607 patients consenting to extended follow-up, median progression-free survival was 10.5 years with rituximab maintenance, compared with 4.1 years for observation (hazard ratio, 0.61; P less than .001). There were more patients with progression-free survival at 3 years, complete response or unconfirmed complete response at 2 years, longer time to next antilymphoma treatment, and later time to next chemotherapy. But the 10-year overall survival was similar in the two groups, as were the quality of life ratings.
In all, 503 patients experienced disease progression. Overall survival after progression was shorter in the rituximab maintenance arm versus the observation arm. Among the approximately 4% of patients experiencing transformation from follicular lymphoma to a more aggressive histology, there was no difference observed in time to transformation. Results were independent of the induction regimen received, response to induction, Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index score, and other clinical factors.
In the safety analysis, there were more grade 3-4 adverse events among the rituximab maintenance patients – primarily cytopenia and infections – more serious adverse events, and more adverse events overall. Fatal adverse events were low in both groups (1.6 vs. 0.6%).
How these results influence practice
Many years ago, a senior mentor of mine taught that “progression-free survival is an important endpoint since the quality of life for patients is generally superior before relapse than afterwards.”
With that mantra playing in my mind and with the reality that discussions about relapse and subsequent treatment are never easy, the results of PRIMA seem straightforward: Rituximab maintenance is beneficial, despite the absence of an overall survival benefit, in a disease with multiple options for subsequent therapy and a long natural history. In this 9-year, final analysis of PRIMA, rituximab maintenance seems to have achieved its goals of deepening responses with low (but not inconsequential) toxicity and delaying substantially those difficult conversations with patients about how to proceed after relapse.
The influence of the final analysis of PRIMA, however, may be more complicated that it would initially seem. Bendamustine-containing regimens were not employed, are commonly used now, and some studies with bendamustine have suggested higher nonrelapse mortality with rituximab maintenance.
Low-grade adverse events take on greater importance for patients on long-term therapy than they do for patients receiving abbreviated treatment, and with noncurative treatment, the higher adverse event profile with 2 years of rituximab maintenance needs to be taken seriously. Induction and maintenance regimens involving rituximab alone, lenalidomide, or obinutuzumab may be preferred for some patients. For all of those reasons, the discussion about rituximab with advanced follicular lymphoma patients remains a long one, demanding detailed descriptions of risks, benefits, limitations of the data, and multiple modern day alternatives to the treatments employed in PRIMA.
Supplemental MRI for dense breast tissue
In the DENSE trial, investigators assigned 40,373 women with extremely dense breast tissue and negative results on screening mammography to be offered either supplemental MRI or mammography screening every other year only. The women were 50-75 years old and were enrolled in the Dutch population-based digital mammography screening program. The primary outcome was the difference in the number of cancers that developed in the 2-year interval between mammograms (N Engl J Med 2019;381:2091-102).
The interval cancer rate was 2.5 per 1,000 screenings among 4,783 women in the “MRI-invitation” group (41% of whom did not actually agree to have an MRI), and 5 per 1,000 in the 32,312 women in the “mammography-only” group, a difference of 2.5 per 1,000 screenings (P less than .001).
Of the 20 interval cancers diagnosed in the MRI-invitation group, 4 were diagnosed in the 59% of women who had undergone MRI (0.8 per 1,000 screenings). The remaining 16 were diagnosed in those who had declined an MRI (4.9 per 1,000 screenings) – virtually identical to the rate of interval cancers in the group that was not invited to have an MRI. This speaks against nonrandom allocation of patients between the mammography-only and the supplemental MRI groups.
Although supplemental MRI was associated with a cancer-detection rate of 16.5 per 1,000 screenings, there was a false positive rate of 8.0% (79.8 per 1,000 screenings). Of the women who underwent a breast biopsy after MRI, 73.7% did not have cancer. Among the women who had MRI-detected cancers, in general, the malignancies diagnosed were smaller, more likely node negative, better differentiated, and more often hormone receptor–positive, compared with those in the mammography-only group.
At the next screening mammogram, the cancer detection rate was lower in the MRI-screened group (2 per 1,000 screenings) than in the MRI–“offered but declined” (7.1 per 1,000 screenings) or mammogram-only groups (6 per 1,000 screenings).
How these results influence practice
American physicians are obligated to inform women with dense breast tissue about the limitations (for them) of conventional mammography, an unquantified, but elevated, risk of breast cancer in women with dense breast tissue, and the fact that there are no universally accepted recommended subsequent steps those women should take.
One side benefit of the requirement to disclose information about breast density, however, is that disclosure can prompt discussions about breast cancer risk reduction – an important discussion with multiple possible health-maintaining interventions.
The DENSE trial is very important news, with potential for even more value in future years. It is finite (2 years of study, with only one MRI scan mandated), narrow (Vopara or BI-RADs breast density grade 4 only), and oligo-institutional (eight participating centers in the Netherlands). Still, it provides randomized, rigorously gathered and analyzed data where there were previously none. Importantly, it answers the question, “So what can I do now, doctor?”
I have some concerns about whether we, as a medical community, have the discipline to restrict application of supplemental MRI screening beyond the population that was studied in the Netherlands. Will we be able to restrain ourselves from ordering MRI scans in women with heterogeneously dense – but not extremely dense – breasts? Will we truly manage patients whose MRI scans had BI-RADs readings of less than 4 in the rigorous, but conservative, fashion employed in the trial? Would we miss fewer significant cancers and subject fewer patients to potential expense and harm with annual mammography, instead of the biennial screening performed in the Netherlands? Does tomo-synthesis improve the interpretation of screening mammograms so much that the interval cancer rate is a lot closer to the rate obtained with supplemental MRI scans? Is the expense of MRI scanning, with the resultant subsequent tests and procedures, justified by the reduction in detecting relatively favorable breast cancers that may not materially impact overall survival?
The DENSE study promises to be a “gift that keeps on giving” as the investigators continue to assess a number of factors including: the value of ongoing supplemental MRI scans (compared with the one-time-only screening reported here); whether there will be a reduction in the advanced cancers and subsequent mortality benefit; the extent of over diagnosis, costs, and impact on quality-of-life; and the applicability of artificial intelligence techniques to reduce false positive MRI results.
While the study may not be practice changing in the United States at the present time, it may be just that as subsequent analyses emerge.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
ASH releases guidelines on managing cardiopulmonary and kidney disease in SCD
ORLANDO – It is good practice to consult with a pulmonary hypertension (PH) expert before referring a patient with sickle cell disease (SCD) for right-heart catheterization or PH evaluation, according to new American Society of Hematology guidelines for the screening and management of cardiopulmonary and kidney disease in patients with SCD.
That “Good Practice” recommendation is one of several included in the evidence-based guidelines published Dec. 10 in Blood Advances and highlighted during a Special Education Session at the annual ASH meeting.
The guidelines provide 10 main recommendations intended to “support patients, clinicians, and other health care professionals in their decisions about screening, diagnosis, and management of cardiopulmonary and renal complications of SCD,” wrote Robert I. Liem, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues.
The recommendations, agreed upon by a multidisciplinary guideline panel, relate to screening, diagnosis, and management of PH, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), hypertension, proteinuria and chronic kidney disease, and venous thromboembolism (VTE). Most are “conditional,” as opposed to “strong,” because of a paucity of direct, high-quality outcomes data, and they are accompanied by the Good Practice Statements, descriptive remarks and caveats based on the available data, as well as suggestions for future research.
At the special ASH session, Ankit A. Desai, MD, highlighted some of the recommendations and discussed considerations for their practical application.
The Good Practice Statement on consulting a specialist before referring a patient for PH relates specifically to Recommendations 2a and 2b on the management of abnormal echocardiography, explained Dr. Desai of Indiana University, Indianapolis.
For asymptomatic children and adults with SCD and an isolated peak tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity (TRJV) of at least 2.5-2.9 m/s on echocardiography, the panel recommends against right-heart catheterization (Recommendation 2a, conditional), he said.
For children and adults with SCD and a peak TRJV of at least 2.5 m/s who also have a reduced 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) and/or elevated N-terminal proB-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), the panel supports right-heart catheterization (Recommendation 2b, conditional).
Dr. Desai noted that the 2.5 m/s threshold was found to be suboptimal when used as the sole criteria for right-heart catheterization. Using that threshold alone is associated with “moderate to large” harms, such as starting inappropriate PH-specific therapies and/or performing unnecessary right-heart catheterization. However, when used in combination with 6MWD, the predictive capacity improved significantly, and the risk for potential harm was low, he explained.
Another Good Practice Statement included in the guidelines, and relevant to these recommendations on managing abnormal echocardiography, addresses the importance of basing decisions about the need for right-heart catheterization on echocardiograms obtained at steady state rather than during acute illness, such as during hospitalization for pain or acute chest syndrome.
This is in part because of technical factors, Dr. Desai said.
“We know that repeating [echocardiography] is something that should be considered in patients because ... results vary – sometimes quite a bit – from study to study,” he said.
As for the cutoff values for 6MWD and NT-proBNP, “a decent amount of literature” suggests that less than 333 m and less than 160 pg/ml, respectively, are good thresholds, he said.
“Importantly, this should all be taken in the context of good clinical judgment ... along with discussion with a PH expert,” he added.
The full guidelines are available, along with additional ASH guidelines on immune thrombocytopenia and prevention of venous thromboembolism in surgical hospitalized patients, at the ASH publications website.
Of note, the SCD guidelines on cardiopulmonary disease and kidney disease are one of five sets of SCD guidelines that have been in development; these are the first of those to be published. The remaining four sets of guidelines will address pain, cerebrovascular complications, transfusion, and hematopoietic stem cell transplant. All will be published in Blood Advances, and according to Dr. Liem, the transfusion medicine guidelines have been accepted and should be published in January 2020, followed by those for cerebrovascular complications. Publication of the pain and transplant guidelines are anticipated later in 2020.
Dr. Liem and Dr. Desai reported having no conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – It is good practice to consult with a pulmonary hypertension (PH) expert before referring a patient with sickle cell disease (SCD) for right-heart catheterization or PH evaluation, according to new American Society of Hematology guidelines for the screening and management of cardiopulmonary and kidney disease in patients with SCD.
That “Good Practice” recommendation is one of several included in the evidence-based guidelines published Dec. 10 in Blood Advances and highlighted during a Special Education Session at the annual ASH meeting.
The guidelines provide 10 main recommendations intended to “support patients, clinicians, and other health care professionals in their decisions about screening, diagnosis, and management of cardiopulmonary and renal complications of SCD,” wrote Robert I. Liem, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues.
The recommendations, agreed upon by a multidisciplinary guideline panel, relate to screening, diagnosis, and management of PH, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), hypertension, proteinuria and chronic kidney disease, and venous thromboembolism (VTE). Most are “conditional,” as opposed to “strong,” because of a paucity of direct, high-quality outcomes data, and they are accompanied by the Good Practice Statements, descriptive remarks and caveats based on the available data, as well as suggestions for future research.
At the special ASH session, Ankit A. Desai, MD, highlighted some of the recommendations and discussed considerations for their practical application.
The Good Practice Statement on consulting a specialist before referring a patient for PH relates specifically to Recommendations 2a and 2b on the management of abnormal echocardiography, explained Dr. Desai of Indiana University, Indianapolis.
For asymptomatic children and adults with SCD and an isolated peak tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity (TRJV) of at least 2.5-2.9 m/s on echocardiography, the panel recommends against right-heart catheterization (Recommendation 2a, conditional), he said.
For children and adults with SCD and a peak TRJV of at least 2.5 m/s who also have a reduced 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) and/or elevated N-terminal proB-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), the panel supports right-heart catheterization (Recommendation 2b, conditional).
Dr. Desai noted that the 2.5 m/s threshold was found to be suboptimal when used as the sole criteria for right-heart catheterization. Using that threshold alone is associated with “moderate to large” harms, such as starting inappropriate PH-specific therapies and/or performing unnecessary right-heart catheterization. However, when used in combination with 6MWD, the predictive capacity improved significantly, and the risk for potential harm was low, he explained.
Another Good Practice Statement included in the guidelines, and relevant to these recommendations on managing abnormal echocardiography, addresses the importance of basing decisions about the need for right-heart catheterization on echocardiograms obtained at steady state rather than during acute illness, such as during hospitalization for pain or acute chest syndrome.
This is in part because of technical factors, Dr. Desai said.
“We know that repeating [echocardiography] is something that should be considered in patients because ... results vary – sometimes quite a bit – from study to study,” he said.
As for the cutoff values for 6MWD and NT-proBNP, “a decent amount of literature” suggests that less than 333 m and less than 160 pg/ml, respectively, are good thresholds, he said.
“Importantly, this should all be taken in the context of good clinical judgment ... along with discussion with a PH expert,” he added.
The full guidelines are available, along with additional ASH guidelines on immune thrombocytopenia and prevention of venous thromboembolism in surgical hospitalized patients, at the ASH publications website.
Of note, the SCD guidelines on cardiopulmonary disease and kidney disease are one of five sets of SCD guidelines that have been in development; these are the first of those to be published. The remaining four sets of guidelines will address pain, cerebrovascular complications, transfusion, and hematopoietic stem cell transplant. All will be published in Blood Advances, and according to Dr. Liem, the transfusion medicine guidelines have been accepted and should be published in January 2020, followed by those for cerebrovascular complications. Publication of the pain and transplant guidelines are anticipated later in 2020.
Dr. Liem and Dr. Desai reported having no conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – It is good practice to consult with a pulmonary hypertension (PH) expert before referring a patient with sickle cell disease (SCD) for right-heart catheterization or PH evaluation, according to new American Society of Hematology guidelines for the screening and management of cardiopulmonary and kidney disease in patients with SCD.
That “Good Practice” recommendation is one of several included in the evidence-based guidelines published Dec. 10 in Blood Advances and highlighted during a Special Education Session at the annual ASH meeting.
The guidelines provide 10 main recommendations intended to “support patients, clinicians, and other health care professionals in their decisions about screening, diagnosis, and management of cardiopulmonary and renal complications of SCD,” wrote Robert I. Liem, MD, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues.
The recommendations, agreed upon by a multidisciplinary guideline panel, relate to screening, diagnosis, and management of PH, pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), hypertension, proteinuria and chronic kidney disease, and venous thromboembolism (VTE). Most are “conditional,” as opposed to “strong,” because of a paucity of direct, high-quality outcomes data, and they are accompanied by the Good Practice Statements, descriptive remarks and caveats based on the available data, as well as suggestions for future research.
At the special ASH session, Ankit A. Desai, MD, highlighted some of the recommendations and discussed considerations for their practical application.
The Good Practice Statement on consulting a specialist before referring a patient for PH relates specifically to Recommendations 2a and 2b on the management of abnormal echocardiography, explained Dr. Desai of Indiana University, Indianapolis.
For asymptomatic children and adults with SCD and an isolated peak tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity (TRJV) of at least 2.5-2.9 m/s on echocardiography, the panel recommends against right-heart catheterization (Recommendation 2a, conditional), he said.
For children and adults with SCD and a peak TRJV of at least 2.5 m/s who also have a reduced 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) and/or elevated N-terminal proB-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), the panel supports right-heart catheterization (Recommendation 2b, conditional).
Dr. Desai noted that the 2.5 m/s threshold was found to be suboptimal when used as the sole criteria for right-heart catheterization. Using that threshold alone is associated with “moderate to large” harms, such as starting inappropriate PH-specific therapies and/or performing unnecessary right-heart catheterization. However, when used in combination with 6MWD, the predictive capacity improved significantly, and the risk for potential harm was low, he explained.
Another Good Practice Statement included in the guidelines, and relevant to these recommendations on managing abnormal echocardiography, addresses the importance of basing decisions about the need for right-heart catheterization on echocardiograms obtained at steady state rather than during acute illness, such as during hospitalization for pain or acute chest syndrome.
This is in part because of technical factors, Dr. Desai said.
“We know that repeating [echocardiography] is something that should be considered in patients because ... results vary – sometimes quite a bit – from study to study,” he said.
As for the cutoff values for 6MWD and NT-proBNP, “a decent amount of literature” suggests that less than 333 m and less than 160 pg/ml, respectively, are good thresholds, he said.
“Importantly, this should all be taken in the context of good clinical judgment ... along with discussion with a PH expert,” he added.
The full guidelines are available, along with additional ASH guidelines on immune thrombocytopenia and prevention of venous thromboembolism in surgical hospitalized patients, at the ASH publications website.
Of note, the SCD guidelines on cardiopulmonary disease and kidney disease are one of five sets of SCD guidelines that have been in development; these are the first of those to be published. The remaining four sets of guidelines will address pain, cerebrovascular complications, transfusion, and hematopoietic stem cell transplant. All will be published in Blood Advances, and according to Dr. Liem, the transfusion medicine guidelines have been accepted and should be published in January 2020, followed by those for cerebrovascular complications. Publication of the pain and transplant guidelines are anticipated later in 2020.
Dr. Liem and Dr. Desai reported having no conflicts of interest.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASH 2019
PT-Cy bests conventional GVHD prophylaxis
ORLANDO – Posttransplant cyclophosphamide may be superior to conventional immunosuppression as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
A phase 3 trial showed that posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PT-Cy) reduced graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) without affecting relapse. Rates of acute and chronic GVHD were significantly lower among patients who received PT-Cy than among those who received conventional immunosuppression (CIS). Rates of progression/relapse, progression-free survival, and overall survival were similar between the PT-Cy and CIS arms.
These results suggest PT-Cy provides a “long-term benefit and positive impact on quality of life” for patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, according to Annoek E.C. Broers, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Dr. Broers presented the results during the plenary session at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 160 patients with leukemias, lymphomas, myelomas, and other hematologic malignancies. All patients had a matched, related donor or an 8/8 or greater matched, unrelated donor.
The patients were randomized to receive CIS (n = 55) or PT-Cy (n = 105) as GVHD prophylaxis. The CIS regimen consisted of cyclosporine A (from day –3 to 180) and mycophenolic acid (from day 0 to 84). Patients in the PT-Cy arm received cyclophosphamide at 50 mg/kg (days 3 and 4) and cyclosporine A (from day 5 to 70).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms. The median age was 58 years in the CIS arm and 57 years in the PT-Cy arm. A majority of patients were men – 63% and 67%, respectively.
Two patients in the CIS arm received myeloablative conditioning, but all other patients received reduced-intensity conditioning. Most patients in the CIS arm (67%) and the PT-Cy arm (70%) had a matched, unrelated donor. All patients in the CIS arm and 96% in the PT-Cy arm received peripheral blood cell grafts.
PT-Cy significantly reduced the cumulative incidence of acute and chronic GVHD. The incidence of grade 2-4 acute GVHD at 6 months was 48% in the CIS arm and 32% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .014). The incidence of chronic extensive GVHD at 24 months was 50% and 19%, respectively (P = .001).
There were no significant between-arm differences for any other individual endpoint assessed.
“With a median follow-up of 3.2 years, so far, there’s no difference in the cumulative incidence of progression or relapse, nor is there a difference in progression-free or overall survival,” Dr. Broers said.
At 60 months, the rate of relapse/progression was 32% in the PT-Cy arm and 26% in the CIS arm (P = .36). The rate of nonrelapse mortality was 11% and 14%, respectively (P = .53).
At 60 months, the progression-free survival was 60% in the CIS arm and 58% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .67). The overall survival was 69% and 63%, respectively (P = .63).
In addition to assessing endpoints that “determine the success of our transplant strategy,” Dr. Broers said she and her colleagues also looked at a combined endpoint to account for “the effect GVHD has on morbidity and quality of life.” That endpoint is GVHD- and relapse-free survival.
The researchers found that PT-Cy improved GVHD- and relapse-free survival at 12 months. It was 22% in the CIS arm and 45% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .001). PT-Cy conferred this benefit irrespective of donor type, Dr. Broers noted.
Overall, the incidence of adverse events was somewhat higher in the PT-Cy arm (60%) than in the CIS arm (42%). The incidence of infections also was higher in the PT-Cy arm (41%) than in the CIS arm (21%), and this was largely caused by a greater incidence of neutropenic fever with PT-Cy (25% vs. 15%).
The study was funded by the Dutch Cancer Society, and Novartis provided the mycophenolic acid used in the study. Dr. Broers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Broers AEC et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 1.
ORLANDO – Posttransplant cyclophosphamide may be superior to conventional immunosuppression as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
A phase 3 trial showed that posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PT-Cy) reduced graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) without affecting relapse. Rates of acute and chronic GVHD were significantly lower among patients who received PT-Cy than among those who received conventional immunosuppression (CIS). Rates of progression/relapse, progression-free survival, and overall survival were similar between the PT-Cy and CIS arms.
These results suggest PT-Cy provides a “long-term benefit and positive impact on quality of life” for patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, according to Annoek E.C. Broers, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Dr. Broers presented the results during the plenary session at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 160 patients with leukemias, lymphomas, myelomas, and other hematologic malignancies. All patients had a matched, related donor or an 8/8 or greater matched, unrelated donor.
The patients were randomized to receive CIS (n = 55) or PT-Cy (n = 105) as GVHD prophylaxis. The CIS regimen consisted of cyclosporine A (from day –3 to 180) and mycophenolic acid (from day 0 to 84). Patients in the PT-Cy arm received cyclophosphamide at 50 mg/kg (days 3 and 4) and cyclosporine A (from day 5 to 70).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms. The median age was 58 years in the CIS arm and 57 years in the PT-Cy arm. A majority of patients were men – 63% and 67%, respectively.
Two patients in the CIS arm received myeloablative conditioning, but all other patients received reduced-intensity conditioning. Most patients in the CIS arm (67%) and the PT-Cy arm (70%) had a matched, unrelated donor. All patients in the CIS arm and 96% in the PT-Cy arm received peripheral blood cell grafts.
PT-Cy significantly reduced the cumulative incidence of acute and chronic GVHD. The incidence of grade 2-4 acute GVHD at 6 months was 48% in the CIS arm and 32% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .014). The incidence of chronic extensive GVHD at 24 months was 50% and 19%, respectively (P = .001).
There were no significant between-arm differences for any other individual endpoint assessed.
“With a median follow-up of 3.2 years, so far, there’s no difference in the cumulative incidence of progression or relapse, nor is there a difference in progression-free or overall survival,” Dr. Broers said.
At 60 months, the rate of relapse/progression was 32% in the PT-Cy arm and 26% in the CIS arm (P = .36). The rate of nonrelapse mortality was 11% and 14%, respectively (P = .53).
At 60 months, the progression-free survival was 60% in the CIS arm and 58% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .67). The overall survival was 69% and 63%, respectively (P = .63).
In addition to assessing endpoints that “determine the success of our transplant strategy,” Dr. Broers said she and her colleagues also looked at a combined endpoint to account for “the effect GVHD has on morbidity and quality of life.” That endpoint is GVHD- and relapse-free survival.
The researchers found that PT-Cy improved GVHD- and relapse-free survival at 12 months. It was 22% in the CIS arm and 45% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .001). PT-Cy conferred this benefit irrespective of donor type, Dr. Broers noted.
Overall, the incidence of adverse events was somewhat higher in the PT-Cy arm (60%) than in the CIS arm (42%). The incidence of infections also was higher in the PT-Cy arm (41%) than in the CIS arm (21%), and this was largely caused by a greater incidence of neutropenic fever with PT-Cy (25% vs. 15%).
The study was funded by the Dutch Cancer Society, and Novartis provided the mycophenolic acid used in the study. Dr. Broers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Broers AEC et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 1.
ORLANDO – Posttransplant cyclophosphamide may be superior to conventional immunosuppression as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
A phase 3 trial showed that posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PT-Cy) reduced graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) without affecting relapse. Rates of acute and chronic GVHD were significantly lower among patients who received PT-Cy than among those who received conventional immunosuppression (CIS). Rates of progression/relapse, progression-free survival, and overall survival were similar between the PT-Cy and CIS arms.
These results suggest PT-Cy provides a “long-term benefit and positive impact on quality of life” for patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, according to Annoek E.C. Broers, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Dr. Broers presented the results during the plenary session at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 160 patients with leukemias, lymphomas, myelomas, and other hematologic malignancies. All patients had a matched, related donor or an 8/8 or greater matched, unrelated donor.
The patients were randomized to receive CIS (n = 55) or PT-Cy (n = 105) as GVHD prophylaxis. The CIS regimen consisted of cyclosporine A (from day –3 to 180) and mycophenolic acid (from day 0 to 84). Patients in the PT-Cy arm received cyclophosphamide at 50 mg/kg (days 3 and 4) and cyclosporine A (from day 5 to 70).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms. The median age was 58 years in the CIS arm and 57 years in the PT-Cy arm. A majority of patients were men – 63% and 67%, respectively.
Two patients in the CIS arm received myeloablative conditioning, but all other patients received reduced-intensity conditioning. Most patients in the CIS arm (67%) and the PT-Cy arm (70%) had a matched, unrelated donor. All patients in the CIS arm and 96% in the PT-Cy arm received peripheral blood cell grafts.
PT-Cy significantly reduced the cumulative incidence of acute and chronic GVHD. The incidence of grade 2-4 acute GVHD at 6 months was 48% in the CIS arm and 32% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .014). The incidence of chronic extensive GVHD at 24 months was 50% and 19%, respectively (P = .001).
There were no significant between-arm differences for any other individual endpoint assessed.
“With a median follow-up of 3.2 years, so far, there’s no difference in the cumulative incidence of progression or relapse, nor is there a difference in progression-free or overall survival,” Dr. Broers said.
At 60 months, the rate of relapse/progression was 32% in the PT-Cy arm and 26% in the CIS arm (P = .36). The rate of nonrelapse mortality was 11% and 14%, respectively (P = .53).
At 60 months, the progression-free survival was 60% in the CIS arm and 58% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .67). The overall survival was 69% and 63%, respectively (P = .63).
In addition to assessing endpoints that “determine the success of our transplant strategy,” Dr. Broers said she and her colleagues also looked at a combined endpoint to account for “the effect GVHD has on morbidity and quality of life.” That endpoint is GVHD- and relapse-free survival.
The researchers found that PT-Cy improved GVHD- and relapse-free survival at 12 months. It was 22% in the CIS arm and 45% in the PT-Cy arm (P = .001). PT-Cy conferred this benefit irrespective of donor type, Dr. Broers noted.
Overall, the incidence of adverse events was somewhat higher in the PT-Cy arm (60%) than in the CIS arm (42%). The incidence of infections also was higher in the PT-Cy arm (41%) than in the CIS arm (21%), and this was largely caused by a greater incidence of neutropenic fever with PT-Cy (25% vs. 15%).
The study was funded by the Dutch Cancer Society, and Novartis provided the mycophenolic acid used in the study. Dr. Broers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Broers AEC et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 1.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Think twice: Choosing Wisely recommendations on testing to avoid in pediatric hematology
ORLANDO – There’s with some exceptions.
The list, which was produced by an expert panel with representatives from the American Society of Hematology and the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO), includes five tests or procedures that are considered unnecessary. The recommendations were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The five recommendations are:
- Don’t perform routine preoperative hemostatic testing in an otherwise healthy child with no prior personal or family history of bleeding.
- Don’t transfuse platelets in a nonbleeding pediatric patient with a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL, unless other signs of bleeding are present, or if the patient is set to undergo an invasive procedure.
- Don’t order thrombophilia testing on children with venous access-associated thrombosis in the absence of a positive family history.
- Don’t transfuse packed RBCs for iron-deficiency anemia in asymptomatic pediatric patients when there is no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding.
- Don’t routinely administer granulocyte colony–stimulating factor (G-CSF) for empiric treatment of pediatric patients with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia in the absence of recurrent or severe bacterial and/or fungal infections.
This is the third Choosing Wisely list produced by ASH. The group released the first list in 2013 and the second in 2014. But officials at both ASH and ASPHO have received feedback over the years that there should also be a pediatric-focused list in hematology, said Sarah O’Brien, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, and cochair of the expert panel that put together the recommendations.
Hemostatic testing
The panel recommended against preoperative hemostatic screening in healthy children with no personal or family history of excessive bleeding because the test does not effectively predict who will have unexpected surgical bleeding. The testing could instead identify artifacts or disorders unrelated to bleeding risk, such as factor XII deficiency or an infection-associated, transient lupus anticoagulant, according to Veronica H. Flood, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and a member of the expert panel.
Performing this type of testing also adds cost and stress for families, and often delays surgery.
A look at the current literature reveals that there is little evidence to support coagulation testing in healthy children undergoing surgery. “Despite all this evidence, there remain practitioners who perform such screening on a regular basis,” Dr. Flood said.
For physicians concerned about bleeding risk, Dr. Flood said that existing guidelines support taking a bleeding history in preoperative patients. “This may take a little more time, but in the end will result in better results and less expense.”
Platelet transfusion
The panel recommended against platelet transfusion in nonbleeding pediatric patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia and a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL. The caveats for this recommendation are that it does not apply if there are other signs or symptoms of bleeding, if the patient is undergoing an invasive procedure, if the patient is aged 1 year or younger, or if the patient has immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, according to Rachel Bercovitz, MD, of the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a member of the expert panel.
Previous studies on the platelet transfusions in patients with hematologic malignancies have shown that 10,000/mcL is the appropriate threshold, with no difference in bleeding above that number and increased bleeding below it, Dr. Bercovitz said.
Additionally, while platelet transfusion is a safe procedure, Dr. Bercovitz said, it is not without acute and long-term risks.
Cost is also a factor. “Platelets are a limited and expensive resource,” she said.
Thrombophilia testing
Thrombophilia testing in children with a central venous catheter-associated thrombosis was once common practice but should be avoided, explained Leslie J. Raffini, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a member of the expert panel.
Thrombophilia does not influence the initial management of a first episode of provoked venous thrombosis, it does not inform the intensity of duration of anticoagulant therapy, and it does not predict recurrence of venous thrombosis in children, Dr. Raffini said.
In the 2013 Choosing Wisely list, ASH made the same recommendation against testing in adult patients with venous thromboembolism occurring in the setting of major transient risk factors. Thrombophilia testing is also expensive, often has to be repeated, and can be misinterpreted, Dr. Raffini said.
Packed RBC transfusion
The panel recommended against transfusion with packed RBCs for children with iron-deficiency anemia who have no symptoms and no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding. Transfusion is appropriate if children are symptomatic or are hemodynamically unstable, said Patrick T. McGann, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert panel.
Rather than jump to transfusion, Dr. McGann said this group of asymptomatic and hemodynamically stable children should be treated for their iron deficiency through oral or intravenous iron. “This is not about ignoring iron deficiency.”
Both are effective treatments with multiple options available, he said. But sending a child to the hospital for transfusion is a costly option that is stressful for families and only provides a temporary solution to the issue, since treatment of the underlying iron deficiency still needs to be addressed, Dr. McGann said.
G-CSF treatment
The panel also recommended against routine administration of G-CSF in children with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia. Peter E. Newburger, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert guideline panel, said that there is limited evidence available and no published guidelines in this area, so the panel was guided by expert opinion.
In most cases, G-CSF is not necessary because autoimmune neutropenia resolves spontaneously by age 4-5 years and the risk of serious infection is extremely low. Appropriate management includes antibiotics for acute bacterial infection, good dental hygiene, and continued immunizations, Dr. Newburger said.
G-CSF may be appropriate in limited cases to improve quality of life, but it should be started at a low dose of 1-2 mcg/kg.
In cases of serious infection, Dr. Newburger said physicians should consider alternative diagnoses, such as congenital neutropenia or myelodysplastic syndromes.
ORLANDO – There’s with some exceptions.
The list, which was produced by an expert panel with representatives from the American Society of Hematology and the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO), includes five tests or procedures that are considered unnecessary. The recommendations were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The five recommendations are:
- Don’t perform routine preoperative hemostatic testing in an otherwise healthy child with no prior personal or family history of bleeding.
- Don’t transfuse platelets in a nonbleeding pediatric patient with a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL, unless other signs of bleeding are present, or if the patient is set to undergo an invasive procedure.
- Don’t order thrombophilia testing on children with venous access-associated thrombosis in the absence of a positive family history.
- Don’t transfuse packed RBCs for iron-deficiency anemia in asymptomatic pediatric patients when there is no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding.
- Don’t routinely administer granulocyte colony–stimulating factor (G-CSF) for empiric treatment of pediatric patients with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia in the absence of recurrent or severe bacterial and/or fungal infections.
This is the third Choosing Wisely list produced by ASH. The group released the first list in 2013 and the second in 2014. But officials at both ASH and ASPHO have received feedback over the years that there should also be a pediatric-focused list in hematology, said Sarah O’Brien, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, and cochair of the expert panel that put together the recommendations.
Hemostatic testing
The panel recommended against preoperative hemostatic screening in healthy children with no personal or family history of excessive bleeding because the test does not effectively predict who will have unexpected surgical bleeding. The testing could instead identify artifacts or disorders unrelated to bleeding risk, such as factor XII deficiency or an infection-associated, transient lupus anticoagulant, according to Veronica H. Flood, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and a member of the expert panel.
Performing this type of testing also adds cost and stress for families, and often delays surgery.
A look at the current literature reveals that there is little evidence to support coagulation testing in healthy children undergoing surgery. “Despite all this evidence, there remain practitioners who perform such screening on a regular basis,” Dr. Flood said.
For physicians concerned about bleeding risk, Dr. Flood said that existing guidelines support taking a bleeding history in preoperative patients. “This may take a little more time, but in the end will result in better results and less expense.”
Platelet transfusion
The panel recommended against platelet transfusion in nonbleeding pediatric patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia and a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL. The caveats for this recommendation are that it does not apply if there are other signs or symptoms of bleeding, if the patient is undergoing an invasive procedure, if the patient is aged 1 year or younger, or if the patient has immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, according to Rachel Bercovitz, MD, of the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a member of the expert panel.
Previous studies on the platelet transfusions in patients with hematologic malignancies have shown that 10,000/mcL is the appropriate threshold, with no difference in bleeding above that number and increased bleeding below it, Dr. Bercovitz said.
Additionally, while platelet transfusion is a safe procedure, Dr. Bercovitz said, it is not without acute and long-term risks.
Cost is also a factor. “Platelets are a limited and expensive resource,” she said.
Thrombophilia testing
Thrombophilia testing in children with a central venous catheter-associated thrombosis was once common practice but should be avoided, explained Leslie J. Raffini, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a member of the expert panel.
Thrombophilia does not influence the initial management of a first episode of provoked venous thrombosis, it does not inform the intensity of duration of anticoagulant therapy, and it does not predict recurrence of venous thrombosis in children, Dr. Raffini said.
In the 2013 Choosing Wisely list, ASH made the same recommendation against testing in adult patients with venous thromboembolism occurring in the setting of major transient risk factors. Thrombophilia testing is also expensive, often has to be repeated, and can be misinterpreted, Dr. Raffini said.
Packed RBC transfusion
The panel recommended against transfusion with packed RBCs for children with iron-deficiency anemia who have no symptoms and no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding. Transfusion is appropriate if children are symptomatic or are hemodynamically unstable, said Patrick T. McGann, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert panel.
Rather than jump to transfusion, Dr. McGann said this group of asymptomatic and hemodynamically stable children should be treated for their iron deficiency through oral or intravenous iron. “This is not about ignoring iron deficiency.”
Both are effective treatments with multiple options available, he said. But sending a child to the hospital for transfusion is a costly option that is stressful for families and only provides a temporary solution to the issue, since treatment of the underlying iron deficiency still needs to be addressed, Dr. McGann said.
G-CSF treatment
The panel also recommended against routine administration of G-CSF in children with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia. Peter E. Newburger, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert guideline panel, said that there is limited evidence available and no published guidelines in this area, so the panel was guided by expert opinion.
In most cases, G-CSF is not necessary because autoimmune neutropenia resolves spontaneously by age 4-5 years and the risk of serious infection is extremely low. Appropriate management includes antibiotics for acute bacterial infection, good dental hygiene, and continued immunizations, Dr. Newburger said.
G-CSF may be appropriate in limited cases to improve quality of life, but it should be started at a low dose of 1-2 mcg/kg.
In cases of serious infection, Dr. Newburger said physicians should consider alternative diagnoses, such as congenital neutropenia or myelodysplastic syndromes.
ORLANDO – There’s with some exceptions.
The list, which was produced by an expert panel with representatives from the American Society of Hematology and the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology (ASPHO), includes five tests or procedures that are considered unnecessary. The recommendations were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The five recommendations are:
- Don’t perform routine preoperative hemostatic testing in an otherwise healthy child with no prior personal or family history of bleeding.
- Don’t transfuse platelets in a nonbleeding pediatric patient with a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL, unless other signs of bleeding are present, or if the patient is set to undergo an invasive procedure.
- Don’t order thrombophilia testing on children with venous access-associated thrombosis in the absence of a positive family history.
- Don’t transfuse packed RBCs for iron-deficiency anemia in asymptomatic pediatric patients when there is no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding.
- Don’t routinely administer granulocyte colony–stimulating factor (G-CSF) for empiric treatment of pediatric patients with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia in the absence of recurrent or severe bacterial and/or fungal infections.
This is the third Choosing Wisely list produced by ASH. The group released the first list in 2013 and the second in 2014. But officials at both ASH and ASPHO have received feedback over the years that there should also be a pediatric-focused list in hematology, said Sarah O’Brien, MD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, and cochair of the expert panel that put together the recommendations.
Hemostatic testing
The panel recommended against preoperative hemostatic screening in healthy children with no personal or family history of excessive bleeding because the test does not effectively predict who will have unexpected surgical bleeding. The testing could instead identify artifacts or disorders unrelated to bleeding risk, such as factor XII deficiency or an infection-associated, transient lupus anticoagulant, according to Veronica H. Flood, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, and a member of the expert panel.
Performing this type of testing also adds cost and stress for families, and often delays surgery.
A look at the current literature reveals that there is little evidence to support coagulation testing in healthy children undergoing surgery. “Despite all this evidence, there remain practitioners who perform such screening on a regular basis,” Dr. Flood said.
For physicians concerned about bleeding risk, Dr. Flood said that existing guidelines support taking a bleeding history in preoperative patients. “This may take a little more time, but in the end will result in better results and less expense.”
Platelet transfusion
The panel recommended against platelet transfusion in nonbleeding pediatric patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia and a platelet count greater than 10,000/mcL. The caveats for this recommendation are that it does not apply if there are other signs or symptoms of bleeding, if the patient is undergoing an invasive procedure, if the patient is aged 1 year or younger, or if the patient has immune-mediated thrombocytopenia, according to Rachel Bercovitz, MD, of the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a member of the expert panel.
Previous studies on the platelet transfusions in patients with hematologic malignancies have shown that 10,000/mcL is the appropriate threshold, with no difference in bleeding above that number and increased bleeding below it, Dr. Bercovitz said.
Additionally, while platelet transfusion is a safe procedure, Dr. Bercovitz said, it is not without acute and long-term risks.
Cost is also a factor. “Platelets are a limited and expensive resource,” she said.
Thrombophilia testing
Thrombophilia testing in children with a central venous catheter-associated thrombosis was once common practice but should be avoided, explained Leslie J. Raffini, MD, of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a member of the expert panel.
Thrombophilia does not influence the initial management of a first episode of provoked venous thrombosis, it does not inform the intensity of duration of anticoagulant therapy, and it does not predict recurrence of venous thrombosis in children, Dr. Raffini said.
In the 2013 Choosing Wisely list, ASH made the same recommendation against testing in adult patients with venous thromboembolism occurring in the setting of major transient risk factors. Thrombophilia testing is also expensive, often has to be repeated, and can be misinterpreted, Dr. Raffini said.
Packed RBC transfusion
The panel recommended against transfusion with packed RBCs for children with iron-deficiency anemia who have no symptoms and no evidence of hemodynamic instability or active bleeding. Transfusion is appropriate if children are symptomatic or are hemodynamically unstable, said Patrick T. McGann, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert panel.
Rather than jump to transfusion, Dr. McGann said this group of asymptomatic and hemodynamically stable children should be treated for their iron deficiency through oral or intravenous iron. “This is not about ignoring iron deficiency.”
Both are effective treatments with multiple options available, he said. But sending a child to the hospital for transfusion is a costly option that is stressful for families and only provides a temporary solution to the issue, since treatment of the underlying iron deficiency still needs to be addressed, Dr. McGann said.
G-CSF treatment
The panel also recommended against routine administration of G-CSF in children with asymptomatic autoimmune neutropenia. Peter E. Newburger, MD, of Boston Children’s Hospital and a member of the expert guideline panel, said that there is limited evidence available and no published guidelines in this area, so the panel was guided by expert opinion.
In most cases, G-CSF is not necessary because autoimmune neutropenia resolves spontaneously by age 4-5 years and the risk of serious infection is extremely low. Appropriate management includes antibiotics for acute bacterial infection, good dental hygiene, and continued immunizations, Dr. Newburger said.
G-CSF may be appropriate in limited cases to improve quality of life, but it should be started at a low dose of 1-2 mcg/kg.
In cases of serious infection, Dr. Newburger said physicians should consider alternative diagnoses, such as congenital neutropenia or myelodysplastic syndromes.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
The clinical impact of new approvals in sickle cell, MCL
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration – crizanlizumab for sickle cell patients with painful crises and zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients in relapse.
Crizanlizumab
P-selectin is an adhesion molecule expressed on activated vascular endothelial cells and platelets. It is a key molecule in the initiation of leukocyte rolling on vessel walls and promotes firm attachment and extravasation to underlying tissues during inflammation. Up-regulation of P-selectin on endothelial cells and platelets contributes to the cell-cell interactions involved in the pathogenesis of sickle cell pain crises.
The SUSTAIN study was a multisite, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial of two different dosage levels of intravenous crizanlizumab (2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg for 52 weeks), a humanized anti–P-selectin antibody, examining its effect on pain crises in patients with sickle cell disease. The primary endpoint was the annual rate of sickle cell pain crises, with a variety of clinically relevant secondary endpoints. The target population had 2-10 pain crises in the 12 months before enrollment. Patients on a stable dose of hydroxyurea for at least the most recent 3 months were allowed to enter, but if patients were not receiving hydroxyurea, it could not be initiated during the trial. Patients who were undergoing chronic red-cell transfusion therapy were excluded.
Among 198 enrolled patients, 35% did not complete the 52 weeks of treatment. Discontinuations were equally balanced among patients assigned to the high-dose, low-dose, and placebo cohorts. Adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events occurred in 55 patients, with 5 deaths, all of which were unrelated to treatment. Crizanlizumab did not augment hemolysis or bacterial infections.
In the efficacy analysis, patients receiving high-dose crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for sickle cell pain crises, compared with 2.98 visits for placebo patients (P = .01). In comparison with placebo, high-dose crizanlizumab also delayed the first pain crisis after starting treatment (4.1 months vs. 1.4 months), delayed the median time to a second pain crisis, and decreased the median number of pain crises annually.
More than twice as many high-dose crizanlizumab patients had no pain crisis episodes, compared with placebo patients. In general, differences were more striking in patients who were not taking hydroxyurea and who had non–hemoglobin SS disease. Differences in the primary endpoint between low-dose crizanlizumab and placebo were numerically, but not statistically, different.
How these results influence practice
It has been over 20 years since a new agent (hydroxyurea) was approved for sickle cell patients and, despite its use, sickle cell pain crises remain a frequent problem. Pain crises are associated with worse quality of life and increased risk of death. A promising advance is badly needed, especially in an era in which sensitivity to providers’ role in the opioid addiction crisis is highly scrutinized and may contribute to future undertreatment of pain episodes. This is especially true for patients from areas with high levels of opioid misuse.
The SUSTAIN trial was international, multi-institutional, placebo-controlled, and inclusive. These attributes enhance the likelihood that crizanlizumab will enhance patient care in routine practice. As an intravenous agent, monitoring adherence and toxicity are less challenging than with hydroxyurea. Despite these factors, however, there are some concerns. Crizanlizumab was not free of toxicity, quality of life via the Brief Pain Inventory used in the trial was not improved, and changes in the pain-severity and pain-interference domains were small. Treatment in SUSTAIN ensued for 52 weeks, so the emergence of late neutralizing antibodies and late toxicities with longer-term therapy will require careful postmarketing assessment.
These concerns notwithstanding, anyone who has cared for sickle cell patients would be excited about the potential benefits crizanlizumab could bring to patient care.
Zanubrutinib
The FDA has approved zanubrutinib for the treatment of MCL in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy. The approval is based on the results of two studies in which overall response rate was the primary endpoint.
BGB-3111-206 (NCT03206970) was a phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with MCL who received at least one prior therapy. Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120) was a phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation trial of B-cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.
In the phase 2 trial, 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% confidence interval, 74%-91%), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI, 48%-70%) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI, 16.6% to not estimable). In the phase 1/2 dose-escalation trial, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI, 67%-95%), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI, 9%-40%) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI, 12.6% to not estimable). In both trials, median follow-up on study was about 18 months.
The most common adverse reactions were cytopenias, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, bruising, diarrhea, and cough. The most common serious adverse reactions were pneumonia in 11% and hemorrhage in 5% of patients. Of 118 MCL patients, 8 stopped therapy because of an adverse event, most frequently pneumonia (3.4%).
How these results influence practice
Unfortunately, the therapy of recurrent MCL is noncurative, because of the rapid development of treatment resistance. There are multiple single-and multiagent chemotherapy regimens that may be tried, many incorporating immunotherapy options such as anti-CD20- or Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–targeted agents. Given the limited efficacy of these agents, temporary nature of remissions, and paucity of data comparing these various treatment options, participation in clinical trials is encouraged whenever possible.
Outside of a clinical trial, zanubrutinib joins ibrutinib and acalabrutinib as approved single-agent BTK inhibitors for adult MCL patients in relapse. The impressive ORR and response duration reported for zanubrutinib are similar to the results achieved with the other agents, but the toxicity pattern may be slightly different.
As in the treatment of hormonally sensitive breast cancer, clinicians and patients benefit when they have multiple similar, equally efficacious oral agents with slightly different toxicity patterns so that quality of life can be improved and treatment duration maximized before treatment resistance develops and a more toxic and/or inconvenient therapy needs to be employed.
Whether zanubrutinib has benefits beyond those for MCL patients in relapse will depend on the results of confirmatory trials and patient-reported outcome data.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration – crizanlizumab for sickle cell patients with painful crises and zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients in relapse.
Crizanlizumab
P-selectin is an adhesion molecule expressed on activated vascular endothelial cells and platelets. It is a key molecule in the initiation of leukocyte rolling on vessel walls and promotes firm attachment and extravasation to underlying tissues during inflammation. Up-regulation of P-selectin on endothelial cells and platelets contributes to the cell-cell interactions involved in the pathogenesis of sickle cell pain crises.
The SUSTAIN study was a multisite, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial of two different dosage levels of intravenous crizanlizumab (2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg for 52 weeks), a humanized anti–P-selectin antibody, examining its effect on pain crises in patients with sickle cell disease. The primary endpoint was the annual rate of sickle cell pain crises, with a variety of clinically relevant secondary endpoints. The target population had 2-10 pain crises in the 12 months before enrollment. Patients on a stable dose of hydroxyurea for at least the most recent 3 months were allowed to enter, but if patients were not receiving hydroxyurea, it could not be initiated during the trial. Patients who were undergoing chronic red-cell transfusion therapy were excluded.
Among 198 enrolled patients, 35% did not complete the 52 weeks of treatment. Discontinuations were equally balanced among patients assigned to the high-dose, low-dose, and placebo cohorts. Adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events occurred in 55 patients, with 5 deaths, all of which were unrelated to treatment. Crizanlizumab did not augment hemolysis or bacterial infections.
In the efficacy analysis, patients receiving high-dose crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for sickle cell pain crises, compared with 2.98 visits for placebo patients (P = .01). In comparison with placebo, high-dose crizanlizumab also delayed the first pain crisis after starting treatment (4.1 months vs. 1.4 months), delayed the median time to a second pain crisis, and decreased the median number of pain crises annually.
More than twice as many high-dose crizanlizumab patients had no pain crisis episodes, compared with placebo patients. In general, differences were more striking in patients who were not taking hydroxyurea and who had non–hemoglobin SS disease. Differences in the primary endpoint between low-dose crizanlizumab and placebo were numerically, but not statistically, different.
How these results influence practice
It has been over 20 years since a new agent (hydroxyurea) was approved for sickle cell patients and, despite its use, sickle cell pain crises remain a frequent problem. Pain crises are associated with worse quality of life and increased risk of death. A promising advance is badly needed, especially in an era in which sensitivity to providers’ role in the opioid addiction crisis is highly scrutinized and may contribute to future undertreatment of pain episodes. This is especially true for patients from areas with high levels of opioid misuse.
The SUSTAIN trial was international, multi-institutional, placebo-controlled, and inclusive. These attributes enhance the likelihood that crizanlizumab will enhance patient care in routine practice. As an intravenous agent, monitoring adherence and toxicity are less challenging than with hydroxyurea. Despite these factors, however, there are some concerns. Crizanlizumab was not free of toxicity, quality of life via the Brief Pain Inventory used in the trial was not improved, and changes in the pain-severity and pain-interference domains were small. Treatment in SUSTAIN ensued for 52 weeks, so the emergence of late neutralizing antibodies and late toxicities with longer-term therapy will require careful postmarketing assessment.
These concerns notwithstanding, anyone who has cared for sickle cell patients would be excited about the potential benefits crizanlizumab could bring to patient care.
Zanubrutinib
The FDA has approved zanubrutinib for the treatment of MCL in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy. The approval is based on the results of two studies in which overall response rate was the primary endpoint.
BGB-3111-206 (NCT03206970) was a phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with MCL who received at least one prior therapy. Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120) was a phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation trial of B-cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.
In the phase 2 trial, 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% confidence interval, 74%-91%), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI, 48%-70%) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI, 16.6% to not estimable). In the phase 1/2 dose-escalation trial, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI, 67%-95%), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI, 9%-40%) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI, 12.6% to not estimable). In both trials, median follow-up on study was about 18 months.
The most common adverse reactions were cytopenias, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, bruising, diarrhea, and cough. The most common serious adverse reactions were pneumonia in 11% and hemorrhage in 5% of patients. Of 118 MCL patients, 8 stopped therapy because of an adverse event, most frequently pneumonia (3.4%).
How these results influence practice
Unfortunately, the therapy of recurrent MCL is noncurative, because of the rapid development of treatment resistance. There are multiple single-and multiagent chemotherapy regimens that may be tried, many incorporating immunotherapy options such as anti-CD20- or Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–targeted agents. Given the limited efficacy of these agents, temporary nature of remissions, and paucity of data comparing these various treatment options, participation in clinical trials is encouraged whenever possible.
Outside of a clinical trial, zanubrutinib joins ibrutinib and acalabrutinib as approved single-agent BTK inhibitors for adult MCL patients in relapse. The impressive ORR and response duration reported for zanubrutinib are similar to the results achieved with the other agents, but the toxicity pattern may be slightly different.
As in the treatment of hormonally sensitive breast cancer, clinicians and patients benefit when they have multiple similar, equally efficacious oral agents with slightly different toxicity patterns so that quality of life can be improved and treatment duration maximized before treatment resistance develops and a more toxic and/or inconvenient therapy needs to be employed.
Whether zanubrutinib has benefits beyond those for MCL patients in relapse will depend on the results of confirmatory trials and patient-reported outcome data.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration – crizanlizumab for sickle cell patients with painful crises and zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients in relapse.
Crizanlizumab
P-selectin is an adhesion molecule expressed on activated vascular endothelial cells and platelets. It is a key molecule in the initiation of leukocyte rolling on vessel walls and promotes firm attachment and extravasation to underlying tissues during inflammation. Up-regulation of P-selectin on endothelial cells and platelets contributes to the cell-cell interactions involved in the pathogenesis of sickle cell pain crises.
The SUSTAIN study was a multisite, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial of two different dosage levels of intravenous crizanlizumab (2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg for 52 weeks), a humanized anti–P-selectin antibody, examining its effect on pain crises in patients with sickle cell disease. The primary endpoint was the annual rate of sickle cell pain crises, with a variety of clinically relevant secondary endpoints. The target population had 2-10 pain crises in the 12 months before enrollment. Patients on a stable dose of hydroxyurea for at least the most recent 3 months were allowed to enter, but if patients were not receiving hydroxyurea, it could not be initiated during the trial. Patients who were undergoing chronic red-cell transfusion therapy were excluded.
Among 198 enrolled patients, 35% did not complete the 52 weeks of treatment. Discontinuations were equally balanced among patients assigned to the high-dose, low-dose, and placebo cohorts. Adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events occurred in 55 patients, with 5 deaths, all of which were unrelated to treatment. Crizanlizumab did not augment hemolysis or bacterial infections.
In the efficacy analysis, patients receiving high-dose crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for sickle cell pain crises, compared with 2.98 visits for placebo patients (P = .01). In comparison with placebo, high-dose crizanlizumab also delayed the first pain crisis after starting treatment (4.1 months vs. 1.4 months), delayed the median time to a second pain crisis, and decreased the median number of pain crises annually.
More than twice as many high-dose crizanlizumab patients had no pain crisis episodes, compared with placebo patients. In general, differences were more striking in patients who were not taking hydroxyurea and who had non–hemoglobin SS disease. Differences in the primary endpoint between low-dose crizanlizumab and placebo were numerically, but not statistically, different.
How these results influence practice
It has been over 20 years since a new agent (hydroxyurea) was approved for sickle cell patients and, despite its use, sickle cell pain crises remain a frequent problem. Pain crises are associated with worse quality of life and increased risk of death. A promising advance is badly needed, especially in an era in which sensitivity to providers’ role in the opioid addiction crisis is highly scrutinized and may contribute to future undertreatment of pain episodes. This is especially true for patients from areas with high levels of opioid misuse.
The SUSTAIN trial was international, multi-institutional, placebo-controlled, and inclusive. These attributes enhance the likelihood that crizanlizumab will enhance patient care in routine practice. As an intravenous agent, monitoring adherence and toxicity are less challenging than with hydroxyurea. Despite these factors, however, there are some concerns. Crizanlizumab was not free of toxicity, quality of life via the Brief Pain Inventory used in the trial was not improved, and changes in the pain-severity and pain-interference domains were small. Treatment in SUSTAIN ensued for 52 weeks, so the emergence of late neutralizing antibodies and late toxicities with longer-term therapy will require careful postmarketing assessment.
These concerns notwithstanding, anyone who has cared for sickle cell patients would be excited about the potential benefits crizanlizumab could bring to patient care.
Zanubrutinib
The FDA has approved zanubrutinib for the treatment of MCL in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy. The approval is based on the results of two studies in which overall response rate was the primary endpoint.
BGB-3111-206 (NCT03206970) was a phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with MCL who received at least one prior therapy. Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120) was a phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation trial of B-cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.
In the phase 2 trial, 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% confidence interval, 74%-91%), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI, 48%-70%) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI, 16.6% to not estimable). In the phase 1/2 dose-escalation trial, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI, 67%-95%), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI, 9%-40%) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI, 12.6% to not estimable). In both trials, median follow-up on study was about 18 months.
The most common adverse reactions were cytopenias, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, bruising, diarrhea, and cough. The most common serious adverse reactions were pneumonia in 11% and hemorrhage in 5% of patients. Of 118 MCL patients, 8 stopped therapy because of an adverse event, most frequently pneumonia (3.4%).
How these results influence practice
Unfortunately, the therapy of recurrent MCL is noncurative, because of the rapid development of treatment resistance. There are multiple single-and multiagent chemotherapy regimens that may be tried, many incorporating immunotherapy options such as anti-CD20- or Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–targeted agents. Given the limited efficacy of these agents, temporary nature of remissions, and paucity of data comparing these various treatment options, participation in clinical trials is encouraged whenever possible.
Outside of a clinical trial, zanubrutinib joins ibrutinib and acalabrutinib as approved single-agent BTK inhibitors for adult MCL patients in relapse. The impressive ORR and response duration reported for zanubrutinib are similar to the results achieved with the other agents, but the toxicity pattern may be slightly different.
As in the treatment of hormonally sensitive breast cancer, clinicians and patients benefit when they have multiple similar, equally efficacious oral agents with slightly different toxicity patterns so that quality of life can be improved and treatment duration maximized before treatment resistance develops and a more toxic and/or inconvenient therapy needs to be employed.
Whether zanubrutinib has benefits beyond those for MCL patients in relapse will depend on the results of confirmatory trials and patient-reported outcome data.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
Presence
The plan was in motion before I got on the plane.
When your leukemia came back suddenly 3 years after your stem cell transplant, it was devastating. But we had a plan. Your cancer developed a new mutation we could target with a chemotherapy drug. If we got you into a second remission, we could consolidate it by infusing more of your donor’s stem cells.
We met in the hospital, but I was adamant to “keep” you as my patient when you got to the clinic. I made swaps to see you, to get the continuity I value so much but often lose as a fellow, rotating from clinic to hospital to clinic.
I was grateful to see how well you dealt with the chemotherapy. Typically it’s a tough regimen, but you hardly had side effects. Between visits, I would check your blood counts on my phone, watching your blast count fall and your normal blood cells rise. Watching the cancer disappear.
Your lumbar punctures were negative, negative, negative – my favorite word, I told you. I was involved in long email threads coordinating the timing of your stem cell infusion with the remission we were achieving.
We were on our way.
One day, your lumbar puncture came back with a few “atypical” cells. I called the pathologist, and upon further review they were convinced the cells were reactive, not cancer. The next lumbar puncture was normal, but it was hard to ignore.
“Are you worried?” I asked my attending in clinic.
“I’m always worried,” she said. Neither of us truly believed the leukemia was back, but with the odds against us, we pored over every detail, always on the alert for a clue to an outcome we feared.
By now, the stem cell infusion was all set up. The donor was ready; so was the medical team; so were you. It was exciting. I thought of how a different attending described his interest in leukemia: There’s a subset you get to cure. Yes, you were going to be one of them.
Your big day coincided with a vacation I had scheduled months before. I was sorry I would be missing the actual moment, but happy I would come back to good news.
I left my coat and badge at the hospital, packed my bags, and got on the plane. I refrained from immediately checking your blood counts on my phone as soon as we landed. That night, jet lagged, I let myself look before I go to sleep. Relief. Your numbers still looked good.
Every day, I explored. My Internet was spotty during my travels, and when I would I finally get service I would peek at your latest blood tests.
Day 1. Cooled lava canyons. Black sand beaches. Circulating blast count: 0%.
Day 2: Glacier tour. A national park. Geysers. Blast count: 2%.
Day 3: We drive along the shore to see a famous waterfall, where you can climb a set of winding stairs to the top.
I check my phone before we start the climb. No service.
And so we begin. The wind cuts as I count steps. 403, 404, 405 … and 406. We are there. The air is thin, the world quiet. My nose is running from the cold.
We hike a bit, and I glance down again. Still no signal. It’s probably for the best. The scenery is spectacular.
Two miles later, I get service. I open the blood work first. Circulating blast count: 5%. But the other counts are okay. It could still be reactive, I say to myself, though on a deeper level I think of my attending’s words: I’m always worried. The stem cell infusion is scheduled for tomorrow.
I hear the rush of the water hitting the rocks below. Icicles form to our left. Sheep graze on our right. I appreciate the feeling of my muscles aching as we climb, higher and higher, a reminder of where I am and my place in it.
At the very top, we pause to take photos. And I get a signal again. I open the bone marrow biopsy report and skim the pathologist’s words. My eyes glue on the summary: 80% blasts, compatible with relapsed leukemia.
I let out an audible gasp.
Do you know? How will they tell you? I am painfully aware of the distance between us, in so many ways.
I want to be present. And soon I will be back, and I will be visiting in the hospital, and we will be having hard conversations and thinking about hard decisions.
But I’m not there right now. Someone else is. Here, now, I realize what I cannot do. The best way I can be present for you later is to be present where I am now.
I stuff my phone in my backpack and zip it closed. I step carefully forward on the rocks, slippery from the rain. My nose is running again, but not from the cold.
“What do you think?” my partner asks.
“The views are incredible,” I say.
Minor details of this story were changed to protect privacy.
Dr. Yurkiewicz is a fellow in hematology and oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University. Follow her on Twitter @ilanayurkiewicz and listen to her each week on the Blood & Cancer podcast.
The plan was in motion before I got on the plane.
When your leukemia came back suddenly 3 years after your stem cell transplant, it was devastating. But we had a plan. Your cancer developed a new mutation we could target with a chemotherapy drug. If we got you into a second remission, we could consolidate it by infusing more of your donor’s stem cells.
We met in the hospital, but I was adamant to “keep” you as my patient when you got to the clinic. I made swaps to see you, to get the continuity I value so much but often lose as a fellow, rotating from clinic to hospital to clinic.
I was grateful to see how well you dealt with the chemotherapy. Typically it’s a tough regimen, but you hardly had side effects. Between visits, I would check your blood counts on my phone, watching your blast count fall and your normal blood cells rise. Watching the cancer disappear.
Your lumbar punctures were negative, negative, negative – my favorite word, I told you. I was involved in long email threads coordinating the timing of your stem cell infusion with the remission we were achieving.
We were on our way.
One day, your lumbar puncture came back with a few “atypical” cells. I called the pathologist, and upon further review they were convinced the cells were reactive, not cancer. The next lumbar puncture was normal, but it was hard to ignore.
“Are you worried?” I asked my attending in clinic.
“I’m always worried,” she said. Neither of us truly believed the leukemia was back, but with the odds against us, we pored over every detail, always on the alert for a clue to an outcome we feared.
By now, the stem cell infusion was all set up. The donor was ready; so was the medical team; so were you. It was exciting. I thought of how a different attending described his interest in leukemia: There’s a subset you get to cure. Yes, you were going to be one of them.
Your big day coincided with a vacation I had scheduled months before. I was sorry I would be missing the actual moment, but happy I would come back to good news.
I left my coat and badge at the hospital, packed my bags, and got on the plane. I refrained from immediately checking your blood counts on my phone as soon as we landed. That night, jet lagged, I let myself look before I go to sleep. Relief. Your numbers still looked good.
Every day, I explored. My Internet was spotty during my travels, and when I would I finally get service I would peek at your latest blood tests.
Day 1. Cooled lava canyons. Black sand beaches. Circulating blast count: 0%.
Day 2: Glacier tour. A national park. Geysers. Blast count: 2%.
Day 3: We drive along the shore to see a famous waterfall, where you can climb a set of winding stairs to the top.
I check my phone before we start the climb. No service.
And so we begin. The wind cuts as I count steps. 403, 404, 405 … and 406. We are there. The air is thin, the world quiet. My nose is running from the cold.
We hike a bit, and I glance down again. Still no signal. It’s probably for the best. The scenery is spectacular.
Two miles later, I get service. I open the blood work first. Circulating blast count: 5%. But the other counts are okay. It could still be reactive, I say to myself, though on a deeper level I think of my attending’s words: I’m always worried. The stem cell infusion is scheduled for tomorrow.
I hear the rush of the water hitting the rocks below. Icicles form to our left. Sheep graze on our right. I appreciate the feeling of my muscles aching as we climb, higher and higher, a reminder of where I am and my place in it.
At the very top, we pause to take photos. And I get a signal again. I open the bone marrow biopsy report and skim the pathologist’s words. My eyes glue on the summary: 80% blasts, compatible with relapsed leukemia.
I let out an audible gasp.
Do you know? How will they tell you? I am painfully aware of the distance between us, in so many ways.
I want to be present. And soon I will be back, and I will be visiting in the hospital, and we will be having hard conversations and thinking about hard decisions.
But I’m not there right now. Someone else is. Here, now, I realize what I cannot do. The best way I can be present for you later is to be present where I am now.
I stuff my phone in my backpack and zip it closed. I step carefully forward on the rocks, slippery from the rain. My nose is running again, but not from the cold.
“What do you think?” my partner asks.
“The views are incredible,” I say.
Minor details of this story were changed to protect privacy.
Dr. Yurkiewicz is a fellow in hematology and oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University. Follow her on Twitter @ilanayurkiewicz and listen to her each week on the Blood & Cancer podcast.
The plan was in motion before I got on the plane.
When your leukemia came back suddenly 3 years after your stem cell transplant, it was devastating. But we had a plan. Your cancer developed a new mutation we could target with a chemotherapy drug. If we got you into a second remission, we could consolidate it by infusing more of your donor’s stem cells.
We met in the hospital, but I was adamant to “keep” you as my patient when you got to the clinic. I made swaps to see you, to get the continuity I value so much but often lose as a fellow, rotating from clinic to hospital to clinic.
I was grateful to see how well you dealt with the chemotherapy. Typically it’s a tough regimen, but you hardly had side effects. Between visits, I would check your blood counts on my phone, watching your blast count fall and your normal blood cells rise. Watching the cancer disappear.
Your lumbar punctures were negative, negative, negative – my favorite word, I told you. I was involved in long email threads coordinating the timing of your stem cell infusion with the remission we were achieving.
We were on our way.
One day, your lumbar puncture came back with a few “atypical” cells. I called the pathologist, and upon further review they were convinced the cells were reactive, not cancer. The next lumbar puncture was normal, but it was hard to ignore.
“Are you worried?” I asked my attending in clinic.
“I’m always worried,” she said. Neither of us truly believed the leukemia was back, but with the odds against us, we pored over every detail, always on the alert for a clue to an outcome we feared.
By now, the stem cell infusion was all set up. The donor was ready; so was the medical team; so were you. It was exciting. I thought of how a different attending described his interest in leukemia: There’s a subset you get to cure. Yes, you were going to be one of them.
Your big day coincided with a vacation I had scheduled months before. I was sorry I would be missing the actual moment, but happy I would come back to good news.
I left my coat and badge at the hospital, packed my bags, and got on the plane. I refrained from immediately checking your blood counts on my phone as soon as we landed. That night, jet lagged, I let myself look before I go to sleep. Relief. Your numbers still looked good.
Every day, I explored. My Internet was spotty during my travels, and when I would I finally get service I would peek at your latest blood tests.
Day 1. Cooled lava canyons. Black sand beaches. Circulating blast count: 0%.
Day 2: Glacier tour. A national park. Geysers. Blast count: 2%.
Day 3: We drive along the shore to see a famous waterfall, where you can climb a set of winding stairs to the top.
I check my phone before we start the climb. No service.
And so we begin. The wind cuts as I count steps. 403, 404, 405 … and 406. We are there. The air is thin, the world quiet. My nose is running from the cold.
We hike a bit, and I glance down again. Still no signal. It’s probably for the best. The scenery is spectacular.
Two miles later, I get service. I open the blood work first. Circulating blast count: 5%. But the other counts are okay. It could still be reactive, I say to myself, though on a deeper level I think of my attending’s words: I’m always worried. The stem cell infusion is scheduled for tomorrow.
I hear the rush of the water hitting the rocks below. Icicles form to our left. Sheep graze on our right. I appreciate the feeling of my muscles aching as we climb, higher and higher, a reminder of where I am and my place in it.
At the very top, we pause to take photos. And I get a signal again. I open the bone marrow biopsy report and skim the pathologist’s words. My eyes glue on the summary: 80% blasts, compatible with relapsed leukemia.
I let out an audible gasp.
Do you know? How will they tell you? I am painfully aware of the distance between us, in so many ways.
I want to be present. And soon I will be back, and I will be visiting in the hospital, and we will be having hard conversations and thinking about hard decisions.
But I’m not there right now. Someone else is. Here, now, I realize what I cannot do. The best way I can be present for you later is to be present where I am now.
I stuff my phone in my backpack and zip it closed. I step carefully forward on the rocks, slippery from the rain. My nose is running again, but not from the cold.
“What do you think?” my partner asks.
“The views are incredible,” I say.
Minor details of this story were changed to protect privacy.
Dr. Yurkiewicz is a fellow in hematology and oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University. Follow her on Twitter @ilanayurkiewicz and listen to her each week on the Blood & Cancer podcast.
Survey: Cancer-related pain, opioid use up since 2018
Cancer-related pain was more common among patients in 2019 than in 2018, as was the use of prescription opioids, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
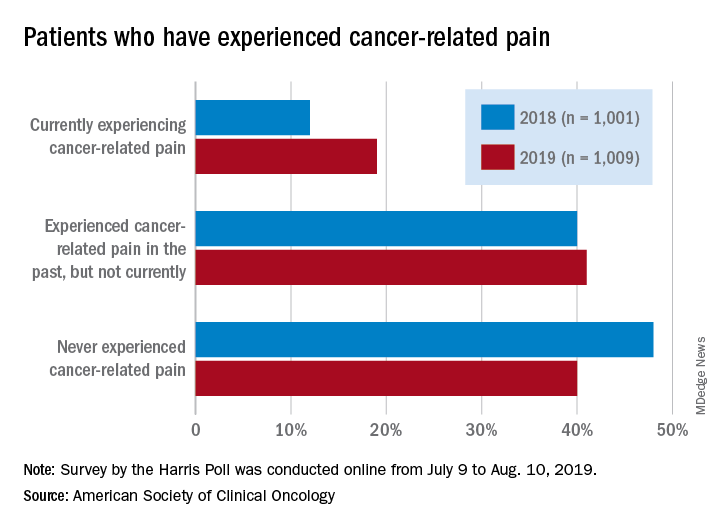
Patients who have/had cancer were significantly more likely to report that they were currently experiencing cancer-related pain in 2019 (19%) than in 2018 (12%), but there was only a slight increase in patients who said that they had experienced cancer-related pain in the past, the society reported in its National Cancer Opinion Survey.
When asked about methods used to manage pain, nausea, and other symptoms, patients diagnosed with cancer most often said that they had not used anything in the last 12 months, although this response was significantly less common in 2019 (48%) than in 2018 (55%). Over-the-counter pain relievers were the most common method used (24% in 2019 and 22% in 2018), followed by vitamins/minerals/herbs (18% in 2019 and 17% in 2018), ASCO said.
Prescription opioids were the third most popular choice for symptom management both years, but use was significantly higher in 2019 (17%) than in 2018 (12%). Also showing a significant increase from 2018 to 2019 was use of medical marijuana, which went from 5% to 10%, ASCO said.
The survey was conducted online for ASCO by the Harris Poll from July 9 to Aug. 10, 2019. The total sample consisted of 4,815 U.S. adults, of whom 1,009 had been diagnosed with cancer.
Cancer-related pain was more common among patients in 2019 than in 2018, as was the use of prescription opioids, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology.

Patients who have/had cancer were significantly more likely to report that they were currently experiencing cancer-related pain in 2019 (19%) than in 2018 (12%), but there was only a slight increase in patients who said that they had experienced cancer-related pain in the past, the society reported in its National Cancer Opinion Survey.
When asked about methods used to manage pain, nausea, and other symptoms, patients diagnosed with cancer most often said that they had not used anything in the last 12 months, although this response was significantly less common in 2019 (48%) than in 2018 (55%). Over-the-counter pain relievers were the most common method used (24% in 2019 and 22% in 2018), followed by vitamins/minerals/herbs (18% in 2019 and 17% in 2018), ASCO said.
Prescription opioids were the third most popular choice for symptom management both years, but use was significantly higher in 2019 (17%) than in 2018 (12%). Also showing a significant increase from 2018 to 2019 was use of medical marijuana, which went from 5% to 10%, ASCO said.
The survey was conducted online for ASCO by the Harris Poll from July 9 to Aug. 10, 2019. The total sample consisted of 4,815 U.S. adults, of whom 1,009 had been diagnosed with cancer.
Cancer-related pain was more common among patients in 2019 than in 2018, as was the use of prescription opioids, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology.

Patients who have/had cancer were significantly more likely to report that they were currently experiencing cancer-related pain in 2019 (19%) than in 2018 (12%), but there was only a slight increase in patients who said that they had experienced cancer-related pain in the past, the society reported in its National Cancer Opinion Survey.
When asked about methods used to manage pain, nausea, and other symptoms, patients diagnosed with cancer most often said that they had not used anything in the last 12 months, although this response was significantly less common in 2019 (48%) than in 2018 (55%). Over-the-counter pain relievers were the most common method used (24% in 2019 and 22% in 2018), followed by vitamins/minerals/herbs (18% in 2019 and 17% in 2018), ASCO said.
Prescription opioids were the third most popular choice for symptom management both years, but use was significantly higher in 2019 (17%) than in 2018 (12%). Also showing a significant increase from 2018 to 2019 was use of medical marijuana, which went from 5% to 10%, ASCO said.
The survey was conducted online for ASCO by the Harris Poll from July 9 to Aug. 10, 2019. The total sample consisted of 4,815 U.S. adults, of whom 1,009 had been diagnosed with cancer.