User login
When Should an IVC Filter Be Used to Treat a DVT?
Case
A 67-year-old man with a history of hypertension presents with a swollen right lower extremity. An ultrasound reveals a DVT, and he is commenced on low-molecular-weight heparin and warfarin. Two days later, he develops slurred speech and right-sided weakness. A head CT reveals an intracranial hemorrhage. When should an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter be utilized for treatment of DVT?
Overview
It is estimated that 350,000 to 600,000 Americans develop a VTE each year.1 Patients with a DVT are at high risk of developing a pulmonary embolism (PE). In a multicenter study, nearly 40% of patients admitted with a DVT had evidence of a PE on ventilation perfusion scan.2 Treatment of a DVT is aimed at preventing the extension of the DVT and embolization.3 The American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) recommends anticoagulation as the primary DVT treatment (Grade 1A).4 However, IVC filters might be considered when anticoagulation is contraindicated.
In 1868, Trousseau created the conceptual model of surgical interruption of the IVC to prevent PE. However, it wasn’t until 1959 by Bottini that the surgical interruption was successfully performed.5 The Mobin-Uddin filter was introduced in 1967 as the first mechanical IVC filter.6 IVC filters mechanically trap the DVT, preventing emboli from traveling into the pulmonary vasculature.7
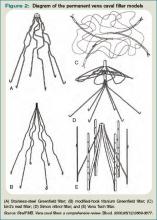
There are two classes of IVC filters: permanent filters and removable filters. Removable filters include both temporary filters and retrievable filters. Temporary filters are attached to a catheter that exits the skin and therefore must be removed due to the risk of infection and embolization.7 Retrievable filters are similar in design to permanent filters but are designed to be removed. However, this must be done with caution, as neointimal hyperplasia can prevent removal or cause vessel wall damage upon removal.8
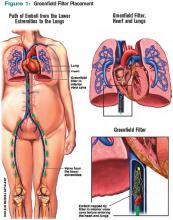
IVC filters are inserted into the vena cava percutaneously via the femoral or jugular approach under fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance (see Figure 1, p. 16). The filters typically are placed infrarenally, unless there is an indication for a suprarenal filter (e.g., renal vein thrombosis or IVC thrombus extending above the renal veins).7 Complete IVC thrombosis is an absolute contraindication to IVC filter placement, and the relative contraindications include significant coagulopathy and bacteremia.9
The incidence of complications related to IVC filter placement is 4% to 11%. Complications include:
- Insertion-site thrombosis;
- IVC thrombosis;
- Recurrent DVT postphlebitic syndrome;
- Filter migration;
- Erosion of the filter through the vessel wall; and
- Vena caval obstruction.10
A review of the National Hospital Discharge Survey database for trends in IVC filter use in the U.S. found a dramatic increase in the use of IVC filters from 1979 to 1999—to 49,000 patients from 2,000 patients with IVC filters in place. The indications for IVC filter use vary such that it is imperative there are well-designed trials and guidelines to guide appropriate use.11
The Evidence
The 2008 ACCP guidelines on VTE management follow a grading system that classifies recommendations as Grade 1 (strong) or Grade 2 (weak), and classifies the quality of evidence as A (high), B (moderate), or C (low).12 The ACCP guidelines’ recommended first-line treatment for a confirmed DVT is anticoagulation with subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin, intravenous unfractionated heparin, monitored subcutaneous heparin, fixed-dose subcutaneous unfractionated heparin, or subcutaneous fondaparinux (all Grade 1A recommendations). The ACCP recommends against the routine use of an IVC filter in addition to anticoagulants (Grade 1A). However, for patients with acute proximal DVT, if anticoagulant therapy is not possible because of the risk of bleeding, IVC filter placement is recommended (Grade 1C). If a patient requires an IVC filter for treatment of an acute DVT as an alternative to anticoagulation, it is recommended to start anticoagulant therapy once the risk of bleeding resolves (Grade 1C).4
The 2008 ACCP guidelines for IVC filter use have a few important changes from the 2004 version. First, the IVC filter placement recommendation for patients with contraindications to anticoagulation was strengthened from Grade 2C to Grade 1C. Second, the 2008 guidelines omitted the early recommendation of IVC filter use for recurrent VTE, despite adequate anticoagulation (Grade 2C).13
Only one randomized study has evaluated the efficacy of IVC filters. All other studies of IVC filters are retrospective or prospective case series.
The PREPIC study randomized 400 patients with proximal DVT considered to be at high risk for PE to receive either an IVC filter or no IVC filter. Additionally, patients were randomized to receive enoxaparin or unfractionated heparin as a bridge to warfarin therapy, which was continued for at least three months. The primary endpoints were recurrent DVT, PE, major bleeding, or death. The patients were followed up at day 12, two years, and then annually up to eight years following randomization.14 At day 12, there were fewer PEs in the group that received filters (OR 0.22, 95% CI, 0.05-0.90). However, at year two, there was no significant difference in PE development in the filter group compared with the no-filter group (OR 0.50, 95% CI, 0.19-1.33).
Additionally, at year two, the filter group was more likely to develop recurrent DVT (OR 1.87, 95% CI, 1.10-3.20). At year eight, there was a significant reduction in the number of PEs in the filter group versus the no-filter group (6.2% vs.15.1%, P=0.008). However, at eight-year followup, IVC filter use was associated with increased DVT (35.7% vs. 27.5%, P=0.042). There was no difference in mortality between the two groups.
In summary, the use of IVC filters was associated with decreased incidence of PE at eight years, offset by higher rates of recurrent DVT and no overall mortality benefit.14,15 Importantly, the indications for IVC filter use in this study differ from the current ACCP guidelines; all patients were given concomitant anticoagulation for at least three months, which might not be possible in patients for whom the ACCP recommends IVC filters.
There are no randomized studies to compare the efficacy of permanent IVC filters and retrievable filters for PE prevention. A retrospective study comparing the clinical effectiveness of the two filter types reported no difference in the rates of symptomatic PE (permanent filter 4% vs. retrievable filter 4.7%, P=0.67) or DVT (11.3% vs. 12.6%, P=0.59). In addition, the frequency of symptomatic IVC thrombosis was similar (1.1% vs. 0.5%, p=0.39).16 A paper reviewing the efficacy of IVC filters reported that permanent filters were associated with a 0%-6.2% rate of PE versus a 0%-1.9% rate with retrievable filters.7 Notably, these studies were not randomized controlled trials—rather, case series—and the indications for IVC filters were not necessarily those currently recommended by the ACCP.
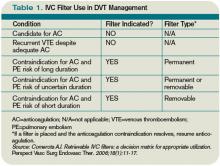
Due to the long-term complications of permanent IVC filters, it is suggested that a retrievable IVC filter be used for patients with temporary contraindications to anticoagulation.17 Comerata et al created a clinical decision-making tool for picking the type of filter to employ. If the duration of contraindication to anticoagulation is short or uncertain, a retrievable filter is recommended.18 Table 1 (p. 15) outlines the recommendations for IVC filter placement.
There are no randomized controlled trials to guide the use of concomitant anticoagulation after filter insertion, although this intervention may be beneficial to prevent DVT propagation, recurrence, or IVC filter thrombosis.5 A meta-analysis of 14 studies evaluating the rates of VTE after IVC filter placement demonstrated a non-statistically significant trend toward fewer VTE events in the patients with an IVC filter and concomitant anticoagulation in comparison with those who solely had an IVC filter (OR 0.64, 95% CI, 0.35-1.2). The duration and degree of anticoagulation was not presented in all of the studies in the meta-analysis, therefore limiting the analysis.19
In addition to the ACCP guidelines, there have been other proposed indications for IVC filter use, including recurrent VTE despite anticoagulation, chronic recurrent PE with pulmonary hypertension, extensive free-floating iliofemoral thrombus, and thrombolysis of ilio-caval thrombus.20 The ACCP guidelines do not specifically address these individual indications, and at this time there are no randomized controlled trials to guide IVC filter use in these cases.
Back to the Case
Our patient developed a significant complication from anticoagulation. Current ACCP guidelines recommend an IVC filter if anticoagulant therapy is contraindicated (Grade 1C). The anticoagulation was discontinued and a retrievable IVC filter was placed. Once a patient no longer has a contraindication for anticoagulation, the ACCP recommends restarting a conventional course of anticoagulation. Thus, once the patient can tolerate anticoagulation, consideration will be given to removal of the retrievable filter.
Bottom Line
An IVC filter should be considered in patients with a DVT who have a contraindication to anticoagulation. Other indications for IVC filter use are not supported by the current literature. TH
Drs. Bhogal and Eid are hospitalist fellows and instructors at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore. Dr. Kantsiper is a hospitalist and assistant professor at Bayview Medical Center.
References
- The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Web site. Available at: www.surgeongeneral.gov/topics/deepvein/. Accessed Jan. 25, 2010.
- Moser KM, Fedullo PR, LitteJohn JK, Crawford R. Frequent asymptomatic pulmonary embolism in patients with deep venous thrombosis. JAMA. 1994;271(3):223-225.
- Bates SM, Ginsberg JS. Treatment of deep vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:268-277.
- Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G, Goldhaber S, Raskob GE, Comerota AJ, American College of Chest Physicians. Antithrombotic therapy for venous theomboembolic disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):454S-545S.
- Becker DM, Philbrick JT, Selby JB. Inferior vena cava filters. Indications, safety, effectiveness. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(10):1985-1994.
- Streiff MB. Vena caval filters: a comprehensive review. Blood. 2000;95(12):3669-3677.
- Chung J, Owen RJ. Using inferior vena cava filters to prevent pulmonary embolism. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(1):49-55.
- Ku GH. Billett HH. Long lives, short indications. The case for removable inferior cava filters. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93(1):17-22.
- Stavropoulos WS. Inferior vena cava filters. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;7(2):91-95.
- Crowther MA. Inferior vena cava filters in the management of venous thromboembolism. Am J Med. 2007;120(10 Suppl 2):S13–S17.
- Stein PD, Kayali F, Olson RE. Twenty-one-year trends in the use of inferior vena cava filters. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(14):1541-1545.
- Guyatt G, Gutterman D, Baumann MH, et al. Grading strength of recommendations and quality of evidence in clinical guidelines: report from an American College of Chest Physicians task force. Chest. 2006;129(1):174-181.
- Büller HR, Agnelli G, Hull RD, Hyers TM, Prins MH, Raskob GE. Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004;126(3 Suppl):401S-428S.
- Decousus H, Leizorovicz A, Parent F, et al. A clinical trial of vena caval filters in the prevention of pulmonary embolism in patients with proximal deep-vein thrombosis. Prévention du Risque d’Embolie Pulmonaire par Interruption Cave Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(7):409-415.
- Decousus H, Barral F, Buchmuller-Cordier A, et al. Participating centers eight-year follow-up of patients with permanent vena cava filters in the prevention of pulmonary embolism: the PREPIC randomization croup. Circulation. 2005;112:416-422.
- Kim HS, Young MJ, Narayan AK, Liddell RP, Streiff MB. A comparison of clinical outcomes with retrievable and permanent inferior vena cava filters. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008:19(3):393-399.
- Houman Fekrazad M, Lopes RD, Stashenko GJ, Alexander JH, Garcia D. Treatment of venous thromboembolism: guidelines translated for the clinician. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2009; 28(3):270–275.
- Comerota AJ. Retrievable IVC filters: a decision matrix for appropriate utilization. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther. 2006;18(1):11-17.
- Ray CE Jr, Prochazka A. The need for anticoagulation following inferior vena cava filter placement: systematic review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008; 31(2):316-324.
- Hajduk B, Tomkowski WZ, Malek G, Davidson BL. Vena cava filter occlusion and venous thromboembolism risk in persistently anticoagulated patients: A prospective, observational cohort study. Chest. 2009.
Case
A 67-year-old man with a history of hypertension presents with a swollen right lower extremity. An ultrasound reveals a DVT, and he is commenced on low-molecular-weight heparin and warfarin. Two days later, he develops slurred speech and right-sided weakness. A head CT reveals an intracranial hemorrhage. When should an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter be utilized for treatment of DVT?
Overview
It is estimated that 350,000 to 600,000 Americans develop a VTE each year.1 Patients with a DVT are at high risk of developing a pulmonary embolism (PE). In a multicenter study, nearly 40% of patients admitted with a DVT had evidence of a PE on ventilation perfusion scan.2 Treatment of a DVT is aimed at preventing the extension of the DVT and embolization.3 The American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) recommends anticoagulation as the primary DVT treatment (Grade 1A).4 However, IVC filters might be considered when anticoagulation is contraindicated.
In 1868, Trousseau created the conceptual model of surgical interruption of the IVC to prevent PE. However, it wasn’t until 1959 by Bottini that the surgical interruption was successfully performed.5 The Mobin-Uddin filter was introduced in 1967 as the first mechanical IVC filter.6 IVC filters mechanically trap the DVT, preventing emboli from traveling into the pulmonary vasculature.7
There are two classes of IVC filters: permanent filters and removable filters. Removable filters include both temporary filters and retrievable filters. Temporary filters are attached to a catheter that exits the skin and therefore must be removed due to the risk of infection and embolization.7 Retrievable filters are similar in design to permanent filters but are designed to be removed. However, this must be done with caution, as neointimal hyperplasia can prevent removal or cause vessel wall damage upon removal.8
IVC filters are inserted into the vena cava percutaneously via the femoral or jugular approach under fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance (see Figure 1, p. 16). The filters typically are placed infrarenally, unless there is an indication for a suprarenal filter (e.g., renal vein thrombosis or IVC thrombus extending above the renal veins).7 Complete IVC thrombosis is an absolute contraindication to IVC filter placement, and the relative contraindications include significant coagulopathy and bacteremia.9
The incidence of complications related to IVC filter placement is 4% to 11%. Complications include:
- Insertion-site thrombosis;
- IVC thrombosis;
- Recurrent DVT postphlebitic syndrome;
- Filter migration;
- Erosion of the filter through the vessel wall; and
- Vena caval obstruction.10
A review of the National Hospital Discharge Survey database for trends in IVC filter use in the U.S. found a dramatic increase in the use of IVC filters from 1979 to 1999—to 49,000 patients from 2,000 patients with IVC filters in place. The indications for IVC filter use vary such that it is imperative there are well-designed trials and guidelines to guide appropriate use.11
The Evidence
The 2008 ACCP guidelines on VTE management follow a grading system that classifies recommendations as Grade 1 (strong) or Grade 2 (weak), and classifies the quality of evidence as A (high), B (moderate), or C (low).12 The ACCP guidelines’ recommended first-line treatment for a confirmed DVT is anticoagulation with subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin, intravenous unfractionated heparin, monitored subcutaneous heparin, fixed-dose subcutaneous unfractionated heparin, or subcutaneous fondaparinux (all Grade 1A recommendations). The ACCP recommends against the routine use of an IVC filter in addition to anticoagulants (Grade 1A). However, for patients with acute proximal DVT, if anticoagulant therapy is not possible because of the risk of bleeding, IVC filter placement is recommended (Grade 1C). If a patient requires an IVC filter for treatment of an acute DVT as an alternative to anticoagulation, it is recommended to start anticoagulant therapy once the risk of bleeding resolves (Grade 1C).4
The 2008 ACCP guidelines for IVC filter use have a few important changes from the 2004 version. First, the IVC filter placement recommendation for patients with contraindications to anticoagulation was strengthened from Grade 2C to Grade 1C. Second, the 2008 guidelines omitted the early recommendation of IVC filter use for recurrent VTE, despite adequate anticoagulation (Grade 2C).13
Only one randomized study has evaluated the efficacy of IVC filters. All other studies of IVC filters are retrospective or prospective case series.
The PREPIC study randomized 400 patients with proximal DVT considered to be at high risk for PE to receive either an IVC filter or no IVC filter. Additionally, patients were randomized to receive enoxaparin or unfractionated heparin as a bridge to warfarin therapy, which was continued for at least three months. The primary endpoints were recurrent DVT, PE, major bleeding, or death. The patients were followed up at day 12, two years, and then annually up to eight years following randomization.14 At day 12, there were fewer PEs in the group that received filters (OR 0.22, 95% CI, 0.05-0.90). However, at year two, there was no significant difference in PE development in the filter group compared with the no-filter group (OR 0.50, 95% CI, 0.19-1.33).
Additionally, at year two, the filter group was more likely to develop recurrent DVT (OR 1.87, 95% CI, 1.10-3.20). At year eight, there was a significant reduction in the number of PEs in the filter group versus the no-filter group (6.2% vs.15.1%, P=0.008). However, at eight-year followup, IVC filter use was associated with increased DVT (35.7% vs. 27.5%, P=0.042). There was no difference in mortality between the two groups.
In summary, the use of IVC filters was associated with decreased incidence of PE at eight years, offset by higher rates of recurrent DVT and no overall mortality benefit.14,15 Importantly, the indications for IVC filter use in this study differ from the current ACCP guidelines; all patients were given concomitant anticoagulation for at least three months, which might not be possible in patients for whom the ACCP recommends IVC filters.
There are no randomized studies to compare the efficacy of permanent IVC filters and retrievable filters for PE prevention. A retrospective study comparing the clinical effectiveness of the two filter types reported no difference in the rates of symptomatic PE (permanent filter 4% vs. retrievable filter 4.7%, P=0.67) or DVT (11.3% vs. 12.6%, P=0.59). In addition, the frequency of symptomatic IVC thrombosis was similar (1.1% vs. 0.5%, p=0.39).16 A paper reviewing the efficacy of IVC filters reported that permanent filters were associated with a 0%-6.2% rate of PE versus a 0%-1.9% rate with retrievable filters.7 Notably, these studies were not randomized controlled trials—rather, case series—and the indications for IVC filters were not necessarily those currently recommended by the ACCP.
Due to the long-term complications of permanent IVC filters, it is suggested that a retrievable IVC filter be used for patients with temporary contraindications to anticoagulation.17 Comerata et al created a clinical decision-making tool for picking the type of filter to employ. If the duration of contraindication to anticoagulation is short or uncertain, a retrievable filter is recommended.18 Table 1 (p. 15) outlines the recommendations for IVC filter placement.
There are no randomized controlled trials to guide the use of concomitant anticoagulation after filter insertion, although this intervention may be beneficial to prevent DVT propagation, recurrence, or IVC filter thrombosis.5 A meta-analysis of 14 studies evaluating the rates of VTE after IVC filter placement demonstrated a non-statistically significant trend toward fewer VTE events in the patients with an IVC filter and concomitant anticoagulation in comparison with those who solely had an IVC filter (OR 0.64, 95% CI, 0.35-1.2). The duration and degree of anticoagulation was not presented in all of the studies in the meta-analysis, therefore limiting the analysis.19
In addition to the ACCP guidelines, there have been other proposed indications for IVC filter use, including recurrent VTE despite anticoagulation, chronic recurrent PE with pulmonary hypertension, extensive free-floating iliofemoral thrombus, and thrombolysis of ilio-caval thrombus.20 The ACCP guidelines do not specifically address these individual indications, and at this time there are no randomized controlled trials to guide IVC filter use in these cases.
Back to the Case
Our patient developed a significant complication from anticoagulation. Current ACCP guidelines recommend an IVC filter if anticoagulant therapy is contraindicated (Grade 1C). The anticoagulation was discontinued and a retrievable IVC filter was placed. Once a patient no longer has a contraindication for anticoagulation, the ACCP recommends restarting a conventional course of anticoagulation. Thus, once the patient can tolerate anticoagulation, consideration will be given to removal of the retrievable filter.
Bottom Line
An IVC filter should be considered in patients with a DVT who have a contraindication to anticoagulation. Other indications for IVC filter use are not supported by the current literature. TH
Drs. Bhogal and Eid are hospitalist fellows and instructors at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore. Dr. Kantsiper is a hospitalist and assistant professor at Bayview Medical Center.
References
- The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Web site. Available at: www.surgeongeneral.gov/topics/deepvein/. Accessed Jan. 25, 2010.
- Moser KM, Fedullo PR, LitteJohn JK, Crawford R. Frequent asymptomatic pulmonary embolism in patients with deep venous thrombosis. JAMA. 1994;271(3):223-225.
- Bates SM, Ginsberg JS. Treatment of deep vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:268-277.
- Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G, Goldhaber S, Raskob GE, Comerota AJ, American College of Chest Physicians. Antithrombotic therapy for venous theomboembolic disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):454S-545S.
- Becker DM, Philbrick JT, Selby JB. Inferior vena cava filters. Indications, safety, effectiveness. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(10):1985-1994.
- Streiff MB. Vena caval filters: a comprehensive review. Blood. 2000;95(12):3669-3677.
- Chung J, Owen RJ. Using inferior vena cava filters to prevent pulmonary embolism. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(1):49-55.
- Ku GH. Billett HH. Long lives, short indications. The case for removable inferior cava filters. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93(1):17-22.
- Stavropoulos WS. Inferior vena cava filters. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;7(2):91-95.
- Crowther MA. Inferior vena cava filters in the management of venous thromboembolism. Am J Med. 2007;120(10 Suppl 2):S13–S17.
- Stein PD, Kayali F, Olson RE. Twenty-one-year trends in the use of inferior vena cava filters. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(14):1541-1545.
- Guyatt G, Gutterman D, Baumann MH, et al. Grading strength of recommendations and quality of evidence in clinical guidelines: report from an American College of Chest Physicians task force. Chest. 2006;129(1):174-181.
- Büller HR, Agnelli G, Hull RD, Hyers TM, Prins MH, Raskob GE. Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004;126(3 Suppl):401S-428S.
- Decousus H, Leizorovicz A, Parent F, et al. A clinical trial of vena caval filters in the prevention of pulmonary embolism in patients with proximal deep-vein thrombosis. Prévention du Risque d’Embolie Pulmonaire par Interruption Cave Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(7):409-415.
- Decousus H, Barral F, Buchmuller-Cordier A, et al. Participating centers eight-year follow-up of patients with permanent vena cava filters in the prevention of pulmonary embolism: the PREPIC randomization croup. Circulation. 2005;112:416-422.
- Kim HS, Young MJ, Narayan AK, Liddell RP, Streiff MB. A comparison of clinical outcomes with retrievable and permanent inferior vena cava filters. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008:19(3):393-399.
- Houman Fekrazad M, Lopes RD, Stashenko GJ, Alexander JH, Garcia D. Treatment of venous thromboembolism: guidelines translated for the clinician. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2009; 28(3):270–275.
- Comerota AJ. Retrievable IVC filters: a decision matrix for appropriate utilization. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther. 2006;18(1):11-17.
- Ray CE Jr, Prochazka A. The need for anticoagulation following inferior vena cava filter placement: systematic review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008; 31(2):316-324.
- Hajduk B, Tomkowski WZ, Malek G, Davidson BL. Vena cava filter occlusion and venous thromboembolism risk in persistently anticoagulated patients: A prospective, observational cohort study. Chest. 2009.
Case
A 67-year-old man with a history of hypertension presents with a swollen right lower extremity. An ultrasound reveals a DVT, and he is commenced on low-molecular-weight heparin and warfarin. Two days later, he develops slurred speech and right-sided weakness. A head CT reveals an intracranial hemorrhage. When should an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter be utilized for treatment of DVT?
Overview
It is estimated that 350,000 to 600,000 Americans develop a VTE each year.1 Patients with a DVT are at high risk of developing a pulmonary embolism (PE). In a multicenter study, nearly 40% of patients admitted with a DVT had evidence of a PE on ventilation perfusion scan.2 Treatment of a DVT is aimed at preventing the extension of the DVT and embolization.3 The American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) recommends anticoagulation as the primary DVT treatment (Grade 1A).4 However, IVC filters might be considered when anticoagulation is contraindicated.
In 1868, Trousseau created the conceptual model of surgical interruption of the IVC to prevent PE. However, it wasn’t until 1959 by Bottini that the surgical interruption was successfully performed.5 The Mobin-Uddin filter was introduced in 1967 as the first mechanical IVC filter.6 IVC filters mechanically trap the DVT, preventing emboli from traveling into the pulmonary vasculature.7
There are two classes of IVC filters: permanent filters and removable filters. Removable filters include both temporary filters and retrievable filters. Temporary filters are attached to a catheter that exits the skin and therefore must be removed due to the risk of infection and embolization.7 Retrievable filters are similar in design to permanent filters but are designed to be removed. However, this must be done with caution, as neointimal hyperplasia can prevent removal or cause vessel wall damage upon removal.8
IVC filters are inserted into the vena cava percutaneously via the femoral or jugular approach under fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance (see Figure 1, p. 16). The filters typically are placed infrarenally, unless there is an indication for a suprarenal filter (e.g., renal vein thrombosis or IVC thrombus extending above the renal veins).7 Complete IVC thrombosis is an absolute contraindication to IVC filter placement, and the relative contraindications include significant coagulopathy and bacteremia.9
The incidence of complications related to IVC filter placement is 4% to 11%. Complications include:
- Insertion-site thrombosis;
- IVC thrombosis;
- Recurrent DVT postphlebitic syndrome;
- Filter migration;
- Erosion of the filter through the vessel wall; and
- Vena caval obstruction.10
A review of the National Hospital Discharge Survey database for trends in IVC filter use in the U.S. found a dramatic increase in the use of IVC filters from 1979 to 1999—to 49,000 patients from 2,000 patients with IVC filters in place. The indications for IVC filter use vary such that it is imperative there are well-designed trials and guidelines to guide appropriate use.11
The Evidence
The 2008 ACCP guidelines on VTE management follow a grading system that classifies recommendations as Grade 1 (strong) or Grade 2 (weak), and classifies the quality of evidence as A (high), B (moderate), or C (low).12 The ACCP guidelines’ recommended first-line treatment for a confirmed DVT is anticoagulation with subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin, intravenous unfractionated heparin, monitored subcutaneous heparin, fixed-dose subcutaneous unfractionated heparin, or subcutaneous fondaparinux (all Grade 1A recommendations). The ACCP recommends against the routine use of an IVC filter in addition to anticoagulants (Grade 1A). However, for patients with acute proximal DVT, if anticoagulant therapy is not possible because of the risk of bleeding, IVC filter placement is recommended (Grade 1C). If a patient requires an IVC filter for treatment of an acute DVT as an alternative to anticoagulation, it is recommended to start anticoagulant therapy once the risk of bleeding resolves (Grade 1C).4
The 2008 ACCP guidelines for IVC filter use have a few important changes from the 2004 version. First, the IVC filter placement recommendation for patients with contraindications to anticoagulation was strengthened from Grade 2C to Grade 1C. Second, the 2008 guidelines omitted the early recommendation of IVC filter use for recurrent VTE, despite adequate anticoagulation (Grade 2C).13
Only one randomized study has evaluated the efficacy of IVC filters. All other studies of IVC filters are retrospective or prospective case series.
The PREPIC study randomized 400 patients with proximal DVT considered to be at high risk for PE to receive either an IVC filter or no IVC filter. Additionally, patients were randomized to receive enoxaparin or unfractionated heparin as a bridge to warfarin therapy, which was continued for at least three months. The primary endpoints were recurrent DVT, PE, major bleeding, or death. The patients were followed up at day 12, two years, and then annually up to eight years following randomization.14 At day 12, there were fewer PEs in the group that received filters (OR 0.22, 95% CI, 0.05-0.90). However, at year two, there was no significant difference in PE development in the filter group compared with the no-filter group (OR 0.50, 95% CI, 0.19-1.33).
Additionally, at year two, the filter group was more likely to develop recurrent DVT (OR 1.87, 95% CI, 1.10-3.20). At year eight, there was a significant reduction in the number of PEs in the filter group versus the no-filter group (6.2% vs.15.1%, P=0.008). However, at eight-year followup, IVC filter use was associated with increased DVT (35.7% vs. 27.5%, P=0.042). There was no difference in mortality between the two groups.
In summary, the use of IVC filters was associated with decreased incidence of PE at eight years, offset by higher rates of recurrent DVT and no overall mortality benefit.14,15 Importantly, the indications for IVC filter use in this study differ from the current ACCP guidelines; all patients were given concomitant anticoagulation for at least three months, which might not be possible in patients for whom the ACCP recommends IVC filters.
There are no randomized studies to compare the efficacy of permanent IVC filters and retrievable filters for PE prevention. A retrospective study comparing the clinical effectiveness of the two filter types reported no difference in the rates of symptomatic PE (permanent filter 4% vs. retrievable filter 4.7%, P=0.67) or DVT (11.3% vs. 12.6%, P=0.59). In addition, the frequency of symptomatic IVC thrombosis was similar (1.1% vs. 0.5%, p=0.39).16 A paper reviewing the efficacy of IVC filters reported that permanent filters were associated with a 0%-6.2% rate of PE versus a 0%-1.9% rate with retrievable filters.7 Notably, these studies were not randomized controlled trials—rather, case series—and the indications for IVC filters were not necessarily those currently recommended by the ACCP.
Due to the long-term complications of permanent IVC filters, it is suggested that a retrievable IVC filter be used for patients with temporary contraindications to anticoagulation.17 Comerata et al created a clinical decision-making tool for picking the type of filter to employ. If the duration of contraindication to anticoagulation is short or uncertain, a retrievable filter is recommended.18 Table 1 (p. 15) outlines the recommendations for IVC filter placement.
There are no randomized controlled trials to guide the use of concomitant anticoagulation after filter insertion, although this intervention may be beneficial to prevent DVT propagation, recurrence, or IVC filter thrombosis.5 A meta-analysis of 14 studies evaluating the rates of VTE after IVC filter placement demonstrated a non-statistically significant trend toward fewer VTE events in the patients with an IVC filter and concomitant anticoagulation in comparison with those who solely had an IVC filter (OR 0.64, 95% CI, 0.35-1.2). The duration and degree of anticoagulation was not presented in all of the studies in the meta-analysis, therefore limiting the analysis.19
In addition to the ACCP guidelines, there have been other proposed indications for IVC filter use, including recurrent VTE despite anticoagulation, chronic recurrent PE with pulmonary hypertension, extensive free-floating iliofemoral thrombus, and thrombolysis of ilio-caval thrombus.20 The ACCP guidelines do not specifically address these individual indications, and at this time there are no randomized controlled trials to guide IVC filter use in these cases.
Back to the Case
Our patient developed a significant complication from anticoagulation. Current ACCP guidelines recommend an IVC filter if anticoagulant therapy is contraindicated (Grade 1C). The anticoagulation was discontinued and a retrievable IVC filter was placed. Once a patient no longer has a contraindication for anticoagulation, the ACCP recommends restarting a conventional course of anticoagulation. Thus, once the patient can tolerate anticoagulation, consideration will be given to removal of the retrievable filter.
Bottom Line
An IVC filter should be considered in patients with a DVT who have a contraindication to anticoagulation. Other indications for IVC filter use are not supported by the current literature. TH
Drs. Bhogal and Eid are hospitalist fellows and instructors at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore. Dr. Kantsiper is a hospitalist and assistant professor at Bayview Medical Center.
References
- The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Web site. Available at: www.surgeongeneral.gov/topics/deepvein/. Accessed Jan. 25, 2010.
- Moser KM, Fedullo PR, LitteJohn JK, Crawford R. Frequent asymptomatic pulmonary embolism in patients with deep venous thrombosis. JAMA. 1994;271(3):223-225.
- Bates SM, Ginsberg JS. Treatment of deep vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:268-277.
- Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G, Goldhaber S, Raskob GE, Comerota AJ, American College of Chest Physicians. Antithrombotic therapy for venous theomboembolic disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):454S-545S.
- Becker DM, Philbrick JT, Selby JB. Inferior vena cava filters. Indications, safety, effectiveness. Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(10):1985-1994.
- Streiff MB. Vena caval filters: a comprehensive review. Blood. 2000;95(12):3669-3677.
- Chung J, Owen RJ. Using inferior vena cava filters to prevent pulmonary embolism. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(1):49-55.
- Ku GH. Billett HH. Long lives, short indications. The case for removable inferior cava filters. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93(1):17-22.
- Stavropoulos WS. Inferior vena cava filters. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;7(2):91-95.
- Crowther MA. Inferior vena cava filters in the management of venous thromboembolism. Am J Med. 2007;120(10 Suppl 2):S13–S17.
- Stein PD, Kayali F, Olson RE. Twenty-one-year trends in the use of inferior vena cava filters. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(14):1541-1545.
- Guyatt G, Gutterman D, Baumann MH, et al. Grading strength of recommendations and quality of evidence in clinical guidelines: report from an American College of Chest Physicians task force. Chest. 2006;129(1):174-181.
- Büller HR, Agnelli G, Hull RD, Hyers TM, Prins MH, Raskob GE. Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004;126(3 Suppl):401S-428S.
- Decousus H, Leizorovicz A, Parent F, et al. A clinical trial of vena caval filters in the prevention of pulmonary embolism in patients with proximal deep-vein thrombosis. Prévention du Risque d’Embolie Pulmonaire par Interruption Cave Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(7):409-415.
- Decousus H, Barral F, Buchmuller-Cordier A, et al. Participating centers eight-year follow-up of patients with permanent vena cava filters in the prevention of pulmonary embolism: the PREPIC randomization croup. Circulation. 2005;112:416-422.
- Kim HS, Young MJ, Narayan AK, Liddell RP, Streiff MB. A comparison of clinical outcomes with retrievable and permanent inferior vena cava filters. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008:19(3):393-399.
- Houman Fekrazad M, Lopes RD, Stashenko GJ, Alexander JH, Garcia D. Treatment of venous thromboembolism: guidelines translated for the clinician. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2009; 28(3):270–275.
- Comerota AJ. Retrievable IVC filters: a decision matrix for appropriate utilization. Perspect Vasc Surg Endovasc Ther. 2006;18(1):11-17.
- Ray CE Jr, Prochazka A. The need for anticoagulation following inferior vena cava filter placement: systematic review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008; 31(2):316-324.
- Hajduk B, Tomkowski WZ, Malek G, Davidson BL. Vena cava filter occlusion and venous thromboembolism risk in persistently anticoagulated patients: A prospective, observational cohort study. Chest. 2009.
In the Literature: March 2010
In This Edition
Literature at a Glance
A guide to this month’s studies
- Statins and postoperative cardiac outcomes
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with mild CHF symptoms
- Oral direct thrombin inhibitor versus warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
- Association of fatigue and medical error
- Effects of chronic inhaled steroid and beta-agonist use in COPD
- Dialysis and functional status in nursing home patients
- Outcomes with different insulin-dosing regimens
- Understanding of disease severity and outcomes in advanced dementia
Fluvastatin Improves Postoperative Cardiac Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Vascular Surgery
Clinical question: Does perioperative fluvastatin decrease adverse cardiac events after vascular surgery?
Background: Patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease who undergo vascular surgery are at high risk for postoperative cardiac events. Studies in nonsurgical populations have shown the beneficial effects of statin therapy on cardiac outcomes. However, no placebo-controlled trials have addressed the effect of statins on postoperative cardiac outcomes.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Single large academic medical center in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: The study looked at 497 statin-naïve patients 40 years or older undergoing non-cardiac vascular surgery. The patients were randomized to 80 mg of extended-release fluvastatin versus placebo; all patients received a beta-blocker. Therapy began preoperatively (median of 37 days) and continued for at least 30 days after surgery. Outcomes were assessed at 30 days post-surgery.
Postoperative myocardial infarction (MI) was significantly less common in the fluvastatin group than with placebo (10.8% vs. 19%, hazard ratio (HR) 0.55, P=0.01). In addition, the treatment group had a lower frequency of death from cardiovascular causes (4.8% vs. 10.1%, HR 0.47, P=0.03). Statin therapy was not associated with an increased rate of adverse events.
Notably, all of the patients enrolled in this study were high-risk patients undergoing high-risk (vascular) surgery. Patients already on statins were excluded.
Further studies are needed to determine whether the findings can be extrapolated to other populations, including nonvascular surgery patients.
Bottom line: Perioperative statin therapy resulted in a significant decrease in postoperative MI and death within 30 days of vascular surgery.
Citation: Schouten O, Boersma E, Hoeks SE, et al. Fluvastatin and perioperative events in patients undergoing vascular surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):980-989.
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Placement Decreases Heart Failure
Clinical question: Does cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) with biventricular pacing decrease cardiac events in patients with reduced ejection fraction (EF) and wide QRS complex but only mild cardiac symptoms?
Background: In patients with severely reduced EF, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) have been shown to improve survival. Meanwhile, CRT decreases heart-failure-related hospitalizations for patients with advanced heart-failure symptoms, EF less than 35%, and intraventricular conduction delay. It is not as clear whether patients with less-severe symptoms benefit from CRT.
Study design: Randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: 110 medical centers in the U.S., Canada, and Europe.
Synopsis: This Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial with Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT-CRT) study randomly assigned 1,820 adults with EF less than 30%, New York Health Association Class I or II congestive heart failure, and in sinus rhythm with QRS greater than 130 msec to receive ICD with CRT or ICD alone. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality or nonfatal heart-failure events. Average followup was 2.4 years.
A 34% reduction in the primary endpoint was found in the ICD-CRT group when compared with the ICD-only group, primarily due to a 41% reduction in heart-failure events. In a subgroup analysis, women and patients with QRS greater than 150 msec experienced particular benefit. Echocardiography one year after device implantation demonstrated significant reductions in left ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volume, and a significant increase in EF with ICD-CRT versus ICD-only (P<0.001).
Bottom line: Compared with ICD alone, CRT in combination with ICD prevented heart-failure events in relatively asymptomatic heart-failure patients with low EF and prolonged QRS.
Citation: Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS, et al. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for the prevention of heart-failure events. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(14):1329-1338.
Dabigatran Is Not Inferior to Warfarin in Atrial Fibrillation
Clinical question: Is dabigatran, an oral thrombin inhibitor, an effective and safe alternative to warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation?
Background: Warfarin reduces the risk of stroke among patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) but requires frequent laboratory monitoring. Dabigatran is an oral direct thrombin inhibitor given in fixed dosages without laboratory monitoring.
Study design: Randomized, multicenter, open-label, noninferiority trial.
Setting: 951 clinical centers in 44 countries.
Synopsis: More than 18,000 patients 65 and older with AF and at least one stroke risk factor were enrolled. The average CHADS2 score was 2.1. Patients were randomized to receive fixed doses of dabigatran (110 mg or 150 mg, twice daily) or warfarin adjusted to an INR of 2.0-3.0. The primary outcomes were a) stroke or systemic embolism and b) major hemorrhage. Median followup was two years.
The annual rates of stroke or systemic embolism for both doses of dabigatran were noninferior to warfarin (P<0.001); higher-dose dabigatran was statistically superior to warfarin (relative risk (RR)=0.66, P<0.001). The annual rate of major hemorrhage was lowest in the lower-dose dabigatran group (RR=0.80, P=0.003 compared with warfarin); the higher-dose dabigatran and warfarin groups had equivalent rates of major bleeding. No increased risk of liver function abnormalities was noted.
Bottom line: Dabigatran appears to be an effective and safe alternative to warfarin in AF patients. If the drug were to be FDA-approved, appropriate patient selection and cost will need to be established.
Citation: Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139-1151.
Resident Fatigue and Distress Contribute to Perceived Medical Errors
Clinical question: Do resident fatigue and distress contribute to medical errors?
Background: In recent years, such measures as work-hour limitations have been implemented to decrease resident fatigue and, it is presumed, medical errors. However, few studies address the relationship between residents’ well-being and self-reported medical errors.
Study design: Prospective six-year longitudinal cohort study.
Setting: Single academic medical center.
Synopsis: The authors had 380 internal-medicine residents complete quarterly surveys to assess fatigue, quality of life, burnout, symptoms of depression, and frequency of perceived medical errors. In a univariate analysis, fatigue/sleepiness, burnout, depression, and overall quality of life measures correlated significantly with self-reported major medical errors. Fatigue/sleepiness and measures of distress additively increased the risk of self-reported errors. Increases in one or both domains were estimated to increase the risk of self-reported errors by as much as 15% to 28%.
The authors studied only self-reported medical errors. It is difficult to know whether these errors directly affected patient outcomes. Additionally, results of this single-site study might not be able to be generalized.
Bottom line: Fatigue and distress contribute to self-perceived medical errors among residents.
Citation: West CP, Tan AD, Habermann TM, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Association of resident fatigue and distress with perceived medical errors. JAMA. 2009;302(12):1294-1300.
Inhaled Corticosteroids Decrease Inflammation in Moderate to Severe COPD
Clinical question: Does long-term inhaled corticosteroid therapy, with and without long-acting beta-agonists, decrease airway inflammation and improve lung function in patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
Background: Guideline-recommended treatment of COPD with inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta-agonists improves symptoms and exacerbation rates; little is known about the impact of these therapies on inflammation and long-term lung function.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Two university medical centers in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: One hundred one steroid-naïve patients, ages 45 to 75 who were current or former smokers with moderate to severe COPD, were randomized to one of four regimens: 1) fluticasone for six months, then placebo for 24 months; 2) fluticasone for 30 months; 3) fluticasone and salmeterol for 30 months; or 4) placebo for 30 months. The primary outcome was inflammatory cell counts in bronchial biopsies/induced sputum. Secondary outcomes included postbronchodilator spirometry, methacholine hyperresponsiveness, and self-reported symptoms and health status. Patients with asthma were excluded.
Short-term fluticasone therapy decreased inflammation and improved forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). Long-term therapy also decreased the rate of FEV1 decline, reduced dyspnea, and improved health status. Discontinuation of therapy at six months led to inflammation relapse with worsened symptoms and increased rate of FEV1 decline. The addition of long-acting beta-agonists did not provide additional anti-inflammatory benefits, but it did improve FEV1 and dyspnea at six months.
Additional studies are needed to further define clinical outcomes and assess the cost benefit of these therapies.
Bottom line: Inhaled corticosteroids decrease inflammation in steroid-naïve patients with moderate to severe COPD and might decrease the rate of lung function decline. Long-acting beta-agonists do not offer additional anti-inflammatory benefit.
Citation: Lapperre TS, Snoeck-Stroband JB, Gosman MM, et al. Effect of fluticasone with and without salmeterol on pulmonary outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(8):517-527.
Initiation of Dialysis Does Not Help Maintain Functional Status in Elderly
Clinical question: Is functional status in the elderly maintained over time after initiating long-term dialysis?
Background: Quality-of-life maintenance often is used as a goal when initiating long-term dialysis in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease. More elderly patients are being offered long-term dialysis treatment. Little is known about the functional status of elderly patients on long-term dialysis.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: U.S. nursing homes.
Synopsis: By cross-linking data from two population-based administrative datasets, this study identified 3,702 nursing home patients (mean 73.4 years) who had started long-term dialysis and whose functional status had been assessed. Activities of daily living assessments before and at three-month intervals after dialysis initiation were compared to see if functional status was maintained.
Within three months of starting dialysis, 61% of patients had a decline in functional status or had died. By one year, only 1 in 8 patients had maintained their pre-dialysis functional status.
Decline in functional status cannot be attributed solely to dialysis because study patients were not compared to patients with chronic kidney disease who were not dialyzed. In addition, these results might not apply to all elderly patients on dialysis, as the functional status of elderly nursing home patients might differ significantly from those living at home.
Bottom line: Functional status is not maintained in most elderly nursing home patients in the first 12 months after long-term dialysis is initiated. Elderly patients considering dialysis treatment should be aware that dialysis might not help maintain functional status and quality of life.
Citation: Kurella Tamura MK, Covinsky KE, Chertow GM, Yaffe C, Landefeld CS, McCulloch CE. Functional status of elderly adults before and after initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1539-1547.
Adding Basal Insulin to Oral Agents in Type 2 Diabetes Might Offer Best Glycemic Control
Clinical question: When added to oral diabetic agents, which insulin regimen (biphasic, prandial or basal) best achieves glycemic control in patients with Type 2 diabetes?
Background: Most patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) require insulin when oral agents provide suboptimal glycemic control. Little is known about which insulin regimen is most effective.
Study design: Three-year, open-label, multicenter trial.
Setting: Fifty-eight clinical centers in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
Synopsis: The authors randomized 708 insulin-naïve DM2 patients (median age 62 years) with HgbA1c 7% to 10% on maximum-dose metformin or sulfonylurea to one of three regimens: biphasic insulin twice daily; prandial insulin three times daily; or basal insulin once daily. Outcomes were HgbA1c, hypoglycemia rates, and weight gain. Sulfonylureas were replaced by another insulin if glycemic control was unacceptable.
The patients were mostly Caucasian and overweight. At three years of followup, median HgbA1c was similar in all groups (7.1% biphasic, 6.8% prandial, 6.9% basal); however, more patients who received prandial or basal insulin achieved HgbA1c less than 6.5% (45% and 43%, respectively) than in the biphasic group (32%).
Hypoglycemia was significantly less frequent in the basal insulin group (1.7 per patient per year versus 3.0 and 5.5 with biphasic and prandial, respectively). Patients gained weight in all groups; the greatest gain was with prandial insulin. At three years, there were no significant between-group differences in blood pressure, cholesterol, albuminuria, or quality of life.
Bottom line: Adding insulin to oral diabetic regimens improves glycemic control. Basal or prandial insulin regimens achieve glycemic targets more frequently than biphasic dosing.
Citation: Holman RR, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, et al. Three-year efficacy of complex insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(18):1736-1747.
Advanced Dementia Is a Terminal Illness with High Morbidity and Mortality
Clinical question: Does understanding the expected clinical course of advanced dementia influence end-of-life decisions by proxy decision-makers?
Background: Advanced dementia is a leading cause of death in the United States, but the clinical course of advanced dementia has not been described in a rigorous, prospective manner. The lack of information might cause risk to be underestimated, and patients might receive suboptimal palliative care.
Study design: Multicenter prospective cohort study.
Setting: Twenty-two nursing homes in a single U.S. city.
Synopsis: The survey examined 323 nursing home residents with advanced dementia. The patients were clinically assessed at baseline and quarterly for 18 months through chart reviews, nursing interviews, and physical examinations. Additionally, their proxies were surveyed regarding their understanding of the subjects’ prognoses.
During the survey period, 41.1% of patients developed pneumonia, 52.6% of patients experienced a febrile episode, and 85.8% of patients developed an eating problem; cumulative all-cause mortality was 54.8%. Adjusted for age, sex, and disease duration, the six-month mortality rate for subjects who had pneumonia was 46.7%; a febrile episode, 44.5%; and an eating problem, 38.6%.
Distressing symptoms, including dyspnea (46.0%) and pain (39.1%), were common. In the last three months of life, 40.7% of subjects underwent at least one burdensome intervention (defined as hospitalization, ED visit, parenteral therapy, or tube feeding).
Subjects whose proxies reported an understanding of the poor prognosis and expected clinical complications of advanced dementia underwent significantly fewer burdensome interventions (adjusted odds ratio 0.12).
Bottom line: Advanced dementia is associated with frequent complications, including infections and eating problems, with high six-month mortality and significant associated morbidity. Patients whose healthcare proxies have a good understanding of the expected clinical course and prognosis receive less-aggressive end-of-life care.
Citation: Mitchell SL, Teno JM, Kiely DK, et al. The clinical course of advanced dementia. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1529-1538. TH
In This Edition
Literature at a Glance
A guide to this month’s studies
- Statins and postoperative cardiac outcomes
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with mild CHF symptoms
- Oral direct thrombin inhibitor versus warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
- Association of fatigue and medical error
- Effects of chronic inhaled steroid and beta-agonist use in COPD
- Dialysis and functional status in nursing home patients
- Outcomes with different insulin-dosing regimens
- Understanding of disease severity and outcomes in advanced dementia
Fluvastatin Improves Postoperative Cardiac Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Vascular Surgery
Clinical question: Does perioperative fluvastatin decrease adverse cardiac events after vascular surgery?
Background: Patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease who undergo vascular surgery are at high risk for postoperative cardiac events. Studies in nonsurgical populations have shown the beneficial effects of statin therapy on cardiac outcomes. However, no placebo-controlled trials have addressed the effect of statins on postoperative cardiac outcomes.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Single large academic medical center in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: The study looked at 497 statin-naïve patients 40 years or older undergoing non-cardiac vascular surgery. The patients were randomized to 80 mg of extended-release fluvastatin versus placebo; all patients received a beta-blocker. Therapy began preoperatively (median of 37 days) and continued for at least 30 days after surgery. Outcomes were assessed at 30 days post-surgery.
Postoperative myocardial infarction (MI) was significantly less common in the fluvastatin group than with placebo (10.8% vs. 19%, hazard ratio (HR) 0.55, P=0.01). In addition, the treatment group had a lower frequency of death from cardiovascular causes (4.8% vs. 10.1%, HR 0.47, P=0.03). Statin therapy was not associated with an increased rate of adverse events.
Notably, all of the patients enrolled in this study were high-risk patients undergoing high-risk (vascular) surgery. Patients already on statins were excluded.
Further studies are needed to determine whether the findings can be extrapolated to other populations, including nonvascular surgery patients.
Bottom line: Perioperative statin therapy resulted in a significant decrease in postoperative MI and death within 30 days of vascular surgery.
Citation: Schouten O, Boersma E, Hoeks SE, et al. Fluvastatin and perioperative events in patients undergoing vascular surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):980-989.
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Placement Decreases Heart Failure
Clinical question: Does cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) with biventricular pacing decrease cardiac events in patients with reduced ejection fraction (EF) and wide QRS complex but only mild cardiac symptoms?
Background: In patients with severely reduced EF, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) have been shown to improve survival. Meanwhile, CRT decreases heart-failure-related hospitalizations for patients with advanced heart-failure symptoms, EF less than 35%, and intraventricular conduction delay. It is not as clear whether patients with less-severe symptoms benefit from CRT.
Study design: Randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: 110 medical centers in the U.S., Canada, and Europe.
Synopsis: This Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial with Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT-CRT) study randomly assigned 1,820 adults with EF less than 30%, New York Health Association Class I or II congestive heart failure, and in sinus rhythm with QRS greater than 130 msec to receive ICD with CRT or ICD alone. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality or nonfatal heart-failure events. Average followup was 2.4 years.
A 34% reduction in the primary endpoint was found in the ICD-CRT group when compared with the ICD-only group, primarily due to a 41% reduction in heart-failure events. In a subgroup analysis, women and patients with QRS greater than 150 msec experienced particular benefit. Echocardiography one year after device implantation demonstrated significant reductions in left ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volume, and a significant increase in EF with ICD-CRT versus ICD-only (P<0.001).
Bottom line: Compared with ICD alone, CRT in combination with ICD prevented heart-failure events in relatively asymptomatic heart-failure patients with low EF and prolonged QRS.
Citation: Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS, et al. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for the prevention of heart-failure events. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(14):1329-1338.
Dabigatran Is Not Inferior to Warfarin in Atrial Fibrillation
Clinical question: Is dabigatran, an oral thrombin inhibitor, an effective and safe alternative to warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation?
Background: Warfarin reduces the risk of stroke among patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) but requires frequent laboratory monitoring. Dabigatran is an oral direct thrombin inhibitor given in fixed dosages without laboratory monitoring.
Study design: Randomized, multicenter, open-label, noninferiority trial.
Setting: 951 clinical centers in 44 countries.
Synopsis: More than 18,000 patients 65 and older with AF and at least one stroke risk factor were enrolled. The average CHADS2 score was 2.1. Patients were randomized to receive fixed doses of dabigatran (110 mg or 150 mg, twice daily) or warfarin adjusted to an INR of 2.0-3.0. The primary outcomes were a) stroke or systemic embolism and b) major hemorrhage. Median followup was two years.
The annual rates of stroke or systemic embolism for both doses of dabigatran were noninferior to warfarin (P<0.001); higher-dose dabigatran was statistically superior to warfarin (relative risk (RR)=0.66, P<0.001). The annual rate of major hemorrhage was lowest in the lower-dose dabigatran group (RR=0.80, P=0.003 compared with warfarin); the higher-dose dabigatran and warfarin groups had equivalent rates of major bleeding. No increased risk of liver function abnormalities was noted.
Bottom line: Dabigatran appears to be an effective and safe alternative to warfarin in AF patients. If the drug were to be FDA-approved, appropriate patient selection and cost will need to be established.
Citation: Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139-1151.
Resident Fatigue and Distress Contribute to Perceived Medical Errors
Clinical question: Do resident fatigue and distress contribute to medical errors?
Background: In recent years, such measures as work-hour limitations have been implemented to decrease resident fatigue and, it is presumed, medical errors. However, few studies address the relationship between residents’ well-being and self-reported medical errors.
Study design: Prospective six-year longitudinal cohort study.
Setting: Single academic medical center.
Synopsis: The authors had 380 internal-medicine residents complete quarterly surveys to assess fatigue, quality of life, burnout, symptoms of depression, and frequency of perceived medical errors. In a univariate analysis, fatigue/sleepiness, burnout, depression, and overall quality of life measures correlated significantly with self-reported major medical errors. Fatigue/sleepiness and measures of distress additively increased the risk of self-reported errors. Increases in one or both domains were estimated to increase the risk of self-reported errors by as much as 15% to 28%.
The authors studied only self-reported medical errors. It is difficult to know whether these errors directly affected patient outcomes. Additionally, results of this single-site study might not be able to be generalized.
Bottom line: Fatigue and distress contribute to self-perceived medical errors among residents.
Citation: West CP, Tan AD, Habermann TM, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Association of resident fatigue and distress with perceived medical errors. JAMA. 2009;302(12):1294-1300.
Inhaled Corticosteroids Decrease Inflammation in Moderate to Severe COPD
Clinical question: Does long-term inhaled corticosteroid therapy, with and without long-acting beta-agonists, decrease airway inflammation and improve lung function in patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
Background: Guideline-recommended treatment of COPD with inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta-agonists improves symptoms and exacerbation rates; little is known about the impact of these therapies on inflammation and long-term lung function.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Two university medical centers in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: One hundred one steroid-naïve patients, ages 45 to 75 who were current or former smokers with moderate to severe COPD, were randomized to one of four regimens: 1) fluticasone for six months, then placebo for 24 months; 2) fluticasone for 30 months; 3) fluticasone and salmeterol for 30 months; or 4) placebo for 30 months. The primary outcome was inflammatory cell counts in bronchial biopsies/induced sputum. Secondary outcomes included postbronchodilator spirometry, methacholine hyperresponsiveness, and self-reported symptoms and health status. Patients with asthma were excluded.
Short-term fluticasone therapy decreased inflammation and improved forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). Long-term therapy also decreased the rate of FEV1 decline, reduced dyspnea, and improved health status. Discontinuation of therapy at six months led to inflammation relapse with worsened symptoms and increased rate of FEV1 decline. The addition of long-acting beta-agonists did not provide additional anti-inflammatory benefits, but it did improve FEV1 and dyspnea at six months.
Additional studies are needed to further define clinical outcomes and assess the cost benefit of these therapies.
Bottom line: Inhaled corticosteroids decrease inflammation in steroid-naïve patients with moderate to severe COPD and might decrease the rate of lung function decline. Long-acting beta-agonists do not offer additional anti-inflammatory benefit.
Citation: Lapperre TS, Snoeck-Stroband JB, Gosman MM, et al. Effect of fluticasone with and without salmeterol on pulmonary outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(8):517-527.
Initiation of Dialysis Does Not Help Maintain Functional Status in Elderly
Clinical question: Is functional status in the elderly maintained over time after initiating long-term dialysis?
Background: Quality-of-life maintenance often is used as a goal when initiating long-term dialysis in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease. More elderly patients are being offered long-term dialysis treatment. Little is known about the functional status of elderly patients on long-term dialysis.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: U.S. nursing homes.
Synopsis: By cross-linking data from two population-based administrative datasets, this study identified 3,702 nursing home patients (mean 73.4 years) who had started long-term dialysis and whose functional status had been assessed. Activities of daily living assessments before and at three-month intervals after dialysis initiation were compared to see if functional status was maintained.
Within three months of starting dialysis, 61% of patients had a decline in functional status or had died. By one year, only 1 in 8 patients had maintained their pre-dialysis functional status.
Decline in functional status cannot be attributed solely to dialysis because study patients were not compared to patients with chronic kidney disease who were not dialyzed. In addition, these results might not apply to all elderly patients on dialysis, as the functional status of elderly nursing home patients might differ significantly from those living at home.
Bottom line: Functional status is not maintained in most elderly nursing home patients in the first 12 months after long-term dialysis is initiated. Elderly patients considering dialysis treatment should be aware that dialysis might not help maintain functional status and quality of life.
Citation: Kurella Tamura MK, Covinsky KE, Chertow GM, Yaffe C, Landefeld CS, McCulloch CE. Functional status of elderly adults before and after initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1539-1547.
Adding Basal Insulin to Oral Agents in Type 2 Diabetes Might Offer Best Glycemic Control
Clinical question: When added to oral diabetic agents, which insulin regimen (biphasic, prandial or basal) best achieves glycemic control in patients with Type 2 diabetes?
Background: Most patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) require insulin when oral agents provide suboptimal glycemic control. Little is known about which insulin regimen is most effective.
Study design: Three-year, open-label, multicenter trial.
Setting: Fifty-eight clinical centers in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
Synopsis: The authors randomized 708 insulin-naïve DM2 patients (median age 62 years) with HgbA1c 7% to 10% on maximum-dose metformin or sulfonylurea to one of three regimens: biphasic insulin twice daily; prandial insulin three times daily; or basal insulin once daily. Outcomes were HgbA1c, hypoglycemia rates, and weight gain. Sulfonylureas were replaced by another insulin if glycemic control was unacceptable.
The patients were mostly Caucasian and overweight. At three years of followup, median HgbA1c was similar in all groups (7.1% biphasic, 6.8% prandial, 6.9% basal); however, more patients who received prandial or basal insulin achieved HgbA1c less than 6.5% (45% and 43%, respectively) than in the biphasic group (32%).
Hypoglycemia was significantly less frequent in the basal insulin group (1.7 per patient per year versus 3.0 and 5.5 with biphasic and prandial, respectively). Patients gained weight in all groups; the greatest gain was with prandial insulin. At three years, there were no significant between-group differences in blood pressure, cholesterol, albuminuria, or quality of life.
Bottom line: Adding insulin to oral diabetic regimens improves glycemic control. Basal or prandial insulin regimens achieve glycemic targets more frequently than biphasic dosing.
Citation: Holman RR, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, et al. Three-year efficacy of complex insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(18):1736-1747.
Advanced Dementia Is a Terminal Illness with High Morbidity and Mortality
Clinical question: Does understanding the expected clinical course of advanced dementia influence end-of-life decisions by proxy decision-makers?
Background: Advanced dementia is a leading cause of death in the United States, but the clinical course of advanced dementia has not been described in a rigorous, prospective manner. The lack of information might cause risk to be underestimated, and patients might receive suboptimal palliative care.
Study design: Multicenter prospective cohort study.
Setting: Twenty-two nursing homes in a single U.S. city.
Synopsis: The survey examined 323 nursing home residents with advanced dementia. The patients were clinically assessed at baseline and quarterly for 18 months through chart reviews, nursing interviews, and physical examinations. Additionally, their proxies were surveyed regarding their understanding of the subjects’ prognoses.
During the survey period, 41.1% of patients developed pneumonia, 52.6% of patients experienced a febrile episode, and 85.8% of patients developed an eating problem; cumulative all-cause mortality was 54.8%. Adjusted for age, sex, and disease duration, the six-month mortality rate for subjects who had pneumonia was 46.7%; a febrile episode, 44.5%; and an eating problem, 38.6%.
Distressing symptoms, including dyspnea (46.0%) and pain (39.1%), were common. In the last three months of life, 40.7% of subjects underwent at least one burdensome intervention (defined as hospitalization, ED visit, parenteral therapy, or tube feeding).
Subjects whose proxies reported an understanding of the poor prognosis and expected clinical complications of advanced dementia underwent significantly fewer burdensome interventions (adjusted odds ratio 0.12).
Bottom line: Advanced dementia is associated with frequent complications, including infections and eating problems, with high six-month mortality and significant associated morbidity. Patients whose healthcare proxies have a good understanding of the expected clinical course and prognosis receive less-aggressive end-of-life care.
Citation: Mitchell SL, Teno JM, Kiely DK, et al. The clinical course of advanced dementia. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1529-1538. TH
In This Edition
Literature at a Glance
A guide to this month’s studies
- Statins and postoperative cardiac outcomes
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients with mild CHF symptoms
- Oral direct thrombin inhibitor versus warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
- Association of fatigue and medical error
- Effects of chronic inhaled steroid and beta-agonist use in COPD
- Dialysis and functional status in nursing home patients
- Outcomes with different insulin-dosing regimens
- Understanding of disease severity and outcomes in advanced dementia
Fluvastatin Improves Postoperative Cardiac Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Vascular Surgery
Clinical question: Does perioperative fluvastatin decrease adverse cardiac events after vascular surgery?
Background: Patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease who undergo vascular surgery are at high risk for postoperative cardiac events. Studies in nonsurgical populations have shown the beneficial effects of statin therapy on cardiac outcomes. However, no placebo-controlled trials have addressed the effect of statins on postoperative cardiac outcomes.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Single large academic medical center in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: The study looked at 497 statin-naïve patients 40 years or older undergoing non-cardiac vascular surgery. The patients were randomized to 80 mg of extended-release fluvastatin versus placebo; all patients received a beta-blocker. Therapy began preoperatively (median of 37 days) and continued for at least 30 days after surgery. Outcomes were assessed at 30 days post-surgery.
Postoperative myocardial infarction (MI) was significantly less common in the fluvastatin group than with placebo (10.8% vs. 19%, hazard ratio (HR) 0.55, P=0.01). In addition, the treatment group had a lower frequency of death from cardiovascular causes (4.8% vs. 10.1%, HR 0.47, P=0.03). Statin therapy was not associated with an increased rate of adverse events.
Notably, all of the patients enrolled in this study were high-risk patients undergoing high-risk (vascular) surgery. Patients already on statins were excluded.
Further studies are needed to determine whether the findings can be extrapolated to other populations, including nonvascular surgery patients.
Bottom line: Perioperative statin therapy resulted in a significant decrease in postoperative MI and death within 30 days of vascular surgery.
Citation: Schouten O, Boersma E, Hoeks SE, et al. Fluvastatin and perioperative events in patients undergoing vascular surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):980-989.
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Placement Decreases Heart Failure
Clinical question: Does cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) with biventricular pacing decrease cardiac events in patients with reduced ejection fraction (EF) and wide QRS complex but only mild cardiac symptoms?
Background: In patients with severely reduced EF, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) have been shown to improve survival. Meanwhile, CRT decreases heart-failure-related hospitalizations for patients with advanced heart-failure symptoms, EF less than 35%, and intraventricular conduction delay. It is not as clear whether patients with less-severe symptoms benefit from CRT.
Study design: Randomized, controlled trial.
Setting: 110 medical centers in the U.S., Canada, and Europe.
Synopsis: This Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial with Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT-CRT) study randomly assigned 1,820 adults with EF less than 30%, New York Health Association Class I or II congestive heart failure, and in sinus rhythm with QRS greater than 130 msec to receive ICD with CRT or ICD alone. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality or nonfatal heart-failure events. Average followup was 2.4 years.
A 34% reduction in the primary endpoint was found in the ICD-CRT group when compared with the ICD-only group, primarily due to a 41% reduction in heart-failure events. In a subgroup analysis, women and patients with QRS greater than 150 msec experienced particular benefit. Echocardiography one year after device implantation demonstrated significant reductions in left ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic volume, and a significant increase in EF with ICD-CRT versus ICD-only (P<0.001).
Bottom line: Compared with ICD alone, CRT in combination with ICD prevented heart-failure events in relatively asymptomatic heart-failure patients with low EF and prolonged QRS.
Citation: Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS, et al. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for the prevention of heart-failure events. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(14):1329-1338.
Dabigatran Is Not Inferior to Warfarin in Atrial Fibrillation
Clinical question: Is dabigatran, an oral thrombin inhibitor, an effective and safe alternative to warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation?
Background: Warfarin reduces the risk of stroke among patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) but requires frequent laboratory monitoring. Dabigatran is an oral direct thrombin inhibitor given in fixed dosages without laboratory monitoring.
Study design: Randomized, multicenter, open-label, noninferiority trial.
Setting: 951 clinical centers in 44 countries.
Synopsis: More than 18,000 patients 65 and older with AF and at least one stroke risk factor were enrolled. The average CHADS2 score was 2.1. Patients were randomized to receive fixed doses of dabigatran (110 mg or 150 mg, twice daily) or warfarin adjusted to an INR of 2.0-3.0. The primary outcomes were a) stroke or systemic embolism and b) major hemorrhage. Median followup was two years.
The annual rates of stroke or systemic embolism for both doses of dabigatran were noninferior to warfarin (P<0.001); higher-dose dabigatran was statistically superior to warfarin (relative risk (RR)=0.66, P<0.001). The annual rate of major hemorrhage was lowest in the lower-dose dabigatran group (RR=0.80, P=0.003 compared with warfarin); the higher-dose dabigatran and warfarin groups had equivalent rates of major bleeding. No increased risk of liver function abnormalities was noted.
Bottom line: Dabigatran appears to be an effective and safe alternative to warfarin in AF patients. If the drug were to be FDA-approved, appropriate patient selection and cost will need to be established.
Citation: Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139-1151.
Resident Fatigue and Distress Contribute to Perceived Medical Errors
Clinical question: Do resident fatigue and distress contribute to medical errors?
Background: In recent years, such measures as work-hour limitations have been implemented to decrease resident fatigue and, it is presumed, medical errors. However, few studies address the relationship between residents’ well-being and self-reported medical errors.
Study design: Prospective six-year longitudinal cohort study.
Setting: Single academic medical center.
Synopsis: The authors had 380 internal-medicine residents complete quarterly surveys to assess fatigue, quality of life, burnout, symptoms of depression, and frequency of perceived medical errors. In a univariate analysis, fatigue/sleepiness, burnout, depression, and overall quality of life measures correlated significantly with self-reported major medical errors. Fatigue/sleepiness and measures of distress additively increased the risk of self-reported errors. Increases in one or both domains were estimated to increase the risk of self-reported errors by as much as 15% to 28%.
The authors studied only self-reported medical errors. It is difficult to know whether these errors directly affected patient outcomes. Additionally, results of this single-site study might not be able to be generalized.
Bottom line: Fatigue and distress contribute to self-perceived medical errors among residents.
Citation: West CP, Tan AD, Habermann TM, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Association of resident fatigue and distress with perceived medical errors. JAMA. 2009;302(12):1294-1300.
Inhaled Corticosteroids Decrease Inflammation in Moderate to Severe COPD
Clinical question: Does long-term inhaled corticosteroid therapy, with and without long-acting beta-agonists, decrease airway inflammation and improve lung function in patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
Background: Guideline-recommended treatment of COPD with inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta-agonists improves symptoms and exacerbation rates; little is known about the impact of these therapies on inflammation and long-term lung function.
Study design: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Two university medical centers in the Netherlands.
Synopsis: One hundred one steroid-naïve patients, ages 45 to 75 who were current or former smokers with moderate to severe COPD, were randomized to one of four regimens: 1) fluticasone for six months, then placebo for 24 months; 2) fluticasone for 30 months; 3) fluticasone and salmeterol for 30 months; or 4) placebo for 30 months. The primary outcome was inflammatory cell counts in bronchial biopsies/induced sputum. Secondary outcomes included postbronchodilator spirometry, methacholine hyperresponsiveness, and self-reported symptoms and health status. Patients with asthma were excluded.
Short-term fluticasone therapy decreased inflammation and improved forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). Long-term therapy also decreased the rate of FEV1 decline, reduced dyspnea, and improved health status. Discontinuation of therapy at six months led to inflammation relapse with worsened symptoms and increased rate of FEV1 decline. The addition of long-acting beta-agonists did not provide additional anti-inflammatory benefits, but it did improve FEV1 and dyspnea at six months.
Additional studies are needed to further define clinical outcomes and assess the cost benefit of these therapies.
Bottom line: Inhaled corticosteroids decrease inflammation in steroid-naïve patients with moderate to severe COPD and might decrease the rate of lung function decline. Long-acting beta-agonists do not offer additional anti-inflammatory benefit.
Citation: Lapperre TS, Snoeck-Stroband JB, Gosman MM, et al. Effect of fluticasone with and without salmeterol on pulmonary outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(8):517-527.
Initiation of Dialysis Does Not Help Maintain Functional Status in Elderly
Clinical question: Is functional status in the elderly maintained over time after initiating long-term dialysis?
Background: Quality-of-life maintenance often is used as a goal when initiating long-term dialysis in elderly patients with end-stage renal disease. More elderly patients are being offered long-term dialysis treatment. Little is known about the functional status of elderly patients on long-term dialysis.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: U.S. nursing homes.
Synopsis: By cross-linking data from two population-based administrative datasets, this study identified 3,702 nursing home patients (mean 73.4 years) who had started long-term dialysis and whose functional status had been assessed. Activities of daily living assessments before and at three-month intervals after dialysis initiation were compared to see if functional status was maintained.
Within three months of starting dialysis, 61% of patients had a decline in functional status or had died. By one year, only 1 in 8 patients had maintained their pre-dialysis functional status.
Decline in functional status cannot be attributed solely to dialysis because study patients were not compared to patients with chronic kidney disease who were not dialyzed. In addition, these results might not apply to all elderly patients on dialysis, as the functional status of elderly nursing home patients might differ significantly from those living at home.
Bottom line: Functional status is not maintained in most elderly nursing home patients in the first 12 months after long-term dialysis is initiated. Elderly patients considering dialysis treatment should be aware that dialysis might not help maintain functional status and quality of life.
Citation: Kurella Tamura MK, Covinsky KE, Chertow GM, Yaffe C, Landefeld CS, McCulloch CE. Functional status of elderly adults before and after initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1539-1547.
Adding Basal Insulin to Oral Agents in Type 2 Diabetes Might Offer Best Glycemic Control
Clinical question: When added to oral diabetic agents, which insulin regimen (biphasic, prandial or basal) best achieves glycemic control in patients with Type 2 diabetes?
Background: Most patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) require insulin when oral agents provide suboptimal glycemic control. Little is known about which insulin regimen is most effective.
Study design: Three-year, open-label, multicenter trial.
Setting: Fifty-eight clinical centers in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
Synopsis: The authors randomized 708 insulin-naïve DM2 patients (median age 62 years) with HgbA1c 7% to 10% on maximum-dose metformin or sulfonylurea to one of three regimens: biphasic insulin twice daily; prandial insulin three times daily; or basal insulin once daily. Outcomes were HgbA1c, hypoglycemia rates, and weight gain. Sulfonylureas were replaced by another insulin if glycemic control was unacceptable.
The patients were mostly Caucasian and overweight. At three years of followup, median HgbA1c was similar in all groups (7.1% biphasic, 6.8% prandial, 6.9% basal); however, more patients who received prandial or basal insulin achieved HgbA1c less than 6.5% (45% and 43%, respectively) than in the biphasic group (32%).
Hypoglycemia was significantly less frequent in the basal insulin group (1.7 per patient per year versus 3.0 and 5.5 with biphasic and prandial, respectively). Patients gained weight in all groups; the greatest gain was with prandial insulin. At three years, there were no significant between-group differences in blood pressure, cholesterol, albuminuria, or quality of life.
Bottom line: Adding insulin to oral diabetic regimens improves glycemic control. Basal or prandial insulin regimens achieve glycemic targets more frequently than biphasic dosing.
Citation: Holman RR, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, et al. Three-year efficacy of complex insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(18):1736-1747.
Advanced Dementia Is a Terminal Illness with High Morbidity and Mortality
Clinical question: Does understanding the expected clinical course of advanced dementia influence end-of-life decisions by proxy decision-makers?
Background: Advanced dementia is a leading cause of death in the United States, but the clinical course of advanced dementia has not been described in a rigorous, prospective manner. The lack of information might cause risk to be underestimated, and patients might receive suboptimal palliative care.
Study design: Multicenter prospective cohort study.
Setting: Twenty-two nursing homes in a single U.S. city.
Synopsis: The survey examined 323 nursing home residents with advanced dementia. The patients were clinically assessed at baseline and quarterly for 18 months through chart reviews, nursing interviews, and physical examinations. Additionally, their proxies were surveyed regarding their understanding of the subjects’ prognoses.
During the survey period, 41.1% of patients developed pneumonia, 52.6% of patients experienced a febrile episode, and 85.8% of patients developed an eating problem; cumulative all-cause mortality was 54.8%. Adjusted for age, sex, and disease duration, the six-month mortality rate for subjects who had pneumonia was 46.7%; a febrile episode, 44.5%; and an eating problem, 38.6%.
Distressing symptoms, including dyspnea (46.0%) and pain (39.1%), were common. In the last three months of life, 40.7% of subjects underwent at least one burdensome intervention (defined as hospitalization, ED visit, parenteral therapy, or tube feeding).
Subjects whose proxies reported an understanding of the poor prognosis and expected clinical complications of advanced dementia underwent significantly fewer burdensome interventions (adjusted odds ratio 0.12).
Bottom line: Advanced dementia is associated with frequent complications, including infections and eating problems, with high six-month mortality and significant associated morbidity. Patients whose healthcare proxies have a good understanding of the expected clinical course and prognosis receive less-aggressive end-of-life care.
Citation: Mitchell SL, Teno JM, Kiely DK, et al. The clinical course of advanced dementia. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1529-1538. TH
Prevent Defense
Three U.S. medical centers have been recognized for innovative approaches to preventing DVT and its potentially fatal complications, which include pulmonary embolism (PE). Central to each of the DVT prevention strategies is a risk assessment tool that is easy to use, built directly into routine care, and linked directly to guideline-recommended choices for prophylaxis.
The University of California at San Diego (UCSD) Medical Center, Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, and the Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center in Washington, D.C., each received the first DVTeamCare Hospital Award. The North American Thrombosis Forum (NATF), in conjunction with pharmaceutical company Eisai Inc., recognized each center’s accomplishment based upon an evaluation by an independent panel of expert judges.

—Gregory A. Maynard, MD, FHM, hospital medicine division chief, University of California at San Diego
The award reflects NATF’s goal of enhancing thrombosis education, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment to improve patient outcomes, says NATF Executive Director Ilene Sussman, PhD. Dr. Sussman notes that DVT affects more than 600,000 Americans annually, kills more than 100,000, and is one of the leading causes of preventable deaths in hospitals. Preventable DVT-related complication is on Medicare’s list of “never events,” for which hospitals will no longer be reimbursed.
UCSD, representing medical centers with more than 200 beds, imbedded its VTE prevention protocol into admission, transfer, and perioperative order sets across all medical and surgical services, says Gregory A. Maynard, MD, FHM, hospital medicine division chief. The protocol flags three levels of DVT risk, notes possible contraindications for a particular kind of patient, and presents a set of options for guideline-recommended prophylaxis. The protocol can be paper- or computer-based. Prompting concurrent intervention is a central component of UCSD’s implementation strategy, “identifying in real-time patients who are not receiving the right DVT prophylaxis and having a front-line nurse or pharmacist intervene appropriately,” Dr. Maynard explains.
The percent of UCSD’s patients on adequate prophylaxis rose to more than 98% in the past two years, up from about 50% before the intervention, while preventable VTE dropped by 85%—about 50 fewer cases per year in a hospital with fewer than 300 beds. “Having DVT prevention protocols such as these in place allows hospitalists to provide better care with less effort by leaving hospitalists free to focus on more complicated patient-care issues,” Dr. Maynard says.
UCSD has partnered with SHM to develop DVT prevention toolkits and mentored collaboratives, with which hospitalists can take the lead on QI projects at their local institutions. SHM’s online VTE Implementation Guide is available at www.hospitalmedicine.org/ResourceRoomRedesign/RR_VTE/VTE_Home.cfm.
Johns Hopkins Hospital, representing medical centers with more than 200 beds, developed a mandatory computer-based decision-support system to facilitate specialty-specific risk-factor assessment and the application of risk-appropriate VTE prophylaxis, says Michael Streiff, MD, FACP, director of Johns Hopkins’ Anticoagulation Management Service and Outpatient Clinic, and a member of its Evidence-Based Practice Center. Before a physician can issue any orders—medications, lab tests, nursing instructions, etc.—using a physician transfer order set, the computerized order-entry system automatically guides them through a concise set of questions about a patient’s DVT risk factors, contraindications for blood thinners, and guideline-recommended prophylaxis choices, Dr. Streiff says.
Since implementing the system, the percent of patients being DVT-risk-stratified within 24 hours of hospital admission rose to more than 90%, and nearly 9 in 10 of the appropriate patients are now receiving risk-appropriate, American College of Chest Physicians-approved DVT prophylaxis, up from about 26% before the intervention, Dr. Streiff notes.
The VA Medical Center in Washington, D.C., representing medical centers with fewer than 200 beds, participated in a mentorship collaborative with UCSD’s Dr. Maynard and designed a seven-step process that walks providers through an evidence-based risk-factor assessment to determine appropriate thromboprophylactic therapy, says Divya Shroff, MD, associate chief of staff, Informatics. The guideline-driven steps are integrated into the VA’s computerized patient medical record system and take no more than 60 seconds to follow, says pharmacy practice resident Jovonne H. Jones, PharmD. The steps include:
- Assess patient DVT risk level;
- Educate patient about the order;
- Identify contraindications, if any;
- Choose prophylaxis drug or device;
- Accept order for drug or device;
- Check if additional prophylactic method is needed; and
- Accept the final order.
After the intervention, the rate at which patients receive appropriate prophylaxis upon admission more than doubled. Twenty VA medical centers around the country are in the process of implementing the system, Jones says.
The award-winning protocols will be presented at an NATF-hosted program April 9 at Harvard Medical School. The protocols and implementation plans will be made available at www.DVTeamCareAward.com to help other hospitals enhance their efforts to prevent DVT. TH
Chris Guadagnino is a freelance medical writer based in Philadelphia.
Three U.S. medical centers have been recognized for innovative approaches to preventing DVT and its potentially fatal complications, which include pulmonary embolism (PE). Central to each of the DVT prevention strategies is a risk assessment tool that is easy to use, built directly into routine care, and linked directly to guideline-recommended choices for prophylaxis.
The University of California at San Diego (UCSD) Medical Center, Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, and the Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center in Washington, D.C., each received the first DVTeamCare Hospital Award. The North American Thrombosis Forum (NATF), in conjunction with pharmaceutical company Eisai Inc., recognized each center’s accomplishment based upon an evaluation by an independent panel of expert judges.

—Gregory A. Maynard, MD, FHM, hospital medicine division chief, University of California at San Diego
The award reflects NATF’s goal of enhancing thrombosis education, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment to improve patient outcomes, says NATF Executive Director Ilene Sussman, PhD. Dr. Sussman notes that DVT affects more than 600,000 Americans annually, kills more than 100,000, and is one of the leading causes of preventable deaths in hospitals. Preventable DVT-related complication is on Medicare’s list of “never events,” for which hospitals will no longer be reimbursed.
UCSD, representing medical centers with more than 200 beds, imbedded its VTE prevention protocol into admission, transfer, and perioperative order sets across all medical and surgical services, says Gregory A. Maynard, MD, FHM, hospital medicine division chief. The protocol flags three levels of DVT risk, notes possible contraindications for a particular kind of patient, and presents a set of options for guideline-recommended prophylaxis. The protocol can be paper- or computer-based. Prompting concurrent intervention is a central component of UCSD’s implementation strategy, “identifying in real-time patients who are not receiving the right DVT prophylaxis and having a front-line nurse or pharmacist intervene appropriately,” Dr. Maynard explains.
The percent of UCSD’s patients on adequate prophylaxis rose to more than 98% in the past two years, up from about 50% before the intervention, while preventable VTE dropped by 85%—about 50 fewer cases per year in a hospital with fewer than 300 beds. “Having DVT prevention protocols such as these in place allows hospitalists to provide better care with less effort by leaving hospitalists free to focus on more complicated patient-care issues,” Dr. Maynard says.
UCSD has partnered with SHM to develop DVT prevention toolkits and mentored collaboratives, with which hospitalists can take the lead on QI projects at their local institutions. SHM’s online VTE Implementation Guide is available at www.hospitalmedicine.org/ResourceRoomRedesign/RR_VTE/VTE_Home.cfm.
Johns Hopkins Hospital, representing medical centers with more than 200 beds, developed a mandatory computer-based decision-support system to facilitate specialty-specific risk-factor assessment and the application of risk-appropriate VTE prophylaxis, says Michael Streiff, MD, FACP, director of Johns Hopkins’ Anticoagulation Management Service and Outpatient Clinic, and a member of its Evidence-Based Practice Center. Before a physician can issue any orders—medications, lab tests, nursing instructions, etc.—using a physician transfer order set, the computerized order-entry system automatically guides them through a concise set of questions about a patient’s DVT risk factors, contraindications for blood thinners, and guideline-recommended prophylaxis choices, Dr. Streiff says.
Since implementing the system, the percent of patients being DVT-risk-stratified within 24 hours of hospital admission rose to more than 90%, and nearly 9 in 10 of the appropriate patients are now receiving risk-appropriate, American College of Chest Physicians-approved DVT prophylaxis, up from about 26% before the intervention, Dr. Streiff notes.
The VA Medical Center in Washington, D.C., representing medical centers with fewer than 200 beds, participated in a mentorship collaborative with UCSD’s Dr. Maynard and designed a seven-step process that walks providers through an evidence-based risk-factor assessment to determine appropriate thromboprophylactic therapy, says Divya Shroff, MD, associate chief of staff, Informatics. The guideline-driven steps are integrated into the VA’s computerized patient medical record system and take no more than 60 seconds to follow, says pharmacy practice resident Jovonne H. Jones, PharmD. The steps include:
- Assess patient DVT risk level;
- Educate patient about the order;
- Identify contraindications, if any;
- Choose prophylaxis drug or device;
- Accept order for drug or device;
- Check if additional prophylactic method is needed; and
- Accept the final order.
After the intervention, the rate at which patients receive appropriate prophylaxis upon admission more than doubled. Twenty VA medical centers around the country are in the process of implementing the system, Jones says.
The award-winning protocols will be presented at an NATF-hosted program April 9 at Harvard Medical School. The protocols and implementation plans will be made available at www.DVTeamCareAward.com to help other hospitals enhance their efforts to prevent DVT. TH
Chris Guadagnino is a freelance medical writer based in Philadelphia.
Three U.S. medical centers have been recognized for innovative approaches to preventing DVT and its potentially fatal complications, which include pulmonary embolism (PE). Central to each of the DVT prevention strategies is a risk assessment tool that is easy to use, built directly into routine care, and linked directly to guideline-recommended choices for prophylaxis.
The University of California at San Diego (UCSD) Medical Center, Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, and the Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center in Washington, D.C., each received the first DVTeamCare Hospital Award. The North American Thrombosis Forum (NATF), in conjunction with pharmaceutical company Eisai Inc., recognized each center’s accomplishment based upon an evaluation by an independent panel of expert judges.

—Gregory A. Maynard, MD, FHM, hospital medicine division chief, University of California at San Diego
The award reflects NATF’s goal of enhancing thrombosis education, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment to improve patient outcomes, says NATF Executive Director Ilene Sussman, PhD. Dr. Sussman notes that DVT affects more than 600,000 Americans annually, kills more than 100,000, and is one of the leading causes of preventable deaths in hospitals. Preventable DVT-related complication is on Medicare’s list of “never events,” for which hospitals will no longer be reimbursed.
UCSD, representing medical centers with more than 200 beds, imbedded its VTE prevention protocol into admission, transfer, and perioperative order sets across all medical and surgical services, says Gregory A. Maynard, MD, FHM, hospital medicine division chief. The protocol flags three levels of DVT risk, notes possible contraindications for a particular kind of patient, and presents a set of options for guideline-recommended prophylaxis. The protocol can be paper- or computer-based. Prompting concurrent intervention is a central component of UCSD’s implementation strategy, “identifying in real-time patients who are not receiving the right DVT prophylaxis and having a front-line nurse or pharmacist intervene appropriately,” Dr. Maynard explains.
The percent of UCSD’s patients on adequate prophylaxis rose to more than 98% in the past two years, up from about 50% before the intervention, while preventable VTE dropped by 85%—about 50 fewer cases per year in a hospital with fewer than 300 beds. “Having DVT prevention protocols such as these in place allows hospitalists to provide better care with less effort by leaving hospitalists free to focus on more complicated patient-care issues,” Dr. Maynard says.
UCSD has partnered with SHM to develop DVT prevention toolkits and mentored collaboratives, with which hospitalists can take the lead on QI projects at their local institutions. SHM’s online VTE Implementation Guide is available at www.hospitalmedicine.org/ResourceRoomRedesign/RR_VTE/VTE_Home.cfm.
Johns Hopkins Hospital, representing medical centers with more than 200 beds, developed a mandatory computer-based decision-support system to facilitate specialty-specific risk-factor assessment and the application of risk-appropriate VTE prophylaxis, says Michael Streiff, MD, FACP, director of Johns Hopkins’ Anticoagulation Management Service and Outpatient Clinic, and a member of its Evidence-Based Practice Center. Before a physician can issue any orders—medications, lab tests, nursing instructions, etc.—using a physician transfer order set, the computerized order-entry system automatically guides them through a concise set of questions about a patient’s DVT risk factors, contraindications for blood thinners, and guideline-recommended prophylaxis choices, Dr. Streiff says.
Since implementing the system, the percent of patients being DVT-risk-stratified within 24 hours of hospital admission rose to more than 90%, and nearly 9 in 10 of the appropriate patients are now receiving risk-appropriate, American College of Chest Physicians-approved DVT prophylaxis, up from about 26% before the intervention, Dr. Streiff notes.
The VA Medical Center in Washington, D.C., representing medical centers with fewer than 200 beds, participated in a mentorship collaborative with UCSD’s Dr. Maynard and designed a seven-step process that walks providers through an evidence-based risk-factor assessment to determine appropriate thromboprophylactic therapy, says Divya Shroff, MD, associate chief of staff, Informatics. The guideline-driven steps are integrated into the VA’s computerized patient medical record system and take no more than 60 seconds to follow, says pharmacy practice resident Jovonne H. Jones, PharmD. The steps include:
- Assess patient DVT risk level;
- Educate patient about the order;
- Identify contraindications, if any;
- Choose prophylaxis drug or device;
- Accept order for drug or device;
- Check if additional prophylactic method is needed; and
- Accept the final order.
After the intervention, the rate at which patients receive appropriate prophylaxis upon admission more than doubled. Twenty VA medical centers around the country are in the process of implementing the system, Jones says.
The award-winning protocols will be presented at an NATF-hosted program April 9 at Harvard Medical School. The protocols and implementation plans will be made available at www.DVTeamCareAward.com to help other hospitals enhance their efforts to prevent DVT. TH
Chris Guadagnino is a freelance medical writer based in Philadelphia.
Transitions of Care Integral to HM Patient Care
Transitions of Care Integral to HM Patient Care
I just finished my internal-medicine training and started a job as a hospitalist. We are a new hospitalist group, and I have been told that “transitions of care” is important to HM groups. I understand that getting information back to the patients’ primary-care physicians (PCPs) is important, but I am worried that I don’t have the whole picture. Is there something I am missing?
E. Parkhurst, MD
Tampa, Fla.
Dr. Hospitalist responds: Congrats on your new job. I am pleased to hear that you are motivated to learn more about transitions of care. It is important to hospitalist groups, but even more important to patients. I suspect your instincts are correct. You have an idea of what is meant by “transitions of care,” but probably do not appreciate all the nuances of the term. I certainly did not when I came out of training many years ago.
Transitions of care is a critical aspect of every patient’s care, and thus should be important to every healthcare provider. Our job is to care for the hospitalized patient and help them navigate through the complex systems of the hospital. How well we guide the patients through these transitions is reflected in their outcomes.
What is the definition of “transitions of care”? I find it useful to think about the patient’s journey when the decision is made to hospitalize the patient. When the patient is hospitalized, it is easy to recognize that the patient’s physical location is different; some, if not all, of the patient’s providers are different, too. The patient might have the same PCP caring for them in the hospital, but the nurses are different. The contrast is more evident if all of the patient’s providers are different. The ED is the point of entry for most patients. This is another location with another group of providers who do not have knowledge of all of the patient’s medical issues.
The hospital discharge is another inevitable transition. Most patients go home, but some will go to another healthcare facility (e.g., rehabilitation hospital) with another group of providers.
As you can see, the admission and discharge from the hospital involves multiple transitions. But multiple transitions also occur within the hospital. The patient could move from the general medical ward to the ICU and back; the patient might spend time in the surgical suite or operating room. Many patients go to radiology or other parts of the hospital for testing or procedures. At each location, the patient has a new group of providers.
But even if a physical location does not change, there could be a transition in care. During the day, one hospitalist or nurse might care for the patient. At night, another group of doctors and nurses are responsible for the patient’s care. Information must be transmitted and received between all of the parties at each transition in order for the appropriate care to proceed.
Effective transitions can improve provider efficiency. Think about how much easier it is to care for a patient whose care you assume when you have a clear understanding of the patient’s issues. Minimizing medical errors and increasing effective communication can reduce medical and legal risks. Effective transitions also minimize the length of hospital stay for the patient and minimize the risk of unnecessary readmission to the hospital. These can result in enhanced financial outcomes.
I think the key to effective and safe transitions of care is to create a mutually-agreed-upon process of communication and a level of expectation from all providers to carry out their role in the process. This is always easier said than done. In fact, the lack of an agreed-upon process often is a common barrier to effective transitions of care. Each participant’s role in the patient’s transitions might compete with another set of agendas.
As you can see, transitions of care is a complex topic, and I have only briefly reviewed it here. For more information, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/boost. TH
Image Source: AMANE KANEKO
Transitions of Care Integral to HM Patient Care
I just finished my internal-medicine training and started a job as a hospitalist. We are a new hospitalist group, and I have been told that “transitions of care” is important to HM groups. I understand that getting information back to the patients’ primary-care physicians (PCPs) is important, but I am worried that I don’t have the whole picture. Is there something I am missing?
E. Parkhurst, MD
Tampa, Fla.
Dr. Hospitalist responds: Congrats on your new job. I am pleased to hear that you are motivated to learn more about transitions of care. It is important to hospitalist groups, but even more important to patients. I suspect your instincts are correct. You have an idea of what is meant by “transitions of care,” but probably do not appreciate all the nuances of the term. I certainly did not when I came out of training many years ago.
Transitions of care is a critical aspect of every patient’s care, and thus should be important to every healthcare provider. Our job is to care for the hospitalized patient and help them navigate through the complex systems of the hospital. How well we guide the patients through these transitions is reflected in their outcomes.
What is the definition of “transitions of care”? I find it useful to think about the patient’s journey when the decision is made to hospitalize the patient. When the patient is hospitalized, it is easy to recognize that the patient’s physical location is different; some, if not all, of the patient’s providers are different, too. The patient might have the same PCP caring for them in the hospital, but the nurses are different. The contrast is more evident if all of the patient’s providers are different. The ED is the point of entry for most patients. This is another location with another group of providers who do not have knowledge of all of the patient’s medical issues.
The hospital discharge is another inevitable transition. Most patients go home, but some will go to another healthcare facility (e.g., rehabilitation hospital) with another group of providers.
As you can see, the admission and discharge from the hospital involves multiple transitions. But multiple transitions also occur within the hospital. The patient could move from the general medical ward to the ICU and back; the patient might spend time in the surgical suite or operating room. Many patients go to radiology or other parts of the hospital for testing or procedures. At each location, the patient has a new group of providers.
But even if a physical location does not change, there could be a transition in care. During the day, one hospitalist or nurse might care for the patient. At night, another group of doctors and nurses are responsible for the patient’s care. Information must be transmitted and received between all of the parties at each transition in order for the appropriate care to proceed.
Effective transitions can improve provider efficiency. Think about how much easier it is to care for a patient whose care you assume when you have a clear understanding of the patient’s issues. Minimizing medical errors and increasing effective communication can reduce medical and legal risks. Effective transitions also minimize the length of hospital stay for the patient and minimize the risk of unnecessary readmission to the hospital. These can result in enhanced financial outcomes.
I think the key to effective and safe transitions of care is to create a mutually-agreed-upon process of communication and a level of expectation from all providers to carry out their role in the process. This is always easier said than done. In fact, the lack of an agreed-upon process often is a common barrier to effective transitions of care. Each participant’s role in the patient’s transitions might compete with another set of agendas.
As you can see, transitions of care is a complex topic, and I have only briefly reviewed it here. For more information, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/boost. TH
Image Source: AMANE KANEKO
Transitions of Care Integral to HM Patient Care
I just finished my internal-medicine training and started a job as a hospitalist. We are a new hospitalist group, and I have been told that “transitions of care” is important to HM groups. I understand that getting information back to the patients’ primary-care physicians (PCPs) is important, but I am worried that I don’t have the whole picture. Is there something I am missing?
E. Parkhurst, MD
Tampa, Fla.
Dr. Hospitalist responds: Congrats on your new job. I am pleased to hear that you are motivated to learn more about transitions of care. It is important to hospitalist groups, but even more important to patients. I suspect your instincts are correct. You have an idea of what is meant by “transitions of care,” but probably do not appreciate all the nuances of the term. I certainly did not when I came out of training many years ago.
Transitions of care is a critical aspect of every patient’s care, and thus should be important to every healthcare provider. Our job is to care for the hospitalized patient and help them navigate through the complex systems of the hospital. How well we guide the patients through these transitions is reflected in their outcomes.
What is the definition of “transitions of care”? I find it useful to think about the patient’s journey when the decision is made to hospitalize the patient. When the patient is hospitalized, it is easy to recognize that the patient’s physical location is different; some, if not all, of the patient’s providers are different, too. The patient might have the same PCP caring for them in the hospital, but the nurses are different. The contrast is more evident if all of the patient’s providers are different. The ED is the point of entry for most patients. This is another location with another group of providers who do not have knowledge of all of the patient’s medical issues.
The hospital discharge is another inevitable transition. Most patients go home, but some will go to another healthcare facility (e.g., rehabilitation hospital) with another group of providers.
As you can see, the admission and discharge from the hospital involves multiple transitions. But multiple transitions also occur within the hospital. The patient could move from the general medical ward to the ICU and back; the patient might spend time in the surgical suite or operating room. Many patients go to radiology or other parts of the hospital for testing or procedures. At each location, the patient has a new group of providers.
But even if a physical location does not change, there could be a transition in care. During the day, one hospitalist or nurse might care for the patient. At night, another group of doctors and nurses are responsible for the patient’s care. Information must be transmitted and received between all of the parties at each transition in order for the appropriate care to proceed.
Effective transitions can improve provider efficiency. Think about how much easier it is to care for a patient whose care you assume when you have a clear understanding of the patient’s issues. Minimizing medical errors and increasing effective communication can reduce medical and legal risks. Effective transitions also minimize the length of hospital stay for the patient and minimize the risk of unnecessary readmission to the hospital. These can result in enhanced financial outcomes.
I think the key to effective and safe transitions of care is to create a mutually-agreed-upon process of communication and a level of expectation from all providers to carry out their role in the process. This is always easier said than done. In fact, the lack of an agreed-upon process often is a common barrier to effective transitions of care. Each participant’s role in the patient’s transitions might compete with another set of agendas.
As you can see, transitions of care is a complex topic, and I have only briefly reviewed it here. For more information, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/boost. TH
Image Source: AMANE KANEKO
ONLINE EXCLUSIVE: Audio interview with HM10 Course Director
Effective Communication Ensures Patient Safety
Effective Communication Ensures Patient Safety
Can you explain to me what is meant by SBAR? I heard this acronym mentioned during a session at HM09, but I did not understand the term.
S. East, MD
Pullman, Wash.
Dr. Hospitalist responds: SBAR (pronounced “ess-bar”) is a standardized method of communication that originated in the Navy’s nuclear submarine program. It stands for:
- Situation: What is happening presently?
- Background: What circumstances led to this situation?
- Assessment: What do I think is the problem?
- Recommendation: What should we do to correct the problem?
The SBAR system was developed to prevent simple communication errors that could lead to global disaster.
Kaiser Permanente of Colorado was among the first to adopt this model of communication among its staff and has since popularized its use in healthcare. Numerous hospitals and healthcare organizations have implemented SBAR as an approach to minimize communication errors between healthcare providers. The idea is that eliminating communication errors between healthcare providers improves patient safety. SBAR encourages all providers (doctors, nurses, pharmacists, etc.) to communicate with a shared mental model for information transfer.
SBAR requires providers to organize their thoughts, understand what it is they want to convey, and make requests in an organized fashion. Adherence to SBAR allows providers to transmit factual information in a concise manner.
Highly effective communication is essential to any hospitalist program. The SBAR approach should not be limited to nurse-doctor communication. I encourage you to implement this tool at your institution.
For more information, an SBAR toolkit is available at www.azhha.org/patient_safety/sbar.aspx. TH
Effective Communication Ensures Patient Safety
Can you explain to me what is meant by SBAR? I heard this acronym mentioned during a session at HM09, but I did not understand the term.
S. East, MD
Pullman, Wash.
Dr. Hospitalist responds: SBAR (pronounced “ess-bar”) is a standardized method of communication that originated in the Navy’s nuclear submarine program. It stands for:
- Situation: What is happening presently?
- Background: What circumstances led to this situation?
- Assessment: What do I think is the problem?
- Recommendation: What should we do to correct the problem?
The SBAR system was developed to prevent simple communication errors that could lead to global disaster.
Kaiser Permanente of Colorado was among the first to adopt this model of communication among its staff and has since popularized its use in healthcare. Numerous hospitals and healthcare organizations have implemented SBAR as an approach to minimize communication errors between healthcare providers. The idea is that eliminating communication errors between healthcare providers improves patient safety. SBAR encourages all providers (doctors, nurses, pharmacists, etc.) to communicate with a shared mental model for information transfer.
SBAR requires providers to organize their thoughts, understand what it is they want to convey, and make requests in an organized fashion. Adherence to SBAR allows providers to transmit factual information in a concise manner.
Highly effective communication is essential to any hospitalist program. The SBAR approach should not be limited to nurse-doctor communication. I encourage you to implement this tool at your institution.
For more information, an SBAR toolkit is available at www.azhha.org/patient_safety/sbar.aspx. TH
Effective Communication Ensures Patient Safety
Can you explain to me what is meant by SBAR? I heard this acronym mentioned during a session at HM09, but I did not understand the term.
S. East, MD
Pullman, Wash.
Dr. Hospitalist responds: SBAR (pronounced “ess-bar”) is a standardized method of communication that originated in the Navy’s nuclear submarine program. It stands for:
- Situation: What is happening presently?
- Background: What circumstances led to this situation?
- Assessment: What do I think is the problem?
- Recommendation: What should we do to correct the problem?
The SBAR system was developed to prevent simple communication errors that could lead to global disaster.
Kaiser Permanente of Colorado was among the first to adopt this model of communication among its staff and has since popularized its use in healthcare. Numerous hospitals and healthcare organizations have implemented SBAR as an approach to minimize communication errors between healthcare providers. The idea is that eliminating communication errors between healthcare providers improves patient safety. SBAR encourages all providers (doctors, nurses, pharmacists, etc.) to communicate with a shared mental model for information transfer.
SBAR requires providers to organize their thoughts, understand what it is they want to convey, and make requests in an organized fashion. Adherence to SBAR allows providers to transmit factual information in a concise manner.
Highly effective communication is essential to any hospitalist program. The SBAR approach should not be limited to nurse-doctor communication. I encourage you to implement this tool at your institution.
For more information, an SBAR toolkit is available at www.azhha.org/patient_safety/sbar.aspx. TH
Growth Spurt
Despite intravenous medication, a young boy in status epilepticus had the pediatric ICU team at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison stumped. The team called for a consult with the Integrative Medicine Program, which works with licensed acupuncturists and has been affiliated with the department of family medicine since 2001. Acupuncture’s efficacy in this setting has not been validated, but it has been shown to ease chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, as well as radiation-induced xerostomia.1,2
Following several treatments by a licensed acupuncturist and continued conventional care, the boy’s seizures subsided and he was transitioned to the medical floor. Did the acupuncture contribute to bringing the seizures under control? “I can’t say that it was the acupuncture—it was probably a function of all the therapies working together,” says David P. Rakel, MD, assistant professor and director of UW’s Integrative Medicine Program.
The UW case illustrates both current trends and the constant conundrum that surrounds hospital-based complementary medicine: Complementary and alternative medicine’s use is increasing in some U.S. hospitals, yet the existing research evidence for the efficacy of its multiple modalities is decidedly mixed.
Even if your hospital does not offer complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), your patients are using CAM at ever-increasing rates. In 1993, 34% of Americans reported using some type of CAM (e.g., supplements, massage therapy, prayer, and so on). That number has almost doubled to 62%.3 Americans spend $47 billion a year—of their own money—for CAM therapies, chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists. And older patients with chronic conditions—the kind of patient hospitalists are most familiar with—tend to try CAM more than younger patients.4
These trends can directly affect hospitalists’ treatment decisions, but they also play a part in how you establish communication and trust with your patients, and how you keep your patients safe from adverse drug interactions. According to the National Academy of Sciences, in order to effectively counsel patients and ensure high-quality comprehensive care, conventional professionals need more CAM-related education.5

—Suzanne Bertisch, MD, MPH, fellow, Harvard Medical School’s Osher Research Center
What Trends Show
In 2007, according to the American Hospital Association, 20.8% of community hospitals offered some type of care or treatment not based on traditional Western allopathic medicine. That’s up from 8.6% of reporting hospitals that offered those services in 1998.
The 1990s saw rapid growth of integrative medicine centers at major research institutions, and the majority of U.S. cancer centers now offer some form of complementary therapy, says Barrie R. Cassileth, MS, PhD, the Laurance S. Rockefeller Chair in Integrative Medicine and chief of the Integrative Medicine Service at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
The 2007 Health Forum/AHA Complementary and Alternative Medicine Survey of Hospitals reported that complementary programs are more common in urban rather than rural hospitals; services vary by hospital size (see Figure 2, above); and the top six modalities offered on an inpatient basis are pet therapy, massage therapy, music/art therapy, guided imagery, acupuncture, and reiki (see “Glossary of Complementary Terms,” above). Eighty-four percent of hospitals offer complementary services due to patient demand, the survey showed.
Joseph Ming-Wah Li, MD, FHM, SHM board member and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the hospital medicine program and associate chief of the division of general medicine and primary care at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, doesn’t see a problem with modalities that can make his patients feel better. Patients at his hospital have access to pet therapy, massage, and acupuncture. “I don’t think these modalities hurt our patients, and there is very little downside, except for potential cost,” says Dr. Li, an SHM board member. “What’s not clear is whether these therapies work or not.”
What’s in a Name?
Numerous therapies and modalities crowd under the CAM umbrella, but most experts classify “complementary” modalities as those used in conjunction with conventional medicine to mitigate symptoms of disease or treatment, whereas “alternative” connotes therapies claiming to treat or cure the underlying disease. Some harmful, dangerous, and dishonest practices fall into the “alternative” category, such as Hulda Clark’s “Zapper” device, which was promoted as a cure for liver flukes, something she says cause everything from diabetes to heart disease. (For more on questionable practices, visit www.quackwatch.com or the National Council Against Health Fraud’s Web site at www.ncahf.org.)
The National Institutes of Health’s National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) defines CAM as a group of “diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not presently considered to be part of conventional medicine.” Dr. Cassileth says the conflation of “complementary and alternative” into one neat acronym—CAM—causes confusion among patients and medical professionals. NCCAM will be changing its name soon, she says, to the National Center for Integrative Medicine, emphasizing the use of adjunctive modalities along with conventional medical treatments.
Hospitalist Suzanne Bertisch, MD, MPH, recently completed a research fellowship at Harvard Medical School’s Osher Research Center. She explains that integrative medicine uses a macro model of health, claiming a middle ground between the traditional, allopathic model of treating disease.
All Kinds of Evidence
Twenty years of complementary medicine research has yielded some information about safety—namely, what works and what doesn’t. For example, saw palmetto has not panned out as an effective treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia; St. John’s wort, useful for mild depression, interferes with many medications, including cyclosporine and warfarin, and should be avoided at least five days prior to surgery.7,8
Since NCCAM’s inception in October 1998, its research portfolio has stirred debate in the scientific community. Part of the disagreement stems from the difficulty of fitting multidimensional interventions, some of which are provider-dependent (e.g., massage or acupuncture), into the gold standard of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, explains Darshan Mehta, MD, MPH, associate director of medical education at the Benson-Henry Institute for Mind Body Medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The manner in which the effectiveness of integrative techniques is assessed requires a higher sophistication of systems research, Dr. Mehta says.
“The way we construe evidence needs to change,” she adds.
Likely to Expand
Most private health plans do not cover complementary services, although Medicare and numerous insurance plans will reimburse treatment in conjunction with physical therapy (e.g., massage) in the outpatient setting. Twenty-three states cover chiropractic care under Medicaid, and Medicare has begun to assess the cost-effectiveness of including acupuncture—especially for postoperative and chemotherapy-associated nausea and vomiting—in its benefits package.9 Other modalities, ranging from aromatherapy to guided imagery training, are paid for largely out-of-pocket.10
Dr. Rakel notes that the delivery of integrative medicine services at UW entails conversations with patients about out-of-pocket payments. “It can pose a barrier to the clinician-patient relationship if you give them acupuncture to help with their chemotherapy-induced nausea and then ask for their credit card,” he says.
Hospitalist Preparation
Most complementary therapies are currently offered on an outpatient basis. Because of this trend, and because they deal with acute conditions, hospitalists are less likely to be involved with complementary or integrative medicine services, says Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center hospitalist Andrew C. Ahn, MD, MPH. But that’s not to say complementary medicine is something hospitalists should ignore; patients arrive at the hospital with CAM regimens in tow. It’s the No. 1 reason, Dr. Ahn says, hospitalists should be knowledgeable and exposed to CAM therapies.
Physicians must understand patient patterns and preferences regarding allopathic and complementary medicine, says Sita Ananth, MHA, director of knowledge services and optimal healing environments at the Samueli Institute in Alexandria, Va., and author of the 2007 AHA report. She points to a 2006 survey conducted by AARP and NCCAM that found almost 70% of respondents did not tell their physicians about their complementary medicine approaches. These patients are within the age range most likely to be cared for by hospitalists, and failure to communicate about complementary treatment, such as supplemental vitamin use, could lead to safety issues. Moreover, without complete disclosure, the patient-physician relationship might not be as open as possible, Dr. Ananth says.
Many acute-care hospitalists do not have formal dietary supplement policies, and less than half of U.S. children’s hospitals require documentation of a check for drug or dietary supplement interaction.11,12 As a safety issue, it is always incumbent on hospitalists, says Dr. Li, to ask about any supplements or therapies patients are trying on their own as part of the history and physical examination. The policy at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Dr. Cassileth says, is that patients on chemotherapy or who are undergoing radiation or facing surgery must avoid herbal dietary supplements.
Beyond Safety
Dr. Bertisch advises hospitalists to pose questions about complementary therapies in an open manner, avoiding antagonistic discussions. “Even when I disagree, I try to guide them to issues about safety and nonsafety, and coax in my concerns,” she says. “The most challenging part about complementary medicine is that patients’ beliefs in these therapies may be so strong that even if the doctor says it won’t work, that will not necessarily change that belief.” A 2001 study in the Archives of Internal Medicine revealed that 70% of respondents would continue to take supplements even if a major study or their physician told them they didn’t work.13
The attraction to complementary medicine often reflects patients’ preferences for a holistic approach to health, says Dr. Ahn, or it may emanate from traditions carried with them from their country of origin. “Once you do understand their reasons for using CAM, then the patient-physician relationship can be significantly strengthened,” he says. With nearly two-thirds of Americans using some form of CAM, hospitalists need to engage in this dialogue.
Dr. Rakel agrees understanding patient culture is vital to uncovering useful information. “Most clinicians would agree that if we can match a therapy to the patient culture and belief system, we are more likely to get buy-in from the patient,” he says.
Dr. Mehta also is a clinical instructor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. He teaches his residents to educate themselves about credentialing, certification, and licensure of complementary providers. He also asks them to maintain an open mind. He says the most important preparation for hospitalists right now is to help educate their patients to be more proactive in their own healthcare. “An engaged patient,” he says, “is better than a disengaged patient.” TH
Gretchen Henkel is a freelance writer based in California.
References
- Deng G, Cassileth BR, Yeung KS. Complementary therapies for cancer-related symptoms. J Support Oncol. 2004;2(5):419-426.
- Kahn ST, Johnstone PA. Management of xerostomia related to radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Oncology. 2005;19(14):1827-1832.
- Barnes PM, Powell-Griner E, McFann K, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults: United States, 2002. Adv Data. 2004;27(343):1-19.
- Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA. 1998;280(18):1569-1575.
- Committee on the Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine by the American Public. Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the United States. Washington, D.C: National Academies Press; 2005.
- Ananth S. 2007 Health Forum/AHA Complementary and Alternative Medicine Survey of Hospitals. Health Forum LLC. 2008.
- Bent S, Kane C, Shinohara K, et al. Saw palmetto for benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(6):557-566.
- Bauer BA. The herbal hospitalist. The Hospitalist. 2006;10(2);16-17.
- Ananth S. Applying integrative healthcare. Explore. 2009;5(2):119-120.
- Eisenberg DM, Kessler RC, Foster C, Norlock FE, Calkins DR, Delbanco TL. Unconventional medicine in the United States. Prevalence, costs, and patterns of use. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:246-52
- Bassie KL, Witmer DR, Pinto B, Bush C, Clark J, Deffenbaugh J Jr. National survey of dietary supplement policies in acute care facilities. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(1):65-70.
- Gardiner P, Phillips RS, Kemper KJ, Legedza A, Henlon S, Woolf AD. Dietary supplements: inpatient policies in US children’s hospitals. Pediatrics. 2008;121(4):e775-781.
- Blendon RJ, DesRoches CM, Benson JM, Brodie M, Altman DE. Americans’ views on the use and regulation of dietary supplements. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(6):805-810.
Top Image Source: TETRA IMAGES
Despite intravenous medication, a young boy in status epilepticus had the pediatric ICU team at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison stumped. The team called for a consult with the Integrative Medicine Program, which works with licensed acupuncturists and has been affiliated with the department of family medicine since 2001. Acupuncture’s efficacy in this setting has not been validated, but it has been shown to ease chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, as well as radiation-induced xerostomia.1,2
Following several treatments by a licensed acupuncturist and continued conventional care, the boy’s seizures subsided and he was transitioned to the medical floor. Did the acupuncture contribute to bringing the seizures under control? “I can’t say that it was the acupuncture—it was probably a function of all the therapies working together,” says David P. Rakel, MD, assistant professor and director of UW’s Integrative Medicine Program.
The UW case illustrates both current trends and the constant conundrum that surrounds hospital-based complementary medicine: Complementary and alternative medicine’s use is increasing in some U.S. hospitals, yet the existing research evidence for the efficacy of its multiple modalities is decidedly mixed.
Even if your hospital does not offer complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), your patients are using CAM at ever-increasing rates. In 1993, 34% of Americans reported using some type of CAM (e.g., supplements, massage therapy, prayer, and so on). That number has almost doubled to 62%.3 Americans spend $47 billion a year—of their own money—for CAM therapies, chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists. And older patients with chronic conditions—the kind of patient hospitalists are most familiar with—tend to try CAM more than younger patients.4
These trends can directly affect hospitalists’ treatment decisions, but they also play a part in how you establish communication and trust with your patients, and how you keep your patients safe from adverse drug interactions. According to the National Academy of Sciences, in order to effectively counsel patients and ensure high-quality comprehensive care, conventional professionals need more CAM-related education.5

—Suzanne Bertisch, MD, MPH, fellow, Harvard Medical School’s Osher Research Center
What Trends Show
In 2007, according to the American Hospital Association, 20.8% of community hospitals offered some type of care or treatment not based on traditional Western allopathic medicine. That’s up from 8.6% of reporting hospitals that offered those services in 1998.
The 1990s saw rapid growth of integrative medicine centers at major research institutions, and the majority of U.S. cancer centers now offer some form of complementary therapy, says Barrie R. Cassileth, MS, PhD, the Laurance S. Rockefeller Chair in Integrative Medicine and chief of the Integrative Medicine Service at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
The 2007 Health Forum/AHA Complementary and Alternative Medicine Survey of Hospitals reported that complementary programs are more common in urban rather than rural hospitals; services vary by hospital size (see Figure 2, above); and the top six modalities offered on an inpatient basis are pet therapy, massage therapy, music/art therapy, guided imagery, acupuncture, and reiki (see “Glossary of Complementary Terms,” above). Eighty-four percent of hospitals offer complementary services due to patient demand, the survey showed.
Joseph Ming-Wah Li, MD, FHM, SHM board member and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the hospital medicine program and associate chief of the division of general medicine and primary care at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, doesn’t see a problem with modalities that can make his patients feel better. Patients at his hospital have access to pet therapy, massage, and acupuncture. “I don’t think these modalities hurt our patients, and there is very little downside, except for potential cost,” says Dr. Li, an SHM board member. “What’s not clear is whether these therapies work or not.”
What’s in a Name?
Numerous therapies and modalities crowd under the CAM umbrella, but most experts classify “complementary” modalities as those used in conjunction with conventional medicine to mitigate symptoms of disease or treatment, whereas “alternative” connotes therapies claiming to treat or cure the underlying disease. Some harmful, dangerous, and dishonest practices fall into the “alternative” category, such as Hulda Clark’s “Zapper” device, which was promoted as a cure for liver flukes, something she says cause everything from diabetes to heart disease. (For more on questionable practices, visit www.quackwatch.com or the National Council Against Health Fraud’s Web site at www.ncahf.org.)
The National Institutes of Health’s National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) defines CAM as a group of “diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not presently considered to be part of conventional medicine.” Dr. Cassileth says the conflation of “complementary and alternative” into one neat acronym—CAM—causes confusion among patients and medical professionals. NCCAM will be changing its name soon, she says, to the National Center for Integrative Medicine, emphasizing the use of adjunctive modalities along with conventional medical treatments.
Hospitalist Suzanne Bertisch, MD, MPH, recently completed a research fellowship at Harvard Medical School’s Osher Research Center. She explains that integrative medicine uses a macro model of health, claiming a middle ground between the traditional, allopathic model of treating disease.
All Kinds of Evidence
Twenty years of complementary medicine research has yielded some information about safety—namely, what works and what doesn’t. For example, saw palmetto has not panned out as an effective treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia; St. John’s wort, useful for mild depression, interferes with many medications, including cyclosporine and warfarin, and should be avoided at least five days prior to surgery.7,8
Since NCCAM’s inception in October 1998, its research portfolio has stirred debate in the scientific community. Part of the disagreement stems from the difficulty of fitting multidimensional interventions, some of which are provider-dependent (e.g., massage or acupuncture), into the gold standard of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, explains Darshan Mehta, MD, MPH, associate director of medical education at the Benson-Henry Institute for Mind Body Medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The manner in which the effectiveness of integrative techniques is assessed requires a higher sophistication of systems research, Dr. Mehta says.
“The way we construe evidence needs to change,” she adds.
Likely to Expand
Most private health plans do not cover complementary services, although Medicare and numerous insurance plans will reimburse treatment in conjunction with physical therapy (e.g., massage) in the outpatient setting. Twenty-three states cover chiropractic care under Medicaid, and Medicare has begun to assess the cost-effectiveness of including acupuncture—especially for postoperative and chemotherapy-associated nausea and vomiting—in its benefits package.9 Other modalities, ranging from aromatherapy to guided imagery training, are paid for largely out-of-pocket.10
Dr. Rakel notes that the delivery of integrative medicine services at UW entails conversations with patients about out-of-pocket payments. “It can pose a barrier to the clinician-patient relationship if you give them acupuncture to help with their chemotherapy-induced nausea and then ask for their credit card,” he says.
Hospitalist Preparation
Most complementary therapies are currently offered on an outpatient basis. Because of this trend, and because they deal with acute conditions, hospitalists are less likely to be involved with complementary or integrative medicine services, says Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center hospitalist Andrew C. Ahn, MD, MPH. But that’s not to say complementary medicine is something hospitalists should ignore; patients arrive at the hospital with CAM regimens in tow. It’s the No. 1 reason, Dr. Ahn says, hospitalists should be knowledgeable and exposed to CAM therapies.
Physicians must understand patient patterns and preferences regarding allopathic and complementary medicine, says Sita Ananth, MHA, director of knowledge services and optimal healing environments at the Samueli Institute in Alexandria, Va., and author of the 2007 AHA report. She points to a 2006 survey conducted by AARP and NCCAM that found almost 70% of respondents did not tell their physicians about their complementary medicine approaches. These patients are within the age range most likely to be cared for by hospitalists, and failure to communicate about complementary treatment, such as supplemental vitamin use, could lead to safety issues. Moreover, without complete disclosure, the patient-physician relationship might not be as open as possible, Dr. Ananth says.
Many acute-care hospitalists do not have formal dietary supplement policies, and less than half of U.S. children’s hospitals require documentation of a check for drug or dietary supplement interaction.11,12 As a safety issue, it is always incumbent on hospitalists, says Dr. Li, to ask about any supplements or therapies patients are trying on their own as part of the history and physical examination. The policy at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Dr. Cassileth says, is that patients on chemotherapy or who are undergoing radiation or facing surgery must avoid herbal dietary supplements.
Beyond Safety
Dr. Bertisch advises hospitalists to pose questions about complementary therapies in an open manner, avoiding antagonistic discussions. “Even when I disagree, I try to guide them to issues about safety and nonsafety, and coax in my concerns,” she says. “The most challenging part about complementary medicine is that patients’ beliefs in these therapies may be so strong that even if the doctor says it won’t work, that will not necessarily change that belief.” A 2001 study in the Archives of Internal Medicine revealed that 70% of respondents would continue to take supplements even if a major study or their physician told them they didn’t work.13
The attraction to complementary medicine often reflects patients’ preferences for a holistic approach to health, says Dr. Ahn, or it may emanate from traditions carried with them from their country of origin. “Once you do understand their reasons for using CAM, then the patient-physician relationship can be significantly strengthened,” he says. With nearly two-thirds of Americans using some form of CAM, hospitalists need to engage in this dialogue.
Dr. Rakel agrees understanding patient culture is vital to uncovering useful information. “Most clinicians would agree that if we can match a therapy to the patient culture and belief system, we are more likely to get buy-in from the patient,” he says.
Dr. Mehta also is a clinical instructor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. He teaches his residents to educate themselves about credentialing, certification, and licensure of complementary providers. He also asks them to maintain an open mind. He says the most important preparation for hospitalists right now is to help educate their patients to be more proactive in their own healthcare. “An engaged patient,” he says, “is better than a disengaged patient.” TH
Gretchen Henkel is a freelance writer based in California.
References
- Deng G, Cassileth BR, Yeung KS. Complementary therapies for cancer-related symptoms. J Support Oncol. 2004;2(5):419-426.
- Kahn ST, Johnstone PA. Management of xerostomia related to radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Oncology. 2005;19(14):1827-1832.
- Barnes PM, Powell-Griner E, McFann K, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults: United States, 2002. Adv Data. 2004;27(343):1-19.
- Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA. 1998;280(18):1569-1575.
- Committee on the Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine by the American Public. Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the United States. Washington, D.C: National Academies Press; 2005.
- Ananth S. 2007 Health Forum/AHA Complementary and Alternative Medicine Survey of Hospitals. Health Forum LLC. 2008.
- Bent S, Kane C, Shinohara K, et al. Saw palmetto for benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(6):557-566.
- Bauer BA. The herbal hospitalist. The Hospitalist. 2006;10(2);16-17.
- Ananth S. Applying integrative healthcare. Explore. 2009;5(2):119-120.
- Eisenberg DM, Kessler RC, Foster C, Norlock FE, Calkins DR, Delbanco TL. Unconventional medicine in the United States. Prevalence, costs, and patterns of use. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:246-52
- Bassie KL, Witmer DR, Pinto B, Bush C, Clark J, Deffenbaugh J Jr. National survey of dietary supplement policies in acute care facilities. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(1):65-70.
- Gardiner P, Phillips RS, Kemper KJ, Legedza A, Henlon S, Woolf AD. Dietary supplements: inpatient policies in US children’s hospitals. Pediatrics. 2008;121(4):e775-781.
- Blendon RJ, DesRoches CM, Benson JM, Brodie M, Altman DE. Americans’ views on the use and regulation of dietary supplements. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(6):805-810.
Top Image Source: TETRA IMAGES
Despite intravenous medication, a young boy in status epilepticus had the pediatric ICU team at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison stumped. The team called for a consult with the Integrative Medicine Program, which works with licensed acupuncturists and has been affiliated with the department of family medicine since 2001. Acupuncture’s efficacy in this setting has not been validated, but it has been shown to ease chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, as well as radiation-induced xerostomia.1,2
Following several treatments by a licensed acupuncturist and continued conventional care, the boy’s seizures subsided and he was transitioned to the medical floor. Did the acupuncture contribute to bringing the seizures under control? “I can’t say that it was the acupuncture—it was probably a function of all the therapies working together,” says David P. Rakel, MD, assistant professor and director of UW’s Integrative Medicine Program.
The UW case illustrates both current trends and the constant conundrum that surrounds hospital-based complementary medicine: Complementary and alternative medicine’s use is increasing in some U.S. hospitals, yet the existing research evidence for the efficacy of its multiple modalities is decidedly mixed.
Even if your hospital does not offer complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), your patients are using CAM at ever-increasing rates. In 1993, 34% of Americans reported using some type of CAM (e.g., supplements, massage therapy, prayer, and so on). That number has almost doubled to 62%.3 Americans spend $47 billion a year—of their own money—for CAM therapies, chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists. And older patients with chronic conditions—the kind of patient hospitalists are most familiar with—tend to try CAM more than younger patients.4
These trends can directly affect hospitalists’ treatment decisions, but they also play a part in how you establish communication and trust with your patients, and how you keep your patients safe from adverse drug interactions. According to the National Academy of Sciences, in order to effectively counsel patients and ensure high-quality comprehensive care, conventional professionals need more CAM-related education.5

—Suzanne Bertisch, MD, MPH, fellow, Harvard Medical School’s Osher Research Center
What Trends Show
In 2007, according to the American Hospital Association, 20.8% of community hospitals offered some type of care or treatment not based on traditional Western allopathic medicine. That’s up from 8.6% of reporting hospitals that offered those services in 1998.
The 1990s saw rapid growth of integrative medicine centers at major research institutions, and the majority of U.S. cancer centers now offer some form of complementary therapy, says Barrie R. Cassileth, MS, PhD, the Laurance S. Rockefeller Chair in Integrative Medicine and chief of the Integrative Medicine Service at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
The 2007 Health Forum/AHA Complementary and Alternative Medicine Survey of Hospitals reported that complementary programs are more common in urban rather than rural hospitals; services vary by hospital size (see Figure 2, above); and the top six modalities offered on an inpatient basis are pet therapy, massage therapy, music/art therapy, guided imagery, acupuncture, and reiki (see “Glossary of Complementary Terms,” above). Eighty-four percent of hospitals offer complementary services due to patient demand, the survey showed.
Joseph Ming-Wah Li, MD, FHM, SHM board member and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the hospital medicine program and associate chief of the division of general medicine and primary care at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, doesn’t see a problem with modalities that can make his patients feel better. Patients at his hospital have access to pet therapy, massage, and acupuncture. “I don’t think these modalities hurt our patients, and there is very little downside, except for potential cost,” says Dr. Li, an SHM board member. “What’s not clear is whether these therapies work or not.”
What’s in a Name?
Numerous therapies and modalities crowd under the CAM umbrella, but most experts classify “complementary” modalities as those used in conjunction with conventional medicine to mitigate symptoms of disease or treatment, whereas “alternative” connotes therapies claiming to treat or cure the underlying disease. Some harmful, dangerous, and dishonest practices fall into the “alternative” category, such as Hulda Clark’s “Zapper” device, which was promoted as a cure for liver flukes, something she says cause everything from diabetes to heart disease. (For more on questionable practices, visit www.quackwatch.com or the National Council Against Health Fraud’s Web site at www.ncahf.org.)
The National Institutes of Health’s National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) defines CAM as a group of “diverse medical and health care systems, practices, and products that are not presently considered to be part of conventional medicine.” Dr. Cassileth says the conflation of “complementary and alternative” into one neat acronym—CAM—causes confusion among patients and medical professionals. NCCAM will be changing its name soon, she says, to the National Center for Integrative Medicine, emphasizing the use of adjunctive modalities along with conventional medical treatments.
Hospitalist Suzanne Bertisch, MD, MPH, recently completed a research fellowship at Harvard Medical School’s Osher Research Center. She explains that integrative medicine uses a macro model of health, claiming a middle ground between the traditional, allopathic model of treating disease.
All Kinds of Evidence
Twenty years of complementary medicine research has yielded some information about safety—namely, what works and what doesn’t. For example, saw palmetto has not panned out as an effective treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia; St. John’s wort, useful for mild depression, interferes with many medications, including cyclosporine and warfarin, and should be avoided at least five days prior to surgery.7,8
Since NCCAM’s inception in October 1998, its research portfolio has stirred debate in the scientific community. Part of the disagreement stems from the difficulty of fitting multidimensional interventions, some of which are provider-dependent (e.g., massage or acupuncture), into the gold standard of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, explains Darshan Mehta, MD, MPH, associate director of medical education at the Benson-Henry Institute for Mind Body Medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The manner in which the effectiveness of integrative techniques is assessed requires a higher sophistication of systems research, Dr. Mehta says.
“The way we construe evidence needs to change,” she adds.
Likely to Expand
Most private health plans do not cover complementary services, although Medicare and numerous insurance plans will reimburse treatment in conjunction with physical therapy (e.g., massage) in the outpatient setting. Twenty-three states cover chiropractic care under Medicaid, and Medicare has begun to assess the cost-effectiveness of including acupuncture—especially for postoperative and chemotherapy-associated nausea and vomiting—in its benefits package.9 Other modalities, ranging from aromatherapy to guided imagery training, are paid for largely out-of-pocket.10
Dr. Rakel notes that the delivery of integrative medicine services at UW entails conversations with patients about out-of-pocket payments. “It can pose a barrier to the clinician-patient relationship if you give them acupuncture to help with their chemotherapy-induced nausea and then ask for their credit card,” he says.
Hospitalist Preparation
Most complementary therapies are currently offered on an outpatient basis. Because of this trend, and because they deal with acute conditions, hospitalists are less likely to be involved with complementary or integrative medicine services, says Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center hospitalist Andrew C. Ahn, MD, MPH. But that’s not to say complementary medicine is something hospitalists should ignore; patients arrive at the hospital with CAM regimens in tow. It’s the No. 1 reason, Dr. Ahn says, hospitalists should be knowledgeable and exposed to CAM therapies.
Physicians must understand patient patterns and preferences regarding allopathic and complementary medicine, says Sita Ananth, MHA, director of knowledge services and optimal healing environments at the Samueli Institute in Alexandria, Va., and author of the 2007 AHA report. She points to a 2006 survey conducted by AARP and NCCAM that found almost 70% of respondents did not tell their physicians about their complementary medicine approaches. These patients are within the age range most likely to be cared for by hospitalists, and failure to communicate about complementary treatment, such as supplemental vitamin use, could lead to safety issues. Moreover, without complete disclosure, the patient-physician relationship might not be as open as possible, Dr. Ananth says.
Many acute-care hospitalists do not have formal dietary supplement policies, and less than half of U.S. children’s hospitals require documentation of a check for drug or dietary supplement interaction.11,12 As a safety issue, it is always incumbent on hospitalists, says Dr. Li, to ask about any supplements or therapies patients are trying on their own as part of the history and physical examination. The policy at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Dr. Cassileth says, is that patients on chemotherapy or who are undergoing radiation or facing surgery must avoid herbal dietary supplements.
Beyond Safety
Dr. Bertisch advises hospitalists to pose questions about complementary therapies in an open manner, avoiding antagonistic discussions. “Even when I disagree, I try to guide them to issues about safety and nonsafety, and coax in my concerns,” she says. “The most challenging part about complementary medicine is that patients’ beliefs in these therapies may be so strong that even if the doctor says it won’t work, that will not necessarily change that belief.” A 2001 study in the Archives of Internal Medicine revealed that 70% of respondents would continue to take supplements even if a major study or their physician told them they didn’t work.13
The attraction to complementary medicine often reflects patients’ preferences for a holistic approach to health, says Dr. Ahn, or it may emanate from traditions carried with them from their country of origin. “Once you do understand their reasons for using CAM, then the patient-physician relationship can be significantly strengthened,” he says. With nearly two-thirds of Americans using some form of CAM, hospitalists need to engage in this dialogue.
Dr. Rakel agrees understanding patient culture is vital to uncovering useful information. “Most clinicians would agree that if we can match a therapy to the patient culture and belief system, we are more likely to get buy-in from the patient,” he says.
Dr. Mehta also is a clinical instructor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. He teaches his residents to educate themselves about credentialing, certification, and licensure of complementary providers. He also asks them to maintain an open mind. He says the most important preparation for hospitalists right now is to help educate their patients to be more proactive in their own healthcare. “An engaged patient,” he says, “is better than a disengaged patient.” TH
Gretchen Henkel is a freelance writer based in California.
References
- Deng G, Cassileth BR, Yeung KS. Complementary therapies for cancer-related symptoms. J Support Oncol. 2004;2(5):419-426.
- Kahn ST, Johnstone PA. Management of xerostomia related to radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Oncology. 2005;19(14):1827-1832.
- Barnes PM, Powell-Griner E, McFann K, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults: United States, 2002. Adv Data. 2004;27(343):1-19.
- Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA. 1998;280(18):1569-1575.
- Committee on the Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine by the American Public. Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the United States. Washington, D.C: National Academies Press; 2005.
- Ananth S. 2007 Health Forum/AHA Complementary and Alternative Medicine Survey of Hospitals. Health Forum LLC. 2008.
- Bent S, Kane C, Shinohara K, et al. Saw palmetto for benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(6):557-566.
- Bauer BA. The herbal hospitalist. The Hospitalist. 2006;10(2);16-17.
- Ananth S. Applying integrative healthcare. Explore. 2009;5(2):119-120.
- Eisenberg DM, Kessler RC, Foster C, Norlock FE, Calkins DR, Delbanco TL. Unconventional medicine in the United States. Prevalence, costs, and patterns of use. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:246-52
- Bassie KL, Witmer DR, Pinto B, Bush C, Clark J, Deffenbaugh J Jr. National survey of dietary supplement policies in acute care facilities. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(1):65-70.
- Gardiner P, Phillips RS, Kemper KJ, Legedza A, Henlon S, Woolf AD. Dietary supplements: inpatient policies in US children’s hospitals. Pediatrics. 2008;121(4):e775-781.
- Blendon RJ, DesRoches CM, Benson JM, Brodie M, Altman DE. Americans’ views on the use and regulation of dietary supplements. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(6):805-810.
Top Image Source: TETRA IMAGES