User login
Fezolinetant looks good for hot flashes in phase 2b trial
NEW ORLEANS – Hot flash frequency was reduced by up to threefold in phase 2b results for fezolinetant, a novel nonhormonal therapy.

The neurokinin-3–receptor (NK3R) antagonist showed a significant reduction of 1.8-2.6 mean hot flashes daily from placebo in twice-daily dosing at the end of 12 weeks, despite a strong 55% response rate to placebo, Graeme Fraser, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Once-daily dosing also significantly dropped the frequency of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms by 2.1-2.6 events daily, compared with placebo at the end of 12 weeks.
“This phase 2b trial was really about looking at different dose levels and looking at the once-daily versus twice-daily dosing,” Dr. Fraser said in a video interview. “The efficacy of both, with regard to once-daily and twice-daily dosing, was clear.”
The investigators looked at doses ranging from 15 mg to 90 mg twice daily and 30-120 mg daily. Significant reductions in frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes were seen at all doses and frequencies at 4 weeks and 12 weeks.
A coprimary endpoint, vasomotor severity, was also significantly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest twice-daily doses. Hot flash severity was similarly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest once-daily doses.
The safety profile was generally good; there were no signs of suicidality, no changes in endometrial thickness judged by ultrasound or endometrial biopsy, and estradiol levels were unchanged. Plasma bone markers, other laboratory values, and electrocardiograms were also unchanged.
A total of nine women experienced asymptomatic elevations in liver enzymes without bilirubin elevation. Most of these elevations were below three times the upper limit of normal.
Across 51 study sites in the United States, a total of 352 women received one dose of study drug and were included in the safety analysis. Efficacy was analyzed for 349 women, and 287 (81%) were considered completers.
Women were included in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study if they were naturally or surgically menopausal and aged 40-65 years, and experiencing at least 50 moderate to severe hot flashes weekly.
Fezolinetant acts on the KNDy neuron by replacing estrogen’s inhibitory effects. “Normally the firing is controlled by estrogen, but of course, in menopause, estrogen levels drop, and that control is lost,” explained Dr. Fraser. Fezolinetant exerts antagonism on the KNDy neuron’s NK3 receptor. “Why that’s important is that this neuron synapses at the thermoregulatory centers of the brain.”
Dr. Fraser said that discussions are underway with regulatory authorities to proceed to phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Fraser is a consultant to Astellas and was formerly a principal in Ogeda, the developer of fezolinetant. Ogeda is now a wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas, which funded the phase 2B trial.
NEW ORLEANS – Hot flash frequency was reduced by up to threefold in phase 2b results for fezolinetant, a novel nonhormonal therapy.

The neurokinin-3–receptor (NK3R) antagonist showed a significant reduction of 1.8-2.6 mean hot flashes daily from placebo in twice-daily dosing at the end of 12 weeks, despite a strong 55% response rate to placebo, Graeme Fraser, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Once-daily dosing also significantly dropped the frequency of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms by 2.1-2.6 events daily, compared with placebo at the end of 12 weeks.
“This phase 2b trial was really about looking at different dose levels and looking at the once-daily versus twice-daily dosing,” Dr. Fraser said in a video interview. “The efficacy of both, with regard to once-daily and twice-daily dosing, was clear.”
The investigators looked at doses ranging from 15 mg to 90 mg twice daily and 30-120 mg daily. Significant reductions in frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes were seen at all doses and frequencies at 4 weeks and 12 weeks.
A coprimary endpoint, vasomotor severity, was also significantly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest twice-daily doses. Hot flash severity was similarly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest once-daily doses.
The safety profile was generally good; there were no signs of suicidality, no changes in endometrial thickness judged by ultrasound or endometrial biopsy, and estradiol levels were unchanged. Plasma bone markers, other laboratory values, and electrocardiograms were also unchanged.
A total of nine women experienced asymptomatic elevations in liver enzymes without bilirubin elevation. Most of these elevations were below three times the upper limit of normal.
Across 51 study sites in the United States, a total of 352 women received one dose of study drug and were included in the safety analysis. Efficacy was analyzed for 349 women, and 287 (81%) were considered completers.
Women were included in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study if they were naturally or surgically menopausal and aged 40-65 years, and experiencing at least 50 moderate to severe hot flashes weekly.
Fezolinetant acts on the KNDy neuron by replacing estrogen’s inhibitory effects. “Normally the firing is controlled by estrogen, but of course, in menopause, estrogen levels drop, and that control is lost,” explained Dr. Fraser. Fezolinetant exerts antagonism on the KNDy neuron’s NK3 receptor. “Why that’s important is that this neuron synapses at the thermoregulatory centers of the brain.”
Dr. Fraser said that discussions are underway with regulatory authorities to proceed to phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Fraser is a consultant to Astellas and was formerly a principal in Ogeda, the developer of fezolinetant. Ogeda is now a wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas, which funded the phase 2B trial.
NEW ORLEANS – Hot flash frequency was reduced by up to threefold in phase 2b results for fezolinetant, a novel nonhormonal therapy.

The neurokinin-3–receptor (NK3R) antagonist showed a significant reduction of 1.8-2.6 mean hot flashes daily from placebo in twice-daily dosing at the end of 12 weeks, despite a strong 55% response rate to placebo, Graeme Fraser, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Once-daily dosing also significantly dropped the frequency of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms by 2.1-2.6 events daily, compared with placebo at the end of 12 weeks.
“This phase 2b trial was really about looking at different dose levels and looking at the once-daily versus twice-daily dosing,” Dr. Fraser said in a video interview. “The efficacy of both, with regard to once-daily and twice-daily dosing, was clear.”
The investigators looked at doses ranging from 15 mg to 90 mg twice daily and 30-120 mg daily. Significant reductions in frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes were seen at all doses and frequencies at 4 weeks and 12 weeks.
A coprimary endpoint, vasomotor severity, was also significantly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest twice-daily doses. Hot flash severity was similarly reduced at 12 weeks for the two highest once-daily doses.
The safety profile was generally good; there were no signs of suicidality, no changes in endometrial thickness judged by ultrasound or endometrial biopsy, and estradiol levels were unchanged. Plasma bone markers, other laboratory values, and electrocardiograms were also unchanged.
A total of nine women experienced asymptomatic elevations in liver enzymes without bilirubin elevation. Most of these elevations were below three times the upper limit of normal.
Across 51 study sites in the United States, a total of 352 women received one dose of study drug and were included in the safety analysis. Efficacy was analyzed for 349 women, and 287 (81%) were considered completers.
Women were included in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study if they were naturally or surgically menopausal and aged 40-65 years, and experiencing at least 50 moderate to severe hot flashes weekly.
Fezolinetant acts on the KNDy neuron by replacing estrogen’s inhibitory effects. “Normally the firing is controlled by estrogen, but of course, in menopause, estrogen levels drop, and that control is lost,” explained Dr. Fraser. Fezolinetant exerts antagonism on the KNDy neuron’s NK3 receptor. “Why that’s important is that this neuron synapses at the thermoregulatory centers of the brain.”
Dr. Fraser said that discussions are underway with regulatory authorities to proceed to phase 3 clinical trials.
Dr. Fraser is a consultant to Astellas and was formerly a principal in Ogeda, the developer of fezolinetant. Ogeda is now a wholly owned subsidiary of Astellas, which funded the phase 2B trial.
REPORTING FROM ENDO 2019
Biomarkers predict VTE risk with menopausal oral hormone therapy
CHICAGO – An elevated baseline D-dimer level is helpful to women and their physicians in clarifying decision making about oral hormone therapy for troublesome menopausal symptoms, Mary Cushman, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
She was lead investigator in a nested case-control study embedded in the landmark Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), which showed that participants who had a baseline D-dimer greater than 0.54 mg/L – putting them in the top 25% – and were randomized to oral menopausal hormone therapy had a 5-year incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) of 6%. That’s 500% higher than in women with a lower D-dimer randomized to placebo.
“The number needed to test for D-dimer in advance of prescribing in order to prevent one VTE over 5 years of hormone therapy was only 33. So this is potentially something in the toolbox you can use in counseling women about oral hormone therapy,” said Dr. Cushman, professor of medicine and pathology and medical director of the thrombosis and hemostasis program at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
The biomarker study included 1,082 WHI participants aged 50-79 years randomized to oral conjugated equine estrogen with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate or to placebo, 215 of whom experienced VTE during a mean 4.1 years of follow-up. Levels of a variety of biomarkers obtained at baseline were assessed in terms of their associated risk of future VTE. The biomarkers included C-reactive protein and procoagulant, anticoagulant, and fibrinolytic factors.
In a logistic regression analysis adjusted for age, race, body mass index, and hysterectomy, the strongest association with VTE was a high D-dimer. That 500% increased risk of VTE with hormone therapy in women with a D-dimer greater than 0.54 mg/L was comparable in magnitude with the risk Dr. Cushman and her coinvestigators previously reported for the combination of factor V Leiden and hormone therapy.
Dr. Cushman and her associates also took a first step towards developing a multibiomarker risk score. They found that WHI participants randomized to hormone therapy who had abnormal baseline values for any three or more of eight biomarkers had a 1,450% greater risk of future VTE than women with zero or one abnormal biomarker who were assigned to placebo. The eight-biomarker panel described in the recently published study comprised D-dimer, factor V Leiden, protein C, total protein S, free protein S, antithrombin, plasmin-antiplasmin complex, and fragment 1.2. However, the investigators indicated the risk score needs further study before it’s ready for adoption in clinical practice (Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2018 Apr 17;2[2]:310-9).
Dr. Cushman noted that, although the main findings of the WHI have largely resulted in abandonment of menopausal hormone therapy for disease prevention, many women still want to take oral hormone therapy for relief of bothersome menopausal symptoms. She tries to steer them instead to safer nonoral formulations. Transdermal estrogen replacement has no associated risk of VTE and doesn’t activate anticoagulation. Neither does vaginal estradiol.
In offering what she called “the 30,000-foot view of the impact of venous thrombosis on women’s health,” Dr. Cushman noted that VTE is the third-most common vascular disease in the United States, with up to 900,000 cases per year. The lifetime risk in women after age 45 is 8.4%. Half of VTEs are provoked and therefore potentially preventable, with common triggers being surgery, cancer, pregnancy, trauma, and immobilization, especially during travel.
In addition, a retrospective study conducted in the Worcester, Mass., area showed that 1-month mortality after VTE remained static in the 5%-10% range during 1999-2009.
“This is a fatal disease, even though we treat it as an outpatient quite a lot,” Dr. Cushman observed.
Common nonfatal complications of VTE include major bleeding in 5%-10% of cases, a recurrence rate of 5%-10% annually, a 20%-40% of the burdensome and not infrequently disabling condition known as postthrombotic syndrome, and a 3%-4% incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Yet despite the seriousness of VTE, awareness about VTE is poor among both patients and physicians, and appropriate prophylaxis is underutilized, she said.
The key to improved primary prevention of VTE, Dr. Cushman continued, is greater attention to modifiable behavioral risk factors, along with more use of prophylactic medication when needed.
The traditional cardiovascular risk factors, like hypertension, smoking, and hyperlipidemia, aren’t relevant to VTE risk. But obesity and sedentary lifestyle have come to be recognized as important modifiable risk factors. In one study of more than 30,000 Americans, the risk of VTE was shown to be reduced by 40% in individuals who exercised at least four times per week, compared with the physically inactive.
And in an analysis led by Dr. Cushman of nearly 21,000 participants over age 45 years with 12.6 years of follow-up in the Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology (LITE), the investigators found that greater levels of all body size measures – not just body mass index, but calf circumference, waist-hip ratio, hip circumference, and others – were associated with increased VTE risk. These associations weren’t affected by levels of circulating biomarkers for inflammation or hypercoagulability, suggesting that it’s obesity per se, with its associated adverse impact on blood flow caused by physical factors, that explains the mechanism underlying obesity as a risk factor for VTE (Thromb Res. 2016 Aug;144:127-32).
At the meeting’s opening ceremonies, AHA President Ivor Benjamin, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, presented Dr. Cushman with the AHA Population Research Prize. She was honored for her “critically acclaimed research utilizing biomarker assessments in population studies to elucidate pathways of disease etiology for the three most common vascular diseases – coronary heart disease, stroke, and venous thromboembolism – as well as their risk factors,” said Dr. Benjamin.
Dr. Cushman reported having no financial conflicts regarding her D-dimer study, which was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
CHICAGO – An elevated baseline D-dimer level is helpful to women and their physicians in clarifying decision making about oral hormone therapy for troublesome menopausal symptoms, Mary Cushman, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
She was lead investigator in a nested case-control study embedded in the landmark Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), which showed that participants who had a baseline D-dimer greater than 0.54 mg/L – putting them in the top 25% – and were randomized to oral menopausal hormone therapy had a 5-year incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) of 6%. That’s 500% higher than in women with a lower D-dimer randomized to placebo.
“The number needed to test for D-dimer in advance of prescribing in order to prevent one VTE over 5 years of hormone therapy was only 33. So this is potentially something in the toolbox you can use in counseling women about oral hormone therapy,” said Dr. Cushman, professor of medicine and pathology and medical director of the thrombosis and hemostasis program at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
The biomarker study included 1,082 WHI participants aged 50-79 years randomized to oral conjugated equine estrogen with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate or to placebo, 215 of whom experienced VTE during a mean 4.1 years of follow-up. Levels of a variety of biomarkers obtained at baseline were assessed in terms of their associated risk of future VTE. The biomarkers included C-reactive protein and procoagulant, anticoagulant, and fibrinolytic factors.
In a logistic regression analysis adjusted for age, race, body mass index, and hysterectomy, the strongest association with VTE was a high D-dimer. That 500% increased risk of VTE with hormone therapy in women with a D-dimer greater than 0.54 mg/L was comparable in magnitude with the risk Dr. Cushman and her coinvestigators previously reported for the combination of factor V Leiden and hormone therapy.
Dr. Cushman and her associates also took a first step towards developing a multibiomarker risk score. They found that WHI participants randomized to hormone therapy who had abnormal baseline values for any three or more of eight biomarkers had a 1,450% greater risk of future VTE than women with zero or one abnormal biomarker who were assigned to placebo. The eight-biomarker panel described in the recently published study comprised D-dimer, factor V Leiden, protein C, total protein S, free protein S, antithrombin, plasmin-antiplasmin complex, and fragment 1.2. However, the investigators indicated the risk score needs further study before it’s ready for adoption in clinical practice (Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2018 Apr 17;2[2]:310-9).
Dr. Cushman noted that, although the main findings of the WHI have largely resulted in abandonment of menopausal hormone therapy for disease prevention, many women still want to take oral hormone therapy for relief of bothersome menopausal symptoms. She tries to steer them instead to safer nonoral formulations. Transdermal estrogen replacement has no associated risk of VTE and doesn’t activate anticoagulation. Neither does vaginal estradiol.
In offering what she called “the 30,000-foot view of the impact of venous thrombosis on women’s health,” Dr. Cushman noted that VTE is the third-most common vascular disease in the United States, with up to 900,000 cases per year. The lifetime risk in women after age 45 is 8.4%. Half of VTEs are provoked and therefore potentially preventable, with common triggers being surgery, cancer, pregnancy, trauma, and immobilization, especially during travel.
In addition, a retrospective study conducted in the Worcester, Mass., area showed that 1-month mortality after VTE remained static in the 5%-10% range during 1999-2009.
“This is a fatal disease, even though we treat it as an outpatient quite a lot,” Dr. Cushman observed.
Common nonfatal complications of VTE include major bleeding in 5%-10% of cases, a recurrence rate of 5%-10% annually, a 20%-40% of the burdensome and not infrequently disabling condition known as postthrombotic syndrome, and a 3%-4% incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Yet despite the seriousness of VTE, awareness about VTE is poor among both patients and physicians, and appropriate prophylaxis is underutilized, she said.
The key to improved primary prevention of VTE, Dr. Cushman continued, is greater attention to modifiable behavioral risk factors, along with more use of prophylactic medication when needed.
The traditional cardiovascular risk factors, like hypertension, smoking, and hyperlipidemia, aren’t relevant to VTE risk. But obesity and sedentary lifestyle have come to be recognized as important modifiable risk factors. In one study of more than 30,000 Americans, the risk of VTE was shown to be reduced by 40% in individuals who exercised at least four times per week, compared with the physically inactive.
And in an analysis led by Dr. Cushman of nearly 21,000 participants over age 45 years with 12.6 years of follow-up in the Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology (LITE), the investigators found that greater levels of all body size measures – not just body mass index, but calf circumference, waist-hip ratio, hip circumference, and others – were associated with increased VTE risk. These associations weren’t affected by levels of circulating biomarkers for inflammation or hypercoagulability, suggesting that it’s obesity per se, with its associated adverse impact on blood flow caused by physical factors, that explains the mechanism underlying obesity as a risk factor for VTE (Thromb Res. 2016 Aug;144:127-32).
At the meeting’s opening ceremonies, AHA President Ivor Benjamin, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, presented Dr. Cushman with the AHA Population Research Prize. She was honored for her “critically acclaimed research utilizing biomarker assessments in population studies to elucidate pathways of disease etiology for the three most common vascular diseases – coronary heart disease, stroke, and venous thromboembolism – as well as their risk factors,” said Dr. Benjamin.
Dr. Cushman reported having no financial conflicts regarding her D-dimer study, which was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
CHICAGO – An elevated baseline D-dimer level is helpful to women and their physicians in clarifying decision making about oral hormone therapy for troublesome menopausal symptoms, Mary Cushman, MD, said at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
She was lead investigator in a nested case-control study embedded in the landmark Women’s Health Initiative (WHI), which showed that participants who had a baseline D-dimer greater than 0.54 mg/L – putting them in the top 25% – and were randomized to oral menopausal hormone therapy had a 5-year incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) of 6%. That’s 500% higher than in women with a lower D-dimer randomized to placebo.
“The number needed to test for D-dimer in advance of prescribing in order to prevent one VTE over 5 years of hormone therapy was only 33. So this is potentially something in the toolbox you can use in counseling women about oral hormone therapy,” said Dr. Cushman, professor of medicine and pathology and medical director of the thrombosis and hemostasis program at the University of Vermont, Burlington.
The biomarker study included 1,082 WHI participants aged 50-79 years randomized to oral conjugated equine estrogen with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate or to placebo, 215 of whom experienced VTE during a mean 4.1 years of follow-up. Levels of a variety of biomarkers obtained at baseline were assessed in terms of their associated risk of future VTE. The biomarkers included C-reactive protein and procoagulant, anticoagulant, and fibrinolytic factors.
In a logistic regression analysis adjusted for age, race, body mass index, and hysterectomy, the strongest association with VTE was a high D-dimer. That 500% increased risk of VTE with hormone therapy in women with a D-dimer greater than 0.54 mg/L was comparable in magnitude with the risk Dr. Cushman and her coinvestigators previously reported for the combination of factor V Leiden and hormone therapy.
Dr. Cushman and her associates also took a first step towards developing a multibiomarker risk score. They found that WHI participants randomized to hormone therapy who had abnormal baseline values for any three or more of eight biomarkers had a 1,450% greater risk of future VTE than women with zero or one abnormal biomarker who were assigned to placebo. The eight-biomarker panel described in the recently published study comprised D-dimer, factor V Leiden, protein C, total protein S, free protein S, antithrombin, plasmin-antiplasmin complex, and fragment 1.2. However, the investigators indicated the risk score needs further study before it’s ready for adoption in clinical practice (Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2018 Apr 17;2[2]:310-9).
Dr. Cushman noted that, although the main findings of the WHI have largely resulted in abandonment of menopausal hormone therapy for disease prevention, many women still want to take oral hormone therapy for relief of bothersome menopausal symptoms. She tries to steer them instead to safer nonoral formulations. Transdermal estrogen replacement has no associated risk of VTE and doesn’t activate anticoagulation. Neither does vaginal estradiol.
In offering what she called “the 30,000-foot view of the impact of venous thrombosis on women’s health,” Dr. Cushman noted that VTE is the third-most common vascular disease in the United States, with up to 900,000 cases per year. The lifetime risk in women after age 45 is 8.4%. Half of VTEs are provoked and therefore potentially preventable, with common triggers being surgery, cancer, pregnancy, trauma, and immobilization, especially during travel.
In addition, a retrospective study conducted in the Worcester, Mass., area showed that 1-month mortality after VTE remained static in the 5%-10% range during 1999-2009.
“This is a fatal disease, even though we treat it as an outpatient quite a lot,” Dr. Cushman observed.
Common nonfatal complications of VTE include major bleeding in 5%-10% of cases, a recurrence rate of 5%-10% annually, a 20%-40% of the burdensome and not infrequently disabling condition known as postthrombotic syndrome, and a 3%-4% incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Yet despite the seriousness of VTE, awareness about VTE is poor among both patients and physicians, and appropriate prophylaxis is underutilized, she said.
The key to improved primary prevention of VTE, Dr. Cushman continued, is greater attention to modifiable behavioral risk factors, along with more use of prophylactic medication when needed.
The traditional cardiovascular risk factors, like hypertension, smoking, and hyperlipidemia, aren’t relevant to VTE risk. But obesity and sedentary lifestyle have come to be recognized as important modifiable risk factors. In one study of more than 30,000 Americans, the risk of VTE was shown to be reduced by 40% in individuals who exercised at least four times per week, compared with the physically inactive.
And in an analysis led by Dr. Cushman of nearly 21,000 participants over age 45 years with 12.6 years of follow-up in the Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology (LITE), the investigators found that greater levels of all body size measures – not just body mass index, but calf circumference, waist-hip ratio, hip circumference, and others – were associated with increased VTE risk. These associations weren’t affected by levels of circulating biomarkers for inflammation or hypercoagulability, suggesting that it’s obesity per se, with its associated adverse impact on blood flow caused by physical factors, that explains the mechanism underlying obesity as a risk factor for VTE (Thromb Res. 2016 Aug;144:127-32).
At the meeting’s opening ceremonies, AHA President Ivor Benjamin, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, presented Dr. Cushman with the AHA Population Research Prize. She was honored for her “critically acclaimed research utilizing biomarker assessments in population studies to elucidate pathways of disease etiology for the three most common vascular diseases – coronary heart disease, stroke, and venous thromboembolism – as well as their risk factors,” said Dr. Benjamin.
Dr. Cushman reported having no financial conflicts regarding her D-dimer study, which was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
REPORTING FROM THE AHA SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Women in the top 25% for D-dimer level before going on menopausal hormone therapy had a 6% incidence of venous thromboembolism over 5 years.
Study details: This was a nested case-control study focused on identifying biomarkers for venous thromboembolism risk which included 1,082 participants in the Women’s Health Initiative randomized to menopausal hormone therapy or placebo.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Is vaginal estrogen used for GSM associated with a higher risk of CVD or cancer?
Expert Commentary
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. December 17, 2018. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001284.
GSM, a chronic and often progressive condition, occurs in almost 50% of postmenopausal women and has been shown to impair sexual function and quality of life.1 Symptoms include vaginal dryness, vulvar or vaginal itching, dyspareunia, urinary urgency or frequency, and increased urinary tract infections. Although lubricants or vaginal moisturizers may be sufficient to treat GSM, targeted hormonal therapy may be needed to improve the symptoms and resolve the underlying cause, due to vaginal hormone loss.
Despite lack of any observational or clinical trial evidence for chronic health disease risks related to low-dose vaginal estrogen use, there remains an US Food and Drug Administration boxed warning on the package label for low-dose vaginal estrogen related to risks of heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, pdementia, and breast cancer. The objective of the investigation by Bhupathiraju and colleagues was to evaluate associations between vaginal estrogen use and health outcomes, including CVD (myocardial infarction, stroke, and pulmonary embolism/deep vein thrombosis), cancer (total invasive, breast, endometrial, ovarian, and colorectal), and hip fracture.
Details of the study
The prospective analysis included 896 postmenopausal current users of vaginal estrogen in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS; 1982–2012), compared with 52,901 nonusers. Eighteen years of follow-up was evaluated. Users of systemic hormone therapy were excluded from the analysis. For the NHS, self-reported data were collected every 2 years on questionnaires for vaginal estrogen use and health outcomes. Investigators used medical records to confirm health outcomes.
After adjusting for covariates, no significant differences in risks were found for CVD, cancer, and hip fracture between users and nonusers of vaginal estrogen, regardless of hysterectomy status.
Key findings
After adjusting for multiple variables (including age, race, physical activity, age at menopause, hysterectomy, aspirin use, parental history of cancer, etc), health outcomes for CVDs, all cancers, and hip fracture were:
- myocardial infarction: hazard ratio (HR), 0.73 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.47–1.13)
- stroke: HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.56–1.29)
- pulmonary embolism/deep vein thrombosis: HR, 1.06 (95% CI, 0.58–1.93)
- hip fracture: HR, 0.91 (95% CI, 0.60–1.38)
- all cancers: HR, 1.05 (95% CI, 0.89–1.25).
Continue to: Health outcomes for specific invasive cancers
Health outcomes for specific invasive cancers (risk for endometrial cancer included only women with an intact uterus) were:
- invasive breast cancer: HR, 1.07 (95% CI, 0.78–1.47)
- ovarian cancer: HR, 1.17 (95% CI, 0.52–2.65)
- endometrial cancer: HR, 1.62 (95% CI, 0.88–2.97)
- colorectal cancer: HR, 0.77 (95% CI, 0.45–1.34).
Study strengths and weaknesses
A causal relationship cannot be proven as the study was observational. However, a strength included the 18 years of follow-up. Women used vaginal estrogen for an average of 3 years, which provided longer-term safety data than available 12-month clinical trial data. Data were collected through self-report on questionnaires every 2 years, which is a drawback; however, participants were registered nurses, who have been shown to provide reliable health-related information. Comparisons between therapies were not possible as data were not collected about type or dosage of vaginal estrogen. Available therapies during the NHS included vaginal estrogen tablets, creams, and an estradiol ring, with higher doses available during earlier parts of the study than the lower doses commonly prescribed in current day.
Overall
The findings from this long-term follow-up of the NHS provide support for the safety of vaginal estrogen for treatment of GSM. No statistically significant increased health risks were found for users of vaginal estrogen, similar to earlier reported findings from the large Women’s Health Initiative.2 Low-dose vaginal estrogen is recommended for treatment of GSM by The North American Menopause Society, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the Endocrine Society.
Absorption of low-dose vaginal estrogen preparations appears minimal, and they are effective and generally safe for the treatment of GSM for women at any age. Progesterone is not recommended with low-dose vaginal estrogen therapies, based primarily on randomized clinical trial safety data of 12 months.3 Postmenopausal bleeding, however, needs to be thoroughly evaluated. For women with breast cancer, include the oncologist in decision making about the use of low-dose vaginal estrogen.
Despite the boxed warning on vaginal estrogen, the findings from this study support the safety of vaginal estrogen use for effective relief of GSM in women with and without a uterus.
JOANN V. PINKERTON, MD, NCMP
- Gandhi J, Chen A, Dagur G, et al. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: an overview of clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, etiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;251:704-711.
- Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
Expert Commentary
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. December 17, 2018. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001284.
GSM, a chronic and often progressive condition, occurs in almost 50% of postmenopausal women and has been shown to impair sexual function and quality of life.1 Symptoms include vaginal dryness, vulvar or vaginal itching, dyspareunia, urinary urgency or frequency, and increased urinary tract infections. Although lubricants or vaginal moisturizers may be sufficient to treat GSM, targeted hormonal therapy may be needed to improve the symptoms and resolve the underlying cause, due to vaginal hormone loss.
Despite lack of any observational or clinical trial evidence for chronic health disease risks related to low-dose vaginal estrogen use, there remains an US Food and Drug Administration boxed warning on the package label for low-dose vaginal estrogen related to risks of heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, pdementia, and breast cancer. The objective of the investigation by Bhupathiraju and colleagues was to evaluate associations between vaginal estrogen use and health outcomes, including CVD (myocardial infarction, stroke, and pulmonary embolism/deep vein thrombosis), cancer (total invasive, breast, endometrial, ovarian, and colorectal), and hip fracture.
Details of the study
The prospective analysis included 896 postmenopausal current users of vaginal estrogen in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS; 1982–2012), compared with 52,901 nonusers. Eighteen years of follow-up was evaluated. Users of systemic hormone therapy were excluded from the analysis. For the NHS, self-reported data were collected every 2 years on questionnaires for vaginal estrogen use and health outcomes. Investigators used medical records to confirm health outcomes.
After adjusting for covariates, no significant differences in risks were found for CVD, cancer, and hip fracture between users and nonusers of vaginal estrogen, regardless of hysterectomy status.
Key findings
After adjusting for multiple variables (including age, race, physical activity, age at menopause, hysterectomy, aspirin use, parental history of cancer, etc), health outcomes for CVDs, all cancers, and hip fracture were:
- myocardial infarction: hazard ratio (HR), 0.73 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.47–1.13)
- stroke: HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.56–1.29)
- pulmonary embolism/deep vein thrombosis: HR, 1.06 (95% CI, 0.58–1.93)
- hip fracture: HR, 0.91 (95% CI, 0.60–1.38)
- all cancers: HR, 1.05 (95% CI, 0.89–1.25).
Continue to: Health outcomes for specific invasive cancers
Health outcomes for specific invasive cancers (risk for endometrial cancer included only women with an intact uterus) were:
- invasive breast cancer: HR, 1.07 (95% CI, 0.78–1.47)
- ovarian cancer: HR, 1.17 (95% CI, 0.52–2.65)
- endometrial cancer: HR, 1.62 (95% CI, 0.88–2.97)
- colorectal cancer: HR, 0.77 (95% CI, 0.45–1.34).
Study strengths and weaknesses
A causal relationship cannot be proven as the study was observational. However, a strength included the 18 years of follow-up. Women used vaginal estrogen for an average of 3 years, which provided longer-term safety data than available 12-month clinical trial data. Data were collected through self-report on questionnaires every 2 years, which is a drawback; however, participants were registered nurses, who have been shown to provide reliable health-related information. Comparisons between therapies were not possible as data were not collected about type or dosage of vaginal estrogen. Available therapies during the NHS included vaginal estrogen tablets, creams, and an estradiol ring, with higher doses available during earlier parts of the study than the lower doses commonly prescribed in current day.
Overall
The findings from this long-term follow-up of the NHS provide support for the safety of vaginal estrogen for treatment of GSM. No statistically significant increased health risks were found for users of vaginal estrogen, similar to earlier reported findings from the large Women’s Health Initiative.2 Low-dose vaginal estrogen is recommended for treatment of GSM by The North American Menopause Society, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the Endocrine Society.
Absorption of low-dose vaginal estrogen preparations appears minimal, and they are effective and generally safe for the treatment of GSM for women at any age. Progesterone is not recommended with low-dose vaginal estrogen therapies, based primarily on randomized clinical trial safety data of 12 months.3 Postmenopausal bleeding, however, needs to be thoroughly evaluated. For women with breast cancer, include the oncologist in decision making about the use of low-dose vaginal estrogen.
Despite the boxed warning on vaginal estrogen, the findings from this study support the safety of vaginal estrogen use for effective relief of GSM in women with and without a uterus.
JOANN V. PINKERTON, MD, NCMP
Expert Commentary
Bhupathiraju SN, Grodstein F, Stampfer MJ, et al. Vaginal estrogen use and chronic disease risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Menopause. December 17, 2018. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001284.
GSM, a chronic and often progressive condition, occurs in almost 50% of postmenopausal women and has been shown to impair sexual function and quality of life.1 Symptoms include vaginal dryness, vulvar or vaginal itching, dyspareunia, urinary urgency or frequency, and increased urinary tract infections. Although lubricants or vaginal moisturizers may be sufficient to treat GSM, targeted hormonal therapy may be needed to improve the symptoms and resolve the underlying cause, due to vaginal hormone loss.
Despite lack of any observational or clinical trial evidence for chronic health disease risks related to low-dose vaginal estrogen use, there remains an US Food and Drug Administration boxed warning on the package label for low-dose vaginal estrogen related to risks of heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, pdementia, and breast cancer. The objective of the investigation by Bhupathiraju and colleagues was to evaluate associations between vaginal estrogen use and health outcomes, including CVD (myocardial infarction, stroke, and pulmonary embolism/deep vein thrombosis), cancer (total invasive, breast, endometrial, ovarian, and colorectal), and hip fracture.
Details of the study
The prospective analysis included 896 postmenopausal current users of vaginal estrogen in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS; 1982–2012), compared with 52,901 nonusers. Eighteen years of follow-up was evaluated. Users of systemic hormone therapy were excluded from the analysis. For the NHS, self-reported data were collected every 2 years on questionnaires for vaginal estrogen use and health outcomes. Investigators used medical records to confirm health outcomes.
After adjusting for covariates, no significant differences in risks were found for CVD, cancer, and hip fracture between users and nonusers of vaginal estrogen, regardless of hysterectomy status.
Key findings
After adjusting for multiple variables (including age, race, physical activity, age at menopause, hysterectomy, aspirin use, parental history of cancer, etc), health outcomes for CVDs, all cancers, and hip fracture were:
- myocardial infarction: hazard ratio (HR), 0.73 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.47–1.13)
- stroke: HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.56–1.29)
- pulmonary embolism/deep vein thrombosis: HR, 1.06 (95% CI, 0.58–1.93)
- hip fracture: HR, 0.91 (95% CI, 0.60–1.38)
- all cancers: HR, 1.05 (95% CI, 0.89–1.25).
Continue to: Health outcomes for specific invasive cancers
Health outcomes for specific invasive cancers (risk for endometrial cancer included only women with an intact uterus) were:
- invasive breast cancer: HR, 1.07 (95% CI, 0.78–1.47)
- ovarian cancer: HR, 1.17 (95% CI, 0.52–2.65)
- endometrial cancer: HR, 1.62 (95% CI, 0.88–2.97)
- colorectal cancer: HR, 0.77 (95% CI, 0.45–1.34).
Study strengths and weaknesses
A causal relationship cannot be proven as the study was observational. However, a strength included the 18 years of follow-up. Women used vaginal estrogen for an average of 3 years, which provided longer-term safety data than available 12-month clinical trial data. Data were collected through self-report on questionnaires every 2 years, which is a drawback; however, participants were registered nurses, who have been shown to provide reliable health-related information. Comparisons between therapies were not possible as data were not collected about type or dosage of vaginal estrogen. Available therapies during the NHS included vaginal estrogen tablets, creams, and an estradiol ring, with higher doses available during earlier parts of the study than the lower doses commonly prescribed in current day.
Overall
The findings from this long-term follow-up of the NHS provide support for the safety of vaginal estrogen for treatment of GSM. No statistically significant increased health risks were found for users of vaginal estrogen, similar to earlier reported findings from the large Women’s Health Initiative.2 Low-dose vaginal estrogen is recommended for treatment of GSM by The North American Menopause Society, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the Endocrine Society.
Absorption of low-dose vaginal estrogen preparations appears minimal, and they are effective and generally safe for the treatment of GSM for women at any age. Progesterone is not recommended with low-dose vaginal estrogen therapies, based primarily on randomized clinical trial safety data of 12 months.3 Postmenopausal bleeding, however, needs to be thoroughly evaluated. For women with breast cancer, include the oncologist in decision making about the use of low-dose vaginal estrogen.
Despite the boxed warning on vaginal estrogen, the findings from this study support the safety of vaginal estrogen use for effective relief of GSM in women with and without a uterus.
JOANN V. PINKERTON, MD, NCMP
- Gandhi J, Chen A, Dagur G, et al. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: an overview of clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, etiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;251:704-711.
- Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
- Gandhi J, Chen A, Dagur G, et al. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: an overview of clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, etiology, evaluation, and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;251:704-711.
- Crandall CJ, Hovey KM, Andrews CA, et al. Breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and cardiovascular events in participants who used vaginal estrogen in the Women's Health Initiative Observational Study. Menopause. 2018;25:11-20.
- The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
Does the type of menopausal HT used increase the risk of venous thromboembolism?
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases. BMJ. 2019;364:k4810.
The Women’s Health Initiative trials, in which menopausal women were randomly assigned to treatment with oral CEE or placebo, found that statistically the largest risk associated with menopausal hormone therapy (HT) was increased VTE.1 Recently, investigators in the United Kingdom (UK) published results of their research aimed at determining the association between the risk of VTE and the use of different types of HT.2
Details of the study
Vinogradova and colleagues used 2 UK primary care research databases, QResearch and Clinical Practice Research Datalink, to identify cases of incident VTE in general practice records, hospital admissions, and mortality records. They identified 80,396 women (aged 40 to 79 years) diagnosed with VTE between 1998 and 2017 and 391,494 control women matched by age and general practice. The mean age of the case and control women was approximately 64 years; the great majority of women were white. Analyses were adjusted for smoking, body mass index (BMI), family history of VTE, and comorbidities associated with VTE.
Types of HT used. The investigators found that 5,795 (7.2%) women with VTE and 21,670 (5.5%) controls were exposed to HT in the 90 days before the index date (the first date of VTE diagnosis for cases became the index date for matched controls). In those exposed to HT:
- 4,915 (85%) cases and 16,938 (78%) controls used oral preparations (including 102 [1.8%] cases and 312 [1.4%] controls who also had transdermal preparations)
- 880 (14%) cases and 4,731 (19%) controls used transdermal HT only.
Association of VTE with HT. Risk of VTE was increased with all oral HT formulations, including combined (estrogen plus progestogen) and estrogen-only preparations. Use of oral CEE (odds ratio [OR], 1.49) and estradiol (OR, 1.27) were both associated with an elevated risk of VTE (P<.05 for both comparisons). In contrast, use of transdermal estradiol (the great majority of which was administered by patch) was not associated with an elevated risk of VTE (OR, 0.96).
Direct comparison of oral estradiol and CEE found that the lower VTE risk with oral estradiol achieved statistical significance (P = .005). Direct comparison of oral and transdermal estrogen revealed an OR of 1.7 for the oral route of administration (P<.001)
Continue to: Study strengths and weaknesses
Study strengths and weaknesses
This study used data from the 2 largest primary care databases in the United Kingdom. Analyses were adjusted for numerous confounding factors, including acute and chronic conditions, lifestyle factors, and social deprivation. Additional sensitivity analyses were conducted and yielded results similar to those of the main analysis.
Several limitations could have resulted in some residual confounding bias. For example, drug exposure information was based on HT prescriptions and not actual use; data on some factors were not available, such as indications for HT, age at menopause, and education level; and for a small proportion of women, some data (smoking status, alcohol consumption, BMI) were missing and had to be imputed for analysis.
Although randomized trials have not compared VTE risk with oral versus transdermal estrogen, prior observational studies have consistently suggested that transdermal estrogen does not elevate VTE risk; this is consistent with the results from this large UK study. In my practice, congruent with the authors’ suggestions, I recommend transdermal rather than oral estrogen for patients (notably, those who are obese) who at baseline have risk factors for VTE. For menopausal women for whom use of oral estrogen is indicated, I recommend estradiol rather than CEE, since estradiol is less expensive and, based on this study’s results, may be safer than CEE.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
- Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women's Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310:1353-1368.
- Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases. BMJ. 2019;364:k4810.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases. BMJ. 2019;364:k4810.
The Women’s Health Initiative trials, in which menopausal women were randomly assigned to treatment with oral CEE or placebo, found that statistically the largest risk associated with menopausal hormone therapy (HT) was increased VTE.1 Recently, investigators in the United Kingdom (UK) published results of their research aimed at determining the association between the risk of VTE and the use of different types of HT.2
Details of the study
Vinogradova and colleagues used 2 UK primary care research databases, QResearch and Clinical Practice Research Datalink, to identify cases of incident VTE in general practice records, hospital admissions, and mortality records. They identified 80,396 women (aged 40 to 79 years) diagnosed with VTE between 1998 and 2017 and 391,494 control women matched by age and general practice. The mean age of the case and control women was approximately 64 years; the great majority of women were white. Analyses were adjusted for smoking, body mass index (BMI), family history of VTE, and comorbidities associated with VTE.
Types of HT used. The investigators found that 5,795 (7.2%) women with VTE and 21,670 (5.5%) controls were exposed to HT in the 90 days before the index date (the first date of VTE diagnosis for cases became the index date for matched controls). In those exposed to HT:
- 4,915 (85%) cases and 16,938 (78%) controls used oral preparations (including 102 [1.8%] cases and 312 [1.4%] controls who also had transdermal preparations)
- 880 (14%) cases and 4,731 (19%) controls used transdermal HT only.
Association of VTE with HT. Risk of VTE was increased with all oral HT formulations, including combined (estrogen plus progestogen) and estrogen-only preparations. Use of oral CEE (odds ratio [OR], 1.49) and estradiol (OR, 1.27) were both associated with an elevated risk of VTE (P<.05 for both comparisons). In contrast, use of transdermal estradiol (the great majority of which was administered by patch) was not associated with an elevated risk of VTE (OR, 0.96).
Direct comparison of oral estradiol and CEE found that the lower VTE risk with oral estradiol achieved statistical significance (P = .005). Direct comparison of oral and transdermal estrogen revealed an OR of 1.7 for the oral route of administration (P<.001)
Continue to: Study strengths and weaknesses
Study strengths and weaknesses
This study used data from the 2 largest primary care databases in the United Kingdom. Analyses were adjusted for numerous confounding factors, including acute and chronic conditions, lifestyle factors, and social deprivation. Additional sensitivity analyses were conducted and yielded results similar to those of the main analysis.
Several limitations could have resulted in some residual confounding bias. For example, drug exposure information was based on HT prescriptions and not actual use; data on some factors were not available, such as indications for HT, age at menopause, and education level; and for a small proportion of women, some data (smoking status, alcohol consumption, BMI) were missing and had to be imputed for analysis.
Although randomized trials have not compared VTE risk with oral versus transdermal estrogen, prior observational studies have consistently suggested that transdermal estrogen does not elevate VTE risk; this is consistent with the results from this large UK study. In my practice, congruent with the authors’ suggestions, I recommend transdermal rather than oral estrogen for patients (notably, those who are obese) who at baseline have risk factors for VTE. For menopausal women for whom use of oral estrogen is indicated, I recommend estradiol rather than CEE, since estradiol is less expensive and, based on this study’s results, may be safer than CEE.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases. BMJ. 2019;364:k4810.
The Women’s Health Initiative trials, in which menopausal women were randomly assigned to treatment with oral CEE or placebo, found that statistically the largest risk associated with menopausal hormone therapy (HT) was increased VTE.1 Recently, investigators in the United Kingdom (UK) published results of their research aimed at determining the association between the risk of VTE and the use of different types of HT.2
Details of the study
Vinogradova and colleagues used 2 UK primary care research databases, QResearch and Clinical Practice Research Datalink, to identify cases of incident VTE in general practice records, hospital admissions, and mortality records. They identified 80,396 women (aged 40 to 79 years) diagnosed with VTE between 1998 and 2017 and 391,494 control women matched by age and general practice. The mean age of the case and control women was approximately 64 years; the great majority of women were white. Analyses were adjusted for smoking, body mass index (BMI), family history of VTE, and comorbidities associated with VTE.
Types of HT used. The investigators found that 5,795 (7.2%) women with VTE and 21,670 (5.5%) controls were exposed to HT in the 90 days before the index date (the first date of VTE diagnosis for cases became the index date for matched controls). In those exposed to HT:
- 4,915 (85%) cases and 16,938 (78%) controls used oral preparations (including 102 [1.8%] cases and 312 [1.4%] controls who also had transdermal preparations)
- 880 (14%) cases and 4,731 (19%) controls used transdermal HT only.
Association of VTE with HT. Risk of VTE was increased with all oral HT formulations, including combined (estrogen plus progestogen) and estrogen-only preparations. Use of oral CEE (odds ratio [OR], 1.49) and estradiol (OR, 1.27) were both associated with an elevated risk of VTE (P<.05 for both comparisons). In contrast, use of transdermal estradiol (the great majority of which was administered by patch) was not associated with an elevated risk of VTE (OR, 0.96).
Direct comparison of oral estradiol and CEE found that the lower VTE risk with oral estradiol achieved statistical significance (P = .005). Direct comparison of oral and transdermal estrogen revealed an OR of 1.7 for the oral route of administration (P<.001)
Continue to: Study strengths and weaknesses
Study strengths and weaknesses
This study used data from the 2 largest primary care databases in the United Kingdom. Analyses were adjusted for numerous confounding factors, including acute and chronic conditions, lifestyle factors, and social deprivation. Additional sensitivity analyses were conducted and yielded results similar to those of the main analysis.
Several limitations could have resulted in some residual confounding bias. For example, drug exposure information was based on HT prescriptions and not actual use; data on some factors were not available, such as indications for HT, age at menopause, and education level; and for a small proportion of women, some data (smoking status, alcohol consumption, BMI) were missing and had to be imputed for analysis.
Although randomized trials have not compared VTE risk with oral versus transdermal estrogen, prior observational studies have consistently suggested that transdermal estrogen does not elevate VTE risk; this is consistent with the results from this large UK study. In my practice, congruent with the authors’ suggestions, I recommend transdermal rather than oral estrogen for patients (notably, those who are obese) who at baseline have risk factors for VTE. For menopausal women for whom use of oral estrogen is indicated, I recommend estradiol rather than CEE, since estradiol is less expensive and, based on this study’s results, may be safer than CEE.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
- Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women's Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310:1353-1368.
- Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases. BMJ. 2019;364:k4810.
- Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women's Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310:1353-1368.
- Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Use of hormone replacement therapy and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases. BMJ. 2019;364:k4810.
Ospemifene, an oral SERM for dyspareunia of menopause: Is it being underutilized?
Estrogen and androgen deficiency from menopause causes vulvovaginal and urogenital changes and a plethora of symptoms, most prominently dyspareunia.
Read the supplement and earn CME credit for your knowledge of the following:
- The pathophysiology of dyspareunia due to vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) of menopause.
- The underrecognition and undertreatment of dyspareunia due to VVA.
- Efficacy results of randomized placebo controlled trials of ospemifene.
- Adverse events associated with ospemifene.
- Safety data of ospemifine as well as other oral selective estrogen receptor modulators and estrogens.
Click on the image above or here to read the supplement and earn credit
Estrogen and androgen deficiency from menopause causes vulvovaginal and urogenital changes and a plethora of symptoms, most prominently dyspareunia.
Read the supplement and earn CME credit for your knowledge of the following:
- The pathophysiology of dyspareunia due to vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) of menopause.
- The underrecognition and undertreatment of dyspareunia due to VVA.
- Efficacy results of randomized placebo controlled trials of ospemifene.
- Adverse events associated with ospemifene.
- Safety data of ospemifine as well as other oral selective estrogen receptor modulators and estrogens.
Click on the image above or here to read the supplement and earn credit
Estrogen and androgen deficiency from menopause causes vulvovaginal and urogenital changes and a plethora of symptoms, most prominently dyspareunia.
Read the supplement and earn CME credit for your knowledge of the following:
- The pathophysiology of dyspareunia due to vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) of menopause.
- The underrecognition and undertreatment of dyspareunia due to VVA.
- Efficacy results of randomized placebo controlled trials of ospemifene.
- Adverse events associated with ospemifene.
- Safety data of ospemifine as well as other oral selective estrogen receptor modulators and estrogens.
Click on the image above or here to read the supplement and earn credit
Soy didn’t up all-cause mortality in breast cancer survivors
A cohort of Chinese women who are breast cancer survivors had no increased mortality from soy intake, according to a new study.
The work adds to the existing body of evidence that women with breast cancer, or risk for breast cancer, don’t need to modify their soy intake to mitigate risk, said the study’s first author, Suzanne C. Ho, PhD.
Speaking at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, Dr. Ho noted that the combination of increasing breast cancer incidence and improved outcome has resulted in larger numbers of breast cancer survivors in Hong Kong, where she is professor emerita at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
The prospective, ongoing study examines the association between soy intake pre- and postdiagnosis and total mortality for Chinese women who are breast cancer survivors. Dr. Ho said that she and her colleagues hypothesized that they would not see higher mortality among women who had higher soy intake – and this was the case.
Of 1,497 breast cancer survivors drawn from two facilities in Hong Kong, those who consumed higher quantities of dietary soy did not have increased risk of all-cause mortality, compared with those in the lowest tertile of soy consumption.
There are theoretical underpinnings for thinking that soy could be a player in cancer risk, but the biochemistry and epidemiology behind the studies are complicated. Estrogen plays a role in human breast cancer, and many modern breast cancer treatments actually dampen endogenous estrogens.
However, epidemiologic data have shown that consumption of soy-based foods – which contain phytoestrogens, primarily in the form of isoflavones – is inversely associated with developing breast cancer.
This is all part of why soy-based foods have been thought of as a mixed bag with regard to breast cancer: Soy isoflavones are, said Dr. Ho, “Natural estrogen receptor modulators that possess both estrogenlike and antiestrogenic properties.”
Other chemicals contained in soy may fight cancer, with effects that are antioxidative and strengthen immune response. Soy constituents also inhibit DNA topoisomerase I and II, proteases, tyrosine kinases, and inositol phosphate, effects that can slow tumor growth. Still, one soy isoflavone, genistein, actually can promote growth of estrogen-dependent tumors in rats, said Dr. Ho
Dr. Ho and her colleagues enrolled Hong Kong residents for the study of mortality among breast cancer survivors. Participants were included if they were Chinese, female, aged 24-77 years, and had their first primary breast cancer histologically confirmed within 12 months of entering the study. Cancer had to be graded below stage III.
Using a 109-item validated food questionnaire, investigators gathered information about participants’ soy intake and general diet for the year prior to breast cancer diagnosis. Other patient characteristics, relevant prognostic information from medical records, and anthropometric data were collected at baseline, and repeated at 18, 36, and 60 months.
The primary outcome measure – all-cause mortality during the follow-up period – was tracked for a mean 50.9 months, with a 78% retention rate for study participants, said Dr. Ho. In total, 96 patients died during follow-up, making up 5.9% of the premenopausal and 7% of the postmenopausal participants.
Statistical analysis corrected for potential confounders, including patient and disease characteristics and treatment modalities, as well as overall energy consumption.
Patients were evenly divided into tertiles of soy isoflavone intake, with cutpoints of 3.77 mg/1,000 kcal and 10.05 mg/1,000 kcal for the lower limit of the two higher tertiles. For the highest tertile, though, mean isoflavone intake was actually 20.87 mg/1,000 kcal.
Patient, disease, and treatment characteristics did not differ significantly among the tertiles.
An adjusted statistical analysis looked at pre- and postmenopausal women separately by tertile of soy isoflavone consumption, setting the hazard ratio for all-cause mortality at 1.00 for women in the lowest tertile of soy consumption.
For premenopausal women in the middle tertile, the HR was 0.45 (95% confidence interval, 0.20-1.00), and 0.86 for those in the highest tertile (95% CI, 0.43-1.72); 782 participants, in all, were premenopausal.
For the 715 postmenopausal women, the HR for those in the middle tertile of soy consumption was 0.94 (95% CI, 0.43-2.05), and 1.11 in the highest (95% CI, 0.54-2.29).
Taking all pre- and postmenopausal participants together, those in the middle tertile of soy isoflavone intake had an all-cause mortality HR of 0.63 (95% CI, 0.37-1.09). For the highest tertile of the full cohort, the HR was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.58-1.55).
Confidence intervals were wide in these findings, but Dr. Ho noted that “moderate soy food intake might be associated with better survival.”
“Prediagnosis soy intake did not increase the risk of all-cause mortality in breast cancer survivors,” said Dr. Ho, findings she called “consistent with the literature that soy consumption does not adversely effect breast cancer survival.”
The study is ongoing, she explained, and “longer follow-up will provide further evidence on the effect of pre- and postdiagnosis soy intake on breast cancer outcomes.”
The study had a homogeneous population of southern Chinese women, with fairly good retention and robust statistical adjustment for confounders. However, it wasn’t possible to assess bioavailability of isoflavones and their metabolites, which can vary according to individual microbiota. Also, researchers did not track whether patients used traditional Chinese medicine.
The World Cancer Research Fund International supported the study. Dr. Ho reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ho S et al. NAMS 2018, Abstract S-23.
A cohort of Chinese women who are breast cancer survivors had no increased mortality from soy intake, according to a new study.
The work adds to the existing body of evidence that women with breast cancer, or risk for breast cancer, don’t need to modify their soy intake to mitigate risk, said the study’s first author, Suzanne C. Ho, PhD.
Speaking at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, Dr. Ho noted that the combination of increasing breast cancer incidence and improved outcome has resulted in larger numbers of breast cancer survivors in Hong Kong, where she is professor emerita at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
The prospective, ongoing study examines the association between soy intake pre- and postdiagnosis and total mortality for Chinese women who are breast cancer survivors. Dr. Ho said that she and her colleagues hypothesized that they would not see higher mortality among women who had higher soy intake – and this was the case.
Of 1,497 breast cancer survivors drawn from two facilities in Hong Kong, those who consumed higher quantities of dietary soy did not have increased risk of all-cause mortality, compared with those in the lowest tertile of soy consumption.
There are theoretical underpinnings for thinking that soy could be a player in cancer risk, but the biochemistry and epidemiology behind the studies are complicated. Estrogen plays a role in human breast cancer, and many modern breast cancer treatments actually dampen endogenous estrogens.
However, epidemiologic data have shown that consumption of soy-based foods – which contain phytoestrogens, primarily in the form of isoflavones – is inversely associated with developing breast cancer.
This is all part of why soy-based foods have been thought of as a mixed bag with regard to breast cancer: Soy isoflavones are, said Dr. Ho, “Natural estrogen receptor modulators that possess both estrogenlike and antiestrogenic properties.”
Other chemicals contained in soy may fight cancer, with effects that are antioxidative and strengthen immune response. Soy constituents also inhibit DNA topoisomerase I and II, proteases, tyrosine kinases, and inositol phosphate, effects that can slow tumor growth. Still, one soy isoflavone, genistein, actually can promote growth of estrogen-dependent tumors in rats, said Dr. Ho
Dr. Ho and her colleagues enrolled Hong Kong residents for the study of mortality among breast cancer survivors. Participants were included if they were Chinese, female, aged 24-77 years, and had their first primary breast cancer histologically confirmed within 12 months of entering the study. Cancer had to be graded below stage III.
Using a 109-item validated food questionnaire, investigators gathered information about participants’ soy intake and general diet for the year prior to breast cancer diagnosis. Other patient characteristics, relevant prognostic information from medical records, and anthropometric data were collected at baseline, and repeated at 18, 36, and 60 months.
The primary outcome measure – all-cause mortality during the follow-up period – was tracked for a mean 50.9 months, with a 78% retention rate for study participants, said Dr. Ho. In total, 96 patients died during follow-up, making up 5.9% of the premenopausal and 7% of the postmenopausal participants.
Statistical analysis corrected for potential confounders, including patient and disease characteristics and treatment modalities, as well as overall energy consumption.
Patients were evenly divided into tertiles of soy isoflavone intake, with cutpoints of 3.77 mg/1,000 kcal and 10.05 mg/1,000 kcal for the lower limit of the two higher tertiles. For the highest tertile, though, mean isoflavone intake was actually 20.87 mg/1,000 kcal.
Patient, disease, and treatment characteristics did not differ significantly among the tertiles.
An adjusted statistical analysis looked at pre- and postmenopausal women separately by tertile of soy isoflavone consumption, setting the hazard ratio for all-cause mortality at 1.00 for women in the lowest tertile of soy consumption.
For premenopausal women in the middle tertile, the HR was 0.45 (95% confidence interval, 0.20-1.00), and 0.86 for those in the highest tertile (95% CI, 0.43-1.72); 782 participants, in all, were premenopausal.
For the 715 postmenopausal women, the HR for those in the middle tertile of soy consumption was 0.94 (95% CI, 0.43-2.05), and 1.11 in the highest (95% CI, 0.54-2.29).
Taking all pre- and postmenopausal participants together, those in the middle tertile of soy isoflavone intake had an all-cause mortality HR of 0.63 (95% CI, 0.37-1.09). For the highest tertile of the full cohort, the HR was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.58-1.55).
Confidence intervals were wide in these findings, but Dr. Ho noted that “moderate soy food intake might be associated with better survival.”
“Prediagnosis soy intake did not increase the risk of all-cause mortality in breast cancer survivors,” said Dr. Ho, findings she called “consistent with the literature that soy consumption does not adversely effect breast cancer survival.”
The study is ongoing, she explained, and “longer follow-up will provide further evidence on the effect of pre- and postdiagnosis soy intake on breast cancer outcomes.”
The study had a homogeneous population of southern Chinese women, with fairly good retention and robust statistical adjustment for confounders. However, it wasn’t possible to assess bioavailability of isoflavones and their metabolites, which can vary according to individual microbiota. Also, researchers did not track whether patients used traditional Chinese medicine.
The World Cancer Research Fund International supported the study. Dr. Ho reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ho S et al. NAMS 2018, Abstract S-23.
A cohort of Chinese women who are breast cancer survivors had no increased mortality from soy intake, according to a new study.
The work adds to the existing body of evidence that women with breast cancer, or risk for breast cancer, don’t need to modify their soy intake to mitigate risk, said the study’s first author, Suzanne C. Ho, PhD.
Speaking at the annual meeting of the North American Menopause Society, Dr. Ho noted that the combination of increasing breast cancer incidence and improved outcome has resulted in larger numbers of breast cancer survivors in Hong Kong, where she is professor emerita at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.
The prospective, ongoing study examines the association between soy intake pre- and postdiagnosis and total mortality for Chinese women who are breast cancer survivors. Dr. Ho said that she and her colleagues hypothesized that they would not see higher mortality among women who had higher soy intake – and this was the case.
Of 1,497 breast cancer survivors drawn from two facilities in Hong Kong, those who consumed higher quantities of dietary soy did not have increased risk of all-cause mortality, compared with those in the lowest tertile of soy consumption.
There are theoretical underpinnings for thinking that soy could be a player in cancer risk, but the biochemistry and epidemiology behind the studies are complicated. Estrogen plays a role in human breast cancer, and many modern breast cancer treatments actually dampen endogenous estrogens.
However, epidemiologic data have shown that consumption of soy-based foods – which contain phytoestrogens, primarily in the form of isoflavones – is inversely associated with developing breast cancer.
This is all part of why soy-based foods have been thought of as a mixed bag with regard to breast cancer: Soy isoflavones are, said Dr. Ho, “Natural estrogen receptor modulators that possess both estrogenlike and antiestrogenic properties.”
Other chemicals contained in soy may fight cancer, with effects that are antioxidative and strengthen immune response. Soy constituents also inhibit DNA topoisomerase I and II, proteases, tyrosine kinases, and inositol phosphate, effects that can slow tumor growth. Still, one soy isoflavone, genistein, actually can promote growth of estrogen-dependent tumors in rats, said Dr. Ho
Dr. Ho and her colleagues enrolled Hong Kong residents for the study of mortality among breast cancer survivors. Participants were included if they were Chinese, female, aged 24-77 years, and had their first primary breast cancer histologically confirmed within 12 months of entering the study. Cancer had to be graded below stage III.
Using a 109-item validated food questionnaire, investigators gathered information about participants’ soy intake and general diet for the year prior to breast cancer diagnosis. Other patient characteristics, relevant prognostic information from medical records, and anthropometric data were collected at baseline, and repeated at 18, 36, and 60 months.
The primary outcome measure – all-cause mortality during the follow-up period – was tracked for a mean 50.9 months, with a 78% retention rate for study participants, said Dr. Ho. In total, 96 patients died during follow-up, making up 5.9% of the premenopausal and 7% of the postmenopausal participants.
Statistical analysis corrected for potential confounders, including patient and disease characteristics and treatment modalities, as well as overall energy consumption.
Patients were evenly divided into tertiles of soy isoflavone intake, with cutpoints of 3.77 mg/1,000 kcal and 10.05 mg/1,000 kcal for the lower limit of the two higher tertiles. For the highest tertile, though, mean isoflavone intake was actually 20.87 mg/1,000 kcal.
Patient, disease, and treatment characteristics did not differ significantly among the tertiles.
An adjusted statistical analysis looked at pre- and postmenopausal women separately by tertile of soy isoflavone consumption, setting the hazard ratio for all-cause mortality at 1.00 for women in the lowest tertile of soy consumption.
For premenopausal women in the middle tertile, the HR was 0.45 (95% confidence interval, 0.20-1.00), and 0.86 for those in the highest tertile (95% CI, 0.43-1.72); 782 participants, in all, were premenopausal.
For the 715 postmenopausal women, the HR for those in the middle tertile of soy consumption was 0.94 (95% CI, 0.43-2.05), and 1.11 in the highest (95% CI, 0.54-2.29).
Taking all pre- and postmenopausal participants together, those in the middle tertile of soy isoflavone intake had an all-cause mortality HR of 0.63 (95% CI, 0.37-1.09). For the highest tertile of the full cohort, the HR was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.58-1.55).
Confidence intervals were wide in these findings, but Dr. Ho noted that “moderate soy food intake might be associated with better survival.”
“Prediagnosis soy intake did not increase the risk of all-cause mortality in breast cancer survivors,” said Dr. Ho, findings she called “consistent with the literature that soy consumption does not adversely effect breast cancer survival.”
The study is ongoing, she explained, and “longer follow-up will provide further evidence on the effect of pre- and postdiagnosis soy intake on breast cancer outcomes.”
The study had a homogeneous population of southern Chinese women, with fairly good retention and robust statistical adjustment for confounders. However, it wasn’t possible to assess bioavailability of isoflavones and their metabolites, which can vary according to individual microbiota. Also, researchers did not track whether patients used traditional Chinese medicine.
The World Cancer Research Fund International supported the study. Dr. Ho reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ho S et al. NAMS 2018, Abstract S-23.
REPORTING FROM NAMS 2018
Key clinical point: Soy consumption did not increase mortality risk in breast cancer survivors.
Major finding: The hazard ratios for all-cause mortality were 0.63 and 0.95 for the two highest tertiles of soy consumption.
Study details: An ongoing prospective cohort study of 1,497 female breast cancer survivors in Hong Kong.
Disclosures: The World Cancer Research Fund International supported the study. Dr. Ho reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ho S et al. NAMS 2018, Abstract S-23.
Most oral HRT linked to increased VTE risk
Transdermal hormone replacement therapy is associated with the lowest risk of venous thromboembolism, yet still is relatively underused compared to oral preparations, researchers say.
Writing in the BMJ, Yana Vinogradova, PhD, of the University of Nottingham (England) and her associates reported the results of two nested case-control studies of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) from Jan. 1998 to Feb. 2017 that altogether included 80,396 women aged 40-79 years with a primary diagnosis of VTE matched to 391,494 female controls.
Overall, 7% of the women with VTE had been exposed to HRT in the 90 days before the index date versus 5.5% of controls.
The greatest increase in risk of VTE, compared with no exposure, was seen with oral conjugated equine estrogen with medroxyprogesterone acetate, which was associated with a more than twofold increase in risk (odds ratio, 2.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.92-2.31; P less than .01).
However transdermal HRT use was not associated with any increase in risk, compared with no HRT exposure. The data even pointed to a slight decrease in risk, which the authors suggested may be the result of some residual confounding or indication bias.
Oral HRT generally was associated with a 58% increased risk of VTE, which amounted to a number needed to harm of 1,076 and nine extra cases of VTE per 10,000 women taking oral HRT.
Dr. Vinogradova and her colleagues noted that the vast majority of women in the study were being prescribed oral HRT for menopausal symptoms despite previous studies showing transdermal HRT has much lower risk.
“When women with menopausal symptoms already have an increased VTE risk because of comorbidities or obesity, these women and their doctors should give greater consideration to transdermal HRT,” they wrote.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, director of the menopause program and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented in an interview, “These data are tremendously reassuring. The reported findings are: 1) reaffirm what we have already known , i.e. that advancing age, higher body mass index, and higher doses of exogenous systemic estrogen therapy are associated with increased risk for VTE; 2) offer greater granularity in risk for VTE with different formulations of estrogens and progestins and different regimens than understood thus far, 3) reaffirm that, unlike oral estrogen, transdermal estrogen formulations in doses commonly utilized in clinical practice are not associated with VTE risk, and 4) provide reassurance that the absolute risk, while exaggerated with oral estrogen or combination estrogen and progestin use, is nonetheless small as reflected in the number needed to harm with oral hormone therapy being 1,076, and the number of extra VTE cases attributable to oral HT being 9 per 10,000 woman years.
“The authors are to be commended on this massive analytic undertaking that allows an improved understanding of HRT-related risk for VTE and offers meaningful guidance to the practitioner,” said Dr. Pal, who was not involved in the study.*
Estrogen-only preparations had a 40% higher risk and combined preparations had a 73% higher risk, compared with no exposure.
In estrogen-only preparations, the lowest risk was seen with estradiol, compared with conjugated equine estrogens or combined preparations.
The lowest risk of VTE among oral preparations was seen with estradiol plus dydrogesterone, which only showed a nonsignificant 18% increase in risk.
In an attempt to account for possible increased risk of VTE, the authors conducted a sensitivity analysis in a subgroup of women who had not previously used anticoagulants, but they found similar results to the main analysis.
“This sensitivity analysis indicates that most of the excluded women had probably used anticoagulants because of atrial fibrillation or hip replacement operations rather than an earlier unrecorded VTE,” they wrote.
One author declared directorship of a clinical software company, but no other conflicts of interest were declared. There was no external funding. Dr. Pal reported that she was a coinvestigator in the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study and on an AMAG Pharmaceuticals advisory board and member of their speaker’s bureau.
SOURCE: Vinogradova Y et al. BMJ. 2019 Jan 9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k4810.
*This article was updated 1/11/19.
Transdermal hormone replacement therapy is associated with the lowest risk of venous thromboembolism, yet still is relatively underused compared to oral preparations, researchers say.
Writing in the BMJ, Yana Vinogradova, PhD, of the University of Nottingham (England) and her associates reported the results of two nested case-control studies of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) from Jan. 1998 to Feb. 2017 that altogether included 80,396 women aged 40-79 years with a primary diagnosis of VTE matched to 391,494 female controls.
Overall, 7% of the women with VTE had been exposed to HRT in the 90 days before the index date versus 5.5% of controls.
The greatest increase in risk of VTE, compared with no exposure, was seen with oral conjugated equine estrogen with medroxyprogesterone acetate, which was associated with a more than twofold increase in risk (odds ratio, 2.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.92-2.31; P less than .01).
However transdermal HRT use was not associated with any increase in risk, compared with no HRT exposure. The data even pointed to a slight decrease in risk, which the authors suggested may be the result of some residual confounding or indication bias.
Oral HRT generally was associated with a 58% increased risk of VTE, which amounted to a number needed to harm of 1,076 and nine extra cases of VTE per 10,000 women taking oral HRT.
Dr. Vinogradova and her colleagues noted that the vast majority of women in the study were being prescribed oral HRT for menopausal symptoms despite previous studies showing transdermal HRT has much lower risk.
“When women with menopausal symptoms already have an increased VTE risk because of comorbidities or obesity, these women and their doctors should give greater consideration to transdermal HRT,” they wrote.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, director of the menopause program and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented in an interview, “These data are tremendously reassuring. The reported findings are: 1) reaffirm what we have already known , i.e. that advancing age, higher body mass index, and higher doses of exogenous systemic estrogen therapy are associated with increased risk for VTE; 2) offer greater granularity in risk for VTE with different formulations of estrogens and progestins and different regimens than understood thus far, 3) reaffirm that, unlike oral estrogen, transdermal estrogen formulations in doses commonly utilized in clinical practice are not associated with VTE risk, and 4) provide reassurance that the absolute risk, while exaggerated with oral estrogen or combination estrogen and progestin use, is nonetheless small as reflected in the number needed to harm with oral hormone therapy being 1,076, and the number of extra VTE cases attributable to oral HT being 9 per 10,000 woman years.
“The authors are to be commended on this massive analytic undertaking that allows an improved understanding of HRT-related risk for VTE and offers meaningful guidance to the practitioner,” said Dr. Pal, who was not involved in the study.*
Estrogen-only preparations had a 40% higher risk and combined preparations had a 73% higher risk, compared with no exposure.
In estrogen-only preparations, the lowest risk was seen with estradiol, compared with conjugated equine estrogens or combined preparations.
The lowest risk of VTE among oral preparations was seen with estradiol plus dydrogesterone, which only showed a nonsignificant 18% increase in risk.
In an attempt to account for possible increased risk of VTE, the authors conducted a sensitivity analysis in a subgroup of women who had not previously used anticoagulants, but they found similar results to the main analysis.
“This sensitivity analysis indicates that most of the excluded women had probably used anticoagulants because of atrial fibrillation or hip replacement operations rather than an earlier unrecorded VTE,” they wrote.
One author declared directorship of a clinical software company, but no other conflicts of interest were declared. There was no external funding. Dr. Pal reported that she was a coinvestigator in the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study and on an AMAG Pharmaceuticals advisory board and member of their speaker’s bureau.
SOURCE: Vinogradova Y et al. BMJ. 2019 Jan 9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k4810.
*This article was updated 1/11/19.
Transdermal hormone replacement therapy is associated with the lowest risk of venous thromboembolism, yet still is relatively underused compared to oral preparations, researchers say.
Writing in the BMJ, Yana Vinogradova, PhD, of the University of Nottingham (England) and her associates reported the results of two nested case-control studies of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) from Jan. 1998 to Feb. 2017 that altogether included 80,396 women aged 40-79 years with a primary diagnosis of VTE matched to 391,494 female controls.
Overall, 7% of the women with VTE had been exposed to HRT in the 90 days before the index date versus 5.5% of controls.
The greatest increase in risk of VTE, compared with no exposure, was seen with oral conjugated equine estrogen with medroxyprogesterone acetate, which was associated with a more than twofold increase in risk (odds ratio, 2.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.92-2.31; P less than .01).
However transdermal HRT use was not associated with any increase in risk, compared with no HRT exposure. The data even pointed to a slight decrease in risk, which the authors suggested may be the result of some residual confounding or indication bias.
Oral HRT generally was associated with a 58% increased risk of VTE, which amounted to a number needed to harm of 1,076 and nine extra cases of VTE per 10,000 women taking oral HRT.
Dr. Vinogradova and her colleagues noted that the vast majority of women in the study were being prescribed oral HRT for menopausal symptoms despite previous studies showing transdermal HRT has much lower risk.
“When women with menopausal symptoms already have an increased VTE risk because of comorbidities or obesity, these women and their doctors should give greater consideration to transdermal HRT,” they wrote.
Lubna Pal, MBBS, director of the menopause program and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., commented in an interview, “These data are tremendously reassuring. The reported findings are: 1) reaffirm what we have already known , i.e. that advancing age, higher body mass index, and higher doses of exogenous systemic estrogen therapy are associated with increased risk for VTE; 2) offer greater granularity in risk for VTE with different formulations of estrogens and progestins and different regimens than understood thus far, 3) reaffirm that, unlike oral estrogen, transdermal estrogen formulations in doses commonly utilized in clinical practice are not associated with VTE risk, and 4) provide reassurance that the absolute risk, while exaggerated with oral estrogen or combination estrogen and progestin use, is nonetheless small as reflected in the number needed to harm with oral hormone therapy being 1,076, and the number of extra VTE cases attributable to oral HT being 9 per 10,000 woman years.
“The authors are to be commended on this massive analytic undertaking that allows an improved understanding of HRT-related risk for VTE and offers meaningful guidance to the practitioner,” said Dr. Pal, who was not involved in the study.*
Estrogen-only preparations had a 40% higher risk and combined preparations had a 73% higher risk, compared with no exposure.
In estrogen-only preparations, the lowest risk was seen with estradiol, compared with conjugated equine estrogens or combined preparations.
The lowest risk of VTE among oral preparations was seen with estradiol plus dydrogesterone, which only showed a nonsignificant 18% increase in risk.
In an attempt to account for possible increased risk of VTE, the authors conducted a sensitivity analysis in a subgroup of women who had not previously used anticoagulants, but they found similar results to the main analysis.
“This sensitivity analysis indicates that most of the excluded women had probably used anticoagulants because of atrial fibrillation or hip replacement operations rather than an earlier unrecorded VTE,” they wrote.
One author declared directorship of a clinical software company, but no other conflicts of interest were declared. There was no external funding. Dr. Pal reported that she was a coinvestigator in the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study and on an AMAG Pharmaceuticals advisory board and member of their speaker’s bureau.
SOURCE: Vinogradova Y et al. BMJ. 2019 Jan 9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k4810.
*This article was updated 1/11/19.
FROM THE BMJ
Key clinical point: Transdermal HRT is not associated with any increase in VTE risk.
Major finding: Conjugated equine estrogen with medroxyprogesterone shows a twofold increase in VTE risk.
Study details: Nested case-control study in 80,396 women and 391,494 female controls.
Disclosures: One author declared directorship of a clinical software company, but no other conflicts of interest were declared. There was no external funding. Dr. Pal reported that she was a coinvestigator in the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study and on an AMAG Pharmaceuticals advisory board and member of their speaker’s bureau.
Source: Vinogradova Y et al. BMJ. 2019 Jan 9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k4810
How does HT in recent and 10+ years past menopause affect atherosclerosis progression?
Expert Commentary
Sriprasert I, Hodis HN, Karim R, et al. Differential effect of plasma estradiol on subclinical atherosclerosis progression in early versus late postmenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:293-300. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01600.
In 2016, the primary findings of the Early versus Late Intervention Trial with Estradiol (ELITE) demonstrated that oral E2 administered to women who were less than 6 years postmenopause slowed progression of subclinical atherosclerosis as assessed by carotid artery intima-media thickness (CIMT), while it had no effect in women who were at least 10 years postmenopause.1
That trial included 643 healthy women without cardiovascular disease who at enrollment had a median age of 55.4 years in the early postmenopause group (median 3.5 years since menopause) and 63.6 years in the late postmenopause group (median 14.3 years since menopause). The study medications were oral estradiol 1 mg daily plus progesterone vaginal gel for women with a uterus or placebo and placebo gel for a median of 5 years.
The investigators found also that, in contrast with CIMT, cardiac computed tomography (CT) measures of atherosclerosis did not differ significantly between the estradiol and placebo groups, regardless of age.1
Posttrial data analysis revealed a new finding
In a secondary analysis of data from the ELITE trial, Sriprasert and colleagues dug deeper to assess the impact of plasma E2 levels on progression of subclinical atherosclerosis.2
Among 596 women (69.6% white non-Hispanic, 8.7% black, 13.3% Hispanic, and 8.4% Asian/Pacific Islander), E2 levels were available in 248 women in early postmenopause (mean age, 54.7 years) and 348 women in late postmenopause (median age, 63.6 years).
For women in the estradiol-treated group, mean E2 levels during the trial as well as change of E2 levels from baseline were significantly higher in the early postmenopause group than in the late postmenopause group, even though both groups had similar adherence based on pill count. For those in the placebo group, mean E2 levels and change of E2 levels from baseline were equivalent in early and late menopause.
In the E2-treated group and the placebo group combined, the mixed effects analysis of the CIMT progression rate (based on the mean E2 level during the trial) demonstrated that a higher level of E2 was inversely associated with the CIMT progression rate in early postmenopausal women (beta coefficient = -0.04 [95% confidence interval (CI), -0.09 to -0.001] μm CIMT per year per 1 pg/mL estradiol; P = .04). However, a higher level of E2 was positively associated (beta coefficient = 0.063 [95% CI, 0.018 to 0.107] μm CIMT per year per 1 pg/mL estradiol; P = .006) with CIMT progression rate in the late postmenopausal women.
Continue to: Bottom line...
Bottom line. E2 levels resulting from administration of oral estradiol were inversely associated with atherosclerosis progression in women in early menopause, but they were positively associated with progression in late postmenopause participants.
WHAT THIS EVIDENCE MEANS FOR PRACTICE
These new findings from a posttrial analysis of ELITE data provide yet further support for the hormone therapy (HT) “timing hypothesis,” which postulates that HT slows atherosclerosis progression in recently menopausal women but has neutral or adverse effects in women who are at least a decade past menopause onset. As the authors suggest, the favorable vascular effects of E2 appear limited to those women (most often in early menopause) who have not yet developed atherosclerosis. Whether or not HT should be considered for cardioprotection remains unresolved (and controversial). By contrast, these data, along with findings from the Women’s Health Initiative,3 provide reassurance regarding the cardiovascular safety of HT when prescribed for recently menopausal women with bothersome vasomotor symptoms.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
References
1. Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Henderson VW, et al; for the ELITE Research Group. Vascular effects of early versus late postmenopausal treatment with estradiol. N Engl J Med. 2016;374;1221-1231.
2. Sriprasert I, Hodis HN, Karim R, et al. Differential effect of plasma estradiol on subclinical atherosclerosis progression in early versus late postmenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:293-300. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01600.
3. Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310:1353-1368.
Expert Commentary
Sriprasert I, Hodis HN, Karim R, et al. Differential effect of plasma estradiol on subclinical atherosclerosis progression in early versus late postmenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:293-300. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01600.
In 2016, the primary findings of the Early versus Late Intervention Trial with Estradiol (ELITE) demonstrated that oral E2 administered to women who were less than 6 years postmenopause slowed progression of subclinical atherosclerosis as assessed by carotid artery intima-media thickness (CIMT), while it had no effect in women who were at least 10 years postmenopause.1
That trial included 643 healthy women without cardiovascular disease who at enrollment had a median age of 55.4 years in the early postmenopause group (median 3.5 years since menopause) and 63.6 years in the late postmenopause group (median 14.3 years since menopause). The study medications were oral estradiol 1 mg daily plus progesterone vaginal gel for women with a uterus or placebo and placebo gel for a median of 5 years.
The investigators found also that, in contrast with CIMT, cardiac computed tomography (CT) measures of atherosclerosis did not differ significantly between the estradiol and placebo groups, regardless of age.1
Posttrial data analysis revealed a new finding
In a secondary analysis of data from the ELITE trial, Sriprasert and colleagues dug deeper to assess the impact of plasma E2 levels on progression of subclinical atherosclerosis.2
Among 596 women (69.6% white non-Hispanic, 8.7% black, 13.3% Hispanic, and 8.4% Asian/Pacific Islander), E2 levels were available in 248 women in early postmenopause (mean age, 54.7 years) and 348 women in late postmenopause (median age, 63.6 years).
For women in the estradiol-treated group, mean E2 levels during the trial as well as change of E2 levels from baseline were significantly higher in the early postmenopause group than in the late postmenopause group, even though both groups had similar adherence based on pill count. For those in the placebo group, mean E2 levels and change of E2 levels from baseline were equivalent in early and late menopause.
In the E2-treated group and the placebo group combined, the mixed effects analysis of the CIMT progression rate (based on the mean E2 level during the trial) demonstrated that a higher level of E2 was inversely associated with the CIMT progression rate in early postmenopausal women (beta coefficient = -0.04 [95% confidence interval (CI), -0.09 to -0.001] μm CIMT per year per 1 pg/mL estradiol; P = .04). However, a higher level of E2 was positively associated (beta coefficient = 0.063 [95% CI, 0.018 to 0.107] μm CIMT per year per 1 pg/mL estradiol; P = .006) with CIMT progression rate in the late postmenopausal women.
Continue to: Bottom line...
Bottom line. E2 levels resulting from administration of oral estradiol were inversely associated with atherosclerosis progression in women in early menopause, but they were positively associated with progression in late postmenopause participants.
WHAT THIS EVIDENCE MEANS FOR PRACTICE
These new findings from a posttrial analysis of ELITE data provide yet further support for the hormone therapy (HT) “timing hypothesis,” which postulates that HT slows atherosclerosis progression in recently menopausal women but has neutral or adverse effects in women who are at least a decade past menopause onset. As the authors suggest, the favorable vascular effects of E2 appear limited to those women (most often in early menopause) who have not yet developed atherosclerosis. Whether or not HT should be considered for cardioprotection remains unresolved (and controversial). By contrast, these data, along with findings from the Women’s Health Initiative,3 provide reassurance regarding the cardiovascular safety of HT when prescribed for recently menopausal women with bothersome vasomotor symptoms.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
References
1. Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Henderson VW, et al; for the ELITE Research Group. Vascular effects of early versus late postmenopausal treatment with estradiol. N Engl J Med. 2016;374;1221-1231.
2. Sriprasert I, Hodis HN, Karim R, et al. Differential effect of plasma estradiol on subclinical atherosclerosis progression in early versus late postmenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:293-300. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01600.
3. Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310:1353-1368.
Expert Commentary
Sriprasert I, Hodis HN, Karim R, et al. Differential effect of plasma estradiol on subclinical atherosclerosis progression in early versus late postmenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:293-300. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01600.
In 2016, the primary findings of the Early versus Late Intervention Trial with Estradiol (ELITE) demonstrated that oral E2 administered to women who were less than 6 years postmenopause slowed progression of subclinical atherosclerosis as assessed by carotid artery intima-media thickness (CIMT), while it had no effect in women who were at least 10 years postmenopause.1
That trial included 643 healthy women without cardiovascular disease who at enrollment had a median age of 55.4 years in the early postmenopause group (median 3.5 years since menopause) and 63.6 years in the late postmenopause group (median 14.3 years since menopause). The study medications were oral estradiol 1 mg daily plus progesterone vaginal gel for women with a uterus or placebo and placebo gel for a median of 5 years.
The investigators found also that, in contrast with CIMT, cardiac computed tomography (CT) measures of atherosclerosis did not differ significantly between the estradiol and placebo groups, regardless of age.1
Posttrial data analysis revealed a new finding
In a secondary analysis of data from the ELITE trial, Sriprasert and colleagues dug deeper to assess the impact of plasma E2 levels on progression of subclinical atherosclerosis.2
Among 596 women (69.6% white non-Hispanic, 8.7% black, 13.3% Hispanic, and 8.4% Asian/Pacific Islander), E2 levels were available in 248 women in early postmenopause (mean age, 54.7 years) and 348 women in late postmenopause (median age, 63.6 years).
For women in the estradiol-treated group, mean E2 levels during the trial as well as change of E2 levels from baseline were significantly higher in the early postmenopause group than in the late postmenopause group, even though both groups had similar adherence based on pill count. For those in the placebo group, mean E2 levels and change of E2 levels from baseline were equivalent in early and late menopause.
In the E2-treated group and the placebo group combined, the mixed effects analysis of the CIMT progression rate (based on the mean E2 level during the trial) demonstrated that a higher level of E2 was inversely associated with the CIMT progression rate in early postmenopausal women (beta coefficient = -0.04 [95% confidence interval (CI), -0.09 to -0.001] μm CIMT per year per 1 pg/mL estradiol; P = .04). However, a higher level of E2 was positively associated (beta coefficient = 0.063 [95% CI, 0.018 to 0.107] μm CIMT per year per 1 pg/mL estradiol; P = .006) with CIMT progression rate in the late postmenopausal women.
Continue to: Bottom line...
Bottom line. E2 levels resulting from administration of oral estradiol were inversely associated with atherosclerosis progression in women in early menopause, but they were positively associated with progression in late postmenopause participants.
WHAT THIS EVIDENCE MEANS FOR PRACTICE
These new findings from a posttrial analysis of ELITE data provide yet further support for the hormone therapy (HT) “timing hypothesis,” which postulates that HT slows atherosclerosis progression in recently menopausal women but has neutral or adverse effects in women who are at least a decade past menopause onset. As the authors suggest, the favorable vascular effects of E2 appear limited to those women (most often in early menopause) who have not yet developed atherosclerosis. Whether or not HT should be considered for cardioprotection remains unresolved (and controversial). By contrast, these data, along with findings from the Women’s Health Initiative,3 provide reassurance regarding the cardiovascular safety of HT when prescribed for recently menopausal women with bothersome vasomotor symptoms.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD
References
1. Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Henderson VW, et al; for the ELITE Research Group. Vascular effects of early versus late postmenopausal treatment with estradiol. N Engl J Med. 2016;374;1221-1231.
2. Sriprasert I, Hodis HN, Karim R, et al. Differential effect of plasma estradiol on subclinical atherosclerosis progression in early versus late postmenopause. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:293-300. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01600.
3. Manson JE, Chlebowski RT, Stefanick ML, et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trials. JAMA. 2013;310:1353-1368.
Managing menopausal vasomotor and genitourinary symptoms after breast cancer
Breast cancer survivors entering menopause face the risk of several menopausal symptoms:
- Hot flashes, the most common symptom, occur in more than 75% of women during menopause and have the potential to persist for as long as 15 years.1 That lengthy interval becomes a major issue for patients, especially when hot flashes are associated with other menopausal symptoms, including sleep disruption, difficulty concentrating, and emotional instability (crying, irritability).
Painful intercourse and loss of interest in sexual activity often develop as a result of vaginal atrophy and dryness.
- Urinary tract symptoms include urgency and, compared to the patient’s history, more frequent infections.
- Bone loss is a concern for many women after breast cancer, especially if they are, or have been, on aromatase inhibitor therapy.
Depression might be related to hormonal changes due to menopause or hormonal therapies, a consequence of merely having a diagnosis of cancer, or an adverse effect of chemotherapy.
In this brief review, I’ll examine options for treating symptoms of menopause by strategy—lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter treatments, and prescription drugs. Separately, I’ll look at options for managing genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM).
CASE 1
Rose is a 56-year-old woman who presents to clinic with a new breast mass, felt on breast self exam. The mass is about 1 cm, mobile, and firm. Diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound confirm a worrisome mass; biopsy returns positive with a 9-mm invasive, estrogen-receptor positive, ductal carcinoma with negative sentinel nodes at the time of lumpectomy. Radiation therapy was completed. She then met with oncology and decided against chemotherapy. Instead, she began an aromatase inhibitor 3 months ago. Bone density showed osteopenia. She presents to your office reporting frequent bothersome hot flashes and disrupted sleep.
Strategy #1: Lifestyle adaptations
First-line interventions for menopausal women who have had breast cancer usually involve taking a critical look at lifestyle and undertaking modifications that can alleviate discomfort. Because overall health is important for women who have had breast cancer, you should, across the spectrum of patients, encourage them to:
- increase physical activity
- reduce body weight by approximately 10% (if overweight or obese)
- reduce alcohol consumption
- stop smoking
- ensure adequate intake of calcium (1,200 mg, preferably by diet)
- optimize the level of vitamin D, including by increasing intake of fresh fish, eggs, and numerous other fortified foods.
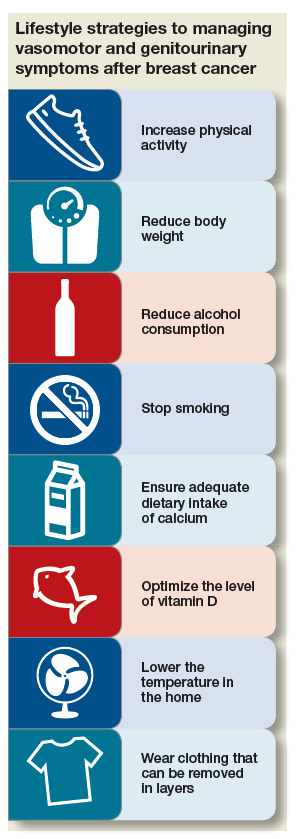
The value of nondrug therapy for hot flashes is difficult to prove. Certain lifestyle changes are sensible, even if not evidence-based, and will help some women (but not others). We suggest that patients try lowering the temperature in the home (65–68˚ at night); running a fan; wearing clothing that can be removed in layers; and avoiding triggers such as spicy food, alcohol, cigarettes, and hot drinks. Hypnosis and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have been shown to help in clinical trials. Measures with benefit and minimal risks, but effectiveness not established, include acupuncture (sham worked as well as traditional), exercise, yoga, paced respiration, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction.
Continue to: Strategy #2: OTC compounds...
Strategy #2: OTC compounds
Over-the-counter products—from soy products to black cohosh to flax seed, and including dong quai, evening primrose oil, maca, omegas, pollen extract, ginseng, and red clover,2 or several compounds formulated in combination—have not been proven to be of more benefit for relieving symptoms of menopause than placebo in randomized trials, and thus might or might not be effective in a given patient. S-equol, a metabolite of a soy isoflavone taken by women who are non-equol producers, is available under the trade name Equelle and has shown some benefit. Note: There is concern that supplements that contain estrogen-like compounds, like soy products, might actually increase the risk of breast cancer. Dietary soy is not felt to be a concern.
Ask questions about the severity of a patient’s hot flashes. When a patient reports hot flashes, and is requesting help to relieve her discomfort, inquire 1) how often she has hot flashes, 2) how severe they are, and 3) how bothered she is by them (not all women are equally troubled, of course). The patient’s answers to these questions will help you decide which treatment option to offer, based on evidence and your experience.
CASE 1 Continued
Rose tried black cohosh OTC without improvement. She was interested in hypnosis but did not find it effective for her. She returned 3 months later stating that she is miserable, exhausted, not getting enough sleep, and her hot flashes and night sweats are affecting both her work and her relationship.
Strategy #3: Prescription medication
When addressing hot flashes, consider whether they occur more at night or during the day, or do not follow a day–night pattern. For women whose hot flashes occur mostly at night, and might therefore make sleeping difficult and cause fatigue and irritability, gabapentin, taken approximately 1 hour before bed, can be helpful. If tolerated without excessive somnolence the next day, the dose can be increased at night or additional doses provided during the day depending on hot flash response. For women who have hot flashes day and night, we often prescribe a low-dose antidepressant from the selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class.
When prescribing an antidepressant, we make a distinction between breast cancer patients who are taking tamoxifen and those who are not, to avoid cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitors in women taking tamoxifen.3 Better choices for women taking tamoxifen include desvenlafaxine, venlafaxine, escitalopram, or gabapentin or pregabalin.
For women with breast cancer who are taking an aromatase inhibitor, and who are also experiencing mood changes with their hot flashes, we often choose a trial of a low-dose antidepressant, either an SSRI or SNRI. One drug is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of hot flashes (but not for mood disorder). This is low-dose salt of paroxetine, 7.5 mg/d, which has the advantage of exerting no adverse effect on libido or weight (but is sometimes difficult to obtain because it is a branded product that might not be covered, or not covered fully, by a given patient’s insurance plan). Other antidepressants can be used in doses lower than needed for depression, with more rapid onset of effect on hot flashes, often within 2 weeks.
Last, transdermal clonidine, an antihypertensive, also has been found to relieve hot flashes.
Continue to: Not a recommended strategy: Systemic hormone therapy
Not a recommended strategy: Systemic hormone therapy
Although hormone therapy is, in general, the gold standard for alleviating hot flashes, it is contraindicated in most women with breast cancer.4 At our institution, we avoid systemic hormone therapy for hot flashes in almost all breast cancer patients.
CASE 2
Sarah first presented with hot flashes that improved while taking escitalopram 10 mg. Her night sweats persisted, however. Gabapentin 300 mg was added to take nightly. With this regimen, she finally felt that she was coping better. Six months later, she reported that she and her long-term partner had not been able to resume vaginal intercourse post–breast cancer treatment because of pain.
The challenge of managing GSM
What if your patient says, “Doctor, I’m really doing OK with my hot flashes, but sex has become painful. I don’t have any interest. I have vaginal dryness, and it’s affecting my quality of life”?
Studies have shown that GSM affects up to 50% of women, and even more than that among women who have had breast cancer.5 The condition interferes with sexual intimacy, disrupts quality of life, and can sour a partnership—significant quality-of-life concerns for breast cancer survivors.
For mild symptoms, encourage patients to apply a lubricant just before intercourse or a vaginal moisturizer twice weekly; moisturizers improve vaginal pH, too. These treatments do not fix the problem of a lack of superficial cells due to estrogen loss, however; to accomplish that, consider prescribing low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy or intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). This strategy is felt to be safe for many breast cancer survivors, as systemic absorption of estrogen is minimal if dosed low, keeping levels in the postmenopausal range.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the Endocrine Society agree that vaginal estrogen therapy may be a good option for many women with breast cancer for whom moisturizers and lubricants are inadequate.6 Delivery options include vaginal creams, tablets, suppositories used 2 or 3 times per week, or the low-dose vaginal estrogen ring, replaced every 3 months. We are concerned about using vaginal estrogen in women who have had aromatase inhibitor (AI) therapy; their estrogen levels are so low that absorbing even a small amount might make a difference in terms of effectiveness of AI. For women who need more than lubricants or vaginal moisturizers, particularly those taking anti-estrogen therapy (aromatase therapy), the use of low-dose vaginal hormones may be considered on an individual basis, but should include the oncologist in decision making.1,3
Beyond low-dose vaginal estrogen therapies, there are additional options that can be considered but with less supporting data for treating GSM in women with breast cancer.
Oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM; Osphena), might be neutral or even protective in its effect on the breast, as demonstrated in preclinical trials.7 In human trials, the drug is approved only for painful intercourse, not for loss of libido, and has not been tested in breast cancer patients.
Intravaginal DHEA (Prasterone), has been on the market for almost 1 year. The drug is approved for treating painful intercourse, but it also reverses vaginal atrophy and alleviates urinary symptoms. Because DHEA is a prohormone, it is converted to estrogen and androgen in the vagina. Again, absorption appears minimal. Intravaginal DHEA does not have the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) black-box warning that vaginal estrogen products do, but it is accompanied by a warning that it has not been tested in women with breast cancer.
Tissue selective estrogen receptor modulator is a conjugated estrogen combined with a third-generation SERM bazedoxifene, which treats hot flashes and reverses vaginal atrophy. This new systemic agent is probably neutral on the breast (at least that is the finding in clinical trials at 2 years8); again, however, it has not been tested in patients with breast cancer.
Continue to: Nonhormone therapies...
Nonhormone therapies
Topical lidocaine for insertional dyspareunia has been studied in postmenopausal women with breast cancer with severe GSM, dyspareunia, increased sexual distress scores, or abnormal sexual function with improvement seen using 4% aqueous lidocaine versus saline applied with a cotton ball to the vestibule for 3 minutes before vaginal penetration.9
Vaginal laser therapy has the potential to ameliorate distressing GSM without the need for local hormone intervention; however, placebo or active-controlled trials and long-term safety follow-up are needed.5
Newly arrived and on the horizon
Where does this review of available treatments leave us? Regrettably, with many women who experience painful intercourse and vaginal dryness despite what is available for treating their problems, and who continue looking to medical science and women’s health care for new options. So, what is coming next for these suffering patients? Here is a quick and selective run-through:
KNDy neurons. For hot flashes, there is the promise of nonhormonal treatment using these neurons, believed to be involved in reproduction by triggering expression of various compounds— particularly neurokinin B, which mediates hot flashes.1
Estetrol. In testing for use in treating hot flashes and its effect on GSM is this pregnancy-associated natural hormone that, importantly, did not stimulate breast cancer in a rat model.2 More evidence of efficacy is needed.
Lasers. For vaginal atrophy, many women are choosing treatment with the laser. Keep in mind, however, that, although lasers are FDA-approved devices, they do not have the FDA’s endorsement for use in vaginal atrophy, and have not been well-tested for their effectiveness for this indication in women with breast cancer who have taken an aromatase inhibitor. ACOG, NAMS, and the Endocrine Society have urged that additional trials be conducted, and have stated that the laser for vaginal atrophy cannot be recommended until there are more data on safety and efficacy.2
Lower-dose soft-gel vaginal estrogen suppositories have recently been approved by the FDA at 4 and 10 µg.3 The formulations are only minimally absorbed, potentially making them a good option for women who have had breast cancer.
Lasofoxifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator not yet approved by the FDA, has been shown to ameliorate vaginal changes.4 The drug is neutral or protective on the breast, but is now being tested in women with resistant breast cancer and unlikely to become available for GSM.
References
1. Anderson RA, Skorupskaite K, Sassarini J. The neurokinin B pathway in the treatment of menopausal hot flushes. Climacteric. 2018;1-4.
2. Gérard C, Mestdagt M, Tskitishvili E, et al. Combined estrogenic and anti-estrogenic properties of estetrol on breast cancer may provide a safe therapeutic window for the treatment of menopausal symptoms. Oncotarget. 2015;6(19):17621–17636.
3. Simon JA, Archer DF, Constantine GD, et al. A vaginal estradiol softgel capsule, TX-004HR, has negligible to very low systemic absorption of estradiol: efficacy and pharmacokinetic data review. Maturitas. 2017;99:51-58.
4. Bachmann G, Gass M, Kagan R, et al. Lasofoxifene (LASO), a next generation selective estrogen response modulator (SERM), improves dyspareunia in postmenopausal women with vaginal atrophy (VA). Menopause. 2005;12:238.
Treatment begins with a conversation
Most importantly, we need to listen to our patients in discomfort because of their menopausal symptoms. Consider proceeding along these lines: “You’ve been treated for breast cancer; now, let’s look at the medical issues that are affecting your quality of life. Are you depressed? Are you having hot flashes? Are you getting enough sleep? Have you stopped having sex or not restarted after your breast cancer treatment? Are you having painful sex or avoiding sex due to fear of pain? Let’s discuss options and work with your oncologist to try to relieve your symptoms and make your life better.”
First-line therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women with a history of breast cancer should start with lifestyle changes and nonhormone therapies. For GSM, lubricants and vaginal moisturizers should be tried first and may be effective. Reassure patients that there are many treatment options, even though not all of them have been well-tested in breast cancer patients, and that new modalities are under investigation and review (see “Newly arrived and on the horizon,”). Become familiar with published data on the safety and effectiveness of the range of available treatments; guide patients through the process of finding what works best for them; and invite their oncologist into the therapeutic partnership. If you do not feel comfortable with these issues in women who are breast cancer survivors, find a menopause specialist to help, available by zip code at Find a Provider, http://www.menopause.org.
1. The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
2. McGarry K, Geary M, Gopinath V. Beyond estrogen: treatment options for hot flashes. Clin Ther. 2018;40(10):1778-1786.
3. Santen RJ, Stuenkel CA, Davis SR, et al. Managing menopausal symptoms and associated clinical issues in breast cancer survivors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:3647-3661.
4. Faubion SS, Loprinzi CL, Ruddy KJ. Management of hormone deprivation symptoms after cancer. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:1133-1146.
5. Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel, et al. 2018;25(6):596-608.
6. American College of Obstertricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Gynecologic Practice, Farrell R. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 659: the use of vaginal estrogen in women with a history of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:e93-e96.
7. Simon JA, Altomare C, Cort S, Jiang W. Overall safety of ospemifene in postmenopausal women from placebocontrolled Phase 2 and 3 trials. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2018;27(1):14-23.
8. Pinkerton JV, Thomas S. Use of SERMs for treatment in postmenopausal women. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;142:142-54.
9. Goetsch MF, Lim JY, Caughey AB. A practical solution for dyspareunia in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3394-3400.
Breast cancer survivors entering menopause face the risk of several menopausal symptoms:
- Hot flashes, the most common symptom, occur in more than 75% of women during menopause and have the potential to persist for as long as 15 years.1 That lengthy interval becomes a major issue for patients, especially when hot flashes are associated with other menopausal symptoms, including sleep disruption, difficulty concentrating, and emotional instability (crying, irritability).
Painful intercourse and loss of interest in sexual activity often develop as a result of vaginal atrophy and dryness.
- Urinary tract symptoms include urgency and, compared to the patient’s history, more frequent infections.
- Bone loss is a concern for many women after breast cancer, especially if they are, or have been, on aromatase inhibitor therapy.
Depression might be related to hormonal changes due to menopause or hormonal therapies, a consequence of merely having a diagnosis of cancer, or an adverse effect of chemotherapy.
In this brief review, I’ll examine options for treating symptoms of menopause by strategy—lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter treatments, and prescription drugs. Separately, I’ll look at options for managing genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM).
CASE 1
Rose is a 56-year-old woman who presents to clinic with a new breast mass, felt on breast self exam. The mass is about 1 cm, mobile, and firm. Diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound confirm a worrisome mass; biopsy returns positive with a 9-mm invasive, estrogen-receptor positive, ductal carcinoma with negative sentinel nodes at the time of lumpectomy. Radiation therapy was completed. She then met with oncology and decided against chemotherapy. Instead, she began an aromatase inhibitor 3 months ago. Bone density showed osteopenia. She presents to your office reporting frequent bothersome hot flashes and disrupted sleep.
Strategy #1: Lifestyle adaptations
First-line interventions for menopausal women who have had breast cancer usually involve taking a critical look at lifestyle and undertaking modifications that can alleviate discomfort. Because overall health is important for women who have had breast cancer, you should, across the spectrum of patients, encourage them to:
- increase physical activity
- reduce body weight by approximately 10% (if overweight or obese)
- reduce alcohol consumption
- stop smoking
- ensure adequate intake of calcium (1,200 mg, preferably by diet)
- optimize the level of vitamin D, including by increasing intake of fresh fish, eggs, and numerous other fortified foods.

The value of nondrug therapy for hot flashes is difficult to prove. Certain lifestyle changes are sensible, even if not evidence-based, and will help some women (but not others). We suggest that patients try lowering the temperature in the home (65–68˚ at night); running a fan; wearing clothing that can be removed in layers; and avoiding triggers such as spicy food, alcohol, cigarettes, and hot drinks. Hypnosis and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have been shown to help in clinical trials. Measures with benefit and minimal risks, but effectiveness not established, include acupuncture (sham worked as well as traditional), exercise, yoga, paced respiration, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction.
Continue to: Strategy #2: OTC compounds...
Strategy #2: OTC compounds
Over-the-counter products—from soy products to black cohosh to flax seed, and including dong quai, evening primrose oil, maca, omegas, pollen extract, ginseng, and red clover,2 or several compounds formulated in combination—have not been proven to be of more benefit for relieving symptoms of menopause than placebo in randomized trials, and thus might or might not be effective in a given patient. S-equol, a metabolite of a soy isoflavone taken by women who are non-equol producers, is available under the trade name Equelle and has shown some benefit. Note: There is concern that supplements that contain estrogen-like compounds, like soy products, might actually increase the risk of breast cancer. Dietary soy is not felt to be a concern.
Ask questions about the severity of a patient’s hot flashes. When a patient reports hot flashes, and is requesting help to relieve her discomfort, inquire 1) how often she has hot flashes, 2) how severe they are, and 3) how bothered she is by them (not all women are equally troubled, of course). The patient’s answers to these questions will help you decide which treatment option to offer, based on evidence and your experience.
CASE 1 Continued
Rose tried black cohosh OTC without improvement. She was interested in hypnosis but did not find it effective for her. She returned 3 months later stating that she is miserable, exhausted, not getting enough sleep, and her hot flashes and night sweats are affecting both her work and her relationship.
Strategy #3: Prescription medication
When addressing hot flashes, consider whether they occur more at night or during the day, or do not follow a day–night pattern. For women whose hot flashes occur mostly at night, and might therefore make sleeping difficult and cause fatigue and irritability, gabapentin, taken approximately 1 hour before bed, can be helpful. If tolerated without excessive somnolence the next day, the dose can be increased at night or additional doses provided during the day depending on hot flash response. For women who have hot flashes day and night, we often prescribe a low-dose antidepressant from the selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class.
When prescribing an antidepressant, we make a distinction between breast cancer patients who are taking tamoxifen and those who are not, to avoid cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitors in women taking tamoxifen.3 Better choices for women taking tamoxifen include desvenlafaxine, venlafaxine, escitalopram, or gabapentin or pregabalin.
For women with breast cancer who are taking an aromatase inhibitor, and who are also experiencing mood changes with their hot flashes, we often choose a trial of a low-dose antidepressant, either an SSRI or SNRI. One drug is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of hot flashes (but not for mood disorder). This is low-dose salt of paroxetine, 7.5 mg/d, which has the advantage of exerting no adverse effect on libido or weight (but is sometimes difficult to obtain because it is a branded product that might not be covered, or not covered fully, by a given patient’s insurance plan). Other antidepressants can be used in doses lower than needed for depression, with more rapid onset of effect on hot flashes, often within 2 weeks.
Last, transdermal clonidine, an antihypertensive, also has been found to relieve hot flashes.
Continue to: Not a recommended strategy: Systemic hormone therapy
Not a recommended strategy: Systemic hormone therapy
Although hormone therapy is, in general, the gold standard for alleviating hot flashes, it is contraindicated in most women with breast cancer.4 At our institution, we avoid systemic hormone therapy for hot flashes in almost all breast cancer patients.
CASE 2
Sarah first presented with hot flashes that improved while taking escitalopram 10 mg. Her night sweats persisted, however. Gabapentin 300 mg was added to take nightly. With this regimen, she finally felt that she was coping better. Six months later, she reported that she and her long-term partner had not been able to resume vaginal intercourse post–breast cancer treatment because of pain.
The challenge of managing GSM
What if your patient says, “Doctor, I’m really doing OK with my hot flashes, but sex has become painful. I don’t have any interest. I have vaginal dryness, and it’s affecting my quality of life”?
Studies have shown that GSM affects up to 50% of women, and even more than that among women who have had breast cancer.5 The condition interferes with sexual intimacy, disrupts quality of life, and can sour a partnership—significant quality-of-life concerns for breast cancer survivors.
For mild symptoms, encourage patients to apply a lubricant just before intercourse or a vaginal moisturizer twice weekly; moisturizers improve vaginal pH, too. These treatments do not fix the problem of a lack of superficial cells due to estrogen loss, however; to accomplish that, consider prescribing low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy or intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). This strategy is felt to be safe for many breast cancer survivors, as systemic absorption of estrogen is minimal if dosed low, keeping levels in the postmenopausal range.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the Endocrine Society agree that vaginal estrogen therapy may be a good option for many women with breast cancer for whom moisturizers and lubricants are inadequate.6 Delivery options include vaginal creams, tablets, suppositories used 2 or 3 times per week, or the low-dose vaginal estrogen ring, replaced every 3 months. We are concerned about using vaginal estrogen in women who have had aromatase inhibitor (AI) therapy; their estrogen levels are so low that absorbing even a small amount might make a difference in terms of effectiveness of AI. For women who need more than lubricants or vaginal moisturizers, particularly those taking anti-estrogen therapy (aromatase therapy), the use of low-dose vaginal hormones may be considered on an individual basis, but should include the oncologist in decision making.1,3
Beyond low-dose vaginal estrogen therapies, there are additional options that can be considered but with less supporting data for treating GSM in women with breast cancer.
Oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM; Osphena), might be neutral or even protective in its effect on the breast, as demonstrated in preclinical trials.7 In human trials, the drug is approved only for painful intercourse, not for loss of libido, and has not been tested in breast cancer patients.
Intravaginal DHEA (Prasterone), has been on the market for almost 1 year. The drug is approved for treating painful intercourse, but it also reverses vaginal atrophy and alleviates urinary symptoms. Because DHEA is a prohormone, it is converted to estrogen and androgen in the vagina. Again, absorption appears minimal. Intravaginal DHEA does not have the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) black-box warning that vaginal estrogen products do, but it is accompanied by a warning that it has not been tested in women with breast cancer.
Tissue selective estrogen receptor modulator is a conjugated estrogen combined with a third-generation SERM bazedoxifene, which treats hot flashes and reverses vaginal atrophy. This new systemic agent is probably neutral on the breast (at least that is the finding in clinical trials at 2 years8); again, however, it has not been tested in patients with breast cancer.
Continue to: Nonhormone therapies...
Nonhormone therapies
Topical lidocaine for insertional dyspareunia has been studied in postmenopausal women with breast cancer with severe GSM, dyspareunia, increased sexual distress scores, or abnormal sexual function with improvement seen using 4% aqueous lidocaine versus saline applied with a cotton ball to the vestibule for 3 minutes before vaginal penetration.9
Vaginal laser therapy has the potential to ameliorate distressing GSM without the need for local hormone intervention; however, placebo or active-controlled trials and long-term safety follow-up are needed.5
Newly arrived and on the horizon
Where does this review of available treatments leave us? Regrettably, with many women who experience painful intercourse and vaginal dryness despite what is available for treating their problems, and who continue looking to medical science and women’s health care for new options. So, what is coming next for these suffering patients? Here is a quick and selective run-through:
KNDy neurons. For hot flashes, there is the promise of nonhormonal treatment using these neurons, believed to be involved in reproduction by triggering expression of various compounds— particularly neurokinin B, which mediates hot flashes.1
Estetrol. In testing for use in treating hot flashes and its effect on GSM is this pregnancy-associated natural hormone that, importantly, did not stimulate breast cancer in a rat model.2 More evidence of efficacy is needed.
Lasers. For vaginal atrophy, many women are choosing treatment with the laser. Keep in mind, however, that, although lasers are FDA-approved devices, they do not have the FDA’s endorsement for use in vaginal atrophy, and have not been well-tested for their effectiveness for this indication in women with breast cancer who have taken an aromatase inhibitor. ACOG, NAMS, and the Endocrine Society have urged that additional trials be conducted, and have stated that the laser for vaginal atrophy cannot be recommended until there are more data on safety and efficacy.2
Lower-dose soft-gel vaginal estrogen suppositories have recently been approved by the FDA at 4 and 10 µg.3 The formulations are only minimally absorbed, potentially making them a good option for women who have had breast cancer.
Lasofoxifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator not yet approved by the FDA, has been shown to ameliorate vaginal changes.4 The drug is neutral or protective on the breast, but is now being tested in women with resistant breast cancer and unlikely to become available for GSM.
References
1. Anderson RA, Skorupskaite K, Sassarini J. The neurokinin B pathway in the treatment of menopausal hot flushes. Climacteric. 2018;1-4.
2. Gérard C, Mestdagt M, Tskitishvili E, et al. Combined estrogenic and anti-estrogenic properties of estetrol on breast cancer may provide a safe therapeutic window for the treatment of menopausal symptoms. Oncotarget. 2015;6(19):17621–17636.
3. Simon JA, Archer DF, Constantine GD, et al. A vaginal estradiol softgel capsule, TX-004HR, has negligible to very low systemic absorption of estradiol: efficacy and pharmacokinetic data review. Maturitas. 2017;99:51-58.
4. Bachmann G, Gass M, Kagan R, et al. Lasofoxifene (LASO), a next generation selective estrogen response modulator (SERM), improves dyspareunia in postmenopausal women with vaginal atrophy (VA). Menopause. 2005;12:238.
Treatment begins with a conversation
Most importantly, we need to listen to our patients in discomfort because of their menopausal symptoms. Consider proceeding along these lines: “You’ve been treated for breast cancer; now, let’s look at the medical issues that are affecting your quality of life. Are you depressed? Are you having hot flashes? Are you getting enough sleep? Have you stopped having sex or not restarted after your breast cancer treatment? Are you having painful sex or avoiding sex due to fear of pain? Let’s discuss options and work with your oncologist to try to relieve your symptoms and make your life better.”
First-line therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women with a history of breast cancer should start with lifestyle changes and nonhormone therapies. For GSM, lubricants and vaginal moisturizers should be tried first and may be effective. Reassure patients that there are many treatment options, even though not all of them have been well-tested in breast cancer patients, and that new modalities are under investigation and review (see “Newly arrived and on the horizon,”). Become familiar with published data on the safety and effectiveness of the range of available treatments; guide patients through the process of finding what works best for them; and invite their oncologist into the therapeutic partnership. If you do not feel comfortable with these issues in women who are breast cancer survivors, find a menopause specialist to help, available by zip code at Find a Provider, http://www.menopause.org.
Breast cancer survivors entering menopause face the risk of several menopausal symptoms:
- Hot flashes, the most common symptom, occur in more than 75% of women during menopause and have the potential to persist for as long as 15 years.1 That lengthy interval becomes a major issue for patients, especially when hot flashes are associated with other menopausal symptoms, including sleep disruption, difficulty concentrating, and emotional instability (crying, irritability).
Painful intercourse and loss of interest in sexual activity often develop as a result of vaginal atrophy and dryness.
- Urinary tract symptoms include urgency and, compared to the patient’s history, more frequent infections.
- Bone loss is a concern for many women after breast cancer, especially if they are, or have been, on aromatase inhibitor therapy.
Depression might be related to hormonal changes due to menopause or hormonal therapies, a consequence of merely having a diagnosis of cancer, or an adverse effect of chemotherapy.
In this brief review, I’ll examine options for treating symptoms of menopause by strategy—lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter treatments, and prescription drugs. Separately, I’ll look at options for managing genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM).
CASE 1
Rose is a 56-year-old woman who presents to clinic with a new breast mass, felt on breast self exam. The mass is about 1 cm, mobile, and firm. Diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound confirm a worrisome mass; biopsy returns positive with a 9-mm invasive, estrogen-receptor positive, ductal carcinoma with negative sentinel nodes at the time of lumpectomy. Radiation therapy was completed. She then met with oncology and decided against chemotherapy. Instead, she began an aromatase inhibitor 3 months ago. Bone density showed osteopenia. She presents to your office reporting frequent bothersome hot flashes and disrupted sleep.
Strategy #1: Lifestyle adaptations
First-line interventions for menopausal women who have had breast cancer usually involve taking a critical look at lifestyle and undertaking modifications that can alleviate discomfort. Because overall health is important for women who have had breast cancer, you should, across the spectrum of patients, encourage them to:
- increase physical activity
- reduce body weight by approximately 10% (if overweight or obese)
- reduce alcohol consumption
- stop smoking
- ensure adequate intake of calcium (1,200 mg, preferably by diet)
- optimize the level of vitamin D, including by increasing intake of fresh fish, eggs, and numerous other fortified foods.

The value of nondrug therapy for hot flashes is difficult to prove. Certain lifestyle changes are sensible, even if not evidence-based, and will help some women (but not others). We suggest that patients try lowering the temperature in the home (65–68˚ at night); running a fan; wearing clothing that can be removed in layers; and avoiding triggers such as spicy food, alcohol, cigarettes, and hot drinks. Hypnosis and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) have been shown to help in clinical trials. Measures with benefit and minimal risks, but effectiveness not established, include acupuncture (sham worked as well as traditional), exercise, yoga, paced respiration, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction.
Continue to: Strategy #2: OTC compounds...
Strategy #2: OTC compounds
Over-the-counter products—from soy products to black cohosh to flax seed, and including dong quai, evening primrose oil, maca, omegas, pollen extract, ginseng, and red clover,2 or several compounds formulated in combination—have not been proven to be of more benefit for relieving symptoms of menopause than placebo in randomized trials, and thus might or might not be effective in a given patient. S-equol, a metabolite of a soy isoflavone taken by women who are non-equol producers, is available under the trade name Equelle and has shown some benefit. Note: There is concern that supplements that contain estrogen-like compounds, like soy products, might actually increase the risk of breast cancer. Dietary soy is not felt to be a concern.
Ask questions about the severity of a patient’s hot flashes. When a patient reports hot flashes, and is requesting help to relieve her discomfort, inquire 1) how often she has hot flashes, 2) how severe they are, and 3) how bothered she is by them (not all women are equally troubled, of course). The patient’s answers to these questions will help you decide which treatment option to offer, based on evidence and your experience.
CASE 1 Continued
Rose tried black cohosh OTC without improvement. She was interested in hypnosis but did not find it effective for her. She returned 3 months later stating that she is miserable, exhausted, not getting enough sleep, and her hot flashes and night sweats are affecting both her work and her relationship.
Strategy #3: Prescription medication
When addressing hot flashes, consider whether they occur more at night or during the day, or do not follow a day–night pattern. For women whose hot flashes occur mostly at night, and might therefore make sleeping difficult and cause fatigue and irritability, gabapentin, taken approximately 1 hour before bed, can be helpful. If tolerated without excessive somnolence the next day, the dose can be increased at night or additional doses provided during the day depending on hot flash response. For women who have hot flashes day and night, we often prescribe a low-dose antidepressant from the selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class.
When prescribing an antidepressant, we make a distinction between breast cancer patients who are taking tamoxifen and those who are not, to avoid cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitors in women taking tamoxifen.3 Better choices for women taking tamoxifen include desvenlafaxine, venlafaxine, escitalopram, or gabapentin or pregabalin.
For women with breast cancer who are taking an aromatase inhibitor, and who are also experiencing mood changes with their hot flashes, we often choose a trial of a low-dose antidepressant, either an SSRI or SNRI. One drug is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of hot flashes (but not for mood disorder). This is low-dose salt of paroxetine, 7.5 mg/d, which has the advantage of exerting no adverse effect on libido or weight (but is sometimes difficult to obtain because it is a branded product that might not be covered, or not covered fully, by a given patient’s insurance plan). Other antidepressants can be used in doses lower than needed for depression, with more rapid onset of effect on hot flashes, often within 2 weeks.
Last, transdermal clonidine, an antihypertensive, also has been found to relieve hot flashes.
Continue to: Not a recommended strategy: Systemic hormone therapy
Not a recommended strategy: Systemic hormone therapy
Although hormone therapy is, in general, the gold standard for alleviating hot flashes, it is contraindicated in most women with breast cancer.4 At our institution, we avoid systemic hormone therapy for hot flashes in almost all breast cancer patients.
CASE 2
Sarah first presented with hot flashes that improved while taking escitalopram 10 mg. Her night sweats persisted, however. Gabapentin 300 mg was added to take nightly. With this regimen, she finally felt that she was coping better. Six months later, she reported that she and her long-term partner had not been able to resume vaginal intercourse post–breast cancer treatment because of pain.
The challenge of managing GSM
What if your patient says, “Doctor, I’m really doing OK with my hot flashes, but sex has become painful. I don’t have any interest. I have vaginal dryness, and it’s affecting my quality of life”?
Studies have shown that GSM affects up to 50% of women, and even more than that among women who have had breast cancer.5 The condition interferes with sexual intimacy, disrupts quality of life, and can sour a partnership—significant quality-of-life concerns for breast cancer survivors.
For mild symptoms, encourage patients to apply a lubricant just before intercourse or a vaginal moisturizer twice weekly; moisturizers improve vaginal pH, too. These treatments do not fix the problem of a lack of superficial cells due to estrogen loss, however; to accomplish that, consider prescribing low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy or intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). This strategy is felt to be safe for many breast cancer survivors, as systemic absorption of estrogen is minimal if dosed low, keeping levels in the postmenopausal range.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the Endocrine Society agree that vaginal estrogen therapy may be a good option for many women with breast cancer for whom moisturizers and lubricants are inadequate.6 Delivery options include vaginal creams, tablets, suppositories used 2 or 3 times per week, or the low-dose vaginal estrogen ring, replaced every 3 months. We are concerned about using vaginal estrogen in women who have had aromatase inhibitor (AI) therapy; their estrogen levels are so low that absorbing even a small amount might make a difference in terms of effectiveness of AI. For women who need more than lubricants or vaginal moisturizers, particularly those taking anti-estrogen therapy (aromatase therapy), the use of low-dose vaginal hormones may be considered on an individual basis, but should include the oncologist in decision making.1,3
Beyond low-dose vaginal estrogen therapies, there are additional options that can be considered but with less supporting data for treating GSM in women with breast cancer.
Oral ospemifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM; Osphena), might be neutral or even protective in its effect on the breast, as demonstrated in preclinical trials.7 In human trials, the drug is approved only for painful intercourse, not for loss of libido, and has not been tested in breast cancer patients.
Intravaginal DHEA (Prasterone), has been on the market for almost 1 year. The drug is approved for treating painful intercourse, but it also reverses vaginal atrophy and alleviates urinary symptoms. Because DHEA is a prohormone, it is converted to estrogen and androgen in the vagina. Again, absorption appears minimal. Intravaginal DHEA does not have the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) black-box warning that vaginal estrogen products do, but it is accompanied by a warning that it has not been tested in women with breast cancer.
Tissue selective estrogen receptor modulator is a conjugated estrogen combined with a third-generation SERM bazedoxifene, which treats hot flashes and reverses vaginal atrophy. This new systemic agent is probably neutral on the breast (at least that is the finding in clinical trials at 2 years8); again, however, it has not been tested in patients with breast cancer.
Continue to: Nonhormone therapies...
Nonhormone therapies
Topical lidocaine for insertional dyspareunia has been studied in postmenopausal women with breast cancer with severe GSM, dyspareunia, increased sexual distress scores, or abnormal sexual function with improvement seen using 4% aqueous lidocaine versus saline applied with a cotton ball to the vestibule for 3 minutes before vaginal penetration.9
Vaginal laser therapy has the potential to ameliorate distressing GSM without the need for local hormone intervention; however, placebo or active-controlled trials and long-term safety follow-up are needed.5
Newly arrived and on the horizon
Where does this review of available treatments leave us? Regrettably, with many women who experience painful intercourse and vaginal dryness despite what is available for treating their problems, and who continue looking to medical science and women’s health care for new options. So, what is coming next for these suffering patients? Here is a quick and selective run-through:
KNDy neurons. For hot flashes, there is the promise of nonhormonal treatment using these neurons, believed to be involved in reproduction by triggering expression of various compounds— particularly neurokinin B, which mediates hot flashes.1
Estetrol. In testing for use in treating hot flashes and its effect on GSM is this pregnancy-associated natural hormone that, importantly, did not stimulate breast cancer in a rat model.2 More evidence of efficacy is needed.
Lasers. For vaginal atrophy, many women are choosing treatment with the laser. Keep in mind, however, that, although lasers are FDA-approved devices, they do not have the FDA’s endorsement for use in vaginal atrophy, and have not been well-tested for their effectiveness for this indication in women with breast cancer who have taken an aromatase inhibitor. ACOG, NAMS, and the Endocrine Society have urged that additional trials be conducted, and have stated that the laser for vaginal atrophy cannot be recommended until there are more data on safety and efficacy.2
Lower-dose soft-gel vaginal estrogen suppositories have recently been approved by the FDA at 4 and 10 µg.3 The formulations are only minimally absorbed, potentially making them a good option for women who have had breast cancer.
Lasofoxifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator not yet approved by the FDA, has been shown to ameliorate vaginal changes.4 The drug is neutral or protective on the breast, but is now being tested in women with resistant breast cancer and unlikely to become available for GSM.
References
1. Anderson RA, Skorupskaite K, Sassarini J. The neurokinin B pathway in the treatment of menopausal hot flushes. Climacteric. 2018;1-4.
2. Gérard C, Mestdagt M, Tskitishvili E, et al. Combined estrogenic and anti-estrogenic properties of estetrol on breast cancer may provide a safe therapeutic window for the treatment of menopausal symptoms. Oncotarget. 2015;6(19):17621–17636.
3. Simon JA, Archer DF, Constantine GD, et al. A vaginal estradiol softgel capsule, TX-004HR, has negligible to very low systemic absorption of estradiol: efficacy and pharmacokinetic data review. Maturitas. 2017;99:51-58.
4. Bachmann G, Gass M, Kagan R, et al. Lasofoxifene (LASO), a next generation selective estrogen response modulator (SERM), improves dyspareunia in postmenopausal women with vaginal atrophy (VA). Menopause. 2005;12:238.
Treatment begins with a conversation
Most importantly, we need to listen to our patients in discomfort because of their menopausal symptoms. Consider proceeding along these lines: “You’ve been treated for breast cancer; now, let’s look at the medical issues that are affecting your quality of life. Are you depressed? Are you having hot flashes? Are you getting enough sleep? Have you stopped having sex or not restarted after your breast cancer treatment? Are you having painful sex or avoiding sex due to fear of pain? Let’s discuss options and work with your oncologist to try to relieve your symptoms and make your life better.”
First-line therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women with a history of breast cancer should start with lifestyle changes and nonhormone therapies. For GSM, lubricants and vaginal moisturizers should be tried first and may be effective. Reassure patients that there are many treatment options, even though not all of them have been well-tested in breast cancer patients, and that new modalities are under investigation and review (see “Newly arrived and on the horizon,”). Become familiar with published data on the safety and effectiveness of the range of available treatments; guide patients through the process of finding what works best for them; and invite their oncologist into the therapeutic partnership. If you do not feel comfortable with these issues in women who are breast cancer survivors, find a menopause specialist to help, available by zip code at Find a Provider, http://www.menopause.org.
1. The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
2. McGarry K, Geary M, Gopinath V. Beyond estrogen: treatment options for hot flashes. Clin Ther. 2018;40(10):1778-1786.
3. Santen RJ, Stuenkel CA, Davis SR, et al. Managing menopausal symptoms and associated clinical issues in breast cancer survivors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:3647-3661.
4. Faubion SS, Loprinzi CL, Ruddy KJ. Management of hormone deprivation symptoms after cancer. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:1133-1146.
5. Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel, et al. 2018;25(6):596-608.
6. American College of Obstertricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Gynecologic Practice, Farrell R. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 659: the use of vaginal estrogen in women with a history of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:e93-e96.
7. Simon JA, Altomare C, Cort S, Jiang W. Overall safety of ospemifene in postmenopausal women from placebocontrolled Phase 2 and 3 trials. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2018;27(1):14-23.
8. Pinkerton JV, Thomas S. Use of SERMs for treatment in postmenopausal women. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;142:142-54.
9. Goetsch MF, Lim JY, Caughey AB. A practical solution for dyspareunia in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3394-3400.
1. The NAMS 2017 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
2. McGarry K, Geary M, Gopinath V. Beyond estrogen: treatment options for hot flashes. Clin Ther. 2018;40(10):1778-1786.
3. Santen RJ, Stuenkel CA, Davis SR, et al. Managing menopausal symptoms and associated clinical issues in breast cancer survivors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:3647-3661.
4. Faubion SS, Loprinzi CL, Ruddy KJ. Management of hormone deprivation symptoms after cancer. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:1133-1146.
5. Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel, et al. 2018;25(6):596-608.
6. American College of Obstertricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Gynecologic Practice, Farrell R. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 659: the use of vaginal estrogen in women with a history of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127:e93-e96.
7. Simon JA, Altomare C, Cort S, Jiang W. Overall safety of ospemifene in postmenopausal women from placebocontrolled Phase 2 and 3 trials. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2018;27(1):14-23.
8. Pinkerton JV, Thomas S. Use of SERMs for treatment in postmenopausal women. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;142:142-54.
9. Goetsch MF, Lim JY, Caughey AB. A practical solution for dyspareunia in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3394-3400.
To prevent fractures, treating only women with osteoporosis is not enough
The conventional bone mineral density threshold for initiating treatment to prevent fragility fractures is a T-score of less than -2.5 (the World Health Organization criteria for osteoporosis).1 However, most fractures experienced by postmenopausal women occur not in osteoporotic women but in those with low bone mass (osteopenia).2
Investigators in New Zealand recently published the results of a randomized controlled trial they conducted to determine the efficacy of zoledronate (zoledronic acid) in preventing fractures in postmenopausal women.3 They enrolled women age 65 years or older with osteopenia of the hip and randomly assigned the participants to 4 intravenous infusions of 5 mg zoledronic acid or placebo at 18-month intervals for 6 years.
Zoledronic acid reduced fracture risk
The trial included 2,000 postmenopausal women (mean age at baseline, 71 years; 94% European ethnicity) with a T-score of -1.0 to -2.5 at either the total hip or the femoral neck on either side. Both hips were assessed. The women received either zoledronic acid treatment or placebo in a 1:1 ratio. Candidates were excluded if they regularly used bone-active drugs in the previous year.
Fragility fractures were noted in 190 women in the placebo group and in 122 women treated with zoledronic acid (hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.50–0.79, P<.001). The number of women that would need to be treated to prevent the occurrence of a fracture in 1 woman was 15.
Compared with placebo, zoledronic acid also lowered the risk of nonvertebral, symptomatic, and vertebral fractures as well as height loss (P≤.003 for these 4 comparisons). Relatively few adverse events occurred with zoledronic acid treatment. No atypical femoral fractures or cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw occurred in either group.
Trial closes the knowledge gap regarding treatment thresholds
This trial’s findings underscore the importance of age as a risk factor for fragility fracture and clarify that pharmacologic treatment is appropriate not only for women with osteoporosis but also for older postmenopausal women with osteopenia.
As the authors point out, administration of zoledronic acid less often than annually can be highly effective in preventing fractures; they recommend future trials of administration of this intravenous bisphosphonate at intervals less frequent than 18 months. Although the absence of atypical femoral fractures or cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw is reassuring, the authors note that their trial was underpowered to assess these uncommon events.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to [email protected]. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- World Health Organization. WHO Scientific Group on the assessment of osteoporosis at primary health care level. Summary meeting report, Brussels, Belgium, 5-7 May 2004. https://www. who.int/chp/topics/Osteoporosis.pdf. Accessed November 19, 2018.
- Siris ES, Chen YT, Abbott TA, et al. Bone mineral density thresholds for pharmacological intervention to prevent fractures. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:1108-1112.
- Reid IR, Horne AM, Mihov B, et al. Fracture prevention with zoledronate in older women with osteopenia. N Engl J Med. 2018. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1808082.
The conventional bone mineral density threshold for initiating treatment to prevent fragility fractures is a T-score of less than -2.5 (the World Health Organization criteria for osteoporosis).1 However, most fractures experienced by postmenopausal women occur not in osteoporotic women but in those with low bone mass (osteopenia).2
Investigators in New Zealand recently published the results of a randomized controlled trial they conducted to determine the efficacy of zoledronate (zoledronic acid) in preventing fractures in postmenopausal women.3 They enrolled women age 65 years or older with osteopenia of the hip and randomly assigned the participants to 4 intravenous infusions of 5 mg zoledronic acid or placebo at 18-month intervals for 6 years.
Zoledronic acid reduced fracture risk
The trial included 2,000 postmenopausal women (mean age at baseline, 71 years; 94% European ethnicity) with a T-score of -1.0 to -2.5 at either the total hip or the femoral neck on either side. Both hips were assessed. The women received either zoledronic acid treatment or placebo in a 1:1 ratio. Candidates were excluded if they regularly used bone-active drugs in the previous year.
Fragility fractures were noted in 190 women in the placebo group and in 122 women treated with zoledronic acid (hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.50–0.79, P<.001). The number of women that would need to be treated to prevent the occurrence of a fracture in 1 woman was 15.
Compared with placebo, zoledronic acid also lowered the risk of nonvertebral, symptomatic, and vertebral fractures as well as height loss (P≤.003 for these 4 comparisons). Relatively few adverse events occurred with zoledronic acid treatment. No atypical femoral fractures or cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw occurred in either group.
Trial closes the knowledge gap regarding treatment thresholds
This trial’s findings underscore the importance of age as a risk factor for fragility fracture and clarify that pharmacologic treatment is appropriate not only for women with osteoporosis but also for older postmenopausal women with osteopenia.
As the authors point out, administration of zoledronic acid less often than annually can be highly effective in preventing fractures; they recommend future trials of administration of this intravenous bisphosphonate at intervals less frequent than 18 months. Although the absence of atypical femoral fractures or cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw is reassuring, the authors note that their trial was underpowered to assess these uncommon events.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to [email protected]. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
The conventional bone mineral density threshold for initiating treatment to prevent fragility fractures is a T-score of less than -2.5 (the World Health Organization criteria for osteoporosis).1 However, most fractures experienced by postmenopausal women occur not in osteoporotic women but in those with low bone mass (osteopenia).2
Investigators in New Zealand recently published the results of a randomized controlled trial they conducted to determine the efficacy of zoledronate (zoledronic acid) in preventing fractures in postmenopausal women.3 They enrolled women age 65 years or older with osteopenia of the hip and randomly assigned the participants to 4 intravenous infusions of 5 mg zoledronic acid or placebo at 18-month intervals for 6 years.
Zoledronic acid reduced fracture risk
The trial included 2,000 postmenopausal women (mean age at baseline, 71 years; 94% European ethnicity) with a T-score of -1.0 to -2.5 at either the total hip or the femoral neck on either side. Both hips were assessed. The women received either zoledronic acid treatment or placebo in a 1:1 ratio. Candidates were excluded if they regularly used bone-active drugs in the previous year.
Fragility fractures were noted in 190 women in the placebo group and in 122 women treated with zoledronic acid (hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.50–0.79, P<.001). The number of women that would need to be treated to prevent the occurrence of a fracture in 1 woman was 15.
Compared with placebo, zoledronic acid also lowered the risk of nonvertebral, symptomatic, and vertebral fractures as well as height loss (P≤.003 for these 4 comparisons). Relatively few adverse events occurred with zoledronic acid treatment. No atypical femoral fractures or cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw occurred in either group.
Trial closes the knowledge gap regarding treatment thresholds
This trial’s findings underscore the importance of age as a risk factor for fragility fracture and clarify that pharmacologic treatment is appropriate not only for women with osteoporosis but also for older postmenopausal women with osteopenia.
As the authors point out, administration of zoledronic acid less often than annually can be highly effective in preventing fractures; they recommend future trials of administration of this intravenous bisphosphonate at intervals less frequent than 18 months. Although the absence of atypical femoral fractures or cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw is reassuring, the authors note that their trial was underpowered to assess these uncommon events.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to [email protected]. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.
- World Health Organization. WHO Scientific Group on the assessment of osteoporosis at primary health care level. Summary meeting report, Brussels, Belgium, 5-7 May 2004. https://www. who.int/chp/topics/Osteoporosis.pdf. Accessed November 19, 2018.
- Siris ES, Chen YT, Abbott TA, et al. Bone mineral density thresholds for pharmacological intervention to prevent fractures. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:1108-1112.
- Reid IR, Horne AM, Mihov B, et al. Fracture prevention with zoledronate in older women with osteopenia. N Engl J Med. 2018. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1808082.
- World Health Organization. WHO Scientific Group on the assessment of osteoporosis at primary health care level. Summary meeting report, Brussels, Belgium, 5-7 May 2004. https://www. who.int/chp/topics/Osteoporosis.pdf. Accessed November 19, 2018.
- Siris ES, Chen YT, Abbott TA, et al. Bone mineral density thresholds for pharmacological intervention to prevent fractures. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:1108-1112.
- Reid IR, Horne AM, Mihov B, et al. Fracture prevention with zoledronate in older women with osteopenia. N Engl J Med. 2018. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1808082.