User login
Does BSO status affect health outcomes for women taking estrogen for menopause?
Do health effects of menopausal estrogen therapy differ between women with bilateral oophorectomy versus those with conserved ovaries? To answer this question a group of investigators performed a subanalysis of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) Estrogen-Alone Trial,1 which included 40 clinical centers across the United States. They examined estrogen therapy outcomes by bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) status, with additional stratification by 10-year age groups in 9,939 women aged 50 to 79 years with prior hysterectomy and known oophorectomy status. In the WHI trial, women were randomly assigned to conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) 0.625 mg/d or placebo for a median of 7.2 years. Investigators assessed the incidence of coronary heart disease and invasive breast cancer (the trial’s 2 primary end points), all-cause mortality, and a “global index”—these end points plus stroke, pulmonary embolism, colorectal cancer, and hip fracture—during the intervention phase and 18-year cumulative follow-up.
OBG Management caught up with lead author JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP, to discuss the study’s results.
OBG Management : How many women undergo BSO with their hysterectomy?
Dr. JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP: Of the 425,000 women who undergo hysterectomy in the United States for benign reasons each year,2,3 about 40% of them undergo BSO—so between 150,000 and 200,000 women per year undergo BSO with their hysterectomy.4,5
OBG Management : Although BSO is performed with hysterectomy to minimize patients’ future ovarian cancer risk, does BSO have health risks of its own, and how has estrogen been shown to affect these risks?
Dr. Manson: First, yes, BSO has been associated with health risks, especially when it is performed at a young age, such as before age 45. It has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, and all-cause mortality. According to observational studies, estrogen therapy appears to offset many of these risks, particularly those related to heart disease and osteoporosis (the evidence is less clear on cognitive deficits).5
OBG Management : What did you find in your trial when you randomly assigned women in the age groups of 50 to 79 who underwent hysterectomy with and without BSO to estrogen therapy or placebo?
Dr. Manson: The WHI is the first study to be conducted in a randomized trial setting to analyze the health risks and benefits of estrogen therapy according to whether or not women had their ovaries removed. What we found was that the woman’s age had a strong influence on the effects of estrogen therapy among women who had BSO but only a negligible effect among women who had conserved ovaries. Overall, across the full age range, the effects of estrogen therapy did not differ substantially between women who had a BSO and those who had their ovaries conserved.
However, there were major differences by age group among the women who had BSO. A significant 32% reduction in all-cause mortality emerged during the 18-year follow-up period among the younger women (below age 60) who had BSO when they received estrogen therapy as compared with placebo. By contrast, the women who had conserved ovaries did not have this significant reduction in all-cause mortality, or in most of the other outcomes on estrogen compared with placebo. Overall, the effects of estrogen therapy tended to be relatively neutral in the women with conserved ovaries.
Now, the reduction in all-cause mortality with estrogen therapy was particularly pronounced among women who had BSO before age 45. They had a 40% statistically significant reduction in all-cause mortality with estrogen therapy compared with placebo. Also, among the women with BSO, there was a strong association between the timing of estrogen initiation and the magnitude of reduction in mortality. Women who started the estrogen therapy within 10 years of having the BSO had a 34% significant reduction in all-cause mortality, and those who started estrogen more than 20 years after having their ovaries removed had no reduction in mortality.
Continue to:
OBG Management : Do your data give support to the timing hypothesis?
Dr. Manson: Yes, our findings do support a timing hypothesis that was particularly pronounced for women who underwent BSO. It was the women who had early surgical menopause (before age 45) and those who started the estrogen therapy within 10 years of having their ovaries removed who had the greatest reduction in all-cause mortality and the most favorable benefit-risk profile from hormone therapy. So, the results do lend support to the timing hypothesis.
By contrast, women who had BSO at hysterectomy and began hormone therapy at age 70 or older had net adverse effects from hormone therapy. They posted a 40% increase in the global index—which is a summary measure of adverse effects on cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other major health outcomes. So, the women with BSO who were randomized in the trial at age 70 and older, had unfavorable results from estrogen therapy and an increase in the global index, in contrast to the women who were below age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
OBG Management : Given your study findings, in which women would you recommend estrogen therapy? And are there groups of women in which you would advise avoiding estrogen therapy?
Dr. Manson: Current guidelines6,7 recommend estrogen therapy for women who have early menopause, particularly an early surgical menopause and BSO prior to the average age at natural menopause. Unless the woman has contraindications to estrogen therapy, the recommendations are to treat with estrogen until the average age of menopause—until about age 50 to 51.
Our study findings provide reassurance that, if a woman continues to have indications for estrogen (vasomotor symptoms, or other indications for estrogen therapy), there is relative safety of continuing estrogen-alone therapy through her 50s, until age 60. For example, a woman who, after the average age of menopause continues to have vasomotor symptoms, or if she has bone health problems, our study would suggest that estrogen therapy would continue to have a favorable benefit-risk profile until at least the age of 60. Decisions would have to be individualized, especially after age 60, with shared decision-making particularly important for those decisions. (Some women, depending on their risk profile, may continue to be candidates for estrogen therapy past age 60.)
So, this study provides reassurance regarding use of estrogen therapy for women in their 50s if they have had BSO. Actually, the women who had conserved ovaries also had relative safety with estrogen therapy until age 60. They just didn’t show the significant benefits for all-cause mortality. Overall, their pattern of health-related benefits and risks was neutral. Thus, if vasomotor symptom management, quality of life benefits, or bone health effects are sought, taking hormone therapy is a quite reasonable choice for these women.
By contrast, women who have had a BSO and are age 70 or older should really avoid initiating estrogen therapy because it would follow a prolonged period of estrogen deficiency, or very low estrogen levels, and these women appeared to have a net adverse effect from initiating hormone therapy (with increases in the global index found).
Continue to:
OBG Management : Did taking estrogen therapy prior to trial enrollment make a difference when it came to study outcomes?
Dr. Manson: We found minimal if any effect in our analyses. In fact, even the women who did not have prior (pre-randomization) use of estrogen therapy tended to do well on estrogen-alone therapy if they were younger than age 60. This was particularly true for the women who had BSO. Even if they had not used estrogen previously, and they were many years past the BSO, they still did well on estrogen therapy if they were below age 60.
1. Manson JE, Aragaki AK, Bassuk SS. Menopausal estrogen-alone therapy and health outcomes in women with and without bilateral oophorectomy: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2019 September 10. doi:10.7326/M19-0274.
2. Einarsson J. Are hysterectomy volumes in the US really falling? Contemporary OB/GYN. 1 September 2017. www.contemporaryobgyn.net/gynecology/are-hysterectomy-volumes-us-really-falling. November 4, 2019.
3. Temkin SM, Minasian L, Noone AM. The end of the hysterectomy epidemic and endometrial cancer incidence: what are the unintended consequences of declining hysterectomy rates? Front Oncol. 2016;6:89.
4. Doll KM, Dusetzina SB, Robinson W. Trends in inpatient and outpatient hysterectomy and oophorectomy rates among commercially insured women in the United States, 2000-2014. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:876-877.
5. Adelman MR, Sharp HT. Ovarian conservation vs removal at the time of benign hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:269-279.
6. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 141: management of menopausal symptoms [published corrections appear in: Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(1):166. and Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(3):604]. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
7. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
Do health effects of menopausal estrogen therapy differ between women with bilateral oophorectomy versus those with conserved ovaries? To answer this question a group of investigators performed a subanalysis of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) Estrogen-Alone Trial,1 which included 40 clinical centers across the United States. They examined estrogen therapy outcomes by bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) status, with additional stratification by 10-year age groups in 9,939 women aged 50 to 79 years with prior hysterectomy and known oophorectomy status. In the WHI trial, women were randomly assigned to conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) 0.625 mg/d or placebo for a median of 7.2 years. Investigators assessed the incidence of coronary heart disease and invasive breast cancer (the trial’s 2 primary end points), all-cause mortality, and a “global index”—these end points plus stroke, pulmonary embolism, colorectal cancer, and hip fracture—during the intervention phase and 18-year cumulative follow-up.
OBG Management caught up with lead author JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP, to discuss the study’s results.
OBG Management : How many women undergo BSO with their hysterectomy?
Dr. JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP: Of the 425,000 women who undergo hysterectomy in the United States for benign reasons each year,2,3 about 40% of them undergo BSO—so between 150,000 and 200,000 women per year undergo BSO with their hysterectomy.4,5
OBG Management : Although BSO is performed with hysterectomy to minimize patients’ future ovarian cancer risk, does BSO have health risks of its own, and how has estrogen been shown to affect these risks?
Dr. Manson: First, yes, BSO has been associated with health risks, especially when it is performed at a young age, such as before age 45. It has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, and all-cause mortality. According to observational studies, estrogen therapy appears to offset many of these risks, particularly those related to heart disease and osteoporosis (the evidence is less clear on cognitive deficits).5
OBG Management : What did you find in your trial when you randomly assigned women in the age groups of 50 to 79 who underwent hysterectomy with and without BSO to estrogen therapy or placebo?
Dr. Manson: The WHI is the first study to be conducted in a randomized trial setting to analyze the health risks and benefits of estrogen therapy according to whether or not women had their ovaries removed. What we found was that the woman’s age had a strong influence on the effects of estrogen therapy among women who had BSO but only a negligible effect among women who had conserved ovaries. Overall, across the full age range, the effects of estrogen therapy did not differ substantially between women who had a BSO and those who had their ovaries conserved.
However, there were major differences by age group among the women who had BSO. A significant 32% reduction in all-cause mortality emerged during the 18-year follow-up period among the younger women (below age 60) who had BSO when they received estrogen therapy as compared with placebo. By contrast, the women who had conserved ovaries did not have this significant reduction in all-cause mortality, or in most of the other outcomes on estrogen compared with placebo. Overall, the effects of estrogen therapy tended to be relatively neutral in the women with conserved ovaries.
Now, the reduction in all-cause mortality with estrogen therapy was particularly pronounced among women who had BSO before age 45. They had a 40% statistically significant reduction in all-cause mortality with estrogen therapy compared with placebo. Also, among the women with BSO, there was a strong association between the timing of estrogen initiation and the magnitude of reduction in mortality. Women who started the estrogen therapy within 10 years of having the BSO had a 34% significant reduction in all-cause mortality, and those who started estrogen more than 20 years after having their ovaries removed had no reduction in mortality.
Continue to:
OBG Management : Do your data give support to the timing hypothesis?
Dr. Manson: Yes, our findings do support a timing hypothesis that was particularly pronounced for women who underwent BSO. It was the women who had early surgical menopause (before age 45) and those who started the estrogen therapy within 10 years of having their ovaries removed who had the greatest reduction in all-cause mortality and the most favorable benefit-risk profile from hormone therapy. So, the results do lend support to the timing hypothesis.
By contrast, women who had BSO at hysterectomy and began hormone therapy at age 70 or older had net adverse effects from hormone therapy. They posted a 40% increase in the global index—which is a summary measure of adverse effects on cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other major health outcomes. So, the women with BSO who were randomized in the trial at age 70 and older, had unfavorable results from estrogen therapy and an increase in the global index, in contrast to the women who were below age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
OBG Management : Given your study findings, in which women would you recommend estrogen therapy? And are there groups of women in which you would advise avoiding estrogen therapy?
Dr. Manson: Current guidelines6,7 recommend estrogen therapy for women who have early menopause, particularly an early surgical menopause and BSO prior to the average age at natural menopause. Unless the woman has contraindications to estrogen therapy, the recommendations are to treat with estrogen until the average age of menopause—until about age 50 to 51.
Our study findings provide reassurance that, if a woman continues to have indications for estrogen (vasomotor symptoms, or other indications for estrogen therapy), there is relative safety of continuing estrogen-alone therapy through her 50s, until age 60. For example, a woman who, after the average age of menopause continues to have vasomotor symptoms, or if she has bone health problems, our study would suggest that estrogen therapy would continue to have a favorable benefit-risk profile until at least the age of 60. Decisions would have to be individualized, especially after age 60, with shared decision-making particularly important for those decisions. (Some women, depending on their risk profile, may continue to be candidates for estrogen therapy past age 60.)
So, this study provides reassurance regarding use of estrogen therapy for women in their 50s if they have had BSO. Actually, the women who had conserved ovaries also had relative safety with estrogen therapy until age 60. They just didn’t show the significant benefits for all-cause mortality. Overall, their pattern of health-related benefits and risks was neutral. Thus, if vasomotor symptom management, quality of life benefits, or bone health effects are sought, taking hormone therapy is a quite reasonable choice for these women.
By contrast, women who have had a BSO and are age 70 or older should really avoid initiating estrogen therapy because it would follow a prolonged period of estrogen deficiency, or very low estrogen levels, and these women appeared to have a net adverse effect from initiating hormone therapy (with increases in the global index found).
Continue to:
OBG Management : Did taking estrogen therapy prior to trial enrollment make a difference when it came to study outcomes?
Dr. Manson: We found minimal if any effect in our analyses. In fact, even the women who did not have prior (pre-randomization) use of estrogen therapy tended to do well on estrogen-alone therapy if they were younger than age 60. This was particularly true for the women who had BSO. Even if they had not used estrogen previously, and they were many years past the BSO, they still did well on estrogen therapy if they were below age 60.
Do health effects of menopausal estrogen therapy differ between women with bilateral oophorectomy versus those with conserved ovaries? To answer this question a group of investigators performed a subanalysis of the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) Estrogen-Alone Trial,1 which included 40 clinical centers across the United States. They examined estrogen therapy outcomes by bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) status, with additional stratification by 10-year age groups in 9,939 women aged 50 to 79 years with prior hysterectomy and known oophorectomy status. In the WHI trial, women were randomly assigned to conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) 0.625 mg/d or placebo for a median of 7.2 years. Investigators assessed the incidence of coronary heart disease and invasive breast cancer (the trial’s 2 primary end points), all-cause mortality, and a “global index”—these end points plus stroke, pulmonary embolism, colorectal cancer, and hip fracture—during the intervention phase and 18-year cumulative follow-up.
OBG Management caught up with lead author JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP, to discuss the study’s results.
OBG Management : How many women undergo BSO with their hysterectomy?
Dr. JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, NCMP: Of the 425,000 women who undergo hysterectomy in the United States for benign reasons each year,2,3 about 40% of them undergo BSO—so between 150,000 and 200,000 women per year undergo BSO with their hysterectomy.4,5
OBG Management : Although BSO is performed with hysterectomy to minimize patients’ future ovarian cancer risk, does BSO have health risks of its own, and how has estrogen been shown to affect these risks?
Dr. Manson: First, yes, BSO has been associated with health risks, especially when it is performed at a young age, such as before age 45. It has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, and all-cause mortality. According to observational studies, estrogen therapy appears to offset many of these risks, particularly those related to heart disease and osteoporosis (the evidence is less clear on cognitive deficits).5
OBG Management : What did you find in your trial when you randomly assigned women in the age groups of 50 to 79 who underwent hysterectomy with and without BSO to estrogen therapy or placebo?
Dr. Manson: The WHI is the first study to be conducted in a randomized trial setting to analyze the health risks and benefits of estrogen therapy according to whether or not women had their ovaries removed. What we found was that the woman’s age had a strong influence on the effects of estrogen therapy among women who had BSO but only a negligible effect among women who had conserved ovaries. Overall, across the full age range, the effects of estrogen therapy did not differ substantially between women who had a BSO and those who had their ovaries conserved.
However, there were major differences by age group among the women who had BSO. A significant 32% reduction in all-cause mortality emerged during the 18-year follow-up period among the younger women (below age 60) who had BSO when they received estrogen therapy as compared with placebo. By contrast, the women who had conserved ovaries did not have this significant reduction in all-cause mortality, or in most of the other outcomes on estrogen compared with placebo. Overall, the effects of estrogen therapy tended to be relatively neutral in the women with conserved ovaries.
Now, the reduction in all-cause mortality with estrogen therapy was particularly pronounced among women who had BSO before age 45. They had a 40% statistically significant reduction in all-cause mortality with estrogen therapy compared with placebo. Also, among the women with BSO, there was a strong association between the timing of estrogen initiation and the magnitude of reduction in mortality. Women who started the estrogen therapy within 10 years of having the BSO had a 34% significant reduction in all-cause mortality, and those who started estrogen more than 20 years after having their ovaries removed had no reduction in mortality.
Continue to:
OBG Management : Do your data give support to the timing hypothesis?
Dr. Manson: Yes, our findings do support a timing hypothesis that was particularly pronounced for women who underwent BSO. It was the women who had early surgical menopause (before age 45) and those who started the estrogen therapy within 10 years of having their ovaries removed who had the greatest reduction in all-cause mortality and the most favorable benefit-risk profile from hormone therapy. So, the results do lend support to the timing hypothesis.
By contrast, women who had BSO at hysterectomy and began hormone therapy at age 70 or older had net adverse effects from hormone therapy. They posted a 40% increase in the global index—which is a summary measure of adverse effects on cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other major health outcomes. So, the women with BSO who were randomized in the trial at age 70 and older, had unfavorable results from estrogen therapy and an increase in the global index, in contrast to the women who were below age 60 or within 10 years of menopause.
OBG Management : Given your study findings, in which women would you recommend estrogen therapy? And are there groups of women in which you would advise avoiding estrogen therapy?
Dr. Manson: Current guidelines6,7 recommend estrogen therapy for women who have early menopause, particularly an early surgical menopause and BSO prior to the average age at natural menopause. Unless the woman has contraindications to estrogen therapy, the recommendations are to treat with estrogen until the average age of menopause—until about age 50 to 51.
Our study findings provide reassurance that, if a woman continues to have indications for estrogen (vasomotor symptoms, or other indications for estrogen therapy), there is relative safety of continuing estrogen-alone therapy through her 50s, until age 60. For example, a woman who, after the average age of menopause continues to have vasomotor symptoms, or if she has bone health problems, our study would suggest that estrogen therapy would continue to have a favorable benefit-risk profile until at least the age of 60. Decisions would have to be individualized, especially after age 60, with shared decision-making particularly important for those decisions. (Some women, depending on their risk profile, may continue to be candidates for estrogen therapy past age 60.)
So, this study provides reassurance regarding use of estrogen therapy for women in their 50s if they have had BSO. Actually, the women who had conserved ovaries also had relative safety with estrogen therapy until age 60. They just didn’t show the significant benefits for all-cause mortality. Overall, their pattern of health-related benefits and risks was neutral. Thus, if vasomotor symptom management, quality of life benefits, or bone health effects are sought, taking hormone therapy is a quite reasonable choice for these women.
By contrast, women who have had a BSO and are age 70 or older should really avoid initiating estrogen therapy because it would follow a prolonged period of estrogen deficiency, or very low estrogen levels, and these women appeared to have a net adverse effect from initiating hormone therapy (with increases in the global index found).
Continue to:
OBG Management : Did taking estrogen therapy prior to trial enrollment make a difference when it came to study outcomes?
Dr. Manson: We found minimal if any effect in our analyses. In fact, even the women who did not have prior (pre-randomization) use of estrogen therapy tended to do well on estrogen-alone therapy if they were younger than age 60. This was particularly true for the women who had BSO. Even if they had not used estrogen previously, and they were many years past the BSO, they still did well on estrogen therapy if they were below age 60.
1. Manson JE, Aragaki AK, Bassuk SS. Menopausal estrogen-alone therapy and health outcomes in women with and without bilateral oophorectomy: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2019 September 10. doi:10.7326/M19-0274.
2. Einarsson J. Are hysterectomy volumes in the US really falling? Contemporary OB/GYN. 1 September 2017. www.contemporaryobgyn.net/gynecology/are-hysterectomy-volumes-us-really-falling. November 4, 2019.
3. Temkin SM, Minasian L, Noone AM. The end of the hysterectomy epidemic and endometrial cancer incidence: what are the unintended consequences of declining hysterectomy rates? Front Oncol. 2016;6:89.
4. Doll KM, Dusetzina SB, Robinson W. Trends in inpatient and outpatient hysterectomy and oophorectomy rates among commercially insured women in the United States, 2000-2014. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:876-877.
5. Adelman MR, Sharp HT. Ovarian conservation vs removal at the time of benign hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:269-279.
6. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 141: management of menopausal symptoms [published corrections appear in: Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(1):166. and Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(3):604]. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
7. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
1. Manson JE, Aragaki AK, Bassuk SS. Menopausal estrogen-alone therapy and health outcomes in women with and without bilateral oophorectomy: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2019 September 10. doi:10.7326/M19-0274.
2. Einarsson J. Are hysterectomy volumes in the US really falling? Contemporary OB/GYN. 1 September 2017. www.contemporaryobgyn.net/gynecology/are-hysterectomy-volumes-us-really-falling. November 4, 2019.
3. Temkin SM, Minasian L, Noone AM. The end of the hysterectomy epidemic and endometrial cancer incidence: what are the unintended consequences of declining hysterectomy rates? Front Oncol. 2016;6:89.
4. Doll KM, Dusetzina SB, Robinson W. Trends in inpatient and outpatient hysterectomy and oophorectomy rates among commercially insured women in the United States, 2000-2014. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:876-877.
5. Adelman MR, Sharp HT. Ovarian conservation vs removal at the time of benign hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:269-279.
6. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 141: management of menopausal symptoms [published corrections appear in: Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(1):166. and Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(3):604]. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:202-216.
7. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause. 2017;24:728-753.
Product Update: Addyi alcohol ban lifted, fezolinetant trial, outcomes tracker, comfort gown
FDA REMOVES ALCOHOL BAN WITH ADDYI
Sprout Pharmaceuticals announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has removed their contraindication on alcohol use with Addyi® (flibanserin). Addyi was approved in 2015 and is an oral nonhormonal pill for acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women. Patients are advised to discontinue drinking alcohol at least 2 hours before taking Addyi at bedtime or skip the Addyi dose that evening.
The FDA also removed the requirement, under its Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, for health care practitioners or pharmacies to be certified to prescribe or dispense Addyi. Sprout says that to make all labeling elements consistent with the FDA’s findings the boxed warning will change and the medication guide will be updated and included under the REMS.
The most commonly reported adverse events among patients taking Addyi are dizziness, sleepiness, nausea, fatigue, insomnia, and dry mouth. Addyi is contraindicated in patients taking moderate or strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors and in those with hepatic impairment.
FOR MORE INFORMATION AND THE FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION AND MEDICATION GUIDE, VISIT: www.addyi.com
FEZOLINETANT FOR VMS
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov, TRIAL IDENTIFIERS NCT04003155, NCT04003142, AND NCT04003389
SOLUTIONS FOR OUTCOME TRACKING
DrChrono and OutcomeMD announce a partnership to track and analyze patient outcome data and confounding factors. DrChrono is an electronic health record (EHR) system, and OutcomeMD is a software solution that uses literature-validated patient-reported outcome instruments to score and track a patient’s symptom severity and inform treatment decisions for users.
Via a HIPAA compliant process, patients answer a list of questions that are accessed through a web link on their mobile or desktop devices. OutcomeMD summarizes the symptoms into a score that displays to both the physician and patient. Patients’ answers and scores are pushed to the clinician’s DrChrono EHR medical note.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: www.outcomemd.com
Continue to: NEW MATERNITY GOWN...
NEW MATERNITY GOWN
ImageFIRST launched a new maternity gown for expecting mothers. The Comfort Care® Maternity Gown is a lightweight, premium polyester/nylon fabric that front snaps to allow for skin-to-skin access and optional breastfeeding. The gown also includes shoulder snaps and a full cut for extra coverage and to accommodate a variety of body types, says ImageFIRST.
ImageFIRST is a national linen rental provider. It developed the Comfort Care® Maternity Gown with input from labor and delivery departments to best meet the needs of expecting mothers. It also says that a portion of the proceeds from each gown rental will be donated to the National Pediatric Cancer Foundation.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: www.imagefirst.com
FDA REMOVES ALCOHOL BAN WITH ADDYI
Sprout Pharmaceuticals announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has removed their contraindication on alcohol use with Addyi® (flibanserin). Addyi was approved in 2015 and is an oral nonhormonal pill for acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women. Patients are advised to discontinue drinking alcohol at least 2 hours before taking Addyi at bedtime or skip the Addyi dose that evening.
The FDA also removed the requirement, under its Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, for health care practitioners or pharmacies to be certified to prescribe or dispense Addyi. Sprout says that to make all labeling elements consistent with the FDA’s findings the boxed warning will change and the medication guide will be updated and included under the REMS.
The most commonly reported adverse events among patients taking Addyi are dizziness, sleepiness, nausea, fatigue, insomnia, and dry mouth. Addyi is contraindicated in patients taking moderate or strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors and in those with hepatic impairment.
FOR MORE INFORMATION AND THE FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION AND MEDICATION GUIDE, VISIT: www.addyi.com
FEZOLINETANT FOR VMS
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov, TRIAL IDENTIFIERS NCT04003155, NCT04003142, AND NCT04003389
SOLUTIONS FOR OUTCOME TRACKING
DrChrono and OutcomeMD announce a partnership to track and analyze patient outcome data and confounding factors. DrChrono is an electronic health record (EHR) system, and OutcomeMD is a software solution that uses literature-validated patient-reported outcome instruments to score and track a patient’s symptom severity and inform treatment decisions for users.
Via a HIPAA compliant process, patients answer a list of questions that are accessed through a web link on their mobile or desktop devices. OutcomeMD summarizes the symptoms into a score that displays to both the physician and patient. Patients’ answers and scores are pushed to the clinician’s DrChrono EHR medical note.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: www.outcomemd.com
Continue to: NEW MATERNITY GOWN...
NEW MATERNITY GOWN
ImageFIRST launched a new maternity gown for expecting mothers. The Comfort Care® Maternity Gown is a lightweight, premium polyester/nylon fabric that front snaps to allow for skin-to-skin access and optional breastfeeding. The gown also includes shoulder snaps and a full cut for extra coverage and to accommodate a variety of body types, says ImageFIRST.
ImageFIRST is a national linen rental provider. It developed the Comfort Care® Maternity Gown with input from labor and delivery departments to best meet the needs of expecting mothers. It also says that a portion of the proceeds from each gown rental will be donated to the National Pediatric Cancer Foundation.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: www.imagefirst.com
FDA REMOVES ALCOHOL BAN WITH ADDYI
Sprout Pharmaceuticals announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has removed their contraindication on alcohol use with Addyi® (flibanserin). Addyi was approved in 2015 and is an oral nonhormonal pill for acquired, generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women. Patients are advised to discontinue drinking alcohol at least 2 hours before taking Addyi at bedtime or skip the Addyi dose that evening.
The FDA also removed the requirement, under its Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program, for health care practitioners or pharmacies to be certified to prescribe or dispense Addyi. Sprout says that to make all labeling elements consistent with the FDA’s findings the boxed warning will change and the medication guide will be updated and included under the REMS.
The most commonly reported adverse events among patients taking Addyi are dizziness, sleepiness, nausea, fatigue, insomnia, and dry mouth. Addyi is contraindicated in patients taking moderate or strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors and in those with hepatic impairment.
FOR MORE INFORMATION AND THE FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION AND MEDICATION GUIDE, VISIT: www.addyi.com
FEZOLINETANT FOR VMS
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov, TRIAL IDENTIFIERS NCT04003155, NCT04003142, AND NCT04003389
SOLUTIONS FOR OUTCOME TRACKING
DrChrono and OutcomeMD announce a partnership to track and analyze patient outcome data and confounding factors. DrChrono is an electronic health record (EHR) system, and OutcomeMD is a software solution that uses literature-validated patient-reported outcome instruments to score and track a patient’s symptom severity and inform treatment decisions for users.
Via a HIPAA compliant process, patients answer a list of questions that are accessed through a web link on their mobile or desktop devices. OutcomeMD summarizes the symptoms into a score that displays to both the physician and patient. Patients’ answers and scores are pushed to the clinician’s DrChrono EHR medical note.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: www.outcomemd.com
Continue to: NEW MATERNITY GOWN...
NEW MATERNITY GOWN
ImageFIRST launched a new maternity gown for expecting mothers. The Comfort Care® Maternity Gown is a lightweight, premium polyester/nylon fabric that front snaps to allow for skin-to-skin access and optional breastfeeding. The gown also includes shoulder snaps and a full cut for extra coverage and to accommodate a variety of body types, says ImageFIRST.
ImageFIRST is a national linen rental provider. It developed the Comfort Care® Maternity Gown with input from labor and delivery departments to best meet the needs of expecting mothers. It also says that a portion of the proceeds from each gown rental will be donated to the National Pediatric Cancer Foundation.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: www.imagefirst.com
Ovarian cryopreservation should no longer be experimental
PHILADELPHIA – Ovarian tissue cryopreservation should no longer be considered experimental, Sherman J. Silber, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
That claim is based on more than 20 years of experience at his center performing the procedure and results he presented from patients for whom frozen ovarian tissue has been reimplanted resulting in a spontaneous pregnancy.
“For prepubertal girls with cancer and for patients who have already had a preliminary round of chemotherapy, ovarian tissue freezing is the only method available to preserve their fertility,” said Dr. Silber, of the Infertility Center of St. Louis in Chesterfield, Missouri. “It is also the only method available to preserve their fertility.”
“I have very strong feelings about this,” he added. “It has huge societal implications for insurance payments.”
Dr. Silber presented results of ovarian tissue freezing and reimplantation at his center beginning in 1997, where 115 patients between the ages of 2 and 35 years underwent the procedure using the same technique. Of these patients, 14 women came back years later to have their frozen ovary cortex reimplanted. Dr. Silber and his group followed these patients monthly for more than 2 years after reimplantation for signs of return of menses, hormonal changes, pregnancy, and live birth.
Most of the patients who chose ovarian tissue freezing had cancer. Eight patients underwent the procedure after being diagnosed with solid tissue cancer and three had leukemia, while two patients underwent ovarian tissue freezing due to premature ovarian failure, and one because of multiple sclerosis. Patients who underwent reimplantation were menopausal for at least 3 years, said Dr. Silber.
Dr. Silber also described the technique used for reimplantation. After the cortical tissue was thawed, the tissue was quilted into one piece from three to five slices using 9-0 nylon interrupted sutures. The quilted tissue was then sutured to the medulla after the surgeon completely removed the dead cortex from the other ovary. “Hemostasis was achieved with micro bipolar forceps,” said Dr. Silber. “Constant irrigation was employed with pulsed heparinized media because we wanted to avoid adhesions, and we wanted to try for spontaneous pregnancy rather than IVF.”
“Then, we put [the quilted ovarian slices] on to the medulla on the other side in such a way that the fallopian tube would be able to reach and catch any egg that’s ovulated during that time,” he added.
Dr. Silber and his group found that, over time, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels sharply decreased to normal or near-normal levels between 69 days and 133 days after the procedure while Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels dramatically rose to higher levels between 133 days and 227 days post-procedure before dropping to very low levels, “and the AMH remained at low levels despite the fact that [transplants] would last 8 to 10 years,” said Dr. Silber.
Of the 14 cases where frozen ovarian tissue was reimplanted, 11 patients (78%) achieved pregnancy, 10 patients (71%) delivered healthy babies, and 1 patient (9%) experienced a miscarriage. All patients had spontaneous pregnancies, and none used in vitro fertilization (IVF), noted Dr. Silber. There were 2 patients who had four children from transplanted ovarian tissue, and 2 of 3 patients with leukemia had a total of five children.
Additionally, Dr. Silber’s group examined the literature for other examples of ovarian tissue reimplantation after cryopreservation to determine how many live births resulted from the procedure. They found an additional 170 live births in addition to the 15 live births at their center, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 31% to 71% in different studies. Cancer was not transmitted from mother to child in any case, said Dr. Silber.
Compared with egg freezing, there is a benefit to performing ovarian tissue freezing, even after chemotherapy has begun, noted Dr. Silber. The cost of ovarian tissue freezing is also roughly one-tenth that of egg freezing, and the procedure is less burdensome than multiple cycles with the potential for ovarian hyperstimulation, and it restores the hormone function and the fertility of eggs after reimplantation.
“Because the greater primordial follicle recruitment decreases as the ovarian reserve decreases, you can put a piece of ovary tissue back every 8 years, and a woman can have endocrine function until she’s 100 years old,” said Dr. Silber.
Dr. Silber reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Silber SJ. ASRM 2019. Abstract O-203.
PHILADELPHIA – Ovarian tissue cryopreservation should no longer be considered experimental, Sherman J. Silber, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
That claim is based on more than 20 years of experience at his center performing the procedure and results he presented from patients for whom frozen ovarian tissue has been reimplanted resulting in a spontaneous pregnancy.
“For prepubertal girls with cancer and for patients who have already had a preliminary round of chemotherapy, ovarian tissue freezing is the only method available to preserve their fertility,” said Dr. Silber, of the Infertility Center of St. Louis in Chesterfield, Missouri. “It is also the only method available to preserve their fertility.”
“I have very strong feelings about this,” he added. “It has huge societal implications for insurance payments.”
Dr. Silber presented results of ovarian tissue freezing and reimplantation at his center beginning in 1997, where 115 patients between the ages of 2 and 35 years underwent the procedure using the same technique. Of these patients, 14 women came back years later to have their frozen ovary cortex reimplanted. Dr. Silber and his group followed these patients monthly for more than 2 years after reimplantation for signs of return of menses, hormonal changes, pregnancy, and live birth.
Most of the patients who chose ovarian tissue freezing had cancer. Eight patients underwent the procedure after being diagnosed with solid tissue cancer and three had leukemia, while two patients underwent ovarian tissue freezing due to premature ovarian failure, and one because of multiple sclerosis. Patients who underwent reimplantation were menopausal for at least 3 years, said Dr. Silber.
Dr. Silber also described the technique used for reimplantation. After the cortical tissue was thawed, the tissue was quilted into one piece from three to five slices using 9-0 nylon interrupted sutures. The quilted tissue was then sutured to the medulla after the surgeon completely removed the dead cortex from the other ovary. “Hemostasis was achieved with micro bipolar forceps,” said Dr. Silber. “Constant irrigation was employed with pulsed heparinized media because we wanted to avoid adhesions, and we wanted to try for spontaneous pregnancy rather than IVF.”
“Then, we put [the quilted ovarian slices] on to the medulla on the other side in such a way that the fallopian tube would be able to reach and catch any egg that’s ovulated during that time,” he added.
Dr. Silber and his group found that, over time, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels sharply decreased to normal or near-normal levels between 69 days and 133 days after the procedure while Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels dramatically rose to higher levels between 133 days and 227 days post-procedure before dropping to very low levels, “and the AMH remained at low levels despite the fact that [transplants] would last 8 to 10 years,” said Dr. Silber.
Of the 14 cases where frozen ovarian tissue was reimplanted, 11 patients (78%) achieved pregnancy, 10 patients (71%) delivered healthy babies, and 1 patient (9%) experienced a miscarriage. All patients had spontaneous pregnancies, and none used in vitro fertilization (IVF), noted Dr. Silber. There were 2 patients who had four children from transplanted ovarian tissue, and 2 of 3 patients with leukemia had a total of five children.
Additionally, Dr. Silber’s group examined the literature for other examples of ovarian tissue reimplantation after cryopreservation to determine how many live births resulted from the procedure. They found an additional 170 live births in addition to the 15 live births at their center, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 31% to 71% in different studies. Cancer was not transmitted from mother to child in any case, said Dr. Silber.
Compared with egg freezing, there is a benefit to performing ovarian tissue freezing, even after chemotherapy has begun, noted Dr. Silber. The cost of ovarian tissue freezing is also roughly one-tenth that of egg freezing, and the procedure is less burdensome than multiple cycles with the potential for ovarian hyperstimulation, and it restores the hormone function and the fertility of eggs after reimplantation.
“Because the greater primordial follicle recruitment decreases as the ovarian reserve decreases, you can put a piece of ovary tissue back every 8 years, and a woman can have endocrine function until she’s 100 years old,” said Dr. Silber.
Dr. Silber reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Silber SJ. ASRM 2019. Abstract O-203.
PHILADELPHIA – Ovarian tissue cryopreservation should no longer be considered experimental, Sherman J. Silber, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
That claim is based on more than 20 years of experience at his center performing the procedure and results he presented from patients for whom frozen ovarian tissue has been reimplanted resulting in a spontaneous pregnancy.
“For prepubertal girls with cancer and for patients who have already had a preliminary round of chemotherapy, ovarian tissue freezing is the only method available to preserve their fertility,” said Dr. Silber, of the Infertility Center of St. Louis in Chesterfield, Missouri. “It is also the only method available to preserve their fertility.”
“I have very strong feelings about this,” he added. “It has huge societal implications for insurance payments.”
Dr. Silber presented results of ovarian tissue freezing and reimplantation at his center beginning in 1997, where 115 patients between the ages of 2 and 35 years underwent the procedure using the same technique. Of these patients, 14 women came back years later to have their frozen ovary cortex reimplanted. Dr. Silber and his group followed these patients monthly for more than 2 years after reimplantation for signs of return of menses, hormonal changes, pregnancy, and live birth.
Most of the patients who chose ovarian tissue freezing had cancer. Eight patients underwent the procedure after being diagnosed with solid tissue cancer and three had leukemia, while two patients underwent ovarian tissue freezing due to premature ovarian failure, and one because of multiple sclerosis. Patients who underwent reimplantation were menopausal for at least 3 years, said Dr. Silber.
Dr. Silber also described the technique used for reimplantation. After the cortical tissue was thawed, the tissue was quilted into one piece from three to five slices using 9-0 nylon interrupted sutures. The quilted tissue was then sutured to the medulla after the surgeon completely removed the dead cortex from the other ovary. “Hemostasis was achieved with micro bipolar forceps,” said Dr. Silber. “Constant irrigation was employed with pulsed heparinized media because we wanted to avoid adhesions, and we wanted to try for spontaneous pregnancy rather than IVF.”
“Then, we put [the quilted ovarian slices] on to the medulla on the other side in such a way that the fallopian tube would be able to reach and catch any egg that’s ovulated during that time,” he added.
Dr. Silber and his group found that, over time, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels sharply decreased to normal or near-normal levels between 69 days and 133 days after the procedure while Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels dramatically rose to higher levels between 133 days and 227 days post-procedure before dropping to very low levels, “and the AMH remained at low levels despite the fact that [transplants] would last 8 to 10 years,” said Dr. Silber.
Of the 14 cases where frozen ovarian tissue was reimplanted, 11 patients (78%) achieved pregnancy, 10 patients (71%) delivered healthy babies, and 1 patient (9%) experienced a miscarriage. All patients had spontaneous pregnancies, and none used in vitro fertilization (IVF), noted Dr. Silber. There were 2 patients who had four children from transplanted ovarian tissue, and 2 of 3 patients with leukemia had a total of five children.
Additionally, Dr. Silber’s group examined the literature for other examples of ovarian tissue reimplantation after cryopreservation to determine how many live births resulted from the procedure. They found an additional 170 live births in addition to the 15 live births at their center, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 31% to 71% in different studies. Cancer was not transmitted from mother to child in any case, said Dr. Silber.
Compared with egg freezing, there is a benefit to performing ovarian tissue freezing, even after chemotherapy has begun, noted Dr. Silber. The cost of ovarian tissue freezing is also roughly one-tenth that of egg freezing, and the procedure is less burdensome than multiple cycles with the potential for ovarian hyperstimulation, and it restores the hormone function and the fertility of eggs after reimplantation.
“Because the greater primordial follicle recruitment decreases as the ovarian reserve decreases, you can put a piece of ovary tissue back every 8 years, and a woman can have endocrine function until she’s 100 years old,” said Dr. Silber.
Dr. Silber reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Silber SJ. ASRM 2019. Abstract O-203.
REPORTING FROM ASRM 2019
What does the REPLENISH trial reveal about E2/P4’s ability to affect VMS and sleep and appropriate dosing for smokers?
The REPLENISH trial evaluated the oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone (E2/P4) softgel capsule (TX-001HR; 1 mg E2/100 mg P4) approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in October 2018 as Bijuva (TherapeuticsMD) for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS) due to menopause. In separate subanalyses presented at the annual Scientific Meeting of the North American Menopause Society in Chicago, Illinois (September 25-28, 2019), researchers examined E2/P4’s ability to address VMS according to age and body mass index (BMI), ability to address sleep, and appropriate dosing in smokers versus nonsmokers.
REPLENISH
The REPLENISH trial was a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of E2/P4 for the treatment of VMS in 1,835 postmenopausal women aged 40 to 65 years with a uterus. Women with moderate to severe VMS (≥7/day or ≥50/week) were randomly assigned to E2/P4 (mg/mg) 1/100, 0.5/100, 0.5/50, 0.25/50, or placebo.1
E2/P4 and VMS according to age and BMI
Percent changes in the weekly frequency and severity of moderate to severe VMS from baseline to weeks 4 and 12 versus placebo were analyzed by age (<55 and ≥55 years) and BMI in the study participants.1 The BMI subgroups had similar baseline VMS, but women in the younger age group had higher baseline frequency of moderate to severe VMS than women in the older age group.
Age. The percent changes in VMS frequency from baseline for women treated with E2/P4 were similar at weeks 4 and 12 between age groups. While subgroup analyses were not powered for statistical significance, significant differences were observed between E2/P4 dosages and placebo at week 12. For VMS severity, the percent changes from baseline for women treated with E2/P4 ranged from 16% to 22% at week 4 and 24% to 51% for either age group at week 12.
BMI. When analyzed by BMI, larger percent reductions from baseline in VMS frequency and severity were observed with E2/P4 dosaging versus placebo, with some groups meeting statistical significance at both weeks 4 and 12.
The authors concluded that their subgroup analyses show a consistency of efficacy for VMS frequency and severity among the different age group and BMI populations of women treated with E2/P4.
E2/P4 and sleep outcomes
Participants in the REPLENISH trial took 2 surveys related to sleep—the Medical Outcomes Study (MOS)-Sleep, a 12-item questionnaire measuring 6 sleep dimensions, and the Menopause-specific Quality of Life (MENQOL), which included a “difficulty sleeping” item.2 Except for women treated with E2/P4 0.25/50 at week 12, women receiving E2/P4 reported significantly better change in the MOS-Sleep total, as well as better ratings on sleep problems and disturbance subscales, than women treated with placebo at week 12 and months 6 and 12. The incidence of somnolence was low with E2/P4 treatment. In addition, sleep mediation models showed that E2/P4 improved MOS-sleep disturbances indirectly through improvements in VMS. The study authors concluded that women taking E2/P4 for moderate to severe VMS may experience improved sleep.
Smoking and E2/P4 dosage
Among postmenopausal women, smoking has been shown to reduce the efficacy of hormone therapy.3 Researchers found that nonsmokers (never or past smokers) may benefit more from a lower E2/P4 dosage than current smokers (<15 cigarettes per day).4 (Women smoking ≥15 cigarettes per day or any e-cigarettes were excluded from REPLENISH). Compared with nonsmokers taking placebo, nonsmokers taking any dosage of E2/P4 had a significant and clinically meaningful reduction in VMS frequency and severity beginning at week 4 and maintained through week 12 (except for the E2/P4 dosage of 0.5/50 at week 4 for severity). By contrast, current smokers in any E2/P4 group had no significant VMS improvements from baseline to weeks 4 and 12 compared with placebo, and proportions of smokers who did measure some response to treatment (at both ≥50% and ≥75% levels) were not different from placebo at weeks 4 and 12. In addition, current smokers had significantly lower median levels of systemic estradiol and estrone concentrations with all E2/P4 treatment groups than did nonsmokers, despite both groups having similar estradiol and estrone concentrations at baseline.
- Bitner D, Brightman R, Graham S, et al. E2/P4 capsules effectively treat vasomotor symptoms irrespective of age and BMI. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Kaunitz AM, Kagan R, Graham S, et al. Oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone (E2/P4) improved sleep outcomes in the REPLENISH trial. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Jensen J, Christiansen C, Rodbro P. Cigarette smoking, serum estrogens, and bone loss during hormone-replacement therapy after menopause. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:973-975.
- Constantine GD, Santoro N, Graham S, et al. Nonsmokers may benefit from lower doses of an oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone capsule—data from the REPLENISH trial. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
The REPLENISH trial evaluated the oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone (E2/P4) softgel capsule (TX-001HR; 1 mg E2/100 mg P4) approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in October 2018 as Bijuva (TherapeuticsMD) for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS) due to menopause. In separate subanalyses presented at the annual Scientific Meeting of the North American Menopause Society in Chicago, Illinois (September 25-28, 2019), researchers examined E2/P4’s ability to address VMS according to age and body mass index (BMI), ability to address sleep, and appropriate dosing in smokers versus nonsmokers.
REPLENISH
The REPLENISH trial was a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of E2/P4 for the treatment of VMS in 1,835 postmenopausal women aged 40 to 65 years with a uterus. Women with moderate to severe VMS (≥7/day or ≥50/week) were randomly assigned to E2/P4 (mg/mg) 1/100, 0.5/100, 0.5/50, 0.25/50, or placebo.1
E2/P4 and VMS according to age and BMI
Percent changes in the weekly frequency and severity of moderate to severe VMS from baseline to weeks 4 and 12 versus placebo were analyzed by age (<55 and ≥55 years) and BMI in the study participants.1 The BMI subgroups had similar baseline VMS, but women in the younger age group had higher baseline frequency of moderate to severe VMS than women in the older age group.
Age. The percent changes in VMS frequency from baseline for women treated with E2/P4 were similar at weeks 4 and 12 between age groups. While subgroup analyses were not powered for statistical significance, significant differences were observed between E2/P4 dosages and placebo at week 12. For VMS severity, the percent changes from baseline for women treated with E2/P4 ranged from 16% to 22% at week 4 and 24% to 51% for either age group at week 12.
BMI. When analyzed by BMI, larger percent reductions from baseline in VMS frequency and severity were observed with E2/P4 dosaging versus placebo, with some groups meeting statistical significance at both weeks 4 and 12.
The authors concluded that their subgroup analyses show a consistency of efficacy for VMS frequency and severity among the different age group and BMI populations of women treated with E2/P4.
E2/P4 and sleep outcomes
Participants in the REPLENISH trial took 2 surveys related to sleep—the Medical Outcomes Study (MOS)-Sleep, a 12-item questionnaire measuring 6 sleep dimensions, and the Menopause-specific Quality of Life (MENQOL), which included a “difficulty sleeping” item.2 Except for women treated with E2/P4 0.25/50 at week 12, women receiving E2/P4 reported significantly better change in the MOS-Sleep total, as well as better ratings on sleep problems and disturbance subscales, than women treated with placebo at week 12 and months 6 and 12. The incidence of somnolence was low with E2/P4 treatment. In addition, sleep mediation models showed that E2/P4 improved MOS-sleep disturbances indirectly through improvements in VMS. The study authors concluded that women taking E2/P4 for moderate to severe VMS may experience improved sleep.
Smoking and E2/P4 dosage
Among postmenopausal women, smoking has been shown to reduce the efficacy of hormone therapy.3 Researchers found that nonsmokers (never or past smokers) may benefit more from a lower E2/P4 dosage than current smokers (<15 cigarettes per day).4 (Women smoking ≥15 cigarettes per day or any e-cigarettes were excluded from REPLENISH). Compared with nonsmokers taking placebo, nonsmokers taking any dosage of E2/P4 had a significant and clinically meaningful reduction in VMS frequency and severity beginning at week 4 and maintained through week 12 (except for the E2/P4 dosage of 0.5/50 at week 4 for severity). By contrast, current smokers in any E2/P4 group had no significant VMS improvements from baseline to weeks 4 and 12 compared with placebo, and proportions of smokers who did measure some response to treatment (at both ≥50% and ≥75% levels) were not different from placebo at weeks 4 and 12. In addition, current smokers had significantly lower median levels of systemic estradiol and estrone concentrations with all E2/P4 treatment groups than did nonsmokers, despite both groups having similar estradiol and estrone concentrations at baseline.
The REPLENISH trial evaluated the oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone (E2/P4) softgel capsule (TX-001HR; 1 mg E2/100 mg P4) approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in October 2018 as Bijuva (TherapeuticsMD) for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms (VMS) due to menopause. In separate subanalyses presented at the annual Scientific Meeting of the North American Menopause Society in Chicago, Illinois (September 25-28, 2019), researchers examined E2/P4’s ability to address VMS according to age and body mass index (BMI), ability to address sleep, and appropriate dosing in smokers versus nonsmokers.
REPLENISH
The REPLENISH trial was a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of E2/P4 for the treatment of VMS in 1,835 postmenopausal women aged 40 to 65 years with a uterus. Women with moderate to severe VMS (≥7/day or ≥50/week) were randomly assigned to E2/P4 (mg/mg) 1/100, 0.5/100, 0.5/50, 0.25/50, or placebo.1
E2/P4 and VMS according to age and BMI
Percent changes in the weekly frequency and severity of moderate to severe VMS from baseline to weeks 4 and 12 versus placebo were analyzed by age (<55 and ≥55 years) and BMI in the study participants.1 The BMI subgroups had similar baseline VMS, but women in the younger age group had higher baseline frequency of moderate to severe VMS than women in the older age group.
Age. The percent changes in VMS frequency from baseline for women treated with E2/P4 were similar at weeks 4 and 12 between age groups. While subgroup analyses were not powered for statistical significance, significant differences were observed between E2/P4 dosages and placebo at week 12. For VMS severity, the percent changes from baseline for women treated with E2/P4 ranged from 16% to 22% at week 4 and 24% to 51% for either age group at week 12.
BMI. When analyzed by BMI, larger percent reductions from baseline in VMS frequency and severity were observed with E2/P4 dosaging versus placebo, with some groups meeting statistical significance at both weeks 4 and 12.
The authors concluded that their subgroup analyses show a consistency of efficacy for VMS frequency and severity among the different age group and BMI populations of women treated with E2/P4.
E2/P4 and sleep outcomes
Participants in the REPLENISH trial took 2 surveys related to sleep—the Medical Outcomes Study (MOS)-Sleep, a 12-item questionnaire measuring 6 sleep dimensions, and the Menopause-specific Quality of Life (MENQOL), which included a “difficulty sleeping” item.2 Except for women treated with E2/P4 0.25/50 at week 12, women receiving E2/P4 reported significantly better change in the MOS-Sleep total, as well as better ratings on sleep problems and disturbance subscales, than women treated with placebo at week 12 and months 6 and 12. The incidence of somnolence was low with E2/P4 treatment. In addition, sleep mediation models showed that E2/P4 improved MOS-sleep disturbances indirectly through improvements in VMS. The study authors concluded that women taking E2/P4 for moderate to severe VMS may experience improved sleep.
Smoking and E2/P4 dosage
Among postmenopausal women, smoking has been shown to reduce the efficacy of hormone therapy.3 Researchers found that nonsmokers (never or past smokers) may benefit more from a lower E2/P4 dosage than current smokers (<15 cigarettes per day).4 (Women smoking ≥15 cigarettes per day or any e-cigarettes were excluded from REPLENISH). Compared with nonsmokers taking placebo, nonsmokers taking any dosage of E2/P4 had a significant and clinically meaningful reduction in VMS frequency and severity beginning at week 4 and maintained through week 12 (except for the E2/P4 dosage of 0.5/50 at week 4 for severity). By contrast, current smokers in any E2/P4 group had no significant VMS improvements from baseline to weeks 4 and 12 compared with placebo, and proportions of smokers who did measure some response to treatment (at both ≥50% and ≥75% levels) were not different from placebo at weeks 4 and 12. In addition, current smokers had significantly lower median levels of systemic estradiol and estrone concentrations with all E2/P4 treatment groups than did nonsmokers, despite both groups having similar estradiol and estrone concentrations at baseline.
- Bitner D, Brightman R, Graham S, et al. E2/P4 capsules effectively treat vasomotor symptoms irrespective of age and BMI. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Kaunitz AM, Kagan R, Graham S, et al. Oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone (E2/P4) improved sleep outcomes in the REPLENISH trial. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Jensen J, Christiansen C, Rodbro P. Cigarette smoking, serum estrogens, and bone loss during hormone-replacement therapy after menopause. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:973-975.
- Constantine GD, Santoro N, Graham S, et al. Nonsmokers may benefit from lower doses of an oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone capsule—data from the REPLENISH trial. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Bitner D, Brightman R, Graham S, et al. E2/P4 capsules effectively treat vasomotor symptoms irrespective of age and BMI. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Kaunitz AM, Kagan R, Graham S, et al. Oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone (E2/P4) improved sleep outcomes in the REPLENISH trial. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Jensen J, Christiansen C, Rodbro P. Cigarette smoking, serum estrogens, and bone loss during hormone-replacement therapy after menopause. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:973-975.
- Constantine GD, Santoro N, Graham S, et al. Nonsmokers may benefit from lower doses of an oral 17β-estradiol/progesterone capsule—data from the REPLENISH trial. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
Postmenopausal women would benefit from clinician-initiated discussion of GSM symptoms
Researchers from Kaiser Permanente Northwest and Oregon Health & Science University, both in Portland, performed a secondary analysis of a survey of postmenopausal women conducted to assess the impact of a health system intervention on genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). They presented their results at the recent annual Scientific Meeting of the North American Menopause Society in Chicago, Illinois (September 25-28, 2019). The intervention included clinician education and computer support tools and was assessed in a clinic-based, cluster-randomized trial in which primary care and gynecology clinics either received the intervention or did not. Women received follow-up 2 weeks after a well-woman visit with a survey that elicited vulvovaginal, sexual, and urinary symptoms with bother.
About 45% of those responding to the survey (N = 1,533) reported 1 or more vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) symptoms—on average described as somewhat or moderately bothersome—but less than half of those women (39%) discussed their symptom(s) at their well-woman visit. Typically it was the woman, rather than the clinician, who initiated the discussion of the VVA symptom(s) (59% vs 22%, respectively). About 16% of women reported that both parties brought up the symptom(s). Most women (83%) were satisfied with the VVA symptom discussion. Of the women not having such a discussion, 18% wished that one had occurred. A VVA symptom discussion was positively associated with clinicians providing written materials, suggesting lubricants or vaginal estrogen, and providing a referral. Therefore, there is a greater role for clinician-initiated screening for GSM, the study authors concluded.
- Clark AL, Bulkley JE, Bennett AT, et al. Discussion of vulvovaginal health at postmenopausal well woman visit—patient characteristics and visit experiences. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
Researchers from Kaiser Permanente Northwest and Oregon Health & Science University, both in Portland, performed a secondary analysis of a survey of postmenopausal women conducted to assess the impact of a health system intervention on genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). They presented their results at the recent annual Scientific Meeting of the North American Menopause Society in Chicago, Illinois (September 25-28, 2019). The intervention included clinician education and computer support tools and was assessed in a clinic-based, cluster-randomized trial in which primary care and gynecology clinics either received the intervention or did not. Women received follow-up 2 weeks after a well-woman visit with a survey that elicited vulvovaginal, sexual, and urinary symptoms with bother.
About 45% of those responding to the survey (N = 1,533) reported 1 or more vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) symptoms—on average described as somewhat or moderately bothersome—but less than half of those women (39%) discussed their symptom(s) at their well-woman visit. Typically it was the woman, rather than the clinician, who initiated the discussion of the VVA symptom(s) (59% vs 22%, respectively). About 16% of women reported that both parties brought up the symptom(s). Most women (83%) were satisfied with the VVA symptom discussion. Of the women not having such a discussion, 18% wished that one had occurred. A VVA symptom discussion was positively associated with clinicians providing written materials, suggesting lubricants or vaginal estrogen, and providing a referral. Therefore, there is a greater role for clinician-initiated screening for GSM, the study authors concluded.
Researchers from Kaiser Permanente Northwest and Oregon Health & Science University, both in Portland, performed a secondary analysis of a survey of postmenopausal women conducted to assess the impact of a health system intervention on genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). They presented their results at the recent annual Scientific Meeting of the North American Menopause Society in Chicago, Illinois (September 25-28, 2019). The intervention included clinician education and computer support tools and was assessed in a clinic-based, cluster-randomized trial in which primary care and gynecology clinics either received the intervention or did not. Women received follow-up 2 weeks after a well-woman visit with a survey that elicited vulvovaginal, sexual, and urinary symptoms with bother.
About 45% of those responding to the survey (N = 1,533) reported 1 or more vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) symptoms—on average described as somewhat or moderately bothersome—but less than half of those women (39%) discussed their symptom(s) at their well-woman visit. Typically it was the woman, rather than the clinician, who initiated the discussion of the VVA symptom(s) (59% vs 22%, respectively). About 16% of women reported that both parties brought up the symptom(s). Most women (83%) were satisfied with the VVA symptom discussion. Of the women not having such a discussion, 18% wished that one had occurred. A VVA symptom discussion was positively associated with clinicians providing written materials, suggesting lubricants or vaginal estrogen, and providing a referral. Therefore, there is a greater role for clinician-initiated screening for GSM, the study authors concluded.
- Clark AL, Bulkley JE, Bennett AT, et al. Discussion of vulvovaginal health at postmenopausal well woman visit—patient characteristics and visit experiences. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
- Clark AL, Bulkley JE, Bennett AT, et al. Discussion of vulvovaginal health at postmenopausal well woman visit—patient characteristics and visit experiences. Poster presented at: North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting; September 25-28, 2019; Chicago, IL.
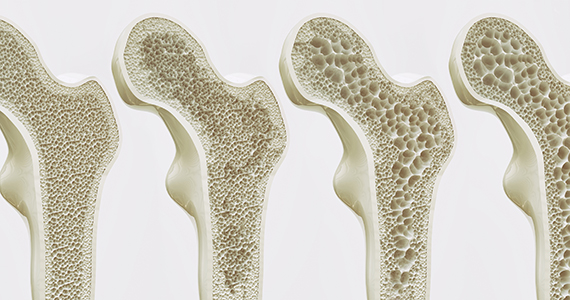
Can we discern optimal long-term osteoporosis treatment for women?
In a recent systematic review, Fink and colleagues attempted to summarize the published evidence of the efficacy and safety of long-term (> 3 years) therapy for osteoporosis.1 Unfortunately, they arrived at very limited and tentative conclusions because, as they point out, of the paucity of such evidence.
Why long-term studies stop short
Only 3 of the several tens of placebo-controlled fracture end-point studies (about 58 trials and observational studies) that Fink and colleagues reviewed evaluated treatment for more than 3 years. The nonavailability of longer-term studies is the direct consequence of a requirement by regulatory agencies for a 3-year fracture end-point study in order to register a new drug for osteoporosis. Hence, longer, placebo-controlled studies do not benefit the industry sponsor, and enrolling patients with osteoporosis or who are at high risk for fracture in any, much less long, placebo-controlled trials is now considered to be unethical.
What the authors did observe
From this limited set of information with which to evaluate, Fink and colleagues observed that long-term therapy with raloxifene reduces the risk of vertebral fractures but is associated with thromboembolic complications. In addition, treatment for more than 3 years with bisphosphonates reduces the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures but may increase risk of rare adverse events (including femoral shaft fractures with atypical radiographic features).
The bisphosphonate holiday. The authors refer to the even more limited evidence about the effects of discontinuing bisphosphonate therapy. Unlike the rapid loss of bone mass density (BMD) and fracture protection upon stopping estrogen or denosumab, the offset of these treatment benefits is slower when bisphosphonates are discontinued. This, coupled with concern about increasing risk with long-term bisphosphonate therapy, led to the confusing concept of a “bisphosphonate holiday.” While recommendations to consider temporary discontinuation of bisphosphonates in patients at low risk for fracture have been made by expert panels,2 very little information exists about the benefits/risks of this strategy, how long the treatment interruption should be, or how to decide when and with what to restart therapy. Unfortunately, overall, Fink and colleagues’ observations provide little practical guidance for clinicians.
Continue to: What we can learn from longer term and recent studies of ideal treatment...
What we can learn from longer term and recent studies of ideal treatment
Since we have no “cure” for osteoporosis, and since the benefits of therapy, including protection from fractures, abate upon stopping treatment (as they do when we stop treating hypertension or diabetes), very long term if not lifelong management is required for patients with osteoporosis. Persistent or even greater reduction of fracture risk with treatment up to 10 years, compared with the rate of fracture in the placebo or treated group during the first 3 years of the study, has been observed with zoledronate and denosumab.3-5 Denosumab was not included in the systematic review by Fink and colleagues since the pivotal fracture trial with that agent was placebo-controlled for only 3 years.6
Sequential drug treatment may be best. Fink and colleagues also did not consider new evidence, which suggests that the use of osteoporosis drugs in sequence—rather than a single agent for a long time—may be the most effective management strategy.7,8
More consideration should be given to the use of estrogen and raloxifene in younger postmenopausal women at risk for vertebral but not hip fracture.
Only treat high-risk patients. Using osteoporosis therapies to only treat patients at high risk for fracture will optimize the benefit:risk ratio and cost-effectiveness of therapy.
Bisphosphonate holidays may not be as important as once thought. BMD and fracture risk reduction does not improve after 5 years of bisphosphonate therapy, and longer treatment may increase the risk of atypic
Hip BMD may serve as indicator for treatment decisions. Recent evidence indicating that the change in hip BMD with treatment or the level of hip BMD achieved on treatment correlates with fracture risk reduction may provide a useful clinical target to guide treatment decisions.9,10
Because we have a lack of pristine evidence does not mean that we shouldn’t treat osteoporosis; we have to do the best we can with the limited evidence we have. Therapy must be individualized, for we are not just treating osteoporosis, we are treating patients with osteoporosis.
- Fink HA, MacDonald R, Forte ML, et al. Long-term drug therapy and drug discontinuations and holidays for osteoporosis fracture prevention: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171:37-50.
- Adler RA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Bauer DC, et al. Managing osteoporosis in patients on long-term bisphosphonate treatment: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31:16-35.
- Black DM, Reid IR, Cauley JA, et al. The effect of 6 versus 9 years of zoledronic acid treatment in osteoporosis: a randomized second extension to the HORIZON-Pivotal Fracture Trial (PFT). J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30:934-944.
- Bone HG, Wagman RB, Brandi ML, et al. 10 years of denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the phase 3 randomised FREEDOM trial and open-label extension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:513-523.
- Ferrari S, Butler PW, Kendler DL, et al. Further nonvertebral fracture reduction beyond 3 years for up to 10 years of denosumab treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:3450-3461.
- Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, et al. Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:756-765.
- Cosman F, Nieves JW, Dempster DW. Treatment sequence matters: anabolic and antiresorptive therapy for osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32:198-202.
- Hanley DA, McClung MR, Davison KS, et al; Writing Group for the Western Osteoporosis Alliance. Western Osteoporosis Alliance Clinical Practice Series: evaluating the balance of benefits and risks of long-term osteoporosis therapies. Am J Med. 2017;130:862.e1-862.e7.
- Bouxsein ML, Eastell R, Lui LY, et al; FNIH Bone Quality Project. Change in bone density and reduction in fracture risk: a meta-regression of published trials. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:632-642.
- Ferrari S, Libanati C, Lin CJF, et al. Relationship between bone mineral density T-score and nonvertebral fracture risk over 10 years of denosumab treatment. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:1033-1040.
In a recent systematic review, Fink and colleagues attempted to summarize the published evidence of the efficacy and safety of long-term (> 3 years) therapy for osteoporosis.1 Unfortunately, they arrived at very limited and tentative conclusions because, as they point out, of the paucity of such evidence.
Why long-term studies stop short
Only 3 of the several tens of placebo-controlled fracture end-point studies (about 58 trials and observational studies) that Fink and colleagues reviewed evaluated treatment for more than 3 years. The nonavailability of longer-term studies is the direct consequence of a requirement by regulatory agencies for a 3-year fracture end-point study in order to register a new drug for osteoporosis. Hence, longer, placebo-controlled studies do not benefit the industry sponsor, and enrolling patients with osteoporosis or who are at high risk for fracture in any, much less long, placebo-controlled trials is now considered to be unethical.
What the authors did observe
From this limited set of information with which to evaluate, Fink and colleagues observed that long-term therapy with raloxifene reduces the risk of vertebral fractures but is associated with thromboembolic complications. In addition, treatment for more than 3 years with bisphosphonates reduces the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures but may increase risk of rare adverse events (including femoral shaft fractures with atypical radiographic features).
The bisphosphonate holiday. The authors refer to the even more limited evidence about the effects of discontinuing bisphosphonate therapy. Unlike the rapid loss of bone mass density (BMD) and fracture protection upon stopping estrogen or denosumab, the offset of these treatment benefits is slower when bisphosphonates are discontinued. This, coupled with concern about increasing risk with long-term bisphosphonate therapy, led to the confusing concept of a “bisphosphonate holiday.” While recommendations to consider temporary discontinuation of bisphosphonates in patients at low risk for fracture have been made by expert panels,2 very little information exists about the benefits/risks of this strategy, how long the treatment interruption should be, or how to decide when and with what to restart therapy. Unfortunately, overall, Fink and colleagues’ observations provide little practical guidance for clinicians.
Continue to: What we can learn from longer term and recent studies of ideal treatment...
What we can learn from longer term and recent studies of ideal treatment
Since we have no “cure” for osteoporosis, and since the benefits of therapy, including protection from fractures, abate upon stopping treatment (as they do when we stop treating hypertension or diabetes), very long term if not lifelong management is required for patients with osteoporosis. Persistent or even greater reduction of fracture risk with treatment up to 10 years, compared with the rate of fracture in the placebo or treated group during the first 3 years of the study, has been observed with zoledronate and denosumab.3-5 Denosumab was not included in the systematic review by Fink and colleagues since the pivotal fracture trial with that agent was placebo-controlled for only 3 years.6
Sequential drug treatment may be best. Fink and colleagues also did not consider new evidence, which suggests that the use of osteoporosis drugs in sequence—rather than a single agent for a long time—may be the most effective management strategy.7,8
More consideration should be given to the use of estrogen and raloxifene in younger postmenopausal women at risk for vertebral but not hip fracture.
Only treat high-risk patients. Using osteoporosis therapies to only treat patients at high risk for fracture will optimize the benefit:risk ratio and cost-effectiveness of therapy.
Bisphosphonate holidays may not be as important as once thought. BMD and fracture risk reduction does not improve after 5 years of bisphosphonate therapy, and longer treatment may increase the risk of atypic
Hip BMD may serve as indicator for treatment decisions. Recent evidence indicating that the change in hip BMD with treatment or the level of hip BMD achieved on treatment correlates with fracture risk reduction may provide a useful clinical target to guide treatment decisions.9,10
Because we have a lack of pristine evidence does not mean that we shouldn’t treat osteoporosis; we have to do the best we can with the limited evidence we have. Therapy must be individualized, for we are not just treating osteoporosis, we are treating patients with osteoporosis.
In a recent systematic review, Fink and colleagues attempted to summarize the published evidence of the efficacy and safety of long-term (> 3 years) therapy for osteoporosis.1 Unfortunately, they arrived at very limited and tentative conclusions because, as they point out, of the paucity of such evidence.
Why long-term studies stop short
Only 3 of the several tens of placebo-controlled fracture end-point studies (about 58 trials and observational studies) that Fink and colleagues reviewed evaluated treatment for more than 3 years. The nonavailability of longer-term studies is the direct consequence of a requirement by regulatory agencies for a 3-year fracture end-point study in order to register a new drug for osteoporosis. Hence, longer, placebo-controlled studies do not benefit the industry sponsor, and enrolling patients with osteoporosis or who are at high risk for fracture in any, much less long, placebo-controlled trials is now considered to be unethical.
What the authors did observe
From this limited set of information with which to evaluate, Fink and colleagues observed that long-term therapy with raloxifene reduces the risk of vertebral fractures but is associated with thromboembolic complications. In addition, treatment for more than 3 years with bisphosphonates reduces the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures but may increase risk of rare adverse events (including femoral shaft fractures with atypical radiographic features).
The bisphosphonate holiday. The authors refer to the even more limited evidence about the effects of discontinuing bisphosphonate therapy. Unlike the rapid loss of bone mass density (BMD) and fracture protection upon stopping estrogen or denosumab, the offset of these treatment benefits is slower when bisphosphonates are discontinued. This, coupled with concern about increasing risk with long-term bisphosphonate therapy, led to the confusing concept of a “bisphosphonate holiday.” While recommendations to consider temporary discontinuation of bisphosphonates in patients at low risk for fracture have been made by expert panels,2 very little information exists about the benefits/risks of this strategy, how long the treatment interruption should be, or how to decide when and with what to restart therapy. Unfortunately, overall, Fink and colleagues’ observations provide little practical guidance for clinicians.
Continue to: What we can learn from longer term and recent studies of ideal treatment...
What we can learn from longer term and recent studies of ideal treatment
Since we have no “cure” for osteoporosis, and since the benefits of therapy, including protection from fractures, abate upon stopping treatment (as they do when we stop treating hypertension or diabetes), very long term if not lifelong management is required for patients with osteoporosis. Persistent or even greater reduction of fracture risk with treatment up to 10 years, compared with the rate of fracture in the placebo or treated group during the first 3 years of the study, has been observed with zoledronate and denosumab.3-5 Denosumab was not included in the systematic review by Fink and colleagues since the pivotal fracture trial with that agent was placebo-controlled for only 3 years.6
Sequential drug treatment may be best. Fink and colleagues also did not consider new evidence, which suggests that the use of osteoporosis drugs in sequence—rather than a single agent for a long time—may be the most effective management strategy.7,8
More consideration should be given to the use of estrogen and raloxifene in younger postmenopausal women at risk for vertebral but not hip fracture.
Only treat high-risk patients. Using osteoporosis therapies to only treat patients at high risk for fracture will optimize the benefit:risk ratio and cost-effectiveness of therapy.
Bisphosphonate holidays may not be as important as once thought. BMD and fracture risk reduction does not improve after 5 years of bisphosphonate therapy, and longer treatment may increase the risk of atypic
Hip BMD may serve as indicator for treatment decisions. Recent evidence indicating that the change in hip BMD with treatment or the level of hip BMD achieved on treatment correlates with fracture risk reduction may provide a useful clinical target to guide treatment decisions.9,10
Because we have a lack of pristine evidence does not mean that we shouldn’t treat osteoporosis; we have to do the best we can with the limited evidence we have. Therapy must be individualized, for we are not just treating osteoporosis, we are treating patients with osteoporosis.
- Fink HA, MacDonald R, Forte ML, et al. Long-term drug therapy and drug discontinuations and holidays for osteoporosis fracture prevention: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171:37-50.
- Adler RA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Bauer DC, et al. Managing osteoporosis in patients on long-term bisphosphonate treatment: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31:16-35.
- Black DM, Reid IR, Cauley JA, et al. The effect of 6 versus 9 years of zoledronic acid treatment in osteoporosis: a randomized second extension to the HORIZON-Pivotal Fracture Trial (PFT). J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30:934-944.
- Bone HG, Wagman RB, Brandi ML, et al. 10 years of denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the phase 3 randomised FREEDOM trial and open-label extension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:513-523.
- Ferrari S, Butler PW, Kendler DL, et al. Further nonvertebral fracture reduction beyond 3 years for up to 10 years of denosumab treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:3450-3461.
- Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, et al. Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:756-765.
- Cosman F, Nieves JW, Dempster DW. Treatment sequence matters: anabolic and antiresorptive therapy for osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32:198-202.
- Hanley DA, McClung MR, Davison KS, et al; Writing Group for the Western Osteoporosis Alliance. Western Osteoporosis Alliance Clinical Practice Series: evaluating the balance of benefits and risks of long-term osteoporosis therapies. Am J Med. 2017;130:862.e1-862.e7.
- Bouxsein ML, Eastell R, Lui LY, et al; FNIH Bone Quality Project. Change in bone density and reduction in fracture risk: a meta-regression of published trials. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:632-642.
- Ferrari S, Libanati C, Lin CJF, et al. Relationship between bone mineral density T-score and nonvertebral fracture risk over 10 years of denosumab treatment. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:1033-1040.
- Fink HA, MacDonald R, Forte ML, et al. Long-term drug therapy and drug discontinuations and holidays for osteoporosis fracture prevention: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171:37-50.
- Adler RA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Bauer DC, et al. Managing osteoporosis in patients on long-term bisphosphonate treatment: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31:16-35.
- Black DM, Reid IR, Cauley JA, et al. The effect of 6 versus 9 years of zoledronic acid treatment in osteoporosis: a randomized second extension to the HORIZON-Pivotal Fracture Trial (PFT). J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30:934-944.
- Bone HG, Wagman RB, Brandi ML, et al. 10 years of denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from the phase 3 randomised FREEDOM trial and open-label extension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:513-523.
- Ferrari S, Butler PW, Kendler DL, et al. Further nonvertebral fracture reduction beyond 3 years for up to 10 years of denosumab treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:3450-3461.
- Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, et al. Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:756-765.
- Cosman F, Nieves JW, Dempster DW. Treatment sequence matters: anabolic and antiresorptive therapy for osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32:198-202.
- Hanley DA, McClung MR, Davison KS, et al; Writing Group for the Western Osteoporosis Alliance. Western Osteoporosis Alliance Clinical Practice Series: evaluating the balance of benefits and risks of long-term osteoporosis therapies. Am J Med. 2017;130:862.e1-862.e7.
- Bouxsein ML, Eastell R, Lui LY, et al; FNIH Bone Quality Project. Change in bone density and reduction in fracture risk: a meta-regression of published trials. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:632-642.
- Ferrari S, Libanati C, Lin CJF, et al. Relationship between bone mineral density T-score and nonvertebral fracture risk over 10 years of denosumab treatment. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34:1033-1040.
Try testosterone for some women with sexual dysfunction, but not others
A new international position statement on testosterone therapy for women concludes that a trial of testosterone is appropriate for postmenopausal women with hypoactive sexual desire dysfunction (HSDD) and that its use for any other condition, symptom, or reason is not supported by available evidence.
The seven-page position statement, developed by an international task force of experts from the Endocrine Society, the American College of Gynecologists and Obstetricians, and multiple other medical societies, also emphasized that blood concentrations of testosterone should approximate premenopausal physiological conditions.
“When testosterone therapy is given, the resultant blood levels should not be above those seen in healthy young women,” said lead author Susan Ruth Davis, PhD, MBBS, of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, in a press release issued by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Davis is president of the International Menopause Society, which coordinated the panel.
The statement was published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism and three other medical journals.
Margaret E. Wierman, MD, who represented the Endocrine Society on the task force, said in an interview that there has been “growing concern about testosterone being prescribed for a variety of signs and symptoms without data to support” such use. At the same time, there is significant concern about the ongoing lack of approved formulations licensed specifically for women, she said.
In part, the statement is about a renewed “call to industry to make some [female-specific] formulations so that we can examine other potential roles of testosterone in women,” said Dr. Wierman, professor of medicine and physiology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and chief of endocrinology at the Rocky Mountain Regional Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Aurora.
“Testosterone may be useful [for indications other than HSDD], but we don’t know. There may be no [breast or cardiovascular disease risk], but we don’t know,” she said. “And without a formulation to study potential benefits and risks, it’s good to be cautious. It’s good to really outline where we have data and where we don’t.”
The Endocrine Society’s 2014 clinical practice guideline on androgen therapy in women, for which Dr. Wierman was the lead author, also recommended against the off-label use of testosterone for sexual dysfunction other than HSDD or for any other reason, such as cognitive, cardiovascular, metabolic, or bone health. As with the new statement, the society’s position statement was guided by an international, multisociety task force, albeit a smaller one.
For the new global position statement, the task force’s review of evidence includes a recently published systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial data – of at least 12 weeks’ duration – on the use of testosterone for sexual function, cardiometabolic variables, cognitive measures, and musculoskeletal health. Some of the data from the randomized controlled trials were unpublished.
The meta-analysis, led by Dr. Davis and published in July in the Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, found that, compared with placebo or a comparator (such as estrogen, with or without progesterone), testosterone in either oral or transdermal form significantly improved sexual function in postmenopausal women. However, data about the effects of testosterone for other indications, its long-term safety, and its use in premenopausal women, were insufficient for drawing any conclusions (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Jul 25. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587[19]30189-5).
In addition, testosterone administered orally – but not nonorally (patch or cream) – was associated with adverse lipid profiles, Dr. Davis and her colleagues reported.
Another systematic review and meta-analysis, published in Fertility and Sterility in 2017 and included in the task force’s evidence review, focused specifically on transdermal testosterone for menopausal women with HSDD, with or without estrogen and progestin therapy. It also showed short-term efficacy in terms of improvement in sexual function, as well as short-term safety (Fertil Steril. 2017;107(2):475-82).
The new position statement warns about the lack of long-term safety data, stating that “safety data for testosterone in physiologic doses are not available beyond 24 months of treatment.”
In the short term, testosterone therapy for postmenopausal women (in doses approximating testosterone concentrations for premenopausal women), is associated with mild increases in acne and body/facial hair growth in some women, but not with alopecia, clitoromegaly, or voice change. Short-term transdermal therapy also does not seem to affect breast cancer risk or have any significant effects on lipid profiles, the statement says.
The panel points out, however, that randomized controlled trials with testosterone therapy have excluded women who are at high risk of cardiometabolic disease, and that women with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer have also been excluded from randomized trials of testosterone in women with HSDD. This is a “big issue,” said Dr. Wierman, and means that recommendations regarding the effect of testosterone in postmenopausal women with HSDD may not be generalizable to possible at-risk subpopulations.
The panel endorsed testosterone therapy specifically for women with HSDD because most of the studies reporting on sexual function have recruited women with diagnosed HSDD. Demonstrated benefits of testosterone in these cases include improved sexual desire, arousal, orgasm, and pleasure, and reduced concerns and distress about sex. HSDD should be diagnosed after formal biopsychosocial assessment, the statement notes.
“We don’t completely understand the control of sexual function in women, but it’s very dependent on estrogen status. And it’s also dependent on psychosocial factors, emotional health, relationship issues, and physical issues,” Dr. Wierman said in the interview.
“In practice, we look at all these issues, and we first optimize estrogen status. Once that’s done, and we’ve looked at all the other components of sexual function, then we can consider off-label use of testosterone,” she said. “If there’s no response in 3-6 months, we stop it.”
Testosterone levels do not correlate with sexual dysfunction, Dr. Wierman emphasized, and direct assays for the measurement of total and free testosterone are unreliable. The statement acknowledges that but still recommends measurement of testosterone using direct assays, in cases in which liquid/gas chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry assay (which has “high accuracy and reproducibility”) are not available. This is “to exclude high baseline concentrations and also to exclude supraphysiological concentrations during treatment,” the panel said.
Most endocrinologists and other experts who prescribe testosterone therapy for women use an approved male formulation off label and adjust it – an approach that the panel says is reasonable as long as hormone concentrations are “maintained in the physiologic female range.”
Compounded “bioidentical” testosterone therapy “cannot be recommended for the treatment of HSDD because of the lack of evidence for safety and efficacy,” the statement says.
“A big concern of many endocrinologists,” Dr. Wierman added, “is the recent explosion of using pharmacological levels of both estrogen and testosterone in either [injections] or pellets.” The Endocrine Society and other societies have alerted the Food and Drug Administration to “this new cottage industry, which may have significant side effects and risks for our patients,” she said.
Dr. Wierman reported received funding from Corcept Therapeutics, Novartis, and the Cancer League of Colorado, and honoraria or consultation fees from Pfizer to review ASPIRE grant applications for studies of acromegaly as well as Endocrine Society honorarium for teaching in the Endocrine Board Review and Clinical Endocrine Update. Dr. Davis reported receiving funding from a National Health and Medical Research Council Project Grant, a National Breast Foundation accelerator grant, and the Grollo-Ruzenne Foundation, as well as honoraria from Besins and Pfizer Australia. She has been a consultant to Besins Healthcare, Mayne Pharmaceuticals, Lawley Pharmaceuticals, and Que Oncology. Disclosures for other authors of the position statement are listed with the statement.
SOURCE: Davis SR et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep 2. doi: 10.1210/jc.2019-01603.
A new international position statement on testosterone therapy for women concludes that a trial of testosterone is appropriate for postmenopausal women with hypoactive sexual desire dysfunction (HSDD) and that its use for any other condition, symptom, or reason is not supported by available evidence.
The seven-page position statement, developed by an international task force of experts from the Endocrine Society, the American College of Gynecologists and Obstetricians, and multiple other medical societies, also emphasized that blood concentrations of testosterone should approximate premenopausal physiological conditions.
“When testosterone therapy is given, the resultant blood levels should not be above those seen in healthy young women,” said lead author Susan Ruth Davis, PhD, MBBS, of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, in a press release issued by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Davis is president of the International Menopause Society, which coordinated the panel.
The statement was published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism and three other medical journals.
Margaret E. Wierman, MD, who represented the Endocrine Society on the task force, said in an interview that there has been “growing concern about testosterone being prescribed for a variety of signs and symptoms without data to support” such use. At the same time, there is significant concern about the ongoing lack of approved formulations licensed specifically for women, she said.
In part, the statement is about a renewed “call to industry to make some [female-specific] formulations so that we can examine other potential roles of testosterone in women,” said Dr. Wierman, professor of medicine and physiology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and chief of endocrinology at the Rocky Mountain Regional Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Aurora.
“Testosterone may be useful [for indications other than HSDD], but we don’t know. There may be no [breast or cardiovascular disease risk], but we don’t know,” she said. “And without a formulation to study potential benefits and risks, it’s good to be cautious. It’s good to really outline where we have data and where we don’t.”
The Endocrine Society’s 2014 clinical practice guideline on androgen therapy in women, for which Dr. Wierman was the lead author, also recommended against the off-label use of testosterone for sexual dysfunction other than HSDD or for any other reason, such as cognitive, cardiovascular, metabolic, or bone health. As with the new statement, the society’s position statement was guided by an international, multisociety task force, albeit a smaller one.
For the new global position statement, the task force’s review of evidence includes a recently published systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial data – of at least 12 weeks’ duration – on the use of testosterone for sexual function, cardiometabolic variables, cognitive measures, and musculoskeletal health. Some of the data from the randomized controlled trials were unpublished.
The meta-analysis, led by Dr. Davis and published in July in the Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, found that, compared with placebo or a comparator (such as estrogen, with or without progesterone), testosterone in either oral or transdermal form significantly improved sexual function in postmenopausal women. However, data about the effects of testosterone for other indications, its long-term safety, and its use in premenopausal women, were insufficient for drawing any conclusions (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Jul 25. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587[19]30189-5).
In addition, testosterone administered orally – but not nonorally (patch or cream) – was associated with adverse lipid profiles, Dr. Davis and her colleagues reported.
Another systematic review and meta-analysis, published in Fertility and Sterility in 2017 and included in the task force’s evidence review, focused specifically on transdermal testosterone for menopausal women with HSDD, with or without estrogen and progestin therapy. It also showed short-term efficacy in terms of improvement in sexual function, as well as short-term safety (Fertil Steril. 2017;107(2):475-82).
The new position statement warns about the lack of long-term safety data, stating that “safety data for testosterone in physiologic doses are not available beyond 24 months of treatment.”
In the short term, testosterone therapy for postmenopausal women (in doses approximating testosterone concentrations for premenopausal women), is associated with mild increases in acne and body/facial hair growth in some women, but not with alopecia, clitoromegaly, or voice change. Short-term transdermal therapy also does not seem to affect breast cancer risk or have any significant effects on lipid profiles, the statement says.
The panel points out, however, that randomized controlled trials with testosterone therapy have excluded women who are at high risk of cardiometabolic disease, and that women with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer have also been excluded from randomized trials of testosterone in women with HSDD. This is a “big issue,” said Dr. Wierman, and means that recommendations regarding the effect of testosterone in postmenopausal women with HSDD may not be generalizable to possible at-risk subpopulations.
The panel endorsed testosterone therapy specifically for women with HSDD because most of the studies reporting on sexual function have recruited women with diagnosed HSDD. Demonstrated benefits of testosterone in these cases include improved sexual desire, arousal, orgasm, and pleasure, and reduced concerns and distress about sex. HSDD should be diagnosed after formal biopsychosocial assessment, the statement notes.
“We don’t completely understand the control of sexual function in women, but it’s very dependent on estrogen status. And it’s also dependent on psychosocial factors, emotional health, relationship issues, and physical issues,” Dr. Wierman said in the interview.
“In practice, we look at all these issues, and we first optimize estrogen status. Once that’s done, and we’ve looked at all the other components of sexual function, then we can consider off-label use of testosterone,” she said. “If there’s no response in 3-6 months, we stop it.”
Testosterone levels do not correlate with sexual dysfunction, Dr. Wierman emphasized, and direct assays for the measurement of total and free testosterone are unreliable. The statement acknowledges that but still recommends measurement of testosterone using direct assays, in cases in which liquid/gas chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry assay (which has “high accuracy and reproducibility”) are not available. This is “to exclude high baseline concentrations and also to exclude supraphysiological concentrations during treatment,” the panel said.
Most endocrinologists and other experts who prescribe testosterone therapy for women use an approved male formulation off label and adjust it – an approach that the panel says is reasonable as long as hormone concentrations are “maintained in the physiologic female range.”
Compounded “bioidentical” testosterone therapy “cannot be recommended for the treatment of HSDD because of the lack of evidence for safety and efficacy,” the statement says.
“A big concern of many endocrinologists,” Dr. Wierman added, “is the recent explosion of using pharmacological levels of both estrogen and testosterone in either [injections] or pellets.” The Endocrine Society and other societies have alerted the Food and Drug Administration to “this new cottage industry, which may have significant side effects and risks for our patients,” she said.
Dr. Wierman reported received funding from Corcept Therapeutics, Novartis, and the Cancer League of Colorado, and honoraria or consultation fees from Pfizer to review ASPIRE grant applications for studies of acromegaly as well as Endocrine Society honorarium for teaching in the Endocrine Board Review and Clinical Endocrine Update. Dr. Davis reported receiving funding from a National Health and Medical Research Council Project Grant, a National Breast Foundation accelerator grant, and the Grollo-Ruzenne Foundation, as well as honoraria from Besins and Pfizer Australia. She has been a consultant to Besins Healthcare, Mayne Pharmaceuticals, Lawley Pharmaceuticals, and Que Oncology. Disclosures for other authors of the position statement are listed with the statement.
SOURCE: Davis SR et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep 2. doi: 10.1210/jc.2019-01603.
A new international position statement on testosterone therapy for women concludes that a trial of testosterone is appropriate for postmenopausal women with hypoactive sexual desire dysfunction (HSDD) and that its use for any other condition, symptom, or reason is not supported by available evidence.
The seven-page position statement, developed by an international task force of experts from the Endocrine Society, the American College of Gynecologists and Obstetricians, and multiple other medical societies, also emphasized that blood concentrations of testosterone should approximate premenopausal physiological conditions.
“When testosterone therapy is given, the resultant blood levels should not be above those seen in healthy young women,” said lead author Susan Ruth Davis, PhD, MBBS, of Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, in a press release issued by the Endocrine Society. Dr. Davis is president of the International Menopause Society, which coordinated the panel.
The statement was published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism and three other medical journals.
Margaret E. Wierman, MD, who represented the Endocrine Society on the task force, said in an interview that there has been “growing concern about testosterone being prescribed for a variety of signs and symptoms without data to support” such use. At the same time, there is significant concern about the ongoing lack of approved formulations licensed specifically for women, she said.
In part, the statement is about a renewed “call to industry to make some [female-specific] formulations so that we can examine other potential roles of testosterone in women,” said Dr. Wierman, professor of medicine and physiology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and chief of endocrinology at the Rocky Mountain Regional Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Aurora.
“Testosterone may be useful [for indications other than HSDD], but we don’t know. There may be no [breast or cardiovascular disease risk], but we don’t know,” she said. “And without a formulation to study potential benefits and risks, it’s good to be cautious. It’s good to really outline where we have data and where we don’t.”
The Endocrine Society’s 2014 clinical practice guideline on androgen therapy in women, for which Dr. Wierman was the lead author, also recommended against the off-label use of testosterone for sexual dysfunction other than HSDD or for any other reason, such as cognitive, cardiovascular, metabolic, or bone health. As with the new statement, the society’s position statement was guided by an international, multisociety task force, albeit a smaller one.
For the new global position statement, the task force’s review of evidence includes a recently published systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial data – of at least 12 weeks’ duration – on the use of testosterone for sexual function, cardiometabolic variables, cognitive measures, and musculoskeletal health. Some of the data from the randomized controlled trials were unpublished.
The meta-analysis, led by Dr. Davis and published in July in the Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, found that, compared with placebo or a comparator (such as estrogen, with or without progesterone), testosterone in either oral or transdermal form significantly improved sexual function in postmenopausal women. However, data about the effects of testosterone for other indications, its long-term safety, and its use in premenopausal women, were insufficient for drawing any conclusions (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Jul 25. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587[19]30189-5).
In addition, testosterone administered orally – but not nonorally (patch or cream) – was associated with adverse lipid profiles, Dr. Davis and her colleagues reported.
Another systematic review and meta-analysis, published in Fertility and Sterility in 2017 and included in the task force’s evidence review, focused specifically on transdermal testosterone for menopausal women with HSDD, with or without estrogen and progestin therapy. It also showed short-term efficacy in terms of improvement in sexual function, as well as short-term safety (Fertil Steril. 2017;107(2):475-82).
The new position statement warns about the lack of long-term safety data, stating that “safety data for testosterone in physiologic doses are not available beyond 24 months of treatment.”
In the short term, testosterone therapy for postmenopausal women (in doses approximating testosterone concentrations for premenopausal women), is associated with mild increases in acne and body/facial hair growth in some women, but not with alopecia, clitoromegaly, or voice change. Short-term transdermal therapy also does not seem to affect breast cancer risk or have any significant effects on lipid profiles, the statement says.
The panel points out, however, that randomized controlled trials with testosterone therapy have excluded women who are at high risk of cardiometabolic disease, and that women with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer have also been excluded from randomized trials of testosterone in women with HSDD. This is a “big issue,” said Dr. Wierman, and means that recommendations regarding the effect of testosterone in postmenopausal women with HSDD may not be generalizable to possible at-risk subpopulations.
The panel endorsed testosterone therapy specifically for women with HSDD because most of the studies reporting on sexual function have recruited women with diagnosed HSDD. Demonstrated benefits of testosterone in these cases include improved sexual desire, arousal, orgasm, and pleasure, and reduced concerns and distress about sex. HSDD should be diagnosed after formal biopsychosocial assessment, the statement notes.
“We don’t completely understand the control of sexual function in women, but it’s very dependent on estrogen status. And it’s also dependent on psychosocial factors, emotional health, relationship issues, and physical issues,” Dr. Wierman said in the interview.
“In practice, we look at all these issues, and we first optimize estrogen status. Once that’s done, and we’ve looked at all the other components of sexual function, then we can consider off-label use of testosterone,” she said. “If there’s no response in 3-6 months, we stop it.”
Testosterone levels do not correlate with sexual dysfunction, Dr. Wierman emphasized, and direct assays for the measurement of total and free testosterone are unreliable. The statement acknowledges that but still recommends measurement of testosterone using direct assays, in cases in which liquid/gas chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry assay (which has “high accuracy and reproducibility”) are not available. This is “to exclude high baseline concentrations and also to exclude supraphysiological concentrations during treatment,” the panel said.
Most endocrinologists and other experts who prescribe testosterone therapy for women use an approved male formulation off label and adjust it – an approach that the panel says is reasonable as long as hormone concentrations are “maintained in the physiologic female range.”
Compounded “bioidentical” testosterone therapy “cannot be recommended for the treatment of HSDD because of the lack of evidence for safety and efficacy,” the statement says.
“A big concern of many endocrinologists,” Dr. Wierman added, “is the recent explosion of using pharmacological levels of both estrogen and testosterone in either [injections] or pellets.” The Endocrine Society and other societies have alerted the Food and Drug Administration to “this new cottage industry, which may have significant side effects and risks for our patients,” she said.
Dr. Wierman reported received funding from Corcept Therapeutics, Novartis, and the Cancer League of Colorado, and honoraria or consultation fees from Pfizer to review ASPIRE grant applications for studies of acromegaly as well as Endocrine Society honorarium for teaching in the Endocrine Board Review and Clinical Endocrine Update. Dr. Davis reported receiving funding from a National Health and Medical Research Council Project Grant, a National Breast Foundation accelerator grant, and the Grollo-Ruzenne Foundation, as well as honoraria from Besins and Pfizer Australia. She has been a consultant to Besins Healthcare, Mayne Pharmaceuticals, Lawley Pharmaceuticals, and Que Oncology. Disclosures for other authors of the position statement are listed with the statement.
SOURCE: Davis SR et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep 2. doi: 10.1210/jc.2019-01603.
FROM JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM
Higher BMD linked to family history of diabetes in postmenopausal women
according to results of a study.
Lijuan Yang, MD, of First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou (China) Medical University and colleagues reported the results in Menopause. The cross-sectional study included 892 normoglycemic postmenopausal women, of whom 147 had a first-degree FHD; the mean age was 55 years among both those with and those without first-degree FHD. The investigators assessed BMDs of the femoral neck and lumbar spine with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and insulin resistance with Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR).
Lumbar spine BMD was higher in those with first-degree FHD than in those without, at 1.077 and 1.034 g/cm2, respectively; femoral neck BMD was similarly higher at 0.89 vs. 0.85 g/cm2, respectively. HOMA-IR also was higher among those with first-degree FHD than among those without, at 1.85 and 1.60, respectively.
Spearman’s correlation analyses showed that lumbar spine BMD was positively associated with first-degree FHD (P = .008) and HOMA-IR (P = .041), as was femoral neck BMD (P = .013 and P = .005, respectively). Results of multiple stepwise regression analysis showed that first-degree FHD and HOMA-IR were independent factors positively associated with femoral neck BMD (P = .029 and P = .0009, respectively) and lumbar spine BMD (P = .029 and P = .002).
“The present study demonstrated that lumbar spine BMD and femoral neck BMD were positively associated with HOMA-IR in postmenopausal women and that individuals with a first-degree FHD were more likely to have high HOMA-IR,” the investigators said. “We suggest that the elevated BMD in individuals with a first-degree FHD could be attributed to insulin resistance,” which appears to be inherited by persons with a first-degree FHD.
The authors noted that the cross-sectional design is a limitations of this study. They suggested future studies might investigate the relationship between insulin resistance and bone development in these populations by assessing osteocalcin and P1NP.
The study received funding or support from National Key R&D Program of China and from the Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau. The authors did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Yang L et al. Menopause. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001396.
according to results of a study.
Lijuan Yang, MD, of First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou (China) Medical University and colleagues reported the results in Menopause. The cross-sectional study included 892 normoglycemic postmenopausal women, of whom 147 had a first-degree FHD; the mean age was 55 years among both those with and those without first-degree FHD. The investigators assessed BMDs of the femoral neck and lumbar spine with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and insulin resistance with Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR).
Lumbar spine BMD was higher in those with first-degree FHD than in those without, at 1.077 and 1.034 g/cm2, respectively; femoral neck BMD was similarly higher at 0.89 vs. 0.85 g/cm2, respectively. HOMA-IR also was higher among those with first-degree FHD than among those without, at 1.85 and 1.60, respectively.
Spearman’s correlation analyses showed that lumbar spine BMD was positively associated with first-degree FHD (P = .008) and HOMA-IR (P = .041), as was femoral neck BMD (P = .013 and P = .005, respectively). Results of multiple stepwise regression analysis showed that first-degree FHD and HOMA-IR were independent factors positively associated with femoral neck BMD (P = .029 and P = .0009, respectively) and lumbar spine BMD (P = .029 and P = .002).
“The present study demonstrated that lumbar spine BMD and femoral neck BMD were positively associated with HOMA-IR in postmenopausal women and that individuals with a first-degree FHD were more likely to have high HOMA-IR,” the investigators said. “We suggest that the elevated BMD in individuals with a first-degree FHD could be attributed to insulin resistance,” which appears to be inherited by persons with a first-degree FHD.
The authors noted that the cross-sectional design is a limitations of this study. They suggested future studies might investigate the relationship between insulin resistance and bone development in these populations by assessing osteocalcin and P1NP.
The study received funding or support from National Key R&D Program of China and from the Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau. The authors did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Yang L et al. Menopause. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001396.
according to results of a study.
Lijuan Yang, MD, of First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou (China) Medical University and colleagues reported the results in Menopause. The cross-sectional study included 892 normoglycemic postmenopausal women, of whom 147 had a first-degree FHD; the mean age was 55 years among both those with and those without first-degree FHD. The investigators assessed BMDs of the femoral neck and lumbar spine with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and insulin resistance with Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR).
Lumbar spine BMD was higher in those with first-degree FHD than in those without, at 1.077 and 1.034 g/cm2, respectively; femoral neck BMD was similarly higher at 0.89 vs. 0.85 g/cm2, respectively. HOMA-IR also was higher among those with first-degree FHD than among those without, at 1.85 and 1.60, respectively.
Spearman’s correlation analyses showed that lumbar spine BMD was positively associated with first-degree FHD (P = .008) and HOMA-IR (P = .041), as was femoral neck BMD (P = .013 and P = .005, respectively). Results of multiple stepwise regression analysis showed that first-degree FHD and HOMA-IR were independent factors positively associated with femoral neck BMD (P = .029 and P = .0009, respectively) and lumbar spine BMD (P = .029 and P = .002).
“The present study demonstrated that lumbar spine BMD and femoral neck BMD were positively associated with HOMA-IR in postmenopausal women and that individuals with a first-degree FHD were more likely to have high HOMA-IR,” the investigators said. “We suggest that the elevated BMD in individuals with a first-degree FHD could be attributed to insulin resistance,” which appears to be inherited by persons with a first-degree FHD.
The authors noted that the cross-sectional design is a limitations of this study. They suggested future studies might investigate the relationship between insulin resistance and bone development in these populations by assessing osteocalcin and P1NP.
The study received funding or support from National Key R&D Program of China and from the Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau. The authors did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Yang L et al. Menopause. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001396.
FROM MENOPAUSE
Product Update: Osphena’s NDA, new hysteroscope, TempSure RF technology, Resilient stirrup covers
OSPHENA HAS NEW INDICATION
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.osphena.com/.
NEW 3-IN-1 HYSTEROSCOPE
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://gynsurgicalsolutions.com/product/omni-hysteroscope/.
SURGICAL RF TECHNOLOGY
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.cynosure.com/tempsure-platform.
PROFESSIONAL FOOT SUPPORTS
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.comenitymed.com.
OSPHENA HAS NEW INDICATION
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.osphena.com/.
NEW 3-IN-1 HYSTEROSCOPE
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://gynsurgicalsolutions.com/product/omni-hysteroscope/.
SURGICAL RF TECHNOLOGY
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.cynosure.com/tempsure-platform.
PROFESSIONAL FOOT SUPPORTS
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.comenitymed.com.
OSPHENA HAS NEW INDICATION
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.osphena.com/.
NEW 3-IN-1 HYSTEROSCOPE
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://gynsurgicalsolutions.com/product/omni-hysteroscope/.
SURGICAL RF TECHNOLOGY
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.cynosure.com/tempsure-platform.
PROFESSIONAL FOOT SUPPORTS
FOR MORE INFORMATION, VISIT: https://www.comenitymed.com.
Hormone therapy and cognition: What is best for the midlife brain?
CASE HT for vasomotor symptoms in perimenopausal woman with cognitive concerns
Jackie is a 49-year-old woman. Her body mass index is 33 kg/m2, and she has mild hypertension that is effectively controlled with antihypertensive medications. Otherwise, she is in good health.During her annual gynecologic exam, she reports that for the past 9 months her menstrual cycles have not been as regular as they used to be and that 3 months ago she skipped a cycle. She is having bothersome vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and is concerned about her memory. She says she is forgetful at work and in social situations. During a recent presentation, she could not remember the name of one of her former clients. At a work happy hour, she forgot the name of her coworker’s husband, although she did remember it later after returning home.
Her mother has Alzheimer disease (AD), and Jackie worries about whether she, too, might be developing dementia and whether her memory will fail her in social situations.
She is concerned about using hormone therapy (HT) for her vasomotor symptoms because she has heard that it can lead to breast cancer and/or AD.
How would you advise her?
HT remains the most effective treatment for bothersome VMS, but concerns about its cognitive safety persist. Such concerns, and indeed a black-box warning about the risk of dementia with HT use, initially arose following the 2003 publication of the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of HT for the primary prevention of dementia in women aged 65 years and older at baseline.1 The study found that combination estrogen/progestin therapy was associated with a 2-fold increase in dementia when compared with placebo.
One of the critical questions arising even before WHIMS was whether the cognitive risks associated with HT that were seen in WHIMS apply to younger women. Attempting to answer the question and adding fuel to the fire are the results of a recent case-control study from Finland.2 This study compared HT use in Finnish women with and without AD and found that HT use was higher among Finnish women with AD compared with those without AD, regardless of age. The authors concluded, “Our data must be implemented into information for the present and future users of HT, even though the absolute risk increase is small.”
However, given the limitations inherent to observational and registry studies, and the contrasting findings of 3 high-quality, randomized controlled trials (RCTs; more details below), providers actually can reassure younger peri- and postmenopausal women about the cognitive safety of HT.3 They also can explain to patients that cognitive symptoms like the ones described in the case example are normal and provide general guidance to midlife women on how to optimize brain health.

Continue to: Closer look at WHI and RCT research pinpoints cognitively neutral HT...
Closer look at WHI and RCT research pinpoints cognitively neutral HT
In WHIMS, the combination of conjugated equine estrogen (CEE; 0.625 mg/d) plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA; 2.5 mg/d) led to a doubling of the risk of all-cause dementia compared with placebo in a sample of 4,532 women aged 65 years and older at baseline.1 CEE alone (0.625 mg) did not lead to an increased risk of all-cause dementia.4
Whether those formulations led to cognitive impairment in younger postmenopausal women was the focus of WHIMS-Younger (WHIMS-Y), which involved WHI participants aged 50 to 55 years at baseline.5 Results revealed neutral cognitive effects (ie, no differences in cognitive performance in women randomly assigned to HT or placebo) in women tested 7.2 years after the end of the WHI trial. WHIMS-Y findings indicated that there were no sustained cognitive risks of CEE or CEE/MPA therapy. Two randomized, placebo-controlled trials involving younger postmenopausal women yielded similar findings.6,7 HT shown to produce cognitively neutral effects during active treatment included transdermal estradiol plus micronized progesterone,6 CEE plus progesterone,6 and oral estradiol plus vaginal progesterone gel.7 The findings of these randomized trials are critical for guiding decisions regarding the cognitive risks of HT in early postmenopausal women (TABLE 1).
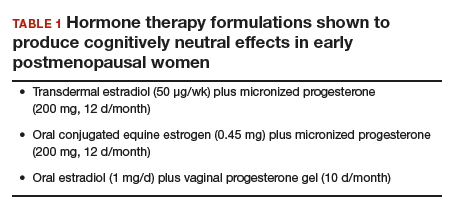
What about women with VMS?
A key gap in knowledge about the cognitive effects of HT is whether HT confers cognitive advantages to women with bothersome VMS. This is a striking absence given that the key indication for HT is the treatment of VMS. While some symptomatic women were included in the trials of HT in younger postmenopausal women described above, no large trial to date has selectively enrolled women with moderate-to-severe VMS to determine if HT is cognitively neutral, beneficial, or detrimental in that group. Some studies involving midlife women have found associations between VMS (as measured with ambulatory skin conductance monitors) and multiple measures of brain health, including memory performance,8 small ischemic lesions on structural brain scans,9 and altered brain function.10 In a small trial of a nonhormonal intervention for VMS, improvement in VMS following the intervention was directly related to improvement in memory performance.11 The reliability of these findings continues to be evaluated but raises the hypothesis that VMS treatments might improve memory in midlife women.
Memory complaints common among midlife women
About 60% of women report an undesirable change in memory performance at midlife as compared with earlier in their lives.12,13 Complaints of forgetfulness are higher in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women compared with premenopausal women, even when those women are similar in age.14 Two large prospective studies found that memory performance decreases during the perimenopause and then rebounds, suggesting a transient decrease in memory.15,16 Although cognitive complaints are common among women in their 40s and 50s, AD is rare in that age group. The risk is largely limited to those women with a parent who developed dementia before age 65, as such cases suggest a familial form of AD.
Continue to: What causes cognitive difficulties during midlife?
What causes cognitive difficulties during midlife?
First, some cognitive decline is expected at midlife based on increasing age. Second, above and beyond the role of chronologic aging (ie, getting one year older each year), ovarian aging plays a role. A role of estrogen was verified in clinical trials showing that memory decreased following oophorectomy in premenopausal women in their 40s but returned to presurgical levels following treatment with estrogen therapy (ET).17 Cohort studies indicate that women who undergo oophorectomy before the typical age of menopause are at increased risk for cognitive impairment or dementia, but those who take ET after oophorectomy until the typical age of menopause do not show that risk.18
Third, cognitive problems are linked not only to VMS but also to sleep disturbance, depressed mood, and increased anxiety—all of which are common in midlife women.15,19 Lastly, health factors play a role. Hypertension, obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and smoking are associated with adverse brain changes at midlife.20
Giving advice to your patients
First, normalize the cognitive complaints, noting that some cognitive changes are an expected part of aging for all people regardless of whether they are male or female. Advise that while the best studies indicate that these cognitive lapses are especially common in perimenopausal women, they appear to be temporary; women are likely to resume normal cognitive function once the hormonal changes associated with menopause subside.15,16 Note that the one unknown is the role that VMS play in memory problems and that some studies indicate a link between VMS and cognitive problems. Women may experience some cognitive improvement if VMS are effectively treated.
Advise patients that the Endocrine Society, the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the International Menopause Society all have published guidelines saying that the benefits of HT outweigh the risks for most women aged 50 to 60 years.21 For concerns about the cognitive adverse effects of HT, discuss the best quality evidence—that which comes from randomized trials—which shows no harmful effects of HT in midlife women.5-7 Especially reassuring is that one of these high-quality studies was conducted by the same researchers who found that HT can be risky in older women (ie, the WHI Investigators).5
Going one step further: Protecting brain health
As primary care providers to midlife women, ObGyns can go one step further and advise patients on how to proactively nurture their brain health. Great evidence-based resources for information on maintaining brain health include the Alzheimer’s Association (https://www.alz.org) and the Women’s Brain Health Initiative (https://womensbrainhealth.org). Primary prevention of AD begins decades before the typical age of an AD diagnosis, and many risk factors for AD are modifiable.22 Patients can keep their brains healthy through myriad approaches including treating hypertension, reducing body mass index, engaging in regular aerobic exercise (brisk walking is fine), eating a Mediterranean diet, maintaining an active social life, and engaging in novel challenging activities like learning a new language or a new skill like dancing.20
Also important is the overlap between cognitive issues, mood, and alcohol use. In the opening case, Jackie mentions alcohol use and social withdrawal. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), low-risk drinking for women is defined as no more than 3 drinks on any single day and no more than 7 drinks per week.23 Heavy alcohol use not only affects brain function but also mood, and depressed mood can lead women to drink excessively.24
In addition, Jackie’s mother has AD, and that stressor can contribute to depressed feelings, especially if Jackie is involved in caregiving. A quick screen for depression with an instrument like the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ-2; TABLE 2)25 can rule out a more serious mood disorder—an approach that is particularly important for patients with a history of major depression, as 58% of those patients experience a major depressive episode during the menopausal transition.26 For this reason, it is important to ask patients like Jackie if they have a history of depression; if they do and were treated medically, consider prescribing the antidepressant that worked in the past. For information on menopause and mood-related issues, providers can access new guidelines from NAMS and the National Network of Depression Centers (NNDC).27 There is also a handy patient information sheet to accompany those guidelines on the NAMS website (https://www.menopause.org/).
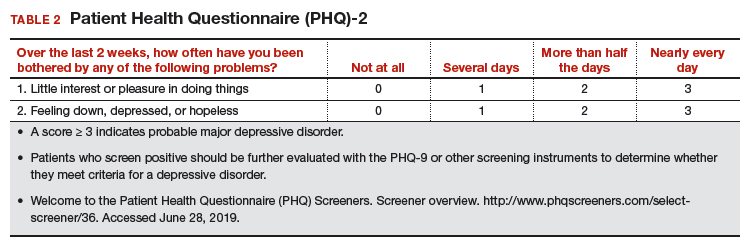
Continue to: CASE Resolved...
CASE Resolved
When approaching Jackie, most importantly, I would normalize her experience and tell her that memory problems are common in the menopausal transition, especially for women with bothersome VMS. Research suggests that the memory problems she is experiencing are related to hormonal changes and not to AD, and that her memory will likely improve once she has transitioned through the menopause. I would tell her that AD is rare at midlife unless there is a family history of early onset of AD (before age 65), and I would verify the age at which her mother was diagnosed to confirm that it was late-onset AD.
For now, I would recommend that she be prescribed HT for her bothersome hot flashes using one of the “safe” formulations in the Table on page 24. I also would tell her that there is much she can do to lower her risk of AD and that it is best to start now as she enters her 50s because that is when AD changes typically start in the brain, and she can start to prevent those changes now.
I would tell her that experts in the field of AD agree that these lifestyle interventions are currently the best way to prevent AD and that the more of them she engages in, the more her brain will benefit. I would advise her to continue to manage her hypertension and to consider ways of lowering her BMI to enhance her brain health. Engaging in regular brisk walking or other aerobic exercise, as well as incorporating more of the Mediterranean diet into her daily food intake would also benefit her brain. As a working woman, she is exercising her brain, and she should consider other cognitively challenging activities to keep her brain in good shape.
I would follow up with her in a few months to see if her memory functioning is better. If it is not, and if her VMS continue to be bothersome, I would increase her dose of HT. Only if her VMS are treated but her memory problems are getting worse would I screen her with a Mini-Mental State Exam and refer her to a neurologist for an evaluation.
- Shumaker SA, Legault C, Rapp SR, et al. Estrogen plus progestin and the incidence of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in postmenopausal women: the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;289:2651-2662.
- Savolainen-Peltonen H, Rahkola-Soisalo P, Hoti F, et al. Use of postmenopausal hormone therapy and risk of Alzheimer’s disease in Finland: nationwide case-control study. BMJ. 2019;364:1665.
- Maki PM, Girard LM, Manson JE. Menopausal hormone therapy and cognition. BMJ. 2019;364:1877.
- Shumaker SA, Legault C, Kuller L, et al. Conjugated equine estrogens and incidence of probable dementia and mild cognitive impairment in postmenopausal women: Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study. JAMA. 2004;291:2947-2958.
- Espeland MA, Shumaker SA, Leng I, et al. Long-term effects on cognitive function of postmenopausal hormone therapy prescribed to women aged 50 to 55 years. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1429-1436.
- Gleason CE, Dowling NM, Wharton W, et al. Effects of hormone therapy on cognition and mood in recently postmenopausal women: findings from the randomized, controlled KEEPS-cognitive and affective study. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001833.
- Henderson VW, St. John JA, Hodis HN, et al. Cognitive effects of estradiol after menopause: a randomized trial of the timing hypothesis. Neurology. 2016;87:699-708.
- Maki PM, Drogos LL, Rubin LH, et al. Objective hot flashes are negatively related to verbal memory performance in midlife women. Menopause. 2008;15:848-856.
- Thurston RC, Aizenstein HJ, Derby CA, et al. Menopausal hot flashes and white matter hyperintensities. Menopause. 2016;23:27-32.
- Thurston RC, Maki PM, Derby CA, et al. Menopausal hot flashes and the default mode network. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:1572-1578.e1.
- Maki PM, Rubin LH, Savarese A, et al. Stellate ganglion blockade and verbal memory in midlife women: evidence from a randomized trial. Maturitas. 2016;92:123-129.
- Woods NF, Mitchell ES, Adams C. Memory functioning among midlife women: observations from the Seattle Midlife Women’s Health Study. Menopause. 2000;7:257-265.
- Sullivan Mitchell E, Fugate Woods N. Midlife women’s attributions about perceived memory changes: observations from the Seattle Midlife Women’s Health Study. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2001;10:351-362.
- Gold EB, Sternfeld B, Kelsey JL, et al. Relation of demographic and lifestyle factors to symptoms in a multi-racial/ethnic population of women 40-55 years of age. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;152:463-473.
CASE HT for vasomotor symptoms in perimenopausal woman with cognitive concerns
Jackie is a 49-year-old woman. Her body mass index is 33 kg/m2, and she has mild hypertension that is effectively controlled with antihypertensive medications. Otherwise, she is in good health.During her annual gynecologic exam, she reports that for the past 9 months her menstrual cycles have not been as regular as they used to be and that 3 months ago she skipped a cycle. She is having bothersome vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and is concerned about her memory. She says she is forgetful at work and in social situations. During a recent presentation, she could not remember the name of one of her former clients. At a work happy hour, she forgot the name of her coworker’s husband, although she did remember it later after returning home.
Her mother has Alzheimer disease (AD), and Jackie worries about whether she, too, might be developing dementia and whether her memory will fail her in social situations.
She is concerned about using hormone therapy (HT) for her vasomotor symptoms because she has heard that it can lead to breast cancer and/or AD.
How would you advise her?
HT remains the most effective treatment for bothersome VMS, but concerns about its cognitive safety persist. Such concerns, and indeed a black-box warning about the risk of dementia with HT use, initially arose following the 2003 publication of the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of HT for the primary prevention of dementia in women aged 65 years and older at baseline.1 The study found that combination estrogen/progestin therapy was associated with a 2-fold increase in dementia when compared with placebo.
One of the critical questions arising even before WHIMS was whether the cognitive risks associated with HT that were seen in WHIMS apply to younger women. Attempting to answer the question and adding fuel to the fire are the results of a recent case-control study from Finland.2 This study compared HT use in Finnish women with and without AD and found that HT use was higher among Finnish women with AD compared with those without AD, regardless of age. The authors concluded, “Our data must be implemented into information for the present and future users of HT, even though the absolute risk increase is small.”
However, given the limitations inherent to observational and registry studies, and the contrasting findings of 3 high-quality, randomized controlled trials (RCTs; more details below), providers actually can reassure younger peri- and postmenopausal women about the cognitive safety of HT.3 They also can explain to patients that cognitive symptoms like the ones described in the case example are normal and provide general guidance to midlife women on how to optimize brain health.

Continue to: Closer look at WHI and RCT research pinpoints cognitively neutral HT...
Closer look at WHI and RCT research pinpoints cognitively neutral HT
In WHIMS, the combination of conjugated equine estrogen (CEE; 0.625 mg/d) plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA; 2.5 mg/d) led to a doubling of the risk of all-cause dementia compared with placebo in a sample of 4,532 women aged 65 years and older at baseline.1 CEE alone (0.625 mg) did not lead to an increased risk of all-cause dementia.4
Whether those formulations led to cognitive impairment in younger postmenopausal women was the focus of WHIMS-Younger (WHIMS-Y), which involved WHI participants aged 50 to 55 years at baseline.5 Results revealed neutral cognitive effects (ie, no differences in cognitive performance in women randomly assigned to HT or placebo) in women tested 7.2 years after the end of the WHI trial. WHIMS-Y findings indicated that there were no sustained cognitive risks of CEE or CEE/MPA therapy. Two randomized, placebo-controlled trials involving younger postmenopausal women yielded similar findings.6,7 HT shown to produce cognitively neutral effects during active treatment included transdermal estradiol plus micronized progesterone,6 CEE plus progesterone,6 and oral estradiol plus vaginal progesterone gel.7 The findings of these randomized trials are critical for guiding decisions regarding the cognitive risks of HT in early postmenopausal women (TABLE 1).

What about women with VMS?
A key gap in knowledge about the cognitive effects of HT is whether HT confers cognitive advantages to women with bothersome VMS. This is a striking absence given that the key indication for HT is the treatment of VMS. While some symptomatic women were included in the trials of HT in younger postmenopausal women described above, no large trial to date has selectively enrolled women with moderate-to-severe VMS to determine if HT is cognitively neutral, beneficial, or detrimental in that group. Some studies involving midlife women have found associations between VMS (as measured with ambulatory skin conductance monitors) and multiple measures of brain health, including memory performance,8 small ischemic lesions on structural brain scans,9 and altered brain function.10 In a small trial of a nonhormonal intervention for VMS, improvement in VMS following the intervention was directly related to improvement in memory performance.11 The reliability of these findings continues to be evaluated but raises the hypothesis that VMS treatments might improve memory in midlife women.
Memory complaints common among midlife women
About 60% of women report an undesirable change in memory performance at midlife as compared with earlier in their lives.12,13 Complaints of forgetfulness are higher in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women compared with premenopausal women, even when those women are similar in age.14 Two large prospective studies found that memory performance decreases during the perimenopause and then rebounds, suggesting a transient decrease in memory.15,16 Although cognitive complaints are common among women in their 40s and 50s, AD is rare in that age group. The risk is largely limited to those women with a parent who developed dementia before age 65, as such cases suggest a familial form of AD.
Continue to: What causes cognitive difficulties during midlife?
What causes cognitive difficulties during midlife?
First, some cognitive decline is expected at midlife based on increasing age. Second, above and beyond the role of chronologic aging (ie, getting one year older each year), ovarian aging plays a role. A role of estrogen was verified in clinical trials showing that memory decreased following oophorectomy in premenopausal women in their 40s but returned to presurgical levels following treatment with estrogen therapy (ET).17 Cohort studies indicate that women who undergo oophorectomy before the typical age of menopause are at increased risk for cognitive impairment or dementia, but those who take ET after oophorectomy until the typical age of menopause do not show that risk.18
Third, cognitive problems are linked not only to VMS but also to sleep disturbance, depressed mood, and increased anxiety—all of which are common in midlife women.15,19 Lastly, health factors play a role. Hypertension, obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and smoking are associated with adverse brain changes at midlife.20
Giving advice to your patients
First, normalize the cognitive complaints, noting that some cognitive changes are an expected part of aging for all people regardless of whether they are male or female. Advise that while the best studies indicate that these cognitive lapses are especially common in perimenopausal women, they appear to be temporary; women are likely to resume normal cognitive function once the hormonal changes associated with menopause subside.15,16 Note that the one unknown is the role that VMS play in memory problems and that some studies indicate a link between VMS and cognitive problems. Women may experience some cognitive improvement if VMS are effectively treated.
Advise patients that the Endocrine Society, the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the International Menopause Society all have published guidelines saying that the benefits of HT outweigh the risks for most women aged 50 to 60 years.21 For concerns about the cognitive adverse effects of HT, discuss the best quality evidence—that which comes from randomized trials—which shows no harmful effects of HT in midlife women.5-7 Especially reassuring is that one of these high-quality studies was conducted by the same researchers who found that HT can be risky in older women (ie, the WHI Investigators).5
Going one step further: Protecting brain health
As primary care providers to midlife women, ObGyns can go one step further and advise patients on how to proactively nurture their brain health. Great evidence-based resources for information on maintaining brain health include the Alzheimer’s Association (https://www.alz.org) and the Women’s Brain Health Initiative (https://womensbrainhealth.org). Primary prevention of AD begins decades before the typical age of an AD diagnosis, and many risk factors for AD are modifiable.22 Patients can keep their brains healthy through myriad approaches including treating hypertension, reducing body mass index, engaging in regular aerobic exercise (brisk walking is fine), eating a Mediterranean diet, maintaining an active social life, and engaging in novel challenging activities like learning a new language or a new skill like dancing.20
Also important is the overlap between cognitive issues, mood, and alcohol use. In the opening case, Jackie mentions alcohol use and social withdrawal. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), low-risk drinking for women is defined as no more than 3 drinks on any single day and no more than 7 drinks per week.23 Heavy alcohol use not only affects brain function but also mood, and depressed mood can lead women to drink excessively.24
In addition, Jackie’s mother has AD, and that stressor can contribute to depressed feelings, especially if Jackie is involved in caregiving. A quick screen for depression with an instrument like the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ-2; TABLE 2)25 can rule out a more serious mood disorder—an approach that is particularly important for patients with a history of major depression, as 58% of those patients experience a major depressive episode during the menopausal transition.26 For this reason, it is important to ask patients like Jackie if they have a history of depression; if they do and were treated medically, consider prescribing the antidepressant that worked in the past. For information on menopause and mood-related issues, providers can access new guidelines from NAMS and the National Network of Depression Centers (NNDC).27 There is also a handy patient information sheet to accompany those guidelines on the NAMS website (https://www.menopause.org/).

Continue to: CASE Resolved...
CASE Resolved
When approaching Jackie, most importantly, I would normalize her experience and tell her that memory problems are common in the menopausal transition, especially for women with bothersome VMS. Research suggests that the memory problems she is experiencing are related to hormonal changes and not to AD, and that her memory will likely improve once she has transitioned through the menopause. I would tell her that AD is rare at midlife unless there is a family history of early onset of AD (before age 65), and I would verify the age at which her mother was diagnosed to confirm that it was late-onset AD.
For now, I would recommend that she be prescribed HT for her bothersome hot flashes using one of the “safe” formulations in the Table on page 24. I also would tell her that there is much she can do to lower her risk of AD and that it is best to start now as she enters her 50s because that is when AD changes typically start in the brain, and she can start to prevent those changes now.
I would tell her that experts in the field of AD agree that these lifestyle interventions are currently the best way to prevent AD and that the more of them she engages in, the more her brain will benefit. I would advise her to continue to manage her hypertension and to consider ways of lowering her BMI to enhance her brain health. Engaging in regular brisk walking or other aerobic exercise, as well as incorporating more of the Mediterranean diet into her daily food intake would also benefit her brain. As a working woman, she is exercising her brain, and she should consider other cognitively challenging activities to keep her brain in good shape.
I would follow up with her in a few months to see if her memory functioning is better. If it is not, and if her VMS continue to be bothersome, I would increase her dose of HT. Only if her VMS are treated but her memory problems are getting worse would I screen her with a Mini-Mental State Exam and refer her to a neurologist for an evaluation.
CASE HT for vasomotor symptoms in perimenopausal woman with cognitive concerns
Jackie is a 49-year-old woman. Her body mass index is 33 kg/m2, and she has mild hypertension that is effectively controlled with antihypertensive medications. Otherwise, she is in good health.During her annual gynecologic exam, she reports that for the past 9 months her menstrual cycles have not been as regular as they used to be and that 3 months ago she skipped a cycle. She is having bothersome vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and is concerned about her memory. She says she is forgetful at work and in social situations. During a recent presentation, she could not remember the name of one of her former clients. At a work happy hour, she forgot the name of her coworker’s husband, although she did remember it later after returning home.
Her mother has Alzheimer disease (AD), and Jackie worries about whether she, too, might be developing dementia and whether her memory will fail her in social situations.
She is concerned about using hormone therapy (HT) for her vasomotor symptoms because she has heard that it can lead to breast cancer and/or AD.
How would you advise her?
HT remains the most effective treatment for bothersome VMS, but concerns about its cognitive safety persist. Such concerns, and indeed a black-box warning about the risk of dementia with HT use, initially arose following the 2003 publication of the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of HT for the primary prevention of dementia in women aged 65 years and older at baseline.1 The study found that combination estrogen/progestin therapy was associated with a 2-fold increase in dementia when compared with placebo.
One of the critical questions arising even before WHIMS was whether the cognitive risks associated with HT that were seen in WHIMS apply to younger women. Attempting to answer the question and adding fuel to the fire are the results of a recent case-control study from Finland.2 This study compared HT use in Finnish women with and without AD and found that HT use was higher among Finnish women with AD compared with those without AD, regardless of age. The authors concluded, “Our data must be implemented into information for the present and future users of HT, even though the absolute risk increase is small.”
However, given the limitations inherent to observational and registry studies, and the contrasting findings of 3 high-quality, randomized controlled trials (RCTs; more details below), providers actually can reassure younger peri- and postmenopausal women about the cognitive safety of HT.3 They also can explain to patients that cognitive symptoms like the ones described in the case example are normal and provide general guidance to midlife women on how to optimize brain health.

Continue to: Closer look at WHI and RCT research pinpoints cognitively neutral HT...
Closer look at WHI and RCT research pinpoints cognitively neutral HT
In WHIMS, the combination of conjugated equine estrogen (CEE; 0.625 mg/d) plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA; 2.5 mg/d) led to a doubling of the risk of all-cause dementia compared with placebo in a sample of 4,532 women aged 65 years and older at baseline.1 CEE alone (0.625 mg) did not lead to an increased risk of all-cause dementia.4
Whether those formulations led to cognitive impairment in younger postmenopausal women was the focus of WHIMS-Younger (WHIMS-Y), which involved WHI participants aged 50 to 55 years at baseline.5 Results revealed neutral cognitive effects (ie, no differences in cognitive performance in women randomly assigned to HT or placebo) in women tested 7.2 years after the end of the WHI trial. WHIMS-Y findings indicated that there were no sustained cognitive risks of CEE or CEE/MPA therapy. Two randomized, placebo-controlled trials involving younger postmenopausal women yielded similar findings.6,7 HT shown to produce cognitively neutral effects during active treatment included transdermal estradiol plus micronized progesterone,6 CEE plus progesterone,6 and oral estradiol plus vaginal progesterone gel.7 The findings of these randomized trials are critical for guiding decisions regarding the cognitive risks of HT in early postmenopausal women (TABLE 1).

What about women with VMS?
A key gap in knowledge about the cognitive effects of HT is whether HT confers cognitive advantages to women with bothersome VMS. This is a striking absence given that the key indication for HT is the treatment of VMS. While some symptomatic women were included in the trials of HT in younger postmenopausal women described above, no large trial to date has selectively enrolled women with moderate-to-severe VMS to determine if HT is cognitively neutral, beneficial, or detrimental in that group. Some studies involving midlife women have found associations between VMS (as measured with ambulatory skin conductance monitors) and multiple measures of brain health, including memory performance,8 small ischemic lesions on structural brain scans,9 and altered brain function.10 In a small trial of a nonhormonal intervention for VMS, improvement in VMS following the intervention was directly related to improvement in memory performance.11 The reliability of these findings continues to be evaluated but raises the hypothesis that VMS treatments might improve memory in midlife women.
Memory complaints common among midlife women
About 60% of women report an undesirable change in memory performance at midlife as compared with earlier in their lives.12,13 Complaints of forgetfulness are higher in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women compared with premenopausal women, even when those women are similar in age.14 Two large prospective studies found that memory performance decreases during the perimenopause and then rebounds, suggesting a transient decrease in memory.15,16 Although cognitive complaints are common among women in their 40s and 50s, AD is rare in that age group. The risk is largely limited to those women with a parent who developed dementia before age 65, as such cases suggest a familial form of AD.
Continue to: What causes cognitive difficulties during midlife?
What causes cognitive difficulties during midlife?
First, some cognitive decline is expected at midlife based on increasing age. Second, above and beyond the role of chronologic aging (ie, getting one year older each year), ovarian aging plays a role. A role of estrogen was verified in clinical trials showing that memory decreased following oophorectomy in premenopausal women in their 40s but returned to presurgical levels following treatment with estrogen therapy (ET).17 Cohort studies indicate that women who undergo oophorectomy before the typical age of menopause are at increased risk for cognitive impairment or dementia, but those who take ET after oophorectomy until the typical age of menopause do not show that risk.18
Third, cognitive problems are linked not only to VMS but also to sleep disturbance, depressed mood, and increased anxiety—all of which are common in midlife women.15,19 Lastly, health factors play a role. Hypertension, obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and smoking are associated with adverse brain changes at midlife.20
Giving advice to your patients
First, normalize the cognitive complaints, noting that some cognitive changes are an expected part of aging for all people regardless of whether they are male or female. Advise that while the best studies indicate that these cognitive lapses are especially common in perimenopausal women, they appear to be temporary; women are likely to resume normal cognitive function once the hormonal changes associated with menopause subside.15,16 Note that the one unknown is the role that VMS play in memory problems and that some studies indicate a link between VMS and cognitive problems. Women may experience some cognitive improvement if VMS are effectively treated.
Advise patients that the Endocrine Society, the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), and the International Menopause Society all have published guidelines saying that the benefits of HT outweigh the risks for most women aged 50 to 60 years.21 For concerns about the cognitive adverse effects of HT, discuss the best quality evidence—that which comes from randomized trials—which shows no harmful effects of HT in midlife women.5-7 Especially reassuring is that one of these high-quality studies was conducted by the same researchers who found that HT can be risky in older women (ie, the WHI Investigators).5
Going one step further: Protecting brain health
As primary care providers to midlife women, ObGyns can go one step further and advise patients on how to proactively nurture their brain health. Great evidence-based resources for information on maintaining brain health include the Alzheimer’s Association (https://www.alz.org) and the Women’s Brain Health Initiative (https://womensbrainhealth.org). Primary prevention of AD begins decades before the typical age of an AD diagnosis, and many risk factors for AD are modifiable.22 Patients can keep their brains healthy through myriad approaches including treating hypertension, reducing body mass index, engaging in regular aerobic exercise (brisk walking is fine), eating a Mediterranean diet, maintaining an active social life, and engaging in novel challenging activities like learning a new language or a new skill like dancing.20
Also important is the overlap between cognitive issues, mood, and alcohol use. In the opening case, Jackie mentions alcohol use and social withdrawal. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), low-risk drinking for women is defined as no more than 3 drinks on any single day and no more than 7 drinks per week.23 Heavy alcohol use not only affects brain function but also mood, and depressed mood can lead women to drink excessively.24
In addition, Jackie’s mother has AD, and that stressor can contribute to depressed feelings, especially if Jackie is involved in caregiving. A quick screen for depression with an instrument like the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ-2; TABLE 2)25 can rule out a more serious mood disorder—an approach that is particularly important for patients with a history of major depression, as 58% of those patients experience a major depressive episode during the menopausal transition.26 For this reason, it is important to ask patients like Jackie if they have a history of depression; if they do and were treated medically, consider prescribing the antidepressant that worked in the past. For information on menopause and mood-related issues, providers can access new guidelines from NAMS and the National Network of Depression Centers (NNDC).27 There is also a handy patient information sheet to accompany those guidelines on the NAMS website (https://www.menopause.org/).

Continue to: CASE Resolved...
CASE Resolved
When approaching Jackie, most importantly, I would normalize her experience and tell her that memory problems are common in the menopausal transition, especially for women with bothersome VMS. Research suggests that the memory problems she is experiencing are related to hormonal changes and not to AD, and that her memory will likely improve once she has transitioned through the menopause. I would tell her that AD is rare at midlife unless there is a family history of early onset of AD (before age 65), and I would verify the age at which her mother was diagnosed to confirm that it was late-onset AD.
For now, I would recommend that she be prescribed HT for her bothersome hot flashes using one of the “safe” formulations in the Table on page 24. I also would tell her that there is much she can do to lower her risk of AD and that it is best to start now as she enters her 50s because that is when AD changes typically start in the brain, and she can start to prevent those changes now.
I would tell her that experts in the field of AD agree that these lifestyle interventions are currently the best way to prevent AD and that the more of them she engages in, the more her brain will benefit. I would advise her to continue to manage her hypertension and to consider ways of lowering her BMI to enhance her brain health. Engaging in regular brisk walking or other aerobic exercise, as well as incorporating more of the Mediterranean diet into her daily food intake would also benefit her brain. As a working woman, she is exercising her brain, and she should consider other cognitively challenging activities to keep her brain in good shape.
I would follow up with her in a few months to see if her memory functioning is better. If it is not, and if her VMS continue to be bothersome, I would increase her dose of HT. Only if her VMS are treated but her memory problems are getting worse would I screen her with a Mini-Mental State Exam and refer her to a neurologist for an evaluation.
- Shumaker SA, Legault C, Rapp SR, et al. Estrogen plus progestin and the incidence of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in postmenopausal women: the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;289:2651-2662.
- Savolainen-Peltonen H, Rahkola-Soisalo P, Hoti F, et al. Use of postmenopausal hormone therapy and risk of Alzheimer’s disease in Finland: nationwide case-control study. BMJ. 2019;364:1665.
- Maki PM, Girard LM, Manson JE. Menopausal hormone therapy and cognition. BMJ. 2019;364:1877.
- Shumaker SA, Legault C, Kuller L, et al. Conjugated equine estrogens and incidence of probable dementia and mild cognitive impairment in postmenopausal women: Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study. JAMA. 2004;291:2947-2958.
- Espeland MA, Shumaker SA, Leng I, et al. Long-term effects on cognitive function of postmenopausal hormone therapy prescribed to women aged 50 to 55 years. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1429-1436.
- Gleason CE, Dowling NM, Wharton W, et al. Effects of hormone therapy on cognition and mood in recently postmenopausal women: findings from the randomized, controlled KEEPS-cognitive and affective study. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001833.
- Henderson VW, St. John JA, Hodis HN, et al. Cognitive effects of estradiol after menopause: a randomized trial of the timing hypothesis. Neurology. 2016;87:699-708.
- Maki PM, Drogos LL, Rubin LH, et al. Objective hot flashes are negatively related to verbal memory performance in midlife women. Menopause. 2008;15:848-856.
- Thurston RC, Aizenstein HJ, Derby CA, et al. Menopausal hot flashes and white matter hyperintensities. Menopause. 2016;23:27-32.
- Thurston RC, Maki PM, Derby CA, et al. Menopausal hot flashes and the default mode network. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:1572-1578.e1.
- Maki PM, Rubin LH, Savarese A, et al. Stellate ganglion blockade and verbal memory in midlife women: evidence from a randomized trial. Maturitas. 2016;92:123-129.
- Woods NF, Mitchell ES, Adams C. Memory functioning among midlife women: observations from the Seattle Midlife Women’s Health Study. Menopause. 2000;7:257-265.
- Sullivan Mitchell E, Fugate Woods N. Midlife women’s attributions about perceived memory changes: observations from the Seattle Midlife Women’s Health Study. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2001;10:351-362.
- Gold EB, Sternfeld B, Kelsey JL, et al. Relation of demographic and lifestyle factors to symptoms in a multi-racial/ethnic population of women 40-55 years of age. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;152:463-473.
- Shumaker SA, Legault C, Rapp SR, et al. Estrogen plus progestin and the incidence of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in postmenopausal women: the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;289:2651-2662.
- Savolainen-Peltonen H, Rahkola-Soisalo P, Hoti F, et al. Use of postmenopausal hormone therapy and risk of Alzheimer’s disease in Finland: nationwide case-control study. BMJ. 2019;364:1665.
- Maki PM, Girard LM, Manson JE. Menopausal hormone therapy and cognition. BMJ. 2019;364:1877.
- Shumaker SA, Legault C, Kuller L, et al. Conjugated equine estrogens and incidence of probable dementia and mild cognitive impairment in postmenopausal women: Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study. JAMA. 2004;291:2947-2958.
- Espeland MA, Shumaker SA, Leng I, et al. Long-term effects on cognitive function of postmenopausal hormone therapy prescribed to women aged 50 to 55 years. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1429-1436.
- Gleason CE, Dowling NM, Wharton W, et al. Effects of hormone therapy on cognition and mood in recently postmenopausal women: findings from the randomized, controlled KEEPS-cognitive and affective study. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001833.
- Henderson VW, St. John JA, Hodis HN, et al. Cognitive effects of estradiol after menopause: a randomized trial of the timing hypothesis. Neurology. 2016;87:699-708.
- Maki PM, Drogos LL, Rubin LH, et al. Objective hot flashes are negatively related to verbal memory performance in midlife women. Menopause. 2008;15:848-856.
- Thurston RC, Aizenstein HJ, Derby CA, et al. Menopausal hot flashes and white matter hyperintensities. Menopause. 2016;23:27-32.
- Thurston RC, Maki PM, Derby CA, et al. Menopausal hot flashes and the default mode network. Fertil Steril. 2015;103:1572-1578.e1.
- Maki PM, Rubin LH, Savarese A, et al. Stellate ganglion blockade and verbal memory in midlife women: evidence from a randomized trial. Maturitas. 2016;92:123-129.
- Woods NF, Mitchell ES, Adams C. Memory functioning among midlife women: observations from the Seattle Midlife Women’s Health Study. Menopause. 2000;7:257-265.
- Sullivan Mitchell E, Fugate Woods N. Midlife women’s attributions about perceived memory changes: observations from the Seattle Midlife Women’s Health Study. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2001;10:351-362.
- Gold EB, Sternfeld B, Kelsey JL, et al. Relation of demographic and lifestyle factors to symptoms in a multi-racial/ethnic population of women 40-55 years of age. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;152:463-473.