User login
PCI or not, mortality climbs with post-ACS bleeding complications
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.
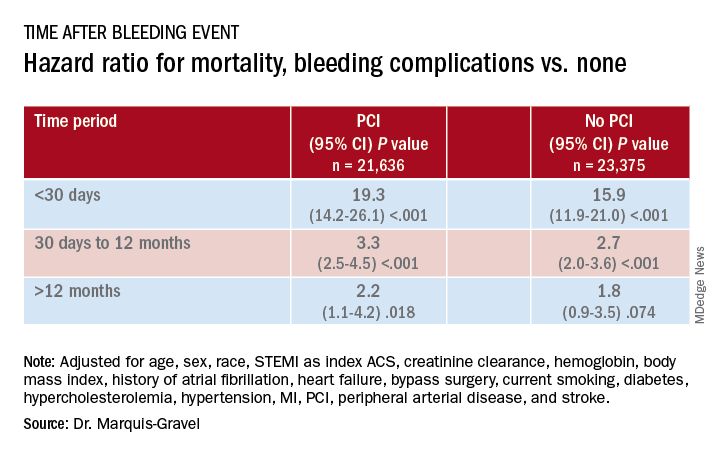
Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.

Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.

Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Acetaminophen beats fentanyl in STEMI
Swapping out intravenous fentanyl in favor of IV acetaminophen in patients with ST-elevation MI (STEMI) provides comparable pain relief but with desirably higher blood levels of ticagrelor both immediately after primary percutaneous intervention and 1 hour post procedure.
That’s according to results of the Dutch ON-TIME 3 trial, presented by Anne H. Tavenier, MD, at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Our trial results have implications for the prehospital treatment of STEMI patients,” said Dr. Tavenier, a cardiologist at the Isala Clinic in Zwolle, the Netherlands.
The explanation for the success of this novel STEMI pain management strategy? The synthetic opioid fentanyl impairs gastrointestinal absorption of oral P2Y12 receptor antagonists such as ticagrelor. Opiates do so as well, whereas acetaminophen does not, she explained.
The potent platelet inhibition provided by oral P2Y12 inhibitors is crucial to successful primary PCI for STEMI. But these platelet inhibitory effects are inherently slowed in STEMI patients owing to hemodynamic changes and delayed GI absorption. And even though both American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association and European Society of Cardiology guidelines recommend the use of opioids for pain control in STEMI patients, the fact is that these medications further delay the absorption of oral P2Y12 inhibitors. And this delay is further exacerbated by the nausea and vomiting which are common side effects of IV fentanyl, she continued.
The impetus for the ON-TIME 3 trial was straightforward, the cardiologist said: “For years, STEMI patients have been treated with morphine or morphinelike drugs like fentanyl because of pain or sympathetic stress. To date, trials investigating alternative analgesics to opioids have been scarce.”
ON-TIME 3 was a multicenter, open-label, phase 4 clinical trial in which 195 STEMI patients with a self-reported pain score of at least 4 on a 0-10 scale received crushed ticagrelor in the ambulance along with either 1,000 mg of IV acetaminophen or fentanyl at 1-2 mcg/kg.
Ticagrelor blood levels were significantly higher in the IV acetaminophen group when measured just prior to primary PCI (151 ng/mL versus 60 ng/mL in the IV fentanyl group; immediately after PCI (326 versus 115 ng/mL), and 1 hour post PCI (488 versus 372 ng/mL).
However, there was no significant between-group difference in levels of platelet reactivity units measured immediately after primary PCI, Dr. Tavenier added.
Discussant Christoph K. Naber, MD, PhD, confessed that prior to ON-TIME 3 he was unaware that administering opioids to STEMI patients results in delayed absorption of oral P2Y12 inhibitors. Upon delving into the literature, however, he found that this is indeed a well-documented problem.
“The open question I have about this very elegant trial is whether the increased P2Y12 levels will translate into a measurable difference in clinical outcomes,” said Dr. Naber, an interventional cardiologist at the Wilhemshaven (Germany) Clinic.
The answer to that question would require a larger, longer-term trial. And he’s disinclined to wait around for that to happen.
“I think when we look at the risk balance, the risk of switching from an opioid to acetaminophen, if it works for the patient, is rather low. So this might be something to introduce in my practice,” the cardiologist said.
Dr. Tavenier and Dr. Naber reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tavenier AH. EuroPCR 2020.
Swapping out intravenous fentanyl in favor of IV acetaminophen in patients with ST-elevation MI (STEMI) provides comparable pain relief but with desirably higher blood levels of ticagrelor both immediately after primary percutaneous intervention and 1 hour post procedure.
That’s according to results of the Dutch ON-TIME 3 trial, presented by Anne H. Tavenier, MD, at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Our trial results have implications for the prehospital treatment of STEMI patients,” said Dr. Tavenier, a cardiologist at the Isala Clinic in Zwolle, the Netherlands.
The explanation for the success of this novel STEMI pain management strategy? The synthetic opioid fentanyl impairs gastrointestinal absorption of oral P2Y12 receptor antagonists such as ticagrelor. Opiates do so as well, whereas acetaminophen does not, she explained.
The potent platelet inhibition provided by oral P2Y12 inhibitors is crucial to successful primary PCI for STEMI. But these platelet inhibitory effects are inherently slowed in STEMI patients owing to hemodynamic changes and delayed GI absorption. And even though both American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association and European Society of Cardiology guidelines recommend the use of opioids for pain control in STEMI patients, the fact is that these medications further delay the absorption of oral P2Y12 inhibitors. And this delay is further exacerbated by the nausea and vomiting which are common side effects of IV fentanyl, she continued.
The impetus for the ON-TIME 3 trial was straightforward, the cardiologist said: “For years, STEMI patients have been treated with morphine or morphinelike drugs like fentanyl because of pain or sympathetic stress. To date, trials investigating alternative analgesics to opioids have been scarce.”
ON-TIME 3 was a multicenter, open-label, phase 4 clinical trial in which 195 STEMI patients with a self-reported pain score of at least 4 on a 0-10 scale received crushed ticagrelor in the ambulance along with either 1,000 mg of IV acetaminophen or fentanyl at 1-2 mcg/kg.
Ticagrelor blood levels were significantly higher in the IV acetaminophen group when measured just prior to primary PCI (151 ng/mL versus 60 ng/mL in the IV fentanyl group; immediately after PCI (326 versus 115 ng/mL), and 1 hour post PCI (488 versus 372 ng/mL).
However, there was no significant between-group difference in levels of platelet reactivity units measured immediately after primary PCI, Dr. Tavenier added.
Discussant Christoph K. Naber, MD, PhD, confessed that prior to ON-TIME 3 he was unaware that administering opioids to STEMI patients results in delayed absorption of oral P2Y12 inhibitors. Upon delving into the literature, however, he found that this is indeed a well-documented problem.
“The open question I have about this very elegant trial is whether the increased P2Y12 levels will translate into a measurable difference in clinical outcomes,” said Dr. Naber, an interventional cardiologist at the Wilhemshaven (Germany) Clinic.
The answer to that question would require a larger, longer-term trial. And he’s disinclined to wait around for that to happen.
“I think when we look at the risk balance, the risk of switching from an opioid to acetaminophen, if it works for the patient, is rather low. So this might be something to introduce in my practice,” the cardiologist said.
Dr. Tavenier and Dr. Naber reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tavenier AH. EuroPCR 2020.
Swapping out intravenous fentanyl in favor of IV acetaminophen in patients with ST-elevation MI (STEMI) provides comparable pain relief but with desirably higher blood levels of ticagrelor both immediately after primary percutaneous intervention and 1 hour post procedure.
That’s according to results of the Dutch ON-TIME 3 trial, presented by Anne H. Tavenier, MD, at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
“Our trial results have implications for the prehospital treatment of STEMI patients,” said Dr. Tavenier, a cardiologist at the Isala Clinic in Zwolle, the Netherlands.
The explanation for the success of this novel STEMI pain management strategy? The synthetic opioid fentanyl impairs gastrointestinal absorption of oral P2Y12 receptor antagonists such as ticagrelor. Opiates do so as well, whereas acetaminophen does not, she explained.
The potent platelet inhibition provided by oral P2Y12 inhibitors is crucial to successful primary PCI for STEMI. But these platelet inhibitory effects are inherently slowed in STEMI patients owing to hemodynamic changes and delayed GI absorption. And even though both American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association and European Society of Cardiology guidelines recommend the use of opioids for pain control in STEMI patients, the fact is that these medications further delay the absorption of oral P2Y12 inhibitors. And this delay is further exacerbated by the nausea and vomiting which are common side effects of IV fentanyl, she continued.
The impetus for the ON-TIME 3 trial was straightforward, the cardiologist said: “For years, STEMI patients have been treated with morphine or morphinelike drugs like fentanyl because of pain or sympathetic stress. To date, trials investigating alternative analgesics to opioids have been scarce.”
ON-TIME 3 was a multicenter, open-label, phase 4 clinical trial in which 195 STEMI patients with a self-reported pain score of at least 4 on a 0-10 scale received crushed ticagrelor in the ambulance along with either 1,000 mg of IV acetaminophen or fentanyl at 1-2 mcg/kg.
Ticagrelor blood levels were significantly higher in the IV acetaminophen group when measured just prior to primary PCI (151 ng/mL versus 60 ng/mL in the IV fentanyl group; immediately after PCI (326 versus 115 ng/mL), and 1 hour post PCI (488 versus 372 ng/mL).
However, there was no significant between-group difference in levels of platelet reactivity units measured immediately after primary PCI, Dr. Tavenier added.
Discussant Christoph K. Naber, MD, PhD, confessed that prior to ON-TIME 3 he was unaware that administering opioids to STEMI patients results in delayed absorption of oral P2Y12 inhibitors. Upon delving into the literature, however, he found that this is indeed a well-documented problem.
“The open question I have about this very elegant trial is whether the increased P2Y12 levels will translate into a measurable difference in clinical outcomes,” said Dr. Naber, an interventional cardiologist at the Wilhemshaven (Germany) Clinic.
The answer to that question would require a larger, longer-term trial. And he’s disinclined to wait around for that to happen.
“I think when we look at the risk balance, the risk of switching from an opioid to acetaminophen, if it works for the patient, is rather low. So this might be something to introduce in my practice,” the cardiologist said.
Dr. Tavenier and Dr. Naber reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Tavenier AH. EuroPCR 2020.
REPORTING FROM EUROPCR 2020
Post-PCI mortality higher in Blacks vs. Whites, regardless of comorbidities
A combined analysis of 10 prospective trials, intended to shed light on racial disparities in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) outcomes, saw sharply higher risks of death and myocardial infarction (MI) for Blacks compared with Whites.
The burden of comorbidities, including diabetes, was greater for Hispanics and Blacks, compared with Whites, but only in Blacks were PCI outcomes significantly worse even after controlling for such conditions and other baseline risk factors.
The analysis based on more than 22,000 patients was published July 6 in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions,with lead author Mordechai Golomb, MD, Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York.
In the study based on patient-level data from the different trials, the adjusted risk of MI after PCI was increased 45% at 1 year and 55% after 5 years for Blacks, compared with Whites. Their risk of death at 1 year was doubled, and their risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) was up by 28% at 5 years.
“Improving health care and outcomes for minorities is essential, and we are hopeful that our work may help direct these efforts, senior author Gregg W. Stone, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“But this won’t happen without active, concerted efforts to promote change and opportunity, a task for government, regulators, payers, hospital administrators, physicians, and all health care providers,” he said. “Understanding patient outcomes according to race and ethnicity is essential to optimize health for all patients,” but “most prior studies in this regard have looked at population-based data.”
In contrast, the current study used hospital source records – which are considered more accurate than administrative databases – and event coding reports, Dr. Stone said, plus angiographic core laboratory analyses for all patients, which allows “an independent assessment of the extent and type of coronary artery disease and procedural outcomes.”
The analysis “demonstrated that even when upfront treatments are presumably similar [across racial groups] in a clinical trial setting, longitudinal outcomes still differ by race,” Michael Nanna, MD, said in an interview.
The “troubling” results “highlight the persistence of racial disparities in health care and the need to renew our focus on closing these gaps [and] is yet another call to action for clinicians, researchers, and the health care system at large,” said Dr. Nanna, of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., and lead author on an editorial accompanying the published analysis.
Of the 10 randomized controlled trials included in the study, which encompassed 22,638 patients, 9 were stent comparisons and 1 compared antithrombotic regimens in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS), the authors noted. The median follow-up was about 1,100 days.
White patients made up 90.9% of the combined cohort, Black patients comprised 4.1%, Hispanics 2.1%, and Asians 1.8% – figures that “confirm the well-known fact that minority groups are underrepresented in clinical trials,” Dr. Stone said.
There were notable demographic and clinical differences at baseline between the four groups.
For example, Black patients tended to be younger than White, Hispanic, and Asian patients. Black and Hispanic patients were also less likely to be male, compared with White patients.
Both Black and Hispanic patients had more comorbidities than Whites did at baseline, the authors observe. For example, Black and Hispanic patients had a greater body mass index, compared with Whites, whereas it was lower for Asians; and they had more diabetes and more hypertension than Whites (P < .0001 for all differences). Hispanics were more likely to have ACS at baseline, compared with Whites, and less likely to have stable coronary artery disease (CAD) (P < .0001 for all differences). Similar proportions of Blacks and of Whites had stable CAD (about 32% of each) and ACS (about 68% in both cases). Rates of hyperlipidemia and stable CAD were greater and rates of ACS was lower in Asians than the other three race groups (P < .0001 for each difference). In adjusted analysis, the risk of MACE at 5 years was significantly increased for Blacks, compared with Whites (hazard ratio, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.57; P = .01). The same applied to MI (HR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.15-2.09; P = .004). At 1 year, Blacks showed higher risks for death (HR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.26-3.36; P = .004) and for MI (HR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.01-2.10; P = .045), compared with Whites.
No significant increases in risk for outcomes at 1 and 5 years were seen for Hispanics or Asians, compared with Whites.
Covariates in the analyses included age, sex, body mass index, diabetes, current smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, history of MI or coronary revascularization, clinical CAD presentation, category of stent, and race stratified by study.
Even with underlying genotypic differences between Blacks and Whites, much of the difference in risk for outcomes “should have been accounted for when the researchers adjusted for these clinical phenotypes,” the editorial notes.
Some of the difference in risk must have derived from uncontrolled-for variables, and “[b]eyond genetics, it is clear that race is also a surrogate for other socioeconomic factors that influence both medical care and patient outcomes,” the editorialists wrote.
The adjusted analysis, noted Golomb et al, suggests “that for Hispanic patients, the excess risk for adverse clinical outcomes may have been attributable to a higher prevalence of risk factors. In contrast, the excess risk for adverse clinical outcomes for Black patients persisted even after adjustment for baseline risk factors.”
As such, they agreed: “The observed increased risk may be explained by differences that are not fully captured in traditional cardiovascular risk factor assessment, including socioeconomic differences and education, treatment compliance rates, and yet-to-be-elucidated genetic differences and/or other factors.”
Dr. Stone said that such socioeconomic considerations may include reduced access to care and insurance coverage; lack of preventive care, disease awareness, and education; delayed presentation; and varying levels of provided care.
“Possible genetic or environmental-related differences in the development and progression of atherosclerosis and other disease processes” may also be involved.
“Achieving representative proportions of minorities in clinical trials is essential but has proved challenging,” Dr. Stone said. “We must ensure that adequate numbers of hospitals and providers that are serving these patients participate in multicenter trials, and trust has to be developed so that minority populations have confidence to enroll in studies.”
Dr. Stone reported holding equity options in Ancora, Qool Therapeutics, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, the Biostar family of funds, SpectraWave, Orchestro Biomed, Aria, Cardiac Success, the MedFocus family of funds, and Valfix and receiving consulting fees from Valfix, TherOx, Vascular Dynamics, Robocath, HeartFlow, Gore Ablative Solutions, Miracor, Neovasc, W-Wave, Abiomed, and others. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Nanna reports no relevant financial relationships; other coauthor disclosures are provided with the editorial.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A combined analysis of 10 prospective trials, intended to shed light on racial disparities in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) outcomes, saw sharply higher risks of death and myocardial infarction (MI) for Blacks compared with Whites.
The burden of comorbidities, including diabetes, was greater for Hispanics and Blacks, compared with Whites, but only in Blacks were PCI outcomes significantly worse even after controlling for such conditions and other baseline risk factors.
The analysis based on more than 22,000 patients was published July 6 in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions,with lead author Mordechai Golomb, MD, Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York.
In the study based on patient-level data from the different trials, the adjusted risk of MI after PCI was increased 45% at 1 year and 55% after 5 years for Blacks, compared with Whites. Their risk of death at 1 year was doubled, and their risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) was up by 28% at 5 years.
“Improving health care and outcomes for minorities is essential, and we are hopeful that our work may help direct these efforts, senior author Gregg W. Stone, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“But this won’t happen without active, concerted efforts to promote change and opportunity, a task for government, regulators, payers, hospital administrators, physicians, and all health care providers,” he said. “Understanding patient outcomes according to race and ethnicity is essential to optimize health for all patients,” but “most prior studies in this regard have looked at population-based data.”
In contrast, the current study used hospital source records – which are considered more accurate than administrative databases – and event coding reports, Dr. Stone said, plus angiographic core laboratory analyses for all patients, which allows “an independent assessment of the extent and type of coronary artery disease and procedural outcomes.”
The analysis “demonstrated that even when upfront treatments are presumably similar [across racial groups] in a clinical trial setting, longitudinal outcomes still differ by race,” Michael Nanna, MD, said in an interview.
The “troubling” results “highlight the persistence of racial disparities in health care and the need to renew our focus on closing these gaps [and] is yet another call to action for clinicians, researchers, and the health care system at large,” said Dr. Nanna, of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., and lead author on an editorial accompanying the published analysis.
Of the 10 randomized controlled trials included in the study, which encompassed 22,638 patients, 9 were stent comparisons and 1 compared antithrombotic regimens in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS), the authors noted. The median follow-up was about 1,100 days.
White patients made up 90.9% of the combined cohort, Black patients comprised 4.1%, Hispanics 2.1%, and Asians 1.8% – figures that “confirm the well-known fact that minority groups are underrepresented in clinical trials,” Dr. Stone said.
There were notable demographic and clinical differences at baseline between the four groups.
For example, Black patients tended to be younger than White, Hispanic, and Asian patients. Black and Hispanic patients were also less likely to be male, compared with White patients.
Both Black and Hispanic patients had more comorbidities than Whites did at baseline, the authors observe. For example, Black and Hispanic patients had a greater body mass index, compared with Whites, whereas it was lower for Asians; and they had more diabetes and more hypertension than Whites (P < .0001 for all differences). Hispanics were more likely to have ACS at baseline, compared with Whites, and less likely to have stable coronary artery disease (CAD) (P < .0001 for all differences). Similar proportions of Blacks and of Whites had stable CAD (about 32% of each) and ACS (about 68% in both cases). Rates of hyperlipidemia and stable CAD were greater and rates of ACS was lower in Asians than the other three race groups (P < .0001 for each difference). In adjusted analysis, the risk of MACE at 5 years was significantly increased for Blacks, compared with Whites (hazard ratio, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.57; P = .01). The same applied to MI (HR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.15-2.09; P = .004). At 1 year, Blacks showed higher risks for death (HR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.26-3.36; P = .004) and for MI (HR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.01-2.10; P = .045), compared with Whites.
No significant increases in risk for outcomes at 1 and 5 years were seen for Hispanics or Asians, compared with Whites.
Covariates in the analyses included age, sex, body mass index, diabetes, current smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, history of MI or coronary revascularization, clinical CAD presentation, category of stent, and race stratified by study.
Even with underlying genotypic differences between Blacks and Whites, much of the difference in risk for outcomes “should have been accounted for when the researchers adjusted for these clinical phenotypes,” the editorial notes.
Some of the difference in risk must have derived from uncontrolled-for variables, and “[b]eyond genetics, it is clear that race is also a surrogate for other socioeconomic factors that influence both medical care and patient outcomes,” the editorialists wrote.
The adjusted analysis, noted Golomb et al, suggests “that for Hispanic patients, the excess risk for adverse clinical outcomes may have been attributable to a higher prevalence of risk factors. In contrast, the excess risk for adverse clinical outcomes for Black patients persisted even after adjustment for baseline risk factors.”
As such, they agreed: “The observed increased risk may be explained by differences that are not fully captured in traditional cardiovascular risk factor assessment, including socioeconomic differences and education, treatment compliance rates, and yet-to-be-elucidated genetic differences and/or other factors.”
Dr. Stone said that such socioeconomic considerations may include reduced access to care and insurance coverage; lack of preventive care, disease awareness, and education; delayed presentation; and varying levels of provided care.
“Possible genetic or environmental-related differences in the development and progression of atherosclerosis and other disease processes” may also be involved.
“Achieving representative proportions of minorities in clinical trials is essential but has proved challenging,” Dr. Stone said. “We must ensure that adequate numbers of hospitals and providers that are serving these patients participate in multicenter trials, and trust has to be developed so that minority populations have confidence to enroll in studies.”
Dr. Stone reported holding equity options in Ancora, Qool Therapeutics, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, the Biostar family of funds, SpectraWave, Orchestro Biomed, Aria, Cardiac Success, the MedFocus family of funds, and Valfix and receiving consulting fees from Valfix, TherOx, Vascular Dynamics, Robocath, HeartFlow, Gore Ablative Solutions, Miracor, Neovasc, W-Wave, Abiomed, and others. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Nanna reports no relevant financial relationships; other coauthor disclosures are provided with the editorial.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A combined analysis of 10 prospective trials, intended to shed light on racial disparities in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) outcomes, saw sharply higher risks of death and myocardial infarction (MI) for Blacks compared with Whites.
The burden of comorbidities, including diabetes, was greater for Hispanics and Blacks, compared with Whites, but only in Blacks were PCI outcomes significantly worse even after controlling for such conditions and other baseline risk factors.
The analysis based on more than 22,000 patients was published July 6 in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions,with lead author Mordechai Golomb, MD, Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York.
In the study based on patient-level data from the different trials, the adjusted risk of MI after PCI was increased 45% at 1 year and 55% after 5 years for Blacks, compared with Whites. Their risk of death at 1 year was doubled, and their risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) was up by 28% at 5 years.
“Improving health care and outcomes for minorities is essential, and we are hopeful that our work may help direct these efforts, senior author Gregg W. Stone, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“But this won’t happen without active, concerted efforts to promote change and opportunity, a task for government, regulators, payers, hospital administrators, physicians, and all health care providers,” he said. “Understanding patient outcomes according to race and ethnicity is essential to optimize health for all patients,” but “most prior studies in this regard have looked at population-based data.”
In contrast, the current study used hospital source records – which are considered more accurate than administrative databases – and event coding reports, Dr. Stone said, plus angiographic core laboratory analyses for all patients, which allows “an independent assessment of the extent and type of coronary artery disease and procedural outcomes.”
The analysis “demonstrated that even when upfront treatments are presumably similar [across racial groups] in a clinical trial setting, longitudinal outcomes still differ by race,” Michael Nanna, MD, said in an interview.
The “troubling” results “highlight the persistence of racial disparities in health care and the need to renew our focus on closing these gaps [and] is yet another call to action for clinicians, researchers, and the health care system at large,” said Dr. Nanna, of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., and lead author on an editorial accompanying the published analysis.
Of the 10 randomized controlled trials included in the study, which encompassed 22,638 patients, 9 were stent comparisons and 1 compared antithrombotic regimens in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS), the authors noted. The median follow-up was about 1,100 days.
White patients made up 90.9% of the combined cohort, Black patients comprised 4.1%, Hispanics 2.1%, and Asians 1.8% – figures that “confirm the well-known fact that minority groups are underrepresented in clinical trials,” Dr. Stone said.
There were notable demographic and clinical differences at baseline between the four groups.
For example, Black patients tended to be younger than White, Hispanic, and Asian patients. Black and Hispanic patients were also less likely to be male, compared with White patients.
Both Black and Hispanic patients had more comorbidities than Whites did at baseline, the authors observe. For example, Black and Hispanic patients had a greater body mass index, compared with Whites, whereas it was lower for Asians; and they had more diabetes and more hypertension than Whites (P < .0001 for all differences). Hispanics were more likely to have ACS at baseline, compared with Whites, and less likely to have stable coronary artery disease (CAD) (P < .0001 for all differences). Similar proportions of Blacks and of Whites had stable CAD (about 32% of each) and ACS (about 68% in both cases). Rates of hyperlipidemia and stable CAD were greater and rates of ACS was lower in Asians than the other three race groups (P < .0001 for each difference). In adjusted analysis, the risk of MACE at 5 years was significantly increased for Blacks, compared with Whites (hazard ratio, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.05-1.57; P = .01). The same applied to MI (HR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.15-2.09; P = .004). At 1 year, Blacks showed higher risks for death (HR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.26-3.36; P = .004) and for MI (HR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.01-2.10; P = .045), compared with Whites.
No significant increases in risk for outcomes at 1 and 5 years were seen for Hispanics or Asians, compared with Whites.
Covariates in the analyses included age, sex, body mass index, diabetes, current smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, history of MI or coronary revascularization, clinical CAD presentation, category of stent, and race stratified by study.
Even with underlying genotypic differences between Blacks and Whites, much of the difference in risk for outcomes “should have been accounted for when the researchers adjusted for these clinical phenotypes,” the editorial notes.
Some of the difference in risk must have derived from uncontrolled-for variables, and “[b]eyond genetics, it is clear that race is also a surrogate for other socioeconomic factors that influence both medical care and patient outcomes,” the editorialists wrote.
The adjusted analysis, noted Golomb et al, suggests “that for Hispanic patients, the excess risk for adverse clinical outcomes may have been attributable to a higher prevalence of risk factors. In contrast, the excess risk for adverse clinical outcomes for Black patients persisted even after adjustment for baseline risk factors.”
As such, they agreed: “The observed increased risk may be explained by differences that are not fully captured in traditional cardiovascular risk factor assessment, including socioeconomic differences and education, treatment compliance rates, and yet-to-be-elucidated genetic differences and/or other factors.”
Dr. Stone said that such socioeconomic considerations may include reduced access to care and insurance coverage; lack of preventive care, disease awareness, and education; delayed presentation; and varying levels of provided care.
“Possible genetic or environmental-related differences in the development and progression of atherosclerosis and other disease processes” may also be involved.
“Achieving representative proportions of minorities in clinical trials is essential but has proved challenging,” Dr. Stone said. “We must ensure that adequate numbers of hospitals and providers that are serving these patients participate in multicenter trials, and trust has to be developed so that minority populations have confidence to enroll in studies.”
Dr. Stone reported holding equity options in Ancora, Qool Therapeutics, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, the Biostar family of funds, SpectraWave, Orchestro Biomed, Aria, Cardiac Success, the MedFocus family of funds, and Valfix and receiving consulting fees from Valfix, TherOx, Vascular Dynamics, Robocath, HeartFlow, Gore Ablative Solutions, Miracor, Neovasc, W-Wave, Abiomed, and others. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Nanna reports no relevant financial relationships; other coauthor disclosures are provided with the editorial.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Tendyne device shows promise for mitral annular calcification
Transcatheter implantation of the Tendyne mitral valve replacement device for treatment of mitral regurgitation in patients at prohibitive surgical risk because of severe mitral annular calcification showed considerable promise in a small feasibility study, Paul Sorajja, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
There is a huge unmet need for safe and effective therapies for severe mitral annular calcification (MAC).
“Severe MAC often precludes surgical treatment, and there’s a poor prognosis in patients with MAC and mitral regurgitation when untreated, with 2-year survival of about 60% in some studies,” noted Dr. Sorajja, a cardiologist at the Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation.
Attempts at repurposing transcatheter aortic valves for use in the mitral location have been largely unsatisfactory, he added.
The 6-month outcomes in the 11 patients who received the Tendyne device in the multicenter U.S. feasibility study featured low rates of mortality and nonfatal adverse events, elimination of mitral regurgitation, marked improvement on quality of life measures, and a mean gradient of 4.1 mm Hg. The acute procedural outcomes were encouraging as well.
“We had technical success in 11 of 11 patients, no procedural mortality or left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, no valve embolization or malposition, and no conversion to open heart surgery,” he said.
There was one death caused by mesenteric ischemia 16 days post Tendyne implantation. One patient experienced a nondisabling stroke at day 4. Two patients developed new-onset atrial fibrillation, one of whom cardioverted to sinus rhythm. And one patient had a moderate paravalvular leak that resolved with placement of a plug at 3 months. There were no MIs.
At baseline, 9 of 11 patients were New York Heart Association functional class III and the others were class II. At 6 months, six patients were class I, four were class II, and one was class III. The average score on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire improved from 45.9 at baseline to 65.5 at 1 month, 77.4 at 3 months, and 70.3 at 6 months.
This was a highly selected study population with a Society of Thoracic Surgery Predicted Risk of Mortality score of 9.03%. Part of the screening process for study participation involved preprocedural CT imaging with simulated device overlay in order to identify candidates who were likely to have an optimal device fit.
Discussant Francesco Maisano, MD, was impressed by how well this simulation resembled the actual results as depicted in side-by-side pre- and postprocedural CT images presented by Dr. Sorajja.
“What really surprised me was the correlation between preprocedural simulation data and the actual CT scan after the procedure. This trial shows that the simulation works, and also that Tendyne is a great alternative to aortic valve-in-MAC for these very-high-risk patients,” said Dr. Maisano, professor of cardiac surgery at the University of Zürich and a pioneer of catheter-based mitral and tricuspid interventions.
Earlier this year the Tendyne device was approved in Europe for patients with mitral regurgitation who aren’t candidates for surgical valve replacement or transcatheter mitral valve repair. The approval does not, however, extend to MAC. The Abbott device remains investigational in the United States, where the pivotal SUMMIT trial is underway. In one arm of the trial, patients with mitral regurgitation are being randomized to the investigational Tendyne device or to Abbott’s MitraClip, which is approved for that indication. In the other arm, patients with severe MAC at prohibitive surgical risk will get the Tendyne device. Results are expected in 2020.
Dr. Sorajja reported receiving research grants from and serving as a consultant to Abbott, the feasibility study sponsor, as well as to several other medical device companies, as did Dr. Maisano.
Transcatheter implantation of the Tendyne mitral valve replacement device for treatment of mitral regurgitation in patients at prohibitive surgical risk because of severe mitral annular calcification showed considerable promise in a small feasibility study, Paul Sorajja, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
There is a huge unmet need for safe and effective therapies for severe mitral annular calcification (MAC).
“Severe MAC often precludes surgical treatment, and there’s a poor prognosis in patients with MAC and mitral regurgitation when untreated, with 2-year survival of about 60% in some studies,” noted Dr. Sorajja, a cardiologist at the Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation.
Attempts at repurposing transcatheter aortic valves for use in the mitral location have been largely unsatisfactory, he added.
The 6-month outcomes in the 11 patients who received the Tendyne device in the multicenter U.S. feasibility study featured low rates of mortality and nonfatal adverse events, elimination of mitral regurgitation, marked improvement on quality of life measures, and a mean gradient of 4.1 mm Hg. The acute procedural outcomes were encouraging as well.
“We had technical success in 11 of 11 patients, no procedural mortality or left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, no valve embolization or malposition, and no conversion to open heart surgery,” he said.
There was one death caused by mesenteric ischemia 16 days post Tendyne implantation. One patient experienced a nondisabling stroke at day 4. Two patients developed new-onset atrial fibrillation, one of whom cardioverted to sinus rhythm. And one patient had a moderate paravalvular leak that resolved with placement of a plug at 3 months. There were no MIs.
At baseline, 9 of 11 patients were New York Heart Association functional class III and the others were class II. At 6 months, six patients were class I, four were class II, and one was class III. The average score on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire improved from 45.9 at baseline to 65.5 at 1 month, 77.4 at 3 months, and 70.3 at 6 months.
This was a highly selected study population with a Society of Thoracic Surgery Predicted Risk of Mortality score of 9.03%. Part of the screening process for study participation involved preprocedural CT imaging with simulated device overlay in order to identify candidates who were likely to have an optimal device fit.
Discussant Francesco Maisano, MD, was impressed by how well this simulation resembled the actual results as depicted in side-by-side pre- and postprocedural CT images presented by Dr. Sorajja.
“What really surprised me was the correlation between preprocedural simulation data and the actual CT scan after the procedure. This trial shows that the simulation works, and also that Tendyne is a great alternative to aortic valve-in-MAC for these very-high-risk patients,” said Dr. Maisano, professor of cardiac surgery at the University of Zürich and a pioneer of catheter-based mitral and tricuspid interventions.
Earlier this year the Tendyne device was approved in Europe for patients with mitral regurgitation who aren’t candidates for surgical valve replacement or transcatheter mitral valve repair. The approval does not, however, extend to MAC. The Abbott device remains investigational in the United States, where the pivotal SUMMIT trial is underway. In one arm of the trial, patients with mitral regurgitation are being randomized to the investigational Tendyne device or to Abbott’s MitraClip, which is approved for that indication. In the other arm, patients with severe MAC at prohibitive surgical risk will get the Tendyne device. Results are expected in 2020.
Dr. Sorajja reported receiving research grants from and serving as a consultant to Abbott, the feasibility study sponsor, as well as to several other medical device companies, as did Dr. Maisano.
Transcatheter implantation of the Tendyne mitral valve replacement device for treatment of mitral regurgitation in patients at prohibitive surgical risk because of severe mitral annular calcification showed considerable promise in a small feasibility study, Paul Sorajja, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
There is a huge unmet need for safe and effective therapies for severe mitral annular calcification (MAC).
“Severe MAC often precludes surgical treatment, and there’s a poor prognosis in patients with MAC and mitral regurgitation when untreated, with 2-year survival of about 60% in some studies,” noted Dr. Sorajja, a cardiologist at the Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation.
Attempts at repurposing transcatheter aortic valves for use in the mitral location have been largely unsatisfactory, he added.
The 6-month outcomes in the 11 patients who received the Tendyne device in the multicenter U.S. feasibility study featured low rates of mortality and nonfatal adverse events, elimination of mitral regurgitation, marked improvement on quality of life measures, and a mean gradient of 4.1 mm Hg. The acute procedural outcomes were encouraging as well.
“We had technical success in 11 of 11 patients, no procedural mortality or left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, no valve embolization or malposition, and no conversion to open heart surgery,” he said.
There was one death caused by mesenteric ischemia 16 days post Tendyne implantation. One patient experienced a nondisabling stroke at day 4. Two patients developed new-onset atrial fibrillation, one of whom cardioverted to sinus rhythm. And one patient had a moderate paravalvular leak that resolved with placement of a plug at 3 months. There were no MIs.
At baseline, 9 of 11 patients were New York Heart Association functional class III and the others were class II. At 6 months, six patients were class I, four were class II, and one was class III. The average score on the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire improved from 45.9 at baseline to 65.5 at 1 month, 77.4 at 3 months, and 70.3 at 6 months.
This was a highly selected study population with a Society of Thoracic Surgery Predicted Risk of Mortality score of 9.03%. Part of the screening process for study participation involved preprocedural CT imaging with simulated device overlay in order to identify candidates who were likely to have an optimal device fit.
Discussant Francesco Maisano, MD, was impressed by how well this simulation resembled the actual results as depicted in side-by-side pre- and postprocedural CT images presented by Dr. Sorajja.
“What really surprised me was the correlation between preprocedural simulation data and the actual CT scan after the procedure. This trial shows that the simulation works, and also that Tendyne is a great alternative to aortic valve-in-MAC for these very-high-risk patients,” said Dr. Maisano, professor of cardiac surgery at the University of Zürich and a pioneer of catheter-based mitral and tricuspid interventions.
Earlier this year the Tendyne device was approved in Europe for patients with mitral regurgitation who aren’t candidates for surgical valve replacement or transcatheter mitral valve repair. The approval does not, however, extend to MAC. The Abbott device remains investigational in the United States, where the pivotal SUMMIT trial is underway. In one arm of the trial, patients with mitral regurgitation are being randomized to the investigational Tendyne device or to Abbott’s MitraClip, which is approved for that indication. In the other arm, patients with severe MAC at prohibitive surgical risk will get the Tendyne device. Results are expected in 2020.
Dr. Sorajja reported receiving research grants from and serving as a consultant to Abbott, the feasibility study sponsor, as well as to several other medical device companies, as did Dr. Maisano.
REPORTING FROM EUROPCR 2020
Bariatric embolotherapy helps shed pounds in obese patients
Transcatheter bariatric embolotherapy (TBE) provides sustained weight loss without serious adverse effects among obese patients, results of a pilot sham-controlled study suggest.
At 6-month follow-up, the patients receiving the intervention had lost 7.4 kg (16.3 lbs), compared with 3.0 kg (6.6 lbs) in those randomized to a sham procedure in an intention-to-treat analysis (P = .034).
Results were similar in a per-protocol analysis (9.4 kg/20.7 lbs vs. 1.9 kg/4.1 lbs; P = .0002).
Weight loss after embolotherapy was sustained over 12 months, falling 7.8 kg (17.1 lbs) from baseline in the intention-to-treat population (P = .0011) and 9.3 kg (20.5 lbs) in the per-protocol population (P = .0005).
Safety events after TBE were mild nausea or vomiting, reported Vivek Reddy, MD, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City. Five participants had minor, asymptomatic ulcers that required no additional treatment.
“In this randomized pilot trial, we established the proof of principle that transcatheter bariatric embolotherapy of the left gastric artery is safe and it promotes clinically significant weight loss,” he concluded at PCR e-Course, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions 2020.
Although bariatric surgery is highly effective, he noted that the associated morbidity and mortality limit its use to the severely obese with a body mass index (BMI) typically over 40 kg/m2.
TBE is a minimally invasive approach that uses a custom occlusion balloon microcatheter and robotic manifold to inject 300- to 500-mcm beads to the left gastric artery. Preclinical and case studies suggest it promotes weight loss by reducing ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating hormone secreted from the gastric fundus, Dr. Reddy said.
The study enrolled 44 patients (aged 21-60 years) with a BMI of 35-55, excluding those with prior bariatric surgery and a history of ulcers, type 2 diabetes, chronic aspirin or nonsteroidal inflammatory use, and active Helicobacter pylori infection.
A total of 40 patients were randomly assigned to TBE or a sham procedure, in which lidocaine was applied to the femoral area and propofol infused for 1 hour. The two groups were well matched, with a mean age of 45 vs. 46 years, weight of 110 kg vs. 119 kg, and BMI of 39 vs. 40, Dr. Reddy noted.
Embolotherapy was performed at a single center in Prague, and, on average, took 82.3 minutes and used 127 mL of contrast, 163 Gy/cm2 radiation, and 4.2 mL of microspheres. A single vessel was injected in 80% of cases.
The intention-to-treat population comprised 19 TBE and 18 control subjects, and the per-protocol population comprised 15 TBE and 16 control subjects, after the exclusion of patients in whom embolotherapy was unsuccessful or incomplete or who withdrew consent.
All patients received endoscopy at baseline and 1 week, as well as an intensive 19-session lifestyle and dietary education intervention out to 6 months.
Patients who underwent TBE had significant improvement in hunger scores at 6 and 12 months, compared with baseline. Similarly, quality of life improved across all six domains, including significant gains in physical function, self-esteem, and overall quality of life at both time points, Dr. Reddy reported.
Dr. Reddy disclosed receiving research support from Endobar Solutions.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transcatheter bariatric embolotherapy (TBE) provides sustained weight loss without serious adverse effects among obese patients, results of a pilot sham-controlled study suggest.
At 6-month follow-up, the patients receiving the intervention had lost 7.4 kg (16.3 lbs), compared with 3.0 kg (6.6 lbs) in those randomized to a sham procedure in an intention-to-treat analysis (P = .034).
Results were similar in a per-protocol analysis (9.4 kg/20.7 lbs vs. 1.9 kg/4.1 lbs; P = .0002).
Weight loss after embolotherapy was sustained over 12 months, falling 7.8 kg (17.1 lbs) from baseline in the intention-to-treat population (P = .0011) and 9.3 kg (20.5 lbs) in the per-protocol population (P = .0005).
Safety events after TBE were mild nausea or vomiting, reported Vivek Reddy, MD, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City. Five participants had minor, asymptomatic ulcers that required no additional treatment.
“In this randomized pilot trial, we established the proof of principle that transcatheter bariatric embolotherapy of the left gastric artery is safe and it promotes clinically significant weight loss,” he concluded at PCR e-Course, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions 2020.
Although bariatric surgery is highly effective, he noted that the associated morbidity and mortality limit its use to the severely obese with a body mass index (BMI) typically over 40 kg/m2.
TBE is a minimally invasive approach that uses a custom occlusion balloon microcatheter and robotic manifold to inject 300- to 500-mcm beads to the left gastric artery. Preclinical and case studies suggest it promotes weight loss by reducing ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating hormone secreted from the gastric fundus, Dr. Reddy said.
The study enrolled 44 patients (aged 21-60 years) with a BMI of 35-55, excluding those with prior bariatric surgery and a history of ulcers, type 2 diabetes, chronic aspirin or nonsteroidal inflammatory use, and active Helicobacter pylori infection.
A total of 40 patients were randomly assigned to TBE or a sham procedure, in which lidocaine was applied to the femoral area and propofol infused for 1 hour. The two groups were well matched, with a mean age of 45 vs. 46 years, weight of 110 kg vs. 119 kg, and BMI of 39 vs. 40, Dr. Reddy noted.
Embolotherapy was performed at a single center in Prague, and, on average, took 82.3 minutes and used 127 mL of contrast, 163 Gy/cm2 radiation, and 4.2 mL of microspheres. A single vessel was injected in 80% of cases.
The intention-to-treat population comprised 19 TBE and 18 control subjects, and the per-protocol population comprised 15 TBE and 16 control subjects, after the exclusion of patients in whom embolotherapy was unsuccessful or incomplete or who withdrew consent.
All patients received endoscopy at baseline and 1 week, as well as an intensive 19-session lifestyle and dietary education intervention out to 6 months.
Patients who underwent TBE had significant improvement in hunger scores at 6 and 12 months, compared with baseline. Similarly, quality of life improved across all six domains, including significant gains in physical function, self-esteem, and overall quality of life at both time points, Dr. Reddy reported.
Dr. Reddy disclosed receiving research support from Endobar Solutions.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transcatheter bariatric embolotherapy (TBE) provides sustained weight loss without serious adverse effects among obese patients, results of a pilot sham-controlled study suggest.
At 6-month follow-up, the patients receiving the intervention had lost 7.4 kg (16.3 lbs), compared with 3.0 kg (6.6 lbs) in those randomized to a sham procedure in an intention-to-treat analysis (P = .034).
Results were similar in a per-protocol analysis (9.4 kg/20.7 lbs vs. 1.9 kg/4.1 lbs; P = .0002).
Weight loss after embolotherapy was sustained over 12 months, falling 7.8 kg (17.1 lbs) from baseline in the intention-to-treat population (P = .0011) and 9.3 kg (20.5 lbs) in the per-protocol population (P = .0005).
Safety events after TBE were mild nausea or vomiting, reported Vivek Reddy, MD, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City. Five participants had minor, asymptomatic ulcers that required no additional treatment.
“In this randomized pilot trial, we established the proof of principle that transcatheter bariatric embolotherapy of the left gastric artery is safe and it promotes clinically significant weight loss,” he concluded at PCR e-Course, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions 2020.
Although bariatric surgery is highly effective, he noted that the associated morbidity and mortality limit its use to the severely obese with a body mass index (BMI) typically over 40 kg/m2.
TBE is a minimally invasive approach that uses a custom occlusion balloon microcatheter and robotic manifold to inject 300- to 500-mcm beads to the left gastric artery. Preclinical and case studies suggest it promotes weight loss by reducing ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating hormone secreted from the gastric fundus, Dr. Reddy said.
The study enrolled 44 patients (aged 21-60 years) with a BMI of 35-55, excluding those with prior bariatric surgery and a history of ulcers, type 2 diabetes, chronic aspirin or nonsteroidal inflammatory use, and active Helicobacter pylori infection.
A total of 40 patients were randomly assigned to TBE or a sham procedure, in which lidocaine was applied to the femoral area and propofol infused for 1 hour. The two groups were well matched, with a mean age of 45 vs. 46 years, weight of 110 kg vs. 119 kg, and BMI of 39 vs. 40, Dr. Reddy noted.
Embolotherapy was performed at a single center in Prague, and, on average, took 82.3 minutes and used 127 mL of contrast, 163 Gy/cm2 radiation, and 4.2 mL of microspheres. A single vessel was injected in 80% of cases.
The intention-to-treat population comprised 19 TBE and 18 control subjects, and the per-protocol population comprised 15 TBE and 16 control subjects, after the exclusion of patients in whom embolotherapy was unsuccessful or incomplete or who withdrew consent.
All patients received endoscopy at baseline and 1 week, as well as an intensive 19-session lifestyle and dietary education intervention out to 6 months.
Patients who underwent TBE had significant improvement in hunger scores at 6 and 12 months, compared with baseline. Similarly, quality of life improved across all six domains, including significant gains in physical function, self-esteem, and overall quality of life at both time points, Dr. Reddy reported.
Dr. Reddy disclosed receiving research support from Endobar Solutions.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chewed prasugrel for primary PCI? Forget it!
And cangrelor, in turn, is superior to oral prasugrel, according to the randomized FABOLUS FASTER trial, Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
Moreover, contrary to conventional wisdom, chewed prasugrel (Effient) proved no better than swallowing the tablets whole for platelet inhibition, said Dr. Valgimigli, an interventional cardiologist at the University of Bern (Switzerland).
He explained that standard administration of the newer oral P2Y12 inhibitors prasugrel and ticagrelor (Brilinta) in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ST-elevation MI (STEMI) does not provide optimal early inhibition of platelet aggregation. The parenteral antiplatelet drugs tirofiban and cangrelor have been shown to provide faster and more prolonged inhibition of platelet aggregation than the oral P2Y12 inhibitors.
But there has been no head-to-head comparative data for the glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitor tirofiban (Aggrastat) and the P2Y12 inhibitor cangrelor (Kengreal) in the setting of primary PCI for STEMI. This was the impetus for FABOLUS FASTER, the first study to compare the pharmacodynamic effects of the two parenteral antiplatelet agents. The trial also looked at how these potent parenteral drugs, compared with chewed prasugrel, another previously unexamined yet highly practical issue.
The three-center, multinational, open-label FABOLUS FASTER trial randomized 122 patients undergoing primary PCI for STEMI to one of three arms: a standard intravenous bolus and 2-hour infusion of either the P2Y12 inhibitor cangrelor (Kengreal) or the glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitor tirofiban (Aggrastat), followed in either case by 60 mg of oral prasugrel, or a third arm in which patients didn’t receive either drug but were instead randomized to a 60-mg loading dose of chewed or whole prasugrel tablets.
The primary study endpoint was inhibition of platelet aggregation at 30 minutes as measured by light transmittance aggregometry in response to 20 mcmol/L of adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
Tirofiban was the unequivocal winner with 95% inhibition, as compared with 34.1% with cangrelor, 10.5% with chewed prasugrel, and 6.3% with prasugrel swallowed whole, even though the concentration of prasugrel’s active metabolite was far greater at 62.3 ng/mL after prasugrel was chewed, compared with 17.1 ng/mL when swallowed in integral tablet form.
The rate of nonresponsiveness to tirofiban as defined by greater than 59% platelet aggregation was zero for tirofiban during its 2-hour infusion, then a scant 8% thereafter during repeated testing at 3 and 4-6 hours. In contrast, the cangrelor nonresponsiveness rate was 50%-58% during the 2-hour infusion, rising to 82% at 3 hours.
FABOLUS FASTER, while not powered for clinical endpoints, might nevertheless have important clinical implications, according to Dr. Valgimigli. First, the superiority of the intravenous drugs tirofiban and cangrelor over prasugrel for early, strong platelet inhibition underscores the importance of giving parenteral antiplatelet drugs over oral therapy during the acute phase of STEMI therapy. Moreover, tirofiban’s outstanding performance – and the high residual platelet reactivity associated with cangrelor – makes a strong case for large comparative, randomized trials of the two drugs, with hard clinical endpoints.
Discussant Christoph K. Naber, MD, PhD, opined that he personally doesn’t consider the FABOLUS FASTER results practice changing, for a couple of reasons.
“Platelet inhibition measured by ADP in vitro is not necessarily related to true effects in vivo. We know that platelets are activated by multiple mechanisms, and the ADP pathway is just one of them,” said Dr. Naber, an interventional cardiologist at the Wilhemshaven (Germany) Clinic.
Also, there’s a good reason why no glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitors are approved for treatment of STEMI, and why tirofiban, despite its impressive antiplatelet effects, is currently largely reserved for bailout situations, such as complex lesions with large thrombus burden. It’s because tirofiban’s potent antiplatelet activity is accompanied by a high risk of bleeding, he added.
However, Dr. Valgimigli noted that this conviction about excessive bleeding risk is mainly based on older studies in which glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitors were administered for prolonged duration through femoral access sites. He argued that it’s time for large clinical trials examining the risk/benefit ratio of short infusion of these agents in the contemporary practice of primary PCI for STEMI.
Simultaneously with Dr. Valgimigli’s presentation, the FABOLUS FASTER results were published online (Circulation. 2020 Jun 27; doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046928).
Dr. Valgimigli reported that Medicure, the sponsor of the FABOLUS FASTER trial, provided an institutional research grant to conduct the study. He also disclosed receiving research grants and personal fees outside the scope of this study from a dozen pharmaceutical and medical device companies. Dr. Naber reported having no financial conflicts.
And cangrelor, in turn, is superior to oral prasugrel, according to the randomized FABOLUS FASTER trial, Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
Moreover, contrary to conventional wisdom, chewed prasugrel (Effient) proved no better than swallowing the tablets whole for platelet inhibition, said Dr. Valgimigli, an interventional cardiologist at the University of Bern (Switzerland).
He explained that standard administration of the newer oral P2Y12 inhibitors prasugrel and ticagrelor (Brilinta) in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ST-elevation MI (STEMI) does not provide optimal early inhibition of platelet aggregation. The parenteral antiplatelet drugs tirofiban and cangrelor have been shown to provide faster and more prolonged inhibition of platelet aggregation than the oral P2Y12 inhibitors.
But there has been no head-to-head comparative data for the glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitor tirofiban (Aggrastat) and the P2Y12 inhibitor cangrelor (Kengreal) in the setting of primary PCI for STEMI. This was the impetus for FABOLUS FASTER, the first study to compare the pharmacodynamic effects of the two parenteral antiplatelet agents. The trial also looked at how these potent parenteral drugs, compared with chewed prasugrel, another previously unexamined yet highly practical issue.
The three-center, multinational, open-label FABOLUS FASTER trial randomized 122 patients undergoing primary PCI for STEMI to one of three arms: a standard intravenous bolus and 2-hour infusion of either the P2Y12 inhibitor cangrelor (Kengreal) or the glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitor tirofiban (Aggrastat), followed in either case by 60 mg of oral prasugrel, or a third arm in which patients didn’t receive either drug but were instead randomized to a 60-mg loading dose of chewed or whole prasugrel tablets.
The primary study endpoint was inhibition of platelet aggregation at 30 minutes as measured by light transmittance aggregometry in response to 20 mcmol/L of adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
Tirofiban was the unequivocal winner with 95% inhibition, as compared with 34.1% with cangrelor, 10.5% with chewed prasugrel, and 6.3% with prasugrel swallowed whole, even though the concentration of prasugrel’s active metabolite was far greater at 62.3 ng/mL after prasugrel was chewed, compared with 17.1 ng/mL when swallowed in integral tablet form.
The rate of nonresponsiveness to tirofiban as defined by greater than 59% platelet aggregation was zero for tirofiban during its 2-hour infusion, then a scant 8% thereafter during repeated testing at 3 and 4-6 hours. In contrast, the cangrelor nonresponsiveness rate was 50%-58% during the 2-hour infusion, rising to 82% at 3 hours.
FABOLUS FASTER, while not powered for clinical endpoints, might nevertheless have important clinical implications, according to Dr. Valgimigli. First, the superiority of the intravenous drugs tirofiban and cangrelor over prasugrel for early, strong platelet inhibition underscores the importance of giving parenteral antiplatelet drugs over oral therapy during the acute phase of STEMI therapy. Moreover, tirofiban’s outstanding performance – and the high residual platelet reactivity associated with cangrelor – makes a strong case for large comparative, randomized trials of the two drugs, with hard clinical endpoints.
Discussant Christoph K. Naber, MD, PhD, opined that he personally doesn’t consider the FABOLUS FASTER results practice changing, for a couple of reasons.
“Platelet inhibition measured by ADP in vitro is not necessarily related to true effects in vivo. We know that platelets are activated by multiple mechanisms, and the ADP pathway is just one of them,” said Dr. Naber, an interventional cardiologist at the Wilhemshaven (Germany) Clinic.
Also, there’s a good reason why no glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitors are approved for treatment of STEMI, and why tirofiban, despite its impressive antiplatelet effects, is currently largely reserved for bailout situations, such as complex lesions with large thrombus burden. It’s because tirofiban’s potent antiplatelet activity is accompanied by a high risk of bleeding, he added.
However, Dr. Valgimigli noted that this conviction about excessive bleeding risk is mainly based on older studies in which glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitors were administered for prolonged duration through femoral access sites. He argued that it’s time for large clinical trials examining the risk/benefit ratio of short infusion of these agents in the contemporary practice of primary PCI for STEMI.
Simultaneously with Dr. Valgimigli’s presentation, the FABOLUS FASTER results were published online (Circulation. 2020 Jun 27; doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046928).
Dr. Valgimigli reported that Medicure, the sponsor of the FABOLUS FASTER trial, provided an institutional research grant to conduct the study. He also disclosed receiving research grants and personal fees outside the scope of this study from a dozen pharmaceutical and medical device companies. Dr. Naber reported having no financial conflicts.
And cangrelor, in turn, is superior to oral prasugrel, according to the randomized FABOLUS FASTER trial, Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
Moreover, contrary to conventional wisdom, chewed prasugrel (Effient) proved no better than swallowing the tablets whole for platelet inhibition, said Dr. Valgimigli, an interventional cardiologist at the University of Bern (Switzerland).
He explained that standard administration of the newer oral P2Y12 inhibitors prasugrel and ticagrelor (Brilinta) in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for ST-elevation MI (STEMI) does not provide optimal early inhibition of platelet aggregation. The parenteral antiplatelet drugs tirofiban and cangrelor have been shown to provide faster and more prolonged inhibition of platelet aggregation than the oral P2Y12 inhibitors.
But there has been no head-to-head comparative data for the glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitor tirofiban (Aggrastat) and the P2Y12 inhibitor cangrelor (Kengreal) in the setting of primary PCI for STEMI. This was the impetus for FABOLUS FASTER, the first study to compare the pharmacodynamic effects of the two parenteral antiplatelet agents. The trial also looked at how these potent parenteral drugs, compared with chewed prasugrel, another previously unexamined yet highly practical issue.
The three-center, multinational, open-label FABOLUS FASTER trial randomized 122 patients undergoing primary PCI for STEMI to one of three arms: a standard intravenous bolus and 2-hour infusion of either the P2Y12 inhibitor cangrelor (Kengreal) or the glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitor tirofiban (Aggrastat), followed in either case by 60 mg of oral prasugrel, or a third arm in which patients didn’t receive either drug but were instead randomized to a 60-mg loading dose of chewed or whole prasugrel tablets.
The primary study endpoint was inhibition of platelet aggregation at 30 minutes as measured by light transmittance aggregometry in response to 20 mcmol/L of adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
Tirofiban was the unequivocal winner with 95% inhibition, as compared with 34.1% with cangrelor, 10.5% with chewed prasugrel, and 6.3% with prasugrel swallowed whole, even though the concentration of prasugrel’s active metabolite was far greater at 62.3 ng/mL after prasugrel was chewed, compared with 17.1 ng/mL when swallowed in integral tablet form.
The rate of nonresponsiveness to tirofiban as defined by greater than 59% platelet aggregation was zero for tirofiban during its 2-hour infusion, then a scant 8% thereafter during repeated testing at 3 and 4-6 hours. In contrast, the cangrelor nonresponsiveness rate was 50%-58% during the 2-hour infusion, rising to 82% at 3 hours.
FABOLUS FASTER, while not powered for clinical endpoints, might nevertheless have important clinical implications, according to Dr. Valgimigli. First, the superiority of the intravenous drugs tirofiban and cangrelor over prasugrel for early, strong platelet inhibition underscores the importance of giving parenteral antiplatelet drugs over oral therapy during the acute phase of STEMI therapy. Moreover, tirofiban’s outstanding performance – and the high residual platelet reactivity associated with cangrelor – makes a strong case for large comparative, randomized trials of the two drugs, with hard clinical endpoints.
Discussant Christoph K. Naber, MD, PhD, opined that he personally doesn’t consider the FABOLUS FASTER results practice changing, for a couple of reasons.
“Platelet inhibition measured by ADP in vitro is not necessarily related to true effects in vivo. We know that platelets are activated by multiple mechanisms, and the ADP pathway is just one of them,” said Dr. Naber, an interventional cardiologist at the Wilhemshaven (Germany) Clinic.
Also, there’s a good reason why no glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitors are approved for treatment of STEMI, and why tirofiban, despite its impressive antiplatelet effects, is currently largely reserved for bailout situations, such as complex lesions with large thrombus burden. It’s because tirofiban’s potent antiplatelet activity is accompanied by a high risk of bleeding, he added.
However, Dr. Valgimigli noted that this conviction about excessive bleeding risk is mainly based on older studies in which glycoprotein IIb/IIIA inhibitors were administered for prolonged duration through femoral access sites. He argued that it’s time for large clinical trials examining the risk/benefit ratio of short infusion of these agents in the contemporary practice of primary PCI for STEMI.
Simultaneously with Dr. Valgimigli’s presentation, the FABOLUS FASTER results were published online (Circulation. 2020 Jun 27; doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046928).
Dr. Valgimigli reported that Medicure, the sponsor of the FABOLUS FASTER trial, provided an institutional research grant to conduct the study. He also disclosed receiving research grants and personal fees outside the scope of this study from a dozen pharmaceutical and medical device companies. Dr. Naber reported having no financial conflicts.
REPORTING FROM EUROPCR 2020
Once again, no survival benefit with PCI, surgery in stable CAD
Coronary revascularization does not confer a survival advantage over initial medical therapy in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) but reduces unstable angina, according to a new study-level meta-analysis.
Routine upfront revascularization is also associated with less spontaneous myocardial infarction but this is at the cost of increased procedural infarctions, reported lead investigator Sripal Bangalore, MD, of New York University.
“These relationships should be taken into consideration for shared decision-making for the management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease,” he said in a late-breaking trial session at PCR e-Course 2020, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EuroPCR).
The results, simultaneously published in Circulation, are consistent with last year’s ISCHEMIA trial and other contemporary trials, such as COURAGE, FAME 2, and BARI 2D, that have failed to show a reduction in mortality with revascularization alone in SIHD. Guidelines continue, however, to recommend revascularization to improve survival in SIHD based on trials performed in the 1980s when medical therapy was limited, Dr. Bangalore observed.
The updated meta-analysis included 14 randomized controlled trials, including the aforementioned, and 14,877 patients followed for a weighted mean of 4.5 years. Most trials enrolled patients who had preserved left ventricular function and low symptom burden (Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class I/II).
In the revascularization group, 87.5% of patients underwent any revascularization. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was the first procedure in 71.3% and bypass surgery the first choice in 16.2%. In eight trials, stents were used in at least 50% of PCI patients; drug-eluting stents were mainly used in FAME 2, ISCHEMIA, and ISCHEMIA-CKD.
In eight trials, statins were used in at least 50% of patients. Nearly 1 in 3 patients (31.9%) treated initially with medical therapy underwent revascularization during follow-up.
Results show no reduction in mortality risk with routine revascularization in the overall analysis (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.09) or when analyzed by whether studies did or did not use stents (P for interaction = .85).
Trial sequential analysis also showed that the cumulative z-curve crossed the futility boundary, “suggesting we have great data to show that there is lack of even a 10% reduction in death with revascularization,” Dr. Bangalore said.
Results were very similar for cardiovascular death (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.80-1.06), including when analyzed by study stent status (P for interaction = .60).
There was no significant reduction in overall MI risk with revascularization, although a borderline significant 11% decrease in MIs was found in the contemporary stent era trials (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.998).
Revascularization was associated with a 148% increase in the risk of procedural MI (RR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.86-3.31) but reduced risk of spontaneous MI (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.67-0.85).
Unstable angina was reduced in patients undergoing revascularization (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.45-0.92), driven by a 55% reduction in the contemporary stent era trials. Freedom from angina was also greater with routine revascularization but the difference was modest, Dr. Bangalore said. There was no difference between the two strategies in heart failure or stroke.
“This meta-analysis is well done but really doesn’t change what we already know,” Rasha Al-Lamee, MBBS, of Imperial College, London, said in an interview. “The most important message is that intervention in stable CAD does not change survival. We don’t need to rush to intervene: We have time to plan the best strategy for each patient and to modify our plans based on their response.”
The analysis addresses some of the issues with previous meta-analyses that have included trials that were not strictly stable CAD trials such as SWISSI-2, COMPARE-ACUTE, and DANAMI-3-PRIMULTI, she noted. “However a study like this is only as good as the trials that are included. We must remember that unblinded trials really cannot be used to accurately assess endpoints that are prone to bias such as unstable angina and freedom from angina.”
Following the presentation, dedicated discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, of the University of Catania (Italy) said, “We have seen beyond any doubt that there is no difference in mortality. For cardiovascular death, it’s pretty much the same. It’s a little bit more mixed and nuanced, the story of myocardial infarction.”
“Additional science is needed to understand the prognostic implications,” he said. “Of course we know that spontaneous myocardial infarction is bad, but I’m not so sure about periprocedural MI. Is this something that is as important as spontaneous myocardial infarction?”
The meta-analysis is the largest ever performed, but there was clinical heterogeneity in the individual studies, especially in the definition of MI, Dr. Capodanno observed. Because of the use of trial-level data rather than patient-level data, the analysis also could not account for adherence to treatment or the effect of stent type or medication dosage.
The MI issue really depends on the trial definition of MI, Dr. Al-Lamee said. “We need long-term follow-up from ISCHEMIA to understand what it means for our patients. While revascularization clearly increases procedural MI rates, it also results in lower spontaneous MI rates with no impact on overall MI or death,” she said. “We will only know if these MIs are important if we see what impact they have in the long term.”
Although the meta-analysis combined data from several decades, it’s likely that the outdated revascularization techniques in the older trials are balanced out by the outdated medical therapy in the same trials, Dr. Al-Lamee observed.
The new findings can certainly be used in patient-physician discussions, with more follow-up from ISCHEMIA to provide additional insights, she said.
“We will of course hear more about the placebo-controlled efficacy of PCI in the blinded ORBITA-2 trial. And I would really like to see some of the older studies of patients and perceptions of the effect of PCI repeated,” Dr. Al-Lamee said. “Now we have more data, are we informing our patients and referrers correctly of the impact of our procedures, and do they truly choose revascularization with a true awareness of what it does and does not do?”
Dr. Bangalore reported grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Abbott Vascular; and serving on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Meril, SMT, Pfizer, Amgen, and Reata. Dr. Al-Lamee reported speaker’s honorarium from Philips Volcano and Menarini Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Capodanno has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary revascularization does not confer a survival advantage over initial medical therapy in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) but reduces unstable angina, according to a new study-level meta-analysis.
Routine upfront revascularization is also associated with less spontaneous myocardial infarction but this is at the cost of increased procedural infarctions, reported lead investigator Sripal Bangalore, MD, of New York University.
“These relationships should be taken into consideration for shared decision-making for the management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease,” he said in a late-breaking trial session at PCR e-Course 2020, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EuroPCR).
The results, simultaneously published in Circulation, are consistent with last year’s ISCHEMIA trial and other contemporary trials, such as COURAGE, FAME 2, and BARI 2D, that have failed to show a reduction in mortality with revascularization alone in SIHD. Guidelines continue, however, to recommend revascularization to improve survival in SIHD based on trials performed in the 1980s when medical therapy was limited, Dr. Bangalore observed.
The updated meta-analysis included 14 randomized controlled trials, including the aforementioned, and 14,877 patients followed for a weighted mean of 4.5 years. Most trials enrolled patients who had preserved left ventricular function and low symptom burden (Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class I/II).
In the revascularization group, 87.5% of patients underwent any revascularization. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was the first procedure in 71.3% and bypass surgery the first choice in 16.2%. In eight trials, stents were used in at least 50% of PCI patients; drug-eluting stents were mainly used in FAME 2, ISCHEMIA, and ISCHEMIA-CKD.
In eight trials, statins were used in at least 50% of patients. Nearly 1 in 3 patients (31.9%) treated initially with medical therapy underwent revascularization during follow-up.
Results show no reduction in mortality risk with routine revascularization in the overall analysis (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.09) or when analyzed by whether studies did or did not use stents (P for interaction = .85).
Trial sequential analysis also showed that the cumulative z-curve crossed the futility boundary, “suggesting we have great data to show that there is lack of even a 10% reduction in death with revascularization,” Dr. Bangalore said.
Results were very similar for cardiovascular death (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.80-1.06), including when analyzed by study stent status (P for interaction = .60).
There was no significant reduction in overall MI risk with revascularization, although a borderline significant 11% decrease in MIs was found in the contemporary stent era trials (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.998).
Revascularization was associated with a 148% increase in the risk of procedural MI (RR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.86-3.31) but reduced risk of spontaneous MI (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.67-0.85).
Unstable angina was reduced in patients undergoing revascularization (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.45-0.92), driven by a 55% reduction in the contemporary stent era trials. Freedom from angina was also greater with routine revascularization but the difference was modest, Dr. Bangalore said. There was no difference between the two strategies in heart failure or stroke.
“This meta-analysis is well done but really doesn’t change what we already know,” Rasha Al-Lamee, MBBS, of Imperial College, London, said in an interview. “The most important message is that intervention in stable CAD does not change survival. We don’t need to rush to intervene: We have time to plan the best strategy for each patient and to modify our plans based on their response.”
The analysis addresses some of the issues with previous meta-analyses that have included trials that were not strictly stable CAD trials such as SWISSI-2, COMPARE-ACUTE, and DANAMI-3-PRIMULTI, she noted. “However a study like this is only as good as the trials that are included. We must remember that unblinded trials really cannot be used to accurately assess endpoints that are prone to bias such as unstable angina and freedom from angina.”
Following the presentation, dedicated discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, of the University of Catania (Italy) said, “We have seen beyond any doubt that there is no difference in mortality. For cardiovascular death, it’s pretty much the same. It’s a little bit more mixed and nuanced, the story of myocardial infarction.”
“Additional science is needed to understand the prognostic implications,” he said. “Of course we know that spontaneous myocardial infarction is bad, but I’m not so sure about periprocedural MI. Is this something that is as important as spontaneous myocardial infarction?”
The meta-analysis is the largest ever performed, but there was clinical heterogeneity in the individual studies, especially in the definition of MI, Dr. Capodanno observed. Because of the use of trial-level data rather than patient-level data, the analysis also could not account for adherence to treatment or the effect of stent type or medication dosage.
The MI issue really depends on the trial definition of MI, Dr. Al-Lamee said. “We need long-term follow-up from ISCHEMIA to understand what it means for our patients. While revascularization clearly increases procedural MI rates, it also results in lower spontaneous MI rates with no impact on overall MI or death,” she said. “We will only know if these MIs are important if we see what impact they have in the long term.”
Although the meta-analysis combined data from several decades, it’s likely that the outdated revascularization techniques in the older trials are balanced out by the outdated medical therapy in the same trials, Dr. Al-Lamee observed.
The new findings can certainly be used in patient-physician discussions, with more follow-up from ISCHEMIA to provide additional insights, she said.
“We will of course hear more about the placebo-controlled efficacy of PCI in the blinded ORBITA-2 trial. And I would really like to see some of the older studies of patients and perceptions of the effect of PCI repeated,” Dr. Al-Lamee said. “Now we have more data, are we informing our patients and referrers correctly of the impact of our procedures, and do they truly choose revascularization with a true awareness of what it does and does not do?”
Dr. Bangalore reported grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Abbott Vascular; and serving on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Meril, SMT, Pfizer, Amgen, and Reata. Dr. Al-Lamee reported speaker’s honorarium from Philips Volcano and Menarini Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Capodanno has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary revascularization does not confer a survival advantage over initial medical therapy in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) but reduces unstable angina, according to a new study-level meta-analysis.
Routine upfront revascularization is also associated with less spontaneous myocardial infarction but this is at the cost of increased procedural infarctions, reported lead investigator Sripal Bangalore, MD, of New York University.
“These relationships should be taken into consideration for shared decision-making for the management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease,” he said in a late-breaking trial session at PCR e-Course 2020, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EuroPCR).
The results, simultaneously published in Circulation, are consistent with last year’s ISCHEMIA trial and other contemporary trials, such as COURAGE, FAME 2, and BARI 2D, that have failed to show a reduction in mortality with revascularization alone in SIHD. Guidelines continue, however, to recommend revascularization to improve survival in SIHD based on trials performed in the 1980s when medical therapy was limited, Dr. Bangalore observed.
The updated meta-analysis included 14 randomized controlled trials, including the aforementioned, and 14,877 patients followed for a weighted mean of 4.5 years. Most trials enrolled patients who had preserved left ventricular function and low symptom burden (Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class I/II).
In the revascularization group, 87.5% of patients underwent any revascularization. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was the first procedure in 71.3% and bypass surgery the first choice in 16.2%. In eight trials, stents were used in at least 50% of PCI patients; drug-eluting stents were mainly used in FAME 2, ISCHEMIA, and ISCHEMIA-CKD.
In eight trials, statins were used in at least 50% of patients. Nearly 1 in 3 patients (31.9%) treated initially with medical therapy underwent revascularization during follow-up.
Results show no reduction in mortality risk with routine revascularization in the overall analysis (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.09) or when analyzed by whether studies did or did not use stents (P for interaction = .85).
Trial sequential analysis also showed that the cumulative z-curve crossed the futility boundary, “suggesting we have great data to show that there is lack of even a 10% reduction in death with revascularization,” Dr. Bangalore said.
Results were very similar for cardiovascular death (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.80-1.06), including when analyzed by study stent status (P for interaction = .60).
There was no significant reduction in overall MI risk with revascularization, although a borderline significant 11% decrease in MIs was found in the contemporary stent era trials (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.998).
Revascularization was associated with a 148% increase in the risk of procedural MI (RR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.86-3.31) but reduced risk of spontaneous MI (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.67-0.85).
Unstable angina was reduced in patients undergoing revascularization (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.45-0.92), driven by a 55% reduction in the contemporary stent era trials. Freedom from angina was also greater with routine revascularization but the difference was modest, Dr. Bangalore said. There was no difference between the two strategies in heart failure or stroke.
“This meta-analysis is well done but really doesn’t change what we already know,” Rasha Al-Lamee, MBBS, of Imperial College, London, said in an interview. “The most important message is that intervention in stable CAD does not change survival. We don’t need to rush to intervene: We have time to plan the best strategy for each patient and to modify our plans based on their response.”
The analysis addresses some of the issues with previous meta-analyses that have included trials that were not strictly stable CAD trials such as SWISSI-2, COMPARE-ACUTE, and DANAMI-3-PRIMULTI, she noted. “However a study like this is only as good as the trials that are included. We must remember that unblinded trials really cannot be used to accurately assess endpoints that are prone to bias such as unstable angina and freedom from angina.”
Following the presentation, dedicated discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, of the University of Catania (Italy) said, “We have seen beyond any doubt that there is no difference in mortality. For cardiovascular death, it’s pretty much the same. It’s a little bit more mixed and nuanced, the story of myocardial infarction.”
“Additional science is needed to understand the prognostic implications,” he said. “Of course we know that spontaneous myocardial infarction is bad, but I’m not so sure about periprocedural MI. Is this something that is as important as spontaneous myocardial infarction?”
The meta-analysis is the largest ever performed, but there was clinical heterogeneity in the individual studies, especially in the definition of MI, Dr. Capodanno observed. Because of the use of trial-level data rather than patient-level data, the analysis also could not account for adherence to treatment or the effect of stent type or medication dosage.
The MI issue really depends on the trial definition of MI, Dr. Al-Lamee said. “We need long-term follow-up from ISCHEMIA to understand what it means for our patients. While revascularization clearly increases procedural MI rates, it also results in lower spontaneous MI rates with no impact on overall MI or death,” she said. “We will only know if these MIs are important if we see what impact they have in the long term.”
Although the meta-analysis combined data from several decades, it’s likely that the outdated revascularization techniques in the older trials are balanced out by the outdated medical therapy in the same trials, Dr. Al-Lamee observed.
The new findings can certainly be used in patient-physician discussions, with more follow-up from ISCHEMIA to provide additional insights, she said.
“We will of course hear more about the placebo-controlled efficacy of PCI in the blinded ORBITA-2 trial. And I would really like to see some of the older studies of patients and perceptions of the effect of PCI repeated,” Dr. Al-Lamee said. “Now we have more data, are we informing our patients and referrers correctly of the impact of our procedures, and do they truly choose revascularization with a true awareness of what it does and does not do?”
Dr. Bangalore reported grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Abbott Vascular; and serving on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Meril, SMT, Pfizer, Amgen, and Reata. Dr. Al-Lamee reported speaker’s honorarium from Philips Volcano and Menarini Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Capodanno has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Two-stent technique shown superior for complex coronary bifurcations
A systematic two-stent approach to complex coronary bifurcation lesions led to significantly improved clinical outcomes at 1 year, compared with the long-popular provisional stenting technique, in the first randomized trial to prospectively validate a standardized definition of what constitutes a complex bifurcation.
Since the double-kissing (DK) crush technique was employed in 78% of the systematic two-stent procedures, and the two-stent approach provided superior outcomes, it’s reasonable to infer that the DK crush is the preferred technique in patients with truly complex coronary bifurcation lesions (CBLs), Shao-Liang Chen, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
He presented the results of the DEFINITION II trial, a multinational trial in which 653 patients at 49 medical centers who fulfilled the criteria for complex CBLs were randomized to a systematic two-stent approach or provisional stenting, with a second stent deployed by interventionalists as needed. Dr. Chen, director of the cardiology department and deputy president of Nanjing (China) Medical University, and coworkers had previously published their standardized criteria for CBLs (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Nov;7[11]:1266-76), which they developed by analysis of a large bifurcation cohort; however, until the DEFINITION II trial, the criteria had never been used in a prospective randomized trial.
According to the standardized definition developed by Dr. Chen and associates, complex coronary bifurcation lesions must meet one major and two minor criteria.
Major criteria:
- A side branch lesion length of at least 10 mm with a diameter stenosis of 70% or more for distal left main bifurcation lesions.
- For non–left main bifurcation lesions, a side branch diameter stenosis of at least 90% along with a side branch lesion length of at least 10 mm.
Minor criteria:
- Moderate to severe calcification multiple lesions
- Bifurcation angle of <45 degrees or >70 degrees
- Thrombus-containing lesions
- Main vessel residual diameter <2.5 mm
- Main vessel lesion length of at least 25 mm
Interventionalists were strongly encouraged to utilize the DK crush or culotte stenting techniques in patients randomized to the systematic two-stent approach. In contrast, in the provisional stenting group, where 23% of patients received a second stent, that stent was placed using the T and small protrusion technique 64% of the time.
The primary endpoint was the target lesion failure rate at 1-year of follow-up. Target lesion failure was a composite comprising cardiac death, target vessel MI, and clinically driven target vessel revascularization. The rate was 6.1% in the systematic two-stent group and 11.4% with provisional stenting, for a highly significant 48% relative risk reduction. The difference was driven largely by the systematic two-stent group’s lower rates of target vessel MI – 3.0% versus 7.1% with provisional stenting – and target lesion revascularization, with rates of 2.4% and 5.5%, respectively.
“The underlying mechanisms for the increased target vessel MI rate after the provisional stenting technique are unclear, and further study is urgently warranted,” Dr. Chen said.
There were no significant between-group differences in all-cause mortality or cardiac death, although both endpoints were numerically less frequent in the two-stent group.
The primary safety outcome was the 12-month rate of definite or probable stent thrombosis. This occurred in 1.2% of the systematic two-stent group and 2.5% of the provisional stent patients, a nonsignificant difference.
Discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, declared the DEFINITE II trial to be “another success for this DK crush technique everyone is talking about recently.”
He noted that, in a recent meta-analysis of 21 randomized, controlled trials including 5,711 patients with bifurcation lesions treated using five different percutaneous coronary intervention techniques, DK crush stood out from the pack. Particularly impressive was the finding that the target lesion revascularization rate in patients treated using the DK crush technique was 64% lower than with provisional stenting (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Jun 22;13[12]:1432-44).
Dr. Capodanno said that, although the DEFINITE II results were strongly positive in favor of the systematic two-stent approach and DK crush technique, he’s not convinced of the generalizability of the study results.
“These investigators are very expert in this technique. They invented it. They’ve been using it for 10 years. So of course you may expect excellent results when you have masters of this technique,” observed Dr. Capodanno, a cardiologist at the University of Catania (Italy).
Independent replication of the DEFINITE II findings is needed. Fortunately, two ongoing randomized trials are addressing the issue of how to best treat bifurcation lesions. The EBC-MAIN trial is comparing the provisional approach with the systematic two-stent strategy in patients with left main bifurcation lesions; the study will include the DK crush as well as culotte and TAP PCI techniques, with a primary endpoint consisting of the 12-month rate of death, MI, and target lesion revascularization. And the BBK-3 trial will compare systematic two-stent strategies pitting the culotte against the DK crush, with the primary endpoint being the 9-month rate of angiographic restenosis by quantitative coronary angiography.
“After these trials are complete, we’ll probably know much more about the tailoring of bifurcation techniques for particular patients,” according to Dr. Capodanno.
Simultaneous with Dr. Chen’s presentation, the results of the DEFINITION II trial were published online (Eur Heart J. 2020 Jun 26.doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa543).
Dr. Chen and Dr. Capodanno reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding the study, which was funded mainly by the National Science Foundation of China.
A systematic two-stent approach to complex coronary bifurcation lesions led to significantly improved clinical outcomes at 1 year, compared with the long-popular provisional stenting technique, in the first randomized trial to prospectively validate a standardized definition of what constitutes a complex bifurcation.
Since the double-kissing (DK) crush technique was employed in 78% of the systematic two-stent procedures, and the two-stent approach provided superior outcomes, it’s reasonable to infer that the DK crush is the preferred technique in patients with truly complex coronary bifurcation lesions (CBLs), Shao-Liang Chen, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
He presented the results of the DEFINITION II trial, a multinational trial in which 653 patients at 49 medical centers who fulfilled the criteria for complex CBLs were randomized to a systematic two-stent approach or provisional stenting, with a second stent deployed by interventionalists as needed. Dr. Chen, director of the cardiology department and deputy president of Nanjing (China) Medical University, and coworkers had previously published their standardized criteria for CBLs (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Nov;7[11]:1266-76), which they developed by analysis of a large bifurcation cohort; however, until the DEFINITION II trial, the criteria had never been used in a prospective randomized trial.
According to the standardized definition developed by Dr. Chen and associates, complex coronary bifurcation lesions must meet one major and two minor criteria.
Major criteria:
- A side branch lesion length of at least 10 mm with a diameter stenosis of 70% or more for distal left main bifurcation lesions.
- For non–left main bifurcation lesions, a side branch diameter stenosis of at least 90% along with a side branch lesion length of at least 10 mm.
Minor criteria:
- Moderate to severe calcification multiple lesions
- Bifurcation angle of <45 degrees or >70 degrees
- Thrombus-containing lesions
- Main vessel residual diameter <2.5 mm
- Main vessel lesion length of at least 25 mm
Interventionalists were strongly encouraged to utilize the DK crush or culotte stenting techniques in patients randomized to the systematic two-stent approach. In contrast, in the provisional stenting group, where 23% of patients received a second stent, that stent was placed using the T and small protrusion technique 64% of the time.
The primary endpoint was the target lesion failure rate at 1-year of follow-up. Target lesion failure was a composite comprising cardiac death, target vessel MI, and clinically driven target vessel revascularization. The rate was 6.1% in the systematic two-stent group and 11.4% with provisional stenting, for a highly significant 48% relative risk reduction. The difference was driven largely by the systematic two-stent group’s lower rates of target vessel MI – 3.0% versus 7.1% with provisional stenting – and target lesion revascularization, with rates of 2.4% and 5.5%, respectively.
“The underlying mechanisms for the increased target vessel MI rate after the provisional stenting technique are unclear, and further study is urgently warranted,” Dr. Chen said.
There were no significant between-group differences in all-cause mortality or cardiac death, although both endpoints were numerically less frequent in the two-stent group.
The primary safety outcome was the 12-month rate of definite or probable stent thrombosis. This occurred in 1.2% of the systematic two-stent group and 2.5% of the provisional stent patients, a nonsignificant difference.
Discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, declared the DEFINITE II trial to be “another success for this DK crush technique everyone is talking about recently.”
He noted that, in a recent meta-analysis of 21 randomized, controlled trials including 5,711 patients with bifurcation lesions treated using five different percutaneous coronary intervention techniques, DK crush stood out from the pack. Particularly impressive was the finding that the target lesion revascularization rate in patients treated using the DK crush technique was 64% lower than with provisional stenting (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Jun 22;13[12]:1432-44).
Dr. Capodanno said that, although the DEFINITE II results were strongly positive in favor of the systematic two-stent approach and DK crush technique, he’s not convinced of the generalizability of the study results.
“These investigators are very expert in this technique. They invented it. They’ve been using it for 10 years. So of course you may expect excellent results when you have masters of this technique,” observed Dr. Capodanno, a cardiologist at the University of Catania (Italy).
Independent replication of the DEFINITE II findings is needed. Fortunately, two ongoing randomized trials are addressing the issue of how to best treat bifurcation lesions. The EBC-MAIN trial is comparing the provisional approach with the systematic two-stent strategy in patients with left main bifurcation lesions; the study will include the DK crush as well as culotte and TAP PCI techniques, with a primary endpoint consisting of the 12-month rate of death, MI, and target lesion revascularization. And the BBK-3 trial will compare systematic two-stent strategies pitting the culotte against the DK crush, with the primary endpoint being the 9-month rate of angiographic restenosis by quantitative coronary angiography.
“After these trials are complete, we’ll probably know much more about the tailoring of bifurcation techniques for particular patients,” according to Dr. Capodanno.
Simultaneous with Dr. Chen’s presentation, the results of the DEFINITION II trial were published online (Eur Heart J. 2020 Jun 26.doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa543).
Dr. Chen and Dr. Capodanno reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding the study, which was funded mainly by the National Science Foundation of China.
A systematic two-stent approach to complex coronary bifurcation lesions led to significantly improved clinical outcomes at 1 year, compared with the long-popular provisional stenting technique, in the first randomized trial to prospectively validate a standardized definition of what constitutes a complex bifurcation.
Since the double-kissing (DK) crush technique was employed in 78% of the systematic two-stent procedures, and the two-stent approach provided superior outcomes, it’s reasonable to infer that the DK crush is the preferred technique in patients with truly complex coronary bifurcation lesions (CBLs), Shao-Liang Chen, MD, reported at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions.
He presented the results of the DEFINITION II trial, a multinational trial in which 653 patients at 49 medical centers who fulfilled the criteria for complex CBLs were randomized to a systematic two-stent approach or provisional stenting, with a second stent deployed by interventionalists as needed. Dr. Chen, director of the cardiology department and deputy president of Nanjing (China) Medical University, and coworkers had previously published their standardized criteria for CBLs (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Nov;7[11]:1266-76), which they developed by analysis of a large bifurcation cohort; however, until the DEFINITION II trial, the criteria had never been used in a prospective randomized trial.
According to the standardized definition developed by Dr. Chen and associates, complex coronary bifurcation lesions must meet one major and two minor criteria.
Major criteria:
- A side branch lesion length of at least 10 mm with a diameter stenosis of 70% or more for distal left main bifurcation lesions.
- For non–left main bifurcation lesions, a side branch diameter stenosis of at least 90% along with a side branch lesion length of at least 10 mm.
Minor criteria:
- Moderate to severe calcification multiple lesions
- Bifurcation angle of <45 degrees or >70 degrees
- Thrombus-containing lesions
- Main vessel residual diameter <2.5 mm
- Main vessel lesion length of at least 25 mm
Interventionalists were strongly encouraged to utilize the DK crush or culotte stenting techniques in patients randomized to the systematic two-stent approach. In contrast, in the provisional stenting group, where 23% of patients received a second stent, that stent was placed using the T and small protrusion technique 64% of the time.
The primary endpoint was the target lesion failure rate at 1-year of follow-up. Target lesion failure was a composite comprising cardiac death, target vessel MI, and clinically driven target vessel revascularization. The rate was 6.1% in the systematic two-stent group and 11.4% with provisional stenting, for a highly significant 48% relative risk reduction. The difference was driven largely by the systematic two-stent group’s lower rates of target vessel MI – 3.0% versus 7.1% with provisional stenting – and target lesion revascularization, with rates of 2.4% and 5.5%, respectively.
“The underlying mechanisms for the increased target vessel MI rate after the provisional stenting technique are unclear, and further study is urgently warranted,” Dr. Chen said.
There were no significant between-group differences in all-cause mortality or cardiac death, although both endpoints were numerically less frequent in the two-stent group.
The primary safety outcome was the 12-month rate of definite or probable stent thrombosis. This occurred in 1.2% of the systematic two-stent group and 2.5% of the provisional stent patients, a nonsignificant difference.
Discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, declared the DEFINITE II trial to be “another success for this DK crush technique everyone is talking about recently.”
He noted that, in a recent meta-analysis of 21 randomized, controlled trials including 5,711 patients with bifurcation lesions treated using five different percutaneous coronary intervention techniques, DK crush stood out from the pack. Particularly impressive was the finding that the target lesion revascularization rate in patients treated using the DK crush technique was 64% lower than with provisional stenting (JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Jun 22;13[12]:1432-44).
Dr. Capodanno said that, although the DEFINITE II results were strongly positive in favor of the systematic two-stent approach and DK crush technique, he’s not convinced of the generalizability of the study results.
“These investigators are very expert in this technique. They invented it. They’ve been using it for 10 years. So of course you may expect excellent results when you have masters of this technique,” observed Dr. Capodanno, a cardiologist at the University of Catania (Italy).
Independent replication of the DEFINITE II findings is needed. Fortunately, two ongoing randomized trials are addressing the issue of how to best treat bifurcation lesions. The EBC-MAIN trial is comparing the provisional approach with the systematic two-stent strategy in patients with left main bifurcation lesions; the study will include the DK crush as well as culotte and TAP PCI techniques, with a primary endpoint consisting of the 12-month rate of death, MI, and target lesion revascularization. And the BBK-3 trial will compare systematic two-stent strategies pitting the culotte against the DK crush, with the primary endpoint being the 9-month rate of angiographic restenosis by quantitative coronary angiography.
“After these trials are complete, we’ll probably know much more about the tailoring of bifurcation techniques for particular patients,” according to Dr. Capodanno.
Simultaneous with Dr. Chen’s presentation, the results of the DEFINITION II trial were published online (Eur Heart J. 2020 Jun 26.doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa543).
Dr. Chen and Dr. Capodanno reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding the study, which was funded mainly by the National Science Foundation of China.
FROM EUROPCR 2020
Renal denervation response similar regardless of CV risks, comorbidities
In a new analysis of international registry data, renal denervation resulted in similar reduced blood pressure levels in patients with varying high-risk comorbidities and across a range of cardiovascular risk scores.
At 3 years, 24-hour systolic BP was reduced by an average of –8.9 mm Hg overall, with slightly higher or lower readings seen in those with higher cardiovascular risk scores (–10.4 mm Hg) and 65 years or older (–10.2 mm Hg). Similar reductions were seen in those with resistant hypertension (–8.7 mm Hg), diabetes (–8.6 mm Hg), isolated systolic hypertension (–10.1 mm Hg), chronic kidney disease (–10.1 mm Hg), or atrial fibrillation (–10.0 mm Hg).
“In the largest international registry of its kind, the efficacy of renal denervation was similar in patients with and without baseline conditions associated with increased sympathetic activity and irrespective of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease] risk,” first author Felix Mahfoud, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Mahfoud, from University Hospital of Saarland, Homburg, Germany, and colleagues published their analysis in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The article reported a post hoc analysis of data from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry (GSR), an international, Medtronic-funded effort that includes 2,652 patients with uncontrolled hypertension treated with a Symplicity denervation system. Data were obtained from 196 centers in 45 countries.
“Blood pressure reductions were durable and sustained to 3 years and the rates of new-onset, end-stage renal disease and elevation in serum creatinine levels were very low in patients at high and low [cardiovascular] risk,” reported Dr. Mahfoud.
As expected, adverse event rates were higher for patients with higher baseline cardiovascular risk. “Elevated rates were also seen in patients with [atrial fibrillation] and diabetes, identifying these subgroups who might derive even greater clinical benefit from improved BP control using renal denervation,” said Dr. Mahfoud.
Asked which patients might be optimal candidates for renal denervation, Dr. Mahfoud recommended the technology for “patients with uncontrolled hypertension on medication, patients with nonadherence, unwillingness, or intolerability to medication, and patients with combined systolic and diastolic hypertension.”
Analyses limited by incomplete data
Stephen C. Textor, MD, has concerns over the amount of missing data in the GSR database and its continued use as a repository of information on renal denervation.
“I am a bit lukewarm on this paper in part because of the nature of the registry data they’re using,” he added in an interview. “The problem I see is that the registry is not terribly uniform as to what information they collect on each patient, not terribly uniform in terms of how the procedure is performed, and not terribly uniform on how they follow up patients.”
Indeed, the post hoc subgroup analyses represent only a limited subset because of incomplete data, added Dr. Textor, a nephrologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“Remarkably, only 504 [patients] had “matched” data for office [systolic BP] levels at the time points defined in the report,” he wrote in an editorial comment accompanying the registry report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Jun 16;75[23]:2889-91).
Similarly, the researchers were able to calculate baseline atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk scores in only 1,485 patients (56% of total), primarily because of missing cholesterol measurements.
“They simply did these paired comparison that may have included a couple hundred cases, and on average, there were no differences in response, but what I would have liked to see is a multivariate analysis, where you have all the data on everybody and look at what are the factors that impact response?” Dr. Textor said in the interview.
“They really couldn’t do that because they just, they’re just too many holes in the data,” he added.
On the bright side, Dr. Textor noted that, while the impact overall on systolic BP was “modest,” the standard deviations in some cases were large, indicating that some people had large reductions of systolic BP of more than 30-40 mm Hg.
“There is a belief out there that there are some people that really benefit from this, but how to identify them has been the question,” Dr. Textor said.
Enthusiasm for renal denervation plummeted after results from the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 showed the procedure failing to meet its efficacy endpoint in resistant hypertension. The procedure was associated with a 14–mm Hg fall in systolic BP, compared with an 11–mm Hg drop in the “sham” control group (N Engl J Med. 2014 Apr 10;370:1393-401). However, post hoc analysis of the trial revealed significant shortcomings in design and execution.
No renal denervation device is approved in the United States. The Symplicity device used in this registry is approved in the European Union.
In early 2020, the Food and Drug Administration promised a rigorous review of new renal denervation trials. Subsequently, primary results from the SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED pivotal trial were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology in March and showed promising efficacy.
SPYRAL HTN OFF-MED was designed in collaboration with the FDA to obtain meaningful evidence of whether renal denervation performed with the Symplicity Spyral multielectrode catheter (Medtronic Vascular) could reduce BP in patients not taking antihypertensive medication.
Dr. Mahfoud reported he has received speaking honoraria from Medtronic and ReCor. Two other authors are employees of Medtronic. Dr. Textor reported no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper. The Global SYMPLICITY Registry is funded by Medtronic Vascular.
SOURCE: Mahfoud F et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 June 16;75:2879-88.
This article was updated 6/16/20.
In a new analysis of international registry data, renal denervation resulted in similar reduced blood pressure levels in patients with varying high-risk comorbidities and across a range of cardiovascular risk scores.
At 3 years, 24-hour systolic BP was reduced by an average of –8.9 mm Hg overall, with slightly higher or lower readings seen in those with higher cardiovascular risk scores (–10.4 mm Hg) and 65 years or older (–10.2 mm Hg). Similar reductions were seen in those with resistant hypertension (–8.7 mm Hg), diabetes (–8.6 mm Hg), isolated systolic hypertension (–10.1 mm Hg), chronic kidney disease (–10.1 mm Hg), or atrial fibrillation (–10.0 mm Hg).
“In the largest international registry of its kind, the efficacy of renal denervation was similar in patients with and without baseline conditions associated with increased sympathetic activity and irrespective of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease] risk,” first author Felix Mahfoud, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Mahfoud, from University Hospital of Saarland, Homburg, Germany, and colleagues published their analysis in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The article reported a post hoc analysis of data from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry (GSR), an international, Medtronic-funded effort that includes 2,652 patients with uncontrolled hypertension treated with a Symplicity denervation system. Data were obtained from 196 centers in 45 countries.
“Blood pressure reductions were durable and sustained to 3 years and the rates of new-onset, end-stage renal disease and elevation in serum creatinine levels were very low in patients at high and low [cardiovascular] risk,” reported Dr. Mahfoud.
As expected, adverse event rates were higher for patients with higher baseline cardiovascular risk. “Elevated rates were also seen in patients with [atrial fibrillation] and diabetes, identifying these subgroups who might derive even greater clinical benefit from improved BP control using renal denervation,” said Dr. Mahfoud.
Asked which patients might be optimal candidates for renal denervation, Dr. Mahfoud recommended the technology for “patients with uncontrolled hypertension on medication, patients with nonadherence, unwillingness, or intolerability to medication, and patients with combined systolic and diastolic hypertension.”
Analyses limited by incomplete data
Stephen C. Textor, MD, has concerns over the amount of missing data in the GSR database and its continued use as a repository of information on renal denervation.
“I am a bit lukewarm on this paper in part because of the nature of the registry data they’re using,” he added in an interview. “The problem I see is that the registry is not terribly uniform as to what information they collect on each patient, not terribly uniform in terms of how the procedure is performed, and not terribly uniform on how they follow up patients.”
Indeed, the post hoc subgroup analyses represent only a limited subset because of incomplete data, added Dr. Textor, a nephrologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“Remarkably, only 504 [patients] had “matched” data for office [systolic BP] levels at the time points defined in the report,” he wrote in an editorial comment accompanying the registry report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Jun 16;75[23]:2889-91).
Similarly, the researchers were able to calculate baseline atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk scores in only 1,485 patients (56% of total), primarily because of missing cholesterol measurements.
“They simply did these paired comparison that may have included a couple hundred cases, and on average, there were no differences in response, but what I would have liked to see is a multivariate analysis, where you have all the data on everybody and look at what are the factors that impact response?” Dr. Textor said in the interview.
“They really couldn’t do that because they just, they’re just too many holes in the data,” he added.
On the bright side, Dr. Textor noted that, while the impact overall on systolic BP was “modest,” the standard deviations in some cases were large, indicating that some people had large reductions of systolic BP of more than 30-40 mm Hg.
“There is a belief out there that there are some people that really benefit from this, but how to identify them has been the question,” Dr. Textor said.
Enthusiasm for renal denervation plummeted after results from the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 showed the procedure failing to meet its efficacy endpoint in resistant hypertension. The procedure was associated with a 14–mm Hg fall in systolic BP, compared with an 11–mm Hg drop in the “sham” control group (N Engl J Med. 2014 Apr 10;370:1393-401). However, post hoc analysis of the trial revealed significant shortcomings in design and execution.
No renal denervation device is approved in the United States. The Symplicity device used in this registry is approved in the European Union.
In early 2020, the Food and Drug Administration promised a rigorous review of new renal denervation trials. Subsequently, primary results from the SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED pivotal trial were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology in March and showed promising efficacy.
SPYRAL HTN OFF-MED was designed in collaboration with the FDA to obtain meaningful evidence of whether renal denervation performed with the Symplicity Spyral multielectrode catheter (Medtronic Vascular) could reduce BP in patients not taking antihypertensive medication.
Dr. Mahfoud reported he has received speaking honoraria from Medtronic and ReCor. Two other authors are employees of Medtronic. Dr. Textor reported no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper. The Global SYMPLICITY Registry is funded by Medtronic Vascular.
SOURCE: Mahfoud F et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 June 16;75:2879-88.
This article was updated 6/16/20.
In a new analysis of international registry data, renal denervation resulted in similar reduced blood pressure levels in patients with varying high-risk comorbidities and across a range of cardiovascular risk scores.
At 3 years, 24-hour systolic BP was reduced by an average of –8.9 mm Hg overall, with slightly higher or lower readings seen in those with higher cardiovascular risk scores (–10.4 mm Hg) and 65 years or older (–10.2 mm Hg). Similar reductions were seen in those with resistant hypertension (–8.7 mm Hg), diabetes (–8.6 mm Hg), isolated systolic hypertension (–10.1 mm Hg), chronic kidney disease (–10.1 mm Hg), or atrial fibrillation (–10.0 mm Hg).
“In the largest international registry of its kind, the efficacy of renal denervation was similar in patients with and without baseline conditions associated with increased sympathetic activity and irrespective of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease] risk,” first author Felix Mahfoud, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Mahfoud, from University Hospital of Saarland, Homburg, Germany, and colleagues published their analysis in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The article reported a post hoc analysis of data from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry (GSR), an international, Medtronic-funded effort that includes 2,652 patients with uncontrolled hypertension treated with a Symplicity denervation system. Data were obtained from 196 centers in 45 countries.
“Blood pressure reductions were durable and sustained to 3 years and the rates of new-onset, end-stage renal disease and elevation in serum creatinine levels were very low in patients at high and low [cardiovascular] risk,” reported Dr. Mahfoud.
As expected, adverse event rates were higher for patients with higher baseline cardiovascular risk. “Elevated rates were also seen in patients with [atrial fibrillation] and diabetes, identifying these subgroups who might derive even greater clinical benefit from improved BP control using renal denervation,” said Dr. Mahfoud.
Asked which patients might be optimal candidates for renal denervation, Dr. Mahfoud recommended the technology for “patients with uncontrolled hypertension on medication, patients with nonadherence, unwillingness, or intolerability to medication, and patients with combined systolic and diastolic hypertension.”
Analyses limited by incomplete data
Stephen C. Textor, MD, has concerns over the amount of missing data in the GSR database and its continued use as a repository of information on renal denervation.
“I am a bit lukewarm on this paper in part because of the nature of the registry data they’re using,” he added in an interview. “The problem I see is that the registry is not terribly uniform as to what information they collect on each patient, not terribly uniform in terms of how the procedure is performed, and not terribly uniform on how they follow up patients.”
Indeed, the post hoc subgroup analyses represent only a limited subset because of incomplete data, added Dr. Textor, a nephrologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“Remarkably, only 504 [patients] had “matched” data for office [systolic BP] levels at the time points defined in the report,” he wrote in an editorial comment accompanying the registry report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Jun 16;75[23]:2889-91).
Similarly, the researchers were able to calculate baseline atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk scores in only 1,485 patients (56% of total), primarily because of missing cholesterol measurements.
“They simply did these paired comparison that may have included a couple hundred cases, and on average, there were no differences in response, but what I would have liked to see is a multivariate analysis, where you have all the data on everybody and look at what are the factors that impact response?” Dr. Textor said in the interview.
“They really couldn’t do that because they just, they’re just too many holes in the data,” he added.
On the bright side, Dr. Textor noted that, while the impact overall on systolic BP was “modest,” the standard deviations in some cases were large, indicating that some people had large reductions of systolic BP of more than 30-40 mm Hg.
“There is a belief out there that there are some people that really benefit from this, but how to identify them has been the question,” Dr. Textor said.
Enthusiasm for renal denervation plummeted after results from the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 showed the procedure failing to meet its efficacy endpoint in resistant hypertension. The procedure was associated with a 14–mm Hg fall in systolic BP, compared with an 11–mm Hg drop in the “sham” control group (N Engl J Med. 2014 Apr 10;370:1393-401). However, post hoc analysis of the trial revealed significant shortcomings in design and execution.
No renal denervation device is approved in the United States. The Symplicity device used in this registry is approved in the European Union.
In early 2020, the Food and Drug Administration promised a rigorous review of new renal denervation trials. Subsequently, primary results from the SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED pivotal trial were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology in March and showed promising efficacy.
SPYRAL HTN OFF-MED was designed in collaboration with the FDA to obtain meaningful evidence of whether renal denervation performed with the Symplicity Spyral multielectrode catheter (Medtronic Vascular) could reduce BP in patients not taking antihypertensive medication.
Dr. Mahfoud reported he has received speaking honoraria from Medtronic and ReCor. Two other authors are employees of Medtronic. Dr. Textor reported no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper. The Global SYMPLICITY Registry is funded by Medtronic Vascular.
SOURCE: Mahfoud F et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 June 16;75:2879-88.
This article was updated 6/16/20.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Ventricular tachycardia storm responds to magnetic stimulation
In a pilot study of five patients with ventricular tachycardia (VT) storm that was refractory to antiarrhythmic drug therapy, treatment with noninvasive transcutaneous magnetic stimulation (TCMS) was associated with a lower arrhythmia burden.
The five patients were men aged 40 to 68 years with VT storm, defined as at least three episodes of sustained VT in the preceding 24 hours. The patients experienced a drop in both sustained and nonsustained VT with TCMS.
The study “aimed at developing a novel system for noninvasively and nondestructively interrupting the sympathetic tone,” corresponding author Timothy M. Markman, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “We demonstrated that the technique was safe and that there was a strong signal of efficacy,” he added.
“We know that interrupting the sympathetic tone in these patients is beneficial,” said Markman, “but our strategies for doing so are mostly invasive and associated with a significant risk profile.”
The research letter was published online May 5 in the Journal of the American Medical Association. It was also presented during the virtual Heart Rhythm Society 2020 conference.
Growing body of evidence
Numerous studies have linked autonomic neuromodulation, including local blockade of the left stellate ganglion, with a reduction of cardiac sympathetic input in patients with VT storm, the authors write.
“This adds to a growing body of literature that autonomic neuromodulation is a valuable tool in the management of arrhythmias,” said Markman.
The use of magnetic stimulation to treat arrhythmias by targeting cardiac sympathetic innervation has been demonstrated in animal studies. The authors note that, to their knowledge, this is the first study involving humans.
Evidence suggests that TCMS may serve as a bridge for patients with difficult-to- treat VT to reduce VT and eliminate antiarrhythmic drug therapies and the associated risks, the authors say.
A lower VT burden
Five participants were included in the study. The patients were followed from March 2019 to June 2019. All had experienced at least three episodes of sustained VT (>30 sec) in the 24 hours preceding treatment. Patients with implantable cardiac devices were excluded.
The investigators used a figure 8 TCMS coil that was attached to a magnetic stimulation system positioned lateral to the C7 spinous process in approximation of the left stellate ganglion. TCMS was delivered at 80% of the left trapezius motor threshold at a frequency of 0.9 Hz for 60 minutes, the authors write. For one patient (patient no. 4), TCMS was shut off after 17 minutes, owing to the coil’s overheating. That resulted in the patient’s not being able to complete the protocol, they note.
Patients were monitored during and immediately after treatment for adverse events, including hemodynamic compromise, local discomfort, and skin irritation.
Results showed that compared to the 24-hour baseline period, sustained VT was reduced from 99 to five episodes, and nonsustained VT was reduced from 150 to 58 episodes in the 48 hours following TCMS.
In addition, 41 total external shocks were performed at the 24-hour baseline before TCMS. No external shocks were performed 48 hours after TCMS treatment.
Of the three patients who were not under sedation, none reported discomfort from TCMS.
Before TCMS treatment began, VT was refractory to a mean (SD) of 2.5 (2.1) antiarrhythmic drugs per patient. Within the 48-hour follow-up, patients received a mean of 1.2 (0.7) antiarrhythmic drugs. No additional antiarrhythmic drug was added, the authors note. Only patient no. 4, who did not complete the protocol, underwent ablation 36 hours post enrollment, they add.
The authors note some limitations, such as small case number. Markman told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology that enrollment of patients in a randomized, sham-controlled trial to demonstrate efficacy is underway.
Physiology studies to evaluate the effects of this therapy while optimizing the technical aspects of the delivery of transcutaneous magnetic stimulation are also being conducted, he adds. Other limitations include the absence of control measures and exclusion of patients with implantable cardiac devices.
A potential addition to treatment
Gordon F. Tomaselli, MD, past president of the American Heart Association and current dean of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, who was not involved in the research, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology that “the results are kind of interesting; it actually changes the function in the ganglion in the neck that actually innervates the heart, excites the heart, if you will.
“Clearly it wasn’t something that was just happening while this therapy was applied, but instead there’s some changes made when the sympathetic ganglion is targeted,” Tomaselli said. “They’re changing it functionally somehow, reducing the stimulating input to the heart, and in doing so, reducing the frequency of arrhythmias.”
Tomaselli suggested TCMS might be helpful in choosing among alternative treatments, such as sympathetic denervation. “It might also be a way to decide whether or not somebody might benefit, for example, from permanent dissection,” he said. “If you do this therapy, if it quiets things down but then it comes back after a while, you may consider denervation of that ganglion.”
Tomaselli adds that this treatment might be applied in different ways. “In some future iteration, it could even be implantable, could be patient activated or automatically activated ― for example, if a rapid heart rate is detected, that kind of thing.”
He noted that “there may be applications of this ultra-low frequency to other arrythmias, more common arrythmias, less life-threatening arrythmias, like atrial fibrillation; so there are a number of ways you might consider using this to treat cardiac rhythm disturbances by targeting the nervous system.”
Nazarian has consulted for Siemens, CardioSolv, and Circle Software and is a principle investigator for research funding to the University of Pennsylvania from Biosense-Webster, Siemens, ImriCor, and the National Institutes of Health. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a pilot study of five patients with ventricular tachycardia (VT) storm that was refractory to antiarrhythmic drug therapy, treatment with noninvasive transcutaneous magnetic stimulation (TCMS) was associated with a lower arrhythmia burden.
The five patients were men aged 40 to 68 years with VT storm, defined as at least three episodes of sustained VT in the preceding 24 hours. The patients experienced a drop in both sustained and nonsustained VT with TCMS.
The study “aimed at developing a novel system for noninvasively and nondestructively interrupting the sympathetic tone,” corresponding author Timothy M. Markman, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “We demonstrated that the technique was safe and that there was a strong signal of efficacy,” he added.
“We know that interrupting the sympathetic tone in these patients is beneficial,” said Markman, “but our strategies for doing so are mostly invasive and associated with a significant risk profile.”
The research letter was published online May 5 in the Journal of the American Medical Association. It was also presented during the virtual Heart Rhythm Society 2020 conference.
Growing body of evidence
Numerous studies have linked autonomic neuromodulation, including local blockade of the left stellate ganglion, with a reduction of cardiac sympathetic input in patients with VT storm, the authors write.
“This adds to a growing body of literature that autonomic neuromodulation is a valuable tool in the management of arrhythmias,” said Markman.
The use of magnetic stimulation to treat arrhythmias by targeting cardiac sympathetic innervation has been demonstrated in animal studies. The authors note that, to their knowledge, this is the first study involving humans.
Evidence suggests that TCMS may serve as a bridge for patients with difficult-to- treat VT to reduce VT and eliminate antiarrhythmic drug therapies and the associated risks, the authors say.
A lower VT burden
Five participants were included in the study. The patients were followed from March 2019 to June 2019. All had experienced at least three episodes of sustained VT (>30 sec) in the 24 hours preceding treatment. Patients with implantable cardiac devices were excluded.
The investigators used a figure 8 TCMS coil that was attached to a magnetic stimulation system positioned lateral to the C7 spinous process in approximation of the left stellate ganglion. TCMS was delivered at 80% of the left trapezius motor threshold at a frequency of 0.9 Hz for 60 minutes, the authors write. For one patient (patient no. 4), TCMS was shut off after 17 minutes, owing to the coil’s overheating. That resulted in the patient’s not being able to complete the protocol, they note.
Patients were monitored during and immediately after treatment for adverse events, including hemodynamic compromise, local discomfort, and skin irritation.
Results showed that compared to the 24-hour baseline period, sustained VT was reduced from 99 to five episodes, and nonsustained VT was reduced from 150 to 58 episodes in the 48 hours following TCMS.

In addition, 41 total external shocks were performed at the 24-hour baseline before TCMS. No external shocks were performed 48 hours after TCMS treatment.
Of the three patients who were not under sedation, none reported discomfort from TCMS.
Before TCMS treatment began, VT was refractory to a mean (SD) of 2.5 (2.1) antiarrhythmic drugs per patient. Within the 48-hour follow-up, patients received a mean of 1.2 (0.7) antiarrhythmic drugs. No additional antiarrhythmic drug was added, the authors note. Only patient no. 4, who did not complete the protocol, underwent ablation 36 hours post enrollment, they add.
The authors note some limitations, such as small case number. Markman told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology that enrollment of patients in a randomized, sham-controlled trial to demonstrate efficacy is underway.
Physiology studies to evaluate the effects of this therapy while optimizing the technical aspects of the delivery of transcutaneous magnetic stimulation are also being conducted, he adds. Other limitations include the absence of control measures and exclusion of patients with implantable cardiac devices.
A potential addition to treatment
Gordon F. Tomaselli, MD, past president of the American Heart Association and current dean of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, who was not involved in the research, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology that “the results are kind of interesting; it actually changes the function in the ganglion in the neck that actually innervates the heart, excites the heart, if you will.
“Clearly it wasn’t something that was just happening while this therapy was applied, but instead there’s some changes made when the sympathetic ganglion is targeted,” Tomaselli said. “They’re changing it functionally somehow, reducing the stimulating input to the heart, and in doing so, reducing the frequency of arrhythmias.”
Tomaselli suggested TCMS might be helpful in choosing among alternative treatments, such as sympathetic denervation. “It might also be a way to decide whether or not somebody might benefit, for example, from permanent dissection,” he said. “If you do this therapy, if it quiets things down but then it comes back after a while, you may consider denervation of that ganglion.”
Tomaselli adds that this treatment might be applied in different ways. “In some future iteration, it could even be implantable, could be patient activated or automatically activated ― for example, if a rapid heart rate is detected, that kind of thing.”
He noted that “there may be applications of this ultra-low frequency to other arrythmias, more common arrythmias, less life-threatening arrythmias, like atrial fibrillation; so there are a number of ways you might consider using this to treat cardiac rhythm disturbances by targeting the nervous system.”
Nazarian has consulted for Siemens, CardioSolv, and Circle Software and is a principle investigator for research funding to the University of Pennsylvania from Biosense-Webster, Siemens, ImriCor, and the National Institutes of Health. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a pilot study of five patients with ventricular tachycardia (VT) storm that was refractory to antiarrhythmic drug therapy, treatment with noninvasive transcutaneous magnetic stimulation (TCMS) was associated with a lower arrhythmia burden.
The five patients were men aged 40 to 68 years with VT storm, defined as at least three episodes of sustained VT in the preceding 24 hours. The patients experienced a drop in both sustained and nonsustained VT with TCMS.
The study “aimed at developing a novel system for noninvasively and nondestructively interrupting the sympathetic tone,” corresponding author Timothy M. Markman, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “We demonstrated that the technique was safe and that there was a strong signal of efficacy,” he added.
“We know that interrupting the sympathetic tone in these patients is beneficial,” said Markman, “but our strategies for doing so are mostly invasive and associated with a significant risk profile.”
The research letter was published online May 5 in the Journal of the American Medical Association. It was also presented during the virtual Heart Rhythm Society 2020 conference.
Growing body of evidence
Numerous studies have linked autonomic neuromodulation, including local blockade of the left stellate ganglion, with a reduction of cardiac sympathetic input in patients with VT storm, the authors write.
“This adds to a growing body of literature that autonomic neuromodulation is a valuable tool in the management of arrhythmias,” said Markman.
The use of magnetic stimulation to treat arrhythmias by targeting cardiac sympathetic innervation has been demonstrated in animal studies. The authors note that, to their knowledge, this is the first study involving humans.
Evidence suggests that TCMS may serve as a bridge for patients with difficult-to- treat VT to reduce VT and eliminate antiarrhythmic drug therapies and the associated risks, the authors say.
A lower VT burden
Five participants were included in the study. The patients were followed from March 2019 to June 2019. All had experienced at least three episodes of sustained VT (>30 sec) in the 24 hours preceding treatment. Patients with implantable cardiac devices were excluded.
The investigators used a figure 8 TCMS coil that was attached to a magnetic stimulation system positioned lateral to the C7 spinous process in approximation of the left stellate ganglion. TCMS was delivered at 80% of the left trapezius motor threshold at a frequency of 0.9 Hz for 60 minutes, the authors write. For one patient (patient no. 4), TCMS was shut off after 17 minutes, owing to the coil’s overheating. That resulted in the patient’s not being able to complete the protocol, they note.
Patients were monitored during and immediately after treatment for adverse events, including hemodynamic compromise, local discomfort, and skin irritation.
Results showed that compared to the 24-hour baseline period, sustained VT was reduced from 99 to five episodes, and nonsustained VT was reduced from 150 to 58 episodes in the 48 hours following TCMS.

In addition, 41 total external shocks were performed at the 24-hour baseline before TCMS. No external shocks were performed 48 hours after TCMS treatment.
Of the three patients who were not under sedation, none reported discomfort from TCMS.
Before TCMS treatment began, VT was refractory to a mean (SD) of 2.5 (2.1) antiarrhythmic drugs per patient. Within the 48-hour follow-up, patients received a mean of 1.2 (0.7) antiarrhythmic drugs. No additional antiarrhythmic drug was added, the authors note. Only patient no. 4, who did not complete the protocol, underwent ablation 36 hours post enrollment, they add.
The authors note some limitations, such as small case number. Markman told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology that enrollment of patients in a randomized, sham-controlled trial to demonstrate efficacy is underway.
Physiology studies to evaluate the effects of this therapy while optimizing the technical aspects of the delivery of transcutaneous magnetic stimulation are also being conducted, he adds. Other limitations include the absence of control measures and exclusion of patients with implantable cardiac devices.
A potential addition to treatment
Gordon F. Tomaselli, MD, past president of the American Heart Association and current dean of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, who was not involved in the research, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology that “the results are kind of interesting; it actually changes the function in the ganglion in the neck that actually innervates the heart, excites the heart, if you will.
“Clearly it wasn’t something that was just happening while this therapy was applied, but instead there’s some changes made when the sympathetic ganglion is targeted,” Tomaselli said. “They’re changing it functionally somehow, reducing the stimulating input to the heart, and in doing so, reducing the frequency of arrhythmias.”
Tomaselli suggested TCMS might be helpful in choosing among alternative treatments, such as sympathetic denervation. “It might also be a way to decide whether or not somebody might benefit, for example, from permanent dissection,” he said. “If you do this therapy, if it quiets things down but then it comes back after a while, you may consider denervation of that ganglion.”
Tomaselli adds that this treatment might be applied in different ways. “In some future iteration, it could even be implantable, could be patient activated or automatically activated ― for example, if a rapid heart rate is detected, that kind of thing.”
He noted that “there may be applications of this ultra-low frequency to other arrythmias, more common arrythmias, less life-threatening arrythmias, like atrial fibrillation; so there are a number of ways you might consider using this to treat cardiac rhythm disturbances by targeting the nervous system.”
Nazarian has consulted for Siemens, CardioSolv, and Circle Software and is a principle investigator for research funding to the University of Pennsylvania from Biosense-Webster, Siemens, ImriCor, and the National Institutes of Health. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.












