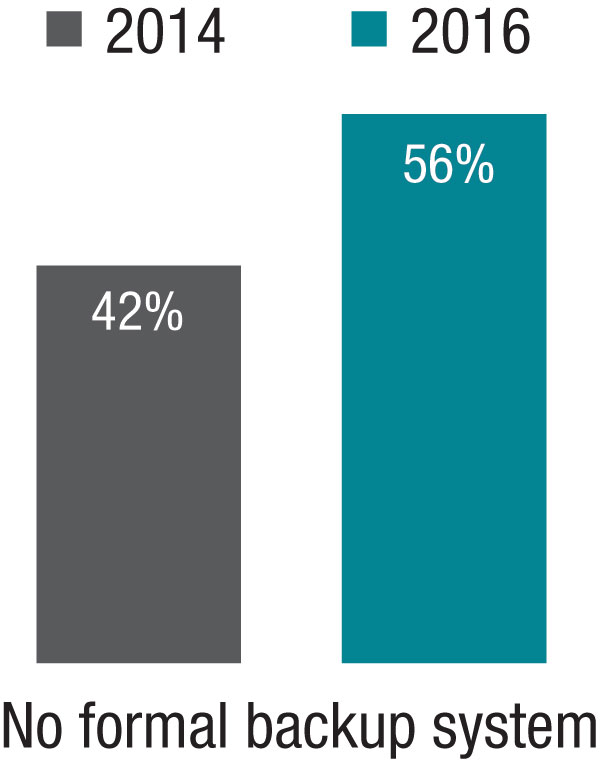User login
The Hospitalist only
Revisiting citizenship bonus and surge capacity
I devoted an entire column to the idea of a citizenship bonus in November 2011. At that time I expressed some ambivalence about its effectiveness. Since then I’ve become disenchanted and think it may do more harm than good.
SHM’s 2016 State of Hospital Medicine (SOHM) Report, based on 2015 data, shows that 46% of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) connect some portion of bonus dollars to a provider’s citizenship.1 This is a relatively new phenomenon in the last 5 years or so. My anecdotal experience is that it isn’t limited to hospitalists; it is pretty common for doctors in any specialty who are employed by a hospital or other large organization.
HMGs vary in their definitions of what constitutes citizenship, but usually include things like committee participation, lectures, grand rounds presentations, community talks, research publications.
Our hospitalist group at my hospital has well-defined criteria that require attendance at more than 75% of meetings as a “light switch” (pays nothing itself, but “turns on” availability to citizenship bonus). Bonus dollars are paid for success in any one of several activities, such as making an in-person visit to two PCP offices or completing a meaningful project related to practice operations or clinical care.
I’ve been a supporter of a citizenship bonus for a long time, but two things have made me ambivalent or even opposed to it. The first is a book by Daniel Pink titled Drive: The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us. It’s a short and very thought-provoking book summarizing research that suggests the effect of providing external rewards like compensation is to “…extinguish intrinsic motivation, diminish performance, crush creativity, and crowd out good behavior.”
The second reason for my ambivalence is my experience working with a lot of HMGs around the country. Those that have a citizenship bonus don’t seem to realize improved operations, more engaged doctors, or lower turnover, and so on. In fact, my experience is that the bonus tends to do exactly what Pink says – steer individuals and the group as a whole away from what is desired.
I’m not ready to say a citizenship bonus is always a bad idea. But it sure seems like it works out badly for many or most groups.
But if you do have a citizenship bonus, then don’t make the mistake of tying it to very basic expectations of the job, like attending group meetings or completing chart documentation on time. Doing those things should never be seen as a reason for a bonus.
Jeopardy (‘surge’) staffing: Not catching on?
As I write, influenza has swept through our region, and my hospital – like most along the west coast – is experiencing incredibly high volumes. I enter the building through a patient care unit that has been mothballed for several years, but today people from building maintenance were busy getting it ready for patients. The hospital is offering various incentives for patient care staff to work extra shifts to manage this volume surge, and our hospitalists have days with encounters near or at our highest-ever level. So surge capacity is once again on my mind.
But if every hospitalist in the group went from, say, 156 to 190 shifts annually, the practice might be able to staff every day with an additional provider without adding staff or spending more money. And a doc’s average day would be less busy, which for some people (okay, not very many) would be a worthwhile trade-off. I realize this is a tough sell and to many people it sounds crazy.
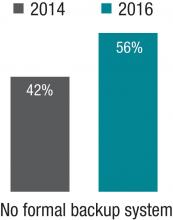
The 2014 SOHM showed 42% of HMGs had “no formal backup system,” and this had climbed to 58% in the 2016 Report. I don’t know if jeopardy or surge backup systems are really becoming less common, but it seems pretty clear they aren’t becoming more common. So it’s worth thinking about whether there is a practical way to remove inhibitors of surge capacity.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is cofounder and past president of SHM, and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is course co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at [email protected].
Endnotes
1. Note that this is down from 2014, when 64% of groups reported having a citizenship element in their bonus. But I’m skeptical this is a real trend of decreasing popularity and suspect the drop is mostly explained by a much larger portion of respondents in this particular survey coming from hospitalist management companies which I think much less often have a citizenship bonus.
I devoted an entire column to the idea of a citizenship bonus in November 2011. At that time I expressed some ambivalence about its effectiveness. Since then I’ve become disenchanted and think it may do more harm than good.
SHM’s 2016 State of Hospital Medicine (SOHM) Report, based on 2015 data, shows that 46% of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) connect some portion of bonus dollars to a provider’s citizenship.1 This is a relatively new phenomenon in the last 5 years or so. My anecdotal experience is that it isn’t limited to hospitalists; it is pretty common for doctors in any specialty who are employed by a hospital or other large organization.
HMGs vary in their definitions of what constitutes citizenship, but usually include things like committee participation, lectures, grand rounds presentations, community talks, research publications.
Our hospitalist group at my hospital has well-defined criteria that require attendance at more than 75% of meetings as a “light switch” (pays nothing itself, but “turns on” availability to citizenship bonus). Bonus dollars are paid for success in any one of several activities, such as making an in-person visit to two PCP offices or completing a meaningful project related to practice operations or clinical care.
I’ve been a supporter of a citizenship bonus for a long time, but two things have made me ambivalent or even opposed to it. The first is a book by Daniel Pink titled Drive: The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us. It’s a short and very thought-provoking book summarizing research that suggests the effect of providing external rewards like compensation is to “…extinguish intrinsic motivation, diminish performance, crush creativity, and crowd out good behavior.”
The second reason for my ambivalence is my experience working with a lot of HMGs around the country. Those that have a citizenship bonus don’t seem to realize improved operations, more engaged doctors, or lower turnover, and so on. In fact, my experience is that the bonus tends to do exactly what Pink says – steer individuals and the group as a whole away from what is desired.
I’m not ready to say a citizenship bonus is always a bad idea. But it sure seems like it works out badly for many or most groups.
But if you do have a citizenship bonus, then don’t make the mistake of tying it to very basic expectations of the job, like attending group meetings or completing chart documentation on time. Doing those things should never be seen as a reason for a bonus.
Jeopardy (‘surge’) staffing: Not catching on?
As I write, influenza has swept through our region, and my hospital – like most along the west coast – is experiencing incredibly high volumes. I enter the building through a patient care unit that has been mothballed for several years, but today people from building maintenance were busy getting it ready for patients. The hospital is offering various incentives for patient care staff to work extra shifts to manage this volume surge, and our hospitalists have days with encounters near or at our highest-ever level. So surge capacity is once again on my mind.
But if every hospitalist in the group went from, say, 156 to 190 shifts annually, the practice might be able to staff every day with an additional provider without adding staff or spending more money. And a doc’s average day would be less busy, which for some people (okay, not very many) would be a worthwhile trade-off. I realize this is a tough sell and to many people it sounds crazy.
The 2014 SOHM showed 42% of HMGs had “no formal backup system,” and this had climbed to 58% in the 2016 Report. I don’t know if jeopardy or surge backup systems are really becoming less common, but it seems pretty clear they aren’t becoming more common. So it’s worth thinking about whether there is a practical way to remove inhibitors of surge capacity.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is cofounder and past president of SHM, and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is course co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at [email protected].
Endnotes
1. Note that this is down from 2014, when 64% of groups reported having a citizenship element in their bonus. But I’m skeptical this is a real trend of decreasing popularity and suspect the drop is mostly explained by a much larger portion of respondents in this particular survey coming from hospitalist management companies which I think much less often have a citizenship bonus.
I devoted an entire column to the idea of a citizenship bonus in November 2011. At that time I expressed some ambivalence about its effectiveness. Since then I’ve become disenchanted and think it may do more harm than good.
SHM’s 2016 State of Hospital Medicine (SOHM) Report, based on 2015 data, shows that 46% of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) connect some portion of bonus dollars to a provider’s citizenship.1 This is a relatively new phenomenon in the last 5 years or so. My anecdotal experience is that it isn’t limited to hospitalists; it is pretty common for doctors in any specialty who are employed by a hospital or other large organization.
HMGs vary in their definitions of what constitutes citizenship, but usually include things like committee participation, lectures, grand rounds presentations, community talks, research publications.
Our hospitalist group at my hospital has well-defined criteria that require attendance at more than 75% of meetings as a “light switch” (pays nothing itself, but “turns on” availability to citizenship bonus). Bonus dollars are paid for success in any one of several activities, such as making an in-person visit to two PCP offices or completing a meaningful project related to practice operations or clinical care.
I’ve been a supporter of a citizenship bonus for a long time, but two things have made me ambivalent or even opposed to it. The first is a book by Daniel Pink titled Drive: The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us. It’s a short and very thought-provoking book summarizing research that suggests the effect of providing external rewards like compensation is to “…extinguish intrinsic motivation, diminish performance, crush creativity, and crowd out good behavior.”
The second reason for my ambivalence is my experience working with a lot of HMGs around the country. Those that have a citizenship bonus don’t seem to realize improved operations, more engaged doctors, or lower turnover, and so on. In fact, my experience is that the bonus tends to do exactly what Pink says – steer individuals and the group as a whole away from what is desired.
I’m not ready to say a citizenship bonus is always a bad idea. But it sure seems like it works out badly for many or most groups.
But if you do have a citizenship bonus, then don’t make the mistake of tying it to very basic expectations of the job, like attending group meetings or completing chart documentation on time. Doing those things should never be seen as a reason for a bonus.
Jeopardy (‘surge’) staffing: Not catching on?
As I write, influenza has swept through our region, and my hospital – like most along the west coast – is experiencing incredibly high volumes. I enter the building through a patient care unit that has been mothballed for several years, but today people from building maintenance were busy getting it ready for patients. The hospital is offering various incentives for patient care staff to work extra shifts to manage this volume surge, and our hospitalists have days with encounters near or at our highest-ever level. So surge capacity is once again on my mind.
But if every hospitalist in the group went from, say, 156 to 190 shifts annually, the practice might be able to staff every day with an additional provider without adding staff or spending more money. And a doc’s average day would be less busy, which for some people (okay, not very many) would be a worthwhile trade-off. I realize this is a tough sell and to many people it sounds crazy.
The 2014 SOHM showed 42% of HMGs had “no formal backup system,” and this had climbed to 58% in the 2016 Report. I don’t know if jeopardy or surge backup systems are really becoming less common, but it seems pretty clear they aren’t becoming more common. So it’s worth thinking about whether there is a practical way to remove inhibitors of surge capacity.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is cofounder and past president of SHM, and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is course co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at [email protected].
Endnotes
1. Note that this is down from 2014, when 64% of groups reported having a citizenship element in their bonus. But I’m skeptical this is a real trend of decreasing popularity and suspect the drop is mostly explained by a much larger portion of respondents in this particular survey coming from hospitalist management companies which I think much less often have a citizenship bonus.
Turnover rate for hospitalist groups trending downward
According to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report based on 2015 data, the median physician turnover rate for hospital medicine groups (HMGs) serving adults only is 6.9%, lower compared with results from prior surveys. Particularly, turnover in 2010 was more than double the current rate (see Figure 1). This steady decline over the years is intriguing, yet encouraging, since hospital medicine is well known for its high turnover compared to other specialties.
Similarly, results from State of Hospital Medicine surveys also reveal a consistent trend for groups with no turnover. As expected, lower turnover rate usually parallels with higher percentage of groups with no turnover. This year, 40.2% of hospitalist groups reported no physician turnover at all, continuing the upward trend from 2014 (38.1%) and 2012 (36%). It is speculating that these groups are not just simply fortunate, but rather work zealously to build a strong internal culture within the group and proactively create a shared vision, values, accountability, and career goals. 
Sources in search of why providers leave a practice and advice on specific strategies to retain them are abundant. To secure retention, at a minimum, employers, leaders, or administrators should pay close attention to such basic factors as work schedules, workload, and compensation – and even consider using national and regional data from the State of Hospital Medicine Report for benchmarking to remain attractive and competitive in the market. Low or no turnover rate indicates workforce stability and program credibility, and allows cost saving as the overall estimated cost of turnover (losing a provider and hiring another one) ranges from $400,000 to $600,000 per provider.1
The turnover data further delineates differences based on academic status, Medicare Indirect Medical Education (IME) program status, and geographic region. For instance, the academic groups consistently report a higher turnover rate, compared with the nonacademic groups. The latter mirrors the overall decreasing trend of physician turnover. Non-teaching hospitals also score significantly higher on the number of groups with no turnover (42% as opposed to 24%-27% for teaching hospitals). Geographically, HMGs in the South and Midwest regions of the United States are the winners this year, with more than 50% of the groups reporting no turnover at all.
Specific information regarding turnover for nurse practitioners and physician assistants (NPs/PAs) can also be found in the report. This rate has been increasing slightly compared with the past, with a subsequent drop in the percentage of groups reporting no turnover. Yet, the overall percentage with no turnover for NPs/PAs remains impressively high at 62%.
The turnover rates for HMGs serving both adults and children, and groups serving children only, appear somewhat similar to those of groups serving adults only, though we cannot reliably analyze the data, elucidate significant differences, or detect any meaningful trends from these two groups because of insufficient numbers of responders.
The downward trend of hospitalist turnover found in SHM’s 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report is reassuring, indicative of a higher retention rate and an extended stability for many programs. Although some hospitalists continue to shop around, most leaders and employers of HMGs work endlessly to strengthen their programs in hope to minimize turnover. The promising data likely reflect such effort. Hopefully, this trend will continue when the next State of Hospital Medicine report comes out.
Dr. Vuong is a hospitalist at HealthPartners Medical Group in St Paul, Minn., and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota. He is a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
Reference
1. Frenz, D (2016). The staggering costs of physician turnover. Today’s Hospitalist.
According to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report based on 2015 data, the median physician turnover rate for hospital medicine groups (HMGs) serving adults only is 6.9%, lower compared with results from prior surveys. Particularly, turnover in 2010 was more than double the current rate (see Figure 1). This steady decline over the years is intriguing, yet encouraging, since hospital medicine is well known for its high turnover compared to other specialties.
Similarly, results from State of Hospital Medicine surveys also reveal a consistent trend for groups with no turnover. As expected, lower turnover rate usually parallels with higher percentage of groups with no turnover. This year, 40.2% of hospitalist groups reported no physician turnover at all, continuing the upward trend from 2014 (38.1%) and 2012 (36%). It is speculating that these groups are not just simply fortunate, but rather work zealously to build a strong internal culture within the group and proactively create a shared vision, values, accountability, and career goals. 
Sources in search of why providers leave a practice and advice on specific strategies to retain them are abundant. To secure retention, at a minimum, employers, leaders, or administrators should pay close attention to such basic factors as work schedules, workload, and compensation – and even consider using national and regional data from the State of Hospital Medicine Report for benchmarking to remain attractive and competitive in the market. Low or no turnover rate indicates workforce stability and program credibility, and allows cost saving as the overall estimated cost of turnover (losing a provider and hiring another one) ranges from $400,000 to $600,000 per provider.1
The turnover data further delineates differences based on academic status, Medicare Indirect Medical Education (IME) program status, and geographic region. For instance, the academic groups consistently report a higher turnover rate, compared with the nonacademic groups. The latter mirrors the overall decreasing trend of physician turnover. Non-teaching hospitals also score significantly higher on the number of groups with no turnover (42% as opposed to 24%-27% for teaching hospitals). Geographically, HMGs in the South and Midwest regions of the United States are the winners this year, with more than 50% of the groups reporting no turnover at all.
Specific information regarding turnover for nurse practitioners and physician assistants (NPs/PAs) can also be found in the report. This rate has been increasing slightly compared with the past, with a subsequent drop in the percentage of groups reporting no turnover. Yet, the overall percentage with no turnover for NPs/PAs remains impressively high at 62%.
The turnover rates for HMGs serving both adults and children, and groups serving children only, appear somewhat similar to those of groups serving adults only, though we cannot reliably analyze the data, elucidate significant differences, or detect any meaningful trends from these two groups because of insufficient numbers of responders.
The downward trend of hospitalist turnover found in SHM’s 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report is reassuring, indicative of a higher retention rate and an extended stability for many programs. Although some hospitalists continue to shop around, most leaders and employers of HMGs work endlessly to strengthen their programs in hope to minimize turnover. The promising data likely reflect such effort. Hopefully, this trend will continue when the next State of Hospital Medicine report comes out.
Dr. Vuong is a hospitalist at HealthPartners Medical Group in St Paul, Minn., and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota. He is a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
Reference
1. Frenz, D (2016). The staggering costs of physician turnover. Today’s Hospitalist.
According to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report based on 2015 data, the median physician turnover rate for hospital medicine groups (HMGs) serving adults only is 6.9%, lower compared with results from prior surveys. Particularly, turnover in 2010 was more than double the current rate (see Figure 1). This steady decline over the years is intriguing, yet encouraging, since hospital medicine is well known for its high turnover compared to other specialties.
Similarly, results from State of Hospital Medicine surveys also reveal a consistent trend for groups with no turnover. As expected, lower turnover rate usually parallels with higher percentage of groups with no turnover. This year, 40.2% of hospitalist groups reported no physician turnover at all, continuing the upward trend from 2014 (38.1%) and 2012 (36%). It is speculating that these groups are not just simply fortunate, but rather work zealously to build a strong internal culture within the group and proactively create a shared vision, values, accountability, and career goals. 
Sources in search of why providers leave a practice and advice on specific strategies to retain them are abundant. To secure retention, at a minimum, employers, leaders, or administrators should pay close attention to such basic factors as work schedules, workload, and compensation – and even consider using national and regional data from the State of Hospital Medicine Report for benchmarking to remain attractive and competitive in the market. Low or no turnover rate indicates workforce stability and program credibility, and allows cost saving as the overall estimated cost of turnover (losing a provider and hiring another one) ranges from $400,000 to $600,000 per provider.1
The turnover data further delineates differences based on academic status, Medicare Indirect Medical Education (IME) program status, and geographic region. For instance, the academic groups consistently report a higher turnover rate, compared with the nonacademic groups. The latter mirrors the overall decreasing trend of physician turnover. Non-teaching hospitals also score significantly higher on the number of groups with no turnover (42% as opposed to 24%-27% for teaching hospitals). Geographically, HMGs in the South and Midwest regions of the United States are the winners this year, with more than 50% of the groups reporting no turnover at all.
Specific information regarding turnover for nurse practitioners and physician assistants (NPs/PAs) can also be found in the report. This rate has been increasing slightly compared with the past, with a subsequent drop in the percentage of groups reporting no turnover. Yet, the overall percentage with no turnover for NPs/PAs remains impressively high at 62%.
The turnover rates for HMGs serving both adults and children, and groups serving children only, appear somewhat similar to those of groups serving adults only, though we cannot reliably analyze the data, elucidate significant differences, or detect any meaningful trends from these two groups because of insufficient numbers of responders.
The downward trend of hospitalist turnover found in SHM’s 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report is reassuring, indicative of a higher retention rate and an extended stability for many programs. Although some hospitalists continue to shop around, most leaders and employers of HMGs work endlessly to strengthen their programs in hope to minimize turnover. The promising data likely reflect such effort. Hopefully, this trend will continue when the next State of Hospital Medicine report comes out.
Dr. Vuong is a hospitalist at HealthPartners Medical Group in St Paul, Minn., and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota. He is a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
Reference
1. Frenz, D (2016). The staggering costs of physician turnover. Today’s Hospitalist.
‘I can handle it’– The state of hospitalist group backup systems
It took my hospital medicine group (HMG) 20 years to implement a formal backup system. Of all the reasons we resisted creating a backup system, foremost was that we did not want to mandate additional work. Because our compensation model did not have a mechanism to financially reward hospitalists for unexpectedly having to come in on unscheduled work days (other than the work relative value units generated by seeing patients), there was not enough motivational energy to get a system started.
It turns out our group is not unlike many other HMGs across the nation. According to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine report (SoHM), 58.3% of adult-only HMGs, 72.2% of pediatric-only HMGs, and 52.6% of HMGs serving both adults and children did not have staffing backup systems. Interestingly, the report also showed that for groups serving adults only, academic HMGs were more likely to have formal backup systems in place (62.6%, compared with 37.3% in nonacademic HMGs).
The reason most HMGs create backup systems is to have a consistent and fair approach for dealing with unanticipated absences and/or high-volume census. In addition to creating a safety net, implementing a backup system addresses the common problem of the same hospitalists disproportionately filling in during times of crisis.
Although our group created a formal backup system starting January 2015, it is not comprehensive and deals only with high patient volumes occurring during the late evening and night hours. Hospitalists rotate through a schedule, taking a week of backup call for which no additional compensation is offered. Then, if they are actually called to come in, an hourly stipend is paid in addition to work RVUs generated. Implementing a backup system was not necessarily a popular idea. Nevertheless, the system has successfully remained in place. Triggering the system infrequently, having a clear set of criteria for when to activate backup, and providing additional compensation for the additional work are key factors in our system’s success.

When data from the 2016 SoHM report are compared with the 2014 SoHM report, the proportion of groups with formal backup systems actually decreases for both adults-only HMGs and HMGs serving both adults and children. For adult-only HMGs, there was a decline to 41.8% from 57.6%. For adult/pediatric HMGs, there was a decline to 47.4% from 58.8%. It also is notable that pediatric HMGs in particular are much less likely to have formal backup systems, only 27.8%, which has changed little since the last survey (28.8 % in 2014).
All in all, the reasons for the decline in backup systems are unclear. Possibly, the decrease is because of issues surrounding compensation, as approximately one-third of survey respondents with backup systems received no additional compensation. But in my view, it’s more likely that the reason for the decreased percentage of groups with backup systems has to do with differences in the particular set of HMGs that responded to the survey this year.
Dr. Stephan is a hospitalist at Abbott Northwestern Hospital in Minneapolis and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
It took my hospital medicine group (HMG) 20 years to implement a formal backup system. Of all the reasons we resisted creating a backup system, foremost was that we did not want to mandate additional work. Because our compensation model did not have a mechanism to financially reward hospitalists for unexpectedly having to come in on unscheduled work days (other than the work relative value units generated by seeing patients), there was not enough motivational energy to get a system started.
It turns out our group is not unlike many other HMGs across the nation. According to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine report (SoHM), 58.3% of adult-only HMGs, 72.2% of pediatric-only HMGs, and 52.6% of HMGs serving both adults and children did not have staffing backup systems. Interestingly, the report also showed that for groups serving adults only, academic HMGs were more likely to have formal backup systems in place (62.6%, compared with 37.3% in nonacademic HMGs).
The reason most HMGs create backup systems is to have a consistent and fair approach for dealing with unanticipated absences and/or high-volume census. In addition to creating a safety net, implementing a backup system addresses the common problem of the same hospitalists disproportionately filling in during times of crisis.
Although our group created a formal backup system starting January 2015, it is not comprehensive and deals only with high patient volumes occurring during the late evening and night hours. Hospitalists rotate through a schedule, taking a week of backup call for which no additional compensation is offered. Then, if they are actually called to come in, an hourly stipend is paid in addition to work RVUs generated. Implementing a backup system was not necessarily a popular idea. Nevertheless, the system has successfully remained in place. Triggering the system infrequently, having a clear set of criteria for when to activate backup, and providing additional compensation for the additional work are key factors in our system’s success.

When data from the 2016 SoHM report are compared with the 2014 SoHM report, the proportion of groups with formal backup systems actually decreases for both adults-only HMGs and HMGs serving both adults and children. For adult-only HMGs, there was a decline to 41.8% from 57.6%. For adult/pediatric HMGs, there was a decline to 47.4% from 58.8%. It also is notable that pediatric HMGs in particular are much less likely to have formal backup systems, only 27.8%, which has changed little since the last survey (28.8 % in 2014).
All in all, the reasons for the decline in backup systems are unclear. Possibly, the decrease is because of issues surrounding compensation, as approximately one-third of survey respondents with backup systems received no additional compensation. But in my view, it’s more likely that the reason for the decreased percentage of groups with backup systems has to do with differences in the particular set of HMGs that responded to the survey this year.
Dr. Stephan is a hospitalist at Abbott Northwestern Hospital in Minneapolis and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
It took my hospital medicine group (HMG) 20 years to implement a formal backup system. Of all the reasons we resisted creating a backup system, foremost was that we did not want to mandate additional work. Because our compensation model did not have a mechanism to financially reward hospitalists for unexpectedly having to come in on unscheduled work days (other than the work relative value units generated by seeing patients), there was not enough motivational energy to get a system started.
It turns out our group is not unlike many other HMGs across the nation. According to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine report (SoHM), 58.3% of adult-only HMGs, 72.2% of pediatric-only HMGs, and 52.6% of HMGs serving both adults and children did not have staffing backup systems. Interestingly, the report also showed that for groups serving adults only, academic HMGs were more likely to have formal backup systems in place (62.6%, compared with 37.3% in nonacademic HMGs).
The reason most HMGs create backup systems is to have a consistent and fair approach for dealing with unanticipated absences and/or high-volume census. In addition to creating a safety net, implementing a backup system addresses the common problem of the same hospitalists disproportionately filling in during times of crisis.
Although our group created a formal backup system starting January 2015, it is not comprehensive and deals only with high patient volumes occurring during the late evening and night hours. Hospitalists rotate through a schedule, taking a week of backup call for which no additional compensation is offered. Then, if they are actually called to come in, an hourly stipend is paid in addition to work RVUs generated. Implementing a backup system was not necessarily a popular idea. Nevertheless, the system has successfully remained in place. Triggering the system infrequently, having a clear set of criteria for when to activate backup, and providing additional compensation for the additional work are key factors in our system’s success.

When data from the 2016 SoHM report are compared with the 2014 SoHM report, the proportion of groups with formal backup systems actually decreases for both adults-only HMGs and HMGs serving both adults and children. For adult-only HMGs, there was a decline to 41.8% from 57.6%. For adult/pediatric HMGs, there was a decline to 47.4% from 58.8%. It also is notable that pediatric HMGs in particular are much less likely to have formal backup systems, only 27.8%, which has changed little since the last survey (28.8 % in 2014).
All in all, the reasons for the decline in backup systems are unclear. Possibly, the decrease is because of issues surrounding compensation, as approximately one-third of survey respondents with backup systems received no additional compensation. But in my view, it’s more likely that the reason for the decreased percentage of groups with backup systems has to do with differences in the particular set of HMGs that responded to the survey this year.
Dr. Stephan is a hospitalist at Abbott Northwestern Hospital in Minneapolis and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
U.S. health care policy: What lies ahead?
The New Year brings new leadership in the United States, with President-elect Donald Trump taking office later this month. With a Republican-controlled Congress, party leaders have the opportunity to shape the nation’s policies around conservative ideals. This includes health care.
Since the Affordable Care Act (ACA) was passed in 2010, Republicans have vowed to repeal and replace it. This could be their opportunity.
However, “there is no clear coalescence around specific policy reforms that would replace the Affordable Care Act,” says Christine Eibner, PhD, a senior economist at Rand and a professor at the Pardee Rand Graduate School.
As a candidate, Trump did little to advance policy ideas around health care. Meanwhile, House Speaker Paul Ryan (R-Wis.) and others have, over the years, proposed reforms with which Trump may or may not agree.
“The Republicans now have a hard issue in their hands,” says Allison Hoffman, JD, professor of law at UCLA School of Law and an expert on health care law and policy. “It was hard before the Affordable Care Act, and it will be hard after. There is not an easy solution.”
By 2016, the ACA had expanded health coverage to 20 million people through Medicaid and private insurance on health care marketplaces. It extended the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance Trust Fund. It accelerated the pace of delivery system and payment reform through creation of the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation.
The law, however, has not been without its challenges.
“It was a strong achievement to get 20 million people insured, but it’s not clear that it bent the cost curve,” says Dr. Eibner. “There are high premiums on the individual market and still 31 million people without coverage. There is still opportunity to improve.”
Where we stand January 2017
Whether the Republicans can or will repeal the ACA in its entirety and improve it remains unknown. But, the experts say, the landmark law has left its mark on the American health care system.
“Everyone is complaining about the uncertainty created by the election, but we have been dealing with a highly uncertain environment for many years,” says Ron Greeno, MD, FCCP, MHM, senior advisor for medical affairs at TeamHealth, chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee, and SHM president-elect. “There will be changes, but things were going to change no matter the outcome of the election. It continues to require tolerance for change and tolerance for uncertainty.”
In an analysis for the Commonwealth Fund, Dr. Eibner investigated the economic implications of aspects of Trump’s plans as a candidate. Using a computer model that incorporates economic theory and data to simulate the effects of health policy changes, Dr. Eibner found that Trump’s plans (full repeal alone or repeal with tax deductions for health care premiums, Medicaid block grants, or selling health insurance across state lines) would increase the number of uninsured people by 16 million to 25 million, disproportionately impact low-income and sicker patients, expose individual market enrollees to higher out-of-pocket costs, and increase the federal deficit by $0.5 billion to $41 billion.1 The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates full repeal could increase the federal deficit by $137 billion to $353 billion by 2025.2 Rep. Ryan’s plan, A Better Way, proposes providing people more control over their health care, giving tax credits instead of subsidies for premiums, capping the employer-sponsored health insurance tax exclusion, and expanding use of health savings accounts.3 However, Rep. Ryan’s plan “doesn’t reduce the cost of health care. It puts more onus on individuals, and their costs go up,” Ms. Hoffman says. “The weight of that will be more on people who have preexisting conditions.”
Joshua Lenchus, DO, RPh, FACP, SFHM, a member of SHM’s Public Policy Committee and hospitalist at the University of Miami/Jackson Memorial Hospital in Florida, is no fan of entitlement programs like Medicaid but says, “The safety-net hospital where I work would rather have people covered with something than nothing.”
Dr. Lenchus is optimistic that economic reforms under Trump will lead to more jobs, increasing the number of people covered by employer plans. “The economy drives health care reform,” he says. “He has to up his ante now and show people that he can stimulate job growth in this country so we don’t have this middle class that is continuously squeezed.”
Dr. Greeno and Ms. Hoffman, who is also a faculty associate at the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research and vice chair of the Insurance Law Section of the Association of American Law Schools, suggest hospitalists get involved as rules are being shaped and written.
“We want to help reform the delivery system, and we want it to be done right and to be done fairly. We want to have say in how our patients are treated,” Dr. Greeno says.
Key provisions: A delicate balance
Many people equate the ACA with the individual mandate, which requires nearly all Americans to purchase health insurance or pay a fine. The federal government provides subsidies to enrollees between 138% and 400% of the federal poverty level so their out-of-pocket costs never exceed a defined threshold even if premiums go up. These could be on the chopping block.
“The last bill Congress passed to repeal the Affordable Care Act, which Obama vetoed, repealed the individual mandate and subsidies for people to buy insurance,” Ms. Hoffman says. “If they do repeal it, private insurance through the exchanges will crumble.”
Mr. Trump’s tax deductions to offset premium costs are based on income, making them more generous for higher-income earners than low-income ones, Hoffman adds.
As a result, she says, people may choose high-deductible plans and face high out-of-pocket costs if they do seek care.
“It’s asking individuals to save by deciding how they’re going to ration care, where someone says they’re not going to go to the doctor today or fill a prescription drug they need,” Ms. Hoffman says.
Meanwhile, Mr. Trump has said he would like to keep the provision of the ACA that bans insurers from denying individuals with preexisting conditions. This, experts agree, may not be possible if other parts of the law are repealed and not replaced with similar protections for insurers.
“If you try to keep the rules about not including preexisting conditions and get rid of subsidies and the individual mandate, it just won’t work,” Ms. Hoffman says. “You end up with extraordinarily expensive health insurance.”
Rep. Ryan’s plan would prohibit insurers from denying patients with preexisting conditions but only if patients maintain continuous coverage, with a single open-enrollment period. He has promised to provide at least $25 billion in federal funding for state high-risk pools.
Prior to the passage of the ACA, 35 states offered high-risk pools to people excluded from the individual market. The Kaiser Family Foundation shows the net annual losses in these states averaged $5,510 per enrollee in 2011. Premiums ranged from 100% to 200% higher than non–high-risk group coverage. Government subsidies to cover losses amounted to $1 billion in each state.4
Meanwhile, both Mr. Trump and Rep. Ryan have proposed profound changes for Medicaid. Dr. Greeno calls this a “massive political challenge” unless they can provide an alternative way to cover people who currently rely on the federal-state entitlement, as well as those who gained coverage through ACA expansion. Currently, 70 million people are enrolled in Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program.5 Through Mr. Trump’s suggested block grants, states would receive a fixed amount of money to administer their program with increased flexibility. Rep. Ryan’s plan calls for enrollment caps that would distribute a dollar amount to each participant in the program with no limit on the number of enrollees. Either would be adjusted for inflation.
States could implement work requirements for beneficiaries or ask them to pay a small amount toward their premiums. Expansion states could also lower the Medicaid threshold below 138%.
Some states will struggle to provide for all their enrollees, Ms. Hoffman says, particularly since health spending generally outpaces inflation. Dr. Lenchus is more optimistic. “I believe states that didn’t expand Medicaid, one way or another, will figure out a way to deal with that population,” he says.
And … Medicare
The other entitlement program facing abrupt change is Medicare, typically considered the third rail of American politics.
“This is the hot political moment,” Ms. Hoffman says. “This is the point where the Republicans think they can tick off their wish list. For many Republicans, this kind of entitlement program is the opposite of what they believe in.”
Though Mr. Trump has said before he would not alter Medicare, he remained quiet on this point in the aftermath of the election. Repealing the ACA would affect Medicare by potentially reopening the Part D prescription drug doughnut hole and eliminating some of the savings provisions in the law. In fact, the CBO estimates Medicare’s direct spending would increase $802 billion between 2016 and 2025.1 Rep. Ryan has talked about privatizing Medicare by offering seniors who rely on it vouchers to apply toward private insurance.
“At the highest level, it’s moving Medicare from a defined benefit to a defined contribution program,” Ms. Hoffman says. “It shifts financial risk from the federal government onto beneficiaries. If Medicare spending continues to grow faster than the rest of the economy, Medicare beneficiaries will pay more and more.”
Seniors may also find themselves rationing or skimping on care.
Despite Rep. Ryan’s statements to the contrary, Medicare is not broken because of the ACA, Ms. Hoffman says. Its solvency has been prolonged, and though the reasons are not clear, Medicare spending has slowed since the passage of the ACA.6
MACRA launch
Another key factor in the health care policy landscape is MACRA, the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act, which fundamentally shifts the way the government administrates and reimburses physicians for health care. MACRA begins in 2017. Dr. Greeno is concerned that changes to the ACA will impact the testing of payment models CMS is testing.
“There are hundreds of hospitals and thousands of physicians already invested in different models, so I don’t expect anybody has any desire to pull the rug from under physicians who are testing alternative payment models [APMs],” he says. “MACRA was passed on a strong bipartisan vote, and it created an APM track. Obviously, Congress intended APM models to continue to expand.”
Dr. Greeno says hospitalists are helping “shape these models,” working with the CMS and the Physician-Focused Payment Model Technical Advisory Committee (PTAC) “to ensure physicians participate in APMs and feel engaged rather than being a worker in a model someone else controls.”
On the campaign trail, Mr. Trump spoke of importing pharmaceuticals from overseas in an effort to control high prices. This policy is no longer part of his online plan. He also proposes allowing the sale of health insurance across state lines.
“It would be giving enrollees in states with stricter regulations the opportunity to circumvent to a looser state, which undermines the state with the stricter regulations,” Dr. Eibner says. “That would really create winners and losers. People who are healthy can buy a policy in a state with looser regulations, and their costs would likely fall. But someone sicker and older, it would be harder.”
Ms. Hoffman defines such a plan as a “race to the bottom.” Without well-established networks of physicians and hospitals, startup costs in new states are prohibitive, and many insurers may not wish to compete across state lines, she adds.
Repeal of the ACA could also limit some of the health benefits it required of plans on the individual market. For example, policymakers might be allowed to strip the contraceptive coverage regulation, which provides for free birth control.
“The reality is a lot of things changing in health care now were changing before the Affordable Care Act passed – PQRS, value-based purchasing, hospital-acquired infections,” Dr. Greeno says. “MACRA will continue the journey away from fee-for-service toward outcome-based models.”
At such a pivotal time, he strongly encourages hospitalists to join SHM if they are not already members and to get involved in SHM’s Grassroots Network.
“For a society of our age – young – and size, we’ve been tremendously impactful in helping with delivery system reform,” Dr. Greeno says. “I think it’s because we’re supporting change, not trying to stop it. We just want it to be intelligent change.”
He also is “convinced” hospitalists will be “critical to the redesign of the health care system. Since we are going to be taking care of the majority of hospitalized adult patients in hospitals, hospitalists want to have our say.”
Kelly April Tyrrell is a freelance writer in Madison, Wis.
References
1. Eibner C. Donald Trump’s health care reform proposals: Anticipated effects on insurance coverage, out-of-pocket costs, and the federal deficit. The Commonweath Fund website. Available at: http://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2016/sep/trump-presidential-health-care-proposal. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
2. Budgetary and economic effects of repealing the Affordable Care Act. Congressional Budget Office website. Available at: https://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/114th-congress-2015-2016/reports/50252-Effects_of_ACA_Repeal.pdf. Accessed Nov. 15, 2016.
3. Our vision for a confident America. A Better Way website. Available at: http://abetterway.speaker.gov. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
4. Pollitz K. High-risk pools for uninsurable individuals. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Available at: http://kff.org/health-reform/issue-brief/high-risk-pools-for-uninsurable-individuals/. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
5. How accessible is individual health insurance for consumers in less-than-ideal health? Kaiser Family Foundation website. Available at: https://kaiserfamilyfoundation.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/how-accessible-is-individual-health-insurance-for-consumer-in-less-than-perfect-health-report.pdf. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
6. The Affordable Care Act and Medicare. The Commonwealth Fund website. Available at: http://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/fund-reports/2015/jun/medicare-affordable-care-act Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
The New Year brings new leadership in the United States, with President-elect Donald Trump taking office later this month. With a Republican-controlled Congress, party leaders have the opportunity to shape the nation’s policies around conservative ideals. This includes health care.
Since the Affordable Care Act (ACA) was passed in 2010, Republicans have vowed to repeal and replace it. This could be their opportunity.
However, “there is no clear coalescence around specific policy reforms that would replace the Affordable Care Act,” says Christine Eibner, PhD, a senior economist at Rand and a professor at the Pardee Rand Graduate School.
As a candidate, Trump did little to advance policy ideas around health care. Meanwhile, House Speaker Paul Ryan (R-Wis.) and others have, over the years, proposed reforms with which Trump may or may not agree.
“The Republicans now have a hard issue in their hands,” says Allison Hoffman, JD, professor of law at UCLA School of Law and an expert on health care law and policy. “It was hard before the Affordable Care Act, and it will be hard after. There is not an easy solution.”
By 2016, the ACA had expanded health coverage to 20 million people through Medicaid and private insurance on health care marketplaces. It extended the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance Trust Fund. It accelerated the pace of delivery system and payment reform through creation of the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation.
The law, however, has not been without its challenges.
“It was a strong achievement to get 20 million people insured, but it’s not clear that it bent the cost curve,” says Dr. Eibner. “There are high premiums on the individual market and still 31 million people without coverage. There is still opportunity to improve.”
Where we stand January 2017
Whether the Republicans can or will repeal the ACA in its entirety and improve it remains unknown. But, the experts say, the landmark law has left its mark on the American health care system.
“Everyone is complaining about the uncertainty created by the election, but we have been dealing with a highly uncertain environment for many years,” says Ron Greeno, MD, FCCP, MHM, senior advisor for medical affairs at TeamHealth, chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee, and SHM president-elect. “There will be changes, but things were going to change no matter the outcome of the election. It continues to require tolerance for change and tolerance for uncertainty.”
In an analysis for the Commonwealth Fund, Dr. Eibner investigated the economic implications of aspects of Trump’s plans as a candidate. Using a computer model that incorporates economic theory and data to simulate the effects of health policy changes, Dr. Eibner found that Trump’s plans (full repeal alone or repeal with tax deductions for health care premiums, Medicaid block grants, or selling health insurance across state lines) would increase the number of uninsured people by 16 million to 25 million, disproportionately impact low-income and sicker patients, expose individual market enrollees to higher out-of-pocket costs, and increase the federal deficit by $0.5 billion to $41 billion.1 The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates full repeal could increase the federal deficit by $137 billion to $353 billion by 2025.2 Rep. Ryan’s plan, A Better Way, proposes providing people more control over their health care, giving tax credits instead of subsidies for premiums, capping the employer-sponsored health insurance tax exclusion, and expanding use of health savings accounts.3 However, Rep. Ryan’s plan “doesn’t reduce the cost of health care. It puts more onus on individuals, and their costs go up,” Ms. Hoffman says. “The weight of that will be more on people who have preexisting conditions.”
Joshua Lenchus, DO, RPh, FACP, SFHM, a member of SHM’s Public Policy Committee and hospitalist at the University of Miami/Jackson Memorial Hospital in Florida, is no fan of entitlement programs like Medicaid but says, “The safety-net hospital where I work would rather have people covered with something than nothing.”
Dr. Lenchus is optimistic that economic reforms under Trump will lead to more jobs, increasing the number of people covered by employer plans. “The economy drives health care reform,” he says. “He has to up his ante now and show people that he can stimulate job growth in this country so we don’t have this middle class that is continuously squeezed.”
Dr. Greeno and Ms. Hoffman, who is also a faculty associate at the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research and vice chair of the Insurance Law Section of the Association of American Law Schools, suggest hospitalists get involved as rules are being shaped and written.
“We want to help reform the delivery system, and we want it to be done right and to be done fairly. We want to have say in how our patients are treated,” Dr. Greeno says.
Key provisions: A delicate balance
Many people equate the ACA with the individual mandate, which requires nearly all Americans to purchase health insurance or pay a fine. The federal government provides subsidies to enrollees between 138% and 400% of the federal poverty level so their out-of-pocket costs never exceed a defined threshold even if premiums go up. These could be on the chopping block.
“The last bill Congress passed to repeal the Affordable Care Act, which Obama vetoed, repealed the individual mandate and subsidies for people to buy insurance,” Ms. Hoffman says. “If they do repeal it, private insurance through the exchanges will crumble.”
Mr. Trump’s tax deductions to offset premium costs are based on income, making them more generous for higher-income earners than low-income ones, Hoffman adds.
As a result, she says, people may choose high-deductible plans and face high out-of-pocket costs if they do seek care.
“It’s asking individuals to save by deciding how they’re going to ration care, where someone says they’re not going to go to the doctor today or fill a prescription drug they need,” Ms. Hoffman says.
Meanwhile, Mr. Trump has said he would like to keep the provision of the ACA that bans insurers from denying individuals with preexisting conditions. This, experts agree, may not be possible if other parts of the law are repealed and not replaced with similar protections for insurers.
“If you try to keep the rules about not including preexisting conditions and get rid of subsidies and the individual mandate, it just won’t work,” Ms. Hoffman says. “You end up with extraordinarily expensive health insurance.”
Rep. Ryan’s plan would prohibit insurers from denying patients with preexisting conditions but only if patients maintain continuous coverage, with a single open-enrollment period. He has promised to provide at least $25 billion in federal funding for state high-risk pools.
Prior to the passage of the ACA, 35 states offered high-risk pools to people excluded from the individual market. The Kaiser Family Foundation shows the net annual losses in these states averaged $5,510 per enrollee in 2011. Premiums ranged from 100% to 200% higher than non–high-risk group coverage. Government subsidies to cover losses amounted to $1 billion in each state.4
Meanwhile, both Mr. Trump and Rep. Ryan have proposed profound changes for Medicaid. Dr. Greeno calls this a “massive political challenge” unless they can provide an alternative way to cover people who currently rely on the federal-state entitlement, as well as those who gained coverage through ACA expansion. Currently, 70 million people are enrolled in Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program.5 Through Mr. Trump’s suggested block grants, states would receive a fixed amount of money to administer their program with increased flexibility. Rep. Ryan’s plan calls for enrollment caps that would distribute a dollar amount to each participant in the program with no limit on the number of enrollees. Either would be adjusted for inflation.
States could implement work requirements for beneficiaries or ask them to pay a small amount toward their premiums. Expansion states could also lower the Medicaid threshold below 138%.
Some states will struggle to provide for all their enrollees, Ms. Hoffman says, particularly since health spending generally outpaces inflation. Dr. Lenchus is more optimistic. “I believe states that didn’t expand Medicaid, one way or another, will figure out a way to deal with that population,” he says.
And … Medicare
The other entitlement program facing abrupt change is Medicare, typically considered the third rail of American politics.
“This is the hot political moment,” Ms. Hoffman says. “This is the point where the Republicans think they can tick off their wish list. For many Republicans, this kind of entitlement program is the opposite of what they believe in.”
Though Mr. Trump has said before he would not alter Medicare, he remained quiet on this point in the aftermath of the election. Repealing the ACA would affect Medicare by potentially reopening the Part D prescription drug doughnut hole and eliminating some of the savings provisions in the law. In fact, the CBO estimates Medicare’s direct spending would increase $802 billion between 2016 and 2025.1 Rep. Ryan has talked about privatizing Medicare by offering seniors who rely on it vouchers to apply toward private insurance.
“At the highest level, it’s moving Medicare from a defined benefit to a defined contribution program,” Ms. Hoffman says. “It shifts financial risk from the federal government onto beneficiaries. If Medicare spending continues to grow faster than the rest of the economy, Medicare beneficiaries will pay more and more.”
Seniors may also find themselves rationing or skimping on care.
Despite Rep. Ryan’s statements to the contrary, Medicare is not broken because of the ACA, Ms. Hoffman says. Its solvency has been prolonged, and though the reasons are not clear, Medicare spending has slowed since the passage of the ACA.6
MACRA launch
Another key factor in the health care policy landscape is MACRA, the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act, which fundamentally shifts the way the government administrates and reimburses physicians for health care. MACRA begins in 2017. Dr. Greeno is concerned that changes to the ACA will impact the testing of payment models CMS is testing.
“There are hundreds of hospitals and thousands of physicians already invested in different models, so I don’t expect anybody has any desire to pull the rug from under physicians who are testing alternative payment models [APMs],” he says. “MACRA was passed on a strong bipartisan vote, and it created an APM track. Obviously, Congress intended APM models to continue to expand.”
Dr. Greeno says hospitalists are helping “shape these models,” working with the CMS and the Physician-Focused Payment Model Technical Advisory Committee (PTAC) “to ensure physicians participate in APMs and feel engaged rather than being a worker in a model someone else controls.”
On the campaign trail, Mr. Trump spoke of importing pharmaceuticals from overseas in an effort to control high prices. This policy is no longer part of his online plan. He also proposes allowing the sale of health insurance across state lines.
“It would be giving enrollees in states with stricter regulations the opportunity to circumvent to a looser state, which undermines the state with the stricter regulations,” Dr. Eibner says. “That would really create winners and losers. People who are healthy can buy a policy in a state with looser regulations, and their costs would likely fall. But someone sicker and older, it would be harder.”
Ms. Hoffman defines such a plan as a “race to the bottom.” Without well-established networks of physicians and hospitals, startup costs in new states are prohibitive, and many insurers may not wish to compete across state lines, she adds.
Repeal of the ACA could also limit some of the health benefits it required of plans on the individual market. For example, policymakers might be allowed to strip the contraceptive coverage regulation, which provides for free birth control.
“The reality is a lot of things changing in health care now were changing before the Affordable Care Act passed – PQRS, value-based purchasing, hospital-acquired infections,” Dr. Greeno says. “MACRA will continue the journey away from fee-for-service toward outcome-based models.”
At such a pivotal time, he strongly encourages hospitalists to join SHM if they are not already members and to get involved in SHM’s Grassroots Network.
“For a society of our age – young – and size, we’ve been tremendously impactful in helping with delivery system reform,” Dr. Greeno says. “I think it’s because we’re supporting change, not trying to stop it. We just want it to be intelligent change.”
He also is “convinced” hospitalists will be “critical to the redesign of the health care system. Since we are going to be taking care of the majority of hospitalized adult patients in hospitals, hospitalists want to have our say.”
Kelly April Tyrrell is a freelance writer in Madison, Wis.
References
1. Eibner C. Donald Trump’s health care reform proposals: Anticipated effects on insurance coverage, out-of-pocket costs, and the federal deficit. The Commonweath Fund website. Available at: http://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2016/sep/trump-presidential-health-care-proposal. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
2. Budgetary and economic effects of repealing the Affordable Care Act. Congressional Budget Office website. Available at: https://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/114th-congress-2015-2016/reports/50252-Effects_of_ACA_Repeal.pdf. Accessed Nov. 15, 2016.
3. Our vision for a confident America. A Better Way website. Available at: http://abetterway.speaker.gov. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
4. Pollitz K. High-risk pools for uninsurable individuals. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Available at: http://kff.org/health-reform/issue-brief/high-risk-pools-for-uninsurable-individuals/. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
5. How accessible is individual health insurance for consumers in less-than-ideal health? Kaiser Family Foundation website. Available at: https://kaiserfamilyfoundation.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/how-accessible-is-individual-health-insurance-for-consumer-in-less-than-perfect-health-report.pdf. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
6. The Affordable Care Act and Medicare. The Commonwealth Fund website. Available at: http://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/fund-reports/2015/jun/medicare-affordable-care-act Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
The New Year brings new leadership in the United States, with President-elect Donald Trump taking office later this month. With a Republican-controlled Congress, party leaders have the opportunity to shape the nation’s policies around conservative ideals. This includes health care.
Since the Affordable Care Act (ACA) was passed in 2010, Republicans have vowed to repeal and replace it. This could be their opportunity.
However, “there is no clear coalescence around specific policy reforms that would replace the Affordable Care Act,” says Christine Eibner, PhD, a senior economist at Rand and a professor at the Pardee Rand Graduate School.
As a candidate, Trump did little to advance policy ideas around health care. Meanwhile, House Speaker Paul Ryan (R-Wis.) and others have, over the years, proposed reforms with which Trump may or may not agree.
“The Republicans now have a hard issue in their hands,” says Allison Hoffman, JD, professor of law at UCLA School of Law and an expert on health care law and policy. “It was hard before the Affordable Care Act, and it will be hard after. There is not an easy solution.”
By 2016, the ACA had expanded health coverage to 20 million people through Medicaid and private insurance on health care marketplaces. It extended the solvency of the Medicare Hospital Insurance Trust Fund. It accelerated the pace of delivery system and payment reform through creation of the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation.
The law, however, has not been without its challenges.
“It was a strong achievement to get 20 million people insured, but it’s not clear that it bent the cost curve,” says Dr. Eibner. “There are high premiums on the individual market and still 31 million people without coverage. There is still opportunity to improve.”
Where we stand January 2017
Whether the Republicans can or will repeal the ACA in its entirety and improve it remains unknown. But, the experts say, the landmark law has left its mark on the American health care system.
“Everyone is complaining about the uncertainty created by the election, but we have been dealing with a highly uncertain environment for many years,” says Ron Greeno, MD, FCCP, MHM, senior advisor for medical affairs at TeamHealth, chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee, and SHM president-elect. “There will be changes, but things were going to change no matter the outcome of the election. It continues to require tolerance for change and tolerance for uncertainty.”
In an analysis for the Commonwealth Fund, Dr. Eibner investigated the economic implications of aspects of Trump’s plans as a candidate. Using a computer model that incorporates economic theory and data to simulate the effects of health policy changes, Dr. Eibner found that Trump’s plans (full repeal alone or repeal with tax deductions for health care premiums, Medicaid block grants, or selling health insurance across state lines) would increase the number of uninsured people by 16 million to 25 million, disproportionately impact low-income and sicker patients, expose individual market enrollees to higher out-of-pocket costs, and increase the federal deficit by $0.5 billion to $41 billion.1 The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates full repeal could increase the federal deficit by $137 billion to $353 billion by 2025.2 Rep. Ryan’s plan, A Better Way, proposes providing people more control over their health care, giving tax credits instead of subsidies for premiums, capping the employer-sponsored health insurance tax exclusion, and expanding use of health savings accounts.3 However, Rep. Ryan’s plan “doesn’t reduce the cost of health care. It puts more onus on individuals, and their costs go up,” Ms. Hoffman says. “The weight of that will be more on people who have preexisting conditions.”
Joshua Lenchus, DO, RPh, FACP, SFHM, a member of SHM’s Public Policy Committee and hospitalist at the University of Miami/Jackson Memorial Hospital in Florida, is no fan of entitlement programs like Medicaid but says, “The safety-net hospital where I work would rather have people covered with something than nothing.”
Dr. Lenchus is optimistic that economic reforms under Trump will lead to more jobs, increasing the number of people covered by employer plans. “The economy drives health care reform,” he says. “He has to up his ante now and show people that he can stimulate job growth in this country so we don’t have this middle class that is continuously squeezed.”
Dr. Greeno and Ms. Hoffman, who is also a faculty associate at the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research and vice chair of the Insurance Law Section of the Association of American Law Schools, suggest hospitalists get involved as rules are being shaped and written.
“We want to help reform the delivery system, and we want it to be done right and to be done fairly. We want to have say in how our patients are treated,” Dr. Greeno says.
Key provisions: A delicate balance
Many people equate the ACA with the individual mandate, which requires nearly all Americans to purchase health insurance or pay a fine. The federal government provides subsidies to enrollees between 138% and 400% of the federal poverty level so their out-of-pocket costs never exceed a defined threshold even if premiums go up. These could be on the chopping block.
“The last bill Congress passed to repeal the Affordable Care Act, which Obama vetoed, repealed the individual mandate and subsidies for people to buy insurance,” Ms. Hoffman says. “If they do repeal it, private insurance through the exchanges will crumble.”
Mr. Trump’s tax deductions to offset premium costs are based on income, making them more generous for higher-income earners than low-income ones, Hoffman adds.
As a result, she says, people may choose high-deductible plans and face high out-of-pocket costs if they do seek care.
“It’s asking individuals to save by deciding how they’re going to ration care, where someone says they’re not going to go to the doctor today or fill a prescription drug they need,” Ms. Hoffman says.
Meanwhile, Mr. Trump has said he would like to keep the provision of the ACA that bans insurers from denying individuals with preexisting conditions. This, experts agree, may not be possible if other parts of the law are repealed and not replaced with similar protections for insurers.
“If you try to keep the rules about not including preexisting conditions and get rid of subsidies and the individual mandate, it just won’t work,” Ms. Hoffman says. “You end up with extraordinarily expensive health insurance.”
Rep. Ryan’s plan would prohibit insurers from denying patients with preexisting conditions but only if patients maintain continuous coverage, with a single open-enrollment period. He has promised to provide at least $25 billion in federal funding for state high-risk pools.
Prior to the passage of the ACA, 35 states offered high-risk pools to people excluded from the individual market. The Kaiser Family Foundation shows the net annual losses in these states averaged $5,510 per enrollee in 2011. Premiums ranged from 100% to 200% higher than non–high-risk group coverage. Government subsidies to cover losses amounted to $1 billion in each state.4
Meanwhile, both Mr. Trump and Rep. Ryan have proposed profound changes for Medicaid. Dr. Greeno calls this a “massive political challenge” unless they can provide an alternative way to cover people who currently rely on the federal-state entitlement, as well as those who gained coverage through ACA expansion. Currently, 70 million people are enrolled in Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program.5 Through Mr. Trump’s suggested block grants, states would receive a fixed amount of money to administer their program with increased flexibility. Rep. Ryan’s plan calls for enrollment caps that would distribute a dollar amount to each participant in the program with no limit on the number of enrollees. Either would be adjusted for inflation.
States could implement work requirements for beneficiaries or ask them to pay a small amount toward their premiums. Expansion states could also lower the Medicaid threshold below 138%.
Some states will struggle to provide for all their enrollees, Ms. Hoffman says, particularly since health spending generally outpaces inflation. Dr. Lenchus is more optimistic. “I believe states that didn’t expand Medicaid, one way or another, will figure out a way to deal with that population,” he says.
And … Medicare
The other entitlement program facing abrupt change is Medicare, typically considered the third rail of American politics.
“This is the hot political moment,” Ms. Hoffman says. “This is the point where the Republicans think they can tick off their wish list. For many Republicans, this kind of entitlement program is the opposite of what they believe in.”
Though Mr. Trump has said before he would not alter Medicare, he remained quiet on this point in the aftermath of the election. Repealing the ACA would affect Medicare by potentially reopening the Part D prescription drug doughnut hole and eliminating some of the savings provisions in the law. In fact, the CBO estimates Medicare’s direct spending would increase $802 billion between 2016 and 2025.1 Rep. Ryan has talked about privatizing Medicare by offering seniors who rely on it vouchers to apply toward private insurance.
“At the highest level, it’s moving Medicare from a defined benefit to a defined contribution program,” Ms. Hoffman says. “It shifts financial risk from the federal government onto beneficiaries. If Medicare spending continues to grow faster than the rest of the economy, Medicare beneficiaries will pay more and more.”
Seniors may also find themselves rationing or skimping on care.
Despite Rep. Ryan’s statements to the contrary, Medicare is not broken because of the ACA, Ms. Hoffman says. Its solvency has been prolonged, and though the reasons are not clear, Medicare spending has slowed since the passage of the ACA.6
MACRA launch
Another key factor in the health care policy landscape is MACRA, the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act, which fundamentally shifts the way the government administrates and reimburses physicians for health care. MACRA begins in 2017. Dr. Greeno is concerned that changes to the ACA will impact the testing of payment models CMS is testing.
“There are hundreds of hospitals and thousands of physicians already invested in different models, so I don’t expect anybody has any desire to pull the rug from under physicians who are testing alternative payment models [APMs],” he says. “MACRA was passed on a strong bipartisan vote, and it created an APM track. Obviously, Congress intended APM models to continue to expand.”
Dr. Greeno says hospitalists are helping “shape these models,” working with the CMS and the Physician-Focused Payment Model Technical Advisory Committee (PTAC) “to ensure physicians participate in APMs and feel engaged rather than being a worker in a model someone else controls.”
On the campaign trail, Mr. Trump spoke of importing pharmaceuticals from overseas in an effort to control high prices. This policy is no longer part of his online plan. He also proposes allowing the sale of health insurance across state lines.
“It would be giving enrollees in states with stricter regulations the opportunity to circumvent to a looser state, which undermines the state with the stricter regulations,” Dr. Eibner says. “That would really create winners and losers. People who are healthy can buy a policy in a state with looser regulations, and their costs would likely fall. But someone sicker and older, it would be harder.”
Ms. Hoffman defines such a plan as a “race to the bottom.” Without well-established networks of physicians and hospitals, startup costs in new states are prohibitive, and many insurers may not wish to compete across state lines, she adds.
Repeal of the ACA could also limit some of the health benefits it required of plans on the individual market. For example, policymakers might be allowed to strip the contraceptive coverage regulation, which provides for free birth control.
“The reality is a lot of things changing in health care now were changing before the Affordable Care Act passed – PQRS, value-based purchasing, hospital-acquired infections,” Dr. Greeno says. “MACRA will continue the journey away from fee-for-service toward outcome-based models.”
At such a pivotal time, he strongly encourages hospitalists to join SHM if they are not already members and to get involved in SHM’s Grassroots Network.
“For a society of our age – young – and size, we’ve been tremendously impactful in helping with delivery system reform,” Dr. Greeno says. “I think it’s because we’re supporting change, not trying to stop it. We just want it to be intelligent change.”
He also is “convinced” hospitalists will be “critical to the redesign of the health care system. Since we are going to be taking care of the majority of hospitalized adult patients in hospitals, hospitalists want to have our say.”
Kelly April Tyrrell is a freelance writer in Madison, Wis.
References
1. Eibner C. Donald Trump’s health care reform proposals: Anticipated effects on insurance coverage, out-of-pocket costs, and the federal deficit. The Commonweath Fund website. Available at: http://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2016/sep/trump-presidential-health-care-proposal. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
2. Budgetary and economic effects of repealing the Affordable Care Act. Congressional Budget Office website. Available at: https://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/114th-congress-2015-2016/reports/50252-Effects_of_ACA_Repeal.pdf. Accessed Nov. 15, 2016.
3. Our vision for a confident America. A Better Way website. Available at: http://abetterway.speaker.gov. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
4. Pollitz K. High-risk pools for uninsurable individuals. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Available at: http://kff.org/health-reform/issue-brief/high-risk-pools-for-uninsurable-individuals/. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
5. How accessible is individual health insurance for consumers in less-than-ideal health? Kaiser Family Foundation website. Available at: https://kaiserfamilyfoundation.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/how-accessible-is-individual-health-insurance-for-consumer-in-less-than-perfect-health-report.pdf. Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
6. The Affordable Care Act and Medicare. The Commonwealth Fund website. Available at: http://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/fund-reports/2015/jun/medicare-affordable-care-act Accessed Nov. 17, 2016.
Effective hospitalist roles for NPs, PAs
I’m often asked about effective roles for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs), collectively known as advanced practice clinicians (APCs). My first response is always the same: They have much to contribute and can be effective members of hospitalist groups. Most hospital medicine groups (HMGs) should think about having them in their staffing mix if they don’t already.
Yet despite all that NPs/PAs can offer, my experience is that many (even most) hospitalist groups fail to develop roles that optimize their APCs’ skills.
An October 2016 study in the Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management adds additional data to help think about this issue. You may have seen the study mentioned in several news articles and blogs. Most summarized the study along the lines of “using high levels of PA staffing results in lower hospital costs per case.” Framing it this way is awfully misleading, so I’ll go a little deeper here.
Study context
The study, “A Comparison of Conventional and Expanded Physician Assistant Hospitalist Staffing Models at a Community Hospital,” is a retrospective analysis of performance measures from two hospitalist groups at Anne Arundel Medical Center (AAMC) in Annapolis, Md.1 One HMG is employed by the hospital. The other, called MDICS, is a private company that contracts with AAMC as well as approximately 13 other hospitals and 40 rehabilitation facilities. Tim Capstack, MD, is the AAMC medical director for MDICS and lead author of the study (representing a potential conflict of interest acknowledged in the article). Barry Meisenberg, MD, is a coauthor, a hospitalist in the AAMC-employed group, and chair for quality improvement and health care systems research at AAMC.
Tim told me by phone that both groups have practiced at AAMC for more than 10 years and enjoy a collegial relationship. Both groups employ PAs and pair them with a single physician in a dyad arrangement each day. Tim’s MDICS group, the “expanded PA” group, staffs each day shift with three physicians and three PAs, compared with the nine physicians and two PAs in the hospital-employed “conventional” group. The MDICS PAs are responsible for more patients each day than their conventional-group counterparts and, during the January 2012 to July 2013 study period, averaged 14.2 patients versus 8.3, respectively.
Over the course of the study, PAs in the expanded PA group saw and billed 36% of patient visits independently, compared with 5.9% for the conventional group.
Notable study findings
I think the main value of this study is in showing that the expanded PA group had rates of readmission, inpatient mortality, length of stay, and consultant use that weren’t statistically different from the conventional group.
The workloads and years of experience of doctors and PAs in each group were similar. And while there were some differences in the patients each group cared for, they seem unlikely to have a significant influence on outcomes. Clearly, there are many unmeasured variables (e.g., culture, morale, and leadership) in each group that could have influenced the outcomes, so this one study at one hospital doesn’t provide a definitive answer about appropriate APC staffing levels. However, it didn’t uncover big differences in the measured outcomes.
And this study did show that higher levels of PA staffing were associated with lower hospital charges per case. Although the difference was a modest 3%, it was statistically significant (P less than .001). I’m skeptical there is causation here; this more likely is just correlation.
It would be great to see a larger study of this.
Information applications
So does this study support the idea that HMGs can or should increase APC staffing and workload significantly to realize lower hospital cost per case and not harm patient outcomes? Not so fast!
This study only compared two hospitalist groups at one hospital. It’s probably not very generalizable.
And as described in the paper, and stressed by Tim talking with me by phone, the outcomes of their expanded PA model likely have a lot to do with their very careful recruiting and screening of experienced PAs before hiring them, not to mention a lengthy and deliberate on-boarding process (summarized in the article) to support their ability to perform well. Groups that are not as thoughtful and deliberate in how they hire and position APCs to contribute to the practice may not perform as well.
Why study only PAs? What about NPs? Tim told me that his group is agnostic regarding the training background of the APCs they hire; he suspects an identical study with NPs rather than PAs in each hospitalist group would probably yield very similar results. I see this the same way. Although there are differences in background and training between NPs and PAs, I think personal traits like years of experience in various health care settings and the ability to work efficiently are more important than training background.
A practical approach
Any group who thinks this study is evidence that adding more APCs and having them manage a higher number of patients relatively independently will go well in any setting is mistaken. But it does offer a story of one place where, with careful planning and execution, it went OK.
In my view, the real take-home message is to think carefully to ensure any APCs in your group have professionally satisfying roles that position them to contribute effectively. While common, I think configuring APCs and physicians as rounding dyads often ends up underperforming and not working out well because of inefficiency. When well executed, as is apparently the case in this study, it can be fine. But my experience is that positioning APCs to assume primary responsibility for some clinical activities, such as covering the observation unit or serving as an evening admitter/cross-cover provider (all with appropriate physician collaboration and backup), more reliably turns out well.
Reference
Capstack TM, Seguija C, Vollono LM, Moser JD, Meisenberg BR, Michtalik HJ. A comparison of conventional and expanded physician assistant hospitalist staffing models at a community hospital. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2016;23(10):455-61.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is co-founder and past president of SHM and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at [email protected].
I’m often asked about effective roles for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs), collectively known as advanced practice clinicians (APCs). My first response is always the same: They have much to contribute and can be effective members of hospitalist groups. Most hospital medicine groups (HMGs) should think about having them in their staffing mix if they don’t already.
Yet despite all that NPs/PAs can offer, my experience is that many (even most) hospitalist groups fail to develop roles that optimize their APCs’ skills.
An October 2016 study in the Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management adds additional data to help think about this issue. You may have seen the study mentioned in several news articles and blogs. Most summarized the study along the lines of “using high levels of PA staffing results in lower hospital costs per case.” Framing it this way is awfully misleading, so I’ll go a little deeper here.
Study context
The study, “A Comparison of Conventional and Expanded Physician Assistant Hospitalist Staffing Models at a Community Hospital,” is a retrospective analysis of performance measures from two hospitalist groups at Anne Arundel Medical Center (AAMC) in Annapolis, Md.1 One HMG is employed by the hospital. The other, called MDICS, is a private company that contracts with AAMC as well as approximately 13 other hospitals and 40 rehabilitation facilities. Tim Capstack, MD, is the AAMC medical director for MDICS and lead author of the study (representing a potential conflict of interest acknowledged in the article). Barry Meisenberg, MD, is a coauthor, a hospitalist in the AAMC-employed group, and chair for quality improvement and health care systems research at AAMC.
Tim told me by phone that both groups have practiced at AAMC for more than 10 years and enjoy a collegial relationship. Both groups employ PAs and pair them with a single physician in a dyad arrangement each day. Tim’s MDICS group, the “expanded PA” group, staffs each day shift with three physicians and three PAs, compared with the nine physicians and two PAs in the hospital-employed “conventional” group. The MDICS PAs are responsible for more patients each day than their conventional-group counterparts and, during the January 2012 to July 2013 study period, averaged 14.2 patients versus 8.3, respectively.
Over the course of the study, PAs in the expanded PA group saw and billed 36% of patient visits independently, compared with 5.9% for the conventional group.
Notable study findings
I think the main value of this study is in showing that the expanded PA group had rates of readmission, inpatient mortality, length of stay, and consultant use that weren’t statistically different from the conventional group.
The workloads and years of experience of doctors and PAs in each group were similar. And while there were some differences in the patients each group cared for, they seem unlikely to have a significant influence on outcomes. Clearly, there are many unmeasured variables (e.g., culture, morale, and leadership) in each group that could have influenced the outcomes, so this one study at one hospital doesn’t provide a definitive answer about appropriate APC staffing levels. However, it didn’t uncover big differences in the measured outcomes.
And this study did show that higher levels of PA staffing were associated with lower hospital charges per case. Although the difference was a modest 3%, it was statistically significant (P less than .001). I’m skeptical there is causation here; this more likely is just correlation.
It would be great to see a larger study of this.
Information applications
So does this study support the idea that HMGs can or should increase APC staffing and workload significantly to realize lower hospital cost per case and not harm patient outcomes? Not so fast!
This study only compared two hospitalist groups at one hospital. It’s probably not very generalizable.
And as described in the paper, and stressed by Tim talking with me by phone, the outcomes of their expanded PA model likely have a lot to do with their very careful recruiting and screening of experienced PAs before hiring them, not to mention a lengthy and deliberate on-boarding process (summarized in the article) to support their ability to perform well. Groups that are not as thoughtful and deliberate in how they hire and position APCs to contribute to the practice may not perform as well.
Why study only PAs? What about NPs? Tim told me that his group is agnostic regarding the training background of the APCs they hire; he suspects an identical study with NPs rather than PAs in each hospitalist group would probably yield very similar results. I see this the same way. Although there are differences in background and training between NPs and PAs, I think personal traits like years of experience in various health care settings and the ability to work efficiently are more important than training background.
A practical approach
Any group who thinks this study is evidence that adding more APCs and having them manage a higher number of patients relatively independently will go well in any setting is mistaken. But it does offer a story of one place where, with careful planning and execution, it went OK.
In my view, the real take-home message is to think carefully to ensure any APCs in your group have professionally satisfying roles that position them to contribute effectively. While common, I think configuring APCs and physicians as rounding dyads often ends up underperforming and not working out well because of inefficiency. When well executed, as is apparently the case in this study, it can be fine. But my experience is that positioning APCs to assume primary responsibility for some clinical activities, such as covering the observation unit or serving as an evening admitter/cross-cover provider (all with appropriate physician collaboration and backup), more reliably turns out well.
Reference
Capstack TM, Seguija C, Vollono LM, Moser JD, Meisenberg BR, Michtalik HJ. A comparison of conventional and expanded physician assistant hospitalist staffing models at a community hospital. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2016;23(10):455-61.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is co-founder and past president of SHM and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at [email protected].
I’m often asked about effective roles for nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs), collectively known as advanced practice clinicians (APCs). My first response is always the same: They have much to contribute and can be effective members of hospitalist groups. Most hospital medicine groups (HMGs) should think about having them in their staffing mix if they don’t already.
Yet despite all that NPs/PAs can offer, my experience is that many (even most) hospitalist groups fail to develop roles that optimize their APCs’ skills.
An October 2016 study in the Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management adds additional data to help think about this issue. You may have seen the study mentioned in several news articles and blogs. Most summarized the study along the lines of “using high levels of PA staffing results in lower hospital costs per case.” Framing it this way is awfully misleading, so I’ll go a little deeper here.
Study context
The study, “A Comparison of Conventional and Expanded Physician Assistant Hospitalist Staffing Models at a Community Hospital,” is a retrospective analysis of performance measures from two hospitalist groups at Anne Arundel Medical Center (AAMC) in Annapolis, Md.1 One HMG is employed by the hospital. The other, called MDICS, is a private company that contracts with AAMC as well as approximately 13 other hospitals and 40 rehabilitation facilities. Tim Capstack, MD, is the AAMC medical director for MDICS and lead author of the study (representing a potential conflict of interest acknowledged in the article). Barry Meisenberg, MD, is a coauthor, a hospitalist in the AAMC-employed group, and chair for quality improvement and health care systems research at AAMC.
Tim told me by phone that both groups have practiced at AAMC for more than 10 years and enjoy a collegial relationship. Both groups employ PAs and pair them with a single physician in a dyad arrangement each day. Tim’s MDICS group, the “expanded PA” group, staffs each day shift with three physicians and three PAs, compared with the nine physicians and two PAs in the hospital-employed “conventional” group. The MDICS PAs are responsible for more patients each day than their conventional-group counterparts and, during the January 2012 to July 2013 study period, averaged 14.2 patients versus 8.3, respectively.
Over the course of the study, PAs in the expanded PA group saw and billed 36% of patient visits independently, compared with 5.9% for the conventional group.
Notable study findings
I think the main value of this study is in showing that the expanded PA group had rates of readmission, inpatient mortality, length of stay, and consultant use that weren’t statistically different from the conventional group.
The workloads and years of experience of doctors and PAs in each group were similar. And while there were some differences in the patients each group cared for, they seem unlikely to have a significant influence on outcomes. Clearly, there are many unmeasured variables (e.g., culture, morale, and leadership) in each group that could have influenced the outcomes, so this one study at one hospital doesn’t provide a definitive answer about appropriate APC staffing levels. However, it didn’t uncover big differences in the measured outcomes.
And this study did show that higher levels of PA staffing were associated with lower hospital charges per case. Although the difference was a modest 3%, it was statistically significant (P less than .001). I’m skeptical there is causation here; this more likely is just correlation.
It would be great to see a larger study of this.
Information applications
So does this study support the idea that HMGs can or should increase APC staffing and workload significantly to realize lower hospital cost per case and not harm patient outcomes? Not so fast!
This study only compared two hospitalist groups at one hospital. It’s probably not very generalizable.
And as described in the paper, and stressed by Tim talking with me by phone, the outcomes of their expanded PA model likely have a lot to do with their very careful recruiting and screening of experienced PAs before hiring them, not to mention a lengthy and deliberate on-boarding process (summarized in the article) to support their ability to perform well. Groups that are not as thoughtful and deliberate in how they hire and position APCs to contribute to the practice may not perform as well.
Why study only PAs? What about NPs? Tim told me that his group is agnostic regarding the training background of the APCs they hire; he suspects an identical study with NPs rather than PAs in each hospitalist group would probably yield very similar results. I see this the same way. Although there are differences in background and training between NPs and PAs, I think personal traits like years of experience in various health care settings and the ability to work efficiently are more important than training background.
A practical approach
Any group who thinks this study is evidence that adding more APCs and having them manage a higher number of patients relatively independently will go well in any setting is mistaken. But it does offer a story of one place where, with careful planning and execution, it went OK.
In my view, the real take-home message is to think carefully to ensure any APCs in your group have professionally satisfying roles that position them to contribute effectively. While common, I think configuring APCs and physicians as rounding dyads often ends up underperforming and not working out well because of inefficiency. When well executed, as is apparently the case in this study, it can be fine. But my experience is that positioning APCs to assume primary responsibility for some clinical activities, such as covering the observation unit or serving as an evening admitter/cross-cover provider (all with appropriate physician collaboration and backup), more reliably turns out well.
Reference
Capstack TM, Seguija C, Vollono LM, Moser JD, Meisenberg BR, Michtalik HJ. A comparison of conventional and expanded physician assistant hospitalist staffing models at a community hospital. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2016;23(10):455-61.
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988. He is co-founder and past president of SHM and principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants. He is co-director for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. Write to him at [email protected].
Promoting the Health of Healthcare Employees
Provisions in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) encourage hospitals to work with their communities to improve population health. Like so many things, these efforts can and should begin at home—in this case, the hospital itself. Health and wellness programs for healthcare workers need to be emphasized, according to “Health and Wellness Programs for Hospital Employees: Results from a 2015 American Hospital Association Survey.”1
Such efforts allow healthcare workers to lead by example.
“To help create a culture of health, hospitals and health systems can provide leadership, and hospital employees can be role models, for health and wellness in their communities,” according to the report. “Developing health and wellness strategies and programs at hospitals will help establish an environment that provides the support, resources, and incentives for hospital employees to serve as such role models.”
Developing health and wellness programs can also help hospitals achieve the public health goals of the Healthy People 2020 initiative from the Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
To find out how hospitals are doing in this work, the 26-question survey was done in 2010 and again in 2015 and sent to approximately 6,000 hospitals in the United States. Response rate was 15% in 2010 and 18% in 2015. Some of the findings include:
- About the same number of hospitals have a health and wellness program or other initiative(s) for employees (86% in 2010 and 87% in 2015); however, the types of health and wellness programs and benefits that hospitals offer to their employees increased.
- The number of hospitals with 70% to 90% or more of employees participating in health and wellness programs increased from 19% in 2010 to 31% in 2015.
- The number of hospitals offering health and wellness programs to people in the community increased from 19% in 2010 to 66% in 2015.
- The number of hospitals offering incentives for participating in health and wellness programs increased as did the value of incentives, with more hospitals giving $500 or more to employees (7% in 2010 and 29% in 2015).
Reference
- Health Research & Educational Trust. Health and wellness programs for hospital employees: results from a 2015 American Hospital Association survey. Hospitals in Pursuit of Excellence website.
Provisions in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) encourage hospitals to work with their communities to improve population health. Like so many things, these efforts can and should begin at home—in this case, the hospital itself. Health and wellness programs for healthcare workers need to be emphasized, according to “Health and Wellness Programs for Hospital Employees: Results from a 2015 American Hospital Association Survey.”1
Such efforts allow healthcare workers to lead by example.
“To help create a culture of health, hospitals and health systems can provide leadership, and hospital employees can be role models, for health and wellness in their communities,” according to the report. “Developing health and wellness strategies and programs at hospitals will help establish an environment that provides the support, resources, and incentives for hospital employees to serve as such role models.”
Developing health and wellness programs can also help hospitals achieve the public health goals of the Healthy People 2020 initiative from the Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
To find out how hospitals are doing in this work, the 26-question survey was done in 2010 and again in 2015 and sent to approximately 6,000 hospitals in the United States. Response rate was 15% in 2010 and 18% in 2015. Some of the findings include:
- About the same number of hospitals have a health and wellness program or other initiative(s) for employees (86% in 2010 and 87% in 2015); however, the types of health and wellness programs and benefits that hospitals offer to their employees increased.
- The number of hospitals with 70% to 90% or more of employees participating in health and wellness programs increased from 19% in 2010 to 31% in 2015.
- The number of hospitals offering health and wellness programs to people in the community increased from 19% in 2010 to 66% in 2015.
- The number of hospitals offering incentives for participating in health and wellness programs increased as did the value of incentives, with more hospitals giving $500 or more to employees (7% in 2010 and 29% in 2015).
Reference
- Health Research & Educational Trust. Health and wellness programs for hospital employees: results from a 2015 American Hospital Association survey. Hospitals in Pursuit of Excellence website.
Provisions in the Affordable Care Act (ACA) encourage hospitals to work with their communities to improve population health. Like so many things, these efforts can and should begin at home—in this case, the hospital itself. Health and wellness programs for healthcare workers need to be emphasized, according to “Health and Wellness Programs for Hospital Employees: Results from a 2015 American Hospital Association Survey.”1
Such efforts allow healthcare workers to lead by example.
“To help create a culture of health, hospitals and health systems can provide leadership, and hospital employees can be role models, for health and wellness in their communities,” according to the report. “Developing health and wellness strategies and programs at hospitals will help establish an environment that provides the support, resources, and incentives for hospital employees to serve as such role models.”
Developing health and wellness programs can also help hospitals achieve the public health goals of the Healthy People 2020 initiative from the Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
To find out how hospitals are doing in this work, the 26-question survey was done in 2010 and again in 2015 and sent to approximately 6,000 hospitals in the United States. Response rate was 15% in 2010 and 18% in 2015. Some of the findings include:
- About the same number of hospitals have a health and wellness program or other initiative(s) for employees (86% in 2010 and 87% in 2015); however, the types of health and wellness programs and benefits that hospitals offer to their employees increased.
- The number of hospitals with 70% to 90% or more of employees participating in health and wellness programs increased from 19% in 2010 to 31% in 2015.
- The number of hospitals offering health and wellness programs to people in the community increased from 19% in 2010 to 66% in 2015.
- The number of hospitals offering incentives for participating in health and wellness programs increased as did the value of incentives, with more hospitals giving $500 or more to employees (7% in 2010 and 29% in 2015).
Reference
- Health Research & Educational Trust. Health and wellness programs for hospital employees: results from a 2015 American Hospital Association survey. Hospitals in Pursuit of Excellence website.
Tips for Working with Difficult Doctors
As a hospitalist, caring for critically ill or injured patients can be stressful and demanding. Working with difficult doctors, those who exhibit intimidating and disruptive behaviors such as verbal outbursts and physical threats as well as passive activities such as refusing to perform assigned tasks, can make the work environment even more challenging.1 Some docs are routinely reluctant—or refuse—to answer questions or return phone calls or pages. Some communicate in condescending language or voice intonation; some are brutally impatient.1
The most difficult doctors to work with are those who are not aligned with the hospital’s or treatment team’s goals and those who aren’t open to feedback and coaching, says Rob Zipper, MD, MMM, SFHM, regional chief medical officer of Sound Physicians, based in Tacoma, Wash.
“If physicians are aware of a practice’s guidelines and goals but simply won’t comply with them, it makes it harder on everyone else who is pulling the ship in the same direction,” he says.
Unruly physicians don’t just annoy their coworkers. According to a sentinel event alert from The Joint Commission, they can:
- foster medical errors;
- contribute to poor patient satisfaction;
- contribute to preventable adverse outcomes;
- increase the cost of care;
- undermine team effectiveness; and
- cause qualified clinicians, administrators, and managers to seek new positions in more professional environments.1
“These issues are all connected,” says Stephen R. Nichols, MD, chief of clinical operations performance at the Schumacher Group in Brownwood, Texas. “Disruptive behaviors create mitigated communications and dissatisfaction among staff, which bleeds over into other aspects that are involved secondarily.”
Stephen M. Paskoff, Esq., president and CEO of ELI in Atlanta, can attest to the most severe consequences of bad behavior on patient care.
At one institution, a surgeon’s disruptive behavior lead to a coworker forgetting to perform a procedure and a patient dying.2 In another incident, the emergency department stopped calling on a medical subspecialist who was predictably abusive. The subspecialist knew how to treat a specific patient with an unusual intervention. Since the specialist was not consulted initially, the patient ended up in the intensive care unit.2
One bad hospitalist can bring down the reputation of an entire team.
“Many programs are incentivized based on medical staff and primary-care physicians’ perceptions of their care, so there are direct and indirect consequences,” Dr. Zipper says.
The bottom line, says Felix Aguirre, MD, SFHM, vice president of medical affairs at IPC Healthcare in North Hollywood, Calif., is that it only takes one bad experience to tarnish a group, but it takes many positive experiences to erase the damage.
The Roots of Evil
Intimidating and disruptive behavior stems from both individual and systemic factors. Care providers who exhibit characteristics such as self-centeredness, immaturity, or defensiveness can be more prone to unprofessional behavior. They can lack interpersonal, coping, or conflict-management skills.1
Systemic factors are marked by pressures related to increased productivity demands, cost-containment requirements, embedded hierarchies, and fear of litigation in the healthcare environment. These pressures can be further exacerbated by changes to or differences in the authority, autonomy, empowerment, and roles or values of professionals on the healthcare team as well as by the continual daily changes in shifts, rotations, and interdepartmental support staff. This dynamic creates challenges for interprofessional communication and development of trust among team members.1
According to The Joint Commission, intimidating and disruptive behaviors are often manifested by healthcare professionals in positions of power.1 But other members of the care team can be problematic as well.
“In my experience, conflicts usually revolve around different perspectives and objectives, even if both parties are acting respectfully,” Dr. Zipper says. “Sometimes, however, providers or other care team members are tired or stressed and don’t behave professionally.”
Paskoff, who has more than 40 years of experience in healthcare-related workplace issues, including serving as an investigator for the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, says some doctors learn bad behaviors from their mentors and that behaviors can be passed down through generations because they are tolerated.
“When I asked one physician who had outstanding training and an outstanding technical reputation how he became abusive, he said, ‘I learned from the best.’” Paskoff was actually able to track the doctor’s training to the late 1800s and physicians who were known for similar behaviors.
Confronting Those Who Misbehave
Dr. Zipper says physicians should confront behavioral issues directly.
“I will typically discuss a complaint with a doctor privately, and ask him or her what happened without being accusatory,” he says. “I try to provide as much concrete and objective information as I can. The doctor needs to know that you are trying to help him or her succeed. That said, if something is clearly bad behavior, feedback should be direct and include a statement such as, ‘This is not how we behave in this practice.’”
At times, it may not be possible to discuss an emergent matter, such as during a code blue.
“However, I will often ask if anyone on the code team has any ideas or concerns before ending the code,” Dr. Nichols says. “Then after the critical time has passed, it is important to debrief and reconnect with the team, especially the less-experienced members who may have lingering concerns.”
For many employees, however, it is difficult to report disruptive behaviors. This is due to a fear of retaliation and the stigma associated with “blowing the whistle” on a colleague as well as a general reluctance to confront an intimidator.1
If an employee cannot muster the courage to confront a disruptive coworker or if the issue isn’t resolved by talking with the difficult individual, an employee should be a good citizen and report bad behavior to the appropriate hospital authority in a timely manner, says A. Kevin Troutman, Esq., a partner at Fisher Phillips in Houston and a former healthcare human resources executive.
Hospitals accredited by The Joint Commission are required to create a code of conduct that defines disruptive and inappropriate behaviors. In addition, leaders must create and implement a process for managing these behaviors.1
Helping Difficult Doctors
After a physician or another employee has been called out for bad behavior, steps need to be taken to correct the problem. Robert Fuller, Esq., an attorney with Nelson Hardiman, LLP, in Los Angeles, has found a positive-oriented intervention called “the 3-Ds”—which stands for diagnose, design, and do—that has been a successful tool for achieving positive change. The strategy involves a supervisor and employee mutually developing a worksheet to diagnose the problem. Next, they design a remediation and improvement plan. Finally, they implement the plan and specify dates to achieve certain milestones. Coworkers should be informed of the plan and be urged to support it.
“Make it clear that the positive aspect of this plan turns to progressive discipline, including termination, if the employee doesn’t improve or abandons the plan of action,” Fuller says. In most cases, troublemakers will make a sincere effort to control disruptive tendencies.
Troutman suggests enlisting the assistance of a respected peer.
“Have a senior-level doctor help the noncompliant physician understand why his or her behavior creates problems for everyone, including the doctor himself,” he says. “Also, consider connecting compensation and other rewards to job performance, which encompasses good behavior and good citizenship within the organization. Make expectations and consequences clear.”
If an employee has a recent change in behavior, ask if there is a reason.
“It is my experience that sudden changes in behaviors are often the result of a personal or clinical issue, so it is important and humane to make certain that there is not some other cause for the change before assuming someone is simply being disruptive or difficult,” Dr. Nichols says.
Many healthcare institutions are now setting up centers of professionalism. Paskoff reports that The Center for Professionalism and Peer Support (CPPS) was created in 2008 at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston to educate the hospital community regarding professionalism and manage unprofessional behavior.3 CPPS has established standards of behavior and a framework to deal with difficult behaviors.
“An employee is told what he or she is doing wrong, receives counseling, and is given resources to improve,” he explains. “If an employee doesn’t improve, he or she is told that the behavior won’t be tolerated.”
Dismissing Bad Employees
After addressing the specifics of unacceptable behavior and explaining the consequences of repeating it, leadership should monitor subsequent conduct and provide feedback.
“If the employee commits other violations or behaves badly, promptly address the misconduct again and make it clear that further such actions will not be tolerated,” Troutman says. “Expect immediate and sustained improvement and compliance. Be consistent, and if bad conduct continues after an opportunity to improve, do not prolong anyone’s suffering. Instead, terminate the disruptive employee. When you do, make the reasons clear.”
Karen Appold is a medical writer in Pennsylvania.
References
- Behaviors that undermine a culture of safety. The Joint Commission website. Accessed April 17, 2015.
- Whittemore AD, New England Society for Vascular Surgery. The impact of professionalism on safe surgical care. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45(2):415-419.
- Shapiro J, Whittemore A, Tsen LC. Instituting a culture of professionalism: the establishment of a center for professionalism and peer support. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2014;40(4):168-177.
As a hospitalist, caring for critically ill or injured patients can be stressful and demanding. Working with difficult doctors, those who exhibit intimidating and disruptive behaviors such as verbal outbursts and physical threats as well as passive activities such as refusing to perform assigned tasks, can make the work environment even more challenging.1 Some docs are routinely reluctant—or refuse—to answer questions or return phone calls or pages. Some communicate in condescending language or voice intonation; some are brutally impatient.1
The most difficult doctors to work with are those who are not aligned with the hospital’s or treatment team’s goals and those who aren’t open to feedback and coaching, says Rob Zipper, MD, MMM, SFHM, regional chief medical officer of Sound Physicians, based in Tacoma, Wash.
“If physicians are aware of a practice’s guidelines and goals but simply won’t comply with them, it makes it harder on everyone else who is pulling the ship in the same direction,” he says.
Unruly physicians don’t just annoy their coworkers. According to a sentinel event alert from The Joint Commission, they can:
- foster medical errors;
- contribute to poor patient satisfaction;
- contribute to preventable adverse outcomes;
- increase the cost of care;
- undermine team effectiveness; and
- cause qualified clinicians, administrators, and managers to seek new positions in more professional environments.1
“These issues are all connected,” says Stephen R. Nichols, MD, chief of clinical operations performance at the Schumacher Group in Brownwood, Texas. “Disruptive behaviors create mitigated communications and dissatisfaction among staff, which bleeds over into other aspects that are involved secondarily.”
Stephen M. Paskoff, Esq., president and CEO of ELI in Atlanta, can attest to the most severe consequences of bad behavior on patient care.
At one institution, a surgeon’s disruptive behavior lead to a coworker forgetting to perform a procedure and a patient dying.2 In another incident, the emergency department stopped calling on a medical subspecialist who was predictably abusive. The subspecialist knew how to treat a specific patient with an unusual intervention. Since the specialist was not consulted initially, the patient ended up in the intensive care unit.2
One bad hospitalist can bring down the reputation of an entire team.
“Many programs are incentivized based on medical staff and primary-care physicians’ perceptions of their care, so there are direct and indirect consequences,” Dr. Zipper says.
The bottom line, says Felix Aguirre, MD, SFHM, vice president of medical affairs at IPC Healthcare in North Hollywood, Calif., is that it only takes one bad experience to tarnish a group, but it takes many positive experiences to erase the damage.
The Roots of Evil
Intimidating and disruptive behavior stems from both individual and systemic factors. Care providers who exhibit characteristics such as self-centeredness, immaturity, or defensiveness can be more prone to unprofessional behavior. They can lack interpersonal, coping, or conflict-management skills.1
Systemic factors are marked by pressures related to increased productivity demands, cost-containment requirements, embedded hierarchies, and fear of litigation in the healthcare environment. These pressures can be further exacerbated by changes to or differences in the authority, autonomy, empowerment, and roles or values of professionals on the healthcare team as well as by the continual daily changes in shifts, rotations, and interdepartmental support staff. This dynamic creates challenges for interprofessional communication and development of trust among team members.1
According to The Joint Commission, intimidating and disruptive behaviors are often manifested by healthcare professionals in positions of power.1 But other members of the care team can be problematic as well.
“In my experience, conflicts usually revolve around different perspectives and objectives, even if both parties are acting respectfully,” Dr. Zipper says. “Sometimes, however, providers or other care team members are tired or stressed and don’t behave professionally.”
Paskoff, who has more than 40 years of experience in healthcare-related workplace issues, including serving as an investigator for the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, says some doctors learn bad behaviors from their mentors and that behaviors can be passed down through generations because they are tolerated.
“When I asked one physician who had outstanding training and an outstanding technical reputation how he became abusive, he said, ‘I learned from the best.’” Paskoff was actually able to track the doctor’s training to the late 1800s and physicians who were known for similar behaviors.
Confronting Those Who Misbehave
Dr. Zipper says physicians should confront behavioral issues directly.
“I will typically discuss a complaint with a doctor privately, and ask him or her what happened without being accusatory,” he says. “I try to provide as much concrete and objective information as I can. The doctor needs to know that you are trying to help him or her succeed. That said, if something is clearly bad behavior, feedback should be direct and include a statement such as, ‘This is not how we behave in this practice.’”
At times, it may not be possible to discuss an emergent matter, such as during a code blue.
“However, I will often ask if anyone on the code team has any ideas or concerns before ending the code,” Dr. Nichols says. “Then after the critical time has passed, it is important to debrief and reconnect with the team, especially the less-experienced members who may have lingering concerns.”
For many employees, however, it is difficult to report disruptive behaviors. This is due to a fear of retaliation and the stigma associated with “blowing the whistle” on a colleague as well as a general reluctance to confront an intimidator.1
If an employee cannot muster the courage to confront a disruptive coworker or if the issue isn’t resolved by talking with the difficult individual, an employee should be a good citizen and report bad behavior to the appropriate hospital authority in a timely manner, says A. Kevin Troutman, Esq., a partner at Fisher Phillips in Houston and a former healthcare human resources executive.
Hospitals accredited by The Joint Commission are required to create a code of conduct that defines disruptive and inappropriate behaviors. In addition, leaders must create and implement a process for managing these behaviors.1
Helping Difficult Doctors
After a physician or another employee has been called out for bad behavior, steps need to be taken to correct the problem. Robert Fuller, Esq., an attorney with Nelson Hardiman, LLP, in Los Angeles, has found a positive-oriented intervention called “the 3-Ds”—which stands for diagnose, design, and do—that has been a successful tool for achieving positive change. The strategy involves a supervisor and employee mutually developing a worksheet to diagnose the problem. Next, they design a remediation and improvement plan. Finally, they implement the plan and specify dates to achieve certain milestones. Coworkers should be informed of the plan and be urged to support it.
“Make it clear that the positive aspect of this plan turns to progressive discipline, including termination, if the employee doesn’t improve or abandons the plan of action,” Fuller says. In most cases, troublemakers will make a sincere effort to control disruptive tendencies.
Troutman suggests enlisting the assistance of a respected peer.
“Have a senior-level doctor help the noncompliant physician understand why his or her behavior creates problems for everyone, including the doctor himself,” he says. “Also, consider connecting compensation and other rewards to job performance, which encompasses good behavior and good citizenship within the organization. Make expectations and consequences clear.”
If an employee has a recent change in behavior, ask if there is a reason.
“It is my experience that sudden changes in behaviors are often the result of a personal or clinical issue, so it is important and humane to make certain that there is not some other cause for the change before assuming someone is simply being disruptive or difficult,” Dr. Nichols says.
Many healthcare institutions are now setting up centers of professionalism. Paskoff reports that The Center for Professionalism and Peer Support (CPPS) was created in 2008 at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston to educate the hospital community regarding professionalism and manage unprofessional behavior.3 CPPS has established standards of behavior and a framework to deal with difficult behaviors.
“An employee is told what he or she is doing wrong, receives counseling, and is given resources to improve,” he explains. “If an employee doesn’t improve, he or she is told that the behavior won’t be tolerated.”
Dismissing Bad Employees
After addressing the specifics of unacceptable behavior and explaining the consequences of repeating it, leadership should monitor subsequent conduct and provide feedback.
“If the employee commits other violations or behaves badly, promptly address the misconduct again and make it clear that further such actions will not be tolerated,” Troutman says. “Expect immediate and sustained improvement and compliance. Be consistent, and if bad conduct continues after an opportunity to improve, do not prolong anyone’s suffering. Instead, terminate the disruptive employee. When you do, make the reasons clear.”
Karen Appold is a medical writer in Pennsylvania.
References
- Behaviors that undermine a culture of safety. The Joint Commission website. Accessed April 17, 2015.
- Whittemore AD, New England Society for Vascular Surgery. The impact of professionalism on safe surgical care. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45(2):415-419.
- Shapiro J, Whittemore A, Tsen LC. Instituting a culture of professionalism: the establishment of a center for professionalism and peer support. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2014;40(4):168-177.
As a hospitalist, caring for critically ill or injured patients can be stressful and demanding. Working with difficult doctors, those who exhibit intimidating and disruptive behaviors such as verbal outbursts and physical threats as well as passive activities such as refusing to perform assigned tasks, can make the work environment even more challenging.1 Some docs are routinely reluctant—or refuse—to answer questions or return phone calls or pages. Some communicate in condescending language or voice intonation; some are brutally impatient.1
The most difficult doctors to work with are those who are not aligned with the hospital’s or treatment team’s goals and those who aren’t open to feedback and coaching, says Rob Zipper, MD, MMM, SFHM, regional chief medical officer of Sound Physicians, based in Tacoma, Wash.
“If physicians are aware of a practice’s guidelines and goals but simply won’t comply with them, it makes it harder on everyone else who is pulling the ship in the same direction,” he says.
Unruly physicians don’t just annoy their coworkers. According to a sentinel event alert from The Joint Commission, they can:
- foster medical errors;
- contribute to poor patient satisfaction;
- contribute to preventable adverse outcomes;
- increase the cost of care;
- undermine team effectiveness; and
- cause qualified clinicians, administrators, and managers to seek new positions in more professional environments.1
“These issues are all connected,” says Stephen R. Nichols, MD, chief of clinical operations performance at the Schumacher Group in Brownwood, Texas. “Disruptive behaviors create mitigated communications and dissatisfaction among staff, which bleeds over into other aspects that are involved secondarily.”
Stephen M. Paskoff, Esq., president and CEO of ELI in Atlanta, can attest to the most severe consequences of bad behavior on patient care.
At one institution, a surgeon’s disruptive behavior lead to a coworker forgetting to perform a procedure and a patient dying.2 In another incident, the emergency department stopped calling on a medical subspecialist who was predictably abusive. The subspecialist knew how to treat a specific patient with an unusual intervention. Since the specialist was not consulted initially, the patient ended up in the intensive care unit.2
One bad hospitalist can bring down the reputation of an entire team.
“Many programs are incentivized based on medical staff and primary-care physicians’ perceptions of their care, so there are direct and indirect consequences,” Dr. Zipper says.
The bottom line, says Felix Aguirre, MD, SFHM, vice president of medical affairs at IPC Healthcare in North Hollywood, Calif., is that it only takes one bad experience to tarnish a group, but it takes many positive experiences to erase the damage.
The Roots of Evil
Intimidating and disruptive behavior stems from both individual and systemic factors. Care providers who exhibit characteristics such as self-centeredness, immaturity, or defensiveness can be more prone to unprofessional behavior. They can lack interpersonal, coping, or conflict-management skills.1
Systemic factors are marked by pressures related to increased productivity demands, cost-containment requirements, embedded hierarchies, and fear of litigation in the healthcare environment. These pressures can be further exacerbated by changes to or differences in the authority, autonomy, empowerment, and roles or values of professionals on the healthcare team as well as by the continual daily changes in shifts, rotations, and interdepartmental support staff. This dynamic creates challenges for interprofessional communication and development of trust among team members.1
According to The Joint Commission, intimidating and disruptive behaviors are often manifested by healthcare professionals in positions of power.1 But other members of the care team can be problematic as well.
“In my experience, conflicts usually revolve around different perspectives and objectives, even if both parties are acting respectfully,” Dr. Zipper says. “Sometimes, however, providers or other care team members are tired or stressed and don’t behave professionally.”
Paskoff, who has more than 40 years of experience in healthcare-related workplace issues, including serving as an investigator for the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, says some doctors learn bad behaviors from their mentors and that behaviors can be passed down through generations because they are tolerated.
“When I asked one physician who had outstanding training and an outstanding technical reputation how he became abusive, he said, ‘I learned from the best.’” Paskoff was actually able to track the doctor’s training to the late 1800s and physicians who were known for similar behaviors.
Confronting Those Who Misbehave
Dr. Zipper says physicians should confront behavioral issues directly.
“I will typically discuss a complaint with a doctor privately, and ask him or her what happened without being accusatory,” he says. “I try to provide as much concrete and objective information as I can. The doctor needs to know that you are trying to help him or her succeed. That said, if something is clearly bad behavior, feedback should be direct and include a statement such as, ‘This is not how we behave in this practice.’”
At times, it may not be possible to discuss an emergent matter, such as during a code blue.
“However, I will often ask if anyone on the code team has any ideas or concerns before ending the code,” Dr. Nichols says. “Then after the critical time has passed, it is important to debrief and reconnect with the team, especially the less-experienced members who may have lingering concerns.”
For many employees, however, it is difficult to report disruptive behaviors. This is due to a fear of retaliation and the stigma associated with “blowing the whistle” on a colleague as well as a general reluctance to confront an intimidator.1
If an employee cannot muster the courage to confront a disruptive coworker or if the issue isn’t resolved by talking with the difficult individual, an employee should be a good citizen and report bad behavior to the appropriate hospital authority in a timely manner, says A. Kevin Troutman, Esq., a partner at Fisher Phillips in Houston and a former healthcare human resources executive.
Hospitals accredited by The Joint Commission are required to create a code of conduct that defines disruptive and inappropriate behaviors. In addition, leaders must create and implement a process for managing these behaviors.1
Helping Difficult Doctors
After a physician or another employee has been called out for bad behavior, steps need to be taken to correct the problem. Robert Fuller, Esq., an attorney with Nelson Hardiman, LLP, in Los Angeles, has found a positive-oriented intervention called “the 3-Ds”—which stands for diagnose, design, and do—that has been a successful tool for achieving positive change. The strategy involves a supervisor and employee mutually developing a worksheet to diagnose the problem. Next, they design a remediation and improvement plan. Finally, they implement the plan and specify dates to achieve certain milestones. Coworkers should be informed of the plan and be urged to support it.
“Make it clear that the positive aspect of this plan turns to progressive discipline, including termination, if the employee doesn’t improve or abandons the plan of action,” Fuller says. In most cases, troublemakers will make a sincere effort to control disruptive tendencies.
Troutman suggests enlisting the assistance of a respected peer.
“Have a senior-level doctor help the noncompliant physician understand why his or her behavior creates problems for everyone, including the doctor himself,” he says. “Also, consider connecting compensation and other rewards to job performance, which encompasses good behavior and good citizenship within the organization. Make expectations and consequences clear.”
If an employee has a recent change in behavior, ask if there is a reason.
“It is my experience that sudden changes in behaviors are often the result of a personal or clinical issue, so it is important and humane to make certain that there is not some other cause for the change before assuming someone is simply being disruptive or difficult,” Dr. Nichols says.
Many healthcare institutions are now setting up centers of professionalism. Paskoff reports that The Center for Professionalism and Peer Support (CPPS) was created in 2008 at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston to educate the hospital community regarding professionalism and manage unprofessional behavior.3 CPPS has established standards of behavior and a framework to deal with difficult behaviors.
“An employee is told what he or she is doing wrong, receives counseling, and is given resources to improve,” he explains. “If an employee doesn’t improve, he or she is told that the behavior won’t be tolerated.”
Dismissing Bad Employees
After addressing the specifics of unacceptable behavior and explaining the consequences of repeating it, leadership should monitor subsequent conduct and provide feedback.
“If the employee commits other violations or behaves badly, promptly address the misconduct again and make it clear that further such actions will not be tolerated,” Troutman says. “Expect immediate and sustained improvement and compliance. Be consistent, and if bad conduct continues after an opportunity to improve, do not prolong anyone’s suffering. Instead, terminate the disruptive employee. When you do, make the reasons clear.”
Karen Appold is a medical writer in Pennsylvania.
References
- Behaviors that undermine a culture of safety. The Joint Commission website. Accessed April 17, 2015.
- Whittemore AD, New England Society for Vascular Surgery. The impact of professionalism on safe surgical care. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45(2):415-419.
- Shapiro J, Whittemore A, Tsen LC. Instituting a culture of professionalism: the establishment of a center for professionalism and peer support. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2014;40(4):168-177.