User login
Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin-Free for 24 Months After Novel Endoscopic Procedure
TOPLINE:
VIENNA, AUSTRIA —
METHODOLOGY:
- ReCET technology, manufactured by Endogenex, uses a specialized catheter that ablates the duodenal mucosa with electroporation, enhancing sensitivity to endogenous insulin.
- In the first-in-human study, a total of 14 participants (aged 28-75 years; body mass index, 24-40) underwent the ReCET procedure. They then followed a 2-week isocaloric liquid diet, after which they were initiated on semaglutide and gradually titrated up to 1 mg/wk.
- Patients were followed for a total of 24 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 14 participants, 12 (86%) no longer required insulin at the 6- and 12-month follow-ups.
- At the 24-month follow-up, 11 patients were still insulin-free while maintaining A1c levels below 7.5%. (One patient withdrew consent at 18 months.)
- Semaglutide at the maximum dose was well-tolerated by 93% of participants. One patient experienced nausea that limited titration to the maximum dose. There were no serious adverse events to the ReCET procedure.
- Researchers have started the EMINENT-2 trial that will compare the use of ReCET with a sham procedure. All patients will still receive semaglutide.
IN PRACTICE:
- “These findings are very encouraging, suggesting that ReCET is a safe and feasible procedure that, when combined with semaglutide, can effectively eliminate the need for insulin therapy,” said the study’s lead author.
- It’s a novel way of treating type 2 diabetes using a single endoscopic procedure instead of repeated insulin injections, Busch explained. “But we do need to consider whether repeat treatment will be necessary because I don’t believe this will be forever.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Celine Busch, MBBS, a PhD candidate in gastroenterology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and was presented (abstract OP049) at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024 in Vienna, Austria, on October 14, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included the small sample size, uncontrolled nature, and bias due to combination therapy.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received an unrestricted research grant from Endogenex. No other relevant disclosures were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
VIENNA, AUSTRIA —
METHODOLOGY:
- ReCET technology, manufactured by Endogenex, uses a specialized catheter that ablates the duodenal mucosa with electroporation, enhancing sensitivity to endogenous insulin.
- In the first-in-human study, a total of 14 participants (aged 28-75 years; body mass index, 24-40) underwent the ReCET procedure. They then followed a 2-week isocaloric liquid diet, after which they were initiated on semaglutide and gradually titrated up to 1 mg/wk.
- Patients were followed for a total of 24 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 14 participants, 12 (86%) no longer required insulin at the 6- and 12-month follow-ups.
- At the 24-month follow-up, 11 patients were still insulin-free while maintaining A1c levels below 7.5%. (One patient withdrew consent at 18 months.)
- Semaglutide at the maximum dose was well-tolerated by 93% of participants. One patient experienced nausea that limited titration to the maximum dose. There were no serious adverse events to the ReCET procedure.
- Researchers have started the EMINENT-2 trial that will compare the use of ReCET with a sham procedure. All patients will still receive semaglutide.
IN PRACTICE:
- “These findings are very encouraging, suggesting that ReCET is a safe and feasible procedure that, when combined with semaglutide, can effectively eliminate the need for insulin therapy,” said the study’s lead author.
- It’s a novel way of treating type 2 diabetes using a single endoscopic procedure instead of repeated insulin injections, Busch explained. “But we do need to consider whether repeat treatment will be necessary because I don’t believe this will be forever.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Celine Busch, MBBS, a PhD candidate in gastroenterology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and was presented (abstract OP049) at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024 in Vienna, Austria, on October 14, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included the small sample size, uncontrolled nature, and bias due to combination therapy.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received an unrestricted research grant from Endogenex. No other relevant disclosures were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
VIENNA, AUSTRIA —
METHODOLOGY:
- ReCET technology, manufactured by Endogenex, uses a specialized catheter that ablates the duodenal mucosa with electroporation, enhancing sensitivity to endogenous insulin.
- In the first-in-human study, a total of 14 participants (aged 28-75 years; body mass index, 24-40) underwent the ReCET procedure. They then followed a 2-week isocaloric liquid diet, after which they were initiated on semaglutide and gradually titrated up to 1 mg/wk.
- Patients were followed for a total of 24 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 14 participants, 12 (86%) no longer required insulin at the 6- and 12-month follow-ups.
- At the 24-month follow-up, 11 patients were still insulin-free while maintaining A1c levels below 7.5%. (One patient withdrew consent at 18 months.)
- Semaglutide at the maximum dose was well-tolerated by 93% of participants. One patient experienced nausea that limited titration to the maximum dose. There were no serious adverse events to the ReCET procedure.
- Researchers have started the EMINENT-2 trial that will compare the use of ReCET with a sham procedure. All patients will still receive semaglutide.
IN PRACTICE:
- “These findings are very encouraging, suggesting that ReCET is a safe and feasible procedure that, when combined with semaglutide, can effectively eliminate the need for insulin therapy,” said the study’s lead author.
- It’s a novel way of treating type 2 diabetes using a single endoscopic procedure instead of repeated insulin injections, Busch explained. “But we do need to consider whether repeat treatment will be necessary because I don’t believe this will be forever.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Celine Busch, MBBS, a PhD candidate in gastroenterology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and was presented (abstract OP049) at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024 in Vienna, Austria, on October 14, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included the small sample size, uncontrolled nature, and bias due to combination therapy.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received an unrestricted research grant from Endogenex. No other relevant disclosures were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GPs Urged to Embed Lifestyle Medicine into Primary Care
LIVERPOOL — “Healthy doctors make healthy patients”, stated a GP during a workshop at the Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP) annual meeting. The session aimed to encourage GPs to embed lifestyle medicine into primary care through collaborative action.
Callum Leese from Aberfeldy Medical Practice in Scotland, who is also a lecturer at the University of Dundee for the Scottish Clinical Research Excellence Development Scheme (SCREDS), discussed the benefits of lifestyle medicine services in addressing lifestyle-related diseases, reducing their contribution towards the prevalence of chronic conditions, and helping prevent premature mortality.
Leese is leading a project to make Aberfeldy the healthiest town in Scotland by promoting physical activities, such as the 2-km, 5-km, and 7-km Santa Stride walking group in November, and a recent food festival to encourage healthy cooking and eating. “There’s loads of things that can be done to try and inspire change,” he said. “The research is fairly unequivocal in that healthy doctors make healthy patients,” Leese asserted. “The most important thing we can do is target our doctors and our nurses and make them advocates for what we want to see with our patients.”
Speaking to this news organization, he emphasized that, “if the doctors are moving, they’re much more likely to promote it, and if they’re eating well, they’re much more likely to be able to be evangelistic.”
Physical Activity Advice Shows High Return
About one-third of the population in the United Kingdom are physically inactive, which costs the economy £7.2 billion, with £1 billion attributed directly to the NHS, he informed the workshop.
As an honorary support fellow in physical activity and lifestyle medicine at the RCGP, Leese specializes in integrating physical activity into primary care settings. “We know it’s cost effective. If we compare it to smoking cessation advice, we know that we need to give advice to one person about 50 times for one person to stop smoking in primary care. But for physical activity, you need to give advice to 12 people for one person to increase their physical activity levels to meet the guidance,” he noted.
Leese stressed the importance of short but effective discussions between GPs and patients. He gave examples of online resources to recommend to patients, such as Moving Medicine, which aims to help healthcare professionals integrate physical activity into routine clinical conversations, or the RCGP toolkit (the Physical Activity Hub). “It really takes 1 minute of asking if the patient has ever considered being more active, and briefly explaining that being more active might have really significant outcomes for their condition,” he said.
In primary care, most patients who need to be more physically activity are directed toward 12-week exercise referral schemes, and sometimes we use social prescribing, for example, inviting patients to walk in groups, Leese explained. “However, despite the best intentions, about 78% of GPs aren’t doing it [advising on physical activity] regularly,” he noted. He cited four main challenges: lack of time, knowledge, resources, and financial support.
Geographical Variation in Social Prescribing
Social prescribing, which links patients with non–medical community support, also varies widely across the United Kingdom. “Social prescribing is a real example of that because it’s really well established in some places and not in others,” Leese remarked. He noted that inner-city and rural areas often have different needs. Contrary to some expectations, city dwellers are sometimes more active than those living in rural areas because despite having lots of green space for physical activity, “they tend to park the car outside the front door and park again right outside their place of work, whereas in London, for example, you can persuade people to get off a stop early on the Tube or a stop early in the bus.”
MAN v FAT 5-a-side Football
Leese also emphasized the importance of innovation in implementing lifestyle medicine, pointing out that nonmedical personnel, social prescribers, and health coaches can alleviate time pressures on GPs.
Citing an example of a physical activity-related intervention, he described a UK-wide organization developed for men in the 40s-50s age group, called MAN v FAT, which involves a novel weight-related way of playing five-a-side football. Players have a weigh-in before each game and teams are rewarded with points on the pitch for every pound lost as a team since their last match.
However, Leese acknowledged the need to tailor physical activity advice to different age groups. For example, “in an 80-year-old, physical activity might improve their balance and they’re less likely to fall and break something.”
Lifestyle Clinics
Leese cited the PCN Lifestyle Clinics, originating from the Leamington Primary Care Network (PCN), as an example of successful lifestyle medicine integration to help address the needs of people living with chronic conditions. “We don’t want to prescribe a model, but we can draw on a program run by the Leamington Spa PCN, that involves four group sessions of 6-10 people focused on lifestyle,” he said.
The weekly group-based sessions are run by a GP, a health and wellbeing coach, a dietitian, and a psychiatrist. Together, they cover four aspects of lifestyle and health comprising individual challenges, how community influences behavior and vice versa, food and nutrition, and physical activity for health and wellbeing.
“We try to debunk some of those myths around nutrition, compared with diet, and physical activity, compared with exercise. So, for example, the idea that exercise is usually considered to be using an elliptical cross-trainer whereas physical activity, which might be just dancing in your kitchen while you’re making dinner, is something that can be done more easily,” explained Leese.
Physical activities include running and swimming in collaboration with a leisure center. “It’s an amazing program,” he remarked.
Outcomes from 142 patients who attended the Lifestyle Clinic at a North Leamington GP practice over 14 months showed that 53% gained confidence in making lifestyle changes, 60% noticed a positive impact on their physical health, and 77% reported positive impacts on their mental health.
GP Embraces Lifestyle Medicine
Rachel Burnett, a GP from Park Medical Practice in Derby, a delegate who attended the session, commented on the central idea of incorporating lifestyle medicine into primary care practice. She told this news organization that, “I think it could prevent a lot of ill health and therefore a lot of health inequalities just by embedding lifestyle medicine into our work. To hear about the Leamington Spa project and how it›s been a success was really inspiring.”
Referring to her own practice, Burnett said: “My patients are familiar with the way I go on and on about lifestyle measures, but I believe the way forward is with group sessions because we need to give the same advice to a large number of patients, for example, with prediabetes. This could save time and resource, and I think patients who are more likely to make the changes will actually attend the sessions so we’re not wasting our breath.”
Neither Leese nor Burnett declared any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LIVERPOOL — “Healthy doctors make healthy patients”, stated a GP during a workshop at the Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP) annual meeting. The session aimed to encourage GPs to embed lifestyle medicine into primary care through collaborative action.
Callum Leese from Aberfeldy Medical Practice in Scotland, who is also a lecturer at the University of Dundee for the Scottish Clinical Research Excellence Development Scheme (SCREDS), discussed the benefits of lifestyle medicine services in addressing lifestyle-related diseases, reducing their contribution towards the prevalence of chronic conditions, and helping prevent premature mortality.
Leese is leading a project to make Aberfeldy the healthiest town in Scotland by promoting physical activities, such as the 2-km, 5-km, and 7-km Santa Stride walking group in November, and a recent food festival to encourage healthy cooking and eating. “There’s loads of things that can be done to try and inspire change,” he said. “The research is fairly unequivocal in that healthy doctors make healthy patients,” Leese asserted. “The most important thing we can do is target our doctors and our nurses and make them advocates for what we want to see with our patients.”
Speaking to this news organization, he emphasized that, “if the doctors are moving, they’re much more likely to promote it, and if they’re eating well, they’re much more likely to be able to be evangelistic.”
Physical Activity Advice Shows High Return
About one-third of the population in the United Kingdom are physically inactive, which costs the economy £7.2 billion, with £1 billion attributed directly to the NHS, he informed the workshop.
As an honorary support fellow in physical activity and lifestyle medicine at the RCGP, Leese specializes in integrating physical activity into primary care settings. “We know it’s cost effective. If we compare it to smoking cessation advice, we know that we need to give advice to one person about 50 times for one person to stop smoking in primary care. But for physical activity, you need to give advice to 12 people for one person to increase their physical activity levels to meet the guidance,” he noted.
Leese stressed the importance of short but effective discussions between GPs and patients. He gave examples of online resources to recommend to patients, such as Moving Medicine, which aims to help healthcare professionals integrate physical activity into routine clinical conversations, or the RCGP toolkit (the Physical Activity Hub). “It really takes 1 minute of asking if the patient has ever considered being more active, and briefly explaining that being more active might have really significant outcomes for their condition,” he said.
In primary care, most patients who need to be more physically activity are directed toward 12-week exercise referral schemes, and sometimes we use social prescribing, for example, inviting patients to walk in groups, Leese explained. “However, despite the best intentions, about 78% of GPs aren’t doing it [advising on physical activity] regularly,” he noted. He cited four main challenges: lack of time, knowledge, resources, and financial support.
Geographical Variation in Social Prescribing
Social prescribing, which links patients with non–medical community support, also varies widely across the United Kingdom. “Social prescribing is a real example of that because it’s really well established in some places and not in others,” Leese remarked. He noted that inner-city and rural areas often have different needs. Contrary to some expectations, city dwellers are sometimes more active than those living in rural areas because despite having lots of green space for physical activity, “they tend to park the car outside the front door and park again right outside their place of work, whereas in London, for example, you can persuade people to get off a stop early on the Tube or a stop early in the bus.”
MAN v FAT 5-a-side Football
Leese also emphasized the importance of innovation in implementing lifestyle medicine, pointing out that nonmedical personnel, social prescribers, and health coaches can alleviate time pressures on GPs.
Citing an example of a physical activity-related intervention, he described a UK-wide organization developed for men in the 40s-50s age group, called MAN v FAT, which involves a novel weight-related way of playing five-a-side football. Players have a weigh-in before each game and teams are rewarded with points on the pitch for every pound lost as a team since their last match.
However, Leese acknowledged the need to tailor physical activity advice to different age groups. For example, “in an 80-year-old, physical activity might improve their balance and they’re less likely to fall and break something.”
Lifestyle Clinics
Leese cited the PCN Lifestyle Clinics, originating from the Leamington Primary Care Network (PCN), as an example of successful lifestyle medicine integration to help address the needs of people living with chronic conditions. “We don’t want to prescribe a model, but we can draw on a program run by the Leamington Spa PCN, that involves four group sessions of 6-10 people focused on lifestyle,” he said.
The weekly group-based sessions are run by a GP, a health and wellbeing coach, a dietitian, and a psychiatrist. Together, they cover four aspects of lifestyle and health comprising individual challenges, how community influences behavior and vice versa, food and nutrition, and physical activity for health and wellbeing.
“We try to debunk some of those myths around nutrition, compared with diet, and physical activity, compared with exercise. So, for example, the idea that exercise is usually considered to be using an elliptical cross-trainer whereas physical activity, which might be just dancing in your kitchen while you’re making dinner, is something that can be done more easily,” explained Leese.
Physical activities include running and swimming in collaboration with a leisure center. “It’s an amazing program,” he remarked.
Outcomes from 142 patients who attended the Lifestyle Clinic at a North Leamington GP practice over 14 months showed that 53% gained confidence in making lifestyle changes, 60% noticed a positive impact on their physical health, and 77% reported positive impacts on their mental health.
GP Embraces Lifestyle Medicine
Rachel Burnett, a GP from Park Medical Practice in Derby, a delegate who attended the session, commented on the central idea of incorporating lifestyle medicine into primary care practice. She told this news organization that, “I think it could prevent a lot of ill health and therefore a lot of health inequalities just by embedding lifestyle medicine into our work. To hear about the Leamington Spa project and how it›s been a success was really inspiring.”
Referring to her own practice, Burnett said: “My patients are familiar with the way I go on and on about lifestyle measures, but I believe the way forward is with group sessions because we need to give the same advice to a large number of patients, for example, with prediabetes. This could save time and resource, and I think patients who are more likely to make the changes will actually attend the sessions so we’re not wasting our breath.”
Neither Leese nor Burnett declared any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LIVERPOOL — “Healthy doctors make healthy patients”, stated a GP during a workshop at the Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP) annual meeting. The session aimed to encourage GPs to embed lifestyle medicine into primary care through collaborative action.
Callum Leese from Aberfeldy Medical Practice in Scotland, who is also a lecturer at the University of Dundee for the Scottish Clinical Research Excellence Development Scheme (SCREDS), discussed the benefits of lifestyle medicine services in addressing lifestyle-related diseases, reducing their contribution towards the prevalence of chronic conditions, and helping prevent premature mortality.
Leese is leading a project to make Aberfeldy the healthiest town in Scotland by promoting physical activities, such as the 2-km, 5-km, and 7-km Santa Stride walking group in November, and a recent food festival to encourage healthy cooking and eating. “There’s loads of things that can be done to try and inspire change,” he said. “The research is fairly unequivocal in that healthy doctors make healthy patients,” Leese asserted. “The most important thing we can do is target our doctors and our nurses and make them advocates for what we want to see with our patients.”
Speaking to this news organization, he emphasized that, “if the doctors are moving, they’re much more likely to promote it, and if they’re eating well, they’re much more likely to be able to be evangelistic.”
Physical Activity Advice Shows High Return
About one-third of the population in the United Kingdom are physically inactive, which costs the economy £7.2 billion, with £1 billion attributed directly to the NHS, he informed the workshop.
As an honorary support fellow in physical activity and lifestyle medicine at the RCGP, Leese specializes in integrating physical activity into primary care settings. “We know it’s cost effective. If we compare it to smoking cessation advice, we know that we need to give advice to one person about 50 times for one person to stop smoking in primary care. But for physical activity, you need to give advice to 12 people for one person to increase their physical activity levels to meet the guidance,” he noted.
Leese stressed the importance of short but effective discussions between GPs and patients. He gave examples of online resources to recommend to patients, such as Moving Medicine, which aims to help healthcare professionals integrate physical activity into routine clinical conversations, or the RCGP toolkit (the Physical Activity Hub). “It really takes 1 minute of asking if the patient has ever considered being more active, and briefly explaining that being more active might have really significant outcomes for their condition,” he said.
In primary care, most patients who need to be more physically activity are directed toward 12-week exercise referral schemes, and sometimes we use social prescribing, for example, inviting patients to walk in groups, Leese explained. “However, despite the best intentions, about 78% of GPs aren’t doing it [advising on physical activity] regularly,” he noted. He cited four main challenges: lack of time, knowledge, resources, and financial support.
Geographical Variation in Social Prescribing
Social prescribing, which links patients with non–medical community support, also varies widely across the United Kingdom. “Social prescribing is a real example of that because it’s really well established in some places and not in others,” Leese remarked. He noted that inner-city and rural areas often have different needs. Contrary to some expectations, city dwellers are sometimes more active than those living in rural areas because despite having lots of green space for physical activity, “they tend to park the car outside the front door and park again right outside their place of work, whereas in London, for example, you can persuade people to get off a stop early on the Tube or a stop early in the bus.”
MAN v FAT 5-a-side Football
Leese also emphasized the importance of innovation in implementing lifestyle medicine, pointing out that nonmedical personnel, social prescribers, and health coaches can alleviate time pressures on GPs.
Citing an example of a physical activity-related intervention, he described a UK-wide organization developed for men in the 40s-50s age group, called MAN v FAT, which involves a novel weight-related way of playing five-a-side football. Players have a weigh-in before each game and teams are rewarded with points on the pitch for every pound lost as a team since their last match.
However, Leese acknowledged the need to tailor physical activity advice to different age groups. For example, “in an 80-year-old, physical activity might improve their balance and they’re less likely to fall and break something.”
Lifestyle Clinics
Leese cited the PCN Lifestyle Clinics, originating from the Leamington Primary Care Network (PCN), as an example of successful lifestyle medicine integration to help address the needs of people living with chronic conditions. “We don’t want to prescribe a model, but we can draw on a program run by the Leamington Spa PCN, that involves four group sessions of 6-10 people focused on lifestyle,” he said.
The weekly group-based sessions are run by a GP, a health and wellbeing coach, a dietitian, and a psychiatrist. Together, they cover four aspects of lifestyle and health comprising individual challenges, how community influences behavior and vice versa, food and nutrition, and physical activity for health and wellbeing.
“We try to debunk some of those myths around nutrition, compared with diet, and physical activity, compared with exercise. So, for example, the idea that exercise is usually considered to be using an elliptical cross-trainer whereas physical activity, which might be just dancing in your kitchen while you’re making dinner, is something that can be done more easily,” explained Leese.
Physical activities include running and swimming in collaboration with a leisure center. “It’s an amazing program,” he remarked.
Outcomes from 142 patients who attended the Lifestyle Clinic at a North Leamington GP practice over 14 months showed that 53% gained confidence in making lifestyle changes, 60% noticed a positive impact on their physical health, and 77% reported positive impacts on their mental health.
GP Embraces Lifestyle Medicine
Rachel Burnett, a GP from Park Medical Practice in Derby, a delegate who attended the session, commented on the central idea of incorporating lifestyle medicine into primary care practice. She told this news organization that, “I think it could prevent a lot of ill health and therefore a lot of health inequalities just by embedding lifestyle medicine into our work. To hear about the Leamington Spa project and how it›s been a success was really inspiring.”
Referring to her own practice, Burnett said: “My patients are familiar with the way I go on and on about lifestyle measures, but I believe the way forward is with group sessions because we need to give the same advice to a large number of patients, for example, with prediabetes. This could save time and resource, and I think patients who are more likely to make the changes will actually attend the sessions so we’re not wasting our breath.”
Neither Leese nor Burnett declared any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CGM With Geriatric Care Simplifies T1D Management in Seniors
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of CGM use enhanced by geriatric principles in adults aged ≥ 65 years with T1D and at least two episodes of hypoglycemia (blood glucose level, < 70 mg/dL for ≥ 20 minutes over 2 weeks), who were either CGM-naive or CGM users prior to the study.
- Participants were randomly assigned to an intervention group using CGM with geriatric principles (ie, adjusting goals based on overall health and simplifying regimens based on CGM patterns and clinical characteristics) or a control group receiving usual care by their endocrinologist.
- The primary outcome was the change in duration of hypoglycemia from baseline to 6 months.
- A cost-effectiveness analysis was also performed for the intervention using a healthcare sector perspective, considering the cost of CGM devices and the cost of medical staff time.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers included 131 participants (mean age, 71 years), of whom 68 were in the intervention group (35 CGM-naive) and 63 in the control group (23 CGM-naive).
- The intervention group showed a median reduction of 2.6% in the duration of hypoglycemia vs a 0.3% reduction in the control group (median difference, −2.3%; P < .001).
- This reduction was observed in both CGM users (median difference, −1.2%) and CGM-naive participants (median difference, −2.8%) in the intervention group.
- No significant difference in A1c levels was observed between the intervention and control groups, indicating that CGM enhanced with geriatric principles did not worsen glycemic control.
- The intervention was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $71,623 per quality-adjusted life-year and was cost-effective for CGM-naive participants but at a lower level owing to the high cost of the CGM device.
IN PRACTICE:
“Personalization of goals and simplification of complex regimens can be combined with CGM use to improve management of type 1 diabetes in older adults,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Medha N. Munshi, MD, Joslin Diabetes Center, Boston. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included a relatively small sample size and an ethnically homogeneous and highly educated cohort, which may have limited the generalizability of its findings. Additionally, the study did not measure adherence to individual simplification strategies, which may have hindered the quantification of behavioral changes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Two authors declared serving as consultants for pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of CGM use enhanced by geriatric principles in adults aged ≥ 65 years with T1D and at least two episodes of hypoglycemia (blood glucose level, < 70 mg/dL for ≥ 20 minutes over 2 weeks), who were either CGM-naive or CGM users prior to the study.
- Participants were randomly assigned to an intervention group using CGM with geriatric principles (ie, adjusting goals based on overall health and simplifying regimens based on CGM patterns and clinical characteristics) or a control group receiving usual care by their endocrinologist.
- The primary outcome was the change in duration of hypoglycemia from baseline to 6 months.
- A cost-effectiveness analysis was also performed for the intervention using a healthcare sector perspective, considering the cost of CGM devices and the cost of medical staff time.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers included 131 participants (mean age, 71 years), of whom 68 were in the intervention group (35 CGM-naive) and 63 in the control group (23 CGM-naive).
- The intervention group showed a median reduction of 2.6% in the duration of hypoglycemia vs a 0.3% reduction in the control group (median difference, −2.3%; P < .001).
- This reduction was observed in both CGM users (median difference, −1.2%) and CGM-naive participants (median difference, −2.8%) in the intervention group.
- No significant difference in A1c levels was observed between the intervention and control groups, indicating that CGM enhanced with geriatric principles did not worsen glycemic control.
- The intervention was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $71,623 per quality-adjusted life-year and was cost-effective for CGM-naive participants but at a lower level owing to the high cost of the CGM device.
IN PRACTICE:
“Personalization of goals and simplification of complex regimens can be combined with CGM use to improve management of type 1 diabetes in older adults,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Medha N. Munshi, MD, Joslin Diabetes Center, Boston. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included a relatively small sample size and an ethnically homogeneous and highly educated cohort, which may have limited the generalizability of its findings. Additionally, the study did not measure adherence to individual simplification strategies, which may have hindered the quantification of behavioral changes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Two authors declared serving as consultants for pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of CGM use enhanced by geriatric principles in adults aged ≥ 65 years with T1D and at least two episodes of hypoglycemia (blood glucose level, < 70 mg/dL for ≥ 20 minutes over 2 weeks), who were either CGM-naive or CGM users prior to the study.
- Participants were randomly assigned to an intervention group using CGM with geriatric principles (ie, adjusting goals based on overall health and simplifying regimens based on CGM patterns and clinical characteristics) or a control group receiving usual care by their endocrinologist.
- The primary outcome was the change in duration of hypoglycemia from baseline to 6 months.
- A cost-effectiveness analysis was also performed for the intervention using a healthcare sector perspective, considering the cost of CGM devices and the cost of medical staff time.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers included 131 participants (mean age, 71 years), of whom 68 were in the intervention group (35 CGM-naive) and 63 in the control group (23 CGM-naive).
- The intervention group showed a median reduction of 2.6% in the duration of hypoglycemia vs a 0.3% reduction in the control group (median difference, −2.3%; P < .001).
- This reduction was observed in both CGM users (median difference, −1.2%) and CGM-naive participants (median difference, −2.8%) in the intervention group.
- No significant difference in A1c levels was observed between the intervention and control groups, indicating that CGM enhanced with geriatric principles did not worsen glycemic control.
- The intervention was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $71,623 per quality-adjusted life-year and was cost-effective for CGM-naive participants but at a lower level owing to the high cost of the CGM device.
IN PRACTICE:
“Personalization of goals and simplification of complex regimens can be combined with CGM use to improve management of type 1 diabetes in older adults,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Medha N. Munshi, MD, Joslin Diabetes Center, Boston. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included a relatively small sample size and an ethnically homogeneous and highly educated cohort, which may have limited the generalizability of its findings. Additionally, the study did not measure adherence to individual simplification strategies, which may have hindered the quantification of behavioral changes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Two authors declared serving as consultants for pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide a Potential Treatment Option for Opioid Use Disorder?
Semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) is associated with a significantly lower risk for overdose in individuals with opioid use disorder (OUD), new research shows.
The findings suggest that the drug may be a promising treatment option for OUD, adding to the growing evidence of the potential psychiatric benefits of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) inhibitors.
“Our study provided real-world evidence suggesting that semaglutide could have benefits in preventing opioid overdose and treating opioid use disorder,” co–lead author Rong Xu, PhD, director of the Center for Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview.
However, Xu cautioned that this evidence is preliminary and randomized clinical trials are required to confirm these findings.
The study published online in a research letter on September 25 in JAMA Network Open.
New Addiction Meds an Urgent Priority
Investigators analyzed electronic medical records from 33,006 patients with type 2 diabetes and OUD who were prescribed one of eight antidiabetic medications between 2017 and 2023.
Drugs included in the study were semaglutide, insulin, metformin, albiglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones.
Participants in the semaglutide and each comparison group were matched for certain covariates at baseline, such as socioeconomic status and OUD medications.
After 1 year, semaglutide was associated with a 42%-68% lower risk for opioid overdose than other antidiabetic medications, including other GLP-1s (range of hazard ratio [HR]: HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.12-0.89; to HR, 0.58; 95%CI, 0.38-0.87).
Xu noted a number of study limitations including the effect of possible confounders and sole reliance on prescription data.
However, the findings are in line with those of prior studies showing that semaglutide may be associated with lower rates of alcohol and nicotine use, she said.
Earlier this year, Xu, along with National Institute on Drug Abuse Director Nora Volkow, MD, and colleagues, published a retrospective cohort study of nearly 84,000 patients with obesity. That analysis showed that semaglutide was associated with a significantly lower risk of new alcohol use disorder diagnoses.
In a previous editorial by Xu and Volkow that summarized the research to-date on GLP-1s for nicotine, alcohol, and substance use disorders, they note that “closing the addiction treatment gap and discovering new, more effective addiction medications are urgent priorities. In this regard, investigating the potential of GLP-1 analogue medications to treat substance use disorder deserves fast and rigorous testing.”
Caution Warranted
Commenting on the study, Riccardo De Giorgi, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Oxford in England, said at this point, “we have to be very careful about how we interpret these data.”
In August, De Giorgi published a study showing that semaglutide was associated with reduced risk for several neurologic and psychiatric outcomes including dementia and nicotine misuse.
While there is enough observational evidence linking GLP-1 medications with reduced SUD risk, he noted that “now is the time to move on and conduct some randomized clinical trials, specifically testing our hypothesis in people who have psychiatric disorders.”
De Giorgi also called for mechanistic studies of semaglutide and other so that researchers could learn more about how it works to reduce cravings. “Instead of going from bench to bed, we need to go back to the bench,” he said.
As previously reported, De Giorgi recently called on experts in the field to actively explore the potential of GLP-1 inhibitors for mental illness.
The study was funded by National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institute on Aging, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health. Xu reported no relevant financial relationships. De Giorgi reported receiving funding from the National Institute for Health Research Oxford Health Biomedical Research Centre.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) is associated with a significantly lower risk for overdose in individuals with opioid use disorder (OUD), new research shows.
The findings suggest that the drug may be a promising treatment option for OUD, adding to the growing evidence of the potential psychiatric benefits of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) inhibitors.
“Our study provided real-world evidence suggesting that semaglutide could have benefits in preventing opioid overdose and treating opioid use disorder,” co–lead author Rong Xu, PhD, director of the Center for Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview.
However, Xu cautioned that this evidence is preliminary and randomized clinical trials are required to confirm these findings.
The study published online in a research letter on September 25 in JAMA Network Open.
New Addiction Meds an Urgent Priority
Investigators analyzed electronic medical records from 33,006 patients with type 2 diabetes and OUD who were prescribed one of eight antidiabetic medications between 2017 and 2023.
Drugs included in the study were semaglutide, insulin, metformin, albiglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones.
Participants in the semaglutide and each comparison group were matched for certain covariates at baseline, such as socioeconomic status and OUD medications.
After 1 year, semaglutide was associated with a 42%-68% lower risk for opioid overdose than other antidiabetic medications, including other GLP-1s (range of hazard ratio [HR]: HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.12-0.89; to HR, 0.58; 95%CI, 0.38-0.87).
Xu noted a number of study limitations including the effect of possible confounders and sole reliance on prescription data.
However, the findings are in line with those of prior studies showing that semaglutide may be associated with lower rates of alcohol and nicotine use, she said.
Earlier this year, Xu, along with National Institute on Drug Abuse Director Nora Volkow, MD, and colleagues, published a retrospective cohort study of nearly 84,000 patients with obesity. That analysis showed that semaglutide was associated with a significantly lower risk of new alcohol use disorder diagnoses.
In a previous editorial by Xu and Volkow that summarized the research to-date on GLP-1s for nicotine, alcohol, and substance use disorders, they note that “closing the addiction treatment gap and discovering new, more effective addiction medications are urgent priorities. In this regard, investigating the potential of GLP-1 analogue medications to treat substance use disorder deserves fast and rigorous testing.”
Caution Warranted
Commenting on the study, Riccardo De Giorgi, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Oxford in England, said at this point, “we have to be very careful about how we interpret these data.”
In August, De Giorgi published a study showing that semaglutide was associated with reduced risk for several neurologic and psychiatric outcomes including dementia and nicotine misuse.
While there is enough observational evidence linking GLP-1 medications with reduced SUD risk, he noted that “now is the time to move on and conduct some randomized clinical trials, specifically testing our hypothesis in people who have psychiatric disorders.”
De Giorgi also called for mechanistic studies of semaglutide and other so that researchers could learn more about how it works to reduce cravings. “Instead of going from bench to bed, we need to go back to the bench,” he said.
As previously reported, De Giorgi recently called on experts in the field to actively explore the potential of GLP-1 inhibitors for mental illness.
The study was funded by National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institute on Aging, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health. Xu reported no relevant financial relationships. De Giorgi reported receiving funding from the National Institute for Health Research Oxford Health Biomedical Research Centre.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Semaglutide (Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) is associated with a significantly lower risk for overdose in individuals with opioid use disorder (OUD), new research shows.
The findings suggest that the drug may be a promising treatment option for OUD, adding to the growing evidence of the potential psychiatric benefits of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) inhibitors.
“Our study provided real-world evidence suggesting that semaglutide could have benefits in preventing opioid overdose and treating opioid use disorder,” co–lead author Rong Xu, PhD, director of the Center for Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview.
However, Xu cautioned that this evidence is preliminary and randomized clinical trials are required to confirm these findings.
The study published online in a research letter on September 25 in JAMA Network Open.
New Addiction Meds an Urgent Priority
Investigators analyzed electronic medical records from 33,006 patients with type 2 diabetes and OUD who were prescribed one of eight antidiabetic medications between 2017 and 2023.
Drugs included in the study were semaglutide, insulin, metformin, albiglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, liraglutide, lixisenatide, dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones.
Participants in the semaglutide and each comparison group were matched for certain covariates at baseline, such as socioeconomic status and OUD medications.
After 1 year, semaglutide was associated with a 42%-68% lower risk for opioid overdose than other antidiabetic medications, including other GLP-1s (range of hazard ratio [HR]: HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.12-0.89; to HR, 0.58; 95%CI, 0.38-0.87).
Xu noted a number of study limitations including the effect of possible confounders and sole reliance on prescription data.
However, the findings are in line with those of prior studies showing that semaglutide may be associated with lower rates of alcohol and nicotine use, she said.
Earlier this year, Xu, along with National Institute on Drug Abuse Director Nora Volkow, MD, and colleagues, published a retrospective cohort study of nearly 84,000 patients with obesity. That analysis showed that semaglutide was associated with a significantly lower risk of new alcohol use disorder diagnoses.
In a previous editorial by Xu and Volkow that summarized the research to-date on GLP-1s for nicotine, alcohol, and substance use disorders, they note that “closing the addiction treatment gap and discovering new, more effective addiction medications are urgent priorities. In this regard, investigating the potential of GLP-1 analogue medications to treat substance use disorder deserves fast and rigorous testing.”
Caution Warranted
Commenting on the study, Riccardo De Giorgi, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Oxford in England, said at this point, “we have to be very careful about how we interpret these data.”
In August, De Giorgi published a study showing that semaglutide was associated with reduced risk for several neurologic and psychiatric outcomes including dementia and nicotine misuse.
While there is enough observational evidence linking GLP-1 medications with reduced SUD risk, he noted that “now is the time to move on and conduct some randomized clinical trials, specifically testing our hypothesis in people who have psychiatric disorders.”
De Giorgi also called for mechanistic studies of semaglutide and other so that researchers could learn more about how it works to reduce cravings. “Instead of going from bench to bed, we need to go back to the bench,” he said.
As previously reported, De Giorgi recently called on experts in the field to actively explore the potential of GLP-1 inhibitors for mental illness.
The study was funded by National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institute on Aging, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health. Xu reported no relevant financial relationships. De Giorgi reported receiving funding from the National Institute for Health Research Oxford Health Biomedical Research Centre.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Is Metformin An Unexpected Ally Against Long COVID?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have shown that metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces severe COVID-19 and postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also referred to as long COVID, in adults.
- A retrospective cohort analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection and the subsequent incidence of PASC.
- Researchers used data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) and National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) electronic health record (EHR) databases to identify adults (age, ≥ 21 years) with T2D prescribed a diabetes medication within the past 12 months.
- Participants were categorized into those using metformin (metformin group) and those using other noninsulin diabetes medications such as sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones (the comparator group); those who used glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the incidence of PASC or death within 180 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, defined using International Classification of Diseases U09.9 diagnosis code and/or computable phenotype defined by a predicted probability of > 75% for PASC using a machine learning model trained on patients diagnosed using U09.9 (PASC computable phenotype).
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers identified 51,385 and 37,947 participants from the N3C and PCORnet datasets, respectively.
- Metformin use was associated with a 21% lower risk for death or PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P < .001) and a 15% lower risk using the PASC computable phenotype (P < .001) in the N3C dataset than non-metformin use.
- In the PCORnet dataset, the risk for death or PASC was 13% lower using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P = .08) with metformin use vs non-metformin use, whereas the risk did not differ significantly between the groups when using the PASC computable phenotype (P = .58).
- The incidence of PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code for the metformin and comparator groups was similar between the two datasets (1.6% and 2.0% in N3C and 2.2 and 2.6% in PCORnet, respectively).
- However, when using the computable phenotype, the incidence rates of PASC for the metformin and comparator groups were 4.8% and 5.2% in N3C and 25.2% and 24.2% in PCORnet, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“The incidence of PASC was lower when defined by [International Classification of Diseases] code, compared with a computable phenotype in both databases,” the authors wrote. “This may reflect the challenges of clinical care for adults needing chronic medication management and the likelihood of those adults receiving a formal PASC diagnosis.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Steven G. Johnson, PhD, Institute for Health Informatics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data had several limitations, including the inability to examine a dose-dependent relationship and the lack of information on whether medications were taken before, during, or after the acute infection. The outcome definition involved the need for a medical encounter and, thus, may not capture data on all patients experiencing symptoms of PASC. The analysis focused on the prevalent use of chronic medications, limiting the assessment of initiating metformin in those diagnosed with COVID-19.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health Agreement as part of the RECOVER research program. One author reported receiving salary support from the Center for Pharmacoepidemiology and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies. Another author reported receiving grant support and consulting contracts, being involved in expert witness engagement, and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, diabetes management, and medical device companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have shown that metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces severe COVID-19 and postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also referred to as long COVID, in adults.
- A retrospective cohort analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection and the subsequent incidence of PASC.
- Researchers used data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) and National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) electronic health record (EHR) databases to identify adults (age, ≥ 21 years) with T2D prescribed a diabetes medication within the past 12 months.
- Participants were categorized into those using metformin (metformin group) and those using other noninsulin diabetes medications such as sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones (the comparator group); those who used glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the incidence of PASC or death within 180 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, defined using International Classification of Diseases U09.9 diagnosis code and/or computable phenotype defined by a predicted probability of > 75% for PASC using a machine learning model trained on patients diagnosed using U09.9 (PASC computable phenotype).
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers identified 51,385 and 37,947 participants from the N3C and PCORnet datasets, respectively.
- Metformin use was associated with a 21% lower risk for death or PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P < .001) and a 15% lower risk using the PASC computable phenotype (P < .001) in the N3C dataset than non-metformin use.
- In the PCORnet dataset, the risk for death or PASC was 13% lower using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P = .08) with metformin use vs non-metformin use, whereas the risk did not differ significantly between the groups when using the PASC computable phenotype (P = .58).
- The incidence of PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code for the metformin and comparator groups was similar between the two datasets (1.6% and 2.0% in N3C and 2.2 and 2.6% in PCORnet, respectively).
- However, when using the computable phenotype, the incidence rates of PASC for the metformin and comparator groups were 4.8% and 5.2% in N3C and 25.2% and 24.2% in PCORnet, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“The incidence of PASC was lower when defined by [International Classification of Diseases] code, compared with a computable phenotype in both databases,” the authors wrote. “This may reflect the challenges of clinical care for adults needing chronic medication management and the likelihood of those adults receiving a formal PASC diagnosis.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Steven G. Johnson, PhD, Institute for Health Informatics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data had several limitations, including the inability to examine a dose-dependent relationship and the lack of information on whether medications were taken before, during, or after the acute infection. The outcome definition involved the need for a medical encounter and, thus, may not capture data on all patients experiencing symptoms of PASC. The analysis focused on the prevalent use of chronic medications, limiting the assessment of initiating metformin in those diagnosed with COVID-19.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health Agreement as part of the RECOVER research program. One author reported receiving salary support from the Center for Pharmacoepidemiology and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies. Another author reported receiving grant support and consulting contracts, being involved in expert witness engagement, and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, diabetes management, and medical device companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have shown that metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces severe COVID-19 and postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also referred to as long COVID, in adults.
- A retrospective cohort analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection and the subsequent incidence of PASC.
- Researchers used data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) and National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) electronic health record (EHR) databases to identify adults (age, ≥ 21 years) with T2D prescribed a diabetes medication within the past 12 months.
- Participants were categorized into those using metformin (metformin group) and those using other noninsulin diabetes medications such as sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones (the comparator group); those who used glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the incidence of PASC or death within 180 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, defined using International Classification of Diseases U09.9 diagnosis code and/or computable phenotype defined by a predicted probability of > 75% for PASC using a machine learning model trained on patients diagnosed using U09.9 (PASC computable phenotype).
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers identified 51,385 and 37,947 participants from the N3C and PCORnet datasets, respectively.
- Metformin use was associated with a 21% lower risk for death or PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P < .001) and a 15% lower risk using the PASC computable phenotype (P < .001) in the N3C dataset than non-metformin use.
- In the PCORnet dataset, the risk for death or PASC was 13% lower using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P = .08) with metformin use vs non-metformin use, whereas the risk did not differ significantly between the groups when using the PASC computable phenotype (P = .58).
- The incidence of PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code for the metformin and comparator groups was similar between the two datasets (1.6% and 2.0% in N3C and 2.2 and 2.6% in PCORnet, respectively).
- However, when using the computable phenotype, the incidence rates of PASC for the metformin and comparator groups were 4.8% and 5.2% in N3C and 25.2% and 24.2% in PCORnet, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“The incidence of PASC was lower when defined by [International Classification of Diseases] code, compared with a computable phenotype in both databases,” the authors wrote. “This may reflect the challenges of clinical care for adults needing chronic medication management and the likelihood of those adults receiving a formal PASC diagnosis.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Steven G. Johnson, PhD, Institute for Health Informatics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data had several limitations, including the inability to examine a dose-dependent relationship and the lack of information on whether medications were taken before, during, or after the acute infection. The outcome definition involved the need for a medical encounter and, thus, may not capture data on all patients experiencing symptoms of PASC. The analysis focused on the prevalent use of chronic medications, limiting the assessment of initiating metformin in those diagnosed with COVID-19.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health Agreement as part of the RECOVER research program. One author reported receiving salary support from the Center for Pharmacoepidemiology and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies. Another author reported receiving grant support and consulting contracts, being involved in expert witness engagement, and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, diabetes management, and medical device companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nobel Prize in Medicine Awarded to MicroRNA Researchers
Victor Ambros, PhD, a researcher at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School, Worcester, and Gary Ruvkun, PhD, professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts, discovered microRNAs, a new class of RNA molecules.
“Their groundbreaking discovery in the small worm Caenorhabditis elegans revealed a completely new principle of gene regulation. This turned out to be essential for multicellular organisms, including humans,” said the Nobel Assembly in a statement.
Protein Expression
Genetic information flows from DNA during transcription to messenger RNA (mRNA) and then to protein biosynthesis. In that stage, mRNAs are translated so that proteins are produced according to the genetic instructions stored in the DNA.
Different cell types or tissues express unique sets of proteins, however. This specialized expression results from precise regulation of gene activity, so that in each cell type, only the correct set of genes is active. In this way, for example, muscle cells, intestinal cells, and various types of nerve cells can fulfill their functions.
Furthermore, gene activity must constantly be fine-tuned to adapt cell functions to changing conditions in our body and environment. When gene regulation goes awry, it can lead to serious outcomes such as cancer, diabetes, or autoimmune diseases. Therefore, understanding the regulation of gene activity has been an important goal for many decades.
In the 1960s, researchers had shown that specialized proteins called transcription factors bind to specific regions of DNA and control the flow of genetic information by determining which mRNAs are produced. Since that time, thousands of transcription factors have been identified. For a long time, scientists thought that the main principles of gene regulation were understood.
Roundworm Research
In the late 1980s, Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun were postdoctoral researchers in the laboratory of Robert Horvitz, PhD, who received the Nobel Prize in 2002 with Sydney Brenner and John Sulston. In Dr. Horvitz’s laboratory, they studied the relatively inconspicuous, 1-mm long roundworm C elegans.
Despite its small size, C elegans has many specialized cell types such as nerve and muscle cells that are also found in larger, more complex animals. These features make it a popular animal model.
Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun were interested in genes that ensure that different cell types develop at the right time. They examined two mutated worm strains, lin-4 and lin-14, that exhibited defects in the temporal activation of specific genes during development. The laureates wanted to identify mutated genes and understand their function.
Dr. Ambros had previously shown that lin-4 appeared to be a negative regulator of lin-14. But how lin-14 activity was blocked was unknown.
Collaboration Yields Breakthrough
After his postdoctoral years, Dr. Ambros analyzed the lin-4 mutant in his newly established laboratory at Harvard University. Systematic mapping allowed the cloning of the gene and led to an unexpected result: lin-4 produced an unusually short RNA molecule that lacked a code for protein synthesis. These surprising results suggested that this small RNA from lin-4 was responsible for inhibiting lin-14.
At the same time, Dr. Ruvkun, in his newly founded laboratory at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, studied the regulation of lin-14. In contradiction to the current understanding of gene regulation, he showed that it was not the production of lin-14 mRNA that was inhibited by lin-4. The regulation seems to occur at a later stage in the gene expression process, namely through the shutdown of protein synthesis. In addition, a section in lin-14 mRNA was discovered to be necessary for inhibition by lin-4.
The two laureates compared their results, leading to a groundbreaking discovery. The short lin-4 sequence matched complementary sequences in the relevant section of the lin-14 mRNA. Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun conducted further experiments showing that the lin-4 microRNA silences lin-14 by binding to the complementary sequences of its mRNA, thus blocking the production of the lin-14 protein. A new principle of gene regulation, mediated by a previously unknown type of RNA, the microRNA, had been discovered.
Subdued Initial Response
The results were published in Cell in 1993 and initially received little attention. However, interest grew in 2000 when Dr. Ruvkun’s research group published the discovery of another microRNA encoded by let-7.
In contrast to lin-4, let-7 was highly conserved and present throughout the animal kingdom. The article sparked great interest. In the following years, hundreds of microRNAs were identified. Today, researchers know that there are more than 1000 genes for various microRNAs in humans and that gene regulation by microRNAs is found in all multicellular organisms.
In addition to mapping new microRNAs, experiments by several research groups have elucidated fundamental mechanisms. Their binding leads to inhibition of protein synthesis or degradation of mRNA. Interestingly, a single microRNA can regulate the expression of many genes. Conversely, a single gene can be regulated by multiple microRNAs, thus coordinating and fine-tuning entire gene networks.
The cellular machinery for producing functional microRNAs is also used to produce other small RNA molecules in plants and animals, for example, as a means of protecting plants from viral infections. Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2006, described RNA interference, in which specific mRNA molecules are inactivated by the addition of double-stranded RNA molecules to cells.
Small RNAs, Great Importance
Gene regulation by microRNA has likely existed for hundreds of millions of years. This mechanism has enabled the evolution of increasingly complex organisms.
From genetic research, it is known that cells and tissues do not develop normally without microRNAs. Abnormal regulation can lead to cancer. Mutations in genes encoding microRNAs cause, among other things, congenital deafness and eye and skeletal diseases. And mutations in one of the proteins required for microRNA production lead to the DICER1 syndrome, a rare but severe syndrome associated with cancer in various organs and tissues.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Victor Ambros, PhD, a researcher at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School, Worcester, and Gary Ruvkun, PhD, professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts, discovered microRNAs, a new class of RNA molecules.
“Their groundbreaking discovery in the small worm Caenorhabditis elegans revealed a completely new principle of gene regulation. This turned out to be essential for multicellular organisms, including humans,” said the Nobel Assembly in a statement.
Protein Expression
Genetic information flows from DNA during transcription to messenger RNA (mRNA) and then to protein biosynthesis. In that stage, mRNAs are translated so that proteins are produced according to the genetic instructions stored in the DNA.
Different cell types or tissues express unique sets of proteins, however. This specialized expression results from precise regulation of gene activity, so that in each cell type, only the correct set of genes is active. In this way, for example, muscle cells, intestinal cells, and various types of nerve cells can fulfill their functions.
Furthermore, gene activity must constantly be fine-tuned to adapt cell functions to changing conditions in our body and environment. When gene regulation goes awry, it can lead to serious outcomes such as cancer, diabetes, or autoimmune diseases. Therefore, understanding the regulation of gene activity has been an important goal for many decades.
In the 1960s, researchers had shown that specialized proteins called transcription factors bind to specific regions of DNA and control the flow of genetic information by determining which mRNAs are produced. Since that time, thousands of transcription factors have been identified. For a long time, scientists thought that the main principles of gene regulation were understood.
Roundworm Research
In the late 1980s, Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun were postdoctoral researchers in the laboratory of Robert Horvitz, PhD, who received the Nobel Prize in 2002 with Sydney Brenner and John Sulston. In Dr. Horvitz’s laboratory, they studied the relatively inconspicuous, 1-mm long roundworm C elegans.
Despite its small size, C elegans has many specialized cell types such as nerve and muscle cells that are also found in larger, more complex animals. These features make it a popular animal model.
Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun were interested in genes that ensure that different cell types develop at the right time. They examined two mutated worm strains, lin-4 and lin-14, that exhibited defects in the temporal activation of specific genes during development. The laureates wanted to identify mutated genes and understand their function.
Dr. Ambros had previously shown that lin-4 appeared to be a negative regulator of lin-14. But how lin-14 activity was blocked was unknown.
Collaboration Yields Breakthrough
After his postdoctoral years, Dr. Ambros analyzed the lin-4 mutant in his newly established laboratory at Harvard University. Systematic mapping allowed the cloning of the gene and led to an unexpected result: lin-4 produced an unusually short RNA molecule that lacked a code for protein synthesis. These surprising results suggested that this small RNA from lin-4 was responsible for inhibiting lin-14.
At the same time, Dr. Ruvkun, in his newly founded laboratory at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, studied the regulation of lin-14. In contradiction to the current understanding of gene regulation, he showed that it was not the production of lin-14 mRNA that was inhibited by lin-4. The regulation seems to occur at a later stage in the gene expression process, namely through the shutdown of protein synthesis. In addition, a section in lin-14 mRNA was discovered to be necessary for inhibition by lin-4.
The two laureates compared their results, leading to a groundbreaking discovery. The short lin-4 sequence matched complementary sequences in the relevant section of the lin-14 mRNA. Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun conducted further experiments showing that the lin-4 microRNA silences lin-14 by binding to the complementary sequences of its mRNA, thus blocking the production of the lin-14 protein. A new principle of gene regulation, mediated by a previously unknown type of RNA, the microRNA, had been discovered.
Subdued Initial Response
The results were published in Cell in 1993 and initially received little attention. However, interest grew in 2000 when Dr. Ruvkun’s research group published the discovery of another microRNA encoded by let-7.
In contrast to lin-4, let-7 was highly conserved and present throughout the animal kingdom. The article sparked great interest. In the following years, hundreds of microRNAs were identified. Today, researchers know that there are more than 1000 genes for various microRNAs in humans and that gene regulation by microRNAs is found in all multicellular organisms.
In addition to mapping new microRNAs, experiments by several research groups have elucidated fundamental mechanisms. Their binding leads to inhibition of protein synthesis or degradation of mRNA. Interestingly, a single microRNA can regulate the expression of many genes. Conversely, a single gene can be regulated by multiple microRNAs, thus coordinating and fine-tuning entire gene networks.
The cellular machinery for producing functional microRNAs is also used to produce other small RNA molecules in plants and animals, for example, as a means of protecting plants from viral infections. Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2006, described RNA interference, in which specific mRNA molecules are inactivated by the addition of double-stranded RNA molecules to cells.
Small RNAs, Great Importance
Gene regulation by microRNA has likely existed for hundreds of millions of years. This mechanism has enabled the evolution of increasingly complex organisms.
From genetic research, it is known that cells and tissues do not develop normally without microRNAs. Abnormal regulation can lead to cancer. Mutations in genes encoding microRNAs cause, among other things, congenital deafness and eye and skeletal diseases. And mutations in one of the proteins required for microRNA production lead to the DICER1 syndrome, a rare but severe syndrome associated with cancer in various organs and tissues.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Victor Ambros, PhD, a researcher at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School, Worcester, and Gary Ruvkun, PhD, professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts, discovered microRNAs, a new class of RNA molecules.
“Their groundbreaking discovery in the small worm Caenorhabditis elegans revealed a completely new principle of gene regulation. This turned out to be essential for multicellular organisms, including humans,” said the Nobel Assembly in a statement.
Protein Expression
Genetic information flows from DNA during transcription to messenger RNA (mRNA) and then to protein biosynthesis. In that stage, mRNAs are translated so that proteins are produced according to the genetic instructions stored in the DNA.
Different cell types or tissues express unique sets of proteins, however. This specialized expression results from precise regulation of gene activity, so that in each cell type, only the correct set of genes is active. In this way, for example, muscle cells, intestinal cells, and various types of nerve cells can fulfill their functions.
Furthermore, gene activity must constantly be fine-tuned to adapt cell functions to changing conditions in our body and environment. When gene regulation goes awry, it can lead to serious outcomes such as cancer, diabetes, or autoimmune diseases. Therefore, understanding the regulation of gene activity has been an important goal for many decades.
In the 1960s, researchers had shown that specialized proteins called transcription factors bind to specific regions of DNA and control the flow of genetic information by determining which mRNAs are produced. Since that time, thousands of transcription factors have been identified. For a long time, scientists thought that the main principles of gene regulation were understood.
Roundworm Research
In the late 1980s, Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun were postdoctoral researchers in the laboratory of Robert Horvitz, PhD, who received the Nobel Prize in 2002 with Sydney Brenner and John Sulston. In Dr. Horvitz’s laboratory, they studied the relatively inconspicuous, 1-mm long roundworm C elegans.
Despite its small size, C elegans has many specialized cell types such as nerve and muscle cells that are also found in larger, more complex animals. These features make it a popular animal model.
Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun were interested in genes that ensure that different cell types develop at the right time. They examined two mutated worm strains, lin-4 and lin-14, that exhibited defects in the temporal activation of specific genes during development. The laureates wanted to identify mutated genes and understand their function.
Dr. Ambros had previously shown that lin-4 appeared to be a negative regulator of lin-14. But how lin-14 activity was blocked was unknown.
Collaboration Yields Breakthrough
After his postdoctoral years, Dr. Ambros analyzed the lin-4 mutant in his newly established laboratory at Harvard University. Systematic mapping allowed the cloning of the gene and led to an unexpected result: lin-4 produced an unusually short RNA molecule that lacked a code for protein synthesis. These surprising results suggested that this small RNA from lin-4 was responsible for inhibiting lin-14.
At the same time, Dr. Ruvkun, in his newly founded laboratory at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, studied the regulation of lin-14. In contradiction to the current understanding of gene regulation, he showed that it was not the production of lin-14 mRNA that was inhibited by lin-4. The regulation seems to occur at a later stage in the gene expression process, namely through the shutdown of protein synthesis. In addition, a section in lin-14 mRNA was discovered to be necessary for inhibition by lin-4.
The two laureates compared their results, leading to a groundbreaking discovery. The short lin-4 sequence matched complementary sequences in the relevant section of the lin-14 mRNA. Dr. Ambros and Dr. Ruvkun conducted further experiments showing that the lin-4 microRNA silences lin-14 by binding to the complementary sequences of its mRNA, thus blocking the production of the lin-14 protein. A new principle of gene regulation, mediated by a previously unknown type of RNA, the microRNA, had been discovered.
Subdued Initial Response
The results were published in Cell in 1993 and initially received little attention. However, interest grew in 2000 when Dr. Ruvkun’s research group published the discovery of another microRNA encoded by let-7.
In contrast to lin-4, let-7 was highly conserved and present throughout the animal kingdom. The article sparked great interest. In the following years, hundreds of microRNAs were identified. Today, researchers know that there are more than 1000 genes for various microRNAs in humans and that gene regulation by microRNAs is found in all multicellular organisms.
In addition to mapping new microRNAs, experiments by several research groups have elucidated fundamental mechanisms. Their binding leads to inhibition of protein synthesis or degradation of mRNA. Interestingly, a single microRNA can regulate the expression of many genes. Conversely, a single gene can be regulated by multiple microRNAs, thus coordinating and fine-tuning entire gene networks.
The cellular machinery for producing functional microRNAs is also used to produce other small RNA molecules in plants and animals, for example, as a means of protecting plants from viral infections. Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2006, described RNA interference, in which specific mRNA molecules are inactivated by the addition of double-stranded RNA molecules to cells.
Small RNAs, Great Importance
Gene regulation by microRNA has likely existed for hundreds of millions of years. This mechanism has enabled the evolution of increasingly complex organisms.
From genetic research, it is known that cells and tissues do not develop normally without microRNAs. Abnormal regulation can lead to cancer. Mutations in genes encoding microRNAs cause, among other things, congenital deafness and eye and skeletal diseases. And mutations in one of the proteins required for microRNA production lead to the DICER1 syndrome, a rare but severe syndrome associated with cancer in various organs and tissues.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lifestyle Medicine: Not Just for the Wealthy
Primary care clinicians understand that addressing lifestyle-related chronic disease health disparities in minority and lower-income communities is a significant opportunity to alleviate unnecessary suffering. Disparate health outcomes associated with underlying comorbidities during the COVID pandemic exposed the urgency of this problem.
When it comes to delivering evidence-based therapeutic lifestyle behavior interventions to these populations, however, there is a misconception that lifestyle medicine is only for the wealthy. Such a misconception needlessly widens the gap in health disparities because the truth is that everyone deserves access to lifestyle medicine. Fortunately, there are numerous successful examples of delivering these services to underresourced patients. We can all contribute to narrowing health inequities by sourcing increasingly abundant lifestyle medicine resources.
All patients’ lived experiences are unique, and there is a wide range of potential challenges to achieving lifestyle behavior change. Ignoring these obstacles is a disservice to patients and almost certainly results in treatment failure. Requirements to document SDOH have been a tremendous initial step.
The next step is to have conversations with every patient about the powerful outcomes of even small lifestyle changes. All too often, clinicians forgo conversations on lifestyle change with patients affected by adverse SDOH and assume that social obstacles automatically mean that patients are neither willing nor able to attempt behavior modification. Instead, it is an opportunity for clinicians, particularly those certified in lifestyle medicine, to meet patients where they are, work with them to identify solutions, and provide referrals to community-based organizations with resources to help.
Small Steps to Big Changes
Not all lifestyle behavior interventions need to be programmatic or time intensive. Clinicians can guide patients toward simple but specific actions that can make a difference in health outcomes over time. Small steps, like eating one can of beans or two bags of frozen leafy greens each week, are a good start toward adjusted eating patterns. The American College of Lifestyle Medicine offers a whole-food, plant-predominant meal guide to share with patients.
Individuals can increase their physical activity in their living rooms by doing sit-to-stands or balancing on one leg. Deep breathing and establishing a sleep routine are other lifestyle behavior changes without a price tag.
It is true that early adopters of lifestyle medicine often had difficulty practicing in underresourced communities. Those practitioners were forced to operate on a cash-pay basis, making access to care cost-prohibitive for many patients. However, board certification has been available since 2017, and lifestyle medicine is being integrated into medical schools and residency programs. Many such board-certified clinicians now work in large health systems and bill under the usual methods. There are also frameworks, such as the community-engaged lifestyle medicine model, showing how to treat patients affected by adverse SDOH effectively.
For example, patients at risk for malnutrition because of illnesses like chronic kidney disease, cancer, and heart failure receive medically tailored meals and access to a registered dietitian through a partnership between UC San Diego Health and Mama’s Kitchen. In Pennsylvania’s Lehigh Valley, where 1 in 10 of the approximately 700,000 residents face food insecurity, the Kellyn Foundation delivers fresh food through the Eat Real Food Mobile Market and offers whole-food, plant-predominant cooking classes, interactive elementary school programs focused on healthy lifestyle choices, and therapeutic lifestyle-change programs in community locations. Three months after launching new mobile market sites in Allentown, 1200 households were utilizing $15 weekly food vouchers through the program. Lifestyle medicine clinicians serve inner-city and rural areas in independent practices, large health systems, and community-based practice activities.
To improve access to lifestyle medicine in underresourced communities, more clinicians trained and certified in lifestyle medicine are needed. The Health Equity Achieved through Lifestyle Medicine Initiative supports a diverse lifestyle medicine workforce by offering scholarships to clinicians underrepresented in medicine and is working to train and certify at least one physician within each of the 1400 federally qualified health centers where clinicians are on the front lines of delivering care to the most underserved populations.
A meaningful first step for clinicians to address health disparities is to screen patients for and document SDOH. The American Academy of Family Physicians offers useful tools to screen patients, identify community-based resources, and help patients create action plans to overcome health risks and improve outcomes. In a promising trend to better support addressing SDOH in clinical care, the 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule included new codes to support this effort.
Not every patient will be ready or willing to begin a lifestyle medicine treatment plan. Still, all of them will be grateful for the opportunity to decide for themselves. If we are invested in narrowing health inequities, lifestyle medicine and behavior change must be a topic in clinical encounters with all our patients.
Dr. Collings, director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development, and past president, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, California, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care clinicians understand that addressing lifestyle-related chronic disease health disparities in minority and lower-income communities is a significant opportunity to alleviate unnecessary suffering. Disparate health outcomes associated with underlying comorbidities during the COVID pandemic exposed the urgency of this problem.
When it comes to delivering evidence-based therapeutic lifestyle behavior interventions to these populations, however, there is a misconception that lifestyle medicine is only for the wealthy. Such a misconception needlessly widens the gap in health disparities because the truth is that everyone deserves access to lifestyle medicine. Fortunately, there are numerous successful examples of delivering these services to underresourced patients. We can all contribute to narrowing health inequities by sourcing increasingly abundant lifestyle medicine resources.
All patients’ lived experiences are unique, and there is a wide range of potential challenges to achieving lifestyle behavior change. Ignoring these obstacles is a disservice to patients and almost certainly results in treatment failure. Requirements to document SDOH have been a tremendous initial step.
The next step is to have conversations with every patient about the powerful outcomes of even small lifestyle changes. All too often, clinicians forgo conversations on lifestyle change with patients affected by adverse SDOH and assume that social obstacles automatically mean that patients are neither willing nor able to attempt behavior modification. Instead, it is an opportunity for clinicians, particularly those certified in lifestyle medicine, to meet patients where they are, work with them to identify solutions, and provide referrals to community-based organizations with resources to help.
Small Steps to Big Changes
Not all lifestyle behavior interventions need to be programmatic or time intensive. Clinicians can guide patients toward simple but specific actions that can make a difference in health outcomes over time. Small steps, like eating one can of beans or two bags of frozen leafy greens each week, are a good start toward adjusted eating patterns. The American College of Lifestyle Medicine offers a whole-food, plant-predominant meal guide to share with patients.
Individuals can increase their physical activity in their living rooms by doing sit-to-stands or balancing on one leg. Deep breathing and establishing a sleep routine are other lifestyle behavior changes without a price tag.
It is true that early adopters of lifestyle medicine often had difficulty practicing in underresourced communities. Those practitioners were forced to operate on a cash-pay basis, making access to care cost-prohibitive for many patients. However, board certification has been available since 2017, and lifestyle medicine is being integrated into medical schools and residency programs. Many such board-certified clinicians now work in large health systems and bill under the usual methods. There are also frameworks, such as the community-engaged lifestyle medicine model, showing how to treat patients affected by adverse SDOH effectively.
For example, patients at risk for malnutrition because of illnesses like chronic kidney disease, cancer, and heart failure receive medically tailored meals and access to a registered dietitian through a partnership between UC San Diego Health and Mama’s Kitchen. In Pennsylvania’s Lehigh Valley, where 1 in 10 of the approximately 700,000 residents face food insecurity, the Kellyn Foundation delivers fresh food through the Eat Real Food Mobile Market and offers whole-food, plant-predominant cooking classes, interactive elementary school programs focused on healthy lifestyle choices, and therapeutic lifestyle-change programs in community locations. Three months after launching new mobile market sites in Allentown, 1200 households were utilizing $15 weekly food vouchers through the program. Lifestyle medicine clinicians serve inner-city and rural areas in independent practices, large health systems, and community-based practice activities.
To improve access to lifestyle medicine in underresourced communities, more clinicians trained and certified in lifestyle medicine are needed. The Health Equity Achieved through Lifestyle Medicine Initiative supports a diverse lifestyle medicine workforce by offering scholarships to clinicians underrepresented in medicine and is working to train and certify at least one physician within each of the 1400 federally qualified health centers where clinicians are on the front lines of delivering care to the most underserved populations.
A meaningful first step for clinicians to address health disparities is to screen patients for and document SDOH. The American Academy of Family Physicians offers useful tools to screen patients, identify community-based resources, and help patients create action plans to overcome health risks and improve outcomes. In a promising trend to better support addressing SDOH in clinical care, the 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule included new codes to support this effort.
Not every patient will be ready or willing to begin a lifestyle medicine treatment plan. Still, all of them will be grateful for the opportunity to decide for themselves. If we are invested in narrowing health inequities, lifestyle medicine and behavior change must be a topic in clinical encounters with all our patients.
Dr. Collings, director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development, and past president, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, California, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care clinicians understand that addressing lifestyle-related chronic disease health disparities in minority and lower-income communities is a significant opportunity to alleviate unnecessary suffering. Disparate health outcomes associated with underlying comorbidities during the COVID pandemic exposed the urgency of this problem.
When it comes to delivering evidence-based therapeutic lifestyle behavior interventions to these populations, however, there is a misconception that lifestyle medicine is only for the wealthy. Such a misconception needlessly widens the gap in health disparities because the truth is that everyone deserves access to lifestyle medicine. Fortunately, there are numerous successful examples of delivering these services to underresourced patients. We can all contribute to narrowing health inequities by sourcing increasingly abundant lifestyle medicine resources.
All patients’ lived experiences are unique, and there is a wide range of potential challenges to achieving lifestyle behavior change. Ignoring these obstacles is a disservice to patients and almost certainly results in treatment failure. Requirements to document SDOH have been a tremendous initial step.
The next step is to have conversations with every patient about the powerful outcomes of even small lifestyle changes. All too often, clinicians forgo conversations on lifestyle change with patients affected by adverse SDOH and assume that social obstacles automatically mean that patients are neither willing nor able to attempt behavior modification. Instead, it is an opportunity for clinicians, particularly those certified in lifestyle medicine, to meet patients where they are, work with them to identify solutions, and provide referrals to community-based organizations with resources to help.
Small Steps to Big Changes
Not all lifestyle behavior interventions need to be programmatic or time intensive. Clinicians can guide patients toward simple but specific actions that can make a difference in health outcomes over time. Small steps, like eating one can of beans or two bags of frozen leafy greens each week, are a good start toward adjusted eating patterns. The American College of Lifestyle Medicine offers a whole-food, plant-predominant meal guide to share with patients.
Individuals can increase their physical activity in their living rooms by doing sit-to-stands or balancing on one leg. Deep breathing and establishing a sleep routine are other lifestyle behavior changes without a price tag.
It is true that early adopters of lifestyle medicine often had difficulty practicing in underresourced communities. Those practitioners were forced to operate on a cash-pay basis, making access to care cost-prohibitive for many patients. However, board certification has been available since 2017, and lifestyle medicine is being integrated into medical schools and residency programs. Many such board-certified clinicians now work in large health systems and bill under the usual methods. There are also frameworks, such as the community-engaged lifestyle medicine model, showing how to treat patients affected by adverse SDOH effectively.
For example, patients at risk for malnutrition because of illnesses like chronic kidney disease, cancer, and heart failure receive medically tailored meals and access to a registered dietitian through a partnership between UC San Diego Health and Mama’s Kitchen. In Pennsylvania’s Lehigh Valley, where 1 in 10 of the approximately 700,000 residents face food insecurity, the Kellyn Foundation delivers fresh food through the Eat Real Food Mobile Market and offers whole-food, plant-predominant cooking classes, interactive elementary school programs focused on healthy lifestyle choices, and therapeutic lifestyle-change programs in community locations. Three months after launching new mobile market sites in Allentown, 1200 households were utilizing $15 weekly food vouchers through the program. Lifestyle medicine clinicians serve inner-city and rural areas in independent practices, large health systems, and community-based practice activities.
To improve access to lifestyle medicine in underresourced communities, more clinicians trained and certified in lifestyle medicine are needed. The Health Equity Achieved through Lifestyle Medicine Initiative supports a diverse lifestyle medicine workforce by offering scholarships to clinicians underrepresented in medicine and is working to train and certify at least one physician within each of the 1400 federally qualified health centers where clinicians are on the front lines of delivering care to the most underserved populations.
A meaningful first step for clinicians to address health disparities is to screen patients for and document SDOH. The American Academy of Family Physicians offers useful tools to screen patients, identify community-based resources, and help patients create action plans to overcome health risks and improve outcomes. In a promising trend to better support addressing SDOH in clinical care, the 2024 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule included new codes to support this effort.
Not every patient will be ready or willing to begin a lifestyle medicine treatment plan. Still, all of them will be grateful for the opportunity to decide for themselves. If we are invested in narrowing health inequities, lifestyle medicine and behavior change must be a topic in clinical encounters with all our patients.
Dr. Collings, director of lifestyle medicine, Silicon Valley Medical Development, and past president, American College of Lifestyle Medicine, Mountain View, California, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Time-Restricted Eating Is Not a Metabolic Magic Bullet
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
One out of three American adults — about 100 million people in this country — have the metabolic syndrome. I’m showing you the official criteria here, but essentially this is a syndrome of insulin resistance and visceral adiposity that predisposes us to a host of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and even dementia.
The metabolic syndrome is, fundamentally, a lifestyle disease. There is a direct line between our dietary habits and the wide availability of carbohydrate-rich, highly processed foods, and the rise in the syndrome in the population.
A saying I learned from one of my epidemiology teachers comes to mind: “Lifestyle diseases require lifestyle reinterventions.” But you know what? I’m not so sure anymore.
I’ve been around long enough to see multiple dietary fads come and go with varying efficacy. I grew up in the low-fat era, probably the most detrimental time to our national health as food manufacturers started replacing fats with carbohydrates, driving much of the problem we’re faced with today.
But I was also around for the Atkins diet and the low-carb craze — a healthier approach, all things being equal. And I’ve seen variants of these: the paleo diet (essentially a low-carb, high-protein diet based on minimally processed foods) and the Mediterranean diet, which sought to replace some percentage of fats with healthier fats.
And, of course, there is time-restricted eating.
Time-restricted eating, a variant of intermittent fasting, has the advantage of being very simple. No cookbooks, no recipes. Eat what you want — but limit it to certain hours in the day, ideally a window of less than 10 hours, such as 8 a.m. to 6 p.m.
When it comes to weight loss, the diets that work tend to work because they reduce calorie intake. I know, people will get angry about this, but thermodynamics is not just a good idea, it’s the law.
But weight loss is not the only reason we need to eat healthier. What we eat can impact our health in multiple ways; certain foods lead to more atherosclerosis, more inflammation, increased strain on the kidney and liver, and can affect our glucose homeostasis.
So I was really interested when I saw this article, “Time-Restricted Eating in Adults With Metabolic Syndrome,” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine October 1, which examined the effect of time-restricted eating on the metabolic syndrome itself. Could this lifestyle intervention cure this lifestyle disease?
In the study, 108 individuals, all of whom had the metabolic syndrome but not full-blown diabetes, were randomized to usual care — basically, nutrition education — vs time-restricted eating. In that group, participants were instructed to reduce their window of eating by at least 4 hours to achieve an 8- to 10-hour eating window. The groups were followed for 3 months.
Now, before we get to the results, it’s important to remember that the success of a lifestyle intervention trial is quite dependent on how well people adhere to the lifestyle intervention. Time-restricted eating is not as easy as taking a pill once a day.
The researchers had participants log their consumption using a smartphone app to confirm whether they were adhering to that restricted eating window.
Broadly speaking, they did. At baseline, both groups had an eating window of about 14 hours a day — think 7 a.m. to 9 p.m. The intervention group reduced that to just under 10 hours, with 10% of days falling outside of the target window.
Lifestyle change achieved, the primary outcome was the change in hemoglobin A1c at 3 months. A1c integrates the serum glucose over time and is thus a good indicator of the success of the intervention in terms of insulin resistance. But the effect was, honestly, disappointing.
Technically, the time-restricted-eating group had a greater A1c change than the control group — by 0.1 percentage points. On average, they went from a baseline A1c of 5.87 to a 3-month A1c of 5.75.
Other metabolic syndrome markers were equally lackluster: no difference in fasting glucose, mean glucose, or fasting insulin.
There was some weight change. The control group, which got that dietary education, lost 1.5% of body weight over the 3 months. The time-restricted-eating group lost 3.3% — about 7 pounds, which is reasonable.
With that weight loss came statistically significant, albeit modest improvements in BMI, body fat percentage, and LDL cholesterol.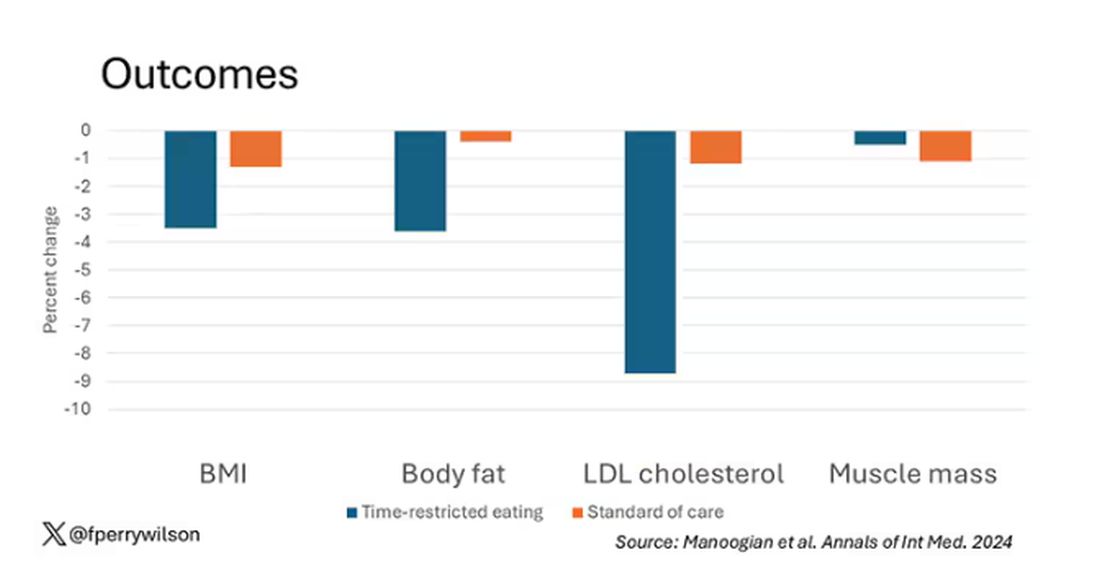
Of interest, despite the larger weight loss in the intermittent-fasting group, there was no difference in muscle mass loss, which is encouraging.
Taken together, we can say that, yes, it seems like time-restricted eating can help people lose some weight. This is essentially due to the fact that people eat fewer calories when they do time-restricted eating, as you can see here.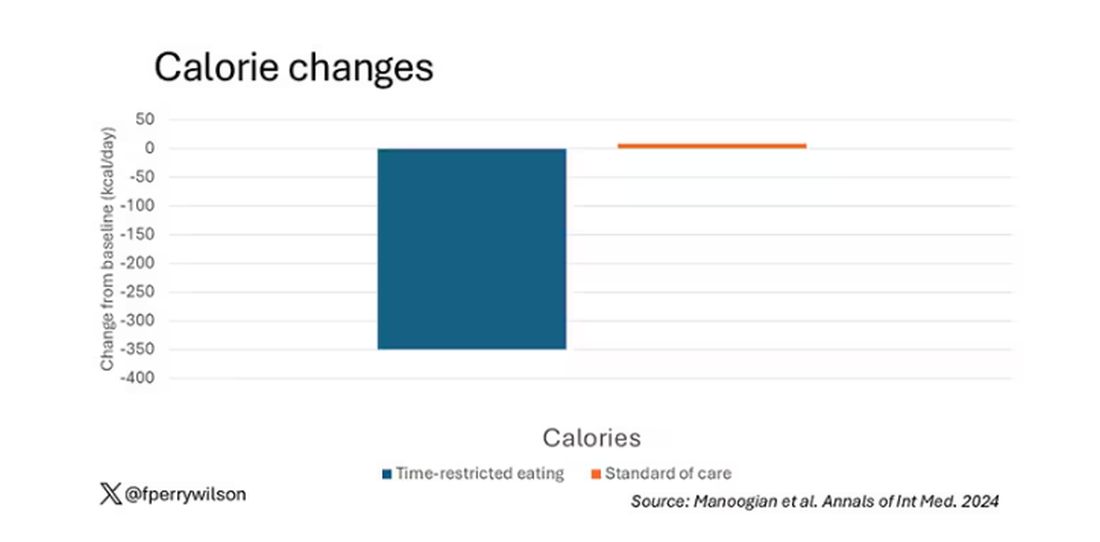
But, in the end, this trial examined whether this relatively straightforward lifestyle intervention would move the needle in terms of metabolic syndrome, and the data are not very compelling for that.
This graph shows how many of those five factors for metabolic syndrome the individuals in this trial had from the start to the end. You see that, over the 3 months, seven people in the time-restricted-eating group moved from having three criteria to two or one — being “cured” of metabolic syndrome, if you will. Nine people in the standard group were cured by that definition. Remember, they had to have at least three to have the syndrome and thus be eligible for the trial. 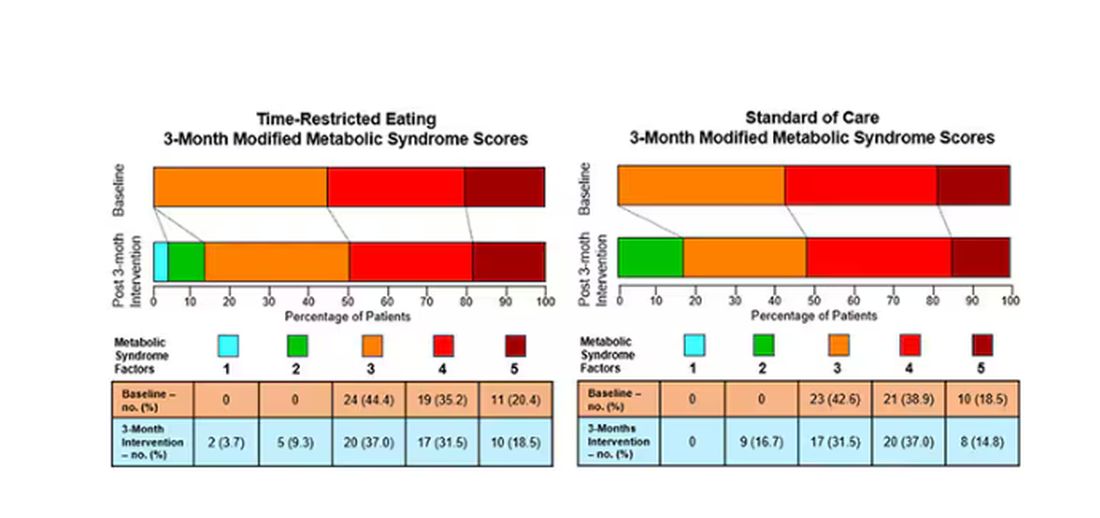
So If it just leads to weight loss by forcing people to consume less calories, then we need to acknowledge that we probably have better methods to achieve this same end. Ten years ago, I would have said that lifestyle change is the only way to end the epidemic of the metabolic syndrome in this country. Today, well, we live in a world of GLP-1 weight loss drugs. It is simply a different world now. Yes, they are expensive. Yes, they have side effects. But we need to evaluate them against the comparison. And so far, lifestyle changes alone are really no comparison.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
One out of three American adults — about 100 million people in this country — have the metabolic syndrome. I’m showing you the official criteria here, but essentially this is a syndrome of insulin resistance and visceral adiposity that predisposes us to a host of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and even dementia.
The metabolic syndrome is, fundamentally, a lifestyle disease. There is a direct line between our dietary habits and the wide availability of carbohydrate-rich, highly processed foods, and the rise in the syndrome in the population.
A saying I learned from one of my epidemiology teachers comes to mind: “Lifestyle diseases require lifestyle reinterventions.” But you know what? I’m not so sure anymore.
I’ve been around long enough to see multiple dietary fads come and go with varying efficacy. I grew up in the low-fat era, probably the most detrimental time to our national health as food manufacturers started replacing fats with carbohydrates, driving much of the problem we’re faced with today.
But I was also around for the Atkins diet and the low-carb craze — a healthier approach, all things being equal. And I’ve seen variants of these: the paleo diet (essentially a low-carb, high-protein diet based on minimally processed foods) and the Mediterranean diet, which sought to replace some percentage of fats with healthier fats.
And, of course, there is time-restricted eating.
Time-restricted eating, a variant of intermittent fasting, has the advantage of being very simple. No cookbooks, no recipes. Eat what you want — but limit it to certain hours in the day, ideally a window of less than 10 hours, such as 8 a.m. to 6 p.m.
When it comes to weight loss, the diets that work tend to work because they reduce calorie intake. I know, people will get angry about this, but thermodynamics is not just a good idea, it’s the law.
But weight loss is not the only reason we need to eat healthier. What we eat can impact our health in multiple ways; certain foods lead to more atherosclerosis, more inflammation, increased strain on the kidney and liver, and can affect our glucose homeostasis.
So I was really interested when I saw this article, “Time-Restricted Eating in Adults With Metabolic Syndrome,” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine October 1, which examined the effect of time-restricted eating on the metabolic syndrome itself. Could this lifestyle intervention cure this lifestyle disease?
In the study, 108 individuals, all of whom had the metabolic syndrome but not full-blown diabetes, were randomized to usual care — basically, nutrition education — vs time-restricted eating. In that group, participants were instructed to reduce their window of eating by at least 4 hours to achieve an 8- to 10-hour eating window. The groups were followed for 3 months.
Now, before we get to the results, it’s important to remember that the success of a lifestyle intervention trial is quite dependent on how well people adhere to the lifestyle intervention. Time-restricted eating is not as easy as taking a pill once a day.
The researchers had participants log their consumption using a smartphone app to confirm whether they were adhering to that restricted eating window.
Broadly speaking, they did. At baseline, both groups had an eating window of about 14 hours a day — think 7 a.m. to 9 p.m. The intervention group reduced that to just under 10 hours, with 10% of days falling outside of the target window.
Lifestyle change achieved, the primary outcome was the change in hemoglobin A1c at 3 months. A1c integrates the serum glucose over time and is thus a good indicator of the success of the intervention in terms of insulin resistance. But the effect was, honestly, disappointing.
Technically, the time-restricted-eating group had a greater A1c change than the control group — by 0.1 percentage points. On average, they went from a baseline A1c of 5.87 to a 3-month A1c of 5.75.
Other metabolic syndrome markers were equally lackluster: no difference in fasting glucose, mean glucose, or fasting insulin.
There was some weight change. The control group, which got that dietary education, lost 1.5% of body weight over the 3 months. The time-restricted-eating group lost 3.3% — about 7 pounds, which is reasonable.
With that weight loss came statistically significant, albeit modest improvements in BMI, body fat percentage, and LDL cholesterol.
Of interest, despite the larger weight loss in the intermittent-fasting group, there was no difference in muscle mass loss, which is encouraging.
Taken together, we can say that, yes, it seems like time-restricted eating can help people lose some weight. This is essentially due to the fact that people eat fewer calories when they do time-restricted eating, as you can see here.
But, in the end, this trial examined whether this relatively straightforward lifestyle intervention would move the needle in terms of metabolic syndrome, and the data are not very compelling for that.
This graph shows how many of those five factors for metabolic syndrome the individuals in this trial had from the start to the end. You see that, over the 3 months, seven people in the time-restricted-eating group moved from having three criteria to two or one — being “cured” of metabolic syndrome, if you will. Nine people in the standard group were cured by that definition. Remember, they had to have at least three to have the syndrome and thus be eligible for the trial. 
So If it just leads to weight loss by forcing people to consume less calories, then we need to acknowledge that we probably have better methods to achieve this same end. Ten years ago, I would have said that lifestyle change is the only way to end the epidemic of the metabolic syndrome in this country. Today, well, we live in a world of GLP-1 weight loss drugs. It is simply a different world now. Yes, they are expensive. Yes, they have side effects. But we need to evaluate them against the comparison. And so far, lifestyle changes alone are really no comparison.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
One out of three American adults — about 100 million people in this country — have the metabolic syndrome. I’m showing you the official criteria here, but essentially this is a syndrome of insulin resistance and visceral adiposity that predisposes us to a host of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and even dementia.
The metabolic syndrome is, fundamentally, a lifestyle disease. There is a direct line between our dietary habits and the wide availability of carbohydrate-rich, highly processed foods, and the rise in the syndrome in the population.
A saying I learned from one of my epidemiology teachers comes to mind: “Lifestyle diseases require lifestyle reinterventions.” But you know what? I’m not so sure anymore.
I’ve been around long enough to see multiple dietary fads come and go with varying efficacy. I grew up in the low-fat era, probably the most detrimental time to our national health as food manufacturers started replacing fats with carbohydrates, driving much of the problem we’re faced with today.
But I was also around for the Atkins diet and the low-carb craze — a healthier approach, all things being equal. And I’ve seen variants of these: the paleo diet (essentially a low-carb, high-protein diet based on minimally processed foods) and the Mediterranean diet, which sought to replace some percentage of fats with healthier fats.
And, of course, there is time-restricted eating.
Time-restricted eating, a variant of intermittent fasting, has the advantage of being very simple. No cookbooks, no recipes. Eat what you want — but limit it to certain hours in the day, ideally a window of less than 10 hours, such as 8 a.m. to 6 p.m.
When it comes to weight loss, the diets that work tend to work because they reduce calorie intake. I know, people will get angry about this, but thermodynamics is not just a good idea, it’s the law.
But weight loss is not the only reason we need to eat healthier. What we eat can impact our health in multiple ways; certain foods lead to more atherosclerosis, more inflammation, increased strain on the kidney and liver, and can affect our glucose homeostasis.
So I was really interested when I saw this article, “Time-Restricted Eating in Adults With Metabolic Syndrome,” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine October 1, which examined the effect of time-restricted eating on the metabolic syndrome itself. Could this lifestyle intervention cure this lifestyle disease?
In the study, 108 individuals, all of whom had the metabolic syndrome but not full-blown diabetes, were randomized to usual care — basically, nutrition education — vs time-restricted eating. In that group, participants were instructed to reduce their window of eating by at least 4 hours to achieve an 8- to 10-hour eating window. The groups were followed for 3 months.
Now, before we get to the results, it’s important to remember that the success of a lifestyle intervention trial is quite dependent on how well people adhere to the lifestyle intervention. Time-restricted eating is not as easy as taking a pill once a day.
The researchers had participants log their consumption using a smartphone app to confirm whether they were adhering to that restricted eating window.
Broadly speaking, they did. At baseline, both groups had an eating window of about 14 hours a day — think 7 a.m. to 9 p.m. The intervention group reduced that to just under 10 hours, with 10% of days falling outside of the target window.
Lifestyle change achieved, the primary outcome was the change in hemoglobin A1c at 3 months. A1c integrates the serum glucose over time and is thus a good indicator of the success of the intervention in terms of insulin resistance. But the effect was, honestly, disappointing.
Technically, the time-restricted-eating group had a greater A1c change than the control group — by 0.1 percentage points. On average, they went from a baseline A1c of 5.87 to a 3-month A1c of 5.75.
Other metabolic syndrome markers were equally lackluster: no difference in fasting glucose, mean glucose, or fasting insulin.
There was some weight change. The control group, which got that dietary education, lost 1.5% of body weight over the 3 months. The time-restricted-eating group lost 3.3% — about 7 pounds, which is reasonable.
With that weight loss came statistically significant, albeit modest improvements in BMI, body fat percentage, and LDL cholesterol.
Of interest, despite the larger weight loss in the intermittent-fasting group, there was no difference in muscle mass loss, which is encouraging.
Taken together, we can say that, yes, it seems like time-restricted eating can help people lose some weight. This is essentially due to the fact that people eat fewer calories when they do time-restricted eating, as you can see here.
But, in the end, this trial examined whether this relatively straightforward lifestyle intervention would move the needle in terms of metabolic syndrome, and the data are not very compelling for that.
This graph shows how many of those five factors for metabolic syndrome the individuals in this trial had from the start to the end. You see that, over the 3 months, seven people in the time-restricted-eating group moved from having three criteria to two or one — being “cured” of metabolic syndrome, if you will. Nine people in the standard group were cured by that definition. Remember, they had to have at least three to have the syndrome and thus be eligible for the trial. 
So If it just leads to weight loss by forcing people to consume less calories, then we need to acknowledge that we probably have better methods to achieve this same end. Ten years ago, I would have said that lifestyle change is the only way to end the epidemic of the metabolic syndrome in this country. Today, well, we live in a world of GLP-1 weight loss drugs. It is simply a different world now. Yes, they are expensive. Yes, they have side effects. But we need to evaluate them against the comparison. And so far, lifestyle changes alone are really no comparison.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Detecting Type 2 Diabetes Through Voice: How Does It Work?
An international study, Colive Voice, presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 conference, shows that These results “open up possibilities for developing a first-line, noninvasive, and rapid screening tool for T2D, feasible with just a few seconds of voice recording on a smartphone or during consultations,” explained the study’s principal investigator Guy Fagherazzi, PhD, a diabetes epidemiologist at the Luxembourg Institute of Health, in an interview with this news organization.
How did the idea of detecting diabetes through voice come about?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we began analyzing voice recordings from patients with chronic diseases. We wanted to find solutions to assess people’s health remotely, without physical contact. We quickly realized that this approach could be extended to other diseases. Because my main research focus has always been diabetes, I looked into how voice characteristics might correlate with diabetes. Previous studies had indicated that patients with diabetes have distinct voices compared with the general population, and this insight formed the starting point.
What mechanism could explain why patients with T2D have different voice characteristics?
It’s challenging to pinpoint a single factor that would explain why patients with T2D have different voices from those without diabetes. Several factors are involved.
Some biological mechanisms, especially those affecting the vascular system, influence symptoms in people with metabolic diseases such as diabetes. For example, people with T2D have more frequent cardiorespiratory fatigue. Obesity and overweight are also key factors, as these conditions can slightly alter vocal parameters compared with people of normal weight. Hypertension, common in patients with T2D, adds to the complexity.
Neurologic complications can affect the nerves and muscles involved in voice production, particularly the vocal cords.
Therefore, respiratory fatigue, neuropathies, and other conditions such as dehydration and gastric acid reflux, which are more common in patients with diabetes, can contribute to differences in voice.
These differences might not be noticeable to the human ear. That’s why we often don’t notice the link between voice and diabetes. However, technological advancements in signal processing and artificial intelligence allow us to extract a large amount of information from these subtle variations. By analyzing these small differences, we can detect diabetes with a reasonable degree of accuracy.
In your study, you mention that voice tone can indicate diabetic status. Could you elaborate?
Yes, voice tone can be affected, though it’s a complex, multidimensional phenomenon.
Patients who have had diabetes for 5-10 years, or longer, tend to have a rougher voice than those without diabetes of the same age and gender. In our study, we were able to extract many voice characteristics from the raw audio signal, which is why it’s difficult to isolate one specific factor that stands out.
Is there a difference in voice changes between patients with well-managed diabetes and those whose disease is uncontrolled?
The roughness of the voice tends to increase with the duration of diabetes. It’s more noticeable in people with poorly controlled diabetes. Our hypothesis, based on the results we presented at the EASD conference, is that fluctuations in blood sugar levels, both hypo- and hyperglycemia, may cause short-term changes in the voice. There are also many subtle, rapid changes that could potentially be detected, though we haven’t confirmed this yet. We’re currently conducting additional studies to explore this.
Why did you ask participants to read a passage from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
We used a highly standardized approach. Participants completed several recordings, including holding the sound “Aaaaaa” for as long as possible in one breath. They also read a passage, which helps us better distinguish between patients with and those without diabetes. This method works slightly better than other sounds typically used for analyzing diseases. We chose this particular text in the participant’s native language because it’s neutral and doesn’t trigger emotional fluctuations. Because Colive Voice is an international, multilingual study, we use official translations in various languages.
Your research focuses on T2D. Do you plan to study type 1 diabetes (T1D) as well?
We believe that individuals with T1D also exhibit voice changes over time. However, our current focus is on T2D because our goal is to develop large-scale screening methods. T1D, typically diagnosed in childhood, requires different screening approaches. For now, our research mainly involves adults.
Were there any gender differences in the accuracy of your voice analysis?
Yes, voice studies generally show that women have different vocal signatures from men, partly owing to hormonal fluctuations that affect pitch and tone. Detecting differences between healthy individuals and those with diabetes can sometimes be more challenging in women, depending on the condition. In our study, we achieved about 70% accuracy for women compared with 75% for men.
The EASD results focused on a US-based population. When can we expect data from France?
We started with the US because we could quickly gather a large number of patients. Now, we’re expanding to global and language-specific analyses. French data are certainly a priority, and we’re working on it. We encourage people to participate — it takes only 20 minutes and contributes to innovative research on noninvasive diabetes detection. Participants can sign up at www.colivevoice.org
Dr. Fagherazzi heads the Deep Digital Phenotyping laboratory and the Department of Precision Health at the Luxembourg Institute of Health. His research focuses on integrating new technologies and digital data into diabetes research. He has declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An international study, Colive Voice, presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 conference, shows that These results “open up possibilities for developing a first-line, noninvasive, and rapid screening tool for T2D, feasible with just a few seconds of voice recording on a smartphone or during consultations,” explained the study’s principal investigator Guy Fagherazzi, PhD, a diabetes epidemiologist at the Luxembourg Institute of Health, in an interview with this news organization.
How did the idea of detecting diabetes through voice come about?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we began analyzing voice recordings from patients with chronic diseases. We wanted to find solutions to assess people’s health remotely, without physical contact. We quickly realized that this approach could be extended to other diseases. Because my main research focus has always been diabetes, I looked into how voice characteristics might correlate with diabetes. Previous studies had indicated that patients with diabetes have distinct voices compared with the general population, and this insight formed the starting point.
What mechanism could explain why patients with T2D have different voice characteristics?
It’s challenging to pinpoint a single factor that would explain why patients with T2D have different voices from those without diabetes. Several factors are involved.
Some biological mechanisms, especially those affecting the vascular system, influence symptoms in people with metabolic diseases such as diabetes. For example, people with T2D have more frequent cardiorespiratory fatigue. Obesity and overweight are also key factors, as these conditions can slightly alter vocal parameters compared with people of normal weight. Hypertension, common in patients with T2D, adds to the complexity.
Neurologic complications can affect the nerves and muscles involved in voice production, particularly the vocal cords.
Therefore, respiratory fatigue, neuropathies, and other conditions such as dehydration and gastric acid reflux, which are more common in patients with diabetes, can contribute to differences in voice.
These differences might not be noticeable to the human ear. That’s why we often don’t notice the link between voice and diabetes. However, technological advancements in signal processing and artificial intelligence allow us to extract a large amount of information from these subtle variations. By analyzing these small differences, we can detect diabetes with a reasonable degree of accuracy.
In your study, you mention that voice tone can indicate diabetic status. Could you elaborate?
Yes, voice tone can be affected, though it’s a complex, multidimensional phenomenon.
Patients who have had diabetes for 5-10 years, or longer, tend to have a rougher voice than those without diabetes of the same age and gender. In our study, we were able to extract many voice characteristics from the raw audio signal, which is why it’s difficult to isolate one specific factor that stands out.
Is there a difference in voice changes between patients with well-managed diabetes and those whose disease is uncontrolled?
The roughness of the voice tends to increase with the duration of diabetes. It’s more noticeable in people with poorly controlled diabetes. Our hypothesis, based on the results we presented at the EASD conference, is that fluctuations in blood sugar levels, both hypo- and hyperglycemia, may cause short-term changes in the voice. There are also many subtle, rapid changes that could potentially be detected, though we haven’t confirmed this yet. We’re currently conducting additional studies to explore this.
Why did you ask participants to read a passage from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
We used a highly standardized approach. Participants completed several recordings, including holding the sound “Aaaaaa” for as long as possible in one breath. They also read a passage, which helps us better distinguish between patients with and those without diabetes. This method works slightly better than other sounds typically used for analyzing diseases. We chose this particular text in the participant’s native language because it’s neutral and doesn’t trigger emotional fluctuations. Because Colive Voice is an international, multilingual study, we use official translations in various languages.
Your research focuses on T2D. Do you plan to study type 1 diabetes (T1D) as well?
We believe that individuals with T1D also exhibit voice changes over time. However, our current focus is on T2D because our goal is to develop large-scale screening methods. T1D, typically diagnosed in childhood, requires different screening approaches. For now, our research mainly involves adults.
Were there any gender differences in the accuracy of your voice analysis?
Yes, voice studies generally show that women have different vocal signatures from men, partly owing to hormonal fluctuations that affect pitch and tone. Detecting differences between healthy individuals and those with diabetes can sometimes be more challenging in women, depending on the condition. In our study, we achieved about 70% accuracy for women compared with 75% for men.
The EASD results focused on a US-based population. When can we expect data from France?
We started with the US because we could quickly gather a large number of patients. Now, we’re expanding to global and language-specific analyses. French data are certainly a priority, and we’re working on it. We encourage people to participate — it takes only 20 minutes and contributes to innovative research on noninvasive diabetes detection. Participants can sign up at www.colivevoice.org
Dr. Fagherazzi heads the Deep Digital Phenotyping laboratory and the Department of Precision Health at the Luxembourg Institute of Health. His research focuses on integrating new technologies and digital data into diabetes research. He has declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An international study, Colive Voice, presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 conference, shows that These results “open up possibilities for developing a first-line, noninvasive, and rapid screening tool for T2D, feasible with just a few seconds of voice recording on a smartphone or during consultations,” explained the study’s principal investigator Guy Fagherazzi, PhD, a diabetes epidemiologist at the Luxembourg Institute of Health, in an interview with this news organization.
How did the idea of detecting diabetes through voice come about?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we began analyzing voice recordings from patients with chronic diseases. We wanted to find solutions to assess people’s health remotely, without physical contact. We quickly realized that this approach could be extended to other diseases. Because my main research focus has always been diabetes, I looked into how voice characteristics might correlate with diabetes. Previous studies had indicated that patients with diabetes have distinct voices compared with the general population, and this insight formed the starting point.
What mechanism could explain why patients with T2D have different voice characteristics?
It’s challenging to pinpoint a single factor that would explain why patients with T2D have different voices from those without diabetes. Several factors are involved.
Some biological mechanisms, especially those affecting the vascular system, influence symptoms in people with metabolic diseases such as diabetes. For example, people with T2D have more frequent cardiorespiratory fatigue. Obesity and overweight are also key factors, as these conditions can slightly alter vocal parameters compared with people of normal weight. Hypertension, common in patients with T2D, adds to the complexity.
Neurologic complications can affect the nerves and muscles involved in voice production, particularly the vocal cords.
Therefore, respiratory fatigue, neuropathies, and other conditions such as dehydration and gastric acid reflux, which are more common in patients with diabetes, can contribute to differences in voice.
These differences might not be noticeable to the human ear. That’s why we often don’t notice the link between voice and diabetes. However, technological advancements in signal processing and artificial intelligence allow us to extract a large amount of information from these subtle variations. By analyzing these small differences, we can detect diabetes with a reasonable degree of accuracy.
In your study, you mention that voice tone can indicate diabetic status. Could you elaborate?
Yes, voice tone can be affected, though it’s a complex, multidimensional phenomenon.
Patients who have had diabetes for 5-10 years, or longer, tend to have a rougher voice than those without diabetes of the same age and gender. In our study, we were able to extract many voice characteristics from the raw audio signal, which is why it’s difficult to isolate one specific factor that stands out.
Is there a difference in voice changes between patients with well-managed diabetes and those whose disease is uncontrolled?
The roughness of the voice tends to increase with the duration of diabetes. It’s more noticeable in people with poorly controlled diabetes. Our hypothesis, based on the results we presented at the EASD conference, is that fluctuations in blood sugar levels, both hypo- and hyperglycemia, may cause short-term changes in the voice. There are also many subtle, rapid changes that could potentially be detected, though we haven’t confirmed this yet. We’re currently conducting additional studies to explore this.
Why did you ask participants to read a passage from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
We used a highly standardized approach. Participants completed several recordings, including holding the sound “Aaaaaa” for as long as possible in one breath. They also read a passage, which helps us better distinguish between patients with and those without diabetes. This method works slightly better than other sounds typically used for analyzing diseases. We chose this particular text in the participant’s native language because it’s neutral and doesn’t trigger emotional fluctuations. Because Colive Voice is an international, multilingual study, we use official translations in various languages.
Your research focuses on T2D. Do you plan to study type 1 diabetes (T1D) as well?
We believe that individuals with T1D also exhibit voice changes over time. However, our current focus is on T2D because our goal is to develop large-scale screening methods. T1D, typically diagnosed in childhood, requires different screening approaches. For now, our research mainly involves adults.
Were there any gender differences in the accuracy of your voice analysis?
Yes, voice studies generally show that women have different vocal signatures from men, partly owing to hormonal fluctuations that affect pitch and tone. Detecting differences between healthy individuals and those with diabetes can sometimes be more challenging in women, depending on the condition. In our study, we achieved about 70% accuracy for women compared with 75% for men.
The EASD results focused on a US-based population. When can we expect data from France?
We started with the US because we could quickly gather a large number of patients. Now, we’re expanding to global and language-specific analyses. French data are certainly a priority, and we’re working on it. We encourage people to participate — it takes only 20 minutes and contributes to innovative research on noninvasive diabetes detection. Participants can sign up at www.colivevoice.org
Dr. Fagherazzi heads the Deep Digital Phenotyping laboratory and the Department of Precision Health at the Luxembourg Institute of Health. His research focuses on integrating new technologies and digital data into diabetes research. He has declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2024
Cannabis Use Rising in Diabetes: What Do Endos Need to Know?
A recent US prevalence study estimated that 9% adults with diabetes used cannabis in the last month, a 33.7% increase between 2021 and 2022. Nearly half (48.9%) of users were younger than 50 years.
Cannabis use is also increasing sharply among those aged 65 years or older, many of whom have diabetes and other chronic conditions. In this demographic, the perceived risk surrounding regular cannabis use has dropped significantly, even as the data tell another story — that they are particularly at risk from emergency department visits for cannabis poisoning.
As legalization continues and cannabis products proliferate, endocrinologists will likely face more patients of all ages seeking advice about its use. Yet with few evidence-based resources to turn to, endocrinologists advising patients in this area are mostly left fending for themselves.
Evidence ‘Limited’
“The evidence on cannabis is limited mainly because of its scheduling in the United States,” Jay Shubrook, DO, a professor and diabetologist at College of Osteopathic Medicine, Touro University California, in Vallejo, California, told this news organization.
“It was declared to be a schedule I drug in the 1970s, which meant it was ‘dangerous’ and ‘had no medical benefit.’ This made it hard to access and study in human trials.”
That will likely change soon. On May 16, 2024, the US Department of Justice submitted a proposal to move marijuana from a schedule I to a schedule III drug under the Controlled Substances Act, emphasizing its accepted medical use. If approved, the door will open to more investigators seeking to study the effects of cannabis.
Yet, even in Canada, where recreational use has been legal since 2018 and cannabis is sold widely with government support, there are little hard data to guide practice. In 2019, Diabetes Canada issued a position statement on recreational cannabis use in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). It sought to evaluate the effects of cannabis on metabolic factors and diabetes complications, as well as self-management behaviors in those aged 13 years or older.
The authors noted that five of the six studies upon which the statement was based did not consider or report the routes of cannabis administration, which have differing risks. In addition, their recommendations were based on grade D evidence and consensus.
What Patients Are Taking
Cannabis — also known as marijuana, weed, pot, or bud — refers to the dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. The plant contains more than 100 compounds, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the euphoric “high,” and other active compounds, including cannabidiol (CBD), which by itself is not mind-altering.
Cannabis can be ingested in several ways. It can be smoked (ie, joints, blunts, pipes, and water pipes), ingested in edible form (mixed or infused into foods), and inhaled using electronic vaporizing devices (ie, e-cigarettes or vape pens).
Compounds in cannabis can also be extracted to make oils and concentrates that can be vaped or inhaled. Smoking oils, concentrates, and extracts from the cannabis plant, known as “dabbing,” are on the rise in the United States.
There are no validated or standard dosage recommendations for cannabis strains and formulations, THC/CBD ratios, or modes of administration. Therefore, the Canadian Pharmacists Association prepared a guide for finding a safe and effective dose for medical purposes. GoodRx, a website with information on prescription drug prices, says that larger doses of THC pose greater risks, noting that the potency of cannabis has increased from 4% in 1995 to about 14% in 2019.
Potential Risks and Benefits: Canadian and US Perspectives
Health and safety risks vary with each of the different ways of using cannabis for individuals with and without diabetes, depending on a host of patient- and product-specific factors.
In a recent article proposing a “THC unit” for Canada’s legal cannabis market, researchers reported that consumers lack familiarity with THC levels, don’t know what constitutes a “low” or “high” THC amount, have trouble dosing, overconsume, and commonly experience adverse health events from cannabis use.
A recent study suggested that most clinicians are similarly uninformed, with “a lack of knowledge of beneficial effects, adverse effects, and of how to advise patients,” even for medical cannabis.
Diabetes Canada takes a stab at summarizing what’s known with respect to cannabis and diabetes, stating that:
“Research on recreational cannabis use suggests it may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors. The safety of recreational cannabis use has not been demonstrated, whereas regular cannabis use is associated with worsening glycemic control, more diabetes-related complications, and poorer self-care behaviors, such as adequate glucose monitoring, adherence to medications, and compliance with dietary and physical activity recommendations for people living with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.”
The American Diabetes Association’s information on cannabis consists of a patient-oriented article on CBD oil. The article stated:
“There’s a lot of hype surrounding CBD oil and diabetes. There is no noticeable effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers continue to study the effects of CBD on diabetes in animal studies.”
It concludes that:
“Although many claims continue to be made about CBD oil, there is little evidence of any benefit. It’s certainly not an alternative to traditional diabetes management. The safety of CBD is also unknown — it may have dangerous side effects that we won’t know about unless further research is done.”
A Roundup of Recent Studies
A smattering of recent studies have touched on various aspects of cannabis consumption and diabetes.
Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and co-director of CUChange at the University of Colorado Boulder, has been evaluating cannabis use in young adults (ages 21-40 years) in the SONIC study. Dr. Bryan reported at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions that cannabis users were more likely to have a lower body mass index and less likely to develop T2D. Furthermore, chronic cannabis users were less likely to have measures of inflammation and no loss of insulin sensitivity.
Another study by Dr. Bryan’s group found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
Similarly positive results were found in a 15-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of THC/CBD spray for neuropathic pain among treatment-resistant patients. The investigators reported that “clinically important improvements” were seen in pain, sleep quality, and subjective impressions of pain. Another small study of inhaled cannabis in treatment-refractory patients found a dose-dependent reduction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain.
Findings from a 9-year longitudinal study of approximately 18,000 Swedish men and women suggested no association between cannabis and subsequent T2D development after controlling for age, although these authors also called for longer follow-up and more detailed information about cannabis use to make “more robust” conclusions.
On the other side of the spectrum, a “rapid” review of recreational cannabis use in people with T1D and T2D found that recreational cannabis use may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors and may increase risks for peripheral arterial occlusion, myocardial infarction, and renal disease. However, the authors cautioned that more robust research is needed to confirm the potential impact of cannabis on diabetes.
How to Advise Patients
When Dr. Shubrook was working with patients with diabetes in his family medicine practice in Ohio, cannabis wasn’t legal.
“’Don’t ask, don’t tell’ was the way we handled it then,” he said.
By contrast, in California, where he’s currently located, “it’s pretty well accepted and legal, and patients volunteer information about use, even if it’s recreational,” he said. “Realizing this was something we could talk about was really eye-opening to me.”
Talking to patients about cannabis use is a “20-minute conversation that details what they’re doing,” he said. He proceeds by asking questions: Are you using for recreational or medicinal purposes? What do you take? What do you take it for? Does it work?
“People will tell you,” Dr. Shubrook said. “They know exactly what it works or doesn’t work for and how it affects their glucose control, which in most cases is only minimally.”
He tells patients he would prefer they don’t inhale cannabis, given the risks posed to the lungs.
“Edibles may have a slower onset of effect, but depending on what they’re adding it to, glucose might be affected,” he noted. “And I have seen that chronic use can lead to hyperemesis syndrome.”
Overall, he said, “Take the time to talk to your patients about cannabis — it will allow them to be honest with you, and you can improve the specificity and safety of its use. If cannabis is legal in your state, encourage people to go to legal dispensaries, which will reduce the risk of it being laced with another drug that could increase the danger of use.”
A recent US prevalence study found that people with diabetes who use cannabis likely engage in other substance and psychoactive substance use, including tobacco use, binge drinking, and misuse of opioids and stimulants.
“Use of these additional substances could further exacerbate the health risks associated with diabetes and also emphasizes the importance of addressing polysubstance use among adults with diabetes,” the study’s author Benjamin H. Han, MD, Division of Geriatrics, Gerontology and Palliative Care, Department of Medicine, US San Diego School of Medicine in La Jolla, California, told this news organization.
“We were surprised at how strong the associations were, especially with use of substances that can increase cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Han added. “And given the strong association we found between cannabis use and use of other psychoactive substances in diabetes, clinicians must screen all their patients for psychoactive substance use.”
Diabetes Canada’s position paper states that despite the limited evidence, “there were sufficient data to begin developing recommendations for type 1 and type 2 diabetes about education, counseling, and management related to recreational cannabis use.”
Their recommendations include the following:
- Healthcare professionals should engage their patients in discussions about substance use on a regular basis, with a nonjudgmental approach.
- The use of recreational cannabis is not recommended for adolescents and adults with diabetes.
- People with T1D should avoid recreational cannabis use because of the increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- For adults with T1D or T2D who intend to use cannabis recreationally, individualized assessment and counseling should be offered to inform them of the general risks of cannabis, with a focus on harm reduction and reduction of the risk for potential adverse effects on diabetes management and complications.
- People with T1D or T2D should be offered education on and encouraged to read public information available through resources from various Canadian health authorities about the general risks of cannabis use to reduce the risk for nondiabetes-related adverse effects of cannabis consumption.
Of note, in 2018, the Canadian government produced an exhaustive compendium of information on cannabis for healthcare professionals that includes information relevant to managing patients with diabetes.
Dr. Shubrook and Dr. Han reported no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent US prevalence study estimated that 9% adults with diabetes used cannabis in the last month, a 33.7% increase between 2021 and 2022. Nearly half (48.9%) of users were younger than 50 years.
Cannabis use is also increasing sharply among those aged 65 years or older, many of whom have diabetes and other chronic conditions. In this demographic, the perceived risk surrounding regular cannabis use has dropped significantly, even as the data tell another story — that they are particularly at risk from emergency department visits for cannabis poisoning.
As legalization continues and cannabis products proliferate, endocrinologists will likely face more patients of all ages seeking advice about its use. Yet with few evidence-based resources to turn to, endocrinologists advising patients in this area are mostly left fending for themselves.
Evidence ‘Limited’
“The evidence on cannabis is limited mainly because of its scheduling in the United States,” Jay Shubrook, DO, a professor and diabetologist at College of Osteopathic Medicine, Touro University California, in Vallejo, California, told this news organization.
“It was declared to be a schedule I drug in the 1970s, which meant it was ‘dangerous’ and ‘had no medical benefit.’ This made it hard to access and study in human trials.”
That will likely change soon. On May 16, 2024, the US Department of Justice submitted a proposal to move marijuana from a schedule I to a schedule III drug under the Controlled Substances Act, emphasizing its accepted medical use. If approved, the door will open to more investigators seeking to study the effects of cannabis.
Yet, even in Canada, where recreational use has been legal since 2018 and cannabis is sold widely with government support, there are little hard data to guide practice. In 2019, Diabetes Canada issued a position statement on recreational cannabis use in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). It sought to evaluate the effects of cannabis on metabolic factors and diabetes complications, as well as self-management behaviors in those aged 13 years or older.
The authors noted that five of the six studies upon which the statement was based did not consider or report the routes of cannabis administration, which have differing risks. In addition, their recommendations were based on grade D evidence and consensus.
What Patients Are Taking
Cannabis — also known as marijuana, weed, pot, or bud — refers to the dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. The plant contains more than 100 compounds, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the euphoric “high,” and other active compounds, including cannabidiol (CBD), which by itself is not mind-altering.
Cannabis can be ingested in several ways. It can be smoked (ie, joints, blunts, pipes, and water pipes), ingested in edible form (mixed or infused into foods), and inhaled using electronic vaporizing devices (ie, e-cigarettes or vape pens).
Compounds in cannabis can also be extracted to make oils and concentrates that can be vaped or inhaled. Smoking oils, concentrates, and extracts from the cannabis plant, known as “dabbing,” are on the rise in the United States.
There are no validated or standard dosage recommendations for cannabis strains and formulations, THC/CBD ratios, or modes of administration. Therefore, the Canadian Pharmacists Association prepared a guide for finding a safe and effective dose for medical purposes. GoodRx, a website with information on prescription drug prices, says that larger doses of THC pose greater risks, noting that the potency of cannabis has increased from 4% in 1995 to about 14% in 2019.
Potential Risks and Benefits: Canadian and US Perspectives
Health and safety risks vary with each of the different ways of using cannabis for individuals with and without diabetes, depending on a host of patient- and product-specific factors.
In a recent article proposing a “THC unit” for Canada’s legal cannabis market, researchers reported that consumers lack familiarity with THC levels, don’t know what constitutes a “low” or “high” THC amount, have trouble dosing, overconsume, and commonly experience adverse health events from cannabis use.
A recent study suggested that most clinicians are similarly uninformed, with “a lack of knowledge of beneficial effects, adverse effects, and of how to advise patients,” even for medical cannabis.
Diabetes Canada takes a stab at summarizing what’s known with respect to cannabis and diabetes, stating that:
“Research on recreational cannabis use suggests it may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors. The safety of recreational cannabis use has not been demonstrated, whereas regular cannabis use is associated with worsening glycemic control, more diabetes-related complications, and poorer self-care behaviors, such as adequate glucose monitoring, adherence to medications, and compliance with dietary and physical activity recommendations for people living with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.”
The American Diabetes Association’s information on cannabis consists of a patient-oriented article on CBD oil. The article stated:
“There’s a lot of hype surrounding CBD oil and diabetes. There is no noticeable effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers continue to study the effects of CBD on diabetes in animal studies.”
It concludes that:
“Although many claims continue to be made about CBD oil, there is little evidence of any benefit. It’s certainly not an alternative to traditional diabetes management. The safety of CBD is also unknown — it may have dangerous side effects that we won’t know about unless further research is done.”
A Roundup of Recent Studies
A smattering of recent studies have touched on various aspects of cannabis consumption and diabetes.
Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and co-director of CUChange at the University of Colorado Boulder, has been evaluating cannabis use in young adults (ages 21-40 years) in the SONIC study. Dr. Bryan reported at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions that cannabis users were more likely to have a lower body mass index and less likely to develop T2D. Furthermore, chronic cannabis users were less likely to have measures of inflammation and no loss of insulin sensitivity.
Another study by Dr. Bryan’s group found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
Similarly positive results were found in a 15-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of THC/CBD spray for neuropathic pain among treatment-resistant patients. The investigators reported that “clinically important improvements” were seen in pain, sleep quality, and subjective impressions of pain. Another small study of inhaled cannabis in treatment-refractory patients found a dose-dependent reduction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain.
Findings from a 9-year longitudinal study of approximately 18,000 Swedish men and women suggested no association between cannabis and subsequent T2D development after controlling for age, although these authors also called for longer follow-up and more detailed information about cannabis use to make “more robust” conclusions.
On the other side of the spectrum, a “rapid” review of recreational cannabis use in people with T1D and T2D found that recreational cannabis use may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors and may increase risks for peripheral arterial occlusion, myocardial infarction, and renal disease. However, the authors cautioned that more robust research is needed to confirm the potential impact of cannabis on diabetes.
How to Advise Patients
When Dr. Shubrook was working with patients with diabetes in his family medicine practice in Ohio, cannabis wasn’t legal.
“’Don’t ask, don’t tell’ was the way we handled it then,” he said.
By contrast, in California, where he’s currently located, “it’s pretty well accepted and legal, and patients volunteer information about use, even if it’s recreational,” he said. “Realizing this was something we could talk about was really eye-opening to me.”
Talking to patients about cannabis use is a “20-minute conversation that details what they’re doing,” he said. He proceeds by asking questions: Are you using for recreational or medicinal purposes? What do you take? What do you take it for? Does it work?
“People will tell you,” Dr. Shubrook said. “They know exactly what it works or doesn’t work for and how it affects their glucose control, which in most cases is only minimally.”
He tells patients he would prefer they don’t inhale cannabis, given the risks posed to the lungs.
“Edibles may have a slower onset of effect, but depending on what they’re adding it to, glucose might be affected,” he noted. “And I have seen that chronic use can lead to hyperemesis syndrome.”
Overall, he said, “Take the time to talk to your patients about cannabis — it will allow them to be honest with you, and you can improve the specificity and safety of its use. If cannabis is legal in your state, encourage people to go to legal dispensaries, which will reduce the risk of it being laced with another drug that could increase the danger of use.”
A recent US prevalence study found that people with diabetes who use cannabis likely engage in other substance and psychoactive substance use, including tobacco use, binge drinking, and misuse of opioids and stimulants.
“Use of these additional substances could further exacerbate the health risks associated with diabetes and also emphasizes the importance of addressing polysubstance use among adults with diabetes,” the study’s author Benjamin H. Han, MD, Division of Geriatrics, Gerontology and Palliative Care, Department of Medicine, US San Diego School of Medicine in La Jolla, California, told this news organization.
“We were surprised at how strong the associations were, especially with use of substances that can increase cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Han added. “And given the strong association we found between cannabis use and use of other psychoactive substances in diabetes, clinicians must screen all their patients for psychoactive substance use.”
Diabetes Canada’s position paper states that despite the limited evidence, “there were sufficient data to begin developing recommendations for type 1 and type 2 diabetes about education, counseling, and management related to recreational cannabis use.”
Their recommendations include the following:
- Healthcare professionals should engage their patients in discussions about substance use on a regular basis, with a nonjudgmental approach.
- The use of recreational cannabis is not recommended for adolescents and adults with diabetes.
- People with T1D should avoid recreational cannabis use because of the increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- For adults with T1D or T2D who intend to use cannabis recreationally, individualized assessment and counseling should be offered to inform them of the general risks of cannabis, with a focus on harm reduction and reduction of the risk for potential adverse effects on diabetes management and complications.
- People with T1D or T2D should be offered education on and encouraged to read public information available through resources from various Canadian health authorities about the general risks of cannabis use to reduce the risk for nondiabetes-related adverse effects of cannabis consumption.
Of note, in 2018, the Canadian government produced an exhaustive compendium of information on cannabis for healthcare professionals that includes information relevant to managing patients with diabetes.
Dr. Shubrook and Dr. Han reported no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent US prevalence study estimated that 9% adults with diabetes used cannabis in the last month, a 33.7% increase between 2021 and 2022. Nearly half (48.9%) of users were younger than 50 years.
Cannabis use is also increasing sharply among those aged 65 years or older, many of whom have diabetes and other chronic conditions. In this demographic, the perceived risk surrounding regular cannabis use has dropped significantly, even as the data tell another story — that they are particularly at risk from emergency department visits for cannabis poisoning.
As legalization continues and cannabis products proliferate, endocrinologists will likely face more patients of all ages seeking advice about its use. Yet with few evidence-based resources to turn to, endocrinologists advising patients in this area are mostly left fending for themselves.
Evidence ‘Limited’
“The evidence on cannabis is limited mainly because of its scheduling in the United States,” Jay Shubrook, DO, a professor and diabetologist at College of Osteopathic Medicine, Touro University California, in Vallejo, California, told this news organization.
“It was declared to be a schedule I drug in the 1970s, which meant it was ‘dangerous’ and ‘had no medical benefit.’ This made it hard to access and study in human trials.”
That will likely change soon. On May 16, 2024, the US Department of Justice submitted a proposal to move marijuana from a schedule I to a schedule III drug under the Controlled Substances Act, emphasizing its accepted medical use. If approved, the door will open to more investigators seeking to study the effects of cannabis.
Yet, even in Canada, where recreational use has been legal since 2018 and cannabis is sold widely with government support, there are little hard data to guide practice. In 2019, Diabetes Canada issued a position statement on recreational cannabis use in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). It sought to evaluate the effects of cannabis on metabolic factors and diabetes complications, as well as self-management behaviors in those aged 13 years or older.
The authors noted that five of the six studies upon which the statement was based did not consider or report the routes of cannabis administration, which have differing risks. In addition, their recommendations were based on grade D evidence and consensus.
What Patients Are Taking
Cannabis — also known as marijuana, weed, pot, or bud — refers to the dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. The plant contains more than 100 compounds, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the euphoric “high,” and other active compounds, including cannabidiol (CBD), which by itself is not mind-altering.
Cannabis can be ingested in several ways. It can be smoked (ie, joints, blunts, pipes, and water pipes), ingested in edible form (mixed or infused into foods), and inhaled using electronic vaporizing devices (ie, e-cigarettes or vape pens).
Compounds in cannabis can also be extracted to make oils and concentrates that can be vaped or inhaled. Smoking oils, concentrates, and extracts from the cannabis plant, known as “dabbing,” are on the rise in the United States.
There are no validated or standard dosage recommendations for cannabis strains and formulations, THC/CBD ratios, or modes of administration. Therefore, the Canadian Pharmacists Association prepared a guide for finding a safe and effective dose for medical purposes. GoodRx, a website with information on prescription drug prices, says that larger doses of THC pose greater risks, noting that the potency of cannabis has increased from 4% in 1995 to about 14% in 2019.
Potential Risks and Benefits: Canadian and US Perspectives
Health and safety risks vary with each of the different ways of using cannabis for individuals with and without diabetes, depending on a host of patient- and product-specific factors.
In a recent article proposing a “THC unit” for Canada’s legal cannabis market, researchers reported that consumers lack familiarity with THC levels, don’t know what constitutes a “low” or “high” THC amount, have trouble dosing, overconsume, and commonly experience adverse health events from cannabis use.
A recent study suggested that most clinicians are similarly uninformed, with “a lack of knowledge of beneficial effects, adverse effects, and of how to advise patients,” even for medical cannabis.
Diabetes Canada takes a stab at summarizing what’s known with respect to cannabis and diabetes, stating that:
“Research on recreational cannabis use suggests it may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors. The safety of recreational cannabis use has not been demonstrated, whereas regular cannabis use is associated with worsening glycemic control, more diabetes-related complications, and poorer self-care behaviors, such as adequate glucose monitoring, adherence to medications, and compliance with dietary and physical activity recommendations for people living with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.”
The American Diabetes Association’s information on cannabis consists of a patient-oriented article on CBD oil. The article stated:
“There’s a lot of hype surrounding CBD oil and diabetes. There is no noticeable effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers continue to study the effects of CBD on diabetes in animal studies.”
It concludes that:
“Although many claims continue to be made about CBD oil, there is little evidence of any benefit. It’s certainly not an alternative to traditional diabetes management. The safety of CBD is also unknown — it may have dangerous side effects that we won’t know about unless further research is done.”
A Roundup of Recent Studies
A smattering of recent studies have touched on various aspects of cannabis consumption and diabetes.
Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and co-director of CUChange at the University of Colorado Boulder, has been evaluating cannabis use in young adults (ages 21-40 years) in the SONIC study. Dr. Bryan reported at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions that cannabis users were more likely to have a lower body mass index and less likely to develop T2D. Furthermore, chronic cannabis users were less likely to have measures of inflammation and no loss of insulin sensitivity.
Another study by Dr. Bryan’s group found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
Similarly positive results were found in a 15-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of THC/CBD spray for neuropathic pain among treatment-resistant patients. The investigators reported that “clinically important improvements” were seen in pain, sleep quality, and subjective impressions of pain. Another small study of inhaled cannabis in treatment-refractory patients found a dose-dependent reduction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain.
Findings from a 9-year longitudinal study of approximately 18,000 Swedish men and women suggested no association between cannabis and subsequent T2D development after controlling for age, although these authors also called for longer follow-up and more detailed information about cannabis use to make “more robust” conclusions.
On the other side of the spectrum, a “rapid” review of recreational cannabis use in people with T1D and T2D found that recreational cannabis use may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors and may increase risks for peripheral arterial occlusion, myocardial infarction, and renal disease. However, the authors cautioned that more robust research is needed to confirm the potential impact of cannabis on diabetes.
How to Advise Patients
When Dr. Shubrook was working with patients with diabetes in his family medicine practice in Ohio, cannabis wasn’t legal.
“’Don’t ask, don’t tell’ was the way we handled it then,” he said.
By contrast, in California, where he’s currently located, “it’s pretty well accepted and legal, and patients volunteer information about use, even if it’s recreational,” he said. “Realizing this was something we could talk about was really eye-opening to me.”
Talking to patients about cannabis use is a “20-minute conversation that details what they’re doing,” he said. He proceeds by asking questions: Are you using for recreational or medicinal purposes? What do you take? What do you take it for? Does it work?
“People will tell you,” Dr. Shubrook said. “They know exactly what it works or doesn’t work for and how it affects their glucose control, which in most cases is only minimally.”
He tells patients he would prefer they don’t inhale cannabis, given the risks posed to the lungs.
“Edibles may have a slower onset of effect, but depending on what they’re adding it to, glucose might be affected,” he noted. “And I have seen that chronic use can lead to hyperemesis syndrome.”
Overall, he said, “Take the time to talk to your patients about cannabis — it will allow them to be honest with you, and you can improve the specificity and safety of its use. If cannabis is legal in your state, encourage people to go to legal dispensaries, which will reduce the risk of it being laced with another drug that could increase the danger of use.”
A recent US prevalence study found that people with diabetes who use cannabis likely engage in other substance and psychoactive substance use, including tobacco use, binge drinking, and misuse of opioids and stimulants.
“Use of these additional substances could further exacerbate the health risks associated with diabetes and also emphasizes the importance of addressing polysubstance use among adults with diabetes,” the study’s author Benjamin H. Han, MD, Division of Geriatrics, Gerontology and Palliative Care, Department of Medicine, US San Diego School of Medicine in La Jolla, California, told this news organization.
“We were surprised at how strong the associations were, especially with use of substances that can increase cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Han added. “And given the strong association we found between cannabis use and use of other psychoactive substances in diabetes, clinicians must screen all their patients for psychoactive substance use.”
Diabetes Canada’s position paper states that despite the limited evidence, “there were sufficient data to begin developing recommendations for type 1 and type 2 diabetes about education, counseling, and management related to recreational cannabis use.”
Their recommendations include the following:
- Healthcare professionals should engage their patients in discussions about substance use on a regular basis, with a nonjudgmental approach.
- The use of recreational cannabis is not recommended for adolescents and adults with diabetes.
- People with T1D should avoid recreational cannabis use because of the increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- For adults with T1D or T2D who intend to use cannabis recreationally, individualized assessment and counseling should be offered to inform them of the general risks of cannabis, with a focus on harm reduction and reduction of the risk for potential adverse effects on diabetes management and complications.
- People with T1D or T2D should be offered education on and encouraged to read public information available through resources from various Canadian health authorities about the general risks of cannabis use to reduce the risk for nondiabetes-related adverse effects of cannabis consumption.
Of note, in 2018, the Canadian government produced an exhaustive compendium of information on cannabis for healthcare professionals that includes information relevant to managing patients with diabetes.
Dr. Shubrook and Dr. Han reported no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.

