User login
Vitamin B1 May Reduce Constipation in Adults
TOPLINE:
Increased dietary intake of vitamin B1 is associated with a lower prevalence of constipation, particularly among men and individuals without hypertension or diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data from 2005-2010 involving 10,371 adults aged ≥ 20 years.
- Participants provided information on fecal characteristics and bowel movement frequency, which was documented for 30 days prior to data collection.
- Constipation was established by either frequency of bowel movements (fewer than three per week) or stool consistency (Bristol Stool Scale type 1 or 2).
- Data on vitamin B1 intake were collected through 24-hour total nutritional intake recall interviews. Patients were divided into three groups based on their level of B1 intake: 0.064-1.21 mg, 1.21-1.76 mg, and 1.76-12.61 mg.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 10.8% of participants were identified as having constipation.
- Greater dietary vitamin B1 intake was associated with a 23% reduction in constipation risk (P = .034).
- Additionally, a subgroup analysis found that higher B1 intake was associated with a reduction in constipation risk of 20% in men, 16% in people without hypertension, and 14% in those without diabetes.
IN PRACTICE:
“This association suggests that enhanced intake of vitamin B1 through diet may facilitate softer stools and heightened intestinal motility, thereby potentially alleviating constipation symptoms. Consequently, healthcare professionals are advised to prioritize the promotion of a well-balanced diet as an initial therapeutic approach, preceding medical interventions,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Wenyi Du, the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou Stomatological Hospital, Suzhou, China, and Wuxi People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi Medical Center, Wuxi, China, was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
A causal relationship could not be established between vitamin B1 intake and constipation owing to the cross-sectional nature of the study. The study relied on patient interviews and patient self-reported data. Additionally, 24-hour dietary recalls may not have accurately reflected the long-term eating habits of the participants.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no specific funding source. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Increased dietary intake of vitamin B1 is associated with a lower prevalence of constipation, particularly among men and individuals without hypertension or diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data from 2005-2010 involving 10,371 adults aged ≥ 20 years.
- Participants provided information on fecal characteristics and bowel movement frequency, which was documented for 30 days prior to data collection.
- Constipation was established by either frequency of bowel movements (fewer than three per week) or stool consistency (Bristol Stool Scale type 1 or 2).
- Data on vitamin B1 intake were collected through 24-hour total nutritional intake recall interviews. Patients were divided into three groups based on their level of B1 intake: 0.064-1.21 mg, 1.21-1.76 mg, and 1.76-12.61 mg.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 10.8% of participants were identified as having constipation.
- Greater dietary vitamin B1 intake was associated with a 23% reduction in constipation risk (P = .034).
- Additionally, a subgroup analysis found that higher B1 intake was associated with a reduction in constipation risk of 20% in men, 16% in people without hypertension, and 14% in those without diabetes.
IN PRACTICE:
“This association suggests that enhanced intake of vitamin B1 through diet may facilitate softer stools and heightened intestinal motility, thereby potentially alleviating constipation symptoms. Consequently, healthcare professionals are advised to prioritize the promotion of a well-balanced diet as an initial therapeutic approach, preceding medical interventions,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Wenyi Du, the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou Stomatological Hospital, Suzhou, China, and Wuxi People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi Medical Center, Wuxi, China, was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
A causal relationship could not be established between vitamin B1 intake and constipation owing to the cross-sectional nature of the study. The study relied on patient interviews and patient self-reported data. Additionally, 24-hour dietary recalls may not have accurately reflected the long-term eating habits of the participants.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no specific funding source. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Increased dietary intake of vitamin B1 is associated with a lower prevalence of constipation, particularly among men and individuals without hypertension or diabetes.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data from 2005-2010 involving 10,371 adults aged ≥ 20 years.
- Participants provided information on fecal characteristics and bowel movement frequency, which was documented for 30 days prior to data collection.
- Constipation was established by either frequency of bowel movements (fewer than three per week) or stool consistency (Bristol Stool Scale type 1 or 2).
- Data on vitamin B1 intake were collected through 24-hour total nutritional intake recall interviews. Patients were divided into three groups based on their level of B1 intake: 0.064-1.21 mg, 1.21-1.76 mg, and 1.76-12.61 mg.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 10.8% of participants were identified as having constipation.
- Greater dietary vitamin B1 intake was associated with a 23% reduction in constipation risk (P = .034).
- Additionally, a subgroup analysis found that higher B1 intake was associated with a reduction in constipation risk of 20% in men, 16% in people without hypertension, and 14% in those without diabetes.
IN PRACTICE:
“This association suggests that enhanced intake of vitamin B1 through diet may facilitate softer stools and heightened intestinal motility, thereby potentially alleviating constipation symptoms. Consequently, healthcare professionals are advised to prioritize the promotion of a well-balanced diet as an initial therapeutic approach, preceding medical interventions,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Wenyi Du, the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou Stomatological Hospital, Suzhou, China, and Wuxi People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi Medical Center, Wuxi, China, was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
A causal relationship could not be established between vitamin B1 intake and constipation owing to the cross-sectional nature of the study. The study relied on patient interviews and patient self-reported data. Additionally, 24-hour dietary recalls may not have accurately reflected the long-term eating habits of the participants.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no specific funding source. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes-Related Outcomes and Costs Have Mostly Improved
TOPLINE:
Over the past 20 years in Denmark, the incidence of type 2 diabetes–related outcomes and many treatment-related harms have both decreased without increased medication expenses despite an aging and more comorbid population; however, challenges remain.
METHODOLOGY:
- Analysis of data from 461,805 individuals in the Danish population with type 2 diabetes between 2002 and 2020.
- Multivariate analyses adjusted for potential confounders, including age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
TAKEAWAY:
- The population grew 2.7-fold from 2002 to 2020 (n = 113,105 to 306,962), the median age increased from 66 to 68 years, and the mean number of diseases per person increased from 5.2 to 8.8, with an increase in Charlson Comorbidity Index from 1.78 to 1.93.
- After adjustments, mortality per 1000 person-years decreased by 28% from 2002 to 2020, with the largest risk reduction, 63%, in acute myocardial infarction.
- The mean number of annually redeemed medications per person increased from 8.1 to 9.0, with statin and antihypertensive use increasing to 65% and 69%, respectively.
- Antiplatelet medication (aspirin and clopidogrel) use peaked at 48% in 2009 and dropped to 31% in 2020.
- Anticoagulant (warfarin and direct-acting oral anticoagulants) use gradually increased from 5% in 2002 to 14% in 2020.
- For glucose-lowering treatment, there was a shift away from using sulfonylureas to metformin and other medications.
- Diagnoses of hypoglycemia, falls, and gastric bleeding decreased over the study period, but incidences of volume depletion, ketoacidosis, infections, and electrolyte imbalances requiring hospitalization increased.
- Cumulative expenses for the population increased from €132,000,000 to €327,000,000 (approximately $144,406,680 to $357,734,730), corresponding to a 148% increase over the study period.
- However, the average medication cost per individual was 8% less in 2020 compared with 2002 despite increasing medication use, mainly driven by reduced costs of antiplatelets, antihypertensives, and statins, among others.
- In contrast, expenses for glucose-lowering medications have gradually increased, with the average more than doubling (138% increase) from €220 ($240) in 2002 to €524 ($573) in 2020.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although these trends suggest improvements in rational pharmacotherapy, they cannot be solely attributed to improved pharmacotherapy and appear to be multifactorial,” the authors wrote.
“Advancements in diabetes management have improved the balance between medication benefits, harms, and costs ... Remaining challenges, such as an increased risk of ketoacidosis and electrolyte imbalances as well as rising costs for glucose-lowering medications, highlight the importance of individualized treatment and continuous risk-benefits evaluations,” they added.
SOURCE:
This study was conducted by Karl Sebastian Johansson, of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Copenhagen University Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues and was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Analysis was confined to events diagnosed in hospital-based inpatient and outpatient settings, not primary healthcare. Only predefined adverse events were analyzed.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Capital Region of Denmark. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Over the past 20 years in Denmark, the incidence of type 2 diabetes–related outcomes and many treatment-related harms have both decreased without increased medication expenses despite an aging and more comorbid population; however, challenges remain.
METHODOLOGY:
- Analysis of data from 461,805 individuals in the Danish population with type 2 diabetes between 2002 and 2020.
- Multivariate analyses adjusted for potential confounders, including age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
TAKEAWAY:
- The population grew 2.7-fold from 2002 to 2020 (n = 113,105 to 306,962), the median age increased from 66 to 68 years, and the mean number of diseases per person increased from 5.2 to 8.8, with an increase in Charlson Comorbidity Index from 1.78 to 1.93.
- After adjustments, mortality per 1000 person-years decreased by 28% from 2002 to 2020, with the largest risk reduction, 63%, in acute myocardial infarction.
- The mean number of annually redeemed medications per person increased from 8.1 to 9.0, with statin and antihypertensive use increasing to 65% and 69%, respectively.
- Antiplatelet medication (aspirin and clopidogrel) use peaked at 48% in 2009 and dropped to 31% in 2020.
- Anticoagulant (warfarin and direct-acting oral anticoagulants) use gradually increased from 5% in 2002 to 14% in 2020.
- For glucose-lowering treatment, there was a shift away from using sulfonylureas to metformin and other medications.
- Diagnoses of hypoglycemia, falls, and gastric bleeding decreased over the study period, but incidences of volume depletion, ketoacidosis, infections, and electrolyte imbalances requiring hospitalization increased.
- Cumulative expenses for the population increased from €132,000,000 to €327,000,000 (approximately $144,406,680 to $357,734,730), corresponding to a 148% increase over the study period.
- However, the average medication cost per individual was 8% less in 2020 compared with 2002 despite increasing medication use, mainly driven by reduced costs of antiplatelets, antihypertensives, and statins, among others.
- In contrast, expenses for glucose-lowering medications have gradually increased, with the average more than doubling (138% increase) from €220 ($240) in 2002 to €524 ($573) in 2020.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although these trends suggest improvements in rational pharmacotherapy, they cannot be solely attributed to improved pharmacotherapy and appear to be multifactorial,” the authors wrote.
“Advancements in diabetes management have improved the balance between medication benefits, harms, and costs ... Remaining challenges, such as an increased risk of ketoacidosis and electrolyte imbalances as well as rising costs for glucose-lowering medications, highlight the importance of individualized treatment and continuous risk-benefits evaluations,” they added.
SOURCE:
This study was conducted by Karl Sebastian Johansson, of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Copenhagen University Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues and was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Analysis was confined to events diagnosed in hospital-based inpatient and outpatient settings, not primary healthcare. Only predefined adverse events were analyzed.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Capital Region of Denmark. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Over the past 20 years in Denmark, the incidence of type 2 diabetes–related outcomes and many treatment-related harms have both decreased without increased medication expenses despite an aging and more comorbid population; however, challenges remain.
METHODOLOGY:
- Analysis of data from 461,805 individuals in the Danish population with type 2 diabetes between 2002 and 2020.
- Multivariate analyses adjusted for potential confounders, including age, sex, and socioeconomic status.
TAKEAWAY:
- The population grew 2.7-fold from 2002 to 2020 (n = 113,105 to 306,962), the median age increased from 66 to 68 years, and the mean number of diseases per person increased from 5.2 to 8.8, with an increase in Charlson Comorbidity Index from 1.78 to 1.93.
- After adjustments, mortality per 1000 person-years decreased by 28% from 2002 to 2020, with the largest risk reduction, 63%, in acute myocardial infarction.
- The mean number of annually redeemed medications per person increased from 8.1 to 9.0, with statin and antihypertensive use increasing to 65% and 69%, respectively.
- Antiplatelet medication (aspirin and clopidogrel) use peaked at 48% in 2009 and dropped to 31% in 2020.
- Anticoagulant (warfarin and direct-acting oral anticoagulants) use gradually increased from 5% in 2002 to 14% in 2020.
- For glucose-lowering treatment, there was a shift away from using sulfonylureas to metformin and other medications.
- Diagnoses of hypoglycemia, falls, and gastric bleeding decreased over the study period, but incidences of volume depletion, ketoacidosis, infections, and electrolyte imbalances requiring hospitalization increased.
- Cumulative expenses for the population increased from €132,000,000 to €327,000,000 (approximately $144,406,680 to $357,734,730), corresponding to a 148% increase over the study period.
- However, the average medication cost per individual was 8% less in 2020 compared with 2002 despite increasing medication use, mainly driven by reduced costs of antiplatelets, antihypertensives, and statins, among others.
- In contrast, expenses for glucose-lowering medications have gradually increased, with the average more than doubling (138% increase) from €220 ($240) in 2002 to €524 ($573) in 2020.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although these trends suggest improvements in rational pharmacotherapy, they cannot be solely attributed to improved pharmacotherapy and appear to be multifactorial,” the authors wrote.
“Advancements in diabetes management have improved the balance between medication benefits, harms, and costs ... Remaining challenges, such as an increased risk of ketoacidosis and electrolyte imbalances as well as rising costs for glucose-lowering medications, highlight the importance of individualized treatment and continuous risk-benefits evaluations,” they added.
SOURCE:
This study was conducted by Karl Sebastian Johansson, of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Copenhagen University Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues and was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Analysis was confined to events diagnosed in hospital-based inpatient and outpatient settings, not primary healthcare. Only predefined adverse events were analyzed.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Capital Region of Denmark. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For Richer, for Poorer: Low-Carb Diets Work for All Incomes
For 3 years, Ajala Efem’s type 2 diabetes was so poorly controlled that her blood sugar often soared northward of 500 mg/dL despite insulin shots three to five times a day. She would experience dizziness, vomiting, severe headaches, and the neuropathy in her feet made walking painful. She was also — literally — frothing at the mouth. The 47-year-old single mother of two adult children with mental disabilities feared that she would die.
Ms. Efem lives in the South Bronx, which is among the poorest areas of New York City, where the combined rate of prediabetes and diabetes is close to 30%, the highest rate of any borough in the city.
She had to wait 8 months for an appointment with an endocrinologist, but that visit proved to be life-changing. She lost 28 pounds and got off 15 medications in a single month. She did not join a gym or count calories; she simply changed the food she ate and adopted a low-carb diet.
“I went from being sick to feeling so great,” she told her endocrinologist recently: “My feet aren’t hurting; I’m not in pain; I’m eating as much as I want, and I really enjoy my food so much.”
Ms. Efem’s life-changing visit was with Mariela Glandt, MD, at the offices of Essen Health Care. One month earlier, Dr. Glandt’s company, OwnaHealth, was contracted by Essen to conduct a 100-person pilot program for endocrinology patients. Essen is the largest Medicaid provider in New York City, and “they were desperate for an endocrinologist,” said Dr. Glandt, who trained at Columbia University in New York. So she came — all the way from Madrid, Spain. She commutes monthly, staying for a week each visit.
Dr. Glandt keeps up this punishing schedule because, as she explains, “it’s such a high for me to see these incredible transformations.” Her mostly Black and Hispanic patients are poor and lack resources, yet they lose significant amounts of weight, and their health issues resolve.
“Food is medicine” is an idea very much in vogue. The concept was central to the landmark White House Conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in 2022 and is now the focus of a number of a wide range of government programs. Recently, the Senate held a hearing aimed at further expanding food as medicine programs.
Still, only a single randomized controlled clinical trial has been conducted on this nutritional approach, with unexpectedly disappointing results. In the mid-Atlantic region, 456 food-insecure adults with type 2 diabetes were randomly assigned to usual care or the provision of weekly groceries for their entire families for about 1 year. Provisions for a Mediterranean-style diet included whole grains, fruits and vegetables, lean protein, low-fat dairy products, cereal, brown rice, and bread. In addition, participants received dietary consultations. Yet, those who got free food and coaching did not see improvements in their average blood sugar (the study’s primary outcome), and their low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels appeared to have worsened.
“To be honest, I was surprised,” the study’s lead author, Joseph Doyle, PhD, professor at the Sloan School of Management at MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, told me. “I was hoping we would show improved outcomes, but the way to make progress is to do well-randomized trials to find out what works.”
I was not surprised by these results because a recent rigorous systematic review and meta-analysis in The BMJ did not show a Mediterranean-style diet to be the most effective for glycemic control. And Ms. Efem was not in fact following a Mediterranean-style diet.
Ms. Efem’s low-carb success story is anecdotal, but Dr. Glandt has an established track record from her 9 years’ experience as the medical director of the eponymous diabetes center she founded in Tel Aviv. A recent audit of 344 patients from the center found that after 6 months of following a very low–carbohydrate diet, 96.3% of those with diabetes saw their A1c fall from a median 7.6% to 6.3%. Weight loss was significant, with a median drop of 6.5 kg (14 pounds) for patients with diabetes and 5.7 kg for those with prediabetes. The diet comprises 5%-10% of calories from carbs, but Dr. Glandt does not use numeric targets with her patients.
Blood pressure, triglycerides, and liver enzymes also improved. And though LDL cholesterol went up by 8%, this result may have been offset by an accompanying 13% rise in HDL cholesterol. Of the 78 patients initially on insulin, 62 were able to stop this medication entirely.
Although these results aren’t from a clinical trial, they’re still highly meaningful because the current dietary standard of care for type 2 diabetes can only slow the progression of the disease, not cause remission. Indeed, the idea that type 2 diabetes could be put into remission was not seriously considered by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) until 2009. By 2019, an ADA report concluded that “[r]educing overall carbohydrate intake for individuals with diabetes has demonstrated the most evidence for improving glycemia.” In other words, the best way to improve the key factor in diabetes is to reduce total carbohydrates. Yet, the ADA still advocates filling one quarter of one’s plate with carbohydrate-based foods, an amount that will prevent remission. Given that the ADA’s vision statement is “a life free of diabetes,” it seems negligent not to tell people with a deadly condition that they can reverse this diagnosis.
A 2023 meta-analysis of 42 controlled clinical trials on 4809 patients showed that a very low–carbohydrate ketogenic diet (keto) was “superior” to alternatives for glycemic control. A more recent review of 11 clinical trials found that this diet was equal but not superior to other nutritional approaches in terms of blood sugar control, but this review also concluded that keto led to greater increases in HDL cholesterol and lower triglycerides.
Dr. Glandt’s patients in the Bronx might not seem like obvious low-carb candidates. The diet is considered expensive and difficult to sustain. My interviews with a half dozen patients revealed some of these difficulties, but even for a woman living in a homeless shelter, the obstacles are not insurmountable.
Jerrilyn, who preferred that I use only her first name, lives in a shelter in Queens. While we strolled through a nearby park, she told me about her desire to lose weight and recover from polycystic ovary syndrome, which terrified her because it had caused dramatic hair loss. When she landed in Dr. Glandt’s office at age 28, she weighed 180 pounds.
Less than 5 months later, Jerrilyn had lost 25 pounds, and her period had returned with some regularity. She said she used “food stamps,” known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), to buy most of her food at local delis because the meals served at the shelter were too heavy in starches. She starts her day with eggs, turkey bacon, and avocado.
“It was hard to give up carbohydrates because in my culture [Latina], we have nothing but carbs: rice, potatoes, yuca,” Jerrilyn shared. She noticed that carbs make her hungrier, but after 3 days of going low-carb, her cravings diminished. “It was like getting over an addiction,” she said.
Jerrilyn told me she’d seen many doctors but none as involved as Dr. Glandt. “It feels awesome to know that I have a lot of really useful information coming from her all the time.” The OwnaHealth app tracks weight, blood pressure, blood sugar, ketones, meals, mood, and cravings. Patients wear continuous glucose monitors and enter other information manually. Ketone bodies are used to measure dietary adherence and are obtained through finger pricks and test strips provided by OwnaHealth. Dr. Glandt gives patients her own food plan, along with free visual guides to low-carbohydrate foods by dietdoctor.com.
Dr. Glandt also sends her patients for regular blood work. She says she does not frequently see a rise in LDL cholesterol, which can sometimes occur on a low-carbohydrate diet. This effect is most common among people who are lean and fit. She says she doesn’t discontinue statins unless cholesterol levels improve significantly.
Samuel Gonzalez, age 56, weighed 275 pounds when he walked into Dr. Glandt’s office this past November. His A1c was 9.2%, but none of his previous doctors had diagnosed him with diabetes. “I was like a walking bag of sugar!” he joked.
A low-carbohydrate diet seemed absurd to a Puerto Rican like himself: “Having coffee without sugar? That’s like sacrilegious in my culture!” exclaimed Mr. Gonzalez. Still, he managed, with SNAP, to cook eggs and bacon for breakfast and some kind of protein for dinner. He keeps lunch light, “like tuna fish,” and finds checking in with the OwnaHealth app to be very helpful. “Every day, I’m on it,” he said. In the past 7 months, he’s lost 50 pounds, normalized his cholesterol and blood pressure levels, and lowered his A1c to 5.5%.
Mr. Gonzalez gets disability payments due to a back injury, and Ms. Efem receives government payments because her husband died serving in the military. Ms. Efem says her new diet challenges her budget, but Mr. Gonzalez says he manages easily.
Mélissa Cruz, a 28-year-old studying to be a nail technician while also doing back office work at a physical therapy practice, says she’s stretched thin. “I end up sad because I can’t put energy into looking up recipes and cooking for me and my boyfriend,” she told me. She’ll often cook rice and plantains for him and meat for herself, but “it’s frustrating when I’m low on funds and can’t figure out what to eat.”
Low-carbohydrate diets have a reputation for being expensive because people often start eating pricier foods, like meat and cheese, to replace cheaper starchy foods such as pasta and rice.
A 2019 cost analysis published in Nutrition & Dietetics compared a low-carbohydrate dietary pattern with the New Zealand government’s recommended guidelines (which are almost identical to those in the United States) and found that it cost only an extra $1.27 in US dollars per person per day. One explanation is that protein and fat are more satiating than carbohydrates, so people who mostly consume these macronutrients often cut back on snacks like packaged chips, crackers, and even fruits. Also, those on a ketogenic diet usually cut down on medications, so the additional $1.27 daily is likely offset by reduced spending at the pharmacy.
It’s not just Bronx residents with low socioeconomic status (SES) who adapt well to low-carbohydrate diets. Among Alabama state employees with diabetes enrolled in a low-carbohydrate dietary program provided by a company called Virta, the low SES population had the best outcomes. Virta also published survey data in 2023 showing that participants in a program with the Veteran’s Administration did not find additional costs to be an obstacle to dietary adherence. In fact, some participants saw cost reductions due to decreased spending on processed snacks and fast foods.
Ms. Cruz told me she struggles financially, yet she’s still lost nearly 30 pounds in 5 months, and her A1c went from 7.1% down to 5.9%, putting her diabetes into remission. Equally motivating for her are the improvements she’s seen in other hormonal issues. Since childhood, she’s had acanthosis, a condition that causes the skin to darken in velvety patches, and more recently, she developed severe hirsutism to the point of growing sideburns. “I had tried going vegan and fasting, but these just weren’t sustainable for me, and I was so overwhelmed with counting calories all the time.” Now, on a low-carbohydrate diet, which doesn’t require calorie counting, she’s finally seeing both these conditions improve significantly.
When I last checked in with Ms. Cruz, she said she had “kind of ghosted” Dr. Glandt due to her work and school constraints, but she hadn’t abandoned the diet. She appreciated, too, that Dr. Glandt had not given up on her and kept calling and messaging. “She’s not at all like a typical doctor who would just tell me to lose weight and shake their head at me,” Ms. Cruz said.
Because Dr. Glandt’s approach is time-intensive and high-touch, it might seem impractical to scale up, but Dr. Glandt’s app uses artificial intelligence to help with communications thus allowing her, with help from part-time health coaches, to care for patients.
This early success in one of the United States’ poorest and sickest neighborhoods should give us hope that type 2 diabetes need not to be a progressive irreversible disease, even among the disadvantaged.
OwnaHealth’s track record, along with that of Virta and other similar low-carbohydrate medical practices also give hope to the food-is-medicine idea. Diabetes can go into remission, and people can be healed, provided that health practitioners prescribe the right foods. And in truth, it’s not a diet. It’s a way of eating that must be maintained. The sustainability of low-carbohydrate diets has been a point of contention, but the Virta trial, with 38% of patients sustaining remission at 2 years, showed that it’s possible. (OwnaHealth, for its part, offers long-term maintenance plans to help patients stay very low-carb permanently.)
Given the tremendous costs and health burden of diabetes, this approach should no doubt be the first line of treatment for doctors and the ADA. The past two decades of clinical trial research have demonstrated that remission of type 2 diabetes is possible through diet alone. It turns out that for metabolic diseases, only certain foods are truly medicine.
Tools and Tips for Clinicians:
- Free two-page keto starter’s guide by OwnaHealth; Dr. Glandt uses this guide with her patients.
- Illustrated low-carb guides by dietdoctor.com
- Free low-carbohydrate starter guide by the Michigan Collaborative for Type 2 Diabetes
- Low-Carb for Any Budget, a free digital booklet by Mark Cucuzzella, MD, and Kristie Sullivan, PhD
- Recipe and meal ideas from Ruled.me, Keto-Mojo.com, and
Dr. Teicholz is the founder of Nutrition Coalition, an independent nonprofit dedicated to ensuring that US dietary guidelines align with current science. She disclosed receiving book royalties from The Big Fat Surprise, and received honorarium not exceeding $2000 for speeches from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For 3 years, Ajala Efem’s type 2 diabetes was so poorly controlled that her blood sugar often soared northward of 500 mg/dL despite insulin shots three to five times a day. She would experience dizziness, vomiting, severe headaches, and the neuropathy in her feet made walking painful. She was also — literally — frothing at the mouth. The 47-year-old single mother of two adult children with mental disabilities feared that she would die.
Ms. Efem lives in the South Bronx, which is among the poorest areas of New York City, where the combined rate of prediabetes and diabetes is close to 30%, the highest rate of any borough in the city.
She had to wait 8 months for an appointment with an endocrinologist, but that visit proved to be life-changing. She lost 28 pounds and got off 15 medications in a single month. She did not join a gym or count calories; she simply changed the food she ate and adopted a low-carb diet.
“I went from being sick to feeling so great,” she told her endocrinologist recently: “My feet aren’t hurting; I’m not in pain; I’m eating as much as I want, and I really enjoy my food so much.”
Ms. Efem’s life-changing visit was with Mariela Glandt, MD, at the offices of Essen Health Care. One month earlier, Dr. Glandt’s company, OwnaHealth, was contracted by Essen to conduct a 100-person pilot program for endocrinology patients. Essen is the largest Medicaid provider in New York City, and “they were desperate for an endocrinologist,” said Dr. Glandt, who trained at Columbia University in New York. So she came — all the way from Madrid, Spain. She commutes monthly, staying for a week each visit.
Dr. Glandt keeps up this punishing schedule because, as she explains, “it’s such a high for me to see these incredible transformations.” Her mostly Black and Hispanic patients are poor and lack resources, yet they lose significant amounts of weight, and their health issues resolve.
“Food is medicine” is an idea very much in vogue. The concept was central to the landmark White House Conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in 2022 and is now the focus of a number of a wide range of government programs. Recently, the Senate held a hearing aimed at further expanding food as medicine programs.
Still, only a single randomized controlled clinical trial has been conducted on this nutritional approach, with unexpectedly disappointing results. In the mid-Atlantic region, 456 food-insecure adults with type 2 diabetes were randomly assigned to usual care or the provision of weekly groceries for their entire families for about 1 year. Provisions for a Mediterranean-style diet included whole grains, fruits and vegetables, lean protein, low-fat dairy products, cereal, brown rice, and bread. In addition, participants received dietary consultations. Yet, those who got free food and coaching did not see improvements in their average blood sugar (the study’s primary outcome), and their low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels appeared to have worsened.
“To be honest, I was surprised,” the study’s lead author, Joseph Doyle, PhD, professor at the Sloan School of Management at MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, told me. “I was hoping we would show improved outcomes, but the way to make progress is to do well-randomized trials to find out what works.”
I was not surprised by these results because a recent rigorous systematic review and meta-analysis in The BMJ did not show a Mediterranean-style diet to be the most effective for glycemic control. And Ms. Efem was not in fact following a Mediterranean-style diet.
Ms. Efem’s low-carb success story is anecdotal, but Dr. Glandt has an established track record from her 9 years’ experience as the medical director of the eponymous diabetes center she founded in Tel Aviv. A recent audit of 344 patients from the center found that after 6 months of following a very low–carbohydrate diet, 96.3% of those with diabetes saw their A1c fall from a median 7.6% to 6.3%. Weight loss was significant, with a median drop of 6.5 kg (14 pounds) for patients with diabetes and 5.7 kg for those with prediabetes. The diet comprises 5%-10% of calories from carbs, but Dr. Glandt does not use numeric targets with her patients.
Blood pressure, triglycerides, and liver enzymes also improved. And though LDL cholesterol went up by 8%, this result may have been offset by an accompanying 13% rise in HDL cholesterol. Of the 78 patients initially on insulin, 62 were able to stop this medication entirely.
Although these results aren’t from a clinical trial, they’re still highly meaningful because the current dietary standard of care for type 2 diabetes can only slow the progression of the disease, not cause remission. Indeed, the idea that type 2 diabetes could be put into remission was not seriously considered by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) until 2009. By 2019, an ADA report concluded that “[r]educing overall carbohydrate intake for individuals with diabetes has demonstrated the most evidence for improving glycemia.” In other words, the best way to improve the key factor in diabetes is to reduce total carbohydrates. Yet, the ADA still advocates filling one quarter of one’s plate with carbohydrate-based foods, an amount that will prevent remission. Given that the ADA’s vision statement is “a life free of diabetes,” it seems negligent not to tell people with a deadly condition that they can reverse this diagnosis.
A 2023 meta-analysis of 42 controlled clinical trials on 4809 patients showed that a very low–carbohydrate ketogenic diet (keto) was “superior” to alternatives for glycemic control. A more recent review of 11 clinical trials found that this diet was equal but not superior to other nutritional approaches in terms of blood sugar control, but this review also concluded that keto led to greater increases in HDL cholesterol and lower triglycerides.
Dr. Glandt’s patients in the Bronx might not seem like obvious low-carb candidates. The diet is considered expensive and difficult to sustain. My interviews with a half dozen patients revealed some of these difficulties, but even for a woman living in a homeless shelter, the obstacles are not insurmountable.
Jerrilyn, who preferred that I use only her first name, lives in a shelter in Queens. While we strolled through a nearby park, she told me about her desire to lose weight and recover from polycystic ovary syndrome, which terrified her because it had caused dramatic hair loss. When she landed in Dr. Glandt’s office at age 28, she weighed 180 pounds.
Less than 5 months later, Jerrilyn had lost 25 pounds, and her period had returned with some regularity. She said she used “food stamps,” known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), to buy most of her food at local delis because the meals served at the shelter were too heavy in starches. She starts her day with eggs, turkey bacon, and avocado.
“It was hard to give up carbohydrates because in my culture [Latina], we have nothing but carbs: rice, potatoes, yuca,” Jerrilyn shared. She noticed that carbs make her hungrier, but after 3 days of going low-carb, her cravings diminished. “It was like getting over an addiction,” she said.
Jerrilyn told me she’d seen many doctors but none as involved as Dr. Glandt. “It feels awesome to know that I have a lot of really useful information coming from her all the time.” The OwnaHealth app tracks weight, blood pressure, blood sugar, ketones, meals, mood, and cravings. Patients wear continuous glucose monitors and enter other information manually. Ketone bodies are used to measure dietary adherence and are obtained through finger pricks and test strips provided by OwnaHealth. Dr. Glandt gives patients her own food plan, along with free visual guides to low-carbohydrate foods by dietdoctor.com.
Dr. Glandt also sends her patients for regular blood work. She says she does not frequently see a rise in LDL cholesterol, which can sometimes occur on a low-carbohydrate diet. This effect is most common among people who are lean and fit. She says she doesn’t discontinue statins unless cholesterol levels improve significantly.
Samuel Gonzalez, age 56, weighed 275 pounds when he walked into Dr. Glandt’s office this past November. His A1c was 9.2%, but none of his previous doctors had diagnosed him with diabetes. “I was like a walking bag of sugar!” he joked.
A low-carbohydrate diet seemed absurd to a Puerto Rican like himself: “Having coffee without sugar? That’s like sacrilegious in my culture!” exclaimed Mr. Gonzalez. Still, he managed, with SNAP, to cook eggs and bacon for breakfast and some kind of protein for dinner. He keeps lunch light, “like tuna fish,” and finds checking in with the OwnaHealth app to be very helpful. “Every day, I’m on it,” he said. In the past 7 months, he’s lost 50 pounds, normalized his cholesterol and blood pressure levels, and lowered his A1c to 5.5%.
Mr. Gonzalez gets disability payments due to a back injury, and Ms. Efem receives government payments because her husband died serving in the military. Ms. Efem says her new diet challenges her budget, but Mr. Gonzalez says he manages easily.
Mélissa Cruz, a 28-year-old studying to be a nail technician while also doing back office work at a physical therapy practice, says she’s stretched thin. “I end up sad because I can’t put energy into looking up recipes and cooking for me and my boyfriend,” she told me. She’ll often cook rice and plantains for him and meat for herself, but “it’s frustrating when I’m low on funds and can’t figure out what to eat.”
Low-carbohydrate diets have a reputation for being expensive because people often start eating pricier foods, like meat and cheese, to replace cheaper starchy foods such as pasta and rice.
A 2019 cost analysis published in Nutrition & Dietetics compared a low-carbohydrate dietary pattern with the New Zealand government’s recommended guidelines (which are almost identical to those in the United States) and found that it cost only an extra $1.27 in US dollars per person per day. One explanation is that protein and fat are more satiating than carbohydrates, so people who mostly consume these macronutrients often cut back on snacks like packaged chips, crackers, and even fruits. Also, those on a ketogenic diet usually cut down on medications, so the additional $1.27 daily is likely offset by reduced spending at the pharmacy.
It’s not just Bronx residents with low socioeconomic status (SES) who adapt well to low-carbohydrate diets. Among Alabama state employees with diabetes enrolled in a low-carbohydrate dietary program provided by a company called Virta, the low SES population had the best outcomes. Virta also published survey data in 2023 showing that participants in a program with the Veteran’s Administration did not find additional costs to be an obstacle to dietary adherence. In fact, some participants saw cost reductions due to decreased spending on processed snacks and fast foods.
Ms. Cruz told me she struggles financially, yet she’s still lost nearly 30 pounds in 5 months, and her A1c went from 7.1% down to 5.9%, putting her diabetes into remission. Equally motivating for her are the improvements she’s seen in other hormonal issues. Since childhood, she’s had acanthosis, a condition that causes the skin to darken in velvety patches, and more recently, she developed severe hirsutism to the point of growing sideburns. “I had tried going vegan and fasting, but these just weren’t sustainable for me, and I was so overwhelmed with counting calories all the time.” Now, on a low-carbohydrate diet, which doesn’t require calorie counting, she’s finally seeing both these conditions improve significantly.
When I last checked in with Ms. Cruz, she said she had “kind of ghosted” Dr. Glandt due to her work and school constraints, but she hadn’t abandoned the diet. She appreciated, too, that Dr. Glandt had not given up on her and kept calling and messaging. “She’s not at all like a typical doctor who would just tell me to lose weight and shake their head at me,” Ms. Cruz said.
Because Dr. Glandt’s approach is time-intensive and high-touch, it might seem impractical to scale up, but Dr. Glandt’s app uses artificial intelligence to help with communications thus allowing her, with help from part-time health coaches, to care for patients.
This early success in one of the United States’ poorest and sickest neighborhoods should give us hope that type 2 diabetes need not to be a progressive irreversible disease, even among the disadvantaged.
OwnaHealth’s track record, along with that of Virta and other similar low-carbohydrate medical practices also give hope to the food-is-medicine idea. Diabetes can go into remission, and people can be healed, provided that health practitioners prescribe the right foods. And in truth, it’s not a diet. It’s a way of eating that must be maintained. The sustainability of low-carbohydrate diets has been a point of contention, but the Virta trial, with 38% of patients sustaining remission at 2 years, showed that it’s possible. (OwnaHealth, for its part, offers long-term maintenance plans to help patients stay very low-carb permanently.)
Given the tremendous costs and health burden of diabetes, this approach should no doubt be the first line of treatment for doctors and the ADA. The past two decades of clinical trial research have demonstrated that remission of type 2 diabetes is possible through diet alone. It turns out that for metabolic diseases, only certain foods are truly medicine.
Tools and Tips for Clinicians:
- Free two-page keto starter’s guide by OwnaHealth; Dr. Glandt uses this guide with her patients.
- Illustrated low-carb guides by dietdoctor.com
- Free low-carbohydrate starter guide by the Michigan Collaborative for Type 2 Diabetes
- Low-Carb for Any Budget, a free digital booklet by Mark Cucuzzella, MD, and Kristie Sullivan, PhD
- Recipe and meal ideas from Ruled.me, Keto-Mojo.com, and
Dr. Teicholz is the founder of Nutrition Coalition, an independent nonprofit dedicated to ensuring that US dietary guidelines align with current science. She disclosed receiving book royalties from The Big Fat Surprise, and received honorarium not exceeding $2000 for speeches from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For 3 years, Ajala Efem’s type 2 diabetes was so poorly controlled that her blood sugar often soared northward of 500 mg/dL despite insulin shots three to five times a day. She would experience dizziness, vomiting, severe headaches, and the neuropathy in her feet made walking painful. She was also — literally — frothing at the mouth. The 47-year-old single mother of two adult children with mental disabilities feared that she would die.
Ms. Efem lives in the South Bronx, which is among the poorest areas of New York City, where the combined rate of prediabetes and diabetes is close to 30%, the highest rate of any borough in the city.
She had to wait 8 months for an appointment with an endocrinologist, but that visit proved to be life-changing. She lost 28 pounds and got off 15 medications in a single month. She did not join a gym or count calories; she simply changed the food she ate and adopted a low-carb diet.
“I went from being sick to feeling so great,” she told her endocrinologist recently: “My feet aren’t hurting; I’m not in pain; I’m eating as much as I want, and I really enjoy my food so much.”
Ms. Efem’s life-changing visit was with Mariela Glandt, MD, at the offices of Essen Health Care. One month earlier, Dr. Glandt’s company, OwnaHealth, was contracted by Essen to conduct a 100-person pilot program for endocrinology patients. Essen is the largest Medicaid provider in New York City, and “they were desperate for an endocrinologist,” said Dr. Glandt, who trained at Columbia University in New York. So she came — all the way from Madrid, Spain. She commutes monthly, staying for a week each visit.
Dr. Glandt keeps up this punishing schedule because, as she explains, “it’s such a high for me to see these incredible transformations.” Her mostly Black and Hispanic patients are poor and lack resources, yet they lose significant amounts of weight, and their health issues resolve.
“Food is medicine” is an idea very much in vogue. The concept was central to the landmark White House Conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in 2022 and is now the focus of a number of a wide range of government programs. Recently, the Senate held a hearing aimed at further expanding food as medicine programs.
Still, only a single randomized controlled clinical trial has been conducted on this nutritional approach, with unexpectedly disappointing results. In the mid-Atlantic region, 456 food-insecure adults with type 2 diabetes were randomly assigned to usual care or the provision of weekly groceries for their entire families for about 1 year. Provisions for a Mediterranean-style diet included whole grains, fruits and vegetables, lean protein, low-fat dairy products, cereal, brown rice, and bread. In addition, participants received dietary consultations. Yet, those who got free food and coaching did not see improvements in their average blood sugar (the study’s primary outcome), and their low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels appeared to have worsened.
“To be honest, I was surprised,” the study’s lead author, Joseph Doyle, PhD, professor at the Sloan School of Management at MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, told me. “I was hoping we would show improved outcomes, but the way to make progress is to do well-randomized trials to find out what works.”
I was not surprised by these results because a recent rigorous systematic review and meta-analysis in The BMJ did not show a Mediterranean-style diet to be the most effective for glycemic control. And Ms. Efem was not in fact following a Mediterranean-style diet.
Ms. Efem’s low-carb success story is anecdotal, but Dr. Glandt has an established track record from her 9 years’ experience as the medical director of the eponymous diabetes center she founded in Tel Aviv. A recent audit of 344 patients from the center found that after 6 months of following a very low–carbohydrate diet, 96.3% of those with diabetes saw their A1c fall from a median 7.6% to 6.3%. Weight loss was significant, with a median drop of 6.5 kg (14 pounds) for patients with diabetes and 5.7 kg for those with prediabetes. The diet comprises 5%-10% of calories from carbs, but Dr. Glandt does not use numeric targets with her patients.
Blood pressure, triglycerides, and liver enzymes also improved. And though LDL cholesterol went up by 8%, this result may have been offset by an accompanying 13% rise in HDL cholesterol. Of the 78 patients initially on insulin, 62 were able to stop this medication entirely.
Although these results aren’t from a clinical trial, they’re still highly meaningful because the current dietary standard of care for type 2 diabetes can only slow the progression of the disease, not cause remission. Indeed, the idea that type 2 diabetes could be put into remission was not seriously considered by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) until 2009. By 2019, an ADA report concluded that “[r]educing overall carbohydrate intake for individuals with diabetes has demonstrated the most evidence for improving glycemia.” In other words, the best way to improve the key factor in diabetes is to reduce total carbohydrates. Yet, the ADA still advocates filling one quarter of one’s plate with carbohydrate-based foods, an amount that will prevent remission. Given that the ADA’s vision statement is “a life free of diabetes,” it seems negligent not to tell people with a deadly condition that they can reverse this diagnosis.
A 2023 meta-analysis of 42 controlled clinical trials on 4809 patients showed that a very low–carbohydrate ketogenic diet (keto) was “superior” to alternatives for glycemic control. A more recent review of 11 clinical trials found that this diet was equal but not superior to other nutritional approaches in terms of blood sugar control, but this review also concluded that keto led to greater increases in HDL cholesterol and lower triglycerides.
Dr. Glandt’s patients in the Bronx might not seem like obvious low-carb candidates. The diet is considered expensive and difficult to sustain. My interviews with a half dozen patients revealed some of these difficulties, but even for a woman living in a homeless shelter, the obstacles are not insurmountable.
Jerrilyn, who preferred that I use only her first name, lives in a shelter in Queens. While we strolled through a nearby park, she told me about her desire to lose weight and recover from polycystic ovary syndrome, which terrified her because it had caused dramatic hair loss. When she landed in Dr. Glandt’s office at age 28, she weighed 180 pounds.
Less than 5 months later, Jerrilyn had lost 25 pounds, and her period had returned with some regularity. She said she used “food stamps,” known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), to buy most of her food at local delis because the meals served at the shelter were too heavy in starches. She starts her day with eggs, turkey bacon, and avocado.
“It was hard to give up carbohydrates because in my culture [Latina], we have nothing but carbs: rice, potatoes, yuca,” Jerrilyn shared. She noticed that carbs make her hungrier, but after 3 days of going low-carb, her cravings diminished. “It was like getting over an addiction,” she said.
Jerrilyn told me she’d seen many doctors but none as involved as Dr. Glandt. “It feels awesome to know that I have a lot of really useful information coming from her all the time.” The OwnaHealth app tracks weight, blood pressure, blood sugar, ketones, meals, mood, and cravings. Patients wear continuous glucose monitors and enter other information manually. Ketone bodies are used to measure dietary adherence and are obtained through finger pricks and test strips provided by OwnaHealth. Dr. Glandt gives patients her own food plan, along with free visual guides to low-carbohydrate foods by dietdoctor.com.
Dr. Glandt also sends her patients for regular blood work. She says she does not frequently see a rise in LDL cholesterol, which can sometimes occur on a low-carbohydrate diet. This effect is most common among people who are lean and fit. She says she doesn’t discontinue statins unless cholesterol levels improve significantly.
Samuel Gonzalez, age 56, weighed 275 pounds when he walked into Dr. Glandt’s office this past November. His A1c was 9.2%, but none of his previous doctors had diagnosed him with diabetes. “I was like a walking bag of sugar!” he joked.
A low-carbohydrate diet seemed absurd to a Puerto Rican like himself: “Having coffee without sugar? That’s like sacrilegious in my culture!” exclaimed Mr. Gonzalez. Still, he managed, with SNAP, to cook eggs and bacon for breakfast and some kind of protein for dinner. He keeps lunch light, “like tuna fish,” and finds checking in with the OwnaHealth app to be very helpful. “Every day, I’m on it,” he said. In the past 7 months, he’s lost 50 pounds, normalized his cholesterol and blood pressure levels, and lowered his A1c to 5.5%.
Mr. Gonzalez gets disability payments due to a back injury, and Ms. Efem receives government payments because her husband died serving in the military. Ms. Efem says her new diet challenges her budget, but Mr. Gonzalez says he manages easily.
Mélissa Cruz, a 28-year-old studying to be a nail technician while also doing back office work at a physical therapy practice, says she’s stretched thin. “I end up sad because I can’t put energy into looking up recipes and cooking for me and my boyfriend,” she told me. She’ll often cook rice and plantains for him and meat for herself, but “it’s frustrating when I’m low on funds and can’t figure out what to eat.”
Low-carbohydrate diets have a reputation for being expensive because people often start eating pricier foods, like meat and cheese, to replace cheaper starchy foods such as pasta and rice.
A 2019 cost analysis published in Nutrition & Dietetics compared a low-carbohydrate dietary pattern with the New Zealand government’s recommended guidelines (which are almost identical to those in the United States) and found that it cost only an extra $1.27 in US dollars per person per day. One explanation is that protein and fat are more satiating than carbohydrates, so people who mostly consume these macronutrients often cut back on snacks like packaged chips, crackers, and even fruits. Also, those on a ketogenic diet usually cut down on medications, so the additional $1.27 daily is likely offset by reduced spending at the pharmacy.
It’s not just Bronx residents with low socioeconomic status (SES) who adapt well to low-carbohydrate diets. Among Alabama state employees with diabetes enrolled in a low-carbohydrate dietary program provided by a company called Virta, the low SES population had the best outcomes. Virta also published survey data in 2023 showing that participants in a program with the Veteran’s Administration did not find additional costs to be an obstacle to dietary adherence. In fact, some participants saw cost reductions due to decreased spending on processed snacks and fast foods.
Ms. Cruz told me she struggles financially, yet she’s still lost nearly 30 pounds in 5 months, and her A1c went from 7.1% down to 5.9%, putting her diabetes into remission. Equally motivating for her are the improvements she’s seen in other hormonal issues. Since childhood, she’s had acanthosis, a condition that causes the skin to darken in velvety patches, and more recently, she developed severe hirsutism to the point of growing sideburns. “I had tried going vegan and fasting, but these just weren’t sustainable for me, and I was so overwhelmed with counting calories all the time.” Now, on a low-carbohydrate diet, which doesn’t require calorie counting, she’s finally seeing both these conditions improve significantly.
When I last checked in with Ms. Cruz, she said she had “kind of ghosted” Dr. Glandt due to her work and school constraints, but she hadn’t abandoned the diet. She appreciated, too, that Dr. Glandt had not given up on her and kept calling and messaging. “She’s not at all like a typical doctor who would just tell me to lose weight and shake their head at me,” Ms. Cruz said.
Because Dr. Glandt’s approach is time-intensive and high-touch, it might seem impractical to scale up, but Dr. Glandt’s app uses artificial intelligence to help with communications thus allowing her, with help from part-time health coaches, to care for patients.
This early success in one of the United States’ poorest and sickest neighborhoods should give us hope that type 2 diabetes need not to be a progressive irreversible disease, even among the disadvantaged.
OwnaHealth’s track record, along with that of Virta and other similar low-carbohydrate medical practices also give hope to the food-is-medicine idea. Diabetes can go into remission, and people can be healed, provided that health practitioners prescribe the right foods. And in truth, it’s not a diet. It’s a way of eating that must be maintained. The sustainability of low-carbohydrate diets has been a point of contention, but the Virta trial, with 38% of patients sustaining remission at 2 years, showed that it’s possible. (OwnaHealth, for its part, offers long-term maintenance plans to help patients stay very low-carb permanently.)
Given the tremendous costs and health burden of diabetes, this approach should no doubt be the first line of treatment for doctors and the ADA. The past two decades of clinical trial research have demonstrated that remission of type 2 diabetes is possible through diet alone. It turns out that for metabolic diseases, only certain foods are truly medicine.
Tools and Tips for Clinicians:
- Free two-page keto starter’s guide by OwnaHealth; Dr. Glandt uses this guide with her patients.
- Illustrated low-carb guides by dietdoctor.com
- Free low-carbohydrate starter guide by the Michigan Collaborative for Type 2 Diabetes
- Low-Carb for Any Budget, a free digital booklet by Mark Cucuzzella, MD, and Kristie Sullivan, PhD
- Recipe and meal ideas from Ruled.me, Keto-Mojo.com, and
Dr. Teicholz is the founder of Nutrition Coalition, an independent nonprofit dedicated to ensuring that US dietary guidelines align with current science. She disclosed receiving book royalties from The Big Fat Surprise, and received honorarium not exceeding $2000 for speeches from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Testosterone Increases Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Trans Men
TOPLINE:
Long-term gender-affirming hormone treatment with testosterone increases the risk for metabolic syndromes in transmasculine individuals, whereas transfeminine individuals receiving estradiol have a lower risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many transgender individuals receive exogenous sex hormone therapy to reduce gender dysphoria and improve quality of life. These treatments, however, may influence the development of metabolic syndrome.
- This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study investigated the association between gender-affirming hormone treatment and metabolic syndrome scores in transfeminine and transmasculine individuals compared with cisgender men and women not receiving the treatment.
- Overall, 645 transgender participants (mean age at index date, 41.3 years; 494 transfeminine and 151 transmasculine) were matched with 645 cisgender participants (280 women and 365 men) from the Veterans Health Administration.
- Metabolic syndrome scores were calculated based on blood pressure; body mass index (BMI); and levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose.
- Changes in metabolic syndrome scores before and after hormonal transition were compared among transgender and cisgender individuals for the corresponding dates.
TAKEAWAY:
- After hormonal transition, all measured metabolic syndrome components significantly worsened in the transmasculine group (P < .05 for all).
- In contrast, the systolic blood pressure and triglyceride levels decreased, HDL cholesterol levels increased, and BMI showed no significant change in the transfeminine group after hormonal transition.
- The increase in metabolic syndrome scores after vs before the date of hormonal transition was the highest for transmasculine individuals (298.0%; P < .001), followed by cisgender women (108.3%; P < .001), cisgender men (49.3%; P = .02), and transfeminine individuals (3.0%; P = .77).
IN PRACTICE:
“This is relevant for the management of metabolic syndrome risk factors in cisgender and transgender individuals and to potentially predict the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, systolic hypertension, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Leila Hashemi, MD, MS, of the Department of General Internal Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, led this study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Causal inferences could not be drawn because of the study’s observational nature. The transmasculine and cisgender female groups were limited in size, and military veterans have special circumstances not representative of the general population. Minority stress among the transgender veterans was also not considered, which may have affected the health and well-being outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and Office of Research on Women’s Health grants. One author received grants from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Long-term gender-affirming hormone treatment with testosterone increases the risk for metabolic syndromes in transmasculine individuals, whereas transfeminine individuals receiving estradiol have a lower risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many transgender individuals receive exogenous sex hormone therapy to reduce gender dysphoria and improve quality of life. These treatments, however, may influence the development of metabolic syndrome.
- This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study investigated the association between gender-affirming hormone treatment and metabolic syndrome scores in transfeminine and transmasculine individuals compared with cisgender men and women not receiving the treatment.
- Overall, 645 transgender participants (mean age at index date, 41.3 years; 494 transfeminine and 151 transmasculine) were matched with 645 cisgender participants (280 women and 365 men) from the Veterans Health Administration.
- Metabolic syndrome scores were calculated based on blood pressure; body mass index (BMI); and levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose.
- Changes in metabolic syndrome scores before and after hormonal transition were compared among transgender and cisgender individuals for the corresponding dates.
TAKEAWAY:
- After hormonal transition, all measured metabolic syndrome components significantly worsened in the transmasculine group (P < .05 for all).
- In contrast, the systolic blood pressure and triglyceride levels decreased, HDL cholesterol levels increased, and BMI showed no significant change in the transfeminine group after hormonal transition.
- The increase in metabolic syndrome scores after vs before the date of hormonal transition was the highest for transmasculine individuals (298.0%; P < .001), followed by cisgender women (108.3%; P < .001), cisgender men (49.3%; P = .02), and transfeminine individuals (3.0%; P = .77).
IN PRACTICE:
“This is relevant for the management of metabolic syndrome risk factors in cisgender and transgender individuals and to potentially predict the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, systolic hypertension, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Leila Hashemi, MD, MS, of the Department of General Internal Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, led this study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Causal inferences could not be drawn because of the study’s observational nature. The transmasculine and cisgender female groups were limited in size, and military veterans have special circumstances not representative of the general population. Minority stress among the transgender veterans was also not considered, which may have affected the health and well-being outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and Office of Research on Women’s Health grants. One author received grants from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Long-term gender-affirming hormone treatment with testosterone increases the risk for metabolic syndromes in transmasculine individuals, whereas transfeminine individuals receiving estradiol have a lower risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many transgender individuals receive exogenous sex hormone therapy to reduce gender dysphoria and improve quality of life. These treatments, however, may influence the development of metabolic syndrome.
- This retrospective, longitudinal cohort study investigated the association between gender-affirming hormone treatment and metabolic syndrome scores in transfeminine and transmasculine individuals compared with cisgender men and women not receiving the treatment.
- Overall, 645 transgender participants (mean age at index date, 41.3 years; 494 transfeminine and 151 transmasculine) were matched with 645 cisgender participants (280 women and 365 men) from the Veterans Health Administration.
- Metabolic syndrome scores were calculated based on blood pressure; body mass index (BMI); and levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose.
- Changes in metabolic syndrome scores before and after hormonal transition were compared among transgender and cisgender individuals for the corresponding dates.
TAKEAWAY:
- After hormonal transition, all measured metabolic syndrome components significantly worsened in the transmasculine group (P < .05 for all).
- In contrast, the systolic blood pressure and triglyceride levels decreased, HDL cholesterol levels increased, and BMI showed no significant change in the transfeminine group after hormonal transition.
- The increase in metabolic syndrome scores after vs before the date of hormonal transition was the highest for transmasculine individuals (298.0%; P < .001), followed by cisgender women (108.3%; P < .001), cisgender men (49.3%; P = .02), and transfeminine individuals (3.0%; P = .77).
IN PRACTICE:
“This is relevant for the management of metabolic syndrome risk factors in cisgender and transgender individuals and to potentially predict the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, systolic hypertension, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Leila Hashemi, MD, MS, of the Department of General Internal Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, led this study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Causal inferences could not be drawn because of the study’s observational nature. The transmasculine and cisgender female groups were limited in size, and military veterans have special circumstances not representative of the general population. Minority stress among the transgender veterans was also not considered, which may have affected the health and well-being outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and Office of Research on Women’s Health grants. One author received grants from the National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Diabetes Lead to a False-Positive Alcohol Test?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to tell you the story of two patients with diabetes who had false-positive alcohol tests.
The first patient is a patient of mine with type 1 diabetes. He was in a car accident. He hit the car in front of him that hit the car in front of them. Because the cars were quite damaged, the police were summoned.
At the scene, he had a breathalyzer test. He flunked the breathalyzer test, and he was charged with a DUI. The woman in the middle car got out of her car and said her neck hurt. This then rose this to the level of a DUI with injury to one of the other people, and my patient was charged with a felony. He was taken to jail.
He told them at the scene and at the jail that he had type 1 diabetes. The reason this is so important is because type 1 diabetes can cause a false-positive breathalyzer test. In particular, this patient of mine had not been eating all day long. He’d been getting his basal insulin through the pump, but he had not given any bolus doses of insulin. He was actually quite ketotic.
When he was put in jail, they took away his cell phone so he could no longer see his glucose levels, and they took away the controller for his Omnipod system. He basically had no way to give bolus doses of insulin. Fortunately, the Omnipod system lasted for a day and a half just by giving him basal. The jail physicians did not give him insulin until he’d been in jail for 3 days.
This is someone with type 1 diabetes, and their protocol for insulin has something to do with high glucose levels and giving something like a sliding scale of insulin. They were not really prepared for managing somebody with type 1 diabetes who was on an automated insulin delivery system.
I, along with my patient’s parents, worked very hard to get the jail doctors to finally give him Lantus. Inherent in all of this, it made me aware of a number of different issues. The first is that breathalyzer tests can be falsely positive in people with type 1 diabetes if they are ketotic; therefore, people with type 1 diabetes should ask for a blood test to test their alcohol levels if they think it could be a false positive.
Second, we need to actually figure out a way to help people with type 1 diabetes who happen to be in jail or in prison because if they don’t have access to a smartphone, they’re not going to be able to run their devices. We need to make sure that devices have receivers that can be used, particularly continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), because CGM is the standard of care for patients and should be so for people who are incarcerated.
The second case is much shorter and isn’t mine, but it was a letter in The New England Journal of Medicine about a man who was on probation, who was having urine tests to show that he had not been consuming alcohol. He was started on empagliflozin, which, interestingly, made his urine test become falsely positive.
Why? Well, it’s thought it’s because it caused fermentation of the sugar with the bacteria that was in his urine because the people who were processing the sample hadn’t done it correctly, and they kept it out at room temperature for a prolonged period of time before testing it. The urine samples should be kept refrigerated to prevent this from happening.
These are two people who had false-positive tests because they had diabetes. I think it’s important that we realize that this can happen, and we need to help our patients deal with these situations.
Dr. Peters is professor, Department of Clinical Medicine, Keck School of Medicine; Director, University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. She reported conflicts of interest with Abbott Diabetes Care, Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, Zafgen, Dexcom, MannKind, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to tell you the story of two patients with diabetes who had false-positive alcohol tests.
The first patient is a patient of mine with type 1 diabetes. He was in a car accident. He hit the car in front of him that hit the car in front of them. Because the cars were quite damaged, the police were summoned.
At the scene, he had a breathalyzer test. He flunked the breathalyzer test, and he was charged with a DUI. The woman in the middle car got out of her car and said her neck hurt. This then rose this to the level of a DUI with injury to one of the other people, and my patient was charged with a felony. He was taken to jail.
He told them at the scene and at the jail that he had type 1 diabetes. The reason this is so important is because type 1 diabetes can cause a false-positive breathalyzer test. In particular, this patient of mine had not been eating all day long. He’d been getting his basal insulin through the pump, but he had not given any bolus doses of insulin. He was actually quite ketotic.
When he was put in jail, they took away his cell phone so he could no longer see his glucose levels, and they took away the controller for his Omnipod system. He basically had no way to give bolus doses of insulin. Fortunately, the Omnipod system lasted for a day and a half just by giving him basal. The jail physicians did not give him insulin until he’d been in jail for 3 days.
This is someone with type 1 diabetes, and their protocol for insulin has something to do with high glucose levels and giving something like a sliding scale of insulin. They were not really prepared for managing somebody with type 1 diabetes who was on an automated insulin delivery system.
I, along with my patient’s parents, worked very hard to get the jail doctors to finally give him Lantus. Inherent in all of this, it made me aware of a number of different issues. The first is that breathalyzer tests can be falsely positive in people with type 1 diabetes if they are ketotic; therefore, people with type 1 diabetes should ask for a blood test to test their alcohol levels if they think it could be a false positive.
Second, we need to actually figure out a way to help people with type 1 diabetes who happen to be in jail or in prison because if they don’t have access to a smartphone, they’re not going to be able to run their devices. We need to make sure that devices have receivers that can be used, particularly continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), because CGM is the standard of care for patients and should be so for people who are incarcerated.
The second case is much shorter and isn’t mine, but it was a letter in The New England Journal of Medicine about a man who was on probation, who was having urine tests to show that he had not been consuming alcohol. He was started on empagliflozin, which, interestingly, made his urine test become falsely positive.
Why? Well, it’s thought it’s because it caused fermentation of the sugar with the bacteria that was in his urine because the people who were processing the sample hadn’t done it correctly, and they kept it out at room temperature for a prolonged period of time before testing it. The urine samples should be kept refrigerated to prevent this from happening.
These are two people who had false-positive tests because they had diabetes. I think it’s important that we realize that this can happen, and we need to help our patients deal with these situations.
Dr. Peters is professor, Department of Clinical Medicine, Keck School of Medicine; Director, University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. She reported conflicts of interest with Abbott Diabetes Care, Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, Zafgen, Dexcom, MannKind, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to tell you the story of two patients with diabetes who had false-positive alcohol tests.
The first patient is a patient of mine with type 1 diabetes. He was in a car accident. He hit the car in front of him that hit the car in front of them. Because the cars were quite damaged, the police were summoned.
At the scene, he had a breathalyzer test. He flunked the breathalyzer test, and he was charged with a DUI. The woman in the middle car got out of her car and said her neck hurt. This then rose this to the level of a DUI with injury to one of the other people, and my patient was charged with a felony. He was taken to jail.
He told them at the scene and at the jail that he had type 1 diabetes. The reason this is so important is because type 1 diabetes can cause a false-positive breathalyzer test. In particular, this patient of mine had not been eating all day long. He’d been getting his basal insulin through the pump, but he had not given any bolus doses of insulin. He was actually quite ketotic.
When he was put in jail, they took away his cell phone so he could no longer see his glucose levels, and they took away the controller for his Omnipod system. He basically had no way to give bolus doses of insulin. Fortunately, the Omnipod system lasted for a day and a half just by giving him basal. The jail physicians did not give him insulin until he’d been in jail for 3 days.
This is someone with type 1 diabetes, and their protocol for insulin has something to do with high glucose levels and giving something like a sliding scale of insulin. They were not really prepared for managing somebody with type 1 diabetes who was on an automated insulin delivery system.
I, along with my patient’s parents, worked very hard to get the jail doctors to finally give him Lantus. Inherent in all of this, it made me aware of a number of different issues. The first is that breathalyzer tests can be falsely positive in people with type 1 diabetes if they are ketotic; therefore, people with type 1 diabetes should ask for a blood test to test their alcohol levels if they think it could be a false positive.
Second, we need to actually figure out a way to help people with type 1 diabetes who happen to be in jail or in prison because if they don’t have access to a smartphone, they’re not going to be able to run their devices. We need to make sure that devices have receivers that can be used, particularly continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), because CGM is the standard of care for patients and should be so for people who are incarcerated.
The second case is much shorter and isn’t mine, but it was a letter in The New England Journal of Medicine about a man who was on probation, who was having urine tests to show that he had not been consuming alcohol. He was started on empagliflozin, which, interestingly, made his urine test become falsely positive.
Why? Well, it’s thought it’s because it caused fermentation of the sugar with the bacteria that was in his urine because the people who were processing the sample hadn’t done it correctly, and they kept it out at room temperature for a prolonged period of time before testing it. The urine samples should be kept refrigerated to prevent this from happening.
These are two people who had false-positive tests because they had diabetes. I think it’s important that we realize that this can happen, and we need to help our patients deal with these situations.
Dr. Peters is professor, Department of Clinical Medicine, Keck School of Medicine; Director, University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. She reported conflicts of interest with Abbott Diabetes Care, Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, Zafgen, Dexcom, MannKind, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Meet the Pregnancy Challenges of Women With Chronic Conditions
Preconception and prenatal care are more complicated in women with chronic health conditions but attention to disease management and promoting the adoption of a healthier lifestyle can improve outcomes for mothers and infants, according to a growing body of research.
The latest version of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Preconception Checklist, published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, highlights preexisting chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, lupus, and obesity as key factors to address in preconception care through disease management. A growing number of studies support the impact of these strategies on short- and long-term outcomes for mothers and babies, according to the authors.
Meet Glycemic Control Goals Prior to Pregnancy
“Women with diabetes can have healthy pregnancies but need to prepare for pregnancy in advance,” Ellen W. Seely, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical research in the endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If glucose levels are running high in the first trimester, this is associated with an increased risk of birth defects, some of which are very serious,” said Dr. Seely. Getting glucose levels under control reduces the risk of birth defects in women with diabetes close to that of the general population, she said.
The American Diabetes Association has set a goal for women to attain an HbA1c of less than 6.5% before conception, Dr. Seely said. “In addition, some women with diabetes may be on medications that should be changed to another class prior to pregnancy,” she noted. Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes often have hypertension as well, but ACE inhibitors are associated with an increased risk of fetal renal damage that can result in neonatal death; therefore, these medications should be stopped prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely emphasized.
“If a woman with type 2 diabetes is on medications other than insulin, recommendations from the ADA are to change to insulin prior to pregnancy, since we have the most data on the safety profile of insulin use in pregnancy,” she said.
To help women with diabetes improve glycemic control prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely recommends home glucose monitoring, with checks of glucose four times a day, fasting, and 2 hours after each meal, and adjustment of insulin accordingly.
A healthy diet and physical activity remain important components of glycemic control as well. A barrier to proper preconception and prenatal care for women with diabetes is not knowing that a pregnancy should be planned, Dr. Seely said. Discussions about pregnancy should start at puberty for women with diabetes, according to the ADA, and the topic should be raised yearly so women can optimize their health and adjust medications prior to conception.
Although studies of drugs have been done to inform preconception care for women with diabetes, research is lacking in several areas, notably the safety of GLP-1 agonists in pregnancy, said Dr. Seely. “This class of drug is commonly used in type 2 diabetes and the current recommendation is to stop these agents 2 months prior to conception,” she said.
Conceive in Times of Lupus Remission
Advance planning also is important for a healthy pregnancy in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sayna Norouzi, MD, director of the glomerular disease clinic and polycystic kidney disease clinic of Loma Linda University Medical Center, California, said in an interview.
“Lupus mostly affects women of childbearing age and can create many challenges during pregnancy,” said Dr. Norouzi, the corresponding author of a recent review on managing lupus nephritis during pregnancy.
“Women with lupus face an increased risk of pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, problems with fetal growth, stillbirth, and premature birth, and these risks increase based on factors such as disease activity, certain antibodies in the body, and other baseline existing conditions such as high blood pressure,” she said.
“It can be difficult to distinguish between a lupus flare and pregnancy-related issues, so proper management is important,” she noted. The Predictors of Pregnancy Outcome: Biomarkers in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (PROMISSE) study findings indicated a lupus nephritis relapse rate of 7.8% of patients in complete remission and 21% of those in partial remission during pregnancy, said Dr. Norouzi. “Current evidence has shown that SLE patients without lupus nephritis flare in the preconception period have a small risk of relapse during pregnancy,” she said.
Before and during pregnancy, women with lupus should work with their treating physicians to adjust medications for safety, watch for signs of flare, and aim to conceive during a period of lupus remission.
Preconception care for women with lupus nephritis involves a careful review of the medications used to control the disease and protect the kidneys and other organs, said Dr. Norouzi.
“Adjustments,” she said, “should be personalized, taking into account the mother’s health and the safety of the baby. Managing the disease actively during pregnancy may require changes to the treatment plan while minimizing risks,” she noted. However, changing medications can cause challenges for patients, as medications that are safer for pregnancy may lead to new symptoms and side effects, and patients will need to work closely with their healthcare providers to overcome new issues that arise, she added.
Preconception lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise and adopting a healthier diet can help with blood pressure control for kidney disease patients, said Dr. Norouzi.
In the review article, Dr. Norouzi and colleagues noted that preconception counseling for patients with lupus should address common comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, and the risk for immediate and long-term cardiovascular complications.
Benefits of Preconception Obesity Care Extend to Infants
Current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Institute of Medicine advise lifestyle interventions to reduce excessive weight gain during pregnancy and reduce the risk of inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and lipotoxicity that can promote complications in the mother and fetus during pregnancy.
In addition, a growing number of studies suggest that women with obesity who make healthy lifestyle changes prior to conception can reduce obesity-associated risks to their infants.
Adults born to women with obesity are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease and early signs of heart remodeling are identifiable in newborns, Samuel J. Burden, PhD, a research associate in the department of women and children’s health, Kings’ College, London, said in an interview. “It is therefore important to investigate whether intervening either before or during pregnancy by promoting a healthy lifestyle can reduce this adverse impact on the heart and blood vessels,” he said.
In a recent study published in the International Journal of Obesity, Dr. Burden and colleagues examined data from eight studies based on data from five randomized, controlled trials including children of mothers with obesity who engaged in healthy lifestyle interventions of improved diet and increased physical activity prior to and during pregnancy. The study population included children ranging in age from less than 2 months to 3-7 years.
Lifestyle interventions for mothers both before conception and during pregnancy were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling in the children, notably reduced interventricular septal wall thickness. Additionally, five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function showed improvement in blood pressure in children of mothers who took part in the interventions.
Dr. Burden acknowledged that lifestyle changes in women with obesity before conception and during pregnancy can be challenging, but should be encouraged. “During pregnancy, it may also seem unnatural to increase daily physical activity or change the way you are eating.” He emphasized that patients should consult their physicians and follow an established program. More randomized, controlled trials are needed from the preconception period to examine whether the health benefits are greater if the intervention begins prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Burden. However, “the current findings indeed indicate that women with obesity who lead a healthy lifestyle before and during their pregnancy can reduce the degree of unhealthy heart remodeling in their children,” he said.
Dr. Seely, Dr. Norouzi, and Dr. Burden had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Preconception and prenatal care are more complicated in women with chronic health conditions but attention to disease management and promoting the adoption of a healthier lifestyle can improve outcomes for mothers and infants, according to a growing body of research.
The latest version of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Preconception Checklist, published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, highlights preexisting chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, lupus, and obesity as key factors to address in preconception care through disease management. A growing number of studies support the impact of these strategies on short- and long-term outcomes for mothers and babies, according to the authors.
Meet Glycemic Control Goals Prior to Pregnancy
“Women with diabetes can have healthy pregnancies but need to prepare for pregnancy in advance,” Ellen W. Seely, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical research in the endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If glucose levels are running high in the first trimester, this is associated with an increased risk of birth defects, some of which are very serious,” said Dr. Seely. Getting glucose levels under control reduces the risk of birth defects in women with diabetes close to that of the general population, she said.
The American Diabetes Association has set a goal for women to attain an HbA1c of less than 6.5% before conception, Dr. Seely said. “In addition, some women with diabetes may be on medications that should be changed to another class prior to pregnancy,” she noted. Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes often have hypertension as well, but ACE inhibitors are associated with an increased risk of fetal renal damage that can result in neonatal death; therefore, these medications should be stopped prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely emphasized.
“If a woman with type 2 diabetes is on medications other than insulin, recommendations from the ADA are to change to insulin prior to pregnancy, since we have the most data on the safety profile of insulin use in pregnancy,” she said.
To help women with diabetes improve glycemic control prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely recommends home glucose monitoring, with checks of glucose four times a day, fasting, and 2 hours after each meal, and adjustment of insulin accordingly.
A healthy diet and physical activity remain important components of glycemic control as well. A barrier to proper preconception and prenatal care for women with diabetes is not knowing that a pregnancy should be planned, Dr. Seely said. Discussions about pregnancy should start at puberty for women with diabetes, according to the ADA, and the topic should be raised yearly so women can optimize their health and adjust medications prior to conception.
Although studies of drugs have been done to inform preconception care for women with diabetes, research is lacking in several areas, notably the safety of GLP-1 agonists in pregnancy, said Dr. Seely. “This class of drug is commonly used in type 2 diabetes and the current recommendation is to stop these agents 2 months prior to conception,” she said.
Conceive in Times of Lupus Remission
Advance planning also is important for a healthy pregnancy in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sayna Norouzi, MD, director of the glomerular disease clinic and polycystic kidney disease clinic of Loma Linda University Medical Center, California, said in an interview.
“Lupus mostly affects women of childbearing age and can create many challenges during pregnancy,” said Dr. Norouzi, the corresponding author of a recent review on managing lupus nephritis during pregnancy.
“Women with lupus face an increased risk of pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, problems with fetal growth, stillbirth, and premature birth, and these risks increase based on factors such as disease activity, certain antibodies in the body, and other baseline existing conditions such as high blood pressure,” she said.
“It can be difficult to distinguish between a lupus flare and pregnancy-related issues, so proper management is important,” she noted. The Predictors of Pregnancy Outcome: Biomarkers in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (PROMISSE) study findings indicated a lupus nephritis relapse rate of 7.8% of patients in complete remission and 21% of those in partial remission during pregnancy, said Dr. Norouzi. “Current evidence has shown that SLE patients without lupus nephritis flare in the preconception period have a small risk of relapse during pregnancy,” she said.
Before and during pregnancy, women with lupus should work with their treating physicians to adjust medications for safety, watch for signs of flare, and aim to conceive during a period of lupus remission.
Preconception care for women with lupus nephritis involves a careful review of the medications used to control the disease and protect the kidneys and other organs, said Dr. Norouzi.
“Adjustments,” she said, “should be personalized, taking into account the mother’s health and the safety of the baby. Managing the disease actively during pregnancy may require changes to the treatment plan while minimizing risks,” she noted. However, changing medications can cause challenges for patients, as medications that are safer for pregnancy may lead to new symptoms and side effects, and patients will need to work closely with their healthcare providers to overcome new issues that arise, she added.
Preconception lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise and adopting a healthier diet can help with blood pressure control for kidney disease patients, said Dr. Norouzi.
In the review article, Dr. Norouzi and colleagues noted that preconception counseling for patients with lupus should address common comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, and the risk for immediate and long-term cardiovascular complications.
Benefits of Preconception Obesity Care Extend to Infants
Current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Institute of Medicine advise lifestyle interventions to reduce excessive weight gain during pregnancy and reduce the risk of inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and lipotoxicity that can promote complications in the mother and fetus during pregnancy.
In addition, a growing number of studies suggest that women with obesity who make healthy lifestyle changes prior to conception can reduce obesity-associated risks to their infants.
Adults born to women with obesity are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease and early signs of heart remodeling are identifiable in newborns, Samuel J. Burden, PhD, a research associate in the department of women and children’s health, Kings’ College, London, said in an interview. “It is therefore important to investigate whether intervening either before or during pregnancy by promoting a healthy lifestyle can reduce this adverse impact on the heart and blood vessels,” he said.
In a recent study published in the International Journal of Obesity, Dr. Burden and colleagues examined data from eight studies based on data from five randomized, controlled trials including children of mothers with obesity who engaged in healthy lifestyle interventions of improved diet and increased physical activity prior to and during pregnancy. The study population included children ranging in age from less than 2 months to 3-7 years.
Lifestyle interventions for mothers both before conception and during pregnancy were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling in the children, notably reduced interventricular septal wall thickness. Additionally, five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function showed improvement in blood pressure in children of mothers who took part in the interventions.
Dr. Burden acknowledged that lifestyle changes in women with obesity before conception and during pregnancy can be challenging, but should be encouraged. “During pregnancy, it may also seem unnatural to increase daily physical activity or change the way you are eating.” He emphasized that patients should consult their physicians and follow an established program. More randomized, controlled trials are needed from the preconception period to examine whether the health benefits are greater if the intervention begins prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Burden. However, “the current findings indeed indicate that women with obesity who lead a healthy lifestyle before and during their pregnancy can reduce the degree of unhealthy heart remodeling in their children,” he said.
Dr. Seely, Dr. Norouzi, and Dr. Burden had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Preconception and prenatal care are more complicated in women with chronic health conditions but attention to disease management and promoting the adoption of a healthier lifestyle can improve outcomes for mothers and infants, according to a growing body of research.
The latest version of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Preconception Checklist, published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, highlights preexisting chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, lupus, and obesity as key factors to address in preconception care through disease management. A growing number of studies support the impact of these strategies on short- and long-term outcomes for mothers and babies, according to the authors.
Meet Glycemic Control Goals Prior to Pregnancy
“Women with diabetes can have healthy pregnancies but need to prepare for pregnancy in advance,” Ellen W. Seely, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical research in the endocrinology, diabetes, and hypertension division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“If glucose levels are running high in the first trimester, this is associated with an increased risk of birth defects, some of which are very serious,” said Dr. Seely. Getting glucose levels under control reduces the risk of birth defects in women with diabetes close to that of the general population, she said.
The American Diabetes Association has set a goal for women to attain an HbA1c of less than 6.5% before conception, Dr. Seely said. “In addition, some women with diabetes may be on medications that should be changed to another class prior to pregnancy,” she noted. Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes often have hypertension as well, but ACE inhibitors are associated with an increased risk of fetal renal damage that can result in neonatal death; therefore, these medications should be stopped prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely emphasized.
“If a woman with type 2 diabetes is on medications other than insulin, recommendations from the ADA are to change to insulin prior to pregnancy, since we have the most data on the safety profile of insulin use in pregnancy,” she said.
To help women with diabetes improve glycemic control prior to pregnancy, Dr. Seely recommends home glucose monitoring, with checks of glucose four times a day, fasting, and 2 hours after each meal, and adjustment of insulin accordingly.
A healthy diet and physical activity remain important components of glycemic control as well. A barrier to proper preconception and prenatal care for women with diabetes is not knowing that a pregnancy should be planned, Dr. Seely said. Discussions about pregnancy should start at puberty for women with diabetes, according to the ADA, and the topic should be raised yearly so women can optimize their health and adjust medications prior to conception.
Although studies of drugs have been done to inform preconception care for women with diabetes, research is lacking in several areas, notably the safety of GLP-1 agonists in pregnancy, said Dr. Seely. “This class of drug is commonly used in type 2 diabetes and the current recommendation is to stop these agents 2 months prior to conception,” she said.
Conceive in Times of Lupus Remission
Advance planning also is important for a healthy pregnancy in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sayna Norouzi, MD, director of the glomerular disease clinic and polycystic kidney disease clinic of Loma Linda University Medical Center, California, said in an interview.
“Lupus mostly affects women of childbearing age and can create many challenges during pregnancy,” said Dr. Norouzi, the corresponding author of a recent review on managing lupus nephritis during pregnancy.
“Women with lupus face an increased risk of pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, problems with fetal growth, stillbirth, and premature birth, and these risks increase based on factors such as disease activity, certain antibodies in the body, and other baseline existing conditions such as high blood pressure,” she said.
“It can be difficult to distinguish between a lupus flare and pregnancy-related issues, so proper management is important,” she noted. The Predictors of Pregnancy Outcome: Biomarkers in Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (PROMISSE) study findings indicated a lupus nephritis relapse rate of 7.8% of patients in complete remission and 21% of those in partial remission during pregnancy, said Dr. Norouzi. “Current evidence has shown that SLE patients without lupus nephritis flare in the preconception period have a small risk of relapse during pregnancy,” she said.
Before and during pregnancy, women with lupus should work with their treating physicians to adjust medications for safety, watch for signs of flare, and aim to conceive during a period of lupus remission.
Preconception care for women with lupus nephritis involves a careful review of the medications used to control the disease and protect the kidneys and other organs, said Dr. Norouzi.
“Adjustments,” she said, “should be personalized, taking into account the mother’s health and the safety of the baby. Managing the disease actively during pregnancy may require changes to the treatment plan while minimizing risks,” she noted. However, changing medications can cause challenges for patients, as medications that are safer for pregnancy may lead to new symptoms and side effects, and patients will need to work closely with their healthcare providers to overcome new issues that arise, she added.
Preconception lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise and adopting a healthier diet can help with blood pressure control for kidney disease patients, said Dr. Norouzi.
In the review article, Dr. Norouzi and colleagues noted that preconception counseling for patients with lupus should address common comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and dyslipidemia, and the risk for immediate and long-term cardiovascular complications.
Benefits of Preconception Obesity Care Extend to Infants
Current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Institute of Medicine advise lifestyle interventions to reduce excessive weight gain during pregnancy and reduce the risk of inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and lipotoxicity that can promote complications in the mother and fetus during pregnancy.
In addition, a growing number of studies suggest that women with obesity who make healthy lifestyle changes prior to conception can reduce obesity-associated risks to their infants.
Adults born to women with obesity are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease and early signs of heart remodeling are identifiable in newborns, Samuel J. Burden, PhD, a research associate in the department of women and children’s health, Kings’ College, London, said in an interview. “It is therefore important to investigate whether intervening either before or during pregnancy by promoting a healthy lifestyle can reduce this adverse impact on the heart and blood vessels,” he said.
In a recent study published in the International Journal of Obesity, Dr. Burden and colleagues examined data from eight studies based on data from five randomized, controlled trials including children of mothers with obesity who engaged in healthy lifestyle interventions of improved diet and increased physical activity prior to and during pregnancy. The study population included children ranging in age from less than 2 months to 3-7 years.
Lifestyle interventions for mothers both before conception and during pregnancy were associated with significant changes in cardiac remodeling in the children, notably reduced interventricular septal wall thickness. Additionally, five studies of cardiac systolic function and three studies of diastolic function showed improvement in blood pressure in children of mothers who took part in the interventions.
Dr. Burden acknowledged that lifestyle changes in women with obesity before conception and during pregnancy can be challenging, but should be encouraged. “During pregnancy, it may also seem unnatural to increase daily physical activity or change the way you are eating.” He emphasized that patients should consult their physicians and follow an established program. More randomized, controlled trials are needed from the preconception period to examine whether the health benefits are greater if the intervention begins prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Burden. However, “the current findings indeed indicate that women with obesity who lead a healthy lifestyle before and during their pregnancy can reduce the degree of unhealthy heart remodeling in their children,” he said.
Dr. Seely, Dr. Norouzi, and Dr. Burden had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Expanding Use of GLP-1 RAs for Weight Management
To discuss issues related to counseling patients about weight loss with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), I recently posted a case from my own practice. This was a 44-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obesity who wanted to try to lose weight with a GLP-1 RA, having been unsuccessful in maintaining a normal weight with lifestyle change alone.
I am very happy to see a high number of favorable responses to this article, and I also recognize that it was very focused on GLP-1 RA therapy while not addressing the multivariate treatment of obesity.
A healthy lifestyle remains foundational for the management of obesity, and clinicians should guide patients to make constructive choices regarding their diet, physical activity, mental health, and sleep. However, like for our patient introduced in that article, lifestyle changes are rarely sufficient to obtain a goal of sustained weight loss that promotes better health outcomes. A meta-analysis of clinical trials testing lifestyle interventions to lose weight among adults with overweight and obesity found that the relative reduction in body weight in the intervention vs control cohorts was −3.63 kg at 1 year and −2.45 kg at 3 years. More intensive programs with at least 28 interventions per year were associated with slightly more weight loss than less intensive programs.
That is why clinicians and patients have been reaching for effective pharmacotherapy to create better outcomes among adults with obesity. In a national survey of 1479 US adults, 12% reported having used a GLP-1 RA. Diabetes was the most common indication (43%), followed by heart disease (26%) and overweight/obesity (22%).
The high cost of GLP-1 RA therapy was a major barrier to even wider use. Some 54% of participants said that it was difficult to afford GLP-1 RA therapy, and an additional 22% found it very difficult to pay for the drugs. Having health insurance did not alter these figures substantially.
While cost and access remain some of the greatest challenges with the use of GLP-1 RAs, there is hope for change there. In March 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide to reduce the risk for cardiovascular events among patients with overweight and obesity and existing cardiovascular disease. It appears that Medicare will cover semaglutide for that indication, which bucks a trend of more than 20 years during which Medicare Part D would not cover pharmacotherapy for weight loss.
There is bipartisan support in the US Congress to further increase coverage of GLP-1 RAs for obesity, which makes sense. GLP-1 RAs are associated with greater average weight loss than either lifestyle interventions alone or that associated with previous anti-obesity medications. While there are no safety data for these drugs stretching back for 50 or 100 years, clinicians should bear in mind that exenatide was approved for the management of type 2 diabetes in 2005. So, we are approaching two decades of practical experience with these drugs, and it appears clear that the benefits of GLP-1 RAs outweigh any known harms. For the right patient, and with the right kind of guidance by clinicians, GLP-1 RA therapy can have a profound effect on individual and public health.
Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, disclosed ties with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To discuss issues related to counseling patients about weight loss with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), I recently posted a case from my own practice. This was a 44-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obesity who wanted to try to lose weight with a GLP-1 RA, having been unsuccessful in maintaining a normal weight with lifestyle change alone.
I am very happy to see a high number of favorable responses to this article, and I also recognize that it was very focused on GLP-1 RA therapy while not addressing the multivariate treatment of obesity.
A healthy lifestyle remains foundational for the management of obesity, and clinicians should guide patients to make constructive choices regarding their diet, physical activity, mental health, and sleep. However, like for our patient introduced in that article, lifestyle changes are rarely sufficient to obtain a goal of sustained weight loss that promotes better health outcomes. A meta-analysis of clinical trials testing lifestyle interventions to lose weight among adults with overweight and obesity found that the relative reduction in body weight in the intervention vs control cohorts was −3.63 kg at 1 year and −2.45 kg at 3 years. More intensive programs with at least 28 interventions per year were associated with slightly more weight loss than less intensive programs.
That is why clinicians and patients have been reaching for effective pharmacotherapy to create better outcomes among adults with obesity. In a national survey of 1479 US adults, 12% reported having used a GLP-1 RA. Diabetes was the most common indication (43%), followed by heart disease (26%) and overweight/obesity (22%).
The high cost of GLP-1 RA therapy was a major barrier to even wider use. Some 54% of participants said that it was difficult to afford GLP-1 RA therapy, and an additional 22% found it very difficult to pay for the drugs. Having health insurance did not alter these figures substantially.
While cost and access remain some of the greatest challenges with the use of GLP-1 RAs, there is hope for change there. In March 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide to reduce the risk for cardiovascular events among patients with overweight and obesity and existing cardiovascular disease. It appears that Medicare will cover semaglutide for that indication, which bucks a trend of more than 20 years during which Medicare Part D would not cover pharmacotherapy for weight loss.
There is bipartisan support in the US Congress to further increase coverage of GLP-1 RAs for obesity, which makes sense. GLP-1 RAs are associated with greater average weight loss than either lifestyle interventions alone or that associated with previous anti-obesity medications. While there are no safety data for these drugs stretching back for 50 or 100 years, clinicians should bear in mind that exenatide was approved for the management of type 2 diabetes in 2005. So, we are approaching two decades of practical experience with these drugs, and it appears clear that the benefits of GLP-1 RAs outweigh any known harms. For the right patient, and with the right kind of guidance by clinicians, GLP-1 RA therapy can have a profound effect on individual and public health.
Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, disclosed ties with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To discuss issues related to counseling patients about weight loss with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), I recently posted a case from my own practice. This was a 44-year-old woman with hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and obesity who wanted to try to lose weight with a GLP-1 RA, having been unsuccessful in maintaining a normal weight with lifestyle change alone.
I am very happy to see a high number of favorable responses to this article, and I also recognize that it was very focused on GLP-1 RA therapy while not addressing the multivariate treatment of obesity.
A healthy lifestyle remains foundational for the management of obesity, and clinicians should guide patients to make constructive choices regarding their diet, physical activity, mental health, and sleep. However, like for our patient introduced in that article, lifestyle changes are rarely sufficient to obtain a goal of sustained weight loss that promotes better health outcomes. A meta-analysis of clinical trials testing lifestyle interventions to lose weight among adults with overweight and obesity found that the relative reduction in body weight in the intervention vs control cohorts was −3.63 kg at 1 year and −2.45 kg at 3 years. More intensive programs with at least 28 interventions per year were associated with slightly more weight loss than less intensive programs.
That is why clinicians and patients have been reaching for effective pharmacotherapy to create better outcomes among adults with obesity. In a national survey of 1479 US adults, 12% reported having used a GLP-1 RA. Diabetes was the most common indication (43%), followed by heart disease (26%) and overweight/obesity (22%).
The high cost of GLP-1 RA therapy was a major barrier to even wider use. Some 54% of participants said that it was difficult to afford GLP-1 RA therapy, and an additional 22% found it very difficult to pay for the drugs. Having health insurance did not alter these figures substantially.
While cost and access remain some of the greatest challenges with the use of GLP-1 RAs, there is hope for change there. In March 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide to reduce the risk for cardiovascular events among patients with overweight and obesity and existing cardiovascular disease. It appears that Medicare will cover semaglutide for that indication, which bucks a trend of more than 20 years during which Medicare Part D would not cover pharmacotherapy for weight loss.
There is bipartisan support in the US Congress to further increase coverage of GLP-1 RAs for obesity, which makes sense. GLP-1 RAs are associated with greater average weight loss than either lifestyle interventions alone or that associated with previous anti-obesity medications. While there are no safety data for these drugs stretching back for 50 or 100 years, clinicians should bear in mind that exenatide was approved for the management of type 2 diabetes in 2005. So, we are approaching two decades of practical experience with these drugs, and it appears clear that the benefits of GLP-1 RAs outweigh any known harms. For the right patient, and with the right kind of guidance by clinicians, GLP-1 RA therapy can have a profound effect on individual and public health.
Dr. Vega, health sciences clinical professor, Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine, disclosed ties with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Uproar Over Vitamin D Disease-Prevention Guideline
A recent report by this news organization of a vitamin D clinical practice guideline released by the Endocrine Society in June triggered an outpouring of objections in the comments section from doctors and other readers.
A society press release listed the key new recommendations on the use of vitamin D supplementation and screening to reduce disease risks in individuals without established indications for such treatment or testing:
- For healthy adults younger than 75, no supplementation at doses above the recommended dietary intakes.
- Populations that may benefit from higher doses include: children and adolescents 18 and younger to prevent rickets and to reduce risk for respiratory infection, individuals 75 and older to possibly lower mortality risk, “pregnant people” to potentially reduce various risks, and people with prediabetes to potentially reduce risk of progression.
- No routine testing for 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels because outcome-specific benefits based on those levels have not been identified (including screening in people with dark complexion or obesity).
- Based on insufficient evidence, the panel could not determine specific blood-level thresholds for 25-hydroxyvitamin D for adequacy or for target levels for disease prevention.
This news organization covered the guideline release and simultaneous presentation at the Endocrine Society annual meeting. In response to the coverage, more than 200 doctors and other readers expressed concerns about the guideline, and some said outright that they would not follow it (readers quoted below are identified by the usernames they registered with on the website).
One reader who posted as Dr. Joseph Destefano went so far as to call the guideline “dangerous” and “almost ... evil.” Ironically, some readers attacked this news organization, thinking that the coverage implied an endorsement, rather than a news report.
Ignores Potential Benefits
“They address issues dealing only with endocrinology and bone health for the most part,” Dr. Emilio Gonzalez wrote. “However, vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency are not rare, and they impact the treatment of autoimmune disorders, chronic pain control, immunosuppression, cancer prevention, cardiovascular health, etc. There is plenty of literature in this regard.”
“They make these claims as if quality studies contradicting their guidelines have not been out there for years,” Dr. Brian Batcheldor said. “What about the huge demographic with diseases that impact intestinal absorption, eg, Crohn’s and celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, and ulcerative colitis? What about the one in nine that now have autoimmune diseases still awaiting diagnosis? What about night workers or anyone with more restricted access to sun exposure? How about those whose cultural or religious dress code limit skin exposure?”
The latter group was also mentioned in a post from Dr. Eve Finkelstein who said, “They don’t take into account women who are totally covered for religious reasons. They have no skin other than part of their face exposed. It does not make sense not to supplement them. Ignoring women’s health needs seems to be the norm.”
“I don’t think they considered the oral health effects of vitamin D deficiency,” pointed out commenter Corie Lewis. “Excess dental calculus (tartar) from excess calcium/phosphate in saliva significantly increases an individual’s periodontal disease risks (gum disease), and low saliva calcium/phosphate increases dental caries (cavities) risks, which generally indicates an imbalance of the oral microbiome. Vitamin D can help create balance and reduce those oral health risks.”
Noted Kimberley Morris-Windisch, “Having worked in rheumatology and pain for most of my career, I have seen too many people benefit from correcting deficiency of vitamin D. To ignore this is to miss opportunities to improve patient health.” Furthermore, “I find it unlikely that it would only improve mortality after age 75. That makes no sense.”
“Also,” she added, “what is the number [needed] to harm? In my 25 years, I have seen vitamin D toxicity once and an excessively high level without symptoms one other time.”
“WHY? Just WHY?” lamented Anne Kinchen. “Low levels in pregnant women have long-term effects on the developing fetus — higher and earlier rates of osteopenia in female children, weaker immune systems overall. There are just SO many reasons to test. These guidelines for no testing are absurd!”
No Screening, No Need for Decision-Making?
Several readers questioned the society’s rationale for not screening, as expressed by session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it,” Dr. Rosen said. “That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen. ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life. ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Among the reader comments in this regard:
“So misguided. Don’t look because we don’t know what do to with data. That’s the message this article exposes. The recommendation is do nothing. But, doing nothing IS an action — not a default.” (Lisa Tracy)
“So now, you will not screen for vitamin D because you do not know what to do next? See a naturopathic doctor — we know what to do next!” (Dr. Joyce Roberson)
“Gee, how do we treat it? ... What to do? Sounds incompetent at minimum. I suspect it’s vital, easy, and inexpensive ... so hide it.” (Holly Kohley)
“Just because we do not know is not a rationale for not testing. The opposite should be done.” (Dr. JJ Gold)
Caters to Industry?
Many commentators intimated that pharma and/or insurance company considerations played a role in the recommendations. Their comments included the following:
“I have been under the impression people do routine checkups to verify there are no hidden problems. If only some testing is done, the probability of not finding a problem is huge. ... Preventive healthcare should be looking for something to prevent instead of waiting until they can cure it. Of course, it might come back to ‘follow the money.’ It is much more profitable to diagnose and treat than it is to prevent.” (Grace Kyser)
“The current irrational ‘recommendation’ gives insurance companies an excuse to deny ALL tests of vitamin D — even if the proper code is supplied. The result is — people suffer. This recommendation does harm!” (Dr JJ Gold)
“Essentially, they are saying let’s not screen ‘healthy’ individuals and ignore it altogether. Better to wait till they’re old, pregnant, or already sick and diagnosed with a disease. This is the problem with the healthcare in this country.” (Brittney Lesher)
“Until allopathic medicine stops waiting for severe symptoms to develop before even screening for potential health problems, the most expensive healthcare (aka, sick care) system in the world will continue to be content to focus on medical emergencies and ignore prevention. ...” (Dean Raffelock)
“Don’t test? Are you kidding me? Especially when people are supplementing? That is akin to taking a blood pressure medication without measuring blood pressures! ... Don’t test? Don’t supplement? ... I have only one explanation for such nonsense: Pharma lives off sick people, not healthy ones.” (Georg Schlomka)
On a somewhat conciliatory and pointed note, Dr Francesca Luna-Rudin commented, “I would like to remind all of my fellow physicians that recommendations should be regarded as just that, a ‘recommendation.’ As doctors, we can use guidelines and recommendations in our practice, but if a new one is presented that does not make sense or would lead to harm based on our education and training, then we are not bound to follow it!”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent report by this news organization of a vitamin D clinical practice guideline released by the Endocrine Society in June triggered an outpouring of objections in the comments section from doctors and other readers.
A society press release listed the key new recommendations on the use of vitamin D supplementation and screening to reduce disease risks in individuals without established indications for such treatment or testing:
- For healthy adults younger than 75, no supplementation at doses above the recommended dietary intakes.
- Populations that may benefit from higher doses include: children and adolescents 18 and younger to prevent rickets and to reduce risk for respiratory infection, individuals 75 and older to possibly lower mortality risk, “pregnant people” to potentially reduce various risks, and people with prediabetes to potentially reduce risk of progression.
- No routine testing for 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels because outcome-specific benefits based on those levels have not been identified (including screening in people with dark complexion or obesity).
- Based on insufficient evidence, the panel could not determine specific blood-level thresholds for 25-hydroxyvitamin D for adequacy or for target levels for disease prevention.
This news organization covered the guideline release and simultaneous presentation at the Endocrine Society annual meeting. In response to the coverage, more than 200 doctors and other readers expressed concerns about the guideline, and some said outright that they would not follow it (readers quoted below are identified by the usernames they registered with on the website).
One reader who posted as Dr. Joseph Destefano went so far as to call the guideline “dangerous” and “almost ... evil.” Ironically, some readers attacked this news organization, thinking that the coverage implied an endorsement, rather than a news report.
Ignores Potential Benefits
“They address issues dealing only with endocrinology and bone health for the most part,” Dr. Emilio Gonzalez wrote. “However, vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency are not rare, and they impact the treatment of autoimmune disorders, chronic pain control, immunosuppression, cancer prevention, cardiovascular health, etc. There is plenty of literature in this regard.”
“They make these claims as if quality studies contradicting their guidelines have not been out there for years,” Dr. Brian Batcheldor said. “What about the huge demographic with diseases that impact intestinal absorption, eg, Crohn’s and celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, and ulcerative colitis? What about the one in nine that now have autoimmune diseases still awaiting diagnosis? What about night workers or anyone with more restricted access to sun exposure? How about those whose cultural or religious dress code limit skin exposure?”
The latter group was also mentioned in a post from Dr. Eve Finkelstein who said, “They don’t take into account women who are totally covered for religious reasons. They have no skin other than part of their face exposed. It does not make sense not to supplement them. Ignoring women’s health needs seems to be the norm.”
“I don’t think they considered the oral health effects of vitamin D deficiency,” pointed out commenter Corie Lewis. “Excess dental calculus (tartar) from excess calcium/phosphate in saliva significantly increases an individual’s periodontal disease risks (gum disease), and low saliva calcium/phosphate increases dental caries (cavities) risks, which generally indicates an imbalance of the oral microbiome. Vitamin D can help create balance and reduce those oral health risks.”
Noted Kimberley Morris-Windisch, “Having worked in rheumatology and pain for most of my career, I have seen too many people benefit from correcting deficiency of vitamin D. To ignore this is to miss opportunities to improve patient health.” Furthermore, “I find it unlikely that it would only improve mortality after age 75. That makes no sense.”
“Also,” she added, “what is the number [needed] to harm? In my 25 years, I have seen vitamin D toxicity once and an excessively high level without symptoms one other time.”
“WHY? Just WHY?” lamented Anne Kinchen. “Low levels in pregnant women have long-term effects on the developing fetus — higher and earlier rates of osteopenia in female children, weaker immune systems overall. There are just SO many reasons to test. These guidelines for no testing are absurd!”
No Screening, No Need for Decision-Making?
Several readers questioned the society’s rationale for not screening, as expressed by session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it,” Dr. Rosen said. “That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen. ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life. ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Among the reader comments in this regard:
“So misguided. Don’t look because we don’t know what do to with data. That’s the message this article exposes. The recommendation is do nothing. But, doing nothing IS an action — not a default.” (Lisa Tracy)
“So now, you will not screen for vitamin D because you do not know what to do next? See a naturopathic doctor — we know what to do next!” (Dr. Joyce Roberson)
“Gee, how do we treat it? ... What to do? Sounds incompetent at minimum. I suspect it’s vital, easy, and inexpensive ... so hide it.” (Holly Kohley)
“Just because we do not know is not a rationale for not testing. The opposite should be done.” (Dr. JJ Gold)
Caters to Industry?
Many commentators intimated that pharma and/or insurance company considerations played a role in the recommendations. Their comments included the following:
“I have been under the impression people do routine checkups to verify there are no hidden problems. If only some testing is done, the probability of not finding a problem is huge. ... Preventive healthcare should be looking for something to prevent instead of waiting until they can cure it. Of course, it might come back to ‘follow the money.’ It is much more profitable to diagnose and treat than it is to prevent.” (Grace Kyser)
“The current irrational ‘recommendation’ gives insurance companies an excuse to deny ALL tests of vitamin D — even if the proper code is supplied. The result is — people suffer. This recommendation does harm!” (Dr JJ Gold)
“Essentially, they are saying let’s not screen ‘healthy’ individuals and ignore it altogether. Better to wait till they’re old, pregnant, or already sick and diagnosed with a disease. This is the problem with the healthcare in this country.” (Brittney Lesher)
“Until allopathic medicine stops waiting for severe symptoms to develop before even screening for potential health problems, the most expensive healthcare (aka, sick care) system in the world will continue to be content to focus on medical emergencies and ignore prevention. ...” (Dean Raffelock)
“Don’t test? Are you kidding me? Especially when people are supplementing? That is akin to taking a blood pressure medication without measuring blood pressures! ... Don’t test? Don’t supplement? ... I have only one explanation for such nonsense: Pharma lives off sick people, not healthy ones.” (Georg Schlomka)
On a somewhat conciliatory and pointed note, Dr Francesca Luna-Rudin commented, “I would like to remind all of my fellow physicians that recommendations should be regarded as just that, a ‘recommendation.’ As doctors, we can use guidelines and recommendations in our practice, but if a new one is presented that does not make sense or would lead to harm based on our education and training, then we are not bound to follow it!”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent report by this news organization of a vitamin D clinical practice guideline released by the Endocrine Society in June triggered an outpouring of objections in the comments section from doctors and other readers.
A society press release listed the key new recommendations on the use of vitamin D supplementation and screening to reduce disease risks in individuals without established indications for such treatment or testing:
- For healthy adults younger than 75, no supplementation at doses above the recommended dietary intakes.
- Populations that may benefit from higher doses include: children and adolescents 18 and younger to prevent rickets and to reduce risk for respiratory infection, individuals 75 and older to possibly lower mortality risk, “pregnant people” to potentially reduce various risks, and people with prediabetes to potentially reduce risk of progression.
- No routine testing for 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels because outcome-specific benefits based on those levels have not been identified (including screening in people with dark complexion or obesity).
- Based on insufficient evidence, the panel could not determine specific blood-level thresholds for 25-hydroxyvitamin D for adequacy or for target levels for disease prevention.
This news organization covered the guideline release and simultaneous presentation at the Endocrine Society annual meeting. In response to the coverage, more than 200 doctors and other readers expressed concerns about the guideline, and some said outright that they would not follow it (readers quoted below are identified by the usernames they registered with on the website).
One reader who posted as Dr. Joseph Destefano went so far as to call the guideline “dangerous” and “almost ... evil.” Ironically, some readers attacked this news organization, thinking that the coverage implied an endorsement, rather than a news report.
Ignores Potential Benefits
“They address issues dealing only with endocrinology and bone health for the most part,” Dr. Emilio Gonzalez wrote. “However, vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency are not rare, and they impact the treatment of autoimmune disorders, chronic pain control, immunosuppression, cancer prevention, cardiovascular health, etc. There is plenty of literature in this regard.”
“They make these claims as if quality studies contradicting their guidelines have not been out there for years,” Dr. Brian Batcheldor said. “What about the huge demographic with diseases that impact intestinal absorption, eg, Crohn’s and celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, and ulcerative colitis? What about the one in nine that now have autoimmune diseases still awaiting diagnosis? What about night workers or anyone with more restricted access to sun exposure? How about those whose cultural or religious dress code limit skin exposure?”
The latter group was also mentioned in a post from Dr. Eve Finkelstein who said, “They don’t take into account women who are totally covered for religious reasons. They have no skin other than part of their face exposed. It does not make sense not to supplement them. Ignoring women’s health needs seems to be the norm.”
“I don’t think they considered the oral health effects of vitamin D deficiency,” pointed out commenter Corie Lewis. “Excess dental calculus (tartar) from excess calcium/phosphate in saliva significantly increases an individual’s periodontal disease risks (gum disease), and low saliva calcium/phosphate increases dental caries (cavities) risks, which generally indicates an imbalance of the oral microbiome. Vitamin D can help create balance and reduce those oral health risks.”
Noted Kimberley Morris-Windisch, “Having worked in rheumatology and pain for most of my career, I have seen too many people benefit from correcting deficiency of vitamin D. To ignore this is to miss opportunities to improve patient health.” Furthermore, “I find it unlikely that it would only improve mortality after age 75. That makes no sense.”
“Also,” she added, “what is the number [needed] to harm? In my 25 years, I have seen vitamin D toxicity once and an excessively high level without symptoms one other time.”
“WHY? Just WHY?” lamented Anne Kinchen. “Low levels in pregnant women have long-term effects on the developing fetus — higher and earlier rates of osteopenia in female children, weaker immune systems overall. There are just SO many reasons to test. These guidelines for no testing are absurd!”
No Screening, No Need for Decision-Making?
Several readers questioned the society’s rationale for not screening, as expressed by session moderator Clifford J. Rosen, MD, director of Clinical and Translational Research and senior scientist at Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, Maine.
“When clinicians measure vitamin D, then they’re forced to make a decision what to do about it,” Dr. Rosen said. “That’s where questions about the levels come in. And that’s a big problem. So what the panel’s saying is, don’t screen. ... This really gets to the heart of the issue, because we have no data that there’s anything about screening that allows us to improve quality of life. ... Screening is probably not worthwhile in any age group.”
Among the reader comments in this regard:
“So misguided. Don’t look because we don’t know what do to with data. That’s the message this article exposes. The recommendation is do nothing. But, doing nothing IS an action — not a default.” (Lisa Tracy)
“So now, you will not screen for vitamin D because you do not know what to do next? See a naturopathic doctor — we know what to do next!” (Dr. Joyce Roberson)
“Gee, how do we treat it? ... What to do? Sounds incompetent at minimum. I suspect it’s vital, easy, and inexpensive ... so hide it.” (Holly Kohley)
“Just because we do not know is not a rationale for not testing. The opposite should be done.” (Dr. JJ Gold)
Caters to Industry?
Many commentators intimated that pharma and/or insurance company considerations played a role in the recommendations. Their comments included the following:
“I have been under the impression people do routine checkups to verify there are no hidden problems. If only some testing is done, the probability of not finding a problem is huge. ... Preventive healthcare should be looking for something to prevent instead of waiting until they can cure it. Of course, it might come back to ‘follow the money.’ It is much more profitable to diagnose and treat than it is to prevent.” (Grace Kyser)
“The current irrational ‘recommendation’ gives insurance companies an excuse to deny ALL tests of vitamin D — even if the proper code is supplied. The result is — people suffer. This recommendation does harm!” (Dr JJ Gold)
“Essentially, they are saying let’s not screen ‘healthy’ individuals and ignore it altogether. Better to wait till they’re old, pregnant, or already sick and diagnosed with a disease. This is the problem with the healthcare in this country.” (Brittney Lesher)
“Until allopathic medicine stops waiting for severe symptoms to develop before even screening for potential health problems, the most expensive healthcare (aka, sick care) system in the world will continue to be content to focus on medical emergencies and ignore prevention. ...” (Dean Raffelock)
“Don’t test? Are you kidding me? Especially when people are supplementing? That is akin to taking a blood pressure medication without measuring blood pressures! ... Don’t test? Don’t supplement? ... I have only one explanation for such nonsense: Pharma lives off sick people, not healthy ones.” (Georg Schlomka)
On a somewhat conciliatory and pointed note, Dr Francesca Luna-Rudin commented, “I would like to remind all of my fellow physicians that recommendations should be regarded as just that, a ‘recommendation.’ As doctors, we can use guidelines and recommendations in our practice, but if a new one is presented that does not make sense or would lead to harm based on our education and training, then we are not bound to follow it!”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study: AFib May Be Linked to Dementia in T2D
TOPLINE:
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a substantially higher risk for all-cause dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies suggest a potential link between AF and dementia in the broader population, but evidence is scarce in people with diabetes, who are at increased risk for both conditions.
- This longitudinal observational study assessed the association between new-onset AF and dementia in 22,989 patients with T2D (median age at enrollment, 61.0 years; 62.3% men; 86.3% White individuals).
- New-onset AF was identified through hospital admission records using the International Classification of Diseases – 9th Revision (ICD-9) and ICD-10 codes, and dementia cases were identified using an algorithm developed by the UK Biobank.
- Time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to determine the association between incident dementia and new-onset AF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up duration of about 12 years, 844 patients developed all-cause dementia, 342 were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, and 246 had vascular dementia.
- Patients with incident AF had a higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 2.15; 95% CI, 1.80-2.57), Alzheimer’s disease (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.06-1.96), and vascular dementia (HR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.32-4.17) than those without incident AF.
- The results are independent of common dementia risk factors, such as sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle factors.
- The mean time intervals from the onset of AF to all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia were 2.95, 2.81, and 3.37 years, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“AF is a significant risk factor for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes, suggesting the importance of timely and effective treatment of AF, such as early rhythm control strategies and anticoagulant use, in preventing dementia among this demographic,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ying Zhou, PhD, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study could not explore the link between different AF subtypes and dementia owing to its small sample size. The effects of AF treatment on the risk for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes were not considered because of lack of information. The mostly White study population limits the generalizability of the findings to other races and ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a substantially higher risk for all-cause dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies suggest a potential link between AF and dementia in the broader population, but evidence is scarce in people with diabetes, who are at increased risk for both conditions.
- This longitudinal observational study assessed the association between new-onset AF and dementia in 22,989 patients with T2D (median age at enrollment, 61.0 years; 62.3% men; 86.3% White individuals).
- New-onset AF was identified through hospital admission records using the International Classification of Diseases – 9th Revision (ICD-9) and ICD-10 codes, and dementia cases were identified using an algorithm developed by the UK Biobank.
- Time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to determine the association between incident dementia and new-onset AF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up duration of about 12 years, 844 patients developed all-cause dementia, 342 were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, and 246 had vascular dementia.
- Patients with incident AF had a higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 2.15; 95% CI, 1.80-2.57), Alzheimer’s disease (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.06-1.96), and vascular dementia (HR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.32-4.17) than those without incident AF.
- The results are independent of common dementia risk factors, such as sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle factors.
- The mean time intervals from the onset of AF to all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia were 2.95, 2.81, and 3.37 years, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“AF is a significant risk factor for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes, suggesting the importance of timely and effective treatment of AF, such as early rhythm control strategies and anticoagulant use, in preventing dementia among this demographic,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ying Zhou, PhD, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study could not explore the link between different AF subtypes and dementia owing to its small sample size. The effects of AF treatment on the risk for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes were not considered because of lack of information. The mostly White study population limits the generalizability of the findings to other races and ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a substantially higher risk for all-cause dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
METHODOLOGY:
- Studies suggest a potential link between AF and dementia in the broader population, but evidence is scarce in people with diabetes, who are at increased risk for both conditions.
- This longitudinal observational study assessed the association between new-onset AF and dementia in 22,989 patients with T2D (median age at enrollment, 61.0 years; 62.3% men; 86.3% White individuals).
- New-onset AF was identified through hospital admission records using the International Classification of Diseases – 9th Revision (ICD-9) and ICD-10 codes, and dementia cases were identified using an algorithm developed by the UK Biobank.
- Time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to determine the association between incident dementia and new-onset AF.
TAKEAWAY:
- Over a median follow-up duration of about 12 years, 844 patients developed all-cause dementia, 342 were diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, and 246 had vascular dementia.
- Patients with incident AF had a higher risk of developing all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 2.15; 95% CI, 1.80-2.57), Alzheimer’s disease (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.06-1.96), and vascular dementia (HR, 3.11; 95% CI, 2.32-4.17) than those without incident AF.
- The results are independent of common dementia risk factors, such as sociodemographic characteristics and lifestyle factors.
- The mean time intervals from the onset of AF to all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia were 2.95, 2.81, and 3.37 years, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“AF is a significant risk factor for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes, suggesting the importance of timely and effective treatment of AF, such as early rhythm control strategies and anticoagulant use, in preventing dementia among this demographic,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ying Zhou, PhD, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, was published online in Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study could not explore the link between different AF subtypes and dementia owing to its small sample size. The effects of AF treatment on the risk for dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes were not considered because of lack of information. The mostly White study population limits the generalizability of the findings to other races and ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mounjaro Beats Ozempic, So Why Isn’t It More Popular?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 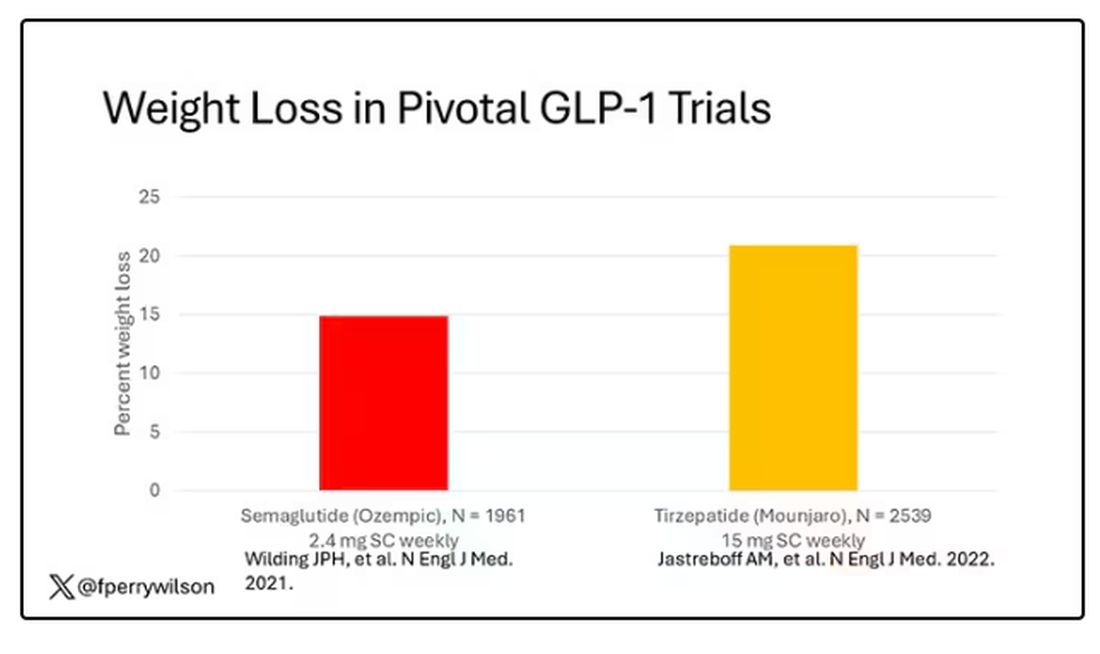
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 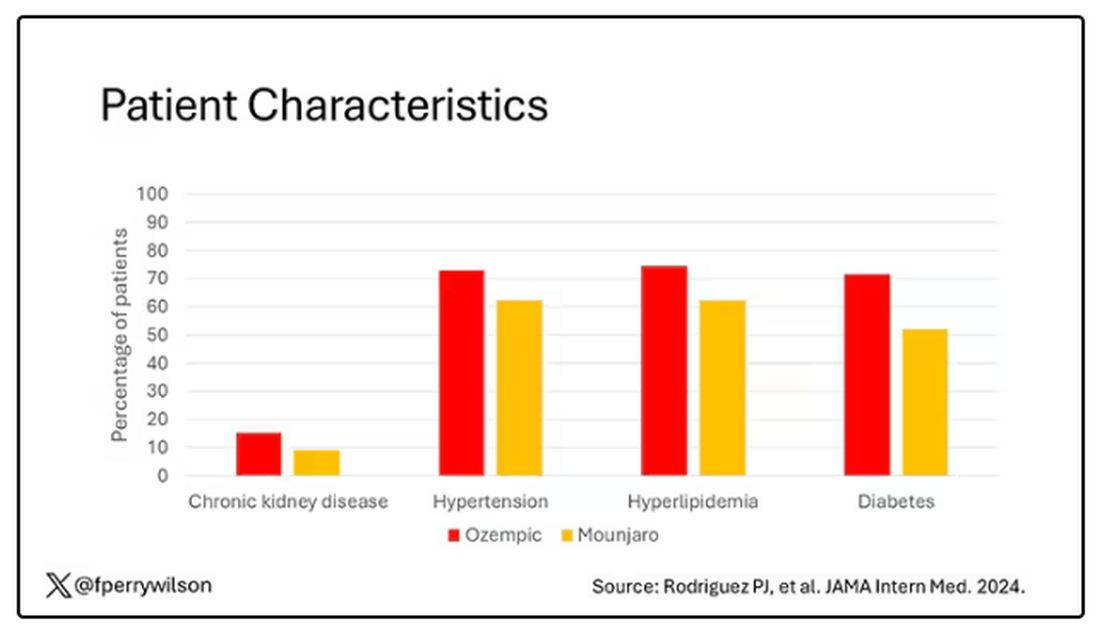
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.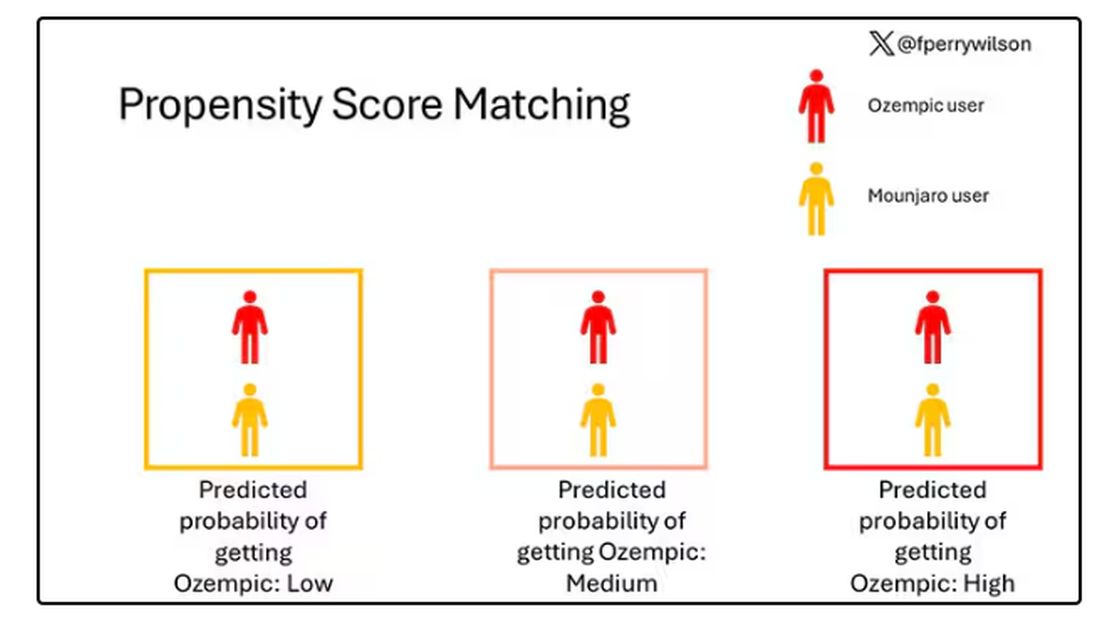
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.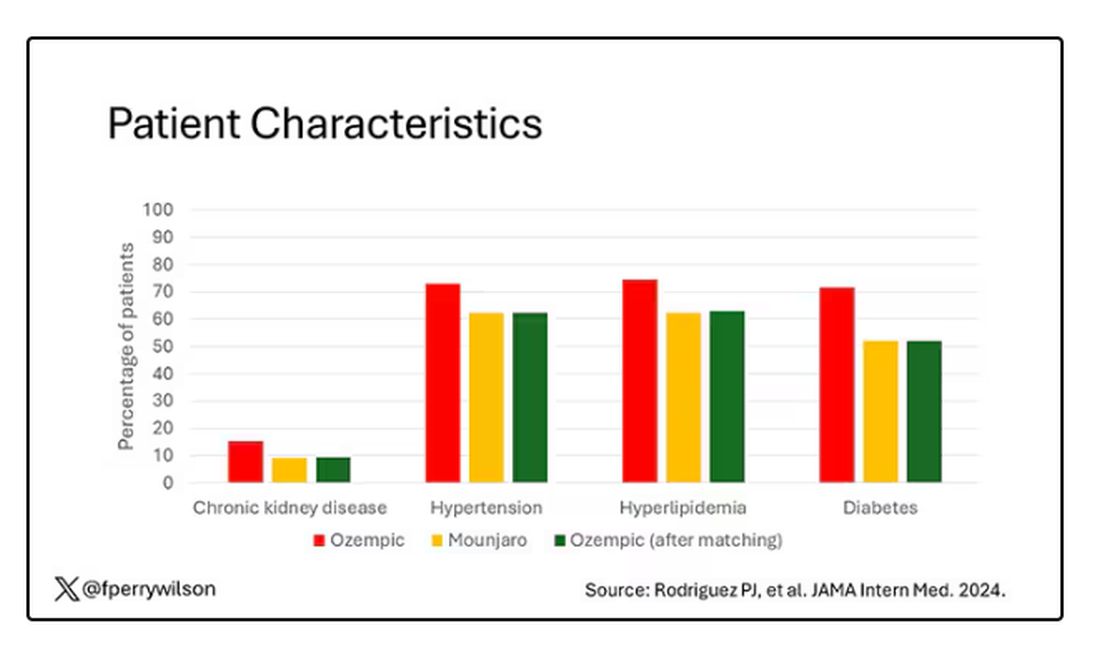
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 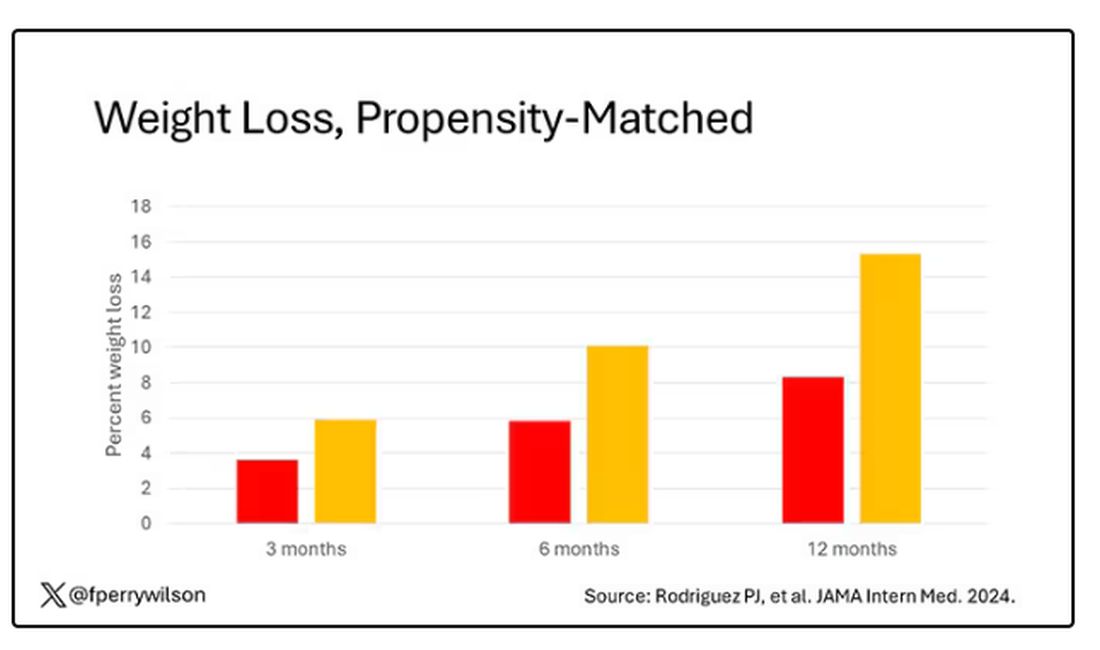
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.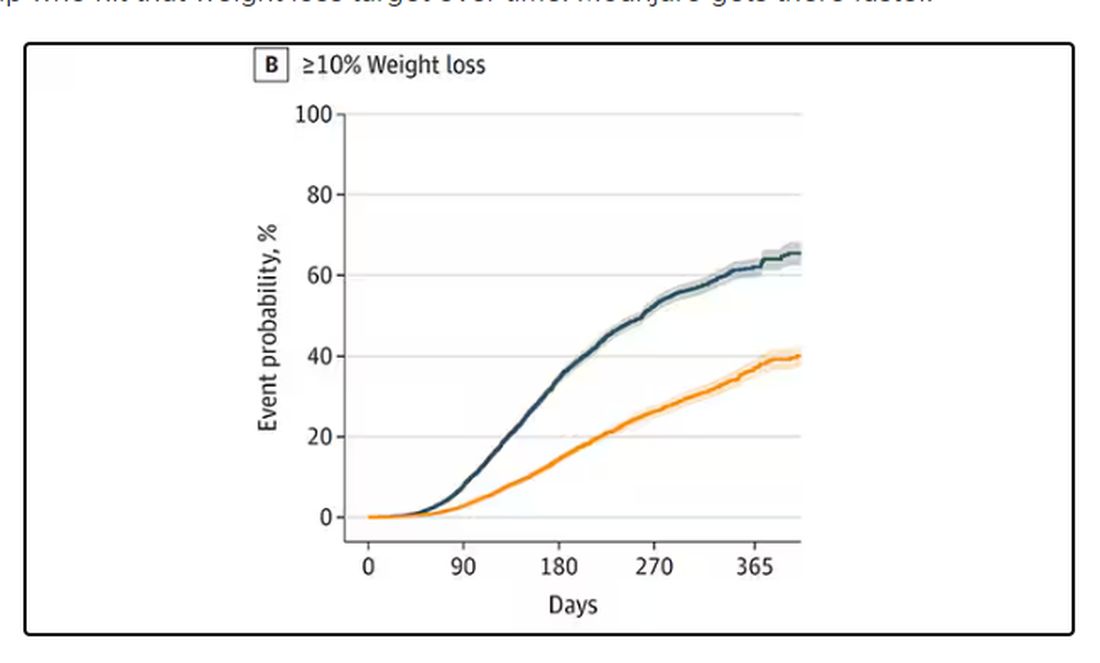
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s July, which means our hospital is filled with new interns, residents, and fellows all eager to embark on a new stage of their career. It’s an exciting time — a bit of a scary time — but it’s also the time when the medical strategies I’ve been taking for granted get called into question. At this point in the year, I tend to get a lot of “why” questions. Why did you order that test? Why did you suspect that diagnosis? Why did you choose that medication?
Meds are the hardest, I find. Sure, I can explain that I prescribed a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist because the patient had diabetes and was overweight, and multiple studies show that this class of drug leads to weight loss and reduced mortality risk. But then I get the follow-up: Sure, but why THAT GLP-1 drug? Why did you pick semaglutide (Ozempic) over tirzepatide (Mounjaro)?
Here’s where I run out of good answers. Sometimes I choose a drug because that’s what the patient’s insurance has on their formulary. Sometimes it’s because it’s cheaper in general. Sometimes, it’s just force of habit. I know the correct dose, I have experience with the side effects — it’s comfortable.
What I can’t say is that I have solid evidence that one drug is superior to another, say from a randomized trial of semaglutide vs tirzepatide. I don’t have that evidence because that trial has never happened and, as I’ll explain in a minute, may never happen at all.
But we might have the next best thing. And the results may surprise you.
Why don’t we see more head-to-head trials of competitor drugs? The answer is pretty simple, honestly: risk management. For drugs that are on patent, like the GLP-1s, conducting a trial without the buy-in of the pharmaceutical company is simply too expensive — we can’t run a trial unless someone provides the drug for free. That gives the companies a lot of say in what trials get done, and it seems that most pharma companies have reached the same conclusion: A head-to-head trial is too risky. Be happy with the market share you have, and try to nibble away at the edges through good old-fashioned marketing.
But if you look at the data that are out there, you might wonder why Ozempic is the market leader. I mean, sure, it’s a heck of a weight loss drug. But the weight loss in the trials of Mounjaro was actually a bit higher. It’s worth noting here that tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is not just a GLP-1 receptor agonist; it is also a gastric inhibitory polypeptide agonist. 
But it’s very hard to compare the results of a trial pitting Ozempic against placebo with a totally different trial pitting Mounjaro against placebo. You can always argue that the patients studied were just too different at baseline — an apples and oranges situation.
Newly published, a study appearing in JAMA Internal Medicine uses real-world data and propensity-score matching to turn oranges back into apples. I’ll walk you through it.
The data and analysis here come from Truveta, a collective of various US healthcare systems that share a broad swath of electronic health record data. Researchers identified 41,222 adults with overweight or obesity who were prescribed semaglutide or tirzepatide between May 2022 and September 2023.
You’d be tempted to just see which group lost more weight over time, but that is the apples and oranges problem. People prescribed Mounjaro were different from people who were prescribed Ozempic. There are a variety of factors to look at here, but the vibe is that the Mounjaro group seems healthier at baseline. They were younger and had less kidney disease, less hypertension, and less hyperlipidemia. They had higher incomes and were more likely to be White. They were also dramatically less likely to have diabetes. 
To account for this, the researchers used a statistical technique called propensity-score matching. Briefly, you create a model based on a variety of patient factors to predict who would be prescribed Ozempic and who would be prescribed Mounjaro. You then identify pairs of patients with similar probability (or propensity) of receiving, say, Ozempic, where one member of the pair got Ozempic and one got Mounjaro. Any unmatched individuals simply get dropped from the analysis.
Thus, the researchers took the 41,222 individuals who started the analysis, of whom 9193 received Mounjaro, and identified the 9193 patients who got Ozempic that most closely matched the Mounjaro crowd. I know, it sounds confusing. But as an example, in the original dataset, 51.9% of those who got Mounjaro had diabetes compared with 71.5% of those who got Ozempic. Among the 9193 individuals who remained in the Ozempic group after matching, 52.1% had diabetes. By matching in this way, you balance your baseline characteristics. Turning apples into oranges. Or, maybe the better metaphor would be plucking the oranges out of a big pile of mostly apples.
Once that’s done, we can go back to do what we wanted to do in the beginning, which is to look at the weight loss between the groups.
What I’m showing you here is the average percent change in body weight at 3, 6, and 12 months across the two drugs in the matched cohort. By a year out, you have basically 15% weight loss in the Mounjaro group compared with 8% or so in the Ozempic group. 
We can slice this a different way as well — asking what percent of people in each group achieve, say, 10% weight loss? This graph examines the percentage of each treatment group who hit that weight loss target over time. Mounjaro gets there faster.
I should point out that this was a so-called “on treatment” analysis: If people stopped taking either of the drugs, they were no longer included in the study. That tends to make drugs like this appear better than they are because as time goes on, you may weed out the people who stop the drug owing to lack of efficacy or to side effects. But in a sensitivity analysis, the authors see what happens if they just treat people as if they were taking the drug for the entire year once they had it prescribed, and the results, while not as dramatic, were broadly similar. Mounjaro still came out on top.
Adverse events— stuff like gastroparesis and pancreatitis — were rare, but rates were similar between the two groups.
It’s great to see studies like this that leverage real world data and a solid statistical underpinning to give us providers actionable information. Is it 100% definitive? No. But, especially considering the clinical trial data, I don’t think I’m going out on a limb to say that Mounjaro seems to be the more effective weight loss agent. That said, we don’t actually live in a world where we can prescribe medications based on a silly little thing like which is the most effective. Especially given the cost of these agents — the patient’s insurance status is going to guide our prescription pen more than this study ever could. And of course, given the demand for this class of agents and the fact that both are actually quite effective, you may be best off prescribing whatever you can get your hands on.
But I’d like to see more of this. When I do have a choice of a medication, when costs and availability are similar, I’d like to be able to answer that question of “why did you choose that one?” with an evidence-based answer: “It’s better.”
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.