User login
according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
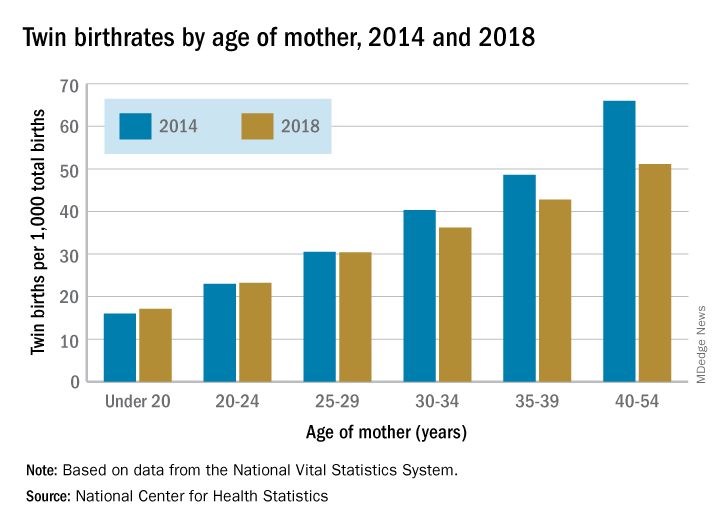
The twin birthrate, which had increased by 79% during 1980-2014, fell by 4% during 2014-2018, but that decline was “not universal across maternal age and race and Hispanic-origin groups,” the NCHS investigators said.
Twin birthrates fell by at least 10% for mothers aged 30 years and older from 2014 to 2018 but held steady for women in their twenties. Over that same period, the twin birthrate fell by a significant 7% among non-Hispanic white women (36.7 to 34.3 per 1,000 total births) but increased just slightly for non-Hispanic black women (40.0 to 40.5 per 1,000) and Hispanic women (24.1 to 24.4), the investigators reported.
For women 30 years and older, the drops in twin births got larger as age increased and were significant for each age group. The rate for women aged 30-34 years fell 10% as it went from 40.3 per 1,000 total births in 2014 to 36.2 per 1,000. The decrease was 12% (from 48.6 per 1,000 to 42.8) for women aged 35-39 and 23% (from 66.0 to 51.1) for those aged 40 years and older, they said based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The rates were basically unchanged for women in their 20s, from 23.0 to 23.2 in 20- to 24-year-olds and 30.5 to 30.4 in 25- to 29-year-olds – but there was a significant increase for the youngest group with rates among those younger than 20 years going from 16.0 to 17.1 per 1,000, the report showed.
according to the National Center for Health Statistics.

The twin birthrate, which had increased by 79% during 1980-2014, fell by 4% during 2014-2018, but that decline was “not universal across maternal age and race and Hispanic-origin groups,” the NCHS investigators said.
Twin birthrates fell by at least 10% for mothers aged 30 years and older from 2014 to 2018 but held steady for women in their twenties. Over that same period, the twin birthrate fell by a significant 7% among non-Hispanic white women (36.7 to 34.3 per 1,000 total births) but increased just slightly for non-Hispanic black women (40.0 to 40.5 per 1,000) and Hispanic women (24.1 to 24.4), the investigators reported.
For women 30 years and older, the drops in twin births got larger as age increased and were significant for each age group. The rate for women aged 30-34 years fell 10% as it went from 40.3 per 1,000 total births in 2014 to 36.2 per 1,000. The decrease was 12% (from 48.6 per 1,000 to 42.8) for women aged 35-39 and 23% (from 66.0 to 51.1) for those aged 40 years and older, they said based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The rates were basically unchanged for women in their 20s, from 23.0 to 23.2 in 20- to 24-year-olds and 30.5 to 30.4 in 25- to 29-year-olds – but there was a significant increase for the youngest group with rates among those younger than 20 years going from 16.0 to 17.1 per 1,000, the report showed.
according to the National Center for Health Statistics.

The twin birthrate, which had increased by 79% during 1980-2014, fell by 4% during 2014-2018, but that decline was “not universal across maternal age and race and Hispanic-origin groups,” the NCHS investigators said.
Twin birthrates fell by at least 10% for mothers aged 30 years and older from 2014 to 2018 but held steady for women in their twenties. Over that same period, the twin birthrate fell by a significant 7% among non-Hispanic white women (36.7 to 34.3 per 1,000 total births) but increased just slightly for non-Hispanic black women (40.0 to 40.5 per 1,000) and Hispanic women (24.1 to 24.4), the investigators reported.
For women 30 years and older, the drops in twin births got larger as age increased and were significant for each age group. The rate for women aged 30-34 years fell 10% as it went from 40.3 per 1,000 total births in 2014 to 36.2 per 1,000. The decrease was 12% (from 48.6 per 1,000 to 42.8) for women aged 35-39 and 23% (from 66.0 to 51.1) for those aged 40 years and older, they said based on data from the National Vital Statistics System.
The rates were basically unchanged for women in their 20s, from 23.0 to 23.2 in 20- to 24-year-olds and 30.5 to 30.4 in 25- to 29-year-olds – but there was a significant increase for the youngest group with rates among those younger than 20 years going from 16.0 to 17.1 per 1,000, the report showed.