User login
but its use “remains low, and that is concerning for maternal and fetal well-being,” said investigators who analyzed one public and one private database.
The two databases showed increases of somewhat different scale. According to Medicaid data on 3,045 pregnancies among SLE women, initiation of hydroxychloroquine rose from 2.7% in 2001 to 7.5% (P = .0002) in 2010. The analysis of data for 2,255 SLE pregnancies from a large commercial insurance database (Optum Clinformatics) showed an increase from 4.9% in 2003 to 13.6% (P = .0001) in 2015, wrote Bonnie L. Bermas, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and her associates. The report was published in Lupus.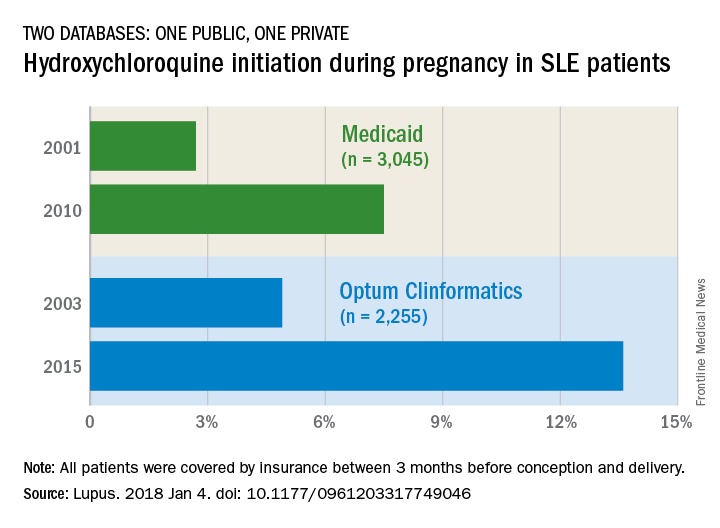
The study was funded by Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School. Dr. Bermas did not report any conflicts. Her associates reported unrelated projects with a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Bermas BL et al. Lupus. 2018 Jan 4. doi: 10.1177/0961203317749046.
but its use “remains low, and that is concerning for maternal and fetal well-being,” said investigators who analyzed one public and one private database.
The two databases showed increases of somewhat different scale. According to Medicaid data on 3,045 pregnancies among SLE women, initiation of hydroxychloroquine rose from 2.7% in 2001 to 7.5% (P = .0002) in 2010. The analysis of data for 2,255 SLE pregnancies from a large commercial insurance database (Optum Clinformatics) showed an increase from 4.9% in 2003 to 13.6% (P = .0001) in 2015, wrote Bonnie L. Bermas, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and her associates. The report was published in Lupus.
The study was funded by Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School. Dr. Bermas did not report any conflicts. Her associates reported unrelated projects with a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Bermas BL et al. Lupus. 2018 Jan 4. doi: 10.1177/0961203317749046.
but its use “remains low, and that is concerning for maternal and fetal well-being,” said investigators who analyzed one public and one private database.
The two databases showed increases of somewhat different scale. According to Medicaid data on 3,045 pregnancies among SLE women, initiation of hydroxychloroquine rose from 2.7% in 2001 to 7.5% (P = .0002) in 2010. The analysis of data for 2,255 SLE pregnancies from a large commercial insurance database (Optum Clinformatics) showed an increase from 4.9% in 2003 to 13.6% (P = .0001) in 2015, wrote Bonnie L. Bermas, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and her associates. The report was published in Lupus.
The study was funded by Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School. Dr. Bermas did not report any conflicts. Her associates reported unrelated projects with a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Bermas BL et al. Lupus. 2018 Jan 4. doi: 10.1177/0961203317749046.
FROM LUPUS